Low Distortion
V
V
FEATURES
Easy to use, single-ended-to-differential conversion
Adjustable output common-mode voltage
Externally adjustable gain
Low harmonic distortion
−94 dBc SFDR @ 5 MHz
−85 dBc SFDR @ 20 MHz
−3 dB bandwidth of 320 MHz, G = +1
Fast settling to 0.01% of 16 ns
Slew rate 1150 V/μs
Fast overdrive recovery of 4 ns
Low input voltage noise of 5 nV/√Hz
1 mV typical offset voltage
Wide supply range +3 V to ±5 V
Low power 90 mW on 5 V
0.1 dB gain flatness to 40 MHz
Available in 8-Lead SOIC and MSOP packages
APPLICATIONS
ADC drivers
Single-ended-to-differential converters
IF and baseband gain blocks
Differential buffers
Line drivers
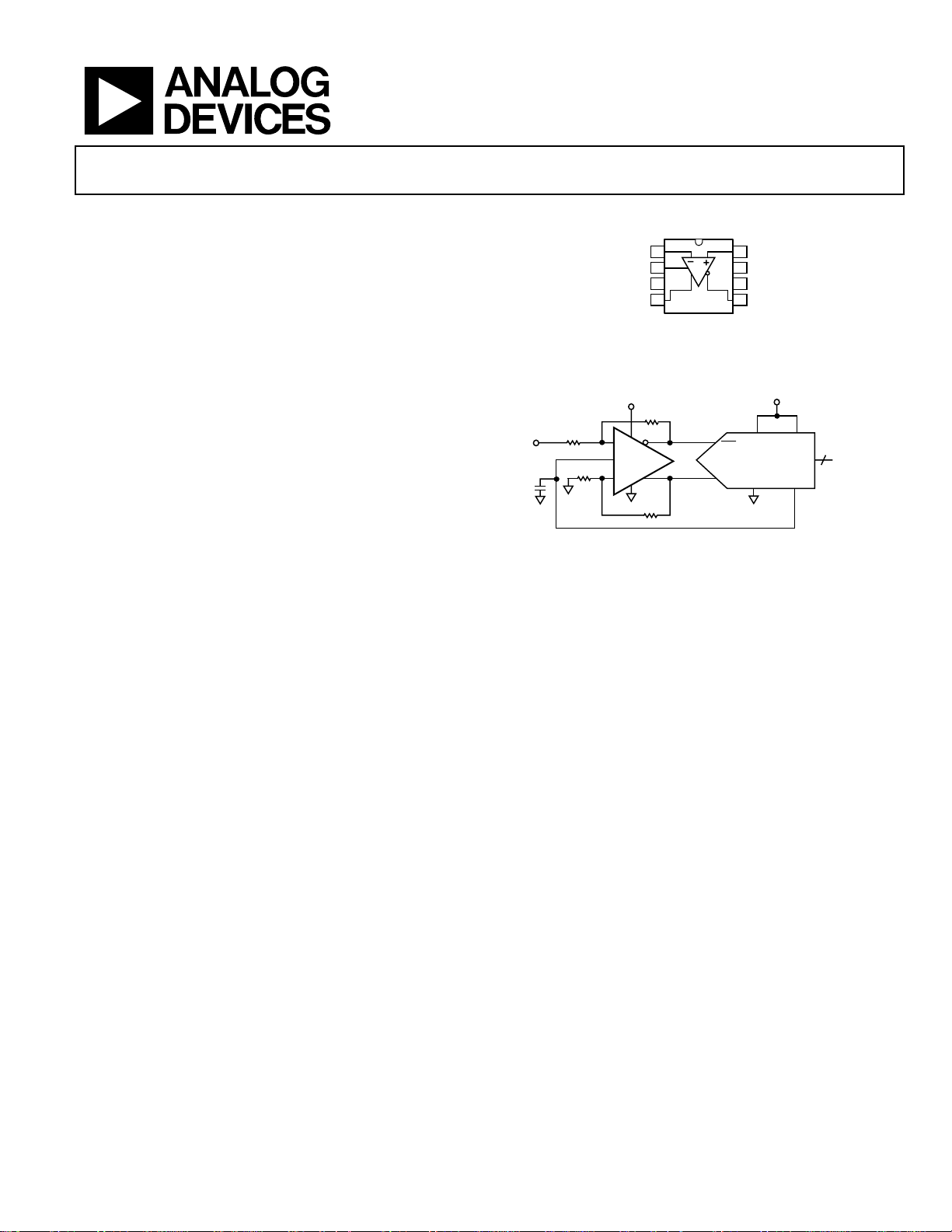
GENERAL DESCRIPTION
Differential ADC Driver
AD8138
PIN CONFIGURATION
–IN
1
V
2
OCM
V+
3
4
+OUT
AD8138
NC = NO CO NNECT
Figure 1.
TYPICAL APPLICATION CIRCUIT
5V
499Ω
499Ω
IN
499Ω
V
OCM
+
AD8138
–
499Ω
Figure 2.
8
7
6
5
AVDD DVDD
AIN
AIN
AVSS
+IN
NC
V–
–OUT
ADC
01073-001
5
DIGITAL
REF
OUTPUTS
01073-002
V
The AD8138 is a major advancement over op amps for
differential signal processing. The AD8138 can be used as a
single-ended-to-differential amplifier or as a differential-todifferential amplifier. The AD8138 is as easy to use as an op
amp and greatly simplifies differential signal amplification and
driving. Manufactured on ADI’s proprietary XFCB bipolar
process, the AD8138 has a −3 dB bandwidth of 320 MHz and
delivers a differential signal with the lowest harmonic distortion
available in a differential amplifier. The AD8138 has a unique
internal feedback feature that provides balanced output gain
and phase matching, suppressing even order harmonics. The
internal feed-back circuit also minimizes any gain error that
would be associated with the mismatches in the external gain
setting resistors.
The AD8138’s differential output helps balance the input to
differential ADCs, maximizing the performance of the ADC.
Rev. F
Information furnished by Analog Devices is believed to be accurate and reliable. However, no
responsibility is assumed by Anal og Devices for its use, nor for any infringements of patents or ot her
rights of third parties that may result from its use. Specifications subject to change without notice. No
license is granted by implication or otherwise under any patent or patent rights of Analog Devices.
Trademarks and registered trademarks are the property of their respective owners.
The AD8138 eliminates the need for a transformer with high
performance ADCs, preserving the low frequency and dc information. The common-mode level of the differential output is
adjustable by a voltage on the V
pin, easily level-shifting the
OCM
input signals for driving single-supply ADCs. Fast overload
recovery preserves sampling accuracy.
The AD8138 distortion performance makes it an ideal ADC
driver for communication systems, with distortion performance
good enough to drive state-of-the-art 10-bit to 16-bit converters
at high frequencies. The AD8138’s high bandwidth and IP3 also
make it appropriate for use as a gain block in IF and baseband
signal chains. The AD8138 offset and dynamic performance
makes it well suited for a wide variety of signal processing and
data acquisition applications.
The AD8138 is available in both SOIC and MSOP packages for
operation over −40°C to +85°C temperatures.
One Technology Way, P.O. Box 9106, Norwood, MA 02062-9106, U.S.A.
Tel: 781.329.4700 www.analog.com
Fax: 781.461.3113 ©2006 Analog Devices, Inc. All rights reserved.

AD8138
TABLE OF CONTENTS
Features.............................................................................................. 1
Theory of Operation ...................................................................... 17
Applications....................................................................................... 1
Pin Configuration............................................................................. 1
Typical Application Circuit ............................................................. 1
General Description ......................................................................... 1
Revision History ............................................................................... 2
Specifications..................................................................................... 3
±D
to ±OUT Specifications...................................................... 3
IN
V
to ±OUT Specifications ..................................................... 4
OCM
±D
to ±OUT Specifications...................................................... 5
IN
V
to ±OUT Specifications ..................................................... 6
OCM
Absolute Maximum Ratings............................................................ 7
Thermal Resistance ...................................................................... 7
ESD Caution.................................................................................. 7
Pin Configuration and Function Descriptions............................. 8
Typical Performance Characteristics ............................................. 9
Test Circuits..................................................................................... 15
Analyzing an Application Circuit ............................................ 17
Setting the Closed-Loop Gain .................................................. 17
Estimating the Output Noise Voltage...................................... 17
The Impact of Mismatches in the Feedback Networks......... 18
Calculating an Application Circuit’s Input Impedance......... 18
Input Common-Mode Voltage Range in Single-Supply
Applications ................................................................................ 18
Setting the Output Common-Mode Voltage.......................... 18
Driving a Capacitive Load......................................................... 18
Layout, Grounding, and Bypassing.............................................. 19
Balanced Transformer Driver....................................................... 20
High Performance ADC Driving ................................................. 21
3 V Operation ................................................................................. 22
Outline Dimensions....................................................................... 23
Ordering Guide .......................................................................... 23
Operational Description................................................................ 16
Definition of Terms.................................................................... 16
REVISION HISTORY
1/06—Rev. E to Rev. F
Changes to Features.......................................................................... 1
Added Thermal Resistance Section and Maximum Power
Dissipation Section........................................................................... 7
Changes to Balanced Transformer Driver Section..................... 20
Changes to Ordering Guide.......................................................... 23
3/03—Rev. D to Rev. E
Changes to Specifications................................................................ 2
Changes to Ordering Guide............................................................ 4
Changes to TPC 16........................................................................... 6
Changes to Table I ............................................................................ 9
Added New Paragraph after Table I ............................................. 10
Updated Outline Dimensions....................................................... 14
7/02—Rev. C to Rev. D
Addition of TPC 35 and TPC 36.....................................................8
6/01—Rev. B to Rev. C
Edits to Specifications ......................................................................2
Edits to Ordering Guide...................................................................4
12/00—Rev. A to Rev. B
9/99—Rev. 0 to Rev. A
3/99—Rev. 0: Initial Version
Rev. F | Page 2 of 24
AD8138
SPECIFICATIONS
±DIN to ±OUT SPECIFICATIONS
At 25°C, VS = ±5 V, V
specifications refer to single-ended input and differential outputs, unless otherwise noted.
Table 1.
Parameter Conditions Min Typ Max Unit
DYNAMIC PERFORMANCE
−3 dB Small Signal Bandwidth V
V
Bandwidth for 0.1 dB Flatness V
Large Signal Bandwidth V
Slew Rate V
Settling Time 0.01%, V
Overdrive Recovery Time VIN = 5 V to 0 V step, G = +2 4 ns
NOISE/HARMONIC PERFORMANCE
Second Harmonic V
V
V
Third Harmonic V
V
V
IMD 20 MHz −77 dBc
IP3 20 MHz 37 dBm
Voltage Noise (RTI) f = 100 kHz to 40 MHz 5 nV/√Hz
Input Current Noise f = 100 kHz to 40 MHz 2 pA/√Hz
INPUT CHARACTERISTICS
Offset Voltage V
T
Input Bias Current 3.5 7 μA
T
Input Resistance Differential 6 MΩ
Common mode 3 MΩ
Input Capacitance 1 pF
Input Common-Mode Voltage −4.7 to +3.4 V
CMRR ∆V
OUTPUT CHARACTERISTICS
Output Voltage Swing Maximum ∆V
Output Current 95 mA
Output Balance Error ∆V
1
Harmonic distortion performance is equal or slightly worse with higher values of R
= 0, G = +1, R
OCM
= 500 Ω, unless otherwise noted. Refer to Figure 39 for test setup and label descriptions. All
L, dm
= 0.5 V p-p, CF = 0 pF 290 320 MHz
OUT
= 0.5 V p-p, CF = 1 pF 225 MHz
OUT
= 0.5 V p-p, CF = 0 pF 30 MHz
OUT
= 2 V p-p, CF = 0 pF 265 MHz
OUT
= 2 V p-p, CF = 0 pF 1150 V/μs
OUT
= 2 V p-p, CF = 1 pF 16 ns
OUT
1
= 2 V p-p, 5 MHz, R
OUT
= 2 V p-p, 20 MHz, R
OUT
= 2 V p-p, 70 MHz, R
OUT
= 2 V p-p, 5 MHz, R
OUT
= 2 V p-p, 20 MHz, R
OUT
= 2 V p-p, 70 MHz, R
OUT
OS, dm
MIN
MIN
OUT, dm
OUT, cm
= V
to T
to T
/2; V
OUT, dm
variation ±4 μV/°C
MAX
variation −0.01 μA/°C
MAX
/∆V
; ∆V
IN, cm
; single-ended output 7.75 V p-p
OUT
/∆V
OUT, dm
; ∆V
= 800 Ω −94 dBc
L, dm
= 800 Ω −87 dBc
L, dm
= 800 Ω −62 dBc
L, dm
= 800 Ω −114 dBc
L, dm
= 800 Ω −85 dBc
L, dm
= 800 Ω −57 dBc
L, dm
= V
= V
DIN+
DIN−
= ±1 V −77 −70 dB
IN, cm
= 1 V −66 dB
OUT, dm
L, dm
= 0 V −2.5 ±1 +2.5 mV
OCM
. See Figure 17 and Figure 18 for more information.
Rev. F | Page 3 of 24
AD8138
V
to ±OUT SPECIFICATIONS
OCM
At 25°C, VS = ±5 V, V
specifications refer to single-ended input and differential outputs, unless otherwise noted.
Table 2.
Parameter Conditions Min Typ Max Unit
DYNAMIC PERFORMANCE
−3 dB Bandwidth 250 MHz
Slew Rate 330 V/μs
INPUT VOLTAGE NOISE (RTI) f = 0.1 MHz to 100 MHz 17 nV/√Hz
DC PERFORMANCE
Input Voltage Range ±3.8 V
Input Resistance 200 kΩ
Input Offset Voltage V
Input Bias Current 0.5 μA
V
CMRR ∆V
OCM
Gain ∆V
POWER SUPPLY
Operating Range ±1.4 ±5.5 V
Quiescent Current 18 20 23 mA
T
Power Supply Rejection Ratio ∆V
OPERATING TEMPERATURE RANGE −40 +85 °C
= 0, G = +1, R
OCM
= 500 Ω, unless otherwise noted. Refer to Figure 39 for test setup and label descriptions. All
L, dm
OS, cm
OUT, dm
OUT, cm
MIN
OUT, dm
= V
to T
; V
= V
= V
OUT, cm
DIN+
DIN–
/∆V
; ∆V
OCM
/∆V
OCM
variation 40 μA/°C
MAX
= ±1 V −75 dB
OCM
; ∆V
= ±1 V 0.9955 1 1.0045 V/V
OCM
= 0 V –3.5 ±1 +3.5 mV
OCM
/∆VS; ∆VS = ±1 V −90 −70 dB
Rev. F | Page 4 of 24
AD8138
±DIN to ±OUT SPECIFICATIONS
At 25°C, VS = 5 V, V
specifications refer to single-ended input and differential output, unless otherwise noted.
Table 3.
Parameter Conditions Min Typ Max Unit
DYNAMIC PERFORMANCE
−3 dB Small Signal Bandwidth V
V
Bandwidth for 0.1 dB Flatness V
Large Signal Bandwidth V
Slew Rate V
Settling Time 0.01%, V
Overdrive Recovery Time VIN = 2.5 V to 0 V step, G = +2 4 ns
NOISE/HARMONIC PERFORMANCE
Second Harmonic V
V
V
Third Harmonic V
V
V
IMD 20 MHz −74 dBc
IP3 20 MHz 35 dBm
Voltage Noise (RTI) f = 100 kHz to 40 MHz 5 nV/√Hz
Input Current Noise f = 100 kHz to 40 MHz 2 pA/√Hz
INPUT CHARACTERISTICS
Offset Voltage V
T
Input Bias Current 3.5 7 μA
T
Input Resistance Differential 6 MΩ
Common mode 3 MΩ
Input Capacitance 1 pF
Input Common-Mode Voltage −0.3 to +3.2 V
CMRR ∆V
OUTPUT CHARACTERISTICS
Output Voltage Swing Maximum ∆V
Output Current 95 mA
Output Balance Error ∆V
1
Harmonic distortion performance is equal or slightly worse with higher values of R
= 2.5 V, G = +1, R
OCM
= 500 Ω, unless otherwise noted. Refer to Figure 39 for test setup and label descriptions. All
L, dm
= 0.5 V p-p, CF = 0 pF 280 310 MHz
OUT
= 0.5 V p-p, CF = 1 pF 225 MHz
OUT
= 0.5 V p-p, CF = 0 pF 29 MHz
OUT
= 2 V p-p, CF = 0 pF 265 MHz
OUT
= 2 V p-p, CF = 0 pF 950 V/μs
OUT
= 2 V p-p, CF = 1 pF 16 ns
OUT
1
= 2 V p-p, 5 MHz, R
OUT
= 2 V p-p, 20 MHz, R
OUT
= 2 V p-p, 70 MHz, R
OUT
= 2 V p-p, 5 MHz, R
OUT
= 2 V p-p, 20 MHz, R
OUT
= 2 V p-p, 70 MHz, R
OUT
OS, dm
MIN
MIN
OUT, dm
OUT, cm
= V
to T
to T
/2; V
OUT, dm
variation ±4 μV/°C
MAX
variation −0.01 μA/°C
MAX
/∆V
; ∆V
IN, cm
; single-ended output 2.9 V p-p
OUT
/∆V
OUT, dm
; ∆V
= 800 Ω −90 dBc
L, dm
= 800 Ω −79 dBc
L, dm
= 800 Ω −60 dBc
L, dm
= 800 Ω −100 dBc
L, dm
= 800 Ω −82 dBc
L, dm
= 800 Ω −53 dBc
L, dm
= V
= V
DIN+
DIN–
= 1 V −77 −70 dB
IN, cm
= 1 V −65 dB
OUT, dm
L, dm
= 0 V −2.5 ±1 +2.5 mV
OCM
. See Figure 17 and Figure 18 for more information.
Rev. F | Page 5 of 24
AD8138
V
TO ±OUT SPECIFICATIONS
OCM
At 25°C, VS = 5 V, V
specifications refer to single-ended input and differential output, unless otherwise noted.
Table 4.
Parameter Conditions Min Typ Max Unit
DYNAMIC PERFORMANCE
−3 dB Bandwidth 220 MHz
Slew Rate 250 V/μs
INPUT VOLTAGE NOISE (RTI) f = 0.1 MHz to 100 MHz 17 nV/√Hz
DC PERFORMANCE
Input Voltage Range 1.0 to 3.8 V
Input Resistance 100 kΩ
Input Offset Voltage V
Input Bias Current 0.5 μA
V
CMRR ∆V
OCM
Gain ∆V
POWER SUPPLY
Operating Range 2.7 11 V
Quiescent Current 15 20 21 mA
T
Power Supply Rejection Ratio ∆V
OPERATING TEMPERATURE RANGE −40 +85 °C
= 2.5 V, G = +1, R
OCM
= 500 Ω, unless otherwise noted. Refer to Figure 39 for test setup and label descriptions. All
L, dm
OS, cm
OUT, dm
OUT, cm
MIN
OUT, dm
= V
to T
; V
= V
= V
OUT, cm
DIN+
DIN–
/∆V
; ∆V
OCM
/∆V
OCM
variation 40 μA/°C
MAX
= 2.5 V ±1 V −70 dB
OCM
; ∆V
= 2.5 V ±1 V 0.9968 1 1.0032 V/V
OCM
= 0 V −5 ±1 +5 mV
OCM
/∆VS; ∆VS = ± 1 V −90 −70 dB
Rev. F | Page 6 of 24
AD8138
ABSOLUTE MAXIMUM RATINGS
Table 5.
Parameter Ratings
Supply Voltage ±5.5 V
V
±VS
OCM
Internal Power Dissipation 550 mW
Operating Temperature Range −40°C to +85°C
Storage Temperature Range −65°C to +150°C
Lead Temperature (Soldering 10 sec) 300°C
Junction Temperature 150°C
Stresses above those listed under Absolute Maximum Ratings
may cause permanent damage to the device. This is a stress
rating only; functional operation of the device at these or any
other conditions above those indicated in the operational
section of this specification is not implied. Exposure to absolute
maximum rating conditions for extended periods may affect
device reliability.
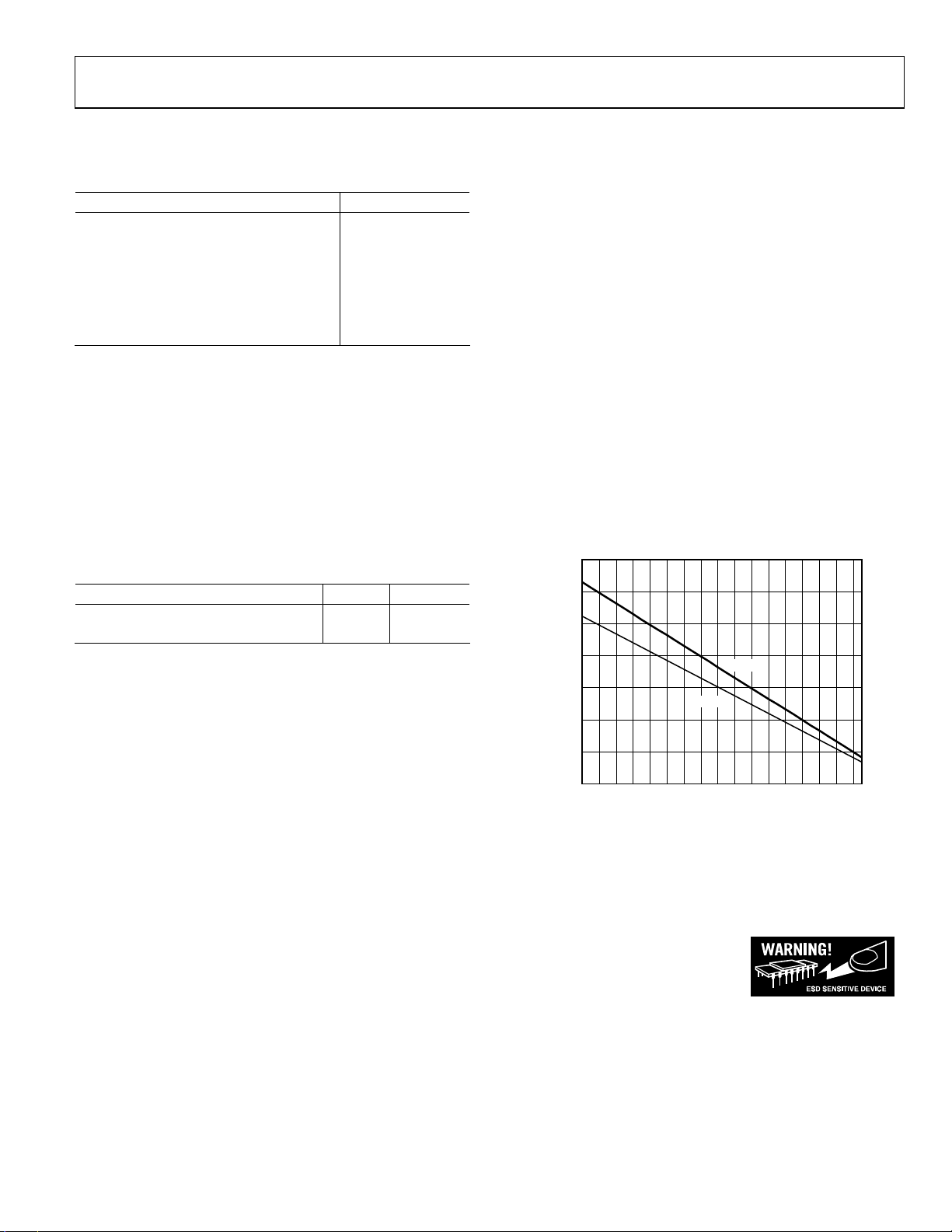
THERMAL RESISTANCE
θJA is specified for the worst-case conditions, that is, θJA is
specified for the device soldered in a circuit board in still air.
The power dissipated in the package (P
quiescent power dissipation and the power dissipated in the
package due to the load drive for all outputs. The quiescent
power is the voltage between the supply pins (V
quiescent current (I
and common-mode currents flowing to the load, as well as
currents flowing through the external feedback networks and
internal common-mode feedback loop. The internal resistor tap
used in the common-mode feedback loop places a negligible
differential load on the output. RMS voltages and currents
should be considered when dealing with ac signals.
Airflow reduces θ
with the package leads from metal traces through holes, ground,
and power planes reduces the θ
Figure 3 shows the maximum safe power dissipation in the
package vs. the ambient temperature for the 8-lead SOIC
(121°C/W) and 8-lead MSOP (θ
JEDEC standard 4-layer board. θ
1.75
Table 6.
Package Type θJA Unit
8-Lead SOIC/4-Layer 121 °C/W
8-Lead MSOP/4-Layer 145 °C/W
Maximum Power Dissipation
1.50
1.25
1.00
0.75
The maximum safe power dissipation in the AD8138 packages
is limited by the associated rise in junction temperature (T
the die. At approximately 150°C, which is the glass transition
temperature, the plastic changes its properties. Even temporarily
exceeding this temperature limit can change the stresses that the
package exerts on the die, permanently shifting the parametric
performance of the AD8138. Exceeding a junction temperature
of 150°C for an extended period can result in changes in the
silicon devices, potentially causing failure.
) on
J
0.50
MAXIMUM POWER DISSIPATION (W)
0.25
0
–40 –30 –20 –10 0 10 20 30 40 50 60 70 80 90 100 110 120
Figure 3. Maximum Power Dissipation vs. Temperature
). The load current consists of the differential
S
. In addition, more metal directly in contact
JA
JA
JA
MSOP
AMBIENT TEMPERATURE (°C)
) is the sum of the
D
) times the
S
.
= 145°C/W) packages on a
values are approximations.
JA
SOIC
01073-049
ESD CAUTION
ESD (electrostatic discharge) sensitive device. Electrostatic charges as high as 4000 V readily accumulate on
the human body and test equipment and can discharge without detection. Although this product features
proprietary ESD protection circuitry, permanent damage may occur on devices subjected to high energy
electrostatic discharges. Therefore, proper ESD precautions are recommended to avoid performance
degradation or loss of functionality.
Rev. F | Page 7 of 24
AD8138
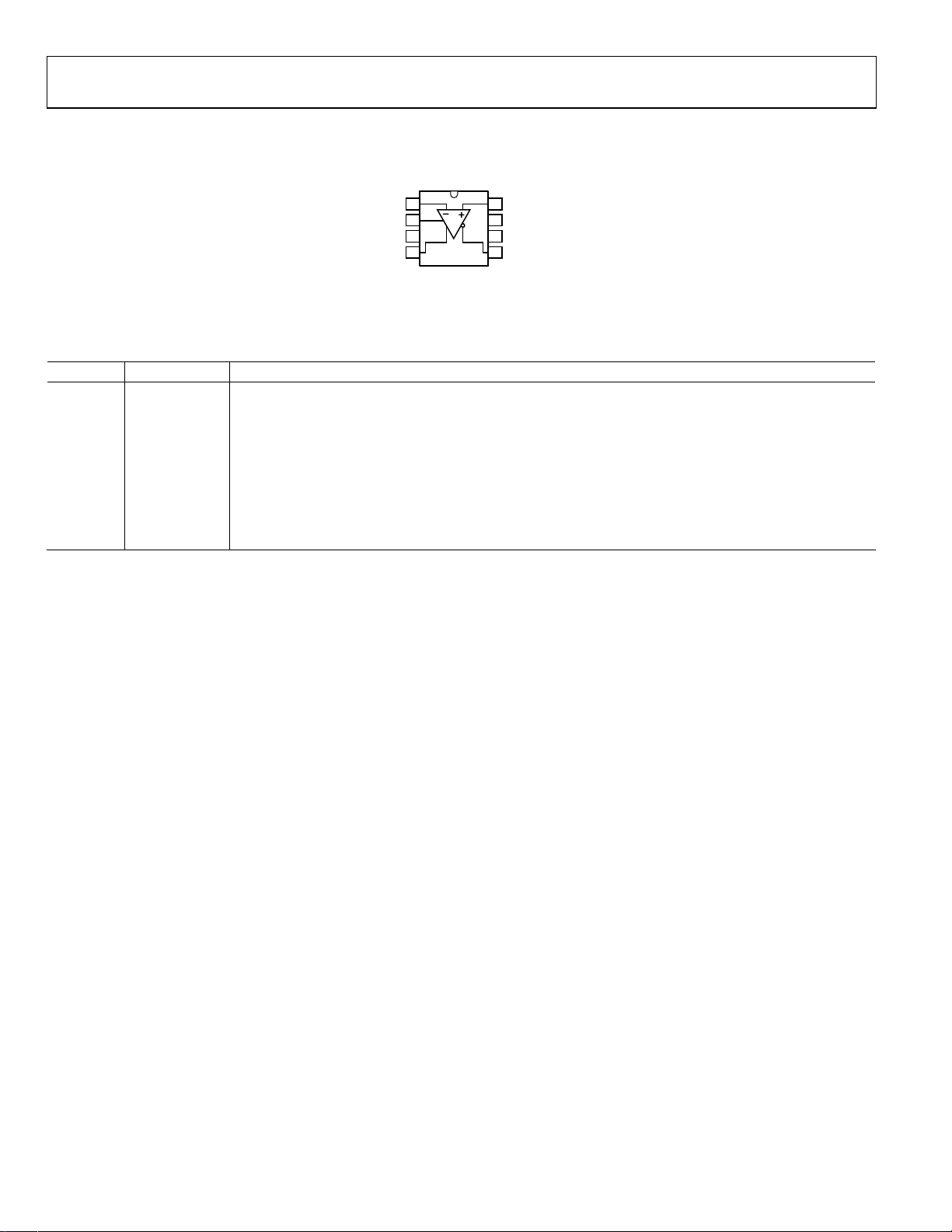
PIN CONFIGURATION AND FUNCTION DESCRIPTIONS
–IN
1
2
V
OCM
V+
3
4
+OUT
AD8138
NC = NO CO NNECT
Figure 4. Pin Configuration
Table 7. Pin Function Descriptions
Pin No. Mnemonic Description
1 −IN Negative Input Summing Node.
2 V
OCM
Voltage applied to this pin sets the common-mode output voltage with a ratio of 1:1. For example,
1 V dc on V
sets the dc bias level on +OUT and −OUT to 1 V.
OCM
3 V+ Positive Supply Voltage.
4 +OUT Positive Output. Note that the voltage at −DIN is inverted at +OUT (see Figure 42).
5 −OUT Negative Output. Note that the voltage at +DIN is inverted at −OUT (see Figure 42).
6 V− Negative Supply Voltage.
7 NC No Connect.
8 +IN Positive Input Summing Node.
+IN
8
NC
7
V–
6
5
–OUT
01073-004
Rev. F | Page 8 of 24
 Loading...
Loading...