Page 1

Nios Ethernet
Development Kit User Guide
101 Innovation Drive
San Jose, CA 95134
(408) 544-7000
http://www.altera.com Document Date: August 2002
Document Version: 3.0
Page 2

Copyright Nios Ethernet Development Kit User Guide
Copyright © 2002 Altera Corporation. All rights reserved. Altera, The Programmable Solutions Company, the stylized Altera logo,
specific device designations, and all other words and logos that are identified as trademarks and/or service marks are, unless
noted otherwise, the trademarks and service marks of Altera Corporation in the U.S. and other countries. All other product or
service names are the property of their respective holders. Altera products are protected under numerous U.S. and foreign patents
and pending applications, mask work rights, and copyrights. Altera warrants performance of its semiconductor
products to current specifications in accordance with Altera’s standard warranty, but reserves the right to make
changes to any products and services at any time without notice. Altera assumes no responsibility or liability
arising out of the application or use of any information, product, or service described herein except as expressly
agreed to in writing by Altera Corporation. Altera customers are advised to obtain the latest version of device
specifications before relying on any published information and before placing orders for products or services.
ii Altera Corporation
UG-NIOSETHERKIT-3.0
Page 3

About this User Guide
This user guide provides the information necessary to get you started
®
using the Nios
Ethernet Development Kit (EDK). This manual provides:
■ An overview of the Nios EDK, its contents, and its intended use
■ A “Getting Started” section with a step-by-step guide to installing the
development tools, installing hardware, and accessing the software
application examples.
■ A “Daughter Card” reference section providing a description of the
daughter card including a functional overview, pinout information,
and descriptions of the PC-board design files included with the kit
■ A software overview introducing you to the C language library,
providing a description of the supported protocols and the general
structure of the provided functions and data structures
■ A plugs library reference describing the software routines
1 For the most current version of this user guide, see
http://www.altera.com/literature/lit-nio.html
Table 1 shows the user guide revision history.
Table 1. User Guide Revision History
Date Description
August 2002 Updated PDF for Ethernet 10/100 kit
April 2002 Updated PDF - new cover for version 2.1
January 2002 PDF only. Added new (adapter_irq) and modified one
(adapter_base_address) parameter for the nr_plugs_initialize
routine. Updated description for nr_plugs_idle routine.
July 2001 initial printed document and PDF - version 1.0
■ Refer to the readme file for new features, system requirements and
installation information.
Altera Corporation iii
Page 4
About this User Guide Nios Ethernet Development Kit User Guide
How to Contact
For the most up-to-date information about Altera® products, go to the
Altera world-wide web site at http://www.altera.com.
Altera
For technical support on this product, go to
http://www.altera.com/mysupport. For additional information about
Altera products, consult the sources shown in Table 2.
Table 2. How to Contact Altera
Information Type USA & Canada All Other Locations
Technical support http://www.altera.com/mysupport/ http://www.altera.com/mysupport/
(800) 800-EPLD (3753)
(7:00 a.m. to 5:00 p.m.
Pacific Time)
Product literature http://www.altera.com http://www.altera.com
Altera literature services lit_req@altera.com (1) lit_req@altera.com (1)
Non-technical customer
service
FTP site ftp.altera.com ftp.altera.com
(800) 767-3753 (408) 544-7000
(408) 544-7000 (1)
(7:00 a.m. to 5:00 p.m.
Pacific Time)
(7:30 a.m. to 5:30 p.m.
Pacific Time)
Note:
(1) You can also contact your local Altera sales office or sales representative.
Documentation
Altera values your feedback. If you would like to provide feedback on this
document—e.g., clarification requests, inaccuracies, or inconsistencies—
Feedback
send e-mail to nios_docs@altera.com.
iv Altera Corporation
Page 5
Nios Ethernet Development Kit User Guide About this User Guide
Typographic
The Nios Ethernet Development Kit User Guide uses the typographic
conventions shown in Table 3.
Conventions
Table 3. Conventions
Visual Cue Meaning
Bold Type with Initial
Capital Letters
bold type External timing parameters, directory names, project names, disk drive names,
Italic Type with Initial
Capital Letters
Italic type Internal timing parameters and variables are shown in italic type. Examples: t
Initial Capital Letters Keyboard keys and menu names are shown with initial capital letters. Examples:
“Subheading Title” References to sections within a document and titles of on-line help topics are shown
Courier type Signal and port names are shown in lowercase Courier type. Examples: data1, tdi,
Command names, dialog box titles, checkbox options, and dialog box options are
shown in bold, initial capital letters. Example: Save As dialog box.
filenames, filename extensions, and software utility names are shown in bold type.
Examples: f
Document titles are shown in italic type with initial capital letters. Example: AN 75:
High-Speed Board Design.
Variable names are enclosed in angle brackets (< >) and shown in italic type. Example:
<file name>, <project name>.pof file.
Delete key, the Options menu.
in quotation marks. Example: “Typographic Conventions.”
input. Active-low signals are denoted by suffix n, e.g., resetn.
, \qdesigns directory, d: drive, chiptrip.gdf file.
MAX
PIA
, n + 1.
Anything that must be typed exactly as it appears is shown in Courier type. For
example: c:\qdesigns\tutorial\chiptrip.gdf. Also, sections of an actual
file, such as a Report File, references to parts of files (e.g., the AHDL keyword
SUBDESIGN), as well as logic function names (e.g., TRI) are shown in Courier.
1., 2., 3., and a., b., c.,... Numbered steps are used in a list of items when the sequence of the items is
important, such as the steps listed in a procedure.
■
v The checkmark indicates a procedure that consists of one step only.
1 The hand points to information that requires special attention.
r The angled arrow indicates you should press the Enter key.
f The feet direct you to more information on a particular topic.
Bullets are used in a list of items when the sequence of the items is not important.
Altera Corporation v
Page 6

Page 7

Contents
About this User Guide ...............................................................................................................................iii
How to Contact Altera .................................................................................................................. iv
Documentation Feedback ............................................................................................................. iv
Typographic Conventions ..............................................................................................................v
Overview .......................................................................................................................................................... 9
Nios Ethernet Development Kit Description ...............................................................................9
Installed Components ...................................................................................................................10
MAC Addresses .............................................................................................................................11
Getting Started ............................................................................................................................................13
Verify Kit Contents ........................................................................................................................ 13
Set Up the Daughter Card ............................................................................................................13
Install the Hardware and Software Files ....................................................................................16
Load the Reference Design ........................................................................................................... 17
Run Example Applications ...........................................................................................................20
The Hello Plugs Application Example ................................................................................20
Configure Your Network Settings ...............................................................................23
The Networked-Based GERMS Monitor Application Example ......................................24
The Simple Web Server Application Example ..................................................................27
Daughter Card ..............................................................................................................................................29
Daughter Card Components ........................................................................................................29
Functional Overview .....................................................................................................................30
Stack Daughter Cards ....................................................................................................................30
SOPC Builder Library Component .............................................................................................. 31
Connector Pinouts ..........................................................................................................................32
Nios System to Daughter Card Pin Map ....................................................................................34
Software Overview .....................................................................................................................................39
Software Description .....................................................................................................................39
System Requirements ............................................................................................................39
Protocols Supported ..............................................................................................................39
Library Features .....................................................................................................................39
Protocols Architecture ...................................................................................................................40
Standards .........................................................................................................................................40
ARP (RFC 826) ........................................................................................................................41
IP (RFC 791) ............................................................................................................................41
Altera Corporation vii
Page 8

Contents Nios Ethernet Development Kit User Guide
ICMP (RFC 792) ......................................................................................................................41
UDP (RFC 768) .......................................................................................................................41
DNS (RFC 1034 & 1035) ........................................................................................................41
TCP (RFC 793) ........................................................................................................................41
Build Options ..................................................................................................................................42
PLUGS_DEBUG (Default Value = 1) .................................................................................. 42
PLUGS_PLUG_COUNT (Default Value = 6) .....................................................................42
PLUGS_ADAPTER_COUNT (Default Value = 2) ............................................................ 42
PLUGS_DNS (Default Value = 1) ........................................................................................42
PLUGS_PING (Default Value = 1) ......................................................................................42
PLUGS_TCP (Default Value = 1) .........................................................................................43
Byte Order .......................................................................................................................................43
Data Structures ...............................................................................................................................44
Payload Descriptions .....................................................................................................................47
Plugs Library Routines ............................................................................................................................. 49
nr_plugs_initialize .........................................................................................................................50
nr_plugs_terminate ........................................................................................................................51
nr_plugs_set_mac_led ...................................................................................................................52
nr_plugs_create ..............................................................................................................................53
typedef int (*nr_plugs_receive_callback_proc) .........................................................................55
nr_plugs_destroy ........................................................................................................................... 57
nr_plugs_connect ...........................................................................................................................58
nr_plugs_send ................................................................................................................................60
nr_plugs_send_to ...........................................................................................................................61
int nr_plugs_listen .........................................................................................................................62
typedef int (*nr_plugs_listen_callback_proc) ............................................................................63
nr_plugs_ip_to_ethernet ...............................................................................................................64
nr_plugs_name_to _ip ...................................................................................................................65
nr_plugs_idle .................................................................................................................................. 66
void nr_plugs_print_ethernet_packet .........................................................................................67
nr_n2h16 ..........................................................................................................................................68
nr_h2n16 ..........................................................................................................................................68
nr_n2h32 ..........................................................................................................................................68
nr_h2n32 ..........................................................................................................................................68
viii Altera Corporation
Page 9

Overview
1
Overview
Nios Ethernet
Development
Kit Description
The Nios Ethernet Development Kit (EDK) includes hardware and
software components that provide network connectivity for your Niosbased embedded systems. The components included in this kit are:
■ A network-interface daughter card that can plug directly into the
Nios development board.
■ An SOPC Builder library component that defines the logic and
interface signals necessary to use the daughter card in a Nios system.
■ A C language library that provides a network-protocol stack. This
library includes support for raw Ethernet, address resolution
protocol (ARP), Internet protocol (IP), Internet control message
protocol (ICMP), user datagram protocol (UDP), and transmission
control protocol (TCP) protocols and utility routines for controlling
the daughter card hardware.
The kit includes APEXTM device hardware reference designs and example
software application programs. These reference designs and application
examples are intended as starting points to be modified by you for your
specific network-enabled application.
The Nios EDK library components and tools can be installed on Solaris,
HP-UX or PC-Windows (NT/2000/XP).
1 The Nios Development Kit, featuring the Nios embedded
processor must be installed before you can use the Nios Ethernet
Development Kit.
The following items are included in the Nios EDK:
■ Nios EDK daughter card based on the SMSC
PHY/MAC chip
■ Male-to-male RJ-45 network cable
■ Female-to-male crossover adapter, used for direct-PC connection
■ Nios EDK CD-ROM
The Nios EDK CD-ROM contains the following files:
■ SOPC library components
■ PC-board schematic and layout files for the Nios EDK daughter card
Altera Corporation 9
TM
LAN91C111
Page 10

Overview Nios Ethernet Development Kit User Guide
■ Example hardware reference design configurations:
– Nios 32-bit CPU for a single daughter card
– Nios 16-bit CPU for a single daughter card
– Nios 32-bit for dual-stacked daughter cards
■ Example software applications:
– Library general demonstration and configuration programs
– Example web server
– Nios 32-bit CPU network-based GERMS monitor application
example
■ Documentation:
– Nios Ethernet Development Kit User Guide
Installed
The Nios EDK CD-ROM includes an InstallShield
®
installation wizard for
Windows workstations, and install scripts for Unix workstations. See
Components
“Install the Hardware and Software Files” on page 16 for step-by-step
installation instructions.
The Nios EDK adds files to your SOPC Builder home <SOPC-HOME>
directory. By default, the install program adds the files to the SOPC
Builder home directory C:\Altera\Excalibur\sopc_builder_2_5. During
installation you have the option to add the SOPC Builder tool to another
directory. In this document, the SOPC Builder home directory is referred
to as <SOPC-HOME>. Below are the directories and files found in the
C:\Altera\Excalibur\sopc_builder_2_5 default directory.
■ The SOPC Builder library component directories are:
–<SOPC-HOME>/components/altera_avalon_cs8900/
–<SOPC-HOME>/components/altera_avalon_lan91c111/
■ The APEX hardware (FPGA) reference designs are:
– <SOPC-HOME>/examples/verilog/nios_dev_board/ethernet/
standard_cs8900_16/
– <SOPC-HOME>/examples/verilog/nios_dev_board/ethernet/
standard_cs8900_32/
– <SOPC-HOME>/examples/verilog/nios_dev_board/ethernet/
standard_cs8900_stacked_32/
– <SOPC-HOME>/examples/verilog/nios_dev_board/ethernet/
standard_lan91c111_16/
– <SOPC-HOME>/examples/verilog/nios_dev_board/ethernet/
standard_lan91c111_32/
– <SOPC-HOME>/examples/verilog/nios_dev_board/ethernet/
standard_lan91c111_stacked_32/
1 To access the .vhdl default directory files, change /verilog/ to
/vhdl/in the default directory files shown for verilog.
10 Altera Corporation
Page 11

Nios Ethernet Development Kit User Guide Overview
■ The PDF documentation files are in:
– <SOPC-HOME>/documents/nedk/
1 For the most current version of this user guide, see
http://www.altera.com/literature/lit-nio.html.
■ A complete set of PC-board manufacturing documents for the
daughter card. This includes all design-files necessary to build and
assemble the daughter card board and components. These
documents are found in following directories:
<SOPC-HOME>/documents/nedk_daughtercard_cs8900/
<SOPC-HOME>/documents/nedk_daughtercard_lan91c111/
1
Overview
f
MAC Addresses
For detailed specifications for the SMSC LAN 91C111 chip, see
http://www.smsc.com/main/catalog/lan91c111.html
For detailed specification for the Cirrus® Logic CS8900A chip, see
http://www.cirrus.com/design/products/overview/detail.cfm?d=
46
The Nios EDK daughter card manufacturing and design documents give
you all the necessary information to build copies of the daughter card
yourself. You may also use these design files to copy and paste sections of
the daughter card design into your own custom PC-board schematic,
layout, or bill of materials (BOM).
All Ethernet devices require a unique 48-bit Ethernet media access control
(MAC) address. All Nios EDK kits ship with the same default MAC
address. This MAC address serves as a placeholder during development.
To obtain your own block of unique Ethernet MAC addresses for your
products, refer to the IEEE web site at
http://www.standards.ieee.org/regauth/oui/index.shtml.
A single Nios EDK system can use the default MAC address on a LAN
without a conflict. However, two Nios EDK systems with the same MAC
address will cause conflicts. If you are using two or more Nios EDK
systems on the same LAN, you must assign a unique Ethernet MAC
address to each system.
The Nios Development Kit and the Nios EDK form a prototyping
platform for creating your custom embedded, networked system. These
development boards, reference designs, and applications allow you to
rapidly prototype your application.
Altera Corporation 11
Page 12

Page 13

Verify Kit
Contents
Getting Started
This section explains how to set up the Nios EDK daughter card, install
the Nios EDK files, load the hardware reference design into the board and
run the Ethernet application examples.
Verify the following items are included in your Nios Ethernet
Development Kit:
■ Nios EDK daughter card based on the SMSC LAN 91C111
PHY/MAC chip
■ Male-to-male RJ-45 network cable
■ Female-to-male crossover adapter, used for direct-PC connection
■ Nios EDK CD-ROM
■ O’Reilly Internet Core Protocols Manual
■ Nios Ethernet Development Kit User Guide
2
Getting Started
Set Up the
Daughter Card
f
The hardware reference designs included with the Nios EDK assume the
daughter card is connected to the prototype connectors JP8, JP9, and JP10
on the Nios development board and that your board is already set up.
If you are setting up your Nios development board for the first time, see
the Nios Embedded Processor Getting Started User Guide.
1. Verify that your Nios board is set up correctly and the power is off.
Altera Corporation 13
Page 14
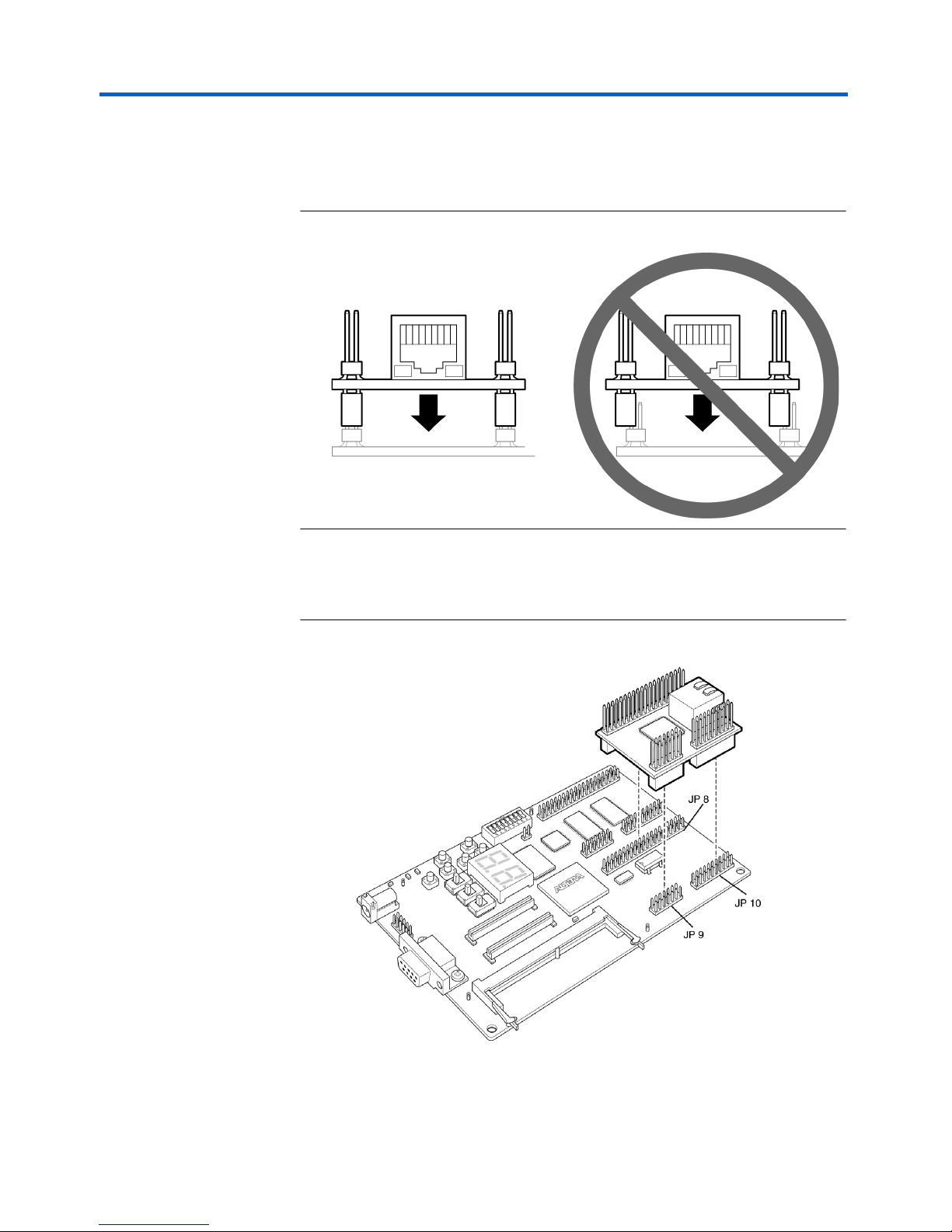
Getting Started Nios Ethernet Development Kit User Guide
1 When connecting the daughter card, make sure you place the
card on the prototype connectors correctly as shown in Figure 1.
If you do not, the board may be permanently damaged.
Figure 1. Correct & Incorrect Daughter Card Connection
2. Place the daughter card on the JP8, JP9, and JP10 prototype
connectors.
Figure 2. Daughter Card Placement for Use with the APEX Reference Design
14 Altera Corporation
Page 15
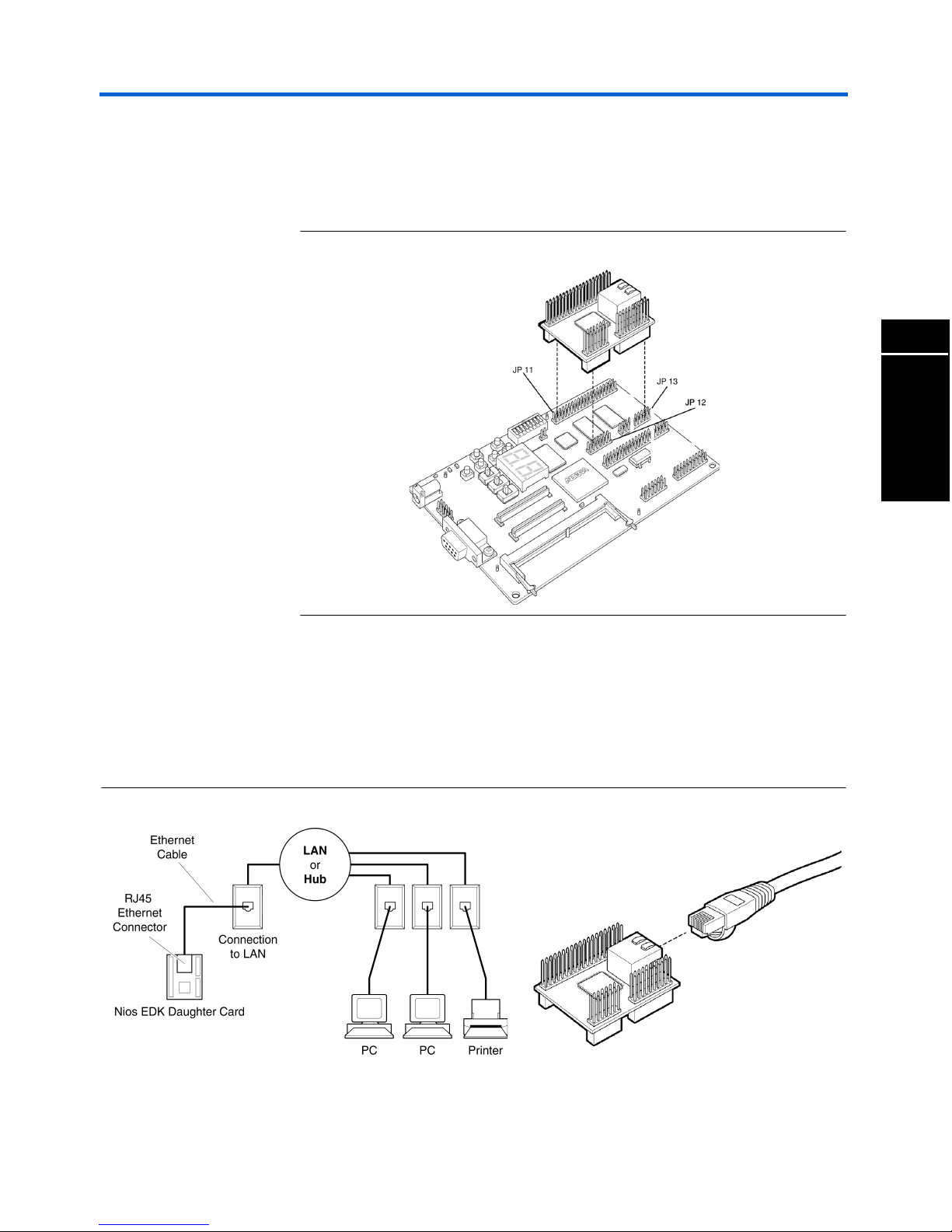
Nios Ethernet Development Kit User Guide Getting Started
1 The daughter card can also be placed on the JP11, JP12, and JP13
prototype connectors. However, the APEX hardware reference
designs shipped with the kit do not target these prototype
connectors and will need to be changed.
Figure 3. Alternative Placement of the Daughter Card
2
Getting Started
3. Connect the network cable to the daughter card.
If you are connected to a LAN or HUB:
Connect the male-to-male networking cable to the RJ-45 connector
on the daughter card as shown in Figure 4.
Figure 4. Using the Nios EDK with a LAN or HUB
Altera Corporation 15
Page 16
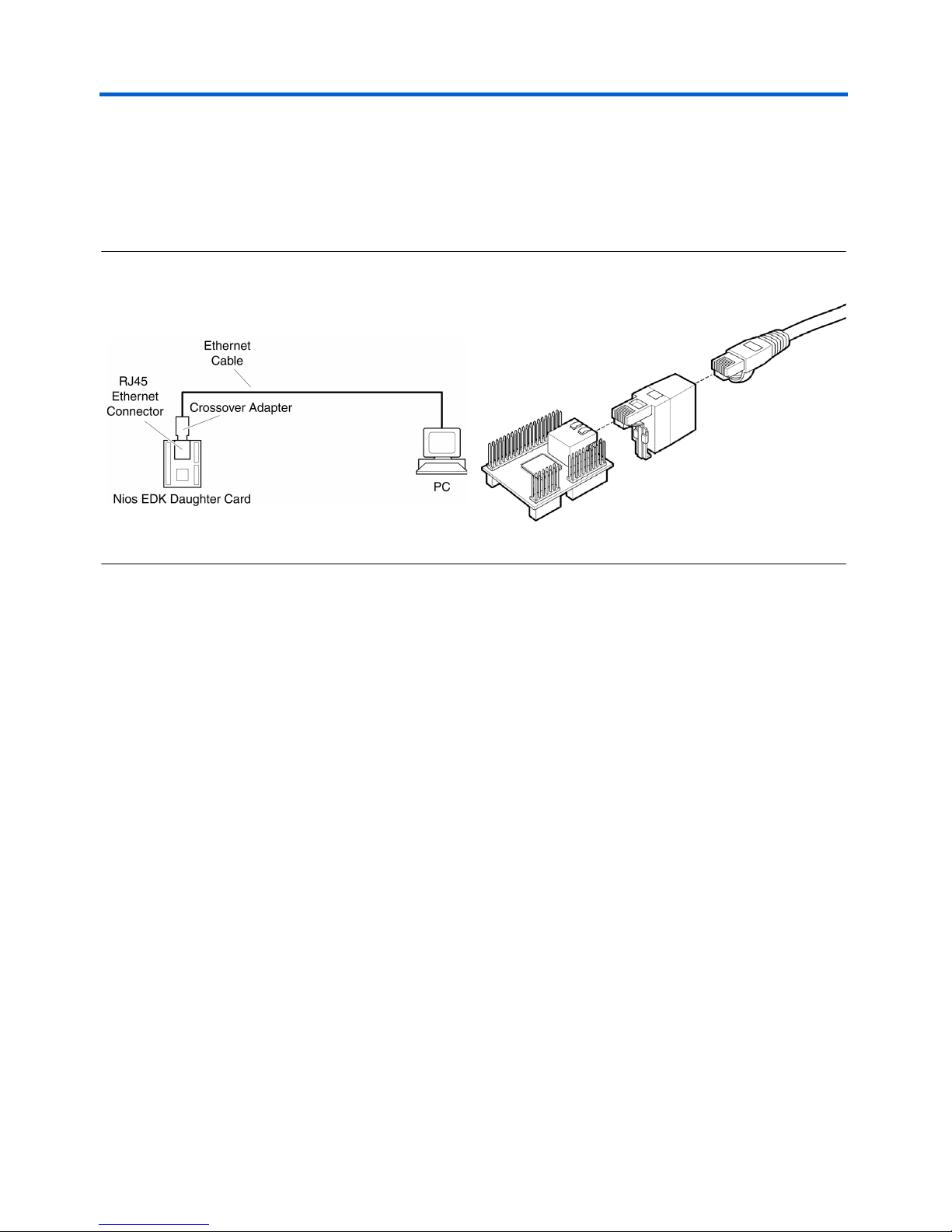
Getting Started Nios Ethernet Development Kit User Guide
If you are not using a LAN or HUB connection and are connected
directly to a workstation or PC Ethernet jack, insert the female-tomale RJ-45 crossover adapter to the networking cable and then
connect the adapter to the RJ-45 on the daughter card as shown in
Figure 5.
Figure 5. Using the Nios EDK with a Workstation or PC Ethernet Jack
Install the
Hardware and
Software Files
f
4. Connect the other end of the networking cable to your Ethernet LAN
or workstation.
The instructions below are for a Windows PC. These instructions assume
you have already installed or upgraded your Nios Development Kit to
version 2.1 or higher.
1. Insert the Nios EDK CD-ROM into your CD-ROM drive. The
InstallShield installer begins automatically.
Unix users: See the readme text file for installation instructions.
16 Altera Corporation
Page 17
Nios Ethernet Development Kit User Guide Getting Started
2. Follow the installation instructions. The screen in Figure 6 appears
when you have completed the installation. Click Finish.
Figure 6. Install Completed
2
Getting Started
Load the
Reference
Design
This section explains how you will use the Quartus
Nios ethernet reference design into the Nios development board. All
instructions assume you are using the Quartus II software.
1. Click the Start Menu > Programs > Altera > Nios Ethernet
Development Kit 2.0 > Nios Ethernet Development Kit Reference
Design.
2. In the Quartus II software, click the Open Programmer icon.
Figure 7. Quartus II Software Icons
Open Programmer Icon
®
II software to load the
Altera Corporation 17
Page 18
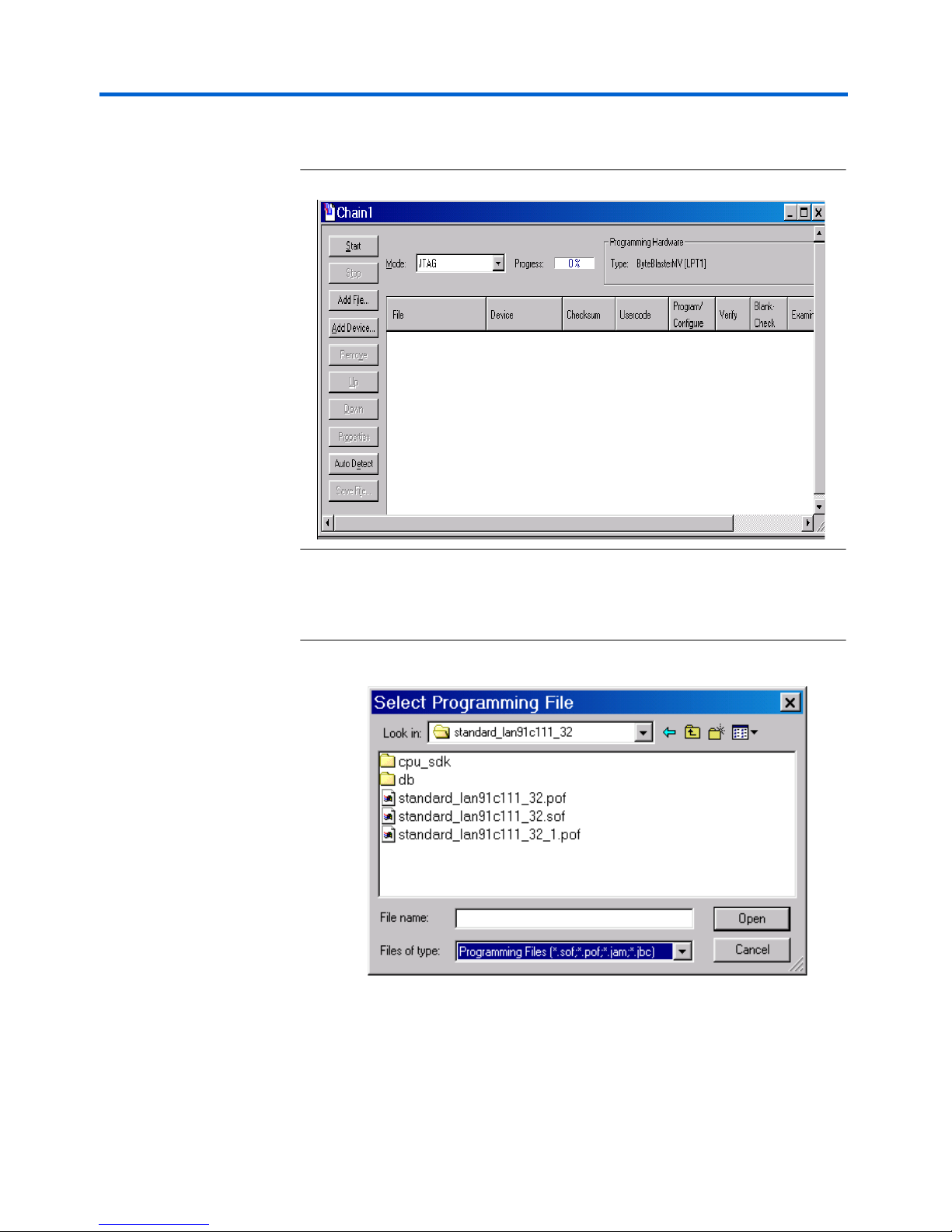
Getting Started Nios Ethernet Development Kit User Guide
The Chain 1 dialog box appears as shown in Figure 8.
Figure 8. Chain 1 Dialog Box
3. Click Add File. The Select File dialog box appears as shown in
Figure 9.
Figure 9. The Select File Dialog Box
18 Altera Corporation
Page 19
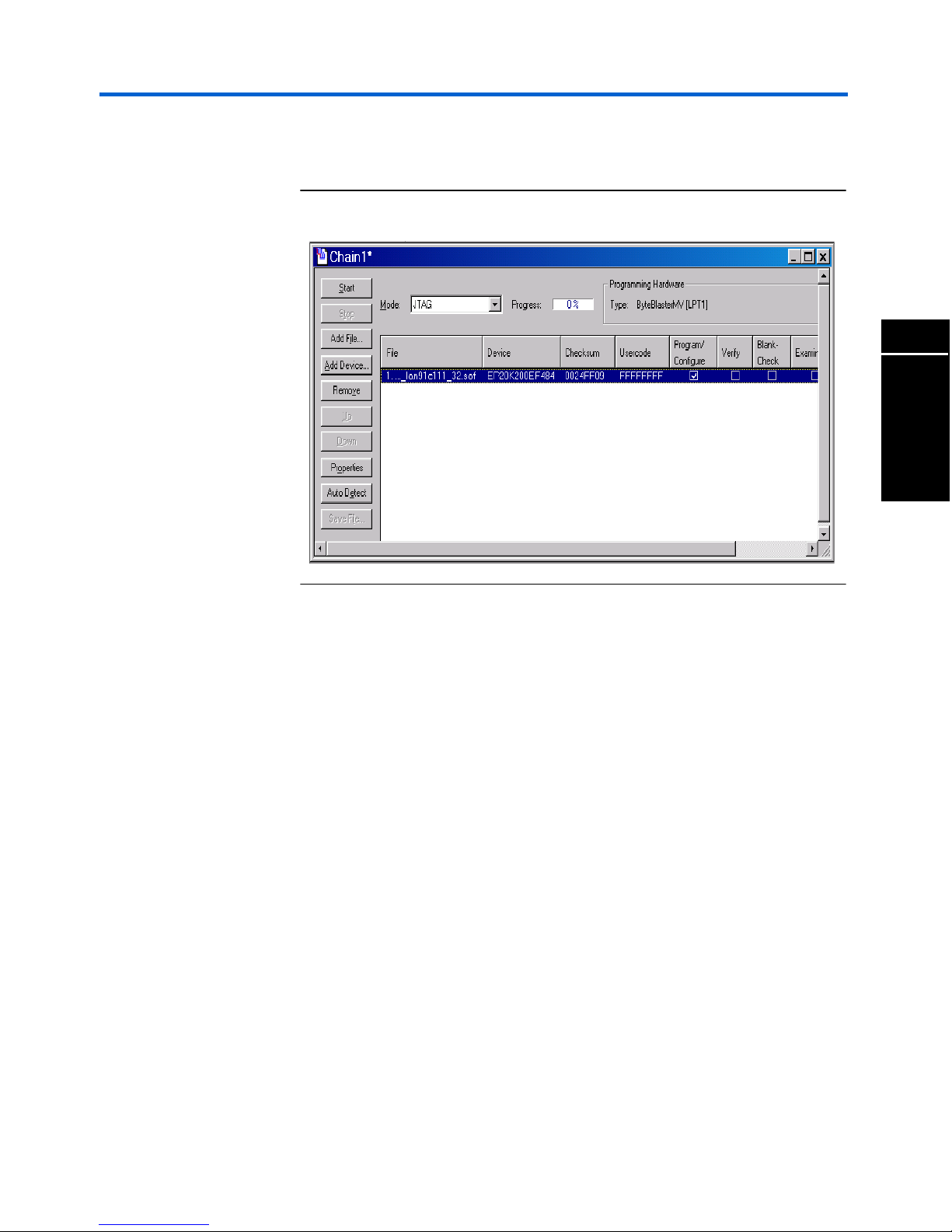
Nios Ethernet Development Kit User Guide Getting Started
4. Double-click the standard_lan91c111_32.sof file and the file appears
in the Chain 1 dialog box as shown in Figure 10.
Figure 10. Chain 1 Dialog Box
2
Getting Started
5. Click the check box in the Program/Configure column as shown in
Figure 10.
6. Check the Programming Hardware section of the screen as shown in
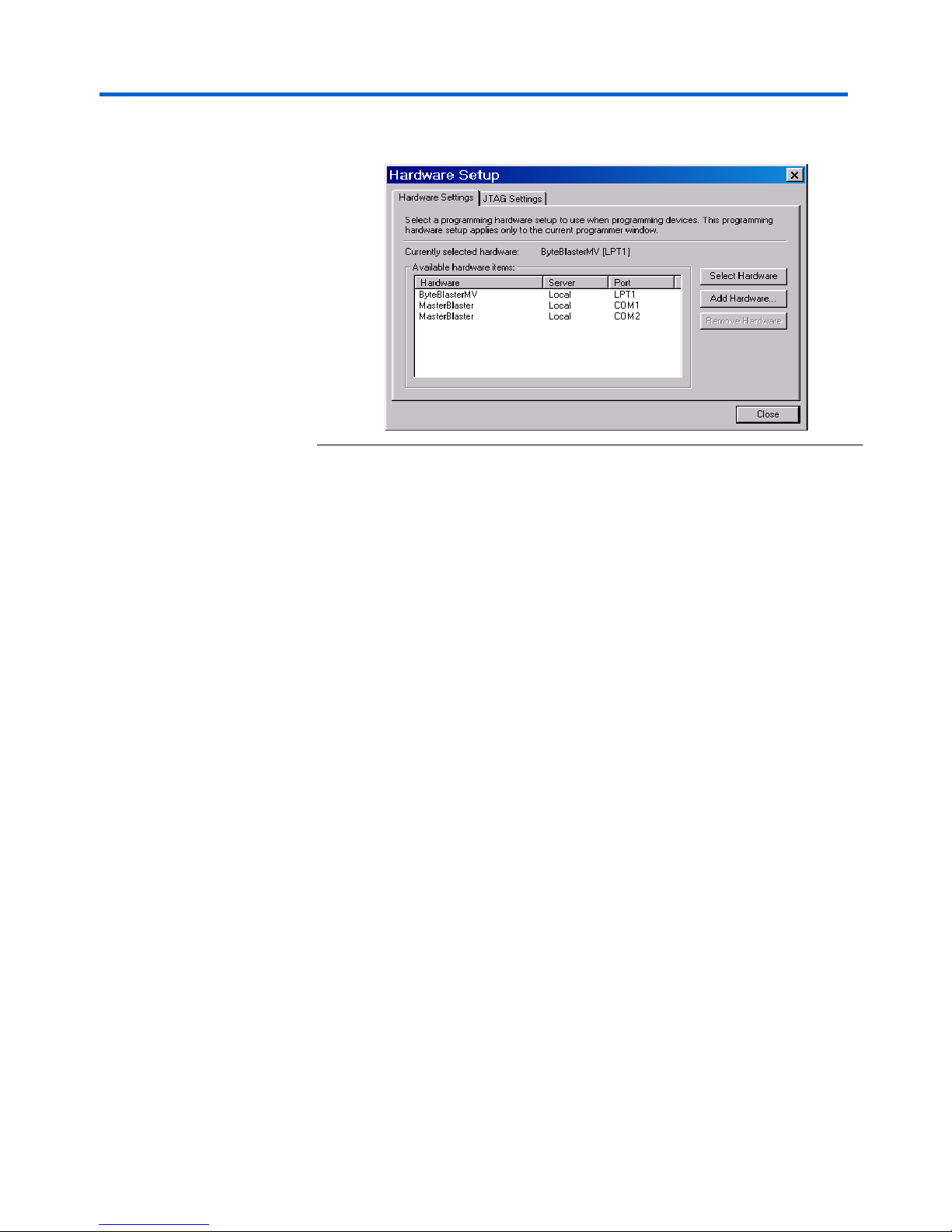
Figure 10. ByteBlasterMV™ should appear in the Type field
selection. To change the type, click Setup and select ByteBlasterMV
from the Hardware Type drop-down list box.
Altera Corporation 19
Page 20
Getting Started Nios Ethernet Development Kit User Guide
Figure 11. ByteBlasterMV Selection
1 If ByteBlasterMV is not an available selection, you will need to
install the ByteBlasterMV driver.
f
f
Run Example
Applications
For information about installing the ByteBlasterMV driver, see the
Quartus II Installation & Licensing for PCs Manual at the Altera web site.
7. In the Chain 1 dailog box, click Start . See Figure 10 on page 19. The
two-digit seven-segment display on the Nios development board
turns off. When the download is completed, the Progress bar reads
100% and the dual seven-segment LED display lights turn on.
If you encounter a JTAG error, see the Nios Embedded Processor
Development Board Data Sheet for information on setting the switches
correctly.
Using the Nios SDK Shell, you will now run the example applications.
Nios software is developed in the Bash environment. If you are unfamiliar
with the Bash environment, refer to the Nios Embedded Processor Software
Development Reference Manual for more information.
The Hello Plugs Application Example
To run Hello Plugs, follow these steps:
1. Click the Start Menu > Programs > Altera > Excalibur Nios 2.1>
Nios SDK Shell. The SDK Shell window appears and displays the
SDK Shell prompt as shown in Figure 12 on page 21.
20 Altera Corporation
Page 21
Nios Ethernet Development Kit User Guide Getting Started
Figure 12. The Nios SDK Shell
2
Getting Started
f
2. At the prompt, type;
cd verilog/nios_dev_board/ethernet/
standard_lan91c111_32/cpu_sdk/src r
1 If you installed the Nios EDK program in another directory,
make the appropriate change in step 2.
3. Type nios-build hello_plugs.c r
The default setting for the nios-run utility is <COM1>. For more
information about specifying another serial port when executing nios-
run,see the Nios Embedded Processor Software Development Reference
Manual.
4. Press SW3 to clear the Nios development board.
5. Type nios-run hello_plugs.srec r
The hello_plugs.srec file begins downloading to the board as
shown in Figure 13.
Altera Corporation 21
Page 22

Getting Started Nios Ethernet Development Kit User Guide
Figure 13. Downloading File to the Development Board
1 If this is the first time you are using the Nios product, the Nios
Peripheral Test Menu could appear. If this menu appears, press
Ctrl+C and then repeat Step 5.
Once the download is completed, the Hello Plugs Main Menu appears as
shown in Figure 14.
Figure 14. The Nios Ethernet Hello Plugs Main Menu
22 Altera Corporation
Page 23

Nios Ethernet Development Kit User Guide Getting Started
Before you can use Hello Plugs, the network-based GERMS monitor, or
the simple web server application examples, you must first configure your
network settings.
Configure Your Network Settings
The instructions for configuring your network settings will only work if
your PC is connected directly to your Nios development board with a
Nios EDK daughter card using an Ethernet cable and crossover adapter.
You can also connect your Ethernet daughter card to your office LAN.
Consult with your system administrator.
1 Do not press r after entering the letters in steps 1 through 3.
1. From the Hello Plugs menu, type a to select Network Settings to set
the network settings of your Ethernet card. The Network Settings
Menu appears as shown in Figure 15.
Figure 15. Configure Your Network Settings
2
Getting Started
2. Type d to select Reset All Settings.
3. Type c to select Enter New Settings. You will then be prompted to
4. Press r to keep the default settings for the ethernet address.
Altera Corporation 23
enter each of the five settings shown above.
Page 24

Getting Started Nios Ethernet Development Kit User Guide
5. Type your PC’s IP address for the IP address. Change the last
number in the IP address up or down one digit (the allowable range
is 2 to 254). For example, if your PC is using IP address 64.3.99.73, set
your Nios EDK to 64.3.99.72 or 64.3.99.74.
1 If you are connecting your Nios EDK to your office LAN, ask
your system administrator for an unused static IP address. If you
are using more than one Nios board on your LAN, give each
board a distinct Ethernet address (MAC address). Below are safe
MAC addresses for you to use:
00:42:00:00:23:00
00:23:23:00:23:23
00:42:42:42:42:00
6. Type your PC’s nameserver address for the nameserver ip address.
1 You will only use the nameserver ip address if your Nios EDK is
connected to a LAN.
7. Use the default setting for the subnet mask.
1 If you are connected to a LAN, use the same subnet mask that
your PC uses.
8. Type the same setting as your PC for the gateway ip address.
1 You will only use the gateway ip address if your Nios EDK is
connected to a LAN.
9. Type b (Save To Flash) after entering all the settings. This writes the
network settings to the Nios development board flash memory.
1 See “nr_plugs_initialize” on page 50 for an explanation about
using these stored settings in your own software applications.
The Networked-Based GERMS Monitor Application Example
To use this application example, you should be familiar with the Nios
GERMS monitor and you must first run the Hello Plugs application to
setup your network parameters. See “The Hello Plugs Application
Example” on page 20 for more information.
24 Altera Corporation
Page 25

Nios Ethernet Development Kit User Guide Getting Started
f
For more information about using the GERMS monitor, refer to the Nios
Embedded Processor Software Development Reference Manual at
http://www.altera.com.
To run the networked-based GERMS monitor application example, follow
these steps:
1. Run the Hello Plugs application to setup your network parameters if
you have not done so already. This only needs to be done once.
2. Press Ctrl+C.
3. Build the GERMS server and client by typing the following
command:
make -f Makefile_nedk all r
4. Press SW3 to clear the development board.
5. Download the GERMS server application .srec by typing the
following command:
nios-run -x germs_server.srec r
2
Getting Started
f
For more information about the nios-run command line options, see the
Nios Embedded Processor Software Development Reference Manual at the
Altera web site.
6. Connect to the GERMS server using the client application by typing
the following command at the prompt:
germs_client -n <Nios IP address> -t r
When running the client, make sure you supply the correct IP
address of the Nios board. This will be the same IP address you
entered when setting your network parameters in Hello Plugs (the
IP address in this example is 137.57.136.179 as shown in Figure 15 on
page 23).
1 Pressing Enter causes a memory dump to display as shown in
Figure 16.
Altera Corporation 25
Page 26

Getting Started Nios Ethernet Development Kit User Guide
Figure 16. Connecting to the GERMS Server
7. Press the ? key + Enter to display the GERMS menu as shown in
Figure 17.
Figure 17. The Nios GERMS Menu
8. To change the dual 7-segment display, type m420:3636 r This
26 Altera Corporation
command confirms your networked GERMS monitor-based
application example is working.
Page 27

Nios Ethernet Development Kit User Guide Getting Started
1 For more information, see the readme_nedk_germs.txt file
included in your kit.
The Simple Web Server Application Example
To use this application example, you must first run the Hello Plugs
application to setup your network parameters. See “The Hello Plugs
Application Example” on page 20 for more information. To run the simple
web server application example, follow these steps:
f
1. Begin by building a flash image of the web pages. To do this, type the
following command:
wosfs_maker.pl exc-nios.gif index.html
template_page.html.template 404_page.html
static_page.html > pages.flash r
2. Store the web pages in flash memory by typing the following
command:
nios-run -x pages.flash r
For more information about the nios-run command-line options, see the
Nios Embedded Processor Software Development Reference Manual found at
the Altera web site.
3. Build the example web server by typing the following command:
nios-build wosfs.c nedk_example_web_server.c r
4. Run the web server by typing the following command:
2
Getting Started
5. Open your web browser to view the web page you built. In the
Altera Corporation 27
nios-run nedk_example_web_server.srec r
Address field, enter the IP address you used as a network settings
for your Ethernet card to display your web page.
Page 28

Page 29

Daughter Card
This section describes the network interface daughter card included in the
Nios EDK.
Daughter Card
Components
The Nios EDK daughter card is a circuit board with the following
components: See Figure 18.
■ A SMSC LAN 91C111 integrated Ethernet 10 Mbit/100 Mbit
PHY/MAC chip
– See http://www.smsc.com/main/catalog/lan91c111.html for
more information about the SMSC LAN91C111 chip
■ A RJ-45 network connector with integrated-transformer magnetics
and Link/LAN LEDs
■ Three female connectors for mounting on the Nios development
board
■ Three male headers for stacking two daughter cards
■ A 25 MHz crystal oscillator that is used by the SMSC LAN 91C111
chip
■ All necessary resistors and capacitors
A complete manufacturing bill of materials for the daughter card is
provided in the installed nedk_daughter_card_documents directory.
Figure 18. The Nios EDK Daughter Card
3
Daughter Card
Altera Corporation 29
RJ-45 connector
LAN91C111
Ethernet
controller
Page 30

Daughter Card Nios Ethernet Development Kit User Guide
Functional
Overview
Stack Daughter
Cards
The main functional component on the Nios EDK daughter card is a
LAN91C111 integrated PHY/MAC chip. See http://www.smsc.com/
main/catalog/lan91c111.html for detailed specifications. The
LAN91C111 presents an ISA-bus interface to the Nios CPU. The necessary
electrical-interface signals are provided on the set of female connectors.
These connectors are compatible with the expansion connector groups on
the Nios development board. The Nios EDK daughter card is compatible
with either the 5-V (JP11, JP12, JP13) or the 3.3-V (JP8, JP9, JP10) expansion
connector groups. The daughter card does not use any 5-V signals.
1 All of the included reference designs use a Nios EDK daughter
card connected to the 3.3-V expansion connector group (JP8, JP9,
and JP10).
1 To use a Nios EDK daughter card connected to the 5-V expansion
connector group, you will need to create a new APEX
configuration with the appropriate pin-assignments.
The Nios EDK daughter card connectors are arranged such that two
daughter cards can be stacked vertically as shown in Figure 19. Two
stacked daughter cards can be accessed via the shared tri-state data bus.
The Nios EDK includes only one daughter card. The electrical interface
does not support stacks more than two cards deep.
Figure 19. Stacked Daughter Cards
30 Altera Corporation
Page 31

Nios Ethernet Development Kit User Guide Daughter Card
SOPC Builder
Library
Component
Figure 20. SOPC Builder Menu
The Nios EDK includes an SOPC Builder library component that provides
all logic and I/O signals necessary for using the daughter card. A library
component is an add-on to the SOPC Builder that makes a new peripheral
available. After the Nios EDK is installed, you will see a new library
component in the SOPC Builder’s menu of available system choices. The
new component is named Ethernet interface (lan91c111). You can add one
or more of these components to your Nios system using SOPC Builder as
shown in Figure 20.
3
Daughter Card
f
Altera Corporation 31
See the Nios Tutorial for more information about the SOPC Builder menus
and the SOPC Builder Data Sheet for a description of the SOPC Builder tool
at the Altera web site.
Page 32

Daughter Card Nios Ethernet Development Kit User Guide
Each Ethernet interface (lan91c111) component in your system will have
an associated group of I/O pins on your system module. A detailed
description of how to connect these system-module I/O pins to the Nios
EDK daughter card can be found at “Nios System to Daughter Card Pin
Map” on page 34. An example of the necessary connections (pin-
assignments) can also be found in the included reference designs.
1 When creating your own system, it is easier to start with one of
the reference designs in the kit and then modify the design as
necessary. This way you know the I/O pins are assigned
correctly
To access two stacked daughter cards, their associated Ethernet interface
(lan91c111) peripherals must be assigned to the same, shared tri-state data
bus.
The LAN91C111 chip should be used in either memory mode or I/Omode. See http://www.smsc.com/main/catalog/lan91c111.html for
more information. The included Ethernet interface (lan91c111) library
component and all associated software libraries use the LAN91C111 chip
in I/O-mode. The electrical interface on the daughter card supports
memory-mode operation, but none of the included Nios EDK interface
logic, reference designs, or software libraries make use of this feature. All
of the examples, software, and documentation in the Nios EDK show the
LAN91C111 being used in I/O-mode.
Connector
Pinouts
This section provides complete pinouts for connectors F8, F9, and F10 on
the Nios EDK daughter card. The Nios CPU accesses the daughter card
through these connectors. Most of the interface pins connect directly to
device pins on the LAN91C111 chip. Where appropriate, the connector
diagrams indicate the name of the LAN91C111 pin that corresponds to
each connector pin. Detailed schematics showing all components and
connections on the daughter card are found at the following site
http://www.smsc.com/main/catalog/lan91c111.html. See Figure 21
through Figure 23.
32 Altera Corporation
Page 33

Nios Ethernet Development Kit User Guide Daughter Card
Figure 21. F2 Connector Pinouts
Figure 22. F1 Connector Pinouts
3
Daughter Card
Altera Corporation 33
Page 34

Daughter Card Nios Ethernet Development Kit User Guide
Figure 23. F3 Connector Pinouts
Nios System to
Daughter Card
Pin Map
Each Ethernet interface (lan91c111) peripheral in your Nios system has an
associated set of I/O pins on your system module. This section describes
how to connect these system-module I/O pins to the daughter card. In
general, you establish these connections by making pin assignments in
your FPGA design. The reference designs included with the kit include
correct pin-assignment information that you can modify for your own
design.
The names given to the system-module I/O ports depends on the name
you provide for the Ethernet interface (lan91c111) peripheral. In Table 4
and Table 5, <your_name> indicates the name you assigned to this
component. The name for some system-module I/O ports also depends
on the tri-state bus you have selected for this peripheral. In Table 4 and
Table 5, <your_bus_name> indicates the name of the bus to which you
assigned this Ethernet interface (lan91c111) peripheral.
34 Altera Corporation
Page 35

Nios Ethernet Development Kit User Guide Daughter Card
Table 4. Nios 32-bit CPU System Module I/O Port Name and Daughter
Card Pin Name
Daughter Card Pin Name 32-bit CPU System Module I/O Port Name
AEN GND (logic 0)
INT (lower) irq_to_the <your_name> of lower card
INT (upper) irq_to_the <your_name> of upper card
IOR_n (upper) ior_n to the <your_name> of the upper card
IOW_n (upper) iow_n to the <your_name> of the upper card
IOCHRDY N/C
IOR_n (lower) ior_n to the <your_name> of the lower card
IOW_n (lower) iow_n to the <your_name> of the lower card
LDEV_n N/C
LOOPBACK N/C
RESET (system module reset_n)
SA0 GND (logic 0)
SA1 <your_bus_name>_address [2]
SA2 <your_bus_name>_address [3]
SA3 <your_bus_name>_address [4]
SA4 GND (logic 0)
SA5 GND (logic 0)
SA6 GND (logic 0)
SA7 GND (logic 0)
SA8 VCC (logic 1)
SA9 VCC (logic 1)
SA10 GND (logic 0)
SA11 GND (logic 0)
SBHE_n GND (logic 0)
SD0 <your_bus_name>_data [0]
SD1 <your_bus_name>_data [1]
SD2 <your_bus_name>_data [2]
SD3 <your_bus_name>_data [3]
SD4 <your_bus_name>_data [4]
SD5 <your_bus_name>_data [5]
SD6 <your_bus_name>_data [6]
SD7 <your_bus_name>_data [7]
SD8 <your_bus_name>_data [8]
SD9 <your_bus_name>_data [9]
SD10 <your_bus_name>_data [10]
SD11 <your_bus_name>_data [11]
3
Daughter Card
Altera Corporation 35
Page 36

Daughter Card Nios Ethernet Development Kit User Guide
Table 4. Nios 32-bit CPU System Module I/O Port Name and Daughter
Card Pin Name
Daughter Card Pin Name 32-bit CPU System Module I/O Port Name
SD12 <your_bus_name>_data [12]
SD13 <your_bus_name>_data [13]
SD14 <your_bus_name>_data [14]
SD15 <your_bus_name>_data [15]
If you are connecting an Ethernet interface (lan91c111) peripheral
component to the upper of the two stacked daughter cards, then
substitute (upper) for (lower) in the left column of the above table.
1 For pin assignments, refer to the Quartus II software design file.
36 Altera Corporation
Page 37

Nios Ethernet Development Kit User Guide Daughter Card
Table 5. Nios 16-bit CPU System Module I/O Port Name and Daughter Card
Pin Name
Daughter Card Pin Name 16-bit CPU System Module I/O Port Name
SD[15..0] <your_bus_name>_data
SA[3] <your_bus_name>_address [3]
SA[2] <your_bus_name>_address [2]
SA[1] <your_bus_name>_address [1]
SHBE_n <your_bus_name>_byteenablen[1]
IOR_n (lower) ior_n_to_the_<your_name>
IOW_n (lower) iow_n_to_the_<your_name>
INTRQ0 (lower) irq_to_the_<your_name>
RESET ~(system module reset_n)
MEMW_n constant Logic-1
MEMR_n constant Logic-1
SA[9..8] constant Logic-1
SA[11..10] constant Logic-0
SA[7..4] constant Logic-0
SA[0] constant Logic-0
CHIPSEL_n (lower) constant Logic-0
CHIPSEL_n (upper) constant Logic-0
3
Daughter Card
If you are connecting an Ethernet interface (lan91c111) peripheral
component to the upper of the two stacked daughter cards, then
substitute (upper) for (lower) in the left column of the above table.
1 For pin assignments, refer to the Quartus II software design file.
Altera Corporation 37
Page 38

Page 39

Software Overview
Software
Description
The software library included in the Nios EDK is called the Plugs Library.
The Plugs Library allows your software to use network protocols for
transmitting and receiving data. The information in this chapter is
applicable to the LAN91C111 PHY/MAC chip.
System Requirements
■ Nios CPU
■ 20 Kbytes code footprint
■ 8 Kbytes data footprint
■ Nios Timer peripheral named timer 1
Protocols Supported
■ Raw Ethernet
■ Address resolution protocol (ARP)
■ Internet protocol (IP)
■ Internet control message protocol (ICMP)
■ User datagram protocol (UDP)
■ Transmission control protocol (TCP)
Library Features
■ Access to low-level packets
■ Access to high-level packet payloads
■ Conforms to RFCs
■ Allows you to open connections and send data with only a few lines
of code
■ Is similar to the Unix standard sockets routines
■ Each plug can be set to print debug information for either transmit or
receive data
1 The Plugs Library requires your system to have a Timer
peripheral named timer 1.
The customized software development kit for the LAN91C111 Ethernetadapter peripherals contains the Plugs Library and example applications.
This library contains single-threaded routines that rely on polling.
Altera Corporation 39
4
Overview
Software
Page 40

Software Overview Nios Ethernet Development Kit User Guide
Protocols
Architecture
Figure 24 shows the relationships between the library-supported Nios
EDK protocols.
Figure 24. Nios EDK Protocol Structure
hello_plugs.c
ARP Scanner
ARP
PING
ICMP
UDP
IP
TELNET
World Wide Web
TCP
Standards
Raw Ethernet
PLUGS LIBRARY
The protocols supported by the Plugs Library adhere to the standards
recommended by the RFCs at http://www.ietf.org.
The Nios EDK supports Ethernet and 802.3 packets. To send an 802.3
packet, the application has to construct all fields explicitly. Higher-level
protocols do not support 802.3, and uses Ethernet instead. Nios EDK does
NOT support trailer encapsulation as documented in RFC 893.
The library routines send and receive Ethernet packets to and from
arbitrary 48-bit MAC addresses. Higher-level protocols such as ICMP,
UDP, and TCP use Ethernet transparently.
40 Altera Corporation
Page 41

Nios Ethernet Development Kit User Guide Software Overview
ARP (RFC 826)
Library routines are provided to query the LAN for the Ethernet address
of a particular remote IP address, and to respond to queries for the local
IP address. Other protocols like IP use ARP transparently.
IP (RFC 791)
Nios EDK encapsulates IP on Ethernet (RFC 894). Library routines are
provided for sending and receiving IP packets to and from a user-defined
32-bit remote IP address. Higher-level protocols like ICMP, UDP, and
TCP use IP transparently.
■ The Nios EDK does not support IP packet fragmentation.
■ The Nios EDK supports IPv4.
ICMP (RFC 792)
The Plugs Library can respond to an ICMP echo request (ping). Library
routines are provided to send and receive ICMP error messages.
UDP (RFC 768)
UDP is a low-level packet format built on top of IP. Library routines are
provided to send and receive UDP packets to and from an arbitrary 32-bit
remote IP address and 16-bit port number. Higher-level protocols like
DNS use UDP transparently.
DNS (RFC 1034 & 1035)
Library routines are provided to transmit a DNS query for a host name to
a specified name server. If the host name is found, the name server returns
the associated IP address requested. The Nios EDK supports UDP
encapsulation of DNS and does not support TCP encapsulation of DNS.
TCP (RFC 793)
TCP is a connection-oriented protocol built on top of IP. Library routines
are provided to open a TCP connection to an arbitrary 32-bit IP address
and 16-bit port. This protocol receives requests for incoming connections,
accepts or denies requests for incoming connections, transmits and
receives bytes on an established connection, and closes an established
connection.
4
Overview
Software
Altera Corporation 41
Page 42

Software Overview Nios Ethernet Development Kit User Guide
Build Options
The following build options are provided for modulating the features and
the footprint of the Plugs Library.
PLUGS_DEBUG (Default Value = 1)
This build option may be set to zero, to disable all debug-printing
features, or 1 or 2 to enables debug-printing for plugs that are created with
the ne_plugs_flag_debug_rx or ne_plugs_flag_debug_tx flags
set. When set to zero, no printing code is linked to the plug.
PLUGS_PLUG_COUNT (Default Value = 6)
This build option sets the maximum number of plugs that you can create.
The library can handle a maximum of 32 plugs. The library itself uses 2 or
3 ports per adapter for managing ARP, pings, and DNS. Changing this
option affects the amount of static storage used by the library.
1 When using a stacked reference design (two adapters), it is
necessary to increase the default value number. The
recommended value is 10.
PLUGS_ADAPTER_COUNT (Default Value = 2)
The Plugs Library can support multiple network adapters. This build
option sets the maximum number of adapters that can be used. It affects
the amount of static storage used by the library.
PLUGS_DNS (Default Value = 1)
The Plugs Library lets you establish connections to a remote network
device using either its name or its IP address. If you use its name, the Plugs
Library contacts a domain name server to translate it into an IP address. If
your application does not need to establish outgoing connections (the
application is a server only), or uses IP addresses only, then this build
option can be set to zero to omit the code that implements name lookups.
PLUGS_PING (Default Value = 1)
In general, every network device should respond to an ICMP echo request
message (ping). You can disable a ping response to save a small amount
of code space by setting this build option to zero.
42 Altera Corporation
Page 43

Nios Ethernet Development Kit User Guide Software Overview
PLUGS_TCP (Default Value = 1)
If your application does not use TCP for any of its plugs, you can disable
it and save a small amount of code space by setting this build option to
zero.
Byte Order
Network-byte order is big endian. The Nios CPU byte order is little
endian. Because of this, packet header numbers reside in memory in
reverse order. This is often desirable for comparing the packet header
numbers to other packet header numbers being sent over the network.
The normal ordering for a particular CPU is called host ordering.
It is important to know whether a particular integer in memory or a
register is in host order or network order when using the Nios EDK Plugs
Library.
Some parameters to routines in the Plugs Library are given in network
order, and others are given in host order. To distinguish between network
order and host order, the following data types are declared:
typedef unsigned char host_8
typedef unsigned short host_16
typedef unsigned long host_32
typedef unsigned char net_8
typedef unsigned short net_16
typedef unsigned long net_32
Altera Corporation 43
4
Overview
Software
Page 44

Software Overview Nios Ethernet Development Kit User Guide
Data Structures
ns_plugs_network_setting
Structure: typedef struct
{
net_48 ethernet_address;
short pad;
net_32 ip_address;
net_32 nameserver_ip_address;
} ns_plugs_network_settings;
Description: This structure is used to configure an adapter with all the
necessary network information. It is passed to the Plugs
Library routine nr_plugs_initialize() for each
adapter.
Structure member:
ethernet_address This is a 48-bit value in network-byte order. Every
Ethernet card must have a unique 48-bit MAC address.
(These addresses are managed by the IEEE. Information
on obtaining a legal Ethernet MAC address can be found
at www.ieee.org; search for OUI, Organizationally Unique
Identifier)
pad This member is unused.
ip_address This is a 32-bit IP address in network-byte order. It should
be an unused IP address within the range of the LAN
connection to the Nios-based device
nameserver_ip_address This is a 32-bit IP address in network-byte order. If your
Nios-based device needs to establish connections with
remote network devices using their DNS names (using the
remote_name parameter of the Plugs Library
nr_plugs_connect() or nr_plugs_name_to_ip()
routines), then you must provide the name server’s IP
address for the Plugs Library to use.
.
44 Altera Corporation
Page 45

Nios Ethernet Development Kit User Guide Software Overview
ns_plugs_network_setting
subnet_mask This is a 32-bit value in network-byte order. This mask val-
ue is used to determine if a particular remote network device is on the same LAN as the Nios-based device. If any
bits of the Nios-based device’s IP address differ from any
bits of the remote network device’s IP address, and the
corresponding subnet mask bit is set, then the remote device is not on the LAN. The Plugs Library sends packets
for remote devices that are not on the LAN to the local
gateway.
gateway_ip_address This is a 32-bit value in network-byte order. If the Nios-
based device is communicating with devices that are not
on the LAN, it must send packets to the gateway. The
gateway is then responsible for routing packets appropriately.
Altera Corporation 45
4
Overview
Software
Page 46

Software Overview Nios Ethernet Development Kit User Guide
ns_plugs_persistent_network_settings
Structure: typedef struct
{
long settings_index; // 0..3
ns_plugs_network_settings settings[4];
} ns_plugs_persistent_network_settings;
Description: The example programs that use the Plugs Library make use
of nonvolatile network settings stored in the Flash memory.
The program hello_plugs.c lets you enter up to four sets
of network settings, and use these setting interchangeably.
The default location in the Flash memory on the Nios
development board is 0x00106000. You can direct the Plugs
Library routine nr_plugs_initialize() to use the
nonvolatile network settings selected by the
settings_index member by passing zero for the settings
parameter.
Structure member:
setting_index An integer that ranges from 0 to 3. This index determines
which of the 4 stored network settings to use.
setting An array of four elements of type
ns_plugs_network_settings. Up to four complete
network settings can be stored in the Flash memory; the one
that is used is determined by the settings_index
member.
46 Altera Corporation
Page 47

Nios Ethernet Development Kit User Guide Software Overview
Payload
Descriptions
Table 6. Nios EDK Protocol Payload Descriptions
Protocol Payload Description Payload Protocol Type Maximum Payload
Ethernet Header portion of Ethernet packet followed
by any other contents
ARP Header portion of ARP packet, which is the
payload portion of the Ethernet packet
IP Payload portion of the IP packet unsigned char * 1024
ICMP Header portion of the ICMP packet ns_icmp_packet * 1024
UDP Payload portion of the UDP packet unsigned char * 1024
TCP Sequential bytes from the stream unsigned char * 512
Each protocol treats a different part of the raw Ethernet packet as the
payload. The payload is the part of the packet passed to the receive
callback procedure. The callback procedure can access the payload and all
encapsulating header information. Table 6 below describes which part of
the packet is treated as the payload for each of the supported protocols.
Size (bytes)
ns_ethernet_packet * 1500
ns_arp_packet * 28
Altera Corporation 47
4
Overview
Software
Page 48

Page 49

Plugs Library Routines
Table 7 lists and describes the Nios plugs library routines.
Table 7. Nios Plugs Library
Routine Description
nr_plugs_initialize Initializes the plugs library
nr_plugs_terminate Terminates the plugs library
nr_plugs_set_mac_led Controls the LED on the RJ-45 jack
nr_plugs_create Allocates a plug
typedef int (*nr_plugs_receive_callback_proc) Application-provided callback routine to receive data
nr_plugs_destroy Deallocates a plug
nr_plugs_connect Associates a plug with a remote IP address and port on the
network
nr_plugs_send Sends a packet to the connected remote-network device
nr_plugs_send_to Sends a packet to a specified IP address and port
nr_plugs_listen Tells a plug to wait for an incoming TCP connection request
typedef int (*nr_plugs_listen_callback_proc) Application-provided callback routine to accept or reject a TCP
connection request
nr_plugs_ip_to_ethernet Converts an IP address to an Ethernet address
nr_plugs_name_to_ip Uses name server to convert a remote-network device name to
an IP address
nr_plugs_idle Polls all network adapters for incoming packets and dispatches
the packets to the receive callback routines
nr_plugs_print_ethernet_packet Prints an Ethernet packet report
nr_n2h16 Translates a network-short integer to a short integer
nr_h2n16 Translates a short integer to a network-short integer
nr_n2h32 Translates a network-long integer to a long integer
nr_h2n32 Translates a long integer to a network-long integer
5
Plugs Library
Altera Corporation 49
Page 50

Plugs Library Routines Nios Ethernet Development Kit User Guide
nr_plugs_initialize
Syntax: int nr_plugs_initialize
(
long flags,
ns_plugs_network_settings *network_settings,
void *adapter_base_address,
int adapter_irq,
ns_plugs_adapter_description *adapter_description
);
Description: This routine can either initialize the plugs library or add an
additional adapter to the plugs library. Each adapter is completely
distinct from each other. If you are using more than one adapter,
each adapter should be added using this routine before calling
any other routine. Each adapter has its own network settings (IP
address, netmask, etc.) Only the first adapter added can perform
DNS lookups.
Parameters: flags This can be 0 or ne_plugs_flag_add_adapter. If it is
ne_plugs_flag_add_adapter, then only the adapter is
initialized and added to the plugs library list of available adapters.
The first adapter has an index number of zero, the second adapter
has an index number of one, and so forth. Some other routines
use this index number to specify a particular adapter.
network_setting A pointer to a structure of type ns_plugs_network_settings
to configure this adapter. If the network_setting is NULL, the
network settings will be retrieved from the Flash memory.
adapter_base_address The hardware address of the adapter peripheral device, if
applicable.
adapter_irq The interrupt number of the ethernet hardware device. If this
parameter is set to zero, interrupts are not enabled and the
adapter is not instructed to enter interrupt mode.
adapter_description A pointer to a structure of type
ns_plugs_adapter_description, that determines the low-
level driver routines for this adapter.
Return Value: The return value is zero for success or a negative value for failure.
Include: plugs.h
50 Altera Corporation
Page 51

Nios Ethernet Development Kit User Guide Plugs Library Routines
nr_plugs_terminate
Syntax: nr_plug_terminate(void)
(
void
);
Description: Call this routine when you are done using the plugs library.
If you need to reinitialize the plugs library with different
network settings, call this routine first before reinitializing.
Parameters: None
Return Value: The return value will be zero for success or a negative val-
ue for failure.
Include: plugs.h
Altera Corporation 51
5
Plugs Library
Page 52

Plugs Library Routines Nios Ethernet Development Kit User Guide
nr_plugs_set_mac_led
Syntax: int nr_plug_set_mac_led
(
int adapter_index,
int led_onoff
);
Description: This routine controls the LED present on most Ethernet
jacks. If a particular adapter does not have a LED on the
Ethernet jack, this routine does nothing. The LAN91C111
LED’s default behavior is to be on if it is connected to a
network, or off if it is not connected to a network.
Parameters:
adapter_index The index number of the adapter to control.
on_off This parameter can have one of three values. Zero turns
the LED off, one turns the LED on and negative one returns the LED to its default behavior as specified for the
particular adapter.
Return Value: The return value will be zero for success or a negative val-
ue for failure.
Include: plugs.h
52 Altera Corporation
Page 53

Nios Ethernet Development Kit User Guide Plugs Library Routines
nr_plugs_create
Syntax: int nr_plugs_create
(
int *plugs_handle_out,
int protocol,
host_16 port,
nr_plugs_receive_callback_proc callback,
void *callback_context,
long flags
);
Description: This routine creates a plug. A plug is a logical endpoint for
network communications. A plug is in some ways similar
to a traditional UNIX socket. When you create a plug, you
specify its protocol, and if applicable to the particular protocol, its port number. You must also specify a callback
procedure. The callback procedure is called whenever
data arrives over the network for this plug. A plug is associated with exactly one adapter.
Parameters:
plugs_handle_out This parameter is a pointer to an integer that contains a
reference to the new plug. The new plug reference is used
to specify this particular plug to other plugs library routines.
protocol This parameter specifies which network protocol the plug
can receive and transmit. The possible values for this parameter are as follows:
ne_plugs_ethernet
ne_plugs_arp
ne_plugs_ip
ne_plugs_icmp
ne_plugs_udp
ne_plugs_tcp
port If the plug’s protocol is UDP or TCP, then the plug must be
associated with a particular port number. If this parameter
is zero, an unused port number will be chosen for you.
5
Plugs Library
Altera Corporation 53
Page 54

Plugs Library Routines Nios Ethernet Development Kit User Guide
callback When data arrives for this plug, your callback routine is
called with the data. The parameters of the callback routine are documented under
nr_plugs_receive_callback_proc.
callback _context This parameter is passed unmodified to your callback rou-
tine. It can be used to carry state information to your callback routine.
flags Multiple flags should be grouped together using the OR in-
struction with the vertical-bar operator. If you are using
more than one adapter, an integer between 0 and 15 can
be added to the value for the flags parameter. This indicates the index number of the adapter associated with the
plug. If you are using only one adapter, then its index is always zero. Flags can be any combination of the following:
ne_plugs_flag_ethernet_broadcast
If the plug is Ethernet protocol, this flag transmits outgoing
packets as broadcast messages.
ne_plugs_flag_ethernet_all
If the plug is Ethernet protocol, this plug receives all packets, regardless of whether their Ethernet address matches
this adapter’s address.
ne_plugs_flag_debug_rx
This flag prints debugging information for each packet received by this plug. The debugging information is printed
using printf(), and appears on the same serial port as
other printf() output.
ne_plugs_flag_debug_tx
This flag prints debugging information for each packet
transmitted by this plug. The debugging information is
printed using printf(), and appears on the same serial
port as other printf() output.
Return Value: The return value will be zero for success or a negative val-
ue for failure.
Include: plugs.h
54 Altera Corporation
Page 55

Nios Ethernet Development Kit User Guide Plugs Library Routines
typedef int (*nr_plugs_receive_callback_proc)
Syntax: typedef int (*nr_plug_receive_callback_proc)
(
int plug_handle
void *context,
ns_plugs_packet *p,
void *payload,
int payload_length
);
Description: This is a routine you provide when you create a plug. The
plugs library will call this routine whenever a packet arrives for the plug. The plug receives the packet’s payload
and length and also a pointer to a list containing the packet header for each network protocol layer used by the incoming packet.
Parameters:
plug_handle A reference to the plug that is receiving a packet.
context The value passed for the parameter named
callback_context in nr_plugs_create().
p A pointer to an array of entries. These entries can be in-
dexed by the various network protocol enumeration constants (the same constants used to specify the network
protocol in nr_plugs_create()). Each entry consists
of two fields, as follows:
typedef struct
{
void *header;
int length;
} ns_plugs_packet;
The header field is a pointer to the first byte of the header
for that protocol layer. If the header pointer is zero, then
the packet does not conform to the indexed protocol. The
length is the combined length of the header and payload
for that protocol layer.
5
Plugs Library
Altera Corporation 55
Page 56

Plugs Library Routines Nios Ethernet Development Kit User Guide
p For example, suppose you created a plug that was using
the TCP protocol. When your callback routine is called,
you could examine the enclosing Ethernet packet header
by reading at location p[ne_plugs_ethernet].head-
er. You could also examine the enclosing IP packet header by reading at location p[ne_plugs_ip].header.
However, the values for p[ne_plugs_arp].header,
p[ne_plugs_icmp].header, and
p[ne_plugs_udp].header will all be zero, because
these protocols are not a part of a TCP packet.
The header field is a pointer to the first byte of the header
for that protocol layer. If the header pointer is zero, then
the packet does not conform to the indexed protocol. The
length is the combined length of the header and payload
for that protocol layer.
For example, suppose you created a plug that was using
the TCP protocol. When your callback routine is called,
you could examine the enclosing Ethernet packet header
by reading at location p[ne_plugs_ethernet].head-
er. You could also examine the enclosing IP packet header by reading at location p[ne_plugs_ip].header.
However, the values for p[ne_plugs_arp].header,
p[ne_plugs_icmp].header, and
p[ne_plugs_udp].header will all be zero, because
these protocols are not a part of a TCP packet.
payload A pointer to the meaningful payload portion of the packet
to be received by this plug. In the case of TCP and UDP,
the payload contains the bytes transmitted.
payload_length The length of the payload. In the case of TCP and UDP
protocol, this is the number of bytes transmitted.
Return Value: The return value will be zero for success or a negative val-
ue for failure.
Include: plugs.h
56 Altera Corporation
Page 57

Nios Ethernet Development Kit User Guide Plugs Library Routines
nr_plugs_destroy
Syntax: int nr_plugs_destroy
(
int plug_handle,
);
Description: Deallocates a plug. When you no longer need a plug, call
this routine to deallocate any resources associated with
the discarded plug.
Parameters:
plug_handle A reference to the plug you are eliminating.
Return Value: The return value will be zero for success or a negative val-
ue for failure.
Include: plugs.h
Altera Corporation 57
5
Plugs Library
Page 58

Plugs Library Routines Nios Ethernet Development Kit User Guide
nr_plugs_connect
Syntax: int nr_plug_connect
(
int plug_handle,
char *remote_name,
host_32 remote_ip_address,
host_16 remote_port
);
Description: This routine associates a plug with a particular remote IP address
and port on the network. If the plug is using TCP, then this routine
will perform the necessary network transaction to establish a connection with the remote host. If the connection cannot be established, an error is returned. If the plug is not using TCP, then the
remote address and port are stored in the plug’s state as the default destination for packets.
This routine can be used to allow packets to be received from any
remote-network device (only if the plug does not use TCP), by
connecting to IP address –1, port –1. This routine can be useful
when providing a UDP service.
If the plug uses TCP, this routine closes an existing TCP connection. To close a connection on a TCP plug, call this routine with a
remote IP address of 0 and a remote port of 0.
Parameters:
plug_handle A reference to the plug you are connecting
remote_name A pointer to a string containing the name of a remote-network de-
vice (for example, http://www.altera.com). The routine will attempt to resolve the name to an IP address by using the DNS
server associated with the first adapter installed. This parameter
may be zero, in which case, the remote_ip_address parame-
ter is used instead.
remote_ip_address A 32-bit value that is an IP address of a remote-network device.
This parameter is ignored if a remote name is provided for the
remote_name parameter.
remote_port If the port uses UDP or TCP, this parameter specifies the port
number of the connection on the remote-network device.
Return Value: The return value will be zero for success or a negative value for
failure.
58 Altera Corporation
Page 59

Nios Ethernet Development Kit User Guide Plugs Library Routines
Include: plugs.h
1 Transmission to another plug on the same Nios system will not
succeed and loopback is not supported.
Altera Corporation 59
5
Plugs Library
Page 60

Plugs Library Routines Nios Ethernet Development Kit User Guide
nr_plugs_send
Syntax: int nr_plugs_send
(
int plug_handle,
void *data,
int data_length,
long flags
);
Description: This routine transmits a packet of data using a particular
plug. Before you call this routine, you must call
nr_plugs_connect() to associate the plug with a particular remote-network device.
Parameters:
plug_handle A reference to a plug.
data The payload to send.
data_length The number of bytes in the payload.
flags This parameter augments the flags specified by
nr_plugs_create(). Typically this is used to add
ne_flag_debug_tx to one particular transmission.
Return Value: The return result will be zero for success or a negative val-
ue for failure.
Include: plugs.h
60 Altera Corporation
Page 61

Nios Ethernet Development Kit User Guide Plugs Library Routines
nr_plugs_send_to
Syntax: int nr_plugs_send_to
(
int plug_handle,
void *data,
int data_length,
long flags,
net_32 ip_address, //
net_16 port //
);
Description: This routine is identical to nr_plugs_send(), with the
|net order
|net order
addition of a destination IP address and port. When a plug
uses UDP, you can easily send a packet to any destination using this routine. Do not use this routine on a plug using TCP.
Parameters:
plug_handle A reference to a plug.
data The payload to send.
data_length The number of bytes in the payload.
flags This parameter augments the flags specified by
nr_plugs_create(). Typically this routine is used to
add ne_plugs_flag_debug_tx to a particular transmission.
ip_ address The IP address of a remote-network device. The packet is
transmitted to this remote-network device.
port If the plug uses UDP, the packet transmits to this port on
the remote-network device.
Return Value: The return value will be zero for success or a negative val-
ue for failure.
5
Plugs Library
Include: plugs.h
Altera Corporation 61
Page 62

Plugs Library Routines Nios Ethernet Development Kit User Guide
int nr_plugs_listen
Syntax: int nr_plugs_listen
(
int plug_handle,
nr_plugs_listen_callback_proc callback,
void *callback_context
);
Description: Only call this routine if the plug uses TCP. This routine
tells the plug to wait for an incoming TCP connection request. If the plug is already connected to a remote-network device, the connection is closed immediately when
this routine is called. When a connection request is received, the callback routine you provide is called and can
accept or reject the connection request.
If there is an existing TCP connection established on this
plug, the connection is closed and the plug begins to wait
for an incoming TCP connection request.
You may create multiple TCP plugs for the same port.
When a connection request is received, each of the plugs’
callback routines will be called and the first plug to accept
the connection will be connected.
Parameters:
plugs_handle A reference to the plug.
callback A routine you provide to accept or decline an incoming
TCP connection request. You may pass zero for this parameter and any incoming TCP connection request will be
accepted.
callback_context This parameter is passed unmodified to your callback rou-
tine. It can be used to carry state information to your routine.
Return Value: The return value will be zero for success or a negative val-
ue for failure.
Include: plugs.h
62 Altera Corporation
Page 63

Nios Ethernet Development Kit User Guide Plugs Library Routines
typedef int (*nr_plugs_listen_callback_proc)
Syntax: typedef int (*nr_plugs_listen_callback_proc)
(
int plug_handle,
void *context,
host_32 remote_ip_address,
host_16 remote_port
);
Description: This is a routine you provide when you allow a TCP plug to
accept connections using the nr_plugs_listen()rou-
tine. This routine can accept or decline the connection by returning a zero (meaning no error occurred — accept the
connection) or a negative value (meaning an error did occur
— do not accept the connection).
Parameters:
plug_handle A reference to a plug.
context The value passed for the parameter named
callback_context in nr_plugs_listen().
remote_ip_address The IP address of the remote-network device attempting to
connect to this plug.
remote_port The port on the remote-network device attempting to con-
nect to this plug.
Return Value: Your routine should return zero to accept the incoming con-
nection request, or a negative value to reject the connection
request.
Include: plugs.h
5
Plugs Library
Altera Corporation 63
Page 64

Plugs Library Routines Nios Ethernet Development Kit User Guide
nr_plugs_ip_to_ethernet
Syntax: int nr_plugs_ip_to_ethernet
(
int adapter_index,
net_32 ip_address,
net_48 *ethernet_address_out,
long flags
);
Description: When this routine is given an IP address, it discovers
which is the correct Ethernet address for the packets being sent. When the IP address is on the LAN, the Ethernet
address is the address for the network device; otherwise,
the Ethernet address is the address for the local gateway.
Parameters:
adapter_index The index number for the adapter being used.
ip_address An IP address of a remote-network device.
ethernet_address_out A pointer to a 48-bit Ethernet address. This routine will fill
out this structure with the discovered Ethernet address.
flags This flag can be 0 or ne_plugs_flag_debug_tx. If the
flag is ne_plugs_flag_debug_tx and the operation
fails, then a message is printed.
Return Value: The return value will be zero for success or a negative val-
ue for failure.
Include: plugs.h
64 Altera Corporation
Page 65

Nios Ethernet Development Kit User Guide Plugs Library Routines
nr_plugs_name_to _ip
Syntax: int nr_plugs_name_to_ip
(
char *host_name,
net_32 *host_ip_address_out
);
Description: When this routine is given the name of a remote-network
device it queries the name server to find out the IP address. This routine uses adapter number 0.
Parameters:
host_name A pointer to a string containing the name of a network de-
vice.
host_ip_address_out A pointer to a 32-bit IP address. This routine will fill out this
value with the discovered IP address.
Return Value: The return value will be zero for success or a negative val-
ue for failure.
Include: plugs.h
5
Plugs Library
Altera Corporation 65
Page 66

Plugs Library Routines Nios Ethernet Development Kit User Guide
nr_plugs_idle
Syntax: int nr_plugs_idle(void)
(
void
);
Description: If interrupts are not enabled, then this routine must be
called frequently in your program’s inner loop, or from a
timer interrupt routine. It polls the hardware device for incoming packets, and dispatches them via each plug’s callback routine.
Parameters: None
Return Value: The return value will be negative if any errors occur.
Include: plugs.h
66 Altera Corporation
Page 67

Nios Ethernet Development Kit User Guide Plugs Library Routines
void nr_plugs_print_ethernet_packet
Syntax: void nr_plugs_print_ethernet_packet(void)
(
ns_plugs_ethernet_packet *p,
int length,
char *title
);
Description: This routine prints an Ethernet packet in a friendly, hu-
man-readable format.
Parameters:
p A pointer to an Ethernet packet.
length The length of the Ethernet packet.
title A short string printed at the beginning of each line.
Return Value: The return value will be zero for success or a negative val-
ue for failure.
Include: plugs.h
5
Plugs Library
Altera Corporation 67
Page 68

Plugs Library Routines Nios Ethernet Development Kit User Guide
The following routines and macros are for your general use, and are
required when you are translating between host-byte ordering and
network-byte ordering for Nios EDK-network programming.
1 Network-byte ordering is always big-endian and Nios host-byte
ordering is little-endian.
nr_n2h16
Syntax: nr_n2h16(net_16 value)
Parameters: A network-short integer
Description: Translates a network-short integer to a short integer.
Equivalent Macro: nm_n2h16(host_16)
nr_h2n16
Syntax: nr_h2n16(host_16 value)
Parameters: A short integer
Description: Translates a short integer to a network-short integer.
Equivalent Macro: nm_h2n16(host_16)
nr_n2h32
Syntax: nr_n2h32(net_32 value)
Parameters: A network-long integer
Description: Translates a network-long integer to a long integer.
Equivalent Macro: nm_n2h32(host_32)
nr_h2n32
Syntax: nr_h2n32(host_32 value)
Parameters: A long integer
Description: Translates a long integer to a network-long integer.
Equivalent Macro: nm_h2n32(host_32)
68 Altera Corporation
 Loading...
Loading...