Analog Devices AD797 d Datasheet
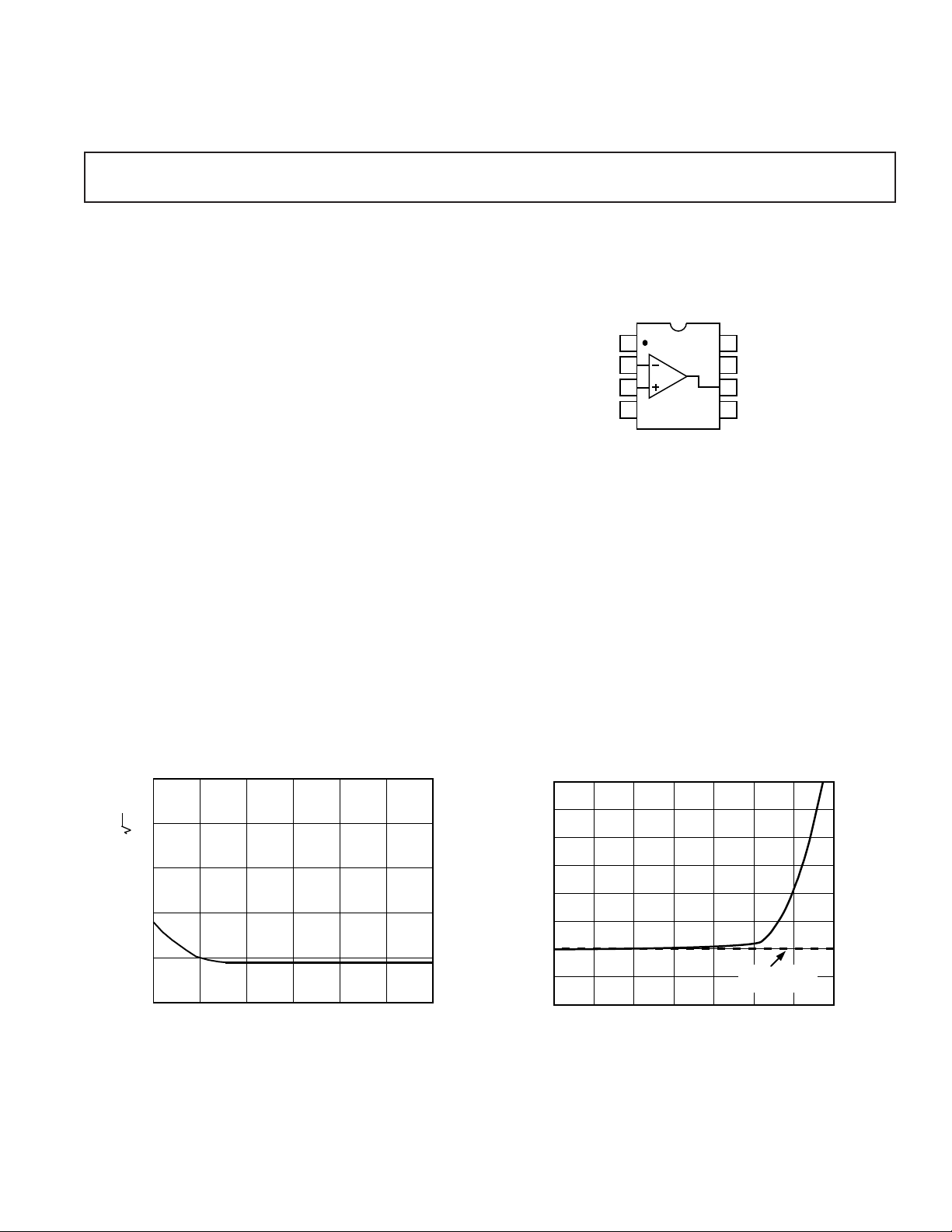
Ultralow Distortion,
–90
–130
300k
–120
300100
–110
–100
100k30k10k3k1k
FREQUENCY – Hz
THD – dB
MEASUREMENT
LIMIT
0.001
0.0003
0.0001
THD – %
a
FEATURES
Low Noise
0.9 nV/÷Hz typ (1.2 nV/÷Hz max) Input Voltage
Noise at 1 kHz
50 nV p-p Input Voltage Noise, 0.1 Hz to 10 Hz
Low Distortion
–120 dB Total Harmonic Distortion at 20 kHz
Excellent AC Characteristics
800 ns Settling Time to 16 Bits (10 V Step)
110 MHz Gain Bandwidth (G = 1000)
8 MHz Bandwidth (G = 10)
280 kHz Full Power Bandwidth at 20 V p-p
20 V/s Slew Rate
Excellent DC Precision
80 V max Input Offset Voltage
1.0 V/ⴗC V
Specified for ⴞ5 V and ⴞ15 V Power Supplies
High Output Drive Current of 50 mA
APPLICATIONS
Professional Audio Preamplifiers
IR, CCD, and Sonar Imaging Systems
Spectrum Analyzers
Ultrasound Preamplifiers
Seismic Detectors
⌺⌬ ADC/DAC Buffers
PRODUCT DESCRIPTION
The AD797 is a very low noise, low distortion operational
amplifier ideal for use as a preamplifier. The low noise of
0.9 nV/÷Hz and low total harmonic distortion of –120 dB at
audio bandwidths give the AD797 the wide dynamic range
OS
Drift
Ultralow Noise Op Amp
AD797*
CONNECTION DIAGRAM
8-Pin Plastic Mini-DIP (N)
and SOIC (R) Packages
DECOMPENSATION &
DISTORTION
8
NEUTRALIZATION
+V
7
S
6
OUTPUT
5
OFFSET NULL
–V
–IN
+IN
1
AD797
2
3
4
S
TOP VIEW
OFFSET NULL
necessary for preamps in microphones and mixing consoles.
Furthermore, the AD797’s excellent slew rate of 20 V/ms and
110 MHz gain bandwidth make it highly suitable for low frequency ultrasound applications.
The AD797 is also useful in IR and Sonar Imaging applications
where the widest dynamic range is necessary. The low distortion and 16-bit settling time of the AD797 make it ideal for
buffering the inputs to ⌺⌬ ADCs or the outputs of high resolution DACs especially when they are used in critical applications
such as seismic detection and spectrum analyzers. Key features
such as a 50 mA output current drive and the specified power
supply voltage range of ±5 to ±15 Volts make the AD797 an
excellent general purpose amplifier.
5
Hz
4
3
2
1
INPUT VOLTAGE NOISE – nV/
0
100
10
FREQUENCY – Hz
10M
1M100k10k1k
AD797 Voltage Noise Spectral Density
*Patent pending.
REV. D
Information furnished by Analog Devices is believed to be accurate and
reliable. However, no responsibility is assumed by Analog Devices for its
use, nor for any infringements of patents or other rights of third parties that
may result from its use. No license is granted by implication or otherwise
under any patent or patent rights of Analog Devices.
THD vs. Frequency
One Technology Way, P.O. Box 9106, Norwood, MA 02062-9106, U.S.A.
Tel: 781/329-4700 www.analog.com
Fax: 781/326-8703 © Analog Devices, Inc., 2002
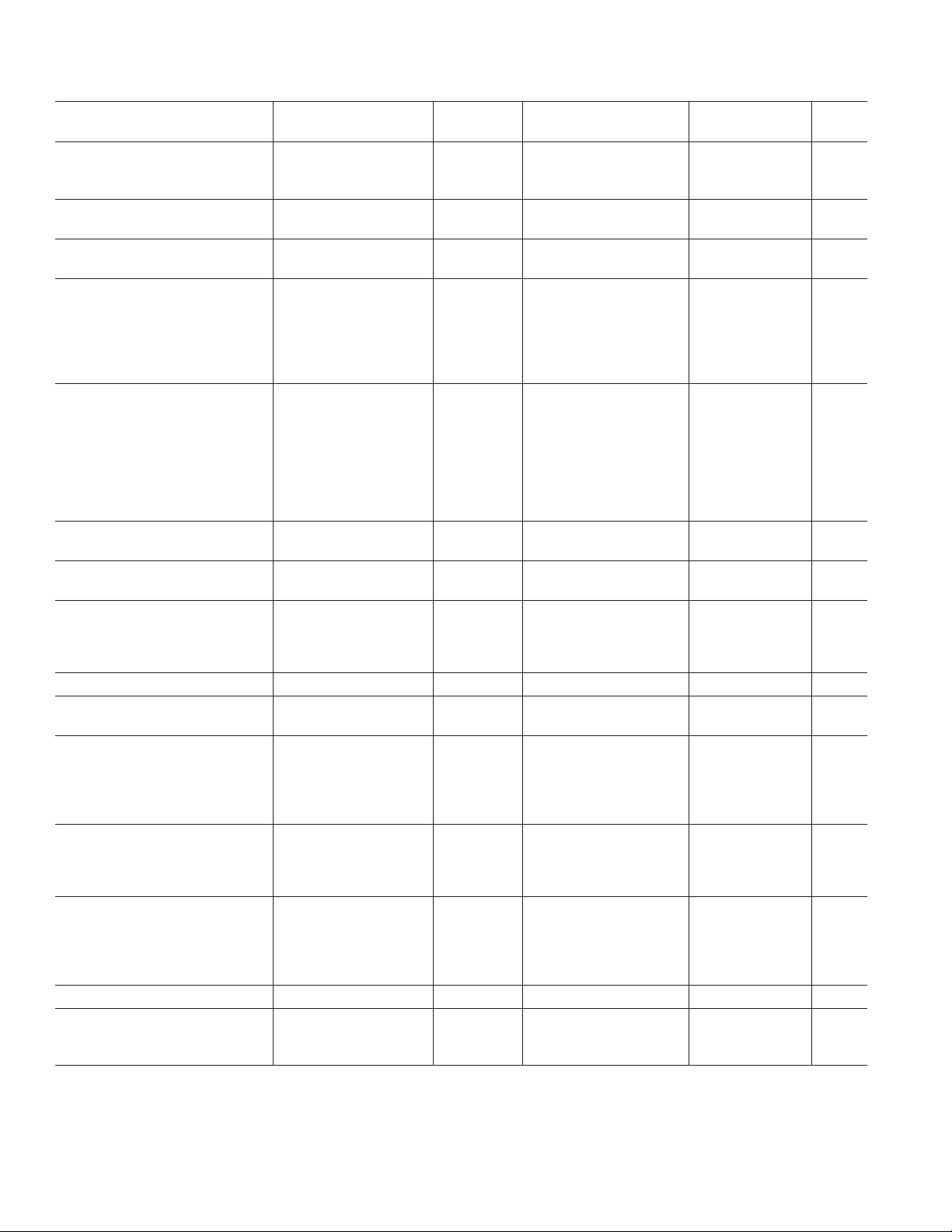
AD797–SPECIFICATIONS
(@ TA = +25ⴗC and VS = ⴞ15 V dc, unless otherwise noted)
AD797A AD797B
Model Conditions V
S
Min Typ Max Min Typ Max Units
INPUT OFFSET VOLTAGE ± 5 V, ± 15 V 25 80 10 40 mV
T
MIN
to T
MAX
50 125/180 30 60 mV
Offset Voltage Drift ± 5 V, ± 15 V 0.2 1.0 0.2 0.6 mV/∞C
INPUT BIAS CURRENT ± 5 V, ± 15 V 0.25 1.5 0.25 0.9 mA
T
MIN
to T
MAX
0.5 3.0 0.25 2.0 mA
INPUT OFFSET CURRENT ± 5 V, ± 15 V 100 400 80 200 nA
T
OPEN-LOOP GAIN V
to T
MIN
MAX
= ± 10 V ± 15 V
OUT
= 2 kW 120 220 V/mV
R
LOAD
T
to T
MIN
MAX
= 600 W 115 215 V/mV
R
LOAD
T
to T
MIN
MAX
@ 20 kHz
2
16 210 V/mV
15 27 V/mV
14000 20000 14000 20000 V/V
120 600/700 120 300 nA
DYNAMIC PERFORMANCE
Gain Bandwidth Product G = 1000 ± 15 V 110 110 MHz
G = 1000
–3 dB Bandwidth G = 10 ± 15 V 8 8 MHz
Full Power Bandwidth
2
VO = 20 V p-p,
R
Slew Rate R
1
= 1 kW±15 V 280 280 kHz
LOAD
= 1 kW±15 V 12.5 20 12.5 20 V/ms
LOAD
± 15 V 450 450 MHz
Settling Time to 0.0015% 10 V Step ± 15 V 800 1200 800 1200 ns
COMMON-MODE REJECTION V
POWER SUPPLY REJECTION V
= CMVR ± 5 V, ± 15 V 114 130 120 130 dB
CM
T
to T
MIN
MAX
= ± 5 V to ± 18 V 114 130 120 130 dB
S
T
to T
MIN
MAX
110 120 114 120 dB
110 120 114 120 dB
INPUT VOLTAGE NOISE f = 0. 1 Hz to 10 Hz ± 15 V 50 50 nV p-p
f = 10 Hz ± 15 V 1.7 1.7 2.5 nV/÷ Hz
f = 1 kHz ± 15 V 0.9 1.2 0.9 1.2 nV/÷Hz
f = 10 Hz–1 MHz ± 15 V 1.0 1.3 1.0 1.2 mV rms
INPUT CURRENT NOISE f = 1 kHz ± 15 V 2.0 2.0 pA/÷Hz
INPUT COMMON-MODE ± 15 V ± 11 ± 12 ± 11 ± 12 V
VOLTAGE RANGE ± 5 V ± 2.5 ±3 ±2.5 ± 3V
OUTPUT VOLTAGE SWING R
Short-Circuit Current ± 5 V, ± 15 V 80 80 mA
Output Current
3
TOTAL HARMONIC DISTORTION R
= 2 kW±15 V ± 12 ± 13 ± 12 ± 13 V
LOAD
= 600 W±15 V ± 11 ± 13 ± 11 ± 13 V
R
LOAD
R
= 600 W±5 V ± 2.5 ±3 ±2.5 ± 3V
LOAD
± 5 V, ± 15 V 30 50 30 50 mA
= 1 kW, CN = 50 pF ± 15 V –98 –90 –98 –90 dB
LOAD
f = 250 kHz, 3 V rms
= 1 kW±15 V –120 –110 –120 –110 dB
R
LOAD
f = 20 kHz, 3 V rms
INPUT CHARACTERISTICS
Input Resistance (Differential) 7.5 7.5 kW
Input Resistance (Common Mode) 100 100 MW
Input Capacitance (Differential)
4
20 20 pF
Input Capacitance (Common Mode) 5 5 pF
OUTPUT RESISTANCE AV = +1, f = 1 kHz 3 3 mW
POWER SUPPLY
Operating Range ± 5 ± 18 ± 5 ±18 V
Quiescent Current ± 5 V, ± 15 V 8.2 10.5 8.2 10.5 mA
NOTES
1
Specified using external decompensation capacitor, see Applications section.
2
Full Power Bandwidth = Slew Rate/2 p V
3
Output Current for |VS – V
4
Differential input capacitance consists of 1.5 pF package capacitance and 18.5 pF from the input differential pair.
Specifications subject to change without notice.
| >4 V, AOL > 200 kW.
OUT
PEAK
.
–2–
REV. D
AD797
WARNING!
ESD SENSITIVE DEVICE
ABSOLUTE MAXIMUM RATINGS
Supply Voltage . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . ± 18 V
Internal Power Dissipation @ +25∞C
Input Voltage . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . ± V
1
2
S
Differential Input Voltage3 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . ± 0.7 V
Output Short Circuit Duration . . . . . . . Indefinite Within max
Internal Power Dissipation
Storage Temperature Range (Cerdip) . . . . . . –65∞C to +150∞C
Storage Temperature Range (N, R Suffix) . . . –65∞C to +125∞C
Operating Temperature Range
AD797A/B . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . –40∞C to +85∞C
Lead Temperature Range (Soldering 60 sec) . . . . . . . .+300∞C
NOTES
1
Stresses above those listed under “Absolute Maximum Ratings” may cause
permanent damage to the device. This is a stress rating only, and functional
operation of the device at these or any other conditions above those indicated in
the operational section of this specification is not implied. Exposure to absolute
maximum rating conditions for extended periods may affect device reliability.
METALLIZATION PHOTO
Contact factory for latest dimensions.
Dimensions shown in inches and (mm).
2
Internal Power Dissipation:
8-Pin SOIC = 0.9 Watts (TA–25∞C)/q
8-Pin Plastic DIP and Cerdip = 1.3 Watts – (TA–25∞C)/q
Thermal Characteristics
8-Pin Plastic DIP Package: qJA = 95∞C/W
8-Pin Small Outline Package: qJA = 155∞C/W
3
The AD797’s inputs are protected by back-to-back diodes. To achieve low noise,
internal current limiting resistors are not incorporated into the design of this
amplifier. If the differential input voltage exceeds ± 0.7 V, the input current should
be limited to less than 25 mA by series protection resistors. Note, however, that
this will degrade the low noise performance of the device.
JA
JA
ORDERING GUIDE
Model Range Description Option
AD797AN –40∞C to +85∞C 8-Pin Plastic DIP N-8
AD797BR –40∞C to +85∞C 8-Pin Plastic SOIC RN-8
AD797BR-REEL –40∞C to +85∞C 8-Pin Plastic SOIC RN-8
AD797BR-REEL7 –40∞C to +85∞C 8-Pin Plastic SOIC RN-8
AD797AR –40∞C to +85∞C 8-Pin Plastic SOIC RN-8
AD797AR-REEL –40∞C to +85∞C 8-Pin Plastic SOIC RN-8
AD797AR-REEL7 –40∞C to +85∞C 8-Pin Plastic SOIC RN-8
Temperature Package Package
NOTE
The AD797 has double layer metal. Only one layer is shown here for clarity.
CAUTION
ESD (electrostatic discharge) sensitive device. Electrostatic charges as high as 4000 V readily
accumulate on the human body and test equipment and can discharge without detection.
Although the AD797 features proprietary ESD protection circuitry, permanent damage may
occur on devices subjected to high energy electrostatic discharges. Therefore, proper ESD
precautions are recommended to avoid performance degradation or loss of functionality.
REV. D
–3–
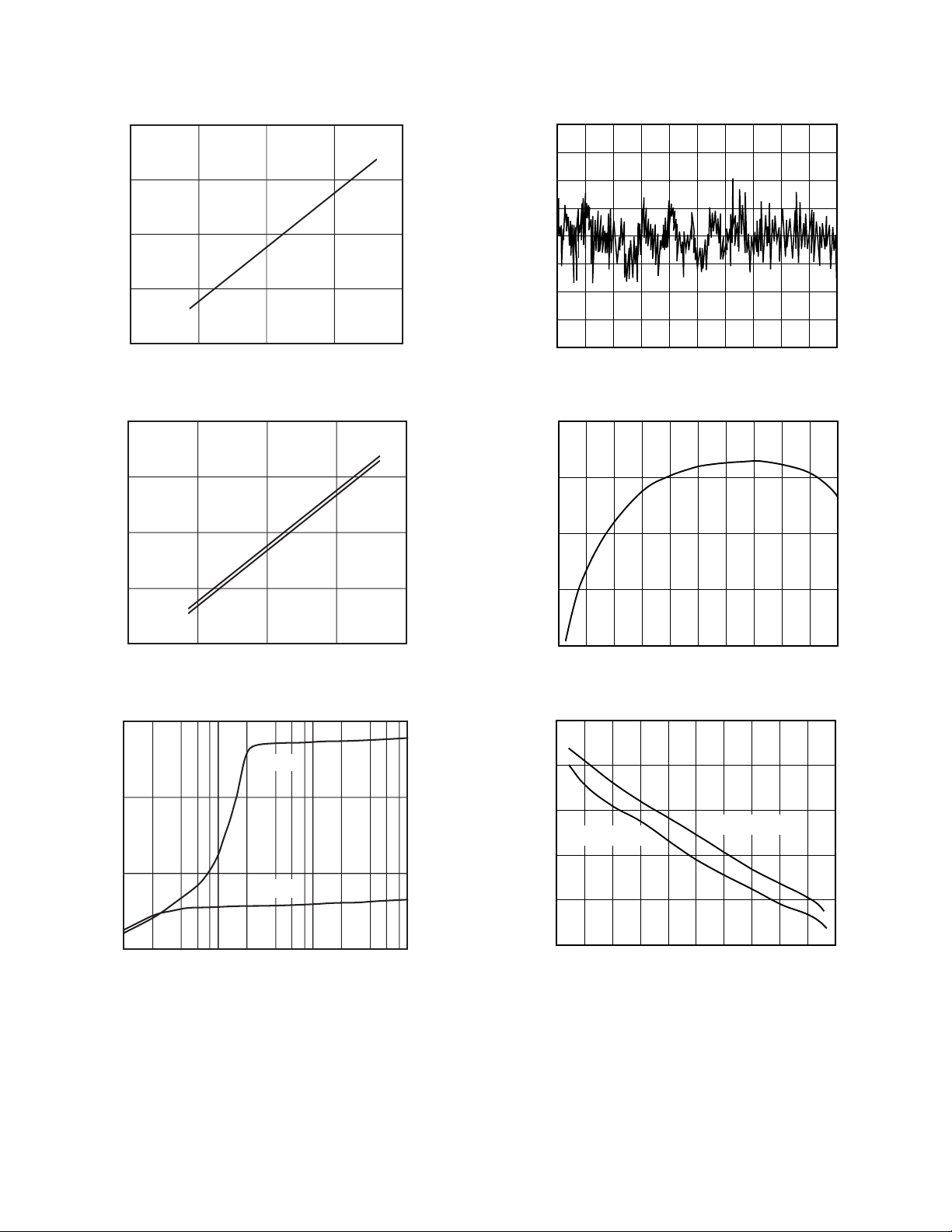
AD797–Typical Performance Characteristics
20
15
10
5
INPUT COMMON-MODE RANGE – ±Volts
0
0
5
SUPPLY VOLTAGE – ±Volts
10
15
20
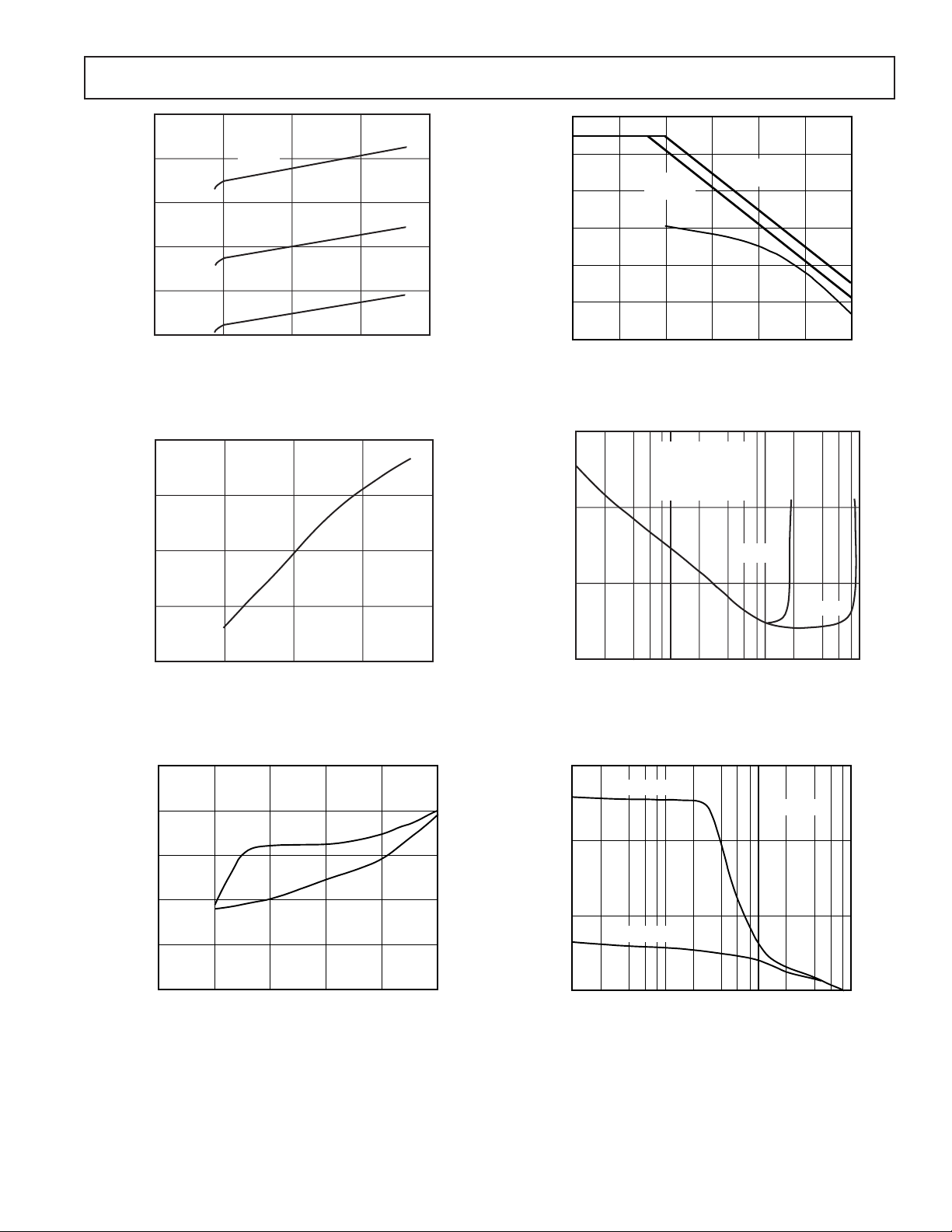
Figure 1. Common-Mode Voltage Range vs. Supply
20
15
10
5
OUTPUT VOLTAGE SWING – ±Volts
0
–V
OUT
0
5
SUPPLY VOLTAGE – ±Volts
+V
OUT
10
15
20
Figure 2. Output Voltage Swing vs. Supply
30
VERTICAL SCALE – 0.01mV/DIV
HORIZONTAL SCALE – 5 sec/DIV
Figure 4. 0.1 Hz to 10 Hz Noise
0.0
–0.5
–1.0
–1.5
INPUT BIAS CURRENT – mA
–2.0
–60 140–40 100 120806040200–20
TEMPERATURE – ∞C
Figure 5. Input Bias Current vs. Temperature
140
V = ±15V
S
20
10
OUTPUT VOLTAGE SWING – Volts p-p
0
10 100 10k1k
V = ±5V
S
LOAD RESISTANCE –
W
Figure 3. Output Voltage Swing vs. Load Resistance
–4–
120
100
SINK CURRENT
80
60
SHORT CIRCUIT CURRENT – mA
40
–40
–60
TEMPERATURE – ∞C
SOURCE CURRENT
6040200–20
80
140
120100
Figure 6. Short Circuit Current vs. Temperature
REV. D
AD797
0
±5V SUPPLIES
±15V SUPPLIES
R
L
= 600 W
11
10
9
8
7
QUIESCENT SUPPLY CURRENT – mA
6
+125°C
+25°C
–55°C
10
SUPPLY VOLTAGE – ±Volts
205015
Figure 7. Quiescent Supply Current vs. Supply Voltage
12
FREQ = 1kHz
= 600W
R
L
G = +10
9
6
3
OUTPUT VOLTAGE – Volts rms
140
120
100
80
60
POWER SUPPLY REJECTION – dB
40
20
10
1
PSR
–SUPPLY
FREQUENCY – Hz
PSR
+SUPPLY
CMR
150
125
100
75
50
100k10k1k100
1M
Figure 10. Power Supply and Common-Mode Rejection
vs. Frequency
–60
RL = 600
W
G = +10
FREQ = 10kHz
NOISE BW = 100kHz
–80
V
= ±5V
S
THD + NOISE – dB
–100
V
= ±15V
S
COMMON MODE REJECTION – dB
0
0
±5
SUPPLY VOLTAGE –Volts
±10
±15
Figure 8. Output Voltage vs. Supply for 0.01% Distortion
1.0
0.8
0.0015%
0.6
0.01%
0.4
SETTLING TIME – ms
0.2
0.0
0
Figure 9. Settling Time vs. Step Size (±)
2
STEP SIZE – Volts
864
±20
–120
0.01 0.1 101.0
OUTPUT LEVEL – Volts
Figure 11. Total Harmonic Distortion (THD) + Noise vs.
Output Level
10
Figure 12. Large Signal Frequency Response
REV. D
–5–
 Loading...
Loading...