

©2000 Antares Audio Technologies. All Rights Reserved.
Antares Audio Technologies
231 Technology Circle, Scotts Valley, California 95066 USA
voice: (831) 461 7800
fax: (831) 461 7801
service: (831) 461 7814
web: www.antarestech.com
Printed in USA Rev 1.0-10/00

Contents
Getting Started
Welcome 5
Tech Support 6
A few words from Dr. Andy 7
Introducing the ATR-1a Chapter 1
Background 9
So what exactly is it? 9
A little bit about pitch 10
Some pitch terminology 10
How the ATR-1a determines pitch 11
How the ATR-1a corrects pitch 12
Program Mode vs. Song Mode 13
Setting Up the ATR-1a Chapter 2
Setting up the ATR-1a 15
Panel Controls and Chapter 3
Connectors
Front panel 17
Back panel 19
Display Screens and Chapter 4
Menu Pages
Flash screen 20
Mode pages 20
Program Edit pages 22
Speed page 23
Make Scale from MIDI page 24
Scale page 24
Vibrato page 26

Program Name page 27
Save Program page 27
Song Edit pages 27
Song Speed page 28
Song Items page 28
Song Vibrato page 29
Song Name page 30
Save Song page 30
System Edit pages 30
Bass Mode page 31
Sensitivity and LCD page 31
Foot Switch and Detune page 32
MIDI page 1 33
MIDI page 2 34
MIDI page 3 35
MIDI page 4 35
MIDI page 5 36
Owner Message page 36
Creative Applications Chapter 5 37
Appendix
Factory Programs 40
Scale and Chord Guides 41
MIDI SysEx message formats 44
MIDI SysEx message examples 47
MIDI Implementation Chart 50
ATR-1a Specifications 51
Index 52

Welcome!
On behalf of everyone at Antares Audio Technologies, we’d like to offer
both our thanks and congratulations on your decision to purchase the
absolute best intonation correction hardware in the world.
Before you proceed much farther, we’d like to strongly encourage you to
fill out and return the ATR-1a registration card. As an ATR-1a owner, you
are entitled to receive notification of any firmware upgrades, technical
support, and advance announcements of upcoming products. But we
can’t send you stuff unless we know who and where you are. So please,
send it in.
At Antares, we are committed to excellence in quality, customer service,
and technological innovation. With your purchase of the ATR-1a, you
have created a relationship with Antares which we hope will be long
and gratifying. Let us know what you think. You can count on us to
listen to you.
Again, thanks.
The Whole Antares Crew
5

Technical Support
In the unlikely event that you experience a problem using your ATR-1a,
try the following:
1. Make another quick scan through this manual. Who knows? You may
have stumbled onto some feature that you didn’t notice the first time
through.
2. Check our web page for tips, techniques, or any late-breaking
information: www.antarestech.com
3. Call your local Antares dealer.
4. Call us at (831) 461-7814 Monday through Friday between 9am and
5pm USA Pacific Standard Time.
5. Email us at: techsupport@antarestech.com
For options 3, 4 and 5, please be prepared to provide the serial number of
your ATR-1a.
6

A few words fr om Dr. Andy
I remember, as if it were yesterday, sitting in my junior high school band,
happily playing away on my flute, when I noticed that our conductor was
screaming and jumping up and down on the podium. What was this
about? Suddenly, I realized she was screaming at me. And just in time too
— since I was able to duck and watch a baton fly past my head, missing
me by inches. “Why [expletive] can’t you play in tune?” she asked. But I
was in tune. Everybody else was out of tune. It was then I began to learn
about intonation.
Many artists struggle with intonation. An entire concert can be spoiled by
a single sour note. Many of our most celebrated entertainers spend hours
in the studio doing retake after retake, trying to sing expressively and in
tune. Afterwards, their producers spend yet more time trying to correct
intonation problems using inadequate tools.
The ATR-1a is dramatically changing all of that. Because of the ATR-1a,
sessions can focus on feeling and expression, rather than retakes. Studio
hours are reduced and production costs are lowered. Even artists in live
performance situations can concentrate on interpretation, confident that
any pitch inaccuracies will be caught and corrected before they make it
out to the audience.
What’s more, the ATR-1a is incredibly easy to use (a fact attested to by the
thinness of this manual). So fire up your ATR-1a, invest a half hour or so in
reading the following pages, and prepare to make intonation problems a
thing of the past.
Andy Hildebrand Ph.D.
Founder and Chief Scientist
andy@antarestech.com
7

8

Chapter 1:
Introducing the ATR-1a
Some background
In 1997, Antares first introduced the ground-breaking Auto-Tune Pitch
Correcting Plug-In for ProTools™ (followed a bit later by the VST and
stand-alone versions). Here was a tool that actually corrected the pitch
of vocals and other solo instruments, in real time, without distortion or
artifacts, while preserving all of the expressive nuance of the original
performance. Recording Magazine called Auto-Tune a “Holy Grail of
recording.” And went on to say, “Bottom line, Auto-Tune is amazing...
Everyone with a Mac should have this program.” In fact, we know of
quite a few people who bought kilo-buck ProTools systems just to be
able to run Auto-Tune.
While Auto-Tune has met with tremendous success, we were immediately
barraged with requests for a self-contained “Auto-Tune-in-a-box.” The
result is the ATR-1a which you have presumably just purchased.
So what exactly is it?
The ATR-1a is a rack-mountable hardware implementation of Antares’s
Auto-Tune pitch correcting software. Like Auto-Tune, the ATR-1a employs
state-of-the-art digital signal processing algorithms (many, interestingly
enough, drawn from the geophysical industry) to continuously detect the
pitch of a periodic input signal (typically a solo voice or instrument) and
instantly and seamlessly change it to a desired pitch (defined by any of a
number of user-programmable scales).
In addition, the ATR-1a, befitting its easy portability, includes a number
of new features that make it particularly powerful in live performance
situations. These include a new Song Mode that lets the ATR-1a follow
even the most complex harmonic song structures, foot switch control of
Scale selection and Bypass Mode, as well as MIDI control of every ATR-1a
parameter.
9
A little bit about pitch
Pitch is typically associated with our perception of the “highness” or
“lowness” of a particular sound. Our perception of pitch ranges from the
very general (the high pitch of hissing steam, the low pitch of the rumble
of an earthquake) to the very specific (the exact pitch of a solo singer or
violinist). There is, of course, a wide range of variation in the middle. A
symphony orchestra playing a scale in unison, for example, results in an
extremely complex waveform, yet you are still able to easily sense the
pitch.
The vocalists and the solo instruments that the ATR-1a is designed to
process have a very clearly defined quality of pitch. The sound-generating
mechanism of these sources is a vibrating element (vocal chords, a string,
an air column, etc.). The sound that is thus generated can be graphically
represented as a waveform (a graph of the sound’s pressure over time)
that is periodic. This means that each cycle of waveform repeats itself
fairly exactly, as in the periodic waveform shown in the diagram below:
Because of its periodic nature, this sound’s pitch can be easily identified
and processed by the ATR-1a.
Other sounds are more complex. This waveform:
is of a violin section playing a single tone. Our ears still sense a specific
pitch, but the waveform does not repeat itself. This waveform is a summation of a number of individually periodic violins. The summation is nonperiodic because the individual violins are slightly out of tune with respect
to one another. Because of this lack of periodicity, the ATR-1a would not
be able to process this sound.
Some pitch terminology
The pitch of a periodic waveform is defined as the number of times the
periodic element repeats in one second. This is measured in Hertz (abbreviated Hz.). For example, the pitch of A3 (the A above middle C on a
piano) is traditionally 440Hz (although that standard varies by a few Hz.
in various parts of the world).
10

Pitches are often described relative to one another as intervals, or ratios of
frequency. For example, two pitches are said to be one octave apart if
their frequencies differ by a factor of two. Pitch ratios are measured in
units called cents. There are 1200 cents per octave. For example, two tones
that are 2400 cents apart are two octaves apart.
The traditional twelve-tone Equal Tempered Scale that is used (or rather
approximated) in 99.9% of all Western tonal music consists of tones that
are, by definition, 100 cents apart. This interval of 100 cents is called a
semitone.
How the ATR-1a detects pitch
In order for the ATR-1a to automatically correct pitch, it must first detect
the pitch of the input sound. Calculating the pitch of a periodic waveform
is a straighforward process. Simply measure the time between repetitions
of the waveform. Divide this time into one, and you have the frequency in
Hertz. The ATR-1a does exactly this: It looks for a periodically repeating
waveform and calculates the time interval between repetitions.
The pitch detection algorithm in the ATR-1a is virtually instantaneous. It
can recognize the repetition in a periodic sound within a few cycles. This
usually occurs before the sound has sufficient amplitude to be heard. Used
in combination with a slight processing delay (no greater than 4 milliseconds), the output pitch can be detected and corrected without artifacts in
a seamless and continuous fashion.
The ATR-1a was designed to detect and correct pitches up to the pitch C6.
If the input pitch is higher than C6, the ATR-1a will often interpret the
pitch an octave lower. This is because it interprets a two cycle repetition as
a one cycle repetition. On the low end, the ATR-1a will detect pitches as
low as A0 (55Hz) in its normal mode and down to 25Hz when Bass Mode is
selected. This range of pitches allows intonation correction to be performed on all vocals and almost all instruments.
Of course, the ATR-1a will not detect pitch when the input waveform is
not periodic. As demonstrated above, the ATR-1a will fail to tune up even
a unison violin section. But this can also occasionally be a problem with
solo voice and solo instruments as well. Consider, for example, an exceptionally breathy voice, or a voice recorded in an unavoidably noisy environment. The added signal is non-periodic, and the ATR-1a will have
difficulty determining the pitch of the composite (voice + noise) sound.
Luckily, there is a control (the SENSITIVITY control, discussed in Chapter 4)
that will let the ATR-1a be a bit more casual about what it considers
“periodic.” Experimenting with this setting will often allow the ATR-1a to
track even noisy signals.
11

How the ATR-1a corrects pitch
The ATR-1a works by continuously tracking the pitch of an input sound
and comparing it to a user-defined scale. The scale tone closest to the
input is continuously identified. If the input pitch exactly matches the scale
tone, no correction is applied. If the input pitch varies from the desired
scale pitch, an output pitch is generated which is closer to the scale tone
than the input pitch. (The exact amount of correction is controlled by the
Speed parameter, described below and in Chapter 4.)
Scales
The heart of the ATR-1a’s pitch correction is the Scale. The ATR-1a allows
you to program 50 different Scales. For each Scale you can define which
notes will sound and which won’t. And for each note that will sound, you
can decide whether the ATR-1a will apply pitch correction to input pitches
near that note or leave those pitches uncorrected.
Speed
You also have control over how rapidly, in time, the pitch adjustment is
made toward the scale tone. This is set with the SPEED control (see
Chapter 4 for more details).
• Fast SPEED settings are more appropriate for short duration notes and
for mechanical instruments, like an oboe or clarinet, whose pitch
typically changes almost instantly. A fast enough setting will also
minimize or completely remove a vibrato.
12
• Slow SPEED settings, on the other hand, are appropriate for longer
notes where you want expressive pitch gestures (like vibrato) to come
through at the output and for vocal and instrumental styles that are
typified by gradual slides (portamento) between pitches. An appropriately selected slow setting can leave a vibrato unmodified while the
average pitch is accurately adjusted to be in-tune.
Vibrato
The ATR-1a can also apply a vibrato to the input sound. You can program
the vibrato depth, vibrato rate and the onset delay of the vibrato (or even
control it in real time via MIDI). You can also choose the shape of the pitch
variation in the vibrato (sine, ramp or square). By combining a fast Speed
setting with the ATR-1a Vibrato settings, you can even remove a
performer’s own vibrato and replace it with the ATR-1a’s programmed
vibrato, all in real time. Also, unusual combinations of Vibrato Waveform,
Rate and Depth settings can be used for some interesting special effects.
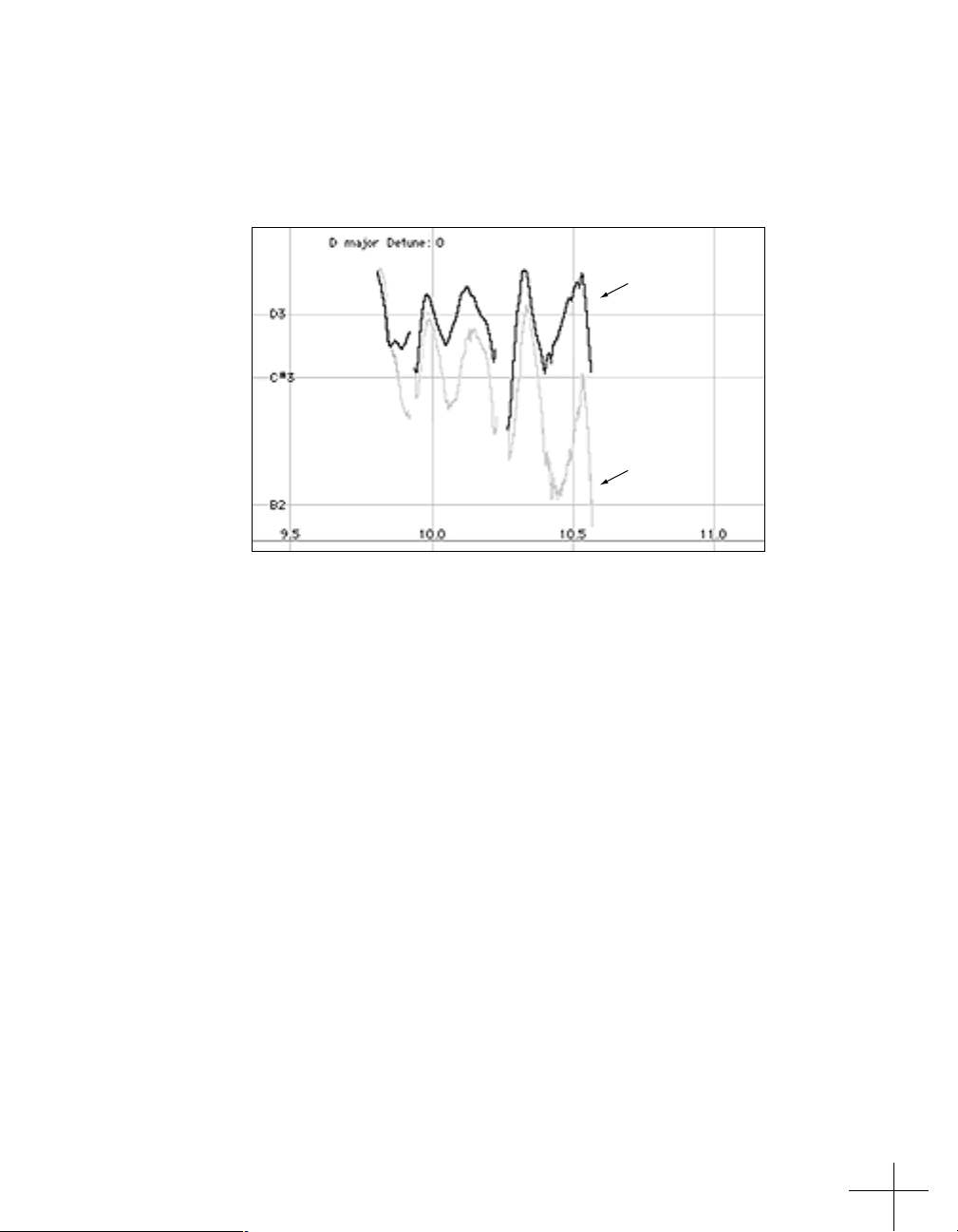
An example
As an example, consider this before-and-after graphic representation of
the pitch of a vocal phrase that contains both vibrato and expressive
gestures.
CORRECTED
BY ATR-1
ORIGINAL
PERFORMANCE
In the original performance, we can see that although the final note
should be centered around D, the vocalist allowed the tail of the note to
fall nearly three semitones flat. The “after” plot is the result of passing
this phrase through the ATR-1a with a Program consisting of a D Major
Scale (with C
causes the pitch center to be moved to D, while still retaining the vibrato
and expressive gestures. (Setting C
the ATR-1a from trying to correct the seriously flat tail of the last note to
those pitches. See Chapter 4 for more details.)
and B set to ”Blank”) and a Speed setting of 10. That Speed
and B to ”Blank” is necessary to keep
Program Mode vs. Song Mode
At its top level, the ATR-1a operates in one of two modes, Program Mode
or Song Mode. Which mode you use depends upon your application and,
to some extent, how radical are the required corrections.
Program Mode
In Program Mode, you call up one of the ATR-1a’s 50 individual Programs
to control the correction algorithm. Each Program consists of a Scale, a
Speed setting and Vibrato settings. You can step through Programs with a
foot switch or via MIDI.
Use Program Mode when a single scale (or maybe two) is all that’s required
for a particular correction.
13

If a performance is quite close to begin with and only requires minor
correction (i.e., never more that 50 cents), it’s often sufficient to simply
choose the Chromatic scale, set Speed to about 10 and leave it there.
If you are working in the studio to correct an already recorded track, you
might use Program Mode to deal with the track one section at a time,
stoping to change Programs between sections.
Song Mode
Song Mode offers a more elaborate set of controls primarily designed to
facilitate the use of the ATR-1a in a live performance situation, whether in
actual concert or during tracking in the studio.
The ATR-1a provides 20 Songs. For each Song, you can program a series of
up to 15 Song Steps. Each Step can contain a Program (with associated
scale) or one of a number of navigation controls (See Chapter 4 for
details). In performance you move from Song Step to Song Step via the
foot switch or MIDI. You can also call up different Songs via MIDI Program
Change messages.
Each Song also contains its own Speed and Vibrato settings that override
those settings in the individual Programs. In this way, an individual
Program’s scale can be used in any number of songs, each with different
Speed and Vibrato settings. (To accomplish the same thing in Program
Mode would require you to create multiple Programs, each with the
identical scale but with the different Speed and Vibrato settings. Very
inefficient. )
14
There is of course no hard and fast rule for which mode to use in any
particular situation. Try out both modes and use what feels comfortable
to you.

Chapter 2:
Setting Up the ATR-1a
Setting up the ATR-1a is a very straightforward.
1. Find a suitable location. The ATR-1a is designed to be mounted in a
standard 19-inch equipment rack.
2. Confirm that the included power supply is correct for the electricity in
your part of the world. If you are not sure, or the power supply has a
plug that is incompatible with your wall sockets, contact your local
Antares dealer for help.
Important! Do not attempt to modify the supply or use any other supply that is not
specifically intended for the ATR-1a.
3. First, connect the power supply’s 7-pin DIN connector to the AC INPUT
jack on the rear of the ATR-1a. Then plug the power supply into an AC
outlet.
4. Connect a balanced or unbalanced audio input to one of the INPUT
jacks (see Chapter 4 for details).
5. Connect a cable to one of the OUTPUT jacks and route the output as
appropriate for your application.
6. If you will be controlling your ATR-1a via MIDI, connect a MIDI cable
from your MIDI source to the ATR-1a’s MIDI IN jack.
An Important Note: Unless you plan to be defining the ATR-1a’s target
pitches via MIDI, be sure that MIDI NOTE MODE is set to OFF in the System
Edit pages (see page 29 for details). If MIDI NOTE MODE is set to ON and
no MIDI note data is present, the ATR-1a will pass through all audio
unprocessed, regardless of the settings of the Program Scale Page —
giving the impression that the ATR-1a is not functioning.
An Important Note About Grounding: The ATR-1a is an extremely quiet piece
of gear. When properly connected and grounded, noise and hum will be
inaudible. However, as you’re no doubt well aware, every studio has its own
unique quirks when it comes to connections, grounding and noise. For the
absolute best sonic performance, ensure that your input and output are fully
balanced.
15

An Important Note About Monitoring: If the ATR-1a is used to pitch-
correct an artist’s performance in real time, it is very important that the
performer is able to monitor their original signal, not the pitch-corrected
signal. Trying to react musically to the processed signal will drive them
crazy and, in most cases, drive them farther off pitch.
16

Chapter 3:
Panel Controls and Connectors
As you have almost certainly noticed, the ATR-1a has relatively few controls.
We’ll cover them here.
1 2
3 4 5 6 7 8 9
The Front Panel
1 Non-existent Power Switch That’s right. There isn’t one. The ATR-1a is
designed to remain on continuously. You can, of course, plug it in to a
switched power strip or power conditioner if you like, but leaving it on
all the time will do it no harm.
10
2 LCD An easy-to-read 20 character by 2 line display. You can set the
optimum viewing angle in the System menu (See Chapter 4).
3 Data Entry Knob As the name implies, turn it to enter data.
4 CURSOR Buttons The cursor buttons let you move the cursor in the LCD
display from field to field so that you can change the field’s value using
the knob.
5 PROGRAMS Button Press this button to edit a Program or Song. It is
state-sensitive. That is, if you are in Program Mode when you press this
button, you will be taken to the Program Edit pages. If you are in Song
Mode, you will be taken to the Song Edit pages. The accompanying LED
lights to remind you that you are in an edit mode. When the LED is lit,
press the PROGRAMS buttom again to exit the Program Mode.
6 PAGE Button While in Program, Song or System Edit Mode, press this
button to cycle sequentially through the available edit pages. You can
only move in one direction, but there are so few pages in each mode
that you are never more than a few presses away from where you want
to be.
17

7 SYSTEM Button Press this button to set various parameters that affect
the ATR-1a’s overall functionality (MIDI response, LCD contrast, etc.)
The accompanying LED lights to remind you that you are in System Edit
Mode. When the LED is lit, press the SYSTEM buttom again to exit the
System Edit Mode.
8 BYPASS Button Press the Bypass button to pass audio through the
ATR-1a without any pitch correction or other processing. Switching the
Bypass state will not cause any audio artifacts, so it can be used in
performance or in the middle of a recorded track. The ATR-1a can also
be placed into Bypass Mode via a footswitch (see below) or by MIDI.
The accompanying LED lights to remind you that you are in Bypass
Mode, whether the mode was initiated by the Bypass button, the foot
switch, a Song Step Item or MIDI.
9 SIGNAL LEVEL Meter These six LEDs light to indicate the input signal
level in dBs. Ideally, you should adjust the input to the highest level that
does not consistently cause the top red LED to light. (The red LED lights
at a level of -3dB. Digital clipping, which introduces a particularly nastysounding distortion, will occur if the input exceeds 0dB.)
10 PITCH CHANGE Meter These LEDs indicate, in real time, the amount of
pitch correction being applied to change the input pitch to the target
pitch. The green LEDs indicate that the input is flat and that positive
correction is being applied. Conversely, the yellow LEDs indicate that
the input is sharp and that negative correction is required. They are
labeled in cents (i.e., 100ths of a semitone).
18

54321
The Back Panel
1 AC POWER INPUT Plug the 7-pin DIN connector from the included
power supply in here. Do NOT use a supply which is not expressly
intended for the ATR-1a (even if you could find one with the that
weird plug on it). Bad things could happen.
2 MIDI IN Connect the MIDI Out from a MIDI keyboard, sequencer, or
other MIDI source in here.
3 FOOT SWITCH Plug in a foot switch here. A 1/4-inch TS (tip-sleeve)
plug is required. There are two varieties of foot switch: those that are
shorted by default and those that are open by default. You should plug
in your foot switch and then power on the ATR-1a. The ATR-1a will
detect which kind of foot switch you have and behave accordingly.
4 BALANCED LINE INPUTS Inputs can be 1/4-inch TRS (tip-ring-sleeve)
Phone, 1/4-inch TS (tip-sleeve) Phone or female XLR.
Note: The XLR input is NOT a microphone input. A line level signal is required.
Also Note: If you use a 1/4-inch TS plug, the input will of course not be balanced.
Yet Another Note: The two inputs will not mix two signals. Plugging in a phone plug will
disconnect the XLR input.
5 LINE OUTPUTs Outputs can be 1/4-inch TS (tip-sleeve) Phone Unbal-
anced or male XLR Balanced.
19

Chapter 4:
Display Screens and Menu Pages
Flash Screen
ATR-1a version 1.3
ATR-1a Processor
The Flash Screen appears for a few moments after the ATR-1a is powered
on. The first line displays the firmware version. The second line can display
any message that will fit in 20 characters. As it comes from the factory, the
ATR-1a displays the rather unimaginative message above. However, you
can create your own (much more clever) message in one of the SYSTEM
pages (see page 36).
Mode Pages
The ATR-1a operates in one of two modes: Program Mode or Song Mode.
When powered on, the ATR-1a reverts to the mode to which it was last
set. (When initially powered on from the factory, the ATR-1a will be
Program Mode.)
Program Mode Main Screen
In Program Mode, this Main Screen (the page visible when the Program
and System LEDs are not lit) appears:
PROGRAM
XX:aaaaaaaaaaaaa
where XX is the program number and aaaaaaaaaaaaa is the program
name. In Program Mode, the parameters of the selected program govern
the pitch correction algorithm.
20

To select a Program, move the cursor to the Program Number field and use
the data knob to choose the desired Program.
If the Program Mode Main Screen is displayed and MIDI Program Changes
are enabled in the SYSTEM menu, a MIDI Program Change command of 1–
50 will select the corresponding Program.
If the Program Mode Main Screen is displayed and the Foot Switch is set to
STEP in the SYSTEM menu, pressing the foot switch will step to the next
higher numbered Program.
To move to Song Mode (see below), move the cursor to the top line and
use the data knob to select Song Mode.
Song Mode Main Screen
When in Song Mode, this Main Screen appears as follows:
Song:XXaaaaaaaaaaaaa
Step:YYbbbbbbbbbbbbb
where XX is the song number, aaaaaaaaaaaaa is the song name, YY is the
Song Step number and bbbbbbbbbbbbb displays the name of the Program
or navigation message at Step YY.
To select a Song, move the cursor to the Song Number field and use the
data knob to choose the desired Song.
If the Song Mode Main Screen is displayed and MIDI Program Changes are
enabled in the SYSTEM menu, a MIDI Program Change command of 1–20
will select the corresponding Song.
If the Song Mode Main Screen is displayed and the Foot Switch is set to
STEP in the SYSTEM menu, pressing the Foot Switch will step to the next
non-”0" Song Step in the Song’s Step list.
When in Song Mode, the Speed and Vibrato settings programmed for the
selected Song override the Speed and Vibrato settings in any Programs
called up by Song Steps.
21

Each Song Step must contain one of the following items:
ITEM CODE MAIN SCREEN STEP DISPLAY
0 (no program)
## (Program number) the program name
B (B bypass)
<- (<- loop)
E (E end)
-> (-> link)
Please note: In the Song Mode main screen, the Cursor buttons can be used to move
the cursor to the YY field and the data knob can then be used to select
any Song Step and display the item programmed for that step. However, when the MIDI increment message or the foot switch step functions are used, the Song Steps may not necessarily appear sequentially.
Any steps programmed with zeroes are skipped, and the control functions (<-, -> and E) will cause changes in Song Step recall order.
For details on the function of each of these options, see the section on
programming Songs on page 26.
To move to Program Mode, move the cursor to the word SONG on the top
line of the Main Screen and use the data knob to select Program Mode.
Program Edit Pages
Pressing the PROGRAMS button while the Program Mode Main Screen is
displayed will place the ATR-1a in Program Edit Mode. The fields on these
pages allow you to set the parameters which control the ATR-1a pitch
processing algorithm.
To edit a specific Program you must first select that Program as the current
Program. Do that by calling up the appropriate program number on the
Program Mode Main Screen. Then, press the PROGRAMS button (the red
LED under the PROGRAMS button will light). The number of the Program
being edited will always appear in the top left corner of the various
Program Edit pages.
When editing a Program, you progress from one edit page to the next by
pressing the PAGE button.
When you are finished making changes, press the PROGRAMS button
again. You will be prompted to save the changes (see the Save Program
Page, below).
22

Speed Page
The first edit page displayed is the SPEED page:
Program:XX Speed
(0 is fast): yy
The SPEED control determines how rapidly pitch correction is applied to
the incoming sound. Values range from 0 to 25. A value of zero will cause
instantaneous changes from one tone to another and will completely
suppress a vibrato and any purposeful expressive pitch variations (note
that any related volume changes will remain). Values from 6 to 10 are
typical for vocals. Higher values allow more vibrato and other interpretative pitch gestures, but will slow down the rate at which pitch corrections
are made.
Although the above suggestions can be used as starting points, finding
the correct Speed setting for a particular performance is largely a matter
of trial-and-error and depends on such attributes as song tempo, note
duration and vocal style, among others.
Make Scale From MIDI Page
In most cases, you will probably tell the ATR-1a which notes to correct
using the Scale Page described below. However, there may be occasions
when it is not clear exactly what key a melody line is in, or where the line
has too many accidentals to fit comfortably into a conventional scale. For
those occasions, the Make Scale From MIDI function allows you to simply
play the line into the ATR-1a from a MIDI keyboard or sequencer and let
the ATR-1a construct a custom scale containing only those notes that
appear in the line.
Prog:xx Press < to
make scale from MIDI
To use the Make Scale From MIDI function, ensure that your MIDI source is
connected to the ATR-1a’s MIDI input and is transmitting on the same MIDI
channel specified on MIDI Page 1 in the System Edit section. Then press the
left cursor button to begin the process. The following screen is displayed:
xx:
Press PAGE when done
23

Now simply play the melody to be corrected from your keyboard or
sequencer. Tempo and rhythm don’t matter, so take your time and make
sure you don’t play any wrong notes. As each note is played, its name
appears in the top line of the display. Assume, for example, that your
melody starts with D
would look like this:
, B, and then A. After playing those notes the display
xx: D# A B
Press PAGE when done
When you have played the entire melody, press the PAGE button to end
the process and automatically take you to the Scale Page, where you may
further edit your scale as described below.
If you happen to make an error during note entry, or want to try again for
any other reason, continue pressing the PAGE button until you return to
the first screen above and start the process again.
Note: When you start the process by pressing the left cursor key, all notes are
first removed from the current Program’s scale in preparation for
adding just the notes you play. If you then press the PAGE button
without playing any notes, you will be taken to the Scale Page below
which will display a scale with no notes present. In this state, the ATR-1a
will pass all notes with no correction applied. So don’t do that.
Another Note: We realize that there is some possibility of confusion between the
Make Scale From MIDI function and MIDI Note Mode selected on MIDI
Page 1 in the System Edit pages. To clarify: the MIDI Note Mode is used
to specify target pitches in real time while pitch correction is occurring,
while Make Scale From MIDI is used in advance of correction to create a
custom scale for a program.
MIDI Note Mode does not need to (and, in fact, shouldn’t) be enabled
to use the Make Scale From MIDI function. MIDI Note Mode always
overrides the current program’s scale, including one created by the
Make Scale From MIDI function.
Scale Page
24
You tell the ATR-1a exactly which notes you want to correct on the Scale
Page:
XX:CC#DD#EFF#GG#AA#B
By:

This page allows you to specify the scale notes to which the ATR-1a tunes
the input sound. If you have used the Make Scale From MIDI function
described above, the notes input via MIDI will already appear on the page
and can be further edited here. There are 12 notes in this scale, i.e. C, C#,
…etc. Each note in the scale can be set to one of three states:
Tune (i.e., the note name appears in the display, but the “By:” field under
the note is blank): When the input is near a note set to Tune, the ATR-1a
will retune the input to that note.
Bypass (i.e., the note name appears in the display and an “*” appears in
the “By:” field under the note): When the input pitch is close to a note set
to Bypass, the output remains uncorrected.
Blank (i.e., the note name disappears from the display): A note set to
Blank will be omitted from the scale. For example, setting C
to Blank causes a C Major scale to remain. In that case the ATR-1a
A
would always retune the input to the closest note of the C Major scale.
As an example, the following settings result in a D Major scale with no
pitch corrections applied to F
and C:
, D, F, G,
23: C#D E F#G A B
By: * *
Why set Scale notes to “Blank”?
To understand why it is sometimes necessary to set even correct scale notes
to ”Blank,“ let’s look again at the example from Chapter 1.
CORRECTED
BY ATR-1
ORIGINAL
PERFORMANCE
25

Vibrato Page
This phrase is in D Major and, if all the pitch errors were no greater than
about 49 cents, would work fine with a standard D Major scale (D, E, F
A, B, C
last note is so large that with B and C
fell, the ATR-1a would see first C
therefore allow the error to remain. With C
the ATR-1a continues to see D as the target pitch for the entire duration
of the note and therefore pulls the phrase up to the correct pitch.
). However, the pitch error of three semitones at the end of the
present in the Scale, as the pitch
and then B as the target pitch and
and B removed from the Scale,
Prog:XX Dpth Rt Dly
yyyyyy xxx zzz dddd
These parameters allow you to superimpose a vibrato (periodic pitch
variation) onto the output sound. The yyyyyy field allows you to select the
shape of the vibrato’s pitch variation through time. The choices are: (off),
SINE, SQUARE and SAW (sawtooth).
The Dpth (Depth) control varies from 0 to 100 cents, controlling the
amount of pitch variation in the vibrato. The vibrato depth can also be
modulated (controlled) by the MIDI MOD WHEEL input.
Note: The Depth setting is used by the MIDI Mod Wheel controller to define
the maximum modulation. You must have the Depth set to a positive
value and the wave type set to SINE, SQUARE or SAW in order for Mod
Wheel control to work.
The Rt (Rate) control varies from .1 to 9.7 Hz and controls the speed of the
vibrato.
, G,
26
The Dly (Delay) control varies from 0 to 3500 milliseconds, and controlls
the time between the beginning of a new note and the full onset of the
vibrato. For example, if Delay is set to 1000, the first 500 milliseconds of a
new note will contain no vibrato and the next 500 milliseconds will make
a transition from no vibrato to the full vibrato.
The vibrato is restarted each time the ATR-1a detects a new attack (i.e.,
input is detected after some finite period of silence). As long as the input
is sustained without interruption, changing pitch will not restart the
vibrato delay. The vibrato is applied after the effects of the SPEED control.
Hence, even with a slow SPEED value of 10, a SQUARE wave vibrato will
still result in instantaneous changes in pitch.

Program Name Page
This page allows you to name each of your Programs. Typically, you would
name the program after the scale that it contains. Alternatively, you could
name it after the song or portion of a song in which it’s used. Do whatever
helps you best remember what you had in mind when you created the
Program.
Program:XX
Name:aaaaaaaaaaaaa
To enter the name, place the cursor under each character space and use
the data knob to select the appropriate character. Names may be a maximum of 13 characters.
The following characters are available for naming (in this order):
(space) (UPPER CASE LETTERS) (lower case letters) – . / 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 !
“# $ % & ‘ ( ) * + , : ; < = > ? @ [ ¥ ] ^ _ ` { | } -> <-
Save Program Page
Prog:XX Save? To Pgm
YES XX
After you finish examining and/or editing Program Edit parameters, press
the PROGRAMS button again to exit. If you have made any changes, the
Save Program Page appears. You may select YES to save or NO to ignore
changes that have been make (they will then be lost). You may also specify
a Program number to which the new Program is to be saved. If you save to
a different Program number, that Program becomes the current Program
when you return to the Main Page and the original Program remains
unchanged.
Song Edit Pages
As explained in Chapter 1, the ATR-1a’s Song Mode is designed to give you
an easy and flexible way to control, in as much detail as you require,
exactly how the ATR-1a will process each note of a song.
Pressing the PROGRAMS button while the Song Mode main screen is
displayed will place the ATR-1a in Song Edit Mode.
27

To edit a specific Song, you must first select that Song as the current Song.
Do that by calling up the appropriate Song number on the Song Mode
Main Screen. Then, press the PROGRAMS button (the red LED under the
PROGRAMS button will light). The number of the Song being edited will
always appear in the top left corner of the various Song Edit pages.
When editing a Song, you progress from one edit page to the next by
pressing the PAGE button.
When you are finished making changes, press the PROGRAMS button
again. You will be prompted to save the changes (see the Save Song Page,
below).
Song Speed Page
The Song Speed page operates in exactly the same manner as the Program
Speed page described above. However, the Song Speed overrides the
Speed settings of any Programs called up by any of the Song Steps.
Song Items Page
Song:YY Speed
(0 is fast): xxx
28
Song:XX : 1 2 3 4
Programs: 0 0 0 0
Here’s where the action is. The Song Items page allows you to specify a
sequence of Programs along with a variety of options for navigating the
sequence.
To specify the contents of a Song Step, use the cursor buttons to move to
the step number and then use the data knob to select the desired Item for
that Step. Each Song contains 15 Steps. Continuing to press a cursor
button when the cursor has reached the leftmost or rightmost displayed
Step Number will cause additional Step Numbers to cycle across the display .
Each Song Step may contain one of the following Items:
## (A Program Number) While this Song Step is active, the input audio will
be pitch corrected according to the scale associated with this Program. All
other Program parameters (i.e., Speed and Vibrato) will be ignored.
B (Bypass) While this Song Step is active, the ATR-1a is put into Bypass
Mode.

<- (Loop) When a Song Step containing a Loop command becomes active,
the Song immediately resets to Song Step #1. If Song Step #1 contains a
“0” (No Program) item, the Song moves forward to the next non-”0“ Step.
Use Loop when you want to repeat a harmonic structure multiple times.
E (End) When a Song Step containing End becomes active, the ATR-1a
enters Bypass Mode and additional presses of the Foot Switch or MIDI
Increment commands have no affect. The only way to proceed to the next
Song is select a new Song on the front panel or via MIDI program change.
It’s a good idea to put an End command at the end of every Song to avoid
the possibility of accidentally getting lost in your Song list.
-> (Link) When a Song Step containing a Link item becomes active, any
Song Steps in the remainder of the current Song are ignored and the ATR1a moves immediately to the next Song (in numerical order). If Song Step
#1 of the new Song contains a “0” (No Program) item, the Song moves
forward to the next non-”0” Step.
Use Link when your Song requires more than 15 Steps.
0 (No Program) Song Steps containing a No Program Item are ignored
when stepping through a Song using either the Foot Switch or MIDI
Increment commands. (i.e., If Song Step #1 contains a Program Number,
Song Step #2 contains a “0” and Song Step #3 contains another Program
Number, pressing the Foot Switch while on Step #1 will move you immediately to Step #3.)
You can, of course, move to a Song Step containing a “0” Item by using
the the front panel data knob. In that case, no pitch correction will occur
while that Song Step is displayed.
All unprogrammed Song Steps initially default to “0.”
Song Vibrato Page
Song:XX Dpth Rt Dly
yyyyyy xxx zzz dddd
The Song Vibrato page operates in exactly the same manner as the Program Vibrato page described above. However, the Song Vibrato settings
override the Vibrato settings of any Programs called up by any of the Song
Steps.
29

Song Name Page
This page allows you to name each of your Songs.
To enter the name, place the cursor under each character space and use
the data knob to select the appropriate character. Names may be a maximum of 13 characters.
The following characters are available for naming (in this order):
(space) (UPPER CASE LETTERS) (lower case letters) – . / 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 !
“# $ % & ‘ ( ) * + , : ; < = > ? @ [ ¥ ] ^ _ ` { | } -> <-
Save Song Page
After you finish editing and/or examining Song Edit parameters, press the
PROGRAMS button again to exit. If you have made any changes, the Save
Song Page appears. You may select YES to save or NO to ignore changes
that have been made (they will then be lost). You may also specify a Song
number to which the edited Song is to be saved. If you save to a different
Song number, that Song becomes the current Song when you return to
the Main Page and the original Song remains unchanged.
Song:XX
Name:aaaaaaaaaaaaa
Song:XX Save? To Sng
YES XX
System Edit Pages
Pressing the SYSTEM button at any time will place the ATR-1a in System
Edit Mode. The System Edit pages allow you to set parameters which
affect the ATR-1a globally, independent of whichever Song or Program is
currently active.
Note: You can go directly to System Edit Mode from either Program Edit or
Song Edit Mode. Simply press the SYSTEM button. If you have made no
parameter changes to your Program/Song, you will immediately enter
the System Edit pages. If you have made Program or Song parameter
changes, you will first be presented with the Save Song or Save Program
page. After making your choice to save or not, you will then be taken
to the System Edit pages.
30

Bass Mode Page
Note: When Bass Mode is enabled, pitches above A4 may be incorrectly tuned
When editing System parameters, you progress from one edit page to the
next by pressing the PAGE button.
After you have finished making changes, press the SYSTEM button again.
Unlike Program and Song editing, you are not prompted to save the
changes, they are automatically saved for you.
Bass Mode
OFF
When operating in its normal mode, the ATR-1a is reliably able to detect
pitches down to A0 (55Hz). Turning Bass Mode ON lowers the lowest
detectable frequency by about one octave to 25Hz. Since the lowest E
string on a bass guitar is approximately 41Hz, Bass Mode (as its name so
ably implies) allows you to apply pitch correction to those pesky fretless
bass lines as well as other low bass range instruments.
by a perfect fifth. Consequently, it’s a good idea to enable Bass Mode
only while working on pitch correcting bass range instruments and then
turn it OFF again when finished.
Sensitivity and LCD Page
Sensitivity LCD
aa bb
The Sensitivity parameter ranges from 0 to 25 and controls exactly what
its name implies. At settings of 0–9, you will be rude and boorish to those
who love you most, wish harm upon small furry animals, and enjoy the
Jerry Springer Show. From 10–20 you will (in varying degrees), see the
good in every situation, cry openly in public (especially if you are male),
and be in close touch with your inner child. From 21–25 you’ll be in close
touch with everybody’s inner child.
OK, we’re kidding about that. (And those of you who are not in the USA,
please forgive the North American-centric references.)
Actually, in order to accurately identify the pitch of the input, the ATR-1a
requires a periodically repeating waveform, characteristic of a voice or
solo instrument. The Sensitivity control determines how much variation is
allowed in the incoming waveform for the A TR-1a to still consider it periodic.
31

If you are working with a well-isolated solo signal (e.g., tracking in a
studio or off of a multi-track tape) you can typically set the Sensitivity
control to 10 and forget it.
If, on the other hand, your signal is noisy or not well-isolated (as might be
more common in a live performance situation), it may be necessary to
allow more signal variation (higher Sensitivity numbers). However, if you
back off too much, the ATR-1a’s ability to detect pitch may be affected.
As a rule, you should start with settings of about 7 to 10. If you want to
detect only highly stable sounds in low-noise conditions, settings of from 2
to 5 may be appropriate. If there is ambient noise or other interfering
sounds, try settings of from 15 to 20. Values close to zero or 25 are extreme, and will typically not do anything useful.
The LCD parameter lets you set the maximum display contrast for your
viewing angle.
Foot Switch and Detune Page
Foot_Switch Detune
aaaaaa bbbb
The Foot_Switch parameter controls the function of a connected foot
switch.
32
When set to BYPASS, the foot switch functions exactly like the BYPASS
button on the front panel.
When set to STEP, if the Program Mode main screen is displayed, pressing
the foot switch steps to the next higher numbered Program. If the Song
Mode main screen is displayed, pressing the Foot Switch will step to the
next non-”0” Song Step in the Song’s Step List.
The Detune parameter allows you to change the pitch standard of the
ATR-1a from the default A = 440Hz. The values are cents (100 cents = a
semitone). The range of adjustment is from -100 to +100 cents.
The Detune function can be used to tune a vocal performance to some
irreparably out-of-tune instrument (a piano or organ, for example), or to
allow correction to other than the conventional 440Hz standard.
Refer to the following table to convert cents to Hertz relative to 440Hz.

MIDI Page 1
DETUNE SETTING A=HERTZ
-20 435
-16 436
-12 437
-8 438
-4 439
0 440
+4 441
+8 442
+12 443
+16 444
+20 445
This table can be extended in either direction by adding or subtracting 4
cents per Hertz, as appropriate.
Channel Note Sustain
aaaa bbb ccc
The Channel parameter selects the channel over which the ATR-1a receives
MIDI messages. The choices include:
Individual MIDI channels 1–16 If an individual channel is selected, the
ATR-1a will respond to messages received on that channel only and will
ignore any messages on other channels.
OMNI If OMNI is selected, the ATR-1a will respond to messages on any
MIDI channel.
Setting the Note field to ON allows MIDI notes to define the scale used by
the ATR–1. Specifically, when Note is set ON, the scale of the currently
active Program is ignored. Instead, the ATR-1a continuously monitors the
MIDI input for Note On messages. At any instant, the scale used for
correction is defined by all MIDI notes that are on. For example, if MIDI
notes A, C and E are held, the ATR-1a input will be retuned to an A, C or E,
whichever is closest to the input pitch.
33

MIDI Page 2
The source of the MIDI input would typically be a MIDI keyboard or
sequencer, and could consist of chords, scales, or even the exact melody
that the input should be corrected to.
If you will not be defining the ATR-1a’s target pitches via MIDI, be sure
that MIDI NOTE MODE is set to OFF. If MIDI NOTE MODE is set to ON and
no MIDI note data is present, the ATR-1a will pass through all audio
unprocessed, regardless of the settings of the Program Scale Page —
giving the impression that the ATR-1a is not functioning.
When the Sustain parameter is set to ON, the ATR-1a will respond to MIDI
Sustain Pedal commands. Specifically, all notes that are on at the moment
the sustain pedal is depressed will be considered to remain on until the
pedal is released or the note is released, whichever happens later.
Pgm_Chg Bend Mod_Whl
aaa ccc ddd
The Pgm_Chg (Program Change) field, when set to ON, causes the ATR-1a
to respond to MIDI Program Change messages. When the ATR-1a is in
Program Mode, a MIDI Program Change message of 1–50 will select the
corresponding Program. When the ATR-1a is in Song Mode, a MIDI Program Change message of 1–20 will select the corresponding Song. Program Change messages outside of those ranges will have no effect.
34
When Bend is set to ON, the ATR-1a will respond to MIDI Pitch Bend
messages. The maximum range of pitch bend is from -200 to +200 cents
(plus or minus one whole step). This modification is applied in addition to
any pitch correction, vibrato or tuning.
When Mod_Whl (Mod Wheel) is set to ON, the ATR-1a will use MIDI Mod
Wheel messages to control the depth of modulation of any programmed
vibrato.
Note: The Mod Wheel messages can only vary the amount of vibrato from
none to the amount of vibrato set in the Vibrato page of the active
Program or Song. In order for Mod Wheel control to work, you must
have the Program’s or Song’s Depth set to a positive value and the
Wave Type set to SINE, SQUARE or SAW.

MIDI Page 3
MIDI Page 4
These next two MIDI Control pages allow you to assign various MIDI
controllers to set selected ATR-1a parameters in real time. (Note that all
MIDI controller data must be sent on the MIDI Channel set on MIDI Page 1
in order to be recognized.)
Midi Speed Step
Control aaa bbb
Assigning a MIDI Continuous Controller to the Speed parameter allows
that controller to override the current Program or Song Speed setting.
Note that this is simply a temporary override. The Program or Song’s
programmed setting is not affected. Changing to another Program or
Song will cause that Program’s or Song’s Speed parameter to be used.
The available values for this field are OFF or controller numbers 14 to 31.
Step allows the MIDI Data Increment controller (#96) to be used to control
stepping from Program to Program in Program Mode, or stepping among
Song Items in Song mode. The values which can be selected are OFF or 96.
Midi Vib Rate Delay
Control aaa bbb
These parameters allow realtime MIDI control of Vibrato Rate and Delay.
Again, these are simply temporary overrides. The Program’s or Song’s
programmed settings are not affected. Changing to another Program or
Song will cause that Program’s or Song’s Vibrato parameters to be used.
The available values for these fields are “OFF” or controller numbers
14 to 31.
35

MIDI Page 5
SysEx Device Number
aaa
The ATR-1a supports a number of MIDI System Exclusive (SysEx) messages
using the Antares manufacturer ID. (See the SysEx Appendix for details.)
The ATR-1a SysEx device number is similar to the Device ID found in SysEx
Real Time and Non-Real Time messages. By setting each unit to a different
device number, up to sixteen ATR-1as can be independently controlled
with System Exclusive messages.
Values for the Device Number range from 0 to 15.
Owner Message Page
Edit Owner Name:
aaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaa
This page is briefly displayed when the ATR-1a is powered on. This is
where you can show the world just how clever you can be in 20 characters.
Enter your message in exactly the same way that you enter Program and
Song names.
36

Chapter 5:
Creative Applications for the ATR-1a
The ATR-1a works on vocals so well you may think that’s all it can do.
Actually, lots of instruments can use it to great advantage. Fretless bass,
electric violin, trombone, even the theremin, all feature continuous pitch
potential, unconstrained by frets or keys. Here are some other ideas for
using your ATR-1a:
• Produce instant double tracking in one take! Record with two mics,
sending only one signal through the ATR-1a. If you’re going for a tight
double track, set the SPEED rather fast (page one in the PROGRAM
menu) and DETUNE the ATR-1a slightly (page six in the SYSTEM menu).
Increase both of these parameters to broaden the doubled effect. You
can also use some VIBRATO (page three in the PROGRAM menu) to
make a more dynamic effect (small depth and rate values are best, with
medium delay). Of course, you can also decide to record a single virgin
track, and bounce that to another, processing through the ATR-1a. This
way you can dial in the effect while auditioning the mix.
• Recording with two mics (as above) while improvising can also produce
heterophonic effects (the effect of two players and instruments playing
the ‘same’ melody, which actually varies with some different pitch
material). The more constrained your scale is in the ATR-1a, the more
variation there will be between the two performances.
• To set up a drone or ambient aura behind a melodic performance, try
sending some of the signal to the ATR-1a with an extremely constrained
scale (for example, in the key of C: C, F, G, A#) and then on to a lush,
long reverb. The effect produced will be a steady backdrop of chanting
tones behind the main melodic material.
• Don’t be afraid to use just as little of the ATR-1a as you need. It’s quite
possible that a performer has really quite good intonation, but fails
consistently on one or two notes. In this case, use the ATR-1a’s individual BYPASS function (page two, bottom line in the PROGRAM mode)
to bypass all the notes except the one(s) which need the retuning. This
way , the ATR-1a is working in a completely transparent mode, and only
when needed.
37

• The ATR-1a can be used to simulate other singing styles. Many ethnic
styles feature exceptional (almost unbelievable) intonation during fast,
melismatic passages. Setting the SPEED parameter faster than normal
(less than 5), and setting the SCALE to an appropriately exotic mode
(for example, G A A# C# D D# F#) can produce exactly this result (if the
singer improvises with sufficient global panache.)
• You can also create ‘impossible’ effects (like very fast octave leaps) by
creating a SCALE of only one note and setting the SPEED medium fast
(~5). Using a foot pedal, enter bypass mode before beginning the
performance, then engage the ATR-1a while singing an interval of a
fifth or more from the Scale note, and then re-enter Bypass Mode to
continue with the normal performance. This effect can sound quite like
the abruptly beautiful vocal ornaments of the Pygmies.
• Use the Vibrato function to introduce strange, synthetic mannerisms
to your performance. Try the SQUARE or SAW wave with DEPTH of 100,
a RATE which relates to the tempo of the music, and, if you don’t want
to sound constantly hysterical, sufficient DELAY time so that the effect
only happens when you hold out longer notes.
• If you perform with a MIDI sequencer, use the MIDI functions of the
ATR-1a to completely automate the Auto-Tune functions. There are
many ways to do this (all setup parameters are in the SYSTEM menu):
Use MIDI program changes to select the proper ATR-1a programs.
38
Use a continuous MIDI controller to adjust the SPEED parameter.
Use MIDI note data on a dedicated MIDI channel to dynamically
adjust the ATR-1a SCALE settings. The note durations should be
completely legato (no space between ‘chords’) or use the SUSTAIN
pedal to keep the current Scale engaged.
Program the melody with MIDI notes, Pitch Bend and Mod Wheel
data to sound exactly as you want and excercise complete control
over the performer to achieve the precise performance you
imagine. Don’t tell the performer. (Just kidding.)
• Karaoke! Create a Program with a chromatic scale and a Speed setting
of 10–15 to tune up sustained notes while letting everything else
through unaffected. This will work for singers who can manage to stay
within a half semitone of the correct pitch. (If they get farther off than
that, they will be tuned to the wrong note.) Prepare multiple versions
of this Program with different Vibrato settings to help out singers who
don’t use vibrato. Although it’s not always possible, allowing the singer
to monitor the unprocessed signal (maybe through headphones?) will
make things easier for them.

• Use the MIDI Note function to create amazing ornamental flourishes
and trills. Connect a MIDI keyboard and turn on the MIDI Note func-
tion. Set a fast Speed and sing a sustained note while playing the
keyboard. Go crazy!
• While the ATR-1a is not really intended to be a harmonizer, you can
create some very high quality close two-part harmony by singing one
part and using the MIDI Note function to retune what you sing to the
appropriate harmony notes.
39

Appendix
Factory Programs
The ATR-1a comes from the factory pre-programmed with the basic
chromatic, major, and natural minor scales in Programs 1–13 as
listed below. You are, of course, free to overwrite these as you desire.
PROGRAM MAJOR SCALE NATURAL MINOR SCALE
1 (Chromatic)
2 C Major A Minor
3D /C Major B /A Minor
4 D Major B Minor
5E /D Major C Minor
6 E Major D /C Minor
40
7 F Major D Minor
8G /F Major E /D Minor
9 G Major E Minor
10 A /G Major F Minor
11 A Major G /F Minor
12 B /A Major G Minor
13 B Major A /G Minor
14 user defined user defined
… user defined user defined
50 user defined user defined

Scale and Chord Guides
Here are some of the most commonly used scales, modes and chords,
and their associated ATR-1a settings. All spellings use sharps because the
ATR-1a software uses sharps to describe all accidentals (the black notes
on the keyboard).
Scales/Modes reference chart
While the major scale needs no introduction, the others might need some
explanation. For example, the difference between the natural and harmonic minor is only one note, the seventh scale degree. The natural minor
uses a flat seventh and is typically found in most jazz and pop styles. The
harmonic minor uses the raised seventh, sometimes called the ‘leading
tone,’ and is used in classical music styles. The raised seventh also produces
a large interval between the sixth scale degree and the seventh (an
augmented second or three semitones) — this sound is featured often in
Middle Eastern styles. The dorian mode is used in popular music styles
because of the opportunity to use a major subdominant chord in a minor
key (i.e., using an A Major chord in the key of E Minor). The phrygian
mode, which features a lowered second scale degree as its most distinctive
characteristic, is seldom used in popular music, though found fairly often
in world music styles. The mixolydian mode is basically the major scale
with a lowered seventh scale degree, and is often used in rock music.
41

Scales/Modes reference chart
KEY MAJOR NATURAL MINOR
C C D E F G A B C D D# F G G# A#
C /D C D F F G A CC
D D E F G A B C
D /E D F G G A C D D F F G A B C
E E F G A B C D
F F G A A C D E F G G A C C D
F /G F G A B C D FF
G G A B C D E F
G /A G A C C D F G G A B C D E F
A A B C D E F G
A /B A C D D F G A A C C D F F G
B B C D E F G A
Chord reference chart
D
E F G A B
D E F G A A C
E F G A B C D
G
A B C D E
G A A C D D F
A B C D E F G
B C D E F G A
42
KEY MAJOR SEVENTH MAJOR SEVENTH
C C E G C E G A
C /D C F G
D D F AD F
D /E D G A
E E G BE G
F F A C F A C D
F /G F A C
G G B D G B D F G B D F
G /A G C D
A A C EA C
A /B A D F A D F G
B B D F
(7) (MAJ 7)
C F G BC
A C D F A C
D G A C
B D E G B D
F A C EF
C E G B
F G C
D G A D
F A C E
A C
F
G C D F
B D F AB D
E G A C E G
G C D G
A D F A
F A

HARMONIC MINOR DORIAN PHRYGIAN MIXOLYDIAN
C D D F G G BC D D
C D E F G A C C D E F G A BC
D E F G A A C
D F F G A B D D F F G A C C
E F G A B C D
F G G A C C EF G G
F G A B C D F F G A B C D EF
G A A C D D F
G A B C D E G G A B C D F F
A B C D E F G
A C C D F F AA
B C D E F G A
F G A A
D E F G A B C D D F G A A CD E F
E F G A B C D E F G A B C D E F G A B C D
A
G A A C D E F G G A C D D F G A B C D E F
A B C D E F GA A
C C D F G G
B C D E F G A B C D E F G A B C D E F G A
C D D
C C D F G G A
D E F G A B C D F F G A B
D E F G A B C
F F G A C C D
G A B C D E F G A B C D E
G A B C D E F
C D E F G A B C D E F G
A B C D F F G
C D E F G A A
G A B C
D F G G A C C
F G A A C D D
G A C C D F F
A C D D F G G
MINOR MINOR SEVENTH DIMINISHED DIMINISHED AUGMENTED
C D GC D
C E G
D F A D F A C D F G BD F G
D F A
E G B E G B D E G A C
F G CF G
F A C
G A DG A
G B D
A C E A C E G A C D F
A C FA
B D F
(M7) (DIM) SEVENTH (DIM7) (+)
G A
C E G BC
D F A BD
C D F AC D
E G A
F
A C D F A C
C D
F A C EF
D F G A C EG A
G B D F
F G B D F G B D
A C D
G B D F G B D F
C
B D F A B D F G
F G
A C E G A C E G
F A
C E G B C F A
CD F
E G A DE G
F A C E F A C
C
FG B D
A C D GA C
B D F A B D G
C E G
D G B
F A C
G C E
A D F
A
C
F
43

MIDI System Exclusive Message Formats
In the explanations, below, braces < > are used to represent enclosed MIDI
data bytes. Concatenated data is shown by < > < >. Names are also enclosed
in braces as symbolic representations defined further into the explanation.
Values are decimal unless an H is used to denote Hexadecimal values.
For example, the MIDI bytes to select song mode for DEVICE NUMBER 3 are:
F0H, 0, 1, 26H, 3, 1, F7H.
<sys ex message> = <F0H> <manufacturer> <device num>
<message bytes> <F7H>
<manufacturer> = <0 1 26H>
<device num> = one byte in range 0 to 15. Must match
SYSEX DEVICE NUMBER set in the ATR-1a.
<message bytes> = <0> to select program mode.
or <1> to select song mode.
or <2> bypass on
or <3> bypass off
or <4><14><system data>
or <5><31><program data>
or <6><34><song data>
<system data> =
<midi channel> 1 to 16, 0 = OMNI
<midi sustain> controller 0 = off, 1 = on
<program change> controller 0 = off, 1 = on
<midi note> controller 0 = off, 1 = on
<pitch bend> controller 0 = off, 1 = on
<mod wheel> controller 0 = off, 1 = on
<foot switch> 0 = BYPASS, 1 = STEP
<speed controller #> 14 to 31, 13 = OFF
<vibrato rate controller #> 14 to 31, 13 = OFF
<vibrato delay controller #> 14 to 31, 13 = OFF
<step controller #96> 0 = off, 1 = on
<sensitivity> 1 to 25
<detune> 0 to 100
<detune direction> 0 = make sharp, 1 = make flat
<program data> =
<program number> 1 to 50
<speed> 0 to 25
<scale 1>…<scale 12> for C, C#,…: 0=remove, 1 =tune, 2=bypass.
<vibrato type> 0 = off, 1 = SINE, 2 = SQUARE, 3 = SAW
<vibrato depth> 0 to 100 cents
<vibrato rate> 1 to 97 (.1 to 9.7 sec)
44

<vibrato delay> 0 to 25 (see DELAY TABLE, below)
<pgm name 1>…
<pgm name 13> all values between 32 (ASCII blank)
and 7FH
<song data> =
<song number> 1 to 20
<speed> 0 to 25
<vibrato type> 0 = off, 1 = SINE, 2 = SQUARE, 3 = SAW
<vibrato depth> 0 to 100 cents
<vibrato rate> 1 to 97 (.1 to 9.7 sec)
<vibrato delay> 0 to 25 (see DELAY TABLE, below)
<song name 1>…
<song name 13> all values between 32 (ASCII blank)
and 7FH
<program 1>…<program 15> 7CH = B Bypass
7DH = <- Loop
7EH = E End
7FH = -> Link
0 = (empty)
1 to 50 = program number
Transmitting <system data> causes values to be immediately used in the
ATR-1a. Transmitting <program data> or <song data> causes the data to be
put into the ATR-1a permanent memory, but the values do not take effect.
To have those data take effect, you can:
from the front panel:
in Song Mode: a new Song must be selected.
in Program Mode: a new Program must be selected.
from MIDI control:
in Program or Song Mode, send a MIDI program change message to
recall the affected Program or Song. Note that Song or Program downloads don’t change Modes. You must have the correct Mode selected
before transmitting a MIDI program change, or you must transmit a
SysEx message to change to Program or Song Mode, as appropriate.
Note: Due to the necessity of writing parameter changes to EEPROM, a delay of
at least 200 milliseconds is required after the transmission of Song,
Program or System parameter changes.
Note: The ATR-1a does not protect itself against SysEx parameters being out of
range. Unpredictable results may occur if out-of-range SysEx parameters
are received.
45

Vibrato Delay Table
The following table identifies the MIDI controller values required to set
each of the possible Vibrato Delay values:
MIDI VALUE VIBRATO DELAY
(milliseconds)
00
110
220
345
470
5 100
6 140
7 190
8 230
9 270
10 315
11 370
46
12 435
13 510
14 600
15 710
16 830
17 970
18 1140
19 1340
20 1575
21 1850
22 2170
23 2550
24 3000
25 3500

MIDI System Exclusive Message Examples
The following examples are Scripts from Opcode’s Galaxy. They show
System Exclusive Messages which communicate with the ATR-1a.
This message will cause the ATR-1a to select Program Mode.
Put $F0 into Sys_Ex;
Put 0 1 $26 into Antares;
Put 0 into Device_Num;
Put 0 into Mode;
Put $F7 into End_Sys_Ex;
Send Sys_Ex Antares Device_Num ¬
Mode ¬
End_Sys_Ex;
This message will cause the ATR-1a to select Song Mode.
Put $F0 into Sys_Ex;
Put 0 1 $26 into Antares;
Put 0 into Device_Num;
Put 1 into Mode;
Put $F7 into End_Sys_Ex;
Send Sys_Ex Antares Device_Num ¬
Mode ¬
End_Sys_Ex;
This message sets System data in the ATR-1a.
Put $F0 into Sys_Ex;
Put 0 1 $26 into Antares;
Put $F7 into End_Sys_Ex;
Put 0 into Device_Num;
Put 4 into Mode;
Put 14 into Msg_Length;
Put 0 into MIDI_Channel;
Put 0 into MIDI_Sustain;
Put 0 into Pgm_Change;
Put 0 into MIDI_Note;
Put 0 into Pitch_Bend;
Put 0 into Mod_Wheel;
Put 0 into Foot_Switch;
Put 13 into Speed_Controller;
Put 13 into Vib_Rate_Controller;
Put 13 into Vib_Delay_Controller;
47

Put 0 into Step_Controller;
Put 7 into Sensitivity;
Put 0 into Detune;
Put 0 into Detune_Direction;
Send Sys_Ex Antares Device_Num Mode Msg_Length ¬
MIDI_Channel MIDI_Sustain Pgm_Change ¬
MIDI_Note Pitch_Bend Mod_Wheel ¬
Foot_Switch Speed_Controller Vib_Rate_Controller ¬
Vib_Delay_Controller Step_Controller Sensitivity ¬
Detune Detune_Direction¬
End_Sys_Ex;
This message sets Program data in the ATR-1a.
Put $F0 into Sys_Ex;
Put 0 1 $26 into Antares;
Put $F7 into End_Sys_Ex;
Put 0 into Device_Num;
Put 5 into Mode;
Put 31 into Msg_Length;
Put 28 into Pgm_Number;
Put 7 into Speed;
Put 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 into Scale;
Put 0 into Vib_Type;
Put 28 into Vib_Depth;
Put 53 into Vib_Rate;
Put 11 into Vib_Delay;
Put “My Test name.” into Name;
48
Send Sys_Ex Antares Device_Num Mode Msg_Length ¬
Pgm_Number Speed Scale Vib_Type Vib_Depth ¬
Vib_Rate Vib_Delay Name ¬
End_Sys_Ex;
This message sets Song data in the ATR-1a.
Put $F0 into Sys_Ex;
Put 0 1 $26 into Antares;
Put $F7 into End_Sys_Ex;
Put 0 into Device_Num;
Put 6 into Mode;
Put 34 into Msg_Length;
Put 5 into Song_Number;
Put 7 into Speed;

Put 0 into Vib_Type;
Put 28 into Vib_Depth;
Put 53 into Vib_Rate;
Put 11 into Vib_Delay;
Put “My test name.” into Name;
Put 10 11 12 0 $7c $7d $7e $7f 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 into
Programs;
Send Sys_Ex Antares Device_Num Mode Msg_Length ¬
Song_Number Speed Vib_Type Vib_Depth Vib_Rate ¬
Vib_Delay Name Programs ¬
End_Sys_Ex;
49

MIDI Implementation Chart
Model: ATR-1a, version 1.13
FUNCTION TRANSMITTED RECOGNIZED REMARKS
Basic Channel Default M 1–16 Memorized
Mode Default MMModes not used
Note Number M 0–127
Velocity Note On MM
After Touch Keys MM
Pitch Bend Mm
Control Change MmModulation wheel
Program Change Mm1–50 Programs
Changed M 1–16
Messages MM
Altered MM
True voice M 33–96 Pitches retuned
Note Off MM
Channel MM
MmSustain foot switch
MmPitch Bend
M 14–31 Continuous Control
SPEED Control
VIBRATO RATE
VIBRATO DELAY
MmData increment
True number Mm1–20 Songs
50
System Exclusive MmSystem, Program and
Song parameters
System Common Song Position MM
Song Select MM
Tune Request MM
System Real Time Clock MM
Commands MM
Aux Messages Local On/Off MM
All Notes Off MM
Active Sensing MM
System Reset MM
m
= YES M = NO

ATR-1a Specifications
Data format 20-bit linear
Sample rate 46.875 kHz
Frequency response 10Hz–20kHz, +0.06dB/-0.23dB
Distortion + Noise Less than 0.005% (@1kHz)
ADC 20 bit
DAC 24 bit
Inputs XLR: Balanced, 17.9 dBu, 40kΩ
Outputs XLR: Balanced, 17.7 dBu, 470Ω
Controls Data Encoder
Displays 2x20 character LCD
Input power 10.5VAC, 17.25 VAC (x 2)
Power consumption 15 watts
Included accessories Power supply, owner ’s manual
Dimensions Width: 19 inches x height: 1.75 inches x depth: 5 inches
Weight Rack: 4 lbs.
56-bit internal processing
103 dB Dynamic Range (A weighted)
97 dB S/(N+D)
105 dB Dynamic Range (A weighted)
94 dB S/(N+D)
1/4 inch Phone: TRS Balanced, 17.9 dBu, 40kΩ
Unbalanced, 17.9 dBu, 40kΩ
MIDI In: 5-Pin DIN
Footswitch: 1/4 inch Phone
1/4 inch Phone: Unbalanced, 17.7 dBu, 470Ω
TRS Balanced, 11.7 dBu, 470Ω
Cursor Control
Program/Song Edit
Page Select
System Edit
Bypass
Pitch Correction Indicator (LED x 10)
Input Level Indicator (LED x 6)
50Hz or 60Hz
Power supply: 1.3 lbs.
Specifications subject to change without notice.
51

Index
A
AC power input 19
ATR-1, defined 9
Auto-Tune Plug-In 9
B
Back Panel 19
Bass Mode Page 31
Bend 34
BYPASS Button 18
C
cents, defined 11
Cents to Hertz relative chart 32
Channel parameter 33
Chord reference chart 42
Creative applications for the ATR-1 37
Cursor buttons 17
D
Data entry knob 17
Detune 32, 37
Detune parameter 32
Display Screens and Menu Pages 20
Dly (Delay) control 26
double tracking 37
Dpth (Depth) control 26
Dr. Andy 7
E
Email address 6
Equal Tempered Scale 11
F
Factory Programs 40
Firmware version 20
Flash Screen 20
Foot Switch 19, 32
Foot Switch and Detune Page 32
Detune parameter 32
Foot_Switch parameter 32
Foot_Switch parameter 32
Front Panel 17
G
Grounding 15
H
Hertz (Hz.) 10
heterophonic effects 37
Hildebrand, Andy 7
I
Introducing the ATR-1 9
K
Karaoke! 38
L
LCD 17
LCD parameter 32
Line inputs, balanced 19
Line outputs 19
52

M
Make Scale From MIDI Page 23
MIDI Implementation Chart 50
MIDI IN 19
MIDI Page 1 33
Channel parameter 33
Individual MIDI channels 1–16 33
Note field 33
OMNI 33
Sustain parameter 34
MIDI Page 2 34
Bend 34
Mod_Whl (Mod Wheel) 34
Pgm_Chg (Program Change) 34
MIDI Page 3 35
Speed parameter 35
Step parameter 35
MIDI Page 4 35
Delay 35
Vibrato Rate 35
MIDI Page 5 36
SysEx device number 36
MIDI System Exclusive Message Examples 47
MIDI System Exclusive Message Formats 44
Mod_Whl (Mod Wheel) 34
Mode Pages 20
N
Naming
available characters 27, 30
Note field 33
O
OMNI 33
Owner Message Page 36
P
PAGE Button 17
Panel Controls and Connectors 17
Pgm_Chg (Program Change) 34
Pitch 10
correction 12
detection 11
perception 10
ratios 11
PITCH CHANGE Meter 18
Power Switch, non-existent 17
Program Edit Pages 22
Program Mode 13, 20
Program Mode Main Screen 20
Program Name Page 27
PROGRAMS Button 17
R
Rt (Rate) control 26
S
Save Program Page 27
Save Song Page 30
Scale and Chord Guides 41
Scale Page 24
Blank 25
Bypass 25
Tune 25
Why set Scale notes to “Blank”? 25
Scales 12
Scales/Modes reference chart 42
semitone, defined 11
Sensitivity and LCD Page 31
Sensitivity parameter 31
setting display contrast 32
Sensitivity parameter 31
Setting Up the ATR-1 15
SIGNAL LEVEL Meter 18
Song Edit Pages 27
Song Items Page 28
Song Mode 14
Song Mode Main Screen 21
to select a Song 21
Song Name Page 30
Song Speed Page 28
53

Song Step Items 22, 28
## (A Program Number) 28
-> (Link) 29
<- (Loop) 29
0 (No Program) 29
B (Bypass) 28
E (End) 29
Song Vibrato Page 29
Specifications 51
Speed 12
Speed Page 23
Speed parameter 35
Sustain parameter 34
SYSTEM button 18, 30
System Edit Pages 30
T
Technical Support 6
V
Vibrato 12
Vibrato Delay table 46
Vibrato Page 26
Dly (Delay) control 26
Dpth (Depth) control 26
Rt (Rate) control 26
W
waveform examples 10
54
 Loading...
Loading...