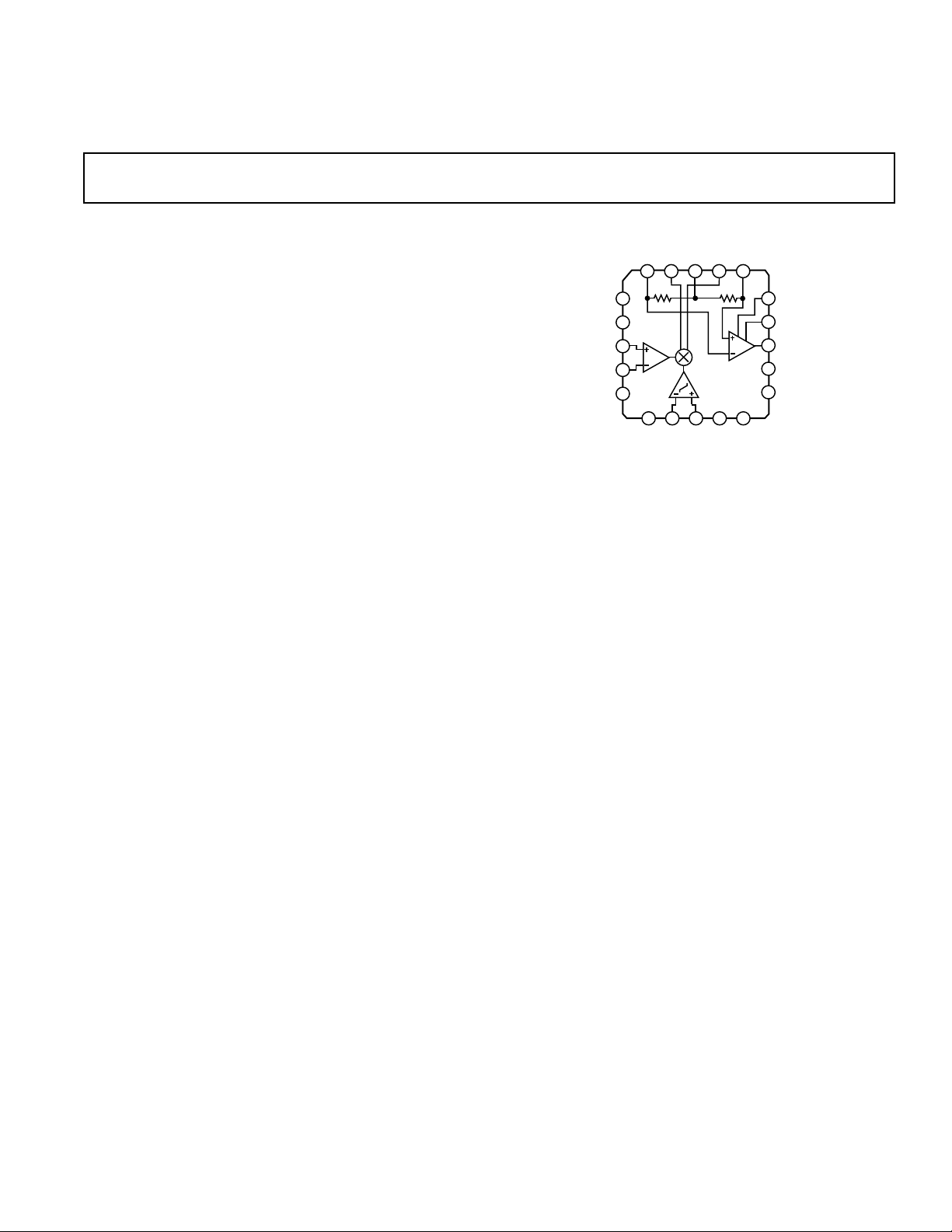
AN
IFN
VP
IFP
AP
GND
VN
RFP
RFN
VN
VP
LON
LOP
VP
GND
BIAS
VN
OUT
VFB
COM
AD831
50Ω
50Ω
139 10 11 12
6
7
8
4
5
14
15
16
17
18
123
19
20
a
Low Distortion Mixer
AD831
FEATURES
FUNCTIONAL BLOCK DIAGRAM
Doubly-Balanced Mixer
Low Distortion
+24 dBm Third Order Intercept (IP3)
+10 dBm 1 dB Compression Point
Low LO Drive Required: –10 dBm
Bandwidth
500 MHz RF and LO Input Bandwidths
250 MHz Differential Current IF Output
DC to >200 MHz Single-Ended Voltage IF Output
Single or Dual Supply Operation
DC Coupled Using Dual Supplies
All Ports May Be DC Coupled
No Lower Frequency Limit—Operation to DC
User-Programmable Power Consumption
APPLICATIONS
High Performance RF/IF Mixer
Direct to Baseband Conversion
Image-Reject Mixers
I/Q Modulators and Demodulators
filtering. When building a quadrature-amplitude modulator or
image reject mixer, the differential current outputs of two
AD831s may be summed by connecting them together.
An integral low noise amplifier provides a single-ended voltage
PRODUCT DESCRIPTION
The AD831 is a low distortion, wide dynamic range, monolithic
mixer for use in such applications as RF to IF down conversion
in HF and VHF receivers, the second mixer in DMR base stations, direct-to-baseband conversion, quadrature modulation and demodulation, and doppler-shift detection in ultrasound imaging applications. The mixer includes an LO driver
and a low-noise output amplifier and provides both user-programmable power consumption and 3rd-order intercept point.
The AD831 provides a +24 dBm third-order intercept point for
–10 dBm LO power, thus improving system performance and
reducing system cost compared to passive mixers, by eliminating
the need for a high power LO driver and its attendant shielding
and isolation problems.
The RF, IF, and LO ports may be dc or ac coupled when the
mixer is operating from ±5 V supplies or ac coupled when operating from a single supply of 9 V minimum. The mixer operates
output and can drive such low impedance loads as filters, 50 Ω
amplifier inputs, and A/D converters. Its small signal bandwidth
exceeds 200 MHz. A single resistor connected between pins
OUT and FB sets its gain. The amplifier’s low dc offset allows
its use in such direct-coupled applications as direct-to-baseband
conversion and quadrature-amplitude demodulation.
The mixer’s SSB noise figure is 10.3 dB at 70 MHz using its
output amplifier and optimum source impedance. Unlike passive mixers, the AD831 has no insertion loss and does not require an external diplexer or passive termination.
A programmable-bias feature allows the user to reduce power
consumption, with a reduction in the 1 dB compression point
and third-order intercept. This permits a tradeoff between dynamic range and power consumption. For example, the AD831
may be used as a second mixer in cellular and two-way radio
base stations at reduced power while still providing a substantial
performance improvement over passive solutions.
with RF and LO inputs as high as 500 MHz.
The mixer’s IF output is available as either a differential current
output or a single-ended voltage output. The differential output
is from a pair of open collectors and may be ac coupled via a
transformer or capacitor to provide a 250 MHz output bandwidth. In down-conversion applications, a single capacitor connected across these outputs implements a low-pass filter to
reduce harmonics directly at the mixer core, simplifying output
REV. B
Information furnished by Analog Devices is believed to be accurate and
reliable. However, no responsibility is assumed by Analog Devices for its
use, nor for any infringements of patents or other rights of third parties
which may result from its use. No license is granted by implication or
otherwise under any patent or patent rights of Analog Devices.
PRODUCT HIGHLIGHTS
1. –10 dBm LO Drive for a +24 dBm Output Referred Third
Order Intercept Point
2. Single-Ended Voltage Output
3. High Port-to-Port Isolation
4. No Insertion Loss
5. Single or Dual Supply Operation
6. 10.3 dB Noise Figure
© Analog Devices, Inc., 1995
One Technology Way, P.O. Box 9106, Norwood. MA 02062-9106, U.S.A.
Tel: 617/329-4700 Fax: 617/326-8703
(TA = +258C and 6VS = 65 V unless otherwise noted;
AD831–SPECIFICA TIONS
all values in dBm assume 50 V load.)
Parameter Conditions Min Typ Max Units
RF INPUT
Bandwidth –10 dBm Signal Level, IP3 ≥ +20 dBm 400 MHz
10.7 MHz IF and High Side Injection
See Figure 1
1 dB Compression Point 10 dBm
Common-Mode Range ±1V
Bias Current DC Coupled 160 500 µA
DC Input Resistance Differential or Common Mode 1.3 kΩ
Capacitance 2pF
IF OUTPUT
Bandwidth Single-Ended Voltage Output, –3 dB
Level = 0 dBm,
RL = 100 Ω 200 MHz
Conversion Gain Terminals OUT and VFB Connected 0 dB
Output Offset Voltage DC Measurement; LO Input Switched ± 1 –40 15 +40 mV
Slew Rate 300 V/µs
Output Voltage Swing R
= 100 Ω, Unity Gain ±1.4 V
L
Short Circuit Current 75 mA
LO INPUT
Bandwidth –10 dBm Input Signal Level 400 MHz
10.7 MHz IF and High Side Injection
Maximum Input Level –1 +1 V
Common-Mode Range –1 +1 V
Minimum Switching Level Differential Input Signal 200 mV p-p
Bias Current DC Coupled 17 50 µA
Resistance Differential or Common Mode 500 Ω
Capacitance 2pF
ISOLATION BETWEEN PORTS
LO to RF LO = 100 MHz, R
LO to IF LO = 100 MHz, R
= 50 Ω, 10.7 MHz IF 70 dB
S
= 50 Ω, 10.7 MHz IF 30 dB
S
RF to IF RF = 100 MHz, RS = 50 Ω, 10.7 MHz IF 45 dB
DISTORTION AND NOISE LO = –10 dBm, f = 100 MHz, IF = 10.7 MHz
3rd Order Intercept Output Referred, ± 100 mV LO Input 24 dBm
2rd Order Intercept Output Referred, ± 100 mV LO Input 62 dBm
1 dB Compression Point R
= 100 Ω, R
L
= ∞ 10 dBm
BIAS
Noise Figure, SSB Matched Input, RF = 70 MHz, IF = 10.7 MHz 10.3 dB
Matched Input, RF = 150 MHz, IF = 10.7 MHz 14 dB
POWER SUPPLIES
Recommended Supply Range Dual Supply ±4.5 ±5.5 V
Single Supply 9 11 V
For Best 3rd Order Intercept Point Performance 100 125 mA
Quiescent Current
1
BIAS Pin Open Circuited
NOTES
1
Quiescent current is programmable.
Specifications subject to change without notice.
–2–
REV. B
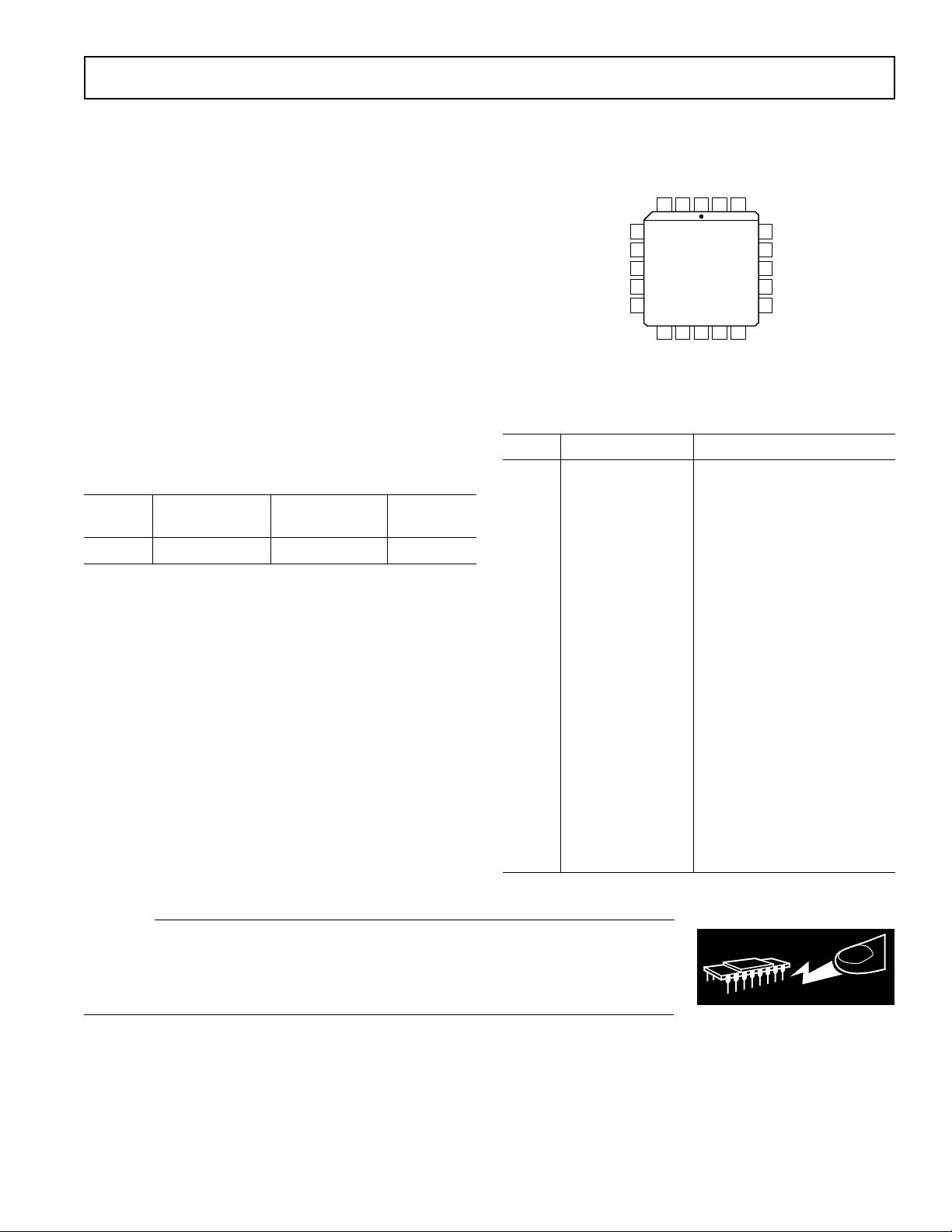
AD831
GND
VN
VN
RFP
RFN
AN
IFN
AP
VP
IFP
VP
LON
GND
LOP
VP
COM
VFB
BIAS
OUT
VN
1931220
4
5
8
6
7
12 1391110
18
17
14
16
15
TOP VIEW
(Not to Scale)
AD831
ABSOLUTE MAXIMUM RATINGS
1
Supply Voltage ±VS . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . ±5.5 V
Input Voltages
RFHI, RFLO . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . ±3 V
LOHI, LOLO . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . ±1 V
Internal Power Dissipation
2
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1200 mW
Operating Temperature Range
AD831A . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . –40°C to +85°C
Storage Temperature Range . . . . . . . . . . . . –65°C to +150°C
Lead Temperature Range (Soldering 60 sec) . . . . . . . . +300°C
NOTES
1
Stresses above those listed under “Absolute Maximum Ratings” may cause
permanent damage to the device. This is a stress rating only and functional
operation of the device at these or any other conditions above those indicated in the
operational section of this specification is not implied. Exposure to absolute
maximum rating conditions for extended periods may affect device reliability.
2
Thermal Characteristics:
20-Pin PLCC Package: θJA = 110°C/Watt; θJC = 20°C/Watt.
Note that the θJA = 110°C/W value is for the package measured while suspended
in still air; mounted on a PC board, the typical value is θ
conduction provided by the AD831’s package being in contact with the board,
which serves as a heat sink.
= 90°C/W due to the
JA
ORDERING GUIDE
Temperature Package Package
Model Range Description Option
AD831AP –40°C to +85°C 20-Lead PLCC P-20A
PIN CONFIGURATION
20-Lead PLCC
PIN DESCRIPTION
Pin Mnemonic Description
1 VP Positive Supply Input
2 IFN Mixer Current Output
3 AN Amplifier Negative Input
4 GND Ground
5 VN Negative Supply Input
6 RFP RF Input
7 RFN RF Input
8 VN Negative Supply Input
9 VP Positive Supply Input
10 LON Local Oscillator Input
11 LOP Local Oscillator Input
12 VP Positive Supply Input
13 GND Ground
14 BIAS Bias Input
15 VN Negative Supply Input
16 OUT Amplifier Output
17 VFB Amplifier Feedback Input
18 COM Amplifier Output Common
19 AP Amplifier Positive Input
20 IFP Mixer Current Output
CAUTION
ESD (electrostatic discharge) sensitive device. Electrostatic charges as high as 4000 V readily
accumulate on the human body and test equipment and can discharge without detection.
Although the AD831 features proprietary ESD protection circuitry, permanent damage may
occur on devices subjected to high energy electrostatic discharges. Therefore, proper ESD
precautions are recommended to avoid performance degradation or loss of functionality.
–3–
REV. B
WARNING!
ESD SENSITIVE DEVICE
AD831–Typical Characteristics
FREQUENCY – MHz
80
70
0
40
30
20
10
50
60
10 1000100
ISOLATION – dB
3 x RF-to-IF
2 x RF-to-IF
RF-to-IF
3 x RF-to-IF
2 x RF-to-IF
RF-to-IF
30
25
20
15
10
THIRD ORDER INTERCEPT – dBm
5
0
10 1000100
FREQUENCY – MHz
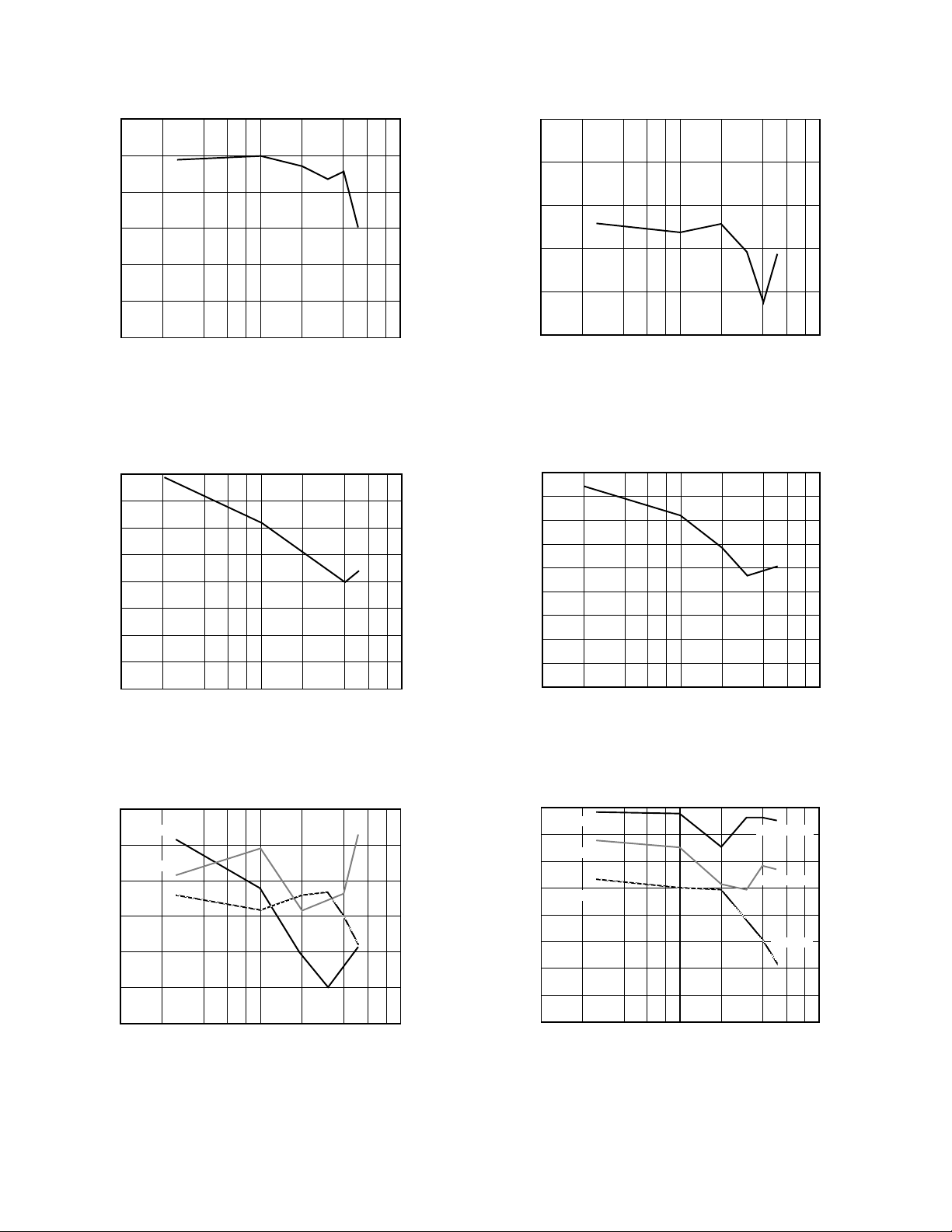
Figure 1. Third-Order Intercept vs. Frequency,
IF Held Constant at 10.7 MHz
80
70
60
50
40
30
ISOLATION – dB
20
10
0
10 1000100
FREQUENCY – MHz
65
64
63
62
61
SECOND ORDER INTERCEPT – dBm
60
10 1000100
FREQUENCY – MHz
Figure 4. Second-Order Intercept vs. Frequency
90
80
70
60
50
40
ISOLATION – dB
30
20
10
0
10 1000100
FREQUENCY – MHz
Figure 2. IF-to-RF Isolation vs. Frequency
60
2 x LO-to-IF
50
3 x LO-to-IF
40
30
ISOLATION – dB
20
10
0
10 1000100
Figure 3. LO-to-IF Isolation vs. Frequency
LO
FREQUENCY – MHz
–4–
Figure 5. LO-to-RF Isolation vs. Frequency
Figure 6. RF-to-IF Isolation vs. Frequency
REV. B
AD831
FREQUENCY – MHz
1dB COMPRESSION POINT – dBm
11
10
7
0 600100 200 300 400 500
9
8
LO LEVEL = –10dBm
IF = 10.7MHz
V
S
= 8V
V
S
= 9V
12
10
8
6
4
1dB COMPRESSION POINT – dBm
2
0
10 1000100
FREQUENCY – MHz
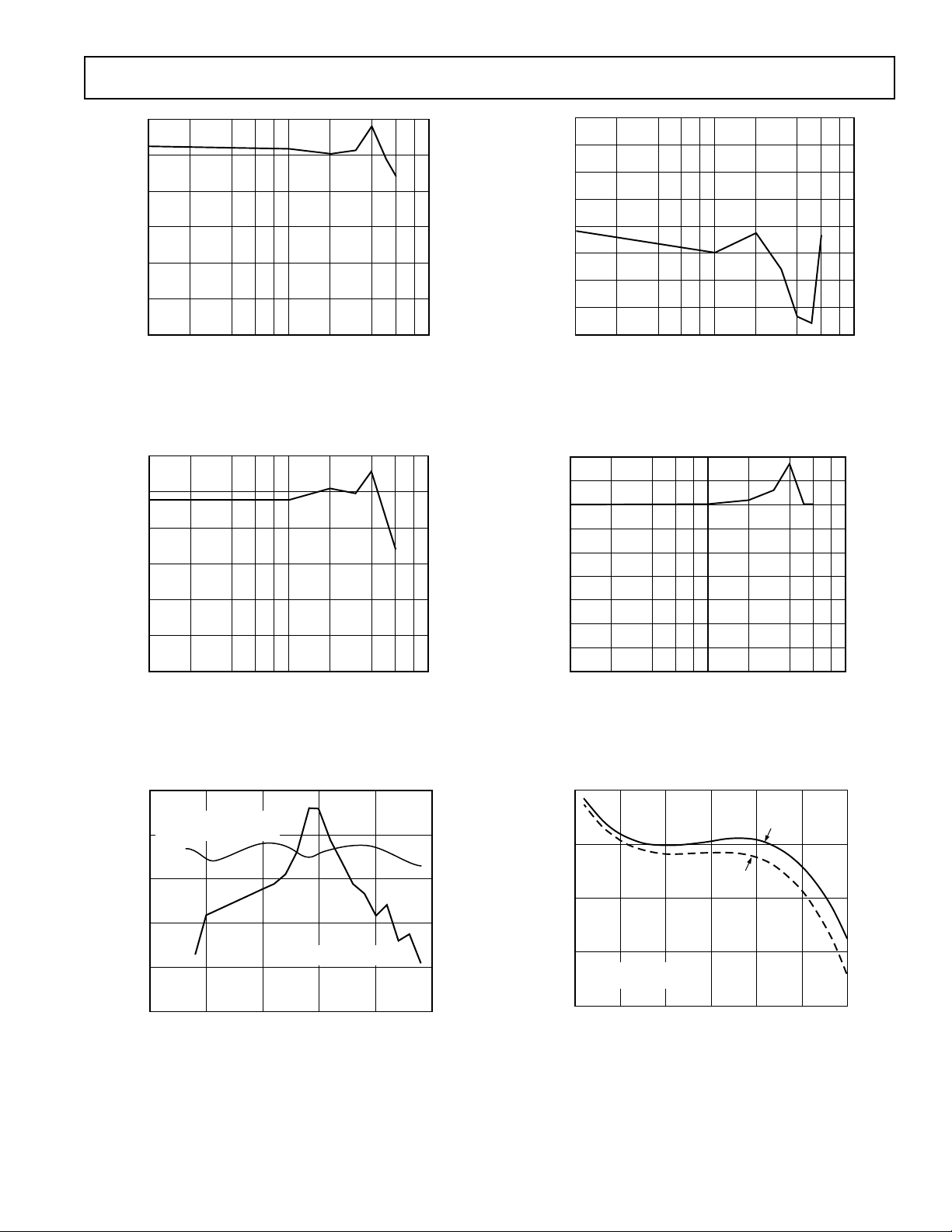
Figure 7. 1 dB Compression Point vs. Frequency, Gain = 1
12
10
8
6
4
1dB COMPRESSION POINT – dBm
2
0
10 1000100
FREQUENCY – MHz
1.00
0.75
0.50
0.25
0.00
–0.25
GAIN ERROR – dB
–0.50
–0.75
–1.00
10 1000100
FREQUENCY – MHz
Figure 10. Gain Error vs. Frequency, Gain = 1
9
8
7
6
5
4
3
2
1dB COMPRESSION POINT – dBm
1
0
10 1000100
FREQUENCY – MHz
Figure 8. 1 dB Compression Point vs. RF Input, Gain = 2
25
MIXER OUTPUT
TRANSFORMER
22
COUPLED PER FIGURE 18
19
16
13
REV. B
THIRD ORDER INTERCEPT – dBm
10
100 350250150 200 300
Figure 9. Third-Order Intercept vs. Frequency , LO Held
Constant at 241 MHz
FREQUENCY – MHz
MIXER PLUS AMPLIFIER,
G = 1
Figure 11. 1 dB Compression Pointvs.Frequency,Gain = 4
Figure 12. Input 1 dB Compression Point vs. Frequency,
Gain = 1, 9 V Single Supply
–5–
 Loading...
Loading...