Page 1

Arria 10 Avalon-MM Interface for PCIe
Solutions
User Guide
Last updated for Altera Complete Design Suite: 15.0
Subscribe
Send Feedback
UG-01145_avm
2015.05.14
101 Innovation Drive
m
San Jose, CA 95134
www.altera.com
Page 2

TOC-2
Contents
Datasheet............................................................................................................. 1-1
Arria 10 Avalon-MM Interface for PCIe Datasheet ...............................................................................1-1
Features ........................................................................................................................................................ 1-2
Release Information ....................................................................................................................................1-6
Device Family Support ...............................................................................................................................1-7
Configurations .............................................................................................................................................1-7
Example Designs..........................................................................................................................................1-9
Debug Features ..........................................................................................................................................1-10
IP Core Verification ..................................................................................................................................1-10
Compatibility Testing Environment ..........................................................................................1-10
Performance and Resource Utilization ..................................................................................................1-10
Recommended Speed Grades ..................................................................................................................1-11
Steps in Creating a Design for PCI Express........................................................................................... 1-11
Getting Started with the Avalon-MM Arria 10 Hard IP for PCI Express .........2-1
Running Qsys .............................................................................................................................................. 2-2
Generating the Example Design ............................................................................................................... 2-3
Understanding Simulation Log File Generation..................................................................................... 2-5
Running a Gate-Level Simulation..............................................................................................................2-5
Simulating the Single DWord Design ......................................................................................................2-5
Generating Quartus II Synthesis Files.......................................................................................................2-6
Creating a Quartus II Project .................................................................................................................... 2-6
Adding Virtual Pin Assignment to the Quartus II Settings File (.qsf)................................................. 2-7
Compiling the Design .................................................................................................................................2-7
Programming a Device ...............................................................................................................................2-7
Understanding Channel Placement Guidelines ..................................................................................... 2-7
Parameter Settings.............................................................................................. 3-1
Arria 10 Avalon-MM System Settings ..................................................................................................... 3-1
Interface System Settings ........................................................................................................................... 3-4
Base Address Register (BAR) Settings ......................................................................................................3-6
Device Identification Registers ..................................................................................................................3-7
PCI Express and PCI Capabilities Parameters ........................................................................................3-8
Device Capabilities ..........................................................................................................................3-8
Error Reporting ...............................................................................................................................3-9
Link Capabilities ........................................................................................................................... 3-10
MSI and MSI-X Capabilities ........................................................................................................3-11
Slot Capabilities .............................................................................................................................3-12
Power Management ......................................................................................................................3-13
Altera Corporation
Page 3

TOC-3
Physical Layout of Hard IP In Arria 10 Devices.................................................4-1
Channel and Pin Placement for the Gen1, Gen2, and Gen3 Data Rates..............................................4-4
Channel Placement and fPLL Usage for the Gen1 and Gen2 Data Rates............................................4-5
Channel Placement and fPLL and ATX PLL Usage for the Gen3 Data Rate...................................... 4-7
64- or 128-Bit Avalon-MM Interface to the Application Layer......................... 5-1
32-Bit Non-Bursting Avalon-MM Control Register Access (CRA) Slave Signals .............................5-3
RX Avalon-MM Master Signals ................................................................................................................5-3
64- or 128-Bit Bursting TX Avalon-MM Slave Signals ..........................................................................5-5
Clock Signals ................................................................................................................................................5-8
Reset...............................................................................................................................................................5-8
Interrupts for Endpoints when Multiple MSI/MSI-X Support Is Enabled .......................................5-10
Hard IP Reconfiguration Interface .........................................................................................................5-11
Physical Layer Interface Signals ..............................................................................................................5-13
Serial Data Signals .........................................................................................................................5-13
PIPE Interface Signals .................................................................................................................. 5-14
Test Signals .................................................................................................................................... 5-19
Registers...............................................................................................................6-1
Correspondence between Configuration Space Registers and the PCIe Specification .....................6-1
Type 0 Configuration Space Registers ..................................................................................................... 6-5
Type 1 Configuration Space Registers ..................................................................................................... 6-6
PCI Express Capability Structures.............................................................................................................6-6
Altera-Defined VSEC Registers................................................................................................................. 6-9
CvP Registers..............................................................................................................................................6-10
64- or 128-Bit Avalon-MM Bridge Register Descriptions .................................................................. 6-13
Avalon-MM to PCI Express Interrupt Registers ......................................................................6-15
Programming Model for Avalon-MM Root Port .................................................................................6-26
Sending a Write TLP .................................................................................................................... 6-27
Sending a Read TLP or Receiving a Non-Posted Completion TLP .......................................6-28
PCI Express to Avalon-MM Interrupt Status and Enable Registers for Root Ports ............6-28
Root Port TLP Data Registers ..................................................................................................... 6-29
Uncorrectable Internal Error Mask Register ........................................................................................ 6-31
Uncorrectable Internal Error Status Register ....................................................................................... 6-32
Correctable Internal Error Mask Register .............................................................................................6-33
Correctable Internal Error Status Register ............................................................................................6-34
Arria 10 Reset and Clocks................................................................................... 7-1
Reset Sequence for Hard IP for PCI Express IP Core and Application Layer ....................................7-2
Clocks ........................................................................................................................................................... 7-4
Clock Domains ................................................................................................................................7-4
Clock Summary ...............................................................................................................................7-6
Interrupts for Endpoints ....................................................................................8-1
Altera Corporation
Page 4

TOC-4
Enabling MSI or Legacy Interrupts .......................................................................................................... 8-2
Generation of Avalon-MM Interrupts .....................................................................................................8-3
Interrupts for Endpoints Using the Avalon-MM Interface with Multiple MSI/MSI-X Support
...................................................................................................................................................................8-3
Error Handling ................................................................................................... 9-1
Physical Layer Errors ..................................................................................................................................9-2
Data Link Layer Errors ...............................................................................................................................9-2
Transaction Layer Errors ...........................................................................................................................9-3
Error Reporting and Data Poisoning ....................................................................................................... 9-6
Uncorrectable and Correctable Error Status Bits ...................................................................................9-7
IP Core Architecture......................................................................................... 10-1
Top-Level Interfaces .................................................................................................................................10-3
Avalon-MM Interface............................................................................................................................... 10-3
Clocks and Reset ....................................................................................................................................... 10-3
Interrupts ................................................................................................................................................... 10-3
PIPE ............................................................................................................................................................ 10-3
Data Link Layer .........................................................................................................................................10-4
Physical Layer ............................................................................................................................................10-6
32-Bit PCI Express Avalon-MM Bridge ................................................................................................ 10-8
Avalon-MM Bridge TLPs .......................................................................................................... 10-11
Avalon-MM-to-PCI Express Write Requests .........................................................................10-11
Avalon-MM-to-PCI Express Upstream Read Requests ........................................................10-11
PCI Express-to-Avalon-MM Read Completions ................................................................... 10-12
PCI Express-to-Avalon-MM Downstream Write Requests ................................................. 10-12
PCI Express-to-Avalon-MM Downstream Read Requests ...................................................10-12
Avalon-MM-to-PCI Express Read Completions ................................................................... 10-13
PCI Express-to-Avalon-MM Address Translation for 32-Bit Bridge ..................................10-13
Minimizing BAR Sizes and the PCIe Address Space .............................................................10-15
Avalon-MM-to-PCI Express Address Translation Algorithm for 32-Bit Addressing ......10-17
Completer Only Single Dword Endpoint ............................................................................................10-19
RX Block .......................................................................................................................................10-20
Avalon-MM RX Master Block .................................................................................................. 10-20
TX Block .......................................................................................................................................10-21
Interrupt Handler Block ............................................................................................................ 10-21
Design Implementation.................................................................................... 11-1
Throughput Optimization................................................................................ 12-1
Altera Corporation
Making Pin Assignments to Assign I/O Standard to Serial Data Pins ..............................................11-1
Recommended Reset Sequence to Avoid Link Training Issues ......................................................... 11-1
SDC Timing Constraints.......................................................................................................................... 11-2
Throughput of Posted Writes ................................................................................................................. 12-3
Throughput of Non-Posted Reads ......................................................................................................... 12-3
Page 5

TOC-5
Optional Features..............................................................................................13-1
Configuration via Protocol (CvP) .......................................................................................................... 13-1
ECRC ..........................................................................................................................................................13-2
ECRC on the RX Path .................................................................................................................. 13-2
ECRC on the TX Path .................................................................................................................. 13-3
Avalon-MM Testbench and Design Example .................................................. 14-1
Arria 10 Avalon-MM Endpoint Testbench ...........................................................................................14-2
Arria 10 Avalon-MM Root Port Testbench ..........................................................................................14-4
Endpoint Design Example........................................................................................................................14-4
BAR/Address Map ........................................................................................................................14-6
Avalon-MM Test Driver Module ........................................................................................................... 14-7
DMA Write Cycles ................................................................................................................................... 14-8
DMA Read Cycles ...................................................................................................................................14-10
Avalon-MM Root Port Design Example .............................................................................................14-12
Root Port BFM ........................................................................................................................................14-14
BFM Memory Map .....................................................................................................................14-16
Configuration Space Bus and Device Numbering ................................................................. 14-16
Configuration of Root Port and Endpoint ..............................................................................14-16
Issuing Read and Write Transactions to the Application Layer .......................................... 14-21
BFM Procedures and Functions ........................................................................................................... 14-22
ebfm_barwr Procedure .............................................................................................................. 14-22
ebfm_barwr_imm Procedure ....................................................................................................14-23
ebfm_barrd_wait Procedure ..................................................................................................... 14-24
ebfm_barrd_nowt Procedure ....................................................................................................14-25
ebfm_cfgwr_imm_wait Procedure ...........................................................................................14-26
ebfm_cfgwr_imm_nowt Procedure ......................................................................................... 14-26
ebfm_cfgrd_wait Procedure ......................................................................................................14-27
ebfm_cfgrd_nowt Procedure .....................................................................................................14-28
BFM Configuration Procedures................................................................................................ 14-29
BFM Shared Memory Access Procedures ............................................................................... 14-31
BFM Log and Message Procedures .......................................................................................... 14-34
Verilog HDL Formatting Functions ........................................................................................ 14-38
Procedures and Functions Specific to the Chaining DMA Design Example......................14-42
Setting Up Simulation.............................................................................................................................14-49
Changing Between Serial and PIPE Simulation ..................................................................... 14-49
Using the PIPE Interface for Gen1 and Gen2 Variants .........................................................14-49
Viewing the Important PIPE Interface Signals........................................................................14-49
Disabling the Scrambler for Gen1 and Gen2 Simulations ....................................................14-49
Disabling 8B/10B Encoding and Decoding for Gen1 and Gen2 Simulations.....................14-50
Debugging .........................................................................................................15-1
Simulation Fails To Progress Beyond Polling.Active State..................................................................15-1
Hardware Bring-Up Issues ......................................................................................................................15-1
Link Training .............................................................................................................................................15-2
Altera Corporation
Page 6

TOC-6
Use Third-Party PCIe Analyzer ..............................................................................................................15-2
BIOS Enumeration Issues ........................................................................................................................15-3
Frequently Asked Questions.............................................................................. A-1
Lane Initialization and Reversal ........................................................................B-1
Additional Information......................................................................................C-1
Revision History for the Avalon-MM Interface......................................................................................C-1
How to Contact Altera............................................................................................................................... C-4
Typographic Conventions......................................................................................................................... C-5
Altera Corporation
Page 7

2015.05.14
Bridge
PCIe Hard IP
Block
PIPE
Interface
PHY IP Core
for PCIe
(PCS/PMA)
Serial Data
Transmission
Application
Layer
(User Logic)
Avalon-MM
Interface
www.altera.com
101 Innovation Drive, San Jose, CA 95134
Datasheet
1
UG-01145_avmm
Subscribe
Send Feedback
Arria 10 Avalon-MM Interface for PCIe Datasheet
Altera® Arria® 10 FPGAs include a configurable, hardened protocol stack for PCI Express
compliant with PCI Express Base Specification 3.0.
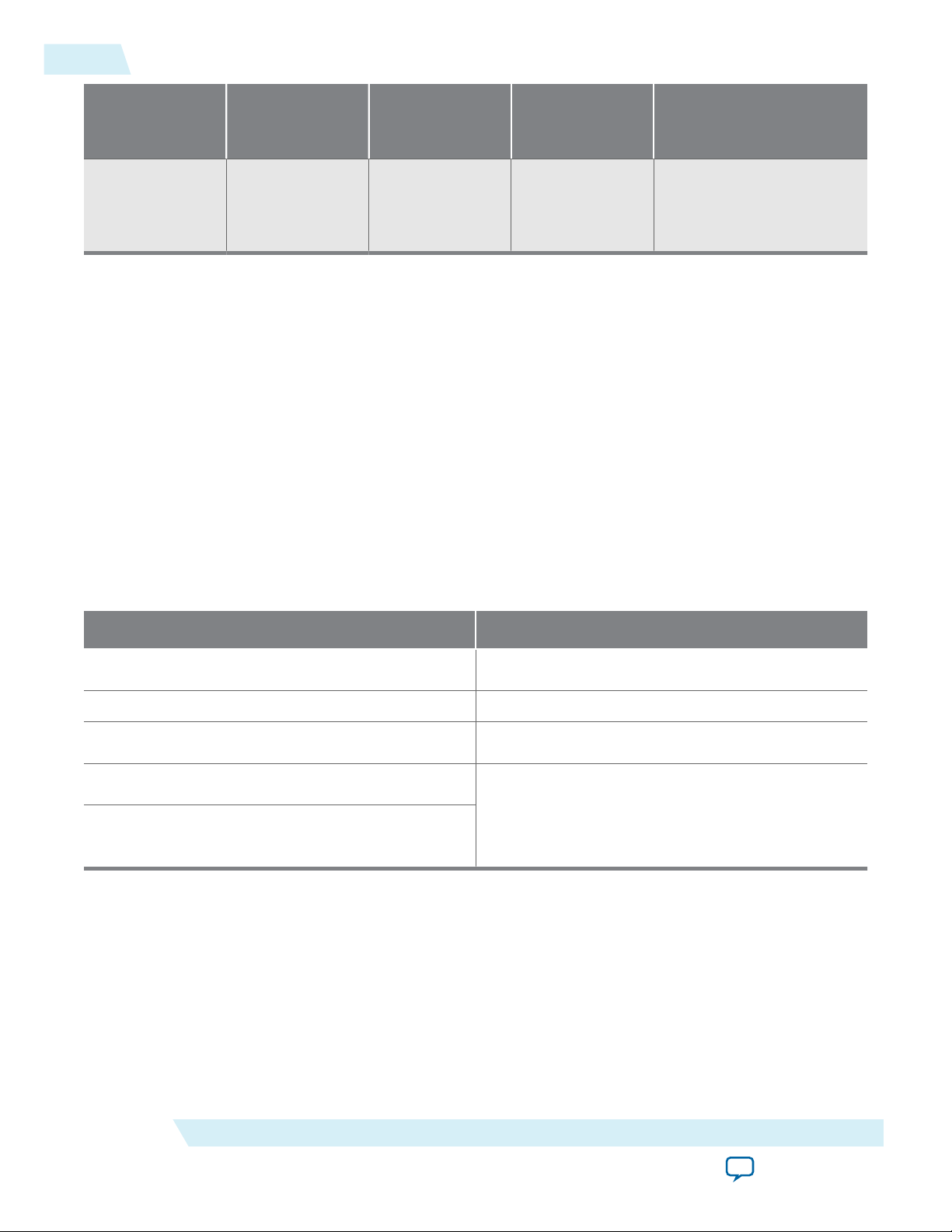
The Hard IP for PCI Express IP core using the Avalon ® Memory-Mapped (Avalon-MM) interface
removes some of the complexities associated with the PCIe protocol. For example, it handles all of the
Transaction Layer Protocol (TLP) encoding and decoding. Consequently, you can complete your design
more quickly. The Avalon-MM interface is implemented as a bridge in soft logic. It is available in Qsys.
Figure 1-1: Arria 10 PCIe Variant with Avalon-MM Interface
The following figure shows the high-level modules and connecting interfaces for this variant.
®
that is
Table 1-1: PCI Express Data Throughput
The following table shows the aggregate bandwidth of a PCI Express link for Gen1, Gen2, and Gen3 for 1, 2, 4,
and 8 lanes. The protocol specifies 2.5 giga-transfers per second for Gen1, 5.0 giga-transfers per second for Gen2,
and 8.0 giga-transfers per second for Gen3. This table provides bandwidths for a single transmit (TX) or receive
(RX) channel. The numbers double for duplex operation. Gen1 and Gen2 use 8B/10B encoding which introduces
a 20% overhead. In contrast, Gen3 uses 128b/130b encoding which reduces the data throughput lost to encoding
to less than 1%.
PCI Express Gen1
(2.5 Gbps)
©
2015 Altera Corporation. All rights reserved. ALTERA, ARRIA, CYCLONE, ENPIRION, MAX, MEGACORE, NIOS, QUARTUS and STRATIX words and logos are
trademarks of Altera Corporation and registered in the U.S. Patent and Trademark Office and in other countries. All other words and logos identified as
trademarks or service marks are the property of their respective holders as described at www.altera.com/common/legal.html. Altera warrants performance
of its semiconductor products to current specifications in accordance with Altera's standard warranty, but reserves the right to make changes to any
products and services at any time without notice. Altera assumes no responsibility or liability arising out of the application or use of any information,
product, or service described herein except as expressly agreed to in writing by Altera. Altera customers are advised to obtain the latest version of device
specifications before relying on any published information and before placing orders for products or services.
Link Width in Gigabits Per Second (Gbps)
x1 x2 x4 x8
2 4 8 16
ISO
9001:2008
Registered
Page 8
1-2
Features
UG-01145_avmm
2015.05.14
Link Width in Gigabits Per Second (Gbps)
x1 x2 x4 x8
PCI Express Gen2
(5.0 Gbps)
PCI Express Gen3
(8.0 Gbps)
Refer to AN 456: PCI Express High Performance Reference Design for more information about calculating
bandwidth for the hard IP implementation of PCI Express in many Altera FPGAs, including the Arria 10
Hard IP for PCI Express IP core.
Related Information
• PCI Express Base Specification 3.0
• AN 456: PCI Express High Performance Reference Design
• Creating a System with Qsys
Features
New features in the Quartus® II 15.0 software release:
• Added Enable Altera Debug Master Endpoint (ADME) parameter to support optional Native PHY
register programming with the Altera System Console.
• Dynamic generation of Qsys design examples using the parameters that you specify.
• Added Root Port support for transmitting messages of length greater than one dword.
4 8 16 32
7.87 15.75 31.51 63
The Arria 10 Hard IP for PCI Express with the Avalon-MM interface supports the following features:
• Complete protocol stack including the Transaction, Data Link, and Physical Layers implemented as
hard IP.
• Support for ×1, ×2, ×4, and ×8 configurations with Gen1, Gen2, or Gen3 lane rates for Root Ports and
Endpoints.
• Dedicated 16 KByte receive buffer.
• Optional support for Configuration via Protocol (CvP) using the PCIe link allowing the I/O and core
bitstreams to be stored separately.
• Support for 32- or 64-bit addressing for the Avalon-MM interface to the Application Layer.
• Qsys example designs demonstrating parameterization, design modules, and connectivity.
• Extended credit allocation settings to better optimize the RX buffer space based on application type.
• Optional end-to-end cyclic redundancy code (ECRC) generation and checking and advanced error
reporting (AER) for high reliability applications.
• Easy to use:
• Flexible configuration.
• No license requirement.
• Example designs to get started.
Altera Corporation
Datasheet
Send Feedback
Page 9
UG-01145_avmm
2015.05.14
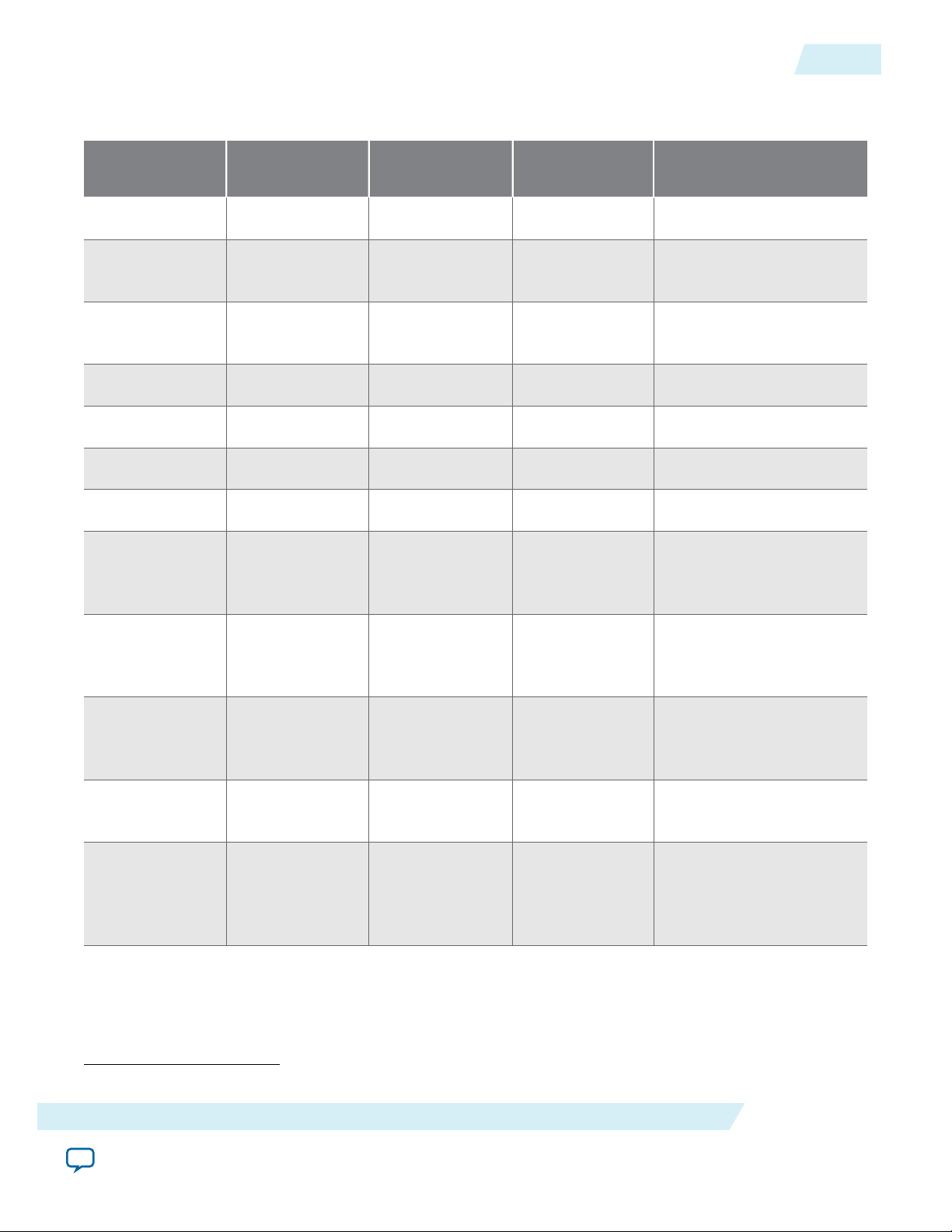
Table 1-2: Feature Comparison for all Hard IP for PCI Express IP Cores
The table compares the features of the four Hard IP for PCI Express IP Cores.
Features
1-3
Feature Avalon-ST Interface Avalon-MM
Interface
Avalon-MM DMA Avalon-ST Interface with SR-
IP Core License Free Free Free Free
Native
Supported Supported Supported Supported
Endpoint
Legacy
Endpoint
(1)
Supported Not Supported Not Supported Not Supported
Root port Supported Supported Not Supported Not Supported
Gen1 ×1, ×2, ×4, ×8 ×1, ×2, ×4, ×8 Not Supported
Gen2 ×1, ×2, ×4, ×8 ×1, ×2, ×4, ×8 ×4, ×8
Gen3 ×1, ×2, ×4, ×8 ×1, ×2, ×4 ×2, ×4, ×8
64-bit Applica‐
Supported Supported Not supported Not supported
×8
×4, ×8
×2, ×4, ×8
tion Layer
interface
IOV
128-bit
Supported Supported Supported Supported
Application
Layer interface
256-bit
Supported Not Supported Supported Supported
Application
Layer interface
Maximum
payload size
Number of tags
128, 256, 512,
1024, 2048 bytes
256 8 16 256
supported for
non-posted
requests
(1)
Not recommended for new designs.
128, 256 bytes 128, 256 bytes 128, 256 bytes
Datasheet
Altera Corporation
Send Feedback
Page 10
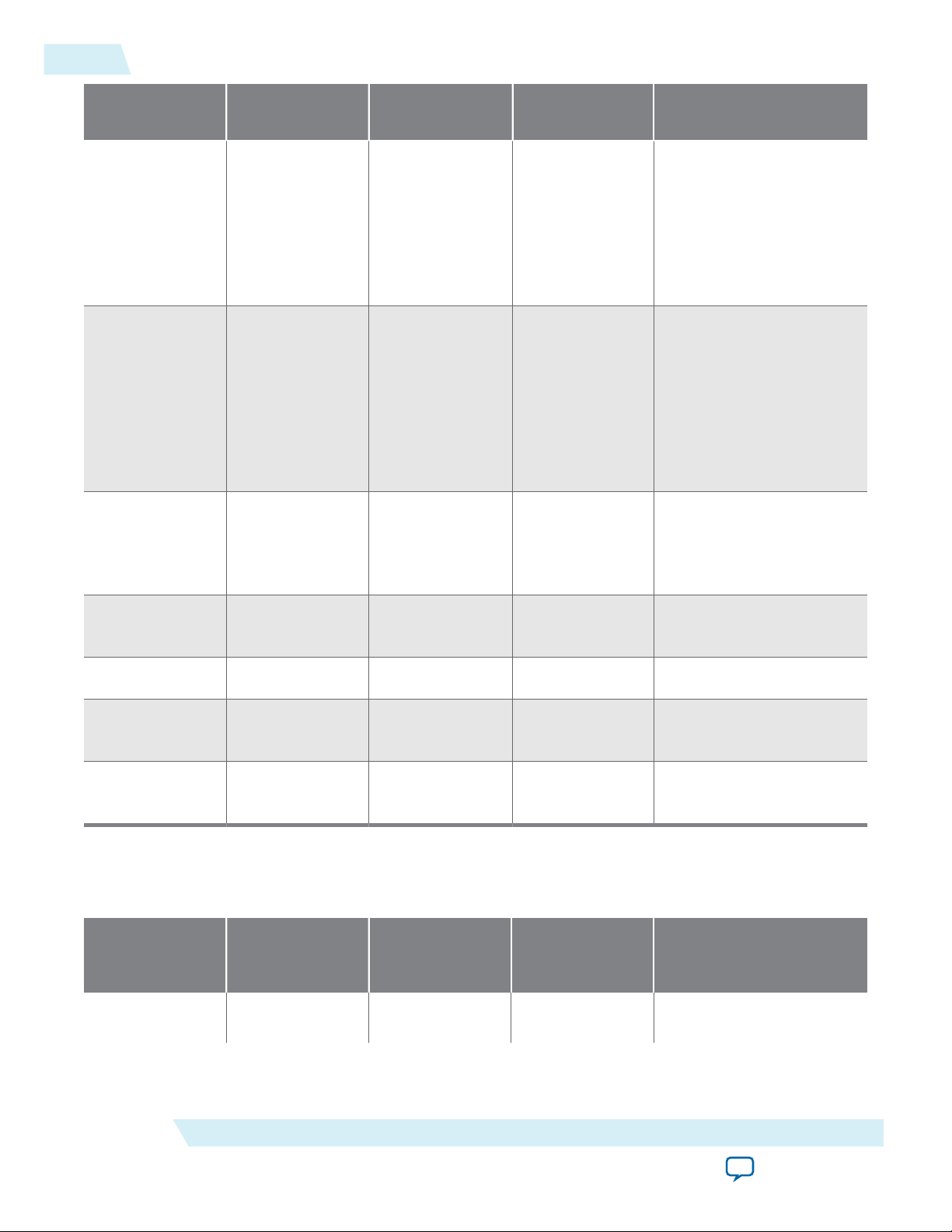
1-4
Features
UG-01145_avmm
2015.05.14
Feature Avalon-ST Interface Avalon-MM
Interface
Automatically
Not supported Supported Supported Not supported
handle out-oforder
completions
(transparent to
the Application
Layer)
Automatically
Not supported Supported Supported Not Supported
handle requests
that cross 4
KByte address
boundary
(transparent to
the Application
Layer)
Polarity
Supported Supported Supported Supported
Inversion of
PIPE interface
signals
Avalon-MM DMA Avalon-ST Interface with SR-
IOV
Number of MSI
requests
1, 2, 4, 8, 16, or 32 1, 2, 4, 8, 16, or 32 1, 2, 4, 8, 16, or 32 1, 2, 4, 8, 16, or 32 (for
Physical Functions)
MSI-X Supported Supported Supported Supported
Legacy
Supported Supported Supported Supported
interrupts
Expansion
Supported Not supported Not supported Not supported
ROM
Table 1-3: TLP Support Comparison for all Hard IP for PCI Express IP Cores
The table compares the TLP types that the four Hard IP for PCI Express IP Cores can transmit. Each entry
indicates whether this TLP type is supported (for transmit) by endpoints (EP), Root Ports (RP), or both (EP/RP).
Transaction Layer
Packet type (TLP)
(transmit support)
Memory Read
Avalon-ST Interface Avalon-MM
Interface
Avalon-MM DMA Avalon-ST Interface with SR-
EP/RP EP/RP EP EP
IOV
Request (Mrd)
Altera Corporation
Datasheet
Send Feedback
Page 11
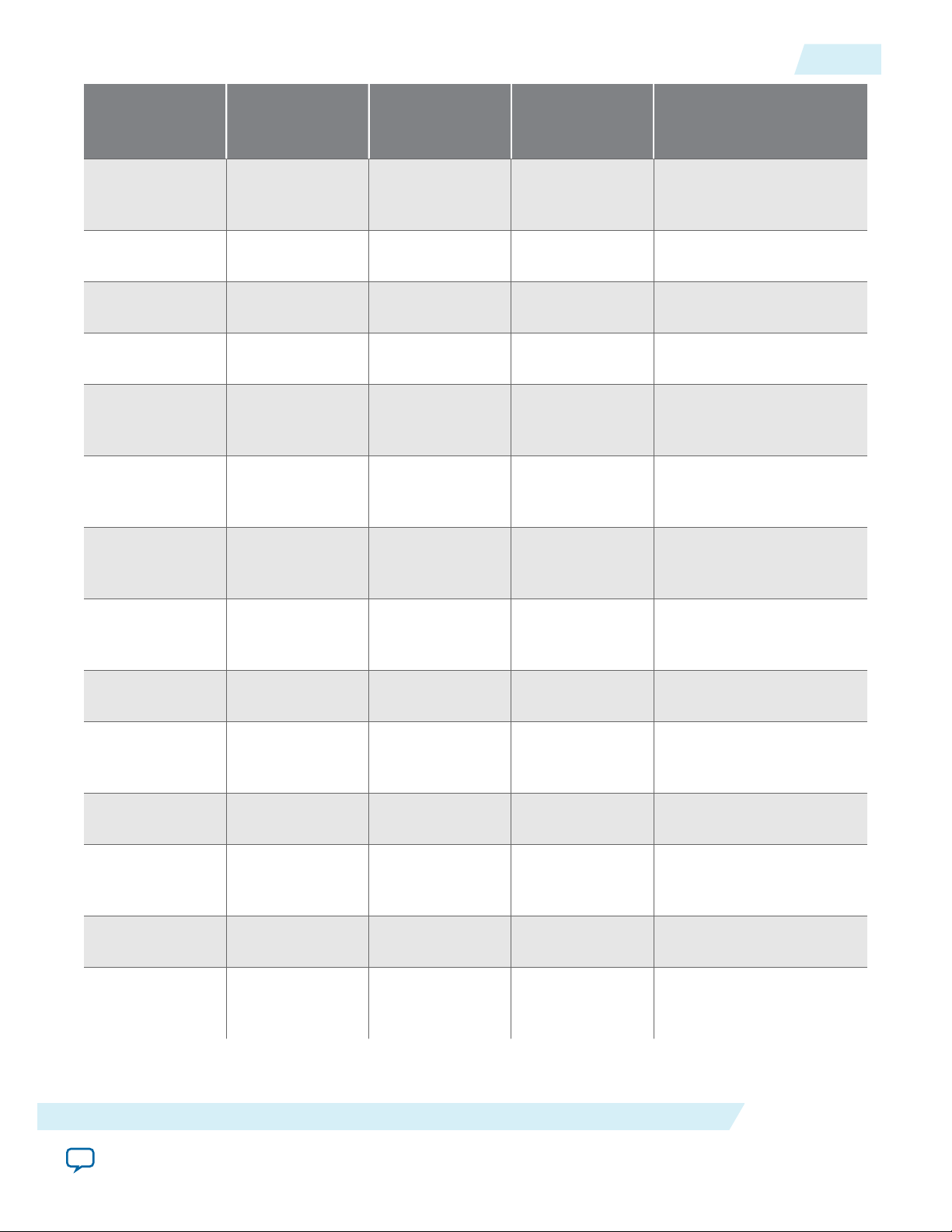
UG-01145_avmm
2015.05.14
Features
1-5
Transaction Layer
Packet type (TLP)
(transmit support)
Memory Read
Lock Request
(MRdLk)
Memory Write
Request (MWr)
I/O Read
Request (IORd)
I/O Write
Request (IOWr)
Config Type 0
Read Request
(CfgRd0)
Config Type 0
Write Request
(CfgWr0)
Config Type 1
Read Request
(CfgRd1)
Avalon-ST Interface Avalon-MM
Interface
Avalon-MM DMA Avalon-ST Interface with SR-
EP/RP EP EP
EP/RP EP/RP EP EP
EP/RP EP/RP EP
EP/RP EP/RP EP
RP RP EP
RP RP EP
RP RP EP
IOV
Config Type 1
Write Request
(CfgWr1)
Message
Request (Msg)
Message
Request with
Data (MsgD)
Completion
(Cpl)
Completion
with Data
(CplD)
CompletionLocked (CplLk)
Completion
Lock with Data
(CplDLk)
RP RP EP
EP/RP EP/RP EP
EP/RP EP/RP EP
EP/RP EP/RP EP EP
EP/RP EP EP
EP/RP EP
EP/RP EP
Datasheet
Altera Corporation
Send Feedback
Page 12
1-6
Release Information
UG-01145_avmm
2015.05.14
Transaction Layer
Packet type (TLP)
(transmit support)
Fetch and Add
Avalon-ST Interface Avalon-MM
EP
AtomicOp
Request
(FetchAdd)
The Arria 10 Avalon-MM Interface for PCIe Solutions User Guide explains how to use this IP core and not
the PCI Express protocol. Although there is inevitable overlap between these two purposes, use this
document only in conjunction with an understanding of the PCI Express Base Specification.
Note: This release provides separate user guides for the different variants. The Related Information
provides links to all versions.
Related Information
• Arria 10 Avalon-ST Interface for PCIe Solutions User Guide
• Arria 10 Avalon-ST Interface with SR-IOV for PCIe Solutions User Guide
• Arria 10 Avalon-MM DMA Interface for PCIe Solutions User Guide
Release Information
Interface
Avalon-MM DMA Avalon-ST Interface with SR-
IOV
Table 1-4: Hard IP for PCI Express Release Information
Item Description
Version 15.0
Release Date May 2015
Ordering Codes No ordering code is required
Product IDs There are no encrypted files for the Arria 10 Hard
IP for PCI Express. The Product ID and Vendor ID
Vendor ID
are not required because this IP core does not
require a license.
Altera Corporation
Datasheet
Send Feedback
Page 13

UG-01145_avmm
2015.05.14
Device Family Support
Table 1-5: Device Family Support
Device Family Support
Device Family Support
1-7
Arria 10
Preliminary. The IP core is verified with prelimi‐
nary timing models for this device family. The IP
core meets all functional requirements, but might
still be undergoing timing analysis for the device
family. It can be used in production designs with
caution.
Other device families Refer to the Altera's PCI Express IP Solutions web
page for support information on other device
families.
Related Information
• Altera's PCI Express IP Solutions web page
Configurations
The Avalon-MM Arria 10 Hard IP for PCI Express includes a full hard IP implementation of the PCI
Express stack comprising the following layers:
• Physical (PHY), including:
• Physical Media Attachment (PMA)
• Physical Coding Sublayer (PCS)
• Media Access Control (MAC)
• Data Link Layer (DL)
• Transaction Layer (TL)
Datasheet
When configured as an Endpoint, the Arria 10 Hard IP for PCI Express using the Avalon-MM supports
memory read and write requests and completions with or without data.
Altera Corporation
Send Feedback
Page 14
Altera FPGA
User Application
Logic
PCIe
Hard IP
RP
PCIe
Hard IP
EP
User Application
Logic
PCI Express Link
Altera FPGA
1-8
Configurations
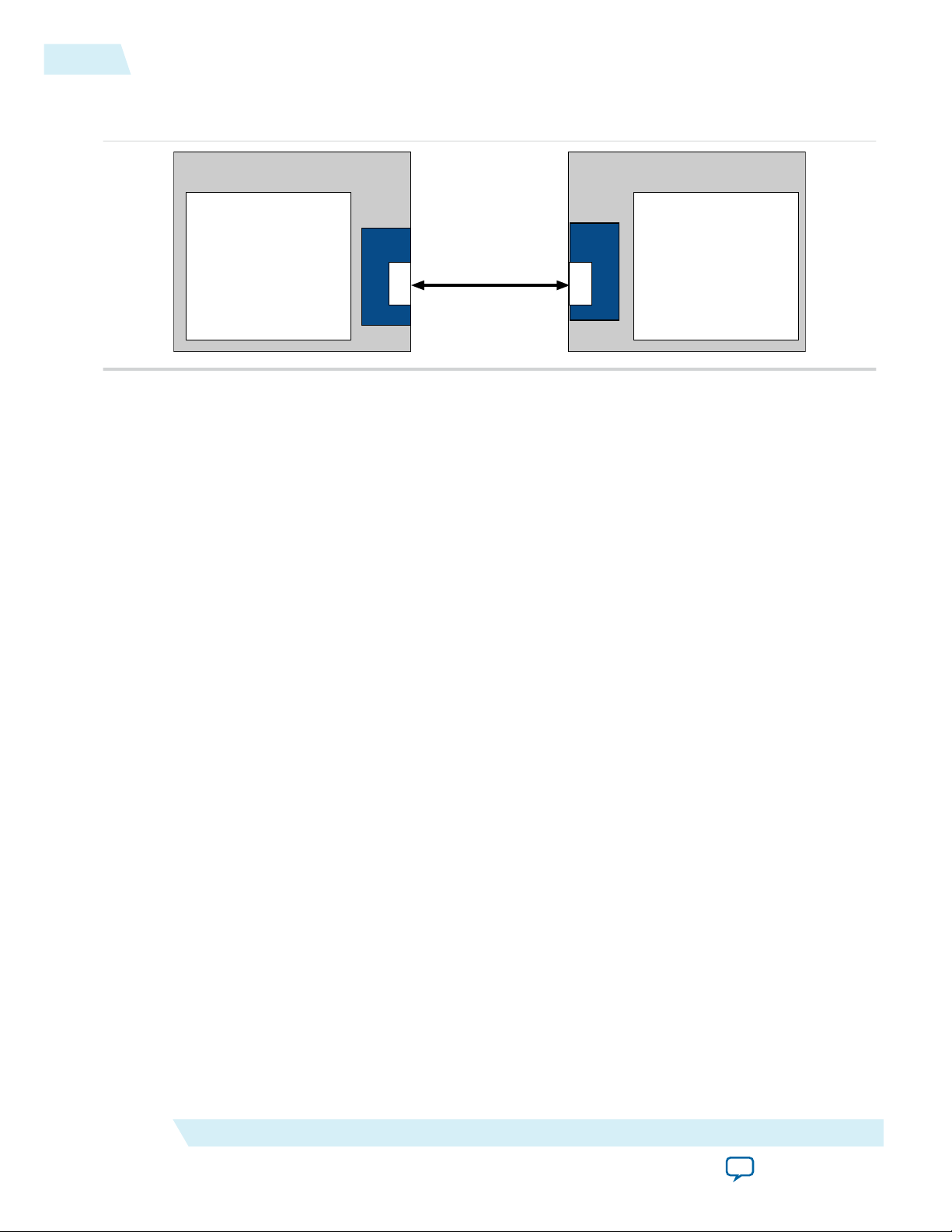
Figure 1-2: PCI Express Application with a Single Root Port and Endpoint
The following figure shows a PCI Express link between two Arria 10 FPGAs.
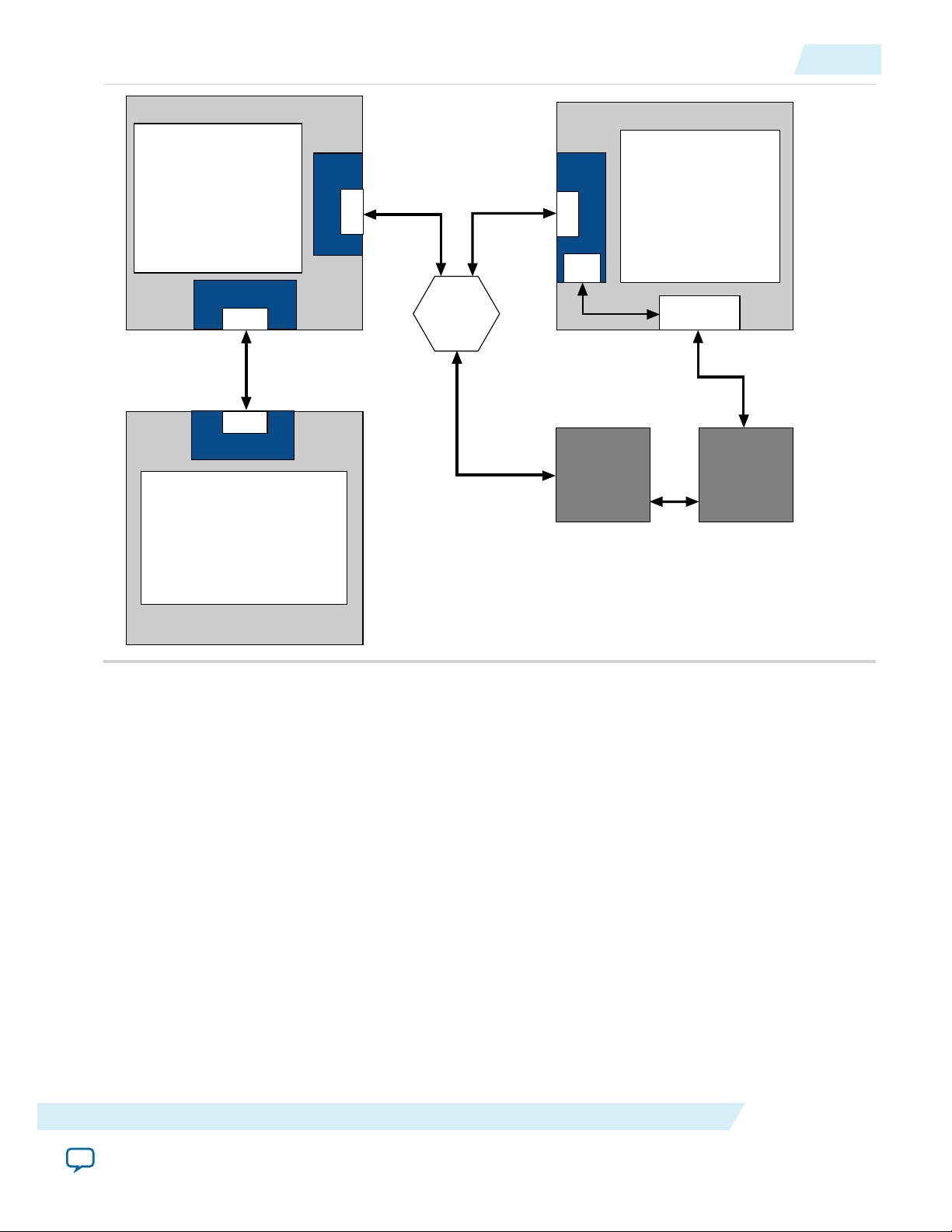
Figure 1-3: PCI Express Application Using Configuration via Protocol
The Arria 10 design below includes the following components:
• A Root Port that connects directly to a second FPGA that includes an Endpoint.
• Two Endpoints that connect to a PCIe switch.
• A host CPU that implements CvP using the PCI Express link connects through the switch. For more
information about configuration over a PCI Express link, refer to Configuration via Protocol (CvP)
on page 13-1.
UG-01145_avmm
2015.05.14
Altera Corporation
Datasheet
Send Feedback
Page 15
PCIe Link
PCIe Hard IP
RP
Switch
PCIe
Hard IP
RP
User Application
Logic
PCIe Hard IP
EP
PCIe Link
PCIe Link
User Application
Logic
Altera FPGA Hard IP for PCI Express
Altera FPGA with Hard IP for PCI Express
Active Serial or
Active Quad
Device Configuration
Configuration via Protocol (CvP)
using the PCI Express Link
Serial or
Quad Flash
USB
Download
cable
PCIe
Hard IP
EP
User
Application
Logic
Altera FPGA with Hard IP for PCI Express
Config
Control
CVP
USB
Host CPU
PCIe
UG-01145_avmm
2015.05.14
Example Designs
1-9
Related Information
Configuration via Protocol (CvP)Implementation in Altera FPGAs User Guide
Example Designs
Qsys example designs are available for the Avalon-MM Arria 10 Hard IP for PCI Express IP Core. You
can download them from the <install_dir>/ip/altera/altera_pcie/altera_pcie_a10_ed/example_design/a10
directory:
When you click the Example Design button in the Parameter Editor, you are prompted to specify the
example design location. After example design generation completes, this directory contains one or two
example designs. One is the example design from the <install_dir> that best matches the current parameter
settings. This example design provides a static DUT. The other example design is a customized example
design that matches your parameter settings exactly; starting in the Quartus II software v15.0, this feature
is available for most but not all IP core variations. If this feature is not available for your particular
parameter settings, the Parameter Editor displays a warning.
Related Information
Getting Started with the Avalon-MM Arria 10 Hard IP for PCI Express on page 2-1
Datasheet
Send Feedback
Altera Corporation
Page 16

1-10
Debug Features
Debug Features
Debug features allow observation and control of the Hard IP for faster debugging of system-level
problems.
Related Information
Debugging on page 15-1
IP Core Verification
To ensure compliance with the PCI Express specification, Altera performs extensive verification. The
simulation environment uses multiple testbenches that consist of industry-standard bus functional
models (BFMs) driving the PCI Express link interface. Altera performs the following tests in the
simulation environment:
• Directed and pseudorandom stimuli are applied to test the Application Layer interface, Configuration
Space, and all types and sizes of TLPs
• Error injection tests that inject errors in the link, TLPs, and Data Link Layer Packets (DLLPs), and
check for the proper responses
• PCI-SIG® Compliance Checklist tests that specifically test the items in the checklist
• Random tests that test a wide range of traffic patterns
UG-01145_avmm
2015.05.14
Altera provides example designs that you can leverage to test your PCBs and complete compliance base
board testing (CBB testing) at PCI-SIG, upon request.
Compatibility Testing Environment
Altera has performed significant hardware testing to ensure a reliable solution. In addition, Altera
internally tests every release with motherboards and PCI Express switches from a variety of manufac‐
turers. All PCI-SIG compliance tests are run with each IP core release.
Performance and Resource Utilization
Because the PCIe protocol stack is implemented in hardened logic, it uses no core device resources (no
ALMs and no embedded memory).
The Avalon-MM soft logic bridge functions as a front end to the hardened protocol stack. The following
table shows the typical device resource utilization for selected configurations using the current version of
the Quartus II software. With the exception of M20K memory blocks, the numbers of ALMs and logic
registers are rounded up to the nearest 50.
Table 1-6: Performance and Resource Utilization Avalon-MM Hard IP for PCI Express
Interface Width ALMs M20K Memory Blocks Logic Registers
Altera Corporation
Avalon-MM Bridge
64 1100 17 1500
Datasheet
Send Feedback
Page 17
UG-01145_avmm
2015.05.14
Interface Width ALMs M20K Memory Blocks Logic Registers
128 1900 25 2900
64 650 8 1000
128 1400 12 2400
64 250 0 350
Related Information
Fitter Resources Reports
Recommended Speed Grades
Recommended speed grades are pending characterization of production Arria 10 devices.
Recommended Speed Grades
Avalon-MM Interface–Completer Only
Avalon-MM–Completer Only Single Dword
1-11
Related Information
• Area and Timing Optimization
• Altera Software Installation and Licensing Manual
• Setting up and Running Analysis and Synthesis
Steps in Creating a Design for PCI Express
Before you begin
Select the PCIe variant that best meets your design requirements.
• Is your design an Endpoint or Root Port?
• What Generation do you intend to implement?
• What link width do you intend to implement?
• What bandwidth does your application require?
• Does your design require CvP?
1. Select parameters for that variant.
2. Simulate using an Altera-provided example design. All of Altera's static PCI Express example designs
are available under <install_dir>/ip/altera/altera_pcie/. Alternatively, generate an example design that
matches your parameter settings, or create a simulation model and use your own custom or thirdparty BFM. The Qsys Generate menu generates simulation models. Altera supports ModelSim-Altera
Datasheet
Altera Corporation
Send Feedback
Page 18

1-12
Steps in Creating a Design for PCI Express
UG-01145_avmm
2015.05.14
for all IP. The PCIe cores support the Aldec RivieraPro, Cadence NCsim, Mentor Graphics ModelSim,
and Synopsys VCS and VCS-MX simulators.
3. Compile your design using the Quartus II software. If the versions of your design and the Quartus II
software you are running do not match, regenerate your PCIe design.
4. Download your design to an Altera development board or your own PCB. Click on the All Develop‐
ment Kits link below for a list of Altera's development boards.
5. Test the hardware. You can use Altera's SignalTap® II Logic Analyzer or a third-party protocol
analyzer to observe behavior.
6. Substitute your Application Layer logic for the Application Layer logic in Altera's testbench. Then
repeat Steps 3–6. In Altera's testbenches, the PCIe core is typically called the DUT (device under test).
The Application Layer logic is typically called APPS.
Related Information
• Parameter Settings on page 3-1
• Getting Started with the Avalon-MM Arria 10 Hard IP for PCI Express on page 2-1
• All Development Kits
Altera Corporation
Datasheet
Send Feedback
Page 19
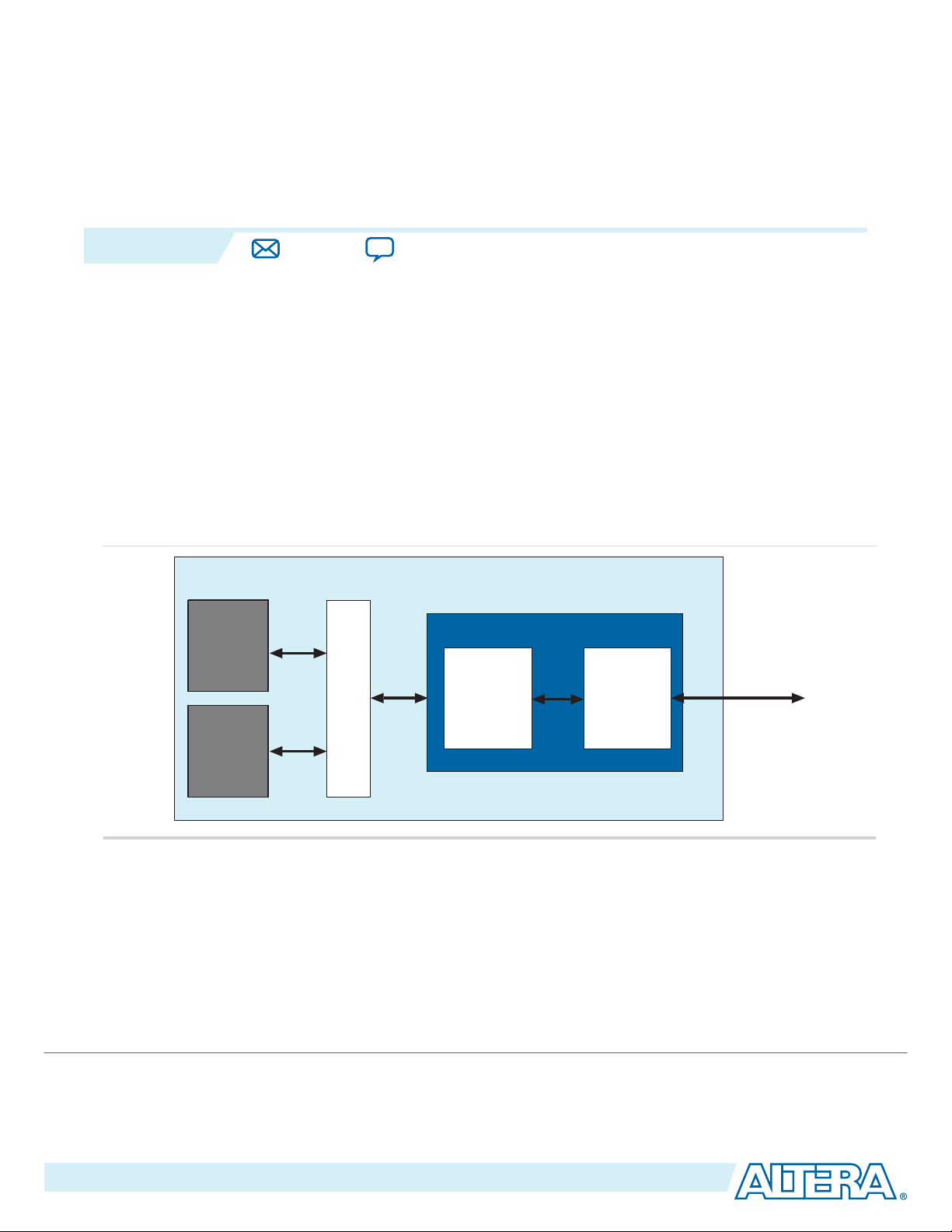
Getting Started with the Avalon‑MM Arria 10
Transaction,
Data Link,
and PHY
Layers
O n-C hip
Memory
DMA
Qsys System Design for PCI Express
PCI Express
Link
PCI
Express
Avalon-MM
Bridge
Interconnect
Avalon-MM Hard IP for PCI Express
www.altera.com
101 Innovation Drive, San Jose, CA 95134
Hard IP for PCI Express
2015.05.14
UG-01145_avmm
Subscribe
This Qsys design example provides detailed step-by-step instructions to generate a Qsys system. When
you install the Quartus II software you also install the IP Library. This installation includes design
examples for the Avalon-MM Arria 10 Hard IP for PCI Express in the <install_dir>/ip/altera/altera_pcie/
altera_pcie_a10_ed/example_design/a10 directory. This walkthrough uses a Gen2 x4 Endpoint,
ep_g2x4_avmm128.qsys.
The design examples contain the following components:
• Avalon-MM Arria 10 Hard IP for PCI Express IP core
• On-Chip memory
• DMA controller
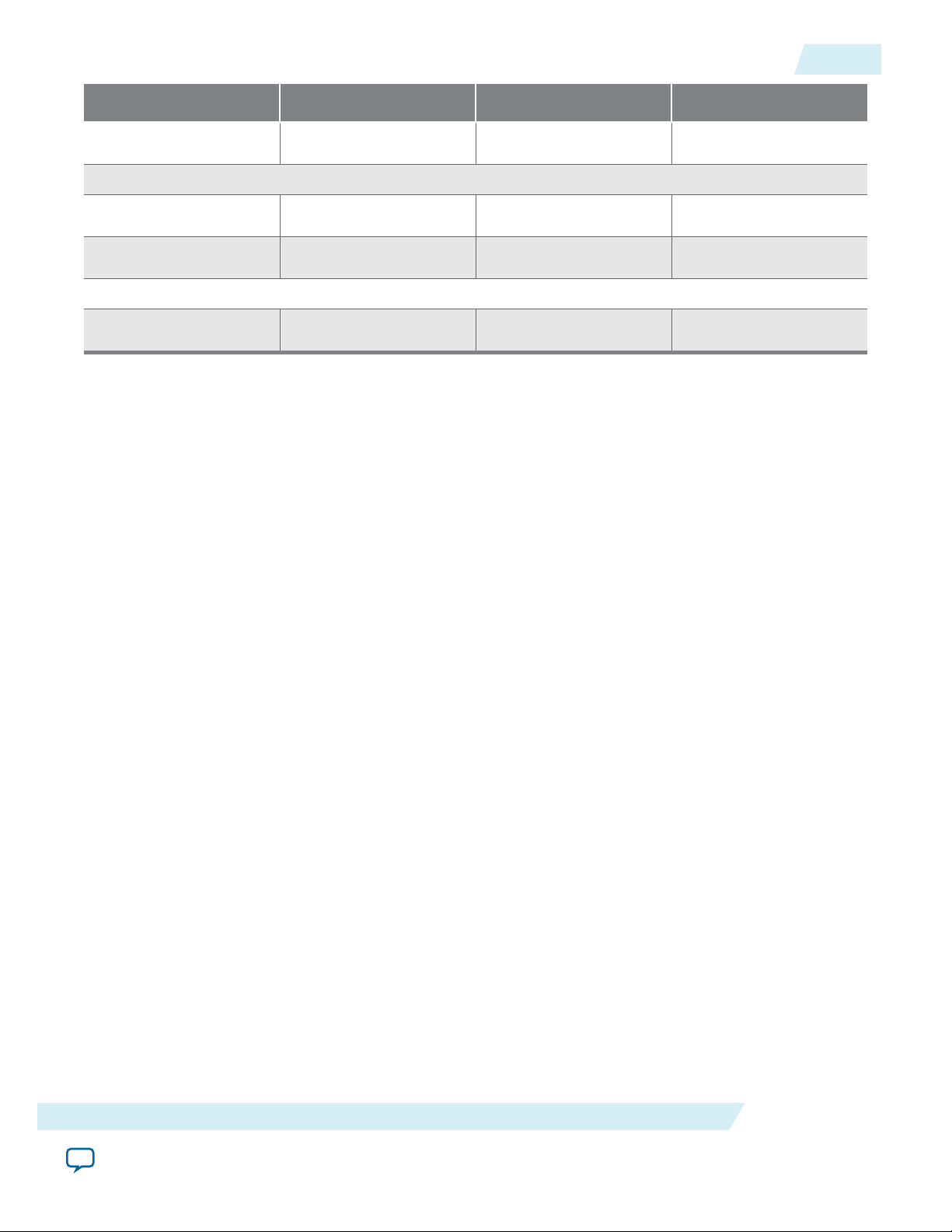
Figure 2-1: Qsys Generated Endpoint
Send Feedback
2
The design example transfers data between an on-chip memory buffer located on the Avalon-MM side
and a PCI Express memory buffer located on the root complex side. The data transfer uses the DMA
component which is programmed by the PCI Express software application running on the Root Complex
processor.
Related Information
©
trademarks of Altera Corporation and registered in the U.S. Patent and Trademark Office and in other countries. All other words and logos identified as
trademarks or service marks are the property of their respective holders as described at www.altera.com/common/legal.html. Altera warrants performance
of its semiconductor products to current specifications in accordance with Altera's standard warranty, but reserves the right to make changes to any
products and services at any time without notice. Altera assumes no responsibility or liability arising out of the application or use of any information,
product, or service described herein except as expressly agreed to in writing by Altera. Altera customers are advised to obtain the latest version of device
specifications before relying on any published information and before placing orders for products or services.
• Generating the Example Design on page 2-3
2015 Altera Corporation. All rights reserved. ALTERA, ARRIA, CYCLONE, ENPIRION, MAX, MEGACORE, NIOS, QUARTUS and STRATIX words and logos are
ISO
9001:2008
Registered
Page 20
2-2
Running Qsys
• Creating a System with Qsys
This document provides an introduction to Qsys.
Running Qsys
1. Choose Programs > Altera > Quartus II><version_number> (Windows Start menu) to run the
Quartus II software. Alternatively, you can also use the Quartus II Web Edition software.
2. On the File menu, select New, then Qsys System File.
3. Open the ep_g2x4_avmm128.qsys example design.
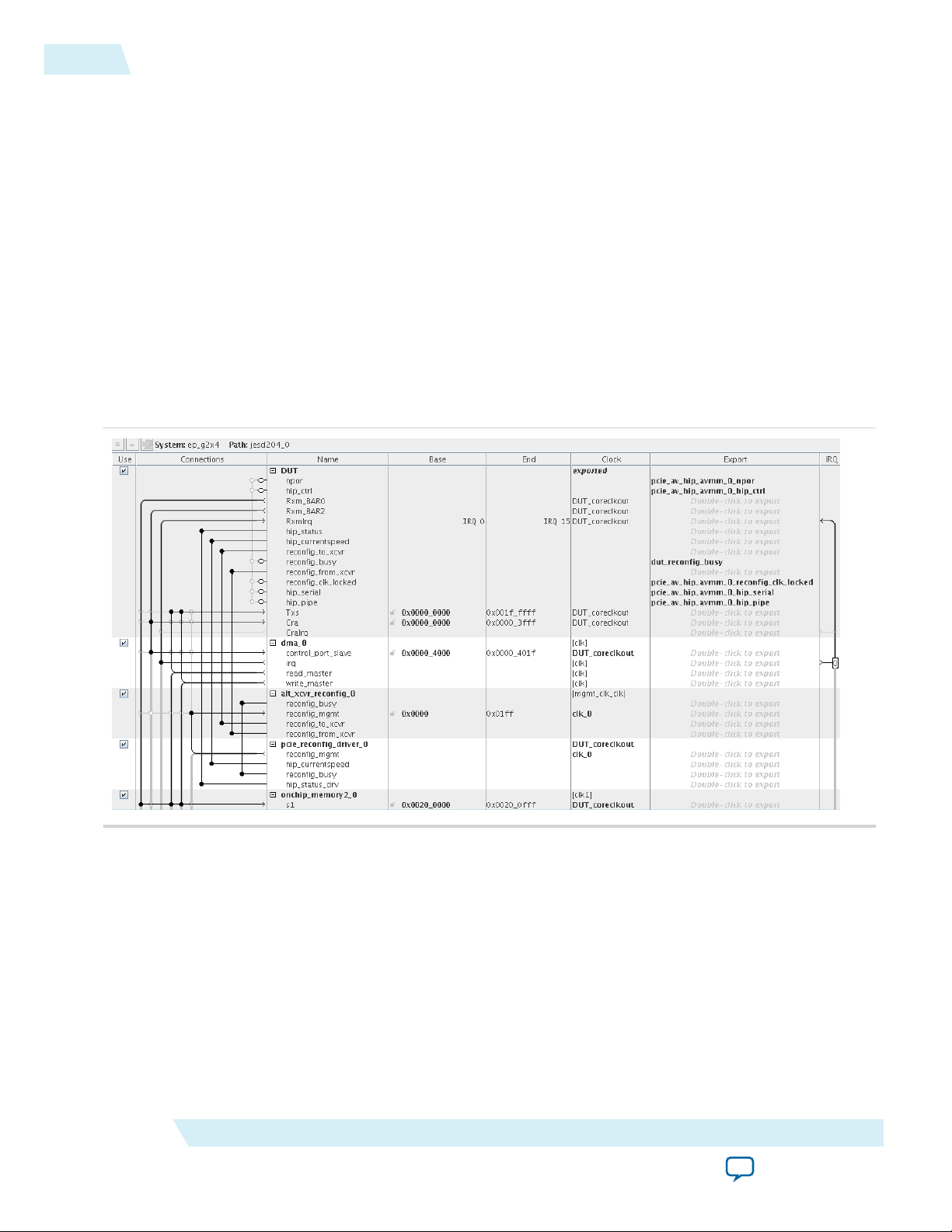
The following figure shows a Qsys system that includes the Transceiver Reconfiguration Controller and
the Altera PCIe Reconfig Driver IP Cores. The Transceiver Reconfiguration Controller performs dynamic
reconfiguration of the analog transceiver settings to optimize signal quality. You must include these
components to the Qsys system to run successfully in hardware.
Figure 2-2: Qsys Avalon-MM Design for PCIe with Transceiver Reconfiguration Components
UG-01145_avmm
2015.05.14
Refer to Creating a System with Qsys in volume 1 of the Quartus II Handbook for more information about
how to use Qsys. For an explanation of each Qsys menu item, refer to About Qsys in Quartus II Help.
Related Information
• Creating a System with Qsys
• About Qsys
Altera Corporation
Getting Started with the Avalon‑MM Arria 10 Hard IP for PCI Express
Send Feedback
Page 21

UG-01145_avmm
2015.05.14
Generating the Example Design
1. On the Generate menu, select Generate Testbench System. The Generation dialog box appears.
2. Under Testbench System, set the following options:
a. For Create testbench Qsys system, select Standard, BFMs for standard Qsys interfaces.
b. For Create testbench simulation model, select Verilog.
3. You can retain the default values for all other parameters.
4. Click Generate.
5. After Qsys reports Generation Completed, click Close.
6. On the File menu, click Save.
The following table lists the testbench and simulation directories Qsys generates.
Table 2-1: Qsys System Generated Directories
Directory Location
Generating the Example Design
2-3
Qsys system
Simulation Directory
<project_dir>/ep_g2x4_avmm128_tb
<project_dir>/ep_g2x4_avmm128_tb/ep_g2x4_tb/sim/
<cad_vendor>
The design example simulation includes the following components and software:
• The Qsys system
• A testbench. You can view this testbench in Qsys by opening <project_dir>/ep_g2x4_avmm128_tb/ep_
g2x4_avmm128_tb.qsys.
• The ModelSim software
Note:
You can also use any other supported third-party simulator to simulate your design.
Complete the following steps to run the Qsys testbench:
1. In a terminal window, change to the <project_dir>/ep_g2x4_avmm128_tb/ep_g2x4_avmm128_tb/sim/
mentor directory.
2. Start the ModelSim® simulator.
3. Type the following commands in a terminal window:
a. do msim_setup.tcl
b. ld_debug
c. run 140000 ns
Getting Started with the Avalon‑MM Arria 10 Hard IP for PCI Express
Send Feedback
Altera Corporation
Page 22

2-4
Generating the Example Design
The driver performs the following transactions with status of the transactions displayed in the ModelSim
simulation message window:
1. Various configuration accesses to the Avalon-MM Arria 10 Hard IP for PCI Express in your system
after the link is initialized
2. Setup of the Address Translation Table for requests that are coming from the DMA component
3. Setup of the DMA controller to read 512 Bytes of data from the Transaction Layer Direct BFM shared
memory
4. Setup of the DMA controller to write the same data back to the Transaction Layer Direct BFM shared
memory
5. Data comparison and report of any mismatch
The following example shows the transcript from a successful simulation run.
Example 2-1: Transcript from ModelSim Simulation of Gen2 x4 Endpoint
# INFO: 3657 ns RP LTSSM State: DETECT.ACTIVE
# INFO: 4425 ns RP LTSSM State: POLLING.ACTIVE
# INFO: 17257 ns RP LTSSM State: DETECT.QUIET
# INFO: 17353 ns RP LTSSM State: DETECT.ACTIVE
# INFO: 17405 ns RP LTSSM State: DETECT.QUIET
# INFO: 17485 ns RP LTSSM State: DETECT.ACTIVE
# INFO: 18249 ns RP LTSSM State: POLLING.ACTIVE
# INFO: 23685 ns RP LTSSM State: DETECT.ACTIVE
# INFO: 28510 ns RP LTSSM State: DETECT.QUIET
. . .
# INFO: 44777 ns RP LTSSM State: POLLING.CONFIG
# INFO: 45865 ns RP LTSSM State: CONFIG.LINKWIDTH.START
# INFO: 46213 ns EP LTSSM State: CONFIG.LINKWIDTH.START
# INFO: 46885 ns EP LTSSM State: CONFIG.LINKWIDTH.ACCEPT
# INFO: 47353 ns RP LTSSM State: CONFIG.LINKWIDTH.ACCEPT
# INFO: 48549 ns RP LTSSM State: CONFIG.LANENUM.WAIT
# INFO: 48825 ns RP LTSSM State: CONFIG.LANENUM.ACCEPT
# INFO: 48869 ns EP LTSSM State: CONFIG.LANENUM.ACCEPT
# INFO: 49145 ns RP LTSSM State: CONFIG.LANENUM.WAIT
# INFO: 49337 ns RP LTSSM State: CONFIG.LANENUM.ACCEPT
# INFO: 49657 ns RP LTSSM State: CONFIG.COMPLETE
# INFO: 50149 ns EP LTSSM State: CONFIG.COMPLETE
# INFO: 51429 ns RP LTSSM State: CONFIG.IDLE
# INFO: 51456 ns EP LTSSM State: CONFIG.IDLE
# INFO: 51609 ns RP LTSSM State: L0
# INFO: 51909 ns EP LTSSM State: L0
. . .
# INFO: 82248 ns Completed configuration of Endpoint BARs.
# INFO: 83016 ns Starting Target Write/Read Test.
# INFO: 83016 ns Target BAR = 0
# INFO: 83016 ns Length = 000512,Start Offset=000000
# INFO: 85264 ns Target Write and Read compared okay
# INFO: 85264 ns Starting DMA Read/Write Test.
# INFO: 85264 ns Setup BAR = 2
# INFO: 85264 ns Length = 000512, Start Offset = 000000
# INFO: 88616 ns Interrupt Monitor: Interrupt INTA Asserted
# INFO: 88616 ns Clear Interrupt INTA
# INFO: 89400 ns Interrupt Monitor: Interrupt INTA Deasserted
# INFO: 92892 ns MSI received!
# INFO: 92896 ns DMA Read and Write compared okay!
# SUCCESS: Simulation stopped due to successful completion!
# Break in Function ebfm_log_stop_sim at ./..//ep_g1x4_avmm64_tb/simulation/
submodules//altpcietb_bfm_log.v line 78
UG-01145_avmm
2015.05.14
Altera Corporation
Getting Started with the Avalon‑MM Arria 10 Hard IP for PCI Express
Send Feedback
Page 23
UG-01145_avmm
2015.05.14
Related Information
Simulating Altera Designs
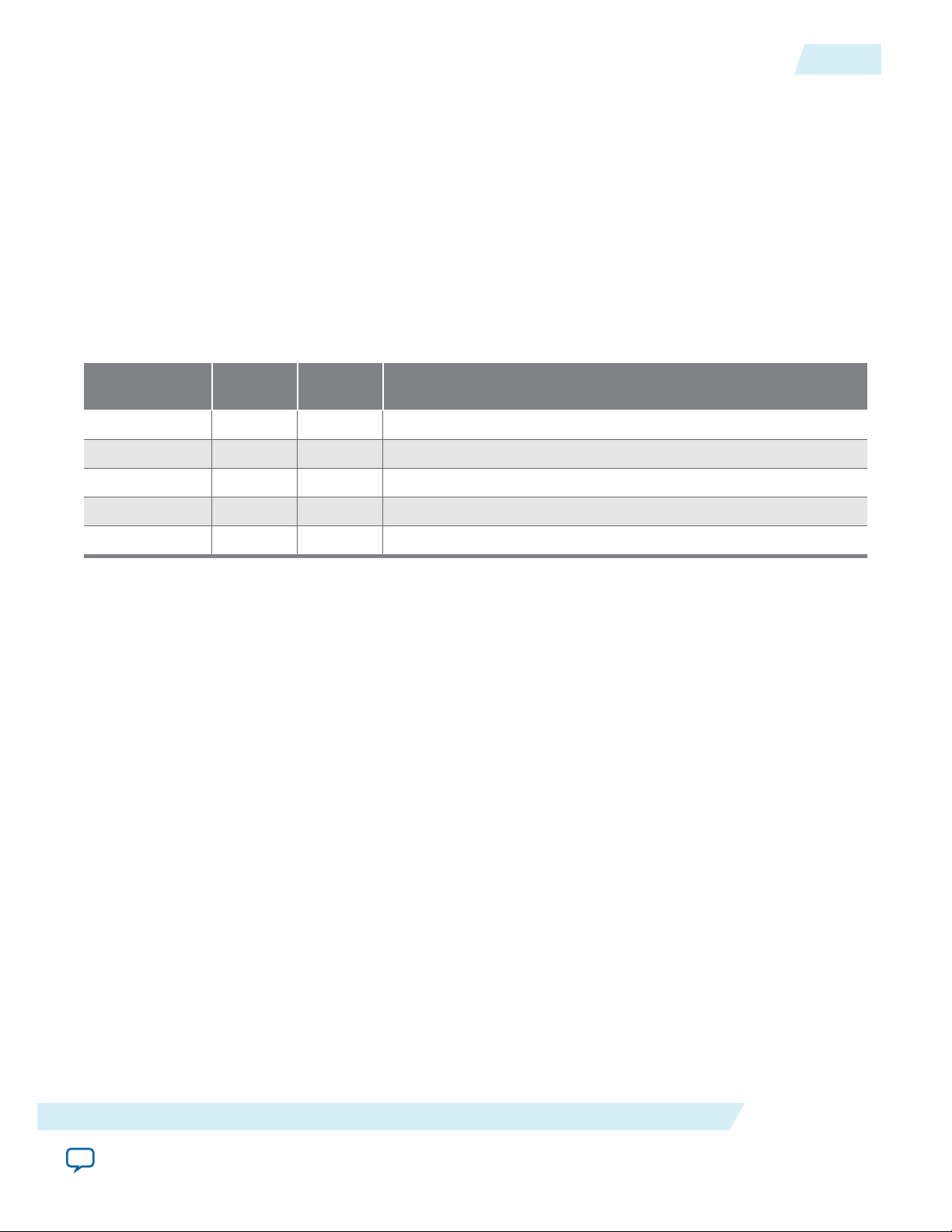
Understanding Simulation Log File Generation
Starting with the Quartus II 14.0 software release, simulation automatically creates a log file, altpcie_
monitor_<dev>_dlhip_tlp_file_log.log in your simulation directory.
Table 2-2: Sample Simulation Log File Entries
Understanding Simulation Log File Generation
2-5
Time TLP Type Payload
(Bytes)
17989 RX CfgRd0 0004 04000001_0000000F_01080008
17989 RX MRd 0000 00000000_00000000_01080000
18021 RX CfgRd0 0004 04000001_0000010F_0108002C
18053 RX CfgRd0 0004 04000001_0000030F_0108003C
18085 RX MRd 0000 00000000_00000000_0108000C
Running a Gate-Level Simulation
The PCI Express testbenches run simulations at the register transfer level (RTL). However, it is possible to
create you own gate-level simulations. Contact your Altera Sales Representative for instructions and an
example that illustrate how to create a gate-level simulation from the RTL testbench.
Simulating the Single DWord Design
You can use the same testbench to simulate the Completer-Only Single Dword IP core by changing the
settings in the driver file.
TLP Header
1. In a terminal window, change to the <variant>_tb/<variant>_tb/altera_pcie_a10_tbed_140/sim/ directory.
2. Open altpcietb_bfm_driver_avmm.v in your text editor.
3. To enable target memory tests and specify the completer-only single dword variant, specify the
following parameters:
a. parameter RUN_TGT_MEM_TST = 1;
b. parameter RUN_DMA_MEM_TST = 0;
c. parameter AVALON_MM_LITE = 1;
4. Change to the <variant>_tb/<variant>_tb/sim/mentor directory.
5. Start the ModelSim simulator.
6. To run the simulation, type the following commands in a terminal window:
Getting Started with the Avalon‑MM Arria 10 Hard IP for PCI Express
Send Feedback
Altera Corporation
Page 24

2-6
Generating Quartus II Synthesis Files
a. do msim_setup.tcl
b. ld_debug (The debug suffix stops optimizations, improving visibility in the ModelSim waveforms.)
c. run 140000 ns
Generating Quartus II Synthesis Files
1. On the Generate menu, select Generate HDL.
2. For Create HDL design files for synthesis, select Verilog.
You can leave the default settings for all other items.
3. Click Generate to generate files for Quartus II synthesis.
4. Click Finish when the generation completes.
Creating a Quartus II Project
You can create a new Quartus II project with the New Project Wizard, which helps you specify the
working directory for the project, assign the project name, and designate the name of the top-level design
entity.
1. On the Quartus II File menu, click then New Project Wizard, then Next.
2. Click Next in the New Project Wizard: Introduction (The introduction does not appear if you
previously turned it off.)
3. On the Directory, Name, Top-Level Entity page, enter the following information:
UG-01145_avmm
2015.05.14
a. For What is the working directory for this project, browse to <project_dir>/ep_g2x4_avmm128/
synth.
b. For What is the name of this project, select ep_g2x4_avmm128.v from the <project_dir>/ep_g2x4_
avmm128/synth directory.
c. For Project Type select Empty project.
4. Click Next.
5. On the Add Files page, add <project_dir>/ep_g2x4_128avmm/ep_g2x4_avmm128.qip to your Quartus II
project.
6. Click Next to display the Family & Device Settings page.
7. On the Device page, choose the following target device family and options:
a. In the Family list, select Arria 10.
b. In the Devices list, select All.
c. In the Available devices list, select the appropriate device. For Arria 10 ES2 development kits, select
10AX115S1F45I3SGE2.
8. Click Next to close this page and display the EDA Tool Settings page.
9. From the Simulation list, select ModelSim. From the Format list, select the HDL language you intend
to use for simulation.
10.Click Next to display the Summary page.
11.Check the Summary page to ensure that you have entered all the information correctly.
Altera Corporation
Getting Started with the Avalon‑MM Arria 10 Hard IP for PCI Express
Send Feedback
Page 25

UG-01145_avmm
2015.05.14
Adding Virtual Pin Assignment to the Quartus II Settings File (.qsf)
Adding Virtual Pin Assignment to the Quartus II Settings File (.qsf)
To compile successfully you must add a virtual pin assignment statement for the PIPE interface to
your .qsf file. The PIPE interface is useful for debugging, but is not a top-level interface of the IP core.
1. Browse to the synthesis directory that includes the .qsf for your project, <project_dir>/ep_g2x4_avmm128/
synth
2. Open ep_g2x4_avmm128.qsf.
3. Add the following assignment statement:
set_instance_assignment -name VIRTUAL_PIN ON -to pcie_a10_hip_0_hip_pipe_*
4. Save the .qsf file.
Compiling the Design
1. Before compiling, you need to make a few changes to your top-level Verilog HDL file to create a design
that you can successfully download to a PCB.
a. In the <project_dir>/ep_g2x4_avmm128/synth/, open ep_g2x4_avmm128.v.
b. Comment out the declaration for pcie_a10_hip_0_hip_ctrl_test_in.
c. Add a wire [31:0] pcie_a10_hip_0_hip_ctrl_test_in declaration to the same the same file.
d. Assign pcie_a10_hip_0_hip_ctrl_test_in = 0x000000A8.
e. Connect pcie_a10_hip_0_hip_ctrl_test_in to the test_in port on the Arria 10 Hard IP for
PCI Express instance.
2. On the Quartus II Processing menu, click Start Compilation.
3. After compilation, expand the TimeQuest Timing Analyzer folder in the Compilation Report. Note
whether the timing constraints are achieved in the Compilation Report.
2-7
If your design does not initially meet the timing constraints, you can find the optimal Fitter settings for
your design by using the Design Space Explorer. To use the Design Space Explorer, click Launch Design
Space Explorer on the Tools menu.
Programming a Device
After you compile your design, you can program your targeted Altera device and verify your design in
hardware.
For more information about programming Altera FPGAs, refer to Quartus II Programmer.
Related Information
Quartus II Programmer
Understanding Channel Placement Guidelines
Arria 10 transceivers are organized in banks of six channels. The transceiver bank boundaries are
important for clocking resources, bonding channels, and fitting. Refer to the Channel Placement for the
Gen1 and Gen2 Data Rates and Channel Placment and fPLL and ATX PLL Usage for the Gen3 Data Rates
for illustrations of channel placement for x1, x2, x4, and x8 variants.
Getting Started with the Avalon‑MM Arria 10 Hard IP for PCI Express
Altera Corporation
Send Feedback
Page 26

2-8
Understanding Channel Placement Guidelines
Related Information
• Channel Placement and fPLL Usage for the Gen1 and Gen2 Data Rates on page 4-5
• Channel Placement and fPLL and ATX PLL Usage for the Gen3 Data Rate on page 4-7
UG-01145_avmm
2015.05.14
Altera Corporation
Getting Started with the Avalon‑MM Arria 10 Hard IP for PCI Express
Send Feedback
Page 27
2015.05.14
www.altera.com
101 Innovation Drive, San Jose, CA 95134
Parameter Settings
3
UG-01145_avmm
Subscribe
Send Feedback
Arria 10 Avalon-MM System Settings
Table 3-1: System Settings for PCI Express
Parameter Value Description
Number of Lanes x1, x2, x4, x8 Specifies the maximum number of lanes supported.
Lane Rate Gen1 (2.5 Gbps)
Gen2 (2.5/5.0 Gbps)
Gen3 (2.5/5.0/8.0
Gbps)
Port type Native Endpoint
Root Port
Legacy endpoint
Specifies the maximum data rate at which the link can operate.
Specifies the port type. Altera recommends Native Endpoint
for all new Endpoint designs. Select Legacy Endpoint only
when you require I/O transaction support for compatibility.
The Endpoint stores parameters in the Type 0 Configuration
Space. The Root Port stores parameters in the Type 1 Configu‐
ration Space.
Application
Interface Type
RX Buffer credit
allocation performance for
received requests
©
2015 Altera Corporation. All rights reserved. ALTERA, ARRIA, CYCLONE, ENPIRION, MAX, MEGACORE, NIOS, QUARTUS and STRATIX words and logos are
trademarks of Altera Corporation and registered in the U.S. Patent and Trademark Office and in other countries. All other words and logos identified as
trademarks or service marks are the property of their respective holders as described at www.altera.com/common/legal.html. Altera warrants performance
of its semiconductor products to current specifications in accordance with Altera's standard warranty, but reserves the right to make changes to any
products and services at any time without notice. Altera assumes no responsibility or liability arising out of the application or use of any information,
product, or service described herein except as expressly agreed to in writing by Altera. Altera customers are advised to obtain the latest version of device
specifications before relying on any published information and before placing orders for products or services.
Avalon-ST
Avalon-MM
Avalon-MM with
DMA
Avalon-ST with SR-
IOV
Minimum
Low
Balanced
Selects either the Avalon-ST interface, Avalon-MM interface,
Avalon-MM with DMA interface, or Avalon-ST with SR-IOV
interface.
Determines the allocation of posted header credits, posted
data credits, non-posted header credits, completion header
credits, and completion data credits in the 16 KByte RX buffer.
The 5 settings allow you to adjust the credit allocation to
ISO
9001:2008
Registered
Page 28

3-2
Arria 10 Avalon-MM System Settings
Parameter Value Description
UG-01145_avmm
2015.05.14
High
Maximum100 MHz
optimize your system. The credit allocation for the selected
setting displays in the message pane.
Refer to the Throughput Optimization chapter for more
information about optimizing performance. The Flow Control
chapter explains how the RX credit allocation and the
Maximum payload RX Buffer credit allocation and the
Maximum payload size that you choose affect the allocation
of flow control credits. You can set the Maximum payload
size parameter on the Device tab.
The Message window dynamically updates the number of
credits for Posted, Non-Posted Headers and Data, and
Completion Headers and Data as you change this selection.
• Minimum—configures the minimum PCIe specification
allowed for non-posted and posted request credits, leaving
most of the RX Buffer space for received completion
header and data. Select this option for variations where
application logic generates many read requests and only
infrequently receives single requests from the PCIe link.
• Low—configures a slightly larger amount of RX Buffer
space for non-posted and posted request credits, but still
dedicates most of the space for received completion header
and data. Select this option for variations where application
logic generates many read requests and infrequently
receives small bursts of requests from the PCIe link. This
option is recommended for typical endpoint applications
where most of the PCIe traffic is generated by a DMA
engine that is located in the endpoint application layer
logic.
• Balanced—configures approximately half the RX Buffer
space to received requests and the other half of the RX
Buffer space to received completions. Select this option for
variations where the received requests and received
completions are roughly equal.
Use 62.5 MHz
application clock
Enable byte
parity ports on
Avalon-ST
interface
Altera Corporation
On/Off This mode is only available only for Gen1 ×1.
On/Off When On, the RX and TX datapaths are parity protected.
Parity is odd.
This parameter is only available for the Avalon-ST Arria 10
Hard IP for PCI Express.
Parameter Settings
Send Feedback
Page 29
UG-01145_avmm
2015.05.14
Arria 10 Avalon-MM System Settings
Parameter Value Description
3-3
Enable multiple
packets per cycle
for the 256-bit
interface
Enable configu‐
ration via PCI
Express (CvP)
Enable credit
consumed
selection port
Enable dynamic
reconfiguration
of PCIE readonly registers
On/Off When On, the 256-bit Avalon-ST interface supports the
transmission of TLPs starting at any 128-bit address
boundary, allowing support for multiple packets in a single
cycle. To support multiple packets per cycle, the Avalon-ST
interface includes 2 start of packet and end of packet signals
for the 256-bit Avalon-ST interfaces. This feature is only
supported for Gen3 x8.
On/Off When On, the Quartus II software places the Endpoint in the
location required for configuration via protocol (CvP). For
more information about CvP, click the Configuration via
Protocol (CvP) link below.
A single hard IP block in each device includes the CvP
functionality. Refer to thePhysical Layout of Hard IP in Arria
10 Devices for more information.
On/Off When you turn on this option, the core includes the tx_cons_
cred_sel port. This parameter does not apply to the Avalon-
MM interface.
On/Off When On, you can use the Hard IP reconfiguration bus to
dynamically reconfigure Hard IP read-only registers. For more
information refer to Hard IP Reconfiguration Interface.
Enable Altera
Debug Master
On/Off When On, you can use the Altera System Console to read and
write the embedded Arria 10 Native PHY registers.
Endpoint
(ADME)
Related Information
• Physical Layout of Hard IP In Arria 10 Devices on page 4-1
• PCI Express Base Specification 3.0
• Arria 10 Transceiver PHY User Guide
Provides information about the ADME feature for Arria 10 devices.
Parameter Settings
Send Feedback
Altera Corporation
Page 30
3-4
Interface System Settings
Interface System Settings
Table 3-2: Interface System Settings
Parameter Value Description
UG-01145_avmm
2015.05.14
Application Interface
width
Avalon-MM address
width
Enable completer-only
Endpoint
64-bit
128-bit
256-bit
32, 64
On/Off
Specifies the data width for the Application Layer to
Transaction Layer interface. Refer to Application Layer
Clock Frequency for All Combinations of Link Width,
Data Rate and Application Layer Interface Widths for all
legal combinations of data width, number of lanes,
Application Layer clock frequency, and data rate. The
Avalon-MM with DMA interface does not support the
64-bit interface width.
Specifies the address width for Avalon-MM RX master
ports that access Avalon-MM slaves in the Avalon
address domain. When you select 32-bit addresses, the
PCI Express Avalon-MM bridge performs address
translation. When you specify 64-bits addresses, no
address translation is performed in either direction. The
destination address specified is forwarded to the
Avalon-MM interface without any changes.
For the Avalon-MM interface with DMA, this value
must be set to 64.
In this mode, the Hard IP can receive requests, but
cannot initiate upstream requests. However, it can
transmit completion packets on the PCI Express TX
link. This mode removes the Avalon-MM TX slave port
and thereby reduces logic utilization.
Enable completer-only
Endpoint with 4-byte
payload
Altera Corporation
On/Off
This is a non-pipelined version of Completer Only
mode. At any time, only a single request can be
outstanding. Single dword completer uses fewer
resources than completer only Endpoint. This variant
is targeted for systems that require simple read and
write register accesses from a host CPU. If you select
this option, the width of the data for RXM BAR masters
is always 32 bits, regardless of the Avalon-MM width.
For the Avalon-MM interface with DMA, this value
must be Off .
Parameter Settings
Send Feedback
Page 31

UG-01145_avmm
2015.05.14
Interface System Settings
Parameter Value Description
3-5
Enable control register
access (CRA) Avalon-MM
slave port
Export MSI/MSI-X
conduit interfaces
Enable PCIe interrupt at
power-on
On/Off
On/Off
On/Off
Allows read and write access to bridge registers from the
interconnect fabric using a specialized slave port. This
option is required for Requester/Completer variants
and optional for Completer Only variants. Enabling
this option allows read and write access to bridge
registers, except in the Completer-Only single dword
variations.
When you turn this option on, the core exports
top-level MSI and MSI-X interfaces that you can use to
implement a Custom Interrupt Handler for MSI and
MSI-X interrupts. For more information about the
Custom Interrupt Handler, refer to Interrupts for End
Points Using the Avalon-MM Interface with Multiple
-
MSI/MSI
X Support. If you turn this option Off, the
core handles interrupts internally.
If you select this option, you must design your own
external descriptor controller. The embedded controller
does not support MSI-X.
When you turn this option on, the Avalon-MM Arria 10
Hard IP for PCI Express enables the interrupt register at
power-up. Turning off this option disables the interrupt
register at power-up. The setting does not affect runtime configuration of the interrupt enable register.
Enable Hard IP Status
Bus when using the
AVMM interface
Address width of
accessible PCIe memory
space
Number of address pages 2, 4, 8, 16, 32, 64,
Parameter Settings
For the Avalon-MM interface with DMA, this value
must be off.
On/Off When you turn this option on, your top-level variant
includes the following top-level signals:
• Link status signals
• ECC error signals
• TX and RX parity error signals
• Completion header and data signals, indicating the
total number of Completion TLPs currently stored in
the RX buffer.
20–64 Specifies the size of the PCIe memory space. The value
you specify sets the width of the TX slave address, txs_
address for 64-bit addresses.
Specifies the number of consecutive address pages in the
128, 256, 512
PCI Express address domain. This parameter is only
necessary for 32-bit addresses.
Altera Corporation
Send Feedback
Page 32

3-6
Base Address Register (BAR) Settings
Parameter Value Description
Size of address pages 4 KByte–4GByte Sets the size of the PCI Express system pages. All pages
must be the same size. This parameter is only necessary
for 32-bit addresses.
Related Information
coreclkout_hip on page 7-5
Base Address Register (BAR) Settings
You can configure up to six 32-bit BARs or three 64-bit BARs.
Table 3-3: BAR Registers
Parameter Value Description
UG-01145_avmm
2015.05.14
Type
Size
Disabled
64-bit prefetchable memory
32-bit non-prefetchable memory
32-bit prefetchable memory
I/O address space
Not configurable
Defining memory as prefetchable allows data in the
region to be fetched ahead anticipating that the
requestor may require more data from the same
region than was originally requested. If you specify
that a memory is prefetchable, it must have the
following 2 attributes:
• Reads do not have side effects
• Write merging is allowed
The 32-bit prefetchable memory and I/O address
space BARs are only available for the Legacy
Endpoint.
Specifies the memory size calculated from other
parameters you enter.
Altera Corporation
Parameter Settings
Send Feedback
Page 33
UG-01145_avmm
2015.05.14
Device Identification Registers
Device Identification Registers
Table 3-4: Device ID Registers
The following table lists the default values of the read-only Device ID registers. You can use the parameter editor
to change the values of these registers. Refer to Type 0 Configuration Space Registers for the layout of the Device
Identification registers.
Register Name Range Default Value Description
Vendor ID 16 bits 0x00000000 Sets the read-only value of the Vendor ID register. This
parameter cannot be set to 0xFFFF, per the PCI Express
Specification.
Address offset: 0x000.
Device ID 16 bits 0x00000000 Sets the read-only value of the Device ID register. This
register is only valid in the Type 0 (Endpoint) Configu‐
ration Space.
Address offset: 0x000.
3-7
Revision ID 8 bits 0x00000000 Sets the read-only value of the Revision ID register.
Address offset: 0x008.
Class code 24 bits 0x00000000 Sets the read-only value of the Class Code register.
Address offset: 0x008.
Subsystem
Vendor ID
16 bits 0x00000000 Sets the read-only value of the Subsystem Vendor ID
register in the PCI Type 0 Configuration Space. This
parameter cannot be set to 0xFFFF per the PCI Express
Base Specification. This value is assigned by PCI-SIG to
the device manufacturer. This register is only valid in
the Type 0 (Endpoint) Configuration Space.
Address offset: 0x02C.
Subsystem
Device ID
16 bits 0x00000000 Sets the read-only value of the Subsystem Device ID
register in the PCI Type 0 Configuration Space.
Address offset: 0x02C
Related Information
PCI Express Base Specification 3.0
Parameter Settings
Send Feedback
Altera Corporation
Page 34

3-8
PCI Express and PCI Capabilities Parameters
PCI Express and PCI Capabilities Parameters
This group of parameters defines various capability properties of the IP core. Some of these parameters
are stored in the PCI Configuration Space - PCI Compatible Configuration Space. The byte offset
indicates the parameter address.
Device Capabilities
Table 3-5: Capabilities Registers
Parameter Possible Values Default Value Description
UG-01145_avmm
2015.05.14
Maximum
payload size
Completion
timeout
range
128 bytes
256 bytes
512 bytes
1024 bytes
2048 bytes
ABCD
BCD
ABC
AB
B
A
None
128 bytes Specifies the maximum payload size supported. This
parameter sets the read-only value of the max payload
size supported field of the Device Capabilities register
(0x084[2:0]). Address: 0x084.
ABCD Indicates device function support for the optional
completion timeout programmability mechanism. This
mechanism allows the system software to modify the
completion timeout value. This field is applicable only to
Root Ports and Endpoints that issue requests on their
own behalf. Completion timeouts are specified and
enabled in the Device Control 2 register (0x0A8) of the
PCI Express Capability Structure Version. For all other
functions this field is reserved and must be hardwired to
0x0000b. Four time value ranges are defined:
• Range A: 50 us to 10 ms
• Range B: 10 ms to 250 ms
• Range C: 250 ms to 4 s
• Range D: 4 s to 64 s
Altera Corporation
Bits are set to show timeout value ranges supported. The
function must implement a timeout value in the range
50 sto 50 ms. The following values specify the range:
• None—Completion timeout programming is not
supported
• 0001 Range A
• 0010 Range B
• 0011 Ranges A and B
• 0110 Ranges B and C
Parameter Settings
Send Feedback
Page 35

UG-01145_avmm
2015.05.14
Parameter Possible Values Default Value Description
Error Reporting
• 0111 Ranges A, B, and C
• 1110 Ranges B, C and D
• 1111 Ranges A, B, C, and D
All other values are reserved. Altera recommends that
the completion timeout mechanism expire in no less
than 10 ms.
3-9
Disable
completion
timeout
On/Off On Disables the completion timeout mechanism. When On,
the core supports the completion timeout disable
mechanism via the PCI Express Device Control
Register 2. The Application Layer logic must
implement the actual completion timeout mechanism
for the required ranges.
Error Reporting
Table 3-6: Error Reporting
Parameter Value Default Value Description
Advanced
error
reporting
(AER)
Enable
ECRC
checking
On/Off Off When On, enables the Advanced Error Reporting (AER)
capability.
On/Off Off When On, enables ECRC checking. Sets the read-only
value of the ECRC check capable bit in the Advanced
Error Capabilities and Control Register. This
parameter requires you to enable the AER capability.
Enable
ECRC
generation
Enable
ECRC
forwarding
on the
Avalon-ST
interface
Parameter Settings
Send Feedback
On/Off Off
When On, enables ECRC generation capability. Sets the
read-only value of the ECRC generation capable bit in
the Advanced Error Capabilities and Control
Register. This parameter requires you to enable the
AER capability.
On/Off Off When On, enables ECRC forwarding to the Application
Layer. On the Avalon-ST RX path, the incoming TLP
contains the ECRC dword
(1)
and the TD bit is set if an
ECRC exists. On the transmit the TLP from the Applica‐
tion Layer must contain the ECRC dword and have the
TD bit set.
Not applicable for Avalon-MM or Avalon-MM DMA
interfaces.
Altera Corporation
Page 36

3-10
Link Capabilities
Parameter Value Default Value Description
UG-01145_avmm
2015.05.14
Track RX
completion
buffer
overflow on
the AvalonST interface
On/Off Off When On, the core includes the rxfx_cplbuf_ovf
output status signal to track the RX posted completion
buffer overflow status.
Not applicable for Avalon-MM or Avalon-MM DMA
interfaces.
Note:
1. Throughout this user guide, the terms word, dword and qword have the same meaning that they have
in the PCI Express Base Specification. A word is 16 bits, a dword is 32 bits, and a qword is 64 bits.
Link Capabilities
Table 3-7: Link Capabilities
Parameter Value Description
Link port
number
Data link layer
active reporting
0x01 Sets the read-only value of the port number field in the Link
Capabilities register.
On/Off
Turn On this parameter for a downstream port, if the
component supports the optional capability of reporting the
DL_Active state of the Data Link Control and Management
State Machine. For a hot-plug capable downstream port (as
indicated by the Hot Plug Capable field of the Slot
Capabilities register), this parameter must be turned On.
For upstream ports and components that do not support this
optional capability, turn Off this option. This parameter is
only supported for the Arria 10 Hard IP for PCI Express in
Root Port mode.
Surprise down
reporting
Altera Corporation
On/Off
Not applicable for Avalon-MM or Avalon-MM DMA
interfaces.
When this option is On, a downstream port supports the
optional capability of detecting and reporting the surprise
down error condition. This parameter is only supported for
the Arria 10 Hard IP for PCI Express in Root Port mode.
Not applicable for Avalon-MM or Avalon-MM DMA
interfaces.
Parameter Settings
Send Feedback
Page 37

UG-01145_avmm
2015.05.14
MSI and MSI-X Capabilities
Parameter Value Description
3-11
Slot clock
configuration
On/Off When On, indicates that the Endpoint or Root Port uses the
same physical reference clock that the system provides on the
connector. When Off, the IP core uses an independent clock
regardless of the presence of a reference clock on the
connector.
MSI and MSI-X Capabilities
Table 3-8: MSI and MSI-X Capabilities
Parameter Value Description
MSI messages
requested
Implement MSIX
1, 2, 4, 8, 16, 32 Specifies the number of messages the Application Layer can
request. Sets the value of the Multiple Message Capable
field of the Message Control register, 0x050[31:16].
MSI-X Capabilities
On/Off When On, enables the MSI-X functionality.
Bit Range
Table size [10:0] System software reads this field to determine the MSI-X Table
size <n>, which is encoded as <n–1>. For example, a returned
value of 2047 indicates a table size of 2048. This field is readonly. Legal range is 0–2047 (211).
Address offset: 0x068[26:16]
Table Offset [31:0] Points to the base of the MSI-X Table. The lower 3 bits of the
table BAR indicator (BIR) are set to zero by software to form a
(1)
. This field is read-only.
Table BAR
Indicator
32-bit qword-aligned offset
[2:0] Specifies which one of a function’s BARs, located beginning at
0x10 in Configuration Space, is used to map the MSI-X table
into memory space. This field is read-only. Legal range is 0–5.
Pending Bit
Array (PBA)
Offset
[31:0] Used as an offset from the address contained in one of the
function’s Base Address registers to point to the base of the
MSI-X PBA. The lower 3 bits of the PBA BIR are set to zero by
software to form a 32-bit qword-aligned offset. This field is
read-only.
Parameter Settings
Send Feedback
Altera Corporation
Page 38

31 19 1 8 17 16 15 14
7
6 5
Physical Slot Number
No Command Completed Support
Electromechanical Interlock Present
Slot Power Limit Scale
Slot Power Limit Value
Hot-Plug Capable
Hot-Plug Surprise
Power Indicator Present
Attention Indicator Present
MRL Sensor Present
Power Controller Present
Attention Button Present
04 3 2 1
3-12
Slot Capabilities
Parameter Value Description
UG-01145_avmm
2015.05.14
Pending BAR
Indicator
[2:0] Specifies the function Base Address registers, located
beginning at 0x10 in Configuration Space, that maps the MSIX PBA into memory space. This field is read-only. Legal range
is 0–5.
Note:
1. Throughout this user guide, the terms word, dword and qword have the same meaning that they have
in the PCI Express Base Specification. A word is 16 bits, a dword is 32 bits, and a qword is 64 bits.
Slot Capabilities
Table 3-9: Slot Capabilities
Parameter Value Description
Use Slot register On/Off The slot capability is required for Root Ports if a slot is implemented
on the port. Slot status is recorded in the PCI Express Capabili-
ties register. This parameter is only supported in Root Port mode.
Defines the characteristics of the slot. You turn on this option by
selecting Enable slot capability. The various bits are defined as
follows:
Slot power scale
Altera Corporation
0–3
Specifies the scale used for the Slot power limit. The following
coefficients are defined:
• 0 = 1.0x
• 1 = 0.1x
• 2 = 0.01x
• 3 = 0.001x
The default value prior to hardware and firmware initialization is
b’00. Writes to this register also cause the port to send the Set_
Slot_Power_Limit Message.
Refer to Section 6.9 of the PCI Express Base Specification Revision for
more information.
Parameter Settings
Send Feedback
Page 39

UG-01145_avmm
2015.05.14
Parameter Value Description
Power Management
3-13
Slot power limit
0–255
In combination with the Slot power scale value, specifies the upper
limit in watts on power supplied by the slot. Refer to Section 7.8.9 of
the PCI Express Base Specification for more information.
Slot number
0-8191
Specifies the slot number.
Power Management
Table 3-10: Power Management Parameters
Parameter Value Description
Endpoint L0s
acceptable
latency
Maximum of 64 ns
Maximum of 128 ns
Maximum of 256 ns
Maximum of 512 ns
Maximum of 1 us
Maximum of 2 us
Maximum of 4 us
No limit
This design parameter specifies the maximum acceptable
latency that the device can tolerate to exit the L0s state for any
links between the device and the root complex. It sets the
read-only value of the Endpoint L0s acceptable latency field of
the Device Capabilities Register (0x084).
This Endpoint does not support the L0s or L1 states. However,
in a switched system there may be links connected to switches
that have L0s and L1 enabled. This parameter is set to allow
system configuration software to read the acceptable latencies
for all devices in the system and the exit latencies for each link
to determine which links can enable Active State Power
Management (ASPM). This setting is disabled for Root Ports.
Endpoint L1
acceptable
latency
Parameter Settings
Maximum of 1 us
Maximum of 2 us
Maximum of 4 us
Maximum of 8 us
Maximum of 16 us
Maximum of 32 us
No limit
The default value of this parameter is 64 ns. This is the safest
setting for most designs.
This value indicates the acceptable latency that an Endpoint
can withstand in the transition from the L1 to L0 state. It is an
indirect measure of the Endpoint’s internal buffering. It sets
the read-only value of the Endpoint L1 acceptable latency field
of the Device Capabilities Register.
This Endpoint does not support the L0s or L1 states. However,
a switched system may include links connected to switches
that have L0s and L1 enabled. This parameter is set to allow
system configuration software to read the acceptable latencies
for all devices in the system and the exit latencies for each link
to determine which links can enable Active State Power
Management (ASPM). This setting is disabled for Root Ports.
The default value of this parameter is 1 µs. This is the safest
setting for most designs.
Altera Corporation
Send Feedback
Page 40

2015.05.14
Transceiver
Bank
Transceiver
Bank
Transceiver
Bank
GXBL1J
Transceiver
Bank
GXBL1I
Transceiver
Bank
GXBL1H
Transceiver
Bank
GXBL1G
Transceiver
Bank
GXBL1F
Transceiver
Bank
Transceiver
Bank
GXBL1D
Transceiver
Bank
GXBL1C
Transceiver
Bank
Transceiver
Bank
Transceiver
Bank
Transceiver
Bank
Transceiver
Bank
Transceiver
Bank
Transceiver
Bank
Transceiver
Bank
Transceiver
Bank
Transceiver
Bank
Transceiver
Bank
Transceiver
Bank
Transceiver
Bank
Transceiver
Bank
GXBR4C
PCIe
Gen3
HIP
(with CvP)
PCIe
Gen3
HIP
PCIe
Gen3
HIP
PCIe
Gen3
HIP
GT 115 UF45
GT 090 UF45
GXBL1E
GXBL1C
GXBL1D
GXBL1E
GXBL1F
GXBL1G
GXBL1H
GXBL1I
GXBL1J
GXBR4D
GXBR4E
GXBR4F
GXBR4G
GXBR4H
GXBR4I
GXBR4J
GXBR4C
GXBR4D
GXBR4E
GXBR4F
GXBR4G
GXBR4H
GXBR4I
GXBR4J
Notes:
(1) Nomenclature of left column bottom transceiver banks always begins with “C”
(2) Nomenclature of right column bottom transceiver banks may begin with “C”, “D”, or “E”.
(1) (2)
www.altera.com
101 Innovation Drive, San Jose, CA 95134
Physical Layout of Hard IP In Arria 10 Devices
4
UG-01145_avmm
Subscribe
Send Feedback
Arria 10 devices include 1–4 hard IP blocks for PCI Express. The bottom left hard IP block includes the
CvP functionality for flip chip packages. For other package types, the CvP functionality is in the bottom
right block.
Figure 4-1: Arria 10 Devices with 96 Transceiver Channels and Four PCIe Hard IP Blocks
©
2015 Altera Corporation. All rights reserved. ALTERA, ARRIA, CYCLONE, ENPIRION, MAX, MEGACORE, NIOS, QUARTUS and STRATIX words and logos are
trademarks of Altera Corporation and registered in the U.S. Patent and Trademark Office and in other countries. All other words and logos identified as
trademarks or service marks are the property of their respective holders as described at www.altera.com/common/legal.html. Altera warrants performance
of its semiconductor products to current specifications in accordance with Altera's standard warranty, but reserves the right to make changes to any
products and services at any time without notice. Altera assumes no responsibility or liability arising out of the application or use of any information,
product, or service described herein except as expressly agreed to in writing by Altera. Altera customers are advised to obtain the latest version of device
specifications before relying on any published information and before placing orders for products or services.
ISO
9001:2008
Registered
Page 41

Transceiver
Bank
Transceiver
Bank
Transceiver
Bank
Transceiver
Bank
Transceiver
Bank
Transceiver
Bank
Transceiver
Bank
Transceiver
Bank
Transceiver
Bank
Transceiver
Bank
Transceiver
Bank
Transceiver
Bank
Transceiver
Bank
Transceiver
Bank
Transceiver
Bank
Transceiver
Bank
Transceiver
Bank
Transceiver
Bank
PCIe
Gen3
Hard IP
(with CvP)
PCIe
Gen3
Hard IP
PCIe
Gen3
Hard IP
GT 115 SF45
GT 090 SF45
GXBL1C
GXBL1D
GXBL1E
GXBL1F
GXBL1G
GXBL1H
GXBL1C
GXBL1E
GXBL1F
GXBL1G
GXBL1H
GXBR4DGXBR4D
GXBR4EGXBR4E
GXBR4FGXBR4F
GXBR4GGXBR4G
GXBR4HGXBR4H
GXBR4IGXBR4I
Notes:
(1) Nomenclature of left column bottom transceiver banks always begins with “C”
(2) Nomenclature of right column bottom transceiver banks may begin with “C”, “D”, or “E”.
(1) (2)
GXBL1D
4-2
Physical Layout of Hard IP In Arria 10 Devices
Figure 4-2: Arria 10 Devices with 72 Transceiver Channels and Four PCIe Hard IP Blocks
UG-01145_avmm
2015.05.14
Altera Corporation
Physical Layout of Hard IP In Arria 10 Devices
Send Feedback
Page 42

Transceiver
Bank
Transceiver
Bank
Transceiver
Bank
Transceiver
Bank
Transceiver
Bank
Transceiver
Bank
Transceiver
Bank
Transceiver
Bank
Transceiver
Bank
Transceiver
Bank
Transceiver
Bank
Transceiver
Bank
Transceiver
Bank
Transceiver
Bank
Transceiver
Bank
Transceiver
Bank
GT 115 NF40
GT 090 NF40
GXBL1C
GXBL1D
GXBL1E
GXBL1F
GXBL1G
GXBL1H
GXBL1I
GXBL1J
Notes:
(1) Nomenclature of left column bottom transceiver banks always begins with “C”
(2) These devices have transceivers only on left hand side of the device.
(1)
PCIe
Gen1 - Gen3
Hard IP
PCIe
Gen1 - Gen3
(with CvP)
Hard IP
Legend:
PCIe Gen1 - Gen3 Hard IP blocks with CvP capabilities
PCIe Gen1 - Gen3 Hard IP blocks without CvP capabilities
UG-01145_avmm
2015.05.14
Figure 4-3: Arria 10 GT Devices with 48 Transceiver Channels and Two PCIe Hard IP Blocks
Physical Layout of Hard IP In Arria 10 Devices
4-3
Refer to the Arria 10 Transceiver Layout in the Arria 10 Transceiver PHY User Guide for comprehensive
figures for Arria 10 GT, GX, and SX devices.
Related Information
Arria 10 Transceiver PHY User Guide
Physical Layout of Hard IP In Arria 10 Devices
Send Feedback
Altera Corporation
Page 43

PMA Channel 5
PMA Channel 4
PMA Channel 3
PMA Channel 2
PMA Channel 0
PMA Channel 3
PMA Channel 2
PMA Channel 1
PMA Channel 0
PCS Channel 5
PCS Channel 4
PCS Channel 3
PCS Channel 2
PCS Channel 0
PCS Channel 3
PCS Channel 2
PCS Channel 1
PCS Channel 0
Hard IP Ch0
PMA Channel 1 PCS Channel 1
PMA Channel 4 PCS Channel 4
PMA Channel 5 PCS Channel 5
Hard IP
for PCIe
<txvr_block_N>_TX/RX_CH4N
PMA Channel 5
PMA Channel 4
PMA Channel 3
PMA Channel 2
PMA Channel 0
PMA Channel 3
PMA Channel 2
PMA Channel 1
PMA Channel 0
PCS Channel 5
PCS Channel 4
PCS Channel 3
PCS Channel 2
PCS Channel 0
PCS Channel 3
PCS Channel 2
PCS Channel 1
PCS Channel 0
Hard IP Ch0
PMA Channel 1 PCS Channel 1
PMA Channel 4 PCS Channel 4
PMA Channel 5 PCS Channel 5
Hard IP
for PCIe
<txvr_block_N>_TX/RX_CH4N
<txvr_block_N>_TX/RX_CH5N
4-4
Channel and Pin Placement for the Gen1, Gen2, and Gen3 Data Rates
UG-01145_avmm
Channel and Pin Placement for the Gen1, Gen2, and Gen3 Data Rates
The following figures illustrate the x1, x2, x4, and x8 channel and pin placements for the Arria 10 Hard IP
for PCI Express.
In these figures, channels that are not used for the PCI Express protocol are available for other protocols.
Unused channels are shown in gray.
Note: In all configurations, physical channel 4 in the PCS connects to logical channel 0 in the hard IP.
You cannot change the channel placements illustrated below.
For the possible values of <txvr_block_N> and <txvr_block_N+1>, refer to the figures that show the
physical location of the Hard IP PCIe blocks in the different types of Arria 10 devices, at the start of this
chapter. For each HIP block, the transceiver block that is adjacent and extends below the HIP block, is
<txvr_block_N>, and the transceiver block that is directly above <txvr_block_N> is <txvr_block_N+1>.
For example, in an Arria 10 device with 96 transceiver channels and four PCIe HIP blocks, if your design
uses the HIP block that supports CvP, <txvr_block_N> is GXB1C and <txvr_block_N+1> is GXB1D.
Figure 4-4: Arria 10 Gen1, Gen2, and Gen3 x1 Channel and Pin Placement
2015.05.14
Figure 4-5: Arria 10 Gen1 Gen2, and Gen3 x2 Channel and Pin Placement
Altera Corporation
Physical Layout of Hard IP In Arria 10 Devices
Send Feedback
Page 44

PMA Channel 5
PMA Channel 4
PMA Channel 3
PMA Channel 0
PMA Channel 3
PMA Channel 2
PMA Channel 1
PMA Channel 0
PCS Channel 5
PCS Channel 4
PCS Channel 3
PCS Channel 0
PCS Channel 3
PCS Channel 2
PCS Channel 1
PCS Channel 0
Hard IP Ch0
PMA Channel 1 PCS Channel 1
PMA Channel 4 PCS Channel 4
PMA Channel 5 PCS Channel 5
PMA Channel 2 PCS Channel 2
Hard IP
for PCIe
<txvr_block_N>_TX/RX_CH4N
<txvr_block_N>_TX/RX_CH5N
<txvr_block_N+1>_TX/RX_CH0N
<txvr_block_N+1>_TX/RX_CH1N
PMA Channel 5
PMA Channel 4
PMA Channel 3
PMA Channel 0
PMA Channel 3
PMA Channel 2
PMA Channel 1
PMA Channel 0
PCS Channel 5
PCS Channel 4
PCS Channel 3
PCS Channel 0
PCS Channel 3
PCS Channel 2
PCS Channel 1
PCS Channel 0
Hard IP
for PCIe
Hard IP Ch0
PMA Channel 1 PCS Channel 1
PMA Channel 4 PCS Channel 4
PMA Channel 5 PCS Channel 5
PMA Channel 2 PCS Channel 2
<txvr_block_N>_TX/RX_CH4N
<txvr_block_N>_TX/RX_CH5N
<txvr_block_N+1>_TX/RX_CH0N
<txvr_block_N+1>_TX/RX_CH1N
<txvr_block_N+1>_TX/RX_CH2N
<txvr_block_N+1>_TX/RX_CH3N
<txvr_block_N+1>_TX/RX_CH4N
<txvr_block_N+1>_TX/RX_CH5N
UG-01145_avmm
2015.05.14
Figure 4-6: Arria 10 Gen1, Gen2, and Gen3 x4 Channel and Pin Placement
Figure 4-7: Arria 10 Gen1, Gen2, and Gen3 x8 Channel and Pin Placement
Channel Placement and fPLL Usage for the Gen1 and Gen2 Data Rates
4-5
Channel Placement and fPLL Usage for the Gen1 and Gen2 Data Rates
The following figures illustrate the x1, x2, x4, and x8 channel placement for the Arria 10 Hard IP for PCI
Express. In these figures, channels that are not used for the PCI Express protocol are available for other
protocols. Unused channels are shown in gray.
Note:
Physical Layout of Hard IP In Arria 10 Devices
Send Feedback
In all configurations, physical channel 4 in the PCS connects to logical channel 0 in the hard IP.
You cannot change the channel placements illustrated below.
Altera Corporation
Page 45

PMA Channel 5
PMA Channel 4
PMA Channel 3
PMA Channel 2
PMA Channel 0
PMA Channel 3
PMA Channel 2
PMA Channel 1
PMA Channel 0
PCS Channel 5
PCS Channel 4
PCS Channel 3
PCS Channel 2
PCS Channel 0
PCS Channel 3
PCS Channel 2
PCS Channel 1
PCS Channel 0
Hard IP Ch0
PMA Channel 1 PCS Channel 1
PMA Channel 4 PCS Channel 4
PMA Channel 5 PCS Channel 5
Hard IP
for PCIe
fPLL1
ATX1 PLL
fPLL0
ATX0 PLL
fPLL1
ATX1 PLL
fPLL0
ATX0 PLL
Master
CGB
PMA Channel 5
PMA Channel 4
PMA Channel 3
PMA Channel 2
PMA Channel 0
PMA Channel 3
PMA Channel 2
PMA Channel 1
PMA Channel 0
PCS Channel 5
PCS Channel 4
PCS Channel 3
PCS Channel 2
PCS Channel 0
PCS Channel 3
PCS Channel 2
PCS Channel 1
PCS Channel 0
Hard IP Ch0
PMA Channel 1 PCS Channel 1
PMA Channel 4 PCS Channel 4
PMA Channel 5 PCS Channel 5
Hard IP
for PCIe
fPLL1
ATX1 PLL
fPLL0
ATX0 PLL
ATX1 PLL
fPLL0
ATX0 PLL
fPLL1
Master
CGB
PMA Channel 5
PMA Channel 4
PMA Channel 3
PMA Channel 0
PMA Channel 3
PMA Channel 2
PMA Channel 1
PMA Channel 0
PCS Channel 5
PCS Channel 4
PCS Channel 3
PCS Channel 0
PCS Channel 3
PCS Channel 2
PCS Channel 1
PCS Channel 0
Hard IP Ch0
PMA Channel 1 PCS Channel 1
PMA Channel 4 PCS Channel 4
PMA Channel 5 PCS Channel 5
PMA Channel 2 PCS Channel 2
Hard IP
for PCIe
fPLL1
ATX1 PLL
ATX0 PLL
fPLL0
ATX1 PLL
fPLL0
ATX0 PLL
Master
CGB
fPLL1
4-6
Channel Placement and fPLL Usage for the Gen1 and Gen2 Data Rates
Figure 4-8: Arria 10 Gen1 and Gen2 x1 Channel Placement
Figure 4-9: Arria 10 Gen1 and Gen2 x2 Channel Placement
UG-01145_avmm
2015.05.14
Figure 4-10: Arria 10 Gen1 and Gen2 x4 Channel Placement
Altera Corporation
Physical Layout of Hard IP In Arria 10 Devices
Send Feedback
Page 46

PMA Channel 5
PMA Channel 4
PMA Channel 3
PMA Channel 0
PMA Channel 3
PMA Channel 2
PMA Channel 1
PMA Channel 0
PCS Channel 5
PCS Channel 4
PCS Channel 3
PCS Channel 0
PCS Channel 3
PCS Channel 2
PCS Channel 1
PCS Channel 0
Hard IP
for PCIe
Hard IP Ch0
PMA Channel 1 PCS Channel 1
PMA Channel 4 PCS Channel 4
PMA Channel 5 PCS Channel 5
PMA Channel 2 PCS Channel 2
fPLL1
ATX1 PLL
ATX0 PLL
ATX1 PLL
fPLL0
ATX0 PLL
fPLL1
fPLL0
Master
CGB
PMA Channel 5
PMA Channel 4
PMA Channel 3
PMA Channel 0
PMA Channel 4
PMA Channel 3
PMA Channel 2
PMA Channel 1
PMA Channel 0
PCS Channel 5
PCS Channel 4
PCS Channel 3
PCS Channel 0
PCS Channel 4
PCS Channel 3
PCS Channel 2
PCS Channel 1
PCS Channel 0
Hard IP
for PCIe
fPLL1
ATX1 PLL
fPLL0
ATX0 PLL
fPLL0
ATX0 PLL
Hard IP Ch0
PMA Channel 1 PCS Channel 1
PMA Channel 2 PCS Channel 2
PMA Channel 5 PCS Channel 5
fPLL1
ATX1 PLL
Master
CGB
UG-01145_avmm
2015.05.14
Channel Placement and fPLL and ATX PLL Usage for the Gen3 Data Rate
Figure 4-11: Gen1 and Gen2 x8 Channel Placement
Channel Placement and fPLL and ATX PLL Usage for the Gen3 Data Rate
The following figures illustrate the x1, x2, x4, and x8 channel placement for the Arria 10 Hard IP for PCI
Express. Gen3 variants must initially train at the Gen1 data rate. Consequently, Gen3 variants require an
fPLL to generate the 2.5 and 5.0 Gbps clocks, and an ATX PLL to generate the 8.0 Gbps clock.
4-7
In these figures, channels that are not used for the PCI Express protocol are available for other protocols.
Unused channels are shown in gray.
In all configurations, physical channel 4 in the PCS connects to logical channel 0 in the hard IP.
Note:
You cannot change the channel placements illustrated below.
Figure 4-12: Arria 10 Gen3 x1 Channel Placement
Physical Layout of Hard IP In Arria 10 Devices
Send Feedback
Altera Corporation
Page 47

PMA Channel 5
PMA Channel 4
PMA Channel 3
PMA Channel 0
PMA Channel 4
PMA Channel 3
PMA Channel 2
PMA Channel 1
PMA Channel 0
PCS Channel 5
PCS Channel 4
PCS Channel 3
PCS Channel 0
PCS Channel 4
PCS Channel 3
PCS Channel 2
PCS Channel 1
PCS Channel 0
Hard IP
for PCIe
fPLL1
ATX1 PLL
fPLL0
ATX0 PLL
fPLL0
ATX0 PLL
Hard IP Ch0
PMA Channel 1 PCS Channel 1
PMA Channel 2 PCS Channel 2
PMA Channel 5 PCS Channel 5
fPLL1
ATX1 PLL
Master
CGB
PMA Channel 5
PMA Channel 4
PMA Channel 3
PMA Channel 0
PMA Channel 5
PMA Channel 4
PMA Channel 3
PMA Channel 2
PMA Channel 1
PMA Channel 0
PCS Channel 5
PCS Channel 4
PCS Channel 3
PCS Channel 0
PCS Channel 5
PCS Channel 4
PCS Channel 3
PCS Channel 2
PCS Channel 1
PCS Channel 0
Hard IP
for PCIe
fPLL1
ATX1 PLL
fPLL0
ATX0 PLL
fPLL1
ATX1 PLL
fPLL0
ATX0 PLL
Hard IP Ch0
PMA Channel 1 PCS Channel 1
PMA Channel 2 PCS Channel 2
Master
CGB
PMA Channel 5
PMA Channel 4
PMA Channel 3
PMA Channel 0
PMA Channel 5
PMA Channel 4
PMA Channel 3
PMA Channel 2
PMA Channel 1
PMA Channel 0
PCS Channel 5
PCS Channel 4
PCS Channel 3
PCS Channel 0
PCS Channel 5
PCS Channel 4
PCS Channel 3
PCS Channel 2
PCS Channel 1
PCS Channel 0
Hard IP
for PCIe
fPLL1
ATX1 PLL
fPLL1
ATX1 PLL
fPLL0
ATX0 PLL
Hard IP Ch0
PMA Channel 1 PCS Channel 1
PMA Channel 2 PCS Channel 2
fPLL0
ATX0 PLL
Master
CGB
4-8
Channel Placement and fPLL and ATX PLL Usage for the Gen3 Data Rate
Figure 4-13: Arria 10 Gen3 x2 Channel Placement
Figure 4-14: Arria 10 Gen3 x4 Channel Placement
UG-01145_avmm
2015.05.14
Figure 4-15: Gen3 x8 Channel Placement
Altera Corporation
Physical Layout of Hard IP In Arria 10 Devices
Send Feedback
Page 48

64- or 128-Bit Avalon-MM Interface to the
www.altera.com
101 Innovation Drive, San Jose, CA 95134
Application Layer
2015.05.14
UG-01145_avmm
Subscribe
This chapter describes the top-level signals of the Arria 10 Hard IP for PCI Express using the Avalon-MM
interface to the Application Layer. The Avalon-MM bridge translates PCI Express read, write and
completion TLPs into standard Avalon-MM read and write commands for the Avalon-MM RX Master
Port interface. For the Avalon-MM TX Slave Port interface, the bridge translates Avalon-MM reads and
writes into PCI Express TLPs. The Avalon-MM read and write commands are the same as those used by
master and slave interfaces to access memories and registers. Consequently, you do not need a detailed
understanding of the PCI Express TLPs to use this Avalon-MM variant.
Send Feedback
5
©
2015 Altera Corporation. All rights reserved. ALTERA, ARRIA, CYCLONE, ENPIRION, MAX, MEGACORE, NIOS, QUARTUS and STRATIX words and logos are
trademarks of Altera Corporation and registered in the U.S. Patent and Trademark Office and in other countries. All other words and logos identified as
trademarks or service marks are the property of their respective holders as described at www.altera.com/common/legal.html. Altera warrants performance
of its semiconductor products to current specifications in accordance with Altera's standard warranty, but reserves the right to make changes to any
products and services at any time without notice. Altera assumes no responsibility or liability arising out of the application or use of any information,
product, or service described herein except as expressly agreed to in writing by Altera. Altera customers are advised to obtain the latest version of device
specifications before relying on any published information and before placing orders for products or services.
ISO
9001:2008
Registered
Page 49

tx_out0[<n>-1:0]
rx_in0[<n>-1:0]
1-Bit Serial
32-Bit
Avalon-MM
CRA
Slave Port
(Optional,
Not available for
Completer-Only
Single Dword)
64- or 128-Bit
Avalon-MM TX
Slave Port
(Not used for
Completer-Only)
Test
Interface
test_in[31:0]
64- or 128-Bit
Avalon-MM RX
Master Port
Clocks
npor
nreset_status
pin_perst
Reset &
Lock Status
refclk
coreclkout_hip
cra_readdata[31:0]
cra_waitrequest
cra_byteenable[3:0]
cra_chipselect
cra_address[14:0]
cra_read
cra_write
cra_writedata[31:0]
txs_writedata[63:0] or [127:0]
txs_busrtcount[6:0]
txs_chipselect
txs_read
txs_write
txs_address[<w>-1:0]
txs_byteenable[<w>-1:0]
txs_readdatavalid
txs_readdata[63:0] or [127:0]
txs_waitrequest
rxm_bar0_write_<n>
rxm_bar0_address_<n>[31:0]
rxm_bar0_writedata_<n>[<w>-1:0]
rxm_bar0_byteenable_<n>[7:0]
rxm_bar0_burstcount_<n>[6:0]
rxm_bar0_waitrequest_<n>
rxm_bar0_read_<n>
rxm_bar0_readdata_<n>[<w>-1:0]
rxm_bar0_readdatavalid
rxm_irq[<m>:0], <m> < 16
cra_irq_irq
64- or 128-Bit Avalon-MM Interface to
Application Layer
Hard IP
Reconfiguration
(Optional)
hip_reconfig_clk
hip_reconfig_rst_n
hip_reconfig_address[9:0]
hip_reconfig_read
hip_reconfig_readdata[15:0]
hip_reconfig_write
hip_reconfig_writedata[15:0]
hip_reconfig_byte_en[1:0]
ser_shift_load
interface_sel
MsiIntfc_o[81:0]
MsiControl_o[15:0]
MsixIntfc_o[15:0]
IntxReq_i
IntxAck_o
Multiple
MSI/MSI-X
txdata0[31:0]
txdatak0[3:0]
txblkst0
rxdata0[31:0]
rxdatak0[3:0]
rxblkst0
txdetectrx0
txelecidle0
txcompl0
rxpolarity0
powerdown0[1:0]
currentcoeff0[17:0]
currentrxpreset0[2:0]
txmargin[2:0]
txswing
txsynchd0[1:0]
rxsyncd[1:0]
rxvalid0
phystatus0
rxelecidle0
rxstatus0[2:0]
simu_mode_pipe
sim_pipe_rate[1:0]
sim_pipe_pclk_in
sim_pipe_pclk_out
sim_pipe_clk250_out
sim_pipe_clk500_out
sim_ltssmstate[4:0]
rxfreqlocked0
rxdataskip0
txdataskip0
eidleinfersel0[2:0]
txdeemph0
Transmit Data
Interface Signals
Receive Data
Interface Signals
Command
Interface Signals
Status
Interface Signals
PIPE
Interface
for Simulation
and Hardware
Debug Using
dl_ltssm[4:0]
SignalTap,
Gen3 version
5-2
64- or 128-Bit Avalon-MM Interface to the Application Layer
Figure 5-1: Signals in 64- or 128-Bit Avalon-MM Interface to the Application Layer
UG-01145_avmm
2015.05.14
Altera Corporation
Note: Signals listed for BAR0 are the same as those for BAR1–BAR5 when those BARs are enabled in the
parameter editor.
Variations using the Avalon-MM interface implement the Avalon-MM protocol described in the Avalon
Interface Specifications. Refer to this specification for information about the Avalon-MM protocol,
including timing diagrams.
Related Information
Avalon Interface Specifications
64- or 128-Bit Avalon-MM Interface to the Application Layer
Send Feedback
Page 50

UG-01145_avmm
2015.05.14
32-Bit Non-Bursting Avalon-MM Control Register Access (CRA) Slave...
32-Bit Non-Bursting Avalon-MM Control Register Access (CRA) Slave Signals
The optional CRA port for the full-featured IP core allows upstream PCI Express devices and external
Avalon-MM masters to access internal control and status registers.
Table 5-1: Avalon-MM CRA Slave Interface Signals
5-3
Signal Name Directio
CraIrq_o
CraReadData_o[31:0]
CraWaitRequest_o
CraAddress_i[13:0]
CraByteEnable_i[3:0]
CraChipSelect_i
CraRead_i
CraWrite_i
Description
n
Output Interrupt request. A port request for an Avalon-MM interrupt.
Output Read data lines
Output Wait request to hold off more requests
Input An address space of 16,384 bytes is allocated for the control
registers. Avalon-MM slave addresses provide address
resolution down to the width of the slave data bus. Because all
addresses are byte addresses, this address logically goes down
to bit 2. Bits 1 and 0 are 0.
Input Byte enable
Input Chip select signal to this slave
Input Read enable
Input Write request
CraWriteData_i[31:0]
Input Write data
RX Avalon-MM Master Signals
This Avalon-MM master port propagates PCI Express requests to the Qsys interconnect fabric. For the
full-feature IP core it propagates requests as bursting reads or writes. A separate Avalon-MM master port
corresponds to each BAR.
64- or 128-Bit Avalon-MM Interface to the Application Layer
Send Feedback
Altera Corporation
Page 51

5-4
RX Avalon-MM Master Signals
Table 5-2: Avalon-MM RX Master Interface Signals
Signals that include Bar number 0 also exist for BAR1–BAR5 when additional BARs are enabled.
Signal Name Direction Description
UG-01145_avmm
2015.05.14
RxmWrite<n>
RxmAddress_<n>_o[31:0]
RxmWriteData_<n>_o[<w>-1:0]
RxmByteEnable_<n>_o[<w>-1:0]
RXMBurstCount_<n>_o[6 or
5:0]
RXMWaitRequest_<n>_o
RXMRead_<n>_o
RXMReadData_<n>_o[<w>-1:0]
Output Asserted by the core to request a write to an Avalon-
MM slave.
Output The address of the Avalon-MM slave being accessed.
Output RX data being written to slave. <w> = 64 or 128 for the
full-featured IP core. <w> = 32 for the completer-only
IP core.
Output Byte enable for write data.
Output The burst count, measured in qwords, of the RX write or
read request. The width indicates the maximum data
that can be requested. The maximum data in a burst is
512 bytes.
Input Asserted by the external Avalon-MM slave to hold data
transfer.
Output Asserted by the core to request a read.
Input Read data returned from Avalon-MM slave in response
to a read request. This data is sent to the IP core through
the TX interface. <w> = 64 or 128 for the full-featured
IP core. <w> = 32 for the completer-only IP core.
RXMReadDataValid_<n>_i
RxmIrq_<n>[<m>:0], <m>< 16
The following figure illustrates the RX master port propagating requests to the Application Layer and also
shows simultaneous, DMA read and write activity
Altera Corporation
Input Asserted by the system interconnect fabric to indicate
that the read data on is valid.
Input Indicates an interrupt request asserted from the system
interconnect fabric. This signal is only available when
the CRA port is enabled. Qsys-generated variations have
as many as 16 individual interrupt signals (<m>≤15). If
rxm_irq_<n>[<m>:0] is asserted on consecutive cycles
without the deassertion of all interrupt inputs, no MSI
message is sent for subsequent interrupts. To avoid
losing interrupts, software must ensure that all interrupt
sources are cleared for each MSI message received.
64- or 128-Bit Avalon-MM Interface to the Application Layer
Send Feedback
Page 52

RxmRead_o
RxmReadDataValid_i
RxmReadData_i[63:0]
RxmResetRequest_o
RxmAddress_o[31:0]
RxmWaitRequest_i
RxmWrite_o
RxmBurstCount_o[9:0]
RxmByteEnable_o[7:0]
RxmWriteData_o[63:0]
RxmIrq_i
TxsWrite_i
TxsWriteData_i[63:0]
TxsBurstCount_i[9:0]
TxsByteEnable_i[7:0]
TxsAddress_i[17:0]
TxsWaitRequest_o
TxsRead_i
TxsReadDataValid_o
TxsReadData_o[63:0]
TxsChipSelect_i
.. . . .
80000100 80000180
010
.
FF FF
. .
000000000002080F
. . . . . . .
001 080
04000 04080 04000
00000 . . 0 .
UG-01145_avmm
2015.05.14
Figure 5-2: Simultaneous DMA Read, DMA Write, and Target Access
64- or 128-Bit Bursting TX Avalon-MM Slave Signals
5-5
64- or 128-Bit Bursting TX Avalon-MM Slave Signals
This optional Avalon-MM bursting slave port propagates requests from the interconnect fabric to the fullfeatured Avalon-MM Arria 10 Hard IP for PCI Express. Requests from the interconnect fabric are
translated into PCI Express request packets. Incoming requests can be up to 512 bytes. For better
performance, Altera recommends using smaller read request size (a maximum of 512 bytes).
64- or 128-Bit Avalon-MM Interface to the Application Layer
Altera Corporation
Send Feedback
Page 53

5-6
64- or 128-Bit Bursting TX Avalon-MM Slave Signals
Table 5-3: Avalon-MM TX Slave Interface Signals
Signal Name Direction Description
UG-01145_avmm
2015.05.14
TxsChipSelect_i
TxsRead_i
TxsWrite_i
TxsWriteData[127 or 63:0]
TxsBurstCount[6 or 5:0]
TxsAddress_i[<w>-1:0]
Input The system interconnect fabric asserts this signal to
select the TX slave port.
Input Read request asserted by the system interconnect fabric
to request a read.
Input Write request asserted by the system interconnect fabric
to request a write.
Input Write data sent by the external Avalon-MM master to
the TX slave port.
Input Asserted by the system interconnect fabric indicating
the amount of data requested. The count unit is the
amount of data that is transferred in a single cycle, that
is, the width of the bus. The burst count is limited to 512
bytes.
Input Address of the read or write request from the external
Avalon-MM master. This address translates to 64-bit or
32-bit PCI Express addresses based on the translation
table. The <w> value is determined when the system is
created.
Altera Corporation
64- or 128-Bit Avalon-MM Interface to the Application Layer
Send Feedback
Page 54

UG-01145_avmm
2015.05.14
64- or 128-Bit Bursting TX Avalon-MM Slave Signals
Signal Name Direction Description
5-7
TxsByteEnable_i[<w>-1:0]
Input Write byte enable for data. A burst must be continuous.
Therefore all intermediate data phases of a burst must
have a byte enable value of 0xFF. The first and final data
phases of a burst can have other valid values.
For the 128-bit interface, the following restrictions
apply:
• All bytes of a single dword must either be enabled or
disabled
• If more than 1 dword is enabled, the enabled dwords
must be contiguous. The following patterns are legal:
• 16'bF000
• 16'b0F00
• 16'b00F0
• 16'b000F
• 16'bFF00
• 16'b0FF0
• 16'b00FF
• 16'bFFF0
• 16'b0FFF
• 16'bFFFF
TxsReadDataValid_o
TxsReadData_o[127 or 63:0]
TxsWaitrequest_o
Output Asserted by the bridge to indicate that read data is valid.
Output The bridge returns the read data on this bus when the
RX read completions for the read have been received
and stored in the internal buffer.
Output Asserted by the bridge to hold off read or write data
when running out of buffer space. If this signal is
asserted during an operation, the master should
maintain the TxsRead_i signal (or TxsWrite_i signal
and TxsWriteData) stable until after TxsWaitrequest_
o is deasserted. txs_Read must be deasserted when
TxsWaitrequest_o is deasserted.
64- or 128-Bit Avalon-MM Interface to the Application Layer
Send Feedback
Altera Corporation
Page 55

5-8
Clock Signals
Clock Signals
Table 5-4: Clock Signals
Signal Direction Description
UG-01145_avmm
2015.05.14
refclk
coreclkout_hip
Related Information
Clocks on page 7-4
Reset
Refer to Reset and Clocks for more information about the reset sequence and a block diagram of the reset
logic.
Table 5-5: Reset Signals
Signal Direction Description
npor
Input Reference clock for the IP core. It must have the frequency
specified under the System Settings heading in the parameter
editor. This is a dedicated free running input clock to the
dedicated REFCLK pin.
Output
This is a fixed frequency clock used by the Data Link and
Transaction Layers.
Input Active low reset signal. In the Altera hardware example designs,
npor is the OR of pin_perst and local_rstn coming from the
software Application Layer. If you do not drive a soft reset signal
from the Application Layer, this signal must be derived from
pin_perst. You cannot disable this signal. Resets the entire IP
Core and transceiver. Asynchronous.
nreset_status
pin_perst
Altera Corporation
This signal is edge, not level sensitive; consequently, you cannot
use a low value on this signal to hold custom logic in reset. For
more information about the reset controller, refer to Reset.
Output
Active low reset signal. It is derived from npor or pin_perstn.
You can use this signal to reset the Application Layer.
Input Active low reset from the PCIe reset pin of the device. pin_perst
resets the datapath and control registers. Configuration via
Protocol (CvP) requires this signal. For more information about
CvP refer to Configuration via Protocol (CvP).
Arria 10 devices can have up to 4 instances of the Hard IP for
PCI Express. Each instance has its own pin_perst signal. You
64- or 128-Bit Avalon-MM Interface to the Application Layer
Send Feedback
Page 56

npor
IO_POF_Load
PCIe_LinkTraining_Enumeration
dl_ltssm[4:0]
detect
detect.active polling.active
L0
UG-01145_avmm
2015.05.14
Signal Direction Description
must connect the pin_perst of each Hard IP instance to the
corresponding nPERST pin of the device. These pins have the
following locations:
• NPERSTL0: bottom left Hard IP and CvP blocks
• NPERSTL1: top left Hard IP block
• NPERSTR0: bottom right Hard IP block
• NPERSTR1: top right Hard IP block
For example, if you are using the Hard IP instance in the bottom
left corner of the device, you must connect pin_perst to
NPERSL0.
For maximum use of the Arria 10 device, Altera recommends
that you use the bottom left Hard IP first. This is the only
location that supports CvP over a PCIe link. If your design does
not require CvP, you may select other Hard IP blocks.
Refer to the appropriate device pinout for correct pin assignment
for more detailed information about these pins. The PCI Express
Card Electromechanical Specification 2.0 specifies this pin
requires 3.3 V. You can drive this 3.3V signal to the nPERST*
even if the V
VCCPGM
of the bank is not 3.3V if the following 2
conditions are met:
Reset
5-9
• The input signal meets the VIH and VIL specification for
LVTTL.
• The input signal meets the overshoot specification for 100°C
operation as defined in the device handbook.
Figure 5-3: Reset and Link Training Timing Relationships
The following figure illustrates the timing relationship between npor and the LTSSM L0 state.
Note:
To meet the 100 ms system configuration time, you must use the fast passive parallel configuration
scheme with CvP and a 32-bit data width (FPP x32) or use the CvP in autonomous mode.
64- or 128-Bit Avalon-MM Interface to the Application Layer
Send Feedback
Altera Corporation
Page 57

5-10
Interrupts for Endpoints when Multiple MSI/MSI‑X Support Is Enabled
Related Information
UG-01145_avmm
• PCI Express Card Electromechanical Specification 2.0
• Configuration via Protocol (CvP) Implementation in Altera FPGAs User Guide
Interrupts for Endpoints when Multiple MSI/MSI‑X Support Is Enabled
Table 5-6: Exported Interrupt Signals for Endpoints when Multiple MSI/MSI‑X Support is Enabled
The following table describes the IP core’s exported interrupt signals when you turn on Enable multiple MSI/
MSI-X support under the Avalon-MM System Settings banner in the parameter editor.
Signal Direction Description
2015.05.14
MsiIntfc_o[81:0]
MsiControl_o[15:0]
MsixIntfc_o[15:0]
Output This bus provides the following MSI address, data, and enabled
signals:
• MsiIntf_o[81]: Master enable
• MsiIntf_o[80}: MSI enable
• MsiIntf_o[79:64]: MSI data
• MsiIntf_o[63:0]: MSI address
Output Provides for system software control of MSI as defined in Section
6.8.1.3 Message Control for MSI in the PCI Local Bus Specifica‐
tion, Rev. 3.0. The following fields are defined:
• MsiControl_o[15:9]: Reserved
• MsiControl_o[8]: Per-vector masking capable
• MsiControl_o[7]: 64-bit address capable
• MsiControl_o[6:4]: Multiple Message Enable
• MsiControl_o[3:1]: MSI Message Capable
• MsiControl_o[0]: MSI Enable.
Output Provides for system software control of MSI-X as defined in
Section 6.8.2.3 Message Control for MSI-X in the PCI Local Bus
Specification, Rev. 3.0. The following fields are defined:
IntxReq_i
Altera Corporation
Input
• MsixIntfc_o[15]: Enable
• MsixIntfc_o[14]: Mask
• MsixIntfc_o[13:11]: Reserved
• MsixIntfc_o[10:0]: Table size
When asserted, the Endpoint is requesting attention from the
interrupt service routine unless MSI or MSI-X interrupts are
enabled. Remains asserted until the device driver clears the
pending request.
64- or 128-Bit Avalon-MM Interface to the Application Layer
Send Feedback
Page 58

clk
IntxReq_i
IntAck_o
clk
IntxReq_i
IntAck_o
UG-01145_avmm
2015.05.14
Hard IP Reconfiguration Interface
Signal Direction Description
5-11
IntxAck_o
Output This signal is the acknowledge for IntxReq_i. It is asserted for at
least one cycle either when either of the following events occur:
• The Assert_INTA message TLP has been transmitted in
response to the assertion of the IntxReq_i.
• The Deassert_INTA message TLP has been transmitted in
response to the deassertion of the IntxReq_i signal.
Refer to the timing diagrams below.
The following figure illustrates interrupt timing for the legacy interface. In this figure the assertion of
IntxReq_i instructs the Hard IP for PCI Express to send an Assert_INTA message TLP.
Figure 5-4: Legacy Interrupt Assertion
The following figure illustrates the timing for deassertion of legacy interrupts. The assertion of IntxReq_i
instructs the Hard IP for PCI Express to send a Deassert_INTA message.
Figure 5-5: Legacy Interrupt Deassertion
Hard IP Reconfiguration Interface
The Hard IP reconfiguration interface is an Avalon-MM slave interface with a 10-bit address and 16-bit
data bus. You can use this bus to dynamically modify the value of configuration registers that are readonly at run time. To ensure proper system operation, reset or repeat device enumeration of the PCI
Express link after changing the value of read-only configuration registers of the Hard IP.
Table 5-7: Hard IP Reconfiguration Signals
Signal Direction Description
hip_reconfig_clk
Input Reconfiguration clock. The frequency range for this clock is 100–
125 MHz.
64- or 128-Bit Avalon-MM Interface to the Application Layer
Send Feedback
Altera Corporation
Page 59

5-12
Hard IP Reconfiguration Interface
Signal Direction Description
UG-01145_avmm
2015.05.14
hip_reconfig_rst_n
hip_reconfig_
address[9:0]
hip_reconfig_read
hip_reconfig_
readdata[15:0]
hip_reconfig_write
hip_reconfig_
writedata[15:0]
hip_reconfig_byte_
en[1:0]
ser_shift_load
Input Active-low Avalon-MM reset. Resets all of the dynamic reconfi‐
guration registers to their default values as described in Hard IP
Reconfiguration Registers.
Input The 10-bit reconfiguration address.
Input Read signal. This interface is not pipelined. You must wait for the
return of the hip_reconfig_readdata[15:0] from the current
read before starting another read operation.
Output 16-bit read data. hip_reconfig_readdata[15:0] is valid on the
third cycle after the assertion of hip_reconfig_read.
Input Write signal.
Input 16-bit write model.
Input Byte enables, currently unused.
Input You must toggle this signal once after changing to user mode
before the first access to read-only registers. This signal should
remain asserted for a minimum of 324 ns after switching to user
mode.
interface_sel
Input A selector which must be asserted when performing dynamic
reconfiguration. Drive this signal low 4 clock cycles after the
release of ser_shif t_load.
Altera Corporation
64- or 128-Bit Avalon-MM Interface to the Application Layer
Send Feedback
Page 60

avmm_clk
hip_reconfig_rst_n
user_mode
ser_shift_load
interface_sel
avmm_wr
avmm_wrdata[15:0]
avmm_rd
avmm_rdata[15:0]
D0D0D1
D1
D2 D3
324 ns
4 clks
4 clks
4 clks
UG-01145_avmm
2015.05.14
Figure 5-6: Hard IP Reconfiguration Bus Timing of Read-Only Registers
Physical Layer Interface Signals
5-13
For a detailed description of the Avalon-MM protocol, refer to the Avalon Memory Mapped Interfaces
chapter in the Avalon Interface Specifications.
Related Information
Avalon Interface Specifications
Physical Layer Interface Signals
Altera provides an integrated solution with the Transaction, Data Link and Physical Layers. The IP
Parameter Editor generates a SERDES variation file, <variation>_serdes.v or .vhd , in addition to the Hard
IP variation file, <variation>.v or .vhd. The SERDES entity is included in the library files for PCI Express.
Serial Data Signals
Table 5-8: 1-Bit Interface Signals
Signal Direction Description
(1)
(1)
Output Transmit output. These signals are the serial outputs of lanes 7–0.
Input Receive input. These signals are the serial inputs of lanes 7–0.
tx_out[7:0]
rx_in[7:0]
64- or 128-Bit Avalon-MM Interface to the Application Layer
Note:
1. The x1 IP core only has lane 0. The x2 IP core only has lanes 1–0. The x4 IP core only has lanes 3–0.
Send Feedback
Altera Corporation
Page 61

5-14
PIPE Interface Signals
Refer to Pin-out Files for Altera Devices for pin-out tables for all Altera devices in .pdf, .txt, and .xls
formats.
Transceiver channels are arranged in groups of six. For GX devices, the lowest six channels on the left side
of the device are labeled GXB_L0, the next group is GXB_L1, and so on. Channels on the right side of the
device are labeled GXB_R0, GXB_R1, and so on. Be sure to connect the Hard IP for PCI Express on the
left side of the device to appropriate channels on the left side of the device, as specified in the Pin-out Files
for Altera Devices.
Related Information
• Physical Layout of Hard IP In Arria 10 Devices on page 4-1
• Pin-out Files for Altera Devices
PIPE Interface Signals
These PIPE signals are available for Gen1, Gen2, and Gen3 variants so that you can simulate using either
the serial or the PIPE interface. Simulation is much faster using the PIPE interface because the PIPE
simulation bypasses the SERDES model . By default, the PIPE interface is 8 bits for Gen1 and Gen2 and 32
bits for Gen3. You can use the PIPE interface for simulation even though your actual design includes a
serial interface to the internal transceivers. However, it is not possible to use the Hard IP PIPE interface in
hardware, including probing these signals using SignalTap® II Embedded Logic Analyzer.
UG-01145_avmm
2015.05.14
Note:
The Altera Root Port BFM bypasses Gen3 Phase 2 and Phase 3 Equalization. However, Gen3
variants can perform Phase 2 and Phase 3 equalization if instructed by a third-party BFM.
In the following table, signals that include lane number 0 also exist for lanes 1-7.
Table 5-9: PIPE Interface Signals
Signal Direction Description
txdata0[31:0]
txdatak0[3:0]
Output Transmit data <n>. This bus transmits data on lane <n>.
Output Transmit data control <n>. This signal serves as the control bit
for txdata <n>. Bit 0 corresponds to the lowest-order byte of
txdata, and so on. A value of 0 indicates a data byte. A value of 1
indicates a control byte. For Gen1 and Gen2 only.
txblkst0
Output For Gen3 operation, indicates the start of a block in the transmit
direction.
txdataskip0 Output For Gen3 operation. Allows the MAC to instruct the TX interface
to ignore the TX data interface for one clock cycle. The following
encodings are defined:
Altera Corporation
• 1’b0: TX data is invalid
• 1’b1: TX data is valid
64- or 128-Bit Avalon-MM Interface to the Application Layer
Send Feedback
Page 62

UG-01145_avmm
2015.05.14
Signal Direction Description
PIPE Interface Signals
5-15
tx_deemph0
Output Transmit de-emphasis selection. The Arria 10 Hard IP for PCI
Express sets the value for this signal based on the indication
received from the other end of the link during the Training
Sequences (TS). You do not need to change this value.
(2)
(2)
Input Receive data <n>. This bus receives data on lane <n>.
Input Receive data >n>. This bus receives data on lane <n>. Bit 0
rxdata0[31:0]
rxdatak[3:0]
corresponds to the lowest-order byte of rxdata, and so on. A
value of 0 indicates a data byte. A value of 1 indicates a control
byte. For Gen1 and Gen2 only.
rxblkst0 Input For Gen3 operation, indicates the start of a block in the receive
direction.
txdetectrx0 Output Transmit detect receive <n>. This signal tells the PHY layer to
start a receive detection operation or to begin loopback.
txelecidle Output Transmit electrical idle <n>. This signal forces the TX output to
electrical idle.
txcompl0 Output Transmit compliance <n>. This signal forces the running
disparity to negative in Compliance Mode (negative COM
character).
rxpolarity0 Output Receive polarity <n>. This signal instructs the PHY layer to
invert the polarity of the 8B/10B receiver decoding block.
powerdown0[1:0] Output Power down <n>. This signal requests the PHY to change its
power state to the specified state (P0, P0s, P1, or P2).
currentcoeff0[17:0]
Output For Gen3, specifies the coefficients to be used by the transmitter.
The 18 bits specify the following coefficients:
• [5:0]: C
• [11:6]: C
• [17:12]: C
currentrxpreset0[2:0]
tx_margin[2:0] Output Transmit V
Output For Gen3 designs, specifies the current preset.
-1
0
+1
margin selection. The value for this signal is based
OD
on the value from the Link Control 2 Register. Available for
simulation only.
64- or 128-Bit Avalon-MM Interface to the Application Layer
Send Feedback
Altera Corporation
Page 63

5-16
PIPE Interface Signals
Signal Direction Description
UG-01145_avmm
2015.05.14
txswing
Output When asserted, indicates full swing for the transmitter voltage.
When deasserted indicates half swing.
txsynchd0[1:0] Output For Gen3 operation, specifies the transmit block type. The
following encodings are defined:
• 2'b01: Ordered Set Block
• 2'b10: Data Block
rxsynchd0[1:0] Input For Gen3 operation, specifies the receive block type. The
following encodings are defined:
• 2'b01: Ordered Set Block
• 2'b10: Data Block
rxvalid0
(1)
Input Receive valid <n>. This signal indicates symbol lock and valid
data on rxdata<n> and rxdatak <n>.
phystatus0
(1)
Input PHY status <n>. This signal communicates completion of several
PHY requests.
rxelecidle0
(1)
Input Receive electrical idle <n>. When asserted, indicates detection of
an electrical idle.
rxstatus0[2:0]
(1)
Input Receive status <n>. This signal encodes receive status, including
error codes for the receive data stream and receiver detection.
simu_mode_pipe Input When set to 1, the PIPE interface is in simulation mode.
sim_pipe_rate[1:0]
Output The 2-bit encodings have the following meanings:
• 2’b00: Gen1 rate (2.5 Gbps)
• 2’b01: Gen2 rate (5.0 Gbps)
• 2’b1X: Gen3 rate (8.0 Gbps)
sim_pipe_pclk_in
Input This clock is used for PIPE simulation only, and is derived from
the refclk. It is the PIPE interface clock used for PIPE mode
simulation.
sim_pipe_pclk_out
Output TX datapath clock to the BFM PHY. pclk_out is derived from
refclk and provides the source synchronous clock for TX data
from the PHY.
sim_pipe_clk250_out
sim_pipe_clk500_out
Output Used to generate pclk.
Output Used to generate pclk.
Altera Corporation
64- or 128-Bit Avalon-MM Interface to the Application Layer
Send Feedback
Page 64

UG-01145_avmm
2015.05.14
Signal Direction Description
PIPE Interface Signals
5-17
sim_pipe_
ltssmstate0[4:0]
Input and
Output
LTSSM state: The LTSSM state machine encoding defines the
following states:
• 5’b00000: Detect.Quiet
• 5’b 00001: Detect.Active
• 5’b00010: Polling.Active
• 5’b 00011: Polling.Compliance
• 5’b 00100: Polling.Configuration
• 5’b00101: Polling.Speed
• 5’b00110: config.LinkwidthsStart
• 5’b 00111: Config.Linkaccept
• 5’b 01000: Config.Lanenumaccept
• 5’b01001: Config.Lanenumwait
• 5’b01010: Config.Complete
• 5’b 01011: Config.Idle
• 5’b01100: Recovery.Rcvlock
• 5’b01101: Recovery.Rcvconfig
• 5’b01110: Recovery.Idle
• 5’b 01111: L0
• 5’b10000: Disable
• 5’b10001: Loopback.Entry
• 5’b10010: Loopback.Active
• 5’b10011: Loopback.Exit
• 5’b10100: Hot.Reset
• 5’b10101: L0s
• 5’b11001: L2.transmit.Wake
• 5’b11010: Speed.Recovery
• 5’b11011: Recovery.Equalization, Phase 0
• 5’b11100: Recovery.Equalization, Phase 1
• 5’b11101: Recovery.Equalization, Phase 2
• 5’b11110: Recovery.Equalization, Phase 3
• 5’b11111: Recovery.Equalization, Done
(1)
rxfreqlocked0
Input When asserted indicates that the pclk_in used for PIPE
simulation is valid.
rxdataskip0 Output For Gen3 operation. Allows the PCS to instruct the RX interface
to ignore the RX data interface for one clock cycle. The following
encodings are defined:
• 1’b0: RX data is invalid
• 1’b1: RX data is valid
64- or 128-Bit Avalon-MM Interface to the Application Layer
Send Feedback
Altera Corporation
Page 65

5-18
PIPE Interface Signals
Signal Direction Description
UG-01145_avmm
2015.05.14
eidleinfersel0[2:0]
Output Electrical idle entry inference mechanism selection. The
following encodings are defined:
• 3'b0xx: Electrical Idle Inference not required in current
LTSSM state
• 3'b100: Absence of COM/SKP Ordered Set in the 128 us
window for Gen1 or Gen2
• 3'b101: Absence of TS1/TS2 Ordered Set in a 1280 UI interval
for Gen1 or Gen2
• 3'b110: Absence of Electrical Idle Exit in 2000 UI interval for
Gen1 and 16000 UI interval for Gen2
• 3'b111: Absence of Electrical idle exit in 128 us window for
Gen1
Notes:
1. These signals are for simulation only. For Quartus II software compilation, these pipe signals can be
left floating.
Altera Corporation
64- or 128-Bit Avalon-MM Interface to the Application Layer
Send Feedback
Page 66

UG-01145_avmm
2015.05.14
Test Signals
Table 5-10: Test Interface Signals
The test_in bus provides run-time control and monitoring of the internal state of the IP core.
Signal Direction Description
Test Signals
5-19
test_in[31:0]
Input The bits of the test_in bus have the following definitions:
• [0]: Simulation mode. This signal can be set to 1 to accelerate
initialization by reducing the value of many initialization
counters.
• [1]: Reserved. Must be set to 1’b0.
• [2]: Descramble mode disable. This signal must be set to 1
during initialization in order to disable data scrambling. You
can use this bit in simulation for both Endpoints and Root
Ports to observe descrambled data on the link. Descrambled
data cannot be used in open systems because the link partner
typically scrambles the data.
• [4:3]: Reserved. Must be set to 4’b01.
• [5]: Compliance test mode. Disable/force compliance mode.
When set, prevents the LTSSM from entering compliance
mode. Toggling this bit controls the entry and exit from the
compliance state, enabling the transmission of Gen1, Gen2
and Gen3 compliance patterns.
• [6]: Forces entry to compliance mode when a timeout is
reached in the polling.active state and not all lanes have
detected their exit condition.
• [7]: Disable low power state negotiation. Altera recommends
setting thist bit.
• [31:8]: Reserved. Set to all 0s.
simu_mode_pipe
Input
When asserted, simulation operates in parallel mode. When
deasserted the simulation is serial.
64- or 128-Bit Avalon-MM Interface to the Application Layer
Send Feedback
Altera Corporation
Page 67

2015.05.14
www.altera.com
101 Innovation Drive, San Jose, CA 95134
Registers
6
UG-01145_avmm
Subscribe
Send Feedback
Correspondence between Configuration Space Registers and the PCIe Specification
Table 6-1: Correspondence between Configuration Space Capability Structures and PCIe Base
Specification Description
For the Type 0 and Type 1 Configuration Space Headers, the first line of each entry lists Type 0 values and the
second line lists Type 1 values when the values differ.
Byte Address Hard IP Configuration Space Register Corresponding Section in PCIe Specification
0x000:0x03C PCI Header Type 0 Configuration Registers Type 0 Configuration Space Header
0x000:0x03C PCI Header Type 1 Configuration Registers Type 1 Configuration Space Header
0x040:0x04C Reserved N/A
0x050:0x05C MSI Capability Structure MSI Capability Structure
0x068:0x070 MSI-X Capability Structure MSI-X Capability Structure
0x070:0x074 Reserved N/A
0x078:0x07C Power Management Capability Structure PCI Power Management Capability
Structure
0x080:0x0B8 PCI Express Capability Structure PCI Express Capability Structure
0x0B8:0x0FC Reserved N/A
0x094:0x0FF Root Port N/A
0x100:0x16C Virtual Channel Capability Structure
Virtual Channel Capability
(Reserved)
©
2015 Altera Corporation. All rights reserved. ALTERA, ARRIA, CYCLONE, ENPIRION, MAX, MEGACORE, NIOS, QUARTUS and STRATIX words and logos are
trademarks of Altera Corporation and registered in the U.S. Patent and Trademark Office and in other countries. All other words and logos identified as
trademarks or service marks are the property of their respective holders as described at www.altera.com/common/legal.html. Altera warrants performance
of its semiconductor products to current specifications in accordance with Altera's standard warranty, but reserves the right to make changes to any
products and services at any time without notice. Altera assumes no responsibility or liability arising out of the application or use of any information,
product, or service described herein except as expressly agreed to in writing by Altera. Altera customers are advised to obtain the latest version of device
specifications before relying on any published information and before placing orders for products or services.
ISO
9001:2008
Registered
Page 68

6-2
Correspondence between Configuration Space Registers and the PCIe...
Byte Address Hard IP Configuration Space Register Corresponding Section in PCIe Specification
0x170:0x17C Reserved N/A
0x180:0x1FC Virtual channel arbitration table (Reserved) VC Arbitration Table
0x200:0x23C Port VC0 arbitration table (Reserved) Port Arbitration Table
0x240:0x27C Port VC1 arbitration table (Reserved) Port Arbitration Table
0x280:0x2BC Port VC2 arbitration table (Reserved) Port Arbitration Table
0x2C0:0x2FC Port VC3 arbitration table (Reserved) Port Arbitration Table
0x300:0x33C Port VC4 arbitration table (Reserved) Port Arbitration Table
0x340:0x37C Port VC5 arbitration table (Reserved) Port Arbitration Table
0x380:0x3BC Port VC6 arbitration table (Reserved) Port Arbitration Table
UG-01145_avmm
2015.05.14
0x3C0:0x3FC Port VC7 arbitration table (Reserved) Port Arbitration Table
0x400:0x7FC Reserved PCIe spec corresponding section name
0x800:0x834 Advanced Error Reporting AER (optional) Advanced Error Reporting Capability
0x838:0xFFF Reserved N/A
0x000 Device ID, Vendor ID Type 0 Configuration Space Header
Type 1 Configuration Space Header
0x004 Status, Command Type 0 Configuration Space Header
Type 1 Configuration Space Header
0x008 Class Code, Revision ID Type 0 Configuration Space Header
Type 1 Configuration Space Header
0x00C BIST, Header Type, Primary Latency Timer,
Cache Line Size
Type 0 Configuration Space Header
Type 1 Configuration Space Header
0x010 Base Address 0 Base Address Registers
0x014 Base Address 1 Base Address Registers
Altera Corporation
Registers
Send Feedback
Page 69

UG-01145_avmm
2015.05.14
Byte Address Hard IP Configuration Space Register Corresponding Section in PCIe Specification
Correspondence between Configuration Space Registers and the PCIe...
6-3
0x018 Base Address 2
Secondary Latency Timer, Subordinate Bus
Number, Secondary Bus Number, Primary
Bus Number
0x01C Base Address 3
Secondary Status, I/O Limit, I/O Base
0x020 Base Address 4
Memory Limit, Memory Base
0x024 Base Address 5
Prefetchable Memory Limit, Prefetchable
Memory Base
0x028 Reserved
Prefetchable Base Upper 32 Bits
0x02C Subsystem ID, Subsystem Vendor ID
Base Address Registers
Secondary Latency Timer, Type 1
Configuration Space Header, Primary
Bus Number
Base Address Registers
Secondary Status Register ,Type 1
Configuration Space Header
Base Address Registers
Type 1 Configuration Space Header
Base Address Registers
Prefetchable Memory Limit, Prefetchable
Memory Base
N/A
Type 1 Configuration Space Header
Type 0 Configuration Space Header
Prefetchable Limit Upper 32 Bits
0x030 I/O Limit Upper 16 Bits, I/O Base Upper 16
Bits
Type 1 Configuration Space Header
Type 0 Configuration Space Header
Type 1 Configuration Space Header
0x034 Reserved, Capabilities PTR Type 0 Configuration Space Header
Type 1 Configuration Space Header
0x038 Reserved N/A
0x03C Interrupt Pin, Interrupt Line
Bridge Control, Interrupt Pin, Interrupt Line
0x050 MSI-Message Control Next Cap Ptr
Type 0 Configuration Space Header
Type 1 Configuration Space Header
MSI and MSI-X Capability Structures
Capability ID
0x054 Message Address MSI and MSI-X Capability Structures
0x058 Message Upper Address MSI and MSI-X Capability Structures
0x05C Reserved Message Data MSI and MSI-X Capability Structures
Registers
Altera Corporation
Send Feedback
Page 70

6-4
Correspondence between Configuration Space Registers and the PCIe...
Byte Address Hard IP Configuration Space Register Corresponding Section in PCIe Specification
UG-01145_avmm
2015.05.14
0x068 MSI-X Message Control Next Cap Ptr
MSI and MSI-X Capability Structures
Capability ID
0x06C MSI-X Table Offset BIR MSI and MSI-X Capability Structures
0x070 Pending Bit Array (PBA) Offset BIR MSI and MSI-X Capability Structures
0x078 Capabilities Register Next Cap PTR Cap ID PCI Power Management Capability
Structure
0x07C Data PM Control/Status Bridge Extensions
Power Management Status & Control
PCI Power Management Capability
Structure
0x800 PCI Express Enhanced Capability Header Advanced Error Reporting Enhanced
Capability Header
0x804 Uncorrectable Error Status Register Uncorrectable Error Status Register
0x808 Uncorrectable Error Mask Register Uncorrectable Error Mask Register
0x80C Uncorrectable Error Severity Register Uncorrectable Error Severity Register
0x810 Correctable Error Status Register Correctable Error Status Register
0x814 Correctable Error Mask Register Correctable Error Mask Register
0x818 Advanced Error Capabilities and Control
Register
Advanced Error Capabilities and Control
Register
0x81C Header Log Register Header Log Register
0x82C Root Error Command Root Error Command Register
0x830 Root Error Status Root Error Status Register
0x834 Error Source Identification Register Correct‐
Error Source Identification Register
able Error Source ID Register
Related Information
PCI Express Base Specification 3.0
Altera Corporation
Registers
Send Feedback
Page 71

0x000
0x004
0x008
0x00C
0x010
0x014
0x018
0x01C
0x020
0x024
0x028
0x02C
0x030
0x034
0x038
0x03C
Device ID Vendor ID
Status
Command
Class Code Revision ID
0x00 Header Type 0x00 Cache Line Size
BAR Registers
BAR Registers
BAR Registers
BAR Registers
BAR Registers
BAR Registers
Reserved
Subsystem Device ID Subsystem Vendor ID
Expansion ROM Base Address
Reserved
Reserved
Capabilities Pointer
0x00 Interrupt Pin Interrupt Line
31
24
23
16
15
8
7
0
UG-01145_avmm
2015.05.14
Type 0 Configuration Space Registers
Figure 6-1: Type 0 Configuration Space Registers - Byte Address Offsets and Layout
Endpoints store configuration data in the Type 0 Configuration Space. The Correspondence between
Configuration Space Registers and the PCIe Specification on page 6-1 lists the appropriate section of
the PCI Express Base Specification that describes these registers.
Type 0 Configuration Space Registers
6-5
Registers
Send Feedback
Altera Corporation
Page 72

0x0000
0x004
Device ID
31
24
23
16
15
8
7
0
0x008
0x00C
0x010
0x014
0x018
0x01C
0x020
0x024
0x028
0x02C
0x030
0x034
0x038
0x03C
Vendor ID
BIST Header Type Primary Latency Timer Cache Line Size
Status Command
Class Code Revision ID
BAR Registers
BAR Registers
Secondary Latency Timer Subordinate Bus Number Secondary Bus Number Primary Bus Number
Secondary Status I/O Limit I/O Base
Memory Limit Memory Base
Prefetchable Base Upper 32 Bits
Prefetchable Limit Upper 32 Bits
I/O Limit Upper 16 Bits I/O Base Upper 16 Bits
Reserved Capabilities Pointer
Expansion ROM Base Address
Bridge Control Interrupt Pin Interrupt Line
Prefetchable Memory Limit Prefetchable Memory Base
0x050
0x054
0x058
Message Control
Configuration MSI Control Status
Register Field Descriptions
Next Cap Ptr
Message Address
Message Upper Address
Reserved Message Data
31
24
23
16
15
8
7
0
0x05C
Capability ID
6-6
Type 1 Configuration Space Registers
Type 1 Configuration Space Registers
Figure 6-2: Type 1 Configuration Space Registers (Root Ports)
UG-01145_avmm
2015.05.14
Altera Corporation
PCI Express Capability Structures
Figure 6-3: MSI Capability Structure
Registers
Send Feedback
Page 73

0x068
0x06C
0x070
Message Control Next Cap Ptr
MSI-X Table Offset
MSI-X Pending Bit Array (PBA) Offset
31 24 23 16 15 8 7 0
Capability ID
3 2
MSI-X
Table BAR
Indicator
MSI-X
Pending
Bit Array
- BAR
Indicator
0x078
0x07C
Capabilities Register Next Cap Ptr
Data
31 24 23 16 15 8 7 0
Capability ID
Power Management Status and Control
PM Control/Status
Bridge Extensions
Byte Offset 31:24 23:16 15:8 7:0
0x800
0x804 Uncorrectable Error Status Register
PCI Express Enhanced Capability Register
Uncorrectable Error Severity Register
Uncorrectable Error Mask Register0x808
0x80C
0x810
0x814
0x818
0x81C
0x82C
0x830
0x834
Correctable Error Status Register
Correctable Error Mask Register
Advanced Error Capabilities and Control Register
Header Log Register
Root Error Command Register
Root Error Status Register
Error Source Identification Register Correctable Error Source Identification Register
UG-01145_avmm
2015.05.14
Figure 6-4: MSI-X Capability Structure
Figure 6-5: Power Management Capability Structure - Byte Address Offsets and Layout
PCI Express Capability Structures
6-7
Figure 6-6: PCI Express AER Extended Capability Structure
Registers
Send Feedback
Altera Corporation
Page 74

0x080
0x084
0x088
0x08C
0x090
0x094
0x098
0x09C
0x0A0
0x0A4
0x0A8
0x0AC
0x0B0
0x0B4
0x0B8
PCI Express Capabilities Register Next Cap Pointer
Device Capabilities
Device Status Device Control
Slot Capabilities
Root Status
Device Compatibilities 2
Link Capabilities 2
Link Status 2
Link Control 2
Slot Capabilities 2
Slot Status 2
Slot Control 2
31
24
23
16
15
8
7
0
PCI Express
Capabilities ID
Link Capabilities
Link Status Link Control
Slot Status
Slot Control
Device Status 2 Device Control 2
Root Capabilities
Root Control
6-8
PCI Express Capability Structures
Figure 6-7: PCI Express Capability Structure - Byte Address Offsets and Layout
In the following table showing the PCI Express Capability Structure, registers that are not applicable to a
device are reserved.
UG-01145_avmm
2015.05.14
Altera Corporation
Registers
Send Feedback
Page 75

0x200
0x204
Next Capability Offset Version
VSEC Length
31
20
19
16
15
8
7
0
Altera-Defined VSEC Capability Header
VSEC ID
Altera-Defined, Vendor-Specific Header
VSEC
Revision
Altera Marker
0x208
JTAG Silicon ID DW0 JTAG Silicon ID0x20C
JTAG Silicon ID DW1 JTAG Silicon ID
0x210
JTAG Silicon ID DW2 JTAG Silicon ID
0x214
JTAG Silicon ID DW3 JTAG Silicon ID
0x218
CvP Status0x21C
CvP Mode Control0x220
CvP Data2 Register0x224
CvP Data Register0x228
CvP Programming Control Register
0x22C
Reserved
0x230
Uncorrectable Internal Error Status Register0x234
Uncorrectable Internal Error Mask Register0x238
Correctable Internal Error Status Register0x23C
User Device or Board Type ID
Correctable Internal Error Mask Register0x240
UG-01145_avmm
2015.05.14
Altera-Defined VSEC Registers
Figure 6-8: VSEC Registers
This extended capability structure supports Configuration via Protocol (CvP) programming and detailed
internal error reporting.
Altera-Defined VSEC Registers
6-9
Table 6-2: Altera‑Defined VSEC Capability Register, 0x200
The Altera-Defined Vendor Specific Extended Capability. This extended capability structure supports
Configuration via Protocol (CvP) programming and detailed internal error reporting.
Bits Register Description Value Access
[15:0] PCI Express Extended Capability ID. Altera-defined value for
[19:16] Version. Altera-defined value for VSEC version. 0x1 RO
VSEC Capability ID.
[31:20] Next Capability Offset. Starting address of the next Capability
Structure implemented, if any.
Registers
Send Feedback
0x000B RO
Variable RO
Altera Corporation
Page 76

6-10
CvP Registers
Table 6-3: Altera‑Defined Vendor Specific Header
You can specify these values when you instantiate the Hard IP. These registers are read-only at run-time.
Bits Register Description Value Access
[15:0] VSEC ID. A user configurable VSEC ID. User entered RO
[19:16] VSEC Revision. A user configurable VSEC revision. Variable RO
[31:20] VSEC Length. Total length of this structure in bytes. 0x044 RO
Table 6-4: Altera Marker Register
Bits Register Description Value Access
UG-01145_avmm
2015.05.14
[31:0] Altera Marker. This read only register is an additional marker. If
you use the standard Altera Programmer software to configure
A Device
Value
the device with CvP, this marker provides a value that the
programming software reads to ensure that it is operating with
the correct VSEC.
Table 6-5: JTAG Silicon ID Register
Bits Register Description Value Access
[127:96]
JTAG Silicon ID DW3
Application
Specific
[95:64]
JTAG Silicon ID DW2
Application
Specific
[63:32]
JTAG Silicon ID DW1
Application
Specific
[31:0] JTAG Silicon ID DW0. This is the JTAG Silicon ID that CvP
programming software reads to determine that the correct SRAM
Application
Specific
object file (.sof) is being used.
RO
RO
RO
RO
RO
Table 6-6: User Device or Board Type ID Register
Bits Register Description Value Access
[15:0] Configurable device or board type ID to specify to CvP the
correct .sof.
CvP Registers
Altera Corporation
Variable RO
Registers
Send Feedback
Page 77

UG-01145_avmm
2015.05.14
Table 6-7: CvP Status
The CvP Status register allows software to monitor the CvP status signals.
Bits Register Description Reset Value Access
[31:26] Reserved 0x00 RO
CvP Registers
6-11
[25] PLD_CORE_READY. From FPGA fabric. This status bit is
Variable RO
provided for debug.
[24] PLD_CLK_IN_USE. From clock switch module to fabric. This
Variable RO
status bit is provided for debug.
[23] CVP_CONFIG_DONE. Indicates that the FPGA control block has
Variable RO
completed the device configuration via CvP and there were
no errors.
[22] Reserved Variable RO
[21] USERMODE. Indicates if the configurable FPGA fabric is in user
Variable RO
mode.
[20] CVP_EN. Indicates if the FPGA control block has enabled CvP
Variable RO
mode.
[19] CVP_CONFIG_ERROR. Reflects the value of this signal from the
Variable RO
FPGA control block, checked by software to determine if
there was an error during configuration.
[18] CVP_CONFIG_READY. Reflects the value of this signal from the
Variable RO
FPGA control block, checked by software during
programming algorithm.
[17:0] Reserved Variable RO
Table 6-8: CvP Mode Control
The CvP Mode Control register provides global control of the CvP operation.
Bits Register Description Reset Value Access
[31:16] Reserved. 0x0000 RO
[15:8] CVP_NUMCLKS.
0x00 RW
This is the number of clocks to send for every CvP data write. Set
this field to one of the values below depending on your configura‐
tion image:
• 0x01 for uncompressed and unencrypted images
• 0x04 for uncompressed and encrypted images
• 0x08 for all compressed images
[7:3] Reserved. 0x0 RO
[2] CVP_FULLCONFIG. Request that the FPGA control block
1’b0 RW
reconfigure the entire FPGA including the Arria 10 Hard IP for
PCI Express, bring the PCIe link down.
Registers
Altera Corporation
Send Feedback
Page 78

6-12
CvP Registers
Bits Register Description Reset Value Access
UG-01145_avmm
2015.05.14
[1] HIP_CLK_SEL. Selects between PMA and fabric clock when USER_
MODE = 1 and PLD_CORE_READY = 1. The following encodings are
defined:
• 1: Selects internal clock from PMA which is required for CVP_
MODE.
• 0: Selects the clock from soft logic fabric. This setting should
only be used when the fabric is configured in USER_MODE with
a configuration file that connects the correct clock.
To ensure that there is no clock switching during CvP, you should
only change this value when the Hard IP for PCI Express has been
idle for 10 µs and wait 10 µs after changing this value before
resuming activity.
[0] CVP_MODE. Controls whether the IP core is in CVP_MODE or normal
mode. The following encodings are defined:
• 1:CVP_MODE is active. Signals to the FPGA control block active
and all TLPs are routed to the Configuration Space. This CVP_
MODE cannot be enabled if CVP_EN = 0.
• 0: The IP core is in normal mode and TLPs are routed to the
FPGA fabric.
Table 6-9: CvP Data Registers
1’b0 RW
1’b0 RW
The following table defines the CvP Data registers. For 64-bit data, the optional CvP Data2 stores the upper 32
bits of data. Programming software should write the configuration data to these registers. If you Every write to
these register sets the data output to the FPGA control block and generates <n> clock cycles to the FPGA control
block as specified by the CVP_NUM_CLKS field in the CvP Mode Control register. Software must ensure that all bytes
in the memory write dword are enabled. You can access this register using configuration writes, alternatively,
when in CvP mode, these registers can also be written by a memory write to any address defined by a memory
space BAR for this device. Using memory writes should allow for higher throughput than configuration writes.
Bits Register Description Reset Value Access
[31:0] Upper 32 bits of configuration data to be transferred to the FPGA
0x00000000 RW
control block to configure the device. You can choose 32- or 64bit data.
[31:0] Lower 32 bits of configuration data to be transferred to the FPGA
0x00000000 RW
control block to configure the device.
Table 6-10: CvP Programming Control Register
This register is written by the programming software to control CvP programming.
Bits Register Description Reset Value Access
[31:2] Reserved. 0x0000 RO
Altera Corporation
Registers
Send Feedback
Page 79

Transaction,
Data Link,
and PHY
Qsys Generated Endpoint (Altera FPGA)
PCI Express Avalon-MM Bridge
Interconnect
Avalon-MM Hard IP for PCI Express
Control and Status Registers
Control Register Access (CRA)
PCIe TLP Address
RX
PCIe
Link
0x0000-0x0FFF: PCIe processors
0x1000-0x1FFF: Addr translation
0x2000-0x2FFF: Root Port TLP Data
0x3000-0x3FFF: Avalon-MM processors
Host
CPU
Avalon-MM
32-Bit Byte Address
Avalon-MM Slave
UG-01145_avmm
2015.05.14
64- or 128-Bit Avalon-MM Bridge Register Descriptions
Bits Register Description Reset Value Access
6-13
[1] START_XFER. Sets the CvP output to the FPGA control block
indicating the start of a transfer.
[0] CVP_CONFIG. When asserted, instructs that the FPGA control
block begin a transfer via CvP.
64- or 128-Bit Avalon-MM Bridge Register Descriptions
The CRA Avalon-MM slave module provides access control and status registers in the PCI Express
Avalon-MM bridge. In addition, it provides access to selected Configuration Space registers and link
status registers in read-only mode. This module is optional. However, you must include it to access the
registers.
The control and status register address space is 16 KBytes. Each 4-KByte sub-region contains a set of
functions, which may be specific to accesses from the PCI Express Root Complex only, from Avalon-MM
processors only, or from both types of processors. Because all accesses come across the interconnect fabric
—requests from the Avalon-MM Arria 10 Hard IP for PCI Express are routed through the interconnect
fabric—hardware does not enforce restrictions to limit individual processor access to specific regions.
However, the regions are designed to enable straight-forward enforcement by processor software. The
following figure illustrates accesses to the Avalon-MM control and status registers from the Host CPU
and PCI Express link.
1’b0 RW
1’b0 RW
Figure 6-9: Accesses to the Avalon-MM Bridge Control and Status Register
Registers
Send Feedback
Altera Corporation
Page 80

6-14
64- or 128-Bit Avalon-MM Bridge Register Descriptions
The following table describes the four subregions.
Table 6-11: Avalon-MM Control and Status Register Address Spaces
AddressRange Address Space Usage
0x0000-0x0FFF Registers typically intended for access by PCI Express link partner only. This includes
PCI Express interrupt enable controls, write access to the PCI Express Avalon-MM
bridge mailbox registers, and read access to Avalon-MM-to-PCI Express mailbox
registers.
0x1000-0x1FFF Avalon-MM-to-PCI Express address translation tables. Depending on the system
design these may be accessed by the PCI Express link partner, Avalon-MM processors,
or both.
0x2000-0x2FFF Root Port request registers. An embedded processor, such as the Nios II processor,
programs these registers to send the data for Configuration TLPs, I/O TLPs, single
dword Memory Read and Write requests, and receive interrupts from an Endpoint.
0x3000-0x3FFF Registers typically intended for access by Avalon-MM processors only. Provides host
access to selected Configuration Space and status registers.
UG-01145_avmm
2015.05.14
Note: The data returned for a read issued to any undefined address in this range is unpredictable.
The following table lists the complete address map for the PCI Express Avalon-MM bridge registers.
Note:
In the following table the text in green are links to the detailed register description
Table 6-12: PCI Express Avalon-MM Bridge Register Map
Address Range Register
0x0040 Avalon-MM to PCI Express Interrupt Status Register
0x0050 Avalon-MM to PCI Express Interrupt Status Enable Register
0x0800–0x081F PCI Express-to-Avalon-MM Mailbox Registers
0x0900–x091F Avalon-MM to PCI Express Mailbox Registers
0x1000–0x1FFF Avalon-MM to PCI Express Address Translation Table
0x2000–0x2FFF Root Port TLP Data Registers
0x3060 Avalon-MM to PCI Express Interrupt Status Registers for Root Ports
0x3060 PCI Express to Avalon-MM Interrupt Status Register for Endpoints
Altera Corporation
Registers
Send Feedback
Page 81

UG-01145_avmm
2015.05.14
Address Range Register
0x3070 INT-X Interrupt Enable Register for Root Ports
0x3070 INT-X Interrupt Enable Register for Endpoints
0x3A00-0x3A1F Avalon-MM to PCI Express Mailbox Registers
0x3B00-0x3B1F PCI Express to Avalon-MM Mailbox Registers
Avalon-MM to PCI Express Interrupt Registers
6-15
0x3C00-0x3C6C
Host (Avalon-MM master) access to selected Configuration Space and status registers.
Avalon-MM to PCI Express Interrupt Registers
Avalon-MM to PCI Express Interrupt Status Registers
These registers contain the status of various signals in the PCI Express Avalon-MM bridge logic and allow
PCI Express interrupts to be asserted when enabled. Only Root Complexes should access these registers;
however, hardware does not prevent other Avalon-MM masters from accessing them.
Table 6-13: Avalon-MM to PCI Express Interrupt Status Register, 0x0040
Bit Name Access Description
[31:24] Reserved N/A N/A
[23]
[22]
[21]
A2P_MAILBOX_INT7
A2P_MAILBOX_INT6
A2P_MAILBOX_INT5
RW1C 1 when the A2P_MAILBOX7 is written to
RW1C 1 when the A2P_MAILBOX6 is written to
RW1C 1 when the A2P_MAILBOX5 is written to
Registers
[20]
[19]
[18]
[17]
[16]
Send Feedback
A2P_MAILBOX_INT4
A2P_MAILBOX_INT3
A2P_MAILBOX_INT2
A2P_MAILBOX_INT1
A2P_MAILBOX_INT0
RW1C 1 when the A2P_MAILBOX4 is written to
RW1C 1 when the A2P_MAILBOX3 is written to
RW1C 1 when the A2P_MAILBOX2 is written to
RW1C 1 when the A2P_MAILBOX1 is written to
RW1C 1 when the A2P_MAILBOX0 is written to
Altera Corporation
Page 82

6-16
Avalon-MM to PCI Express Interrupt Enable Registers
Bit Name Access Description
[15:0] AVL_IRQ_ASSERTED[15:0] RO Current value of the Avalon-MM interrupt
(IRQ) input ports to the Avalon-MM RX
master port:
• 0—Avalon-MM IRQ is not being
signaled.
• 1—Avalon-MM IRQ is being signaled.
A Qsys-generated IP Compiler for PCI
Express has as many as 16 distinct IRQ
input ports. Each AVL_IRQ_ASSERTED[] bit
reflects the value on the corresponding IRQ
input port.
Avalon-MM to PCI Express Interrupt Enable Registers
A PCI Express interrupt can be asserted for any of the conditions registered in the Avalon-MM to PCI
Express Interrupt Status register by setting the corresponding bits in the Avalon-MM-to-PCI Express
Interrupt Enable register. Either MSI or legacy interrupts can be generated as explained in the section
Enabling MSI or Legacy Interrupts
UG-01145_avmm
2015.05.14
Table 6-14: Avalon-MM to PCI Express Interrupt Enable Register, 0x0050
Bits Name Access Description
[31:24] Reserved N/A N/A
[23:16]
A2P_MB_IRQ
RW Enables generation of PCI Express
interrupts when a specified mailbox is
written to by an external Avalon-MM
master.
[4:0]
AVL_IRQ[15:0]
RW Enables generation of PCI Express
interrupts when a specified Avalon-MM
interrupt signal is asserted. Your Qsys
system may have as many as 16
individual input interrupt signals.
Table 6-15: Avalon-MM Interrupt Vector Register - 0x0060
Bits Name Access Description
[31:5] Reserved N/A N/A
Altera Corporation
Registers
Send Feedback
Page 83

UG-01145_avmm
2015.05.14
Bits Name Access Description
PCI Express Mailbox Registers
6-17
[15:0]
AVL_IRQ_Vector
RO Stores the interrupt vector of the system
interconnect fabric. The host software
should read this register after being
interrupted and determine the servicing
priority.
PCI Express Mailbox Registers
The PCI Express Root Complex typically requires write access to a set of PCI Express-to-Avalon-MM
mailbox registers and read-only access to a set of Avalon-MM-to-PCI Express mailbox registers. Eight
mailbox registers are available.
The PCI Express-to-Avalon-MM Mailbox registers are writable at the addresses shown in the following
table. Writing to one of these registers causes the corresponding bit in the Avalon-MM Interrupt
Status register to be set to a one.
Table 6-16: PCI Express-to-Avalon-MM Mailbox Registers, 0x0800–0x081F
Address Name Access Description
0x0800
0x0804
P2A_MAILBOX0
P2A_MAILBOX1
RW PCI Express-to-Avalon-MM Mailbox 0
RW PCI Express-to-Avalon-MM Mailbox 1
0x0808
0x080C
0x0810
0x0814
0x0818
0x081C
P2A_MAILBOX2
P2A_MAILBOX3
P2A_MAILBOX4
P2A_MAILBOX5
P2A_MAILBOX6
P2A_MAILBOX7
RW PCI Express-to-Avalon-MM Mailbox 2
RW PCI Express-to-Avalon-MM Mailbox 3
RW PCI Express-to-Avalon-MM Mailbox 4
RW PCI Express-to-Avalon-MM Mailbox 5
RW PCI Express-to-Avalon-MM Mailbox 6
RW PCI Express-to-Avalon-MM Mailbox 7
The Avalon-MM-to-PCI Express Mailbox registers are read at the addresses shown in the following
table. The PCI Express Root Complex should use these addresses to read the mailbox information after
being signaled by the corresponding bits in the Avalon MM to PCI Express Interrupt Status register.
Table 6-17: Avalon-MM-to-PCI Express Mailbox Registers, 0x0900–0x091F
Address Name Access Description
0x0900 A2P_MAILBOX0 RO Avalon-MM-to-PCI Express Mailbox 0
Registers
Altera Corporation
Send Feedback
Page 84

6-18
Avalon-MM-to-PCI Express Address Translation Table
Address Name Access Description
0x0904 A2P_MAILBOX1 RO Avalon-MM-to-PCI Express Mailbox 1
0x0908 A2P_MAILBOX2 RO Avalon-MM-to-PCI Express Mailbox 2
0x090C A2P_MAILBOX3 RO Avalon-MM-to-PCI Express Mailbox 3
0x0910 A2P_MAILBOX4 RO Avalon-MM-to-PCI Express Mailbox 4
0x0914 A2P_MAILBOX5 RO Avalon-MM-to-PCI Express Mailbox 5
0x0918 A2P_MAILBOX6 RO Avalon-MM-to-PCI Express Mailbox 6
0x091C A2P_MAILBOX7 RO Avalon-MM-to-PCI Express Mailbox 7
Avalon-MM-to-PCI Express Address Translation Table
The Avalon-MM-to-PCI Express address translation table is writable using the CRA slave port. Each
entry in the PCI Express address translation table is 8 bytes wide, regardless of the value in the current
PCI Express address width parameter. Therefore, register addresses are always the same width, regardless
of PCI Express address width.
UG-01145_avmm
2015.05.14
These table entries are repeated for each address specified in the Number of address pages parameter. If
Number of address pages is set to the maximum of 512, 0x1FF8 contains A2P_ADDR_SPACE511 and
A2P_ADDR_MAP_LO511 and 0x1FFC contains A2P_ADDR_MAP_HI511.
Table 6-18: Avalon-MM-to-PCI Express Address Translation Table, 0x1000–0x1FFF
Address Bits Name Access Description
[1:0]
A2P_ADDR_
SPACE0
RW Address space indication for entry 0. The following
encodings are defined:
• 2’b00:. Memory Space, 32-bit PCI Express address.
32-bit header is generated. Address bits 63:32 of the
translation table entries are ignored.
0x1000
• 2’b01: Memory space, 64-bit PCI Express address.
64-bit address header is generated.
• 2’b10: Reserved
• 2’b11: Reserved
[31:2]
0x1004 [31:0]
A2P_ADDR_
MAP_LO0
A2P_ADDR_
MAP_HI0
RW Lower bits of Avalon-MM-to-PCI Express address map
entry 0.
RW Upper bits of Avalon-MM-to-PCI Express address map
entry 0.
Altera Corporation
Registers
Send Feedback
Page 85

UG-01145_avmm
2015.05.14
Address Bits Name Access Description
PCI Express to Avalon-MM Interrupt Status and Enable Registers for...
6-19
[1:0]
A2P_ADDR_
SPACE1
RW Address space indication for entry 1. This entry is
available only if the number of translation table entries
(Number of address pages) is greater than 1.
The same encodings are defined for A2P_ADDR_
0x1008
[31:2]
A2P_ADDR_
MAP_LO1
RW Lower bits of Avalon-MM-to-PCI Express address map
SPACE1 as for A2P_ADDR_SPACE0.:
entry 1.
This entry is only implemented if the number of
address translation table entries is greater than 1.
0x100C [31:0]
A2P_ADDR_
MAP_HI1
RW Upper bits of Avalon-MM-to-PCI Express address map
entry 1.
This entry is only implemented if the number of
address translation table entries is greater than 1.
PCI Express to Avalon-MM Interrupt Status and Enable Registers for Endpoints
The registers in this section contain status of various signals in the PCI Express Avalon-MM bridge logic
and allow Avalon interrupts to be asserted when enabled. A processor local to the interconnect fabric that
processes the Avalon-MM interrupts can access these registers.
These registers must not be accessed by the PCI Express Avalon-MM bridge master ports; however,
Note:
there is nothing in the hardware that prevents a PCI Express Avalon-MM bridge master port from
accessing these registers.
The following table describes the Interrupt Status register when you configure the core as an Endpoint. It
records the status of all conditions that can cause an Avalon-MM interrupt to be asserted.
Table 6-19: PCI Express to Avalon-MM Interrupt Status Register for Endpoints, 0x3060
Bits Name Access Description
0
ERR_PCI_WRITE_FAILURE
RW1C When set to 1, indicates a PCI Express
write failure. This bit can also be cleared
by writing a 1 to the same bit in the
Avalon MM to PCI Express
Interrupt Status register.
1
ERR_PCI_READ_FAILURE
RW1C When set to 1, indicates the failure of a
PCI Express read. This bit can also be
cleared by writing a 1 to the same bit in
the Avalon MM to PCI Express
Interrupt Status register.
Registers
Altera Corporation
Send Feedback
Page 86

6-20
PCI Express to Avalon-MM Interrupt Status and Enable Registers for...
Bits Name Access Description
[15:2] Reserved — —
UG-01145_avmm
2015.05.14
[16]
[17]
[18]
[19]
[20]
[21]
[22]
[23]
P2A_MAILBOX_INT0
P2A_MAILBOX_INT1
P2A_MAILBOX_INT2
P2A_MAILBOX_INT3
P2A_MAILBOX_INT4
P2A_MAILBOX_INT5
P2A_MAILBOX_INT6
P2A_MAILBOX_INT7
RW1C 1 when the P2A_MAILBOX0 is written
RW1C 1 when the P2A_MAILBOX1 is written
RW1C 1 when the P2A_MAILBOX2 is written
RW1C 1 when the P2A_MAILBOX3 is written
RW1C 1 when the P2A_MAILBOX4 is written
RW1C 1 when the P2A_MAILBOX5 is written
RW1C 1 when the P2A_MAILBOX6 is written
RW1C 1 when the P2A_MAILBOX7 is written
[31:24] Reserved — —
An Avalon-MM interrupt can be asserted for any of the conditions noted in the Avalon-MM Interrupt
Status register by setting the corresponding bits in the PCI Express to Avalon-MM Interrupt Enable
register.
PCI Express interrupts can also be enabled for all of the error conditions described. However, it is likely
that only one of the Avalon-MM or PCI Express interrupts can be enabled for any given bit. Typically, a
single process in either the PCI Express or Avalon-MM domain handles the condition reported by the
interrupt.
Table 6-20: INT‑X Interrupt Enable Register for Endpoints, 0x3070
Bits Name Access Description
[31:0]
PCI Express to Avalon-MM
Interrupt Enable
RW When set to 1, enables the interrupt for
the corresponding bit in the PCI
Express to Avalon MM Interrupt
Status register to cause the Avalon
Interrupt signal (cra_Irq_o) to be
asserted.
Only bits implemented in the PCI
Express to Avalon MM Interrupt
Status register are implemented in the
Enable register. Reserved bits cannot be
set to a 1.
Altera Corporation
Registers
Send Feedback
Page 87

UG-01145_avmm
2015.05.14
Avalon-MM Mailbox Registers
A processor local to the interconnect fabric typically requires write access to a set of Avalon-MM-to-PCI
Express Mailbox registers and read-only access to a set of PCI Express-to-Avalon-MM Mailbox
registers. Eight mailbox registers are available.
The Avalon-MM-to-PCI Express Mailbox registers are writable at the addresses shown in the following
table. When the Avalon-MM processor writes to one of these registers the corresponding bit in the
Avalon MM to PCI Express Interrupt Status register is set to 1.
Table 6-21: Avalon-MM to PCI Express Mailbox Registers, 0x3A00–0x3A1F
Address Name Access Description
Avalon-MM Mailbox Registers
6-21
0x3A00
0x3A04
0x3A08
0x3A0C
0x3A10
0x3A14
0x3A18
0x3A1C
A2P_MAILBOX0
A2P_MAILBOX1
A2P _MAILBOX2
A2P _MAILBOX3
A2P _MAILBOX4
A2P _MAILBOX5
A2P _MAILBOX6
A2P_MAILBOX7
RW Avalon-MM-to-PCI Express mailbox 0
RW Avalon-MM-to-PCI Express mailbox 1
RW Avalon-MM-to-PCI Express mailbox 2
RW Avalon-MM-to-PCI Express mailbox 3
RW Avalon-MM-to-PCI Express mailbox 4
RW Avalon-MM-to-PCI Express mailbox 5
RW Avalon-MM-to-PCI Express mailbox 6
RW Avalon-MM-to-PCI Express mailbox 7
The PCI Express-to-Avalon-MM Mailbox registers are read-only at the addresses shown in the
following table. The Avalon-MM processor reads these registers when the corresponding bit in the PCI
Express to Avalon-MM Interrupt Status register is set to 1.
Table 6-22: PCI Express to Avalon-MM Mailbox Registers, 0x3B00–0x3B1F
Registers
Address Name Access
Mode
0x3B00
0x3B04
0x3B08
0x3B0C
0x3B10
Send Feedback
P2A_MAILBOX0
P2A_MAILBOX1
P2A_MAILBOX2
P2A_MAILBOX3
P2A_MAILBOX4
RO PCI Express-to-Avalon-MM mailbox 0
RO PCI Express-to-Avalon-MM mailbox 1
RO PCI Express-to-Avalon-MM mailbox 2
RO PCI Express-to-Avalon-MM mailbox 3
RO PCI Express-to-Avalon-MM mailbox 4
Description
Altera Corporation
Page 88

6-22
Control Register Access (CRA) Avalon-MM Slave Port
UG-01145_avmm
2015.05.14
Address Name Access
Mode
0x3B14
0x3B18
0x3B1C
P2A_MAILBOX5
P2A_MAILBOX6
P2A_MAILBOX7
RO PCI Express-to-Avalon-MM mailbox 5
RO PCI Express-to-Avalon-MM mailbox 6
RO PCI Express-to-Avalon-MM mailbox 7
Control Register Access (CRA) Avalon-MM Slave Port
Table 6-23: Configuration Space Register Descriptions
For registers that are less than 32 bits, the upper bits are unused.
Byte Offset
14'h3C00 cfg_dev_ctrl[15:0]
14'h3C04 cfg_dev_ctrl2[15:0]
Register Dir Description
O cfg_devctrl[15:0] is device control for the PCI
Express capability structure.
O cfg_dev2ctrl[15:0] is device control 2 for the
PCI Express capability structure.
Description
14'h3C08 cfg_link_ctrl[15:0]
14'h3C0C cfg_link_ctrl2[15:0]
O cfg_link_ctrl[15:0]is the primary Link Control
of the PCI Express capability structure.
For Gen2 or Gen3 operation, you must write a 1’b1
to Retrain Link bit (Bit[5] of the cfg_link_ctrl) of
the Root Port to initiate retraining to a higher data
rate after the initial link training to Gen1 L0 state.
Retraining directs the LTSSM to the Recovery state.
Retraining to a higher data rate is not automatic for
the Arria 10 Hard IP for PCI Express IP Core even
if both devices on the link are capable of a higher
data rate.
O cfg_link_ctrl2[31:16] is the secondary Link
Control register of the PCI Express capability
structure for Gen2 operation.
When tl_cfg_addr=2, tl_cfg_ctl returns the
primary and secondary Link Control registers,
{cfg_link_ctrl[15:0], cfg_link_
ctrl2[15:0]}, the primary Link Status register
contents is available on tl_cfg_sts[46:31].
For Gen1 variants, the link bandwidth notification
bit is always set to 0. For Gen2 variants, this bit is
set to 1.
Altera Corporation
Registers
Send Feedback
Page 89

UG-01145_avmm
2015.05.14
Control Register Access (CRA) Avalon-MM Slave Port
6-23
Byte Offset
Register Dir Description
14'h3C10 cfg_prm_cmd[15:0]
14'h3C14 cfg_root_ctrl[7:0]
14'h3C18 cfg_sec_ctrl[15:0]
14'h3C1C cfg_secbus[7:0]
14'h3C20 cfg_subbus[7:0]
14'h3C24 cfg_msi_addr_low[31:0]
14'h3C28 cfg_msi_addr_hi[63:32]
O Base/Primary Command register for the PCI
Configuration Space.
O Root control and status register of the PCI-Express
capability. This register is only available in Root
Port mode.
O Secondary bus Control and Status register of the
PCI-Express capability. This register is only
available in Root Port mode.
O Secondary bus number. Available in Root Port
mode.
O Subordinate bus number. Available in Root Port
mode.
O cfg_msi_add[31:0] is the MSI message address.
O cfg_msi_add[63:32] is the MSI upper message
address.
14'h3C2C cfg_io_bas[19:0]
14'h3C30 cfg_io_lim[19:0]
14'h3C34 cfg_np_bas[11:0]
14'h3C38 cfg_np_lim[11:0]
14'h3C3C cfg_pr_bas_low[31:0]
14'h3C40 cfg_pr_bas_hi[43:32]
O The IO base register of the Type1 Configuration
Space. This register is only available in Root Port
mode.
O The IO limit register of the Type1 Configuration
Space. This register is only available in Root Port
mode.
O The non-prefetchable memory base register of the
Type1 Configuration Space. This register is only
available in Root Port mode.
O The non-prefetchable memory limit register of the
Type1 Configuration Space. This register is only
available in Root Port mode.
O The lower 32 bits of the prefetchable base register of
the Type1 Configuration Space. This register is only
available in Root Port mode.
O The upper 12 bits of the prefetchable base registers
of the Type1 Configuration Space. This register is
only available in Root Port mode.
Registers
Altera Corporation
Send Feedback
Page 90

6-24
Control Register Access (CRA) Avalon-MM Slave Port
UG-01145_avmm
2015.05.14
Byte Offset
Register Dir Description
14'h3C44 cfg_pr_lim_low[31:0]
14'h3C48 cfg_pr_lim_hi[43:32]
14'h3C4C cfg_pmcsr[31:0]
14'h3C50 cfg_msixcsr[15:0]
14'h3C54 cfg_msicsr[15:0]
14'h3C58 cfg_tcvcmap[23:0]
O The lower 32 bits of the prefetchable limit registers
of the Type1 Configuration Space. Available in Root
Port mode.
O The upper 12 bits of the prefetchable limit registers
of the Type1 Configuration Space. Available in Root
Port mode.
O cfg_pmcsr[31:16] is Power Management Control
and cfg_pmcsr[15:0]is the Power Management
Status register.
O MSI-X message control register.
O MSI message control.
O Configuration traffic class (TC)/virtual channel
(VC) mapping. The Application Layer uses this
signal to generate a TLP mapped to the appropriate
channel based on the traffic class of the packet.
14'h3C5C cfg_msi_data[15:0]
14'h3C60 cfg_busdev[12:0]
14'h3C64 ltssm_reg[4:0]
The following encodings are defined:
• cfg_tcvcmap[2:0]: Mapping for TC0 (always 0)
.
• cfg_tcvcmap[5:3]: Mapping for TC1.
• cfg_tcvcmap[8:6]: Mapping for TC2.
• cfg_tcvcmap[11:9]: Mapping for TC3.
• cfg_tcvcmap[14:12]: Mapping for TC4.
• cfg_tcvcmap[17:15]: Mapping for TC5.
• cfg_tcvcmap[20:18]: Mapping for TC6.
• cfg_tcvcmap[23:21]: Mapping for TC7.
O cfg_msi_data[15:0] is message data for MSI.
O Bus/Device Number captured by or programmed in
the Hard IP.
O
Specifies the current LTSSM state. The LTSSM state
machine encoding defines the following states:
• 00000: Detect.Quiet
• 00001: Detect.Active
• 00010: Polling.Active
• 00011: Polling.Compliance
• 00100: Polling.Configuration
Altera Corporation
Registers
Send Feedback
Page 91

UG-01145_avmm
2015.05.14
Control Register Access (CRA) Avalon-MM Slave Port
6-25
Byte Offset
Register Dir Description
• 00101: Polling.Speed
• 00110: config.Linkwidthstart
• 00111: Config.Linkaccept
• 01000: Config.Lanenumaccept
• 01001: Config.Lanenumwait
• 01010: Config.Complete
• 01011: Config.Idle
• 01100: Recovery.Rcvlock
• 01101: Recovery.Rcvconfig
• 01110: Recovery.Idle
• 01111: L0
• 10000: Disable
• 10001: Loopback.Entry
• 10010: Loopback.Active
• 10011: Loopback.Exit
• 10100: Hot.Reset
• 10101: LOs
• 11001: L2.transmit.Wake
• 11010: Speed.Recovery
• 11011: Recovery.Equalization, Phase 0
• 11100: Recovery.Equalization, Phase 1
• 11101: Recovery.Equalization, Phase 2
• 11110: recovery.Equalization, Phase 3
Registers
14'h3C68
current_speed_reg[1:0]
14'h3C6C lane_act_reg[3:0]
O Indicates the current speed of the PCIe link. The
following encodings are defined:
• 2b’00: Undefined
• 2b’01: Gen1
• 2b’10: Gen2
• 2b’11: Gen3
O Lane Active Mode: This signal indicates the number
of lanes that configured during link training. The
following encodings are defined:
• 4’b0001: 1 lane
• 4’b0010: 2 lanes
• 4’b0100: 4 lanes
• 4’b1000: 8 lanes
Altera Corporation
Send Feedback
Page 92

Header 1 [63:32]
Cycle 1
Register 1
Register 0
Register 1
Register 0
Register 1
Register 0
Register 1
Register 0
Register 1
Register 0
Data Unaligned to
QWord Boundary
Data Aligned to
QWord Boundary
Cycle 2
Header 0 [31:0]
Data [63:32]
Header 2 [31:0]
Header 1 [63:32]
Cycle 1
Header 0 [31:0]
Cycle 2
Header 2 [31:0]
Cycle 3
Data [31:0]
Unused, but must
be written
Unused, but must
be written
6-26
Programming Model for Avalon-MM Root Port
Programming Model for Avalon-MM Root Port
The Application Layer writes the Root Port TLP TX Data registers with TLP formatted data for Configu‐
ration Read and Write Requests, Message TLPs, Message TLPs with data payload, I/O Read and Write
Requests, or single dword Memory Read and Write Requests. Software should check the Root Port Link
Status register (offset 0x92) to ensure the Data Link Layer Link Active bit is set to 1'b1 before issuing a
Configuration request to downstream ports.
The Application Layer data must be in the appropriate TLP format with the data payload aligned to the
TLP address. Aligning the payload data to the TLP address may result in the payload data being either
aligned or unaligned to the qword. The following figure illustrates three dword TLPs with data that is
aligned and unaligned to the qword.
Figure 6-10: Layout of Data with 3 Dword Headers
UG-01145_avmm
2015.05.14
Altera Corporation
The following figure illustrates four dword TLPs with data that are aligned and unaligned to the qword.
Send Feedback
Registers
Page 93

Header 1 [63:32]
Cycle 1
Data Unaligned to
QWord Boundary
Data Aligned to
QWord Boundary
Cycle 2
Header 0 [31:0]
Header 3[63:32]
Header 2 [31:0]
Data [63:32]
Header 1 [63:32]
Header 0 [31:0]
Header 2 [31:0]
Cycle 1
Cycle 2
Cycle 3
Cycle 3
Data [31:0]
Unused, but must
be written
Unused, but must
be written
Header 3[63:32]
Register 1
Register 0
Register 1
Register 0
Register 1
Register 0
Register 1
Register 0
Register 1
Register 0
Register 1
Register 0
UG-01145_avmm
2015.05.14
Figure 6-11: Layout of Data with 4 Dword Headers
Sending a Write TLP
6-27
The TX TLP programming model scales with the data width. The Application Layer performs the same
writes for both the 64- and 128-bit interfaces. The Application Layer can only have one outstanding nonposted request at a time. The Application Layer must use tags 16–31 to identify non-posted requests.
For Root Ports, the Avalon-MM bridge does not filter Type 0 Configuration Requests by device
Note:
number. Application Layer software should filter out all requests to Avalon-MM Root Port
registers that are not for device 0. Application Layer software should return an Unsupported
Request Completion Status.
Sending a Write TLP
The Application Layer performs the following sequence of Avalon-MM accesses to the CRA slave port to
send a Memory Write Request:
1. Write the first 32 bits of the TX TLP to RP_TX_REG0.
2. Write the next 32 bits of the TX TLP to RP_TX_REG1.
3. Write the RP_TX_CNTRL.SOP to 1’b1 to push the first two dwords of the TLP into the Root Port TX
FIFO.
4. Repeat Steps 1 and 2. The second write to RP_TX_REG1 is required, even for three dword TLPs with
aligned data.
5. If the packet is complete, write RP_TX_CNTRL to 2’b10 to indicate the end of the packet. If the packet is
not complete, write 2’b00 to RP_TX_CNTRL.
6. Repeat this sequence to program a complete TLP.
When the programming of the TX TLP is complete, the Avalon-MM bridge schedules the TLP with
higher priority than TX TLPs coming from the TX slave port.
Registers
Send Feedback
Altera Corporation
Page 94

6-28
Sending a Read TLP or Receiving a Non-Posted Completion TLP
Sending a Read TLP or Receiving a Non-Posted Completion TLP
The TLPs associated with the Non-Posted TX requests are stored in the RP_RX_CPL FIFO buffer and
subsequently loaded into RP_RXCPL registers. The Application Layer performs the following sequence to
retrieve the TLP.
1. Polls the RP_RXCPL_STA TUS.SOP to determine when it is set to 1’b1.
2. Then RP_RXCPL_STATUS.SOP = 1’b’1, reads RP_RXCPL_REG0 and RP_RXCPL_REG1 to retrieve dword 0
and dword 1 of the TLP.
3. Read the RP_RXCPL_STATUS.EOP.
• If RP_RXCPL_STATUS.EOP = 1’b0, read RP_RXCPL_REG0 and RP_RXCPL_REG1 to retrieve dword 2
and dword 3 of the TLP, then repeat step 3.
• If RP_RXCPL_STATUS.EOP = 1’b1, read RP_RXCPL_REG0 and RP_RXCPL_REG1 to retrieve final
dwords of TLP.
PCI Express to Avalon-MM Interrupt Status and Enable Registers for Root Ports
The Root Port supports MSI, MSI-X and legacy (INTx) interrupts. MSI and MSI-X interrupts are memory
writes from the Endpoint to the Root Port. MSI and MSI-X requests are forwarded to the interconnect
without asserting CraIrq_o.
UG-01145_avmm
2015.05.14
Table 6-24: Avalon‑MM Interrupt Status Registers for Root Ports, 0x3060
Bits Name Access
Mode
[31:5] Reserved — —
[4]
RPRX_CPL_RECEIVED
RW1C Set to 1’b1 when the Root Port has
received a Completion TLP for an
outstanding Non-Posted request from
the TLP Direct channel.
[3]
INTD_RECEIVED
RW1C The Root Port has received INTD from
the Endpoint.
[2]
INTC_RECEIVED
RW1C The Root Port has received INTC from
the Endpoint.
[1]
INTB_RECEIVED
RW1C The Root Port has received INTB from
the Endpoint.
[0]
INTA_RECEIVED
RW1C The Root Port has received INTA from
the Endpoint.
Description
Altera Corporation
Registers
Send Feedback
Page 95

UG-01145_avmm
2015.05.14
Table 6-25: INT‑X Interrupt Enable Register for Root Ports, 0x3070
Root Port TLP Data Registers
6-29
Bit Name Access
Mode
[31:5] Reserved — —
[4]
RPRX_CPL_RECEIVED
RW When set to 1’b1, enables the assertion
of CraIrq_o when the Root Port
Interrupt Status register RPRX_CPL_
RECEIVED bit indicates it has received a
Completion for a Non-Posted request
from the TLP Direct channel.
[3]
INTD_RECEIVED_ENA
RW When set to 1’b1, enables the assertion
of CraIrq_o when the Root Port
Interrupt Status register INTD_
RECEIVED bit indicates it has received
INTD.
[2]
INTC_RECEIVED_ENA
RW When set to 1’b1, enables the assertion
of CraIrq_o when the Root Port
Interrupt Status register INTC_
RECEIVED bit indicates it has received
INTC.
Description
[1]
[0]
INTB_RECEIVED_ENA
INTA_RECEIVED_ENA
Root Port TLP Data Registers
The TLP data registers provide a mechanism for the Application Layer to specify data that the Root Port
uses to construct Configuration TLPs, I/O TLPs, and single dword Memory Reads and Write requests.
The Root Port then drives the TLPs on the TLP Direct Channel to access the Configuration Space, I/O
space, or Endpoint memory.
RW When set to 1’b1, enables the assertion
of CraIrq_o when the Root Port
Interrupt Status register INTB_
RECEIVED bit indicates it has received
INTB.
RW When set to 1’b1, enables the assertion
of CraIrq_o when the Root Port
Interrupt Status register INTA_
RECEIVED bit indicates it has received
INTA.
Registers
Altera Corporation
Send Feedback
Page 96

RX_TX_CNTL
RP_RXCPL_
REG0
RP_RXCPL_
REG1
RP_RXCPL_
STATUS
Control
Register
Access
Slave
Avalon-MM
Master
32
32
32
32
64
64
32
IRQ
RP TX
CTRL
TX
CTRL
RP_TX_FIFO
RP CPL
CTRL
RX
CTRL
RP_RXCPL_FIFO
TLP Direct Channel
to Hard IP for PCIe
Root-Port TLP Data Registers Avalon-MM Bridge -
RX_TX_Reg1
RP_TX_Reg0
6-30
Root Port TLP Data Registers
Figure 6-12: Root Port TLP Data Registers
UG-01145_avmm
2015.05.14
Note: The high performance TLPs implemented by Avalon-MM ports in the Avalon-MM Bridge are also
available for Root Ports. For more information about these TLPs, refer to Avalon-MM Bridge TLPs.
Table 6-26: Root Port TLP Data Registers, 0x2000–0x2FFF
Address Bits Name Access Description
0x2000 [31:0]
0x2004 [31:0]
0x2008
Root-Port Request Registers Address Range: 0x2800-0x2018
[31:2] Reserved — —
[1]
[0]
RP_TX_REG0
RP_TX_REG1
RP_TX_CNTRL.EOP
RP_TX_CNTRL.SOP
W Lower 32 bits of the TX TLP.
W Upper 32 bits of the TX TLP.
W Write 1’b1 to specify the of end a packet.
Writing this bit frees the corresponding
entry in the FIFO.
W Write 1’b1 to specify the start of a packet.
Altera Corporation
Registers
Send Feedback
Page 97

UG-01145_avmm
2015.05.14
Address Bits Name Access Description
Uncorrectable Internal Error Mask Register
Root-Port Request Registers Address Range: 0x2800-0x2018
[31:16] Reserved — —
6-31
[15:8]
[7:2] Reserved — —
[1]
0x2010
[0]
0x2014 [31:0]
0x2018 [31:0]
RP_RXCPL_STATUS
RP_RXCPL_STATUS.EOP
RP_RXCPL_STATUS.SOP
RP_RXCPL_REG0
RP_RXCPL_REG1
R Specifies the number of words in the RX
completion FIFO that contain valid data.
R When 1’b1, indicates that the data for a
Completion TLP is ready to be read by the
Application Layer. The Application Layer
must poll this bit to determine when a
Completion TLP is available.
R When 1’b1, indicates that the final data for
a Completion TLP is ready to be read by
the Application Layer. The Application
Layer must poll this bit to determine when
the final data for a Completion TLP is
available.
RC Lower 32 bits of a Completion TLP.
Reading frees this entry in the FIFO.
RC Upper 32 bits of a Completion TLP.
Reading frees this entry in the FIFO.
Related Information
Avalon-MM Bridge TLPs on page 10-11
Uncorrectable Internal Error Mask Register
Table 6-27: Uncorrectable Internal Error Mask Register
The Uncorrectable Internal Error Mask register controls which errors are forwarded as internal
uncorrectable errors. With the exception of the configuration error detected in CvP mode, all of the errors are
severe and may place the device or PCIe link in an inconsistent state. The configuration error detected in CvP
mode may be correctable depending on the design of the programming software. The access code RWS stands for
Read Write Sticky meaning the value is retained after a soft reset of the IP core.
Bits Register Description Reset Value Access
[31:12] Reserved. 1b’0 RO
Registers
Send Feedback
Altera Corporation
Page 98
6-32
Uncorrectable Internal Error Status Register
Bits Register Description Reset Value Access
[11] Mask for RX buffer posted and completion overflow error. 1b’1 RWS
[10] Reserved 1b’0 RO
UG-01145_avmm
2015.05.14
[9] Mask for parity error detected on Configuration Space to TX bus
1b’1 RWS
interface.
[8] Mask for parity error detected on the TX to Configuration Space
1b’1 RWS
bus interface.
[7] Mask for parity error detected at TX Transaction Layer error. 1b’1 RWS
[6] Reserved 1b’0 RO
[5] Mask for configuration errors detected in CvP mode. 1b’0 RWS
[4] Mask for data parity errors detected during TX Data Link LCRC
1b’1 RWS
generation.
[3] Mask for data parity errors detected on the RX to Configuration
1b’1 RWS
Space Bus interface.
[2] Mask for data parity error detected at the input to the RX Buffer. 1b’1 RWS
[1] Mask for the retry buffer uncorrectable ECC error. 1b’1 RWS
[0] Mask for the RX buffer uncorrectable ECC error. 1b’1 RWS
Uncorrectable Internal Error Status Register
Table 6-28: Uncorrectable Internal Error Status Register
This register reports the status of the internally checked errors that are uncorrectable. When specific errors are
enabled by the Uncorrectable Internal Error Mask register, they are handled as Uncorrectable Internal
Errors as defined in the PCI Express Base Specification 3.0. This register is for debug only. It should only be used to
observe behavior, not to drive custom logic. The access code RW1CS represents Read Write 1 to Clear Sticky.
Bits Register Description
[31:12] Reserved.
[11] When set, indicates an RX buffer overflow condition in a
posted request or Completion
Altera Corporation
Reset
Value
0
0
Access
RW1CS
RO
Registers
Send Feedback
Page 99

UG-01145_avmm
2015.05.14
Correctable Internal Error Mask Register
6-33
Bits Register Description
[10] Reserved.
[9] When set, indicates a parity error was detected on the Configu‐
ration Space to TX bus interface
[8] When set, indicates a parity error was detected on the TX to
Configuration Space bus interface
[7] When set, indicates a parity error was detected in a TX TLP and
the TLP is not sent.
[6] When set, indicates that the Application Layer has detected an
uncorrectable internal error.
[5] When set, indicates a configuration error has been detected in
CvP mode which is reported as uncorrectable. This bit is set
whenever a CVP_CONFIG_ERROR rises while in CVP_MODE.
[4] When set, indicates a parity error was detected by the TX Data
Link Layer.
Reset
Value
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
Access
RO
RW1CS
RW1CS
RW1CS
RW1CS
RW1CS
RW1CS
[3] When set, indicates a parity error has been detected on the RX
0
RW1CS
to Configuration Space bus interface.
[2] When set, indicates a parity error was detected at input to the
0
RW1CS
RX Buffer.
[1] When set, indicates a retry buffer uncorrectable ECC error.
[0] When set, indicates a RX buffer uncorrectable ECC error.
Related Information
0
0
RW1CS
RW1CS
PCI Express Base Specification 3.0
Correctable Internal Error Mask Register
Table 6-29: Correctable Internal Error Mask Register
The Correctab le Internal Error Mask register controls which errors are forwarded as Internal Correctable
Errors. This register is for debug only.
Bits Register Description Reset Value Access
Registers
[31:7] Reserved. 0 RO
Altera Corporation
Send Feedback
Page 100

6-34
Correctable Internal Error Status Register
Bits Register Description Reset Value Access
UG-01145_avmm
2015.05.14
[6] Mask for Corrected Internal Error reported by the Application
1 RWS
Layer.
[5] Mask for configuration error detected in CvP mode. 0 RWS
[4:2] Reserved. 0 RO
[1] Mask for retry buffer correctable ECC error. 1 RWS
[0] Mask for RX Buffer correctable ECC error. 1 RWS
Correctable Internal Error Status Register
Table 6-30: Correctable Internal Error Status Register
The Correctable Internal Error Status register reports the status of the internally checked errors that are
correctable. When these specific errors are enabled by the Correctable Internal Error Mask register, they are
forwarded as Correctable Internal Errors as defined in the PCI Express Base Specification 3.0. This register is for
debug only. It should only be used to observe behavior, not to drive logic custom logic.
Bits Register Description Reset Value Access
[31:6] Reserved. 0 RO
[5] When set, indicates a configuration error has been detected in
0 RW1CS
CvP mode which is reported as correctable. This bit is set
whenever a CVP_CONFIG_ERROR occurs while in CVP_MODE.
[4:2] Reserved. 0 RO
[1] When set, the retry buffer correctable ECC error status indicates
0 RW1CS
an error.
[0] When set, the RX buffer correctable ECC error status indicates an
0 RW1CS
error.
Related Information
PCI Express Base Specification 3.0
Altera Corporation
Registers
Send Feedback
 Loading...
Loading...