Analog Devices AD795 Datasheet
1
2
3
4
8
7
6
5
AD795
NC
–IN
+IN
–V
S
NC
+V
S
OUTPUT
NC
NC = NO CONNECT
Low Power, Low Noise
50
0
5–4
10
–5
30
20
40
43210–1–2–3
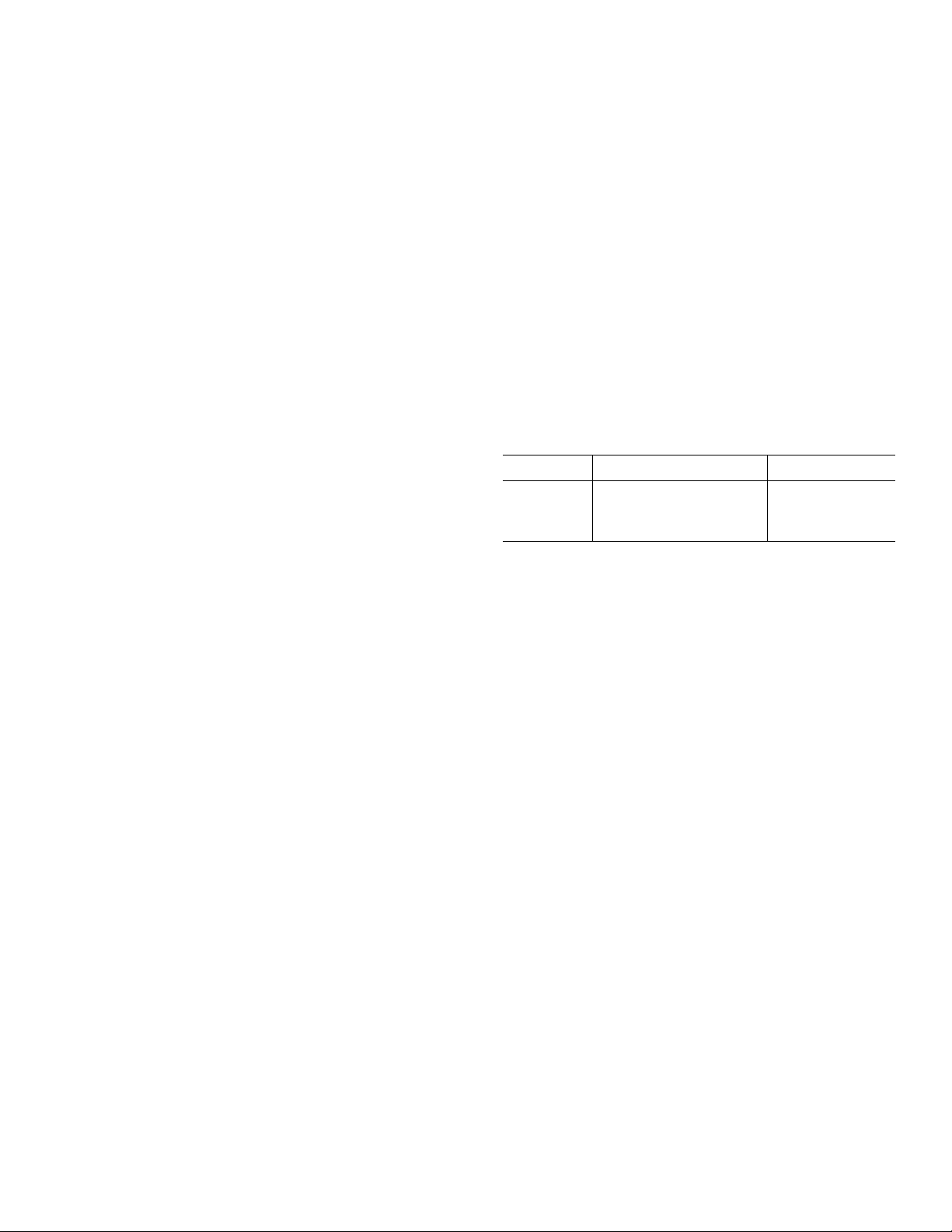
INPUT OFFSET VOLTAGE DRIFT – µV/°C
PERCENTAGE OF UNITS
SAMPLE SIZE = 570
a
FEATURES
Low Power Replacement for Burr-Brown
OPA-111, OPA-121 Op Amps
Low Noise
2.5 mV p-p max, 0.1 Hz to 10 Hz
11 nV/√
0.6 fA/√
High DC Accuracy
250 mV max Offset Voltage
3 mV/8C max Drift
1 pA max Input Bias Current
Low Power: 1.5 mA max Supply Current
Available in Low Cost Plastic Mini-DIP and Surface
Mount (SOIC) Packages
APPLICATIONS
Low Noise Photodiode Preamps
CT Scanners
Precision l-to-V Converters
PRODUCT DESCRIPTION
The AD795 is a low noise, precision, FET input operational
amplifier. It offers both the low voltage noise and low offset drift
of a bipolar input op amp and the very low bias current of a
FET-input device. The 10
insures that input bias current is essentially independent of
common-mode voltage and supply voltage variations.
The AD795 has both excellent dc performance and a guaranteed and tested maximum input voltage noise. It features 1 pA
maximum input bias current and 250 µV maximum offset volt-
age, along with low supply current of 1.5 mA max.
Hz max at 10 kHz
Hz at 1 kHz
1k
14
Ω common-mode impedance
Precision FET Op Amp
AD795
CONNECTION DIAGRAMS
8-Pin Plastic Mini-DIP (N) Package
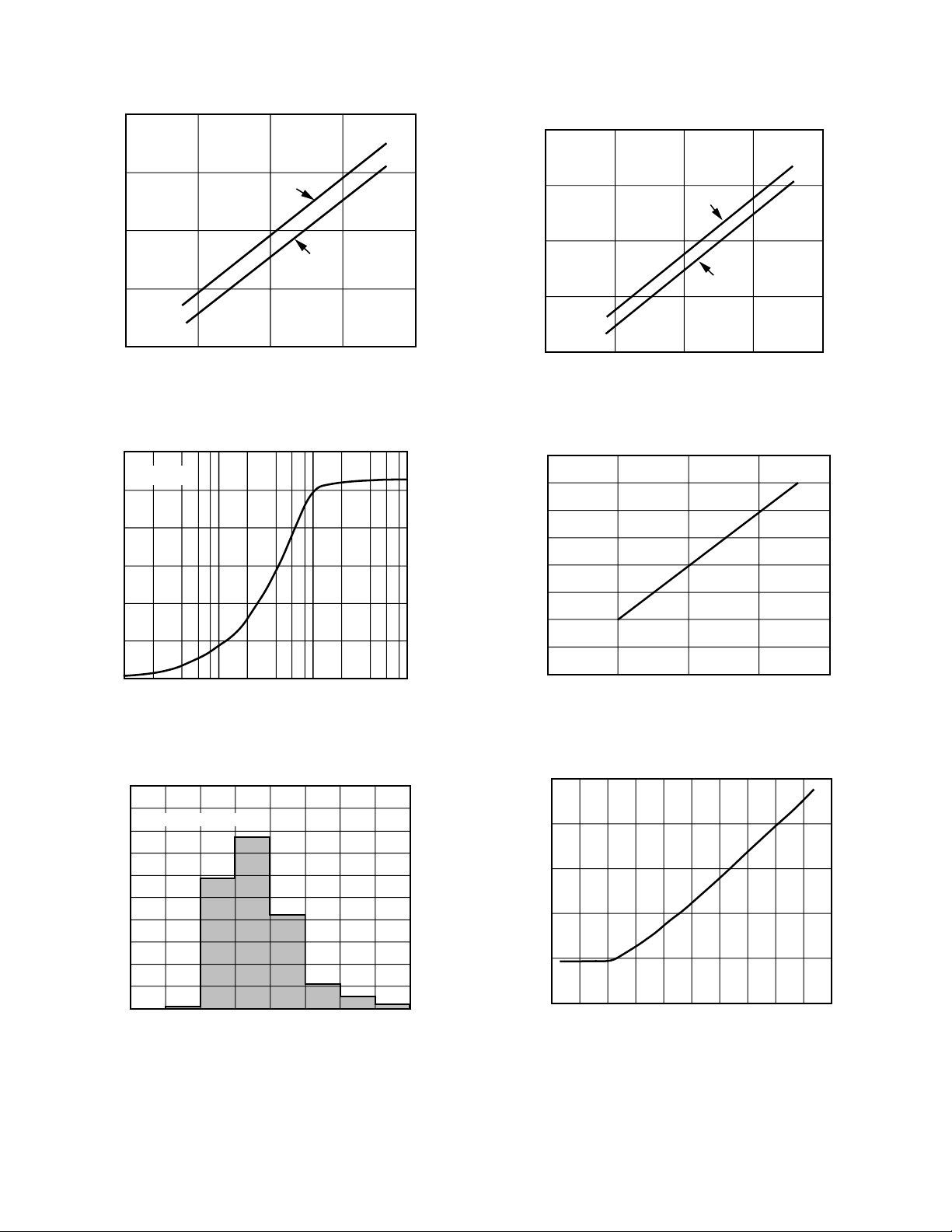
30
Vs = ±15V
25
20
15
10
5
OUTPUT VOLTAGE SWING – Volts p-p
0
10
100 1k
LOAD RESISTANCE –
Ω
8-Pin SOIC (R) Package
Furthermore, the AD795 features a guaranteed low input noise
of 2.5 µV p-p (0.1 Hz to 10 Hz) and a 11 nV/√
level at 10 kHz. The AD795 has a fully specified and tested
input offset voltage drift of only 3 µV/°C max.
The AD795 is useful for many high input impedance, low noise
applications. The AD795J and AD795K are rated over the
commercial temperature range of 0°C to +70°C.
The AD795 is available in 8-pin plastic mini-DIP and 8-pin
surface mount (SOIC) packages.
10k
Hz max noise
REV. A
Information furnished by Analog Devices is believed to be accurate and
reliable. However, no responsibility is assumed by Analog Devices for its
use, nor for any infringements of patents or other rights of third parties
which may result from its use. No license is granted by implication or
otherwise under any patent or patent rights of Analog Devices.
100
10
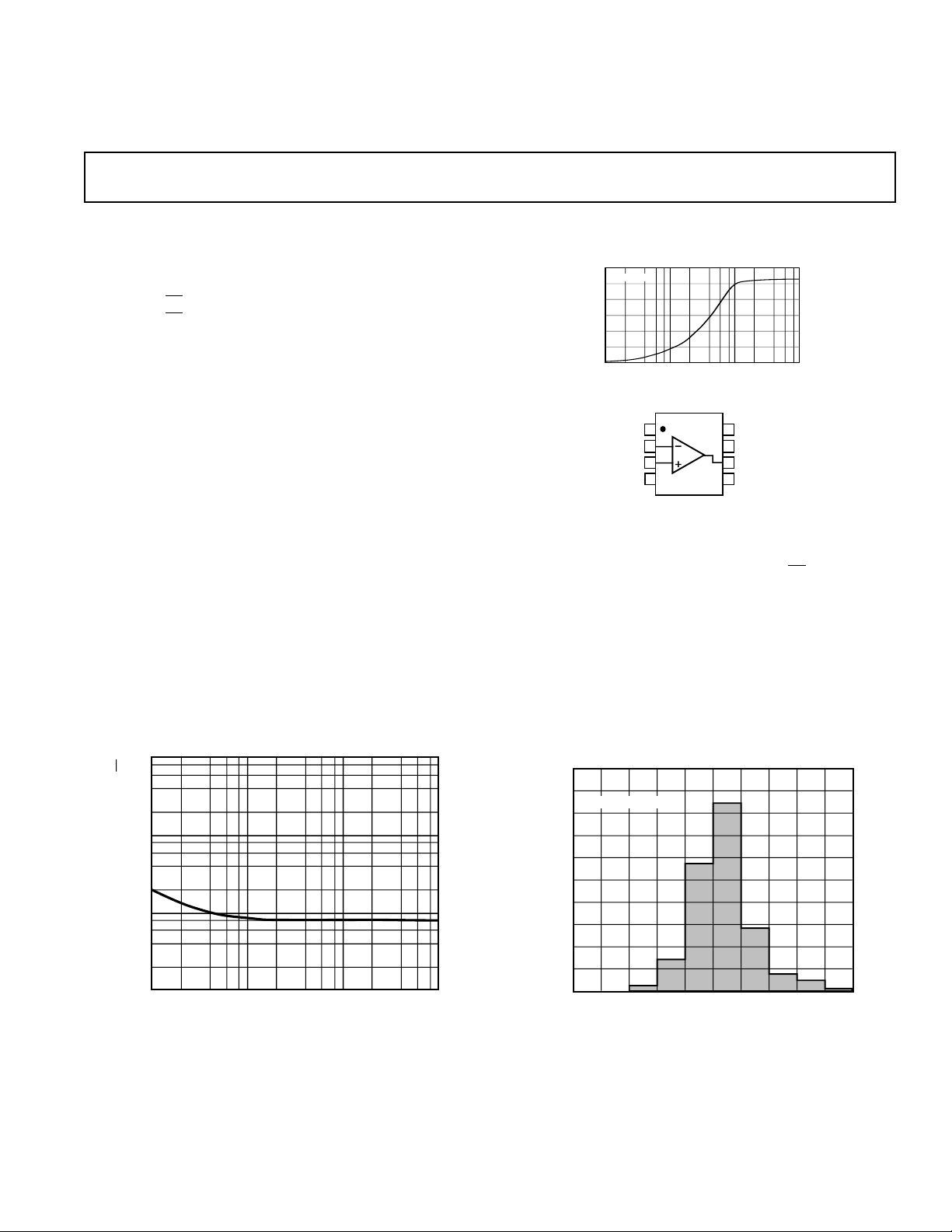
VOLTAGE NOISE SPECTRAL DENSITY – nV/√Hz
1
10 100 10k1k
FREQUENCY – Hz
AD795 Voltage Noise Spectral Density
Typical Distribution of Average Input Offset Voltage Drift
One Technology Way, P.O. Box 9106, Norwood, MA 02062-9106, U.S.A.
Tel: 617/329-4700 Fax: 617/326-8703
AD795–SPECIFICA TIONS
(@ +258C and 615 V dc unless otherwise noted)
AD795JN/JR AD795K
Parameter Conditions Min Typ Max Min Typ Max Units
INPUT OFFSET VOLTAGE
1
Initial Offset 100 500 50 250 µV
Offset T
MIN–TMAX
300 1000 100 400 µV
vs. Temperature 3 10 1 3 µV/°C
vs. Supply (PSRR) 86 110 90 110 dB
vs. Supply (PSRR) T
INPUT BIAS CURRENT
2
MIN–TMAX
84 100 87 100 dB
Either Input VCM = 0 V 1 2/3 1 1 pA
Either Input @ T
=V
MAX
Either Input V
Offset Current V
Offset Current @ T
=V
MAX
OPEN-LOOP GAIN V
= 0 V 23 23 pA
CM
= +10 V 1 1 pA
CM
= 0 V 0.1 1.0 0.1 0.6 pA
CM
= 0 V 2 2 pA
CM
= ±10 V
O
≥ 10 kΩ 110 120 110 120 dB
R
LOAD
R
≥ 10 kΩ 100 108 100 108 dB
LOAD
INPUT VOLTAGE NOISE 0.1 Hz to 10 Hz 1.0 3.3 1.0 2.5 µV p-p
f = 10 Hz 20 50 20 40 nV/√Hz
f = 100 Hz 12 40 12 30 nV/√
f = 1 kHz 11 17 11 15 nV/√
Hz
Hz
f = 10 kHz 9 11 9 11 nV/√Hz
INPUT CURRENT NOISE f = 0.1 Hz to 10 Hz 13 13 fA p-p
f = 1 kHz 0.6 0.6 fA/√Hz
FREQUENCY RESPONSE
Unity Gain, Small Signal G = –1 1.6 1.6 MHz
Full Power Response V
Slow Rate, Unity Gain V
SETTLING TIME
3
= 20 V p-p
O
R
= 2 kΩ 16 16 kHz
LOAD
= 20 V p-p
OUT
R
= 2 kΩ 11V/µs
LOAD
To 0.1% 10 V Step 10 10 µs
To 0.01% 10 V Step 11 11 µs
Overload Recovery
4
50% Overdrive 2 2 µs
Total Harmonic f = 1 kHz
Distortion R1 ≥ 10 kΩ
VO = 3 V rms –108 –108 dB
INPUT IMPEDANCE
Differential V
= ±1 V 1012i210
DIFF
12
i2 ΩipF
Common Mode 1014i2.2 1014i2.2 ΩipF
INPUT VOLTAGE RANGE
Differential
5
±20 ±20 V
Common-Mode Voltage ±10 ±11 ±10 ±11 V
Over Max Operating Temperature ±10 ±10 V
Common-Mode Rejection Ratio V
= ±10 V 90 110 94 110 dB
CM
T
MIN–TMAX
86 100 90 100 dB
OUTPUT CHARACTERISTICS
Voltage R
Current V
≥ 2 kΩ VS –4 VS –2.5 VS –4 VS –2.5 V
LOAD
T
MIN–TMAX
= ±10 V ± 5 ±10 ±5 ±10 mA
OUT
VS –4 VS –4 V
Short Circuit ±15 ±15 mA
POWER SUPPLY
Rated Performance ±15 ±15 V
Operating Range ±4 ±18 ±4 ±18 V
Quiescent Current 1.3 1.5 1.3 1.5 mA
–2–
REV. A
AD795
NOTES
1
Input offset voltage specifications are guaranteed after 5 minutes of operation at TA = +25°C.
2
Bias current specifications are guaranteed maximum at either input after 5 minutes of operation at TA = +25°C. For higher temperature, the current doubles every 10°C.
3
Gain = –1, R1 = 10 kΩ.
4
Defined as the time required for the amplifier’s output to return to normal operation after removal of a 50% overload from the amplifier input.
5
Defined as the maximum continuous voltage between the inputs such that neither input exceeds ±10 V from ground.
All min and max specifications are guaranteed.
Specifications subject to change without notice.
ABSOLUTE MAXIMUM RATINGS
Supply Voltage . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . ±18 V
Internal Power Dissipation
2
(@ TA = +25°C)
1
SOIC Package . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 500 mW
8-Pin Mini-DIP Package . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 750 mW
Input Voltage . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .±V
S
Output Short Circuit Duration . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Indefinite
Differential Input Voltage . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . +V
and –V
S
S
Storage Temperature Range (N, R) . . . . . . . –65°C to +125°C
Operating Temperature Range
AD795J/K . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 0°C to +70°C
NOTES
1
Stresses above those listed under “Absolute Maximum Ratings” may cause
permanent damage to the device. This is a stress rating only and functional
operation of the device at these or any other conditions above those indicated in the
operational section of this specification is not implied. Exposure to absolute
maximum rating conditions for extended periods may affect device reliability.
2
8-Pin Plastic Mini-DIP Package: θJA = 100°C/Watt
8-Pin Small Outline Package: θJA = 155°C/Watt
ESD SUSCEPTIBILITY
ESD (electrostatic discharge) sensitive device. Electrostatic
charges as high as 4000 volts, which readily accumulate on the
human body and on test equipment, can discharge without
detection. Although the AD795 features proprietary ESD protection circuitry, permanent damage may still occur on these
devices if they are subjected to high energy electrostatic discharges. Therefore, proper ESD precautions are recommended
to avoid any performance degradation or loss of functionality.
ORDERING GUIDE
Model Temperature Range Package Option*
AD795JN 0°C to +70°C N-8
AD795KN 0°C to +70°C N-8
AD795JR 0°C to +70°C R-8
*N = Plastic mini-DIP; R = SOIC package.
REV. A
–3–
AD795–Typical Characteristics
OUTPUT VOLTAGE RANGE – ±Volts
SUPPLY VOLTAGE – ±Volts
20
0
020
15
5
5
10
10
15
R
L
= 10k
+V
OUT
–V
OUT
Ω
10
–9
10
–14
140
10
–11
10
–13
–40
10
–12
–60
10
–10
120100806040200–20
INPUT BIAS CURRENT – Amps
TEMPERATURE – °C
20
Ω
= 10k
R
L
15
+V
IN
10
–V
IN
5
INPUT COMMON MODE RANGE – ±Volts
0
020
5
10
15
SUPPLY VOLTAGE – ±Volts
Figure 1. Common-Mode Voltage Range vs. Supply
30
Vs = ±15V
25
20
15
10
5
OUTPUT VOLTAGE SWING – Volts p-p
Figure 2. Output Voltage Range vs. Supply Voltage
1.0
0.95
0.90
0.85
0.80
0.75
0.70
INPUT BIAS CURRENT – pA
0.65
0
10
100 1k
LOAD RESISTANCE –
Ω
10k
0.60
Figure 3. Output Voltage Swing vs. Load Resistance
50
SAMPLE SIZE = 1058
40
30
20
PERCENTAGE OF UNITS
10
0
0
INPUT BIAS CURRENT – pA
1.51.5
Figure 5. Typical Distribution of Input Bias Current
2
Figure 6. Input Bias Current vs. Temperature
0
5
SUPPLY VOLTAGE – ±Volts
1510
Figure 4. Input Bias Current vs. Supply
20
REV. A–4–
VOLTAGE NOISE – µV p-p
SOURCE RESISTANCE – Ω
1k
10
1.0
10
3
10
4
10
9
10
8
10
7
10
6
10
5
Noise Bandwidth: 0.1 to 10Hz
100
FREQUENCY – Hz
1k
10
1.0
100
1 10 10M1M100k10k1k100
VOLTAGE NOISE (REFERRED TO INPUT) – nV/√Hz
1.00
0.95
0.90
0.85
0.80
0.75
0.70
INPUT BIAS CURRENT – pA
0.65
0.60
–10–15
–5
COMMON MODE VOLTAGE – Volts
0
+10+5
+15
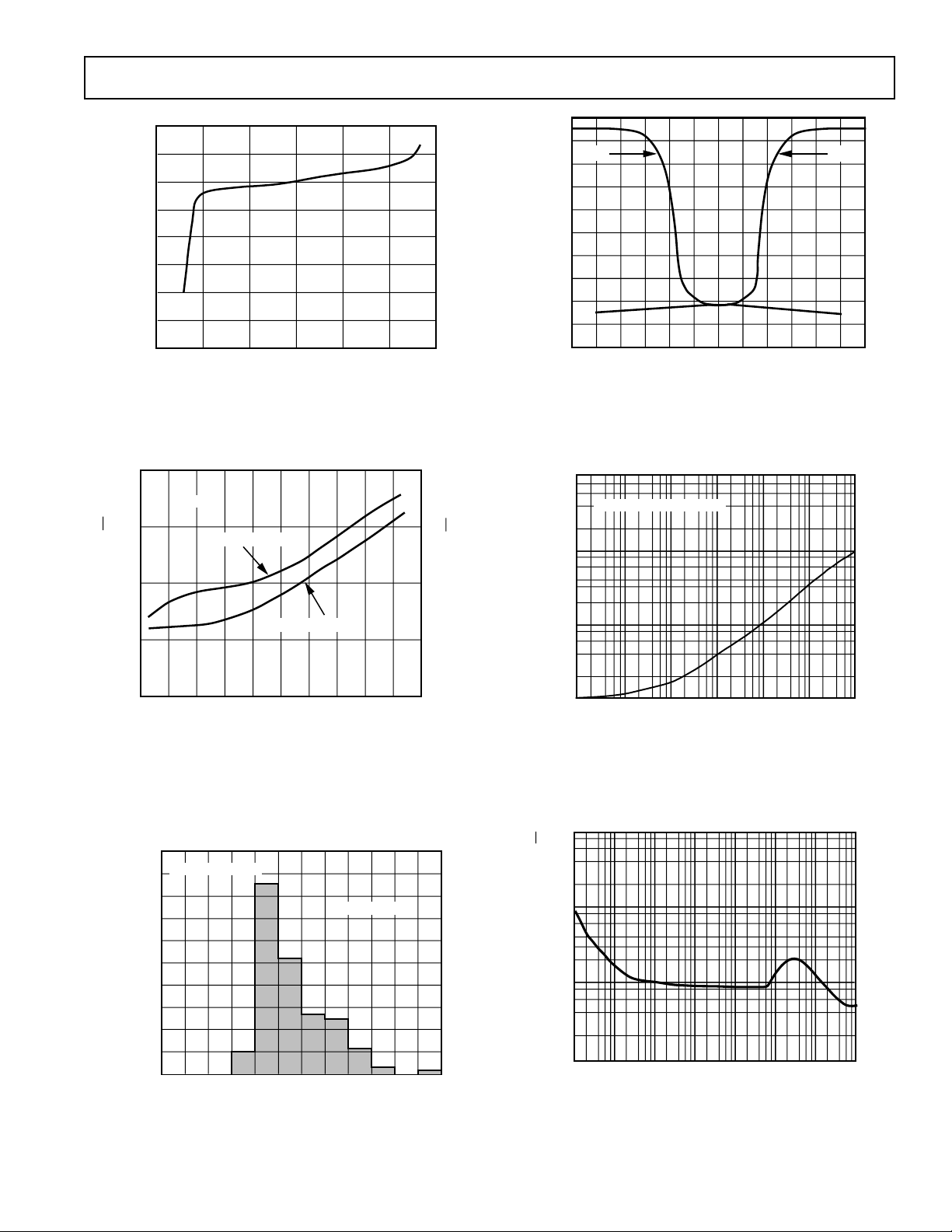
Figure 7. Input Bias Current vs. Common-Mode Voltage
AD795
–4
10
–5
10
–I
IN
–6
10
–7
10
–8
10
–9
10
–10
10
–11
10
INPUT BIAS CURRENT – Amperes
–12
10
–13
10
–14
10
–5
–6
–4 –3
–2 –1
0
12
DIFFERENTIAL INPUT VOLTAGE – ±Volts
Figure 8. Input Bias Current vs. Differential Input Voltage
4
+I
IN
563
140
100
10
1.0
0.1
0.01
CURRENT NOISE – fA/√Hz
15
f = 1kHz
12.5
10
VOLTAGE NOISE – nV/√Hz
7.5
5
–60
–40
VOLTAGE NOISE
–20
CURRENT NOISE
100 120806040200
TEMPERATURE – °C
Figure 9. Voltage and Current Noise Spectral Density vs.
Temperature
50
SAMPLE SIZE = 344
40
f = 0.1 TO 10Hz
Figure 10. Input Voltage Noise vs. Source Resistance
30
20
PERCENTAGE OF UNITS
10
0
0
0.1 TO 10Hz INPUT VOLTAGE NOISE p-p – µV
21
Figure 11. Typical Distribution of Input Voltage Noise
REV. A
3
Figure 12. Input Voltage Noise Spectral Density
–5–
 Loading...
Loading...