Page 1
Engineer-to-Engineer Note EE-235
a
Technical notes on using Analog Devices DSPs, processors and development tools
Contact our technical support at dsp.support@analog.com and at dsptools.support@analog.com
Or vi sit our o n-li ne r esou rces htt p:/ /www.analog.com/ee-notes and http://www.analog.com/processors
An Introduction to Scripting in VisualDSP++®
Contributed by Jason Pound Rev 1 – May 11, 2004
Introduction
VisualDSP++® 3.5 introduces a language-independent scripting host that utilizes the Microsoft®
ActiveX® script host framework. The scripting host permits the use of multiple scripting engines
(languages) that conform to the Microsoft ActiveX script engine framework. Scripting is a powerful and
flexible tool that you can use to extend and customize the built-in capabilities of the IDDE or to automate
repetitive tasks. It is ideal for non-interactive scripting needs such as accessing DSP resources
(reading/writing memory or reading/writing registers), performing repetitive tasks (executing external
tools prior to or after a build completes, or setting registers and memory prior to loading a program), or
running full-blown regression tests. These are only a few examples of what can be done with scripting; the
possibilities are endless. This EE-Note outlines the components involved in scripting and explains how to
use the new scripting capabilities in the IDDE.
A Note About Tcl
Prior to the release of VisualDSP++ 3.5, Tcl (http://www.tcl.tk) was the default scripting language in the
IDDE. Since Tcl is not a true ActiveX script engine, Tcl has been deprecated with release 3.5 and will not
be covered in this EE-Note. Although most Tcl functionality has been maintained for backward
compatibility, no new functionality will be added to the Tcl library going forward.
Supported Languages
The following script languages are officially supported by Analog Devices:
VBScript
A scripting language developed by Microsoft, with syntax based on Visual Basic®. If you already know
Visual Basic or Visual Basic for Applications (VBA), VBScript will be very familiar.
JScript
A scripting language developed by Microsoft that implements the ECMAScript standard. It is a very
powerful interpreted scripting language that is object-based and loosely typed. This will be the most
familiar language to users that are comfortable with C/C++.
Copyright 2004, Analog Devices, Inc. All rights reserved. Analog Devices assumes no responsibility for customer product design or the use or application of
customers’ products or for any infringements of patents or rights of others which may result from Analog Devices assistance. All trademarks and logos are property
of their respective holders. Information furnished by Analog Devices applications and development tools engineers is believed to be accurate and reliable, however
no responsibility is assumed by Analog Devices regarding technical accuracy and topicality of the content provided in Analog Devices’ Engineer-to-Engineer Notes.
Page 2

Although each scripting language has its own syntax, all the scripting languages access the same features
in VisualDSP++. For example, calls to subroutines (methods with no return types) using VBScript do not
use parentheses, even though JScript does.
Although the IDDE permits the use of other scripting languages, Analog Devices Technical
!
The benefits of using the new ActiveX script engines include:
• More language choices
• Better language support and documentation
• Shorter learning curve for users who are already familiar with a language
• Much more powerful API (Automation)
• Better performance and flexibility
Support does not support them at this time.
a
VisualDSP++ Automation API
VisualDSP++ includes a unified programming interface, called the VisualDSP++ Automation API, which
provides all script languages with broad access to all of the capabilities of the IDDE in a languageindependent manner. Automation, formerly called OLE Automation, is a Microsoft COM-based
technology that allows an application to use the services provided by another application (VisualDSP++).
It makes the VisualDSP++ environment programmable by any application that understands Automation.
Since script languages (VBScript or JScript) support the COM interface, they may be used to access to the
Automation API.
When a language is selected as the current language in the Console tab of the IDDE’s Output window, an
instance of the VisualDSP++ application object is created. This object, called
the VisualDSP++ Automation’s methods and properties. The use of this object is shown later in this
document. For detailed information about the Automation API, refer to the online Help, which can be
found at
<VisualDSP install>\help\VisualDSPAutomation.chm.
Idde, is used to easily access
Detecting Installed Languages
By default, under Windows 2000 or later, everything you need for scripting is already installed on the
operating system. However, under Windows 98 and Windows NT, if VisualDSP++ does not automatically
detect any languages, you may have to download
of Internet Explorer, which installs the VBScript and JScript libraries necessary to use the scripting
capabilities. For further information, visit the following Microsoft site:
Microsoft Windows Script 5.6 or upgrade to the latest version
http://www.microsoft.com/scripting
An Introduction to Scripting in VisualDSP++® (EE-235) Page 2 of 18
Page 3

a
Getting Familiar with Scripting
Open VisualDSP++ and click the Console tab of the Output window. To see the list of available
languages, right-click in the Output window and choose
current scripting language.
Figure 1. Language selection menu
The best way to become familiar with the scripting capabilities is to enter a few commands in the Output
window. Type the following lines:
Languages. Choose VBScript to select it as the
a = 5
b = 2
c = a + b
? c
Listing 1. Simple commands
Evaluate expressions by preceding the text with a question mark (?) when a Microsoft activeX
!
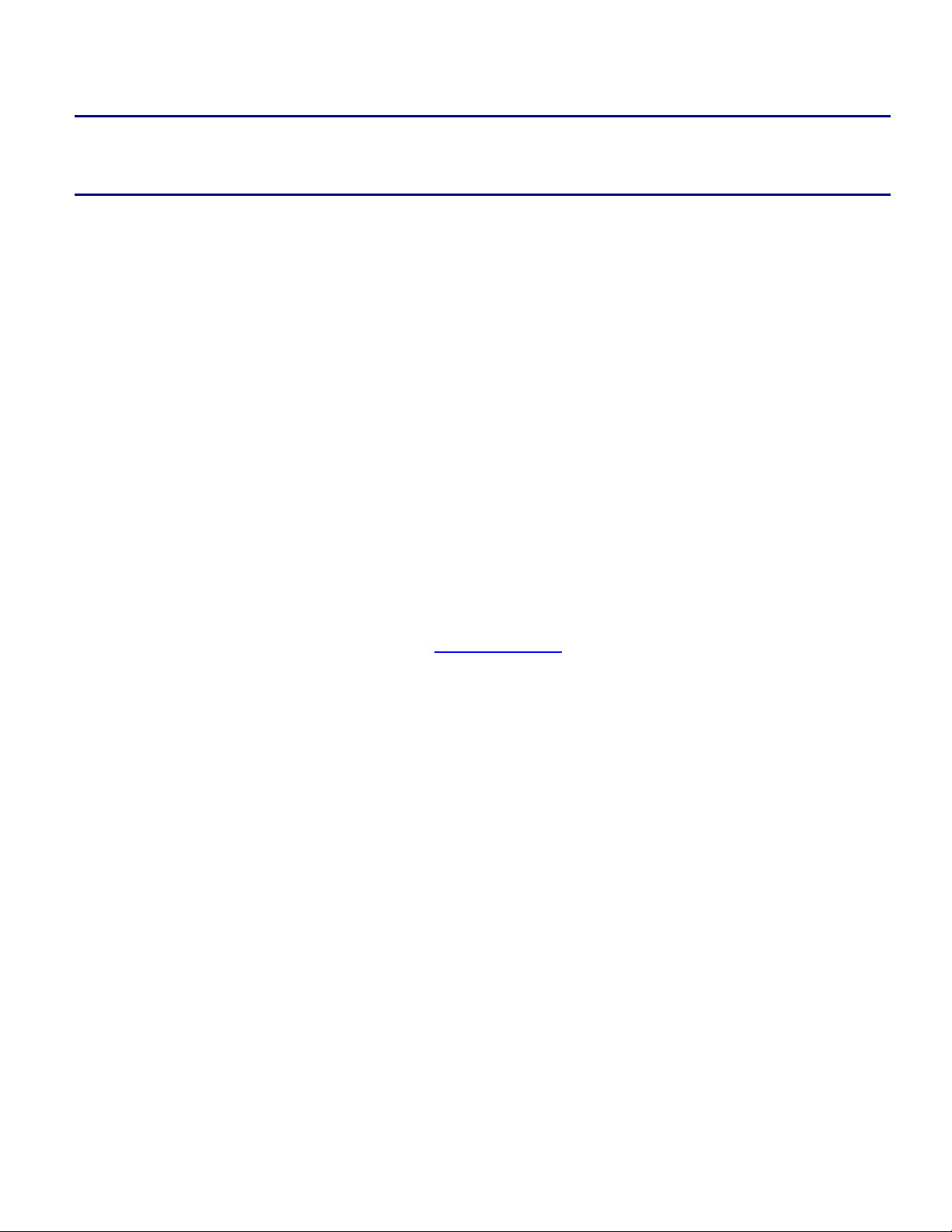
Now, let’s use the Idde object mentioned earlier to access some automation methods and properties. Type
the following commands in the Output window and observe the output for each command:
? Idde.Name
? Idde.ActiveSession.ActiveProcessor.Name
? Idde.ActiveSession.ActiveProcessor.State
Idde.OutputWindow.PrintText “Hello World”, textTypeConsoleNormal
Idde.ActiveSession.ActiveProcessor.Run
Idde.ActiveSession.ActiveProcessor.Halt
script engine is selected.
Listing 2. Idde object commands
An Introduction to Scripting in VisualDSP++® (EE-235) Page 3 of 18
Page 4
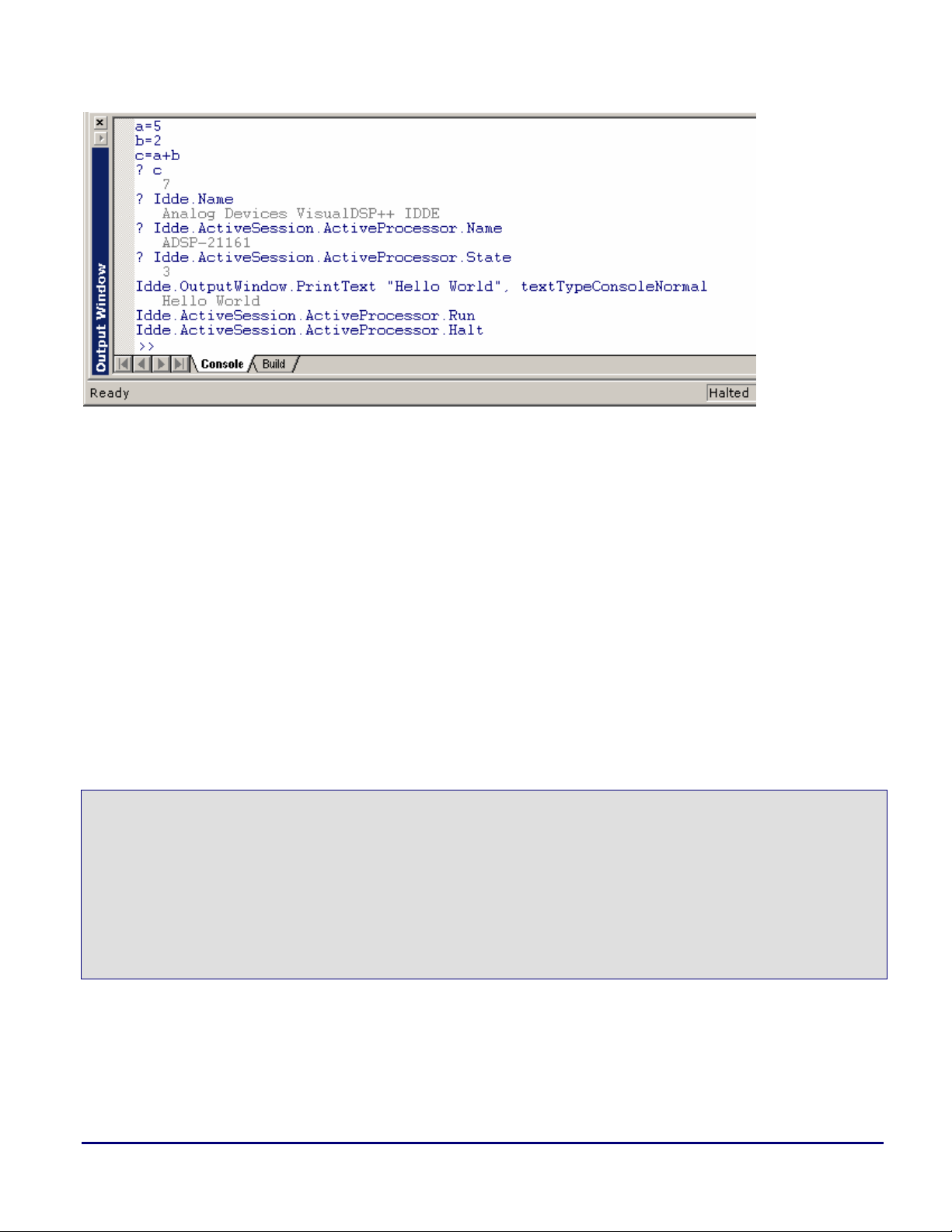
Figure 2. Output window with Idde object commands
Loading a Script
VisualDSP++ provides multiple ways to load a script:
a
• Choose File->Load Script from the IDDE’s main menu
• Choose File->Recent Scripts from the IDDE’s main menu
• Choose Load Script from the Output window’s right-click menu
• Choose Load Script via the right-click menu in an editor window
Following is an example. First, right-click in the Output window, and change the script language to
Open a new document in VisualDSP++ by clicking
into the blank document. Save the file as
been saved, right-click on the
window, type
PrintSessionList() and press Enter. The list of sessions previously created in VisualDSP++
LoadScriptEx.js file in the editor window and choose LoadScript. In the Output
LoadScriptEx.js to a directory of your choice. Once the file has
File->New on the main menu. Copy the following script
should print to the Output window (Figure 3).
function PrintSessionList()
{
SessionList = Idde.SessionList;
for( var i=0; i< SessionList.Count; i++ )
{
Session = SessionList.Item(i);
Idde.OutputWindow.PrintText(Session.Name, 0);
}
}
Listing 3. PrintSessionList code
JScript.
An Introduction to Scripting in VisualDSP++® (EE-235) Page 4 of 18
Page 5
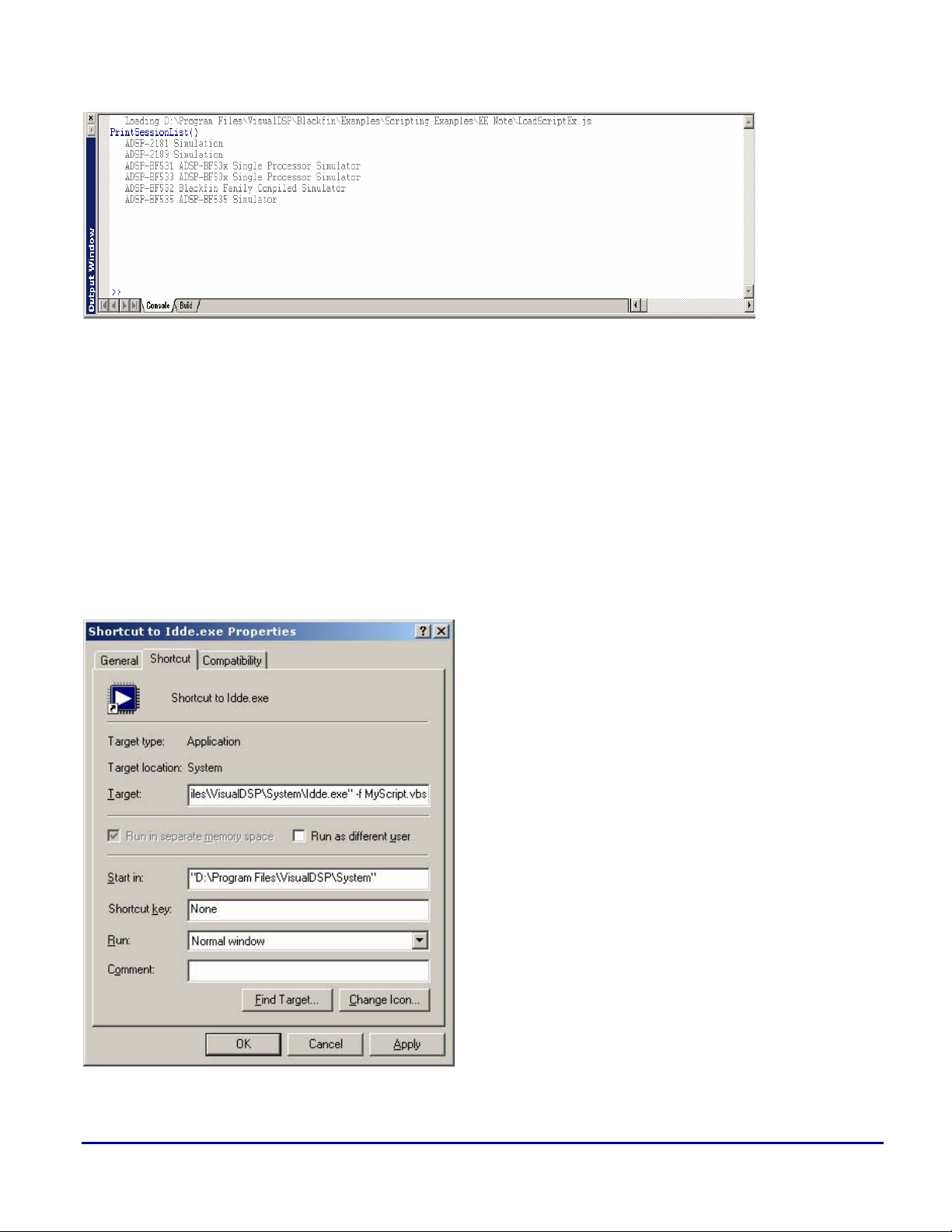
Figure 3. Output window with PrintSessionList output
Code not contained within a function is considered global code and executes immediately after the
!
script is loaded. Code contained within a function is executed only when called within the global
code or when you type the function name into the Output window of the IDDE.
a
Automatically Invoking a Script
A script can automatically be loaded on startup of the IDDE by using the –f parameter and a shortcut to
the
Idde.exe. This is ideal for recurring tasks.
To use this feature, create a shortcut to the
“–f” and file name at the end of the Target field located on the Shortcut tab (Figure 4). Click OK. The next
time the IDDE is started, the script will load automatically.
Idde.exe. Right-click on the shortcut and choose Properties. Place
Figure 4. Specifying a script from the Shortcut tab
An Introduction to Scripting in VisualDSP++® (EE-235) Page 5 of 18
Page 6
a
Creating a Toolbar Button
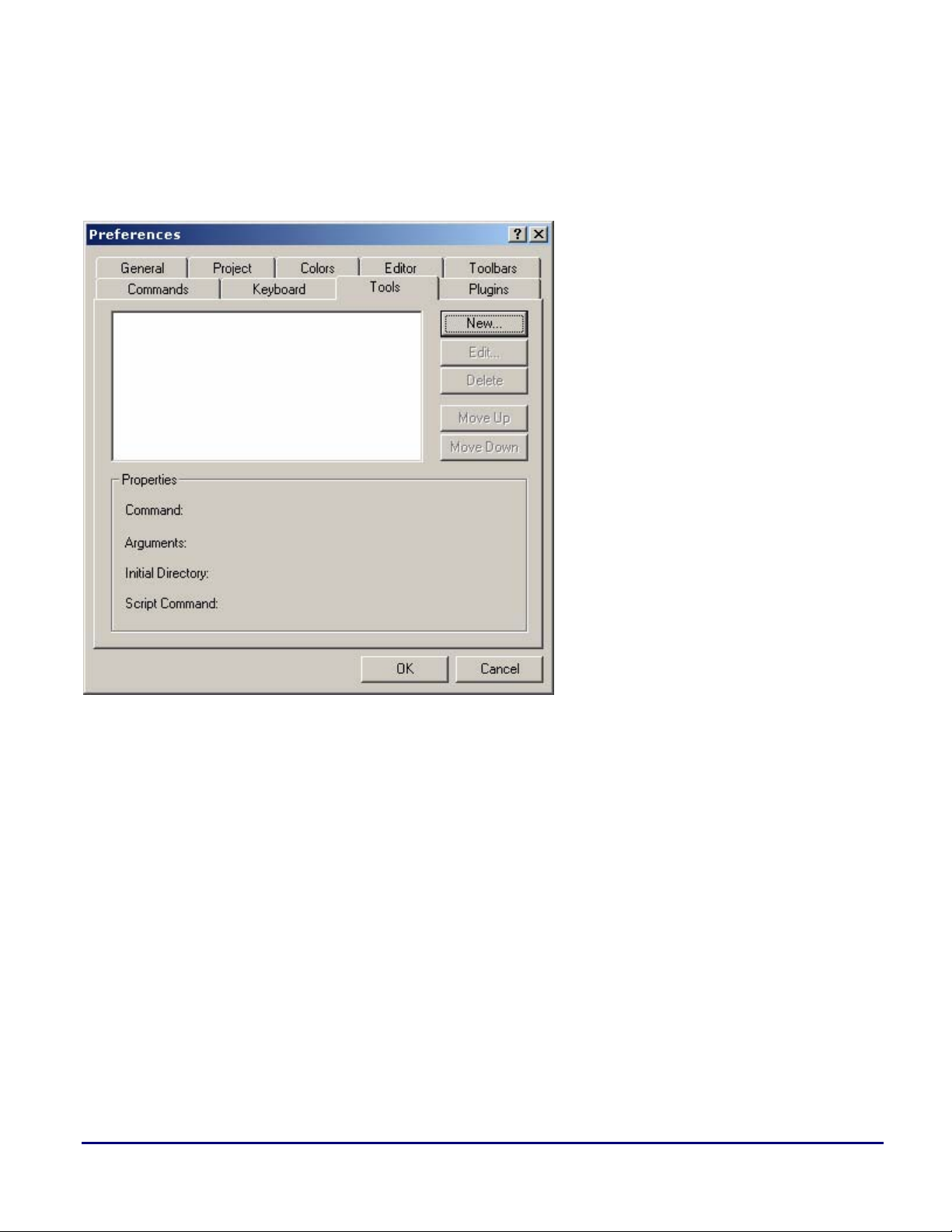
You can map a script to a toolbar button in the IDDE. For example, let’s use the PrintSessionList code
from Listing 3 to create a toolbar button. First, create a tool by choosing
the
Tools tab. Then click New to define the tool.
Settings->Preferences and clicking
Figure 5. Tools tab of the Preferences dialog box
As shown in Figure 6, assign the new tool with the name Print Available Sessions and specify the function to
be executed, PrintSessionList(). Enter the directory where the script is located and select the Script command
option. Click
An Introduction to Scripting in VisualDSP++® (EE-235) Page 6 of 18
OK to save the tool’s settings.
Page 7

Figure 6. Specifying settings for the tool
a
Figure 7. PrintSessionList() tool
The final step is to enable the display of the
Preferences dialog box (
An Introduction to Scripting in VisualDSP++® (EE-235) Page 7 of 18
Settings->Preferences). Select User Tools in the Toolbars list and then click OK to
User Tools toolbar. You do this via the Toolbars tab of the
Page 8

display the toolbar in the IDDE. The User Tools toolbar is now available (Figure 9) and the Print
Available Settings command may be run by clicking the first tool.
a
Figure 8. Toolbars dialog
Figure 9. User Tools toolbar in the IDDE
MenuManger Object
Similar to the built-in Idde object, there is also a built-in MenuManager object. This object allows you to add
menu items to the IDDE’s menu and also allows you to modify the state of the menu items. The following
An Introduction to Scripting in VisualDSP++® (EE-235) Page 8 of 18
Page 9

a
is a simple example (in VBScript) that creates a menu (Figure 10) and declares an event to handle the
menu click.
menuid = MenuManager.AddMenuTail( "&Tools:&My Menu Item", "This is a custom menu item." )
Sub menumanager_OnMenuItemClicked(ByVal MenuID)
If (MenuID = menuid) Then
Idde.OutputWindow.PrintText "My Menu Item was clicked", tabConsole
End If
End Sub
Listing 4. Adding a menu item with the MenuManager object
Figure 10. Custom menu item
Debugging Scripts
The IDDE reports script errors to the Output window. The format of an error message is: File name, Line
number, Column number, Error reason, Error type. Double-clicking on an error line in the Output window
opens the script file and positions the cursor on the line where the error occurred. For example, let’s look
at the following script, which is located in a file named PrintSessionList.vbs:
Set SessionList = Idde.SessionList
For Each Session in SessionList
Idde.OutputWindow.PrintTText Session.Name, textTypeConsoleNormal
Next
Listing 5. Example script file containing an error
Since the line “Idde.OutputWindow.PrintTText Session.Name, textTypeConsoleNormal” contains
a syntax error, an error message would display in the Output window when the file is loaded. Once the
extra “T” is removed, the script will proceed normally.
An Introduction to Scripting in VisualDSP++® (EE-235) Page 9 of 18
Page 10

a
Figure 11. Error message output in the Output window
Enabling the Microsoft Script Debugger
If the Microsoft Script Debugger is already installed on the machine, the Enable Debugger command should
be available from the Output window’s right-click menu. If the debugger is not installed, the command
will be grayed out. To get a copy of the Microsoft Script Debugger, refer to the following Microsoft site:
http://www.microsoft.com/downloads and search for “Script Debugger”.
To enable the script debugger, right-click on the Output window and choose
activate the script debugger to launch when should a script error be encountered or when a command is
typed in the Output window.
Enable Debugger. This will
An Introduction to Scripting in VisualDSP++® (EE-235) Page 10 of 18
Page 11

Figure 12. Enable Debugger menu item
If the PrintSessionList.vbs script above is loaded while the script debugger is enabled, the debugger will
launch and stop on the line containing the error. With the Microsoft script debugger, you can step, run,
halt, set breakpoints, etc. Once you have finished debugging, the focus should return to the IDDE and
show the error message in the Output window.
a
Figure 13. Microsoft Script Debugger
To disable the script debugger, choose Enable Debugger from the Output window’s right-click menu again
and close the debugger.
An Introduction to Scripting in VisualDSP++® (EE-235) Page 11 of 18
Page 12

a
Accessing VisualDSP++ from Another Application
VisualDSP++ can be controlled by another application such as a Visual Basic or C++ program. This
allows Automation aware applications to communicate and control VisualDSP++ and vice versa. As an
example application, a simple script could be written in Microsoft Excel that would connect to a target
board, load a program, set and run to a breakpoint, and then read a block of memory into Excel for data
analysis.
Excel can read
DSP memory through the
VisualDSP++ Automation
API
VisualDSP++ can
also talk to Excel’s
Automation API
Figure 14. Automation aware applications
The syntax of languages varies when creating an instance of VisualDSP++. The following is a sample of
some of the languages and their methods used to create an instance of an object.
Language Syntax
VBScript
JScript
C++
Set app = CreateObject(“VisualDSP.ADspApplication”)
app = new ActiveXObject(“VisualDSP.ADspApplication”)
IADspApplicationPtr pApp( "VisualDSP.ADspApplication" );
Scripting Examples
The VisualDSP++ installation directory includes example scripts in the "Scripting Examples" folder
located under the DSP family name (e.g.,
Blackfin\Examples\Scripting Examples).
An Introduction to Scripting in VisualDSP++® (EE-235) Page 12 of 18
Page 13

a
Scripting References
VisualDSP++ Automation API
For detailed information about the Automation API, refer to the online Help, which can be found at
<VisualDSP install>\help\VisualDSPAutomation.chm.
http://msdn.microsoft.com/scripting
This is a good starting point for learning more about ActiveX scripting. The site includes in-depth
documents that describe the ActiveX technology and languages.
http://msdn.microsoft.com
This is a good starting point for in-depth knowledge on any Microsoft technology including ActiveX
scripting.
http://www.activestate.com
This site offers free, quality-assured language distributions such as perl and python.
news://msnews.microsoft.com/microsoft.public.inetsdk.programming.active_scrptng
This site covers general ActiveX scripting issues.
news://msnews.microsoft.com/microsoft.public.inetsdk.programming.scripting.vbscript
This site covers VBScript related issues.
news://msnews.microsoft.com/microsoft.public.inetsdk.programming.scripting.jscript
This site covers JScript related issues.
Conclusion
This EE-Note shows a fraction of what can be done with scripting. Scripting in VisualDSP++ is a
powerful tool that makes VisualDSP++ a more versatile application and provides users with infinite
possibilities.
An Introduction to Scripting in VisualDSP++® (EE-235) Page 13 of 18
Page 14

a
Appendix A. Example: Project and IDDE Operations in VBScript
The following script example is simple but powerful. It creates a project, creates a file, adds the file to the
project, builds the project, loads the program, runs the program, retrieves the value of a variable within the
program, and then prints the value to the Output widow.
Change the script language to
choosing
File->New on the main menu. Copy the following script into the blank document and save it to a
directory of your choice as
VBScript in the Output window. Open a new document in VisualDSP++ by
EE235ExA.vbs. Right-click on the file in the editor and choose Load Script. This
will start the script.
Exercise caution when using the Idde.Interactive property of the Automation API, as it will
!
suppress all dialog boxes including error messages, making script debugging potentially difficult.
If you use this property in a script, catch errors within the script and set this property back to
EE235ExA.vbs
' Don't show any dialog boxes
Idde.Interactive = False
' Create the project
Set Project = Idde.ProjectList.CreateProject( "EE235Ex", "EE235Ex.dpj" )
' Set the project options
Project.Processor = Idde.ActiveSession.ActiveProcessor.Type
Project.TargetType = "DSP executable file"
Project.ActiveConfiguration = "Debug"
' Create a new file system object.
Set FSO = CreateObject( "Scripting.FileSystemObject" )
' Create the source file.
Set F = FSO.OpenTextFile( "EE235Ex.c", 2, True ) '2 = Writing
' Write the data to the file.
F.Write( "int a, b, nValue;" & vbCrlf & "void main( void )" & vbCrlf & "{"
& vbCrlf & vbTab & "a = 5;" & vbCrlf & vbTab & "b = 3;" & vbCrlf & vbTab & "
nValue = a + b;" & vbCrlf & "}" & vbCrlf )
' Close the file.
F.Close
' Add the file to the project.
Project.AddFile "EE235Ex.c", "Source Files"
' Build the project
Project.Build True
' Get the active processor
Set Processor = Idde.ActiveSession.ActiveProcessor
' Load the program
Processor.LoadProgram Project.TargetFileNameList(0)
True.
An Introduction to Scripting in VisualDSP++® (EE-235) Page 14 of 18
Page 15

' Run the program to the end of main
Processor.Run True
' Get the address of the variable
Address = Processor.MemoryTypeList.FindSymbol("nValue")(0).Address
' Get the memory type
Set MemoryType = Processor.MemoryTypeList.Item(0)
' Read the value of the variable
Set ValueList = MemoryType.GetMemory( Address, 1, 1 )
' Print the value
Idde.OutputWindow.PrintText “The value = “ & ValueList(0).Value, 0
' Show dialog boxes again
Idde.Interactive = True
If Err.Number <> 0 Then
' Show dialog boxes again
Idde.Interactive = True
Idde.OutputWindow.PrintText "An Error occurred.", 3
Err.Clear
End If
a
Listing 1. EE235ExA.vbs
An Introduction to Scripting in VisualDSP++® (EE-235) Page 15 of 18
Page 16

a
Appendix B. Example: Project and IDDE Operations in JScript
The following script example is simple but powerful. It creates a project, creates a file, adds the file to the
project, builds the project, loads the program, runs the program, retrieves the value of a variable within the
program, and then prints the value to the Output widow.
Change the script language to
choosing
File->New on the main menu. Copy the following script into the blank document and save it to a
directory of your choice as
JScript in the Output window. Open a new document in VisualDSP++ by
EE235ExB.js. Right-click on the file in the editor and select Load Script. This will
start the script.
EE235ExB.js
try
{
// Don't show any dialog boxes
Idde.Interactive = false;
// Create the project
Project = Idde.ProjectList.CreateProject( "EE235Ex", "EE235Ex.dpj" )
// Set the project options
Project.Processor = Idde.ActiveSession.ActiveProcessor.Type;
Project.TargetType = "DSP executable file";
Project.ActiveConfiguration = "Debug";
// Create a new file system object.
FSO = new ActiveXObject( "Scripting.FileSystemObject" );
// Create the source file.
F = FSO.CreateTextFile( "EE235Ex.c", true ); //2 = Writing
// Write the data to the file.
F.Write( "int a, b, nValue;" + "\n" + "void main( void )" + "\n" + "{" + "\n" +
"\t" + "a = 5;" + "\n" + "\t" + "b = 3;" + "\n" + "\t" + " nValue = a + b;" +
"\n" + "}" + "\n" );
// Close the file.
F.Close();
// Add the file to the project.
Project.AddFile( "EE235Ex.c", "Source Files" );
// Build the project and wait
Project.Build( true );
// Get the active processor
Processor = Idde.ActiveSession.ActiveProcessor;
// Reset the processor and wait
Processor.Reset( true );
// Load the program
Processor.LoadProgram( Project.TargetFileNameList(0) );
An Introduction to Scripting in VisualDSP++® (EE-235) Page 16 of 18
Page 17

// Run the program to the end of main
Processor.Run( true );
// Get the address of the variable
Address = Processor.MemoryTypeList.FindSymbol("nValue")(0).Address;
// Get the memory type
MemoryType = Processor.MemoryTypeList.Item(0);
// Read the value of the variable
ValueList = MemoryType.GetMemory( Address, 1, 1 );
// Print the value
Idde.OutputWindow.PrintText( "The value = " + ValueList(0).Value, 0 );
// Close the project
Idde.ProjectList.RemoveProject( 0 );
// Show dialog boxes again
Idde.Interactive = true;
}
catch(e)
{
// Show dialog boxes again
Idde.Interactive = true;
Idde.OutputWindow.PrintText( "An Error occurred: " + e.description, 3 );
}
a
Listing 2. EE235ExB.js
An Introduction to Scripting in VisualDSP++® (EE-235) Page 17 of 18
Page 18

a
Appendix C. Example: Saving Projects and Dependencies in VBScript
The following script example illustrates how to load multiple projects and set dependencies on those
projects.
EE235ExC.vbs
‘ get the project list
Set project_list = Idde.ProjectList
‘ empty the project list first
While (project_list.Count > 0)
project_list.RemoveProject 0
WEnd
‘ add the projects
Set project1 = project_list.AddProject("sdram.dpj")
Set project2 = project_list.AddProject(".\CoreA\CoreA.dpj")
Set project3 = project_list.AddProject("..\CoreB\CoreB.dpj")
Set project4 = project_list.AddProject("..\L2\L2.dpj")
Set project5 = project_list.AddProject("..\L3\L3.dpj")
‘ set the dependencies on the projects
Set dependencies = CreateObject( "VisualDSP.ADspStringList" )
dependencies.Add project2.Name
dependencies.Add project3.Name
dependencies.Add project4.Name
dependencies.Add project5.Name
project1.DependentProjectList = dependencies
Listing 3. EE235ExC.vbs
Document History
Revision Description
Rev 1 – May 11, 2004
by J. Pound
Initial Release
An Introduction to Scripting in VisualDSP++® (EE-235) Page 18 of 18
 Loading...
Loading...