NC
NC
NC
+IN1
–IN1
OUT1
–V
S
+V
S
OUT2
–IN2
+IN2
NC
NC
NC
NC
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
15
11
12
13
14
10
AD815
TAB IS
+V
S
NC = NO CONNECT
REFER TO PAGE 3 FOR 24-LEAD SOIC PACKAGE
High Output Current
AMP1
+15V
–15V
R
L
120V
110V
499V
V
OUT
=
40Vp-p
V
IN
=
4Vp-p
1/2
AD815
1/2
AD815
G = +10
100V
100V
AMP2
VD =
40Vp-p
1:2
TRANSFORMER
R
1
= 15V
R2 = 15V
499V
a
FEATURES
Flexible Configuration
Differential Input and Output Driver
or Two Single-Ended Drivers
High Output Power
Power Package
26 dBm Differential Line Drive for ADSL Application
40 V p-p Differential Output Voltage, R
500 mA Minimum Output Drive/Amp, R
Thermally Enhanced SOIC
400 mA Minimum Output Drive/Amp, R
Low Distortion
–66 dB @ 1 MHz THD, R
= 200 ⍀, V
L
0.05% and 0.45ⴗ Differential Gain and Phase, R
(6 Back-Terminated Video Loads)
High Speed
120 MHz Bandwidth (–3 dB)
900 V/s Differential Slew Rate
70 ns Settling Time to 0.1%
Thermal Shutdown
APPLICATIONS
ADSL, HDSL and VDSL Line Interface Driver
Coil or Transformer Driver
CRT Convergence and Astigmatism Adjustment
Video Distribution Amp
Twisted Pair Cable Driver
PRODUCT DESCRIPTION
The AD815 consists of two high speed amplifiers capable of
supplying a minimum of 500 mA. They are typically configured
as a differential driver enabling an output signal of 40 V p-p on
±15 V supplies. This can be increased further with the use of a
–40
VS = 615V
G = +10
–50
–60
V
OUT
= 40V p-p
= 50 ⍀
L
L
L
= 40 V p-p
OUT
= 5 ⍀
= 10 ⍀
= 25 ⍀
L
Differential Driver
AD815
FUNCTIONAL BLOCK DIAGRAM
15-Lead Through-Hole SIP (Y) and Surface-Mount
DDPAK(VR)
coupling transformer with a greater than 1:1 turns ratio. The
low harmonic distortion of –66 dB @ 1 MHz into 200 Ω
combined with the wide bandwidth and high current drive make
the differential driver ideal for communication applications such
as subscriber line interfaces for ADSL, HDSL and VDSL.
The AD815 differential slew rate of 900 V/µs and high load drive
are suitable for fast dynamic control of coils or transformers,
and the video performance of 0.05% and 0.45° differential gain
and phase into a load of 25 Ω enable up to 12 back-terminated
loads to be driven.
Three package styles are available, and all work over the
industrial temperature range (–40°C to +85°C). Maximum
output power is achieved with the power package available for
through-hole mounting (Y) and surface-mounting (VR). The
24-lead SOIC (RB) is capable of driving 26 dBm for full rate
ADSL with proper heat sinking.
–70
RL = 50V
–80
(DIFFERENTIAL)
–90
–100
TOTAL HARMONIC DISTORTION – dBc
–110
REV. B
Information furnished by Analog Devices is believed to be accurate and
reliable. However, no responsibility is assumed by Analog Devices for its
use, nor for any infringements of patents or other rights of third parties
which may result from its use. No license is granted by implication or
otherwise under any patent or patent rights of Analog Devices.
100 10M1k
Total Harmonic Distortion vs. Frequency
10k 100k 1M
FREQUENCY – Hz
RL = 200V
(DIFFERENTIAL)
Subscriber Line Differential Driver
One Technology Way, P.O. Box 9106, Norwood, MA 02062-9106, U.S.A.
Tel: 781/329-4700 World Wide Web Site: http://www.analog.com
Fax: 781/326-8703 © Analog Devices, Inc., 1999
AD815–SPECIFICATIONS
(@ TA = +25ⴗC, VS = ⴞ15 V dc, RFB = 1 k⍀ and R
= 100 ⍀ unless otherwise noted)
LOAD
AD815A
Model Conditions V
S
Min Typ Max Units
DYNAMIC PERFORMANCE
Small Signal Bandwidth (–3 dB) G = +1 ±15 100 120 MHz
G = +1 ±5 90 110 MHz
Bandwidth (0.1 dB) G = +2 ±15 40 MHz
G = +2 ±5 10 MHz
Differential Slew Rate V
= 20 V p-p, G = +2 ±15 800 900 V/µs
OUT
Settling Time to 0.1% 10 V Step, G = +2 ±15 70 ns
NOISE/HARMONIC PERFORMANCE
Total Harmonic Distortion f = 1 MHz, R
Input Voltage Noise f = 10
Input Current Noise (+I
Input Current Noise (–I
) f = 10 kHz, G = +2 ±5, ±15 1.8 pA/√Hz
IN
) f = 10 kHz, G = +2 ±5, ±15 19 pA/√Hz
IN
kHz, G = +2 (Single Ended) ±5, ±15 1.85 nV/√Hz
= 200 Ω, V
LOAD
Differential Gain Error NTSC, G = +2, R
Differential Phase Error NTSC, G = +2, R
= 25 Ω±15 0.05 %
LOAD
= 25 Ω±15 0.45 Degrees
LOAD
= 40 V p-p ±15 –66 dBc
OUT
DC PERFORMANCE
Input Offset Voltage ±558mV
±15 10 15 mV
T
MIN
– T
MAX
30 mV
Input Offset Voltage Drift 20 µV/°C
Differential Offset Voltage ±50.52mV
±15 0.5 4 mV
– T
T
MIN
MAX
5mV
Differential Offset Voltage Drift 10 µV/°C
–Input Bias Current ±5, ±15 10 90 µA
T
MIN
– T
MAX
150 µA
+Input Bias Current ±5, ±15 2 5 µA
T
MIN
– T
MAX
5 µA
Differential Input Bias Current ±5, ±15 10 75 µA
– T
T
MIN
MAX
100 µA
Open-Loop Transresistance ±5, ±15 1.0 5.0 MΩ
T
MIN
– T
MAX
0.5 MΩ
INPUT CHARACTERISTICS
Differential Input Resistance +Input ±15 7 MΩ
–Input 15 Ω
Differential Input Capacitance ±15 1.4 pF
Input Common-Mode Voltage Range ±15 13.5 ±V
±53.5±V
Common-Mode Rejection Ratio T
Differential Common-Mode Rejection Ratio T
MIN
MIN
– T
– T
MAX
MAX
±5, ±15 57 65 dB
±5, ±15 80 100 dB
OUTPUT CHARACTERISTICS
Voltage Swing Single Ended, R
= 25 Ω±15 11.0 11.7 ±V
LOAD
±5 1.1 1.8 ±V
= 50 Ω±15 21 23 ±V
LOAD
±15 22.5 24.5 ±V
Output Current
1, 2
VR, Y R
Differential, R
T
– T
MIN
MAX
= 5 Ω±15 500 750 mA
LOAD
±5 350 400 mA
RB-24 R
= 10 Ω±15 400 500 mA
LOAD
Short Circuit Current ±15 1.0 A
Output Resistance ±15 13 Ω
MATCHING CHARACTERISTICS
Crosstalk f = 1 MHz ±15 –65 dB
POWER SUPPLY
Operating Range
3
T
MIN
– T
MAX
±18 V
Quiescent Current ±52330mA
±15 30 40 mA
– T
T
MIN
MAX
±540mA
±15 55 mA
Power Supply Rejection Ratio T
NOTES
1
Output current is limited in the 24-lead SOIC package to the maximum power dissipation. See absolute maximum ratings and derating curves.
2
See Figure 12 for bandwidth, gain, output drive recommended operation range.
3
Observe derating curves for maximum junction temperature.
Specifications subject to change without notice.
MIN
– T
MAX
±5, ±15 –55 –66 dB
REV. B–2–
AD815
AMBIENT TEMPERATURE – 8C
14
7
4
–50 90–40
MAXIMUM POWER DISSIPATION – Watts
–30 –20 –10 10 20 30 40 50 60 70 80
13
8
6
5
11
9
12
10
0
TJ = 1508C
3
2
1
0
AD815 AVR, AY
θ
JA
= 418C/W
(STILL AIR = 0FT/MIN)
NO HEAT SINK
θ
JA
= 528C/W
(STILL AIR = 0 FT/MIN)
NO HEAT SINK
AD815ARB-24
θ
JA
= 168C/W
SOLDERED DOWN TO
COPPER HEAT SINK
(STILL AIR = 0FT/MIN)
AD815 AVR, AY
WARNING!
ESD SENSITIVE DEVICE
ABSOLUTE MAXIMUM RATINGS
Supply Voltage . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . ±18 V Total
Internal Power Dissipation
2
1
Plastic (Y and VR) . . 3.05 Watts (Observe Derating Curves)
Small Outline (RB) . . 2.4 Watts (Observe Derating Curves)
Input Voltage (Common Mode) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . ±V
S
Differential Input Voltage . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . ±6 V
Output Short Circuit Duration
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Observe Power Derating Curves
Can Only Short to Ground
Storage Temperature Range
Y, VR and RB Package . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . –65°C to +125°C
Operating Temperature Range
AD815A . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . –40°C to +85°C
Lead Temperature Range (Soldering, 10 sec) . . . . . . . +300°C
NOTES
1
Stresses above those listed under Absolute Maximum Ratings may cause perma-
nent damage to the device. This is a stress rating only; functional operation of the
device at these or any other conditions above those indicated in the operational
section of this specification is not implied. Exposure to absolute maximum rating
conditions for extended periods may affect device reliability.
2
Specification is for device in free air with 0 ft/min air flow: 15-Lead Through-Hole
and Surface Mount: θJA = 41°C/W; 24-Lead Surface Mount: θJA = 52°C/W.
PIN CONFIGURATION
24-Lead Thermally-Enhanced SOIC (RB-24)
1
NC
2
NC
3
NC
4
NC
5
THERMAL
HEAT TABS
+V
*
S
+IN1
–IN1
OUT1
–V
*HEAT TABS ARE CONNECTED TO THE POSITIVE SUPPLY.
AD815
6
TOP VIEW
(Not to Scale)
7
8
9
10
11
12
S
NC = NO CONNECT
24
23
22
21
20
19
18
17
16
15
14
13
NC
NC
NC
NC
THERMAL
HEAT TABS
+V
S
+IN2
–IN2
OUT2
+V
S
*
MAXIMUM POWER DISSIPATION
The maximum power that can be safely dissipated by the AD815
is limited by the associated rise in junction temperature. The
maximum safe junction temperature for the plastic encapsulated
parts is determined by the glass transition temperature of the
plastic, about 150°C. Exceeding this limit temporarily may
cause a shift in parametric performance due to a change in the
stresses exerted on the die by the package. Exceeding a junction
temperature of 175°C for an extended period can result in
device failure.
The AD815 has thermal shutdown protection, which guarantees
that the maximum junction temperature of the die remains below a
safe level, even when the output is shorted to ground. Shorting
the output to either power supply will result in device failure.
To ensure proper operation, it is important to observe the
derating curves and refer to the section on power considerations.
It must also be noted that in high (noninverting) gain configurations
(with low values of gain resistor), a high level of input overdrive
can result in a large input error current, which may result in a
significant power dissipation in the input stage. This power
must be included when computing the junction temperature rise
due to total internal power.
Plot of Maximum Power Dissipation vs. Temperature
Model Temperature Range Package Description Package Option
AD815ARB-24 –40°C to +85°C 24-Lead Thermally Enhanced SOIC RB-24
AD815ARB-24-REEL –40°C to +85°C 24-Lead Thermally Enhanced SOIC RB-24
AD815AVR –40°C to +85°C 15-Lead Surface Mount DDPAK VR-15
AD815AY –40°C to +85°C 15-Lead Through-Hole SIP with Staggered Leads and 90° Lead Form Y-15
AD815AYS –40°C to +85°C 15-Lead Through-Hole SIP with Staggered Leads and Straight Lead Form YS-15
AD815-EB Evaluation Board
CAUTION
ESD (electrostatic discharge) sensitive device. Electrostatic charges as high as 4000 V readily
accumulate on the human body and test equipment and can discharge without detection.
Although the AD815 features proprietary ESD protection circuitry, permanent damage may
occur on devices subjected to high energy electrostatic discharges. Therefore, proper ESD
precautions are recommended to avoid performance degradation or loss of functionality.
REV. B –3–
ORDERING GUIDE
AD815–Typical Performance Characteristics
JUNCTION TEMPERATURE – 8C
–40 100–20020406080
36
34
18
SUPPLY CURRENT – mA
26
24
22
20
30
28
32
VS = 615V
VS = 65V
SUPPLY VOLTAGE – 6Volts
33
30
18
0162
TOTAL SUPPLY CURRENT – mA
468101214
27
24
21
TA = +258C
AD815
20
15
10
5
COMMON-MODE VOLTAGE RANGE – 6Volts
0
0205
SUPPLY VOLTAGE – 6Volts
10 15
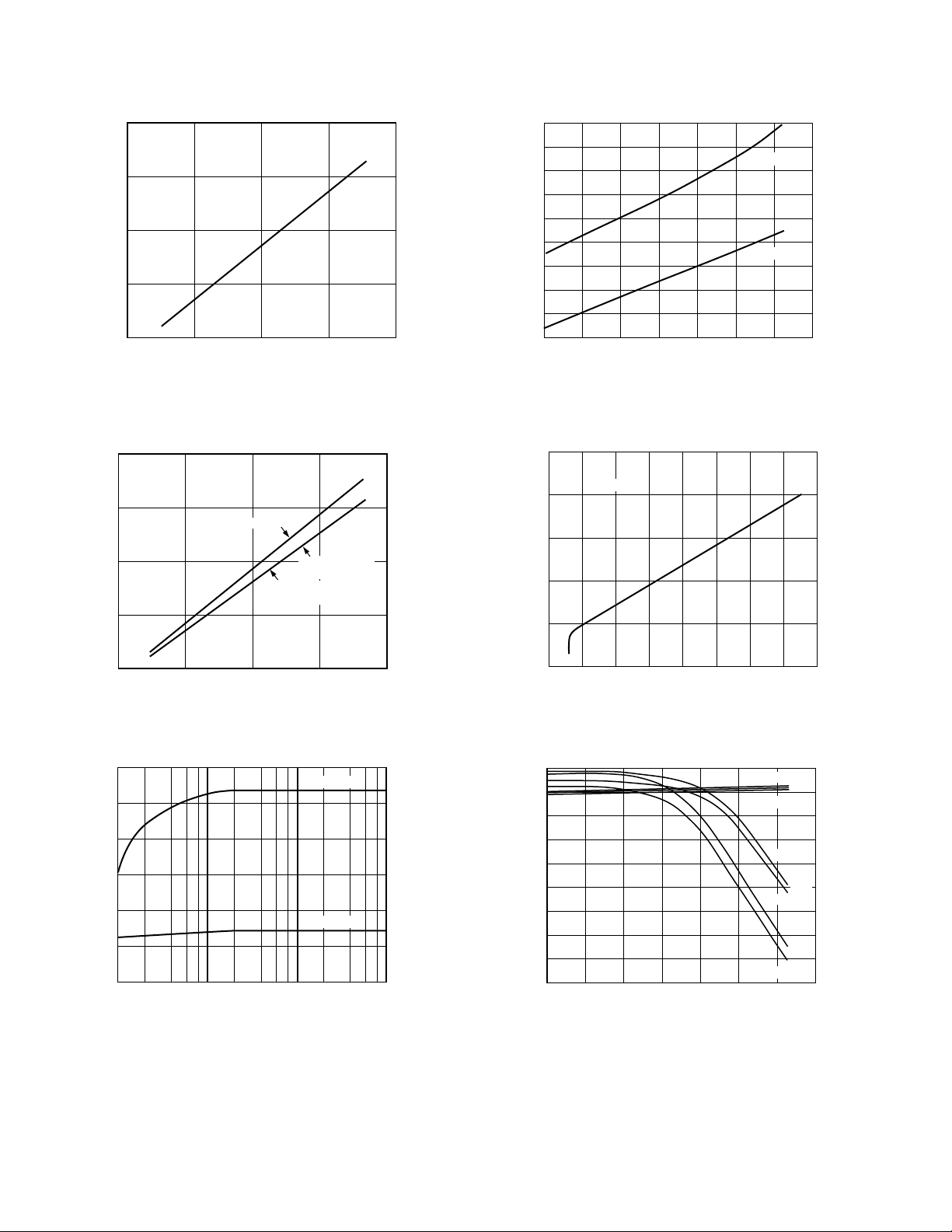
Figure 1. Input Common-Mode Voltage Range vs. Supply
Voltage
Figure 4. Total Supply Current vs. Temperature
40
30
NO LOAD
20
10
SINGLE-ENDED OUTPUT VOLTAGE – V p-p
0
02051015
SUPPLY VOLTAGE – 6Volts
Figure 2. Output Voltage Swing vs. Supply Voltage
30
25
20
15
10
5
SINGLE-ENDED OUTPUT VOLTAGE – Volts p-p
0
10 10k100 1k
LOAD RESISTANCE – (Differential – V) (Single-Ended – V/2)
Figure 3. Output Voltage Swing vs. Load Resistance
RL = 50V
(DIFFERENTIAL)
RL = 25V
(SINGLE-ENDED)
VS = 615V
VS = 65V
80
60
40
20
DIFFERENTIAL OUTPUT VOLTAGE – V p-p
0
Figure 5. Total Supply Current vs. Supply Voltage
60
50
40
30
20
10
DIFFERENTIAL OUTPUT VOLTAGE – Volts p-p
0
10
0
–10
–20
–30
–40
–50
INPUT BIAS CURRENT – mA
–60
–70
–80
–40 100–20 0 20 40 60 80
Figure 6. Input Bias Current vs. Temperature
JUNCTION TEMPERATURE – 8C
SIDE A, B
VS = 615V, 65V
VS = 65V
SIDE B
–I
SIDE A
SIDE B
SIDE A
–I
VS = 615V
+I
B
B
B
REV. B–4–
AD815
LOAD CURRENT – Amps
80
0
–60
40
20
–20
–40
60
–2.0 2.0–1.6 –1.2 –0.8 –0.4
0
0.4 0.8 1.2 1.6
VS =
610V
VS =
65V
RTI OFFSET – mV
VS =
615V
TA = 258C
1kV
1kV
R
L
=
5V
V
OUT
1/2
AD815
100V
49.9V
V
IN
f = 0.1Hz
FREQUENCY – Hz
100
30k 300M100k
CLOSED-LOOP OUTPUT RESISTANCE – V
1M 10M 100M
10
1
0.1
0.01
300k 3M 30M
VS = 65V
VS = 615V
FREQUENCY – MHz
40
0
0146
DIFFERENTIAL OUTPUT VOLTAGE – V p-p
10
30
20
10
RL = 50V
RL = 25V
RL = 1V
24 8 12
RL = 100V
TA = 258C
V
S
= ±15V
0
–2
–4
–6
–8
–10
INPUT OFFSET VOLTAGE – mV
–12
–14
–40 100–20
VS = 615V
020406080
JUNCTION TEMPERATURE – 8C
VS = 65V
Figure 7. Input Offset Voltage vs. Temperature
750
VS = 615V
700
650
600
550
SHORT CIRCUIT CURRENT – mA
500
SOURCE
SINK
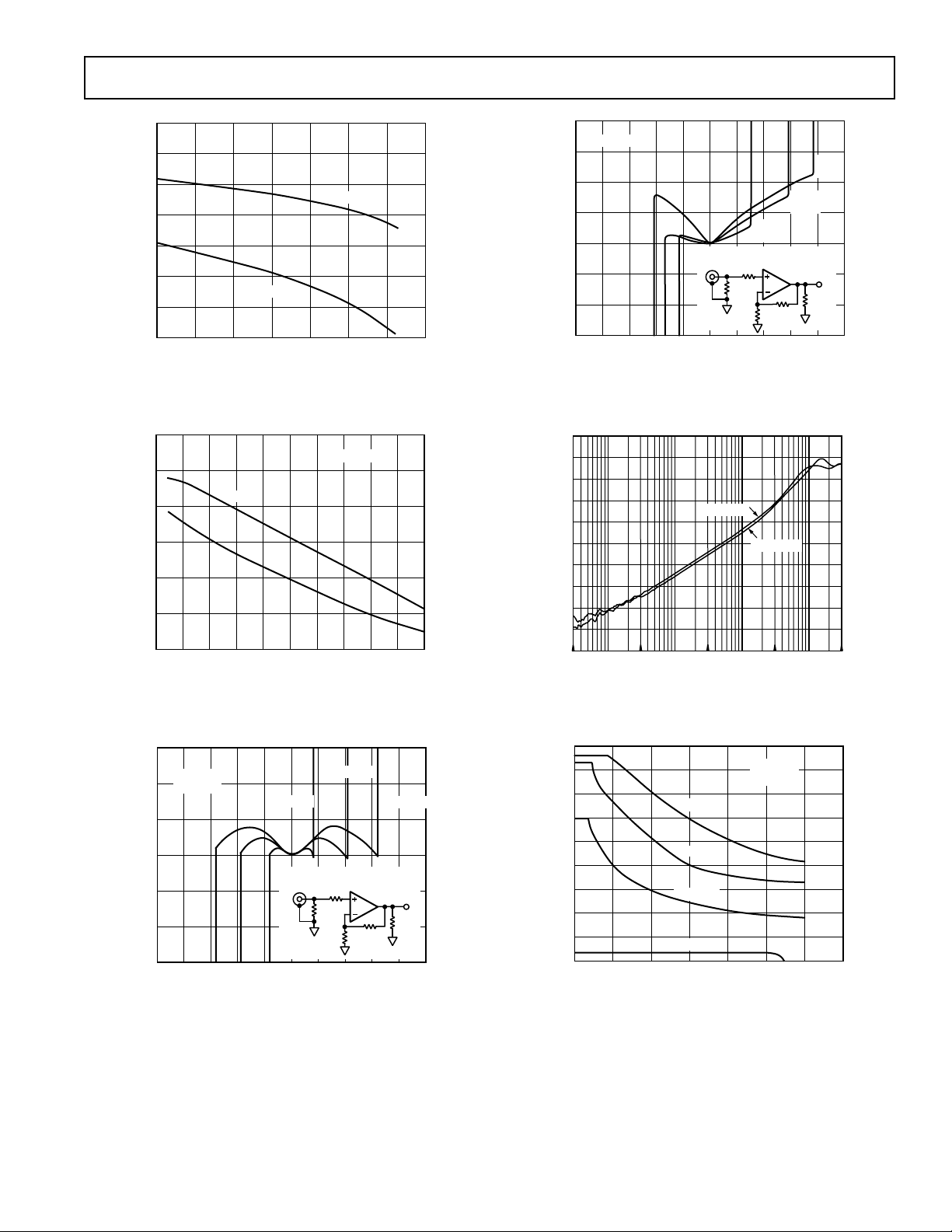
Figure 10. Thermal Nonlinearity vs. Output Current Drive
450
–60 140–40
Figure 8. Short Circuit Current vs. Temperature
15
TA = 258C
10
R
5
0
RTI OFFSET – mV
–5
–10
–15
REV. B –5–
–20 20–16 –12 –8 –4 0 4 8 12 16
Figure 9. Gain Nonlinearity vs. Output Voltage
–20 0 2 0 40 60 80 100 120
JUNCTION TEMPERATURE – 8C
VS = 610V
= 25V
L
V
VS = 65V
V
f = 0.1Hz
– Volts
OUT
IN
100V
49.9V
1kV
1/2
AD815
1kV
VS = 615V
V
OUT
=
R
L
25V
Figure 11. Closed-Loop Output Resistance vs. Frequency
Figure 12. Large Signal Frequency Response
 Loading...
Loading...