
High Speed, Triple Differential Receiver
G
www.BDTIC.com/ADI
FEATURES
High speed: 500 MHz, 2000 V/μs @ G = 1, VO = 2 V p-p
0.1 dB flatness out to 75 MHz
High CMRR: 69 dB @ 10 MHz
High differential input impedance: 1 MΩ
Wide input common-mode range: ± 3.8 V (±5 V supplies)
On-chip gain-setting resistors
C
an be configured for gain of 1 or 2
Fast settling: 15 ns to 0.1% @ 2 V p-p
Low input referred noise: 13nV/√Hz
Disable feature
Small packaging: 32-lead, 5 mm × 5 mm LFCSP
APPLICATIONS
RGB video receivers
YPbPr video receivers
KVM (keyboard, video, mouse)
UTP (unshielded twisted pair) receivers
GND
REF_G
AIN_G
IN+_G
IN–_G
REF_R
GAIN_R
GND
with Comparators
FUNCTIONAL BLOCK DIAGRAM
DIS/PD
REF_B
GAIN_B
IN+_B
IN–_B
GND
C
1
2
+
C
–
3
RR
4
+
–
5
6
+
C
–
7
RR
8
9 10111213141516
GND
R
+
–
+
–
R
AD8145
B
A
–
+
IN–_R
IN+_R
AD8145
S–
GND
V
2526272829303132
24
GND
23
OUT_B
22
OUT_G
21
OUT_R
20
V
19
COMPB_IN+
18
COMPB_IN–
17
GND
GND
S+
GENERAL DESCRIPTION
The AD8145 is a triple, low cost, differential-to-single-ended
receiver specifically designed for receiving red-green-blue
(RGB) video signals over twisted pair cable or differential
printed circuit board traces. It can also be used to receive any
type of analog signal or high speed data transmission. Two
auxiliary comparators with hysteresis are provided, which can
be used to decode video sync signals that are encoded on the
received common-mode voltages, to receive digital signals, or as
general-purpose comparators. The AD8145 can be used in
conjunction with the
ivers to provide a complete low cost solution for RGB over
dr
Category 5 UTP cable applications, including KVM.
The excellent common-mode rejection (69 dB @ 10 MHz) of
e AD8145 allows for the use of low cost, unshielded twisted
th
pair cables in noisy environments.
AD8133 or AD8134 triple differential
COMPA_IN–
COMPA_IN+
COMPB_OUT
COMPA_OUT
Figure 1.
The AD8145 can be configured for a differential-to-single-
d gain of 1 or 2 by connecting the GAIN pin of each
ende
channel to its respective output (G = 1) or connecting it to a
reference voltage (G = 2), which is normally grounded.
A REF input is provided on each channel that allows designers
to
level shift the output signals.
The AD8145 is available in a 5 mm × 5 mm, 32-lead LFCSP and
ted to work over the extended industrial temperature range
is ra
of −40°C to +105°C.
6307-001
Rev. 0
Information furnished by Analog Devices is believed to be accurate and reliable. However, no
responsibility is assumed by Anal og Devices for its use, nor for any infringements of patents or ot her
rights of third parties that may result from its use. Specifications subject to change without notice. No
license is granted by implication or otherwise under any patent or patent rights of Analog Devices.
Trademarks and registered trademarks are the property of their respective owners.
One Technology Way, P.O. Box 9106, Norwood, MA 02062-9106, U.S.A.
Tel: 781.329.4700 www.analog.com
Fax: 781.461.3113 ©2006 Analog Devices, Inc. All rights reserved.

AD8145
www.BDTIC.com/ADI
TABLE OF CONTENTS
Features.............................................................................................. 1
Applications....................................................................................... 1
Functional Block Diagram .............................................................. 1
General Description ......................................................................... 1
Revision History ............................................................................... 2
Specifications..................................................................................... 3
Absolute Maximum Ratings............................................................ 7
Thermal Resistance ...................................................................... 7
ESD Caution.................................................................................. 7
Pin Configuration and Function Description .............................. 8
Typical Performance Characteristics ............................................. 9
Theory of Operation ...................................................................... 14
REVISION HISTORY
10/06—Revision 0: Initial Version
Applications..................................................................................... 15
Overview ..................................................................................... 15
Basic Closed-Loop Gain Configurations ................................ 15
Terminating the Input................................................................ 16
Input Clamping........................................................................... 17
Printed Circuit Board Layout Considerations ....................... 18
Driving a Capacitive Load......................................................... 19
Power-Down ............................................................................... 19
Comparators ............................................................................... 20
Sync Pulse Extraction Using Comparators............................. 20
Outline Dimensions....................................................................... 21
Ordering Guide .......................................................................... 21
Rev. 0 | Page 2 of 24
AD8145
www.BDTIC.com/ADI
SPECIFICATIONS
TA = 25°C, VS = ±5 V, REF = 0 V, RL = 150 Ω, CL = 2 pF, G = 1, T
Table 1.
Parameter Conditions Min Typ Max Unit
DYNAMIC PERFORMANCE
−3 dB Bandwidth V
V
V
V
Bandwidth for 0.1 dB Flatness V
V
Slew Rate V
V
Settling Time V
= 0.2 V p-p 530 MHz
OUT
= 2 V p-p 500 MHz
OUT
= 0.2 V p-p, G = 2 200 MHz
OUT
= 2 V p-p, G = 2 200 MHz
OUT
= 2 V p-p 75 MHz
OUT
= 2 V p-p, G = 2 100 MHz
OUT
= 2 V p-p 2100 V/µs
OUT
= 2 V p-p, G = 2 2100 V/µs
OUT
= 2 V p-p, 0.1% 15 ns
OUT
Output Overdrive Recovery 20 ns
NOISE/DISTORTION
Second Harmonic V
Third Harmonic V
Crosstalk V
= 2 V p-p, 1 MHz −67 dBc
OUT
= 2 V p-p, 1 MHz −88 dBc
OUT
= 2 V p-p, 10 MHz −62 dB
OUT
Input Voltage Noise (RTI) f ≥ 10 kHz 13 nV/√Hz
Differential Gain Error NTSC, 200 IRE, RL ≥ 150 Ω 0.25 %
Differential Phase Error NTSC, 200 IRE, RL ≥ 150 Ω 0.1 Degrees
INPUT CHARACTERISTICS
Common-Mode Rejection DC, VCM = −3.5 V to +3.5 V 81 90 dB
V
V
Common-Mode Voltage Range V
= 1 V p-p, f = 10 MHz 69 dB
CM
= 1 V p-p, f = 100 MHz 41 dB
CM
− V
+IN
Differential Operating Range ±2.5 V
Resistance Differential 1 MΩ
Common mode 1.3 MΩ
Capacitance Differential 1 pF
Common mode 2 pF
DC PERFORMANCE
Closed-Loop Gain DC, G = 2 1.955 1.985 2.020 V/V
Output Offset Voltage G = 2 −17.5 7.0 1.0 mV
T
MIN
to T
Input Bias Current (+IN, −IN) 6 −3.4 −0.9 µA
Input Bias Current Drift T
MIN
to T
Input Offset Current −400 −65 300 nA
OUTPUT PERFORMANCE
Voltage Swing −4.04 3.55 V
Output Current 50 mA
Short-Circuit Current Short to GND, source/sink 195/−230 mA
to T
MIN
= 0 V ±3.5 V
−IN
−18 µV/°C
MAX
(+IN, −IN) 25 nA/°C
MAX
= −40°C to +105°C, unless otherwise noted.
MAX
Rev. 0 | Page 3 of 24

AD8145
www.BDTIC.com/ADI
Parameter Conditions Min Typ Max Unit
COMPARATOR PERFORMANCE
V
OH
V
OL
Input Offset Voltage ±2.5 mV
Hysteresis Width 18 mV
Input Bias Current 1.5 µA
Propagation Delay, t
Propagation Delay, t
Rise Time 10% to 90% 6 ns
Fall Time 10% to 90% 2 ns
POWER-DOWN PERFORMANCE
Power-Down V
Power-Down V
Power-Down I
Power-Down I
Power-Down Assert Time 1 s
POWER SUPPLY
Operating Range 4.5 11 V
Quiescent Current, Positive Supply 48.5 57.5 mA
Disabled 16 19.5 mA
Quiescent Current, Negative Supply −52 −43.5 mA
Disabled −13.9 −11 mA
PSRR, Positive Supply DC −79 −70 dB
PSRR, Negative Supply DC −68 −57 dB
PLH
PHL
IH
IL
IH
IL
RL = 1 kΩ 3.205 3.310 V
RL = 1 kΩ 0.390 0.420 V
6 ns
6 ns
V
V
0.5 µA
−250 µA
− 1.65 V
S+
− 2.65 V
S+
Rev. 0 | Page 4 of 24
AD8145
www.BDTIC.com/ADI
TA = 25°C, VS = ±2.5 V, REF = 0 V, RL = 1 kΩ, CL = 2 pF, G = 1, T
Table 2.
Parameter Conditions Min Typ Max Unit
DYNAMIC PERFORMANCE
−3 dB Bandwidth V
V
V
V
Bandwidth for 0.1 dB Flatness V
V
Slew Rate V
V
Settling Time V
= 0.2 V p-p 450 MHz
OUT
= 2 V p-p 425 MHz
OUT
= 0.2 V p-p, G = 2, RL = 150 Ω 180 MHz
OUT
= 2 V p-p, G = 2, RL = 150 Ω 180 MHz
OUT
= 2 V p-p 53 MHz
OUT
= 2 V p-p, G = 2, RL = 150 Ω 100 MHz
OUT
= 2 V p-p 2000 V/µs
OUT
= 2 V p-p, G = 2, RL = 150 Ω 2000 V/µs
OUT
= 2 V p-p, 0.1% 16 ns
OUT
Output Overdrive Recovery 10 ns
NOISE/DISTORTION
Second Harmonic V
Third Harmonic V
Crosstalk V
= 1 V p-p, 1 MHz −71 dBc
OUT
= 1 V p-p, 1 MHz −76 dBc
OUT
= 1 V p-p, 10 MHz −62 dB
OUT
Input Voltage Noise (RTI) f ≥ 10 kHz 13 nV/√Hz
INPUT CHARACTERISTICS
Common-Mode Rejection DC, VCM = −3.5 V to +3.5 V 78 86 dB
V
V
Common-Mode Voltage Range V
= 1 V p-p, f = 10 MHz 72 dB
CM
= 1 V p-p, f = 100 MHz 43 dB
CM
− V
+IN
−IN
Differential Operating Range ±1.6 V
Resistance Differential 1 MΩ
Common mode 1.3 MΩ
Capacitance Differential 1 pF
Common mode 2 pF
DC PERFORMANCE
Closed-Loop Gain DC, G = 2 1.960 1.985 2.016 V/V
Output Offset Voltage G = 2 −13.5 −4.5 2 mV
T
MIN
to T
Input Bias Current (+IN, −IN) −6 −3.5 −0.9 µA
Input Bias Current Drift T
MIN
to T
Input Offset Current −400 −60 300 nA
OUTPUT PERFORMANCE
Voltage Swing RL = 150 Ω/1 kΩ −1.35 1.3 V
Output Current 25 mA
Short-Circuit Current Short to GND, source/sink 100/−100 mA
POWER-DOWN PERFORMANCE
Power-Down V
Power-Down V
Power-Down I
Power-Down I
IH
IL
IH
IL
V
V
0.25 µA
50 µA
Power-Down Assert Time 1 s
MIN
to T
= −40°C to +105°C, unless otherwise noted.
MAX
= 0 V ±1.25 V
−18 µV/°C
MAX
(+IN, −IN) 25 nA/°C
MAX
− 1.5 V
S+
− 2.5 V
S+
Rev. 0 | Page 5 of 24

AD8145
www.BDTIC.com/ADI
Parameter Conditions Min Typ Max Unit
POWER SUPPLY
Operating Range 4.5 11 V
Quiescent Current, Positive Supply 40 47 mA
Disabled 13.5 16
Quiescent Current, Negative Supply −43.5 −36 mA
Disabled −12.5 −10
PSRR, Positive Supply DC −83 −73 dB
PSRR, Negative Supply DC −67 −62 dB
Rev. 0 | Page 6 of 24
AD8145
www.BDTIC.com/ADI
ABSOLUTE MAXIMUM RATINGS
Table 3.
Parameter Rating
Supply Voltage 12 V
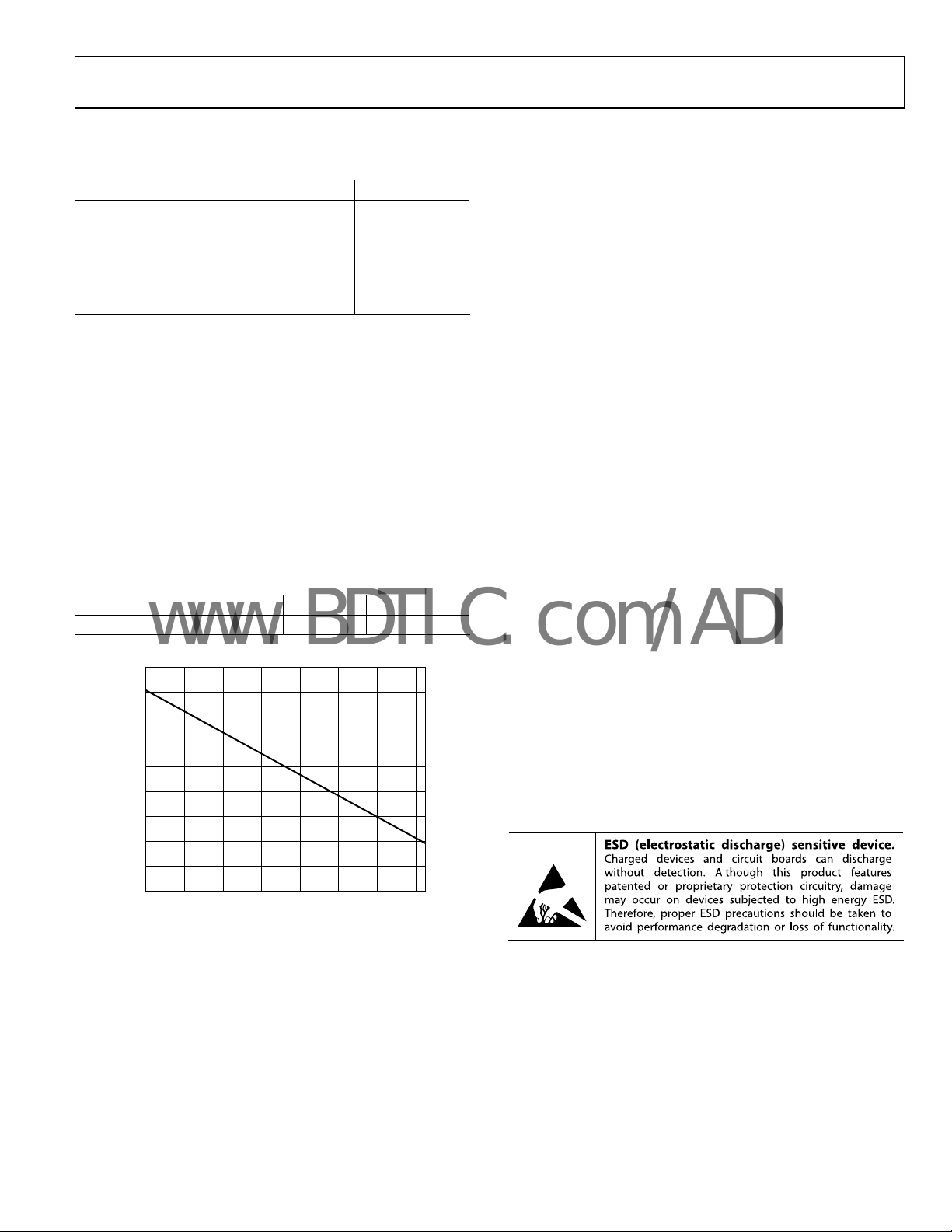
Power Dissipation See Figure 2
Storage Temperature Range –65°C to +125°C
Operating Temperature Range –40°C to +105°C
Lead Temperature Range (Soldering 10 sec) 300°C
Junction Temperature 150°C
Stresses above those listed under Absolute Maximum Ratings
may cause permanent damage to the device. This is a stress
rating only; functional operation of the device at these or any
other conditions above those indicated in the operational
section of this specification is not implied. Exposure to absolute
maximum rating conditions for extended periods may affect
device reliability.
THERMAL RESISTANCE
θJA is specified for the worst-case conditions, that is, θJA is
specified for a device soldered in the circuit board with its
exposed paddle soldered to a pad on the PCB surface, which is
thermally connected to a copper plane.
Table 4. Thermal Resistance
Package Type θJA θ
5 mm × 5 mm, 32-Lead LFCSP 47 8.5 °C/W
4.5
4.0
3.5
3.0
2.5
2.0
1.5
1.0
MAXIMUM POWER DISSIPATION (W)
0.5
0
–40 –20 0 20 40 60 80 100
AMBIENT TEMPERATURE (°C)
Figure 2. Maximum Power Dissipation vs. Temperature for a 4-Layer Board
Unit
JC
06307-002
Maximum Power Dissipation
The maximum safe power dissipation in the AD8145 package is
limited by the associated rise in junction temperature (T
) on
J
the die. At approximately 150°C, which is the glass transition
temperature, the plastic changes its properties. Even temporarily
exceeding this temperature limit can change the stresses that the
package exerts on the die, permanently shifting the parametric
performance of the AD8145. Exceeding a junction temperature
of 150°C for an extended period of time can result in changes in
the silicon devices, potentially causing failure.
The power dissipated in the package (P
) is the sum of the
D
quiescent power dissipation and the power dissipated in the
package due to the load drive for all outputs. The quiescent
power is the voltage between the supply pins (V
quiescent current (I
). The power dissipated due to the load
S
) times the
S
drive depends upon the particular application. For each output,
the power due to load drive is calculated by multiplying the load
current by the associated voltage drop across the device. The
power dissipated due to all of the loads is equal to the sum of
the power dissipation due to each individual load. RMS voltages
and currents must be used in these calculations.
Airflow increases heat dissipation, effectively reducing θ
. Also,
JA
more metal directly in contact with the package leads from
metal traces, through-holes, ground, and power planes reduces
the θ
. The exposed paddle on the underside of the package
JA
must be soldered to a pad on the PCB surface, which is
thermally connected to a copper plane to achieve the specified θ
.
JA
Figure 2 shows the maximum safe power dissipation in the
ackage vs. the ambient temperature for the 32-lead LFCSP
p
(47°C/W) on a JEDEC standard 4-layer board with the
underside paddle soldered to a pad, which is thermally
connected to a PCB plane.
ESD CAUTION
Rev. 0 | Page 7 of 24
AD8145
G
www.BDTIC.com/ADI
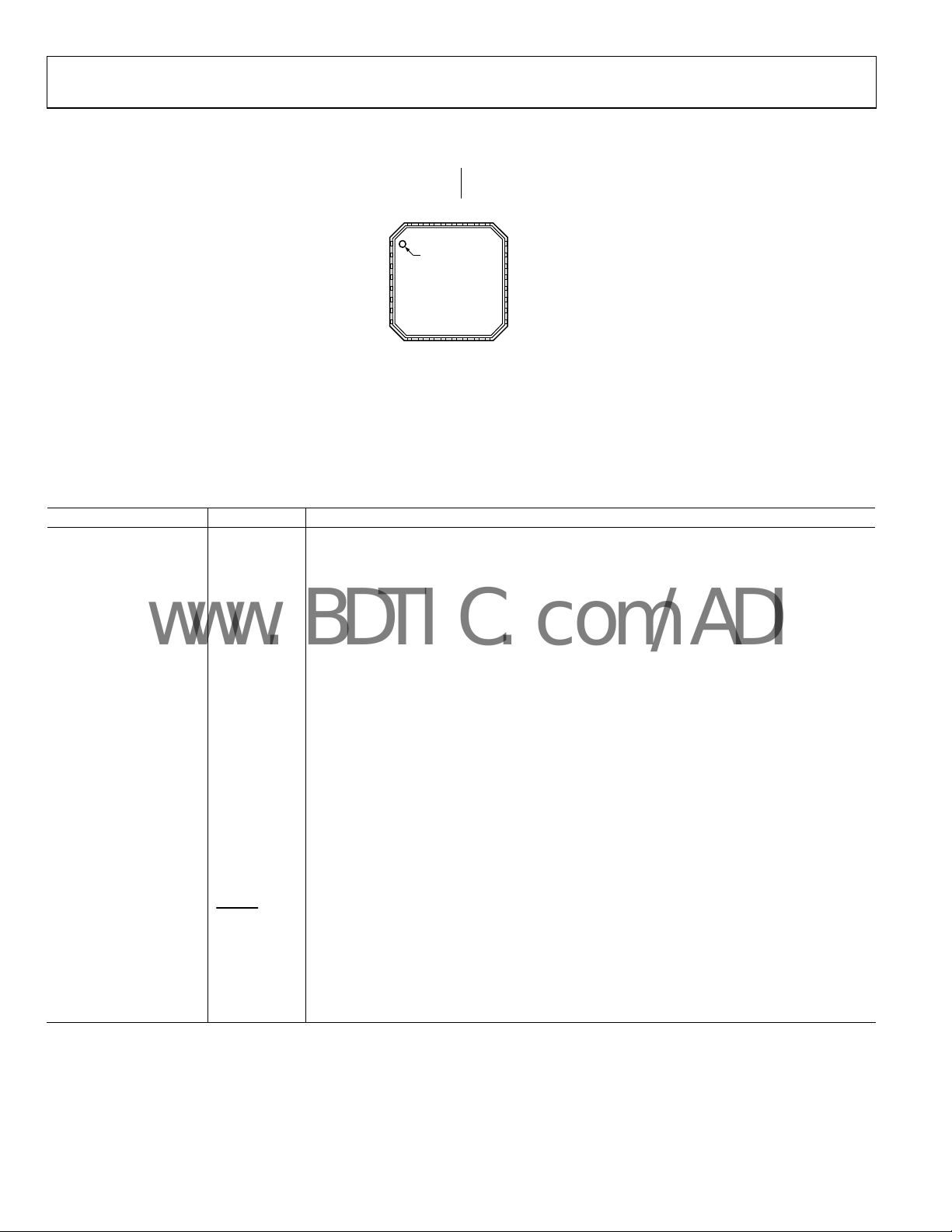
PIN CONFIGURATION AND FUNCTION DESCRIPTION
_B
S–
V
DIS/PD
REF_B
GAIN
IN+_B
IN–_B
GND
30
31
32
GND
26
27
28
29
25
15
14
UT
COMPB_OUT
COMPA_O
24 GND
23 OUT_B
22 OUT_G
21 OUT_R
20 V
19 COMPB_IN+
18 COMPB_IN–
17 GND
16
GND
S+
06307-003
1GND
PIN 1
2REF_G
INDICATO R
3
AIN_G
4IN+_G
AD8145
5IN–_G
TOP VIEW
6REF_R
(Not to Scale)
7GAIN_R
8GND
9
12
13
11
10
ND
G
IN–_R
IN+_R
COMPA_IN–
NOTES
1. EXPOSE D PAD ON UNDERSIDE O F DEVICE
MUST BE CONNECT ED TO GRO UND.
COMPA_IN+
Figure 3. 32-Lead LFCSP Pin Configuration
Table 5. 32-Lead LFCSP Pin Function Descriptions
Pin No. Mnemonic Description
1, 8, 9,16, 17, 24, 25, 32 GND Signal Ground and Thermal Plane Connection. (See the Absolute Maximum Ratings section.)
2 REF_G Reference Input, Green Channel.
3 GAIN_G Gain Connection, Green Channel.
4 IN+_G Noninverting Input, Green Channel.
5 IN−_G Inverting Input, Green Channel.
6 REF_R Reference Input, Red Channel.
7 GAIN_R Gain Connection, Red Channel.
10 IN+_R Noninverting Input, Red Channel.
11 IN−_R Inverting Input, Red Channel.
12 COMPA_IN+ Positive Input, Comparator A.
13 COMPA_IN- Negative Input, Comparator A.
14 COMPA_OUT Output, Comparator A.
15 COMPB_OUT Output, Comparator B.
18 COMPB_IN- Negative Input, Comparator B.
19 COMPB_IN+ Positive Input, Comparator B.
20 VS+ Positive Power Supply.
21 OUT_R Output, Red Channel.
22 OUT_G Output, Green Channel.
23 OUT_B Output, Blue Channel.
26 VS− Negative Power Supply.
27
DIS/PD
Disable/Power Down.
28 REF_B Reference Input, Blue Channel.
29 GAIN_B Gain Connection, Blue Channel.
30 IN+_B Noninverting Input, Blue Channel.
31 IN−_B Inverting Input, Blue Channel.
Exposed Underside Pad GND Signal Ground and Thermal Plane Connection.
Rev. 0 | Page 8 of 24
 Loading...
Loading...