2-Channel, ±10 V Input Range, High
FEATURES
High resolution ADC
24 bits no missing codes
±0.0015% nonlinearity
Optimized for fast channel switching
18-bit p-p resolution (21 bits effective) at 500 Hz
16-bit p-p resolution (19 bits effective) at 2 kHz
14-bit p-p resolution (18 bits effective) at 15 kHz
On-chip per channel system calibration
2 fully differential analog inputs
Input ranges +5 V, ±5 V, +10 V, ±10 V
Overvoltage tolerant
Up to ±16.5 V not affecting adjacent channel
Up to ±50 V absolute maximum
3-wire serial interface
SPI™, QSPI™, MICROWIRE™, and DSP compatible
Schmitt trigger on logic inputs
Single-supply operation
5 V analog supply
3 V or 5 V digital supply
Package: 28-lead TSSOP
APPLICATIONS
PLCs/DCS
Multiplexing applications
Process control
Industrial instrumentation
GENERAL DESCRIPTION
The AD7732 is a high precision, high throughput analog front
end. True 16-bit p-p resolution is achievable with a total
conversion time of 500 µs (2 kHz channel switching), making it
ideally suitable for high resolution multiplexing applications.
The part can be configured via a simple digital interface, which
allows users to balance the noise performance against data
throughput up to a 15.4 kHz.
The analog front end features two fully differential input
channels with unipolar or true bipolar input ranges to ±10 V
while operating from a single +5 V analog supply. The part has
an overrange and underrange detection capability and accepts
an analog input overvoltage to ±16.5 V without degrading the
performance of the adjacent channels.
Throughput, 24-Bit ∑-∆ ADC
AD7732
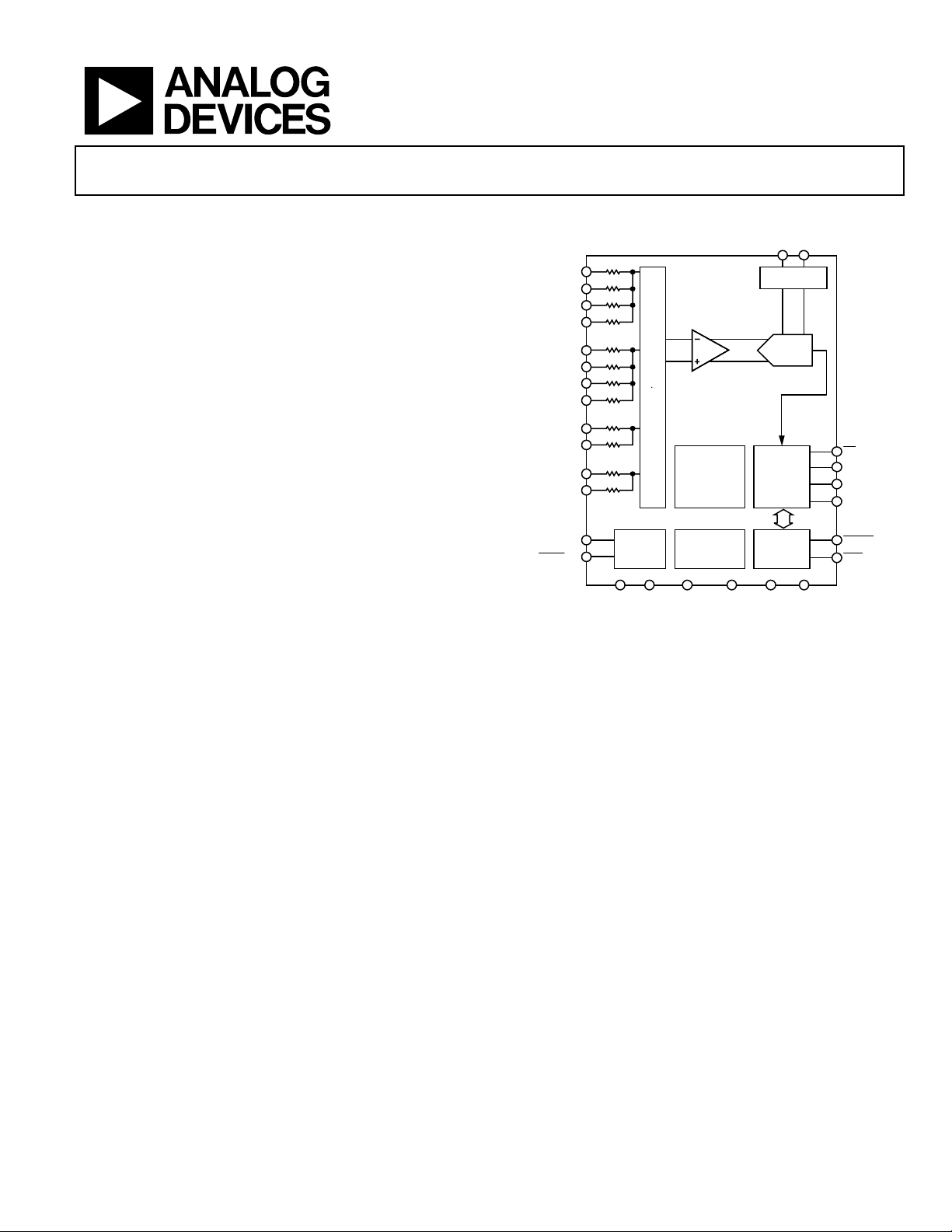
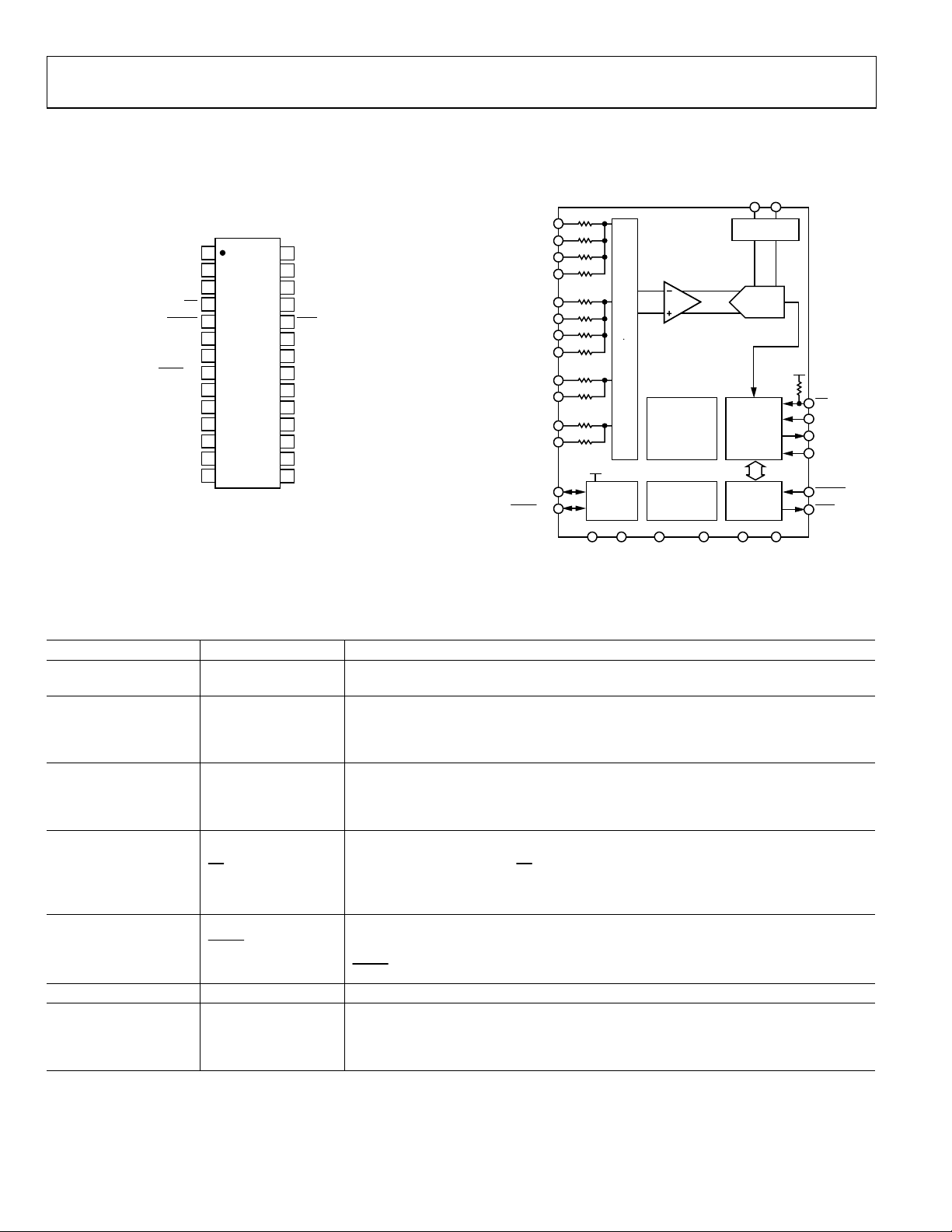
FUNCTIONAL BLOCK DIAGRAM
REFIN(–) REFIN(+)
AIN0(+)
BUFFER
AIN0(–)
MUX
AD7732
AIN1(+)
DD
CALIBRATION
CIRCUITRY
CLOCK
GENERATOR
Figure 1.
AIN1(–)
SYNC/P1
P0
I/O PORT
The differential reference input features “No-Reference” detect
capability. The ADC also supports per channel system
calibration options. The digital serial interface can be
configured for 3-wire operation and is compatible with
microcontrollers and digital signal processors. All interface
inputs are Schmitt triggered.
The part is specified for operation over the extended industrial
temperature range of –40°C to +105°C.
Other parts in the AD7732 family are the AD7734 and
the AD7738.
The AD7734 is similar to AD7732, but its analog front end
features four single-ended input channels.
The AD7738 analog front end is configurable for four fully
differential or eight single-ended input channels, features
0.625 V to 2.5 V bipolar/unipolar input ranges, and accepts a
common-mode input voltage from 200 mV to AVDD – 300 mV.
The AD7738 multiplexer output is pinned out externally,
allowing the user to implement programmable gain or signal
conditioning before being applied to the ADC.
REFERENCE
DETECT
24-BIT
Σ−∆ ADC
SERIAL
INTERFACE
CONTROL
LOGIC
DGNDMCLKINMCLKOUTAGND AV
DV
CS
SCLK
DIN
DOUT
RESET
RDY
DD
Rev. 0
Information furnished by Analog Devices is believed to be accurate and reliable.
However, no responsibility is assumed by Analog Devices for its use, nor for any
infringements of patents or other rights of third parties that may result from its use.
Specifications subject to change without notice. No license is granted by implication
or otherwise under any patent or patent rights of Analog Devices. Trademarks and
registered trademarks are the property of their respective companies.
One Technology Way, P.O. Box 9106, Norwood, MA 02062-9106, U.S.A.
Tel: 781.329.4700 www.analog.com
Fax: 781.326.8703 © 2003 Analog Devices, Inc. All rights reserved.

AD7732
TABLE OF CONTENTS
AD7732—Specifications.................................................................. 3
Mode Register............................................................................. 20
Timing Specifications....................................................................... 6
Absolute Maximum Ratings............................................................ 8
Typical Performance Characteristics ............................................. 9
Output Noise and Resolution Specification................................ 10
Chopping Enabled...................................................................... 10
Chopping Disabled..................................................................... 11
Pin Configurations and Functional Descriptions...................... 12
Register Description....................................................................... 14
Register Access............................................................................ 15
Communications Register......................................................... 15
I/O Port Register......................................................................... 16
Revision Register ........................................................................16
Test Register ................................................................................ 16
ADC Status Register................................................................... 17
Checksum Register..................................................................... 17
Digital Interface Description ........................................................ 22
Hardware ..................................................................................... 22
Reset ............................................................................................. 23
Access the AD7732 Registers.................................................... 23
Single Conversion and Reading Data...................................... 23
Dump Mode................................................................................ 24
Continuous Conversion Mode ................................................. 24
Continuous Read (Continuous Conversion) Mode .............. 25
Circuit Description......................................................................... 26
Analog Front End....................................................................... 26
Analog Input’s Extended Voltage Range ................................. 27
Chopping..................................................................................... 27
Multiplexer, Conversion, and Data Output Timing.............. 28
Sigma-Delta ADC....................................................................... 28
Frequency Response .................................................................. 29
ADC Zero-Scale Calibration Register ..................................... 17
ADC Full-Scale Register............................................................ 17
Channel Data Registers ............................................................. 17
Channel Zero-Scale Calibration Registers.............................. 18
Channel Full-Scale Calibration Registers................................ 18
Channel Status Registers ...........................................................18
Channel Setup Registers............................................................ 19
Channel Conversion Time Registers ....................................... 19
REVISION HISTORY
Revision 0: Initial Version
Voltage Reference Inputs........................................................... 29
Reference Detect......................................................................... 29
I/O Port........................................................................................ 30
Calibration................................................................................... 30
ADC Zero-Scale Self-Calibration ............................................ 30
Per Channel System Calibration .............................................. 30
High Common-Mode Voltage Application............................. 31
Outline Dimensions....................................................................... 32
Rev. 0 | Page 2 of 32
AD7732
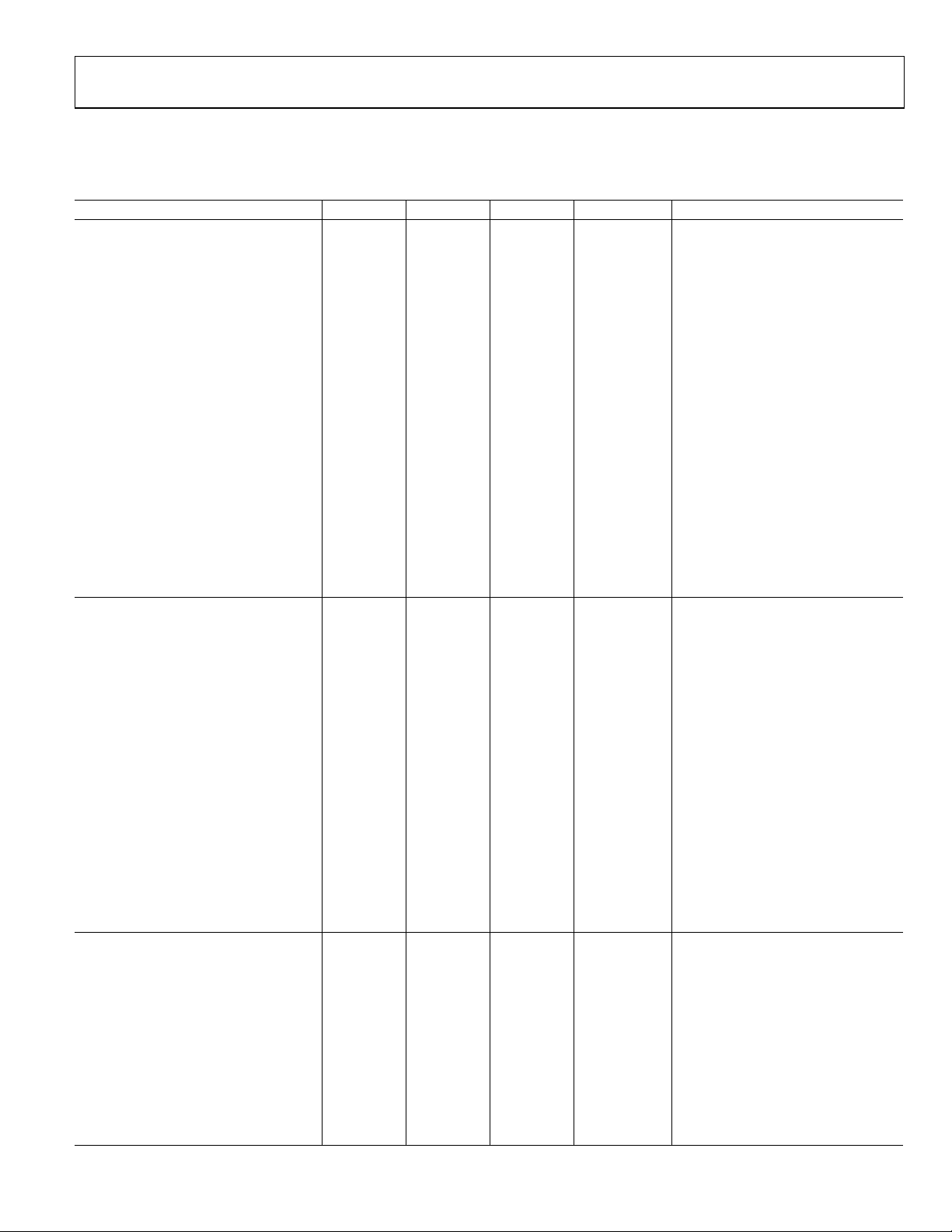
AD7732—SPECIFICATIONS
Table 1. (–40°C to +105°C; AVDD = 5 V ± 5%; DVDD = 2.7 V to 3.6 V, or 5 V ± 5%; BIAS (all), REFIN(+) = 2.5 V;
REFIN(–) = AGND; RA, RB, RC, RD open circuit; AIN Range = ±10 V; f
Parameter Min Typ Max Unit Test Conditions/Comments
ADC PERFORMANCE
CHOPPING ENABLED
Conversion Time Rate 372 12190 Hz Configure via Conv. Time Register
No Missing Codes
1, 2
24 Bits FW ≥ 6 (Conversion Time ≥ 165 µs)
Output Noise
Resolution
Integral Nonlinearity (INL)
Integral Nonlinearity (INL)
1, 2, 3
±0.0003 ±0.0015 % of FSR f
2, 3
±0.0010 ±0.0030 % of FSR f
Offset Error (Unipolar, Bipolar)4 ±10 mV Before Calibration
Offset Drift vs. Temperature1 ±2.5 µV/°C
Gain Error3 ±0.7 % Before Calibration
Gain Drift vs. Temperature1 ±3.2 ppm of FS/°C
Positive Full-Scale Error4 ±0.7 % of FSR Before Calibration
Positive Full-Scale Drift vs. Temp.1 ±3 ppm of FS/°C
Bipolar Negative Full-Scale Error5 ±0.0060 % of FSR After Calibration
Common-Mode Rejection 50 65 dB At DC
Power Supply Sensitivity ±4 ±10 LSB16 At DC, AIN = 7 V, AVDD = 5 V ± 5%
Channel-to-Channel Isolation 100 dB At DC, Maximum ±16.5 V AIN Voltage
ADC PERFORMANCE
CHOPPING DISABLED
Conversion Time Rate 737 15437 Hz Configure via Conv. Time Register
No Missing Codes
1, 2
24 Bits FW ≥ 8 (Conversion Time ≥ 117 µs)
Output Noise See Table 7
Resolution
Integral Nonlinearity (INL)
2, 3
±0.0015 % of FSR
Offset Error (Unipolar, Bipolar)6 ±10 mV Before Calibration
Offset Drift vs. Temperature ±25 µV/°C
Gain Error4 ±0.5 % Before Calibration
Gain Drift vs. Temperature ±5.3 ppm of FS/°C
Positive Full-Scale Error4 ±0.5 % of FSR Before Calibration
Positive Full-Scale Drift vs. Temp. ±4 ppm of FS/°C
Bipolar Negative Full-Scale Error5 ±0.0060 % of FSR After Calibration
Common-Mode Rejection 55 dB At DC
Power Supply Sensitivity ±4 LSB16 At DC, AIN = 7 V, AVDD = 5 V ± 5%
Channel-to-Channel Isolation 100 dB At DC, Maximum ±16.5 V AIN Voltage
ANALOG INPUTS
Analog Input Differential Voltage7
±10 V Range
0 V to +10 V Range 0 to +10 V
±5 V Range
0 V to +5 V Range 0 to +5 V
AIN Absolute Voltage
1, 2, 8
–16.5 +16.5 V
BIAS Voltage1 0 2.5 AVDD V
RA, RB, RC, RD Voltage1 –10.5 +20 V
AIN Impedance
AIN Pin Impedance
1, 9
100 124 kΩ
1, 9
87.5 108.5 kΩ
See
Table 4
See Table 5
and Table 6
See Table 8
and Table 9
±10
±5
V
V
= 6.144 MHz; unless otherwise noted.)
MCLKIN
= 2.5 MHz, VCM = 0 V
MCLKIN
= 6.144 MHz, VCM = 0 V
MCLKIN
Rev. 0 | Page 3 of 32
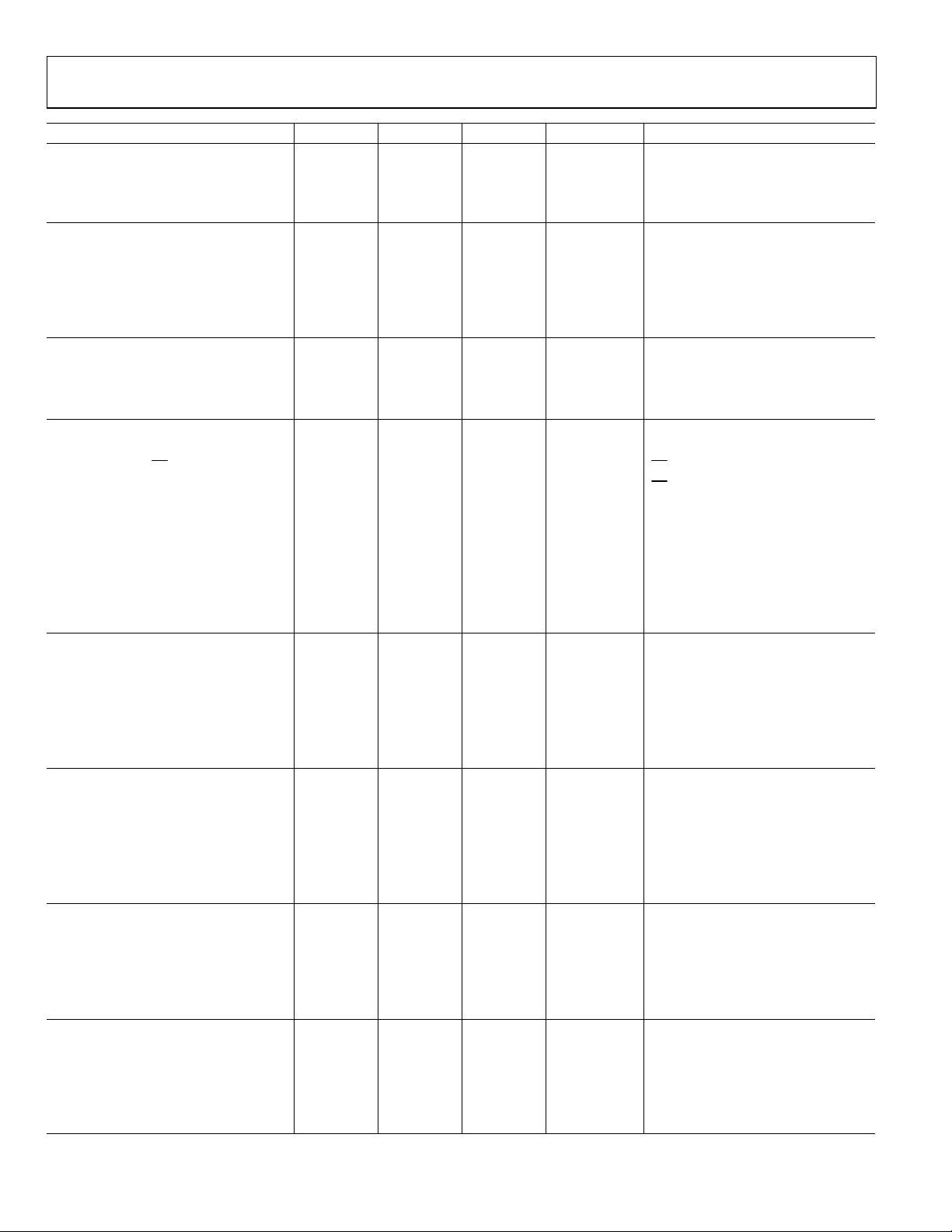
AD7732
Parameter Min Typ Max Unit Test Conditions/Comments
BIAS Pin Impedance
RA, RB, RC, RD Pin Impedance
Input Resistor Matching 0.2 %
Input Resistor Temp. Coefficient –30 ppm/°C
REFERENCE INPUTS
REFIN(+) to REFIN(–) Voltage
NOREF Trigger Voltage 0.5 V NOREF Bit in Channel Status Register
REFIN(+), REFIN(–)
Common-Mode Voltage1 0 AVDD V
Reference Input DC Current11 400 µA
SYSTEM CALIBRATION
Full-Scale Calibration Limit
Zero-Scale Calibration Limit
Input Span
LOGIC INPUTS
Input Current
Input Current CS
–40 µA
Input Capacitance 5 pF
1
V
1.4 2 V DVDD = 5 V
T+
1
V
0.8 1.4 V DVDD = 5 V
T–
VT+ – V
V
1
0.3 0.85 V DVDD = 5 V
T–
1
0.95 2 V DVDD = 3 V
T+
VT– 1 0.4 1.1 V DVDD = 3 V
VT+ – V
1
0.3 0.85 V DVDD = 3 V
T–
MCLK IN ONLY
Input Current
Input Capacitance 5 pF
V
Input Low Voltage 0.8 V DVDD = 5 V
INL
V
Input High Voltage 3.5 V DVDD = 5 V
INH
V
Input Low Voltage 0.4 V DVDD = 3 V
INL
V
Input High Voltage 2.5 V DVDD = 3 V
INH
LOGIC OUTPUTS13
VOL Output Low Voltage 0.4 V I
VOH Output High Voltage 4.0 V I
VOL Output Low Voltage 0.4 V I
VOH Output High Voltage DVDD – 0.6 V I
Floating State Leakage Current
Floating State Leakage Capacitance 3 pF
P0, P1 INPUTS/OUTPUTS Levels Referenced to Analog Supplies
Input Current
V
Input Low Voltage 0.8 V AVDD = 5 V
INL
V
Input High Voltage 3.5 V AVDD = 5 V
INH
VOL Output Low Voltage 0.4 V I
VOH Output High Voltage 4.0 V I
POWER REQUIREMENTS
AVDD–AGND Voltage 4.75 5.25 V
DVDD–DGND Voltage 4.75 5.25 V
2.70 3.60 V
AVDD Current (Normal Mode) 13.5 15.9 mA AVDD = 5 V
DVDD Current (Normal Mode)14 2.8 3.1 mA DVDD = 5 V
1, 9
12.5 15.5
1, 9
25 31
1, 10
2.475 2.5 2.525 V
1, 12
+1.05 × FS
–1.05 × FS
0.8 × FS
V
2.1 × FS
±1
±10
±10
±1
±10
kΩ
kΩ
V
V
µA
µA
µA
µA
µA
CS = DVDD
= DGND, Internal Pull-Up Resistor
CS
= 800 µA, DVDD = 5 V
SINK
= 200 µA, DVDD = 5 V
SOURCE
= 100 µA, DVDD = 3 V
SINK
= 100 µA, DVDD = 3 V
SOURCE
= 7 mA, See Abs. Max. Ratings
SINK
= 200 µA, AVDD = 5 V
SOURCE
Rev. 0 | Page 4 of 32
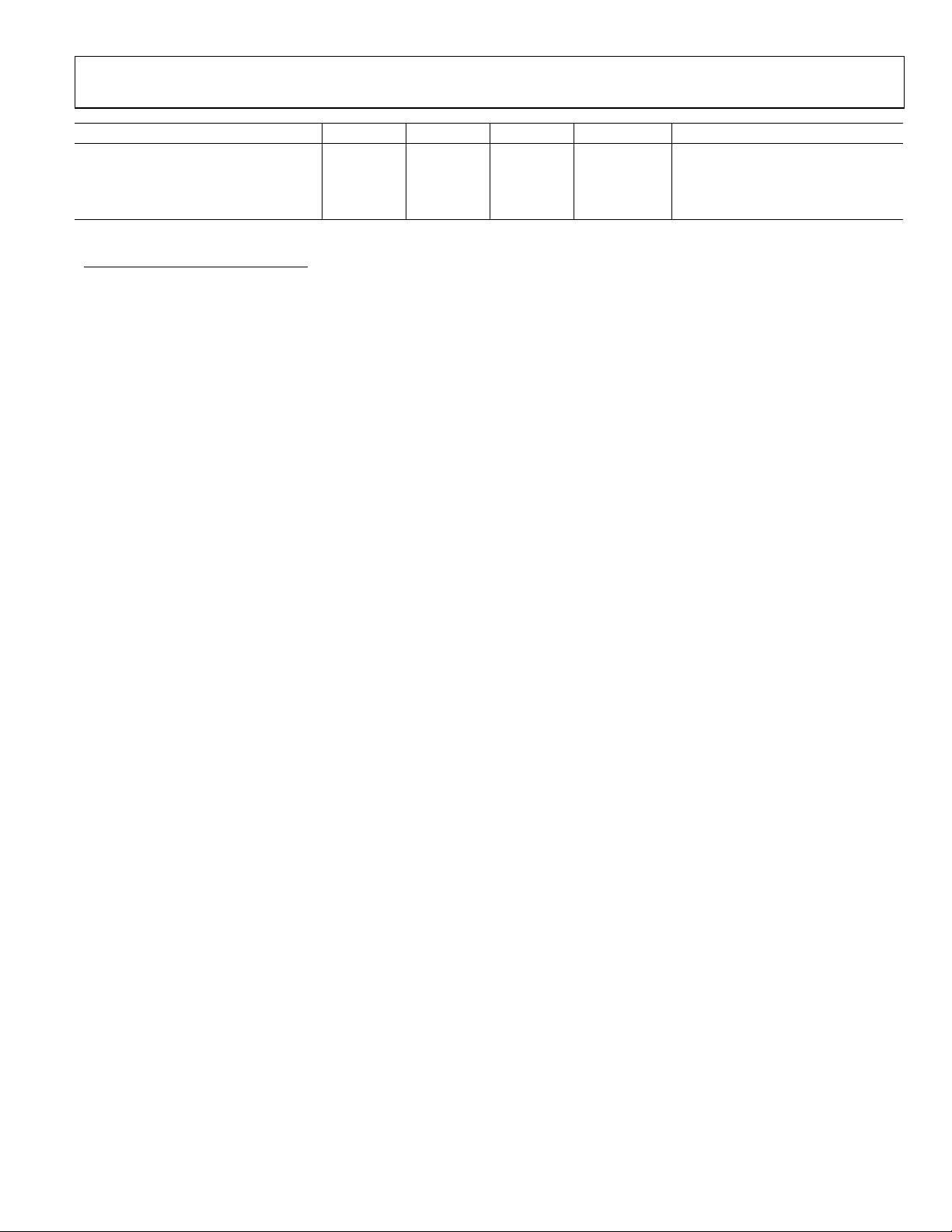
AD7732
Parameter Min Typ Max Unit Test Conditions/Comments
DVDD Current (Normal Mode)
Power Dissipation (Normal Mode)
AVDD+DVDD Current (Standby Mode)15 140 µA
Power Dissipation (Standby Mode)15 750 µW
14
1.0 1.5 mA DVDD = 3 V
14
85 100 mW
1
Specifications are not production tested but guaranteed by design and/or characterization data at initial product release.
2
See Typical Performance Characteristics.
3
VCM = Common-Mode Voltage = 0 V.
4
Specifications before calibration. Channel system calibration reduces these errors to the order of the noise.
5
Applies after the zero-scale and full-scale calibration. The negative full-scale error represents the remaining error after removing the offset and gain error.
6
ADC zero-scale self-calibration reduces this error to ±10 mV. Channel zero-scale system calibration reduces this error to the order of the noise.
7
For specified performance. The output data span corresponds to the specified nominal input voltage range. The ADC is functional outside the nominal input voltage
range, but the performance might degrade. Outside the nominal input voltage range, the OVR bit in the channel status register is set and the channel data register
value depends on the CLAMP bit in the mode register. See the register and circuit descriptions for more details.
8
The AIN absolute voltage of ±16.5 V applies for a nominal VBIAS voltage of +2.5 V. By configuring the BIAS and RA to RD pins differently, the part will work with higher
AIN absolute voltages as long as the internal voltage seen by the multiplexer and the input buffer is within 200 mV to AV
BIAS, and RA to RD pins must never exceed the values specified in the Absolute Maximum Ratings.
9
Pin impedance is from the pin to the internal node. In normal circuit configuration, the analog input total impedance is typically 108.5 kΩ + 15.5 kΩ = 124 kΩ.
10
For specified performance. Part is functional with lower V
11
Dynamic current charging the sigma-delta modulator input switching capacitor.
12
Outside the specified calibration range, calibration is possible but the performance may degrade.
13
These logic output levels apply to the MCLK OUT output when it is loaded with a single CMOS load.
14
With external MCLK, MCLKOUT is disabled (the CLKDIS bit is set in the mode register).
15
External MCLKIN = 0 V or DVDD, Digital Inputs = 0 V or DVDD, and P0 and P1 = 0 V or AV
.
REF
DD.
– 300 mV. Absolute voltage for the AIN,
DD
Rev. 0 | Page 5 of 32
AD7732
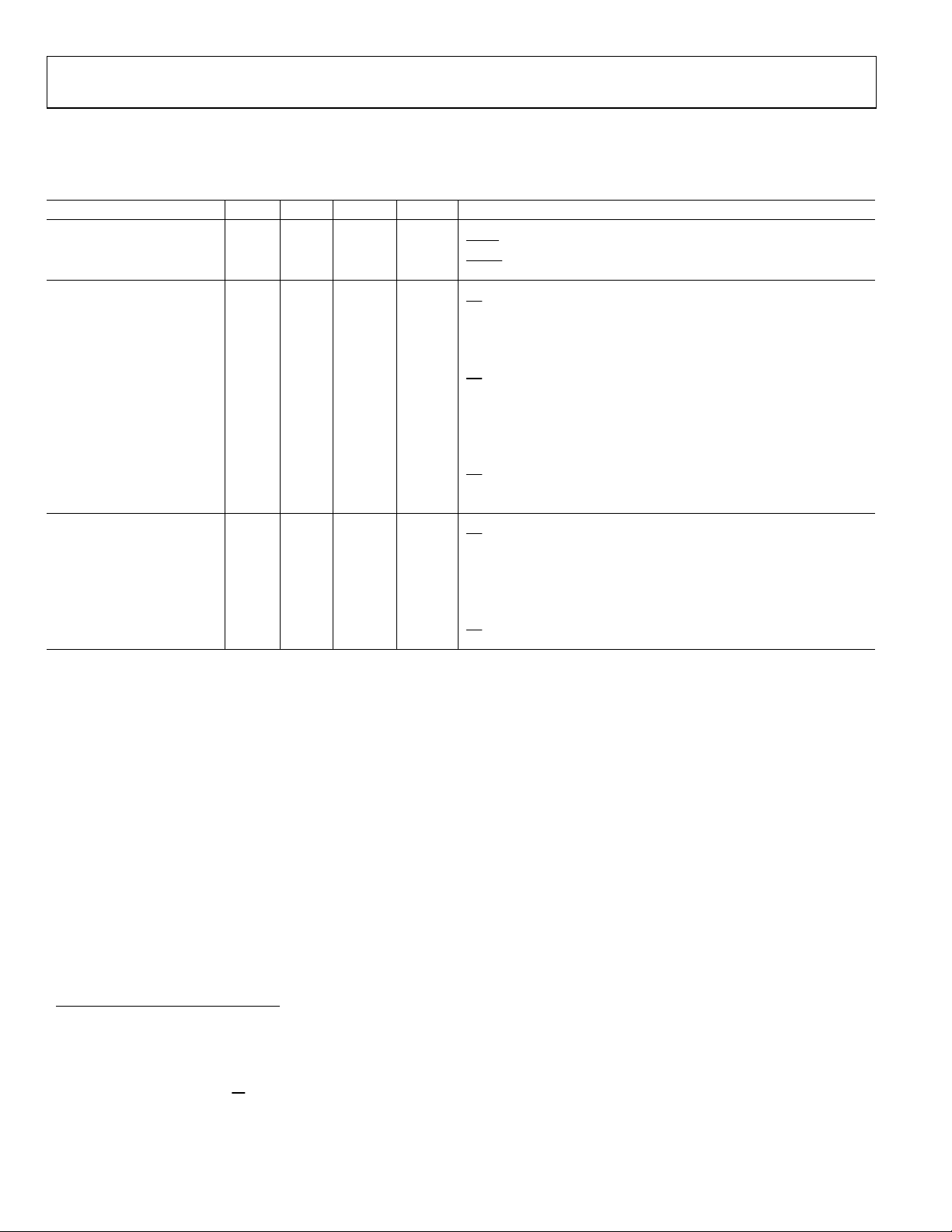
TIMING SPECIFICATIONS
Table 2. (AVDD = 5 V ± 5%; DVDD = 2.7 V to 3.6 V, or 5 V ± 5%; Input Logic 0 = 0 V; Logic 1 = DVDD; unless otherwise
noted.)
Parameter Min Typ Max Unit Test Conditions/Comments
Master Clock Range 1 6.144 MHz
t1 50 ns
t2 500 ns
Read Operation
t4 0 ns
t
0 60 ns DVDD of 4.75 V to 5.25 V
0 80 ns DVDD of 2.7 V to 3.3 V
t
0 60 ns DVDD of 4.75 V to 5.25 V
0 80 ns DVDD of 2.7 V to 3.3 V
t6 50 ns SCLK High Pulsewidth
t7 50 ns SCLK Low Pulsewidth
t8 0 ns
t
Write Operation
t11 0 ns
t12 30 ns Data Valid to SCLK Rising Edge Setup Time
t13 25 ns Data Valid after SCLK Rising Edge Hold Time
t14 50 ns SCLK High Pulsewidth
t15 50 ns SCLK Low Pulsewidth
t16 0 ns
1
Pulsewidth
SYNC
Pulsewidth
RESET
Falling Edge to SCLK Falling Edge Setup Time
CS
2
SCLK Falling Edge to Data Valid Delay
5
2, 3
5A
4
10 80 ns Bus Relinquish Time after SCLK Rising Edge
9
Falling Edge to Data Valid Delay
CS
Rising Edge after SCLK Rising Edge Hold Time
CS
Falling Edge to SCLK Falling Edge Setup
CS
Rising Edge after SCLK Rising Edge Hold Time
CS
1
Sample tested during initial release to ensure compliance. All input signals are specified with tr = tf = 5 ns (10% to 90% of DVDD) and timed from a voltage level of
1.6 V. See and . Figure 2 Figure 3
2
These numbers are measured with the load circuit of and defined as the time required for the output to cross the VOL or VOH limits.
3
This specification is relevant only if CS goes low while SCLK is low.
4
These numbers are derived from the measured time taken by the data output to change 0.5 V when loaded with the circuit of . The measured number is then
extrapolated back to remove effects of charging or discharging the 50 pF capacitor. This means that the times quoted in the Timing Characteristics are the true bus
relinquish times of the part and as such are independent of external bus loading capacitances.
Figure 4
Figure 4
Rev. 0 | Page 6 of 32
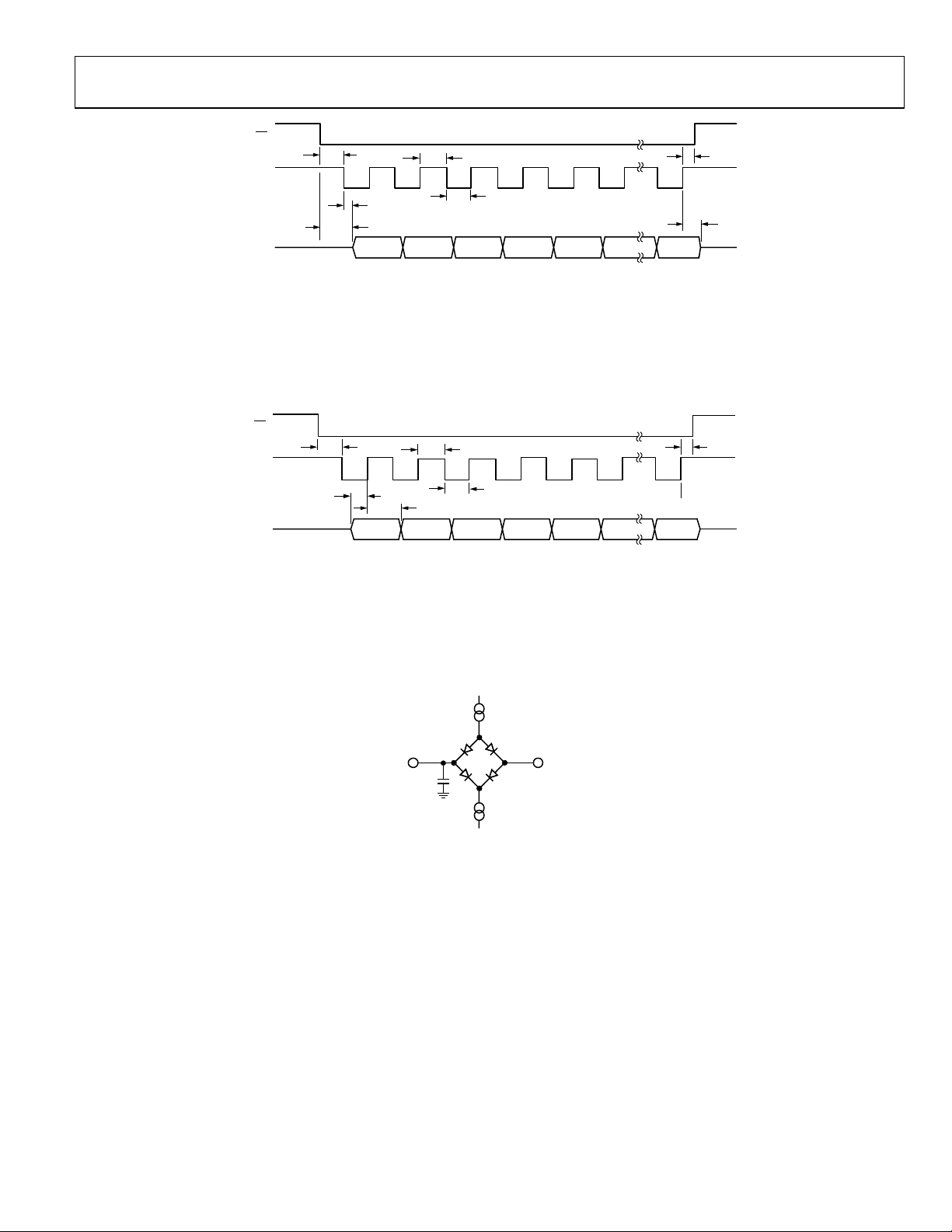
AD7732
SCLK
T
CS
t
4
SCLK
t
5
t
5A
DOUT MSB LSB
t
6
t
7
Figure 2. Read Cycle Timing Diagram
CS
t
DIN
11
t
12
MSB
t
14
t
15
t
13
Figure 3. Write Cycle Timing Diagram
LSB
t
8
t
9
t
16
(800µA AT DVDD = 5V
I
SINK
O OUTPUT
PIN
50pF
100µA AT DV
I
(200µA AT DVDD = 5V
SOURCE
100µA AT DV
1.6V
DD
= 3V)
DD
= 3V)
Figure 4. Load Circuit for Access Time and Bus Relinquish Time
Rev. 0 | Page 7 of 32

AD7732
ABSOLUTE MAXIMUM RATINGS
Table 3. TA = 25°C, unless otherwise noted.
Parameter Rating
AVDD to AGND, DVDD to DGND –0.3 V to +7 V
AGND to DGND –0.3 V to +0.3 V
AVDD to DVDD –5 V to +5 V
AIN to AGND –50 V to +50 V
RA, RB, RC, RD to AGND –11 V to +25 V
BIAS to AGND –0.3 V to AVDD + 0.3 V
REFIN+, REFIN– to AGND –0.3 V to AVDD + 0.3 V
P0, P1 Voltage to AGND –0.3 V to AVDD + 0.3 V
P0, P1 Current (T
P0, P1 Current (T
P0, P1 Current (T
Digital Input Voltage to DGND –0.3 V to DVDD + 0.3 V
Digital Output Voltage to DGND –0.3 V to DVDD + 0.3 V
Operating Temperature Range –40°C to +105°C
Storage Temperature Range –65°C to +150°C
Junction Temperature 150°C
TSSOP Package, Power Dissipation 660 mW
θJA Thermal Impedance
Lead Temperature, Soldering
Vapor Phase (60 sec) 215°C
Infrared (15 sec) 220°C
= 70°C) 8 mA
MAX
= 85°C) 5 mA
MAX
= 105°C) 2.5 mA
MAX
97.9°C/W
Stresses above those listed under Absolute Maximum Ratings may cause permanent damage to the device. This is a stress rating only;
functional operation of the device at these or any other conditions above those indicated in the operational section of this specification is
not implied. Exposure to absolute maximum rating conditions for extended periods may affect device reliability.
Rev. 0 | Page 8 of 32
AD7732
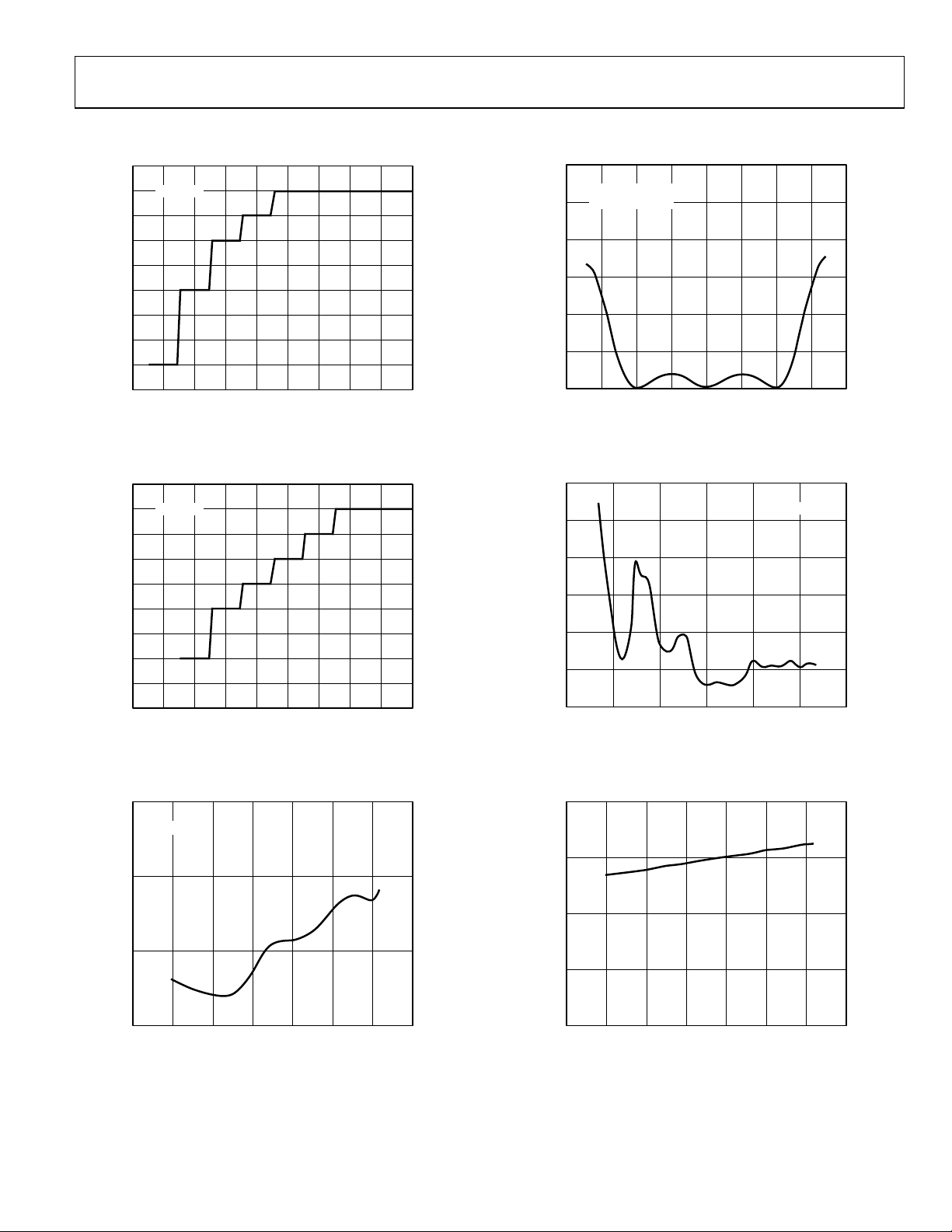
TYPICAL PERFORMANCE CHARACTERISTICS
25
24
CHOP = 1
23
22
21
20
19
NO MISSING CODES
18
17
16
12345678910
FILTER WORD
Figure 5. No Missing Codes Performance, Chopping Enabled
25
24
CHOP = 0
23
22
21
20
19
NO MISSING CODES
18
17
16
12345678910
FILTER WORD
Figure 6. No Missing Codes Performance, Chopping Disabled
15
VCM = 0V
60
MCLK = 6.144MHz
= 0V
V
50
40
30
INL – ppm
20
10
CM
0
–20–15–10–50 5101520
AIN DIFFERENTIAL VOLTAGE – V
Figure 8. Typical INL vs. AIN Differential Voltage, AIN Common-Mode
Voltage = 0 V, MCLK = 6.144 MHz, BIAS(+) = BIAS(–) = 2.5 V
60
50
40
30
INL – ppm
20
10
0
–15 –10 –5 0 5 10 15
AIN COMMON-MODE VOLTAGE – V
MCLK = 6.144MHz
Figure 9. Typical INL vs. AIN Common-Mode Voltage, ±10 V Differential
Signal, MCLK = 6.144 MHz, BIAS(+) = BIAS(–) = 2.5 V
20
10
INL – ppm
5
0
01234567
MCLK FREQUENCY – MHz
Figure 7. Typical INL vs. MCLK Frequency, ±10 V Differential Signal, AIN
Common-Mode Voltage = 0 V, BIAS(+) = BIAS(–) = 2.5 V
Rev. 0 | Page 9 of 32
15
10
CURRENT – mA
DD
+ DV
DD
5
AV
0
01234567
MCLK FREQUENCY – MHz
Figure 10. Typical Supply Current vs. MCLK Frequency,
Normal Operation, Converting
AD7732
OUTPUT NOISE AND RESOLUTION SPECIFICATION
The AD7732 can be operated with chopping enabled or
disabled, allowing the ADC to be programmed to either
optimize the throughput rate and channel switching time or to
optimize the offset drift performance. Noise tables for these two
primary modes of operation are outlined below for a selection
of output rates and settling times.
The AD7732 noise performance depends on the selected
chopping mode, the filter word (FW) value, and the selected
analog input range. The AD7732 noise will not vary
significantly with MCLK frequency.
Chopping Enabled
The first mode, in which the AD7732 is configured with
chopping enabled (CHOP = 1), provides very low noise with
Table 4. Typical Output RMS Noise in µV vs. Conversion Time and Input Range with Chopping Enabled
FW Conversion Time
Register
127 FFh 2686 372 200 9.6
46 AEh 999 1001 520 15.5
22 96h 499 2005 1040 22.7
17 91h 395 2534 1300 26.1
8 88h 207 4826 2500 39.2
6 86h 166 6041 3100 46.0
2 82h 82 12166 6300 120.0
Conversion Time
(µs)
Output Data Rate
(Hz)
lower output rates. Table 4 to Table 6 show the –3 dB
frequencies and typical performance versus the channel
conversion time and equivalent output data rate, respectively.
shows the typical output rms noise. Table 5 shows the typical
effective resolution based on rms noise. Table 6 shows the
typical output peak-to-peak resolution, representing values for
which there will be no code flicker within a 6-sigma limit. The
peak-to-peak resolutions are not calculated based on rms noise
but on peak-to-peak noise.
These typical numbers are generated from 4096 data samples
acquired in continuous conversion mode with an analog input
voltage set to 0 V and MCLK = 6.144 MHz. The conversion
time is selected via the channel conversion time register.
–3 dB Frequency
(Hz)
RMS Noise
(µV)
Table 5. Typical Effective Resolution in Bits vs. Conversion Time and Input Range with Chopping Enabled
Conversion Time
Register
127 FFh 2686 372 200 21.0 20.0 20.0 19.0
46 AEh 999 1001 520 20.3 19.3 19.3 18.3
22 96h 499 2005 1040 19.7 18.7 18.7 17.7
17 91h 395 2534 1300 19.5 18.5 18.5 17.5
8 88h 207 4826 2500 19.0 18.0 18.0 17.0
6 86h 166 6041 3100 18.7 17.7 17.7 16.7
2 82h 82 12166 6300 17.3 16.3 16.3 15.3
(µs)
Output Data Rate
(Hz)
–3 dB Frequency
(Hz)
Input Range/Effective Resolution (Bits) FW Conversion Time
±10 V 0 V to +10 V ±5 V 0 V to +5 V
Table 6. Typical Peak-to-Peak Resolution in Bits vs. Conversion Time and Input Range with Chopping Enabled
Conversion Time
Register
127 FFh 2686 372 200 18.1 17.1 17.1 16.1
46 AEh 999 1001 520 17.4 16.4 16.4 15.4
22 96h 499 2005 1040 16.9 15.9 15.9 14.9
17 91h 395 2534 1300 16.7 15.7 15.7 14.7
8 88h 207 4826 2500 16.2 15.2 15.2 14.2
6 86h 166 6041 3100 15.8 14.8 14.8 13.8
2 82h 82 12166 6300 15.0 13.4 13.4 12.4
(µs)
Output Data Rate
(Hz)
–3 dB Frequency
(Hz)
Input Range/Peak-to-Peak Resolution (Bits) FW Conversion Time
±10 V 0 V to +10 V ±5 V 0 V to +5 V
Rev. 0 | Page 10 of 32

AD7732
Chopping Disabled
The second mode, in which the AD7732 is configured with
chopping disabled (CHOP = 0), provides faster conversion time
while still maintaining high resolution. Table 7 to Table 9 show
the –3 dB frequencies and typical performance versus the
channel conversion time and equivalent output data rate,
respectively. Table 7 shows the typical output rms noise. Table 8
shows the typical effective resolution based on the rms noise.
Table 9 shows the typical output peak-to-peak resolution,
Table 7. Typical Output RMS Noise in µV vs. Conversion Time and Input Range with Chopping Disabled
FW Conversion Time
Register
127 7Fh 1357 737 670 13.2
92 5Ch 992 1008 920 15.5
44 2Ch 492 2032 1850 22.7
35 23h 398 2511 2290 26.3
16 10h 200 4991 2500 39.0
8 08h 117 8545 7780 57.0
3 03h 65 15398 14000 132
Conversion Time
(µs)
Output Data Rate
(Hz)
representing values for which there will be no code flicker
within a 6-sigma limit. The peak-to-peak resolutions are not
calculated based on rms noise but on peak-to-peak noise.
These typical numbers are generated from 4096 data samples
acquired in continuous conversion mode with an analog input
voltage set to 0 V and MCLK = 6.144 MHz. The conversion
time is selected via the channel conversion time register.
–3 dB Frequency
(Hz)
RMS Noise
(µV)
Table 8. Typical Effective Resolution in Bits vs. Conversion Time and Input Range with Chopping Disabled
Conversion Time
Register
127 7Fh 1357 737 670 20.5 19.5 19.5 18.5
92 5Ch 992 1008 920 20.3 19.3 19.3 18.3
44 2Ch 492 2032 1850 19.7 18.7 18.7 17.7
35 23h 398 2511 2290 19.5 18.5 18.5 17.5
16 10h 200 4991 2500 19.0 18.0 18.0 17.0
8 08h 117 8545 7780 18.4 17.4 17.4 16.4
3 03h 65 15398 14000 17.2 16.2 16.2 15.2
(µs)
Output Data Rate
(Hz)
–3 dB Frequency
(Hz)
Input Range/Effective Resolution (Bits) FW Conversion Time
±10 V 0 V to +10 V ±5 V 0 V to +5 V
Table 9. Typical Peak-to-Peak Resolution in Bits vs. Conversion Time and Input Range with Chopping Disabled
Conversion Time
Register
127 7Fh 1357 737 670 17.6 16.6 16.6 15.6
92 5Ch 992 1008 920 17.4 16.4 16.4 15.4
44 2Ch 492 2032 1850 16.8 15.8 15.8 14.8
35 23h 398 2511 2290 16.6 15.6 15.6 14.6
16 10h 200 4991 2500 16.1 15.1 15.1 14.1
8 08h 117 8545 7780 15.5 14.5 14.5 13.5
3 03h 65 15398 14000 14.3 13.3 13.3 12.3
(µs)
Output Data Rate
(Hz)
–3 dB Frequency
(Hz)
Input Range/Peak-to-Peak Resolution (Bits) FW Conversion Time
±10 V 0 V to +10 V ±5 V 0 V to +5 V
Rev. 0 | Page 11 of 32
AD7732
PIN CONFIGURATIONS AND FUNCTIONAL DESCRIPTIONS
1
SCLK
2
MCLKIN
CS
RESET
AV
DD
RA
RB
AIN1(+)
AIN0(+)
P0
10
11
12
13
14
3
4
5
6
AD7732
7
TOP VIEW
(Not to Scale)
8
9
MCLKOUT
SYNC/P1
BIAS1(+)
BIAS0(+)
Figure 11. 28-Lead TSSOP
28
DGND
27
DV
DD
26
DIN
25
DOUT
24
RDY
23
AGND
22
REFIN(–)
21
REFIN(+)
RD
20
RC
19
BIAS1(–)
18
17
AIN1(–)
16
AIN0(–)
15
BIAS0(–)
AIN0(+)
BIAS0(+)
RA
RB
AIN0(–)
BIAS0(–)
RC
RD
AIN1(+)
BIAS1(+)
AIN1(–)
BIAS1(–)
P0
SYNC/P1
R=15.5k
7R
2R
2R
7R
R
2R
2R
7R
R
7R
R
AV
I/O PORT
REFIN(–) REFIN(+)
Ω
BUFFER
MUX
AD7732
CALIBRATION
CIRCUITRY
DD
CLOCK
GENERATOR
REFERENCE
DETECT
24-BIT
Σ−∆
ADC
SERIAL
INTERFACE
CONTROL
LOGIC
DV
DD
CS
SCLK
DIN
DOUT
RESET
RDY
DD
Figure 12. Block Diagram
Table 10. Pin Function Descriptions—28-Lead TSSOP
Pin No. Mnemonic Description
1
SCLK
2
MCLKIN
3
MCLKOUT
4
CS
5
RESET
6 AVDD Analog Positive Supply Voltage. 5 V to AGND nominal.
7
P0
Serial Clock. Schmitt triggered logic input. An external serial clock is applied to this input
to transfer serial data to or from the AD7732.
Master Clock Signal for the ADC. This can be provided in the form of a crystal/resonator
or external clock. A crystal/resonator can be tied across the MCLKIN and MCLKOUT pins.
Alternatively, the MCLKIN pin can be driven with a CMOS compatible clock and
MCLKOUT left unconnected.
When the master clock for the device is a crystal/resonator, the crystal/resonator is
connected between MCLKIN and MCLKOUT. If an external clock is applied to the
MCLKIN, MCLKOUT provides an inverted clock signal or can be switched off to reduce
the device power consumption. MCLK OUT is capable of driving one CMOS load.
Chip Select. Active low Schmitt triggered logic input with an internal pull-up resistor.
With this input hardwired low, the AD7732 can operate in its 3-wire interface mode
using SCLK, DIN, and DOUT. CS
can be used to select the device in systems with more
than one device on the serial bus. It can also be used as an 8-bit frame
synchronization signal.
Schmitt Triggered Logic Input. Active low input that resets the control logic, interface
logic, digital filter, analog modulator, and all on-chip registers of the part to power-on
status. Effectively, everything on the part except the clock oscillator is reset when the
RESET pin is exercised.
Digital Input/Output. The pin direction is determined by the P0 DIR bit; the digital
value can be read/written as the P0 bit in the I/O port register. The digital voltage is
referenced to analog supplies. When configured as an input, the pin should be tied
high or low.
DGNDMCLKINMCLKOUTAGND AV
DV
DD
Rev. 0 | Page 12 of 32

AD7732
Pin No. Mnemonic Description
8
/P1
SYNC
9
10
RA
RB
11
BIAS1(+)
12 AIN1(+) Positive Analog Input Channel 1.
13 AIN0(+) Positive Analog Input Channel 0.
14 BIAS0(+) Voltage Bias for Positive Analog Input 0. This pin has the same function as BIAS1(+).
15 BIAS0(–) Voltage Bias for Negative Analog Input 0. This pin has the same function as BIAS1(+).
16 AIN0(–) Negative Analog Input Channel 0.
17 AIN1(–) Negative Analog Input Channel 1.
18 BIAS1(–) Voltage Bias for Negative Analog Input 1. This pin has the same function as BIAS1(+).
19
20
RC
RD
21
REFIN(+)
22
REFIN(–)
23 AGND Ground Reference Point for Analog Circuitry.
24
RDY
25
DOUT
26
DIN
27 DVDD Digital Supply Voltage, 3 V or 5 V Nominal.
28 DGND Ground Reference Point for Digital Circuitry.
SYNC/Digital Input/Digital Output. The pin direction is determined by the P1 DIR bit;
the digital value can be read/written as the P1 bit in the I/O port register. When the
SYNC bit in the I/O port register is set to 1, the SYNC
/P1 pin can be used to synchronize
the AD7732 modulator and digital filter with other devices in the system. The digital
voltage is referenced to analog supplies. When configured as an input, the pin should be
tied high or low.
RA, in association with RB and BIAS0(+), can be used to level shift the positive analog
input 0. In normal circuit configuration, this pin is left open circuit.
RB, in association with RA and BIAS0(+), can be used to level shift the positive analog
input 0. In normal circuit configuration, this pin is left open circuit.
This input is used to level shift the positive analog input 1. This signal is used to ensure
that the differential signal seen by the internal buffer amplifier is within its commonmode range. BIAS pins will normally be connected to 2.5 V.
RC, in association with RD and BIAS0(–), can be used to level shift the negative analog
input 0. In normal circuit configuration, this pin is left open circuit.
RD, in association with RC and BIAS0(–), can be used to level shift the negative analog
input 0. In normal circuit configuration, this pin is left open circuit.
Positive Terminal of the Differential Reference Input. REFIN(+) voltage potential can lie
anywhere between AV
and AGND. In normal circuit configuration, this pin should be
DD
connected to a 2.5 V reference voltage.
Negative Terminal of the Differential Reference Input. REFIN(–) voltage potential can lie
anywhere between AV
and AGND. In normal circuit configuration, this pin should be
DD
connected to a 0 V reference voltage.
Logic Output. Used as a status output in both conversion mode and calibration mode. In
conversion mode, a falling edge on this output indicates that either any channel or all
channels have unread data available, according to the RDYFN bit in the I/O port register.
In calibration mode, a falling edge on this output indicates that calibration is complete
(see the Digital Interface Description section for more details).
Serial data output with serial data being read from the output shift register on the part.
This output shift register can contain information from any AD7732 register, depending
on the address bits of the communications register.
Serial data input (Schmitt triggered) with serial data being written to the input shift
register on the part. Data from this input shift register is transferred to any AD7732
register, depending on the address bits of the communications register.
Rev. 0 | Page 13 of 32

AD7732
REGISTER DESCRIPTION
Table 11. Register Summary
Register Addr Dir Bit 7 Bit 6 Bit 5 Bit 4 Bit 3 Bit 2 Bit 1 Bit 0
Communications 00 W 0
I/O Port 01 R/W P0 P1 P0 DIR P1 DIR RDYFN 0 0 SYNC
P0 Pin P1 Pin 1 1 0 0 0 0
Revision 02 R Chip Revision Code Chip Generic Code
x x x x 0 1 0 0
Test 03 R/W 24-Bit Manufacturing Test Register
ADC Status 04 R – – – – – RDY1 – RDY0
0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
Checksum 05 R/W 16-Bit Checksum Register
ADC Zero-Scale Calibration 06 R/W 24-Bit ADC Zero-Scale Calibration Register
800000h
ADC Full-Scale 07 R/W 24-Bit ADC Full-Scale Register
800000h
Channel Data1 08, 0A R 16-/24-Bit Data Registers
8000h
Channel Zero-Scale Cal.1 10, 12 R/W 24-Bit Channel Zero-Scale Calibration Registers
800000h
Channel Full-Scale Cal.1 18, 1A R/W 24-Bit Channel Full-Scale Calibration Registers
200000h
Channel Status1 20, 22 R 0 CH1 0 0/P0 RDY/P1 NOREF SIGN OVR
Channel Number 0 0 0 0 0
Channel Setup1 28, 2A R/W 0 0 0 Stat OPT ENABLE 0 RNG1 RNG0
0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
Channel Conversion Time1 30, 32 R/W CHOP FW (7-Bit Filter Word)
1 11h
Mode2 38, 3A R/W MD2 MD1 MD0 CLKDIS DUMP Cont RD 24/16 BIT CLAMP
0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
1
Bit 1 in the communication register specifies the channel number of the register being accessed.
2
There is only one mode register, although the mode register can be accessed in one of two address locations. The address used to write the mode register specifies the
ADC channel on which the mode will be applied. Only address 38h must be used for reading from the mode register.
Table 12. Operational Mode Summary
MD2 MD1 MD0 Mode
0 0 0 Idle Mode
0 0 1 Continuous Conversion Mode
0 1 0 Single Conversion Mode
0 1 1 Power-Down (Standby) Mode
1 0 0 ADC Zero-Scale Self-Calibration
1 0 1 For Future Use
1 1 0 Channel Zero-Scale System Calibration
1 1 1 Channel Full-Scale System Calibration
(hex) Default Value
R/W
6-Bit Register Address
Table 13. Input Range Summary
RNG1 RNG0 Nominal Input Voltage Range
0 0 ±10 V
0 1 0 V to +10 V
1 0 ±5 V
1 1 0 V to +5 V
Rev. 0 | Page 14 of 32

AD7732
Register Access
The AD7732 is configurable through a series of registers. Some
of them configure and control general AD7732 features, while
others are specific to each channel. The register data widths
vary from 8 bits to 24 bits. All registers are accessed through the
communications register, i.e., any communication to the
AD7732 must start with a write to the communications register
specifying which register will be subsequently read or written.
Communications Register
8 Bits, Write-Only Register, Address 00h
All communications to the part must start with a write
operation to the communications register. The data written to
Bit Bit 7 Bit 6 Bit 5 Bit 4 Bit 3 Bit 2 Bit 1 Bit 0
Mnemonic 0
Bit Mnemonic Description
7 0 This bit must be 0 for proper operation.
6
5–0
R/W
Address
A 0 in this bit indicates that the next operation will be a write to a specified register. A 1 in this bit indicates
that the next operation will be a read from a specified register.
Address specifying to which register the read or write operation will be directed. For channel specific registers,
Bit 1 specifies the channel number. When the subsequent operation writes to the Mode register, Bit 1 specifies
the channel selected for operation determined by the mode register value (see Table 14).
Table 14.
Bit 2 Bit 1 Bit 0 Channel Input
0 0 0 0 AIN0(+) – AIN0(–)
0 1 0 1 AIN1(+) – AIN1(–)
R/W
the communications register determines whether the
subsequent operation will be a read or write and to which
register this operation will be directed. The digital interface
defaults to expect write operation to the communications
register after power-on, after reset, or after the subsequent read
or write operation to the selected register is complete. If the
interface sequence is lost, the part can be reset by writing at
CS
least 32 serial clock cycles with DIN high and
all of the parts, including the modulator, filter, interface, and all
registers are reset in this case.) Remember to keep DIN low
while reading 32 bits or more either in continuous read mode or
with the DUMP bit and “24/16” bit in the mode register set.
6-Bit Register Address
low. (Note that
Rev. 0 | Page 15 of 32

AD7732
I/O Port Register
8 Bits, Read/Write Register, Address 01h, Default Value 30h + Digital Input Value × 40h
The bits in this register are used to configure and access the digital I/O port on the AD7732.
Bit Bit 7 Bit 6 Bit 5 Bit 4 Bit 3 Bit 2 Bit 1 Bit 0
Mnemonic P0 P1 P0 DIR P1 DIR RDYFN 0 0 SYNC
Default P0 Pin P1 Pin 1 1 0 0 0 0
Bit Mnemonic Description
7, 6 P0, P1
5, 4 P0 DIR, P1 DIR
3 RDYFN
2, 1 0 These bits must be 0 for proper operation.
0 SYNC
When the P0 and P1 pins are configured as outputs, the P0 and P1 bits determine the pins’ output level. When
the P0 and P1 pins are configured as inputs, the P0 and P1 bits reflect the current input level on the pins.
These bits determine whether the P0 and P1 pins are configured as inputs or outputs. When set to 1, the
corresponding pin will be an input; when reset to 0, the corresponding pin will be an output.
This bit is used to control the function of the RDY
goes low when any channel has unread data. When this bit is set to 1, the RDY
enabled channels have unread data.
This bit enables the SYNC
When the SYNC bit is set to 1, the SYNC
filter with other devices in the system.
pin function. By default, this bit is 0 and SYNC/P1 can be used as a digital I/O pin.
pin can be used to synchronize the AD7732 modulator and digital
pin on the AD7732. When this bit is reset to 0, the RDY pin
pin will only go low if all
Revision Register
8 Bits, Read-Only Register, Address 02h, Default Value 04h + Chip Revision × 10h
Bit Bit 7 Bit 6 Bit 5 Bit 4 Bit 3 Bit 2 Bit 1 Bit 0
Mnemonic Chip Revision Code Chip Generic Code
Default x x x x 0 1 0 0
Bit Mnemonic Description
7–4 Chip Revision Code 4-Bit Factory Chip Revision Code
3–0 Chip Generic Code On the AD7732, these bits will read back as 04h.
Test Register
24 Bits, Read/Write Register, Address 03h
This register is used for testing the part in the manufacturing process. The user must not change the default configuration of this register.
Rev. 0 | Page 16 of 32

AD7732
ADC Status Register
8 Bits, Read-Only Register, Address 04h, Default Value 00h
In conversion modes, the register bits reflect the individual channel status. When a conversion is complete, the corresponding channel
data register is updated and the corresponding RDY bit is set to 1. When the channel data register is read, the corresponding bit is reset to
0. The bit is also reset to 0 when no read operation has taken place and the result of the next conversion is being updated to the channel
data register. Writing to the mode register resets all the bits to 0.
In calibration modes, all the register bits are reset to 0 while a calibration is in progress; all the register bits are set to 1 when the
calibration is complete.
The
The RDY0 bit corresponds to the differential input 0, and the RDY1 bit corresponds to the differential input 1.
Bit Bit 7 Bit 6 Bit 5 Bit 4 Bit 3 Bit 2 Bit 1 Bit 0
Mnemonic – – – – – RDY1 – RDY0
Default 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
Checksum Register
16 Bits, Read/Write Register, Address 05h
This register is described in the Using the
AD7732/AD7734/AD7738 Checksum Register application note
(www.analog.com/UploadedFiles/Application_Notes/71751876
AN626_0.pdf).
ADC Zero-Scale Calibration Register
24 Bits, Read/Write Register, Address 06h, Default Value 800000h
The register holds the ADC zero-scale calibration coefficient.
The value in this register is used in conjunction with the value
in the ADC full-scale calibration register and the corresponding
channel zero-scale and channel full-scale calibration registers to
scale digitally all channels’ conversion results. The value in this
register is updated automatically following the execution of an
ADC zero-scale self-calibration. Writing this register is
possible in the idle mode only (see the Calibration section for
more details).
pin output is related to the content of the ADC status register as defined by the RDYFN bit in the I/O port register.
RDY
Channel Data Registers
16 Bit/24 Bit, Read-Only Registers, Address 08h, 0Ah, Default
Width 16 Bits, Default Value 8000h
These registers contain the most up-to-date conversion results
corresponding to each analog input channel. The 16-bit or 24bit data width can be configured by setting the 16 bit/24 bit in
the mode register. The relevant RDY bit in the channel status
register goes high when the result is updated. The RDY bit will
return low once the data register reading has begun. The
pin can be configured to indicate when any channel has unread
data or waits until all enabled channels have unread data. If any
channel data register read operation is in progress when a new
result is updated, no update of the data register will occur. This
avoids having corrupted data. Reading the status registers can
be associated with reading the data registers in the dump mode.
Reading the status registers is always associated with reading
the data registers in the continuous read mode (see the Digital
Interface Description section for more details).
RDY
ADC Full-Scale Register
24 Bits, Read/Write Register, Address 07h, Default Value 800000h
This register holds the ADC full-scale coefficient. The user is
advised not to change the default configuration of this register.
Rev. 0 | Page 17 of 32

AD7732
Channel Zero-Scale Calibration Registers
Channel Full-Scale Calibration Registers
24 Bits, Read/Write Registers, Address 10h, 12h, Default Value
800000h
These registers hold the particular channel zero-scale
calibration coefficients. The value in these registers is used in
conjunction with the value in the corresponding channel fullscale calibration register, the ADC zero-scale calibration
register, and the ADC full-scale register to digitally scale the
particular channel conversion results. The value in this register
is updated automatically following the execution of a channel
zero-scale system calibration.
The format of the channel zero-scale calibration register is a
sign bit and 22 bits unsigned value. Writing this register is
possible in the idle mode only (see the Calibration section for
more details).
24 Bits, Read/Write Registers, Address 18h, 1Ah, Default Value
200000h
These registers hold the particular channel full-scale calibration
coefficients. The value in these registers is used in conjunction
with the value in the corresponding channel zero-scale
calibration register, the ADC zero-scale calibration register, and
the ADC full-scale register to digitally scale the particular
channel conversion results. The value in this register is updated
automatically following the execution of a channel full-scale
system calibration. Writing this register is possible in the idle
mode only (see the Calibration section for more details).
Channel Status Registers
8 Bits, Read-Only Register, Address 20h, 22h, Default Value 20h × Channel Number
These registers contain individual channel status information and some general AD7732 status information. Reading the status registers
can be associated with reading the data registers in the dump mode. Reading the status registers is always associated with reading the data
registers in the continuous read mode (see the Digital Interface Description section for more details).
Bit Bit 7 Bit 6 Bit 5 Bit 4 Bit 3 Bit 2 Bit 1 Bit 0
Mnemonic 0 CH1 0 0/P0 RDY/P1 NOREF SIGN OVR
Default Channel Number 0 0 0 0 0
Bit Mnemonic Description
7–5 CH1
4 0/P0
3 RDY/P1
2 NOREF
1 SIGN The voltage polarity at the analog input. It will be 0 for a positive voltage and 1 for a negative voltage.
0 OVR
These bits reflect the channel number. This can be used for current channel identification and easier
operation of the dump mode and continuous read mode.
When the status option bit of the corresponding channel setup register is reset to 0, this bit is read as a zero.
When the status option bit is set to 1, this bit reflects the state of the P0 pin, whether it is configured as an
input or an output.
When the status option bit of the corresponding channel setup register is reset to 0, this bit reflects the
selected channel RDY bit in the ADC status register. When the status option bit is set to 1, this bit reflects the
state of the P1 pin, whether it is configured as an input or an output.
This bit indicates the reference input status. If the voltage between the REFIN(+) and REFIN(–) pins is less than
NOREF, the trigger voltage and a conversion is executed, then the NOREF bit goes to 1.
This bit reflects either the overrange or the underrange on the analog input. The bit is set to 1 when the
analog input voltage goes over or under the nominal voltage range (see the Analog Input’s Extended Voltage
Range section).
Rev. 0 | Page 18 of 32

AD7732
Channel Setup Registers
8 Bits, Read/Write Register, Address 28h, 2Ah, Default Value 00h
These registers are used to configure the selected channel, to configure its input voltage range, and to set up the corresponding channel
status register.
Bit Bit 7 Bit 6 Bit 5 Bit 4 Bit 3 Bit 2 Bit 1 Bit 0
Mnemonic 0 0 0 Stat OPT ENABLE 0 RNG1 RNG0
Default 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
Bit Mnemonic Description
7–5 0 These bits must be 0 for proper operation.
4 Stat OPT
3 ENABLE
2 0 This bit must be 0 for proper operation.
1–0 RNG1–RNG0 This is the channel input voltage range (see Table 15).
Table 15.
RNG1 RNG0 Nominal Input Voltage Range
0 0 ±10 V
0 1 0 V to +10 V
1 0 ±5 V
1 1 0 V to +5 V
Status Option. When this bit is set to 1, the P0 and P1 bits in the channel status register will reflect the state of
the P0 and P1 pins. When this bit is reset to 0, the RDY bit in the channel status register will reflect the channel
corresponding to the RDY bit in the ADC status register.
Channel Enable. Set this bit to 1 to enable the channel in the continuous conversion mode. A single
conversion will take place regardless of this bit’s value.
Channel Conversion Time Registers
8 Bits, Read/Write Register, Address 30h, 32h, Default Value 91h
The conversion time registers enable or disable chopping and configure the digital filter for a particular channel. This register value affects
the conversion time, frequency response, and noise performance of the ADC.
Bit Bit 7 Bit 6 Bit 5 Bit 4 Bit 3 Bit 2 Bit 1 Bit 0
Mnemonic CHOP FW (7-Bit Filter Word)
Default 1 11h
Bit Mnemonic Description
7 CHOP Chopping Enable Bit. Set to 1 to apply chopping mode for a particular channel.
6–0 FW
CHOP = 1, single conversion or continuous conversion with one channel enabled.
Conversion Time (µs) = (FW × 128 + 248)/MCLK Frequency (MHz), the FW range is 2 to 127.
CHOP = 1, continuous conversion with two channels enabled.
Conversion Time (µs) = (FW × 128 + 249)/MCLK Frequency (MHz), the FW range is 2 to 127.
CHOP = 0, single conversion or continuous conversion with one channel enabled.
Conversion Time (µs) = (FW × 64 + 206)/MCLK Frequency (MHz), the FW range is 3 to 127.
CHOP = 0, continuous conversion with two channels enabled.
Conversion Time (µs) = (FW × 64 + 207)/MCLK Frequency (MHz), the FW range is 3 to 127.
Rev. 0 | Page 19 of 32

AD7732
Mode Register
8 Bits, Read/Write Register, Address 38h, 3Ah, Default Value 00h
The mode register configures the part and determines its operating mode. Writing to the mode register clears the ADC status register, sets
the
The AD7732 contains only one mode register. Bit 1 of the address is used for writing to the mode register to specify the channel selected
for the operation determined by the MD2 to MD0 bits. Only the address 38h must be used for reading from the mode register.
Bit Bit 7 Bit 6 Bit 5 Bit 4 Bit 3 Bit 2 Bit 1 Bit 0
Mnemonic MD2 MD1 MD0 CLKDIS DUMP Cont RD 24/16 BIT CLAMP
Default 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
Bit Mnemonic Description
7–5 MD2–MD0
4 CLKDIS
3 DUMP
2 Cont RD
1 24/16 BIT
0 CLAMP
MD2 MD1 MD0 Mode Address Used for Mode Register Write Specifies:
0 0 0 Idle Mode
0 0 1 Continuous Conversion Mode The First Channel to Start Converting
0 1 0 Single Conversion Mode Channel to Convert
0 1 1 Power-Down (Standby) Mode
1 0 0 ADC Zero-Scale Self-Calibration Channel Conversion Time Used for the ADC Self-Calibration
1 0 1 For Future Use
1 1 0 Channel Zero-Scale System Calibration Channel to Calibrate
1 1 1 Channel Full-Scale System Calibration Channel to Calibrate
pin to a logic high level, exits all current operations, and starts the mode specified by the mode bits.
RDY
Mode Bits. These three bits determine the AD7732 operation mode. Writing a new value to the mode bits will
exit the part from the mode in which it has been operating and place it in the newly requested mode
immediately. The function of the mode bits is described in more detail below.
Master Clock Output Disable. When this bit is set to 1, the master clock is disabled from appearing at the
MCLKOUT pin and the MCLKOUT pin is in a high impedance state. This allows turning off the MCLKOUT as a
power saving feature. When using an external clock on MCLKIN, the AD7732 continues to have internal clocks
and will convert normally regardless of the CLKDIS bit state. When using a crystal oscillator or ceramic
resonator across the MCLKIN and MCLKOUT pins, the AD7732 clock is stopped and no conversions can take
place when the CLKDIS bit is active. The AD7732 digital interface can still be accessed using the SCLK pin.
DUMP Mode. When this bit is reset to 0, the channel status register and channel data register will be
addressed and read separately. When the DUMP bit is set to 1, the channel status register will be followed
immediately by a read of the channel data register regardless of whether the status or data register has been
addressed through the communication register. The continuous read mode will always be dump mode
reading of the channel status and data register, regardless of the dump bit value (see the Digital Interface
Description section for more details).
When this bit is set to 1, the AD7732 will operate in the continuous read mode (see the Digital Interface
Description section for more details).
The Channel Data Register Data Width Selection Bit. When set to 1, the channel data registers will be 24 bits
wide. When set to 0, the channel data registers will be 16 bits wide.
This bit determines the channel data register’s value when the analog input voltage is outside the nominal
input voltage range. When the CLAMP bit is set to 1, the channel data register will be digitally clamped either
to all 0s or all 1s when the analog input voltage goes outside the nominal input voltage range. When the
CLAMP bit is reset to 0, the data registers reflect the analog input voltage even outside the nominal voltage
range (see the Analog Input’s Extended Voltage Range section).
Rev. 0 | Page 20 of 32

AD7732
MD2 MD1 MD0 Operating Mode
0 0 0
0 0 1
0 1 0
0 1 1
1 0 0
1 0 1 For Future Use.
1 1 0
1 1 1
Idle Mode
The default mode after power-on or reset.
The AD7732 automatically returns to this mode after any calibration or after a single conversion.
Continuous Conversion Mode
The AD7732 performs a conversion on the specified channel. After the conversion is complete, the relevant channel
data register and channel status register are updated, the relevant RDY bit in the ADC status register is set, and the
AD7732 continues converting on the next enabled channel. The part will cycle through all enabled channels until it is
put into another mode or reset. The cycle period will be the sum of all enabled channels’ conversion times, set by the
corresponding channel conversion time registers.
Single Conversion Mode
The AD7732 performs a conversion on the specified channel. After the conversion is complete, the relevant channel
data register and channel status register are updated, the relevant RDY bit in the ADC status register is set, the RDY
goes low, the MD2–MD0 bits are reset, and the AD7732 returns to idle mode. Requesting a single conversion ignores
the channel setup register enable bits; a conversion will be performed even if that channel is disabled.
Power-Down (Standby) Mode
The ADC and the analog front end (internal buffer) go into the power-down mode.
The AD7732 digital interface can still be accessed. The CLKDIS bit works separately, and the MCLKOUT mode is not
affected by the power-down (standby) mode.
ADC Zero-Scale Self-Calibration Mode
A zero-scale self-calibration is performed on internally shorted ADC inputs.
After the calibration is complete, the contents of the ADC zero-scale calibration register are updated, all RDY bits in the
ADC status register are set, the RDY pin goes low, the MD2–MD0 bits are reset, and the AD7732 returns to idle mode.
Channel Zero-Scale System Calibration Mode
A zero-scale system calibration is performed on the selected channel. An external system zero-scale voltage should be
provided at the AD7732 analog input and should remain stable for the duration of the calibration. After the calibration
is complete, the contents of the corresponding channel zero-scale calibration register are updated, all RDY bits in the
ADC status register are set, the RDY
Channel Full-Scale System Calibration Mode
A full-scale system calibration is performed on the selected channel. An external system full-scale voltage should be
provided at the AD7732 analog input and this voltage should remain stable for the duration of the calibration. After
the calibration is complete, the contents of the corresponding channel full-scale calibration register are updated, all
RDY bits in the ADC status register are set, the RDY
to idle mode.
pin goes low, the MD2–MD0 bits are reset, and the AD7732 returns to idle mode.
pin goes low, the MD2–MD0 bits are reset, and the AD7732 returns
pin
Rev. 0 | Page 21 of 32
AD7732
DIGITAL INTERFACE DESCRIPTION
Hardware
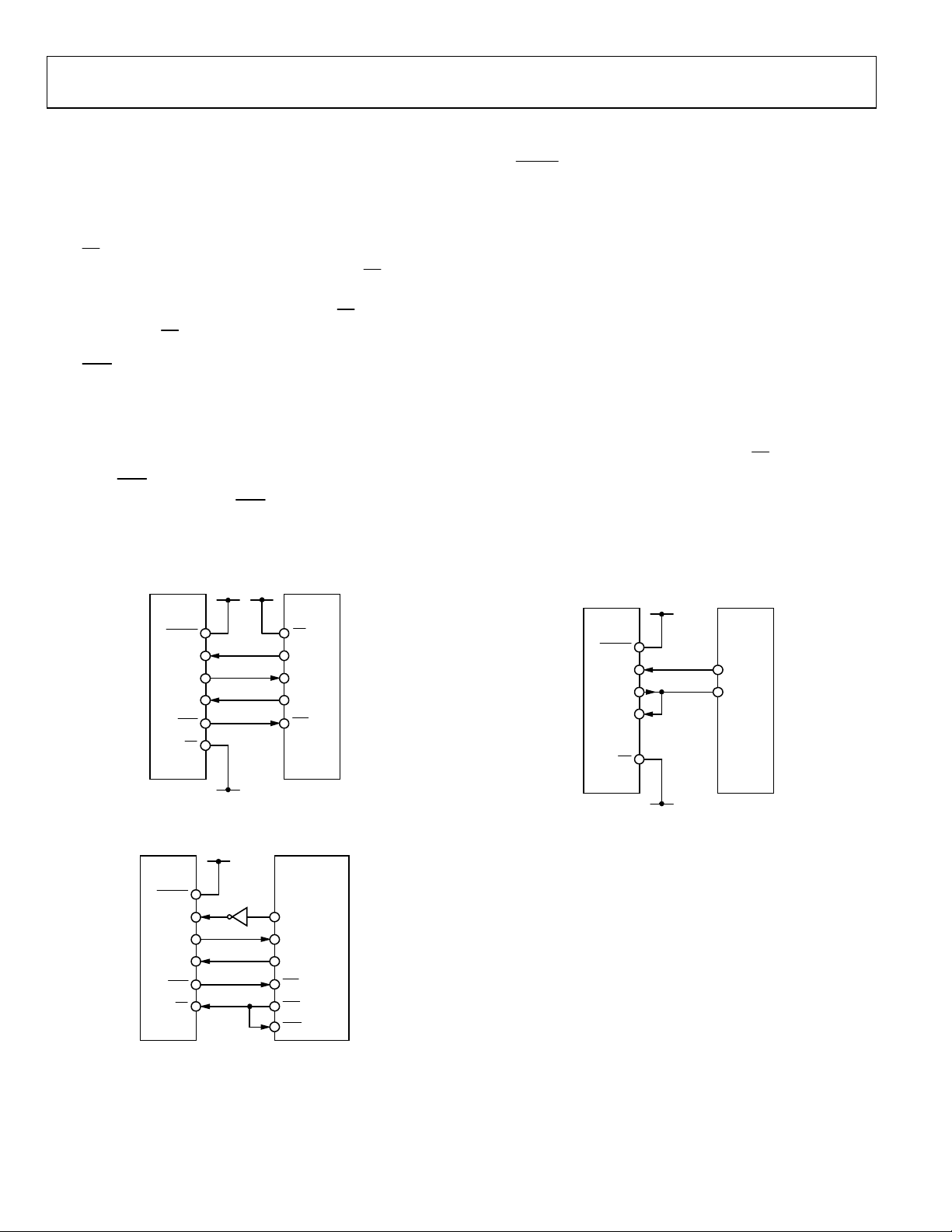
The AD7732 serial interface can be connected to the host device
via the serial interface in several different ways.
pin can be used to select the AD7732 as one of several
The
CS
circuits connected to the host serial interface. When
the AD7732 ignores the SCLK and DIN signals and the DOUT
pin goes to the high impedance state. When the
used, connect the
The
pin can be polled for high-to-low transition or can
RDY
pin to DGND.
CS
drive the host device interrupt input to indicate that the
AD7732 has finished the selected operation and/or new data
from the AD7732 is available. The host system can also wait a
designated time after a given command is written to the device
before reading. Alternatively, the AD7732 status can be polled.
When the
an open circuit. (Note that the
pin is not used in the system, it should be left as
RDY
pin is always an active
RDY
digital output, i.e., it never goes into a high impedance state.)
is high,
CS
signal is not
CS
The
used, connect this pin to DV
pin can be used to reset the AD7732. When not
RESET
.
DD
The AD7732 interface can be reduced to just two wires
connecting the DIN and DOUT pins to a single bidirectional
data line. The second signal in this 2-wire configuration is the
SCLK signal. The host system should change the data line
direction with reference to the AD7732 timing specification
(see the Bus Relinquish Time in Table 2). The AD7732 cannot
operate in the continuous read mode in 2-wire serial interface
configuration.
All the digital interface inputs are Schmitt-Triggered; therefore,
the AD7732 interface features higher noise immunity and can
be easily isolated from the host system via optocouplers.
Figure 13, Figure 14, and Figure 15 outline some of the possible
host device interfaces: SPI without using the
CS
signal
(Figure 13), a DSP interface (Figure 14), and a 2-wire
configuration(Figure 15).
DVDDDV
AD7732
RESET
SCLK
DOUT
DIN
RDY
CS
DGND
Figure 13. AD7732 to Host Device Interface, SPI
DV
AD7732
RESET
SCLK
DOUT
DIN
RDY
CS
Figure 14. AD7732 to Host Device Interface, DSP
DD
68HC11
SS
SCK
MISO
MOSI
INT
DD
ADSP-2105
SCLK
DR
DT
INT
TFS
RFS
DV
CS
DGND
DD
8xC51
P3.1/TXD
P3.0/RXD
AD7732
RESET
SCLK
DOUT
DIN
Figure 15. AD7732 to Host Device Interface, 2-Wire Configuration
Rev. 0 | Page 22 of 32

AD7732
Reset
The AD7732 can be reset by the
pin or by writing a reset
RESET
sequence to the AD7732 serial interface.
The reset sequence is N × 0 + 32 × 1, which could be the data
sequence 00h + FFh + FFh + FFh + FFh in a byte-oriented
interface. The AD7732 also features a power-on reset with a
trip point of 2 V and goes to the defined default state after
power-on.
It is the system designer’s responsibility to prevent an unwanted
write operation to the AD7732. The unwanted write operation
could happen when a spurious clock appears on the SCLK while
pin is low. It should be noted that on system power-on, if
the
CS
the AD7732 interface signals are floating or undefined, the part
can be inadvertently configured into an unknown state. This
could be easily overcome by initiating either a hardware reset
event or a 32 ones reset sequence as the first step in the system
configuration.
Access the AD7732 Registers
All communications to the part start with a write operation to
the communications register followed by either reading or
writing the addressed register.
In a simultaneous read-write interface (such as SPI), write 0 to
the AD7732 while reading data.
Figure 16 shows the AD7732 interface read sequence for the
ADC status register.
CS
SCLK
DIN
DOUT
WRITE
COMMUNICATIONS
REGISTER
Figure 16. Serial Interface Signals—Registers Access
READ
ADC STATUS
REGISTER
Single Conversion and Reading Data
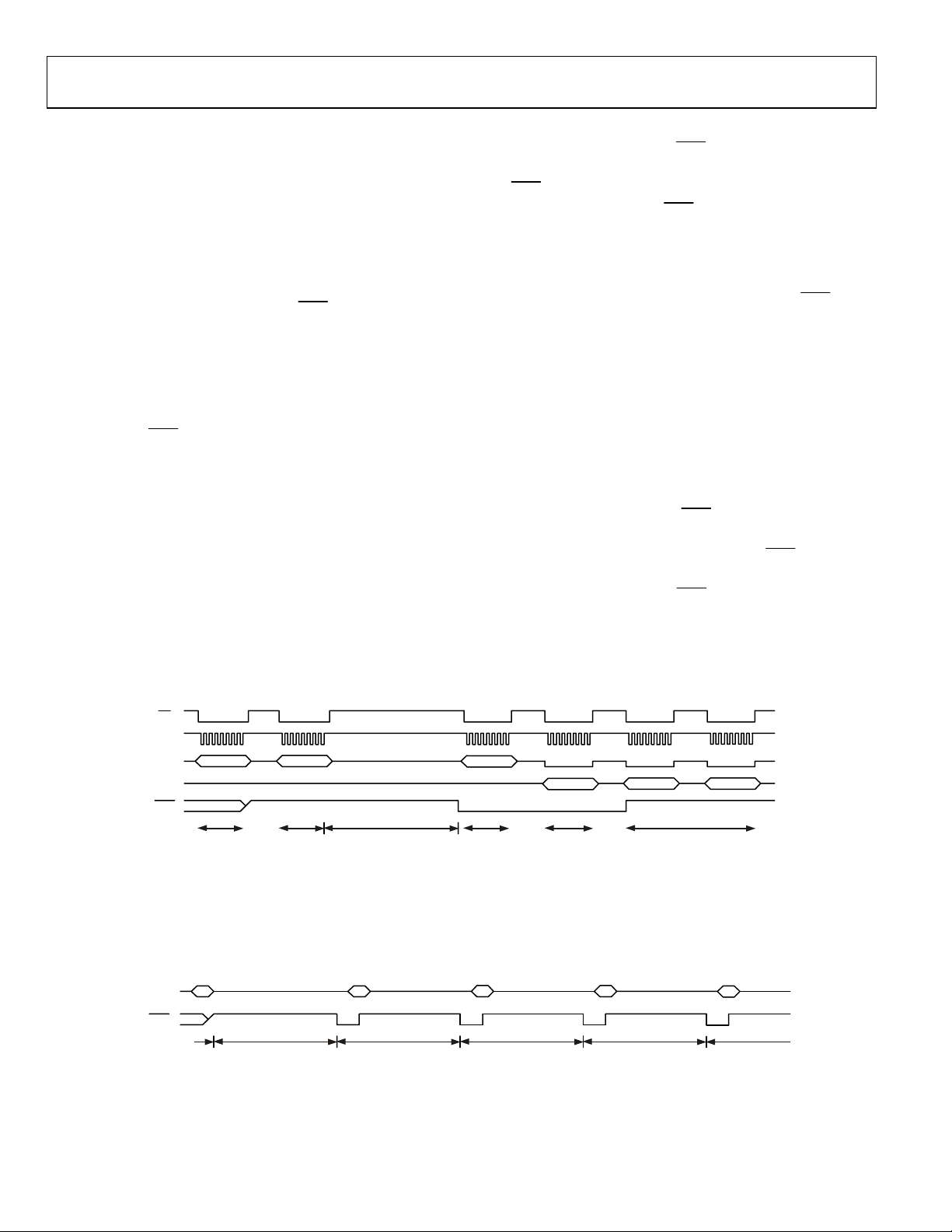
When the mode register is being written, the ADC status byte is
cleared and the
state. When the single conversion command is written to the
mode register, the ADC starts the conversion on the channel
selected by the address of the mode register. After the
conversion is completed, the data register is updated, the mode
register is changed to idle mode, the relevant RDY bit is set,
and the
RDY
pin returns high when the relevant channel data register is
being read.
Figure 17 shows the digital interface signals executing a single
conversion on Channel 0, waiting for the
and reading the Channel 0 data register.
pin goes high, regardless of its previous
RDY
pin goes low. The RDY bit is reset and the
pin to go low,
RDY
RDY
CS
SCLK
DIN
DOUT
RDY
COMMUNICATIONS
38h
WRITE
REGISTER
Figure 17. Serial Interface Signals—Single Conversion Command and 16-Bits Data Reading
40h 48h (00h) (00h)
DATA DATA
WRITE
MODE
REGISTER
CONVERSION TIME READ DATA REGISTER
WRITE
COMMUNICATIONS
REGISTER
Rev. 0 | Page 23 of 32
AD7732
Dump Mode
When the DUMP bit in the mode register is set to 1, the channel
status register will be read immediately by a read of the channel
data register, regardless of whether the status or the data register
has been addressed through the communications register. The
DIN pin should not be high while reading 24-bit data in dump
mode; otherwise, the AD7732 will be reset.
Figure 18 shows the digital interface signals executing a single
conversion on Channel 0, waiting for the
and reading the Channel 0 status register and data register in
the dump mode.
pin to go low,
RDY
The RDY bit is reset when the relevant channel data register is
being read. The behavior of the
pin depends on the
RDY
RDYFN bit in the I/O port register. When the RDYFN bit is 0,
the
the RDYFN bit is set to 1, the
pin goes low when any channel has unread data. When
RDY
pin will only go low if all
RDY
enabled channels have unread data.
If an ADC conversion result has not been read before a new
ADC conversion is completed, the new result will overwrite the
previous one. The relevant RDY bit goes low and the
RDY
pin
goes high for at least 163 MCLK cycles (~26.5 µs), indicating
when the data register is updated and the previous conversion
data is lost.
Continuous Conversion Mode
When the mode register is being written, the ADC status byte is
cleared and the
state. When the continuous conversion command is written to
the mode register, the ADC starts conversion on the channel
selected by the address of the mode register.
After the conversion is complete, the relevant channel data
register and channel status register are updated, the relevant
RDY bit in the ADC status register is set, and the AD7732
continues converting on the next enabled channel. The part will
cycle through all enabled channels until put into another mode
or reset. The cycle period will be the sum of all enabled
channels’ conversion times, set by the corresponding channel
conversion time registers.
pin goes high, regardless of its previous
RDY
CS
SCLK
DIN
DOUT
RDY
38h 48h 48h
If the data register is being read as an ADC conversion
completes, the data register will not be updated with the new
result (to avoid data corruption) and the new conversion
data is lost.
Figure 19 shows the digital interface signal’s sequence for the
continuous conversion mode with Channels 0 and 1 enabled
and the RDYFN bit set to 0. The
pin goes low and the data
RDY
register is read after each conversion. Figure 20 shows a similar
sequence but with the RDYFN bit set to 1. The
RDY
pin goes
low and all data registers are read after all conversions are
completed. Figure 21 shows the
pin when no data are read
RDY
from the AD7732.
(00h) (00h) (00h)
STATUS DATA DATA
WRITE
COMMUNICATIONS
REGISTER
Figure 18. Serial Interface Signals—Single Conversion Command, 16-Bits Data Reading, Dump Mode
WRITE
MODE
REGISTER
CONVERSION TIME READ DATA
WRITE
COMMUNICATIONS
REGISTER
READ
CHANNEL
STATUS
REGISTER
CONTINUOUS
CONVERSION
SERIAL
INTERFACE
RDY
START
READ
DATA
CH0
CH1 CONVERSIONCH0 CONVERSION
Figure 19. Continuous Conversion, CH0 and CH1, RDYFN = 0
Rev. 0 | Page 24 of 32
READ
DATA
CH1
CH0 CONVERSION
READ
DATA
CH0
CH1 CONVERSION
READ
DATA
CH1
CH0 CONVERSION

AD7732
CONTINUOUS
CONVERSION
SERIAL
INTERFACE
RDY
START
CH1 CONVERSIONCH0 CONVERSION
READ
READ
DATA
DATA
CH1
CH0
CH0 CONVERSION
CH1 CONVERSION
READ
READ
DATA
DATA
CH1
CH0
CH0 CONVERSION
Figure 20. Continuous Conversion, CH0 and CH1, RDYFN = 1
START
CONTINUOUS
CONVERSION
SERIAL
INTERFACE
RDY
CH0 CONVERSIONCH1 CONVERSIONCH0 CONVERSION CH1 CONVERSION CH0 CONVERSION
Figure 21. Continuous Conversion, CH0 and CH1, No Data Read
CS
SCLK
DIN 48h 00h
DOUT
RDY
38h 00h
48h
00h
STATUS
00h
DATA
DATA
00h
STATUS
00h
DATA
DATA
WRITE
COMM.
REGISTER
WRITE
MODE
REGISTER
WRITE
COMM.
REGISTER
CONVERSION
ON CH0
COMPLETE
READ
CH0
STATUS
Figure 22. Continuous Conversion, CH0 and CH1, Continuous Read
Continuous Read (Continuous Conversion) Mode
When the Cont RD bit in the mode register is set, the first write
of 48h to the communications register starts the continuous
read mode. As shown in Figure 22, subsequent accesses to the
part sequentially read the channel status and data registers of
the last completed conversion without any further configuration
of the communications register being required.
Note that the continuous conversion bit in the mode register
should be set when entering the continuous read mode.
Note that the continuous read mode is a dump mode reading of
the channel status and data registers regardless of the dump bit
value. Use the channel bits in the channel status register to
check/recognize that channel data is actually being shifted out.
Note that the last completed conversion result is being read.
Therefore the RDYFN bit in the I/O port register should be 0
READ
CH0
DATA
CONVERSION
ON CH1
COMPLETE
READ
CH1
STATUS
READ
CH1
DATA
and reading the result should always start before the next
conversion is completed.
The AD7732 will stay in continuous read mode as long as the
DIN pin is low while the
pin is low; therefore, write 0 to the
CS
AD7732 while reading in continuous read mode. To exit
continuous read mode, take the DIN pin high for at least 100 ns
after a read is complete. (Write 80h to the AD7732 to exit
continuous reading.)
Taking the DIN pin high does not change the Cont RD bit in
the mode register. Therefore, the next write of 48h starts the
continuous read mode again. To completely stop the continuous
read mode, write to the mode register to clear the Cont RD bit.
Rev. 0 | Page 25 of 32
AD7732
CIRCUIT DESCRIPTION
The AD7732 is a sigma-delta ADC that is intended for the
measurement of wide dynamic range, low frequency signals in
industrial process control, instrumentation, and PLC systems.
It contains thin film resistor dividers, a multiplexer, an input
buffer, a sigma-delta (or charge balancing) ADC, a digital filter,
a clock oscillator, a digital I/O port, and a serial
communications interface.
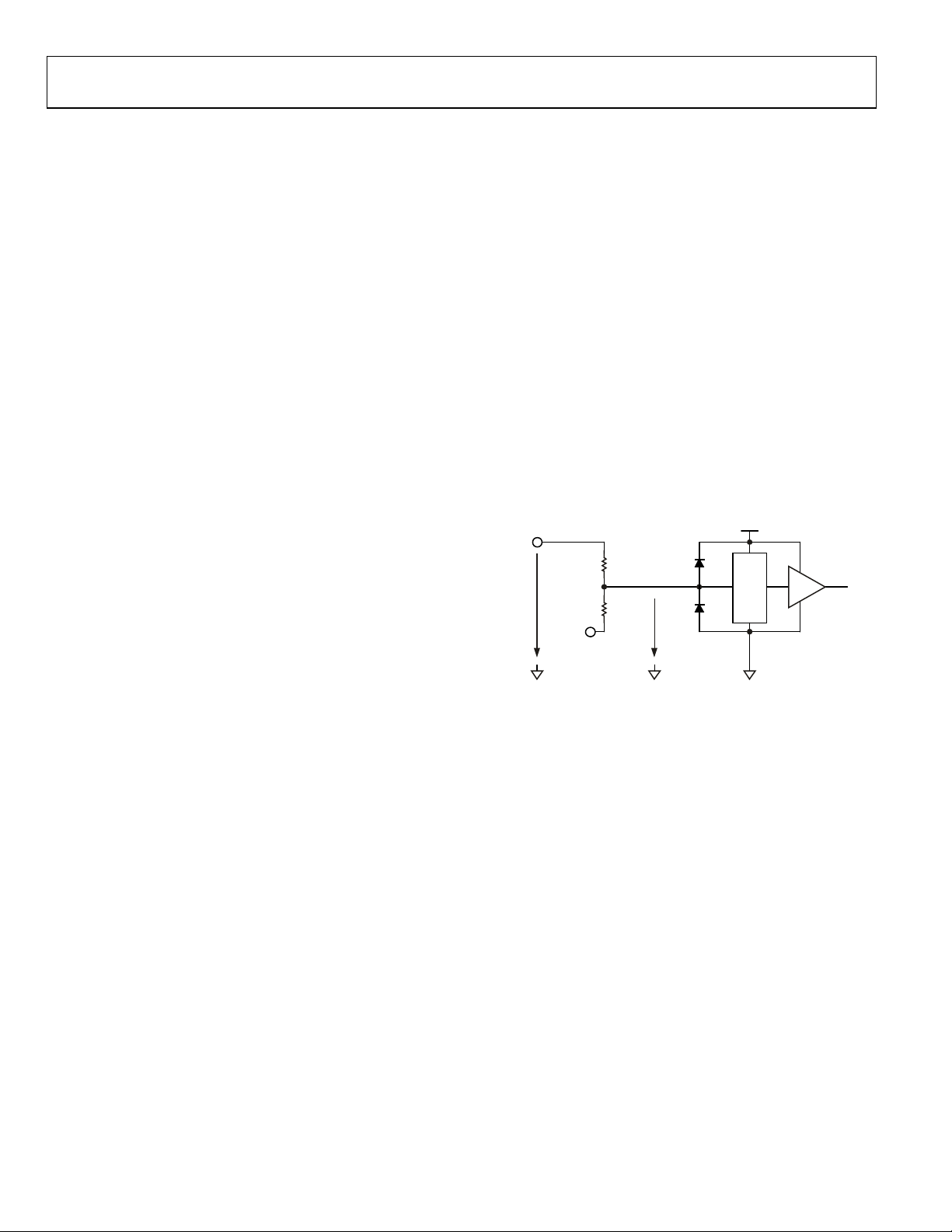
Analog Front End
The AD7732 features two fully differential analog inputs. The
on-chip thin film resistor dividers allow ±10 V, ±5 V, 0 V to +10
V, and 0 V to +5 V input signals to be connected directly to the
analog input pins.
The resistor divider input stage is followed by the multiplexer
and then by a wide bandwidth, fast settling time differential
input buffer capable of driving the dynamic load of a high speed
sigma-delta modulator.
In normal circuit configuration, the BIAS pins are connected to
the 2.5 V (reference) voltage source. This ensures that the
differential signal seen by the internal input buffer is within its
absolute/common-mode range of AGND + 200 mV to
– 300 mV.
AV
DD
The AD7732 AIN differential voltage should be within the
specified nominal (up to ±10 V) input range, otherwise the
performance on channel might degrade (see the Analog Input’s
Extended Voltage Range
The AD7732 INL performance varies with the AIN commonmode voltage (Figure 9). The differential analog input voltage of
±10 V with a common-mode voltage of 0 V means that the AIN
differential voltage is centered around AGND and both AIN(+)
and AIN(–) change within ±5 V respect to AGND. The AD7732
INL also varies with the MCLK frequency (Figure 7).
section).
If the BIAS pins are in normal configuration, the AIN pin
absolute voltage up to ±16.5 V does not degrade the adjacent
channel’s performance. An AIN absolute voltage over ±16.5 V
results in current flowing through the internal protection
diodes located behind the thin film resistors; the adjacent
channel can be affected. By configuring the BIAS and RA to RD
pins differently, the part will work with higher AIN absolute
voltages as long as the internal voltage seen by the multiplexer
and input buffer is within 200 mV to AV
– 300 mV. Absolute
DD
voltage for the AIN, BIAS, and RA to RD pins must never
exceed the values specified in the Absolute Maximum Ratings.
Note that the OVR bit in the channel status register is generated
digitally from the conversion result and indicates the sigmadelta modulator (nominal) overrange. The OVR bit DOES NOT
indicate exceeding the AIN pin absolute/common-mode
voltage limits.
Figure 23 shows the AD7732 analog input internal structure.
PROTECTION
AIN
±10V
BIAS
2.5V
Figure 23. Simplified Analog Input Internal Structure
7R
108.5kΩ
1R
15.5kΩ
DIODES
2.1875V ± 1.25V
AV
DD
MUX
AGND
BUFFER
Rev. 0 | Page 26 of 32

AD7732
Analog Input’s Extended Voltage Range
The AD7732 output data code span corresponds to the nominal
input voltage range. The ADC is functional outside the nominal
input voltage range, but the performance might degrade. The
sigma-delta modulator was designed to fully cover a ±11.6 V
differential input voltage; outside this range, the performance
might degrade more rapidly. The adjacent channels are not
affected by up to ±16.5 V absolute analog input voltage
(Figure 8).
When the CLAMP bit in the mode register is set to 1, the
channel data register will be digitally clamped to either all 0s or
all 1s when the analog input voltage goes outside the nominal
input voltage range.
Table 17. Extended Input Voltage Range, Nominal
Voltage Range 0 V to +10 V, 16 Bits, CLAMP = 0
Input (V) Data (hex) SIGN OVR
11.60006 28F5 0 1
10.00031 0001 0 1
10.00015 0000 0 1
10.00000 FFFF 0 0
0.00015 0001 0 0
0.00000 0000 0 0
–0.00015 0000 1 1
Chopping
As shown in Table 16 and Table 17, when CLAMP = 0, the data
reflects the analog input voltage outside the nominal voltage
range. In this case, the SIGN and OVR bits in the channel status
register should be considered along with the data register value
to decode the actual conversion result.
Note that the OVR bit in the channel status register is generated
digitally from the conversion result and indicates the sigmadelta modulator (nominal) overrange. The OVR bit DOES NOT
indicate exceeding the AIN pin’s absolute voltage limits.
Table 16. Extended Input Voltage Range,
Nominal Voltage Range ±10 V, 16 Bits, CLAMP = 0
Input (V) Data (hex) SIGN OVR
11.60039 147B 0 1
10.00061 0001 0 1
10.00031 0000 0 1
10.00000 FFFF 0 0
0.00031 8001 0 0
0.00000 8000 0 0
–0.00031 7FFF 1 0
–10.00000 0000 1 0
–10.00031 FFFF 1 1
–10.00061 FFFE 1 1
–11.60040 EB85 1 1
With chopping enabled, the multiplexer repeatedly reverses the
ADC inputs. Every output data result is then calculated as an
average of two conversions, the first with the positive and the
second with the negative offset term included. This effectively
removes any offset error of the input buffer and sigma-delta
modulator.
However, chopping is applied only behind the input resistor
divider stage; therefore, chopping does not eliminate the offset
error and drifts caused by the resistors. Figure 24 shows the
channel signal chain with chopping enabled.
AIN(+)
BIAS(+)
AIN(–)
BIAS(–)
BUFFERMULTIPLEXER
Σ−∆
MODULATOR
f
/2
MCLK
Figure 24. Channel Signal Chain Diagram with Chopping Enabled
f
MCLK
/2
DIGITAL
FILTER
Rev. 0 | Page 27 of 32
+
-
CHOPCHOP
SCALI NG
ARITHMETIC
(CALIBRATIONS)
DIGITAL
INTERFACE
OUTPUT DATA
AT THE SELECTED
DATA RATE

AD7732
Multiplexer, Conversion, and Data Output Timing
The specified conversion time includes one or two settling and
sampling periods and a scaling time.
With chopping enabled (Figure 25), a conversion cycle starts
with a settling time of 43 MCLK cycles or 44 MCLK cycles (~7
µs with a 6.144 MHz MCLK) to allow the circuits following the
multiplexer to settle. The sigma-delta modulator then samples
the analog signals and the digital filter processes the digital data
stream. The sampling time depends on FW, i.e., on the channel
conversion time register contents. After another settling of 42
MCLK cycles (~6.8 µs), the sampling time is repeated with a
reversed (chopped) analog input signal. Then, during the
scaling time of 163 MCLK cycles (~26.5 µs), the two results
from the digital filter are averaged, scaled using the calibration
registers, and written into the channel data register.
With chopping disabled (Figure 26), there is only one sampling
time preceded by a settling time of 43 MCLK cycles or
44 MCLK cycles and followed by a scaling time of
163 MCLK cycles.
The
pin goes high during the scaling time, regardless of its
RDY
previous state. The relevant RDY bit is set in the ADC status
register and in the channel status register, and the
RDY
pin goes
low when the channel data register is updated and the channel
conversion cycle is finished. If in continuous conversion mode,
the part will automatically continue with a conversion cycle on
the next enabled channel.
Note that every channel can be configured independently for
conversion time and chopping mode. The overall cycle and
effective per channel data rates depend on all enabled
channel settings.
Sigma-Delta ADC
The AD7732 core consists of a charge balancing sigma-delta
modulator and a digital filter. The architecture is optimized for
fast, fully settled conversion. This allows for fast channel-tochannel switching while maintaining inherently excellent
linearity, high resolution, and low noise.
MULTIPLEXER
– CHANNEL 0
RDY
SETTLING
Figure 25. Multiplexer and Conversion Timing—Continuous Conversion on Several Channels with Chopping Enabled
Figure 26. Multiplexer and Conversion Timing— Continuous Conversion on Several Channels with Chopping Disabled
+ CHANNEL 1
TIME
MULTIPLEXER
CHANNEL 0
RDY
SAMPLING
TIME
SETTLING
TIME
SETTLING
TIME
CONVERSION TIME
CHANNEL 1
SAMPLING
TIME
CONVERSION TIME
– CHANNEL 1
SAMPLING
TIME
SCALING
TIME
SCALING
TIME
Rev. 0 | Page 28 of 32
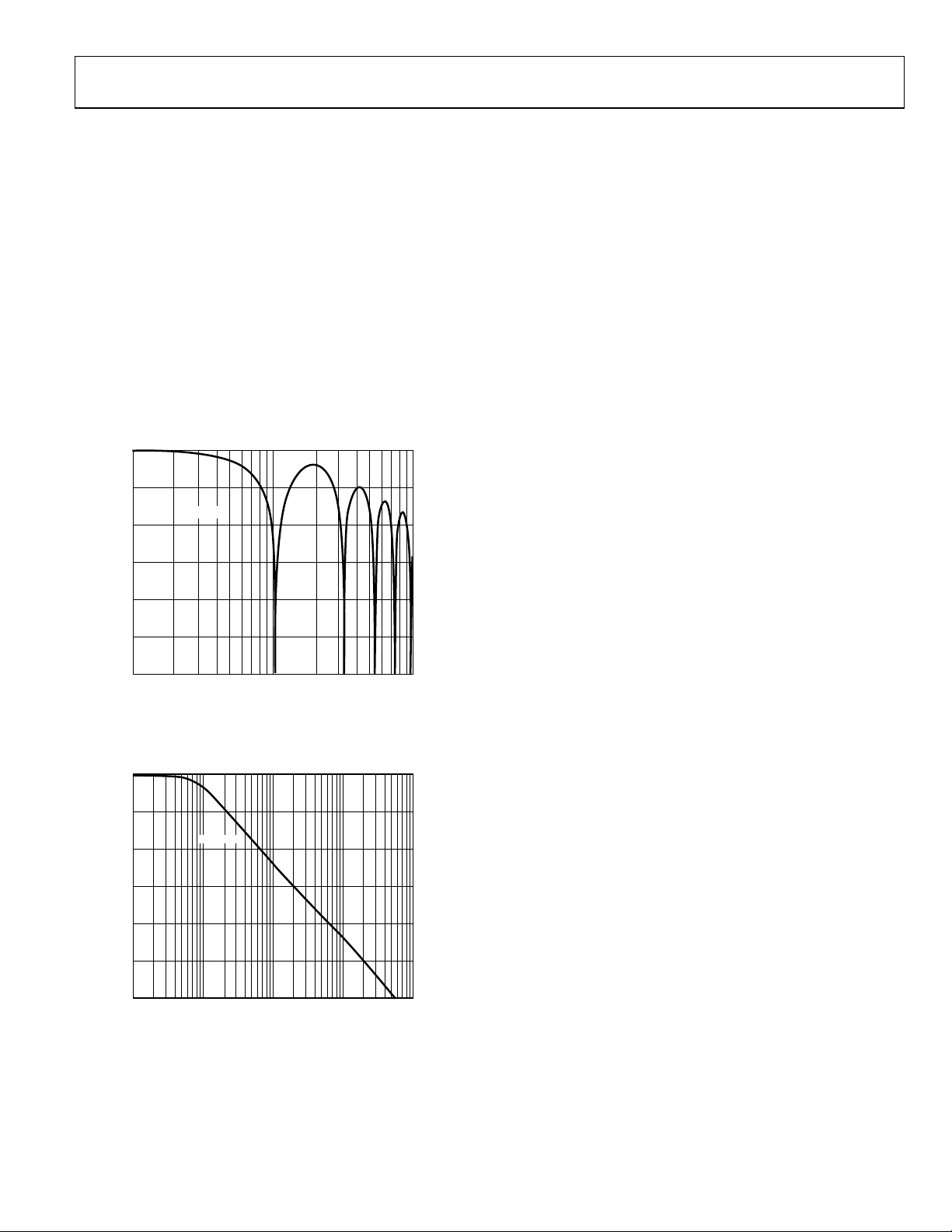
AD7732
Frequency Response
Voltage Reference Inputs
The sigma-delta modulator runs at ½ the MCLK frequency,
which is effectively the sampling frequency. Therefore, the
Nyquist frequency is ¼ the MCLK frequency. The digital filter,
in association with the modulator, features the frequency
response of a first order low-pass filter. The –3 dB point is close
to the frequency of 1/channel conversion time. The roll-off is –
20 dB/dec up to the Nyquist frequency. If chopping is enabled,
the input signal is resampled by chopping. Therefore, the overall
frequency response features notches close to the frequency of
1/channel conversion time. The top envelope is again the ADC
response of –20 dB/dec.
The typical frequency response plots are given in Figure 27
and Figure 28. The plots are normalized to 1/channel
conversion time.
0
–10
CHOP = 1
–20
–30
GAIN – dB
–40
–50
The AD7732 has a differential reference input, REF IN(+) and
REF IN(–). The common-mode range for these inputs is from
AGND to AV
. The nominal differential reference voltage for
DD
specified operation is 2.5 V. Both reference inputs feature
dynamic load. Therefore, the reference inputs should be
connected to a low impedance reference voltage source.
External resistance/capacitance combinations may result in gain
errors on the part.
The output noise performance outlined in Table 4 through
Table 9 is for an analog input of 0 V and is unaffected by noise
on the reference. To obtain the same noise performance as
shown in the noise tables over the full input range requires a
low noise reference source for the AD7732. If the reference
noise in the bandwidth of interest is excessive, it will degrade
the performance of the AD7732.
Recommended reference voltage sources for the AD7732
include the AD780, ADR421, REF43, and REF192. Note that in a
typical connection, the voltage reference must be capable of
sinking current flowing out of the BIAS pins through the
internal resistors if a positive voltage is applied to the analog
input. The AD780 meets this requirement. If the voltage
reference used in an application is not capable of sinking
current, an external resistor (5 kΩ) should be connected in
parallel to the REFIN pins.
–60
0.1 1.0 10.0
NORMALIZED INPUT FREQUENCY
(INPUT FREQUENCY× CONVERSION TIME)
Figure 27. Typical ADC Frequency Response, Chopping Enabled
0
–10
–20
–30
GAIN – dB
–40
–50
–60
Figure 28. Typical ADC Frequency Response, Chopping Disabled
CHOP = 0
1.00.1 10.0 100.0 1000.0
NORMALIZED INPUT FREQUENCY
(INPUT FREQUENCY × CONVERSION TIME)
Reference Detect
The AD7732 includes on-chip circuitry to detect if the part has
a valid reference for conversions. If the voltage between the
REFIN(+) and REFIN(–) pins goes below the NOREF trigger
voltage (0.5 V typ) and the AD7732 is performing a conversion,
the NOREF bit in the channel status register is set.
Rev. 0 | Page 29 of 32

AD7732
I/O Port
The AD7732 P0 pin can be used as a general-purpose digital
I/O pin. The P1 pin (
purpose digital I/O pin or to synchronize the AD7732 with
other devices in the system. When the SYNC bit in the I/O port
register is set and the
process any conversion. If it is put into single conversion mode,
continuous conversion mode, or any calibration mode, the
AD7732 waits until the
operation. This allows conversion to start from a known point
in time, i.e., the rising edge of the
/P1) can be used as a general-
SYNC
pin is low, the AD7732 does not
SYNC
pin goes high and then starts
SYNC
pin.
SYNC
duration is the same as the conversion time configured on the
selected channel. A longer conversion time gives less noise and
yields a more exact calibration; therefore, use at least the default
conversion time to initiate any calibration.
ADC Zero-Scale Self-Calibration
The ADC zero-scale self-calibration can reduce the offset error
in the chopping disabled mode. If repeated after a temperature
change, it can also reduce the offset drift error in the chopping
disabled mode.
The digital P0 and P1 voltage is referenced to the analog
supplies. When configured as inputs, the pins should be tied
high or low.
Calibration
The AD7732 provides zero-scale self-calibration and zero- and
full-scale system calibration capability that can effectively
reduce the offset error and gain error to the order of the noise.
After each conversion, the ADC conversion result is scaled
using the ADC calibration registers and the relevant channel
calibration registers before being written to the data register.
For unipolar ranges:
Data = ((ADC result – ADC ZS Cal. reg.)
× ADC FS Reg./200000h – Ch. ZS Cal. reg.)
× Ch. FS Cal. reg./200000h
For bipolar ranges:
Data = ((ADC result – ADC ZS Cal. reg.)
× ADC FS Reg./400000h + 800000h – Ch. ZS Cal. reg.)
× Ch. FS Cal. reg./200000h
Where the ADC result is in the range of 0 to FFFFFFh.
Note that the channel zero-scale calibration register has the
format of a sign bit and a 22-bit channel offset value. It is
strongly recommended that the user not change the ADC fullscale register.
To start any calibration, write the relevant mode bits to the
AD7732 mode register. After the calibration is complete, the
contents of the corresponding calibration registers are updated,
all RDY bits in the ADC status register are set, the
low, and the AD7732 reverts to idle mode. The calibration
RDY
pin goes
The zero-scale self-calibration is performed on internally
shorted ADC inputs. The negative analog input terminal on the
selected channel is used to set the ADC zero-scale calibration
common mode. Therefore, either the negative terminal of the
selected differential pair or the AINCOM on the single-ended
channel configuration should be driven to a proper commonmode voltage.
It is strongly recommended that the ADC zero-scale calibration
register should only be updated as part of a zero-scale selfcalibration.
Per Channel System Calibration
If the per channel system calibrations are used, these should be
initiated in the following order: a channel zero-scale system
calibration, followed by a channel full-scale system calibration.
The system calibration is affected by the ADC zero-scale and
full-scale calibration registers. Therefore, if both self-calibration
and system calibration are used in the system, an ADC full-scale
self-calibration should be performed first, followed by a system
calibration cycle.
While executing a system calibration, the fully settled system
zero-scale voltage signal or system full-scale voltage signal must
be connected to the selected channel analog inputs.
The per channel calibration registers can be read, stored, or
modified and written back to the AD7732. Note that when
writing the calibration registers the AD7732 must be in idle
mode. Note that outside the specified calibration range,
calibration is possible but the performance may degrade (see
the System Calibration section in Table 1).
Rev. 0 | Page 30 of 32
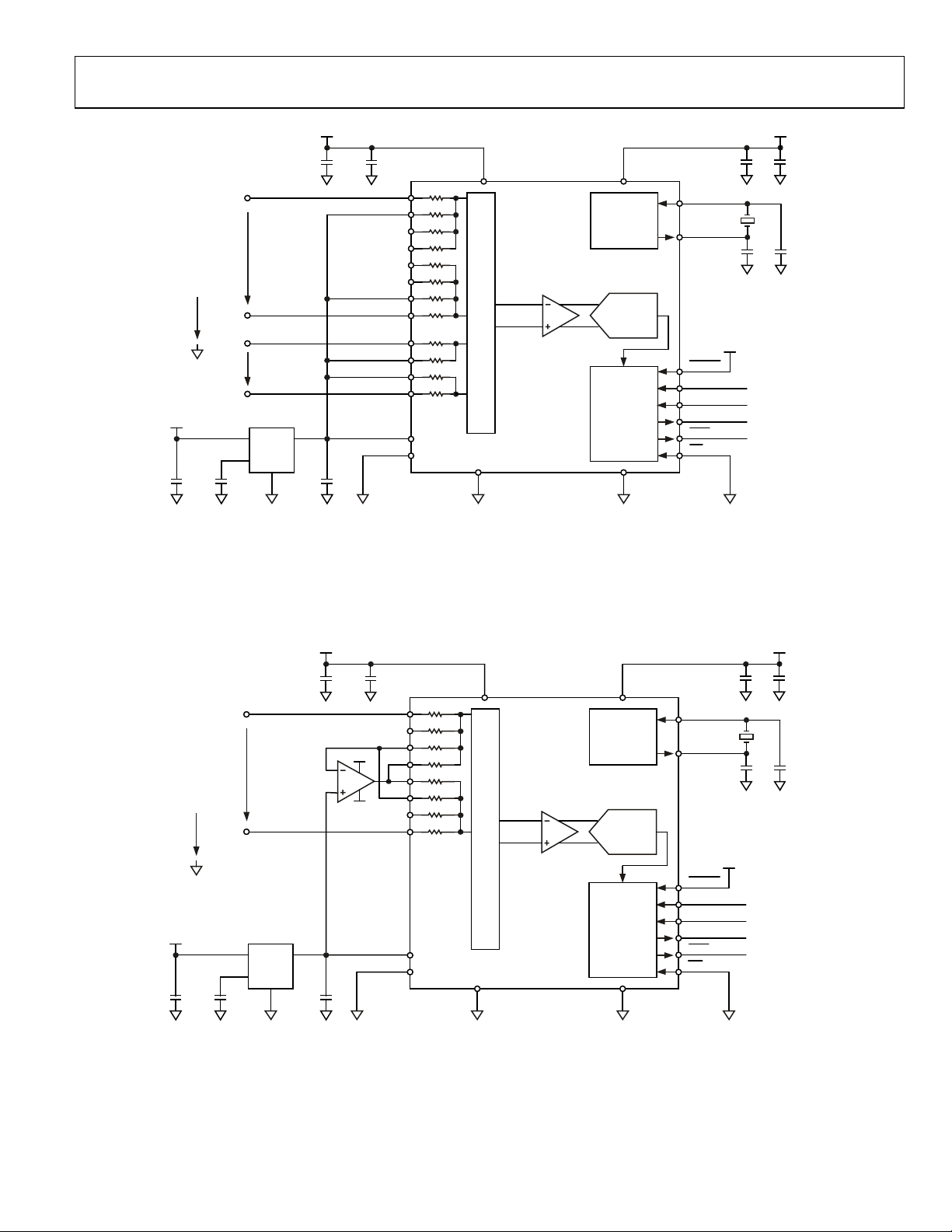
AD7732
E
6.144MHz
DD
HOST
SYSTEM
DV
DD
+
10
µF0.1µF
±11.5V COMMONMODE VOLTAGE
(MAX ±16.5V
ABSOLUTE
VOLTAGE
TO AGND)
AV
DD
TEMP
+
10µF
0.01µF
ANALOG
INPUTS
±10V
DIFFERENTIAL
VOLTAGE
±10V
DIFFERENTIAL
VOLTAGE
AD780
VOUT+VIN
AV
DD
+
+2.5V
+
10
µF 0.1µF
BIAS0(+)
BIAS0(–)
BIAS1(+)
BIAS1(–)
REFIN(+)
REFIN(–)
µF
10
AIN0(+)
RA
RB
RC
RD
AIN0(–)
AIN1(+)
AIN1(–)
7R=108.5k
R=15.5k
R
7R
7R
R
R
7R
AV
DD
Ω
Ω
MUX
BUFFER
AD7732
AGND
DV
DD
CLOCK
GENERATOR
24-BIT
Σ-∆ ADC
SERIAL
INTERFACE
AND
CONTROL
LOGIC
DGND
MCLKIN
MCLKOUT
33pF 33pF
DV
RESET
SCLK
DIN
DOUT
RDY
CS
Figure 29. Typical Connections for the AD7732 Application
High Common-Mode Voltage Application
Using additional thin film resistors on AIN0 and an external operational amplifier with a ±15 V power supply, the AD7732 AIN0 can
easily be configured to accept high common-mode voltages.
6.144MHz
DD
HOST
SYSTEM
DV
DD
+
10µF0.1µF
±37V COMMONMODE VOLTAGE
(±42V ABSOLUTE
MAX VOLTAG
TO AGND)
AV
DD
TEMP
+
10µF
ANALOG
INPUTS
±10V
DIFFERENTIAL
VOLTAGE
0.01µF
AD780
AV
VOUT+VIN
DD
+
10µF 0.1µF
AIN0(+)
BIAS0(+)
+15V
–15V
BIAS0(–)
AIN0(–)
RA
RB
RC
RD
7R=108.5kΩ
R=15.5kΩ
2R
2R
2R
2R
7R
MUX
AV
DD
AD7732
REFIN(+)
+2.5V
REFIN(–)
+
10µF
Figure 30. High Common-Mode Voltage Application
AGND
BUFFER
DV
DD
CLOCK
GENERATOR
24-BIT
Σ-∆ ADC
SERIAL
INTERFACE
AND
CONTROL
LOGIC
DGND
MCLKIN
MCLKOUT
33pF 33pF
DV
RESET
SCLK
DIN
DOUT
RDY
CS
Rev. 0 | Page 31 of 32

AD7732
OUTLINE DIMENSIONS
9.80
9.70
9.60
28
PIN 1
0.15
0.05
COPLANARITY
0.10
0.65
BSC
0.30
0.19
COMPLIANT TO JEDEC STANDARDS MO-153AE
SEATING
PLANE
15
4.50
4.40
4.30
0.20
0.09
6.40 BSC
8°
0°
0.75
0.60
0.45
141
1.20
MAX
Figure 31. 28-Lead This Shrink Small Outline Package [TSSOP] (RU-28)—Dimensions shown in millimeters
ESD CAUTION
ESD (electrostatic discharge) sensitive device. Electrostatic charges as high as 4000 V readily accumulate on the
human body and test equipment and can discharge without detection. Although this product features
proprietary ESD protection circuitry, permanent damage may occur on devices subjected to high energy
electrostatic discharges. Therefore, proper ESD precautions are recommended to avoid performance
degradation or loss of functionality.
Table 18. Ordering Guide
AD7732 Products Temperature Package Package Description Package Outline
AD7732BRU –40°C to +105°C TSSOP-28 RU-28
© 2003 Analog Devices, Inc. All rights reserved. Trademarks and
registered trademarks are the property of their respective companies.
Printed in the U.S.A.
C03070-0-2/03(0)
Rev. 0 | Page 32 of 32
 Loading...
Loading...