a
Audio Processor
SST-Melody®-DAP
FEATURES
16-Bit Fixed-Point Audio Processor (DSP-Based)
Decodes Major Standard Audio Formats
Fixed-Point Implementation for
Using 16-Bit
Decoding:
MPEG 1 Layer I, II, and III (MP3)
AAC 2-Channel Low Complexity
Microsoft WMA
Speech Codecs: MGSM, G.723.1, and Audible Audio
2 Independent Data Address Generators
Powerful Program Sequencer Provides Zero Overhead
Looping Conditional Instruction Execution Programmable 16-Bit Interval Timer with Prescaler 100-Lead
LQFP and 144-Ball Mini-BGA
Supports Postprocessing:
Jazz/Rock/Classic/Pop/Bass
3-Band User Customizable Graphic Equalizer
Supports Major Storage Formats:
SmartMedia Card
DataPlay
SD Card
NAND Flash
Supports DRM (Digital Rights Management) Technologies:
Liquid Audio SP3
Microsoft DRM
DataPlay ContentKey
Supports Standard APIs:
Start Play
Stop Play
Mute Play
Resume Play
Download Song to Flash
Forward to Next Song
Rewind to Previous Song
Delete a Song
Bass/Equalizer
Erase MP3 Flash
Upload Song/Voice from Flash
Rename Flash
Start Record
Stop Record
Report
Get File Information
Seek File
List Number of Songs
Request Song Name
List Number of Voices
Request Voice Note Name
Start Record (G.723.1)
Stop Record (G.723.1)
Start Play (G.723.1)
Stop Play (G.723.1)
(continued on page 2)
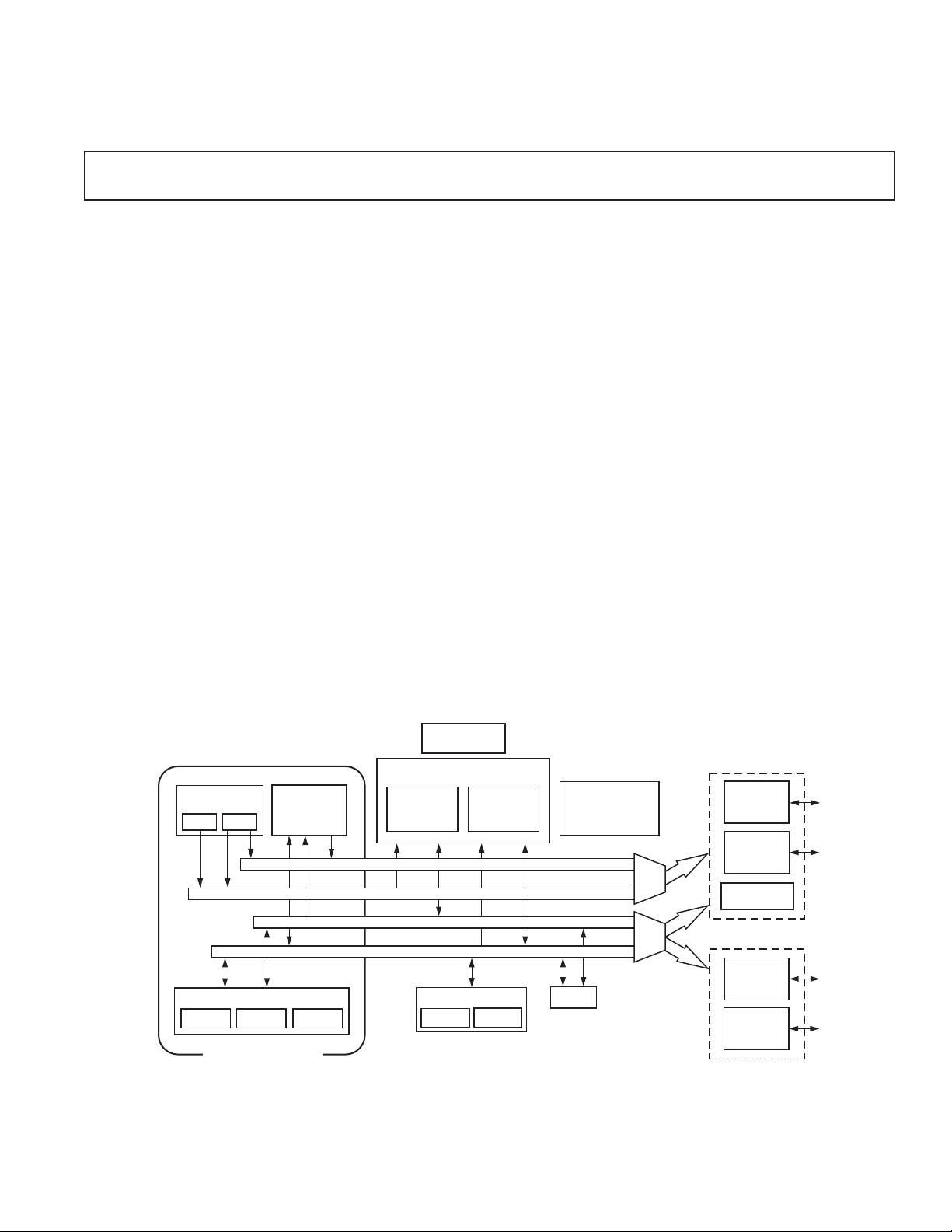
FUNCTIONAL BLOCK DIAGRAM
POWER -DOWN
CONTROL
MEMORY
DATA ADDRESS
GENERATORS
DAG2
DAG1
ARITHMETIC UNITS
ALU
ADSP-2100 BASE
ARCHITECTURE
MAC
PROGRAM
SEQUENCER
SHIFTER
PROGRAM MEMORY ADDRESS
DATA MEMORY ADDRESS
PROGRAM MEMORY DATA
DATA MEMORY DATA
PROGRAM
MEMORY
16K 24 BIT
SERIAL PORTS
SPORT0
REV. 0
Information furnished by Analog Devices is believed to be accurate and
reliable. However, no responsibility is assumed by Analog Devices for its
use, nor for any infringements of patents or other rights of third parties that
may result from its use. No license is granted by implication or otherwise
under any patent or patent rights of Analog Devices.
FULL MEMORY MODE
DATA
MEMORY
16K 16 BIT
SPORT1
One Technology Way, P.O. Box 9106, Norwood, MA 02062-9106, U.S.A.
Tel: 781/329-4700www.analog.com
Fax: 781/326-8703 © Analog Devices, Inc., 2002
PROGRAMMABLE
I/O
AND
FLAGS
TIMER
EXTERNAL
ADDRESS
BUS
EXTERNAL
DATABUS
BYTE DMA
CONTROLLER
OR
EXTERNAL
DATABUS
INTERNAL
DMA
PORT
HOST MODE

SST-Melody-DAP
Mute Play (Voice)
Resume Play (Voice)
Download Voice to Flash
Forward to Next Record
Rewind to Previous Record
Delete a Record
Erase Voice Flash
Version Reporting (G.723.1)
Get G.723.1 Record Information
Rename Voice File
Format Flash
Volume Control
Get Song Name
Get Album Name
Get Singer Name
Get Song Duration
Version Reporting
Supports PC Interface
USB 1.1 Interface
Parallel Port Interface
Other Features:
ID3 Tag Support
SDMI Capable
PERFORMANCE
13.3 ns Instruction Cycle Time @ 2.5 V (Internal)
75 MIPS Sustained Performance
Single-Cycle Instruction Execution
Single-Cycle Context Switch
3-Bus Architecture Allows Dual Operand Fetches in
Every Instruction Cycle
Multifunction Instructions
Power-Down Mode Featuring Low CMOS Standby Power
Dissipation with 200 CLKIN Cycle Recovery from
Power-Down Condition
Low Power Dissipation in Idle Mode
INTEGRATION
ADSP-2100 Family Code Compatible (Easy to Use
Algebraic Syntax), with Instruction Set Extensions
80 Kbytes of On-Chip RAM, Configured as 16K Words
Program Memory RAM
16K Words Data Memory RAM
Dual-Purpose Program Memory for Both Instruction and
Data Storage
Independent ALU, Multiplier/Accumulator, and Barrel
Shifter Computational Units
SYSTEM INTERFACE
Flexible I/O Structure Allows 2.5 V or 3.3 V Operation;
All Inputs Tolerate up to 3.6 V Regardless of Mode
16-Bit Internal DMA Port for High Speed Access to
On-Chip Memory (Mode Selectable)
4 MByte Memory Interface for Storage of Data Tables
and Program Overlays (Mode Selectable)
8-Bit DMA to Byte Memory for Transparent Program
and Data Memory Transfers (Mode Selectable)
I/O Memory Interface with 2048 Locations Supports
Parallel Peripherals (Mode Selectable)
Programmable Memory Strobe and Separate I/O
Memory Space Permits “Glueless” System Design
Programmable Wait State Generation
Two Double-Buffered Serial Ports with Companding
Hardware and Automatic Data Buffering
Automatic Booting of On-Chip Program Memory from
Byte-Wide External Memory, e.g., EPROM, or
through Internal DMA Port
Six External Interrupts
13 Programmable Flag Pins Provide Flexible System
Signaling
UART Emulation through Software SPORT
Reconfiguration
ICE-Port™ Emulator Interface Supports Debugging in
Final Systems
ICE-Port is a trademark of Analog Devices, Inc.
REV. 0–2–

TABLE OF CONTENTS
SST-Melody-DAP
FEATURES . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1
FUNCTIONAL BLOCK DIAGRAM . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1
GENERAL DESCRIPTION . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4
SPECIFICATIONS . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4
Instruction Set Description . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4
RECOMMENDED OPERATING CONDITIONS . . . . . . . 4
ELECTRICAL CHARACTERISTICS . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5
ABSOLUTE MAXIMUM RATINGS . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6
ORDERING INFORMATION . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6
100-LEAD LQFP PIN CONFIGURATION . . . . . . . . . . . . 6
PIN FUNCTION DESCRIPTIONS . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7
TIMING SPECIFICATIONS . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7
GENERAL NOTES . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7
TIMING NOTES . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7
MEMORY TIMING SPECIFICATIONS . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 8
FREQUENCY DEPENDENCY FOR
TIMING SPECIFICATIONS . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 8
POWER DISSIPATION . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 8
Output Drive Currents . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 8
Capacitive Loading . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 9
SOFTWARE ARCHITECTURE . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 10
ARCHITECTURE OVERVIEW . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 10
Serial Ports . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 11
PIN DESCRIPTIONS . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 11
Common-Mode Pins . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 12
Memory Interface Pins . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 13
Full Memory Mode Pins (Mode C = 0) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 13
Host Mode Pins (Mode C = 1) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 13
Interrupts . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 15
LOW POWER OPERATION . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 15
Power-Down . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 15
Idle . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 15
Slow Idle . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 15
SYSTEM INTERFACE . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 16
Clock Signals . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 16
RESET . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 17
Power Supplies . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 17
MODES OF OPERATION . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 17
Setting Memory Mode . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 17
Passive Configuration . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 17
Active Configuration . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 18
IACK Configuration . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 19
MEMORY ARCHITECTURE . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 19
Program Memory . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 19
Data Memory . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 19
Memory Mapped Registers (New to the
SST-Melody-DAP) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 20
I/O Space (Full Memory Mode) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 20
Composite Memory Select (CMS) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 20
Byte Memory Select (BMS) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 20
Byte Memory . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 20
Byte Memory DMA (BDMA, Full Memory Mode) . . . . . 20
Internal Memory DMA Port (IDMA Port; Host Memory
Mode) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 21
Bootstrap Loading (Booting) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 22
IDMA Port Booting . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 22
Bus Request and Bus Grant . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 22
Flag I/O Pins . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 22
OUTLINE DIMENSIONS
100-Lead Metric Thin Plastic Quad Flatpack
(LQFP) (ST-100) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 23
Tables
Table I. Memory Timing Specifications . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 8
Table II. Environmental Conditions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 8
Table III. Power Dissipation Example . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 8
Table IV. Pin Terminations . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 13
Table V. Interrupt Priority and Interrupt Vector Addresses . 15
Table VI. Modes of Operation . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 17
Table VII. PMOVLAY Bits . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 18
Table VIII. DMOVLAY Bits . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 19
Table IX. Wait States . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 20
Table X. Data Formats . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 21
REV. 0
–3–

SST-Melody-DAP
GENERAL DESCRIPTION
The SST-Melody-DAP is a single-chip microcomputer optimized for digital signal processing (DSP) and other high speed
numeric processing applications.
The SST-Melody-DAP combines the ADSP-2100 family base
architecture (three computational units, data address generators, and a program sequencer) with two serial ports, a 16-bit
internal DMA port, a byte DMA port, a programmable timer,
flag I/O, extensive interrupt capabilities, and on-chip program
and data memory.
The SST-Melody-DAP integrates 80 Kbytes of on-chip
memory configured as 16K words (24-bit) of program RAM,
and 16K words (16-bit) of data RAM. Power-down circuitry is
also provided to meet the low power needs of battery-operated
portable equipment. The SST-Melody-DAP is available in a
100-lead LQFP package and 144-ball mini-BGA.
In addition, the SST-Melody-DAP supports new instructions, which include bit manipulations—bit set, bit clear, bit
toggle, bit test—new ALU constants, new multiplication
instruction (x squared), biased rounding, result-free ALU
operations, I/O memory transfers, and global interrupt masking, for increased flexibility. Fabricated in a high speed, low
power, CMOS process, the SST-Melody-DAP operates with a
13.3 ns instruction cycle time. Every instruction can execute in
a single processor cycle.
The SST-Melody-DAP’s flexible architecture and comprehensive instruction set allow the processor to perform multiple
operations in parallel. In one processor cycle, the SST-MelodyDAP can:
• Generate the next program address
• Fetch the next instruction
• Perform one or two data moves
• Update one or two data address pointers
• Perform a computational operation
This takes place while the processor continues to:
• Receive and transmit data through the two serial ports
• Receive and/or transmit data through the internal DMA port
• Receive and/or transmit data through the byte DMA port
• Decrement timer
Instruction Set Description
The SST-Melody-DAP assembly language instruction set has
an algebraic syntax that was designed for ease of coding and
readability.
The assembly language, which takes full advantage of the
processor’s unique architecture, offers the following benefits:
• The algebraic syntax eliminates the need to remember cryptic
assembler mnemonics. For example, a typical arithmetic add
instruction, such as AR = AX0 + AY0, resembles a simple
equation.
• Every instruction assembles into a single, 24-bit word that
can execute in a single instruction cycle.
• The syntax is a superset ADSP-2100 family assembly language and is completely source and object code compatible
with other family members. Programs may need to be relocated to utilize on-chip memory and conform to the
SST-Melody-DAP’s interrupt vector and reset vector map.
• Sixteen condition codes are available. For conditional
jump, call, return, or arithmetic instructions, the condition
can be checked and the operation executed in the same
instruction cycle.
• Multifunction instructions allow parallel execution of an
arithmetic instruction with up to two fetches or one write to
processor memory space during a single instruction cycle.
SPECIFICATIONS
RECOMMENDED OPERATING CONDITIONS
K Grade B Grade
Parameter Min Max Min Max Unit
V
DDINT
V
DDEXT
V
INPUT
T
AMB
Specifications subject to change without notice.
2.37 2.63 2.25 2.75 V
2.37 3.6 2.25 3.6 V
VIL = –0.3 VIH = +3.6 VIL = –0.3 VIH = +3.6 V
0 +70 –40 +85 °C
REV. 0–4–

SST-Melody-DAP
ELECTRICAL CHARACTERISTICS
K/B Grades
Parameter Test Conditions Min Typ Max Unit
V
Hi-Level Input Voltage
IH
VIHHi-Level CLKIN Voltage @ V
VILLo-Level Input Voltage
VOHHi-Level Output Voltage
VOLLo-Level Output Voltage
I
Hi-Level Input Current
IH
I
Lo-Level Input Current
IL
I
Three-State Leakage Current7@ V
OZH
I
Three-State Leakage Current7@ V
OZL
I
Supply Current (Idle)
DD
I
Supply Current (Dynamic)
DD
I
Supply Current (Power-Down)11@ V
DD
C
Input Pin Capacitance
I
COOutput Pin Capacitance
NOTES
1
Bidirectional pins: D0–D3, RFS0, RFS1, SCLK0, SCLK1, TFS0, TFS1, A1–A13, PF0–PF7
2
Input only pins: RESET, BR, DR0, DR1, PWD.
3
Input only pins: CLKIN, RESET, BR, DR0, DR1, PWD
4
Output pins: BG, PMS, DMS, BMS, IOMS, CMS, RD, WR, PWDACK, A0, DT0, DT1, CLKOUT, FL2–0, BGH
5
Although specified for TTL outputs, all ADSP-2185M outputs are CMOS compatible and will drive to V
6
Guaranteed but not tested
7
Three-statable pins: A0–A13, D0–D23, PMS, DMS, BMS, IOMS, CMS, RD, WR, DT0, DT1, SCLK0, SCLK1, TFS0, TFS1, RFS0, RFS1, PF0–PF7
8
0 V on BR
9
IDD measurement taken with all instructions executing from internal memory. 50% of the instructions are multifunctional (types 1, 4, 5, 12, 13, 14), 30% are type 2
and type 6, and 20% are idle instructions.
10
VIN = 0 V and 3 V. For typical figures for supply currents, refer to Power Dissipation section.
11
See Chapter 9 of the ADSP-2100 Family User’s Manual (3rd Edition, 9/95) for details.
12
Output pin capacitance is the capacitive load for any three-stated output pin.
Specifications subject to change without notice.
1, 2
1, 3
1, 4, 5
1, 4, 5
3
3
9
3, 6
6, 7, 11, 12
@ V
@ V
@ V
@ V
@ V
@ V
@ V
@ V
@ V
@ V
9
@ V
@ V
= max
DDINT
= max
DDINT
= min
DDINT
= min, IOH = –0.5 mA
DDEXT
= 3.0 V, IOH = –0.5 mA
DDEXT
= min, IOH = –100 mA
DDEXT
= min, IOL = 2 mA
DDEXT
= max, VIN = 3.6 V 10
DDINT
= max, VIN = 0 V 10
DDINT
= max, VIN = 3.6 V
DDEXT
= max, VIN = 0 V
DDEXT
= 2.5, t
DDINT
= 2.5, t
DDINT
= 2.5, 15 ns10, T
DDINT
= 2.5, 13.3 ns10, T
DDINT
= 2.5, T
DDINT
Power Mode
@ VIN = 2.5 V, fIN = 1.0 MHz, T
@ VIN = 2.5 V, fIN = 1.0 MHz, T
8
8
= 15 ns
CK
= 13.3 ns
CK
AMB
AMB
= 25°C in Lowest
AMB
1.5 V
2.0 V
0.7 V
2.0 V
2.4 V
6
V
– 0.3 V
DDEXT
0.4 V
A
A
10
10
A
A
9mA
10 mA
= 25°C
= 25°C
35 mA
38 mA
100 A
= 25°C8pF
AMB
= 25°C8pF
AMB
and GND, assuming no dc loads.
DDEXT
REV. 0
–5–
SST-Melody-DAP
WARNING!
ESD SENSITIVE DEVICE
ABSOLUTE MAXIMUM RATINGS
Internal Supply Voltage (V
Internal Supply Voltage (V
Input Voltage
2
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . –0.5 V to +4.0 V
Output Voltage Swing
DDINT
DDEXT
3
. . . . . . . . . . –0.5 V to V
1
) . . . . . . . . . –0.3 V to +3.0 V
) . . . . . . . . . –0.3 V to +4.0 V
+ 0.5 V
DDEXT
Operating Temperature Range . . . . . . . . . . . –40°C to +85°C
Storage Temperature Range . . . . . . . . . . . . –65°C to +150°C
Lead Temperature (5 sec) LQFP . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 280°C
NOTES
1
Stresses above those listed under Absolute Maximum Ratings may cause
permanent damage to the device. This is a stress rating only and functional
operation of the device at these or any other conditions above those listed in the
operational sections of this specification is not implied. Exposure to absolute
maximum rating conditions for extended periods may affect device reliability.
2
Applies to bidirectional pins (D0–D3, RFS0, RFS1, SCLK0, SCLK1, TFS0,
TFS1, A1–A13, PF0–PF7) and input only pins (CLKIN, RESET, BR, DR0,
DR1, PWD)
3
Applies to output pins (BG, PMS, DMS, BMS, IOMS, CMS, RD, WR,
PWDACK, A0, DT0, DT1, CLKOUT, FL2–0, BGH)
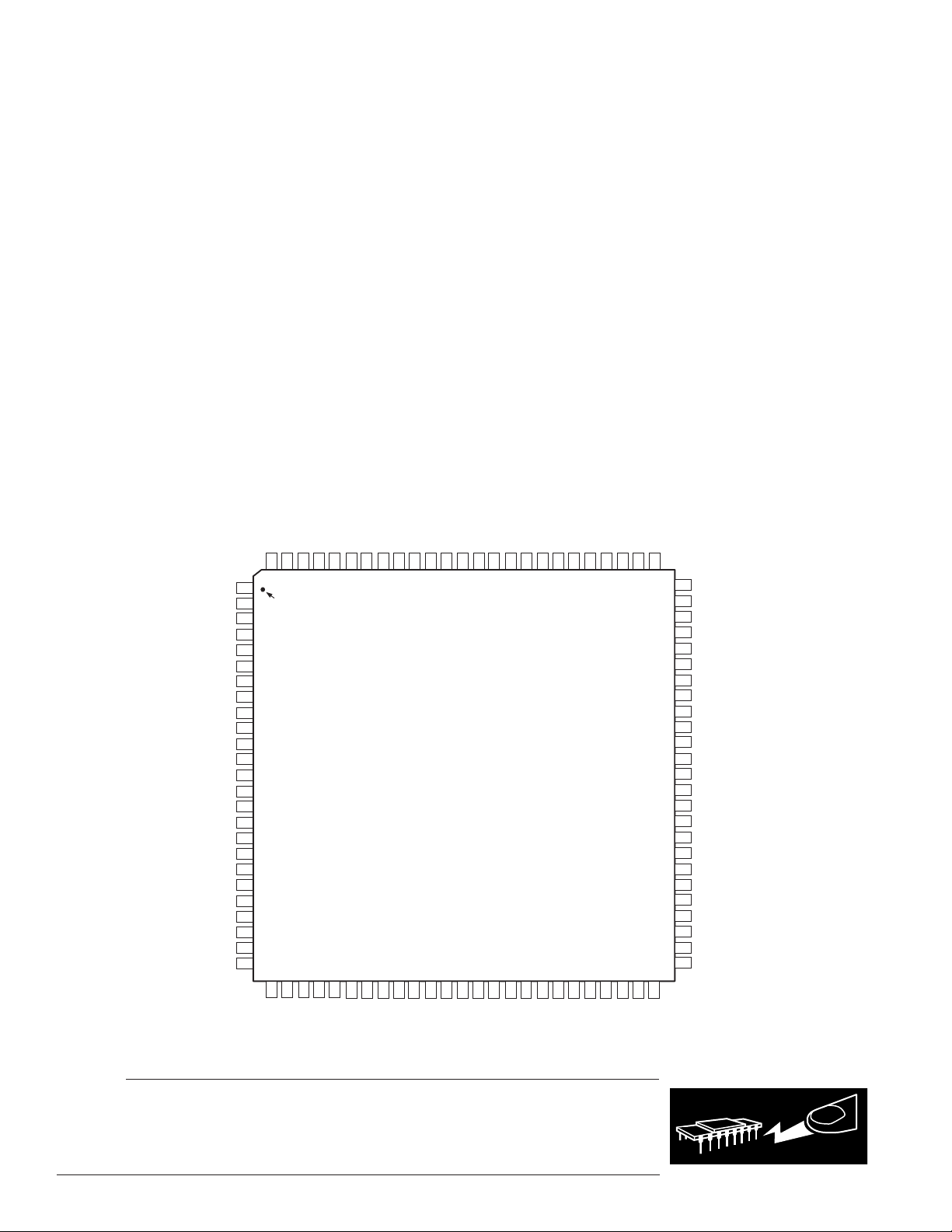
100-LEAD LQFP
PIN CONFIGURATION
DDEXT
V
GND
PWD
PF2 [MODE C]
929190
89
SST-Melody-DAP
TOP VIEW
(Not to Scale)
SCLK0
DDEXT
V
37
DT1/FO
343536
DR0
A4/IAD3
A5/IAD4
GND
A6/IAD5
A7/IAD6
A8/IAD7
A9/IAD8
A10/IAD9
A11/IAD10
A12/IAD11
A13/IAD12
GND
CLKIN
XTAL
V
DDEXT
CLKOUT
GND
V
DDINT
WR
BMS
DMS
PMS
IOMS
CMS
RD
A3/IAD2
A2/IAD1
A1/IAD0A0PWDACK
99989796959493
100
1
PIN 1
2
IDENTIFIER
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
262827
GND
IRQE+PF4
IRQL0+PF5
29
IRQL1+PF6
30
IRQ2+PF7
BGH
PF0 [MODE A]
PF1 [MODE B]
31
33
32
DT0
TFS0
RFS0
ORDERING INFORMATION
The Analog Devices SST-Melody-DAP Reference Design
must be ordered under the part number ADSST-MelodySDK for the
standalone reference design. This includes the
evaluation board with an evaluation copy of the software and
schematics.
Designers of products using this reference design also will be
required to sign a license agreement with the respective license
holder––
i.e., Digital Theater Systems (DTS), Dolby Laboratories, THX Ltd., Microsoft, or SRS Labs––to use the
appropriate code and produce proof to Analog Devices of
having successfully completed the appropriate licensing procedures before final products can be
shipped to them. The final
product will be shipped from Analog Devices and will include
the decoder chipset and software; customers will be required to
sign license agreements with Analog Devices and separately pay
system royalties to the respective license holder.
PF3 [MODE D]
FL0
FL1
FL2
D23
D22
D21
D20
GND
D19
D18
D17
8786858483
88
39
40
38
DR1/FI
TFS1/IRQ1
RFS1/IRQ0
414243
GND
SCLK1
81
82
4445464748
EMS
RESET
ERESET
79
80
EE
ECLK
78
77
49
ELIN
ELOUT
D16
76
50
EINT
75
74
73
72
71
70
69
68
67
66
65
64
63
62
61
60
59
58
57
56
55
54
53
52
51
D15
D14
D13
D12
GND
D11
D10
D9
V
DDEXT
GND
D8
D7/IWR
D6/IRD
D5/IAL
D4/IS
GND
V
DDINT
D3/IACK
D2/IAD15
D1/IAD14
D0/IAD13
BG
EBG
BR
EBR
CAUTION
ESD (electrostatic discharge) sensitive device. Electrostatic charges as high as 4000 V readily
accumulate on the human body and test equipment and can discharge without detection. Although
SST-Melody-DAP
the
features proprietary ESD protection circuitry, permanent damage may
occur on devices subjected to high energy electrostatic discharges. Therefore, proper ESD
precautions are recommended to avoid performance degradation or loss of functionality.
REV. 0–6–
SST-Melody-DAP
The LQFP package pinout is shown in the Pin Function Descriptions. Pin names in bold text replace the plain text named functions
when Mode C = 1. A plus (+) sign separates two functions when either function can be active for either major I/O mode. Signals
enclosed in brackets [ ] are state bits latched from the value of the pin at the deassertion of RESET.
The multiplexed pins DT1/FO, TFS1/IRQ1, RFS1/IRQ0, and DR1/FI are mode selectable by setting Bit 10 (SPORT1 configure) of
the System Control register. If Bit 10 = 1, these pins have serial port functionality. If Bit 10 = 0, these pins are the external interrupt
and flag pins. This bit is set to 1 by default upon reset.
PIN FUNCTION DESCRIPTION
Pin
No. Mnemonic
1 A4/IAD3
2 A5/IAD4
3GND
4 A6/IAD5
5 A7/IAD6
6 A8/IAD7
7 A9/IAD8
8 A10/IAD9
9 A11/IAD10
10 A12/IAD11
11 A13/IAD12
12 GND
13 CLKIN
14 XTAL
15 V
DDEXT
16 CLKOUT
17 GND
18 V
DDINT
19 WR
20 RD
21 BMS
22 DMS
23 PMS
24 IOMS
25 CMS
Pin
No. Mnemonic
26 IRQE+PF4
27 IRQL0+PF5
28 GND
29 IRQL1+PF6
30 IRQ2+PF7
31 DT0
32 TFS0
33 RFS0
34 DR0
35 SCLK0
36 V
DDEXT
37 DT1/FO
38 TFS1/IRQ1
39 RFS1/IRQ0
40 DR1/FI
41 GND
42 SCLK1
43 ERESET
44 RESET
45 EMS
46 EE
47 ECLK
48 ELOUT
49 ELIN
50 EINT
Pin
No. Mnemonic
51 EBR
52 BR
53 EBG
54 BG
55 D0/IAD13
56 D1/IAD14
57 D2/IAD15
58 D3/IACK
59 V
DDINT
60 GND
61 D4/IS
62 D5/IAL
63 D6/IRD
64 D7/IWR
65 D8
66 GND
67 V
DDEXT
68 D9
69 D10
70 D11
71 GND
72 D12
73 D13
74 D14
75 D15
Pin
No. Mnemonic
76 D16
77 D17
78 D18
79 D19
80 GND
81 D20
82 D21
83 D22
84 D23
85 FL2
86 FL1
87 FL0
88 PF3 [MODE D]
89 PF2 [MODE C]
90 V
DDEXT
91 PWD
92 GND
93 PF1 [MODE B]
94 PF0 [MODE A]
95 BGH
96 PWDACK
97 A0
98 A1/IAD0
99 A2/IAD1
100 A3/IAD2
TIMING SPECIFICATIONS
GENERAL NOTES
Use the exact timing information given. Do not attempt to
derive parameters from the addition or subtraction of others.
While addition or subtraction would yield meaningful results for
an individual device, the values given in this data sheet reflect
statistical variations and worst cases. Consequently, the user
cannot meaningfully add up parameters to derive longer times.
TIMING NOTES
Switching characteristics specify how the processor changes its
signals. There is no control over this. Timing circuitry external
to the processor must be designed for compatibility with these
REV. 0
–7–
signal characteristics. Switching characteristics tell what the
processor will do in a given circumstance. Switching characteristics may be used to ensure that any timing requirement of a
device connected to the processor (such as memory) is satisfied.
Timing requirements apply to signals that are controlled by
circuitry external to the processor, such as the data input for a
read operation. Timing requirements guarantee that the processor operates correctly with other devices.
MEMORY TIMING SPECIFICATIONS
Table I shows common memory device specifications and the
corresponding SST-Melody-DAP timing parameters, for your
convenience.
SST-Melody-DAP
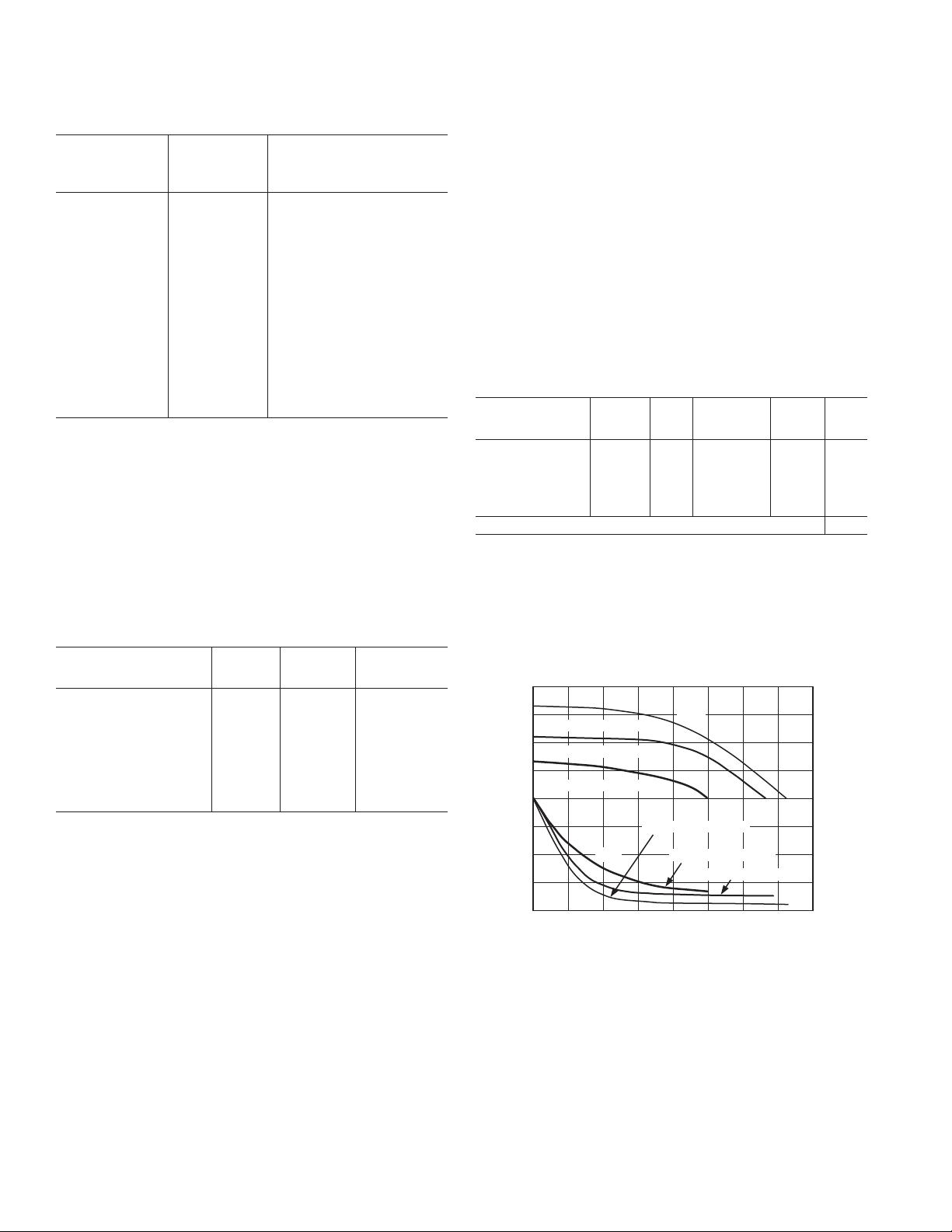
Table I. Memory Timing Specifications
Memory Timing
Device Parameter
Specification Parameter Definition*
Address Setup to t
ASW
A0–A13, xMS Setup
Write Start before WR Low
Address Setup to t
AW
A0–A13, xMS Setup
Write End before WR Deasserted
Address Hold t
WRA
A0–A13, xMS Hold
Time before WR Low
Data Setup Time
Data Hold Time
OE to Data Valid
Address Access t
t
DW
t
DH
t
RDD
AA
Data Setup before WR High
Data Hold after WR High
RD Low to Data Valid
A0–A13, xMS to
Time Data Valid
*xMS = PMS, DMS, CMS, or IOMS.
FREQUENCY DEPENDENCY FOR TIMING SPECIFICATIONS
tCK is defined as 0.5 t
. The SST-Melody-DAP uses an input
CKI
clock with a frequency equal to half the instruction rate. For
example, a 37.50 MHz input clock (which is equivalent to 26.6 ns)
yields a 13.3 ns processor cycle (equivalent to 75 MHz). t
values within the range of 0.5 t
period should be substituted
CKI
CK
for all relevant timing parameters to obtain the specification value.
Example: t
= 0.5 tCK – 2 ns = 0.5 (15 ns) – 2 ns = 5.5 ns
CKH
Table II. Environmental Conditions*
Rating
Description Symbol LQFP Mini-BGA
Thermal Resistance
CA
48°C/W 63.3°C/W
(Case-to-Ambient)
Thermal Resistance
JA
50°C/W 70.7°C/W
(Junction-to-Ambient)
Thermal Resistance
JC
2°C/W 7.4°C/W
(Junction-to-Case)
*Where the Ambient Temperature Rating (T
T
= T
AMB
T
CASE
PD = Power Dissipation in W
– (PD ⫻ CA)
CASE
= Case Temperature in °C
AMB
) is:
POWER DISSIPATION
To determine total power dissipation in a specific application,
the following equation should be applied for each output:
CV f
2
××
DD
C = load capacitance, f = output switching frequency.
Example:
In an application where external data memory is used and no
other outputs are active, power dissipation is calculated as follows:
Assumptions:
•
External data memory is accessed every cycle with 50% of the
address pins switching.
•
External data memory writes occur every other cycle with
50% of the data pins switching.
•
Each address and data pin has a 10 pF total load at the pin.
The application operates at V
•
= 30 ns.
t
CK
Total Power Dissipation = P
P
= internal power dissipation from Power vs. Frequency
INT
+ (C ⫻ V
INT
DDEXT
= 3.3 V and
2
⫻ f)
DDEXT
graph (see Figures 2a through 2c).
(C ⫻ V
2
⫻ f) is calculated for each output:
DDEXT
Table III. Power Dissipation Example
No. of C
V
Parameter Pins (pF) (V) (MHz)
Address 7 10 3.3
Data Output, WR
RD
CLKOUT, DMS
910
1
10
3.3
3.3
2103.3
DDEXT
2
2
2
2
2
f
16.67 12.7
16.67 16.6
16.67 1.8
33.3 7.2
PD
(mW)
Total 38.2
Total power dissipation for this example is P
+ 38.0 mW.
INT
Output Drive Currents
Figure 1 shows typical I–V characteristics for the output
drivers
on the SST-Melody-DAP. The curves represent the
current drive
capability of the output drivers as a function of
output voltage.
80
V
DDEXT
V
VOH
– 3.6V @ –40C
– 2.5V @ +85C
DDEXT
V
– 3.3V @ +25C
DDEXT
60
V
– 3.6V @ –40C
DDEXT
40
V
– 3.3V @ +25C
DDEXT
20
V
– 2.5V @ +85C
DDEXT
0
–20
SOURCE CURRENT – mA
–40
–60
–80
0
VOL
0.5 1.0 1.5 2.0 2.5 3.0 3.5 4.0
SOURCE VOLTAGE – V
Figure 1. Typical Output Driver Characteristics
REV. 0–8–
 Loading...
Loading...