Page 1

AMD M690T/E
Databook
Technical Reference Manual
Rev. 3.10
P/N: 42437_m690t_ds
© 2011 Advanced Micro Devices, Inc
Page 2

Please note that in this databook, references to "DVI" and "HDMI" refer to the capability of the TMDS interface, multiplexed on the PCI Express® external graphics interface,
to enable DVI or HDMI™ through passive enabling circuitries. Any statement in this databook on any DVI or HDMI-related functionality must be understood in that context.
This product incorporates copyright protection technology that is protected by U.S. patents and other intellectual property rights. The use of Rovi Corporation's copy protection
technology in the device must be authorized by Rovi Corporation and is intended for home and other limited pay-per-view uses only, unless otherwise authorized in writing by
Rovi Corporation. Reverse engineering or disassembly is prohibited.
This device may only be sold or distributed to: (i) a Rovi Authorized Buyer, (ii) a customer (PMA Customer) who has executed a Proprietary Materials Agreement (PMA) with
Rovi Corporation that is still in effect, (iii) a contract manufacturer approved by Rovi Coporation to purchase this device on behalf of a Rovi Authorized Buyer or a PMA
Customer, or (iv) a distributor who has executed a Rovi-specified distribution agreement with AMD.
Trademarks
AMD, the AMD Arrow logo, AMD Athlon, AMD Sempron, AMD Turion, Cool'n'Quiet, AMD PowerNow!, AMD Radeon, AMD Avivo, AMD HyperMemory, PowerPlay,
PowerShift, AMD PowerXpress, and combinations thereof, are trademarks of Advanced Micro Devices, Inc.
HDMI is a trademark of HDMI Licensing, LLC.
HyperTransport is a licensed trademark of the HyperTransport Technology Consortium.
Microsoft, Windows, Windows Vista, and DirectX are registered trademarks of Microsoft Corporation.
PCI Express and PCIe are registered trademarks of PCI-SIG.
WinBench is a registered trademark of Ziff Davis, Inc.
Other product names used in this publication are for identification purposes only and may be trademarks of their respective companies.
Disclaimer
The contents of this document are provided in connection with Advanced Micro Devices, Inc. ("AMD") products. AMD makes no representations or warranties with respect
to the accuracy or completeness of the contents of this publication and reserves the right to make changes to specifications and product descriptions at any time without notice.
AMD assumes no liability whatsoever, and disclaims any express or implied warranty, relating to this document including, but not limited to, the implied warranty of
merchantability, fitness for a particular purpose, or infringement of any intellectual property right. AMD shall not be liable for any damage, loss, expense, or claim of loss of
any kind or character (including without limitation direct, indirect, consequential, exemplary, punitive, special, incidental or reliance damages) arising from use of or reliance
on this document. No license, whether express, implied, arising by estoppel, or otherwise, to any intellectual property rights are granted by this publication. Except for AMD
product purchased pursuant to AMD's Standard Terms and Conditions of Sale, and then only as expressly set forth therein, AMD's products are not designed, intended,
authorized or warranted for use as components in systems intended for surgical implant into the body, or in other applications intended to support or sustain life, or in any other
application in which the failure of AMD's product could create a situation where personal injury, death, or severe property or environmental damage may occur. AMD reserves
the right to discontinue or make changes to its products at any time without notice.
© 2011 Advanced Micro Devices, Inc. All rights reserved.
Page 3

Table of Contents
Chapter 1: Overview
1.1 Introducing the M690T .......................................................................................................................................................1-1
1.2 M690E.................................................................................................................................................................................1-2
1.3 M690T Features ..................................................................................................................................................................1-2
1.3.1 CPU HyperTransport™ Interface.........................................................................................................................1-2
1.3.2 Memory Interface .................................................................................................................................................1-2
1.3.3 AMD HyperMemory™ Technology ....................................................................................................................1-2
1.3.4 PCI Express® Interface .......................................................................................................................................1-2
1.3.5 A-Link Express II Interface..................................................................................................................................1-3
1.3.6 2D Acceleration Features .....................................................................................................................................1-3
1.3.7 3D Acceleration Features .....................................................................................................................................1-3
1.3.8 Motion Video Acceleration Features....................................................................................................................1-4
1.3.9 Multiple Display Features ....................................................................................................................................1-4
1.3.10 Integrated LVDS ..................................................................................................................................................1-5
1.3.11 DVI/HDMI™ .......................................................................................................................................................1-6
1.3.12 External Display Support via DVO......................................................................................................................1-6
1.3.13 Power Management Features ...............................................................................................................................1-6
1.3.14 PC Design Guide Compliance..............................................................................................................................1-6
1.3.15 Test Capability Features .......................................................................................................................................1-7
1.3.16 Additional Features ..............................................................................................................................................1-7
1.3.17 Packaging .............................................................................................................................................................1-7
1.4 Software Features................................................................................................................................................................1-7
1.5 Device IDs...........................................................................................................................................................................1-8
1.6 Branding Diagrams .............................................................................................................................................................1-8
1.6.1 Branding Diagram for ASIC Revision A11 .........................................................................................................1-8
1.6.2 Branding Diagram for ASIC Revision A12 and After .........................................................................................1-8
1.7 Part Number Legend .........................................................................................................................................................1-10
1.8 Production Schedule, OPN, and Part Marking .................................................................................................................1-10
1.9 Conventions and Notations ...............................................................................................................................................1-10
1.9.1 Pin Names...........................................................................................................................................................1-10
1.9.2 Pin Types ............................................................................................................................................................1-10
1.9.3 Numeric Representation .....................................................................................................................................1-11
1.9.4 Register Field......................................................................................................................................................1-11
1.9.5 Hyperlinks ..........................................................................................................................................................1-11
1.9.6 Acronyms and Abbreviations .............................................................................................................................1-11
Chapter 2: Functional Descriptions
2.1 Host Interface......................................................................................................................................................................2-2
2.2 Side-port Memory Interface................................................................................................................................................2-3
2.2.1 DDR2 Memory Interface......................................................................................................................................2-3
2.3 LVDS Interface ...................................................................................................................................................................2-6
2.3.1 LVDS Data Mapping............................................................................................................................................2-6
© 2011 Advanced Micro Devices, Inc. 42437 AMD M690T/E Databook 3.10
Proprietary Table of Contents-1
Page 4

2.3.2 LVDS Spread Spectrum ...................................................................................................................................... 2-8
2.4 DVI/HDMI™ ..................................................................................................................................................................... 2-9
2.4.1 DVI/HDMI™ Data Transmission Order and Signal Mapping............................................................................ 2-9
2.4.2 Support for HDMI™ Packet Types ................................................................................................................... 2-12
2.5 VGA DAC Characteristics ............................................................................................................................................... 2-13
2.6 External Clock Chip ......................................................................................................................................................... 2-13
Chapter 3: Pin Descriptions and Strap Options
3.1 Pin Assignment .................................................................................................................................................................. 3-2
3.1.1 M690T Pin Assignment....................................................................................................................................... 3-2
3.2 Interface Block Diagram .................................................................................................................................................... 3-4
3.3 CPU HyperTransport™ Interface .................................................................................................................................... 3-5
3.4 DDR2 Side-port Memory Interface.................................................................................................................................... 3-5
3.5 PCI Express® Interfaces .................................................................................................................................................... 3-6
3.5.1 1 x 8 Lane Interface for External Graphics ......................................................................................................... 3-6
3.5.2 A-Link Express II to Southbridge........................................................................................................................ 3-6
3.5.3 4 x 1 Lane Interface for General Purpose External Devices .............................................................................. 3-6
3.5.4 Miscellaneous PCI Express® Signals ................................................................................................................. 3-7
3.6 Clock Interface ................................................................................................................................................................... 3-7
3.7 CRT and TV Interface........................................................................................................................................................ 3-7
3.8 LVDS Interface (24 Bits) ................................................................................................................................................... 3-8
3.9 DVO Interface for External Display .................................................................................................................................. 3-9
3.10 TMDS Interface Multiplexed on the PCI Express® Graphics Lanes ............................................................................ 3-10
3.11 Power Management Pins................................................................................................................................................3-11
3.12 Miscellaneous Pins..........................................................................................................................................................3-11
3.13 Power Pins...................................................................................................................................................................... 3-12
3.14 Ground Pins.................................................................................................................................................................... 3-13
3.15 Debug Port Signals......................................................................................................................................................... 3-13
3.16 Strapping Options........................................................................................................................................................... 3-14
Chapter 4: Timing Specifications
4.1 CPU HyperTransport™ Bus Timing.................................................................................................................................. 4-1
4.2 HyperTransport™ Reference Clock Timing Parameters ................................................................................................... 4-1
4.3 PCI Express® Differential Clock AC Specifications......................................................................................................... 4-1
4.4 Side-port Memory Timing ................................................................................................................................................. 4-1
4.4.1 Read Cycle DQ/DQS Delay ................................................................................................................................4-1
4.4.2 Write Cycle DQ/DQS Delay ............................................................................................................................... 4-2
4.5 LVDS Timing..................................................................................................................................................................... 4-2
4.6 OSCIN Timing ................................................................................................................................................................... 4-2
4.7 Power Rail Power Up Sequence......................................................................................................................................... 4-4
4.8 LCD Panel Power Up/Down Timing ................................................................................................................................. 4-5
42437 AMD M690T/E Databook 3.10 © 2011 Advanced Micro Devices, Inc.
Table of Contents-2 Proprietary
Page 5

Chapter 5: Electrical Characteristics and Physical Data
5.1 Electrical Characteristics.....................................................................................................................................................5-1
5.1.1 Maximum and Minimum Ratings ........................................................................................................................5-1
5.1.2 DC Characteristics................................................................................................................................................5-2
5.2 M690T Thermal Characteristics .........................................................................................................................................5-5
5.2.1 M690T Thermal Limits ........................................................................................................................................5-5
5.2.2 Thermal Diode Characteristics.............................................................................................................................5-6
5.3 Package Information ...........................................................................................................................................................5-7
5.3.1 Physical Dimensions ............................................................................................................................................5-7
5.3.2 Pressure Specification ..........................................................................................................................................5-9
5.3.3 Board Solder Reflow Process Recommendations ................................................................................................5-9
Chapter 6: Power Management and ACPI
6.1 ACPI Power Management Implementation ........................................................................................................................6-1
6.2 Power Management for the Graphics Controller ................................................................................................................6-2
6.2.1 PCI Function Power States...................................................................................................................................6-2
6.2.2 PCI Power Management Interface........................................................................................................................6-2
6.2.3 Capabilities List Data Structure in PCI Configuration Space ..............................................................................6-2
6.2.4 Register Block Definition.....................................................................................................................................6-3
6.2.5 Capability Identifier: Cap_ID (Offset = 0) ...........................................................................................................6-4
6.2.6 Next Item Pointer .................................................................................................................................................6-5
6.2.7 PMC - Power Management Capabilities (Offset = 2) ..........................................................................................6-5
Chapter 7: Testability
7.1 Test Capability Features......................................................................................................................................................7-1
7.2 Test Interface.......................................................................................................................................................................7-1
7.3 XOR Tree............................................................................................................................................................................7-1
7.3.1 Brief Description of an XOR Tree .......................................................................................................................7-1
7.3.2 Description of the XOR Tree for the M690T .......................................................................................................7-2
7.3.3 XOR Tree Activation ...........................................................................................................................................7-2
7.3.4 XOR Chain for the M690T...................................................................................................................................7-2
7.4 VOH/VOL Test...................................................................................................................................................................7-4
7.4.1 Brief Description of a VOH/VOL Tree................................................................................................................7-4
7.4.2 VOH/VOL Tree Activation..................................................................................................................................7-4
7.4.3 VOH/VOL Pin List...............................................................................................................................................7-5
Appendix A: Pin Listings
A.1 M690T Pin List Sorted by Ball Reference ........................................................................................................................ 1-2
A.2 M690T Pin List Sorted by Pin Name ................................................................................................................................1-6
Appendix B: AMD M690E
B.1 Introduction ....................................................................................................................................................................... 2-1
B.2 Feature Differences between the M690T and M690E ...................................................................................................... 2-1
B.3 DVI-I Support.................................................................................................................................................................... 2-3
B.4 HDMI™ ............................................................................................................................................................................ 2-3
© 2011 Advanced Micro Devices, Inc. 42437 AMD M690T/E Databook 3.10
Proprietary Table of Contents-3
Page 6

B.5 HDCP................................................................................................................................................................................. 2-4
B.6 M690E Display Options .................................................................................................................................................... 2-4
B.7 The LVTM Interface in TMDS Mode............................................................................................................................... 2-5
Appendix C: Revision History
42437 AMD M690T/E Databook 3.10 © 2011 Advanced Micro Devices, Inc.
Table of Contents-4 Proprietary
Page 7

List of Figures
Figure 1-1: M690T Branding Diagram for ASIC Revision A11 .....................................................................................................1-8
Figure 1-2: M690T Branding Diagram for ASIC Revision A12 .....................................................................................................1-9
Figure 1-3: M690T ASIC Part Number Legend ............................................................................................................................1-10
Figure 2-1: M690T Internal Block Diagram ....................................................................................................................................2-1
Figure 2-2: Host Interface Block Diagram ......................................................................................................................................2-2
Figure 2-3: M690T Host Bus Interface Signals ..............................................................................................................................2-3
Figure 2-4: M690T Side-port Memory Interface .............................................................................................................................2-4
Figure 2-5: Single/Dual Channel 24-bit LVDS Data Transmission Ordering .................................................................................2-6
Figure 2-6: Data Transmission Ordering for the TMDS Interface ..................................................................................................2-9
Figure 3-1: M690T Pin Assignment (Left) ......................................................................................................................................3-2
Figure 3-2: M690T Pin Assignment (Right) ....................................................................................................................................3-3
Figure 3-3: M690T Interface Block Diagram ..................................................................................................................................3-4
Figure 4-1: Power Rail Power Up Sequence for the M690T ...........................................................................................................4-4
Figure 4-2.: LCD Panel Power Up/Down Timing ...........................................................................................................................4-5
Figure 5-1: DC Characteristics of the TMDS Interface ...................................................................................................................5-4
Figure 5-2: DC Characteristics of the LVDS Interface ...................................................................................................................5-5
Figure 5-3: M690T Package Outline ...............................................................................................................................................5-7
Figure 5-4: M690T Ball Arrangement .............................................................................................................................................5-8
Figure 5-5: Stencil Opening Recommendations ..............................................................................................................................5-9
Figure 5-6: RoHS/Lead-Free Solder (SAC305/405 Tin-Silver-Copper) Reflow Profile ..............................................................5-10
Figure 6-1: Linked List for Capabilities ..........................................................................................................................................6-5
Figure 7-1: An Example of a Generic XOR Tree ............................................................................................................................7-1
Figure 7-2: Sample of a Generic VOH/VOL Tree ...........................................................................................................................7-4
Figure B-1: M690E Branding Diagram for ASIC Revision A12 ....................................................................................................2-1
Figure B-2: M690T and M690E Analog Display Output Signals ...................................................................................................2-2
Figure B-3: M690E LVTM Interface ..............................................................................................................................................2-3
Figure B-4: Pins for Analog Output on the DVI-I Connector .........................................................................................................2-3
Figure B-5: M690E Display Options ...............................................................................................................................................2-4
Figure B-6: DC Characteristics of the LVTM Interface in TMDS Mode .......................................................................................2-7
42437 AMD M690T/E Databook 3.10 © 2011 Advanced Micro Devices, Inc.
List of Figures-1 Proprietary
Page 8

This page is left blank intentionally.
42437 AMD M690T/E Databook 3.10 © 2011 Advanced Micro Devices, Inc.
List of Figures-2 Proprietary
Page 9

List of Tables
Table 1-1: M690T Device IDs ........................................................................................................................................................ 1-8
Table 1-2: M690T Planned production Schedule, OPN, and Part Marking ................................................................................. 1-10
Table 1-3: Pin Type Codes ........................................................................................................................................................... 1-11
Table 1-4: Acronyms and Abbreviations ...................................................................................................................................... 1-11
Table 2-1: Supported DDR2 Components ...................................................................................................................................... 2-4
Table 2-2: DDR2 Memory Row and Column Addressing .............................................................................................................2-4
Table 2-3: LVDS 24-bit TFT Single Pixel per Clock (Single Channel) Signal Mapping .............................................................. 2-7
Table 2-4: LVDS 24-bit TFT Dual Pixel per Clock (Dual Channel) Signal Mapping ...................................................................2-8
Table 2-5: Single-Link Signal Mapping for DVI/HDMI™ ......................................................................................................... 2-10
Table 2-6: Dual-Link Signal Mapping for DVI ............................................................................................................................ 2-11
Table 2-7: Support for HDMI™ Packet Type ..............................................................................................................................2-12
Table 2-8: VGA DAC Characteristics .......................................................................................................................................... 2-13
Table 3-1: CPU HyperTransport™ Interface .................................................................................................................................. 3-5
Table 3-2: DDR2 Side-port Memory Interface ............................................................................................................................... 3-5
Table 3-3: 1 x 8 Lane PCI Express® Interface for External Graphics ........................................................................................... 3-6
Table 3-4: 1 x 4 Lane A-Link Express II Interface for Southbridge .............................................................................................. 3-6
Table 3-5: 4 x 1 Lane PCI Express® Interface for General Purpose External Devices ................................................................. 3-6
Table 3-6: PCI Express® Interface for Miscellaneous PCI Express® Signals .............................................................................. 3-7
Table 3-7: Clock Interface ..............................................................................................................................................................3-7
Table 3-8: CRT and TV Interface ...................................................................................................................................................3-7
Table 3-9: LVDS Interface ............................................................................................................................................................. 3-8
Table 3-10: DVO Interface ............................................................................................................................................................. 3-9
Table 3-11: TMDS Interface Multiplexed on the PCI Express® Graphics Interface ................................................................... 3-10
Table 3-12: Power Management Pins ........................................................................................................................................... 3-11
Table 3-13: Miscellaneous Pins .................................................................................................................................................... 3-11
Table 3-14: Power Pins ................................................................................................................................................................. 3-12
Table 3-15: Ground Pins ............................................................................................................................................................... 3-13
Table 3-16: M690T Debug Port Signals ....................................................................................................................................... 3-13
Table 3-17: Strap Definitions for the M690T ............................................................................................................................... 3-14
Table 3-18: Strap Definition for GPPSB_LINK_CONFIG .......................................................................................................... 3-15
Table 4-1: HTREFCLK Pad (66.66MHz) Timing Parameters ....................................................................................................... 4-1
Table 4-2: PCI Express® Differential Clock (GFX_CLK, SB_CLK) AC Characteristics ............................................................ 4-1
Table 4-3: Timing Requirements for the LVDS Interface .............................................................................................................. 4-2
Table 4-4: Timing Requirements for the OSCIN Pad ....................................................................................................................4-2
Table 4-5: M690T Power Rail Power Up Sequence Requirements ...............................................................................................4-4
Table 4-6: LCD Power Up/Down Timing ...............................................................................................................................
Table 5-1: Maximum and Minimum Ratings ................................................................................................................................. 5-1
Table 5-2: DC Characteristics for 3.3V TTL Signals .....................................................................................................................5-2
Table 5-3: DC Characteristics for 1.8V TTL Signals .....................................................................................................................5-2
Table 5-4: DC Characteristics for the HTREFCLK Pad (66.66MHz) ............................................................................................ 5-2
Table 5-5: DC Characteristics for the OSCIN Pad (14.3181818MHz) .......................................................................................... 5-2
Table 5-6: DC Characteristics for the DDR2 Interface ..................................................................................................................5-3
Table 5-7: DC Characteristics for the TMDS Interface Multiplexed on the PCI Express® Gfx Lanes ......................................... 5-3
Table 5-8: Electrical Requirements for the LVDS Interface .......................................................................................................... 5-4
Table 5-9: M690T Thermal Limits ................................................................................................................................................. 5-5
Table 5-10: M690T 465-Pin FCBGA Package Physical Dimensions ............................................................................................ 5-7
Table 5-11: Recommended Board Solder Reflow Profile - RoHS/Lead-Free Solder .................................................................. 5-10
Table 6-1: ACPI States Supported by the M690T ..........................................................................................................................6-1
Table 6-2: ACPI Signal Definitions ................................................................................................................................................ 6-1
....... 4-5
42437 AMD M690T/E Databook 3.10 © 2011 Advanced Micro Devices, Inc.
List of Tables-1 Proprietary
Page 10

Table 6-3: Standard PCI Configuration Space Header Type 0 ...................................................................................................... 6-2
Table 6-4: PCI Status Register ....................................................................................................................................................... 6-3
Table 6-5: Capabilities Pointer (CAP_PTR) .................................................................................................................................. 6-3
Table 6-6: Power Management Register Block .............................................................................................................................. 6-3
Table 6-7: Power Management Control/Status Register (PMCSR) ............................................................................................... 6-4
Table 6-8: Capability Identifier (Cap_ID) ...................................................................................................................................... 6-4
Table 6-9: Next Item Pointer (NEXT_ITEM_PTR) ....................................................................................................................... 6-5
Table 6-10: Power Management Capabilities – PMC .................................................................................................................... 6-5
Table 7-1: Pins on the Test Interface .............................................................................................................................................. 7-1
Table 7-2: Example of an XOR Tree .............................................................................................................................................. 7-2
Table 7-3: M690T XOR Tree ......................................................................................................................................................... 7-2
Table 7-4: Truth Table for the VOH/VOL Tree Outputs ............................................................................................................... 7-4
Table 7-5: M690T VOH/VOL Tree ............................................................................................................................................... 7-5
42437 AMD M690T/E Databook 3.10 © 2011 Advanced Micro Devices, Inc.
List of Tables-2 Proprietary
Page 11

1.1 Introducing the M690T
The M690T is a seventh generation Integrated Graphics Processor (IGP) that integrates a DirectX® 9.0 compliant 2D/3D
graphics core and a system controller in a single chip. It is designed to support the AMD Athlon™ 64, AMD Athlon 64
FX, AMD Athlon 64 X2, AMD Sempron™, and AMD Turion™ 64 processors, including both AM2 and S1 socket CPUs.
The CPUs are supported on both high performance and value platforms.
The M690T integrates an AMD Radeon™ X1270 graphics engine, dual display, a TV encoder, an LVDS interface, an
integrated TMDS controller, and Northbridge functionality in a single BGA package. This high level of integration and
scalability is designed to enable manufacturers to offer enthusiast level capabilities and performance while minimizing
board space and system cost.
Robust and Flexible Core Logic Features
The M690T combines graphics and system logic functions in a single chip using a 21mm-body FCBGA package,
minimizing overall solution area. For optimal system and graphics performance, the M690T supports a high speed
HyperTransport™ interface to the AMD processor, running at a data rate of up to 2GT/s and supporting the new
generation of AM2 and S1 socket processors. The M690T is ideally suited to 64-bit operating systems, and supports
platform configurations with greater than 4GB of system memory. The rich PCI Express
M690T, including support for PCI Express external graphics and up to four other PCI Express peripherals, are
complemented by the advanced I/O features of AMD's SB600 Southbridge.
Support for Windows Vista
Chapter 1
Overview
®
expansion capabilities of
®
The M690T delivers an excellent Windows Vista® experience of any integrated graphics and core logic product for the
AMD platform. It incorporates an AMD Radeon™ X700-based graphics core, which provides 3D rendering power to
generate the Windows Vista desktop even under demanding circumstances. In addition, dedicated hardware acceleration
is provided for key new Windows Vista features such as ClearType. This AMD Radeon X700-based graphics technology
also enables great 3D application performance through SmartShader HD, SmoothVision HD, and 3Dc technologies.
Multimedia Capabilities
The M690T incorporates the innovative AMD Avivo™* display architecture, providing users with excellent visual
quality. Advanced scaling and color correction capabilities, along with precision through the entire display pipeline,
ensure an optimal image on CRT monitors, LCD panels, and any other display devices. A TV encoder provides superior
quality, and a TMDS interface, configurable to support DVI/HDMI™ and HDCP, allows compatibility with modern high
definition televisions.
*Note: AMD Avivo™ is a technology platform that includes a broad set of capabilities offered by certain AMD Radeon
products. Full enablement of some AMD Avivo capabilities may require complementary products.
Low Power Consumption and Industry Leading Power Management
The M690T is manufactured using a power efficient 80nm technology, and it supports a wide range of industry standards
and proprietary power management features. In addition to comprehensive support for the ACPI specification and AMD
features such as AMD PowerNow!™, the PowerPlay™ technology (enhanced with new adaptive frame buffer
compression and PowerShift™ features) minimizes the M690T's power consumption by adjusting graphics core
performance and core voltage to the task and usage environment.
Software Compatibility
The graphics driver for the M690T is compatible with AMD Radeon class graphics controllers from AMD. A single
driver can support multiple graphics configurations across AMD's product lines, including the AMD Radeon family and
the AMD chipset family. In addition, this driver compatibility allows the M690T to benefit immediately from AMD's
© 2011 Advanced Micro Devices, Inc. 42437 AMD M690T/E Databook 3.10
Proprietary 1-1
Page 12

software optimization and from the advanced Windows® XP and Windows Vista support available in the AMD Radeon
family drivers.
Note: In some reference documents, the M690T is referred to by its code name "RS690T," which signifies the same
device.
1.2 M690E
The M690T and M690E are the same device with respect to their form, fit, and functionally, except for the differences
described in Appendix B, “AMD M690E.” All information in this databook, unless superseded by the information given in
Appendix B, is applicable to the M690E.
1.3 M690T Features
1.3.1 CPU HyperTransport™ Interface
•
Supports the mobile and desktop AMD Athlon 64/AMD Athlon 64 FX/AMD Athlon X2/AMD Sempron/AMD
Turion 64 processors, including both AM2 and S1 socket CPUs.
• Supports 200, 400, 600, 800, and 1000MHz HyperTransport (HT) interface speeds.
• Supports LDTSTP interface, CPU throttling, and stutter mode.
M690E
1.3.2 Memory Interface
•
Supports an optional dedicated local frame buffer (side-port) of up to 128MB through a 16-bit interface.
• Highly flexible memory architecture allows asymmetric side-port and shared system memory frame buffer sizes.
• Dynamic memory allocation scheme improves performance and reduces power.
• Support for DDR2 system memories up to DDR2-800, with a maximum memory clock speed of 400MHz. Memory
clock is independent of any other clock source and can therefore be set to any frequency equal to or less than
400MHz (DDR2-800), allowing the use of lower speed side-port memories.
• Support for 16Mx16, 32Mx8, 32Mx16, 64Mx8, and 64Mx16 memory devices.
• Asynchronous HyperTransport and memory controller interface speeds.
• Supports DDR SDRAM self refresh mechanism.
• Supports dynamic CKE and ODT for power conservation.
1.3.3 AMD HyperMemory™ Technology
Supports AMD HyperMemory™* technology.
•
* Note: The amount of HyperMemory available includes both dedicated and shared memory and is determined by various
factors. For details, please refer to the product advisory numbered PA_IGPGenC5, available on AMD’s OEM Resource
Center or from your AMD CSS representative.
1.3.4 PCI Express
•
Compliant with the PCI Express (PCIe®) 1.1a Specification.
®
Interface
• Highly flexible PCIe implementation to suit a variety of platform needs.
• A x8 graphics interface, configurable to any of the following modes of support:
• An external graphics device utilizing all 8 lanes (see section 1.3.11“DVI/HDMI™” on page 1-6 for details).
• A TMDS interface, enabling DVI/HDMI.
• A single x1, x2, x4, or x8 general purpose PCIe link.
• Supports programmable lane reversal for the graphics link to ease motherboard layout when the end device does not
support lane reversal.
• A four-port, x4 PCI Express general purpose interface, configurable to one of the following modes of support:
42437 AMD M690T/E Databook 3.10 © 2011 Advanced Micro Devices, Inc.
1-2 Proprietary
Page 13

M690T Features
• Four x1 links.
• Two x2 links.
• One x2 and two x1 links.
• One x4 link.
1.3.5 A-Link Express II Interface
One x4 A-Link Express II interface (PCI Express 1.1 compliant) for connection to an AMD Southbridge, providing
•
more bandwidth than the older A-Link Express interface.
1.3.6 2D Acceleration Features
•
Highly-optimized 128-bit engine, capable of processing multiple pixels per clock.
• Hardware acceleration of Bitblt, Line Draw, Polygon / Rectangle Fill, Bit Masking, Monochrome Expansion,
Panning/Scrolling, Scissoring, and full ROP support (including ROP3).
• Optimized handling of fonts and text using AMD proprietary techniques.
• Hardware acceleration for ClearType font rendering.
• Game acceleration including support for Microsoft's DirectDraw: Double Buffering, Virtual Sprites, Transparent Blit,
and Masked Blit.
• Acceleration in 1/8/15/16/32 bpp modes:
• ClearType mode for 1bpp
• Pseudocolor mode for 8bpp
• ARGB1555 and RGB565 modes for 16bpp
• ARGB8888 mode for 32bpp
• Significant increase in the High-End Graphics WinBench
• Setup of 2D polygons and lines.
• Support for GDI extensions in Windows XP and Windows Vista: Alpha BLT, Transparent BLT, Gradient Fill.
• Hardware cursor (up to 64x64x32bpp), with alpha channel for direct support of Windows XP and Windows Vista
alpha cursor.
1.3.7 3D Acceleration Features
•
Multi-texturing via one texture blending unit per pixel pipes, allowing up to 512 texel reads per pixel in a single pass.
• 3D texture support, including projective 3D textures.
• Comprehensive support for bump mapping: emboss, dot-product, and environment bump maps.
• Precision in anisotropic filtering and bilinear filtering.
• 3D primitive support: points, lines, triangles, lists, strips and quadrilaterals and BLTs with Z compare.
• Texture compositing.
• Hidden surface removal using 16, 24, or 32-bit Z-buffering (maximum Z-buffer depth is 24 bits when stencil buffer
enabled) and Early Z hardware.
• 8-bit stencil buffer.
• Bilinear and trilinear texture filtering.
• Support of Direct3D texture lighting.
• Dithering support in 16bpp for near 24bpp quality in less memory.
• Extensive 3D mode support.
• Anti-aliasing using multi-sampling algorithm with support for 2, 4, and 6 samples.
• Optimized for performance in true color triple buffered 32bpp acceleration modes.
®
score due to capability for C18 color expansion.
© 2011 Advanced Micro Devices, Inc. 42437 AMD M690T/E Databook 3.10
Proprietary 1-3
Page 14

• New generation rendering engine provides top 3D performance.
• Support for OpenGL format for Indirect Vertices in Vertex Walker.
• DirectX 9.0 support (Vertex Shader version 2.0 and Pixel Shader version 2.0):
• Full precision floating point pixel pipeline.
• Support for up to 4 MRTs (Multiple-Render-Targets).
• Support for writing all texture formats from render pipe in floating points (including cube mapes and 3D
textures).
• Support for up to 512bpp formats (4 color case).
• Advanced setup engine, capable of processing 1 polygon (lit and textured) per cycle.
1.3.8 Motion Video Acceleration Features
Enhanced MPEG-2 hardware decode acceleration (SD contents only), including support for:
•
• Integrated general purpose iDCT engine for MPEG2 and DV decode acceleration.
• Integrated MPEG motion compensation engine for decode acceleration.
• Parallel operation of the iDCT and MC and high processing rates with minimal software overhead.
• Supports Microsoft
®
DirectX Video Acceleration (DirectX VA) 2.0 (for SD contents only).
• Provides reduced CPU utilization without incurring the cost of a full MPEG-2 decoder.
• MPEG-4 simple profile support.
• Supports top quality DVD with low CPU usage.
• Hardware-based adaptive de-interlacing filter and scaler provide high quality full-screen and full-speed video
playback. Minimizes the aliasing artifacts along edges usually caused by a conventional deinterlacer/scaler.
M690T Features
1.3.9 Multiple Display Features
General
• Dual independent displays. Possible configurations include:
• CRT and LVDS
• CRT and DVI/HDMI*
• LVDS and DVI/HDMI*
• LVDS and TV (component, composite, or S-Video)
• DVI/HDMI and TV (component, composite, or S-Video)*
• Dual CRT**
• Dual TV**
• CRT and TV**
Notes: * The options require implementation of the TMDS interface that is multiplexed on the PCIe external graphics
interface; see section 1.3.11, “DVI/HDMI™,” on page 1-6.
** The options require implementation of the DVO interface for an external display; see section 1.3.12,
“External Display Support via DVO,” on page 1-6.
• Resolution, refresh rates, and display data can be completely independent for the two display paths.
• Each display controller supports true 30bpp throughout the display pipeline.
• Each display path supports VGA and accelerated modes, video overlay, hardware cursor, hardware icon, and palette
gamma correction.
• Supports both interlaced and non-interlaced displays.
42437 AMD M690T/E Databook 3.10 © 2011 Advanced Micro Devices, Inc.
1-4 Proprietary
Page 15

M690T Features
• Full ratiometric expansion ability is supported for source desktop modes up to 1920 pixels/line.
• Maximum DAC frequency of 400MHz.
• Supports 8, 16, 32 & 64-bpp depths for the main graphics layer:
• For 32-bpp depth, supports xRGB 8:8:8:8, xRGB 2:10:10:10, sCrYCb 8:8:8:8, and xCrYCb 2:10:10:10 data
• For 64-bpp depth, supports xRGB 16:16:16:16 data format.
• Independent gamma, color conversion and correction controls for main graphics layer.
• Support for DDC1 and DDC2B+ for plug and play monitors.
• 8-bit alpha blending of graphics and video overlay.
• Hardware cursor up to 64x64 pixels in 2bpp, full color AND/XOR mix, and full color 8-bit alpha blend.
• Hardware icon up to 128x128 pixels in 2bpp, with two colors, transparent, and inverse transparent. AND/XOR
mixing. Supports 2x2 icon magnification.
• Virtual desktop support.
• Configurable to support flat panel displays or TVs via DVI/HDMI.
• Integrated HD Audio Controller for HDMI audio data.
VGA Output
• Maximum resolutions supported by the VGA output for different refresh rates are:
formats.
• 2048x1536 @85Hz (pixel clock at 388.5MHz) for 4:3 format
• 2560x1440 @75Hz (pixel clock at 397.25MHz) for 16:9 format
• 2456x1536 @60Hz (pixel clock at 320MHz) for 16:10 format
TV Out
• An integrated TV encoder with an on-chip DAC (shared with the CRT analog output) (Note: Simultaneous output for
TV and CRT is not supported).
• 10-bit DAC with 10-tap filter producing scaled, flicker removed, artifact suppressed display on a PAL or NTSC TV
with composite, S-Video, component, and RGB output.
• With the proper BIOS implementation, supports different TV standards including NTSC, NTSC-J, PAL-M, PAL-CN,
PAL-B, PAL-G, PAL-D, PAL-H, PAL-I, PAL-K, and PAL-N.
• Supports Macrovision 7.1 copy protection standard (required by DVD players).
• Supports a maximum resolution of 1024x768 by S-video or composite video output.
• Supports 480i and 576i YUV/YCbCr component output.
• Supports the following formats of YPbPr component output: 480i, 480p, 576i, 576p, 720p, and 1080i.
• Internal adaptive flicker filtering available on both display paths for interlaced TV outputs.
• Supports fully-programmable 2D, adaptive comb filter for composite output.
• TV-out power management support.
• Line 21 Closed Caption and Extended Data Service support for encoding in Vertical Blanking Interval (VBI) of TV
signal.
• CGMS copy management support in VBI through Line-20 and/or Extended Data Service (Line-21 Field 2) for
NTSC, and through Wide Screen Signaling data (WSS) for PAL.
1.3.10 Integrated LVDS
•
Integrated dual-link 24-bit LVDS interface.
• 805 Mbps/channel with 115MHz pixel clock rate per link (230MHz maximum pixel clock).
• FPDI-2 compliant; compatible with receivers from National Semiconductor, Texas Instruments, and THine.
© 2011 Advanced Micro Devices, Inc. 42437 AMD M690T/E Databook 3.10
Proprietary 1-5
Page 16

• OpenLDI compliant excluding DC balancing.
• Programmable internal spread spectrum controller for the signals.
1.3.11 DVI/HDMI™
•
Supports a TMDS interface, enabling DVI or HDMI*, which is multiplexed on the PCIe external graphics interface
(only available if no external graphics card is attached to the PCIe external graphics interface).
• Supports industry standard EIA-861B video modes including 480p, 720p, and 1080i. For a full list of currently
supported modes, contact your AMD CSS representative. Maximum resolutions supported by various modes are:
• Single-link DVI: 1600x1200 @60Hz with pixel clock at 162 MHz and standard timings; 1920x1200 @60Hz
with pixel clock at 154MHz and reduced blanking timings.
• Dual-link DVI: 2560x1600 @60Hz, with pixel clock at 268 MHz (DVI clock at 134 MHz).
• HDMI: 1080i, with pixel clock at 74MHz.
• HDMI basic audio support at 32, 44.1, and 48 kHz. Supports two-channel uncompressed audio and multi-channel
audio compressed to two channels like 5.1 DTS, AC3, etc, for audio bit rates up to 1.5 Mbits/s. HD Audio device
compatible with Microsoft’s HD audio drivers.
• HD Audio device compatible with Microsoft’s HD audio drivers.
• HDCP support on data stream for single-link transmission, with on-chip key storage.**
Notes: * CEC is not supported.
M690T Features
** HDCP content protection is only available to licensed buyers of the technology and can only be enabled when
connected to an HDCP-capable receiver.
1.3.12 External Display Support via DVO
•
Supports an external display via a DVO port (multiplexed with the side-port memory interface and only available
if side-port memory is not implemented).
1.3.13 Power Management Features
•
Supports ACPI states S1, S3, S4, and S5.
• The chip power management support logic supports four device power states defined for the OnNow Architecture—
On, Standby, Suspend, and Off. Each power state can be achieved by software control bits.
• Hardware controlled intelligent clock gating enables clocks only to active functional blocks, and is completely
transparent to software.
• Dynamic self-refresh for the side-port memory.
• Support for AMD Cool'n'Quiet™ technology via FID/VID change.
• Support for AMD PowerNow!™ technology.
• Clocks to every major functional block are controlled by a unique dynamic clock switching technique that is
completely transparent to the software. By turning off the clock to the block that is idle or not used at that point, the
power consumption is significantly reduced during normal operation.
• Supports AMD PowerExpress™, and PowerPlay™ (enhanced with the new PowerShift™ feature).
• Support dynamic lane reduction for the PCIe interfaces, adjusting lane width according to required bandwidth (not
available on the PCIe graphics link when lane reversal is in effect).
1.3.14 PC Design Guide Compliance
The M690T complies with all relevant Windows Logo Program (WLP) requirements from Microsoft for WHQL
certification.
42437 AMD M690T/E Databook 3.10 © 2011 Advanced Micro Devices, Inc.
1-6 Proprietary
Page 17

Software Features
1.3.15 Test Capability Features
The M690T has a variety of test modes and capabilities that provide a very high fault coverage and low DPM (Defect Per
Million) ratio:
• Full scan implementation on the digital core logic through ATPG (Automatic Test Pattern Generation) vectors.
• Dedicated test logic for the on-chip custom memory macros to provide complete coverage on these modules.
• A JTAG test mode to allow board level testing of neighboring devices.
• An EXOR tree test mode on all the digital I/O's to allow for proper soldering verification at the board level.
• A VOH/VOL test mode on all digital I/O’s to allow for proper verification of output high and output low values at the
board level.
• Improved access to the analog modules to allow full evaluation and characterization.
• Improved IDDQ mode support to allow chip evaluation through current leakage measurements.
These test modes can be accessed through the settings on the instruction register of the JTAG circuitry.
1.3.16 Additional Features
•
Integrated spread spectrum PLLs on the memory and LVDS interface.
1.3.17 Packaging
Single chip solution in 80nm, 1.0-1.2V low power CMOS technology.
•
• 465-FCBGA package, 21mmx21mm.
1.4 Software Features
• Supports Microsoft Windows XP and Windows Vista operating systems.
• BIOS ability to read EDID 1.1, 1.2, and 1.3.
• Ability to selectively enable and disable several devices including CRT, LCD, TV, and DFP.
• Register-compatible with VGA standards, BIOS-compatible with VESA VBE2.0.
• Supports corporate manageability requirements such as DMI.
• ACPI support.
• Full Write Combining support for maximum performance of the CPU.
• Full-featured, yet simple Windows utilities:
• Calibration utility for WYSIWYG color
• Independent brightness control of desktop and overlay
• End user diagnostics
• Drivers meet Microsoft's rigorous WHQL criteria and are suitable for systems with the "Designed for Windows"
logos.
• Comprehensive OS and API support.
• Hot-key support (Windows ACPI 1.0b or AMD Event Handler Utility where appropriate).
• Extensive power management support.
• Rotation mode support in software.
• Dual CRTC, simultaneous view, extended desktop support (Windows XP and Windows Vista)
• DirectX 9.0 support.
• Switchable overlay support.
• H.264 playback support.
© 2011 Advanced Micro Devices, Inc. 42437 AMD M690T/E Databook 3.10
Proprietary 1-7
Page 18

1.5 Device IDs
o
GGGGG
YYWWXXV
216TQA6AVA11FG
TAIWAN
RS690T
* YY - Assembly Start Year
WW - Assembly Start Week
XX - Assembly Location
V - Substrate Vendor Code
Part Number (for ASIC revision A11)
Country of Origin
Date and Other Codes*
Wafer Foundry’s Lot Number
AMD Code Name
Artwork
Table 1-1 M690T Device IDs
Value
NB Host ID 0x7910
Internal Graphics ID 0x791F
1.6 Branding Diagrams
1.6.1 Branding Diagram for ASIC Revision A11
Device IDs
Figure 1-1 M690T Branding Diagram for ASIC Revision A11
1.6.2 Branding Diagram for ASIC Revision A12 and After
Note: The branding diagram below does not necessarily contain the latest ASCI revision number for the M690T. Unless specified otherwise, no
information in this databook is specific to the ASIC revision number given in the diagram.
42437 AMD M690T/E Databook 3.10 © 2011 Advanced Micro Devices, Inc.
1-8 Proprietary
Page 19

Branding Diagrams
GGGGGG
YYWWXXV
COO
o
216TQA6AVA12FG
CHIPSET
* YY - Assembly Start Year
WW - Assembly Start Week
XX - Assembly Location
V - Substrate Vendor Code
Part Number (for ASIC revision A12)
Country of Origin
Date and Other Codes*
Wafer Foundry’s Lot Number
AMD Product Type
AMD Logo
“o” indicates pin A1.
Figure 1-2 M690T Branding Diagram for ASIC Revision A12
© 2011 Advanced Micro Devices, Inc. 42437 AMD M690T/E Databook 3.10
Proprietary 1-9
Page 20
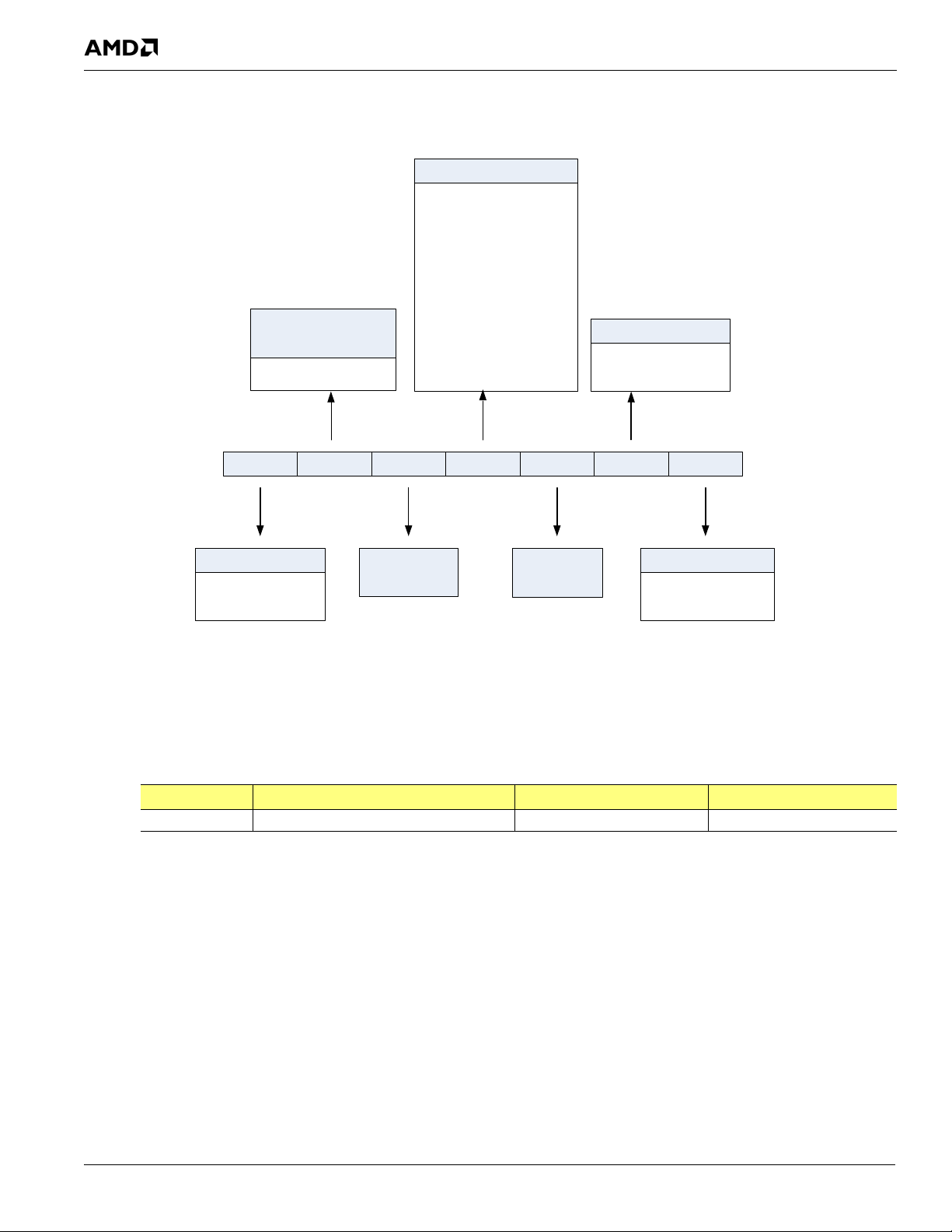
1.7 Part Number Legend
TSMC Fab
216 TQA6 A V A12 F G
215 – Desktop
216 – Mobile
Product Type
TQA6 -M690T
Marketing
Brand Name
Substrate
Revision
N – UMC Fab 8F
M – IBM
C
3
S TSMC Fab
4
F TSMC Fab
5
G
TSMC Fab 6
K TSMC Fab
12
L
TSMC Fab14
W
TSMC WSMC
Q
TSMC WSMC (8B)
T
TSMC Wafer Tech
Foundry Code
ASIC
Revision
Blank – No
F
–
Yes
Flip Chip
K – High Temp
G – Lead Free
Package BOM
–
–
–
–
–
–
–
–
V
–
–
UMC Fab 12A
Part Number Legend
Figure 1-3 M690T ASIC Part Number Legend
1.8 Production Schedule, OPN, and Part Marking
The part marking, planned production schedule, and AMD OPN (ordering numbering) for the M690T are shown in
Table 1-2.
Table 1-2 M690T Planned production Schedule, OPN, and Part Marking
Component Production Availability Date OPN Part Marking
M690T In production now 100-CG1292 216TQA6AVA12FG
1.9 Conventions and Notations
The following conventions are used throughout this manual.
1.9.1 Pin Names
1.9.2 Pin Types
Pins are identified by their pin names or ball references. Multiplexed pins assume alternate “functional names” when they
perform their alternate functions, and these “functional names” are given in Chapter 3, “Pin Descriptions and Strap
Options.”
All active-low signals are identified by the suffix ‘#’ in their names (e.g., LDTSTOP#).
The pins are assigned different codes according to their operational characteristics. These codes are listed in Table 1-3.
42437 AMD M690T/E Databook 3.10 © 2011 Advanced Micro Devices, Inc.
1-10 Proprietary
Page 21
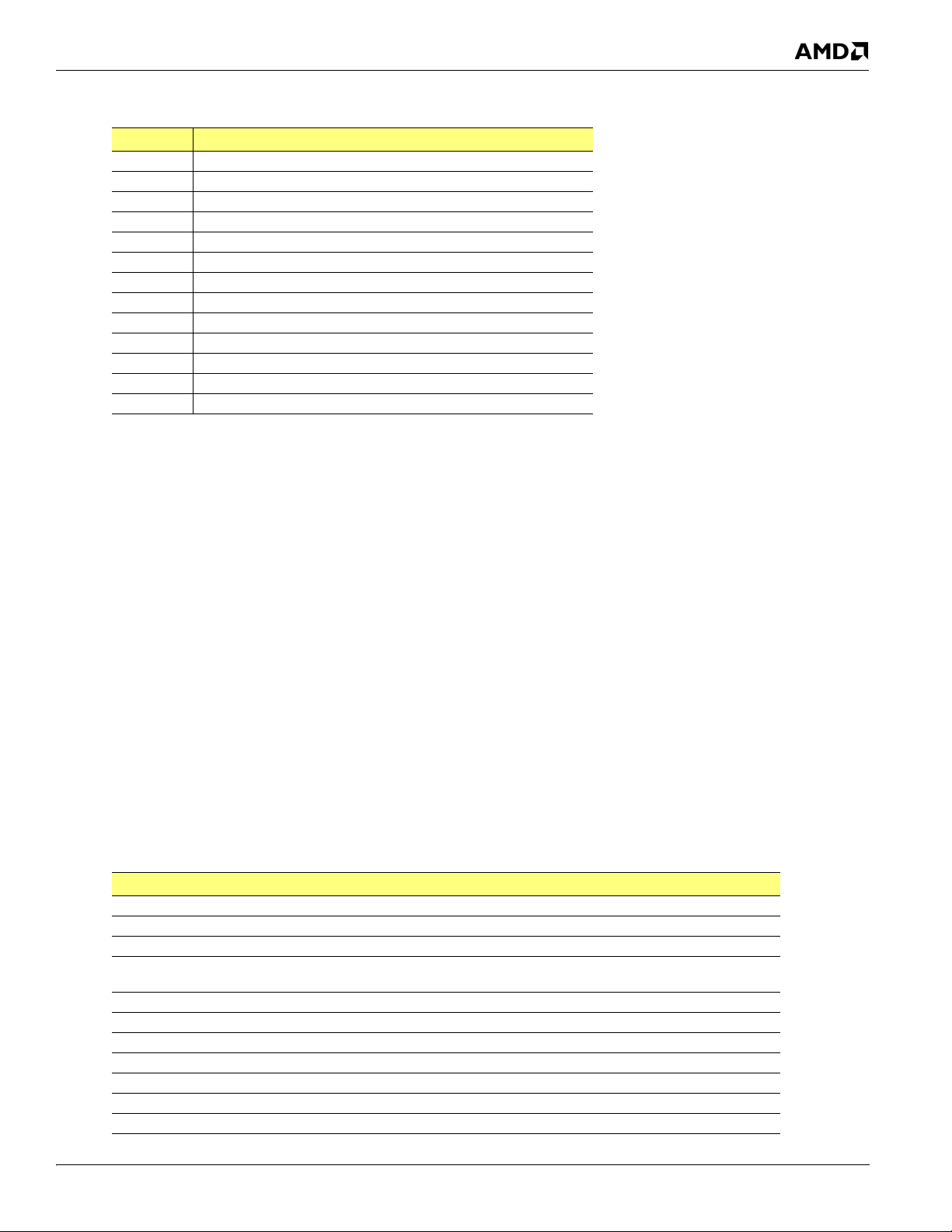
Conventions and Notations
Table 1-3 Pin Type Codes
Code Pin Type
I Digital Input
O Digital Output
OD Open Drain
I/O Bi-Directional Digital Input or Output
M Multifunctional
Pwr Power
Gnd Ground
A-O Analog Output
A-I Analog Input
A-I/O Analog Bi-Directional Input/Output
A-Pwr Analog Power
A-Gnd Analog Ground
Other Pin types not included in any of the categories above
1.9.3 Numeric Representation
Hexadecimal numbers are appended with “h” (Intel assembly-style notation) whenever there is a risk of ambiguity. Other
numbers are in decimal.
Pins of identical functions but different trailing integers (e.g., “CPU_D0, CPU_D1,... CPU_D7”) are referred to
collectively by specifying their integers in square brackets and with colons (i.e., “CPU_D[7:0]”). A similar short-hand
notation is used to indicate bit occupation in a register. For example, NB_COMMAND[15:10] refers to the bit positions
10 through 15 of the NB_COMMAND register.
1.9.4 Register Field
A field of a register is referred to by the format of [Register Name].[Register.Field]. For example,
“NB_MC_CNTL.DISABLE_BYPASS” is the “DISABLE_BYPASS” field of the register “NB_MC_CNTL.”
1.9.5 Hyperlinks
Phrases or sentences in blue italic font are hyperlinks to other parts of the manual. Users of the PDF version of this manual
can click on the links to go directly to the referenced sections, tables, or figures.
1.9.6 Acronyms and Abbreviations
The following is a list of the acronyms and abbreviations used in this manual.
Table 1-4 Acronyms and Abbreviations
Acronym Full Expression
ACPI Advanced Configuration and Power Interface
A-Link-E II A-Link Express II interface between the IGP and the Southbridge.
BGA Ball Grid Array
BIOS
BIST Built In Self Test.
BLT Blit
bpp bits per pixel
CEC Consumer Electronic Control
CPIS Common Panel Interface Specification
CRT Cathode Ray Tube
CSP Chip Scale Package
Basic Input Output System. Initialization code stored in a ROM or Flash RAM used to start up a
system or expansion card.
© 2011 Advanced Micro Devices, Inc. 42437 AMD M690T/E Databook 3.10
Proprietary 1-11
Page 22

Table 1-4 Acronyms and Abbreviations (Continued)
Acronym Full Expression
DAC Digital to Analog Converter
DBI Dynamic Bus Inversion
DDC
DDR Double Data Rate
DFP Digital Flat Panel. Monitor connection standard from VESA.
DPM Defects per Million
DTV Digital TV
DVD Digital Video Disc
DVI
DVS Digital Video Stream
EPROM Erasable Programmable Read Only Memory
FIFO First In, First Out
FPDI Flat Panel Display Interface
GDI Graphics Device Interface
GND Ground
GPIO General Purpose Input/Output
GTL+ Gunning Transceiver Logic
HDCP High-Bandwidth Digital Content Protection
HDMI High Definition Multimedia Interface
HDTV High Definition TV. The 1920x1080 and the 1280x720 modes defined by ATSC.
HPD Hot Plug Detect
iDCT inverse Discrete Cosine Transform
IDDQ Direct Drain Quiescent Current
IGP
JTAG Joint Test Access Group. An IEEE standard.
LVDS Low Voltage Differential Signaling
MB Mega Byte
MPEG
NTSC
PAL Phase Alternate Line. The standard definition TV system used in Europe and other areas.
PCI Peripheral Component Interface
PCIe PCI Express
PCMCIA
PLL Phase Locked Loop
POST Power On Self Test
PD Pull-down Resistor
PU Pull-up Resistor
ROP Raster Operation
SDRAM Synchronous Dynamic RAM
TMDS Transition Minimized Differential Signaling
UMA Unified Memory Architecture
UV Chrominance (also CrCb). Corresponds to the color of a pixel.
UXGA Ultra Extended Graphics Array
VBI Vertical Blank Interval
VESA Video Electronics Standards Association
Display Data Channel. A VESA standard for communicating between a computer system and
attached display devices.
Digital Video Interface. Monitor connection standard from the DDWG (Digital Display Work
Group).
Integrated Graphics Processor. A single device that integrates a graphics processor and a
system controller.
Motion Pictures Experts Group. Refers to compressed video image streams in either MPEG-1
or MPEG-2 formats.
National Television Standards Committee. The standard definition TV system used in North
America and other areas.
Personal Computer Memory Card International Association. It is also the name of a standard
for PC peripherals promoted by the Association.
Conventions and Notations
42437 AMD M690T/E Databook 3.10 © 2011 Advanced Micro Devices, Inc.
1-12 Proprietary
Page 23

Conventions and Notations
Table 1-4 Acronyms and Abbreviations (Continued)
Acronym Full Expression
VGA Video Graphics Adapter
VRM Voltage Regulation Module
© 2011 Advanced Micro Devices, Inc. 42437 AMD M690T/E Databook 3.10
Proprietary 1-13
Page 24

This page is left blank intentionally.
Conventions and Notations
42437 AMD M690T/E Databook 3.10 © 2011 Advanced Micro Devices, Inc.
1-14 Proprietary
Page 25
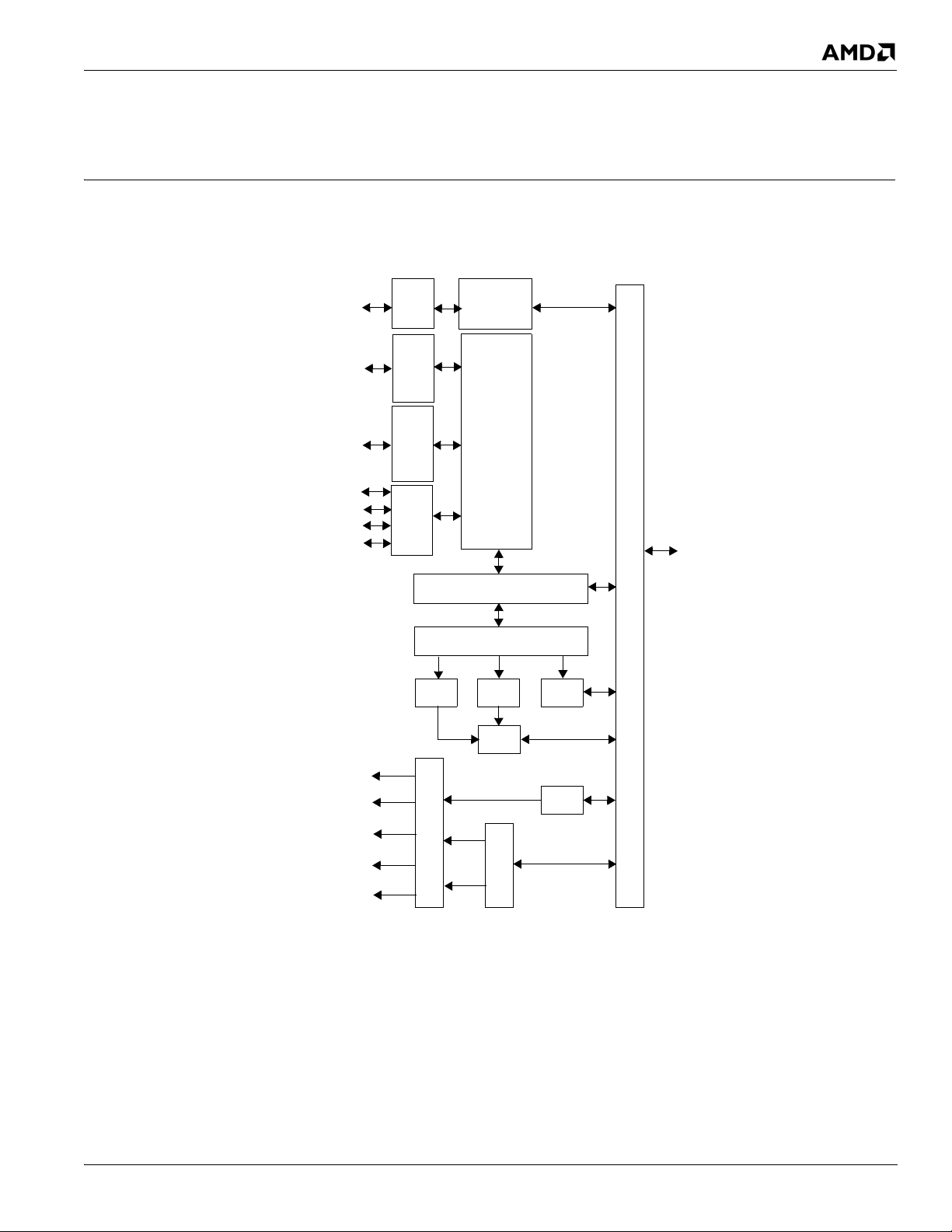
Chapter 2
HyperTransport™
Unit
CPU
Interface
Register Interface
iDCT
Setup
Engine2DEngine
3D
Engine
Overlay
Root
MUX
Display 1& 2
TV-Out
LVDS
CRT
Memory Controller
AMD CPU
BIF
Complex
Optional 16-bit DDR2
Memory Channel
on PCIe® Gfx lanes)
TMDS, enabling DVI/HDM™I (Multiplexed
SB
External
Graphics
A-Link-E II
Gfx Interface
PCIe
®
Interface
(1 x 8 Lanes)
GPP Interface
PCIe
®
(4 x 1 Lanes)
Expansion
Slots or
On-board
Devices
(1 x 4 Lanes)
External Display via DVO
Functional Descriptions
This chapter describes the functional operation of the major interfaces of the M690T system logic chip. Figure 2-1,
“M690T Internal Block Diagram,” illustrates the M690T internal blocks and interfaces.
Figure 2-1 M690T Internal Block Diagram
© 2011 Advanced Micro Devices, Inc. 42437 AMD M690T/E Databook 3.10
Proprietary 2-1
Page 26
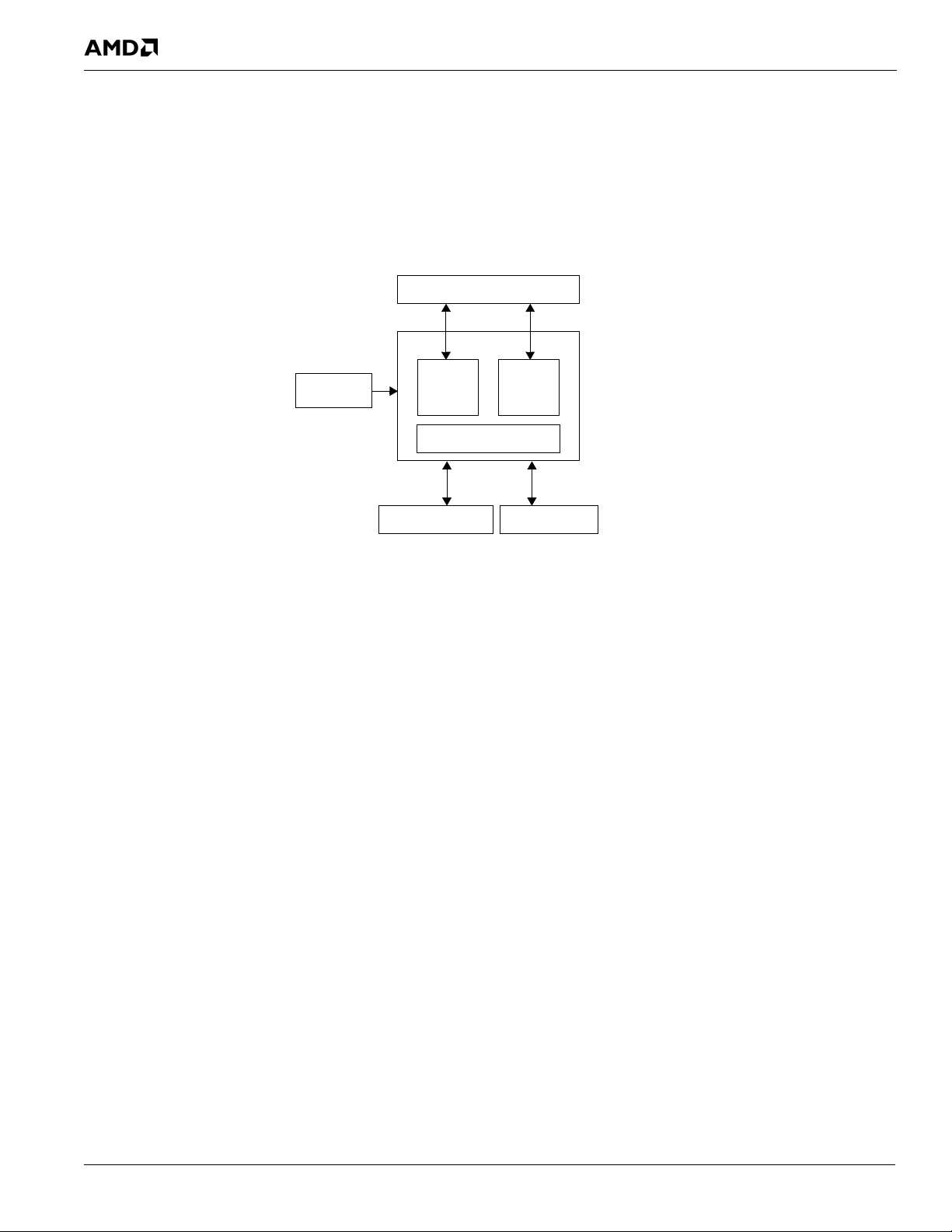
2.1 Host Interface
HT Interface to CPU (PHY)
Configuration
Registers
Root Complex
Memory Controller
LTA
LRA
SCH
Data Link Layer
Protocol/Transaction Layer
The M690T is designed to interface with the AMD Athlon 64/AMD Athlon 64 FX/AMD Athlon X2/AMD
Sempron/AMD Turion 64 processors, including both AM2 and S1 socket CPUs. This section presents an overview of the
HyperTransport™ interface. For a detailed description of the interface, please refer to the HyperTransport I/O Link
Specification from the HyperTransport Consortium. Figure 2-2, “Host Interface Block Diagram,” illustrates the basic
blocks of the host bus interface of the M690T.
Host Interface
Figure 2-2 Host Interface Block Diagram
The HyperTransport (HT) Interface is a high speed, packet-based link implemented on two unidirectional buses. It is a
point-to-point interface where data can flow both upstream and downstream at the same time. The commands, addresses,
and data travel in packets on the HyperTransport link. Lengths of packets are in multiples of four bytes. The HT link
consists of three parts: the physical layer (PHY), the data link layer, and the protocol/transaction layer. The PHY is the
physical interface between the M690T and the CPU. The data link layer includes the initialization and configuration
sequences, periodic redundancy checks, connect/disconnect sequences, and information packet flow controls. The
protocol layer is responsible for maintaining strict ordering rules defined by the HT protocol.
The M690T HyperTransport bus interface consists of 17 unidirectional differential data/control pairs and two differential
clock pairs in each of the upstream and downstream direction. On power up, the HT link is 8 bits wide and runs at a
default speed of 200MT/s. After negotiation, carried out by the HW and SW together, the link width can be brought up to
16 bits and the interface can run up to 2GT/s. The interface is illustrated in Figure 2-3, “M690T Host Bus Interface
Signals,” on page 2-3. The signal name and direction for each signal is shown with respect to the processor. Please note
that the signal names may be different from those used in the pin listing of the M690T. Detailed descriptions of the signals
are given in section 3.3, “CPU HyperTransport™ Interface‚’ on page 3-5.
42437 AMD M690T/E Databook 3.10 © 2011 Advanced Micro Devices, Inc.
2-2 Proprietary
Page 27

Side-port Memory Interface
HT_RXCADN
2
2
M690T
AMD CPU
HT_TXCALP
HT_RXCALN
HT_RXCALP
VDD_HT
HT_TXCALN
HT_RXCADP
HT_RXCTLN
HT_RXCTLP
HT_RXCLKN
HT_RXCLKP
16
16
HT_TXCADN
2
2
HT_TXCADP
HT_TXCTLN
HT_TXCTLP
HT_TXCLKN
HT_TXCLKP
16
16
Figure 2-3 M690T Host Bus Interface Signals
2.2 Side-port Memory Interface
In order to significantly decrease system power and increase graphics performance, the M690T provides an optional
side-port memory interface for dedicated frame buffer memory, to be used exclusively for the integrated graphics core.
The side-port memory interface is designed to significantly reduce system power by allowing the CPU to stay in its lowest
power state during periods of inactivity. Screen refreshes are fetched from the side-port memory, and there is no need to
"wake up" the CPU to fetch screen refresh data.
The M690T memory controller operates in 16-bit mode at very high speed (up to DDR2-800), and has a new
programmable interleaved mode that significantly increases the memory bandwidth and reduces data latency to the
integrated graphics core.
2.2.1 DDR2 Memory Interface
Figure 2-4, “M690T Side-port Memory Interface,” on page 2-4, illustrates the side-port memory interface of the M690T.
The M690T memory controller supports up to 128MB of dedicated side-port frame buffer memory. It controls a single
rank of DDR2 devices in 16-bit memory configuration. It supports device sizes of 256, 512, and 1024 Mbit, and device
widths of x8 and x16. Because the memory controller supplies only one chip select signal, only DDR2 devices with one
chip select are supported. A wide range of DDR2 timing parameters, configurations, and loadings are programmable via
the M690T memory controller configuration registers
© 2011 Advanced Micro Devices, Inc. 42437 AMD M690T/E Databook 3.10
Proprietary 2-3
Page 28

Data Mask MEM_DM[1:0]
Data MEM_DQ[15:0]
2
4
16
M690T Side-port Memory
Interface
Data Strobes MEM_DQS[1:0]P/N
Un-buffered DDR2 SDRAM
MEM_CKE, MEM_RAS#,
Differential Clocks MEM_CKP/MEM_CKN
4
2
MEM_CAS#, MEM_WE#
14
Address MEM_A[13:0]
1
Chip Select MEM_CS#
1
On-Die Termination MEM_ODT
3
Bank Address MEM_BA[2:0]
MEM_CALN
MEM_CALP
VDD_MEM
Side-port Memory Interface
Figure 2-4 M690T Side-port Memory Interface
2.2.1.1 Supported DDR2 Components
The memory controller supports DDR2 SDRAM chips in several configurations. These chips are organized in banks,
rows (or pages), and columns. The supported DDR2 components have four or eight banks. Table 2-1 lists the supported
memory components.
Table 2-1 Supported DDR2 Components
DDR2 SDRAM
Config Mbits CS Mode Bank Bits Row Bits Col Bits
16Mbits x 16 256 4 2 13 9 32
32Mbits x 8 256 5 2 13 10 64
32Mbits x 16 512 10 2 13 10 64
64Mbits x 8 512 6 2 14 10 128
64Mbits x 16 1024 11 3 13 10 128
Mbytes
2.2.1.2 Row and Column Addressing
Table 2-2 shows how the physical address P (after taking out the bank bit) is used to provide the row and column
addressing for each size of DDR2 memories.
Table 2-2 DDR2 Memory Row and Column Addressing
Row P10 P14 P13 P12 P11 P22 P21 P20 P19 P18 P17 P16 P15
Column - - PC - P9P8 P7P6P5P4P3 P2 P1
Row P23 P14 P13 P12 P11 P22 P21 P20 P19 P18 P17 P16 P15
Column - - PCP10P9P8P7P6P5P4P3 P2 P1
A13 A12 A11 A10 A9 A8 A7 A6 A5 A4 A3 A2 A1 A0
16Mbits x16 devices
32Mbits x8 devices
Address
42437 AMD M690T/E Databook 3.10 © 2011 Advanced Micro Devices, Inc.
2-4 Proprietary
Page 29
Side-port Memory Interface
A13 A12 A11 A10 A9 A8 A7 A6 A5 A4 A3 A2 A1 A0
Row P23 P14 P13 P12 P11 P22 P21 P20 P19 P18 P17 P16 P15
Column - - PCP10P9P8P7P6P5P4P3 P2 P1
Row
Column
Row
Column
Note: PC = precharge flag
P24 P23 P14 P13 P12 P11 P22 P21 P20 P19 P18 P17 P16 P15
- - PC P10 P9 P8 P7 P6 P5 P4 P3 P2 P1
P23 P14 P13 P12 P11 P22 P21 P20 P19 P18 P17 P16 P15
- - PC P10 P9 P8 P7 P6 P5 P4 P3 P2 P1
Address
32Mbits x16 devices
64Mbits x8 devices
64Mbits x16 devices
© 2011 Advanced Micro Devices, Inc. 42437 AMD M690T/E Databook 3.10
Proprietary 2-5
Page 30
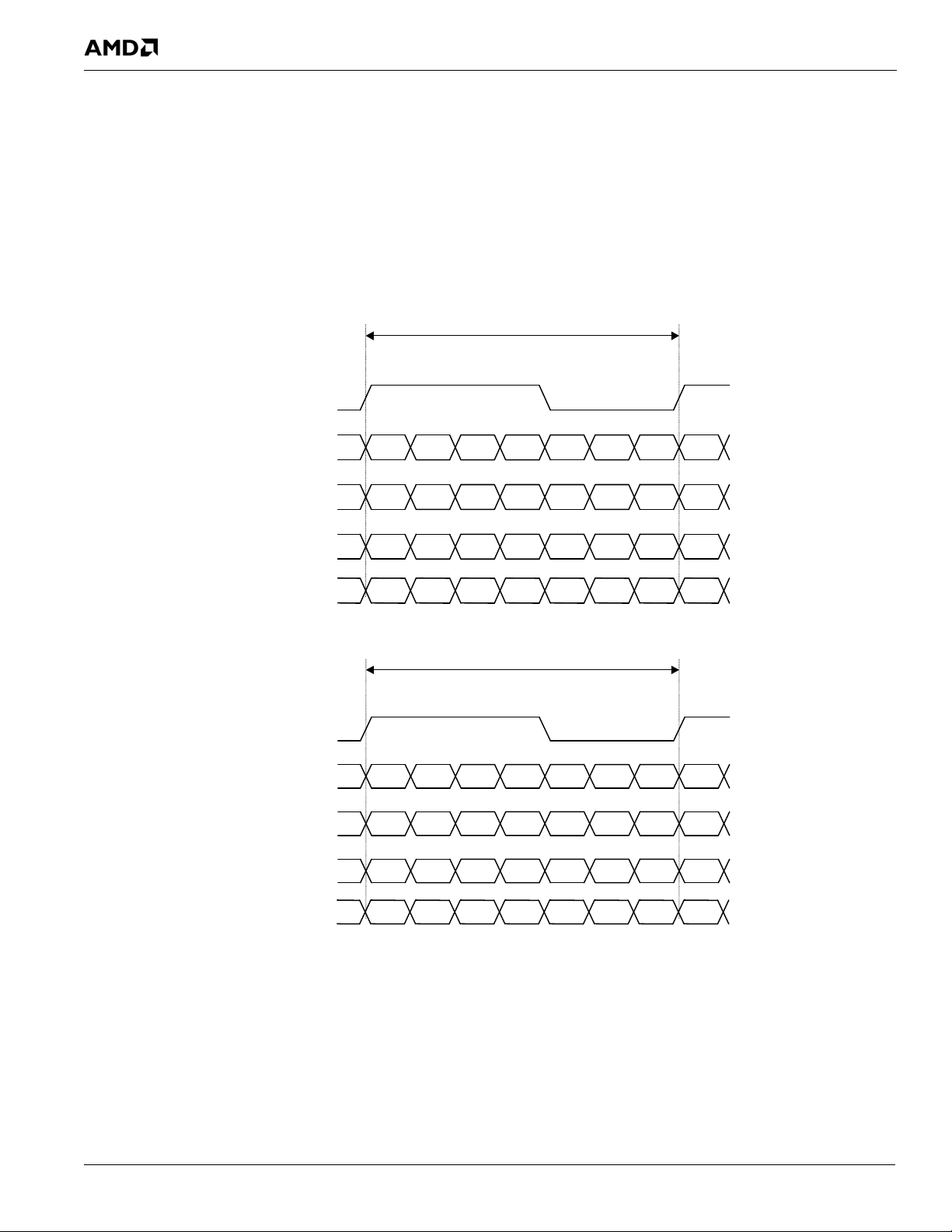
2.3 LVDS Interface
LP1C1
LP1C2LP1C3
T Cycle
LP1C4LP1C5LP1C6LP1C7
TXOUT_L0-/+
LP2C1
LP2C2LP2C3LP2C4LP2C5LP2C6LP2C7
TXOUT_L1-/+
LP3C1
LP3C2LP3C3LP3C4LP3C5LP3C6LP3C7TXOUT_L2-/+
TXCLK_L-/+
LP4C1
LP4C2LP4C3LP4C4LP4C5LP4C6LP4C7
TXOUT_L3-/+
UP1C1
UP1C2UP1C3
T Cycle
UP1C4UP1C5UP1C6UP1C7TXOUT_U0-/+
UP2C1
UP2C2UP2C3UP2C4UP2C5UP2C6UP2C7
TXOUT_U1-/+
UP3C1
UP3C2UP3C3UP3C4UP3C5UP3C6UP3C7
TXOUT_U2-/+
TXCLK_U-/+
UP4C1
UP4C2UP4C3UP4C4UP4C5UP4C6UP4C7
TXOUT_U3-/+
The M690T contains a dual-channel 24-bit LVDS interface. Notice that for designs implementing only a single LVDS
channel, the LOWER channel of the interface should be used.
2.3.1 LVDS Data Mapping
Figure 2-5 below shows the transmission ordering of the LVDS signals on the lower and the upper data channels.
The signal mappings for single and dual channel transmission are shown in Table 2-3 and Table 2-4 respectively.
LVDS Interface
Figure 2-5 Single/Dual Channel 24-bit LVDS Data Transmission Ordering
42437 AMD M690T/E Databook 3.10 © 2011 Advanced Micro Devices, Inc.
2-6 Proprietary
Page 31

LVDS Interface
Table 2-3 LVDS 24-bit TFT Single Pixel per Clock (Single Channel) Signal Mapping
TX Signal 24-bit
LP1C1 R0
LP1C2 R1
LP1C3 R2
LP1C4 R3
LP1C5 R4
LP1C6 R5
LP1C7 G0
LP2C1 G1
LP2C2 G2
LP2C3 G3
LP2C4 G4
LP2C5 G5
LP2C6 B0
LP2C7 B1
LP3C1 B2
LP3C2 B3
LP3C3 B4
LP3C4 B5
LP3C5 HSYNC
LP3C6 VSYNC
LP3C7 ENABLE
LP4C1 R6
LP4C2 R7
LP4C3 G6
LP4C4 G7
LP4C5 B6
LP4C6 B7
LP4C7 Reserved
© 2011 Advanced Micro Devices, Inc. 42437 AMD M690T/E Databook 3.10
Proprietary 2-7
Page 32

Table 2-4 LVDS 24-bit TFT Dual Pixel per Clock (Dual Channel) Signal Mapping
TX Signal 24-bit TX Signal 24-bit
LP1C1 Ro0 UP1C1 Re0
LP1C2 Ro1 UP1C2 Re1
LP1C3 Ro2 UP1C3 Re2
LP1C4 Ro3 UP1C4 Re3
LP1C5 Ro4 UP1C5 Re4
LP1C6 Ro5 UP1C6 Re5
LP1C7 Go0 UP1C7 Ge0
LP2C1 Go1 UP2C1 Ge1
LP2C2 Go2 UP2C2 Ge2
LP2C3 Go3 UP2C3 Ge3
LP2C4 Go4 UP2C4 Ge4
LP2C5 Go5 UP2C5 Ge5
LP2C6 Bo0 UP2C6 Be0
LP2C7 Bo1 UP2C7 Be1
LP3C1 Bo2 UP3C1 Be2
LP3C2 Bo3 UP3C2 Be3
LP3C3 Bo4 UP3C3 Be4
LP3C4 Bo5 UP3C4 Be5
LP3C5 HSYNC UP3C5 (from the register)
LP3C6 VSYNC UP3C6 (from the register)
LP3C7 ENABLE UP3C7 (from the register)
LP4C1 Ro6 UP4C1 Re6
LP4C2 Ro7 UP4C2 Re7
LP4C3 Go6 UP4C3 Ge6
LP4C4 Go7 UP4C4 Ge7
LP4C5 Bo6 UP4C5 Be6
LP4C6 Bo7 UP4C6 Be7
LP4C7 Reserved UP4C7 Reserved
LVDS Interface
Note: Signal names with letter 'o' mean 'odd' pixel or the first pixel on the panel, and signal names with letter 'e' mean
'even' pixel or the second pixel on the panel.
2.3.2 LVDS Spread Spectrum
The M690T has an internal LVDS spread spectrum controller capable of generating a frequency modulated profile for the
LVDS signals. The amount of spread (center spread of up to +/-2.5% and down spread of up to 5%) and the modulation
frequency (in the range of 20-50kHz) are programmable through the LVDS registers.
42437 AMD M690T/E Databook 3.10 © 2011 Advanced Micro Devices, Inc.
2-8 Proprietary
Page 33

DVI/HDMI™
TX0P
TX0M
TX1P
TX1M
TX2P
TX2M
TXCP
TXCM
TG9TG8TG7TG6TG5TG4TG3TG2TG1TG0
Depending upon state of HSYNC and VSYNC
Depending upon encoded Green channel pixel dataDepending upon state of PLL_SYNC and CTL1
Depending upon state of CTL2 and CTL3
TR1TR0 TR2 TR3 TR4 TR5 TR6 TR7 TR8 TR9
Depending upon encoded Red channel pixel data
TB0 TB1 TB2 TB3 TB4 TB5 TB6 TB7 TB8 TB9
Depending upon encoded Blue channel pixel data
Various control and audio (for HDMI™ only) signals
Various control and audio (for HDMI™ only) signals
Various control and audio (for HDMI™ only) signals
Encoded Red Channel Pixel Data
Encoded Green Channel Pixel Data
Encoded Blue Channel Pixel Data
2.4 DVI/HDMI™
2.4.1 DVI/HDMI™ Data Transmission Order and Signal Mapping
The M690T also contains a dual-link TMDS interface, multiplexed on the PCI Express® (PCIe®) graphics lanes. Figure
2-6
below shows the transmission ordering of the signals on the interface. The multiplexing relationships between the
PCIe external graphics signals and the TMDS signals are given in
PCI Express® Graphics Lanes‚’ on page 3-10
.
section 3.10, “TMDS Interface Multiplexed on the
Figure 2-6 Data Transmission Ordering for the TMDS Interface
For dual-link mode, which is for DVI only, the same transmission order applies to data channels on the second link, with
the first link transmitting data for even pixels and the second link for odd pixels. See
Mapping for DVI,” on page 2-11
The signal mapping for the transmission is shown in
2-10
, and Table 2-6, “Dual-Link Signal Mapping for DVI,” on page 2-11.
for details.
Table 2-5, “Single-Link Signal Mapping for DVI/HDMI™,” on page
Table 2-6, “Dual-Link Signal
© 2011 Advanced Micro Devices, Inc. 42437 AMD M690T/E Databook 3.10
Proprietary 2-9
Page 34

Table 2-5 Single-Link Signal Mapping for DVI/HDMI™
DVI/HDMI™
DVI/HDMI™
Functional Name
TX0M/P Phase 1 B0
TX1M/P Phase 1 G0
TX2M/P Phase 1 R0
Note: H/VSYNC are transmitted on TX0M/P(Blue) channel during blank.
Data Phase Signal
Phase 2 B1
Phase 3 B2
Phase 4 B3
Phase 5 B4
Phase 6 B5
Phase 7 B6
Phase 8 B7
Phase 9 B8
Phase 10 B9
Phase 2 G1
Phase 3 G2
Phase 4 G3
Phase 5 G4
Phase 6 G5
Phase 7 G6
Phase 8 G7
Phase 9 G8
Phase 10 G9
Phase 2 R1
Phase 3 R2
Phase 4 R3
Phase 5 R4
Phase 6 R5
Phase 7 R6
Phase 8 R7
Phase 9 R8
Phase 10 R9
42437 AMD M690T/E Databook 3.10 © 2011 Advanced Micro Devices, Inc.
2-10 Proprietary
Page 35

DVI/HDMI™
Table 2-6 Dual-Link Signal Mapping for DVI
DVI Functional
Notes:
- H/VSYNC are transmitted on TX0M/P(Blue) channel during blank.
- For DVI dual-link mode, the first active data pixel is defined as pixel#0 (an even pixel), as opposed to the DVI specifications.
Link 1 Link 2
Name
TX0M/P Phase 1 EVEN_B0 TX3M/P Phase 1 ODD_B0
TX1M/P Phase 1 EVEN_G0 TX4M/P Phase 1 ODD_G0
TX2M/P Phase 1 EVEN_R0 TX5M/P Phase 1 ODD_R0
Data Phase Signal
Phase 2 EVEN_B1 Phase 2 ODD_B1
Phase 3 EVEN_B2 Phase 3 ODD_B2
Phase 4 EVEN_B3 Phase 4 ODD_B3
Phase 5 EVEN_B4 Phase 5 ODD_B4
Phase 6 EVEN_B5 Phase 6 ODD_B5
Phase 7 EVEN_B6 Phase 7 ODD_B6
Phase 8 EVEN_B7 Phase 8 ODD_B7
Phase 9 EVEN_B8 Phase 9 ODD_B8
Phase 10 EVEN_B9 Phase 10 ODD_B9
Phase 2 EVEN_G1 Phase 2 ODD_G1
Phase 3 EVEN_G2 Phase 3 ODD_G2
Phase 4 EVEN_G3 Phase 4 ODD_G3
Phase 5 EVEN_G4 Phase 5 ODD_G4
Phase 6 EVEN_G5 Phase 6 ODD_G5
Phase 7 EVEN_G6 Phase 7 ODD_G6
Phase 8 EVEN_G7 Phase 8 ODD_G7
Phase 9 EVEN_G8 Phase 9 ODD_G8
Phase 10 EVEN_G9 Phase 10 ODD_G9
Phase 2 EVEN_R1 Phase 2 ODD_R1
Phase 3 EVEN_R2 Phase 3 ODD_R2
Phase 4 EVEN_R3 Phase 4 ODD_R3
Phase 5 EVEN_R4 Phase 5 ODD_R4
Phase 6 EVEN_R5 Phase 6 ODD_R5
Phase 7 EVEN_R6 Phase 7 ODD_R6
Phase 8 EVEN_R7 Phase 8 ODD_R7
Phase 9 EVEN_R8 Phase 9 ODD_R8
Phase 10 EVEN_R9 Phase 10 ODD_R9
DVI Functional
Name
Data Phase Signal
© 2011 Advanced Micro Devices, Inc. 42437 AMD M690T/E Databook 3.10
Proprietary 2-11
Page 36

2.4.2 Support for HDMI™ Packet Types
Table 2-7 Support for HDMI™ Packet Type
DVI/HDMI™
Packet
Value
0x00 Null Yes
0x01
0x02 Audio Sample Yes
0x03 General Control No
0x04 ACP Packet Yes* — Audio content protection information.
0x05 ISRC1 Packet Yes
0x06 ISRC2 Packet Yes
0x07 Reserved N/A N/A N/A
InfoFrame Packet Type
HDMI™ IDEIA-861B
0x80 0x00 Vendor-Specific Yes* — —
0x81 0x01 AVI Yes
0x82 0x02
0x83 0x03 Audio Yes
0x84 0x04 MPEG Source Yes
* Note: These packet types are supported using generic packet types. A maximum of two of them can be supported simultaneously.
Packet Type
Audio Clock
Regeneration
ID
Source Product
Descriptor
Supported
or Not
Yes
Yes * — —
Source Comment
Inserted by hardware if no packets in
horizontal active on line 2 (can be disabled
by software).
Inserted by hardware or video driver.
Contents from register bits or combination
of register bits and hardware control.
Inserted in horizontal blank.
Audio samples come from HD audio DMA.
Channel status from HD audio and video
registers.
Inserted in horizontal blank whenever audio
FIFO contains data.
Sending and contents controlled by video
driver.
Inserted (on even frames only in interlaced
mode) when requested by software or
whenever AVMUTE status changes.
Inserted in horizontal active on line selected
by software.
Controlled by video driver.
Inserted in horizontal active on line selected
by software.
Software controlled.
Inserted in horizontal active on line selected
by software.
Controlled by video driver.
Inserted in horizontal active on line selected
by software.
Inserted in horizontal active on line selected
by software.
Contents from registers written by video
and HD audio drivers.
Sent only when HD audio enables audio
(video driver can also disable).
Software controlled.
Inserted in horizontal active on line selected
by software.
Sent when required to meet
maximum time between data island
specification.
For transmitting UPC or ISRC codes.
Implement if ISRC1 is used.
For colorimetry, repetition count,
video format, picture formatting.
For channel counts, sampling
frequency, etc.
For bit rate, field repeat, frame type
—
—
—
42437 AMD M690T/E Databook 3.10 © 2011 Advanced Micro Devices, Inc.
2-12 Proprietary
Page 37

VGA DAC Characteristics
2.5 VGA DAC Characteristics
Table 2-8 VGA DAC Characteristics
Parameter Min Typ Max Notes
Resolution 10 bits - - 1
Maximum PS/2 setting Output Voltage - 0.7V - 1
Maximum PS/2 setting Output Current - 18.7mA - 1
Full Scale Error +8% / -3% - +10% 2, 3
DAC to DAC Correlation -2% - +2% 1, 4
Differential Linearity -2 LSB - +2 LSB 1, 5
Integral Linearity -2 LSB - +2 LSB 1, 5
Rise Time (10% to 90%) 0.58ns - 1.7ns 1, 6
Full Scale Settling Time - TBA - 1, 7, 8
Glitch Energy - TBA - 1, 8
Monotonicity - - - 9
Notes:
1 Tested over the operating temperature range at nominal supply voltage, with an Iref of -1.50mA (Iref is the level of the current flowing
out of the RSET resistor).
2 Tested over the operating temperature range at reduced supply voltage, with an Iref of -1.50mA (Iref is the level of the current flowing
out of the RSET resistor).
3 Full scale error from the value predicted by the design equations.
4 About the mid-point of the distribution of the three DACs measured at full scale deflection.
5 Linearity measured from the best fit line through the DAC characteristics. Monotonicity guaranteed.
6 Load = 37.5 + 20pF with Iref = -1.50 mA (Iref is the current flowing out of the RSET resistor).
7 Measured from the end of the overshoot to the point where the amplitude of the video ringing is down to +/-5% of the final steady state
value.
8 This parameter is sampled, not 100% tested.
9 Monotonicity is guaranteed.
2.6 External Clock Chip
On the M690T platform, an external clock chip provides the reference clock to the CPU (for generating the CPU internal
clocks) and a reference clock to the M690T (for generating the HyperTransport, PCI Express, and A-Link Express II
clocks). For more information about supported clock chips, please consult your AMD CSS representative.
© 2011 Advanced Micro Devices, Inc. 42437 AMD M690T/E Databook 3.10
Proprietary 2-13
Page 38

This page is left blank intentionally.
External Clock Chip
42437 AMD M690T/E Databook 3.10 © 2011 Advanced Micro Devices, Inc.
2-14 Proprietary
Page 39

Chapter 3
Pin Descriptions and Strap Options
This chapter gives the pin descriptions and the strap options for the M690T. To jump to a topic of interest, use the
following list of hyperlinked cross references:
“Pin Assignment” on page 3-2
“Interface Block Diagram” on page 3-4
“CPU HyperTransport™ Interface” on page 3-5
“DDR2 Side-port Memory Interface” on page 3-5
“PCI Express® Interfaces” on page 3-6:
“1 x 8 Lane Interface for External Graphics” on page 3-6
“A-Link Express II to Southbridge” on page 3-6
“4 x 1 Lane Interface for General Purpose External Devices” on page 3-6
“Miscellaneous PCI Express® Signals” on page 3-7
“Clock Interface” on page 3-7
“CRT and TV Interface” on page 3-7
“LVDS Interface (24 Bits)” on page 3-8
“DVO Interface for External Display” on page 3-9
“TMDS Interface Multiplexed on the PCI Express® Graphics Lanes” on page 3-10
“Power Management Pins” on page 3-11
“Miscellaneous Pins” on page 3-11
“Power Pins” on page 3-12
“Ground Pins” on page 3-13
“Debug Port Signals” on page 3-13
“Strapping Options” on page 3-14
© 2011 Advanced Micro Devices, Inc. 42437 AMD M690T/E Databook 3.10
Proprietary 3-1
Page 40

3.1 Pin Assignment
3.1.1 M690T Pin Assignment
Figure 3-1 and Figure 3-2 below show the pin assignment for the M690T.
The figures below only represent the relative ball positions. For the actual physical layout of the balls, please refer to
Figure 5-4, “M690T Ball Arrangement,” on page 5- 8.
12345678910111213
A
B
C
D
E
F
G
H
J
K
L
M
N
P
R
T
U
V
W
Y
AA
AB
AC
AD
AE
VSSA I2C_CLK STRP_DATA VDD_CORE DACHSYNC DACSDA VDD_CORE DFT_GPIO5 VDD_CORE PLLVDD18 PLLVDD12 LVDDR18D TXOU T_L1N
VDDA_12 BMREQ# DDC_DATA I2C_DATA ALLOW_LDTSTOP DACSCL VSS DFT_GPIO4 VDD_CORE PLLVSS OSCIN LVDDR18D TXOUT_L1P
VDDA_12 TVCLKIN TESTMODE VSS LDTSTOP# DACVSYNC DFT_GPIO3 DFT_GPIO2 VDD_CORE SYSRESET# POWERGOOD LVDDR33 LVDDR33
VDDA_12 VDDA_12 VDDA_12 VSS DFT_GPIO0 DFT_GPIO1 VDD_CORE VDDR3 LVS SR
GFX_CLKN VDDA_12 VDDA_12 VDDA_12 VDD_PLL VSS VDDR3 LVDS _D IGO N
VSSA GFX_CLKP VSSA VDDA_12 VDD_PLL VSS_P LL VSS LVDS_BLEN
SB_CLKP SB_CLKN VSSA GFX_RX0N GFX_RX0P VSSA VDDA_12 VSS_PLL VSS LVDS_BLON
VSSA GFX_TX0N VSSA VDD_CORE VSS
GFX_TX0P VSSA VSSA GFX_RX2P GFX_RX2N VSSA GFX_RX1N GFX_RX1P VDD_CORE VSS
GFX_TX1N GFX_TX1P GFX_TX2P
GFX_TX3P GFX_TX3N GFX_TX2N GFX_RX4P GFX_RX4N VSSA GFX_RX3N GFX_RX3P VDDA_12 VDD_CORE VSS VDD_CORE
VDDA_12_PKG VSSA VSSA GFX_RX6P GFX_RX6N VSSA GFX_RX5N GFX_RX5P VDDA_12 VSS VDD_CORE VSS
GFX_TX4N GFX_TX4P VSSA VDD_CORE VSS VDD_CORE
GFX_TX5N GFX_TX5P GFX_TX6P GPP_RX2P GPP_RX2N VS SA GFX _RX7N GFX_RX7P VSSA VSS VDD_CORE VSS
GFX_TX7P GFX_TX7N GFX_TX6N GPP_RX 3P GPP_RX3N VSSA GPP_RX0 P GPP_RX0N VSSA VDD_CORE VSS VDD_CORE
VSSA VSSA VSSA
GPP_TX2N GPP_TX2 P VSSA GPP_RX1P GPP_RX1N VSSA VDDA_12 VDD_CORE VDD_CORE
GPP_TX3N GPP_TX3 P GPP_TX0P SB_RX1P VSS MEM_CS#
GPP_TX1P GPP_TX1N GPP_TX0N SB_RX3P SB_RX3N VSSA VDDA_12 SB_RX1N MEM_COMPN MEM_A0
VSSA SB_TX3P SB_TX3N SB_RX2P SB_RX2N VSSA MEM_ODT MEM_COMPP VSS
SB_TX2P SB_TX2N VSSA VSSA VDD_MEM MEM_A13 MEM_A8
SB_TX1P SB_TX1N VDDA_12 VDDA_12 SB_RX0N SB_RX0P VDD_MEM MEM_A3 MEM_A2
SB_TX0P SB_TX0N VDDA_12 NC VDDA_12 VSSA VDD_MEM VDD_MEM MEM_A9 VSS MEM_BA0 VSS MEM_DQ2
VSSA VDDA_12 VDDA_12_P KG NC
VSSA VDDA_12 PCE_CALRN PCE_CALRP
12345678910111213
THERMALDIODE_
P
THERMALDIODE_
N
Pin Assignment
VDD_MEM VDD_MEM VDD_MEM MEM_A12 MEM_A1 ME M_BA2 MEM_CKE MEM_DQ0
VDD_MEM VDD_MEM VDD_MEM MEM_A7 MEM_A10 ME M_BA1 MEM_VREF MEM_DQ1
CPU Interface
A-Link Express interface
Clock Interface
Side-port Memory/DVO
CRT and TV Interface
External graphics Interface
LVDS Interface
General Purpose External Device Interface
Power Management Interface
Powers
Grounds
Others
Figure 3-1 M690T Pin Assignment (Left)
42437 AMD M690T/E Databook 3.10 © 2011 Advanced Micro Devices, Inc.
3-2 Proprietary
Page 41

Pin Assignment
14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25
LVSS R TXOUT_U0P LVSSR TXOUT_U2N TXOUT_U3P VDD_CORE AVDDDI AVD DQ AVSS Q VSS HT_RXCALP VSS A
TXOUT_L0P TXOUT_L0N TXOUT_U0N TXOUT_U2P TXOUT_ U3N VDD_CORE AVS SDI RSET AVDD HTREFCLK HTPVDD HTPVSS B
TMDS_HPD LVSSR LVSSR TXOUT_U1P TXOUT_U1N LVSS R Y C AVD D HTTSTCLK HT_RXCALN HT_TXCALP C
LPVDD TXCLK_LN TXOUT_L3P COMP VDD_CORE VDD_HT_PKG VSS HT_TXCALN VSS D
LPVSS TXCLK_LP TXOUT_L3N RED HT_TXCAD1P HT_TXCAD0P HT_TXCAD0N E
LVSS R LVS SR VSS GREEN HT_TXCAD8P HT_TXCAD8N HT_TXCAD1N HT_TXCAD2N HT_TXCAD2P F
TXOUT_L2N TXCLK_UN AV SSN BLUE VDD_CORE HT_TXCAD10N HT_TXCAD10P VSS VSS HT_TXCAD3P G
TXOUT_L2P TXCLK_UP AV SS N VSS HT_TXCAD3N VSS H
VDD_18 VDD_18 VDD_CORE HT_TXCAD9P HT_TXCAD9N VSS HT_TXCAD4P HT_TXCLK0P HT_TXCLK0N J
VSS VDD_CORE VDD_CORE HT_TXCAD11P HT_TXCAD11N VSS HT_TXCLK1P HT_TXCLK1N VSS VSS HT_TXCAD6P L
VDD_CORE VSS VSS HT_TXCAD12P HT_TXCAD12N VSS H T_TXCAD13N HT_TXCAD13P VSS HT_TXCAD6N VSS M
VSS VDD_CORE HT_TXCTLP HT_TXCAD7P HT_TXCAD7N N
VDD_CORE VSS VDD_CORE HT_TXCAD14P HT_TXCAD14N VSS HT_TXCAD15P HT_TXCAD15N HT_TXCTLN HT_RXCTLP HT_RXCTLN P
VSS VDD_CORE VSS HT_RXCAD15N HT_RXCAD15P VSS HT_RXCAD14P HT_RXCAD14N VSS VSS HT_RXCAD7N R
VDD_CORE VDD_CORE HT_RXCA D12P HT_RXCAD12N VSS HT_RXCAD13N HT_RXCAD13P HT_RXCAD5N HT_RXCAD6N HT_RXCAD6P U
VSS MEM_CKN HT_RXCAD5P HT_RXCAD4P HT_RXCAD4N V
MEM_A4 MEM_CKP VSS HT_RXCA D11P HT_RXCAD11N HT_RXCLK1P HT_RXCLK1N VSS VSS HT_RXCLK0N W
MEM_A11 MEM_CAS# IOPLLVSS HT_RXCAD8N VSS VSS HT_RXCLK0P VSS Y
VSS MEM_RAS# IOPLLVDD18 HT_RXCAD8P HT_RXCAD9N HT_RXCAD2N HT_RXCAD3N HT _RXCAD3P AA
MEM_A6 MEM_A5 IOPLLVDD12 VSS HT_RXCAD9P HT_RXCAD10N HT_RXCAD2P HT_RXCAD1P HT_RXCAD1N AB
MEM_WE# MEM_DQ4 MEM_DM0 MEM_DQ9 VSS MEM_DQ12 MEM_DQS 1N HT_RXCAD10P VSS VSS HT_RXCAD0P HT_RXCAD0N AC
MEM_DQ3 MEM_DQ5 MEM_D Q8 MEM_DQS0N MEM_DQ10 MEM_DM1 MEM_DQ14 MEM_DQS1P VDD_HT VDD_HT VDD_HT VSS AD
VSS MEM_DQ6 MEM_DQ7 MEM_DQS0P VSS MEM_DQ11 MEM_DQ13 MEM_DQ15 VDD_HT VDD_HT VDD_HT VDD_HT AE
14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25
HT_TXCAD4N HT_TXCAD5N HT_TXCAD5P K
VSS HT_RXCAD7P VSS T
CPU Interface
A-Link Express interface
Clock Interface
Side-port Memory/DVO
CRT and TV Interface
External graphics Interface
LVDS Interface
General Purpose External Device Interface
Power Management Interface
Powers
Grounds
Others
Figure 3-2 M690T Pin Assignment (Right)
© 2011 Advanced Micro Devices, Inc. 42437 AMD M690T/E Databook 3.10
Proprietary 3-3
Page 42

3.2 Interface Block Diagram
HT_RXCAD[15:0]P, HT_RXCAD[15:0]N
HT_RXCLK[1:0]P, HT_RXCLK[1:0]N
HT_RXCTLP, HT_RXCTLN
HT_TXCTLP, HT_TXCTLN
HT_RXCALP, HT_RXCALN
HT_TXCALP, HT_TXCALN
HT_TXCLK[1:0]P, HT_TXCLK[1:0]N
HT_TXCAD[15:0]P, HT_TXCAD[15:0]N
SB_TX[3:0]P, SB_TX[3:0]N
SB_RX[3:0]P, SB_RX[3:0]N
SB_CLKP, SB_CLKN
TXOUT_U0N, TXOUT_U0P
TXOUT_U1N, TXOUT_U1P
TXOUT_U2N, TXOUT_U2P
TXCLK_LN, TXCLK_LP
TXOUT_L0N, TXOUT_L0P
TXCLK_UN, TXCLK_UP
TXOUT_L1N, TXOUT_L1P
TXOUT_L2N, TXOUT_L2P
GFX_TX[7:0]P, GFX_TX[7:0]N
GFX_RX[7:0]P, GFX_RX[7:0]N
GFX_CLKP, GFX_CLKN
MEM_DM[1:0]
MEM_A[13:0]
MEM_CKE
MEM_CKP, MEM_CKN
MEM_RAS#
TESTMODE
THERMALDIDOE_N,
TVCLKIN
OSCIN
SYSRESET#
POWERGOOD
VDD_18
VDDR3
PLLVDD18
VDD_CORE
VDDA_12
MEM_CS#
C
Y
COMP
RSET
RED
GREEN
DACSCL
DACSDA
DACHSYNC
DACVSYNC
BLUE
THERMALDIODE_P
HyperTransport
Interface
LVDS
Interface
A-Link Express
Interface
Power
Management
Interface
Misc. Signals
PCIe
®
External
Graphics or
TMDS
Interface
CRT and
TV-out
Interface
Clock
Interface
Power
Side-port
Memory/DVO
VDD_HT
MEM_CAS#
LVDS_DIGON
LVDS_BLON
PCIe®
Interface
for General
Purpose
External
Devices
GPP_TX[3:0]P, GPP_TX[3:0]N
GPP_RX[3:0]P, GPP_RX[3:0]N
PCE_CALRP
Misc. PCIe®
Signals
PCE_CALRN
MEM_DQ[15:0]
HTREFCLK
LDTSTOP#
ALLOW_LDTSTOP
I2C_CLK
BMREQ#
DDC_DATA
I2C_DATA
STRP_DATA
DFT_GPIO[5:0]
TMDS_HPD
HTTSTCLK
PLLVDD12
VDD_PLL
MEM_DQS[1:0]P, MEM_DQS[1:0]N
MEM_WE#
AVDD
AVDDDI
LVDDR33
LPVDD
HTPVDD
LVDDR18D
AVDDQ
VDD_HT_PKG
VDDA_12_PKG
Grounds
MEM_ODT
MEM_COMPP, MEM_COMPN
MEM_VREF
IOPLLVDD12
IOPLLVDD18
VDD_MEM
MEM_BA[2:0]
LVDS_BLEN
VSSA
AVSSN
LPVSS
LVSSR
AVSSQ
PLLVSS
AVSSDI
VSS
VSS_PLL
HTPVSS
The figure below shows the different interfaces on the M690T. Interface names in blue are hyperlinks to the
corresponding sections in this chapter.
Interface Block Diagram
42437 AMD M690T/E Databook 3.10 © 2011 Advanced Micro Devices, Inc.
3-4 Proprietary
Figure 3-3 M690T Interface Block Diagram
Page 43

CPU HyperTransport™ Interface
3.3 CPU HyperTransport™ Interface
Table 3-1 CPU HyperTransport™ Interface
Pin Name Type
HT_RXCAD[15:0]P,
HT_RXCAD[15:0]N
HT_RXCLK[1:0]P,
HT_RXCLK[1:0]N
HT_RXCTLP,
HT_RXCTLN
HT_TXCAD[15:0]P,
HT_TXCAD[15:0]N
HT_TXCLK[1:0]P,
HT_TXCLK[1:0]N
HT_TXCTLP,
HT_TXCTLN
HT_RXCALN Other VDDHT VSS Receiver Calibration Resistor to VDD_HT power rail.
HT_RXCALP Other VDDHT VSS Receiver Calibration Resistor to Ground
HT_TXCALP Other VDDHT VSS Transmitter Calibration Resistor to HTTX_CALN
HT_TXCALN Other VDDHT VSS Transmitter Calibration Resistor to HTTX_CALP
I VDDHT VSS Receiver Command, Address, and Data Differential Pairs
I VDDHT VSS
I VDDHT VSS
O VDDHT VSS Transmitter Command, Address, and Data Differential Pairs
O VDDHT VSS
O VDDHT VSS
Power
Domain
3.4 DDR2 Side-port Memory Interface
A DVO port for supporting an external display is multiplexed with the side-port memory interface. See section 3.9, “DVO
Interface for External Display,” on page 3- 9
Table 3-2 DDR2 Side-port Memory Interface
Ground
Domain
for details.
Functional Description
Receiver Clock Signal Differential Pair. Forwarded clock signal. Each byte of
RXCAD uses a different clock signal. Data is transferred on each clock edge.
Receiver Control Differential Pair. For distinguishing control packets from data
packets.
Transmitter Clock Signal Differential Pair. Each byte of TXCAD uses a different
clock signal. Data is transferred on each clock edge.
Transmitter Control Differential Pair. Forwarded clock signal. For
distinguishing control packets from data packets.
Pin Name Type
MEM_A[13:0] O VDD_MEM VSS None
MEM_BA[2:0] O VDD_MEM VSS None Memory Bank Address
MEM_RAS# O VDD_MEM VSS None Row Address Strobe
MEM_CAS# O VDD_MEM VSS None Column Address Strobe
MEM_WE# O VDD_MEM VSS None Write Enable Strobe
MEM_CKE O VDD_MEM VSS None Clock Enable
MEM_CKP O VDD_MEM VSS None Memory Differential Positive Clock
MEM_CKN O VDD_MEM VSS None Memory Differential Negative Clock
MEM_CS# O VDD_MEM VSS None Chip Select
MEM_ODT O VDD_MEM VSS None On-die Termination
MEM_DQ[15:0] I/O VDD_MEM VSS None Memory Data Bus. Supports SSTL2 and SSTL3.
MEM_DM[1:0] I/O VDD_MEM VSS None Data masks for each byte during memory write cycles
MEM_DQS[1:0]P I/O VDD_MEM VSS None
MEM_DQS[1:0]N I/O VDD_MEM VSS None Do not connect.
Power
Domain
Ground
Domain
Integrated
Termination
Functional Description
Memory Address Bus. Provides the multiplexed row and column
addresses to the memories.
Memory Data Strobes. These are bi-directional data strobes for
latching read/write data.
© 2011 Advanced Micro Devices, Inc. 42437 AMD M690T/E Databook 3.10
Proprietary 3-5
Page 44

Table 3-2 DDR2 Side-port Memory Interface (Continued)
PCI Express® Interfaces
Pin Name Type
MEM_COMPP,
MEM_COMPN
MEM_VREF Other – VSS None
Other VDD_MEM VSS None
Power
Domain
Ground
Domain
3.5 PCI Express® Interfaces
3.5.1 1 x 8 Lane Interface for External Graphics
Table 3-3 1 x 8 Lane PCI Express® Interface for External Graphics
Pin Name Type
GFX_TX[7:0]P,
GFX_TX[7:0]N
GFX_RX[7:0]P,
GFX_RX[7:0]N
GFX_REFCLKP,
GFX_REFCLKN
O VDD_PCIE VSS_PCIE
Power
Domain
I VDD_PCIE VSS_PCIE
I VDD_PCIE VSS_PCIE
Ground
Domain
Integrated
Termination
50 between
complements
50 between
complements
50 between
complements
Integrated
Termination
Functional Description
Memory interface compensation pins for N and P channel
devices. Connect through resistors to VDD_MEM and ground
respectively (refer to the reference schematics for the proper
resistor values).
Reference voltage. It supplies the threshold value for
distinguishing between “1” and “0” on a memory signal. Typical
value is 0.5*VDD_MEM.
Functional Description
Transmit Data Differential Pairs. Connect to external connector for
an external graphics card on the motherboard (if implemented).
Receive Data Differential Pairs. Connect to external connector for an
external graphics card on the motherboard (if implemented).
Clock Differential Pairs. Connect to external clock generator when
an external graphics card is implemented.
3.5.2 A-Link Express II to Southbridge
Table 3-4 1 x 4 Lane A-Link Express II Interface for Southbridge
Pin Name Type
SB_TX[3:0]P,
SB_TX[3:0]N
SB_RX[3:0]P,
SB_RX[3:0]N
SB_CLKP,
SB_CLKN
O VDD_PCIE VSS_PCIE
Power
Domain
I VDD_PCIE VSS_PCIE
I VDD_PCIE VSS_PCIE
Ground
Domain
Integrated
Termination
50 between
complements
50 between
complements
50 between
complements
Functional Description
Transmit Data Differential Pairs. Connect to the corresponding
Receive Data Differential pairs on the Southbridge.
Receive Data Differential Pairs. Connect to the corresponding
Transmit Data Differential pairs on the Southbridge.
Clock Differential Pair. Connect to an external clock generator on
the motherboard.
3.5.3 4 x 1 Lane Interface for General Purpose External Devices
Table 3-5 4 x 1 Lane PCI Express® Interface for General Purpose External Devices
Pin Name Type
GPP_TX[3:0]P,
GPP_TX[3:0]N
GPP_RX[3:0]P,
GPP_RX[3:0]N
O VDD_PCIE VSS_PCIE
Power
Domain
I VDD_PCIE VSS_PCIE
Ground
Domain
Integrated
Termination
50 between
complements
50 between
complements
Functional Description
Transmit Data Differential Pairs. Connect to external connectors on
the motherboard for add-in card or ExpressCard support.
Receive Data Differential Pairs. Connect to external connectors on
the motherboard for add-in card or ExpressCard support.
42437 AMD M690T/E Databook 3.10 © 2011 Advanced Micro Devices, Inc.
3-6 Proprietary
Page 45

Clock Interface
3.5.4 Miscellaneous PCI Express® Signals
Table 3-6 PCI Express® Interface for Miscellaneous PCI Express® Signals
Pin Name Type
PCE_CALRN Other VDD_PCIE VSS_PCIE
PCE_CALRP Other VDD_PCIE VSS_PCIE
3.6 Clock Interface
Table 3-7 Clock Interface
Pin Name Type
TVCLKIN I VDDR3 VSS –
HTREFCLK I HTPVDD HTPVSS - HyperTransport 66MHz reference clock from external clock source
HTTSTCLK I HTPVDD HTPVSS -
GFX_REFCLKP,
GFX_REFCLKN
SB_CLKP,
SB_CLKN
OSCIN I VDDR3 VSS Disabled
Power
Domain
Power
Domain
I VDDPCIE VSSAPCIE
I VDDPCIE VSSAPCIE
Ground
Domain
Ground
Domain
Functional Description
RX Impedance Calibration. Connect to VDD_PCIE on the motherboard with an
external resistor of an appropriate value.
TX Impedance Calibration. Connect to GND on the motherboard with an external
resistor of an appropriate value.
Integrated
Termination
50 between
complements
50 between
complements
Functional Description
Input pin for reference clock for external TV-out support (3.3V
signaling). SUS_STAT# from the SB can be connected to this signal for
putting the side-port memory into self-refresh before a system warm
reset; that would allow a more graceful reset of the side-port memory
interface.
HyperTransport Bus Test Clock. Drives test clock in test mode.
Connect to ground in functional mode.
Clock Differential Pairs for external graphics. Connect to external clock
generator when an external graphics card is implemented.
Clock Differential Pair for the Southbridge and general purpose PCI
®
Express
the motherboard.
14.3181818MHz Reference clock input from the External Clock chip
(3.3 volt signaling).
(PCIe®) devices. Connect to an external clock generator on
3.7 CRT and TV Interface
Table 3-8 CRT and TV Interface
Pin Name Type
RED A-O AVDD AVSSN – Red for CRT monitor output, Cr or Pr for component video TV output
GREEN A-O AVDD AVSSN – Green for CRT monitor output, or Y for component video TV output
BLUE A-O AVDD AVSSN – Blue for CRT monitor output, Cb or Pb for component video TV output
Y A-O AVDD AVSSN – SVID luminance output for TV out, or Y for component video TV output
C A-O AVDD AV SSN –
COMP A-O AVDD AVSSN – Composite video TV output, or Pb for component video TV output
DACHSYNC A-O VDDR3 VSS
DACVSYNC A-O VDDR3 VSS
RSET Other N/A AVSSQ –
Power
Domain
© 2011 Advanced Micro Devices, Inc. 42437 AMD M690T/E Databook 3.10
Proprietary 3-7
Ground
Domain
Integrated
Termination
50k
programmable:
PU/PD/none
50k
programmable:
PU/PD/none
Functional Description
SVID chrominance output for TV out, or Pr for component video TV
output
Display Horizontal Sync
Display Vertical Sync
DAC internal reference to set full scale DAC current through 1%
resistor to AVSS
Page 46

Table 3-8 CRT and TV Interface (Continued)
LVDS Interface (24 Bits)
Pin Name Type
DACSDA I/O VDDR3 VSS
DACSCL I/O VDDR3 VSS
Power
Domain
3.8 LVDS Interface (24 Bits)
Note: For designs implementing only a single LVDS channel, the LOWER channel of the interface should be used.
Table 3-9 LVDS Interface
Pin Name Type
TXOUT_U0N O
TXOUT_U0P O
TXOUT_U1N O
TXOUT_U1P O
TXOUT_U2N O
TXOUT_U2P O
TXOUT_U3N O
TXOUT_U3P O
TXCLK_UN O
TXCLK_UP O
TXOUT_L0N O
TXOUT_L0P O
TXOUT_L1N O
TXOUT_L1P O
TXOUT_L2N O
TXOUT_L2P O
TXOUT_L3N O
TXOUT_L3P O
TXCLK_LN O
Power
Domain
LVDDR33
LVDDR18D
LVDDR33
LVDDR18D
LVDDR33
LVDDR18D
LVDDR33
LVDDR18D
LVDDR33
LVDDR18D
LVDDR33
LVDDR18D
LVDDR33
LVDDR18D
LVDDR33
LVDDR18D
LVDDR33
LVDDR18D
LVDDR33
LVDDR18D
LVDDR33
LVDDR18D
LVDDR33
LVDDR18D
LVDDR33
LVDDR18D
LVDDR33
LVDDR18D
LVDDR33
LVDDR18D
LVDDR33
LVDDR18D
LVDDR33
LVDDR18D
LVDDR33
LVDDR18D
LVDDR33
LVDDR18D
Ground
Domain
Ground
Domain
LVSSR None
LVSSR None
LVSSR None
LVSSR None
LVSSR None
LVSSR None
LVSSR None
LVSSR None
LVSSR None
LVSSR None
LVSSR None
LVSSR None
LVSSR None
LVSSR None
LVSSR None
LVSSR None
LVSSR None
LVSSR None
LVSSR None
Integrated
Termination
50k
programmable:
PU/PD/none
50k
programmable:
PU/PD/none
Integrated
Termination
Functional Description
I2C Data for display (to video monitor)
2
C Clock for display (to video monitor)
I
Functional Description
LVDS upper data channel 0 (-). Only used in dual-channel LVDS
mode.
LVDS upper data channel 0 (+). Only used in dual-channel LVDS
mode.
LVDS upper data channel 1 (-). Only used in dual-channel LVDS
mode.
LVDS upper data channel 1 (+). Only used in dual-channel LVDS
mode.
LVDS upper data channel 2 (-). Only used in dual-channel LVDS
mode.
LVDS upper data channel 2 (+). Only used in dual-channel LVDS
mode.
LVDS upper data channel 3 (-). Only used in dual-channel LVDS
mode.
LVDS upper data channel 3 (+). Only used in dual-channel LVDS
mode.
LVDS upper clock channel (-). Only used in dual-channel LVDS
mode.
LVDS upper clock channel (+). Only used in dual-channel LVDS
mode.
LVDS lower data channel 0 (-). This channel is used as the
transmitting channel in single-channel LVDS mode.
LVDS lower data channel 0 (+). This channel is used as the
transmitting channel in single-channel LVDS mode.
LVDS lower data channel 1 (-) This channel is used as the
transmitting channel in single-channel LVDS mode.
LVDS lower data channel 1 (+). This channel is used as the
transmitting channel in single-channel LVDS mode.
LVDS lower data channel 2 (-). This channel is used as the
transmitting channel in single-channel LVDS mode.
LVDS lower data channel 2 (+). This channel is used as the
transmitting channel in single-channel LVDS mode.
LVDS lower data channel 3 (-). This channel is used as the
transmitting channel in single-channel LVDS mode.
LVDS lower data channel 3 (+). This channel is used as the
transmitting channel in single-channel LVDS mode.
LVDS lower clock channel (-). This channel is used as the
transmitting channel in single-channel LVDS mode.
42437 AMD M690T/E Databook 3.10 © 2011 Advanced Micro Devices, Inc.
3-8 Proprietary
Page 47

DVO Interface for External Display
Table 3-9 LVDS Interface (Continued)
Pin Name Type
TXCLK_LP O
LVDS_BLON I/O VDDR3 VSS
LVDS_DIGON I/O VDDR3 VSS
LVDS_BLEN I/O VDDR3 VSS
Power
Domain
LVDDR33
LVDDR18D
Ground
Domain
LVSSR None
Integrated
Termination
50k
programmable:
PU/PD/none
50k
programmable:
PU/PD/none
50k
programmable:
PU/PD/none
Functional Description
LVDS lower clock channel (+). This channel is used as the
transmitting channel in single-channel LVDS mode.
Digital panel backlight brightness control. Active high. It controls
backlight on/off or acts as PWM output to adjust brightness.
If LVTMA_BL_MOD_CNTL.LVTMA_BL_MOD_EN = 0, the pin
controls backlight on/off. Otherwise, it is the PWM output to adjust
the brightness.
LVTMA_BL_MOD_CNTL.LVTMA_BL_MOD_LEVEL can be used
to control the backlight level (256 steps) by means of pulse width
modulation. The duty cycle of the backlight signal can be set
through the LVTMA_BL_MOD_CNTL.LVTMA_BL_MOD_LEVEL
bits. For example, setting these bits to a value of 32 will set the
on-time to 32/256*(1/f) and the off-time to (256-32)/256*(1/f),
where f is the XTALIN frequency and is typically 14.318MHz.
Note that the PWM frequency is set by
LVTMA_BL_MOD_CNTL.LVTMA_BL_MOD_RES and
LVTMA_PWRSEQ_REF_DIV.LVTMA_BL_MOD_REF_DIV. The
PWM frequency
= f/((BL_MOD_REF_DIV+1)*(BL_MOD_RES+1)).
For more information, refer to the Register Reference Manual.
In CPIS mode, LVDS_BLON is VARY_BL as defined in CPIS.
PWM mode should be enabled. LVDS_BLEN should be
connected to ENA_BL, which turns the backlight AC inverter
on/off.
Control Panel Digital Power On/Off. Active high.
Enables Backlight for CPIS compliant LCD panels. Active high.
Controlled by the hardware power up/down sequencer. For more
details, refer to
Timing,” on page 4- 5
Figure 4-2, “LCD Panel Power Up/Down
.
3.9 DVO Interface for External Display
The M690T provides a DVO port for supporting an external display. The external DVO port is multiplexed with the
side-port memory interface, and can only be implemented if the side-port memory interface is disabled (see
“Strapping Options,” on page 3- 14
Table 3-10 DVO Interface
Pin Name DVO Function Type Functional Description
MEM_DQ3 DVO_D0 O DVO Data for panel
MEM_DQ5 DVO_D1 O DVO Data for panel
MEM_DQ6 DVO_D2 O DVO Data for panel
MEM_DQ8 DVO_D3 O DVO Data for panel
MEM_DQ7 DVO_D4 O DVO Data for panel
MEM_DQ9 DVO_D5 O DVO Data for panel
MEM_DQ10 DVO_D6 O DVO Data for panel
MEM_DQ11 DVO_D7 O DVO Data for panel
MEM_DM1 DVO_D8 O DVO Data for panel
MEM_DQ13 DVO_D9 O DVO Data for panel
MEM_DQ14 DVO_D10 O DVO Data for panel
MEM_DQ15 DVO_D11 O DVO Data for panel
MEM_DQ2 DVO_DE O DVO Display Enable signal for panel
).
section 3.16,
© 2011 Advanced Micro Devices, Inc. 42437 AMD M690T/E Databook 3.10
Proprietary 3-9
Page 48

TMDS Interface Multiplexed on the PCI Express® Graphics Lanes
Table 3-10 DVO Interface (Continued)
Pin Name DVO Function Type Functional Description
MEM_DQ1 DVO_HSYNC O DVO Horizontal Sync signal for panel
MEM_DQ0 DVO_VSYNC O DVO Vertical Sync signal for panel
MEM_DQS0P DVO_IDCLKP* O DVO Clock Positive
MEM_DQS0N DVO_IDCLKN* O DVO Clock Negative
TMDS_HPD DVO_HPD ** I "Hot Plug" panel detection input pin that monitors if the voltage is
greater than 2.0V on the hot-plugging line.
I2C_CLK DVO_DVI_CLK I/O DDC Clock for the DVO interface
DDC_DATA DVO_DVI_DATA I/O DDC Data for the DVO interface
Notes: * The clock signal and its inverses are required for implementation of the DVO interface.
** Optional for the implementation of the DVO interface.
3.10 TMDS Interface Multiplexed on the PCI Express® Graphics Lanes
The M690T supports a dual-link TMDS interface, enabling DVI/HDMI™, which is multiplexed on the PCIe external
graphics lanes. The TMDS interface is available only if no external graphics card is attached to the PCIe graphics
interface.
HDMI is enabled only through the single-link mode.
Graphics Interface,”
shows the multiplexing relationships between the PCIe external graphics signals and the TMDS
Table 3-11, “TMDS Interface Multiplexed on the PCI Express®
signals.
Table 3-11 TMDS Interface Multiplexed on the PCI Express® Graphics Interface
Pin Name
GFX_TX0P J1 TX2P - 1st Link Red+
GFX_TX0N H2 TX2M - 1st Link Red-
GFX_TX1P K2 TX1P - 1st Link Green+
GFX_TX1N K1 TX1M - 1st Link Green-
GFX_TX2P K3 TX0P - 1st Link Blue+
GFX_TX2N L3 TX0M- 1st Link Blue -
GFX_TX3P L1 TXCP - Clock+
GFX_TX3N L2 TXCM - Clock-
GFX_TX4P N2 TX5P- 2nd Link Red+
GFX_TX4N N1 TX5M - 2nd Link Red-
GFX_TX5P P2 TX4P- 2nd Link Green+
GFX_TX5N P1 TX4M - 2nd Link Green-
GFX_TX6P P3 TX3P - 2nd Link Blue+
GFX_TX6N R3 TX3M - 2nd Link Blue-
Ball
Reference
TMDS Function
42437 AMD M690T/E Databook 3.10 © 2011 Advanced Micro Devices, Inc.
3-10 Proprietary
Page 49

Power Management Pins
3.11 Power Management Pins
Table 3-12 Power Management Pins
Pin Name Type
LDTSTOP# I VDDR3 VSS HyperTransport Stop. Input from the Southbridge to enable and disable the
ALLOW_LDTSTOP OD VDDR3 VSS Output going to the Southbridge to allow LDTSTOP assertions:
SYSRESET# I VDDR3 VSS Global Hardware Reset. This signal comes from the Southbridge.
POWERGOOD I VDDR3 VSS Input from the motherboard signifying that the power to the M690T is up and ready.
3.12 Miscellaneous Pins
Table 3-13 Miscellaneous Pins
Pin Name Type
BMREQ# O VDDR3 VSS –
DFT_GPIO[5:0] I/O VDD_18 VSS – GPIO for DFT purpose.
I2C_CLK I/O VDDR3 VSS
I2C_DATA I/O VDDR3 VSS
DDC_DATA I/O VDDR3 VSS
STRP_DATA I/O VDDR3 VSS
TESTMODE I VDDR3 VSS –
THERMALDIODE_P,
THERMALDIODE_N
TMDS_HPD I/O VDDR3 VSS
Power
Domain
Power
Domain
A-O – – –
Ground
Domain
Ground
Domain
Functional Description
HyperTransport link during system state transitions. For systems requiring power
management. Single-ended.
1 = LDTSTOP# can be asserted
0 = LDTSTOP# has to be de-asserted
Signal high means all power planes are valid. It is not observed internally until it
has been high for more than 6 consecutive REFCLK cycles. The rising edge of this
signal is deglitched. The nominal input high voltage is 3.3V.
Integrated
Termination
50k
programmable:
PU/PD/none
50k
programmable:
PU/PD/none
50k
programmable:
PU/PD/none
50k
programmable:
PU/PD/none
50k
programmable:
PU/PD/none
Functional Description
This output signal to the Southbridge indicates that there is a DMA
request from a PCI Express® Bus device. The signal is not used on
the M690T platforms and should be left unconnected.
2
I
C interface clock signal. Can also be used simultaneously as
DDC interface clock for more than one display. It can also be used
as GPIO.
2
I
C interface data signal. It can also be used as GPIO.
Pin for additional DDC data channel for displays. It makes use of
I2C_CLK to create an I
I2C interface data signal for external EEPROM based strap
loading. Can also be used as GPIO, or as output to the voltage
regulator for pulse-width modulation of M690T’s core voltage.
When high, puts the M690T in test mode and disables the M690T
from operating normally.
Diode connections to external SMBus microcontroller for
monitoring IC thermal characteristics.
TMDS Hot Plug Detect. It monitors the hot-plug line for panel
detection. It is a 3.3V CMOS compatible input. When not used for
hot plug detection, it can also be used as output to the voltage
regulator for pulse-width modulation of various voltages on the
motherboard.
2
C interface. Can also be used as GPIO.
© 2011 Advanced Micro Devices, Inc. 42437 AMD M690T/E Databook 3.10
Proprietary 3-11
Page 50

Table 3-13 Miscellaneous Pins (Continued)
Power Pins
Pin Name Type
VDD_HT_PKG Other VDD_HT VSS –
VDDA_12_PKG Other VDDA_12 VSS –
3.13 Power Pins
Table 3-14 Power Pins
Pin Name Voltage
AVDD 2.5V or 3.3V 2 B22, C22 Dedicated power for the DAC. Effort should be made at the board
AVDDQ 1.8V 1 A21 DAC Bandgap Reference Voltage
AVDDDI 1.8V 1 A20 Dedicated digital power for the DAC
VDD_CORE 1.2V 32 A19, A4, A7, A9, B19, B9,
VDD_18 1.8V 2 J14, J15 Core transform power for GPIOs and power for DFT_GPIOs
VDDA_12 1.2 V 20 AB3, AB4, AC3, AC5, AD2,
VDD_HT 1.2V 7 AAD22, AD23, AD24, AE22,
VDD_MEM 1.8V 10 AA9, AB9, AC7, AC8, AD6,
VDDR3 3.3V 2 D11, E11 I/O power for the following I/O pads:
VDD_PLL 1.2V 2 E7, F7 PCIe interface PLL power
IOPLLVDD12 1.2V 1 AB17 1.2V power for memory I/O PLLs
IOPLLVDD18 1.8V 1 AA17 1.8V power for memory I/O PLLs
LPVDD 1.8V 1 D14 Power for PLL macro.
LVDDR18D 1.8V 2 A12, B12
LVDDR33 3.3V 2 C12, C13
PLLVDD18 1.8V 1 A10 1.8V power for system PLLs
PLLVDD12 1.2V 1 A11 1.2V power for system PLLs
HTPVDD 1.8V 1 B24 Power for HyperTransport interface PLL
Total Power Pin Count 89
Power
Domain
Pin
Count
Ground
Domain
Integrated
Termination
Functional Description
The pin is for connecting a calibration resistor to the VDD_HT
power plane. The VDD_HT_PKG pin is connected to the VDD_HT
power pins via package routing, so that a calibration resistor for the
VDD_HT power plane can be connected to the M690T through the
VDD_HT_PKG pin, and the VDD_HT power plane does not have to
be extended physically for the purpose.
The pins are for connecting calibration resistors to the VDDA_12
power plane. VDDA_12_PKG pins are connected to the VDDA_12
power pins via package routing, so that the calibration resistors for
the VDDA_12 power plane can be connected to the M690T through
the VDDA_12_PKG pins, and the VDDA_12 power plane does not
have to be extended physically for the purpose.
Ball Reference Comments
level to provide as clean a power as possible to this pin to avoid
noise injection, which can affect display quality. Adequate
decoupling should be provided between this pin and AVSS.
Core power
C9, D20, D9, G20, H11, J11,
J19, L11, L13, L15, L17,
M12, M14, N11, N13, N15,
P12, P14, P17, R11, R13,
R15, U11, U12, U14, U15
®
PCIe
interface main I/O power
AE2, B1, C1, D1, D2, D3,
E2, E3, E6, F4, G7, L9, M9,
U7, W7
AE23, AE24, AE25
AD7, AD8, AE6, AE7, AE8
I/O power for HyperTransport interface
Isolated power for side-port memory/DVO and debug I/Os
POWERGOOD, SYSRESET#
42437 AMD M690T/E Databook 3.10 © 2011 Advanced Micro Devices, Inc.
3-12 Proprietary
Page 51

Ground Pins
3.14 Ground Pins
Table 3-15 Ground Pins
Pin Name Pin Count Ball Reference Comments
AVSSN 2 G17, H17 Dedicated analog ground for the DAC
AVSSQ 1 A22 Dedicated ground for the Band Gap Reference. Effort should be
AVSSDI 1 B20 Dedicated digital ground for the DAC (1.8V)
IOPLLVSS 1 Y17 Ground for system PLLs
LPVSS 1 E14 PLL macro ground pin
LVSSR 8 A14, A16, C15, C16, C19,
VSS 64 A23, A25, AA14, AB19, AC10,
VSSA 32 A1, AA3, AA7, AC6, AD1, AE1,
VSS_PLL 2 F9. G9 Ground pin for PCIe
PLLVSS 1 B10 Ground pin for graphics core PLL
HTPVSS 1 B25 Ground pin for HyperTransport interface PLL
Total Ground Pin Count 114
D12, F14, F15
AC12, AC18, AC22, AC23,
AD25, AE14, AE18, B7, C4,
D23, D25, D4, E9, F11, F17,
G11, G23, G24, H12, H23,
H25, J12, J22, L12, L14, L20,
L23, L24, M11, M13, M15,
M17, M20, M23, M25,N12,
N14, P11, P13, P15, P20, R12,
R14, R17, R20, R23, R24,
T23, T25, U20, V11, V14, W17,
W23, W24, Y12,Y22, Y23, Y25
F1, F3, G3, G6, H1, H3, J2, J3,
J6, L6, M2, M3, M6, N3, P6,
P9, R6, R9, T1, T2, T3, U3, U6,
W6, Y1, Y7
made at the board level to provide as clean a ground as possible
to this pin to avoid noise injection, which can affect display quality.
Adequate decoupling should be provided between this pin and
AVDD.
ground pin
Common ground
PCI Express
®
interface ground
®
interface PLL
3.15 Debug Port Signals
In order to fully support debugging of customer platforms, it is mandatory that customer designs allow access to the
signals listed in
For debug ports on the side-port memory signals, an acceptable implementation of an access point will be an opening in
the solder mask for the required signal traces. Adding stubs to side-port memory signals for the purpose is not
recommended. Other signals in the table should be brought out to test points on the motherboard.
Table 3-16 M690T Debug Port Signals
Pin Name Ball Ref Debug Port Name
MEM_A0 W12 Debug0
MEM_A1 AD10 Debug1
MEM_A2 AB12 Debug2
MEM_A3 AB11 Debug3
MEM_A4 W14 Debug4
MEM_A5 AB15 Debug5
MEM_A6 AB14 Debug6
© 2011 Advanced Micro Devices, Inc. 42437 AMD M690T/E Databook 3.10
Proprietary 3-13
Table 3-16, “M690T Debug Port Signals” below.
Page 52

Table 3-16 M690T Debug Port Signals (Continued)
Pin Name Ball Ref Debug Port Name
MEM_A7 AE9 Debug7
MEM_A8 AA12 Debug8
MEM_A9 AC9 Debug9
MEM_A10 AE10 Debug10
MEM_A11 Y14 Debug11
MEM_A12 AD9 Debug12
MEM_A13 AA11 Debug13
MEM_BA0 AC11 Debug14
MEM_BA1 AE11 Debug15
DFT_GPIO2 C8 Debug [programmable*]
DFT_GPIO3 C7 Debug [programmable*]
DFT_GPIO4 B8 Debug [programmable*]
DFT_GPIO5 A8 Debug [programmable*]
LVDS_BLON G12 Debug [programmable*]
LVDS_BLEN F12 Debug [programmable*]
LVDS_DIGON E12 Debug [programmable*]
TMDS_HPD C14 Debug [programmable*]
*Note: The port is programmable into any of Debug0 to Debug15.
Strapping Options
3.16 Strapping Options
The M690T provides strapping options to define specific operating parameters. The strap values are latched into internal
registers after the assertion of the POWERGOOD signal to the M690T.
shows the definitions of all the strap functions. These straps are set by one of the following four methods:
• Allowing the internal pull-up resistors to set all strap values to “1” automatically.
• Attaching pull-down resistors to specific strap pins listed in Table 3-17 to set their values to “0”.
• Downloading the strap values from an I
representative for details).
• Setting through an external debug port, if implemented (contact your AMD CSS representative for details).
All of the straps below are defined active low. They are pulled up internally by default, so that no external pull-ups are
required to select “1”s for those straps. To select “0”s, the strap pins must be pulled down to VSS through resistors.
During reset, the strap pins are undriven, allowing either an internal pull-up to pull a pin to “1” or an external pull-down to
pull a pin to “0.” The values on the strap pins are then latched into the device and used as operational parameters.
However, for debug purposes, those latched values may be overridden through an external debug strap port or by a
bit-stream downloaded from a serial EEPROM.
Table 3-17 Strap Definitions for the M690T
Strap Function Strap Pin Description
STRAP_DEBUG_BUS_EN# DFT_GPIO5 Enables debug bus output via the memory I/O pads.
GPPSB_LINK_CONFIG DFT_GPIO[4:2] Southbridge and General Purpose Link Configuration.
Table 3-17, “Strap Definitions for the M690T,”
2
C serial EEPROM (for debug purpose only; contact your AMD CSS
0: Use the memory data bus for debug bus output
1: Use default values (Default)
(See debug bus specification documents for more details.)
See Table 3-18 below for details.
42437 AMD M690T/E Databook 3.10 © 2011 Advanced Micro Devices, Inc.
3-14 Proprietary
Page 53

Strapping Options
Strap Function Strap Pin Description
LOAD_ROM_STRAPS# DFT_GPIO1 Selects loading of strap values from EEPROM
SIDE_PORT_EN# DFT_GPIO0 Indicates if memory side port is available or not
Table 3-18 Strap Definition for GPPSB_LINK_CONFIG
2
0: I
C master can load strap values from EEPROM if connected, or use default values
if not connected
1: Use default values (Default)
0: Memory side port available
1: Memory side port NOT available (Default). This is the required setting for
supporting the DVO interface.
Strap Pin Value Link Width
DFT_GPIO4 DFT_GPIO3 DFT_GPIO2 SB GPP1 GPP2 GPP3 GPP4
Use register field
111
1 1 0 40000 A
1 0 1 44000 B
1 0 0 42200 C
0 1 1 42110 D
0 1 0 41111 E
Others
Note: The three strap pins are internally pulled up so that if left unconnected on the motherboard, the
M690T will use register field STRAP_BIF_LINK_CONFIG_GPPSB of register StrapsOutputMux_7
(NBMISCIND: 0x67 bit[7:4]) to define the link configuration. The power on default value of this register
corresponds to Configuration E. If the pin straps are used, the GPPSB configuration will then be
determined according to this table and cannot be changed after the system has been powered up.
STRAP_BIF_LINK_CONFIG_GPPSB
of register StrapsOutputMux_7
(NBMISCIND: 0x67 bit[7:4]) to
define link configuration (Default).
Use register field
STRAP_BIF_LINK_CONFIG_GPPSB
of register StrapsOutputMux_7
(NBMISCIND: 0x67 bit[7:4]) to define
link configuration.
Configuration
-
-
© 2011 Advanced Micro Devices, Inc. 42437 AMD M690T/E Databook 3.10
Proprietary 3-15
Page 54

This page intentionally left blank.
Strapping Options
42437 AMD M690T/E Databook 3.10 © 2011 Advanced Micro Devices, Inc.
3-16 Proprietary
Page 55

4.1 CPU HyperTransport™ Bus Timing
For HyperTransport bus timing information, please refer to CPU specifications.
4.2 HyperTransport™ Reference Clock Timing Parameters
Table 4-1 HTREFCLK Pad (66.66MHz) Timing Parameters
Symbol Parameter Min Typ Max Unit Comment
Chapter 4
Timing Specifications
TIP REFCLK Period – 15 – ns
FIP REFCLK Frequency – 66.66 – MHz FIP is the reciprocal of TIP.
TIH REFCLK High Time 2 – – ns –
TIL REFCLK Low Time 2 – – ns –
TIR REFCLK Rise Time – – 1.5 ns –
TIF REFCLK Fall Time – – 1.5 ns –
TIJCC REFCLK Cycle-to-Cycle Jitter Requirement – – 300 ps –
TIJLT
REFCLK Long Term Jitter Requirement
(1s after scope trigger)
––1ns–
4.3 PCI Express® Differential Clock AC Specifications
Table 4-2 PCI Express® Differential Clock (GFX_CLK, SB_CLK) AC Characteristics
Parameter Minimum Maximum Unit
Absolute Minimum Differential Clock Period 9.872 – ns
Rise Time 175 700 ps
Fall time 175 700 ps
Rise/Fall Matching – 20 %
Cycle-to-Cycle Jitter – 125 ps
Duty Cycle 45 55 %
Time intervals measured at 50%
VDDCK threshold point
4.4 Side-port Memory Timing
The M690T’s side-port memory DDR2 interface complies with all the timing requirements given in the JESD79-2B
specification. Please refer to the JEDEC standard for any timing details.
4.4.1 Read Cycle DQ/DQS Delay
During a memory read cycle, there is a DLL inside the M690T that can delay each DQS signal with respect to its byte of
the DQ valid window. This delay ensures adequate setup and hold time to capture the memory data. This DLL delay is
programmable through the following registers:
MCA_DLL_SLAVE_RD_0. MCA_DLL_ADJ_DQSR_0 <NBMCIND : 0xE0[7:0]>
MCA_DLL_SLAVE_RD_1. MCA_DLL_ADJ_DQSR_1 <NBMCIND : 0xE1[7:0]>
© 2011 Advanced Micro Devices, Inc. 42437 AMD M690T/E Databook 3.10
Proprietary 4-1
Page 56

The fraction of strobe delay, in terms of a memory clock period is (24+MCA_DLL_ADJ_DQSR) / 240. For example: if
MCA_DLL_ADJ_DQSR_1 = 36, then DQS1 is delayed by 0.25 x memory_clock_period. So, if the memory clock period
is 5ns, then DQS1 is delayed internally by 1.25ns with respect to DQ[15:8].
4.4.2 Write Cycle DQ/DQS Delay
Similar to a read cycle, during memory write cycle there is a DLL inside the M690T that can delay each DQS signal with
respect to its byte of the DQ valid window. This delay ensures adequate setup and hold time for DQ and DQS to the
memory. This DLL delay is programmable by the following registers in the same manner as with the read cycle:
MCA_DLL_SLAVE_WR_0.MCA_DLL_ADJ_DQ_B0 <NBMCIND : 0xE8[7:0]>
MCA_DLL_SLAVE_WR_1.MCA_DLL_ADJ_DQ_B1 <NBMCIND : 0xE9[7:0]>
Again, the fraction of strobe delay, in terms of a memory clock period is (24+MCA_DLL_ADJ_DQSR) / 240. For
example: if MCA_DLL_ADJ_DQ_B0 = 96, then DQS0 is delayed by 0.5 x memory_clock_period. So, if the memory
clock period is 5ns, then DQS0 is delayed internally by 2.5ns with respect to DQ[7:0].
Depending on the board layout of DQS and DQ signals, it may be necessary to have different delays for each DQS signal.
Layouts of the DQS and DQ signals should follow the rules given in the
Guide.
4.5 LVDS Timing
LVDS Timing
RS690/RS485-Series IGP Motherboard Design
Table 4-3 Timing Requirements for the LVDS Interface
Differential Clock Period 11.7 – 40 ns 1
Differential Clock Frequency 25 – 85 MHz
Frequency of the LVDS PLL VOC 175 – 595 MHz
Differential Clock Cycle-to-Cycle Jitter – – 420 ps 1
Transmitter PLL Reset Time
Transmitter PLL Lock Time
Differential Low-to-High Transition Time
Differential High-to-Low Transition Time
Data Channel to Channel Skew – 100 – ps
Notes:
1 Time intervals measured at 50% LTPVDD18 threshold point.
2 Minimum time to keep LVDS_PLL_RESET asserted.
3 Measured after LVDS_PLL_RESET is de-asserted.
is the bit-time, which is 1/7 of the differential clock period.
4 T
b
4.6 OSCIN Timing
Parameter Min Ty p Max Unit Notes
10 – –
––750
0.26 –
0.26 –
0.3T
0.3T
b
b
s
s
ns 4
ns 4
1,2
1,3
Table 4-4 Timing Requirements for the OSCIN Pad
Symbol Parameter Min Typical Max Unit Note
TIP REFCLK Period 0.037 – 1.1 s1
FIP REFCLK Frequency 0.9 – 27 MHz 2
TIR REFCLK Rise Time – – 1.5 ns
TIF REFCLK Fall Time – – 1.5 ns
42437 AMD M690T/E Databook 3.10 © 2011 Advanced Micro Devices, Inc.
4-2 Proprietary
Page 57

OSCIN Timing
Table 4-4 Timing Requirements for the OSCIN Pad (Continued)
Symbol Parameter Min Typical Max Unit Note
Notes:
1 Time intervals measured at 50% threshold point.
2 FIP is the reciprocal of TIP.
3 FRQD is the tolerance of the frequency input for proper generation of the expected PLL frequencies.
TIJCC REFCLK Cycle-to-Cycle Jitter Requirement – – 300 ps
FRQD Frequency Tolerance – 30 – ppm 3
© 2011 Advanced Micro Devices, Inc. 42437 AMD M690T/E Databook 3.10
Proprietary 4-3
Page 58

4.7 Power Rail Power Up Sequence
T11
T13
T14
1.8V Memory and
Debug I/O Rails
(VDD_MEM)
T12
3.3V Rails
(VDDR3, LVDDR33, AVDD)
1.8V Display and PLL Rails
(PLLVDD18, IOPLLVDD18,
LVDDR18D, LPVDD, AVDDDI,
AVDDQ, HTPVDD, VDD_18)
1.2V PLL Rails
(PLLVDD12, IOPLLVDD12)
1.2V VDD_CORE
Power Rail Power Up Sequence
Table 4-5 M690T Power Rail Power Up Sequence Requirements
Figure 4-1 above only shows the power up sequence for the power rails that the M690T connects to. For a power up
sequence for the whole M690T platform, please refer to the
Figure 4-1 Power Rail Power Up Sequence for the M690T
Symbol Parameter
T11
T12
T13
T14
Notes:
1. Power rails in the same group may require separate power sources. Please refer to the RS690/RS485-series IGP
Motherboard Design Guide for details.
2. There are no specific requirements for the following 1.2V rails: VDD_HT, VDDA_12, and VDD_PLL.
3. For power down, the rails should either be turned off simultaneously or in the reversed order of the above power up
sequence. Variations in speeds of decay due to different capacitor discharge rates can be safely ignored.
3.3V rails ramp high relative to 1.8V
display and PLL rails
1.8V memory and debug rail ramps high
relative to VDD_CORE (1.2V)
1.8V display and PLL rails ramp high
relative to 1.2V PLL rails
1.2V PLL rails ramp high relative to
VDD_CORE (1.2V)
Voltage Difference During Ramping
Minimum (V) Maximum (V)
02.1
0 No restrictions
0 No restrictions
0 No restrictions
RS690/RS485-Series IGP Motherboard Design Guide.
42437 AMD M690T/E Databook 3.10 © 2011 Advanced Micro Devices, Inc.
4-4 Proprietary
Page 59

LCD Panel Power Up/Down Timing
LVDS_DIGON
LVDS DATA/CLOCK
LVDS_BLON
T1 T2 T3 T4
LVDS_BLEN
(CPIS)
PWM
4.8 LCD Panel Power Up/Down Timing
Table 4-6 LCD Power Up/Down Timing
*Note: Values for M, N1, N2, N3 and N4 are programmable through the following registers:
Figure 4-2. LCD Panel Power Up/Down Timing
Parameter Description Time (s)*
T1 Delay from LVDS_DIGON active to LVDS data/clock M*N1
T2 Delay from LVDS data/clock to LVDS_BLON active M*N2
T3 Delay from LVDS_BLON inactive to LVDS inactive M*N3
T4 Delay from LVDS inactive to LVDS_DIGON inactive M*N4
M = LVTMA_PWRSEQ_REF_DIV.LVTMA_PWRSEQ_REF_DIV (1- 255)
N1 = LVTMA_PWRSEQ_DELAY1.LVTMA_PWRUP_DELAY1 (0 - 15)
N2 = LVTMA_PWRSEQ_DELAY1.LVTMA_PWRUP_DELAY2 (0 - 15)
N3 = LVTMA_PWRSEQ_DELAY1.LVTMA_PWRDN_DELAY1 (0 - 15)
N4 = LVTMA_PWRSEQ_DELAY1.LVTMA_PWRDN_DELAY2 (0 - 15)
© 2011 Advanced Micro Devices, Inc. 42437 AMD M690T/E Databook 3.10
Proprietary 4-5
Page 60

This page is left blank intentionally.
LCD Panel Power Up/Down Timing
42437 AMD M690T/E Databook 3.10 © 2011 Advanced Micro Devices, Inc.
4-6 Proprietary
Page 61

Electrical Characteristics and Physical Data
5.1 Electrical Characteristics
Chapter 5
5.1.1 Maximum and Minimum Ratings
Table 5-1 Maximum and Minimum Ratings
Pin Minimum Typical Maximum Unit Comments
VDD_CORE 1.2 1.26 V ASIC core power
VDD_18 1.71 1.8 1.89 V
VDD_MEM 1.71 1.8 1.89 V
VDD_HT 1.14 1.2 1.26 V
VDDR3 3.135 3.3 3.465 V 3.3 Volt I/O power
VDDA_12 1.14 1.2 1.26 V
AVDDDI 1.71 1.8 1.89 V Digital power for DAC
AVDDQ 1.71 1.8 1.89 V
AVDD 3.135 3.3 3.465 V I/O power for DAC
LPVDD 1.71 1.8 1.89 V Power for PLL macro
LVDDR18D 1.71 1.8 1.89 V 1.8V power
LVDDR33 3.135 3.3 3.465 V 3.3V power
PLVDD12 1.14 1.2 1.26 V 1.2V power for system PLLs
PLVDD18 1.71 1.8 1.89 V 1.8V power for system PLLs
IOPLVDD12 1.14 1.2 1.26 V 1.2V power for memory I/O PLLs
IOPLVDD18 1.71 1.8 1.89 V 1.8V power for memory I/O PLLs
HTPVDD 1.71 1.8 1.89 V
Note: Numbers in this table are to be qualified.
Core transform power for GPIOs
and power for DFT_GPIOs
I/O power for the DDR
memory/DVO and debug I/Os
I/O power for HyperTransport
interface
®
PCI Express
power
Band gap reference voltage for
DAC
Power for HyperTransport
interface PLL
Interface main I/O
TM
© 2011 Advanced Micro Devices, Inc. 42437 AMD M690T/E Databook 3.10
Proprietary 5-1
Page 62

Electrical Characteristics
5.1.2 DC Characteristics
Table 5-2 DC Characteristics for 3.3V TTL Signals
Pins Symbol Description Minimum Maximum Unit
ALLOW_LDTSTOP†
BMREQ#†
DACVSYNC
DACSCL*†, DACSDA
DACHSYNC†
DDC_DATA
LVD S_DIG ON
LVDS_BLON
LVDS_BLEN
LDTSTOP#‡
OSCIN‡
I2C_DATA, I2C_CLK*
POWERGOOD‡
STRP_DATA
SYSRESET#‡
TESTMODE‡
TMDS_HPD‡
SUS_STAT#‡
Notes:
‡ Input pins. Output parameters in the table do not apply.
† Output pins. Input parameters in the table do not apply.
* DACSCL and I2C_CLK have different values for IOL and IOH:
DACSCL: IOL=14mA, IOH=5.8mA
Other numbers in this tables are applicable to the two signals.
I2C_CLK: IOL=9.5mA, IOH=3.2mA
VILdc
VIHdc
VOL Output low voltage – 0.35 V
VOH Output high voltage 2.6 – V
IOL Output low current at V=0.1V 2.3* – mA
IOH Output high current at V=VDDR-0.1V 2.2* – mA
DC voltage at PAD pin that will produce
a stable low at the Y pin of macro
DC voltage at PAD pin that will produce
a stable high at the Y pin of macro
–0.6V
1.4 – V
Table 5-3 DC Characteristics for 1.8V TTL Signals
Pins Symbol Description Minimum Maximum Unit
VILdc
VIHdc
DFT_GPIO[5:0]†
* Note: Measured with edge rate of 1s at PAD pin.
Table 5-4 DC Characteristics for the HTREFCLK Pad (66.66MHz)
VOL Output low voltage – 0.59 V
VOH Output high voltage 1.16 – V
IOL Output low current at V=0.1V 1.52 – mA
IOH Output high current at V=VDDR-0.1V 1.79 – mA
DC voltage at PAD pin that will produce
a stable low at the Y pin of macro
DC voltage at PAD pin that will produce
a stable high at the Y pin of macro
– 0.69* V
0.81* – V
Symbol Description Minimum Typical Maximum Comments
VIL Input Low Voltage – 0V 0.2V –
VIH Input High Voltage 1.4V 1.8V – –
VIMAX Maximum Input Voltage – – 2.1V –
Table 5-5 DC Characteristics for the OSCIN Pad (14.3181818MHz)
Symbol Description Minimum Typical Maximum Comments
VIL Input Low Voltage – 0V 0.6V –
VIH Input High Voltage 2.5V 2.6V – –
VIMAX Maximum Input Voltage – – 3.3V –
42437 AMD M690T/E Databook 3.10 © 2011 Advanced Micro Devices, Inc.
5-2 Proprietary
Page 63

Electrical Characteristics
Table 5-6 DC Characteristics for the DDR2 Interface
Symbol Description Minimum Maximum Comments
VIL(dc) DC Input Low Voltage -0.3V VREF-0.15V For DQ and DQS
VIH(dc) DC Input High Voltage VREF + 0.15V VDDQ + 0.3V
VIL(ac) AC Input Low Voltage – VREF - 0.31 For DQ and DQS
VIH(ac) AC Input High Voltage VREF + 0.31V – For DQ and DQS
VUSH
VOSH
VOI Output Low Voltage 0.186V 0.305V I_out = 16.5mA
VOH Output High Voltage 1.90V 2.50V I_out = -16.5mA
VREF DC Input Reference Voltage 1.125V 1.375V
ILI Input Leakage Current 10A15A
ILO Tri-state Leakage Current 10A15A
CIN Input Capacitance 3pF 5pF
Table 5-7 DC Characteristics for the TMDS Interface Multiplexed on the PCI Express® Gfx Lanes
Minimum Voltage Allowed for
Undershoot
Maximum Voltage Allowed for
Overshoot
For DQ and DQS. (VDDQ is I/O voltage
of memory device.)
- 0.3V – For DQ and DQS
– VDDQ + 0.3V
For DQ and DQS. (VDDQ is I/O voltage
of memory device.)
Symbol Parameter Minimum Typical Maximum Unit Note
VH Single-ended High Level Output Voltage AVCC - 10 – AVCC + 10 mV 1
VL Single-ended Low Level Output Voltage AVCC - 600 – AVCC - 400 mV 1
VSW Single-ended Output Swing 400 – 600 mV
VOS Differential Output Overshoot (Ringing) – – 15%*2VSW –
VUS Differential Output Undershoot (Ringing) – – 25%*2VSW –
Notes:
1 AVCC stands for the termination supply voltage of the receiver, which is 3.3V +/- 5%.
2 Figure 5-1 below illustrates some of the DC characteristics of the TMDS interface.
© 2011 Advanced Micro Devices, Inc. 42437 AMD M690T/E Databook 3.10
Proprietary 5-3
Page 64

Electrical Characteristics
VSW
VHmax
VHmin
VLmax
VLmin
2VSW
VOS
VUS
Single-ended Waveforms
Differential Waveform
VOS
VUS
Figure 5-1 DC Characteristics of the TMDS Interface
Table 5-8 Electrical Requirements for the LVDS Interface
Symbol Parameter Minimum Typical Maximum Unit Note
VCM Differential Output Common-mode Voltage 1.125 – 1.375 V 1
DVCM
VH Single-ended High Level Output Voltage VCM + 0.257 – VCM + 0.454 V 1
VL Single-ended Low Level Output Voltage VCM - 0.257 – VCM - 0.454 V 1
VSW Single-ended Output Swing 257 – 454 mV 1
VOS Differential Output Overshoot (Ringing) – – 160 mV 1
VUS Differential Output Undershoot (Ringing) – – 160 mV 1
IDDLP Average Supply Current at – 10.0 – mA 2
IDDLV Average Supply Current at – 100.0 – mA 2
IPDLP Power Down Current at – 10.0 – A3
IPDLV Power Down Current at – 10.0 – A3
Notes:
1 Differential termination is 100 ohms.
2 Measured under typical conditions, at minimum Differential Clock Frequency and maximum LVDS PLL VOC frequency.
3 Measured under typical conditions, based on typical leakage values.
4 Figure 5-2 below illustrates the DC characteristics of the LVDS interface.
Differential Output Common-mode Voltage
Ripple
– – 150 mV 1
42437 AMD M690T/E Databook 3.10 © 2011 Advanced Micro Devices, Inc.
5-4 Proprietary
Page 65

M690T Thermal Characteristics
+257 to
+454mV
-257 to
-454mV
Differential Waveform
VCM = 1.125-
Single-ended Waveforms
Ground
VSW
1.375V
VSW
0V
5.2 M690T Thermal Characteristics
This section describes some key thermal parameters of the M690T. For a detailed discussion on these parameters
and other thermal design descriptions including package level thermal data and analysis, please consult the
Design and Analysis Guidelines for the RS690 Product Family
5.2.1 M690T Thermal Limits
Table 5-9 M690T Thermal Limits
Parameter Minimum Nominal Maximum Unit Note
Operating Case Temperature 0 — 95
Absolute Rated Junction
Temperature
Storage Temperature -40 — 60
Figure 5-2 DC Characteristics of the LVDS Interface
.
— — 125
Thermal
°
C1
°
C2
°
C
© 2011 Advanced Micro Devices, Inc. 42437 AMD M690T/E Databook 3.10
Proprietary 5-5
Page 66

Table 5-9 M690T Thermal Limits (Continued)
V
K T Nln
q
--------------------------------------------
=
Parameter Minimum Nominal Maximum Unit Note
Ambient Temperature 0 — 45
Thermal Design Power — 8 — W 4
Notes:
1 - The maximum operating case temperature is the die geometric top-center temperature measured via a thermocouple based on the
methodology given in the document Thermal Design and Analysis Guidelines for the RS690 Product Family (Chapter 10). This is the
temperature at which the functionality of the chip is qualified.
2 - The maximum absolute rated junction temperature is the junction temperature at which the device can operate without causing
damage to the ASIC. This temperature can be measured via the integrated thermal diode described in the next section.
3 - The ambient temperature is defined as the temperature of the local intake air to the thermal management device. The maximum
ambient temperature is dependent on the heat sink's local ambient conditions as well as the chassis' external ambient, and the value
given here is based on AMD’s reference heat sink solution for the M690T. Refer to Chapter 7 in the Thermal Design and Analysis
Guidelines for the RS690 Product Family for heatsink and thermal design guidelines. Refer to Chapter of the above mentioned
document for details of ambient conditions.
4 - The Thermal Design Power (TDP) is defined as the worst-case power dissipation while running currently available applications at
nominal voltages and at the maximum operating temperature. Since the core power of modern ASICs using 90nm and smaller process
technology can vary significantly, parts specifically screened for higher core power were used for TDP measurement.The TDP is
intended only as a design reference. It is not an absolute maximum power under all conditions. The value shown here is a preliminary
estimate only.
5.2.2 Thermal Diode Characteristics
M690T Thermal Characteristics
°
C3
The M690T has an on-die thermal diode, with its positive and negative terminals connected to the THERMALDIODE_P
and THERMALDIODE_N pins respectively. Combined with a thermal sensor circuit, the diode temperature, and hence
the ASIC temperature, can be derived from a differential voltage reading (
V). The equation relating T to V is given
below:
where:
V = Difference of two base-to-emitter voltage readings, one using current = I and the other using current = N x I
N
= Ratio of the two thermal diode currents (=10 when using an ADI thermal sensor, e.g. ADM 1020, 1030)
= Ideality factor of the diode
K = Boltzman’s Constant
T = Temperature in Kelvin
q = Electron charge
The series resistance of the thermal diode (RT) must be taken into account as it introduces an error in the reading
(for every 1.0
induced, plus any other known fixed error. Measured values of diode ideality factor and series resistance for the
R
T
, approximately 0.8
diode circuit are defined in the
o
C is added to the reading). The sensor circuit should be calibrated to offset the
Thermal Design and Analysis Guidelines for the RS690 Product Family.
42437 AMD M690T/E Databook 3.10 © 2011 Advanced Micro Devices, Inc.
5-6 Proprietary
Page 67

Package Information
MOD-0010 Rev A
5.3 Package Information
5.3.1 Physical Dimensions
Figure 5-3 and Table 5-10 describe the physical dimensions of the M690T package. Figure 5-4 shows the detailed
ball arrangement for the M690T.
Table 5-10 M690T 465-Pin FCBGA Package Physical Dimensions
Ref. Minimum(mm) Typical(mm) Maximum(mm)
Figure 5-3 M690T Package Outline
c 0.96 1.06 1.16
A 2.18 2.33 2.48
A1 0.30 0.40 0.50
A2 0.84 0.87 0.90
b 0.40 0.50 0.60
D1 20.80 21.00 21.20
D2 - 7.33 -
D3 2.00 - -
D4 1.00 - -
E1 20.80 21.00 21.20
E2 - 6.93 -
E3 2.00 - -
E4 1.00 - -
© 2011 Advanced Micro Devices, Inc. 42437 AMD M690T/E Databook 3.10
Proprietary 5-7
Page 68

Table 5-10 M690T 465-Pin FCBGA Package Physical Dimensions (Continued)
Ref. Minimum(mm) Typical(mm) Maximum(mm)
F1 - 19.20 -
F2 - 19.20 -
e (min pitch) - 0.80 -
ddd - - 0.15
Note: Maximum height of SMT components is 0.650 mm.
Package Information
Figure 5-4 M690T Ball Arrangement
42437 AMD M690T/E Databook 3.10 © 2011 Advanced Micro Devices, Inc.
5-8 Proprietary
Page 69

Package Information
Stencil apperture
for solderballs to
be kept at the same
size as the land
pads', except for
the corner balls.
400 m maximum for
the nine corner balls'
openings
400 m maximum for
the nine corner balls'
openings
400 m maximum for
the nine corner balls'
openings
400 m maximum for
the nine corner balls'
openings
5.3.2 Pressure Specification
To avoid damages to the ASIC (die or solder ball joint cracks) caused by improper mechanical assembly of the cooling
device, follow the recommendations below:
• It is recommended that the maximum load that is evenly applied across the contact area between the thermal
management device and the die does not exceed 6 lbf. Note that a total load of 4-6 lbf is adequate to secure the
thermal management device and achieve the lowest thermal contact resistance with a temperature drop across
the thermal interface material of no more than 3°C. Also, the surface flatness of the metal spreader should be
0.001 inch/1 inch.
• Pre-test the assembly fixture with a strain gauge to make sure that the flexing of the final assembled board and
the pressure applying around the ASIC package will not exceed 600 micron strain under any circumstances.
• Ensure that any distortion (bow or twist) of the board after SMT and cooling device assembly is within industry
guidelines (IPC/EIA J-STD-001). For measurement method, refer to the industry approved technique described
in the manual IPC-TM-650, section 2.4.22.
5.3.3 Board Solder Reflow Process Recommendations
5.3.3.1 Stencil Opening Size for Solderball Pads on PCB
It is recommended that the stencil aperture for solderballs be kept at the same size as the land pads' except for the
nine pads at each corner of the ASIC package, for which a maximum size of 400µm is recommended (see
below). This recommendation is based on AMD’s sample land pattern design for the M690T, which is available
5-5
from your AMD CSS representative.
Figure
Figure 5-5 Stencil Opening Recommendations
Proprietary 5-9
© 2011 Advanced Micro Devices, Inc. 42437 AMD M690T/E Databook 3.10
Page 70

5.3.3.2 Reflow Profile
50
250
150
200
100
Peak 245°C max.
220°C
Heating Time
Solder/Part Surface Temperature ( C)
170°C
50
250
150
200
100
C max.
220 C
o
120 - 240 sec max
Heating Time
°
C
60 – 120 sec max
130 C
60 – 80 sec typical
45 – 90 sec max
60 – 80 sec typical
Pre–heating Zone
Soldering Zone
Ramp Rate < 2 C / sec
°
Ramp Rate < 2 C / sec
Soaking Zone
°
A reference reflow profile is given below. Please note the following when using RoHS/lead-free solder (SAC105/305/405
Tin-Silver-Cu):
• The final reflow temperature profile will depend on the type of solder paste and chemistry of flux used in the SMT
process. Modifications to the reference reflow profile may be required in order to accommodate the requirements of
the other components in the application.
• An oven with 10 heating zones or above is recommended.
• To ensure that the reflow profile meets the target specification on both sides of the board, a different profile and oven
recipe for the first and second reflow may be required.
• Mechanical stiffening can be used to minimize board warpage during reflow.
• It is suggested to decrease temperature cooling rate to minimize board warpage.
• This reflow profile applies only to RoHS/lead-free (high temperature) soldering process and it should not be used for
Eutectic solder packages. Damage may result if this condition is violated.
• Maximum 3 reflows are allowed on the same part.
Table 5-11 Recommended Board Solder Reflow Profile - RoHS/Lead-Free Solder
Profiling Stage Temperature Process Range
Overall Preheat Room temp to 220C 2 mins to 4 mins
Soaking Time 130C to 170C Typical 60 – 80 seconds
Liquidus 220C Typical 60 – 80 seconds
Ramp Rate Ramp up and Cooling <2C / second
Peak Max. 245C 235C +/-5C
Temperature at peak
within 5C
Package Information
240C to 245C 10 – 30 seconds
42437 AMD M690T/E Databook 3.10 © 2011 Advanced Micro Devices, Inc.
5-10 Proprietary
Figure 5-6 RoHS/Lead-Free Solder (SAC305/405 Tin-Silver-Copper) Reflow Profile
Page 71

6.1 ACPI Power Management Implementation
This chapter describes the support for ACPI power management provided by the M690T. The M690T supports ACPI
Revision 1.0b. The hardware, system BIOS, video BIOS, and drivers of the M690T have the logic needed for meeting the
power management specifications of PC2001, OnNow, and the Windows Logo Program and Device Requirements
version 2.1.
Table 6-2, “ACPI Signal Definitions,” describes the signals used in the ACPI power management scheme of the M690T.
Table 6-1 ACPI States Supported by the M690T
Graphics States:
D0 Full on, display active.
D1 Display Off. M690T power on. Configuration registers, state, and main memory contents retained.
D3 Hot Similar to D1, with additional power saving and the graphics PLLs shut off.
D3 Cold M690T power off.
Processor States:
S0/C0: Working State Working State. The processor is executing instructions.
S0/C1: Halt CPU Halt state. No instructions are executed. This state has the lowest latency on resume and contributes
S0/C2: Stop Grant
Caches Snoopable
S0/C3: Stop Grant
Caches Not Snoopable
System States:
S1: Standby
Powered On Suspend
S3: Standby
Suspend to RAM
S4: Hibernate
Suspend to Disk
S5: Soft Off System is off. OS re-boots when the system transitions to the working state.
G3: Mechanical Off Occurs when system power (AC or battery) is not present or is unable to keep the system in one of the
Table 6-1, “ACPI States Supported by the M690T,” describes the ACPI states supported by the M690T.
ACPI State Description
minimum power savings.
Stop Grant or Cache Snoopable CPU state. This state offers more power savings but has a higher latency
on resume than the C1 state.
Stop Grant or Cache not Snoopable Sleep state. The CPU’s caches maintain state but ignore any snoops.
This state offers more power savings but has a higher latency on resume than the C1 and C2 states.
System is in Standby mode. This state has low wakeup latency on resume. OEM support of this state is
optional.
System is off but context is saved to RAM. OEM support of this state is optional. System memory is put
into self-refresh.
System is off but context is saved to disk. When the system transitions to the working state, the OS is
resumed without a system re-boot.
other states.
Chapter 6
Power Management and ACPI
Note: Also supported are additional processor power states that are not part of the ACPI specification, e.g. C1E (C1
Enhanced) and C3 pop-up. Please refer to the
SB600 Databook and the RS690 Register Programming Requirements for
more information.
Table 6-2 ACPI Signal Definitions
Signal Name Description Source
ALLOW_LDTSTOP Output to the Southbridge to allow LDTSTOP# assertion. Northbridge
TM
LDTSTOP# HyperTransport
system state transitions.
POWERON# Power on Power switch
RESET# Global Reset Southbridge
Technology Stop: Enables and disables links during
Southbridge
© 2011 Advanced Micro Devices, Inc. 42437 AMD M690T/E Databook 3.10
Proprietary 6-1
Page 72

6.2 Power Management for the Graphics Controller
The M690T supports power management for the embedded graphics device as specified by the PCI Bus Power
Management Interface Specification version 1.0, according to which the integrated graphics core of the M690T qualifies
as a device embedding a single function in the power management system.
6.2.1 PCI Function Power States
There are up to four power states defined for each PCI function associated with each PCI device in the system. These
power states are D0, D1, D2 and D3. D0 (on) consumes the most power while D3 (off) consumes the least. D1 and D2
enable levels of power savings in between those of D0 and D3. The concepts of these power states are universal for all
functions in the system. When transitioned to a given power management state, the intended functional behavior is
dependent upon the type (or class) of the function.
6.2.2 PCI Power Management Interface
The four basic power management operations are:
• Capabilities Reporting
• Power Status Reporting
• Setting Power State
• System Wakeup
All four of these capabilities are required for each power management function with the exception of wakeup event
generation.
Power Management for the Graphics Controller
This section describes the format of the registers in the PCI Configuration Space that are used by these power
management operations. The Status and Capabilities Pointer (CAP_PTR) fields have been highlighted to indicate where
the PCI Power Management features appear in the standard Configuration Space Header.
Table 6-3 Standard PCI Configuration Space Header Type 0
R e g i s t e r F i e l d s ( 3 2 b i t s )
MSB LSB
Device ID Vendor ID 00h (LSB)
Status (with Bit 4 set to 1) Command 04h
Class Code Revision ID 08h
BIST Header Type Latency Timer Cache Line Size 0Ch
Base Address Registers 10h
CardBus CIS Pointer 28h
Subsystem ID Subsystem Vendor ID 2Ch
Expansion ROM Base Address 30h
Reserved CAP_PTR 34h
Reserved 38h
Max_Lat Min_Gnt Interrupt Pin Interrupt Line 3Ch
Offset
14h
18h
1Ch
20h
24h
6.2.3 Capabilities List Data Structure in PCI Configuration Space
The Capabilities bit in the PCI Status register (offset = 06h) indicates whether or not the subject function implements a
linked list of extended capabilities. Specifically, if bit 4 is set, the CAP_PTR register is implemented to give offset to the
first item in the Capabilities link list.
42437 AMD M690T/E Databook 3.10 © 2011 Advanced Micro Devices, Inc.
6-2 Proprietary
Page 73

Power Management for the Graphics Controller
Table 6-4 PCI Status Register
Bits Default Value
15:05----Refer to PCI Local Bus Specification, Revision 2.2
04 1b Read Only This bit indicates whether this function implements a list of extended capabilities
03:00 0h Read Only Reserved
Read/
Write
Description
such as PCI power management. When set, this bit indicates the presence of
Capabilities. A value of 0 implies that this function does not implement
Capabilities.
The location of the Capabilities Pointer (CAP_PTR) depends on the PCI header type. See PCI specification Revision 2.2
for specification of CAP_PTR offsets.
Table 6-5 Capabilities Pointer (CAP_PTR)
Bits Default Value
07:00 50h Read Only The CAP_PTR provides an offset in the PCI Configuration Space of the
Read/
Write
Description
function to access the location of the first item in the Capabilities linked list. The
CAP_PTR offset is DWORD aligned, so that the two least significant bits are
always zeros.
The graphics core implements extended capabilities of the AGP and Power Management. It needs to provide the
standardized register interface. The first entry in the chain of descriptors has to be the PMI descriptor, as this functionality
will be supported even if the M690T operates as a PCI device. The Capabilities Identifier for Power Management is 01h.
6.2.4 Register Block Definition
This section describes the PCI Power Management Interface registers. These registers are implemented inside the Host
Interface (HI) as part of the configuration space of the device (M690T).
Table 6-6 Power Management Register Block
Register Fields Offset
Capabilities ID 00h
Next Item Pointer 01h
Power Management Capabilities (PMC) 02h
Power Management Control/Status Register (PMCSR) 04h
Reserved 06h
The first 16 bits (Capabilities ID [offset = 0] and Next Item Pointer [offset = 1]) are used for the linked list infrastructure.
The next 32 bits (PMC [offset = 2] and PMCSR registers [offset = 4]) are required for compliance with this specification.
As with all PCI configuration registers, these registers may be accessed as bytes, 16-bit words, or 32-bit DWORDs. All of
the write operations to the reserved registers must be treated as no-ops. This implies that the access must be completed
normally on the bus and the data should be discarded. Read accesses to the reserved or the unimplemented registers must
be completed normally and a data value of 0000h should be returned.
© 2011 Advanced Micro Devices, Inc. 42437 AMD M690T/E Databook 3.10
Proprietary 6-3
Page 74

Power Management for the Graphics Controller
Table 6-7 Power Management Control/Status Register (PMCSR)
Field
Name
Power State 1:0 00b This field describes the power state of the graphics core.
Power State 15:2 00h These Read Only bits will return the clock status of each clock tree, generated inside the clock
Bits
Default
(Reset)
States Function
00 = D0 Normal operation, no power savings enabled
01 = D1 Sleeping state 1:
10 = D2 Sleeping state 2
11 = D3 Everything, except Host Interface, is turned off.
block.
The offset for each register is listed as an offset from the beginning of the linked list item that is determined either from
the CAP_PTR (if Power Management is the first item in the list) or the NEXT_ITEM_PTR of the previous item in the list.
6.2.5 Capability Identifier: Cap_ID (Offset = 0)
The Capability Identifier, when read by system software as 01h, indicates that the data structure currently being pointed to
is the PCI Power Management data structure. Each function of a PCI device may have only one item in its capability list
with Cap_ID set to 01h.
Description
Display is off
Host access to DRAM is allowed
Display is off.
All engines are off.
Graphics core does not respond to host accesses to the frame buffer.
Table 6-8 Capability Identifier (Cap_ID)
Bits Default Value
7:0 01h Read Only This field, when set to 01h, identifies the linked list item as being the PCI Power
Read/
Write
Description
Management registers
Figure 6-1, ‘Linked List for Capabilities,” shows the implementation of the capabilities list. The CAP_PTR gives the
location of the first item in the list. PCI Power Management registers have been stated as example in this list (although the
capabilities can be in any order).
• The first byte of each entry is required to be the ID of that capability. The PCI Power Management capability has an
ID of 01h.
• The next byte is a pointer giving an absolute offset in the functions PCI Configuration Space to the next item in the
list and must be DWORD aligned.
• If there are no more entries in the list, the NEXT_ITEM_PTR must be set to 0 to indicate an end of the linked list.
Each capability can then have registers following the NEXT_ITEM_PTR.
The definition of these registers (including layout, size, and bit definitions) is specific to each capability. The PCI Power
Management Register Block is defined in
Figure 6-1, ‘Linked List for Capabilities,” below.
42437 AMD M690T/E Databook 3.10 © 2011 Advanced Micro Devices, Inc.
6-4 Proprietary
Page 75

Power Management for the Graphics Controller
Cap_Ptr = 50h
8 bits
PCI Configuration Header
Offset 34h
025Ch
AGP Capability
0100h
PM Registers
Offset 5Ch
Offset 50h
Figure 6-1 Linked List for Capabilities
6.2.6 Next Item Pointer
The Next Item Pointer register describes the location of the next item in the capability list of the function. The value given
is an offset in the PCI Configuration Space of that function. This register must be set to 00h if the function does not
implement any other capabilities defined by the PCI Specifications for inclusion in the capabilities list, or if power
management is the last item in the list.
Table 6-9 Next Item Pointer (NEXT_ITEM_PTR)
Bits
7:0 80h Read Only This field provides an offset in the PCI Configuration Space of the function pointing to the location
Default
Value
6.2.7 PMC - Power Management Capabilities (Offset = 2)
The Power Management Capabilities register is a 16-bit Read Only register that provides information on the capabilities
of the function related to power management. The information in this register is generally static and is known at design
time.
Table 6-10 Power Management Capabilities – PMC
Bits Default Value
15:11 00111b Read Only This 5-bit field indicates the power states in which the function may assert PME#. A value of
10 1b Read Only M690T supports D2.
Read/
Write
Read/
Write
Description
of next item in the capability list of the function. For Power Management of the M690T, this
pointer is set to 80h and it points to the next capability pointer of the MSI structure.
Description
0b for any bit indicates that the function is not capable of asserting the PME# signal while in
that power state.
bit(11) XXXX1b - PME# can be asserted from D0.
bit(12) XXX1Xb - PME# can be asserted from D1.
bit(13) XX1XXb - PME# can be asserted from D2.
bit(14) X0XXXb - PME# cannot be asserted from D3hot.
bit(15) 0XXXXb - PME# cannot be asserted from D3cold.
© 2011 Advanced Micro Devices, Inc. 42437 AMD M690T/E Databook 3.10
Proprietary 6-5
Page 76

Power Management for the Graphics Controller
Table 6-10 Power Management Capabilities – PMC (Continued)
Bits Default Value
9 1b Read Only M690T supports D1.
8:6 000b Read Only Reserved
5 1b Read Only The Device Specific Initialization bit indicates whether special initialization of this function is
4 0b Read Only Reserved
3 0b Read Only Reserved
2:0 001b Read Only A value of 001b indicates that this function complies with Revision 1.0 of the PCI Power
Read/
Write
Description
required (beyond the standard PCI configuration header) before the generic class device
driver is able to use it. The M690T requires device specific initialization after Reset; this field
must therefore return a value 1 to the system.
Management Interface Specification.
42437 AMD M690T/E Databook 3.10 © 2011 Advanced Micro Devices, Inc.
6-6 Proprietary
Page 77

7.1 Test Capability Features
XOR Start Signal
1
2
3
4
5
6
A
The M690T has integrated test modes and capabilities. These test features cover both the ASIC and board level testing.
The ASIC tests provide a high fault coverage and low DPM (Defect Per Million) ratio of the part. The board level tests
modes can be used for motherboard manufacturing and debug purposes. The following are the test modes of the M690T:
• Full scan implementation on the digital core logic that provides fault coverage through ATPG (Automatic Test Pattern
Generation Vectors).
• Test logic for the on-chip custom memory macros to provide complete coverage on these modules.
• Access to the analog modules and PLLs in the M690T to allow full evaluation and characterization of these modules.
• A JTAG test mode (which is not entirely compliant to the IEEE 1149.1 standard) to allow board level testing of
neighboring devices.
• An XOR TREE test mode on all the digital I/Os to allow for soldering verification at the board level.
• A VOH/VOL test mode on all digital I/Os to allow for verification of output high and output low voltages at the
board level.
These test modes can be accessed through the settings on the instruction register of the JTAG circuitry.
7.2 Test Interface
Table 7-1 Pins on the Test Interface
Chapter 7
Testability
Pin Name Ball number Type Description
TESTMODE C3 I IEEE 1149.1 test port reset
DDC_DATA B3 I TMS: Test Mode Select (IEEE 1149.1 test mode select)
I2C_DATA B4 I TDI: Test Mode Data In (IEEE 1149.1 data in)
I2C_CLK A2 I TCLK: Test Mode Clock (IEEE 1149.1 clock)
TMDS_HPD C14 O TDO: Test Mode Data Out (IEEE 1149.1 data out)
POWERGOOD C11 I I/O Reset
OSCIN B11 I I/O Test Clock
7.3 XOR Tree
7.3.1 Brief Description of an XOR Tree
An example of a generic XOR tree is shown in the Figure 7-1 below.
Figure 7-1 An Example of a Generic XOR Tree
Pin A is assigned to the output direction, and pins 1 through 6 are assigned to the input direction. It can be seen that after
© 2011 Advanced Micro Devices, Inc. 42437 AMD M690T/E Databook 3.10
Proprietary 7-1
Page 78

all pins 1 to 6 are assigned to logic 0 or 1, a logic change in any one of these pins will toggle the output pin A.
XOR Tree
The following is the truth table for the XOR tree shown in
Table 7-2 Example of an XOR Tree
Test Vector
number
10000001
21000000
31100001
41110000
51111001
61111100
71111111
Input Pin 1 Input Pin 2 Input Pin 3 Input Pin 4 Input Pin 5 Input Pin 6 Output Pin A
7.3.2 Description of the XOR Tree for the M690T
The XOR start signal is applied at the TDI pin of the JTAG circuitry and the output of the XOR tree is obtained at the
TDO pin. Refer to
Section 7.3.4 for the list of the signals included on the XOR tree. There is no specific connection order
to the signals on the tree. A toggle of any of these balls in the XOR tree will cause the output to toggle.
7.3.3 XOR Tree Activation
The M690T chip enters the XOR tree test mode by means of the JTAG. First, the 8-bit instruction register of the JTAG is
loaded with the XOR instruction (“00001000”). This instruction assigns the input direction to all the pins except pin TDO,
which is assigned the output direction to serve as the output of the XOR tree. After loading, the JTAG is taken to the
Run-Test state for completion of the XOR tree initialization.
Figure 7-1 The XOR start signal is assumed to be logic 1.
Note: 10MHz clock frequency is recommended for the XOR TREE test mode.
7.3.4 XOR Chain for the M690T
When the XOR tree is activated, any pin on the XOR tree must be either pulled down or pulled up to the I/O voltage of the
pin. Only pins that are
When differential signal pairs are listed as single entries on the XOR tree, opposite input values should be applied to the
two signals in each pair (e.g., for entry no. 13 on the tree, when “1” is applied to HT_RXCAD15P, “0” should be applied
to HT_RXCAD15N).
Table 7-3 M690T XOR Tree
No. Pin Name Ball Ref.
1 LVDS_BLON G12
2 LVDS_BLEN F12
3 LVDS_DIGON E12
4 DACVSYNC C6
5 DACHSYNC A5
6 DACSCL B6
7DFT_GPIO0 D6
8DFT_GPIO1 D7
not on the XOR tree can be left floating.
No. Pin Name Ball Ref.
9DFT_GPIO2 C8
10 DFT_GPIO3 C7
11 D FT_GP IO4 B8
12 DFT_GPIO5 A8
13 HT_RXCAD15N/P R18/R19
14 HT_RXCAD14N/P R22/R21
15 HT_RXCAD13N/P U21/U22
16 HT_RXCAD12N/P U19/U18
42437 AMD M690T/E Databook 3.10 © 2011 Advanced Micro Devices, Inc.
7-2 Proprietary
Page 79

XOR Tree
No. Pin Name Ball Ref.
17 HT_RXCAD11N/P W20/W19
18 HT_RXCAD10N/P AB22/AC21
19 HT_RXCAD9N/P AA20/AB20
20 HT_RXCAD8N/P Y19/AA19
21 HT_RXCAD7N/P R25/T24
22 HT_RXCAD6N/P U24/U25
23 HT_RXCAD5N/P U23/V23
24 HT_RXCAD4N/P V25/V24
25 HT_RXCAD3N/P AA24/AA25
26 HT_RXCAD2N/P AA23/AB23
27 HT_RXCAD1N/P AB25/AB24
28 HT_RXCAD0N/P AC25/AC24
29 HT_RXCTLN/P P25/P24
30 HT_RXCLK1N/P W22/W21
31 HT_RXCLK0N/P W25/Y24
32 GPP_RX3N/P R5/R4
No. Pin Name Ball Ref.
53 MEM_DQ12 AC19
54 MEM_DQ11 AE19
55 MEM_DQ10 AD18
56 MEM_DQ9 AC17
57 MEM_DQ8 AD16
58 MEM_DQ7 AE16
59 MEM_DQ6 AE15
60 MEM_DQ5 AD15
61 MEM_DQ4 AC15
62 MEM_DQ3 AD14
63 MEM_DQ2 AC13
64 MEM_DQ1 AE13
65 MEM_DQ0 AD13
66 MEM_DM1 AD19
67 MEM_DM0 AC16
68 MEM_A13 AA11
33 GPP_RX2N/P P5/P4
34 GPP_RX1N/P U5/U4
35 GPP_RX0N/P R8/R7
36 SB_RX3N/P W5/W4
37 SB_RX2N/P Y5/Y4
38 SB_RX1N/P W9/V9
39 SB_RX0N/P AB6/AB7
40 GFX_RX7N/P P7/P8
41 GFX_RX6N/P M5/M4
42 GFX_RX5N/P M7/M8
43 GFX_RX4N/P L5/L4
44 GFX_RX3N/P L7/L8
45 GFX_RX2N/P J5/J4
46 GFX_RX1N/P J7/J8
47 GFX_RX0N/P G4/G5
48 MEM_DQS1N/P AC20/AD21
49 MEM_DQS0N/P AD17/AE17
69 MEM_A12 AD9
70 MEM_A11 Y14
71 MEM_A10 AE10
72 MEM_A9 AC9
73 MEM_A8 AA12
74 MEM_A7 AE9
75 MEM_A6 AB14
76 MEM_A5 AB15
77 MEM_A4 W14
78 MEM_A3 AB11
79 MEM_A2 AB12
80 MEM_A1 AD10
81 MEM_A0 W12
82 MEM_BA2 AD11
83 MEM_BA1 AE11
84 MEM_BA0 AC11
85 MEM_CAS# Y15
50 MEM_DQ15 AE21
51 MEM_DQ14 AD20
52 MEM_DQ13 AE20
86 MEM_RAS# AA15
87 MEM_WE# AC14
88 MEM_ODT Y9
© 2011 Advanced Micro Devices, Inc. 42437 AMD M690T/E Databook 3.10
Proprietary 7-3
Page 80

No. Pin Name Ball Ref.
1
6
5
4
3
2
VOH/VOL
mode
TEST_ODD
TEST_EVEN
89 MEM_CS# V12
90 MEM_CKE AD12
91 MEM_CKN/P V15/W15
7.4 VOH/VOL Test
7.4.1 Brief Description of a VOH/VOL Tree
The VOH/VOL logic gives signal output on I/Os when test patterns are applied through the TEST_ODD and
TEST_EVEN inputs. Sample of a generic VOH/VOL tree is shown in the
VOH/VOL Test
Figure 7-2 below.
Figure 7-2 Sample of a Generic VOH/VOL Tree
The following is the truth table for the above VOH/VOL tree.
Table 7-4 Truth Table for the VOH/VOL Tree Outputs
Test Vector
Number
1 0 0 000000
2 0 1 010101
3 1 0 101010
4 1 1 111111
Refer to
TEST_ODD
Input
TEST_EVEN
Input
Output
Pin 1
Output
Pin 2
Output
Pin 3
Output
Pin 4
Output
Pin 5
Output
Pin 6
Table 7.4.3, “VOH/VOL Pin List,” on page 7-5 for the list of pins that are on the VOH/VOL tree.
7.4.2 VOH/VOL Tree Activation
To activate the VOH/VOL tree and run a VOH/VOL test, perform the sequence below:
1. Supply a clock at any speed (same or faster than test pattern data rate) to the OSCIN pin as the I/O test clock source.
42437 AMD M690T/E Databook 3.10 © 2011 Advanced Micro Devices, Inc.
7-4 Proprietary
Page 81

VOH/VOL Test
2. Set POWERGOOD to 0.
3. Set TESTMODE to 1.
4. Set DACSDA to 0.
5. Load JTAG instruction register with the instruction 0110 0011.
6. Load JTAG instruction register with the instruction 0010 0111.
7. Set POWERGOOD to 1.
8. Load JTAG instruction register with the instruction 1001 1001.
9. Run test by loading JTAG data register with data 0000 0000 0000 00xy, where bit x is the input value for
TEST_ODD and bit y that for TEST_EVEN (see Table 7-4 above).
10. To end test, load JTAG instruction register with the instruction 0101 1101.
7.4.3 VOH/VOL Pin List
Table 7-5 below shows the M690T VOH/VOL tree. There is no specific order of connection. Under the Control column,
an “ODD” or “EVEN” indicates that the logical output of the pin is same as the “TEST_ODD” or “TEST_EVEN” input
respectively.
When a differential pair appear in the table as a single entry, the output of the positive (“P”) pin is indicated in the Control
column (see last paragraph for explanations), and the output of the negative pin (“N”) will be of the opposite value. E.g.,
for entry no. 1 on the tree, when TEST_EVEN is 1, HT_TXCAD15P will give a value of 1 and HT_TXCAD15N will give
a value of 0.
Table 7-5 M690T VOH/VOL Tree
No. Pin Name Ball Ref. Control
No. Pin Name Ball Ref. Control
1 HT_TXCAD15P/N P21/P22 EVEN
2 HT_TXCAD14P/N P18/P19 ODD
3 HT_TXCAD13P/N M22/M21 EVEN
4 HT_TXCAD12P/N M18/M19 ODD
5 HT_TXCAD11P/N L18/L19 EVEN
6 HT_TXCAD10P/N G22/G21 ODD
7 HT_TXCAD9P/N J20/J21 EVEN
8 HT_TXCAD8P/N F21/F22 ODD
9 HT_TXCTLP/N N23/P23 EVEN
10 HT_TXCAD7P/N N24/N25 ODD
11 HT_TXCAD6P/N L25/M24 EVEN
12 HT_TXCAD5P/N K25/K24 ODD
13 HT_TXCAD4P/N J23/K23 EVEN
14 HT_TXCAD3P/N G25/H24 ODD
15 HT_TXCAD2P/N F25/F24 EVEN
16 HT_TXCAD1P/N E23/F23 ODD
17 HT_TXCAD0P/N E24/E25 EVEN
18 DACSCL B6 ODD
19 DACVSYNC C6 EVEN
20 DACHSYNC A5 ODD
21 LVDS_BLON G12 EVEN
22 LVDS_BLEN F12 ODD
23 LVDS_DIGON E12 EVEN
24 DFT_GPIO5 A8 ODD
25 DFT_GPIO4 B8 EVEN
26 DFT_GPIO3 C7 ODD
27 DFT_GPIO2 C8 EVEN
28 DFT_GPIO1 D7 ODD
29 DFT_GPIO0 D6 EVEN
30 SB_TX3P/N Y2/Y3 ODD
© 2011 Advanced Micro Devices, Inc. 42437 AMD M690T/E Databook 3.10
Proprietary 7-5
Page 82

VOH/VOL Test
No. Pin Name Ball Ref. Control
31 SB_TX2P/N AA1/AA2 EVEN
32 SB_TX1P/N AB1/AB2 ODD
33 SB_TX0P/N AC1/AC2 EVEN
34 GPP_TX3P/N V2/V1 ODD
35 GPP_TX2P/N U2/U1 EVEN
36 GPP_TX1P/N W1/W2 ODD
37 GPP_TX0P/N V3/W3 EVEN
38 GFX_TX7P/N R1/R2 ODD
39 GFX_TX6P/N P3/R3 EVEN
40 GFX_TX5P/N P2/P1 ODD
41 GFX_TX4P/N N2/N1 EVEN
42 GFX_TX3P/N L1/L2 ODD
43 GFX_TX2P/N K3/L3 EVEN
44 GFX_TX1P/N K2/K1 ODD
45 GFX_TX0P/N J1/H2 EVEN
46 MEM_DQS1P AD21 ODD
No. Pin Name Ball Ref. Control
67 MEM_DM1 AD19 EVEN
68 MEM_DM0 AC16 ODD
69 MEM_A13 AA11 EVEN
70 MEM_A12 AD9 ODD
71 MEM_A11 Y14 EVEN
72 MEM_A10 AE10 ODD
73 MEM_A9 AC9 EVEN
74 MEM_A8 AA12 ODD
75 MEM_A7 AE9 EVEN
76 MEM_A6 AB14 ODD
77 MEM_A5 AB15 EVEN
78 MEM_A4 W14 ODD
79 MEM_A3 AB11 EVEN
80 MEM_A2 AB12 ODD
81 MEM_A1 AD10 EVEN
82 MEM_A0 W12 ODD
47 MEM_DQS1N AC20 EVEN
48 MEM_DQS0N AD17 ODD
49 MEM_DQS0P AE17 EVEN
50 MEM_DQ12 AC19 ODD
51 MEM_DQ15 AE21 EVEN
52 MEM_DQ11 AE19 ODD
53 MEM_DQ14 AD20 EVEN
54 MEM_CS# V12 ODD
55 MEM_DQ13 AE20 EVEN
56 MEM_DQ10 AD18 ODD
57 MEM_DQ9 AC17 EVEN
58 MEM_DQ8 AD16 ODD
59 MEM_DQ7 AE16 EVEN
60 MEM_DQ6 AE15 ODD
61 MEM_DQ5 AD15 EVEN
62 MEM_DQ2 AC13 ODD
63 MEM_DQ4 AC15 EVEN
83 MEM_BA2 AD11 EVEN
84 MEM_BA1 AE11 ODD
85 MEM_BA0 AC11 EVEN
86 MEM_CAS# Y15 ODD
87 MEM_RAS# AA15 EVEN
88 MEM_WE# AC14 ODD
89 MEM_ODT Y9 EVEN
90 MEM_CKE AD12 ODD
91 MEM_CKP/N W15/V15 EVEN
64 MEM_DQ1 AE13 ODD
65 MEM_DQ3 AD14 EVEN
66 MEM_DQ0 AD13 ODD
42437 AMD M690T/E Databook 3.10 © 2011 Advanced Micro Devices, Inc.
7-6 Proprietary
Page 83

Appendix A
Pin Listings
This appendix contains pin listings for the M690T sorted in different ways. To go to the listing of interest, use the linked
cross-references below:
“M690T Pin List Sorted by Ball Reference” on page A-2
“M690T Pin List Sorted by Pin Name” on page A-6
© 2011 Advanced Micro Devices, Inc. 42437 AMD M690T/E Databook 3.10
Proprietary A-1
Page 84

A.1 M690T Pin List Sorted by Ball Reference
Table A-1 M690T Pin List Sorted by Ball Reference
Ball
Ref.
A1 VSSA
A10 PLLVDD18
A11 PLLVDD12
A12 LVDDR18D
A13 TXOUT_L1N
A14 LVSSR
A15 TXOUT_U0P
A16 LVSSR
A17 TXOUT_U2N
A18 TXOUT_U3P
A19 VDD_CORE
A2 I2C_CLK
A20 AVDDDI
A21 AVDDQ
A22 AVSSQ
A23 VSS
A24 HT_RXCALP
A25 VSS
A3 STRP_DATA
A4 VDD_CORE
A5 DACHSYNC
A6 DACSDA
A7 VDD_CORE
A8 DFT_GPIO5
A9 VDD_CORE
AA1 SB_TX2P
AA11 MEM_A13
AA12 MEM_A8
AA14 VSS
AA15 MEM_RAS#
AA17 IOPLLVDD18
AA19 HT_RXCAD8P
AA2 SB_TX2N
AA20 HT_RXCAD9N
AA23 HT_RXCAD2N
AA24 HT_RXCAD3N
AA25 HT_RXCAD3P
AA3 VSSA
AA7 VSSA
AA9 VDD_MEM
AB1 SB_TX1P
Pin Name
Ball
Ref.
AB11 MEM_A3
AB12 MEM_A2
AB14 MEM_A6
AB15 MEM_A5
AB17 IOPLLVDD12
AB19 VSS
AB2 SB_TX1N
AB20 HT_RXCAD9P
AB22 HT_RXCAD10N
AB23 HT_RXCAD2P
AB24 HT_RXCAD1P
AB25 HT_RXCAD1N
AB3 VDDA_12
AB4 VDDA_12
AB6 SB_RX0N
AB7 SB_RX0P
AB9 VDD_MEM
AC1 SB_TX0P
AC10 VSS
AC11 MEM_BA0
AC12 VSS
AC13 MEM_DQ2
AC14 MEM_WE#
AC15 MEM_DQ4
AC16 MEM_DM0
AC17 MEM_DQ9
AC18 VSS
AC19 MEM_DQ12
AC2 SB_TX0N
AC20 MEM_DQS1N
AC21 HT_RXCAD10P
AC22 VSS
AC23 VSS
AC24 HT_RXCAD0P
AC25 HT_RXCAD0N
AC3 VDDA_12
AC4 NC
AC5 VDDA_12
AC6 VSSA
AC7 VDD_MEM
AC8 VDD_MEM
Pin Name
Ball
Ref.
AC9 MEM_A9
AD1 VSSA
AD10 MEM_A1
AD11 MEM_BA2
AD12 MEM_CKE
AD13 MEM_DQ0
AD14 MEM_DQ3
AD15 MEM_DQ5
AD16 MEM_DQ8
AD17 MEM_DQS0N
AD18 MEM_DQ10
AD19 MEM_DM1
AD2 VDDA_12
AD20 MEM_DQ14
AD21 MEM_DQS1P
AD22 VDD_HT
AD23 VDD_HT
AD24 VDD_HT
AD25 VSS
AD3 VDDA_12_PKG
AD4 NC
AD5 THERMALDIODE_P
AD6 VDD_MEM
AD7 VDD_MEM
AD8 VDD_MEM
AD9 MEM_A12
AE1 VSSA
AE10 MEM_A10
AE11 MEM_BA1
AE12 MEM_VREF
AE13 MEM_DQ1
AE14 VSS
AE15 MEM_DQ6
AE16 MEM_DQ7
AE17 MEM_DQS0P
AE18 VSS
AE19 MEM_DQ11
AE2 VDDA_12
AE20 MEM_DQ13
AE21 MEM_DQ15
AE22 VDD_HT
Pin Name
42437 AMD M690T/E Databook 3.10 © 2011 Advanced Micro Devices, Inc.
A-2 Proprietary
Page 85

Ball
Ref.
AE23 VDD_HT
AE24 VDD_HT
AE25 VDD_HT
AE3 PCE_CALRN
AE4 PCE_CALRP
AE5 THERMALDIODE_N
AE6 VDD_MEM
AE7 VDD_MEM
AE8 VDD_MEM
AE9 MEM_A7
B1 VDDA_12
B10 PLLVSS
B11 OSCIN
B12 LVDDR18D
B13 TXOUT_L1P
B14 TXOUT_L0P
B15 TXOUT_L0N
B16 TXOUT_U0N
B17 TXOUT_U2P
B18 TXOUT_U3N
B19 VDD_CORE
B2 BMREQ#
B20 AVSSDI
B21 RSET
B22 AVDD
B23 HTREFCLK
B24 HTPVDD
B25 HTPVSS
B3 DDC_DATA
B4 I2C_DATA
B5 ALLOW_LDTSTOP
B6 DACSCL
B7 VSS
B8 DFT_GPIO4
B9 VDD_CORE
C1 VDDA_12
C10 SYSRESET#
C11 POWERGOOD
C12 LVDDR33
C13 LVDDR33
C14 TMDS_HPD
C15 LVSSR
C16 LVSSR
Pin Name
Ball
Ref.
C17 TXOUT_U1P
C18 TXOUT_U1N
C19 LVSSR
C2 TVCLKIN
C20 Y
C21 C
C22 AVDD
C23 HTTSTCLK
C24 HT_RXCALN
C25 HT_TXCALP
C3 TESTMODE
C4 VSS
C5 LDTSTOP#
C6 DACVSYNC
C7 DFT_GPIO3
C8 DFT_GPIO2
C9 VDD_CORE
D1 VDDA_12
D11 VDDR3
D12 LVSSR
D14 LPVDD
D15 TXCLK_LN
D17 TXOUT_L3P
D19 COMP
D2 VDDA_12
D20 VDD_CORE
D22 VDD_HT_PKG
D23 VSS
D24 HT_TXCALN
D25 VSS
D3 VDDA_12
D4 VSS
D6 DFT_GPIO0
D7 DFT_GPIO1
D9 VDD_CORE
E1 GFX_CLKN
E11 VDDR3
E12 LVDS_DIGON
E14 LPVSS
E15 TXCLK_LP
E17 TXOUT_L3N
E19 RED
E2 VDDA_12
Pin Name
Ball
Ref.
E23 HT_TXCAD1P
E24 HT_TXCAD0P
E25 HT_TXCAD0N
E3 VDDA_12
E6 VDDA_12
E7 VDD_PLL
E9 VSS
F1 VSSA
F11 VSS
F12 LVDS_BLEN
F14 LVSSR
F15 LVSSR
F17 VSS
F19 GREEN
F2 GFX_CLKP
F21 HT_TXCAD8P
F22 HT_TXCAD8N
F23 HT_TXCAD1N
F24 HT_TXCAD2N
F25 HT_TXCAD2P
F3 VSSA
F4 VDDA_12
F7 VDD_PLL
F9 VSS_PLL
G1 SB_CLKP
G11 VSS
G12 LVDS_BLON
G14 TXOUT_L2N
G15 TXCLK_UN
G17 AVSSN
G19 BLUE
G2 SB_CLKN
G20 VDD_CORE
G21 HT_TXCAD10N
G22 HT_TXCAD10P
G23 VSS
G24 VSS
G25 HT_TXCAD3P
G3 VSSA
G4 GFX_RX0N
G5 GFX_RX0P
G6 VSSA
G7 VDDA_12
Pin Name
© 2011 Advanced Micro Devices, Inc. 42437 AMD M690T/E Databook 3.10
Proprietary A-3
Page 86

Ball
Ref.
G9 VSS_PLL
H1 VSSA
H11 VDD_CORE
H12 VSS
H14 TXOUT_L2P
H15 TXCLK_UP
H17 AVSSN
H2 GFX_TX0N
H23 VSS
H24 HT_TXCAD3N
H25 VSS
H3 VSSA
J1 GFX_TX0P
J11 VDD_CORE
J12 VSS
J14 VDD_18
J15 VDD_18
J19 VDD_CORE
J2 VSSA
J20 HT_TXCAD9P
J21 HT_TXCAD9N
J22 VSS
J23 HT_TXCAD4P
J24 HT_TXCLK0P
J25 HT_TXCLK0N
J3 VSSA
J4 GFX_RX2P
J5 GFX_RX2N
J6 VSSA
J7 GFX_RX1N
J8 GFX_RX1P
K1 GFX_TX1N
K2 GFX_TX1P
K23 HT_TXCAD4N
K24 HT_TXCAD5N
K25 HT_TXCAD5P
K3 GFX_TX2P
L1 GFX_TX3P
L11 VDD_CORE
L12 VSS
L13 VDD_CORE
L14 VSS
L15 VDD_CORE
L17 VDD_CORE
Pin Name
Ball
Ref.
L18 HT_TXCAD11P
L19 HT_TXCAD11N
L2 GFX_TX3N
L20 VSS
L21 HT_TXCLK1P
L22 HT_TXCLK1N
L23 VSS
L24 VSS
L25 HT_TXCAD6P
L3 GFX_TX2N
L4 GFX_RX4P
L5 GFX_RX4N
L6 VSSA
L7 GFX_RX3N
L8 GFX_RX3P
L9 VDDA_12
M1 VDDA_12_PKG
M11 VSS
M12 VDD_CORE
M13 VSS
M14 VDD_CORE
M15 VSS
M17 VSS
M18 HT_TXCAD12P
M19 HT_TXCAD12N
M2 VSSA
M20 VSS
M21 HT_TXCAD13N
M22 HT_TXCAD13P
M23 VSS
M24 HT_TXCAD6N
M25 VSS
M3 VSSA
M4 GFX_RX6P
M5 GFX_RX6N
M6 VSSA
M7 GFX_RX5N
M8 GFX_RX5P
M9 VDDA_12
N1 GFX_TX4N
N11 VDD_CORE
N12 VSS
N13 VDD_CORE
N14 VSS
Pin Name
Ball
Ref.
N15 VDD_CORE
N2 GFX_TX4P
N23 HT_TXCTLP
N24 HT_TXCAD7P
N25 HT_TXCAD7N
N3 VSSA
P1 GFX_TX5N
P11 VSS
P12 VDD_CORE
P13 VSS
P14 VDD_CORE
P15 VSS
P17 VDD_CORE
P18 HT_TXCAD14P
P19 HT_TXCAD14N
P2 GFX_TX5P
P20 VSS
P21 HT_TXCAD15P
P22 HT_TXCAD15N
P23 HT_TXCTLN
P24 HT_RXCTLP
P25 HT_RXCTLN
P3 GFX_TX6P
P4 GPP_RX2P
P5 GPP_RX2N
P6 VSSA
P7 GFX_RX7N
P8 GFX_RX7P
P9 VSSA
R1 GFX_TX7P
R11 VDD_CORE
R12 VSS
R13 VDD_CORE
R14 VSS
R15 VDD_CORE
R17 VSS
R18 HT_RXCAD15N
R19 HT_RXCAD15P
R2 GFX_TX7N
R20 VSS
R21 HT_RXCAD14P
R22 HT_RXCAD14N
R23 VSS
R24 VSS
Pin Name
42437 AMD M690T/E Databook 3.10 © 2011 Advanced Micro Devices, Inc.
A-4 Proprietary
Page 87

Ball
Ref.
R25 HT_RXCAD7N
R3 GFX_TX6N
R4 GPP_RX3P
R5 GPP_RX3N
R6 VSSA
R7 GPP_RX0P
R8 GPP_RX0N
R9 VSSA
T1 VSSA
T2 VSSA
T23 VSS
T24 HT_RXCAD7P
T25 VSS
T3 VSSA
U1 GPP_TX2N
U11 VDD_CORE
U12 VDD_CORE
U14 VDD_CORE
U15 VDD_CORE
U18 HT_RXCAD12P
U19 HT_RXCAD12N
U2 GPP_TX2P
U20 VSS
U21 HT_RXCAD13N
U22 HT_RXCAD13P
U23 HT_RXCAD5N
U24 HT_RXCAD6N
U25 HT_RXCAD6P
U3 VSSA
U4 GPP_RX1P
U5 GPP_RX1N
U6 VSSA
U7 VDDA_12
V1 GPP_TX3N
V11 VSS
V12 MEM_CS#
V14 VSS
V15 MEM_CKN
V2 GPP_TX3P
V23 HT_RXCAD5P
V24 HT_RXCAD4P
V25 HT_RXCAD4N
V3 GPP_TX0P
Pin Name
Ball
Ref.
V9 SB_RX1P
W1 GPP_TX1P
W11 MEM_COMPN
W12 MEM_A0
W14 MEM_A4
W15 MEM_CKP
W17 VSS
W19 HT_RXCAD11P
W2 GPP_TX1N
W20 HT_RXCAD11N
W21 HT_RXCLK1P
W22 HT_RXCLK1N
W23 VSS
W24 VSS
W25 HT_RXCLK0N
W3 GPP_TX0N
W4 SB_RX3P
W5 SB_RX3N
W6 VSSA
W7 VDDA_12
W9 SB_RX1N
Y1 VSSA
Y11 MEM_COMPP
Y12 VSS
Y14 MEM_A11
Y15 MEM_CAS#
Y17 IOPLLVSS
Y19 HT_RXCAD8N
Y2 SB_TX3P
Y22 VSS
Y23 VSS
Y24 HT_RXCLK0P
Y25 VSS
Y3 SB_TX3N
Y4 SB_RX2P
Y5 SB_RX2N
Y7 VSSA
Y9 MEM_ODT
Pin Name
© 2011 Advanced Micro Devices, Inc. 42437 AMD M690T/E Databook 3.10
Proprietary A-5
Page 88

A.2 M690T Pin List Sorted by Pin Name
Table A-2 M690T Pin List Sorted by Pin Name
Pin Name
ALLOW_LDTSTOP B5
AVD D B22
AVDD C22
AVDDDI A20
AVDDQ A21
AVSSDI B20
AVSSN G17
AVSSN H17
AVSSQ A22
BLUE G19
BMREQ# B2
CC21
COMP D19
DACHSYNC A5
DACSCL B6
DACSDA A6
DACVSYNC C6
DDC_DATA B3
DFT_GPIO0 D6
DFT_GPIO1 D7
DFT_GPIO2 C8
DFT_GPIO3 C7
DFT_GPIO4 B8
DFT_GPIO5 A8
GFX_CLKN E1
GFX_CLKP F2
GFX_RX0N G4
GFX_RX0P G5
GFX_RX1N J7
GFX_RX1P J8
GFX_RX2N J5
GFX_RX2P J4
GFX_RX3N L7
GFX_RX3P L8
GFX_RX4N L5
GFX_RX4P L4
GFX_RX5N M7
GFX_RX5P M8
GFX_RX6N M5
GFX_RX6P M4
GFX_RX7N P7
Ball
Ref.
Pin Name
GFX_RX7P P8
GFX_TX0N H2
GFX_TX0P J1
GFX_TX1N K1
GFX_TX1P K2
GFX_TX2N L3
GFX_TX2P K3
GFX_TX3N L2
GFX_TX3P L1
GFX_TX4N N1
GFX_TX4P N2
GFX_TX5N P1
GFX_TX5P P2
GFX_TX6N R3
GFX_TX6P P3
GFX_TX7N R2
GFX_TX7P R1
GPP_RX0N R8
GPP_RX0P R7
GPP_RX1N U5
GPP_RX1P U4
GPP_RX2N P5
GPP_RX2P P4
GPP_RX3N R5
GPP_RX3P R4
GPP_TX0N W3
GPP_TX0P V3
GPP_TX1N W2
GPP_TX1P W1
GPP_TX2N U1
GPP_TX2P U2
GPP_TX3N V1
GPP_TX3P V2
GREEN F19
HT_RXCAD0N AC25
HT_RXCAD0P AC24
HT_RXCAD10N AB22
HT_RXCAD10P AC21
HT_RXCAD11N W20
HT_RXCAD11P W19
HT_RXCAD12N U19
Ball
Ref.
Pin Name
HT_RXCAD12P U18
HT_RXCAD13N U21
HT_RXCAD13P U22
HT_RXCAD14N R22
HT_RXCAD14P R21
HT_RXCAD15N R18
HT_RXCAD15P R19
HT_RXCAD1N AB25
HT_RXCAD1P AB24
HT_RXCAD2N AA23
HT_RXCAD2P AB23
HT_RXCAD3N AA24
HT_RXCAD3P AA25
HT_RXCAD4N V25
HT_RXCAD4P V24
HT_RXCAD5N U23
HT_RXCAD5P V23
HT_RXCAD6N U24
HT_RXCAD6P U25
HT_RXCAD7N R25
HT_RXCAD7P T24
HT_RXCAD8N Y19
HT_RXCAD8P AA19
HT_RXCAD9N AA20
HT_RXCAD9P AB20
HT_RXCALN C24
HT_RXCALP A24
HT_RXCLK0N W25
HT_RXCLK0P Y24
HT_RXCLK1N W22
HT_RXCLK1P W21
HT_RXCTLN P25
HT_RXCTLP P24
HT_TXCAD0N E25
HT_TXCAD0P E24
HT_TXCAD10N G21
HT_TXCAD10P G22
HT_TXCAD11N L19
HT_TXCAD11P L18
HT_TXCAD12N M19
HT_TXCAD12P M18
Ball
Ref.
42437 AMD M690T/E Databook 3.10 © 2011 Advanced Micro Devices, Inc.
A-6 Proprietary
Page 89

Pin Name
HT_TXCAD13N M21
HT_TXCAD13P M22
HT_TXCAD14N P19
HT_TXCAD14P P18
HT_TXCAD15N P22
HT_TXCAD15P P21
HT_TXCAD1N F23
HT_TXCAD1P E23
HT_TXCAD2N F24
HT_TXCAD2P F25
HT_TXCAD3N H24
HT_TXCAD3P G25
HT_TXCAD4N K23
HT_TXCAD4P J23
HT_TXCAD5N K24
HT_TXCAD5P K25
HT_TXCAD6N M24
HT_TXCAD6P L25
HT_TXCAD7N N25
HT_TXCAD7P N24
HT_TXCAD8N F22
HT_TXCAD8P F21
HT_TXCAD9N J21
HT_TXCAD9P J20
HT_TXCALN D24
HT_TXCALP C25
HT_TXCLK0N J25
HT_TXCLK0P J24
HT_TXCLK1N L22
HT_TXCLK1P L21
HT_TXCTLN P23
HT_TXCTLP N23
HTPVDD B24
HTPVSS B25
HTREFCLK B23
HTTSTCLK C23
I2C_CLK A2
I2C_DATA B4
IOPLLVDD12 AB17
IOPLLVDD18 AA17
IOPLLVSS Y17
LDTSTOP# C5
LPVDD D14
Ball
Ref.
Pin Name
LPVSS E14
LVDDR18D A12
LVDDR18D B12
LVDDR33 C12
LVDDR33 C13
LVDS_BLEN F12
LVDS_BLON G12
LVD S_DIG ON E 12
LVSSR A14
LVSSR A16
LVSSR C15
LVSSR C16
LVSSR C19
LVSSR D12
LVSSR F14
LVSSR F15
MEM_A0 W12
MEM_A1 AD10
MEM_A10 AE10
MEM_A11 Y14
MEM_A12 AD9
MEM_A13 AA11
MEM_A2 AB12
MEM_A3 AB11
MEM_A4 W14
MEM_A5 AB15
MEM_A6 AB14
MEM_A7 AE9
MEM_A8 AA12
MEM_A9 AC9
MEM_BA0 AC11
MEM_BA1 AE11
MEM_BA2 AD11
MEM_CAS# Y15
MEM_CKE AD12
MEM_CKN V15
MEM_CKP W15
MEM_COMPN W11
MEM_COMPP Y11
MEM_CS# V12
MEM_DM0 AC16
MEM_DM1 AD19
MEM_DQ0 AD13
Ball
Ref.
Pin Name
MEM_DQ1 AE13
MEM_DQ10 AD18
MEM_DQ11 AE19
MEM_DQ12 AC19
MEM_DQ13 AE20
MEM_DQ14 AD20
MEM_DQ15 AE21
MEM_DQ2 AC13
MEM_DQ3 AD14
MEM_DQ4 AC15
MEM_DQ5 AD15
MEM_DQ6 AE15
MEM_DQ7 AE16
MEM_DQ8 AD16
MEM_DQ9 AC17
MEM_DQS0N AD17
MEM_DQS0P AE17
MEM_DQS1N AC20
MEM_DQS1P AD21
MEM_ODT Y9
MEM_RAS# AA15
MEM_VREF AE12
MEM_WE# AC14
NC AC4
NC AD4
OSCIN B11
PCE_CALRN AE3
PCE_CALRP AE4
PLLVDD12 A11
PLLVDD18 A10
PLLVSS B10
POWERGOOD C11
RED E19
RSET B21
SB_CLKN G2
SB_CLKP G1
SB_RX0N AB6
SB_RX0P AB7
SB_RX1N W9
SB_RX1P V9
SB_RX2N Y5
SB_RX2P Y4
SB_RX3N W5
Ball
Ref.
© 2011 Advanced Micro Devices, Inc. 42437 AMD M690T/E Databook 3.10
Proprietary A-7
Page 90

Pin Name
SB_RX3P W4
SB_TX0N AC2
SB_TX0P AC1
SB_TX1N AB2
SB_TX1P AB1
SB_TX2N AA2
SB_TX2P AA1
SB_TX3N Y3
SB_TX3P Y2
STRP_DATA A3
SYSRESET# C10
TESTMODE C3
THERMALDIODE_N AE5
THERMALDIODE_P AD5
TMDS_HPD C14
TVCLKIN C2
TXCLK_LN D15
TXCLK_LP E15
TXCLK_UN G15
TXCLK_UP H15
TXOUT_L0N B15
TXOUT_L0P B14
TXOUT_L1N A13
TXOUT_L1P B13
TXOUT_L2N G14
TXOUT_L2P H14
TXOUT_L3N E17
TXOUT_L3P D17
TXOUT_U0N B16
TXOUT_U0P A15
TXOUT_U1N C18
TXOUT_U1P C17
TXOUT_U2N A17
TXOUT_U2P B17
TXOUT_U3N B18
TXOUT_U3P A18
VDD_18 J14
VDD_18 J15
VDD_CORE A19
VDD_CORE A4
VDD_CORE A7
VDD_CORE A9
VDD_CORE B19
VDD_CORE B9
Ball
Ref.
Pin Name
VDD_CORE C9
VDD_CORE D20
VDD_CORE D9
VDD_CORE G20
VDD_CORE H11
VDD_CORE J11
VDD_CORE J19
VDD_CORE L11
VDD_CORE L13
VDD_CORE L15
VDD_CORE L17
VDD_CORE M12
VDD_CORE M14
VDD_CORE N11
VDD_CORE N13
VDD_CORE N15
VDD_CORE P12
VDD_CORE P14
VDD_CORE P17
VDD_CORE R11
VDD_CORE R13
VDD_CORE R15
VDD_CORE U11
VDD_CORE U12
VDD_CORE U14
VDD_CORE U15
VDD_HT AD22
VDD_HT AD23
VDD_HT AD24
VDD_HT AE22
VDD_HT AE23
VDD_HT AE24
VDD_HT AE25
VDD_HT_PKG D22
VDD_MEM AA9
VDD_MEM AB9
VDD_MEM AC7
VDD_MEM AC8
VDD_MEM AD6
VDD_MEM AD7
VDD_MEM AD8
VDD_MEM AE6
VDD_MEM AE7
VDD_MEM AE8
Ball
Ref.
Pin Name
VDD_PLL E7
VDD_PLL F7
VDDA_12 AB3
VDDA_12 AB4
VDDA_12 AC3
VDDA_12 AC5
VDDA_12 AD2
VDDA_12 AE2
VDDA_12 B1
VDDA_12 C1
VDDA_12 D1
VDDA_12 D2
VDDA_12 D3
VDDA_12 E2
VDDA_12 E3
VDDA_12 E6
VDDA_12 F4
VDDA_12 G7
VDDA_12 L9
VDDA_12 M9
VDDA_12 U7
VDDA_12 W7
VDDA_12_PKG AD3
VDDA_12_PKG M1
VDDR3 D11
VDDR3 E11
VSS A23
VSS A25
VSS AA14
VSS AB19
VSS AC10
VSS AC12
VSS AC18
VSS AC22
VSS AC23
VSS AD25
VSS AE14
VSS AE18
VSS B7
VSS C4
VSS D23
VSS D25
VSS D4
VSS E9
Ball
Ref.
42437 AMD M690T/E Databook 3.10 © 2011 Advanced Micro Devices, Inc.
A-8 Proprietary
Page 91

Pin Name
VSS F11
VSS F17
VSS G11
VSS G23
VSS G24
VSS H12
VSS H23
VSS H25
VSS J12
VSS J22
VSS L12
VSS L14
VSS L20
VSS L23
VSS L24
VSS M11
VSS M13
VSS M15
VSS M17
VSS M20
VSS M23
VSS M25
VSS N12
VSS N14
VSS P11
VSS P13
VSS P15
VSS P20
VSS R12
VSS R14
VSS R17
VSS R20
VSS R23
VSS R24
VSS T23
VSS T25
VSS U20
VSS V11
VSS V14
VSS W17
VSS W23
VSS W24
VSS Y12
Ball
Ref.
Pin Name
VSS Y22
VSS Y23
VSS Y25
VSS_PLL F9
VSS_PLL G9
VSSA A1
VSSA AA3
VSSA AA7
VSSA AC6
VSSA AD1
VSSA AE1
VSSA F1
VSSA F3
VSSA G3
VSSA G6
VSSA H1
VSSA H3
VSSA J2
VSSA J3
VSSA J6
VSSA L6
VSSA M2
VSSA M3
VSSA M6
VSSA N3
VSSA P6
VSSA P9
VSSA R6
VSSA R9
VSSA T1
VSSA T2
VSSA T3
VSSA U3
VSSA U6
VSSA W6
VSSA Y1
VSSA Y7
YC20
Ball
Ref.
© 2011 Advanced Micro Devices, Inc. 42437 AMD M690T/E Databook 3.10
Proprietary A-9
Page 92

This page is left blank intentionally.
42437 AMD M690T/E Databook 3.10 © 2011 Advanced Micro Devices, Inc.
A-10 Proprietary
Page 93

B.1 Introduction
GGGGGG
YYWWXXV
COO
o
216EVA6CVA12FG
CHIPSET
* YY - Assembly Start Year
WW - Assembly Start Week
XX - Assembly Location
V - Substrate Vendor Code
Part Number (for ASIC revision A12)
Country of Origin
Date and Other Codes*
Wafer Foundry’s Lot Number
AMD Product Type
AMD Logo
“o” indicates pin A1.
The M690T and M690E are two members of the same AMD RS690-series Northbridge and chipset family. The M690E
and M690T have the same package, pin-out, and fabrication process. All peripheral functions and features are the same as
well, except for the differences explained in
Appendix B
AMD M690E
Section B.2 below.
Figure B-1 M690E Branding Diagram for ASIC Revision A12
Both the M690E and M690T are packaged in the same 21mmx21mm 465-ball FCBGA package. But, the devices’
markings and part numbers are different. The part marking, planned production schedule, and AMD OPN (ordering
number) for the M690E are shown in
Table B-1 Planned Production Schedule, OPN, and Part Marking
Component Production Availability Date OPN Part Marking
M690E Oct 19, 2007 100-CG1408 216EVA6CVA12FG
B.2 Feature Differences between the M690T and M690E
Table B-1.
The M690E is identified and distinguished from the M690T by an e-fuse on the chip. There are no identification registers
that differentiate the two devices.
A) TV Output
The M690T provides SDTV (PAL or NTSC standard, with composite, S-Video (separate luminance and chrominance
channels), or YCbCr 480i (YUV) standard definition component output) and HDTV (YPbPr 480i, 480p, 576i, 576p,
720p, 1080i) outputs through the on-chip DACs that are shared between TV and CRT outputs. Macrovision analog TV
copy protection is supported on all its standard definition and 480p high definition TV outputs.
© 2011 Advanced Micro Devices, Inc. 42437 AMD M690T/E Databook 3.10
Proprietary B-1
Page 94

The M690E, on the other hand, does not provide any sort of analog TV output and does not support Macrovision copy
protection. Despite the lack of TV output, the DACs of the M690E can still be used to provide a high quality CRT output.
The table and figure below summarize the differences between the M690T and M690E in terms of analog TV and
VGA/CRT display outputs.
Table B-2 M690T/E Analog TV and VGA/CRT Support Differences
Analog Output Feature M690T M690E
Composite NTSC/PAL TV Port Available Not Available
S-Video (Y/C) NTSC/PAL TV Port Available Not Available
Component 480i/576i (YUV/YCbCr) TV Port Available Not Available
Component 480p/576p/720p/1080i HDTV (YPbPr) TV
Port
Standard VGA/CRT (RGBHV) Port Available Available
Note: AMD customers MUST have a Macrovision license in place or be authorized by Rovi to purchase
Macrovision-enabled technology before AMD can sell them any M690T chips.
without a Macrovision license.
Figure B-2 M690T and M690E Analog Display Output Signals
Available Not Available
M690E devices can be obtained
Note: For designs using the M690E, the C, Y, and COMP pins on the package do not provide any output and should be
left unconnected on the motherboard.
B) TMDS/DVI Digital Output Multiplexed on the LVDS/TMDS (LVTM) Interface
Both the M690E and M690T support a dual-channel LVDS 24-bit output through its LVDS interface. However, on the
M690E, the interface is enhanced to also support a TMDS/DVI output in place of the LVDS format. An M690E
based-system requires a custom video BIOS to configure the enhanced LVDS/TMDS (LVTM) interface to drive out
either LVDS or TMDS/DVI signals. The video BIOS is available from AMD. The minimum version number for the
LVDS output is 10.55.0.15 and for the TMDS/DVI output is 10.55.0.31. Contact your AMD CSS representative for the
latest video BIOS.
A custom video BIOS and proper signal routing from the LVTM interface to a DVI connector are the only requirements
for the M690E to support a TMDS/DVI output on the LVTM interface. No other register programming is needed. Users
should not attempt to configure the LVTM port by programming the M690E's registers directly.
Features of the TMDS/DVI output include:
• Supports a 30-bit dual-link DVI interface.
• 1650 Mbps/channel with 165MHz pixel clock rate per link (data rate and clock speed to be qualified).
• Supports industry standard EVA-861B video modes including 480p, 720p, and 1080i. For a full list of currently
supported modes, contact your AMD CSS representative.
42437 AMD M690T/E Databook 3.10 © 2011 Advanced Micro Devices, Inc.
B-2 Proprietary
Page 95

TXOUT_U0N/P
TXOUT_U1N/P
TXOUT_U2N/P
TXCLK_LN/P
TXOUT_L0N/P
TXCLK_UN/P
TXOUT_L1N/P
TXOUT_L2N/P
LVDS_DIGON
LVDS_BLON
LVDS_BLEN
LVDS upper data channel 0
LVDS upper data channel 2
LVDS lower clock channel
LVDS lower data channel 0
LVDS upper clock channel
LVDS lower data channel 1
LVDS lower data channel 2
LVDS_DIGON
LVDS_BLON
LVDS_BLEN
LVDS upper data channel 3
TXOUT_U3N/P
LVDS upper data channel 1
TXOUT_U0N/P
TXOUT_U1N/P
TXOUT_U2N/P
TXCLK_LN/P
TXOUT_L0N/P
TXCLK_UN/P
TXOUT_L1N/P
TXOUT_L2N/P
LVDS_DIGON
LVDS_BLON
LVDS_BLEN
TMDS data channel 4
TMDS data channel 0
NC
TMDS data channel 3
TMDS clock channel
TMDS data channel 2
NC
GPIO3
GPIO2
GPIO4
TMDS data channel 1
TXOUT_U3N/P
TMDS data channel 5
TXOUT_L3N/P
LVDS lower data channel 3
TXOUT_L3N/P
NC
LVTM Interface in LVDS Mode
LVTM Interface in TMDS Mode
VGA Signals
Figure B-3 M690E LVTM Interface
Notice that the M690E, like the M690T, can also provide a TMDS/DVI via its TMDS interface that is multiplexed with its
PCI Express
integrated TMDS transmitters—one through the LVTM interface, and the other through the TMDS interface multiplexed
with the PCIe
B.3 DVI-I Support
The M690E has the capability of driving both digital and analog outputs simultaneously to a DVI-I connector. This is
accomplished by routing the RED, GREEN, BLUE, DACHSYNC, DACVSYNC, and AVSSN signals from the M690E’s
CRT output (see
C2(G), C3(B), C4(HS), C5(GND), and Pin 8 (VS) signals (see
Connector,”
For the single-link DVI output portion of the DVI-I connector, AMD recommends using the M690E’s LVTM interface to
provide the DVI output and routing these digital signals (see
inputs on the DVI-I connector. The video BIOS must be configured so that the M690E drives out DVI/TMDS from its
LVTM interface. Display modes supported include desktop resolutions such as 800x600, 1024x768, 1152x864,
B.4 HDMI™
© 2011 Advanced Micro Devices, Inc. 42437 AMD M690T/E Databook 3.10
Proprietary B-3
1280x1024, and 1600x1200 at 16bpp or 32bpp, with 60Hz or 75Hz screen refresh rate.
Creating a DVI-I configuration using the DAC signals (RED, GREEN, BLUE, DACHSYNC, etc.) plus the TMDS output
multiplexed on the PCIe graphics links is supposed to work as well, but the configuration is not recommended since it
cannot be validated using any of AMD's current internal reference boards.
The M690E has an integrated controller that allows support for a single-link HDMI™ (video and audio) transmission on
®
graphics link. As a result, the M690E can provide two single-link DVI-D outputs using its two on-chip
®
graphics interface.
Figure B-2, “M690T and M690E Analog Display Output Signals” ) to the DVI-I connector’s C1(R),
Figure B-4, “Pins for Analog Output on the DVI-I
below).
Figure B-4 Pins for Analog Output on the DVI-I Connector
Figure B-3, “M690E LVTM Interface” ) to the appropriate
Page 96

the LVTM interface. For details on HDMI audio support, please refer to section 1.3.11, “DVI/HDMI™,” on page 1- 6.
HD
Audio
SW
Frame Buffers
A
B
(Live in memory)
Mux
LVDS
TMDS
LVTM Interface
PCIe® x8
TMDS
PCI-E/TMDS Interface
DAC
CRT Interface
SW SW
SW
LVDS Output
or
TMDS output
TMDS output
(or PCI-E GFX Signals)
CRT Output
Notes:
1. Each switch represents 2 possible configuration choices.
2. Each frame buffer output can be routed through the mux to any of the outputs.
3. Each frame buffer has its own resolution, color depth, and refresh rate.
4. TMDS alone is in DVI-D format, and TMDS+Audio is in HDMI format.
5. M690E offers dual DVI by utilizing both TMDS outputs from the LVTM interface and the TMDS interface multiplexed on the
PCIe
®
graphics lanes.
Also, like the M690T, the M690E’s TMDS interface that is multiplexed on its PCIe graphics lanes can also enable HDMI
(single-link only).
Note: The TMDS interface multiplexed on the PCIe graphics lanes cannot enable HDMI when the LVTM interface is
supporting HDMI, and vice versa.
B.5 HDCP
The M690E supports HDCP on data streams for single-link transmission, with on-chip key storage. It is available either
on the DVI/HDMI data stream driven by the LVTM interface or on the data stream driven by the TMDS interface
multiplexed on the PCIe graphics lanes, but both digital outputs cannot be HDCP protected simultaneously.
Note: HDCP content protection is only available to licensed buyers of the technology and can only be enabled when
connected to an HDCP-capable receiver.
B.6 M690E Display Options
The display options possible with the M690E are summarized in Figure B-5 below.
Figure B-5 M690E Display Options
42437 AMD M690T/E Databook 3.10 © 2011 Advanced Micro Devices, Inc.
B-4 Proprietary
Page 97

B.7 The LVTM Interface in TMDS Mode
B.7.1 Pin Descriptions
When the M690E's LVTM Interface is configured to TMDS mode via the video BIOS, the pins take on the functions as
described in
Interface (24 Bits),” on page 3- 8
Table B-3 M690E’s LVTM Interface in TMDS Mode
Table B-3 below. For operation in LVDS mode, please refer to pin descriptions given in section 3.8, “LVDS
.
Pin Name
Functional
Name
TXOUT_L0N TX0M O
TXOUT_L0P TX0P O
TXOUT_L1N TX1M O
TXOUT_L1P TX1P O
TXOUT_L2N TX2M O
TXOUT_L2P TX2P O
TXOUT_L3N TX3M O
TXOUT_L3P TX3P O
TXOUT_U0N TX4M O
TXOUT_U0P TX4P O
TXOUT_U1N TX5M O
TXOUT_U1P TX5P O
TXOUT_U2N – O
TXOUT_U2P – O
TXOUT_U3N – O
TXOUT_U3P – O
TXCLK_LN TXCM O
TXCLK_LP TXCP O
TMDS
Type
Power
Domain
LVDDR33
LVDDR18D
LVDDR33
LVDDR18D
LVDDR33
LVDDR18D
LVDDR33
LVDDR18D
LVDDR33
LVDDR18D
LVDDR33
LVDDR18D
LVDDR33
LVDDR18D
LVDDR33
LVDDR18D
LVDDR33
LVDDR18D
LVDDR33
LVDDR18D
LVDDR33
LVDDR18D
LVDDR33
LVDDR18D
LVDDR33
LVDDR18D
LVDDR33
LVDDR18D
LVDDR33
LVDDR18D
LVDDR33
LVDDR18D
LVDDR33
LVDDR18D
LVDDR33
LVDDR18D
Ground
Domain
VSSLT None TMDS data channel 0 (-)
VSSLT None TMDS data channel 0 (+)
VSSLT None TMDS data channel 1 (-)
VSSLT None TMDS data channel 1 (+)
VSSLT None TMDS data channel 2 (-)
VSSLT None TMDS data channel 2 (+)
VSSLT None
VSSLT None
VSSLT None
VSSLT None
VSSLT None
VSSLT None
VSSLT None Unused. NC.
VSSLT None Unused. NC.
VSSLT None Unused. NC.
VSSLT None Unused. NC.
VSSLT None TMDS clock channel (-)
VSSLT None TMDS clock channel (+)
Integrated
Termination
Functional Description
TMDS data channel 3 (-). The channel is only used
in DVI dual-link mode and is not used for HDMI™
support. NC if unused.
TMDS data channel 3 (+). The channel is only used
in DVI dual-link mode and is not used for HDMI
support. NC if unused.
TMDS data channel 4 (-). The channel is only used
in DVI dual-link mode and is not used for HDMI
support. NC if unused.
TMDS data channel 4 (+) The channel is only used
in DVI dual-link mode and is not used for HDMI
support. NC if unused.
TMDS data channel 5 (-). The channel is only used
in DVI dual-link mode and is not used for HDMI
support. NC if unused.
TMDS data channel 5 (+). The channel is only used
in DVI dual-link mode and is not used for HDMI
support. NC if unused.
© 2011 Advanced Micro Devices, Inc. 42437 AMD M690T/E Databook 3.10
Proprietary B-5
Page 98

Table B-3 M690E’s LVTM Interface in TMDS Mode (Continued)
Pin Name
Functional
Name
TXCLK_UN – O
TXCLK_UP – O
TMDS
Type
Power
Domain
LVDDR33
LVDDR18D
LVDDR33
LVDDR18D
B.7.2 Data Ordering and Signal Mapping
Refer to section 2.4.1, “DVI/HDMI™ Data Transmission Order and Signal Mapping,” on page 2- 9 for the data ordering
and signal mapping for the TMDS/DVI signal output from the LVTM interface on the M690E.
B.7.3 Electrical Characteristics
Table B-4 DC Characteristics for the LVTM Interface in TMDS Mode
Symbol Parameter Min Typical Max Unit Note
VH Single-ended High Level Output Voltage AVCC - 10 – AVCC + 10 mV 1
VL Single-ended Low Level Output Voltage AVCC - 600 – AVCC - 400 mV 1
VSW Single-ended Output Swing 400 – 600 mV
VOS Differential Output Overshoot (Ringing) – – 15%*2VSW –
VUS Differential Output Undershoot (Ringing) – – 25%*2VSW –
IDDLP Average Supply Current at LPVDD – 20.0 – mA 2
IDDLV
IPDLP Power Down Current at LPVDD – 10.0 – A3
IPDLV
Notes:
1 AVCC stands for the termination supply voltage of the receiver, which is 3.3V +/- 5%.
2 Measured under typical conditions, at minimum differential clock frequency and maximum DVI/HDMI™ PLL VOC frequency.
3 Measured under typical conditions, based on typical leakage values.
4 Figure B-6 below illustrates some of the DC Characteristics of the LVTM interface in TMDS mode.
Average Supply Current at LVDDR18D and
LVDDR33
Power Down Current at LVDDR18D and
LVDDR33
Ground
Domain
VSSLT None Unused. NC.
VSSLT None Unused. NC.
Integrated
Termination
– 100.0 – mA 2
– 10.0 – A3
Functional Description
42437 AMD M690T/E Databook 3.10 © 2011 Advanced Micro Devices, Inc.
B-6 Proprietary
Page 99

VSW
VHmax
VHmin
VLmax
VLmin
2VSW
VOS
VUS
Single-ended Waveforms
Differential Waveform
VOS
VUS
Figure B-6 DC Characteristics of the LVTM Interface in TMDS Mode
© 2011 Advanced Micro Devices, Inc. 42437 AMD M690T/E Databook 3.10
Proprietary B-7
Page 100

This page is left blank intentionally.
42437 AMD M690T/E Databook 3.10 © 2011 Advanced Micro Devices, Inc.
B-8 Proprietary
 Loading...
Loading...