X1
X2
Y1
Y2
V
P
OUT
NC
V
N
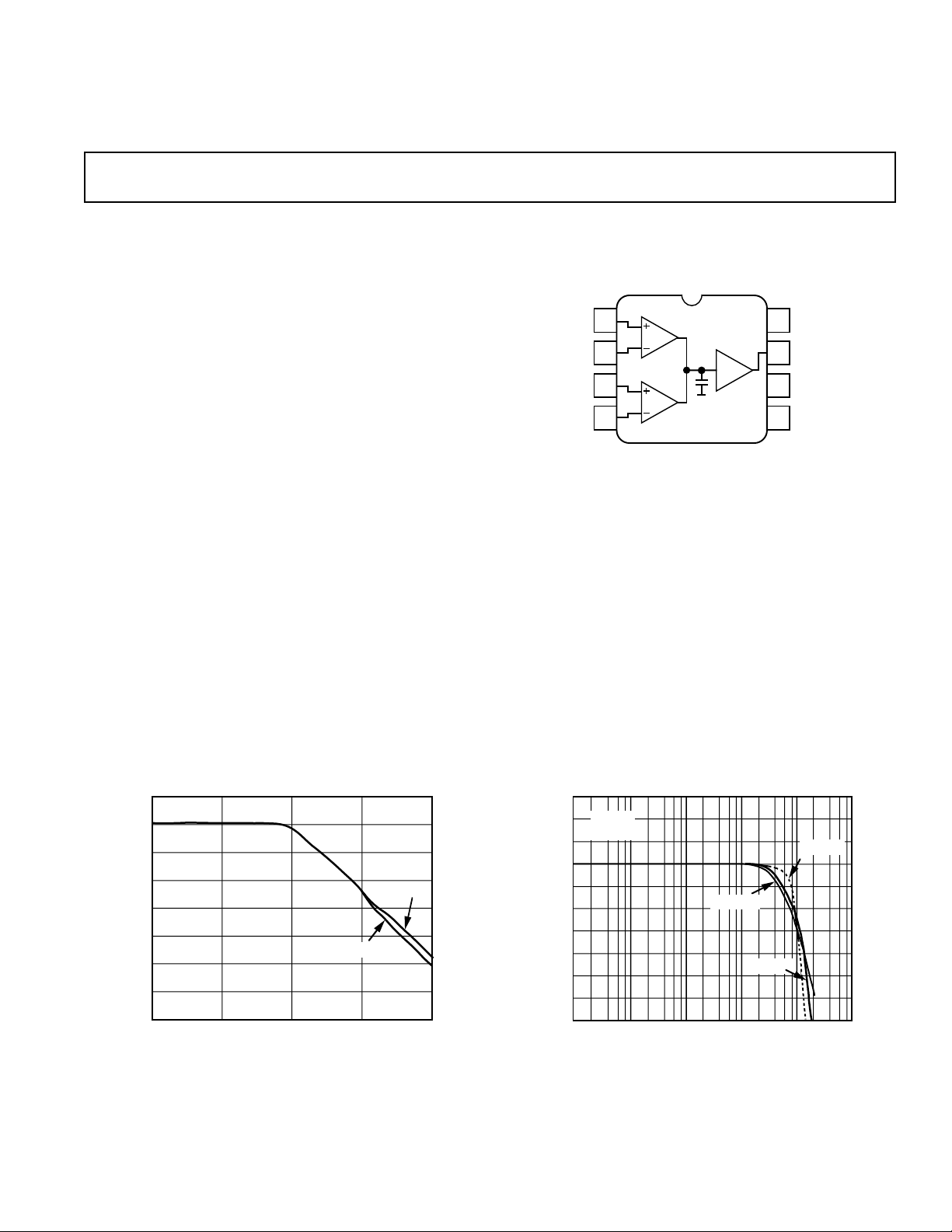
AD830
NC = NO CONNECT
1
2
3
4
8
7
6
5
A=1
V→1
V→1
High Speed, Video
9
–6
–21
100k 1G10M1M10k
–3
0
3
6
–18
–15
–12
–9
FREQUENCY – Hz
GAIN – dB
100M
VS = ±5V
RL = 150Ω
CL = 4.7pF
CL = 15pF
CL = 33pF
a
FEATURES
Differential Amplification
Wide Common-Mode Voltage Range: +12.8 V, –12 V
Differential Voltage Range: 62 V
High CMRR: 60 dB @ 4 MHz
Built-in Differential Clipping Level: 62.3 V
Fast Dynamic Performance
85 MHz Unity Gain Bandwidth
35 ns Settling Time to 0.1%
360 V/ms Slew Rate
Symmetrical Dynamic Response
Excellent Video Specifications
Differential Gain Error: 0.06%
Differential Phase Error: 0.088
15 MHz (0.1 dB) Bandwidth
Flexible Operation
High Output Drive of 650 mA min
Specified with Both 65 V and 615 V Supplies
Low Distortion: THD = –72 dB @ 4 MHz
Excellent DC Performance: 3 mV max Input Offset
Voltage
APPLICATIONS
Differential Line Receiver
High Speed Level Shifter
High Speed In-Amp
Differential to Single Ended Conversion
Resistorless Summation and Subtraction
High Speed A/D Driver
PRODUCT DESCRIPTION
The AD830 is a wideband, differencing amplifier designed for
use at video frequencies but also useful in many other applications. It accurately amplifies a fully differential signal at the
110
Difference Amplifier
AD830
CONNECTION DIAGRAM
8-Pin Plastic Mini-DIP (N),
Cerdip (Q) and SOIC (R) Packages
input and produces an output voltage referred to a user-chosen
level. The undesired common-mode signal is rejected, even at
high frequencies. High impedance inputs ease interfacing to finite source impedances and thus preserve the excellent
common-mode rejection. In many respects, it offers significant
improvements over discrete difference amplifier approaches, in
particular in high frequency common-mode rejection.
The wide common-mode and differential-voltage range of the
AD830 make it particularly useful and flexible in level shifting
applications, but at lower power dissipation than discrete solutions. Low distortion is preserved over the many possible differential and common-mode voltages at the input and output.
Good gain flatness and excellent differential gain of 0.06% and
phase of 0.08° make the AD830 suitable for many video system
applications. Furthermore, the AD830 is suited for general purpose signal processing from dc to 10 MHz.
100
90
80
70
CMRR – dB
60
50
REV. A
Information furnished by Analog Devices is believed to be accurate and
reliable. However, no responsibility is assumed by Analog Devices for its
use, nor for any infringements of patents or other rights of third parties
which may result from its use. No license is granted by implication or
otherwise under any patent or patent rights of Analog Devices.
40
30
1k
Common-Mode Rejection Ratio vs. Frequency
FREQUENCY – Hz
VS = ±15V
VS = ±5V
1M100k10k
10M
Closed-Loop Gain vs. Frequency, Gain = +1
One Technology Way, P.O. Box 9106, Norwood, MA 02062-9106, U.S.A.
Tel: 617/329-4700 Fax: 617/326-8703
AD830–SPECIFICA TIONS
(VS = 615 V, R
= 150 V, C
LOAD
= 5 pF, TA = +258C unless otherwise noted)
LOAD
AD830J/A AD830S
1
Parameter Conditions Min Typ Max Min Typ Max Units
DYNAMIC CHARACTERISTICS
3 dB Small Signal Bandwidth Gain = 1, V
0.1 dB Gain Flatness Frequency Gain = 1, V
= 100 mV rms 75 85 75 85 MHz
OUT
= 100 mV rms 11 15 11 15 MHz
OUT
Differential Gain Error 0 to +0.7 V, Frequency = 4.5 MHz 0.06 0.09 0.06 0.09 %
Differential Phase Error 0 to +0.7 V, Frequency = 4.5 MHz 0.08 0.12 0.08 0.12 Degrees
Slew Rate 2 V Step, R
4 V Step, R
3 dB Large Signal Bandwidth Gain = 1, V
Settling Time, Gain = 1 V
V
OUT
OUT
= 500 Ω 360 360 V/µs
L
= 500 Ω 350 350 V/µs
L
= 1 V rms 38 45 38 45 MHz
OUT
= 2 V Step, to 0.1% 25 25 ns
= 4 V Step, to 0.1% 35 35 ns
Harmonic Distortion 2 V p-p, Frequency = 1 MHz –82 –82 dBc
2 V p-p, Frequency = 4 MHz –72 –72 dBc
Input Voltage Noise Frequency = 10 kHz 27 27 nV/√
Input Current Noise 1.4 1.4 pA/√Hz
DC PERFORMANCE
Offset Voltage Gain = 1 ±1.5 ±3 ±1.5 ±3mV
Gain = 1, T
MIN–TMAX
±5 ±7mV
Open Loop Gain DC 64 69 64 69 dB
Gain Error R
= 1 kΩ, G = ±1 ±0.1 ±0.6 ±0.1 ±0.6 %
L
Peak Nonlinearity, RL= 1 kΩ, –1 V ≤ X ≤ +1 V 0.01 0.03 0.01 0.03 % FS
Gain = 1 –1.5 V ≤ X ≤ +1.5 V 0.035 0.07 0.035 0.07 % FS
–2 V ≤ X ≤ +2 V 0.15 0.4 0.15 0.4 % FS
Input Bias Current V
Input Offset Current VIN = 0 V, T
= 0 V, +25°C to T
IN
V
= 0 V, T
IN
MIN
MIN–TMAX
MAX
510 510µA
713 817µA
0.1 1 0.1 1 µA
INPUT CHARACTERISTICS
Differential Voltage Range V
Differential Clipping Level
2
Common-Mode Voltage Range V
= 0 ±2.0 ±2.0 V
CM
Pins 1 and 2 Inputs Only ±2.1 ±2.3 ±2.1 ±2.3 V
= ±1 V –12.0 +12.8 –12.0 +12.8 V
DM
CMRR DC, Pins 1, 2, ±10 V 90 100 90 100 dB
DC, Pins 1, 2, ±10 V, T
MIN–TMAX
88 86 dB
Frequency = 4 MHz 55 60 55 60 dB
Input Resistance 370 370 kΩ
Input Capacitance 2 2 pF
Hz
OUTPUT CHARACTERISTICS
Output Voltage Swing R
≥ 1 kΩ±12 +13.8, –13.8 ±12 +13.8, –13.8 V
L
RL ≥ 1 kΩ, ±16.5 V
S
±13 +15.3, –14.7 ±13 +15.3, –14.7 V
Short Circuit Current Short to Ground ±80 ±80 mA
Output Current RL = 150 Ω±50 ±50 mA
POWER SUPPLIES
Operating Range ±4 ±16.5 ±4 ±16.5 V
Quiescent Current T
MIN–TMAX
14.5 17 14.5 17 mA
+ PSRR (to VP) DC, G = 1 86 86 dB
– PSRR (to V
PSRR DC, G = 1, ±5 to ±15 V
PSRR DC, G = 1, ±5 to ±15 V
NOTES
1
See Standard Military Drawing 5962-9313001MPA for specifications.
2
Clipping level function on X channel only.
Specifications subject to change without notice.
) DC, G = 1 68 68 dB
N
S
,
T
MIN–TMAX
S
66 71 66 71 dB
62 68 60 68 dB
–2–
REV. A
AD830
(VS = 65 V, R
Parameter Conditions Min Typ Max Min Typ Max Units
DYNAMIC CHARACTERISTICS
3 dB Small Signal Bandwidth Gain = 1, V
0.1 dB Gain Flatness Frequency Gain = 1, V
Differential Gain Error 0 to +0.7 V, Frequency = 4.5 MHz,
Differential Phase Error 0 to +0.7 V, Frequency = 4.5 MHz,
Slew Rate, Gain = 1 2 V Step, R
3 dB Large Signal Bandwidth Gain = 1, V
Settling Time V
Harmonic Distortion 2 V p-p, Frequency = 1 MHz –69 –69 dBc
Input Voltage Noise Frequency = 10 kHz 27 27 nV/√
Input Current Noise 1.4 1.4 pA/√Hz
DC PERFORMANCE
Offset Voltage Gain = 1 ±1.5 ±3 ±1.5 ±3mV
Open Loop Gain DC 60 65 60 65 dB
Unity Gain Accuracy R
Peak Nonlinearity, RL= 1 kΩ –1 V ≤ X ≤ +1 V 0.01 0.03 0.01 0.03 % FS
Input Bias Current V
Input Offset Current VIN = 0 V, T
INPUT CHARACTERISTICS
Differential Voltage Range V
Differential Clipping Level
Common-Mode Voltage Range V
CMRR DC, Pins 1, 2, +4 V to –2 V 90 100 90 100 dB
Input Resistance 370 370 kΩ
Input Capacitance 2 2 pF
OUTPUT CHARACTERISTICS
Output Voltage Swing R
Short Circuit Current Short to Ground –55, +70 –55, +70 mA
Output Current ±40 ±40 mA
= 150 V, C
LOAD
= 5 pF, TA = +258C unless otherwise noted)
LOAD
= 100 mV rms 35 40 35 40 MHz
OUT
= 100 mV rms 5 6.5 5 6.5 MHz
OUT
G = +2 0.14 0.18 0.14 0.18 %
G = +2 0.32 0.4 0.32 0.4 Degrees
= 500 Ω 210 210 V/µs
L
4 V Step, RL = 500 Ω 240 240 V/µs
= 1 V rms 30 36 30 36 MHz
OUT
= 2 V Step, to 0.1% 35 35 ns
OUT
V
= 4 V Step, to 0.1% 48 48 ns
OUT
2 V p-p, Frequency = 4 MHz –56 –56 dBc
Gain = 1, T
= 1 kΩ±0.1 ±0.6 ±0.1 ±0.6 %
L
MIN–TMAX
–1.5 V ≤ X ≤ +1.5 V 0.045 0.07 0.045 0.07 % FS
–2 V ≤ X ≤ +2 V 0.23 0.4 0.23 0.4 % FS
= 0 V, +25°C to T
IN
V
= 0 V, T
IN
= 0 ±2.0 ±2.0 V
2
CM
Pins 1 and 2 Inputs Only ±2.0 ±2.2 ±2.0 ±2.2 V
= ±1 V –2.0 +2.9 –2.0 +2.9 V
DM
MIN
MIN–TMAX
MAX
DC, Pins 1, 2, +4 V to –2 V,
T
MIN–TMAX
Frequency = 4 MHz 55 60 55 60 dB
≥ 150 Ω±3.2 ±3.5 ±3.2 ±3.5 V
L
RL ≥ 150 Ω, ±4 V
S
AD830J/A AD830S
1
±4 ±5mV
510 510µA
713 817µA
0.1 1 0.1 1 µA
88 86 dB
±2.2 +2.7, –2.4 ±2.2 +2.7, –2.4 V
Hz
POWER SUPPLIES
Operating Range ±4 ±16.5 ±4 ±16.5 V
Quiescent Current T
+ PSRR (to V
) DC, G = 1, Offset 86 86 dB
P
MIN–TMAX
13.5 16 13.5 16 mA
– PSRR (to VN) DC, G = 1, Offset 68 68 dB
PSRR (Dual Supply) DC, G = 1, ±5 to ±15 V
S
66 71 66 71 dB
PSRR (Dual Supply) DC, G = 1, ±5 to ±15 VS,
T
MIN–TMAX
NOTES
1
See Standard Military Drawing 5962-9313001MPA for specifications.
2
Clipping level function on X channel only.
Specifications subject to change without notice.
REV. A
62 68 60 68 dB
–3–
AD830
ABSOLUTE MAXIMUM RATINGS
Supply Voltage . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .±18 V
Internal Power Dissipation
2
. . . . . . . Observe Derating Curves
1
Output Short Circuit Duration . . . . Observe Derating Curves
Common-Mode Input Voltage . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .±V
Differential Input Voltage . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .±V
S
S
Storage Temperature Range (Q) . . . . . . . . . –65°C to +150°C
Storage Temperature Range (N) . . . . . . . . . –65°C to +125°C
Storage Temperature Range (R) . . . . . . . . . –65°C to +125°C
Operating Temperature Range
AD830J . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .0°C to +70°C
AD830A . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . –40°C to +85°C
AD830S . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . –55°C to +125°C
Lead Temperature Range (Soldering 60 seconds) . . . +300 °C
NOTES
1
Stresses above those listed under “Absolute Maximum Ratings” may cause
permanent damage to the device. This is a stress rating only and functional
operation of the device at these or any other conditions above those indicated in the
operational section of this specification is not implied. Exposure to absolute
maximum rating conditions for extended periods may affect device reliability.
2
8-Pin Plastic Package: θJA = 90°C/Watt
8-Pin SOIC Package: θJA = 155°C/Watt
8-Pin Cerdip Package: θJA = 110°C/Watt
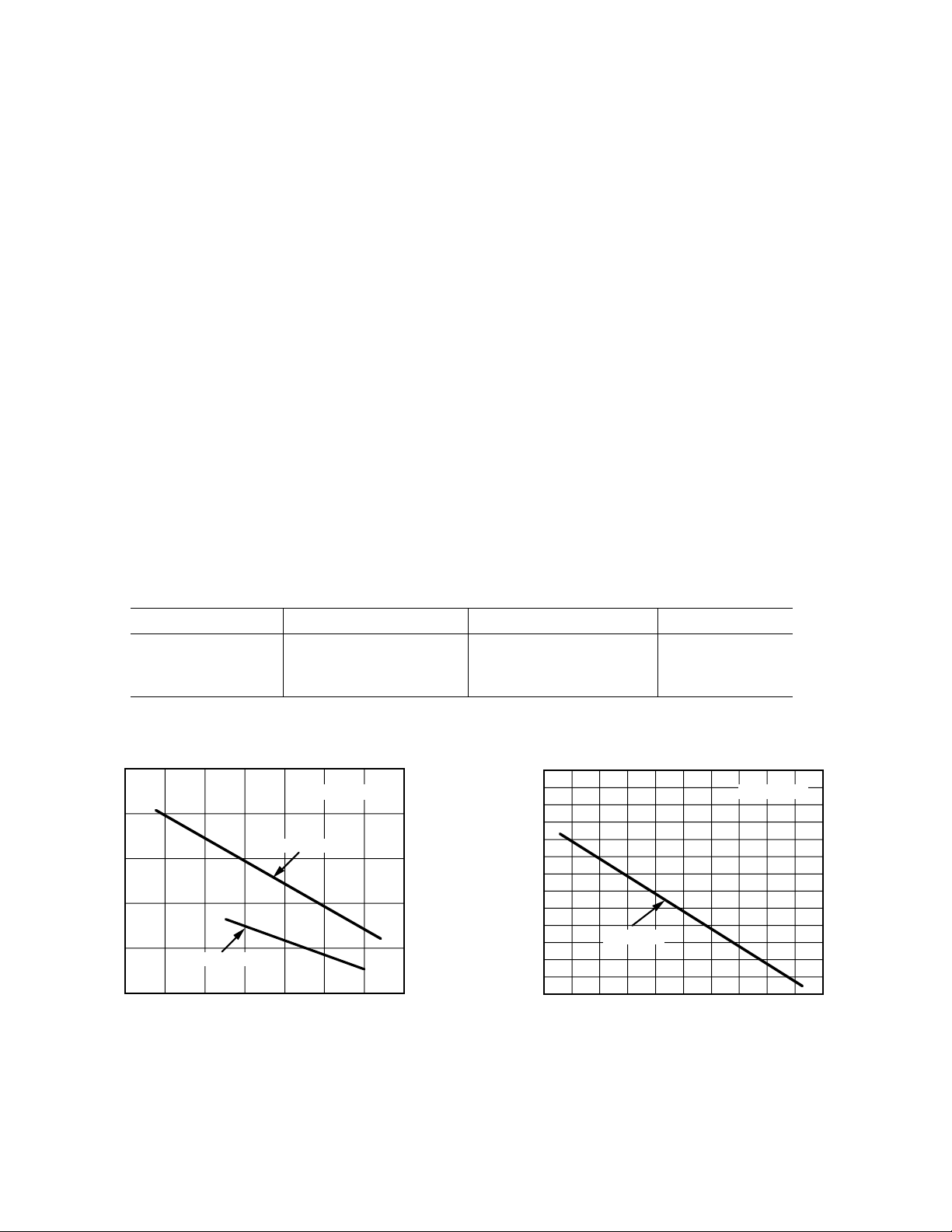
MAXIMUM POWER DISSIPATION
The maximum power that can be safely dissipated by the
AD830 is limited by the associated rise in junction temperature.
For the plastic packages, the maximum safe junction temperature is 145°C. For the cerdip, the maximum junction temperature is 175°C. If these maximums are exceeded momentarily,
proper circuit operation will be restored as soon as the die temperature is reduced. Leaving the AD830 in the “overheated”
condition for an extended period can result in permanent damage to the device. To ensure proper operation, it is important to
observe the recommended derating curves.
While the AD830 output is internally short circuit protected,
this may not be sufficient to guarantee that the maximum junction temperature is not exceeded under all conditions. If the
output is shorted to a supply rail for an extended period, then
the amplifier may be permanently destroyed.
ESD SUSCEPTIBILITY
ESD (electrostatic discharge) sensitive device. Electrostatic
charges as high as 4000 volts, which readily accumulate on the
human body and on test equipment, can discharge without detection. Although the AD830 features proprietary ESD protection circuitry, permanent damage may still occur on these
devices if they are subjected to high energy electrostatic discharges. Therefore, proper ESD precautions are recommended
to avoid any performance degradation or loss of functionality.
ORDERING GUIDE
Model Temperature Range Package Description Package Option
AD830AN –40°C to +85°C 8-Pin Plastic Mini-DIP N-8
AD830JR 0°C to +70°C 8-Pin SOIC R-8
5962-9313001MPA* –55°C to +125°C 8-Pin Cerdip Q-8
*See Standard Military Drawing for specifications.
2.5
2.0
1.5
1.0
0.5
TOTAL POWER DISSIPATION – Watts
0
–50
8-PIN SOIC
–30
AMBIENT TEMPERATURE – °C
8-PIN MINI-DIP
TJ MAX = 145°C
70503010–10
90
3.0
2.8
2.4
2.2
2.0
1.8
1.6
1.4
1.2
1.0
0.8
0.6
TOTAL POWER DISSIPATION – Watts
0.4
0.2
–60
8-PIN CERDIP
–40
AMBIENT TEMPERATURE – °C
TJ MAX = 175°C
100 120806040200–20
140
Maximum Power Dissipation vs. Temperature,
Mini-DlP and SOIC Packages
–4–
Maximum Power Dissipation vs. Temperature,
Cerdip Package
REV. A
Typical Characteristics–
FREQUENCY – Hz
3
–12
–27
100k 100M10M1M10k
–9
–6
–3
0
–24
–21
–18
–15
GAIN – dB
±15V
±5V
1G
±10V
RL = 150Ω
CL = 4.7pF
JUNCTION TEMPERATURE – °C
INPUT OFFSET VOLTAGE – mV
3
–4
140
–1
–3
–40
–2
–60
2
0
1
120100806040200–20
±5V
S
±15V
S
±10V
S
AD830
110
100
90
80
70
CMRR – dB
60
50
40
30
1k
FREQUENCY – Hz
VS = ±5V
1M100k10k
VS = ±15V
10M
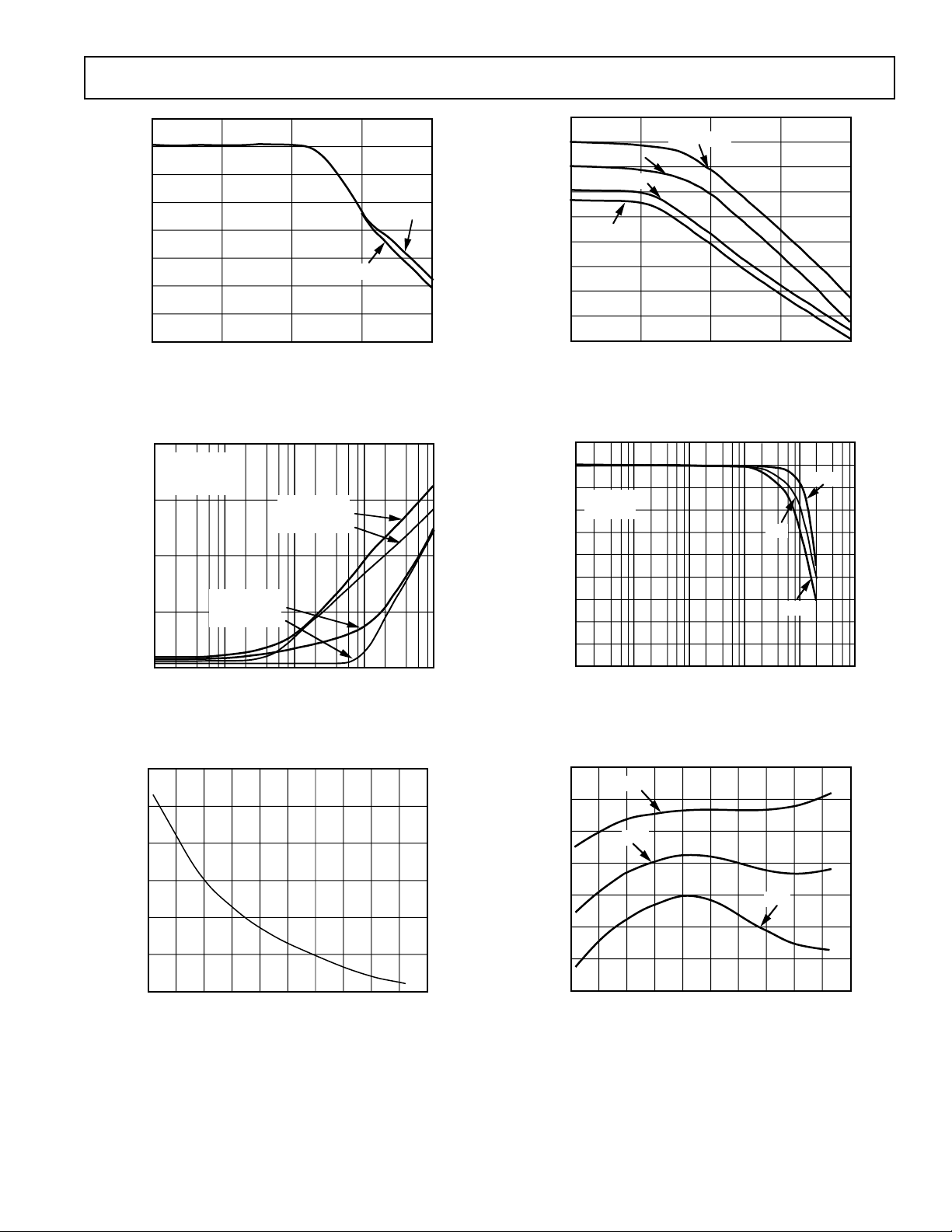
Figure 1. Common-Mode Rejection Ratio vs. Frequency
–50
V
= 2V p-p
OUT
RL = 150Ω
GAIN = +1
–60
–70
±5V SUPPLIES
2ND HARMONIC
3RD HARMONIC
100
90
TO VP @ ±5V
80
TO VN @ ±15V
70
60
TO VN @ ±5V
50
PSRR – dB
40
30
20
10
1k
TO VP @ ±15V
FREQUENCY – Hz
1M100k10k
10M
Figure 4. Power Supply Rejection Ratio vs. Frequency
–80
HARMONIC DISTORTION – dBc
–90
Figure 2. Harmonic Distortion vs. Frequency
9
8
7
6
5
INPUT CURRENT – µA
4
REV. A
3
Figure 3. Input Bias Current vs. Temperature
–40
–60
±15V SUPPLIES
2ND HARMONIC
3RD HARMONIC
10k 10M1M100k1k
FREQUENCY – Hz
JUNCTION TEMPERATURE – °C
Figure 5. Closed-Loop Gain vs. Frequency G = +1
140
120806040 100200–20
Figure 6. Input Offset Voltage vs. Temperature
–5–
 Loading...
Loading...