Page 1

AT-8700XL SERIES SWITCH
USER GUIDE
Software Release 2.6.1
Page 2

AT-8700XL Series Switch User Guide for Software Release 2.6.1
Document Number C613-02030-00 REV B.
Copyright © 2003 Allied Telesyn International Corp.
19800 North Creek Parkway, Suite 200, Bothell, WA 98011, USA.
All rights reserved. No part of this publication may be reproduced without prior written
permission from Allied Telesyn.
Allied Telesyn International Corp. reserves the right to make changes in specifications
and other information contained in this document without prior written notice. The
information provided herein is subject to change without notice. In no event shall Allied
Telesyn be liable for any incidental, special, indirect, or consequential damages
whatsoever, including but not limited to lost profits, arising out of or related to this
manual or the information contained herein, even if Allied Telesyn has been advised of,
known, or should have known, the possibility of such damages.
All trademarks are the property of their respective owner.
Page 3

Contents
CHAPTER 1 Introduction
Why Read this User Guide? ............................................................................... 5
Where To Find More Information ...................................................................... 6
Technical support .............................................................................................. 7
Features of the AT-8700XL Series Switch ........................................................... 7
Warning about FLASH memory ......................................................................... 9
CHAPTER 2
CHAPTER 3
CHAPTER 4
Getting Started with the Command Line Interface (CLI)
This Chapter ................................................................................................... 11
Connecting a Terminal or PC ........................................................................... 12
Terminal Communication Parameters .............................................................. 12
Logging In ...................................................................................................... 13
Assigning an IP Address .................................................................................. 13
Assigning an IP Address .................................................................................. 14
Setting Routes ................................................................................................ 15
Changing a Password ..................................................................................... 16
Choosing a Password ...................................................................................... 16
Using the Commands ..................................................................................... 17
Getting Command Line Help .......................................................................... 18
Setting System Parameters .............................................................................. 18
Getting Started with the Graphical User Interface (GUI)
This Chapter ................................................................................................... 21
What is the GUI? ............................................................................................ 22
Accessing the Switch via the GUI .................................................................... 22
Using the GUI: Navigation and Features .......................................................... 32
Upgrading the GUI ......................................................................................... 38
Troubleshooting .............................................................................................. 39
Operating the switch
This Chapter ................................................................................................... 45
User Accounts and Privileges ........................................................................... 45
Normal Mode and Security Mode ................................................................... 47
Remote Management ..................................................................................... 49
Storing Files in FLASH Memory ........................................................................ 49
Using Scripts ................................................................................................... 50
Loading and Uploading Files ........................................................................... 52
Upgrading Switch Software ............................................................................ 56
Using the Built-in Editor .................................................................................. 60
Page 4

4 AT-8700XL Series Switch User Guide
SNMP and MIBs .............................................................................................. 61
For More About Operations and Facilities ........................................................ 62
CHAPTER 5
CHAPTER 6
Switching
Switch Ports .................................................................................................... 63
Virtual Local Area Networks (VLANs) ............................................................... 65
Generic VLAN Registration Protocol (GVRP) ..................................................... 68
Quality of Service ............................................................................................ 68
Spanning Tree Protocol (STP) ........................................................................... 68
IP Switching .................................................................................................... 69
Routing Information Protocol (RIP) .................................................................. 70
Example output from the SHOW IP RIP command. .......................................... 70
IGMP Snooping .............................................................................................. 70
Triggers ........................................................................................................... 71
Maintenance and Troubleshooting
This Chapter ................................................................................................... 73
How the Switch Starts Up ............................................................................... 74
How to Avoid Problems .................................................................................. 75
What to Do if You Clear FLASH Memory Completely ....................................... 77
What to Do if Passwords are Lost .................................................................... 78
Getting the Most Out of Technical Support ..................................................... 78
Resetting Switch Defaults ............................................................................... 79
Checking Connections Using PING .................................................................. 79
Troubleshooting IP Configurations .................................................................. 80
Troubleshooting DHCP IP Addresses ................................................................ 81
Using Trace Route for IP Traffic ........................................................................ 81
Software Release 2.6.1
C613-02030-00 REV B
Page 5

Chapter 1
Introduction
Welcome to the AT-8700XL Series Advanced Fast Ethernet Switch, combining
wire speed Layer 2 and Layer 3 switching with Quality of Service (QoS)
features such as traffic classifiers and bandwidth limiting.
This guide introduces the AT-8700XL Series Switch and will guide you through
the most common uses and applications of your new switch. Getting started
will not take long—many applications are set up in just a few minutes. If you
have any questions about the switch, contact your authorised distributor or
reseller.
Your AT-8700XL Series Switch is supplied with default settings which allow
you to operate the switch immediately, without any configuration. Even if this
is all you want to do, you should still gain access to the switch configuration, if
only to change the manager password to prevent unauthorised access.
To take advantage of the advanced routing features, you will need to enter
detailed configuration. The switch has both a Command Line Interface (CLI)
and a Graphical User Interface (GUI) for configuration and management.
Before you can use the GUI, you will need to login to the switch and use its CLI
to allocate an IP address to at least one interface.
Why Read this User Guide?
Before you use your switch in a live network, please read this guide. The guide
tells you how to access and use the Command Line Interface (CLI) to configure
the switch software, and how to access and use the switch’s Graphical User
Interface (GUI). It then introduces a number of common switch functions and
how to configure them using the CLI. For information on configuration using
the GUI, see the context-sensitive online GUI help. For more detailed
descriptions of all commands, display outputs, and background information,
see the AT-8700XL Series Software Reference.
This user guide is organised into the following chapters:
■ Chapter 1, Introduction gives an overview of the switch features and of the
documentation supplied with your switch.
■ Chapter 2, Getting Started with the Command Line Interface (CLI) describes
how to gain access to the command line interface.
Page 6

6 AT-8700XL Series Switch User Guide
■ Chapter 3, Getting Started with the Graphical User Interface (GUI) describes
how to access and use the graphical user interface.
■ Chapter 4, Operating the switch introduces general operation, management
and support features, including loading and installing support files and
new releases.
■ Chapter 5, Switching describes how to configure Layer 2 and IP switching
features, including switch ports and VLANs.
■ Chapter 6, Maintenance and Troubleshooting describes some of the commands
you can use to monitor the switch and diagnose faults.
Where To Find More Information
Before installing the switch and any expansion options, read the important
safety information in the Safety and Statutory Information booklet.
Follow the Quick Install Guides’ step-by-step instructions for physically
installing the switch and any expansion options.
The AT-8700XL Series Hardware Reference gives detailed information about the
equipment hardware.
The context-sensitive online GUI help gives descriptions of each page and
element of the GUI.
Once you are familiar with the basic operations of the switch, use the AT-
8700XL Series Software Reference for full descriptions of routing features and
command syntax.
The AT-8700XL Series Switch Documentation Set
The documentation set for the AT-8700XL Series Switch includes:
■ AT-8700XL Series Safety and Statutory Information
■ AT-8700XL Series Quick Install Guide
■ AT-8700XL Series Documentation and Tools CD-ROM, which includes the
following PDF documents:
• AT-8700XL Series Safety and Statutory Information
• AT-8700XL Series Quick Install Guide
•This User Guide
• AT-8700XL Series Hardware Reference
• AT-8700XL Series Software Reference
• Uplink Module Quick Install Guide
• Uplink Module Hardware Reference
Software Release 2.6.1
C613-02030-00 REV B
Page 7
Introduction 7
The CD-ROM also includes:
• AT-TFTP Server for Windows, for downloading software releases,
scripts and other files to or from an AT-8700XL switch.
• Adobe Acrobat Reader for Windows for viewing and printing the
online documentation in PDF format. Get instant access to information
with full-text searching of PDF documents by keyword or phrase.
•Microsoft Internet Explorer.
• A demonstration version of F-Secure’s Secure Shell client for Windows.
• Information about other Allied Telesyn routing and switching
products.
Technical support
For online support for your AT-8700XL Series Switch, see our on-line support
page at http://www.alliedtelesyn.co.nz/support/at8700xl
This site contains the latest switch software releases, patches, GUI resource files
and documentation. Download software upgrades from the Allied Telesyn web
site to your server, and the use the LOAD command to copy them to the
switch’s FLASH memory. Use the SET INSTALL command to enable the new
software (see “Upgrading Switch Software” on page 56 for detailed instructions).
.
If you require further assistance, contact your authorised distributor or reseller.
Features of the AT-8700XL Series Switch
Software support for AT-8700XL Series Switches provides wirespeed Layer 2
and Layer 3 switching, including support for Virtual LANs.
Switching Features
The main Layer 2 features of the switch are:
■ High performance, wire-speed Layer 2 switching (“Switching” on page 63).
■ Packet Forwarding at wire speed.
■ Store and Forward switching mode.
■ Autonegotiation of link speed and duplex mode for 10/100 Mbps speed on
all 100BASE TX ports (“Autonegotiation of Port Speed and Duplex Mode” on
page 64).
■ Automatic, configurable MAC address learning and ageing, supporting up
to 255 static MAC addresses per switch.
Software Release 2.6.1
C613-02030-00 REV B
■ Switch Filtering.
■ Layer 3 Filtering (Switching chapter in the AT-8700XL Series Software
Reference.
■ Broadcast Storm Protection (“Packet Storm Protection” on page 64).
■ Virtual LANs defined by port membership (“Virtual Local Area Networks
(VLANs)” on page 65).
Page 8

8 AT-8700XL Series Switch User Guide
■ Spanning Tree Protocol and Rapid Spanning Tree Protocol (“Spanning Tree
Protocol (STP)” on page 68).
■ Classifiers to sort traffic for QoS and hardware filtering
■ Quality of Service
• DSCP configuration enabling management of DiffServ domains
• Priority queuing
• Bandwidth limiting
■ Port trunking to spread traffic over several links (“Port Trunking” on
page 64).
■ Port mirroring (“Port Mirroring” on page 64).
■ IGMP snooping and Multicast VLAN Registration
Management Features
The following features enhance management of the switch:
■ A sophisticated and configurable event logging facility for monitoring and
alarm notification to single or multiple management centres.
■ Triggers for automatic and timed execution of commands in response to
events.
■ Scripting for automated configuration and centralised management of
configurations.
■ Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP) for IP and IPv6. DHCP lets
you automatically assign IP addresses and other configuration information
to PCs and other hosts on TCP/IP networks.
■ Support for the Simple Network Management Protocol (SNMP), standard
MIBs and the Allied Telesyn Enterprise MIB, enabling the switch to be
managed by a separate SNMP management station.
■ Telnet client and server.
■ Secure Shell remote management.
■ An HTTP client that allows the direct download of files from a web server
to the switch’s FLASH memory.
For complete descriptions of these software features, see the AT-8700XL Series
Software Reference.
Layer 3 and Other Features
AT-8700XL Series Advanced Fast Ethernet Switches provide efficient and costeffective switching, terminal serving and integrated network management
over LANs. All models can run the same software suite and can provide all of
the following functions simultaneously (depending on the hardware
configuration):
■ TCP/IP routing.
■ IP multicasting support including Internet Group Management Protocol
(IGMP), IGMP snooping, IGMP proxy and Multicast VLAN Registration.
■ Ping Polling for determining device reachability and responding when a
device or link goes up or down.
Software Release 2.6.1
C613-02030-00 REV B
Page 9

Introduction 9
■ OSPF and IP RIP routing protocols.
■ ARP, Proxy ARP and Inverse ARP address resolution protocols.
■ Sophisticated packet filtering.
■ Terminal serving using Telnet, with local host nicknames.
■ Integration with a Public Key Infrastructure (PKI).
■ Virtual Router Redundancy Protocol (VRRP).
■ Software Secure Sockets Layer (SSL).
■ 802.1x port authentication.
Warning about FLASH memory
Before you start to configure your switch, note that it is possible to enter
commands that can impact severely on your switch’s performance.
DO NOT clear the FLASH memory completely. The software release files are
stored in FLASH, and clearing FLASH memory would leave no software to run
the switch.
While FLASH is compacting, do not restart the switch or use any commands
that affect the FLASH file subsystem. Do not restart the switch, or create, edit,
load, rename or delete any files until a message confirms that FLASH file
compaction is completed. Interrupting flash compaction may result in damage
to files. Damaged files are likely to prevent the switch from operating correctly.
For more information, see “How to Avoid Problems” on page 75 and “What to Do
if You Clear FLASH Memory Completely” on page 77.
Software Release 2.6.1
C613-02030-00 REV B
Page 10

Page 11

Chapter 2
Getting Started with the Command Line Interface (CLI)
This Chapter
This chapter describes how to access the switch’s CLI, and provides basic
information about configuring the switch, including how to:
■ Physically connect a terminal or PC to the switch (see “Connecting a
Terminal or PC” on page 12 and the Quick Install Guide).
■ Set the Terminal Communication parameters to match the switch’s settings
(see “Terminal Communication Parameters” on page 12).
■ Log in to the switch as a manager (see “Logging In” on page 13).
■ Configure IP addresses on the switch interfaces over which you will
manage the switch. This is necessary if you will access the switch using the
GUI or Telnet (see “Assigning an IP Address” on page 14).
■ Set routes (see “Setting Routes” on page 15)
■ Change the management password to limit unauthorised access to the
switch configuration (see “Changing a Password” on page 16).
■ Use the command line interface to control the switch software, including
creating aliases for often used character sequences (see “Using the
Commands” on page 17).
■ Set the online help file to gain access to command syntax help (see “Getting
Command Line Help” on page 18).
■ Enable any special feature licences (see “Enabling Special Feature Licences”
on page 18).
■ Set the name, location and contact details for the switch (see “Setting
System Parameters” on page 18).
Page 12

12 AT-8700XL Series Switch User Guide
Connecting a Terminal or PC
The first thing to do after physically installing the switch is to start a terminal
or terminal emulation session to access the switch. Then you can use the
command line interface (CLI) to configure the switch. If you wish to configure
the switch using the Graphical User Interface, you must first access the CLI and
assign an IP address to at least one interface.
You can use a PC running terminal emulation software as the manager console
instead of a terminal. Many terminal emulation applications are available for
the PC, but the most readily available is the HyperTerminal application
included in Microsoft® Windows™ 95, Windows™ 98, and Windows™ 2000.
In a normal Windows™ installation HyperTerminal is located in the
Accessories group. In Windows™ 2000, HyperTerminal is located in the Start >
Programs > Accessories > Communications menu.
The key to successfully using terminal emulation software with the switch is to
configure the communications parameters in the terminal emulation software
to match the default settings of the console port on the switch. For instructions
on how to configure HyperTerminal, see the AT-8700XL Series Hardware
Reference.
To start a terminal session, connect to the switch in one of the following ways:
■ Connect a VT100-compatible terminal to the RS-232 Terminal Port (asyn0),
set the communications parameters on the terminal (Table 1 on page 12),
and press [Enter] a few times until the switch’s login prompt appears; OR
■ Connect the COM port of a PC running terminal emulation software such
as Windows Terminal or HyperTerminal to the RS-232 Terminal Port
(asyn0), set the communications parameters on the terminal emulation
software (Table 1 on page 12), and press [Enter] a few times until the
switch’s login prompt appears.
Terminal Communication Parameters
Check that the terminal or modem’s communication settings match the settings
of the asynchronous port. By default, the asynchronous port (also known as the
Console, RS-232, or Config port) on the switch is set to the parameters shown
in Table 1 on page 12:
Table 1: Parameters for terminal communication
Parameter Value
Baud rate 9600
Data bits 8
Parity None
Stop bits 1
Flow control Hardware
Refer to the user manual supplied with the terminal or modem for details of
how to change the communications settings for the terminal or modem.
Software Release 2.6.1
C613-02030-00 REV B
Page 13

Getting Started with the Command Line Interface (CLI) 13
If a modem is connected, configure the switch to make and/or accept calls via
the modem. To set the CDCONTROL parameter to “CONNECT” and the
FLOW parameter to “HARDWARE”, enter the command:
SET ASYN CDCONTROL=CONNECT FLOW=HARDWARE
If the terminal or modem is used with communications settings other than the
default settings, then configure the asynchronous port to match the terminal or
modem settings using the SET ASYN command.
See the switch’s online help or the Interfaces chapter in the AT-8700XL Series
Software Reference for more information on how to configure the asynchronous
port.
Logging In
When you access the switch from a terminal or PC connected to the RS-232
terminal port (asyn0), or via a Telnet or HTTP connection, you must enter a
login name and password to gain access to the command prompt. When the
switch is supplied, it has a manager account with an initial password friend.
Enter your login name at the login prompt:
login: manager
Enter the password at the password prompt:
password: friend
After you log into the manager account you can enter commands from this
document and from the AT-8700XL Series Software Reference.
Assigning an IP Address
To configure the switch to perform IP routing (for example, to access the
Internet) you need to configure IP. You also need to configure IP if you want to
manage the switch from a Telnet session or with the GUI. For detailed
instructions on accessing the switch with the GUI, see “Accessing the Switch
via the GUI” on page 22.
First enable IP, using the command:
ENABLE IP
Then, add an IP address to each of the switch interfaces that you want to
process IP traffic.
Software Release 2.6.1
C613-02030-00 REV B
For the default VLAN, use the command:
ADD IP INTERFACE=vlan1 IPADDRESS=ipadd MASK=mask
where:
■ ipadd is an unused IP address on your LAN.
■ mask is the subnet mask (for example 255.255.255.0)
Page 14

14 AT-8700XL Series Switch User Guide
If IP addresses on your LAN are assigned dynamically by DHCP, you can set
the switch to request an IP address from the DHCP server, using the
commands:
ADD IP INTERFACE=vlan1 IPADDRESS=DHCP
ENABLE IP REMOTEASSIGN
You do not need to set the MASK parameter because the subnet mask received
from the DHCP server is used.
If you use DHCP to assign IP addresses to devices on your LAN, and you want to
manage the switch within this DHCP regime, it is recommended that you set your
DHCP server to always assign the same IP address to the switch. This will enable you
to access the GUI by browsing to that IP address, and will also let you use the switch as
a gateway device for your LAN. If you need the switch's MAC address for this, it can be
displayed using the command SHOW SWITCH.
To change the IP address for an interface, enter the command:
SET IP INTERFACE=interface IPADDRESS=ipadd MASK=ipadd
When you are configuring the switch remotely, if you change the configuration (for
example, the VLAN membership) of the port over which you are configuring, the switch
is likely to break the connection.
For more information about switch ports and Virtual LANs (VLANs), see
Chapter 5, Switching in this document, and the Switching chapter in the
AT-8700XL Series Software Reference. For more information about IP addressing
and switching, see Chapter 5, Switching in this document, and the Internet
Protocol (IP) chapter in the AT-8700XL Series Software Reference.
Assigning an IP Address
To configure the switch to perform IP routing (for example, to access the
Internet) you need to configure IP. You also need to configure IP if you want to
manage the switch from a Telnet session or with the GUI. For detailed
instructions on accessing the switch with the GUI, see “Accessing the Switch via
the GUI” on page 22.
First enable IP, using the command:
ENABLE IP
Then, add an IP address to each of the switch interfaces that you want to
process IP traffic. For example, for Ethernet port 0, use the command:
ADD IP INTERFACE=eth0 IPADDRESS=ipadd MASK=mask
where:
■ ipadd is an unused IP address on your LAN.
■ mask is the subnet mask (for example 255.255.255.0)
Software Release 2.6.1
C613-02030-00 REV B
Page 15

Getting Started with the Command Line Interface (CLI) 15
If IP addresses on your LAN are assigned dynamically by DHCP, you can set
the switch to request an IP address from the DHCP server, using the
commands (for Ethernet port 0, for example):
ADD IP INTERFACE=eth0 IPADDRESS=DHCP
ENABLE IP REMOTEASSIGN
You do not need to set the MASK parameter because the subnet mask received
from the DHCP server is used.
If you use DHCP to assign IP addresses to devices on your LAN, and you want to
manage the switch within this DHCP regime, it is recommended that you set your
DHCP server to always assign the same IP address to the switch. This will enable you
to access the GUI by browsing to that IP address, and will also let you use the switch as
a gateway device for your LAN. If you need the switch's MAC address for this, it can be
displayed using the command SHOW SWITCH.
To change the IP address for an interface, enter the command:
SET IP INTERFACE=interface IPADDRESS=ipadd MASK=ipadd
Setting Routes
The process of routing packets consists of selectively forwarding data packets
from one network to another. Your switch makes a decision to send a packet to
a particular network on information it learns dynamically from listening to the
selected route protocol and on the static information entered as part of the
configuration process. In addition, you can configure user-defined filters to
restrict the way packets are sent.
Your switch maintains a table of routes which holds information about routes
to destinations. The route table tells the switch how to find a remote network or
host. A route is uniquely identified by IP address, network mask, next hop,
ifIndex, protocol and policy. A list of routes comprises all the different routes to
a destination. The routes may have different metrics, next hops, policy or
protocol. A list of routes is uniquely identified by its IP address and net mask.
The routing table is maintained dynamically by using one or more routing
protocols such as RIP, EGP and OSPF. These act to exchange routing
information with other switches or hosts.
You can also add static routes to the route table to define default routes to
external switches or networks and to define subnets.
To add a static route, enter the command:
Software Release 2.6.1
C613-02030-00 REV B
ADD IP ROUTE=ipadd INTERFACE=interface NEXTHOP=ipadd
[CIRCUIT=miox-circuit] [DLCI=dlci]
[MASK=ipadd][METRIC=1..16] [METRIC1=1..16]
[METRIC2=1..65535][POLICY=0..7] [PREFERENCE=0..65535]
To displays the entire routing table, including both static and dynamic routes,
enter the command:
SHOW IP ROUTE
For more information about setting IP routes, see the Internet Protocol (IP)
chapter in the AT-8700XL Series Software Reference.
Page 16

Changing a Password
You should change this password to prevent unauthorised access to the switch.
Enter the command:
SET PASSWORD
The switch prompts you for the current password, for the new password, and
for confirmation of the new password. The password can contain any printable
characters, and must be at least a minimum length, by default six characters.
(To change the default minimum length, see the SET USER command in the
Operations chapter, AT-8700XL Series Software Reference.)
Choosing a Password
All users, including managers, should take care in selecting passwords. Tools
exist that enable hackers to guess or test many combinations of login names
and passwords easily. The User Authentication Facility (UAF) provides some
protection against such attacks by allowing the manager to set the number of
consecutive login failures allowed and a lockout period when the limit is
exceeded.
However, the best protection against password discovery is to select a good
password and keep it secret. When choosing a password:
■ Do make it six or more characters in length. The UAF enforces a minimum
password length, which the manager can change. The default is six
characters.
■ Do include both alphabetic (a–z) and numeric (0–9) characters.
■ Do include both uppercase and lowercase characters. The passwords
stored by the switch are case-sensitive, so “bgz4kal” and “Bgz4Kal” are
different.
■ Do avoid words found in a dictionary, unless combined with other random
alphabetic and numeric characters.
■ Do not use the login name, or the word “password” as the password.
■ Do not use your name, your mother’s name, your spouse’s name, your
pet’s name, or the name of your favourite cologne, actor, food or song.
■ Do not use your birth date, street number or telephone number.
■ Do not write down your password anywhere.
Make sure you remember the new password created as you cannot retrieve a
lost password. Recovery of access to the switch is complex.
Once you have logged into the manager account you are able to enter
commands from this guide and from the AT-8700XL Series Software Reference.
Page 17

Getting Started with the Command Line Interface (CLI) 17
Using the Commands
You control the switch with commands described in this document and in the
AT-8700XL Series Software Reference. While the keywords in commands are not
case sensitive, the values entered for some parameters are (especially
passwords). The switch supports command line editing and recall. Command
line editing functions and keystrokes are shown in Table 2 on page 17.
Table 2: Command line editing functions and keystrokes .
Function VT100 Terminal Dumb terminal
Move cursor within command line ←, → Not available
Delete character to left of cursor [Delete] or [Backspace] [Delete] or [Backspace]
Toggle between insert/overstrike [Ctrl/O] Not available
Clear command line [Ctrl/U] [Ctrl/U]
Recall previous command ↑ or [Ctrl/B] [Ctrl/B]
Recall next command ↓ or [Ctrl/F] [Ctrl/F]
Display command history [Ctrl/C] or
SHOW PORT HISTORY
Clear command history RESET PORT HISTORY RESET PORT HISTORY
Recall matching command [Tab] or [Ctrl/I] [Tab] or [Ctrl/I]
[Ctrl/C]
or SHOW PORT HISTORY
The switch assumes that the width of the terminal screen is 80 characters, and
performs command line wrapping at the 80th column regardless of the setting
of the terminal. To execute a command the cursor does not need to be at the
end of the line. The default editing mode is insert mode. Characters are
inserted at the cursor position and any characters to the right of the cursor are
pushed to the right to make room. In overstrike mode, characters are inserted
at the cursor position and replace any existing characters.
Commands are limited to 1000 characters, excluding the prompt. Path names
of up to 256 characters, including file names, and file names up to 16 characters
long, with extensions of 3 characters, are supported.
Aliases
The command line interface supports aliases. An alias is a short name for an
often-used longer character sequence. When the user presses [Enter] to execute
the command line, the command processor first checks the command line for
aliases and substitutes the replacement text. The command line is then parsed
and processed normally. Alias substitution is not recursive—the command line
is scanned only once for aliases.
Aliases are created and destroyed using the commands:
ADD ALIAS=name STRING=substitution
DELETE ALIAS=name
Software Release 2.6.1
C613-02030-00 REV B
Page 18

18 AT-8700XL Series Switch User Guide
Getting Command Line Help
Online help is available for all switch commands. A multilingual, languageindependent online help facility provides help information via the command:
HELP [topic]
If a topic is not specified, a list of available topics is displayed. The HELP
command displays information from the system help file stored in FLASH
memory. The help file uses a simple mark-up language to identify topics,
access level (USER or MANAGER) and help text. Both standard ASCII and
Unicode character encodings are supported. Alternate help files can be
uploaded and stored in FLASH, then activated using the command:
SET HELP=helpfile
To display the current help file, enter the command:
SHOW SYSTEM
The help file is easily modified, for example to provide detailed site-specific
support information. The mark-up language specification and preprocessor
program are available from your authorised distributor or reseller.
Also, typing a question mark “?” at the end of a partially completed command
displays a list of the parameters that may follow the current command line,
with the minimum abbreviations in uppercase letters (see Figure 1 on page 18).
The current command line is then re-displayed, ready for further input.
Figure 1: Using the question mark character (“?”) to display help for the current command.
Manager > ADD ?
Options : ACC APPletalk BGP CLASSifier BOOTp BRIDge DECnet FRamerelay GRE IP IPX
ISDN LAPD LOG MIOX NTP OSPF PERM PPP RADius SA SCript SNmp STReam STT TRIGger
TACacs USEr X25C X25T TDM
Manager > ADD ACC ?
Options : CALL SCript DOmainname
Manager > ADD ACC CALL ?
Options : DIrection DScript CScript RScript POrt ENcapsulation AUthentication
DOmainname
Setting System Parameters
You can set some general system parameters to ensure the switch’s
compatibility with the public network, and to aid network administration.
Some services, for instance ISDN, use slightly different versions in different
countries. To make sure that the switch uses protocols consistent with the
services it is connected to, set the system territory to the country or region in
which your switch operates. Enter the command:
SET SYSTEM TERRITORY={AUSTRALIA|CHINA|EUROPE|JAPAN|KOREA|
NEWZEALAND|USA}
Software Release 2.6.1
C613-02030-00 REV B
Page 19

Getting Started with the Command Line Interface (CLI) 19
In Australia only: to use the Micro service, SET SYSTEM LOCATION=australia; to
use the OnRamp service, SET SYSTEM LOCATION=europe.
System name, location and contact parameters can help a remote network
administrator identify the switch. By convention the system name is the full
domain name. Set the name of the switch, for example:
SET SYSTEM NAME=nd1.co.nz
the location of the switch, for example:
SET SYSTEM LOCATION=”Head Office, 3rd floor east”
and a contact name and phone number for the network administrator
responsible for the switch, for example:
SET SYSTEM CONTACT=”Anna Brown 03-456 789”
The name, location, and contact are strings 1 to 80 characters in length of any
printable character. If the string includes spaces enclose the string in double
quotes.
Set the switch’s real time clock to the current local time in 24 hour notation
(hh:mm:ss), for example:
SET TIME=14:50:00
and to the current date (dd-mmm-yy, or dd-mmm-yyyy), for example:
SET DATE=29-JAN-02
or
SET DATE=29-JAN-2003
Software Release 2.6.1
C613-02030-00 REV B
Page 20

Page 21

Chapter 3
Getting Started with the Graphical User Interface (GUI)
This Chapter
This chapter describes how to access the switch’s HTTP-based Graphical User
Interface (GUI), and provides basic information about using the GUI,
including:
■ What is the GUI?
• an introduction to the Graphical User Interface
■ Accessing the switch via the GUI:
• browser and PC setup, including interaction with HTTP proxy servers
• establishing a connection to your switch, including an example of
configuring SSL for secure access
• the System Status page, the first GUI page you see
■ Using the GUI: navigation and features:
• an overview of the menus
• using configuration pages, with a description of key elements of GUI
pages
• changing your password
• using the context sensitive online help
• saving your configuration
• combining GUI and CLI configuration
• configuring multiple devices
■ Upgrading the GUI
■ Troubleshooting
• diagnosing and solving connection problems
• using the GUI to troubleshoot the switch’s configuration.
Page 22

22 AT-8700XL Series Switch User Guide
What is the GUI?
The GUI (Graphical User Interface) is a web-based device management tool,
designed to make it easier to configure and monitor the switch. The GUI
provides an alternative to the CLI (Command Line Interface). Its purpose is to
make complicated tasks simpler and regularly performed tasks quicker.
The GUI relies on an HTTP server that runs on the switch, and a web browser
on the host PC. When you use the GUI to configure the switch, the GUI sends
commands to the switch and the switch sends the results back to your browser,
all via HTTP.
The tasks you may perform using the GUI are not as comprehensive as the
command set available on the CLI, but for some protocols, a few clicks of the
mouse will perform many commands.
The GUI is stored on the switch in the form of an embedded resource file, with
file extension
version encoded in the file name.
rsc. Resource files are model-specific, with the model and
Accessing the Switch via the GUI
To use the GUI to configure the switch, you use a web browser to open a
connection to the switch’s HTTP server. Therefore, you need a PC, a web
browser and the switch. Supported browsers and operating systems, and the
settings you need on your PC and browser, are detailed in the following
section. Switch setup is detailed in “Establishing a Connection to the Switch” on
page 24.
Browser and PC Setup
The GUI requires a web browser installed on a PC. Table 3 shows supported
combinations of operating system and browser. A copy of Internet Explorer can
be found on the switch’s Documentation and Tools CD-ROM.
Table 3: Supported browsers and operating systems
IE 5.0 IE 5.5 IE 6.0 NS 6.2.2 NS 6.2.3
Windows 95
Windows 98 !!!
Windows ME !!!!!
Windows 2000 !!!!!
Windows XP !!!!!
!
JavaScript must be enabled. To enable JavaScript in Internet Explorer:
1. From the Tools menu, select Internet Options
2. Select the Security tab
3. Click on the Custom Level button
4. Under the Scripting section, ensure that “Active scripting” is enabled.
Software Release 2.6.1
C613-02030-00 REV B
Page 23
Getting Started with the Graphical User Interface (GUI) 23
To enable JavaScript in Netscape 6.2.x:
1. From the Edit menu, select Preference
2. Select the Advanced menu option.
3. Ensure that the “Enable JavaScript for Navigator” checkbox is checked.
The minimum screen resolution on the PC is 800x600.
HTTP Proxy Servers
An HTTP proxy server provides a security barrier between a private network’s
PCs and the Internet. The PCs send HTTP requests (and other web traffic) to
the server, which then forwards the requests appropriately. Similarly, the server
receives incoming HTTP traffic addressed to a PC on the private network, and
forwards it to the appropriate PC. Proxy servers can be used to block traffic
from undesirable websites, to log traffic flows, and to disallow cookies.
If your browser is configured to use a proxy server, and the switch is on your
side of the proxy server, you will need to set the browser to bypass proxy
entries for the IP address of the appropriate interface on the switch. (See
“Establishing a Connection to the Switch” on page 24 for information about
giving switch interfaces IP addresses.)
To ensure that your network’s security settings are not compromised, see your
network administrator for information about bypassing the proxy server on
your system.
To bypass the proxy server on Internet Explorer, if your browser administration
does not use a script, and the PC and the switch are in the same subnet:
1. From the Tools menu, select Internet Options.
2. Select the Connections tab and click the LAN Settings button.
3. Check the “Bypass proxy server for local addresses” checkbox.
4. If necessary, click the Advanced button and enter a list of local addresses.
To bypass the proxy server on Netscape, if your browser does not use a script:
1. From the Edit menu, select Preferences
2. Click on the Advanced menu option to expand it.
3. Select the Proxies menu option
4. Enter the switch’s IP address in the “No Proxy for” list.
Software Release 2.6.1
C613-02030-00 REV B
Page 24
Establishing a Connection to the Switch
Before you start, consider how the switch fits into your network. If you are
installing a new switch, consider whether you want to configure it before
deploying it into the LAN, or want to configure it in situ. If you want to access
a switch that has already been configured, consider the relative positions of the
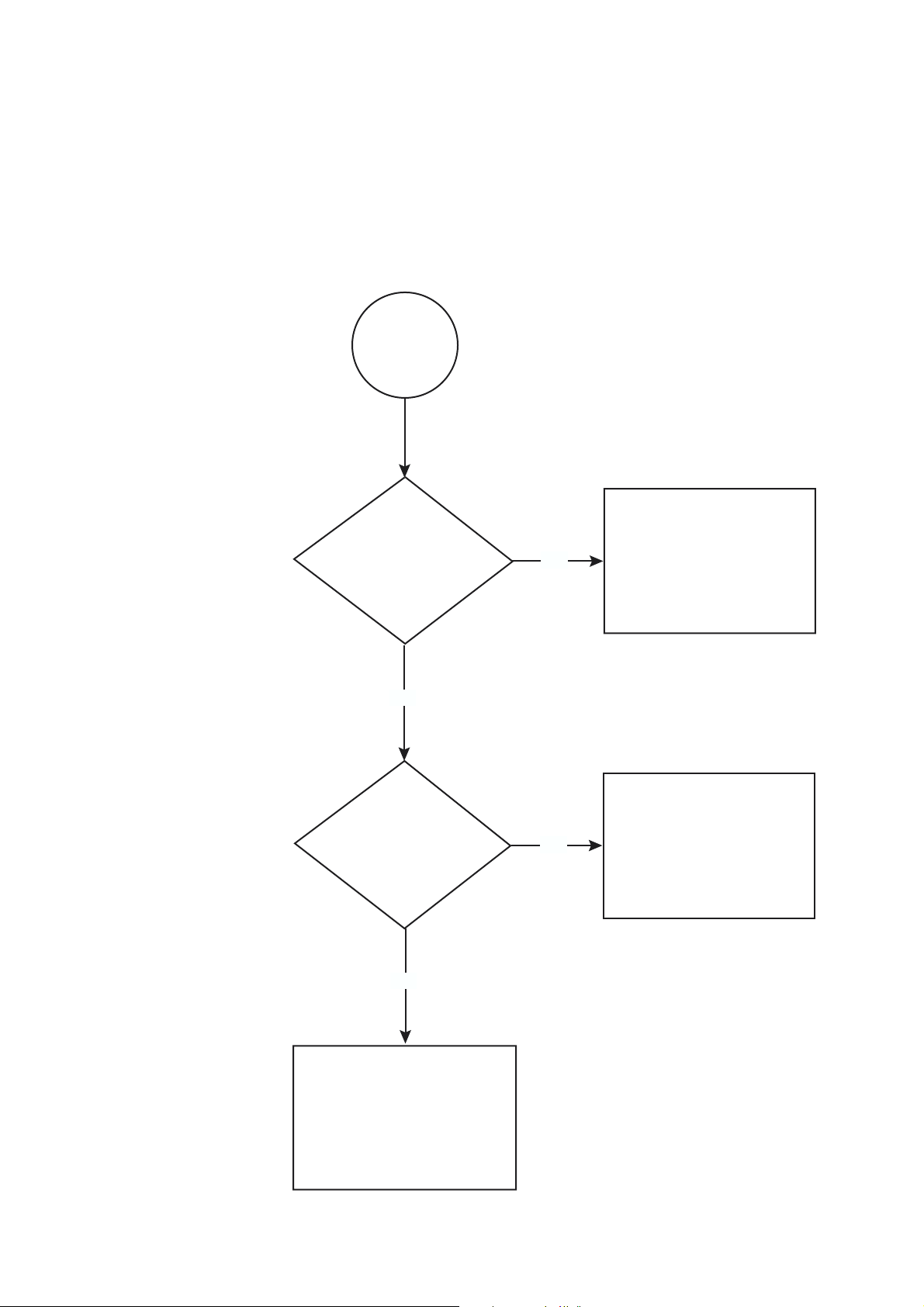
PC and the switch. The flow chart below summarises this process, and the
procedures that follow take you through each possibility in detail.
Figure 2: A summary of the process for establishing a connection via the GUI.
Start here
Determine the IP address
Is the router
already installed and
configured in
the LAN?
Ye s
of an interface on the router
and browse to it.
See “Option 3: Connecting
to an Installed Switch” on
page 28.
No
Do you want
to configure the router
before installing it in
the LAN?
No
Install the router into the LAN,
give it an IP address and
browse to it.
See “Option 2: Installing
the Switch into the LAN”
on page 26.
Connect your PC directly to
the router, give the router an
IP address and browse to it.
Ye s
See “Option 1: Configuring
the Switch before
Installation” on page 25.
Page 25

Getting Started with the Graphical User Interface (GUI) 25
Option 1: Configuring the Switch before Installation
Use this procedure if:
■ You want to configure the switch before installing it in your LAN.
■ You will be installing the switch at a remote office or a customer site and
want to configure it first.
■ You want a dedicated management PC permanently connected to the
switch.
1. Select a PC to browse to the switch from
You can browse to the switch from any PC that is running a supported
operating system with a supported browser installed. See “Browser and
PC Setup” on page 22 for more information.
You need to know the PC’s subnet.
2. Connect the PC to the switch
Use a straight-through Ethernet cable to connect an Ethernet card on the
PC to any one of the switch ports (see Figure 3).
Figure 3: Connecting a PC directly to the switch.
AT-8724XL
Advanced Fast Ethernet Switch
AT-8700XL
You can browse to the switch through any VLAN, as long as you give that VLAN an IP
address (see below). These instructions assume you will use vlan1. The switch ports all
belong to vlan1 by default.
3. Access the switch’s command line interface
Access the CLI from the PC, as described in “Connecting a Terminal or PC”
on page 12.
4. Enable IP
ENABLE IP
5. Assign the vlan1 interface an IP address in the same subnet as the PC
ADD IP INTERFACE=vlan1 IP=ipaddress MASK=mask
Software Release 2.6.1
C613-02030-00 REV B
6. Save the configuration and set the switch to use it on bootup
CREATE CONFIG=your-name.cfg
SET CONFIG=your-name.cfg
7. On the PC, bypass the HTTP proxy server, if necessary
See “HTTP Proxy Servers” on page 23 for more information.
8. Point your web browser at the LAN interface’s IP address
Page 26

26 AT-8700XL Series Switch User Guide
9. At the login prompt, enter the user name and password
The default username is manager:
User Name: manager
Password: friend
The System Status page is displayed (Figure 6 on page 31). Select options
from the sidebar menu to configure and manage the switch.
Option 2: Installing the Switch into the LAN
Use this procedure if:
■ You want to install the switch into the LAN before you configure it.
1. Select a PC to browse to the switch from
You can browse to the switch from any PC that is running a supported
operating system with a supported browser installed, with JavaScript
enabled. See “Browser and PC Setup” on page 22 for more information.
You need to know the PC’s subnet.
2. Plug the switch into the LAN
To i n st al l th e switch into the same subnet as the PC:
Use an Ethernet cable to connect one of the switch ports to a device on the
LAN segment, for example, a hub, router or switch (see Figure 4).
Figure 4: Connecting the switch into the same LAN segment as the PC
AT-8724XL
Advanced Fast Ethernet Switch
AT-8700XL
To i n st al l th e switch into a different subnet than the PC:
Use an Ethernet cable to connect any one of the switch ports to a device on
the LAN segment in which you require the switch to work, for example, a
hub, router or switch (see Figure 5).
Figure 5: Configuring the switch from a PC in another subnet.
gateway
subnet
subnet
AT-8700XL Series Switch
AT-8724XL
Advanced Fast Ethernet Switch
Software Release 2.6.1
C613-02030-00 REV B
Page 27

Getting Started with the Graphical User Interface (GUI) 27
You can browse to the switch through any VLAN, as long as you give that VLAN an IP
address (see below). These instructions assume you will use vlan1. The switch ports all
belong to vlan1 by default.
3. Access the switch’s command line interface
Access the CLI from the PC, as described in “Connecting a Terminal or PC”
on page 12.
4. Enable IP
ENABLE IP
5. Assign the vlan1 interface an IP address
ADD IP INTERFACE=vlan1 IP=ipaddress MASK=mask
If you use DHCP to assign IP addresses to devices on your LAN, and you want to
manage the switch within this DHCP regime, it is recommended that you set your
DHCP server to always assign the same IP address to the switch. This will enable you
to access the GUI by browsing to that IP address, and will also let you use the switch as
a gateway device for your LAN. If you need the switch's MAC address for this, you can
display it using the command SHOW SWITCH. To set the interface to obtain its IP
address by DHCP, use the commands:
ADD IP INTERFACE=VLAN1 IPADDRESS=DHCP and
ENABLE IP REMOTEASSIGN.
6. If the PC you want to browse from is in a different subnet from the switch,
give the switch a route to the PC
ADD IP ROUTE=PC-subnet INTERFACE=vlan1
NEXTHOP=gateway-ipaddress
where:
• PC-subnet is the IP subnet address of the PC. For example, if the PC has
an IP address of 192.168.6.1 and a mask of 255.255.255.0, its subnet
address is 192.168.6.0.
• gateway-ipaddress is the IP address of the gateway device that connects
the PC’s subnet with the switch’s subnet (Figure 5 on page 26).
7. If you want to be able to browse to the GUI securely, configure SSL (Secure
Sockets Layer)
See “Secure Access” on page 29 for more information.
8. Save the configuration and set the switch to use it on bootup
CREATE CONFIG=filename.cfg
SET CONFIG=filename.cfg
9. On the PC, bypass the HTTP proxy server, if necessary
See “HTTP Proxy Servers” on page 23 for more information.
Software Release 2.6.1
C613-02030-00 REV B
10. Point your web browser at the LAN interface’s IP address
For normal access, point your web browser to
http://ip-address
Page 28

For secure access, point your web browser to
https://ip-address
where ip-address is the interface’s IP address.
11. At the login prompt, enter the user name and password
The default username is manager:
User Name: manager
Password: friend
The System Status page is displayed (see Figure 6 on page 31). Select
options from the sidebar menu to configure and manage the switch.
Option 3: Connecting to an Installed Switch
Use this procedure if:
■ At least one interface on the switch already has an IP address, and the
switch is already installed in a LAN.
1. Find out the IP address of the switch’s interface
Ask your system administrator. Alternatively, access the CLI, as described
in “Connecting a Terminal or PC” on page 12, and enter the command:
SHOW IP INTERFACE
You can browse to the switch through any VLAN, as long as you give that VLAN an IP
address (see below). These instructions assume you will use vlan1. The switch ports all
belong to vlan1 by default.
2. Select a PC
You can browse to the GUI from any PC that:
• has an IP address in the same subnet as the switch, or that the switch
has a route to
• is running a supported operating system
• has a supported browser installed, with JavaScript enabled
See “Browser and PC Setup” on page 22 for more information.
3. If necessary, bypass the HTTP proxy server
See “HTTP Proxy Servers” on page 23 for more information.
4. Browse to the switch
For normal access, point your web browser to
http://ip-address
where ip-address is the interface’s IP address.
To access the switch securely if SSL (Secure Sockets Layer) has been
configured on the interface, point your web browser to
https://ip-address
For more information about secure access, see “Secure Access” on page 29.
Page 29

Getting Started with the Graphical User Interface (GUI) 29
5. At the login prompt, enter the user name and password
The default username is manager:
User Name: manager
Password: friend
The System Status page is displayed (see Figure 6 on page 31). Select
options from the sidebar menu to configure and manage the switch.
Secure Access
You can optionally browse to the switch using Secure Sockets Layer (SSL). This
means that sensitive data including passwords and email addresses can not be
accessed by malicious parties. This section details the required configuration.
For information about SSL, refer to the Secure Sockets Layer (SSL) chapter of
your Software Reference.
For this configuration to succeed your switch must have PKI, ISAKMP, SSH and SSL
feature licences. If these licences are not already present on your switch, please contact
your authorised distributor or reseller.
To secure your switch’s HTTP Server with SSL for secure switch
management via the GUI.
1. Create a Security Officer user account
Only a user with Security Officer privilege can enable system security and SSL.
To add a user with the login name “CIPHER”, password “sbr4y3”,
login=yes, and SECURITY OFFICER privilege, use the command:
ADD USER="CIPHER" PASSWORD="sbr4y3"
PRIVILEGE=SECURITYOFFICER Login=yes
CREATE CONFIG=ssl.cfg
RESTART SWITCH
2. Login as a Security Officer
To login as the user with Security Officer privilege called “CIPHER”, use
the command:
LOGIN CIPHER
And then enter the password for “CIPHER”, “sbr4y3”.
3. Enable system security
Software Release 2.6.1
C613-02030-00 REV B
To enable system security, use the command:
ENABLE SYSTEM SECURITY
4. Create an RSA key pair for this switch.
To create an RSA key pair, use the command:
CREATE ENCO KEY=0 TYPE=RSA LENGTH=1024
5. Set the switch’s distinguished name.
Page 30

30 AT-8700XL Series Switch User Guide
To set the switch’s distinguished name to
"cn=switch1,o=my_company,c=us", use the command:
SET SYSTEM DISTINGUISHEDNAME="cn=switch1,
o=my_company,c=us"
6. Set the UTC offset.
To set the Universal Coordinated Time to inform the switch that the
difference between local time and GMT is 7 hours, use the command:
SET LOG UTCOFFSET=7
7. Create a self-signed certificate for the switch.
To create a PKI certificate without contacting a CA for browsing to the GUI,
use the command:
CREATE PKI CERTIFICATE=cer_name KEYPAIR=0
SERIALNUMBER=12345 SUBJECT="cn=172.30.1.105,
o=my_company, c=us"
Using this command creates a certificate that is only suitable for secure switch
management via the GUI. A pop-up message will appear in the browser
window warning that the certificate is not issued by a trusted authority. For
details, see the Public Key Infrastructure (PKI) chapter of your Software
Reference.
8. Load self-signed switch certificate
To load the signed switch certificate onto the switch, use the command:
ADD PKI CERTIFICATE=cer_name LOCATION=cer_name.cer
TRUST=YES
9. Enable SSL on the HTTP server
To enable SSL on the HTTP server with previously created SSL Key and the
port 443, use the command:
SET HTTP SERVER SECURITY=ON SSLKEY=0 PORT=443
10. Configure an IP interface to run SSL over
To configure an IP interface that SSL will be run over, first enable IP using
the command:
ENABLE IP
To mak e VLAN1 the IP interface, and 172.30.1.105 the interface’s IP address,
use the command:
ADD IP INTERFACE=vlan1 IP=172.30.1.105
To add an IP route on this interface with a next hop of 172.30.1.254, use the
command:
ADD IP ROUTE=0.0.0.0 INTERFACE=vlan1 NEXT=172.30.1.254
For this example to succeed, you would have to log in as “cipher” rather than “manager”
when connecting to the switch with a web browser.
Software Release 2.6.1
C613-02030-00 REV B
Page 31

Getting Started with the Graphical User Interface (GUI) 31
System Status
The GUI opens to display the System Status page. Figure 6 points out key
information contained on the page.
Figure 6: The System Status page
Model name
Software release
Help, Save and Exit
Sidebar menu
Port status
System status
Software Release 2.6.1
C613-02030-00 REV B
Page 32

32 AT-8700XL Series Switch User Guide
Using the GUI: Navigation and Features
The GUI consists of a large number of pages, which you navigate between using
the menu on the left of the browser window. This section describes how to use
the GUI, and gives an overview of its functionality.
The Configuration Menu
You can use the GUI to configure:
• the system identity and mail server
• the system time, or NTP (Network Time Protocol)
• triggers, to automatically run scripts at a time you specify or in response
to events you specify
• ping polling, to monitor device reachability and respond to changes in
reachability
• SNMP (Simple Network Management Protocol)
• switch port settings, including mirroring, trunking and storm limits
• 802.1x port security
• VLANs, STP and GARP
• Internet Protocol: interfaces, static routes, the preferences of dynamic
routes, RIP, multicasting, and OSPF
• Quality of Service and traffic filters
Using Configuration Pages
Most protocols are configured by creating or adding an entry - an IP route, a
PIM interface, and so on. For such protocols, configuration with the GUI is
based on sets of three pages: first you see a “summary” page, and from that
you access an “add” page and a “modify” page. Complex protocols are subdivided into different tabs, each with their own summary, add and modify
pages.
Only one person can configure a particular switch with the GUI at a time, to avoid
clashes between configurations. Monitoring and diagnostics pages can be viewed by
more than one user at a time.
Use the menus and buttons on the GUI pages to navigate, not your browser’s buttons,
to ensure that the configuration settings are saved correctly.
The summary page displays a selection table of existing items and information
about them (for example, existing PIM interfaces; see Figure 7 on page 33).
Below the selection table is a row of buttons, labelled Add, Modify and
Remove.
To add a new item, click the Add button. This opens the popup “add” page,
which lets you create a new item (for example, configure a new PIM interface;
see Figure 8 on page 33).
Software Release 2.6.1
C613-02030-00 REV B
Page 33

Getting Started with the Graphical User Interface (GUI) 33
To modify an existing item, select it by clicking on the option button at the
beginning of its entry in the selection table. Then click the Modify button. This
opens the popup “modify” page, which lets you expand or change the
configuration (for example, change the Hello interval for a PIM interface; see
Figure 9 on page 34).
To delete or destroy an item, select it by clicking on the option button at the
beginning of its entry in the selection table. Then click the Remove button.
Figure 7: An example of a configuration page with a selection table
Ta bs
Heading row
Radio button
Add, Modify and
Remove buttons
Select list
Text field
Figure 8: An example of a popup “add” page
Apply and Cancel
Software Release 2.6.1
C613-02030-00 REV B
buttons
Page 34

34 AT-8700XL Series Switch User Guide
Figure 9: An example of a popup “modify” page
Non-editable field
Editable Fields
GUI pages allow you to enter values or select options through a range of field
types. These include:
• text fields, to enter character strings or numbers, especially for fields
where there are few limits on the entries (such as names). See the online
help for valid characters and field length
• select lists, to select one option from a small number of possibilities.
Only valid options are listed. For example, if you are asked to select an
IP interface from a drop-down list, the only interfaces displayed will be
those you have assigned an IP address to
• radio button lists, to choose one of a set of mutually-exclusive options
• checkboxes, to enable or disable features.
Software Release 2.6.1
C613-02030-00 REV B
Page 35

Getting Started with the Graphical User Interface (GUI) 35
Ports Graphic
Pages on which you can select switch ports use a Ports graphic - a visual
representation of the switch ports.To toggle through the selection options, click
on the icon representing the port you want to select or deselect.
Apply Button
An Apply button applies the configuration settings on the page or the section
of the page. The new settings will take effect immediately, but are not
automatically saved. To save the settings after clicking Apply, click the Save
button above the menu.
Cancel Button
A Cancel button closes a popup page without making any changes to the
configuration.
Close Button
A Close button closes a popup page, and conserves any changes that you made
to the settings on the page by clicking on buttons like Add, Modify, Remove or
Apply. Changes you made to editable fields will not be conserved when you
click Close (unless you first clicked Apply).
The Management Menu
You can use the GUI to manage the switch itself, including:
• creating user accounts and enabling system security
• creating and editing files
• backing files up to the switch’s Flash memory or to a PC or TFTP server
• restoring the switch’s configuration from backup
• specifying which software and configuration files the switch uses on
bootup, and displaying the currently-used files
Software Release 2.6.1
C613-02030-00 REV B
• enabling software release and feature licences
• upgrading the switch’s software
Page 36

36 AT-8700XL Series Switch User Guide
The Monitoring Menu
When you browse to the GUI, the sidebar menu opens to display the
monitoring menu, opened at the System > Status. From this menu, you can also
check:
• information about the switch’s hardware
• information about traffic over each port
• the Layer 2 Forwarding Database, which shows the MAC addresses
that the switch ports have learned, and out which port the switch will
switch traffic to each MAC address
• information about Address Resolution Protocol (ARP) entries
•the IP route table
• information about the state of ping polling, including counters
• the log messages that the switch automatically generates. You can also
set up filters to determine where messages are saved to and which
messages are saved.
The Diagnostics Menu
The GUI’s diagnostics pages enable you to troubleshoot network problems and
observe traffic flow, including:
• displaying the number of good and bad packets received and
transmitted over each switch port
• displaying the number of frames related to 802.1x port authentication
received and transmitted over each authenticator and supplicant
• displaying STP and GARP counters
• displaying the number and type of packets received and transmitted by
IP, and discarded by the IP gateway
• displaying the number and type of ICMP and UDP packets received
and transmitted
• displaying the number and type of RIP packets received and
transmitted; and the octets received and transmitted over each IP route
• displaying the contents of the switch’s file system and how much
memory is used and available. You can also delete files
• an interface to the switch’s command line interface, allowing you to
enter CLI commands.
Changing the Password
As a security precaution, change the password as soon as possible.
To change the password of the default Manager account, select Management >
Users from the sidebar menu. Select the Manager account and click Modify.
For information about passwords, see “Changing a Password” on page 16.
Software Release 2.6.1
C613-02030-00 REV B
Page 37

Getting Started with the Graphical User Interface (GUI) 37
Context Sensitive GUI Help
The GUI’s context-sensitive help system is displayed in a pop-up window
which covers the title of the GUI page. You can move the banner to any part of
your screen and/or resize it. To display the help, click on the Help button
Help button
above the sidebar menu or on the page for which you require assistance. Three
types of help are available:
■ Click General Page Info to see brief background and process flow
information. The General Page Info displays when you click the Help
button.
■ Click Page Element Info and roll your mouse over an element, to see
information about that element.
To freeze the banner’s display so that the help does not change when you
move the mouse, press the [Ctrl] key. To unfreeze, press [Ctrl] again. Note
that element information is not available for entries in tables. To see
descriptions of the columns of tables, click Complete Help Page.
■ Click Complete Help Page to see all available information, including the
element information, in a separate printable window.
Save button
Saving Configuration Entered with the GUI
Configuration changes applied using the GUI can be saved to a configuration
script by clicking the Save button at the top of the sidebar menu. A pop-up
Save window gives you the option of saving to the current configuration file,
another existing file, or a new file. You can also choose to use this configuration
at bootup.
When the Save button is red, this indicates that changes have been made to the
configuration and not yet saved. If you attempt to exit the GUI without saving
the configuration, a pop-up window will allow you to choose whether or not to
save.
Combining GUI and CLI Configuration
You can alternate between the GUI and the CLI without difficulty. Note that
GUI pages will not automatically refresh to reflect changes in the CLI
configuration; you must reload the relevant page (for example, by clicking the
Refresh button on your browser).
Configuring Multiple Devices
If you are configuring a number of switches with similar requirements, you
may wish to:
Software Release 2.6.1
C613-02030-00 REV B
1. Configure one device, using either the CLI or the GUI
2. Save that configuration. This creates a configuration file, stored in the
switch’s FLASH memory. The file consists of a sorted list of the CLI
commands that make up the configuration
3. Upload that file to a PC, using either the CLI or the GUI
4. Open the file in a text editor, make changes as required, and download the
file onto each switch you need to configure.
Page 38

38 AT-8700XL Series Switch User Guide
Upgrading the GUI
You can download the latest GUI resource file from the support site at
http://www.alliedtelesyn.co.nz/support/at8700xl
switch is running the most recent release and patch files. The GUI is not part of
the firmware release file, but the most recent resource file will generally only be
compatible with the most recent software release. To check which files the
switch is running, refer to the “Current Install” section of the command:
SHOW INSTALL
If you are updating both the release and the resource file, set the preferred
release and restart the switch before installing the GUI as described below.
To upgrade the GUI
1. If required, delete the old GUI resource file
If required, you can store more than one GUI resource file on the switch at
a time. If you want to delete the previous GUI resource file (for example, to
save memory), you must first disable the GUI, using the command:
DISABLE GUI
. Before you start, ensure that the
Then delete the GUI resource file, using the command:
DELETE FILE=old-gui.rsc
where:
• old-gui.rsc is the name of the GUI resource file that you are replacing.
Wait until FLASH compaction has finished. This will take several minutes.
Do not interrupt the switch’s power supply during FLASH compaction, under
any circumstances.
If you have multiple valid resource files and releases stored on the switch, use the SET
INSTALL command to change the release and resource file the switch uses (see below).
2. Load the new file onto the switch
Download the GUI resource file for your model of switch from the website
to your TFTP server. Do not rename the file.
Resource files use a fixed naming convention, which includes a product code, a language
code and a version code. If you change the GUI resource file’s name, the switch will not
recognise it as a valid file and you will be unable to use it for configuration.
Load the GUI resource file from your TFTP server to the switch, using the
command:
LOAD FILE=filename.rsc SERVER=server
where:
• filename is the name of the GUI resource file, as shown on the support
site for your switch. Do not rename the file.
• server is the IP address of the TFTP server the file is loaded from.
Software Release 2.6.1
C613-02030-00 REV B
Page 39

Getting Started with the Graphical User Interface (GUI) 39
When the switch has loaded the file into its RAM, it displays the message
“File transfer successfully completed”. It then writes the file to FLASH
memory, which takes approximately 30 seconds after the message. Once
the file has been copied to FLASH, you can enter commands that refer to it.
3. Install the new file as the preferred GUI
If you are updating both the release and the resource file, set the preferred
release and restart the switch before installing the GUI as described below.
To set the new GUI resource file as the preferred resource file, use the
command:
SET INSTALL=preferred GUI=filename.rsc
You can use the GUI to load the new resource file onto the switch
(Management > Software > Upgrade), but you need to use the CLI to
install the new file.
If you disabled the GUI to delete the old resource file, enable it again, using
the command:
ENABLE GUI
Check that the new GUI resource file is valid for your device, using the
command:
SHOW GUI
If it is not, or if the file was corrupted during the download, disable the
GUI, delete the file and try again.
4. Point your web browser at the switch’s IP address
Your browser may have a local copy of the old GUI file stored. If so, you
need to delete these temporary files (see “Deleting Temporary Files” on
page 40).
Troubleshooting
The GUI resource file has an 8-digit name, with the file extension rsc. To check
which resource files are present on the switch, use the command:
SHOW FILE
To see which GUI resource file the switch is currently using, and which it will
use on bootup, use the command:
SHOW INSTALL
To display information about the GUI resource file that is currently installed,
use the command:
Software Release 2.6.1
C613-02030-00 REV B
SHOW GUI
In particular, this command lets you check the file’s validity. If the file is invalid
or damaged, download a new file.
To display information about the switch’s HTTP server, use the commands:
SHOW HTTP SERVER
SHOW HTTP SERVER SESSION
Page 40

40 AT-8700XL Series Switch User Guide
Deleting Temporary Files
Browsers store local copies of web pages as temporary files. If you upgrade to a
new GUI resource file, or if you encounter problems in browsing to the GUI,
you may need to delete these files (clear the cache). To clear the cache in
Internet Explorer:
1. From the Tools menu, select Internet Options.
2. On the General tab, click the Delete Files button.
3. The Delete Files dialog box opens. Click the OK button.
To clear the cache in Netscape 6.2.x:
1. From the Edit menu, select Preferences
2. Click on the Advanced menu option to expand it.
3. Select the Cache menu option
4. Click the Clear Memory Cache and Clear Disk Cache buttons.
Accessing the Switch via the GUI
Problem You cannot browse to the switch.
Diagnosis Check if you can ping the switch’s interface from your PC. If you get a
response, this indicates that the interface’s IP address is valid, and that your PC
has a route to it.
Solution
■ If you cannot ping the switch’s interface:
• Check that your PC’s gateway is correct, so that your PC has a route to
the switch.
• The IP address of the switch’s interface may be incorrect. To correct this,
access the CLI and use the IPADDRESS parameter of command SET IP
INTERFACE
• The IP address of the switch’s default gateway may be incorrect, so that
the switch does not have a route back to your PC’s gateway. To correct
this, access the CLI and use the NEXTHOP parameter of the command
ADD IP ROUTE or SET IP ROUTE.
■ If the switch should be dynamically assigned an IP address, check that the
DHCP server can reach the switch, by pinging the switch from the DHCP
server.
■ If your PC accesses the Internet through a proxy server, you may need to
set your browser to bypass the proxy when browsing to the switch’s IP
address range. See “HTTP Proxy Servers” on page 23 for more
information.
■ If you cannot access the GUI because your username or password fails,
check that you are spelling them correctly. The username “manager” will
always be valid. Its default password is “friend”. Note that passwords are
case sensitive.
Software Release 2.6.1
C613-02030-00 REV B
Page 41

Getting Started with the Graphical User Interface (GUI) 41
Problem The GUI is behaving inconsistently, or you cannot access some pages.
Solution
■ Delete your browser’s temporary files (see “Deleting Temporary Files” on
page 40) and try again.
■ Check that you are trying to access the GUI from a supported operating
system and browser combination. See “Browser and PC Setup” on page 22
for more information.
■ Check that JavaScript is enabled.
Problem The GUI does not seem to configure the switch correctly.
Solution
■ Use the buttons on the GUI pages to navigate, not your browser’s Back,
Forward or Refresh buttons. The GUI’s navigation buttons perform aspects
of the configuration.
Tra ff ic F low
Problem No traffic is passing through the switch to or from the LAN, the DMZ or
both.
Solutions
■ Check that the switch’s link to the LAN is functioning, by checking the
interface status (Monitoring) and that the link LED is lit. If the LED is not
lit, or the appropriate interfaces do not have an status of “active”:
• Check that the port is enabled (Configuration > Port > Settings)
• Check that the IP address of the interface is still valid.
• Check that the cables are connected correctly and function correctly.
■ Check the RIP configuration (Configuration > Internet Protocol > RIP).
• Check that the RIP neighbour can reach the switch, by pinging the
switch from the RIP neighbour.
• Any password and authentication settings must be configured on the
neighbour as well as on this switch.
■ Check that the switch is passing the correct DNS information to hosts on
the LAN, if the switch is a DHCP server. If the switch acting as a DHCP
client as well, and therefore is passing on DNS information from another
DHCP server, check that this DHCP server is providing the switch with the
correct information.
Software Release 2.6.1
C613-02030-00 REV B
Page 42

42 AT-8700XL Series Switch User Guide
IP Addresses and DHCP
Problem The switch is enabled as a DHCP server, but cannot assign an IP address to a
host.
Solution
■ Reboot the host machine.
■ Check the host’s TCP/IP settings, to make sure that the host is set to obtain
its IP address dynamically:
In Windows 95/98, click Settings > Control Panel > Network. Select TCP/
IP and click Properties. Click Obtain an IP address automatically.
In Windows 2000, click Settings > Control Panel > Network and Dial-up
Connections > Local Area Connection > Properties. Select Internet
connection (TCP/IP) and click Properties. Click Obtain an IP address
automatically.
■ Check that the switch’s link to the LAN is functioning, by checking the
interface status (Monitoring) and that the link LED is lit (see “Traffic Flow”
on page 41).
Time and NTP
Diagnosis The switch’s time is displayed on the Configuration > System > Time tab. It
will also be included in log packets.
Problem The switch’s time does not change, even though you entered the correct time.
Solution Changing the time is a 3-step process. Select Configuration > System > Time.
First, enter a time that is very shortly in the future (e.g. 20 seconds later than
the current time). Then check Set time. Then wait until precisely the time you
have entered, and click Apply.
Problem The switch is not assigning the time to devices on the LAN.
Solutions
■ Check NTP is enabled (Configuration > System > Time).
■ Check that the NTP peer’s IP address is entered correctly.
■ Check that the NTP peer can reach the switch, by pinging the switch from
the NTP peer.
■ Check that the switch’s link to the LAN is functioning. See “Traffic Flow” on
page 41.
Problem The switch’s clock does not synchronise with the NTP peer.
Solution
■ The switch’s clock can only synchronise with the NTP peer if its initial time
is similar to the NTP peer’s time (after setting the UTC offset). Manually
set the switch’s time so that it is approximately correct, and enable NTP
again.
■ Check that the UTC offset is correct.
Problem The switch’s time is incorrect, even though it assigns the correct time to
devices on the LAN.
Solution The UTC offset is probably incorrect, or needs to be adjusted for the beginning
or end of summer time. To correct this, select Configuration > System > Time
and enter the correct offset.
Software Release 2.6.1
C613-02030-00 REV B
Page 43

Getting Started with the Graphical User Interface (GUI) 43
Loading Software
Problem You have attempted to load a new release file onto the switch, but the load
has failed and you cannot access the switch through the GUI.
Solution 1. Access the switch’s CLI (see “Connecting a Terminal or PC” on page 12).
If the switch has been switched off or has rebooted since you attempted to
load the release file, it will boot up with the default installation. This
contains the commands you require to load a file.
Log into the switch using the manager account and password.
2. Download the release file to the switch. See “Example: Upgrade to a New
Software Release Using TFTP” on page 57 for an example.
Software Release 2.6.1
C613-02030-00 REV B
Page 44

Page 45

Chapter 4
Operating the switch
This Chapter
This chapter introduces basic operations on the switch, including:
■ “User Accounts and Privileges” on page 45
■ “Normal Mode and Security Mode” on page 47
■ “Remote Management” on page 49
■ “Storing Files in FLASH Memory” on page 49
■ “Using Scripts” on page 50
■ “Loading and Uploading Files” on page 52
■ “Upgrading Switch Software” on page 56
■ “Using the Built-in Editor” on page 60
■ “SNMP and MIBs” on page 61
User Accounts and Privileges
The switch software supports three levels of privilege for users: USER,
MANAGER, and SECURITY OFFICER. By default, the switch has one account
(manager) defined with manager privilege and the default password friend. The
commands that a user can execute depends on the user’s privilege level and
whether the switch is operating in normal or security mode (see “Normal Mode
and Security Mode” on page 47). A USER level prompt looks like:
>
while a MANAGER prompt looks like:
Manager >
and a SECURITY OFFICER prompt looks like:
SecOff >
The MANAGER level has access to the full set of commands when the switch is
in normal mode. When the switch is operating in security mode, users with
MANAGER privilege cannot execute a subset of the commands known as the
security commands (see “Normal Mode and Security Mode” on page 47).
Page 46

46 AT-8700XL Series Switch User Guide
In normal mode, a user with manager privilege can create and delete accounts
for users with any of these privilege levels. Users and passwords are managed
by the User Authentication Facility. Users and passwords are authenticated
using an internal database called the User Authentication Database, or by
interrogation of external RADIUS (Remote Authentication Dial In User Service) or
TACACS (Terminal Access Controller Access System) servers.
On the CLI, to use an account with manager privilege, log in to the account by
entering the command:
LOGIN
The switch prompts you to enter a user name and password. To return to USER
mode, enter the command:
LOGOFF
Make sure that you do not leave a manager session unattended. Unauthorised
use of a manager session gives access to the User Authentication Database. To
reduce the risk of unauthorised activity, a subset of manager commands have a
security timer. These commands are shown in Table 4 on page 46. When you
enter one of these commands from a manager session, the security timer is
started and is then restarted each time you enter another of these commands. If
you enter one of these commands after the timer has expired, you are
prompted to re-enter the password. The secure delay timer is by default 60
seconds. If the password is not entered correctly the password prompt is
repeated a set number of times. If the correct password is still not entered a log
message is generated and the session is logged off.
The security timer enables a manager to make successive additions and
modifications to the database at one time without having to re-enter the
password for every command.
The security timer does not provide a foolproof security mechanism. Managers
should always attempt to log out of a manager session before leaving a
terminal unattended.
Table 4: Secure commands controlled by the security timer.
Command Description
ADD TACACS SERVER Adds a TACACS server to the list of TACACS servers used
for user authentication.
ADD USER Adds a user to the User Authentication Database.
DELETE TACACS SERVER Deletes a TACACS server from the list of TACACS servers
used for user authentication.
DELETE USER Deletes a user from the User Authentication Database.
PURGE USER Deletes all users except MANAGER from the User
Authentication Database.
SET MANAGER PORT Assigns a port semipermanent MANAGER privilege.
SET USER Modifies a user record in the User Authentication Database.
If the switch is operating in security mode, the manager must also log in to a user
account with SECURITY OFFICER privilege in order to execute any of the commands
listed in Table 4 on page 46.
Software Release 2.6.1
C613-02030-00 REV B
Page 47

Operating the switch 47
See the Operations chapter in the AT-8700XL Series Software Reference for:
■ More information about managing and using accounts with user, manager
and security officer privileges
■ A full list of commands that require security officer privilege when the
switch is in secure mode
■ Information about enabling a remote security officer.
Normal Mode and Security Mode
The switch operates in one of two modes, either normal mode or security
mode. By default, the switch is in normal mode.
When the switch is in security mode, the command SHOW DEBUG does not display
output of the SHOW FEATURE and SHOW CONFIGURATION DYNAMIC
commands, or the current configuration in the SHOW SYSTEM output unless the
SHOW DEBUG command is entered by a user with security officer privilege.
If you wish to use the following software features you need to enable security
mode:
■ IP authentication
■ Secure Shell (see the Secure Shell chapter, AT-8700XL Series Software
Reference)
■ Encryption (see the Compression and Encryption Services chapter, AT-8700XL
Series Software Reference)
■ Public Key Encryption (PKI) (see the Public Key Infrastructure chapter, AT-
8700XL Series Software Reference)
To enable security mode, first create a user with security officer privilege, then
enter the command:
ENABLE SYSTEM SECURITY_MODE
To access secure functionality you will need to log in again as the security
officer.
When the switch restarts, it restarts in the same normal mode or security mode
as it was before restarting. To restore the switch to normal operating mode,
enter the command:
DISABLE SYSTEM SECURITY_MODE
Software Release 2.6.1
C613-02030-00 REV B
When security mode is disabled, the switch automatically deletes all sensitive
data files, including encryption keys.
To display the current operating mode, enter the command:
SHOW SYSTEM
When the switch is in security mode, a user with security officer privilege is the
only person who can execute commands which affect switch security. Table 5
on page 48 lists commands that only a security officer can execute when the
switch is in security mode. A complete list of commands limited by security
Page 48

48 AT-8700XL Series Switch User Guide
mode are listed in the Operation chapter in the AT-8700XL Series Software
Reference.
Table 5: Commands requiring SECURITY OFFICER privilege when the switch is
operating in security mode .
Command Specific Parameters
ACTIVATE SCR
ADD IP INT
ADD SCR
ADD USER
CREATE CONFIG
CREATE ENCO KEY
CREATE PPP
CREATE PPP TEMPLATE
CREATE SNMP COMMUNITY
DEACTIVATE SCR
DELETE FILE
DELETE SCR
DELETE USER
DISABLE USER
DUMP
EDIT
ENABLE PPP DEBUG
ENABLE PPP TEMPLATE DEBUG
ENABLE SNMP
ENABLE USER
LOAD
MODIFY
PURGE USER
RENAME FILE
RESET ENCO
RESET USER
SET CONFIG
SET INSTALL
SET IP INT
SET PPP
SET PPP TEMPLATE
SET SCR
SET SNMP COMMUNITY
SET USER
SHOW CONFIG
SHOW FILE
SHOW PPP CONFIG
UPLOAD
Software Release 2.6.1
C613-02030-00 REV B
Page 49

Operating the switch 49
Remote Management
You can manage remote switches as easily as you manage the local switch a
terminal is connected to. From a terminal connected to any port (with either
USER or MANAGER privilege), enter the command:
TELNET ipadd
to Telnet to the remote switch, specifying the remote switch’s IP address.
For information about how to set routes and on how you assign an IP address
to your switch, see “Setting Routes” on page 15 and “Assigning an IP Address”
on page 14.
If the connection is successful, a login prompt from the remote switch is
displayed. Login using a login name that has been defined with MANAGER
privilege (such as the default MANAGER login name), and enter the
password.
To return to the local switch and terminate the connection, enter the command:
LOGOFF
For more information about using Telnet, see the Terminal Server chapter in the
AT-8700XL Series Software Reference.
Storing Files in FLASH Memory
When you purchase the switch, the switch software release, the online help
files, and a default configuration file are stored in FLASH memory, where they
are saved even if the switch is powered down. You will use the FLASH
memory to store updated software releases or patches, and files that record the
switch’s configuration. FLASH memory is like a flat file system, with no
subdirectories.
The switch also has Random Access Memory (RAM). The switch software uses
RAM to run the switch. When you enter commands to configure the switch
these commands affect the dynamic configuration in RAM.
FLASH memory is like a flat file system, with no subdirectories.
File names of up to 16 characters long, with extensions of 3 characters (DOS
16.3 format), are supported on the switch. However, files on the switch are
stored in FLASH using the DOS 8.3 format of 8 characters long, with
extensions of 3 characters. For example, the file
be saved as
accessed via two file names, either of which can be used for file management.
extral~1.cfg in the FLASH File System. Therefore, files can be
extralongfilenam.cfg may
Software Release 2.6.1
C613-02030-00 REV B
A translation table, named
16.3 format and DOS 8.3 format. To reconcile file names the switch consults the
translation table which is synchronised with file contents in memory. For more
information about working with files see the Working With Files section,
Operation chapter, AT-8700XL Series Software Reference.
To display the files in FLASH, enter the command:
SHOW FILE
longname.lfn
, converts file names between
DOS
Page 50

50 AT-8700XL Series Switch User Guide
Figure 10: Example output from the SHOW FILE command.
Filename Device Size Created Locks
---------------------------------------------------------------------------28-72.pat flash 111764 05-May-1997 12:41:42 0
28-74ang.rel flash 2013756 09-May-1997 15:58:55 0
28f72-06.pat flash 123268 18-Apr-1997 15:58:16 0
release.lic flash 32 08-May-1997 16:43:49 0
test.cfg flash 1698 09-May-1997 10:39:42 0
sixteenalongfile.scp flash 24 30-May-1997 15:10:12 0
----------------------------------------------------------------------------
The Locks field indicates the number of concurrent software processes using the file.
The switch automatically compacts FLASH memory when a maximum
threshold of deleted files is reached. Compaction frees space for new files by
discarding garbage. A message will appear when FLASH compaction is
activated. Another message appears when FLASH compaction is complete.
While FLASH is compacting, do not restart the switch or use any commands
that affect the FLASH file subsystem. Do not restart the switch, or create, edit,
load, rename or delete any files until a message confirms that FLASH file
compaction is completed. Interrupting flash compaction may result in damage
to files.
Using Scripts
When you start or restart the switch, or when it automatically restarts, it
executes the configuration commands in the boot script. A boot script is a text
file containing a sequence of standard commands that the switch executes at
startup. The default boot script is called
script are limited to 128 characters.
The commands you enter into the switch from the command line affect only
the dynamic configuration in RAM, which is not retained over a power cycle.
The switch does not automatically store these changes in FLASH memory.
When the switch is restarted, it loads the configuration defined by the boot
script, or if the switch was restarted using the RESTART command, any script
file specified in the RESTART command.
boot.cfg. Commands run from a boot
In addition to the boot configuration script that the switch automatically runs
when it restarts, you can run a configuration script manually at any time, by
entering the command:
ACTIVATE SCRIPT=filename
You can also set a trigger to automatically execute a configuration script when
a specified event occurs.
For more information about how to create and run scripts, see the Scripting
chapter in the AT-8700XL Series Software Reference.
For information about creating triggers, see the Trigger Facility chapter in the
AT-8700XL Series Software Reference.
Software Release 2.6.1
C613-02030-00 REV B
Page 51

Operating the switch 51
Saving the Switch’s Configuration
To view the switch’s current dynamic configuration, enter the command:
SHOW CONFIGURATION DYNAMIC
To save any changes made to the dynamic configuration after the switch last
restarted (booted) across a restart or power cycle, and save the modified
configuration as a script file, enter the command:
CREATE CONFIG=filename.scp
To set the switch to execute this script file when it restarts, enter the command:
SET CONFIG=filename.scp
The configuration file created by CREATE CONFIG command records passwords in
encrypted form, not in cleartext.
You can create a script file from any of the switch software commands. These
are the same commands that are used to change the switch’s configuration
dynamically. Manually edit a configuration file using the switch’s built in
editor (see “Using the Built-in Editor” on page 60), or upload it to a PC using the
UPLOAD command (see the Operation chapter, AT-8700XL Series Software
Reference), edit it using any text editor, and download it again. Give
configuration script files an extension of
.scp or .cfg.
To display the name of the configuration file that is set to execute when the
switch restarts, enter the command:
SHOW CONFIG=filename
Storing Multiple Scripts
You can store multiple configuration scripts on the switch. This allows you to
test new configuration scripts once, before setting them as the default
configuration. For example, to test the new configuration script
enter the command:
RESTART SWITCH CONFIG=test.cfg
Storing multiple scripts also allows you to keep a backup switch with
configuration scripts stored on it for every switch in the network to speed up
network recovery time.
test.cfg,
Software Release 2.6.1
C613-02030-00 REV B
Page 52

52 AT-8700XL Series Switch User Guide
Loading and Uploading Files
When you want to upgrade your switch to a new software patch or release, or
use a new configuration file, load files onto the switch using the switch’s
LOADER module. You can also use the LOADER module to upload files, such
as configuration files or log files, from the switch onto a host on the network.
File Naming Conventions
The file subsystem provides a flat file system—directories are not supported.
Files are uniquely identified by a file name of the form:
[device:]filename.ext
where:
■ device specifies the physical memory device on which the file is stored,
FLASH. If device is specified, it must be separated from the rest of the file
name by a colon (“:”). device is optional. If device is not specified, the default
is FLASH.
■ filename is a descriptive name for the file, and may be one to eight
characters in length. Valid characters are lowercase letters (a–z), uppercase
letters (A–Z), digits (0–9) and the hyphen character (-).
■ ext is a file name extension, one to three characters in length. Some file
name extensions are shown in Figure 6 on page 52. Valid characters are
lowercase letters (a–z), uppercase letters (A–Z), digits (0–9) and the hyphen
character (-). The extension is used by the switch to determine the data
type of the file and how to use the file (Table 6 on page 52). If ext is
specified, it must be separated from the filename portion by a period (“.”)
Table 6: File extensions and file types .
Extension File type/function
CER Public Key Infrastructure (PKI) certificate file.
CFG Configuration or boot script.
CRL PKI Certificate Revocation List file.
CSR PKI Certificate Signing Request file.
GIF (Graphics Interchange Format) graphic image file.
HLP CLI help file.
HTM HTML file used by the HTTP server.
INS Stores install information created by using the SET INSTALL
command.
JPG (Joint Photographic Experts Group) graphic image file.
KEY Public portion of an RSA key.
LIC Licence information.
LOG Log file.
MDS Modem script.
REL Software release.
REZ Compressed release.
SCP Script.
Software Release 2.6.1
C613-02030-00 REV B
Page 53

Operating the switch 53
Table 6: File extensions and file types (Continued).
Extension File type/function
SPA Spam Mail Source files, listing email addresses, identified as spam
mail sources, to be blocked by the firewall SMTP proxy, if it is
active.
SPL VPN client.
TXT Generic text file.
VPF Future VPN client.
LFN Extension used for the long file name translation table
You may see files on your switch with file name extensions not listed in Table 6
on page 52. If you require more information about file types and file name
extensions, contact your authorised distributor or reseller.
Do not change the header in a release or patch file. At best, this will cause the
file load or install to fail, at worst the switch could be put into a state where it
will not boot correctly until field service action is taken.
Loading Files
The LOADER module is responsible for loading and storing releases, patches,
PKI certificates and other files into FLASH. The LOADER module uses the
Trivial File Transfer Protocol (TFTP), Hypertext Transfer Protocol (HTTP), or
ZMODEM over an asynchronous port, to retrieve files from a network host.
You can also load text files without using any of these protocols. For
information about using Lightweight Directory Access Protocol (LDAP) to
load PKI certificates or certificate revocation lists (CRLs), see the Operation
chapter in the AT-8700XL Series Software Reference.
The switch’s default download method is TFTP. To load a file onto the switch
from a TFTP server using the TFTP protocol, enter the command:
LOAD [METHOD=TFTP] [DELAY=delay] [DESTFILE=destfilename]
[DESTINATION={BOOTBLOCK|FLASH}] [SERVER={hostname|ipadd}]
[SRCFILE|FILE=filename]
To load a file onto the switch using the HTTP protocol, enter the command:
LOAD [METHOD={HTTP|WEB|WWW}] [DELAY=delay]
[DESTFILE=destfilename] [DESTINATION=BOOTBLOCK|FLASH}]
[HTTPPROXY={hostname|ipadd} [PASSWORD=password]
[PROXYPORT=1..65535]] [SERVER={hostname|ipadd}]
[SERVPORT={1..65535|DEFAULT}] [SRCFILE|FILE=filename]
[USERNAME=username]
Software Release 2.6.1
C613-02030-00 REV B
The switch can only load one file at a time. Wait for the current transfer to
complete before initiating another transfer. To display the default configuration
of the LOADER module, and the progress of any current transfer, enter the
command:
SHOW LOADER
To stop a load at any time, leaving the LOADER module ready to load again,
enter the command:
RESET LOADER
Page 54

54 AT-8700XL Series Switch User Guide
Setting LOADER Defaults
You are likely to repeat the process of downloading files onto the switch using
a similar method each time. You can set defaults for some or all of the LOADER
parameters. You can then use or override some or all of these defaults for each
particular load.
To set LOADER defaults, enter the command:
SET LOADER [ATTRIBUTE={CERT|CRL|CACERT|DEFAULT}]
[BASEOBJECT={dist-name|DEFAULT}] [DELAY={delay|DEFAULT}]
[DESTFILE=dest-filename] [DESTINATION={FLASH|DEFAULT}]
[HTTPPROXY={hostname|ipadd|DEFAULT}]
[METHOD={HTTP|LDAP|TFTP|WEB|WWW|ZMODEM|NONE|DEFAULT}]
[PASSWORD=password] [PROXYPORT={1..65535|DEFAULT}]
[{SCRFILE|FILE}=filename]
[SERVER={host-name|ipadd|DEFAULT}]
[SERVPORT={1..65535|DEFAULT}] [USERNAME=username]
You can set all parameters except DESTFILE, SCRFILE and FILE back to the
factory defaults with the option DEFAULT.
For more information about setting the LOADER defaults on your switch, see
the Operations chapter in the AT-8700XL Series Software Reference.
Example: Load a Patch File Using HTTP
This example loads a patch file onto the switch from a HTTP server on the
network. Before following this procedure, make sure:
■ The HTTP server is operating on a host with an IP address (for example
192.168.1.1) on the network, and that the patch file is in the server’s HTTP
directory.
■ The switch has an IP address (for example 192.168.1.2) on the interface
connecting it to the HTTP server, and that it can communicate with the
server.
■ There is enough space in the switch’s FLASH for the new patch file.
T
o load a patch file
1. Configure the LOADER.
Set the LOADER module with defaults to make the process of
downloading files in future simpler.
SET LOADER METHOD=HTTP SERVER=192.168.1.1
DESTINATION=FLASH
2. Download the patch file.
Download the patch file onto the switch, using the defaults set above.
LOAD FILE=87251-01.paz
When the download has completed, check that the file is in FLASH.
SHOW FILE
This shows the file 87251-01.paz is present.
To activate the patch see “To upgrade to a new patch file:” on page 59.
Software Release 2.6.1
C613-02030-00 REV B
Page 55

Operating the switch 55
Uploading Files From the Switch
The LOADER can upload files from the switch to a network host, using TFTP
or ZMODEM. Upload files using one of the commands:
UPLOAD [METHOD=TFTP] [FILE=filename]
[SERVER={hostname|ipadd}]
UPLOAD [METHOD=ZMODEM] [FILE=filename] [ASYN=port]
The UPLOAD command uses defaults set with the SET LOADER command,
for parameters not specified with the upload command.
You can install Allied Telesyn’s Trivial File Transfer Protocol Server (AT-TFTPD
on any PC or server running Windows. This will provide a simple way to make
files available to all Allied Telesyn routers and layer 3 switches in your
network. The TFTP Server, and a readme file describing how to install and use
it, are provided on the Documentation and Tools CD-ROM.
Example: Upload a Configuration File Using TFTP
This example uploads a configuration file from the switch to a TFTP server on
the network. Before following this procedure, make sure:
■ The TFTP server is operating on a host with an IP address (for example
192.168.1.3) on the network.
■ The switch has a valid IP address (for example 192.168.1.2) on the interface
connecting it to the TFTP server, and that it can communicate with the
server.
■ The configuration file is present in the switch’s FLASH.
To upload a log file:
1. Configure the LOADER.
Set the LOADER module with defaults to make the process of
downloading and uploading files in future simpler.
SET LOADER METHOD=TFTP SERVER=192.168.1.3
2. Upload the configuration file.
Upload the configuration file from the switch into the TFTP directory of the
TFTP server on the network, using the defaults set above.
UPLOAD FILE=filename.cfg
Monitor the load progress.
SHOW LOAD
When the upload is complete, check that the file is in the TFTP directory on
the network host.
Software Release 2.6.1
C613-02030-00 REV B
More information
For more information about loading files onto and uploading files from the
switch, including using LDAP to load PKI certificate information, see the
Operation chapter in the AT-8700XL Series Software Reference.
Page 56

56 AT-8700XL Series Switch User Guide
Upgrading Switch Software
When you first start the switch, it automatically loads the software release from
FLASH memory into RAM, where the CPU uses it to run all the switch’s
software features. The switch may also load a patch file to improve the main
release. The software release and any patch files are current when the switch is
produced at the factory.
When Allied Telesyn makes a new patch or release available, you may want to
upgrade the software on your switch to use a new patch or release file. You can
download the latest software patches, full software releases, and CLI help files
from the website at: http://www.alliedtelesyn.co.nz/support/at8700xl
Make sure you download a patch or release file that matches your switch
model. A patch or release file for an AT-8700XL Series Switch has 87 as the first
two digits of the filename. Patch files have the file extension
files have the file extension
the AT-8700XL has the filename
.rez. For example, the Software Release 2.6.1 for
87-261.rez.
Release and patch files are compressed ASCII files, and consist of a header
followed by a sequence of Motorola S-records containing the actual code for
the release or patch. The header has a standard format, which provides
information about the release or patch to the switch.
.
.paz and release
Do not change the header in a release or patch file. At best, this will cause the
file load or install to fail, at worst the switch could be put into a state where it
will not boot correctly until field service action is taken.
The current release and patch file are set as the preferred install. The switch
also has a very limited version of the software stored in permanent memory
(EPROM). You cannot delete this version as it is the default, or boot install.
When you load a new software release or patch, you can set it to run once, the
next time the switch reboots. This temporary install allows you to test run a
new release or patch once, before you make it the preferred install. If the
temporary install fails the switch will automatically run the preferred install if
there is one, or otherwise the default install, the next time the switch reboots.
When the switch reboots, it checks the install information in a strict order:
• Firstly, the switch checks the temporary install. If a temporary install is
specified, the switch loads it into RAM and runs it. At the same time, it
deletes the temporary install information so it will not load a second
time. This information is deleted even if the temporary install triggers a
fatal condition causing the switch to reboot immediately.
• Secondly, if no temporary install is defined, or the install information is
invalid, the switch checks the preferred install. If present, this install is
loaded. The switch never deletes the preferred install information.
• Thirdly, if neither a temporary install nor a preferred install is specified,
the switch loads the default install. The default install is always present
in the switch because if, for some reason, it is not, the INSTALL module
will restore it.
The preferred install should not be set up with an untested release or patch. It
is advisable to install new releases or patches as the temporary install, and
when the switch boots correctly, to then set up the preferred install with the
new release or patch.
Software Release 2.6.1
C613-02030-00 REV B
Page 57

Operating the switch 57
To change the install information in the switch, enter the command:
SET INSTALL={TEMPORARY|PREFERRED|DEFAULT}
[RELEASE={release-name|EPROM}] [PATCH=patch-name]
For security reasons the SET INSTALL command is only accepted if the user has
SECURITY OFFICER privilege.
When you set a patch file as part of a temporary install or permanent install,
you must also set the corresponding release file in the same command, if it has
not already been set as part of that install. You can set the patch, but not the
release (always EPROM), for the default install.
To delete a temporary install or preferred install, enter the command:
DELETE INSTALL={TEMPORARY|PREFERRED}
If a default install is set, only the patch information is deleted using the
DELETE INSTALL command as the release information must always be left
intact in the default install.
To display the current install information, including which install is currently
running in the switch, and how the install information was checked at the last
reboot, enter the command:
SHOW INSTALL
For more information about INSTALL commands, see the Operations chapter in
the AT-8700XL Series Software Reference.
Example: Upgrade to a New Software Release Using TFTP
This example assumes the switch is correctly configured to allow TFTP to
function. This means that IP is configured and the switch is able to
communicate with the designated TFTP server. The TFTP server is assumed to
function correctly and the release and patch files are assumed present in the
server’s TFTP directory. The switch has no release or patch files, and is running
the EPROM Software Release 2.5.1. The IP address of the server is 172.16.1.1.
The name of the release file being loaded is
To upgrade to a new software release:
1. Configure the LOADER.
The LOADER module is set up with defaults to make the process of
downloading files in future simpler. All release and patch files in this
switch are stored in FLASH.
SET LOADER METHOD=TFTP SERVER=172.16.1.1 DEST=FLASH
87-261.rez.
Software Release 2.6.1
C613-02030-00 REV B
2. Load the new release file onto the switch.
Make sure there is space in FLASH for the new release file. Load the new
file onto your switch. Make sure the release file matches your switch model
(see “Upgrading Switch Software” on page 56). Load any patch files required,
and the help file for the release (see “Loading and Uploading Files” on
page 52). To load the release file using your LOADER default settings,
enter the command:
LOAD FILE=87-261.rez
Page 58

58 AT-8700XL Series Switch User Guide
Wait for the release to load. This can take several minutes, even if you are
loading the file over a high speed link. To see the progress of the load, enter
the command:
SHOW LOAD
To check that the files are successfully loaded, enter the command:
SHOW FILE
3. Enter licence information for the release.
Enter the licence password for the software release.
ENABLE RELEASE=87-261.rez PASSWORD=ce645398fbe
NUMBER=2.6.1
The release licence password is provided by your authorised distributor or
reseller and is unique for the release number, the file name and the switch’s
serial number.
4. Test the release.
Set the new release to run as a temporary install. This sets the switch to
load the new release once only when it reboots.
SET INSTALL=TEMPORARY RELEASE=87-261.rez
If you want to use the current switch configuration again, store the
dynamic configuration as a configuration script file and set the switch to
use this configuration when it restarts. Releases are generally backwardcompatible, so your current configuration should run with little or no
modifications on the later release.
CREATE CONFIG=myconfig.cfg
SET CONFIG=myconfig.cfg
The SET CONFIG information survives the release update.
Reboot the switch.
RESTART REBOOT
The switch reboots, loading the new release file and the specified
configuration. Display the install history, and check that the temporary
release was loaded.
SHOW INSTALL
5. Make the release the default (permanent) release.
If the switch operates correctly with the new release, make the release
permanent.
SET INSTALL=PREFERRED RELEASE=87-261.rez
Every time the switch reboots from now on, it loads the new release from
FLASH.
Software Release 2.6.1
C613-02030-00 REV B
Page 59

Operating the switch 59
Example: Upgrade to a new patch file
Use this procedure to upgrade the software release currently running on the
switch with a new patch. This example assumes that the Software Release 2.6.1
is set as the preferred release. The patch name is this example is
To upgrade to a new patch file:
1. Load the new patch file onto the switch.
Load the new file onto your switch. See “Loading and Uploading Files” on
page 52.
LOAD FILE=87261-01.paz
Check that the file is successfully loaded.
SHOW FILE
2. Test the patch.
Set the release to run as a temporary install, so that it loads the patch once
only the next time it reboots.
SET INSTALL=TEMPORARY RELEASE=87-261.rez
PATCH=87261-01.paz
87261-01.paz.
If you want to use the current switch configuration again, store the
dynamic configuration as a configuration script file, and set the switch to
use this configuration when it restarts.
CREATE CONFIG=myconfig.scp
SET CONFIG=myconfig.scp
Reboot the switch.
RESTART REBOOT
The switch reboots, loading the new patch file and the specified
configuration. Check that the switch operates correctly with the new patch
file.
3. Make the patch part of the default (permanent) release.
If the switch operates correctly with the new patch, make the release
permanent.
SET INSTALL=PREF RELEASE=87-261.rez PATCH=87261-01.paz
Every time the switch reboots from now on, it loads the new release and
patch from FLASH.
Do not set an untested patch as part of the preferred install.
Software Release 2.6.1
C613-02030-00 REV B
Page 60

60 AT-8700XL Series Switch User Guide
Using the Built-in Editor
The AT-8700XL Series Switch has a built-in full-screen text editor for editing
script files stored on the switch file subsystem. Using the text editor you can
run script files manually, or set script files to run automatically at switch
restart, or on trigger events. Figure 11 on page 60 shows a example screen shot
of the text editor. To start the editor with a new file or an existing file, enter the
command:
EDIT [filename]
Figure 11: The editor screen layout.
The editor uses VT100 command sequences and should only be used with a
VT100-compatible terminal, terminal emulation program or Telnet client.
To display editor Help at any time while in the editor press [Ctrl/K,H]; that is,
hold down the Ctrl key and press in turn the K key then the H key.
For more information about the inbuilt editor, see the Operation chapter in the
AT-8700XL Series Software Reference.
Software Release 2.6.1
C613-02030-00 REV B
Page 61

Operating the switch 61
SNMP and MIBs
You can remotely monitor some features of the switch using Simple Network
Management Protocol (SNMP).
For information about the MIBs supported by the switch, see Appendix C:
SNMP MIBs in the AT-8700XL Series Software Reference.
The SNMP agent is disabled by default. To enable SNMP, enter the command:
ENABLE SNMP
SNMP communities are the main configuration item in the switch’s SNMP
agent, and are defined in terms of a list of IP addresses which define the SNMP
application entities (trap hosts and management stations) in the community. To
create an SNMP community, enter the command:
CREATE SNMP COMMUNITY=name [ACCESS={READ|WRITE}]
[TRAPHOST=ipadd] [MANAGER=ipadd]
[OPEN={ON|OFF|YES|NO|TRUE|FALSE}]
The community name is a security feature and you should keep it secure.
To enable the generation of authentication failure traps by the SNMP agent
whenever an SNMP authentication failure occurs, enter the command:
ENABLE SNMP AUTHENTICATE_TRAP
To enable the generation of link state traps for a specified interface, enter the
command:
ENABLE INTERFACE=interface LINKTRAP
where interface is the name of an interface, such as “eth0”.
For more information see the Simple Network Management Protocol (SNMP)
chapter and the Interfaces chapter in the AT-8700XL Series Software Reference.
To display the current state and configuration of the SNMP agent, enter the
command:
SHOW SNMP
For a detailed description of the output from the SHOW SNMP command, see
the Simple Network Management Protocol (SNMP) chapter in the AT-8700XL
Series Software Reference.
Software Release 2.6.1
C613-02030-00 REV B
Page 62

62 AT-8700XL Series Switch User Guide
For More About Operations and Facilities
For more detail about operating the switch, and for full command syntax
definitions, see the Operation chapter in the AT-8700XL Series Software Reference,
including:
■ How to use the User Authentication Facility, RADIUS, TACACs or
TACACS+ for authenticating users who log on to the switch, and ensuring
that only authorised login accounts are used.
■ How to use the HTTP Client, which you can use to download software files
onto the switch, and the HTTP Server.
■ How to use the Mail Subsystem.
■ How to use LDAP to load PKI certificates and CRLs onto your switch.
■ How to use Switch Startup Operations
■ How to use FLASH compaction to regain storage space on the switch. Read
“Warning about FLASH memory” on page 9 before you attempt to do this.
■ How to set aliases to represent common command strings.
■ How to define a remote security officer, so you can manage the security
features remotely via Telnet.
See other chapters in the AT-8700XL Series Software Reference for more
information on how to:
■ Use the logging facility to monitor network activity and to select and
display the results (see the Logging Facility chapter).
■ Use SNMP to manage the switch remotely (see the Simple Network
Management Protocol (SNMP) chapter and Appendix C: SNMP MIBs).
■ Use the command line to create, delete and modify configuration scripts
(see the Scripting chapter).
■ Set up triggers to automatically run specified scripts at specified times, or
at specified events (see the Trigger Facility chapter).
■ Use NTP to synchronise your switch’s time clock with those of other
network devices (see the Network Time Protocol (NTP) chapter).
■ Use software to test whether the switch’s hardware functions correctly (see
the Tes t F a c i li ty chapter).
Software Release 2.6.1
C613-02030-00 REV B
Page 63

Chapter 5
Switching
This section outlines the Layer 2 and IP switching features on the switch, and
how to configure some of them. For more detail, refer to the Switching and
Internet Protocol (IP) chapters in the AT-8700XL Series Switch Software Reference.
Switch Ports
Each switch port is uniquely identified by a port number. The switch supports
a number of features at the physical level that allow it to be connected in a
variety of physical networks. This physical layer (layer 1) versatility includes:
■ Enabling and disabling of ports.
■ Auto negotiation of port speed and duplex mode for all 10/100 BASE
ports.
■ Manual setting of port speed and duplex mode for all 10/100 BASE ports.
■ Link up and link down triggers.
■ Port trunking.
■ Packet storm protection.
■ Port mirroring.
■ Support for SNMP management
Enabling and Disabling Switch Ports
An switch port that is enabled is available for packet reception and
transmission. Its administrative status in the Interfaces MIB is UP. Disabling a
switch port does not affect the STP operation on the port. Enabling a switch
port will allow the port to participate in spanning tree negotiation. A switch
port that has been disabled by the Port Security feature cannot be enabled
using the ENABLE SWITCH PORT command.
To enable or disable a switch port, use the commands:
ENABLE SWITCH PORT={port-list|ALL}
DISABLE SWITCH PORT={port-list|ALL}
Page 64

64 AT-8700XL Series Switch User Guide
Resetting ports at the hardware level discards all frames queued for reception
or transmission on the port, and restarts autonegotiation of port speed and
duplex mode. Ports are reset using the command:
RESET SWITCH PORT={port-list|ALL} [COUNTER]
To display information about switch ports, use the command:
SHOW SWITCH PORT[={port-list|ALL}]
Autonegotiation of Port Speed and Duplex Mode
Each of the switch ports can operate at either 10 Mbps or 100 Mbps, in either
full duplex or half duplex mode. In full duplex mode a port can transmit and
receive data simultaneously, while in half duplex mode the port can either
transmit or receive, but not at the same time. This versatility makes it possible
to connect devices with different speeds and duplex modes to different ports
on the switch. Such versatility also requires that each port on the switch know
which speed and mode to use.
Port Trunking
Port trunking, also known as port bundling or link aggregation, allows a
number of ports to be configured to join together to make a single logical
connection of higher bandwidth. This can be used where a higher performance
link is required, and makes links even more reliable.
Packet Storm Protection
The packet storm protection feature allows you to set limits on the reception
rate of broadcast, multicast and destination lookup failure packets. The
software allows separate limits to be set for each port, beyond which each of
the different packet types are discarded. The software also allows separate
limits to be set for each of the packet types. Which of these options can be
implemented depends on the model of switch hardware.
Port Mirroring
Port mirroring allows traffic being received and transmitted on a switch port to
be sent to another switch port, the mirror port, usually for the purposes of
capturing the data with a protocol analyser. This mirror port is the only switch
port which belongs to no VLANs, and therefore does not participate in any
other switching. Before the mirror port can be set, it must be removed from all
VLANs except the default VLAN. The port cannot be part of a trunk group.
Port Security
The port security feature allows control over the stations connected to each
switch port, by MAC address. If enabled on a port, the switch will learn MAC
addresses up to a user-defined limit from 1 to 256, then lock out all other MAC
Software Release 2.6.1
C613-02030-00 REV B
Page 65

Switching 65
addresses. One of the following options can be specified for the action taken
when an unknown MAC address is detected on a locked port:
■ Discard the packet and take no further action,
■ Discard the packet and notify management with an SNMP trap,
■ Discard the packet, notify management with an SNMP trap and disable the
port.
Virtual Local Area Networks (VLANs)
A Virtual LAN (VLAN) is a logical, software-defined subnetwork. It allows
similar devices on the network to be grouped together into one broadcast
domain, irrespective of their physical position in the network. Multiple VLANs
can be used to group workstations, servers, and other network equipment
connected to the switch, according to similar data and security requirements.
Decoupling logical broadcast domains from the physical wiring topology
offers several advantages, including the ability to:
■ Move devices and people with minimal, or no, reconfiguration
■ Change a device’s broadcast domain and access to resources without
physically moving the device, by software reconfiguration or by moving its
cable from one switch port to another
■ Isolate parts of the network from other parts, by placing them in different
VLANs
■ Share servers and other network resources without losing data isolation or
security
■ Direct broadcast traffic to only those devices which need to receive it, to
reduce traffic across the network
■ Connect 802.1Q-compatible switches together through one port on each
switch
Devices that are members of the same VLAN only exchange data with each
other through the switch’s switching capabilities. To exchange data between
devices in separate VLANs, the switch’s routing capabilities are used. The
switch passes VLAN status information, indicating whether a VLAN is up or
down, to the Internet Protocol (IP) module. IP uses this information to
determine route availability.
The switch has a maximum of 255 VLANs, ranging from a VLAN identifier
(VID) of 1 to 255. When the switch is first powered up, a “default” VLAN is
created and all ports are added to it. In this initial unconfigured state, the
switch will broadcast all the packets it receives to the default VLAN. This
VLAN has a VID of 1 and an interface name of vlan1. It cannot be deleted, and
ports can only be removed from it if they also belong to at least one other
VLAN. The default VLAN cannot be added to any STP, but always belongs to
the default STP. If all the devices on the physical LAN are to belong to the same
logical LAN, that is, the same broadcast domain, then the default settings will
be acceptable, and no additional VLAN configuration is required.
Software Release 2.6.1
C613-02030-00 REV B
Page 66

66 AT-8700XL Series Switch User Guide
Creating VLANs
To briefly summarise the process of creating a VLAN:
1. Create the VLAN.
2. Add tagged ports to the VLAN, if required.
3. Add untagged ports to the VLAN, if required.
To create a VLAN, use the command:
CREATE VLAN=vlan-name VID=2..255
Every port must belong to a VLAN, unless it is the mirror port. By default, all
ports belong to the default VLAN as untagged ports.
To add tagged ports to a VLAN, use the command:
ADD VLAN={vlan-name|1..255} PORT={port-list|ALL} FRAME=TAGGED
A port can be tagged for any number of VLANs.
To add untagged ports to a VLAN, use the command:
ADD VLAN={vlan-name|1..255} PORT={port-list|ALL}
[FRAME=UNTAGGED]
A port can be untagged for zero or one VLAN. A port can only be added to the
default VLAN as an untagged port if it is not untagged for another VLAN. A
port cannot transmit both tagged and untagged frames for the same VLAN
(that is, it cannot be added to a VLAN as both a tagged and an untagged port).
To remove ports from a VLAN, use the command:
DELETE VLAN={vlan-name|1..255} PORT={port-list|ALL}
Removing an untagged port from a VLAN will return it to the default VLAN,
unless it is a tagged port for another static VLAN. An untagged port can only
be deleted from the default VLAN if the port is a tagged port for another static
VLAN.
Ports tagged for some VLANs and left in the default VLAN as untagged ports will
transmit broadcast traffic for the default VLAN. If this is not required, the unnecessary
traffic in the switch can be reduced by deleting those ports from the default VLAN.
To change the tagging status of a port in a VLAN, use the command:
SET VLAN={vlan-name|1..255} PORT={port-list|ALL} FRAME=TAGGED
To destroy a VLAN, use the command:
DESTROY VLAN={vlan-name|2..255|ALL}
VLANs can only be destroyed if no ports belong to them.
To display the VLANs configured on the switch, use the command:
SHOW VLAN[={vlan-name|1..255|ALL}]
Information which may be useful for trouble-shooting a network can be
displayed with the VLAN debugging mode. This is disabled by default, and
Software Release 2.6.1
C613-02030-00 REV B
Page 67

Switching 67
can be enabled for a specified time, disabled, and displayed using the
commands:
ENABLE VLAN={vlan-name|1..255|ALL} DEBUG={PKT|ALL}
[OUTPUT=CONSOLE] [TIMEOUT={1..4000000000|NONE}]
DISABLE VLAN={vlan-name|1..255|ALL} DEBUG={PKT|ALL}
SHOW VLAN DEBUG
To view packet reception and transmission counters for a VLAN, use the
command (see the Interfaces chapter of the switch’s Software Reference):
SHOW INTERFACE=VLANn COUNTER
Summary of VLAN tagging rules
When designing a VLAN and adding ports to VLANs, the following rules
apply.
1. Each port, except for the mirror port, must belong to at least one static
VLAN. By default, a port is an untagged member of the default VLAN.
2. A port can be untagged for zero or one VLAN. A port that is untagged for
a VLAN transmits frames destined for that VLAN without a VLAN tag in
the Ethernet frame.
3. A port can be tagged for zero or more VLANs. A port that is tagged for a
VLAN transmits frames destined for that VLAN with a VLAN tag,
including the numerical VLAN Identifier of the VLAN.
4. A port cannot be untagged and tagged for the same VLAN.
5. The mirror port, if there is one, is not a member of any VLAN.
Protected VLANs
If a VLAN is Protected, Layer 2 traffic between ports that are members of a
Protected VLAN is blocked. Traffic can be Layer 3 switched to another VLAN.
This feature prevents members of a Protected VLAN from communicating with
each other yet still allows members to access another network. Layer 3 Routing
between Ports in a Protected VLAN can be prevented by adding a Layer 3
filter. The Protected VLAN feature also allows all of the members of the
Protected VLAN to be in the same subnet.
A typical application is a hotel installation where each room has a port that can
be used to access the Internet. In this situation it is undesirable to allow
communication between rooms.
To create a Protected VLAN, use the command:
CREATE VLAN=vlan-name VID=2..255 [PROTECTED]
Software Release 2.6.1
C613-02030-00 REV B
VLAN Interaction with STPs and Trunk Groups
VLANs may have ports in more than one STP, when the ports belong to
multiple VLANs. VLANs can belong to multiple STPs.
All the ports in a trunk group must have the same VLAN configuration: they
must belong to the same VLANs and have the same tagging status, and can
only be operated on as a group.
Page 68

68 AT-8700XL Series Switch User Guide
Generic VLAN Registration Protocol (GVRP)
The GARP application GVRP allows switches in a network to dynamically
share VLAN membership information, to reduce the need for statically
configuring all VLAN membership changes on all switches in a network. See
the Generic Attribute Registration Protocol (GARP) chapter in the AT-8700XL
Series Switch Software Reference.
Quality of Service
Quality of Service (QoS) enables you to prioritise traffic and/or limit the
bandwidth available to it. The concept of QoS is a departure from the original
networking protocols, which treated all traffic on the Internet or within a LAN
the same. Without QoS, every different traffic type is equally likely to be
dropped if a link becomes oversubscribed. This approach is now inadequate in
many networks, because traffic levels have increased and networks transport
time-critical applications such as streams of video data. QoS also enables
service providers to easily supply different customers with different amounts
of bandwidth.
Configuring Quality of Service involves two separate stages:
1. Classifying traffic into flows, according to a wide range of criteria.
Classification is performed by the switch’s packet classifier and is not
described in this chapter, but in the Classifier chapter in the AT-8700XL Series
Switch Software Reference.
2. Acting on these traffic flows.
Approaches, methods and commands for this are described in the Quality of
Service chapter in the AT-8700XL Series Switch Software Reference.
Spanning Tree Protocol (STP)
The Spanning Tree Protocol (STP) makes it possible to automatically disable
redundant paths in a network to avoid loops, and enable them when a fault in
the network means they are needed to keep traffic flowing. A sequence of
LANs and switches may be connected together in an arbitrary physical
topology resulting in more than one path between any two switches. If a loop
exists, frames transmitted onto the extended LAN would circulate around the
loop indefinitely, decreasing the performance of the extended LAN. On the
other hand, multiple paths through the extended LAN provide the opportunity
for redundancy and backup in the event of a bridge experiencing a fatal error
condition.
Software Release 2.6.1
C613-02030-00 REV B
Page 69

Switching 69
The spanning tree algorithm ensures that the extended LAN contains no loops
and that all LANs are connected by:
■ Detecting the presence of loops and automatically computing a logical
loop-free portion of the topology, called a spanning tree. The topology is
dynamically pruned to a spanning tree by declaring the ports on a switch
redundant, and placing the ports into a ‘Blocking’ state.
■ Automatically recovering from a switch failure that would partition the
extended LAN by reconfiguring the spanning tree to use redundant paths,
if available.
Spanning Tree and Rapid Spanning Tree Port States
If STP is running in STANDARD mode, then each port can be in one of five
Spanning Tree states, and one of two switch states. If STP is running in RAPID
mode, then each port can be in one of four states. The state of a switch port is
taken into account by STP. To be involved in STP negotiations, STP must be
enabled on the switch, the port must be enabled on the switch, and enabled for
the STP it belongs to.
IP Switching
The switch performs IP routing at wire speed between VLANs that have been
configured as IP interfaces. For example, to add the admin VLAN as an IP
interface, giving it an IP address of 192.168.163.39 in the subnet 192.168.163.0,
first enable IP using the command:
ENABLE IP
Then use either of the following commands:
ADD IP INTERFACE=vlan-admin IPADDRESS=192.168.163.39
MASK=255.255.255.0
ADD IP INTERFACE=vlan11 IPADDRESS=192.168.163.39
MASK=255.255.255.0
The command:
SHOW IP INTERFACE
displays the interfaces enabled for IP routing (Figure 12).
For detailed information about configuring IP, see the Internet Protocol (IP)
chapter in the AT-8700XL Series Software Reference.
Figure 12: Example output from the SHOW IP INTERFACE command.
Interface Type IP Address Bc Fr PArp Filt RIP Met. SAMode IPSc
Pri. Filt Pol.Filt Network Mask MTU VJC GRE OSPF Met. DBcast Mul.
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------LOCAL - Not Set - n - --- - - --
--- ---- - - - --- - - --vlan11 Static 192.168.163.39 1 y On --- 01 Pass --
--- --- 255.255.255.0 1500 - --- 0000000001 No On
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Software Release 2.6.1
C613-02030-00 REV B
Page 70

70 AT-8700XL Series Switch User Guide
Routing Information Protocol (RIP)
Routing protocols such as RIPv1 and RIPv2 can be enabled on a VLAN. For
example, to enable RIPv2 on the admin VLAN, use the command:
ADD IP RIP INTERFACE=vlan11 SEND=RIP2 RECEIVE=BOTH
To display information about RIP (Figure on page 70), use the command:
SHOW IP RIP
Example output from the SHOW IP RIP command.
Interface Circuit/DLCI IP Address Send Receive Demand Auth Password
------------------------------------------------------------------------------vlan11 - - RIP2 BOTH NO NO
ppp0 - 172.16.249.34 RIP1 RIP2 YES PASS ********
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------
IGMP Snooping
IGMP (Internet Group Management Protocol) is used by IP hosts to report their
multicast group memberships to routers and switches. IP hosts join a multicast
group to receive broadcast messages directed to the multicast group address.
IGMP is an IP-based protocol and uses IP addresses to identify both the
multicast groups and the host members. For a VLAN-aware devices, this
means multicast group membership is on a per-VLAN basis. If at least one port
in the VLAN is a member of a multicast group, by default multicast packets
will be flooded onto all ports in the VLAN.
IGMP snooping enables the switch to forward multicast traffic intelligently on
the switch. The switch listens to IGMP membership reports, queries and leave
messages to identify the switch ports that are members of multicast groups.
Multicast traffic will only be forwarded to ports identified as members of the
specific multicast group.
IGMP snooping is performed at Layer 2 on VLAN interfaces automatically. By
default, the switch will only forward traffic out those ports with multicast
listeners, therefore it will not act as a simple hub and flood all multicast traffic
out all ports. IGMP snooping is independent of the IGMP and Layer 3
configuration, so an IP interface does not have to be attached to the VLAN, and
IGMP does not have to be enabled or configured.
IGMP snooping is enabled by default. To disable it, use the command:
DISABLE IGMPSNOOPING
Software Release 2.6.1
C613-02030-00 REV B
Page 71

Switching 71
Triggers
The Trigger Facility can be used to automatically run specified command
scripts when particular triggers are activated. When a trigger is activated by an
event, global parameters and parameters specific to the event are passed to the
script that is run. For a full description of the Trigger Facility, see the Tr i g g er
Facility chapter in the AT-8700XL Series Software Reference.
The switch can generate triggers to activate scripts when a fibre uplink port
loses or gains coherent light. To create or modify a switch trigger, use the
commands:
CREATE TRIGGER=trigger-id MODULE=SWITCH
EVENT={LIGHTOFF|LIGHTON} PORT=port [AFTER=hh:mm]
[BEFORE=hh:mm] [DATE=date|DAYS=day-list] [NAME=name]
[REPEAT={YES|NO|ONCE|FOREVER|count}] [SCRIPT=filename...]
[STATE={ENABLED|DISABLED}] [TEST={YES|NO|ON|OFF}]
SET TRIGGER=trigger-id PORTS={port-list|ALL} [AFTER=hh:mm]
[BEFORE=hh:mm] [DATE=date|DAYS=day-list] [NAME=name]
[REPEAT={YES|NO|ONCE|FOREVER|count}]
[TEST={YES|NO|ON|OFF}]
The following sections list the events that may be specified for the EVENT
parameter, the parameters that may be specified as module-specific-parameters,
and the arguments passed to the script activated by the trigger.
Event LINKDOWN Description The port link specified by the PORT parameter has just gone down. Parameters The following command parameter(s) must be specified in the CREATE/SET
TRIGGER commands:
Parameter Description
PORT=port The port on which the event will activate the trigger.
Script Parameters The trigger passes the following parameter(s) to the script:
Argument Description
%1 The port number of the port which has just gone down.
Event LINKUP Description The port link specified by the PORT parameter has just come up. Parameters The following command parameter(s) must be specified in the CREATE/SET
TRIGGER commands:
Parameter Description
PORT=port The port on which the event will activate the trigger.
Script Parameters The trigger passes the following parameter(s) to the script:
Software Release 2.6.1
C613-02030-00 REV B
Argument Description
%1 The port number of the port which has just come up.
Page 72

Page 73

Chapter 6
Maintenance and Troubleshooting
This Chapter
If you are familiar with networking and switch operations, you may be able to
diagnose and solve some problems yourself.
This chapter gives tips on how to:
■ start your switch (see “How the Switch Starts Up” on page 74).
■ avoid problems (see “How to Avoid Problems” on page 75).
■ reconfigure your switch if you accidentally clear the FLASH memory (see
“What to Do if You Clear FLASH Memory Completely” on page 77).
■ reset passwords if they are lost (see “What to Do if Passwords are Lost” on
page 78).
■ gather information from your switch that support personnel need to
provide accurate support tailored to your situation (see “Getting the Most
Out of Technical Support” on page 78).
■ restart the switch at any time with no configuration (see “Resetting Switch
Defaults” on page 79).
■ check whether there is a connection between the switch and another
routing interface in the network (see “Checking Connections Using PING” on
page 79).
■ troubleshoot problems with DHCP IP addresses if the switch is acting as a
client or as a server (see “Troubleshooting DHCP IP Addresses” on page 81)
■ examine the route that packets pass between two systems running the IP
protocol (see “Using Trace Route for IP Traffic” on page 81).
Information gained from the LEDs on the front panel of the switch is described
in the AT-8700XL Series Hardware Reference.
Page 74
74 AT-8700XL Series Switch User Guide
How the Switch Starts Up
The sequence of operations that the switch performs when it boots are:
1. Perform startup self tests.
2. Perform the install override option.
3. Load the EPROM release as the INSTALL boot.
4. Inspect and check INSTALL information.
5. Load the required release as the main boot.
6. Start the switch.
7. Execute the boot script, if one has been configured.
If a terminal is connected to asyn0, a series of status and progress messages
similar to those shown in Figure 13 on page 74 are displayed during the startup
process.
Figure 13: switch startup messages.
INFO: Self tests beginning.
INFO: RAM test beginning.
PASS: RAM test, 4096k bytes found.
INFO: BBR tests beginning.
PASS: BBR test, 128k bytes found.
PASS: BBR test. Battery OK.
INFO: Self tests complete
INFO: Downloading router software.
Force EPROM download (Y) ?
INFO: Initial download succeeded
INFO: Executing configuration script <boot.cfg>
INFO: Router startup complete
Manager >
The startup self tests check the basic operation of the switch. If your switch
passes these tests the switch should be able to at least proceed far enough to
perform the load of the EPROM release and to start operating.
The install override option is designed to allow a mandatory switch boot from
the EPROM release. The message:
Force EPROM download (Y)?
is displayed on the terminal connected to asyn0 and the switch pauses. If you
do not press a key within a few seconds, the startup process will continue and
all steps in the sequence are executed. If the [Y], [S], [N] or [Ctrl/D] key on the
terminal are pressed immediately after the message is displayed, you can alter
the switch startup process (Table 7 on page 75).
Software Release 2.6.1
C613-02030-00 REV B
Page 75

Maintenance and Troubleshooting 75
Table 7: Switch startup sequence keystrokes.
Pressing key... Forces the switch to...
Y Load the EPROM release, with no patch, and skip straight to step 6.
S Start with the default configuration. Any boot script or NVS
configuration is ignored.
N Configure from NVS, ignoring any boot script.
[Ctrl/D] Enter diagnostics mode.
When you start the switch the EPROM release is always loaded first. The
EPROM release contains all the code required to obtain and check the
INSTALL information. This first boot is known as the INSTALL boot. The
INSTALL information is inspected and the switch is setup to perform another
load. Even if the actual release required is the EPROM release, another load is
always performed. At this point, if a patch load is required, it is also
performed.
The switch startup occurs immediately after the install override option, or after
the INSTALL information check. The INSTALL information check performs a
full startup of switch software and initiates the normal operation of the switch.
Finally, if there is a defined boot script, this script is executed.
How to Avoid Problems
If you perform the following procedures you may help reduce the likelihood
and impact of some future switch events.
Backup software files
Store a backup of the current switch software. If the switch software is
accidentally cleared from the switch’s FLASH memory, you will need to reload
the software release and patch files. If your access to the Internet is via the
switch, then you will need the files on your LAN. You may wish to keep a copy
of the current software and patch files on a TFTP server on your network. You
can download switch software from the website at
http://www.alliedtelesyn.co.nz/support/at8700xl
Backup configuration script
Store a backup of the latest configuration script, in case the configuration file
on the switch is accidentally deleted or damaged.
.
Software Release 2.6.1
C613-02030-00 REV B
Backup switch
If your network has many switches, you may wish to keep a backup switch
ready to replace any switch that malfunctions. When you upgrade the software
release or patch on the other switches in the network, upgrade the backup too.
Store on it one current config script for each switch in your network, so that
when it is needed, you need only set the configuration file with which it boots
to match the switch it replaces.
Page 76

76 AT-8700XL Series Switch User Guide
Configure logging
The logging facility stores log messages for events with a specified severity in a
log file. You can change the size of the log file, and the kind of messages
recorded. You can configure the switch to output log messages in several ways,
including to a remote switch with a specified IP address, or as an email to a
particular email address. The switch can also receive log messages from
another switch. Set the Logging Facility to log and forward the log messages
you need to monitor your network (see the Logging Facility chapter in the AT-
8700XL Series Software Reference). Inspect the log file from time to time, and if
difficulties arise.
FLASH compaction
If the FLASH memory gets filled beyond a certain level, it will automatically
activate FLASH compaction to recover any space that is made available from
deleted files. You can also activate FLASH compaction manually if required.
While FLASH is compacting, do not restart the switch or use any commands
that affect the FLASH file subsystem. Do not restart the switch, or create, edit,
load, rename or delete any files until a message confirms that FLASH file
compaction is completed. Interrupting flash compaction may result in damage
to files. Damaged files are likely to prevent the switch from operating correctly.
Watch for software updates
From time to time patches may be released to improve the function of your
switch software, and new software releases make new features available.
Watch for patches and new software releases on the website at
http://www.alliedtelesyn.co.nz/support/at8700xl
.
Software Release 2.6.1
C613-02030-00 REV B
Page 77

Maintenance and Troubleshooting 77
What to Do if You Clear FLASH Memory Completely
DO NOT clear the FLASH memory completely. The software release files are
stored in FLASH, and clearing it would leave no software to run the switch.
If you accidentally do this, you will need to:
1. Boot with default configuration.
Reboot the switch from a terminal connected to the asynchronous terminal
port (not Telnet). Use the install override to run the default configuration
(see “How the Switch Starts Up” on page 74).
2. Log in.
Log in to the switch using the default password friend for the manager
account.
3. Put current software release on server.
Make sure you have the current software release and patch files on a server
connected to the switch by a switch port. Current software release and
patch files are downloaded from the website at
http://www.alliedtelesyn.co.nz/support/at8700xl
4. Assign an IP address.
Assign an IP address to the switch interface over which the software files
are downloaded (see “Assigning an IP Address” on page 14).
5. Load software files onto switch.
Load the required software and patch onto the switch (see “Loading and
Uploading Files” on page 52).
6. Set the install information.
Set the switch to use the software installed (see “Upgrading Switch Software”
on page 56).
7. Reconfigure the switch.
If you have a copy of the recent configuration file stored on your network,
you can download this onto the switch too. Otherwise you will need to reenter all configuration.
While FLASH is compacting, do not restart the switch or use any commands
that affect the FLASH file subsystem. Do not restart the switch, or create, edit,
load, rename or delete any files until a message confirms that FLASH file
compaction is completed. Interrupting flash compaction may result in damage
to files. Damaged files are likely to prevent the switch from operating correctly.
.
Software Release 2.6.1
C613-02030-00 REV B
If you accidentally restart the switch, or use any commands that affect the
FLASH file subsystem, contact your authorised distributor or reseller. You may
have to return the switch to the factory.
Page 78

78 AT-8700XL Series Switch User Guide
What to Do if Passwords are Lost
If a user forgets their password, to reset the password from an account with
MANAGER privilege, enter the command:
SET USER=login-name PASSWORD=password
You can reset passwords for accounts with MANAGER privilege with the same
command, provided the manager can login to at least one account with
MANAGER privilege.
If you require further assistance contact your authorised distributor or reseller.
Getting the Most Out of Technical Support
For online support for your switch, see our on-line support page at
http://www.alliedtelesyn.co.nz/support/at8700xl
.
If you require further assistance, contact your authorised distributor or reseller.
Gather as much of the following information from your switch and network as
you can. This gives the support personnel as much information as possible to
diagnose and solve your problem. They may ask you to send the information
to them by email.
Gather this information:
■ Your name, organisation and contact details.
■ What is the make and model of your switch? Enter the command:
SHOW SYSTEM
■ Which software release and patch files is your switch running? For
example,
■
What software configuration is currently running? Enter the command:
How is the switch connected to your network? A diagram showing the
■
87-261.rez, 87261-01.paz. Enter the command:
SHOW INSTALL
SHOW CONF DYN
physical configuration of the network your switch is operating in may be
useful.
■ To get debugging output, enter the command:
SHOW DEBUG
■ Depending on the problem, the support personnel may also ask you for the
output from the following commands (see the Monitoring and Fault
Diagnosis section in the Operations chapter, AT-8700XL Series Software
Reference):
SHOW EXCEPTION
SHOW STARTUP
SHOW LOG
SHOW CPU
SHOW BUFFER
Software Release 2.6.1
C613-02030-00 REV B
Page 79

Maintenance and Troubleshooting 79
Resetting Switch Defaults
To restart the switch at any time with no configuration, enter the command:
RESTART SWITCH CONFIG=NONE
If boot.cfg has changed, to set it back to the default configuration by saving
the default dynamic configuration to the
CREATE CONFIG=boot.cfg
boot.cfg file, enter the command:
To set the switch to restart with the boot configuration file, enter the command:
SET CONFIG=boot.cfg
DO NOT clear the FLASH memory completely. The software release files are
stored in FLASH, and clearing it would leave no software to run the switch.
Checking Connections Using PING
If an aspect of the switch’s configuration dependent on access to a server
functions incorrectly, PINGing the server from the switch, and the switch from
the server, is a useful first step in diagnosis.
You can use PING (Packet Internet Groper) to check whether there is a
connection between the switch and another routing interface in the network.
Use the switch’s extended PING command over IPv4, IPv6, IPX and AppleTalk
network protocols. PING sends echo request packets in the chosen format, and
displays responses at the terminal. Enter the command:
PING [{[IPADDRESS=]ipadd|[IPXADDRESS=]network:station|
[APPLEADDRESS=]network.node}] [LENGTH=number]
[NUMBER={number|CONTINUOUS}] [PATTERN=hexnum]
[{SIPADDRESS=ipadd|SIPXADDRESS=network:station|
SAPPLEADDRESS=network.node}] [SCREENOUTPUT={YES|NO}]
[TIMEOUT=number] [TOS=number]
To set PING defaults, enter the command:
SET PING [{[IPADDRESS=]ipadd|[IPXADDRESS=]network:station|
[APPLEADDRESS=]network.node}] [LENGTH=number]
[NUMBER={number|CONTINUOUS}] [PATTERN=hexnum]
[{SIPADDRESS=ipadd|SIPXADDRESS=network:station|SAPPLEADDR
ESS=network.node}] [SCREENOUTPUT={YES|NO}]
[TIMEOUT=number] [TOS=number]
To display the default PING settings and summary information, enter the
command:
Software Release 2.6.1
C613-02030-00 REV B
SHOW PING
The stop a PING that is in progress, enter the command:
STOP PING
If you can PING the end destination, then the physical and layer 2 links are
functioning, and any difficulties are in the network or higher layers.
Page 80

80 AT-8700XL Series Switch User Guide
If PING to the end destination fails, PING intermediate network addresses. If
you can successfully PING some network addresses, and not others, you can
deduce which link in the network is down.
Note that if Network Address Translation (NAT) is configured on the remote switch,
PINGing devices connected to it may give misleading information.
For more information about using PING, see the Internet Protocol (IP) chapter in
the AT-8700XL Series Software Reference.
Troubleshooting IP Configurations
Telnet Fails
1. If Telnet to switch fails
Check that the IP address you used matches the one assigned to the switch.
To check that RIP is configured correctly, enter the command:
SHOW IP RIP
To check that the IP Telnet server is enabled on each switch, enter the
command.
SHOW IP
If the Telnet server is disabled, enable the Telnet server with the command:
ENABLE TELNETSERVER
2. If Telnet to host fails
If Telnet into a host on the remote LAN fails, but works into the remote
switch, check that the IP address you are using is correct. To check that
both switches are gateways, not servers, enter the command:
SHOW IP
The “IP Packet Forwarding” field in the output should be set to “Enabled”.
Refer to the documentation for the host TCP/IP software for more
information about configuring a gateway.
The host’s TCP/IP software should be configured to use the Head Office
switch as its gateway. Refer to the documentation for the host TCP/IP
software for more information about configuring a gateway.
3. Contact your authorised distributor or reseller for assistance
If problems persist, contact your authorised distributor or reseller for
assistance.
Software Release 2.6.1
C613-02030-00 REV B
Page 81

Maintenance and Troubleshooting 81
Troubleshooting DHCP IP Addresses
Your switch is acting as a DHCP client
If your switch is acting as a DHCP client the switch should receive its IP
address dynamically. If your switch is not receiving an IP address, check that
the domain name and host name are correct.
Your switch is acting as a DHCP server
If your switch is not assigning IP addresses to a host, or hosts, on the subnet
perform this procedure:
1. Reboot the host machine, to force it to re-request IP settings.
2. Check the host’s TCP/IP settings.
In Microsoft® Windows™ 95/98, click Settings → Control Panel →
Network. Select TCP/IP and click Properties. Click Obtain an IP address
automatically.
In Microsoft® Windows™ 2000, click Settings → Control Panel →
Network and Dial-up Connections → Local Area Connection →
Properties. Select Internet connection (TCP/IP) and click Properties. Click
Obtain an IP address automatically.
3. Check that the DHCP server has a large enough range of addresses. To
assign a range, enter the command:
CREATE DHCP RANGE
Using Trace Route for IP Traffic
You can use trace route to discover the route that packets pass between two
systems running the IP protocol. Trace route sends an initial UDP packets with
the Time To Live (TTL) field in the IP header set starting at 1. The TTL field is
increased by one for every subsequent packet sent until the destination is
reached. Each hop along the path between two systems responds with a TTL
exceeded packet and from this the path is determined. For more information
about trace route, see the Internet Protocol (IP) chapter in the AT-8700XL Series
Software Reference.
To initiate a trace route, enter the command:
TRACE [[IPADDRESS=]ipadd] [MAXTTL=number] [MINTTL=number]
[NUMBER=number] [PORT=port-number] [SCREENOUTPUT={YES|NO}]
[SOURCE=ipadd] [TIMEOUT=number] [TOS=number]
Any parameters not specified use the defaults configured with a previous
invocation of the command:
Software Release 2.6.1
C613-02030-00 REV B
SET TRACE [[IPADDRESS=]ipadd] [MAXTTL=number] [MINTTL=number]
[NUMBER=number] [PORT=port-number] [SCREENOUTPUT={YES|NO}]
[SOURCE=ipadd] [TIMEOUT=number] [TOS=number]
As each response packet is received a message is displayed on the terminal
device from which the command was entered and the details are recorded. To
display the default configuration and summary information, enter the
command:
SHOW TRACE
To halt a trace route that is in progress, enter the command:
STOP TRACE
 Loading...
Loading...