Allied Telesis AT-8100L-8POE, AT-8100L-8, AT-8100S-16F8-LC, AT-8100S-16F8-SC, AT-8100S-24F-LC User Manual
...Page 1

AT-8100 Series
AT-8100S/24POE
26
25
26R
25R
S2S1
CONSOLE
LINK / ACT
plus
50
49
50R
49R
AT-8100S/48POE
S2S1
CONSOLE
LINK / ACT
plus
2056
S2S1
CONSOLE
LINK / ACT
AT-8100S/16F8-SC
1
TX RX
L/A
2
TX RX
L/A
3
TX RX
L/A
4
L/A
TX RX
5
TX RX
L/A
6
TX RX
L/A
7
TX RX
L/A
8
L/A
TX RX
9
TX RX
L/A
10
TX RX
L/A
11
TX RX
L/A
12
L/A
TX RX
13
TX RX
L/A
14
TX RX
L/A
15
TX RX
L/A
16
L/A
TX RX
17181920212223
24
262526R
25R
2525R
AT-8100S/24F-BiDi
26
26R
1357911131517192123
2 4 6 8 10 12 14 16 18 20 22 24
S2S1
CONSOLE
LINK / ACT
Fast Ethernet Switches
AT-8100L/8
AT-8100L/8POE
AT-8100L/8POE-E
AT-8100S/24C
AT-8100S/24
AT-8100S/24POE
AT-8100S/16F8-SC
AT-8100S/16F8-LC
AT-8100S/24F-LC
AT-8100S/48
AT-8100S/48POE
Management Software
Web Browser User’s Guide
AlliedWare Plus™ Version 2.2.4
613-001612 Rev. A
Page 2

Copyright
Copyright © 2012, Allied Telesis, Inc.
All rights reserved.
This product includes software licensed under the BSD License. As such, the following language applies for those
portions of the software licensed under the BSD License:
Redistribution and use in source and binary forms, with or without modification, are permitted provided that the following
conditions are met:
* Redistributions of source code must retain the above copyright notice, this list of conditions and the following
disclaimer.
* Redistributions in binary form must reproduce the above copyright notice, this list of conditions and the following
disclaimer in the documentation and/or other materials provided with the distribution.
* Neither the name of Allied Telesis, Inc. nor the names of the respective companies above may be used to endorse or
promote products derived from this software without specific prior written permission.
THIS SOFTWARE IS PROVIDED BY THE COPYRIGHT HOLDERS AND CONTRIBUTORS "AS IS" AND ANY
EXPRESS OR IMPLIED WARRANTIES, INCLUDING, BUT NOT LIMITED TO, THE IMPLIED WARRANTIES OF
MERCHANTABILITY AND FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE ARE DISCLAIMED. IN NO EVENT
SHALL THE COPYRIGHT HOLDER OR CONTRIBUTORS BE LIABLE FOR ANY DIRECT, INDIRECT,
INCIDENTAL, SPECIAL, EXEMPLARY, OR CONSEQUENTIAL DAMAGES (INCLUDING, BUT NOT LIMITED
TO, PROCUREMENT OF SUBSTITUTE GOODS OR SERVICES; LOSS OF USE, DATA, OR PROFITS; OR
BUSINESS INTERRUPTION) HOWEVER CAUSED AND ON ANY THEORY OF LIABILITY, WHETHER IN
CONTRACT, STRICT LIABILITY, OR TORT (INCLUDING NEGLIGENCE OR OTHERWISE) ARISING IN ANY
WAY OUT OF THE USE OF THIS SOFTWARE, EVEN IF ADVISED OF THE POSSIBILITY OF SUCH DAMAGE.
Copyright 1989, 1991, 1992 by Carnegie Mellon University. Derivative Work - 1996, 1998-2000. Copyright 1996, 19982000 by The Regents of the University of California - All rights reserved. Copyright (c) 2001-2003 by Networks
Associates Technology, Inc. - All rights reserved. Copyright (c) 2001-2003 by Cambridge Broadband Ltd. - All rights
reserved. Copyright (c) 2003 by Sun Microsystems, Inc. - All rights reserved. Copyright (c) 2003-2005 by Sparta, Inc. All rights reserved. Copyright (c) 2004 by Cisco, Inc. and Information Network Center of Beijing University of Posts and
Telecommunications. - All rights reserved. Copyright (c) 2003 by Fabasoft R&D Software GmbH & Co KG - All rights
reserved. Copyright (c) 2004-2006 by Internet Systems Consortium, Inc. ("ISC") - All rights reserved. Copyright (c)
1995-2003 by Internet Software Consortium - All rights reserved. Copyright (c) 1992-2003 by David Mills - All rights
reserved. Copyright (c) 1995 by Tatu Ylonen <ylo@cs.hut.fi>, Espoo, Finland - All rights reserved. Copyright (c) 1998
by CORE SDI S.A., Buenos Aires, Argentina - All rights reserved. Copyright 1995, 1996 by David Mazieres - All rights
reserved. Copyright 1983, 1990, 1992, 1993, 1995 by The Regents of the University of California - All rights reserved.
Copyright (c) 1995 Patrick Powell - All rights reserved. Copyright (c) 1998-2005 The OpenSSL Project - All rights
reserved. Copyright (C) 1995-1998 Eric Young (eay@cryptsoft.com) - All rights reserved. Copyright (c) 2008, Henry
Kwok - All rights reserved. Copyright (c) 1995, 1998, 1999, 2000, 2001 by Jef Poskanzer <jef@mail.acme.com>. - All
rights reserved.
Some components of the SSH software are provided under a standard 2-term BSD license with the following names as
copyright holders: Markus Friedl, Theo de Raadt, Niels Provos, Dug Song, Aaron Campbell, Damien Miller, Kevin
Steves, Daniel Kouril, Wesley Griffin, Per Allansson, Nils Nordman, and Simon Wilkinson,
Portable OpenSSH includes code from the following copyright holders, also under the 2-term BSD license: Ben
Lindstrom, Tim Rice, Andre Lucas, Chris Adams, Corinna Vinschen, Cray Inc., Denis Parker, Gert Doering, Jakob
Schlyter, Jason Downs, Juha Yrjola, Michael Stone, Network Associates, Solar Designer, Todd C. Miller, Wayne
Schroeder, William Jones, Darren Tucker, Sun Microsystems, The SCO Group.
Some Portable OpenSSH code is licensed under a 3-term BSD style license to the following copyright holders: Todd C.
Miller, Theo de Raadt, Damien Miller, Eric P. Allman, The Regents of the University of California, and Constantin S.
Svintsoff. Some Portable OpenSSH code is licensed under an ISC-style license to the following copyright holders:
Internet Software Consortium, Todd C. Miller, Reyk Floeter, and Chad Mynhier. Some Portable OpenSSH code is
licensed under a MIT-style license to the following copyright holder: Free Software Foundation, Inc.
This product also includes software licensed under the GNU General Public License available from:
http://www.gnu.org/licenses/gpl2.html
Page 3

Allied Telesis is committed to meeting the requirements of the open source licenses including the GNU General Public
License (GPL) and will make all required source code available.
If you would like a copy of the GPL source code contained in this product, please send us a request by registered mail
including a check for US$15 to cover production and shipping costs, and a CD with the GPL code will be mailed to you.
GPL Code Request
Allied Telesis, Inc.
3041 Orchard Parkway
San Jose, Ca
No part of this publication may be reproduced without prior written permission from Allied Telesis, Inc.
Allied Telesis, AlliedWare Plus, and the Allied Telesis logo are trademarks of Allied Telesis, Incorporated. Microsoft and
Internet Explorer are registered trademarks of Microsoft Corporation. All other product names, company names, logos or
other designations mentioned herein are trademarks or registered trademarks of their respective owners.
Allied Telesis, Inc. reserves the right to make changes in specifications and other information contained in this document
without prior written notice. The information provided herein is subject to change without notice. In no event shall Allied
Telesis, Inc. be liable for any incidental, special, indirect, or consequential damages whatsoever, including but not limited
to lost profits, arising out of or related to this manual or the information contained herein, even if Allied Telesis, Inc. has
been advised of, known, or should have known, the possibility of such damages.
lifornia 95134
Page 4

Page 5

Contents
Preface ............................................................................................................................................................ 15
Document Conventions .................................................................................................................................... 16
Downloading Management Software and Web-based Guides ......................................................................... 17
Contacting Allied Telesis .................................................................................................................................. 18
Online Support ........................................................................................................................................... 18
Email and Telephone Support.................................................................................................................... 18
Returning Products .................................................................................................................................... 18
Sales or Corporate Information .................................................................................................................. 18
Management Software Updates................................................................................................................. 18
Chapter 1: AlliedWare Plus™ Version 2.2.4 Web Browser Interface ........................................................ 19
Management Sessions ..................................................................................................................................... 20
Web Manager Accounts ................................................................................................................................... 21
Chapter 2: Starting a Management Session ............................................................................................... 23
Non-secure HTTP and Secure HTTPS Modes................................................................................................. 24
HTTP Mode................................................................................................................................................ 24
HTTPS Mode ............................................................................................................................................. 24
Starting the Initial Web Management Session.................................................................................................. 25
Logging on to the Switch .................................................................................................................................. 27
What to Configure First..................................................................................................................................... 30
Changing the Login Password ................................................................................................................... 30
Assigning a Name to the Switch ................................................................................................................ 30
Changing a Management IP Address ........................................................................................................ 30
Setting System Time .................................................................................................................................. 31
Starting a Web Management Session .............................................................................................................. 32
When You Do Not Know the IP Address of the Switch .............................................................................. 32
When the Switch Does Not Display the Login Page .................................................................................. 33
Logging on to the CLI through the Console Port........................................................................................ 33
Checking for the IP Addresses of the Switch in the CLI............................................................................. 34
Adding an IP Address to the Switch in the CLI .......................................................................................... 34
Checking the Status of HTTP and HTTPS Services in the CLI.................................................................. 34
Enabling HTTP or HTTPS Service in the CLI ............................................................................................ 35
Saving your Changes in the CLI ................................................................................................................ 36
Saving Your Changes....................................................................................................................................... 37
Ending a Web Management Session ............................................................................................................... 38
Chapter 3: Basic Switch Parameters ........................................................................................................... 39
Setting the System Date and Time................................................................................................................... 40
Configuring an SNTP or NTP Server ......................................................................................................... 40
Setting System Time Manually................................................................................................................... 42
Configuring a Telnet or SSH Server ................................................................................................................. 45
Configuring a Remote Log Server .................................................................................................................... 47
Setting the Switch Information.......................................................................................................................... 48
Managing the Configuration File....................................................................................................................... 50
Displaying the Configuration Files.............................................................................................
Configuration File .......................................................................................................... 51
Setting the Activ
e
................. 50
5
Page 6

Contents
Downloading a Configuration File onto Your PC ........................................................................................ 51
Deleting a Configuration ............................................................................................................................. 52
Managing Local User Accounts ........................................................................................................................ 53
Adding a New User Account....................................................................................................................... 53
Changing a User Password........................................................................................................................ 55
Changing the User Privilege.......................................................................................................................56
Deleting a User Account............................................................................................................................. 57
Rebooting a Switch ........................................................................................................................................... 59
Upgrading the Software .................................................................................................................................... 60
Returning the AlliedWare Plus Management Software to the Factory Default Values...................................... 63
Displaying System Information ......................................................................................................................... 64
Chapter 4: Setting Port Parameters ............................................................................................................. 67
Port Numbers on the Switch .............................................................................................................................68
Displaying the Port Parameters ........................................................................................................................69
Changing the Port Settings ............................................................................................................................... 72
Displaying the Storm Control Settings .............................................................................................................. 76
Modifying the Storm Control Settings ............................................................................................................... 78
Chapter 5: Setting Port Statistics ................................................................................................................. 81
Displaying Port Statistics .................................................................................................................................. 82
Displaying Transmit and Receive Port Statistics ........................................................................................ 82
Displaying Receive Statistics...................................................................................................................... 83
Displaying Transmit Statistics..................................................................................................................... 85
Displaying Interface Statistics..................................................................................................................... 87
Clearing Port Statistics...................................................................................................................................... 89
Reloading Statistics .......................................................................................................................................... 90
Chapter 6: Port Mirroring .............................................................................................................................. 91
Overview ........................................................................................................................................................... 92
Displaying Port Mirroring Settings..................................................................................................................... 93
Assigning a Destination Port ............................................................................................................................. 95
Assigning Source Ports and Port Mirroring Values ...........................................................................................96
Deleting Port Mirroring Settings ........................................................................................................................ 98
Chapter 7: Spanning Tree Protocol on a Port ............................................................................................. 99
Overview ......................................................................................................................................................... 100
Displaying Port Spanning Tree Protocol Settings ...........................................................................................101
Modifying Port Spanning Tree Protocol Settings ............................................................................................ 103
Chapter 8: Setting the MAC Address .........................................................................................................107
Displaying the Unicast MAC Addresses ......................................................................................................... 108
Displaying the Multicast MAC Addresses .......................................................................................................110
Assigning a Unicast MAC Address ................................................................................................................. 111
Assigning a Multicast MAC Address ............................................................................................................... 113
Deleting a Unicast MAC Address.................................................................................................................... 115
Deleting a Multicast MAC Address .................................................................................................................116
Chapter 9: Link Aggregation Control Protocol (LACP) ............................................................................117
......
Overview ........................................................................................................................
........................... 118
Displaying LACP Trunks ................................................................................................................................. 119
Adding an LACP Trunk ................................................................................................................................... 121
Modifying an LACP Trunk ............................................................................................................................... 123
Deleting an LACP Trunk ................................................................................................................................. 125
Chapter 10: Setting Static Port Trunks ...................................................................................................... 127
Overview ......................................................................................................................................................... 128
Displaying Static Trunk Settings ..................................................................................................................... 129
6
Page 7

AlliedWare Plus Version 2.2.4 Management Software Web Browser User’s Guide
Adding Static Trunks ...................................................................................................................................... 131
Modifying the Static Trunk Settings ................................................................................................................ 134
Deleting Static Trunks .................................................................................................................................... 137
Chapter 11: Setting Port-based and Tagged VLANs ................................................................................ 139
Overview......................................................................................................................................................... 140
Port-based VLANs ................................................................................................................................... 140
Port VLAN Identifier ................................................................................................................................. 140
Tagged VLANs......................................................................................................................................... 140
Tagged and Untagged Ports .................................................................................................................... 141
Native VLAN............................................................................................................................................. 141
Displaying VLANs........................................................................................................................................... 142
Adding an VLAN ............................................................................................................................................. 143
Modifying VLANs ............................................................................................................................................ 145
Assigning a Native VLAN ............................................................................................................................... 148
Removing an Untagged Port from a VLAN..................................................................................................... 150
Deleting VLANs .............................................................................................................................................. 152
Chapter 12: Spanning Tree Protocols on the Switch ............................................................................... 153
Overview......................................................................................................................................................... 154
Displaying and Modifying Spanning Tree Protocol Settings on the Switch .................................................... 155
Chapter 13: Internet Group Management Protocol (IGMP) Snooping .................................................... 159
Overview......................................................................................................................................................... 160
Displaying and Modifying IGMP Snooping Configuration............................................................................... 161
Disabling IGMP Snooping .............................................................................................................................. 164
Displaying the Routers List............................................................................................................................. 165
Clearing the Routers List ................................................................................................................................ 167
Displaying the Hosts List ................................................................................................................................ 168
Chapter 14: IGMP Snooping Querier ......................................................................................................... 171
Overview......................................................................................................................................................... 172
Assigning Multiple Queriers ..................................................................................................................... 173
Guidelines....................................................................................................................................................... 176
Displaying IGMP Snooping Querier................................................................................................................ 177
Modifying IGMP Snooping Query Interval ...................................................................................................... 179
Chapter 15: Power Over Ethernet (PoE) .................................................................................................... 181
Overview......................................................................................................................................................... 182
Power Sourcing Equipment (PSE) ........................................................................................................... 182
Powered Device (PD)............................................................................................................................... 182
PD Classes .............................................................................................................................................. 182
Port Prioritization...................................................................................................................................... 183
Displaying PoE Port Settings.......................................................................................................................... 184
Modifying PoE Settings Globally .................................................................................................................... 187
Modifying PoE Settings on a Port................................................................................................................... 188
Chapter 16: MAC Address-based Port Security ....................................................................................... 191
Overview......................................................................................................................................................... 192
Static Versus Dynamic Addresses ........................................................................................................... 192
Intrusion Actions....................................................................................................................................... 192
Guidelines ................................................................................................................................................ 193
Displaying the MAC Address-based Port Security Settings ........................................................................
Modifying
the MAC Address-based Port Sec
urity Settings ............................................................................ 196
... 194
Disabling MAC Address-based Port Security Settings ................................................................................... 198
Chapter 17: RADIUS and TACACS+ Clients .............................................................................................. 199
Overview......................................................................................................................................................... 200
7
Page 8

Contents
Remote Manager Accounts ......................................................................................................................200
Accounting Information............................................................................................................................. 201
Configuring RADIUS and TACACS+ ........................................................................................................ 201
Placing RADIUS and TACACS+ Servers in the Client’s List ....................................................................201
Configuring RADIUS for Remote Manager Authentication ............................................................................. 203
Configuring Remote Manager Authentication Using RADIUS..................................................................203
Adding a RADIUS Server .........................................................................................................................206
Configuring TACACS+ for Remote Manager Authentication .......................................................................... 208
Configuring Remote Manager Authentication Using TACACS+............................................................... 208
Adding a TACACS+ Server ...................................................................................................................... 211
Deleting an Authentication Server .................................................................................................................. 213
Chapter 18: 802.1x Port-based Network Access ....................................................................................... 215
Overview ......................................................................................................................................................... 216
Port Roles................................................................................................................................................. 216
Operating Modes ...................................................................................................................................... 217
Dynamic VLAN Assignments.................................................................................................................... 219
Guest VLAN..............................................................................................................................................220
Enabling 802.1x Port-based Authentication on the Switch ............................................................................. 221
Configuring 802.1x Port-based Authentication ............................................................................................... 222
Disabling 802.1x Port-based Authentication on the Switch ............................................................................227
Disabling 802.1x Port-based Authentication on a Port ................................................................................... 228
Chapter 19: Setting IPv4 and IPv6 Addresses ........................................................................................... 229
Overview ......................................................................................................................................................... 230
IP Management Guidelines ...................................................................................................................... 231
Displaying IPv4 Interfaces .............................................................................................................................. 232
Adding an IPv4 Address ................................................................................................................................. 234
Changing an IPv4 Address ............................................................................................................................. 236
Deleting an IPv4 Address ............................................................................................................................... 238
Displaying the IPv6 Interface .......................................................................................................................... 239
Adding an IPv6 Address ................................................................................................................................. 241
Changing IPv6 Addresses .............................................................................................................................. 243
Deleting IPv6 Addresses................................................................................................................................. 245
Chapter 20: Access Control Lists (ACL) .................................................................................................... 247
Overview ......................................................................................................................................................... 248
Classifier Number Ranges........................................................................................................................ 248
Filtering Criteria ........................................................................................................................................ 248
IPv4 Address and Mask............................................................................................................................ 249
Actions......................................................................................................................................................249
How Ingress Packets are Compared Against ACLs ................................................................................. 249
Guidelines.................................................................................................................................................250
Creating an ACL ............................................................................................................................................. 251
Assigning an ACL to Ports .............................................................................................................................. 255
Displaying a List of ACLs ................................................................................................................................ 257
Chapter 21: Setting Static Routes .............................................................................................................. 259
Displaying Static Routes ................................................................................................................................. 260
Adding a Static Route ..................................................................................................................................... 262
Deleting a Static Route ................................................................................................................................... 264
Displaying the Routing Table ...................................................................................................
....................... 265
er 22: Quality of Service (QoS) .........................................................................................................267
apt
Ch
Overview ......................................................................................................................................................... 268
Class Information......................................................................................................................................268
Priority Queue...........................................................................................................................................268
8
Page 9

AlliedWare Plus Version 2.2.4 Management Software Web Browser User’s Guide
Classifier Number Ranges ....................................................................................................................... 268
Filtering Criteria........................................................................................................................................ 269
Actions ..................................................................................................................................................... 269
How Ingress Packets are Selected with Filtering Criteria ........................................................................ 269
Guidelines ................................................................................................................................................ 269
Creating a QoS Policy .................................................................................................................................... 271
Assigning a QoS Policy to Ports..................................................................................................................... 276
Displaying a List of QoS Policies .................................................................................................................... 278
Chapter 23: Setting Dynamic Routes Using RIP ...................................................................................... 279
Overview......................................................................................................................................................... 280
Enabling RIP ............................................................................................................................................ 280
Displaying the RIP Configuration.................................................................................................................... 281
Enabling RIP on a VLAN Interface ................................................................................................................. 283
Changing the RIP Settings ............................................................................................................................. 286
Removing a VLAN Interface from the RIP Configuration ............................................................................... 287
Displaying RIP Statistics................................................................................................................................. 288
Reloading RIP Statistics ................................................................................................................................. 290
Chapter 24: Managing the ARP Table ........................................................................................................ 291
Overview......................................................................................................................................................... 292
ARP Table Management Guidelines........................................................................................................ 292
Displaying the ARP Table............................................................................................................................... 293
Adding a Static ARP Entry.............................................................................................................................. 295
Deleting ARP Entries...................................................................................................................................... 297
Chapter 25: LLDP and LLDP-MED ............................................................................................................. 299
Overview......................................................................................................................................................... 300
Enabling and Configuring LLDP on the Switch............................................................................................... 302
Disabling LLDP on the Switch ........................................................................................................................ 305
Configuring LLDP on a Port............................................................................................................................ 306
Selecting LLDP TLVs on a Port...................................................................................................................... 308
Setting a Location Entry for the LLDP-MED Location TLV............................................................................. 312
Creating a Civic Location Entry................................................................................................................ 312
Creating a Coordinate Location ............................................................................................................... 316
Creating an Emergency Location Identification Number (ELIN) Location................................................ 319
Assigning LLDP Locations to a Port ............................................................................................................... 322
Selecting LLDP-MED TLVs on a Port............................................................................................................. 324
Displaying LLDP Neighbor Information .......................................................................................................... 327
Displaying LLDP Statistics.............................................................................................................................. 329
Displaying Location Entries ............................................................................................................................ 332
Displaying Civic Locations ....................................................................................................................... 332
Displaying Coordinate Locations.............................................................................................................. 333
Displaying ELIN Locations ....................................................................................................................... 334
Displaying LLDP and LLDP-MED Settings..................................................................................................... 335
Displaying the Basic LLDP Configuration ................................................................................................ 335
Displaying LLDP Port Assignments ......................................................................................................... 336
Displaying Port Locations......................................................................................................................... 337
.......
Displaying LLDP TLV ..............................................................................................................
.......... 337
Displaying LLDP-MED TLV...................................................................................................................... 339
Chapter 26: sFlow ........................................................................................................................................ 341
Overview......................................................................................................................................................... 342
Ingress Packet Samples .......................................................................................................................... 342
Packet Counters....................................................................................................................................... 342
sFlow Collectors....................................................................................................................................... 343
Guidelines ................................................................................................................................................ 343
9
Page 10

Contents
Configuring sFlow on a Port............................................................................................................................344
Specifying an sFlow Collector ......................................................................................................................... 346
Enabling sFlow on the Switch ......................................................................................................................... 348
Displaying the sFlow Settings ......................................................................................................................... 349
10
Page 11

Figures
Figure 1: Login Page ............................................................................................................................................................26
Figure 2: Login Page with Entries.........................................................................................................................................27
Figure 3: Dashboard Page ...................................................................................................................................................28
Figure 4: AlliedWare Plus™ Command Line Prompt............................................................................................................34
Figure 5: Displaying the IP Address .....................................................................................................................................34
Figure 6: Displaying the Status of HTTP Service .................................................................................................................35
Figure 7: Displaying the Status of HTTPS Service...............................................................................................................35
Figure 8: System Contact Information Page.........................................................................................................................37
Figure 9: System Settings Tab .............................................................................................................................................41
Figure 10: System Time Settings Page with Network Time Settings Tab ............................................................................41
Figure 11: System Time Settings Page with Date & Time Tab.............................................................................................43
Figure 12: Calendar Page ....................................................................................................................................................44
Figure 13: System Services Page ........................................................................................................................................45
Figure 14: System Contact Information Page.......................................................................................................................48
Figure 15: Configuration Files Page .....................................................................................................................................50
Figure 16: File Download Popup Window of Internet Explorer 8 ..........................................................................................51
Figure 17: User Management Page......................................................................................................................................54
Figure 18: User Management Page with Change Password Tab.........................................................................................55
Figure 19: User Management Page with Change Privilege Tab...........................................................................................56
Figure 20: User Management Page with Delete User Tab...................................................................................................58
Figure 21: User Login page on the Allied Telesis Website ...................................................................................................60
Figure 22: System Upgrade Page ........................................................................................................................................61
Figure 23: Port Number ........................................................................................................................................................68
Figure 24: Switching Tab with Port Tab................................................................................................................................69
Figure 25: Port Configuration Page ......................................................................................................................................70
Figure 26: Port Configuration Modify Page...........................................................................................................................73
Figure 27: Storm Control List Page ......................................................................................................................................76
Figure 28: Storm Control Settings Page...............................................................................................................................78
Figure 29: Port Statistics Page with Tx + Rx Tab.................................................................................................................82
igure 30:
F
Figure 31: Port Statistics with the Transmit Tab...................................................................................................................86
Figure 32: Port Statistics Page with Interface Tab................................................................................................................87
Figure 33: Port Statistics Page with the Reload Page Button...............................................................................................90
Figure 34: Port Mirroring List Page.......................................................................................................................................93
Figure 35: Modify Port Mirroring Page..................................................................................................................................96
Figure 36: Port Spanning Tree Settings Page....................................................................................................................101
Figure 37: Modify Port Spanning Tree Settings Page ........................................................................................................103
Figure 38: Switching Tab....................................................................................................................................................108
Figure 39: Unicast MACs Page ..........................................................................................................................................108
Figure 40: Multicast MACs Page ........................................................................................................................................110
Figure 41: Unicast MAC Address Page..............................................................................................................................111
Figure 42: Multicast MAC Address Page............................................................................................................................113
Figure 43: Switching Tab with Link Aggregation Selected..................................................................................................119
Figure 44: LACP Trunks Page............................................................................................................................................119
Figure 45: Add LACP Trunk Page ......................................................................................................................................121
Figure 46: Modify LACP Trunk Page..................................................................................................................................123
Figure 47: Switching Tab with Static Trunks.......................................................................................................................129
Figure 48: Static Trunks Page ............................................................................................................................................129
Figure 49: Add Static Trunk Page ......................................................................................................................................132
Figure 50: Modify Static Trunk Page ..................................................................................................................................135
Port Statistics with the Receive Tab....................................................................................................................84
11
Page 12

Figures
Figure 51: VLANs Page ......................................................................................................................................................142
Figure 52: Add VLAN Page ................................................................................................................................................143
Figure 53: Modify VLAN Page ............................................................................................................................................146
Figure 54: Native VLAN Page.............................................................................................................................................148
Figure 55: Modify VLAN Page ............................................................................................................................................151
Figure 56: Spanning Tree Settings Page............................................................................................................................155
Figure 57: Switching IGMP Tab..........................................................................................................................................161
Figure 58: IGMP Snooping Page with Configuration Tab ...................................................................................................162
Figure 59: IGMP Snooping Page with Routers List Tab .....................................................................................................165
Figure 60: IGMP Snooping Page with Hosts List Tab.........................................................................................................168
Figure 61: IGMP Snooping Querier with One Querier ........................................................................................................173
Figure 62: IGMP Snooping Querier with Two Queriers ......................................................................................................174
Figure 63: Switching IGMP Tab..........................................................................................................................................177
Figure 64: IGMP Snooping Querier Page ...........................................................................................................................177
Figure 65: Edit IGMP Snooping Querier Page....................................................................................................................179
Figure 66: Switching Tab ....................................................................................................................................................184
Figure 67: PoE Port List Page ............................................................................................................................................185
Figure 68: Modify Port PoE Settings Page .........................................................................................................................188
Figure 69: Security Tab.......................................................................................................................................................194
Figure 70: MAC Based Port Security Page.........................................................................................................................194
Figure 71: Modify MAC Based Port Security Page .............................................................................................................196
Figure 72: Authentication Server Configuration Page with RADIUS Tab ...........................................................................204
Figure 73: Radius Add Page...............................................................................................................................................206
Figure 74: Authentication Server Configuration Page with TACACS+ Tab ........................................................................209
Figure 75: TACACS+ Add Page .........................................................................................................................................212
Figure 76: Example of Port Roles.......................................................................................................................................217
Figure 77: Single Host Mode ..............................................................................................................................................217
Figure 78: Multiple Host Operating Mode ...........................................................................................................................218
Figure 79: Multiple Supplicant Mode.............................................................................................
Figure 80: 802.1x Authentication Page...............................................................................................................................221
Figure 81: Modify 802.1x Authentication Page ...................................................................................................................222
Figure 82: Modify 802.1x Authentication Page Expanded ..................................................................................................223
Figure 83: 802.1x Authentication Page with Status Enabled ..............................................................................................227
Figure 84: Layer 3 Tab .......................................................................................................................................................232
Figure 85: IPv4 Interfaces Page .........................................................................................................................................232
Figure 86: IP Address Configuration Page .........................................................................................................................234
Figure 87: Edit IP Address Configuration Page ..................................................................................................................236
Figure 88: Layer 3 Tab .......................................................................................................................................................239
Figure 89: IPv6 Interface Page ...........................................................................................................................................239
Figure 90: IPv6 Management Configuration Page..............................................................................................................241
Figure 91: Edit IPv6 Management Configuration Page.......................................................................................................243
Figure 92: ACLs and QoS Tab............................................................................................................................................251
Figure 93: Traffic Classifiers Page......................................................................................................................................251
Figure 94: Traffic Classification Page .................................................................................................................................252
Figure 95: Text box for Mirror to Port..................................................................................................................................253
Figure 96: Policies/ACLs Page ...........................................................................................................................................255
Figure 97: Traffic Classifiers Page......................................................................................................................................256
Figure 98: Traffic Classifiers Page......................................................................................................................................257
Figure 99: Layer 3 Tab .......................................................................................................................................................260
Figure 100: Static Routes Page..........................................................................................................................................260
Figure 101: Add Static ARP Page.......................................................................................................................................262
Figure 102: Layer 3 Tab .....................................................................................................................................................265
Figure 103: Routing Table Page.........................................................................................................................................265
Figure 104: ACLs and QoS Tab..........................................................................................................................................271
Figure 105: Traffic Classifiers Page....................................................................................................................................271
Figure 106: Traffic Classification Page ...............................................................................................................................272
Figure 107: Text box for Priority Queue..............................................................................................................................273
Figure 108: Text box for DSCP...........................................................................................................................................273
Figure 109: Text box for CoS..............................................................................................................................................274
Figure 110: Policies/ACLs Page .........................................................................................................................................276
......................................219
12
Page 13

AlliedWare Plus Version 2.2.4 Management Software Web Browser User’s Guide
Figure 111: Traffic Classifier Page .....................................................................................................................................277
Figure 112: Traffic Classifiers Page....................................................................................................................................278
Figure 113: Layer 3 Tab .....................................................................................................................................................281
Figure 114: RIP Configuration Page...................................................................................................................................281
Figure 115: Layer 3 Tab .....................................................................................................................................................283
Figure 116: RIP Interface Page ..........................................................................................................................................284
Figure 117: Layer 3 Tab .....................................................................................................................................................288
Figure 118: RIP Configuration Page...................................................................................................................................288
Figure 119: RIP Statistics Page with the Refresh Button ...................................................................................................290
Figure 120: Switching Tab..................................................................................................................................................293
Figure 121: ARP Table Page..............................................................................................................................................293
Figure 122: Add Static ARP Page ......................................................................................................................................295
Figure 123: Discovery & Monitoring Tab ............................................................................................................................302
Figure 124: LLDP Configuration Page................................................................................................................................303
Figure 125: LLDP Port Config Page ...................................................................................................................................306
Figure 126: Modify LLDP Port Configuration Page.............................................................................................................307
Figure 127: LLDP TLV Tab.................................................................................................................................................308
Figure 128: LLDP TLV Page ..............................................................................................................................................309
Figure 129: Modify LLDP TLV Page...................................................................................................................................310
Figure 130: Locations Tab..................................................................................................................................................313
Figure 131: LLDP Civic Location Page...............................................................................................................................313
Figure 132: LLDP Civic Location Page— Modify................................................................................................................314
Figure 133: LLDP Coordinate Location Page.....................................................................................................................317
Figure 134: LLDP Coordinate Location Page— Modify......................................................................................................318
Figure 135: LLDP ELIN Location List Page........................................................................................................................320
Figure 136: LLDP ELIN Location Page ..............................................................................................................................320
Figure 137: LLDP Port Location Page................................................................................................................................322
Figure 138: Modify LLDP Port Location Page ....................................................................................................................323
Figure 139: LLDP-MED TLV Page .....................................................................................................................................324
Figure 140: Modify LLDP-MED TLV Page..........................................................................................................................325
Figure 141: LLDP Neighbors Information Page..................................................................................................................327
Figure 142: LLDP Statistics Page with Port Statistics Tab .................................................................................................329
Figure 143: LLDP Statistics Page with Summary Tab........................................................................................................330
Figure 144: Discovery &Monitoring Tab .............................................................................................................................344
Figure 145: sFlow Page with the Port Configurations Tab .................................................................................................344
Figure 146: sFlow Port Modify Page...................................................................................................................................345
Figure 147: sFlow Page with Collectors Tab ......................................................................................................................346
Figure 148: sFlow Collector Page.......................................................................................................................................347
13
Page 14

Figures
14
Page 15
Preface
Caution
This manual is the web browser management guide for the AT-8100
Series of Fast Ethernet switches. The instructions in this guide explain how
to start a management session, use the web interface of the AlliedWare
Plus™ Management Software, and configure the features of the switch.
For hardware installation instructions, refer to the AT-8100L and 8100S
Series Fast Ethernet Stand-alone Installation Guide and AT-8100 Series
Fast Ethernet Switches Stack Installation Guide.
This preface contains the following sections:
“Document Conventions” on page 16
“Downloading Management Software and Web-based Guides” on
page 17
“Contacting Allied Telesis” on page 18
The software described in this document may contain certain
encryption/security or cryptographic functionality and for exporting
those products/software, USA export restrictions apply as per 15
C.F.R. Part 730-772 (particularly Part 740.17). At present, as per
United States of America’s export regulations our products/software
cannot be exported to Cuba, Iran, North Korea, North Sudan, or
Syria. If you wish to transfer this software outside the United States
or Canada, please refer to export regulations of USA.
15
Page 16

Document Conventions
Note
Caution
Warning
This document uses the following conventions:
Notes provide additional information.
Cautions inform you that performing or omitting a specific action
may result in equipment damage or loss of data.
Warnings inform you that performing or omitting a specific action
may result in bodily injury.
16
Page 17

AlliedWare Plus Version 2.2.4 Management Software Web Browser User’s Guide
Downloading Management Software and Web-based Guides
Both new releases of management software and product documentation
are available from the Allied Telesis web sites. The management software
is available at www.alliedtelesis.com/support/software. To display all of
the network management software for a product, use the pull-down menu
labeled “All” to select a hardware product model such as “AT-8100S/24.”
Then double click the software version that you want to download onto
your local work station or server.
The installation and user guides for all Allied Telesis products are available
in PDF at www.alliedtelesis.com/support/documentation/. To display
all of the product documentation for a product, use the pull-down menu
labeled “All” to select a hardware product model such as “AT-8100S/48.”
Then double click the document that you want to view. You can view the
documents online or download them onto your local workstation or server.
17
Page 18

Contacting Allied Telesis
This section provides Allied Telesis contact information for technical
support and for sales and corporate information.
Online Support You can request technical support online by accessing the Allied Telesis
Knowledge Base: www.alliedtelesis.com/support/kb.aspx. You can use
the Knowledge Base to submit questions to our technical support staff and
review answers to previously asked questions.
Email and
Telephone
Support
Returning
Products
Sales or
Corporate
Information
Management
Software Updates
For Technical Support via email or telephone, refer to the Allied Telesis
web site at www.alliedtelesis.com. Select your country from the list on
the web site and then select the appropriate tab.
Products for return or repair must first be assigned a return materials
authorization (RMA) number. A product sent to Allied Telesis without an
RMA number will be returned to the sender at the sender’s expense. For
instructions on how to obtain an RMA number, go to our web site at
www.alliedtelesis.com and then select Support and Replacement
Services.
You can contact Allied Telesis for sales or corporate information through
our web site at www.alliedtelesis.com.
New releases of the management software for our managed products are
available from the Allied Telesis web site: www.alliedtelesis.com. For
downloading instructions, see “Downloading Management Software and
Web-based Guides” on page 17.
18
Page 19

Chapter 1
AlliedWare Plus™ Version 2.2.4 Web Browser Interface
This chapter describes the types of management sessions using the
AlliedWare Plus™ management software and the Web interface manager
accounts. See the following sections:
“Management Sessions” on page 20
“Web Manager Accounts” on page 21
19
Page 20

Chapter 1: AlliedWare Plus™ Version 2.2.4 Web Browser Interface
Management Sessions
The AT-8100 series switches provide two management interfaces: the
AlliedWare Plus™ Web interface and Command Line Interface (CLI). This
manual provides procedures that guide you through the AlliedWare Plus™
Web interface.
The initial management session of the switch can be from a management
session either through the Web interface or the CLI. The switch is shipped
from the factory with an IP address assigned and the Web interface (HTTP
service) enabled so that you can start the initial management session
through the Web interface. To start the initial web management session,
see Chapter 2, “Starting a Management Session” on page 23.
The web interface allows access to a subset of the AlliedWare Plus
features. For access to all of the AlliedWare Plus features, you must use
the CLI.
Detailed feature descriptions are not provided in this guide. For thorough
explanations of the features, see the AlliedWare Plus Management
Software Version 2.2.4 Command Line Interface User’s Guide.
20
Page 21

Web Manager Accounts
You must log on to manage the switch. This requires a valid username and
password. The switch comes with one manager account with a username
of “manager” and the default password of “friend.” Both the username and
password are case sensitive. This account gives you access to all
management modes and commands.
In the Web interface, you can create two additional remote manager
accounts. For instructions, see “Managing Local User Accounts” on
page 53. The switch supports up to three manager sessions at one time.
AlliedWare Plus Version 2.2.4 Management Software Web Browser User’s Guide
21
Page 22

Chapter 1: AlliedWare Plus™ Version 2.2.4 Web Browser Interface
22
Page 23

Chapter 2
Starting a Management Session
This chapter describes how to start a management session using the
AlliedWare Plus™ Web interface as well as how to select fields, save your
changes, and end a management session. See the following sections:
“Non-secure HTTP and Secure HTTPS Modes” on page 24
“Starting the Initial Web Management Session” on page 25
“Logging on to the Switch” on page 27
“What to Configure First” on page 30
“Starting a Web Management Session” on page 32
“Saving Your Changes” on page 37
“Ending a Web Management Session” on page 38
For additional information about the web server, see the following chapters
in the AlliedWare Plus Management Software Version 2.2.4 Command
Line Interface User’s Guide:
Non-secure HTTP Web Browser Server
Non-secure HTTP Web Browser Server Commands
Secure HTTPS Web Browser Server
Secure HTTPS Web Browser Server Commands
Starting a Management Session
23
Page 24

Chapter 2: Starting a Management Session
Note
Non-secure HTTP and Secure HTTPS Modes
The switch has a web browser server so that you can remotely manage
the switch over the network from a web browser on your PC. The server
can operate in either plain-text HTTP mode or encrypted HTTPS mode.
To access the switch through a web browser on your PC, either HTTP
service or HTTPS service must be enabled.
HTTP Mode Web browser management sessions of the switch conducted in the HTTP
mode are non-secure because the packets exchanged by the server on
the switch and your management workstation are sent in clear text,
leaving the packets vulnerable to snooping.
The switch shipped from the factory is configured with HTTP service
enabled.
HTTPS Mode Web browser management sessions of the switch conducted in the
HTTPS mode are protected against snooping because the packets
exchanged between the switch and your management workstation are
encrypted. Only the switch and the workstation are able to decipher the
packets.
To access the switch in the HTTPS mode:
The switch must have a HTTPS certificate.
HTTPS service on the switch must be enabled.
Either HTTPS or HTTP service can be enabled at the same time. To
enable HTTPS service, HTTP must be disabled.
To configure the switch with a HTTPS certificate and enable HTTPS
service, you must use the AlliedWare Plus™ Command Line Interface
(CLI). See “Secure HTTPS Web Browser Server” chapter in AlliedWare
Plus Management Software Version 2.2.4 Command Line Interface User’s
Guide.
24
Page 25

AlliedWare Plus Version 2.2.4 Management Software Web Browser User’s Guide
Note
Starting the Initial Web Management Session
This section explains how to start a management session for the first time
using the AlliedWare Plus™ Web interface. The switch shipped from the
factory is configured with an IP address assigned and the Web interface
(HTTP service) enabled.
The switch and your PC must be directly connected through an twistedpair cable, and the IP addresses of the switch and your PC must be
members of the same network. Because the switch is shipped from the
factory with the IP address 169.254.1.1 and the subnet mask 16, you must
assign your PC an IP address in the 169.254.0.0/16 network except
169.254.1.1. In addition, your PC must have a web browser, such as
Windows Explorer, installed.
There are two ways to assign an IP address to your PC:
Manually assign any IP address in the 169.254.0.0/16 network (except
169.254.1.1) to your PC.
Disconnect your PC from a network and let your PC automatically set
an IP address in the 169.254.0.0/16 network. When a PC is
disconnected from a network and no longer connected to a DHCP
server, Windows assigns a random IP address in the
169.254.0.0/16 network to the PC.
If you delete the boot.cfg file and reboot the switch, the factory
default settings are lost. Deleting the boot.cfg file and restarting the
switch restores the switch to its default configuration with HTTP
service disabled and no IP address assigned.
To start a Web management session when the switch has the
default configuration settings, you must use the AlliedWare Plus™
Command Line Interface (CLI) to assign an IP address and enable
HTTP or HTTPS service. For more information about enabling HTTP
or HTTPS service and assigning an management IP address, see
““Starting a Web Management Session” on page 32.”
To start a Web management session using a PC with an IP address in the
169.254.0.0/16 network, perform the following procedure:
1. Connect a RJ-45 plug on a straight-through twisted-pair cable to a
twisted-pair port on the switch.
2. Connect the other RJ-45 plug on the straight-through twisted-pair
cable to a twisted-pair connector on the PC.
25
Page 26
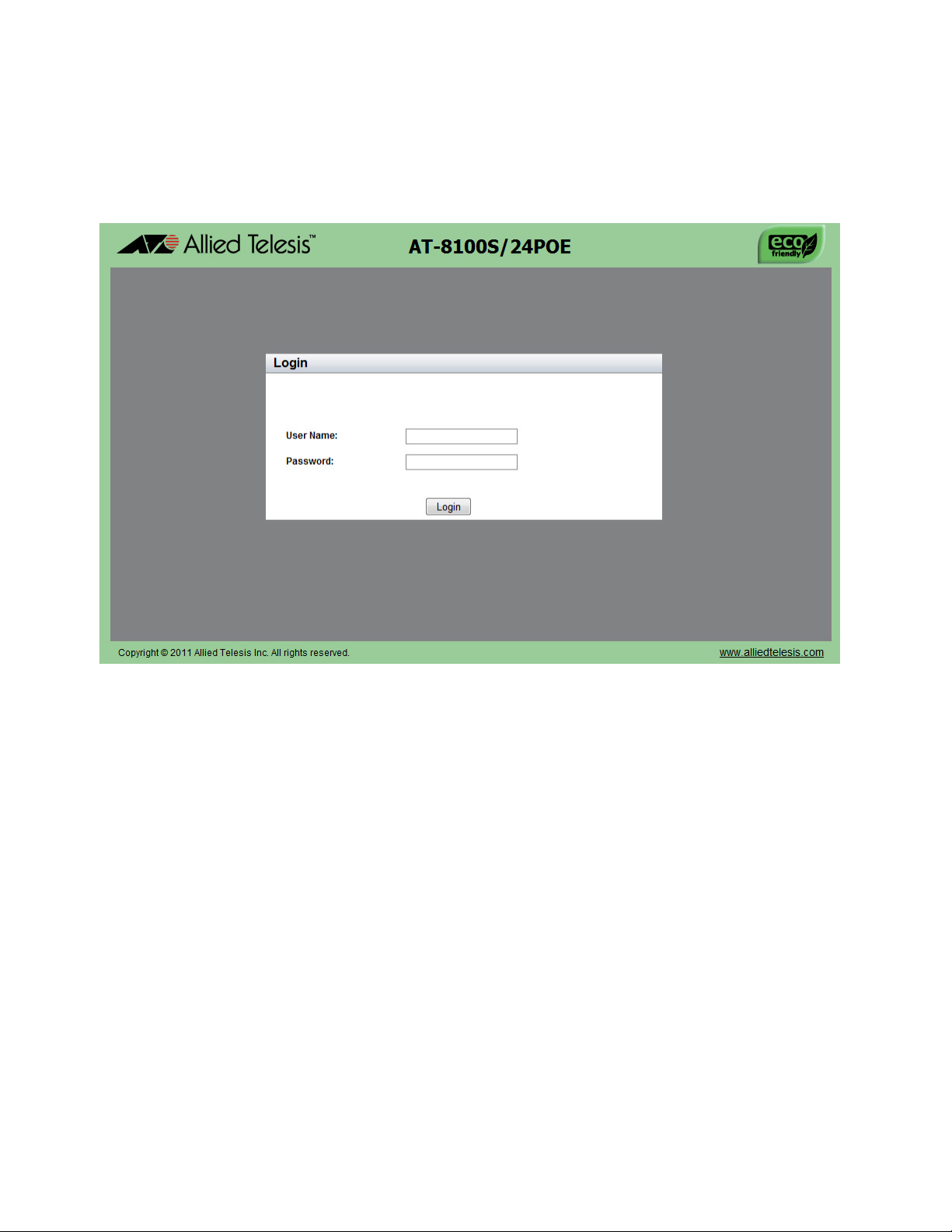
Chapter 2: Starting a Management Session
3. Open a web browser on the PC and enter the following:
http://169.254.1.1
The AT-8100 Login page is displayed as shown in Figure 1.
Figure 1. Login Page
26
Page 27
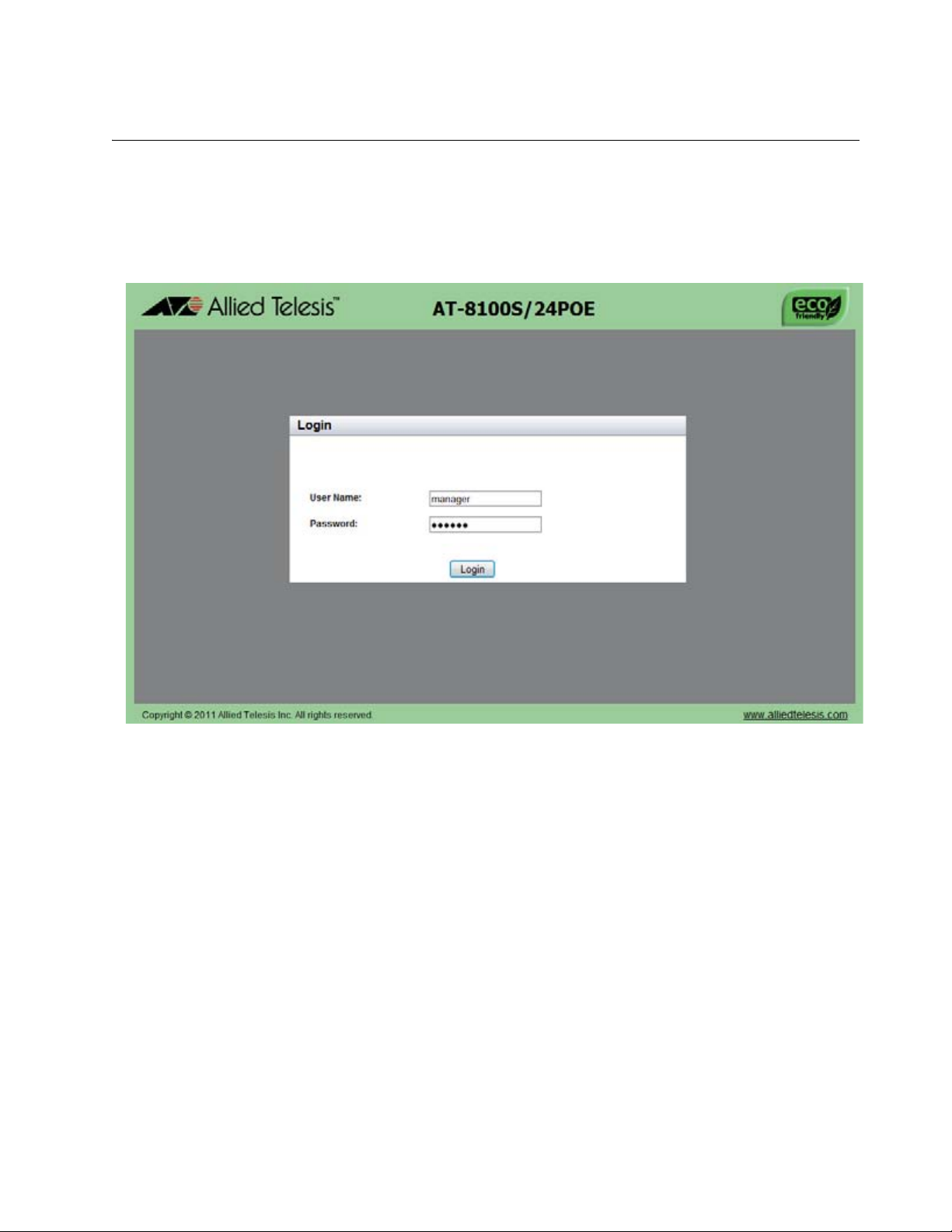
Logging on to the Switch
Once you start the Web interface, the AT-8100 Login page is displayed.
Enter “manager” in the User Name field and “friend” in the Password field
as shown in Figure 2. Then click the Login button.
.
AlliedWare Plus Version 2.2.4 Management Software Web Browser User’s Guide
Figure 2. Login Page with Entries
The Dashboard page is displayed. See Figure 3. The Dashboard page is
the home page of the switch.
27
Page 28
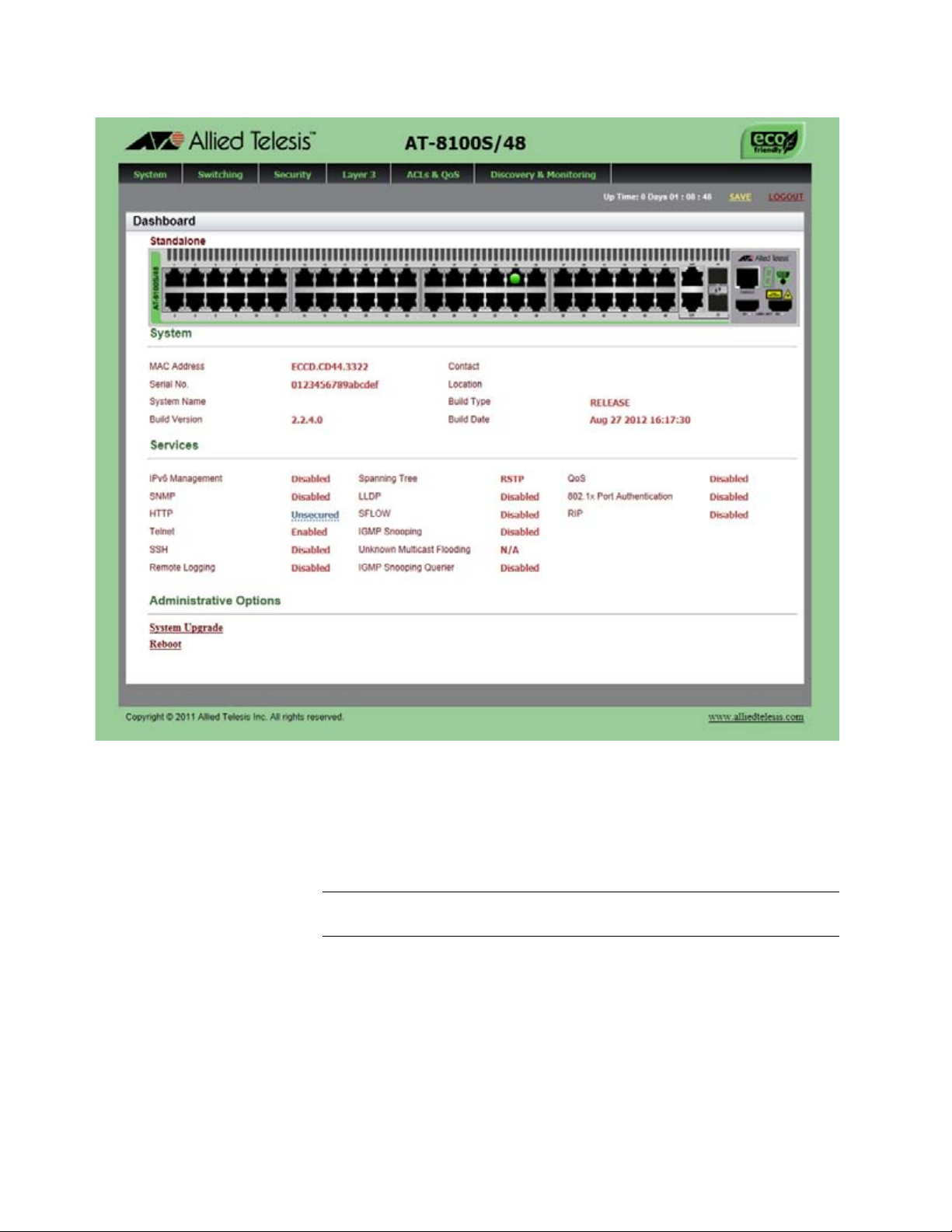
Chapter 2: Starting a Management Session
Note
28
Figure 3. Dashboard Page
The following fields are displayed:
Up Time— Indicates the length of time since the switch was last
reset or power cycled in days, hours, minutes and seconds.
Up Time is displayed on the top-right corner of the screen.
The System section displays the following information:
MAC Address— Indicates the MAC address of the switch.
Serial No.— Lists the unique serial number of the switch.
System Name— Indicates the name of the switch. To specify this
field, see Setting the Switch Information.
Page 29

AlliedWare Plus Version 2.2.4 Management Software Web Browser User’s Guide
Version— Indicates the software version number of the
AlliedWare Plus Management Software.
Contact— Indicates the contact person for the switch. To specify
this field, see Setting the Switch Information.
Location— Indicates the location of the switch. To specify this
field, see Setting the Switch Information.
The Services section displays the following information:
IPv6 Management— Indicates if the IPv6 Management is enabled
or disabled on the switch.
SNMP— Indicates the SNMP setting of the switch.
HTTP— Indicates the HTTP setting of the switch.
Telnet— Indicates if Telnet is enabled or disabled on the switch.
SSH— Indicates if SSH is enabled or disabled on the switch.
Remote Logging— Indicates if the remote logging is enabled or
disabled on the switch.
Spanning Tree— Indicates if STP, RSTP, or MSTP is enabled on
the switch. The default setting is “RSTP.”
QoS— Indicates if QoS is enabled or disabled on the switch.
LLDP— Indicates if LLDP is enabled or disabled on the switch.
sFLOW— Indicates if sFlow is enabled or disabled on the switch.
IGMP Snooping— Indicates if IGMP Snooping is enabled or
disabled on the switch.
IGMP Snooping Querier— Indicates if IGMP Snooping Querier is
enabled or disabled on the switch.
802.1x Port Authentication— Indicates if 802.1x Port
Authentication is enabled or disabled on the switch.
RIP— Indicates if RIP is enabled or disabled on the switch.
The Administration Options section displays the following information:
System Upgrade— Select this field to upgrade your system
software. See “Upgrading the Software” on page 60.
Reboot— Select this field to reboot the switch. For instructions,
see “Rebooting a Switch” on page 59.
29
Page 30

Chapter 2: Starting a Management Session
Note
Note
What to Configure First
Here are a few suggestions on what to configure during your initial
management session on the switch through the Web interface. The initial
management session can be performed through the Command Line
Interface (CLI) as well as the Web interface. For instructions on how to
start a local management session through the CLI, refer to AlliedWare
Plus Management Software Version 2.2.4 Command Line Interface User’s
Guide.
Changing the
Login Password
Assigning a Name
to the Switch
Changing a
Management IP
Address
To protect the switch from unauthorized access, change the password of
the manager account. For instructions on how to change “Changing a
User Password” on page 55.
Write down the new password and keep it in a safe and secure
location. If you forget the manager password, you cannot manage
the switch if there are no other management accounts on the unit. In
this case, contact Allied Telesis Technical Support for assistance.
For instructions on how to create additional management accounts, see
“Adding a New User Account” on page 53.
The switch is easier to identify if you assign it a name. The switch’s name
is displayed on the Dashboard page. To change the name of the switch,
see “Setting the Switch Information” on page 48.
A name can be up to 39 alphanumeric characters. Special characters,
except spaces and quotation marks, are allowed.
The switch shipped from the factory has the IP address 169.254.1.1
assigned. You must change the factory default IP address to an address in
your network. To change the IP address, see “Changing an IPv4 Address”
on page 236. Also, remember to change the IP address of your PC.
When you change the management IP address of the switch, you
lose the connection to the switch. After you change the IP address of
your PC, start a management session again by opening a web
browser on the PC and entering the new IP address of the switch.
Here are the requirements:
You can assign one IPv4 address per VLAN.
The switch can have as many IPv4 addresses as there are VLANs
on the switch.
30
Page 31

AlliedWare Plus Version 2.2.4 Management Software Web Browser User’s Guide
The management IPv4 address can be any IPv4 address assigned
on the switch.
The switch can have only one IPv6 address.
Your PC must have an IP address that belongs to the network
where the management IP address belongs, or have access to the
network where the management IP address belongs.
Setting System
Time
To set the system time either manually or with an NTP server, see “Setting
the System Date and Time” on page 40.
31
Page 32

Chapter 2: Starting a Management Session
Note
Starting a Web Management Session
This section provides how to start a Web management session when the
switch does not have the factory default configuration.
To log on to the switch through the Web interface, enter the IP address of
the switch on the Web browser, such as Windows Explorer, on the PC or
laptop that can access to the switch. If the AlliedWare Plus™ Web
interface comes up, you can skip the rest of this section and continue a
Web management session. If the Web interface does not come up, you
must configure the switch using the AlliedWare Plus™ Command Line
Interface (CLI).
For more information about how to start the Command Line
Interface (CLI), see the AlliedWare Plus Management Software
Version 2.2.4 Command Line Interface User’s Guide.
When You Do
Not Know the IP
Address of the
Switch
There are some cases that you must configure the switch using the CLI to
start a Web management session:
The switch does not have an IP address assigned, or you do not know
the IP address of the switch.
HTTP service on the switch is disabled.
You want to access the switch in the HTTPS mode.
If the switch has no IP address assigned, or you do not know the IP
address of the switch, perform the following steps:
1. “Logging on to the CLI through the Console Port” on page 33.
2. “Checking for the IP Addresses of the Switch in the CLI” on page 34.
3. If the switch does not have any IP address assigned, “Adding an IP
Address to the Switch in the CLI” on page 34.
4. “Checking the Status of HTTP and HTTPS Services in the CLI” on
page 34.
5. “Enabling HTTP or HTTPS Service in the CLI” on page 35.
6. “Saving your Changes in the CLI” on page 36.
32
Page 33

AlliedWare Plus Version 2.2.4 Management Software Web Browser User’s Guide
Note
When the Switch
Does Not Display
the Login Page
When the switch does not display the Web interface even though you
enter the IP address of the switch on the Web browser, you must enable
HTTP or HTTPS service on the switch through the CLI by performing the
following steps:
1. “Logging on to the CLI through the Console Port” on page 33.
Or
Log on to the CLI using the Telnet or SSH protocol.
To start a Telnet or SSH management session, see AlliedWare Plus
Management Software Version 2.2.4 Command Line Interface
User’s Guide.
2. “Checking the Status of HTTP and HTTPS Services in the CLI” on
page 34.
3. “Enabling HTTP or HTTPS Service in the CLI” on page 35.
4. “Saving your Changes in the CLI” on page 36.
Logging on to the
CLI through the
Console Port
To log on to the CLI through the console port on the switch, perform the
following procedure:
1. Connect the RJ-45 connector on the management cable to the console
port on the switch.
2. Connect the other end of the cable to an RS-232 port on a terminal or
a PC with a terminal emulator program.
3. Configure the terminal or terminal emulator program as follows:
Baud rate: 9600
Data bits: 8
Parity: None
Stop bits: 1
Flow control: None
4. Press Enter.
You are prompted for a user name and password.
5. Enter a user name and password. If this is the initial management
session of the switch, enter “manager” as the user name and “friend”
as the password. The user name and password are case sensitive.
33
Page 34

Chapter 2: Starting a Management Session
awplus>
awplus# show ip interface
Interface IP-Address Status Protocol
vlan1-0 192.168.1.3/24 admin up running
The local management session is started when the AlliedWare Plus™
command line prompt is displayed as shown in Figure 4 on page 34.
Figure 4. AlliedWare Plus™ Command Line Prompt
Checking for the
IP Addresses of
the Switch in the
CLI
Adding an IP
Address to the
Switch in the CLI
To check for IP addresses assigned to the switch, enter the following
commands:
awplus> enable
awplus# show ip interface
For a display of this command, see Figure 5.
Figure 5. Displaying the IP Address
When the switch does not have an IP address, assign an IP address and
subnet mask to the switch. The following example assigns the IP address
192.168.1.2. and the subnet mask 24 to VLAN 1:
awplus> enable
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# interface vlan1
awplus(config-if)# ip address 192.168.1.2/24
awplus(config-if)#
Checking the
Status of HTTP
To check if HTTP service is enabled, enter the following commands:
awplus> enable
and HTTPS
Services in the
CLI
34
awplus# show ip http
Figure 6 on page 35 shows an example of the command output.
Page 35

AlliedWare Plus Version 2.2.4 Management Software Web Browser User’s Guide
Note
awplus# show ip http
HTTP server disabled.
HTTPS server enabled. Port: 443
Certificate 1 is active
Issued by: self-signed
Valid from: 5/17/2011 to 5/16/2012
Subject: C=US, ST=California, L=San_Jose, O=Jones_Industries, OU=Sales,
CN=167.214.121.45
Finger print: 3FB9D543 72D8E6F8 2159F35E B634A738
Figure 6. Displaying the Status of HTTP Service
To check whether HTTPS service is enabled, enter the following
commands:
awplus> enable
awplus# show ip https
Figure 7 shows an example of the command output.
Enabling HTTP
or HTTPS
Service in the
CLI
Figure 7. Displaying the Status of HTTPS Service
HTTPS and HTTP services cannot be enabled at the same time. For
example, when HTTP is enabled, HTTPS is disabled.
To enable HTTP service on the switch, enter the following commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# service http
awplus(config)# exit
awplus#
To enable HTTPS, the switch must have a certificate. To configure the
web server in the HTTPS mode, see the “Secure HTTPS Web Browser
Server” chapter in the AlliedWare Plus Management Software Version
2.2.4 Command Line Interface User’s Guide.
35
Page 36

Chapter 2: Starting a Management Session
Saving your
Changes in the
CLI
Save your changes to the startup configuration file by entering the
following commands:
awplus# copy running-config startup-config
Or
awplus# write
36
Page 37

Saving Your Changes
The changes you have made are temporarily stored in the running
configuration file. When you reboot the switch, the information in the
running configuration file is lost. To save your changes after you reboot the
switch, do the following:
AlliedWare Plus Version 2.2.4 Management Software Web Browser User’s Guide
1. Click SAVE
Figure 8 shows the SAVE
Clicking SAVE
.
saves the changes to the startup configuration file.
at the upper right corner of the Web page.
Figure 8. System Contact Information Page
37
Page 38

Chapter 2: Starting a Management Session
Ending a Web Management Session
To end a web management session, select LOGOUT at the top of the web
page. For an example, see the System Contact Information page in Figure
8 on page 37.
38
Page 39

Chapter 3
Basic Switch Parameters
This chapter describes how to set up basic switch operations in the web
interface. See the following sections:
“Setting the System Date and Time” on page 40
“Configuring a Telnet or SSH Server” on page 45
“Configuring a Remote Log Server” on page 47
“Setting the Switch Information” on page 48
“Managing the Configuration File” on page 50
“Managing Local User Accounts” on page 53
“Rebooting a Switch” on page 59
“Upgrading the Software” on page 60
“Returning the AlliedWare Plus Management Software to the Factory
Default Values” on page 63
“Displaying System Information” on page 64
For additional information about basic port settings, see the following
chapters in the AlliedWare Plus Management Software Version 2.2.4
Command Line Interface User’s Guide:
Basic Switch Management
Basic Switch Management Commands
39
Page 40

Chapter 3: Basic Switch Parameters
Note
Note
Setting the System Date and Time
This procedure explains how to set the switch’s date and time. Setting the
date and time is important if you plan to view the events in the switch’s
event log or send events to a syslog server. The correct date and time are
also important if the management software sends traps to a management
workstation or if you plan to create a self-signed SSL certificate. Events,
traps, and self-signed certificates should contain the date and time of
when they occurred or, in the case of certificates, when they were created.
There are two ways to set the switch’s date and time. One method is to set
it manually. This method is not recommended because the date and time
are lost if you reboot the switch.
The second method uses the Simple Network Time Protocol (SNTP). The
AlliedWare Plus Management Software comes with the client version of
this protocol. You can configure the AlliedWare Plus™ software to obtain
the current date and time from a Network Time Protocol (NTP) or SNTP
server located on your network or the Internet.
SNTP is a simplified version of the NTP and uses the same packet
structure as NTP uses. The SNTP client software in the AlliedWare Plus™
Management Software is interoperable with NTP servers.
In order for the management software on the switch to communicate
with an SNTP or NTP server, there must be an interface on the local
subnet from where the switch is reaching the server. The switch
uses the IP address of the interface as its source address when
sending packets to the server.
The default system time on the switch is midnight, January 1, 2000.
Choose from the following procedures:
“Configuring an SNTP or NTP Server” on page 40
“Setting System Time Manually” on page 42
Configuring an
SNTP or NTP
40
To configure SNTP or NTP server, do the following:
1. Select the System tab.
Server
2. From the System ta7b, select System Settings.
The System Settings Tab is displayed in Figure 9.
Page 41

AlliedWare Plus Version 2.2.4 Management Software Web Browser User’s Guide
Figure 9. System Settings Tab
3. From the System tab, select System Settings.
4. Move the cursor to the right and select Time.
The System Time Settings page is displayed.See Figure 10.
Figure 10. System Time Settings Page with Network Time Settings Tab
5. To configure the switch to obtain its date and time from an SNTP or
NTP server on your network or the Internet, specify the following fields:
NTP Status— Select Enabled or Disabled to configure the SNTP
client on the switch. The default is disabled.
41
Page 42

Chapter 3: Basic Switch Parameters
Note
Note
Server IP Address— Specify the IPv4 address of an SNTP or
NTP server.
The IPv4 format is: xxx.xxx.xxx.xxx where x is a decimal number
from 0 to 255.
If the local interface on the switch is obtaining its IP address and
subnet mask from a DHCP server, you can configure the server to
provide the interface with an IP address of an NTP or SNTP server.
If you configured the server to provide this address, then you do not
need to enter it here.
Time Zone— Select the time zone as a measurement of
Greenwich Mean Time (GMT) which is the default setting. Use the
pull-down menu to select the other time zones.
Daylight Saving— Enable or disable the system’s adjustment for
daylight savings time. The default is disabled.
Setting System
Time Manually
The switch does not set daylight saving time (DST) automatically. If
the switch is in a locale that uses DST, you must remember to
enable this in March when DST begins and disable it in October
when DST ends. If the switch is in a locale that does not use DST,
this option should be set to disabled all the time.
6. Click Apply.
If you enabled the SNTP client, the switch immediately polls the SNTP
or SNTP server for the current date and time. (When SNTP is enabled,
the switch automatically polls the server whenever a change is made
to any of the fields on this page.)
7. Click SAVE
to save your changes to the startup configuration file.
To set the system time manually, do the following:
1. Select the System tab.
2. From the System tab, select System Settings.
The System Settings Tab is displayed in Figure 9 on page 41.
3. Move the cursor to the right and select Time.
The System Time Settings page is displayed. See Figure 10 on page
41.
42
Page 43

AlliedWare Plus Version 2.2.4 Management Software Web Browser User’s Guide
4. Select the Date & Time tab.
The System Time Settings page with the Date & Time tab is displayed.
See Figure 11.
Figure 11. System Time Settings Page with Date & Time Tab
5. You have two ways to set the date and time in the Date & Time field.
Use either step 6 or 7.
6. Type in the time and date in the following format:
yyyy-dd-mm hh:mm:ss
7. Select the calendar icon next to he Date & Time field.
The Calendar page is displayed. See Figure 12 on page 44.
43
Page 44

Chapter 3: Basic Switch Parameters
Figure 12. Calendar Page
a. Use the arrows at the top of the Calendar to select the month and
year.
b. Set the time of day using the following format:
hh:mm:ss
c. Click on the day of the month.
8. Click Apply.
9. Click SAVE
to save your changes to the startup configuration file.
44
Page 45

AlliedWare Plus Version 2.2.4 Management Software Web Browser User’s Guide
Configuring a Telnet or SSH Server
The AlliedWare Plus Web Browser interface allows you to configure the
switch as a Telnet or SSH server.
You can use the web browser interface to enable a Telnet server, but not
as a Telnet client. The Telnet client is only supported from the CLI. For
information about how to use a Telnet client, see the AlliedWare Plus
Management Software Version 2.2.4 Command Line Interface User’s
Guide.
To enable an SSH server in the Web interface, you must first create an
encryption key in the CLI interface. Then you can enable the SSH server in
the web interface.
To assign the switch to a Telnet or SSH server, do the following:
1. From the home page, select the System tab.
The System Settings tab is displayed. See Figure 9 on page 41.
2. From the System Settings tab, select Services.
The System Services page is displayed. See Figure 13.
Figure 13. System Services Page
45
Page 46

Chapter 3: Basic Switch Parameters
Note
3. Specify the following fields as necessary:
Telnet— Check the checkbox to enable the Telnet server on the
switch. To disable the server on the switch, uncheck the checkbox.
SSH— Check the checkbox to enable the SSH server on the
switch. To disable the server on the switch, uncheck the checkbox.
Both the Remote Log and Server IP Address fields are used only to
set a remote log server. For information on these fields, see
“Configuring a Remote Log Server” on page 47.
Remote Log— Check the checkbox to enable the switch to send
status and error messages to a remote log server. To disable the
switch to sent messages to a remote log server, uncheck the
checkbox.
Server IP Address— Enter the IPv4 address of the remote log
server if you check the Remote Log checkbox above. Enter the IP
address in the IPv4 format: nnn.nnn.nnn.nnn.
4. Click Apply.
5. Click SAVE
to save your changes to the startup configuration file.
46
Page 47

AlliedWare Plus Version 2.2.4 Management Software Web Browser User’s Guide
Configuring a Remote Log Server
You can use the AlliedWare Plus Web browser interface to assign the
switch to a remote log server, which is part of the Syslog feature. However,
you must use the CLI to view or clear the event log. For information about
the Syslog features, see the SysLog chapters in the AlliedWare Plus
Management Software Version 2.2.4 Command Line Interface User’s
Guide.
To activate remote logging on the switch, do the following:
1. Select the System tab.
The System Settings tab is displayed. See Figure 9 on page 41.
2. From the System Settings tab, select Services.
The System Services page is displayed. See Figure 13 on page 45.
3. Specify the following fields:
Remote Log— Check the checkbox to enable the switch to send
status and error messages to a remote log server. To disable the
switch from sending messages to a remote log server, uncheck the
checkbox.
Server IP Address— Enter the IPv4 address of the remote log
server in the IPv4 format: nnn.nnn.nnn.nnn.
4. Click Apply.
5. Click SAVE
to save your changes to the startup configuration file.
47
Page 48

Chapter 3: Basic Switch Parameters
Setting the Switch Information
This procedure allows you to set information about the switch such as a
switch name, contact person, and location. Assigning a name to the switch
helps you identify your switches when you manage them and help you
avoid performing a configuration procedure on the wrong switch.
To assign a name, contact person, and location to the switch, perform the
following procedure:
1. From the home page, select the System tab.
2. From the System tab, select System Settings.
The System Setting tab is displayed. See Figure 9 on page 41.
3. Move the cursor to the right and select Contact Information.
The System Contact Information page is displayed. See Figure 14.
48
Figure 14. System Contact Information Page
Page 49

AlliedWare Plus Version 2.2.4 Management Software Web Browser User’s Guide
Specify the following fields as necessary:
System Name— Enter a name for the switch, for example, S1 or
Switch2. The name is displayed on the Dashboard page. See
Figure 3 on page 28. The name can be from 1 to 39 characters in
length. Special characters, except spaces and quotation marks,
are allowed. By default, no system name is specified. This field is
optional.
System Contact — Enter the name of a network administrator
responsible for managing the switch. The name can be from 1 to
255 characters; however, only the first 50 characters are displayed
on the Dashboard page. Spaces and special characters, such as
dashes and asterisks are allowed. By default, no system contact is
specified. This field is optional.
System Location— Enter the location of the switch, (for example,
4th Floor - room 402B). The location can be from 1 to 225
characters; however, only the first 50 characters are displayed on
the Dashboard page. Spaces and special characters, such as
dashes and asterisks are allowed. By default, no system location is
specified. This field is optional.
4. Click Apply.
5. Click SAVE
to save your changes to the startup configuration file.
49
Page 50

Chapter 3: Basic Switch Parameters
Managing the Configuration File
Within the web browser interface, you can upload a configuration file on to
the switch, download a configuration file from the switch, delete a
configuration file, and save your changes to the current configuration file.
However, to create a new configuration file, you need to access the switch
through the CLI.
See the following procedures:
“Displaying the Configuration Files” on page 50
“Setting the Active Configuration File” on page 51
“Downloading a Configuration File onto Your PC” on page 51
Displaying the
Configuration
Files
To display a list of the configuration files on the switch, do the following:
1. From the Dashboard page, click the System tab.
The System Settings tab is displayed. See Figure 9 on page 41.
2. From the System tab, select Configuration Files from the pull-down
menu.
For an example of the Configuration Files page, see Figure 15
.
50
Figure 15. Configuration Files Page
Page 51

AlliedWare Plus Version 2.2.4 Management Software Web Browser User’s Guide
The following fields are displayed:
Startup Config— Displays the name of the active boot
configuration file, which for the switch of the example is “boot.cfg.”
File Name— Indicates the name of the configuration file.
File Size— Lists the file size in bytes.
Last Modify— Indicates the date the configuration file was last
modified. The format is year, month, date.
Setting the Active
Configuration
File
Downloading a
Configuration
File onto Your
PC
To specify a file as the startup configuration file, do the following:
1. Use the pull-down menu to select a file as the active configuration file.
2. Click Apply.
The file you select is the active configuration file after you reboot the
switch.
3. Click SAVE
To download a configuration file onto your PC, do the following:
1. Click the System tab.
For an example of the System tab, see Figure 9 on page 41.
2. From the System tab, select Configuration Files.
For an example of the Configuration Files page, See Figure 15 on
page 50.
3. Click Download next to the file name that you want to download.
to save your changes to the startup configuration file.
For an example of the File Download popup window, see Figure 16.
.
Figure 16. File Download Popup Window of Internet Explorer 8
51
Page 52

Chapter 3: Basic Switch Parameters
4. Follow the instructions of your Web browser to select a location and
save the file.
Deleting a
Configuration
To delete a configuration file, do the following:
1. Click the System tab.
For an example of the System tab, see Figure 9 on page 41.
2. From the System tab, select Configuration Files.
For an example of the Configuration Files page, See Figure 15 on
page 50.
3. Click Delete next to the file name that you want to download.
The file is deleted.
4. Click SAVE
to save your changes to the startup configuration file.
52
Page 53

Managing Local User Accounts
The switch comes with one local manager account. The account, which
has the user name “manager” and default password “friend,” is referred to
as a local account because it is the switch that authenticates the user
name and password when a manager logs on using the account.
This section explains how to create additional local user accounts, how to
change passwords and privileges, and how to delete a manager account.
See the following:
“Adding a New User Account” on page 53
“Changing a User Password” on page 55
“Changing the User Privilege” on page 56
“Deleting a User Account” on page 57
The switch also supports remote manager accounts that are authenticated
not by the switch but by a RADIUS or TACACS+ server on your network.
For information, see Chapter 17, “RADIUS and TACACS+ Clients” on
page 199.
AlliedWare Plus Version 2.2.4 Management Software Web Browser User’s Guide
Adding a New
User Account
To add a local user account, do the following:
1. From the home page, click the System tab.
The System Settings tab is displayed, see Figure 9 on page 41.
2. From the System Settings tab, select User Management.
For an example of the User Management page, see Figure 17 on page
54.
53
Page 54

Chapter 3: Basic Switch Parameters
Figure 17. User Management Page
3. Add a new user, do the following:
User Name— Enter a new logon name for the new account. The
name is case sensitive and can contain up to 15 alphanumeric
characters. Spaces and special characters are not allowed.
Password— Enter the password for the new account in plain text.
The password can consist of up to 16 alphanumeric characters
and is case-sensitive. Spaces and special characters are not
allowed.
Privilege— Select a user privilege level from the pull-down menu.
Choose from the following:
Level 15: Management accounts with a user level of 15 have
unrestricted access to the management software.
This is the default setting.
Level 1: Management accounts with a user level of 1 have
restricted access to the management software.
Accounts with this level are allowed to view the
settings on the switch, but not allowed to change
them.
54
Page 55

4. Click Add User.
AlliedWare Plus Version 2.2.4 Management Software Web Browser User’s Guide
Changing a User
Password
5. Click SAVE
To change a user password, do the following:
1. From the home page, click the System tab.
The System Settings Tab is displayed. See Figure 9 on page 41.
2. From the System Settings tab, select User Management.
The User Management page is displayed. See Figure 17 on page 54.
3. From the User Management page, select the Change Password tab.
The User Management page with the Change Password tab is
displayed. See Figure 18.
to save your changes to the startup configuration file.
Figure 18. User Management Page with Change Password Tab
4. Use the pull-down menu next to the User Name field to select a user
name.
The user name must already exist.
55
Page 56

Chapter 3: Basic Switch Parameters
5. Enter a new password in plaintext in the New Password field.
A password can consist of up to 16 alphanumeric characters and is
case-sensitive. Spaces and special characters are not allowed.
6. Re-enter the new password in the Confirm New Password field.
Changing the
User Privilege
7. Click Set Password
8. Click SAVE
To change a privilege of a user, do the following:
1. From the home page, click the System tab.
The System Settings Tab is displayed. See Figure 9 on page 41.
2. From the System Settings tab, select User Management.
The User Management page is displayed. See Figure 17 on page 54.
3. From the User Management page, select the Change Privilege tab.
The User Management page with the Change Privilege tab is
displayed. See Figure 19.
to save your changes to the startup configuration file.
.
56
Figure 19. User Management Page with Change Privilege Tab
Page 57

AlliedWare Plus Version 2.2.4 Management Software Web Browser User’s Guide
4. Use the pull-down menu next to the User Name field to select a user.
5. Use the pull-down menu next the New Privilege field to select a user
privilege level. Choose from the following:
Level 15— Management accounts with a user level of 15 have
unrestricted access to the management software.
Level 1— Management accounts with a user level of 1 have
restricted access to the management software. Accounts with this
level are allowed to view the settings on the switch, but not allowed
to change them.
6. Click Set Privilege.
Deleting a User
Account
7. Click SAVE
to save your changes to the startup configuration file.
To delete a user account from the switch, do the following:
1. From the home page, click the System tab.
The System Settings Tab is displayed. See Figure 9 on page 41.
2. From the System Settings tab, select User Management.
The User Management page is displayed. See Figure 17 on page 54.
3. From the User Management page, select the Delete User tab.
The User Management page with the Delete User tab is displayed.
See Figure 20 on page 58.
57
Page 58

Chapter 3: Basic Switch Parameters
Figure 20. User Management Page with Delete User Tab
4. Use the pull-down menu to select a user.
5. Click Delete User.
6. Click SAVE
to save your changes to the startup configuration file.
58
Page 59

Rebooting a Switch
Note
Note
AlliedWare Plus Version 2.2.4 Management Software Web Browser User’s Guide
Resetting the switch ends your web browser management session. To
continue managing the switch, you must login again.
All unsaved changes are discarded when you reset a switch. To
save your changes to the startup configuration file, click SAVE.
To reboot a switch, perform the following procedure:
1. Select the System Tab.
The System Settings Tab is displayed. See Figure 9 on page 41.
2. From the System Settings tab, select Dashboard.
The Dashboard Page is displayed. See Figure 3 on page 28.
3. Select Reboot
A confirmation prompt is displayed that indicates that the connection to
the web is lost during a reboot.
4. Click OK to reset the switch or Cancel to cancel the procedure.
The switch does not forward packets while it initializes the
AlliedWare Plus™ software and loads its active configuration file.
This process takes between 20 seconds to 2 minutes to complete,
depending on the number and types of commands in the
configuration file.
at the bottom of the page.
59
Page 60

Chapter 3: Basic Switch Parameters
Upgrading the Software
The latest version of the AlliedWare Plus™ software is available from the
Allied Telesis web site. You can download the software image file on your
workstation and upload the file onto the switch.
To upgrade the AlliedWare Plus software, perform the following
procedure:
1. Open a new browser and enter the following:
http://www.alliedtelesis.com/support/software
The Allied Telesis Software Download page is displayed.
2. Select your hardware product model, such as “AT-8100S/24,” from the
pull-down menu next to the Product field.
3. Click the software file that you want to upload to the switch.
The User Login page is displayed. See Figure 21.
60
Figure 21. User Login page on the Allied Telesis Website
Page 61

AlliedWare Plus Version 2.2.4 Management Software Web Browser User’s Guide
Note
Note
4. Enter your email address and password, then click the Sign In button.
If you do not know your password, click the Create Account link and
follow the instructions on the page.
5. Download the software image file to your workstation.
6. Go back to the AT-8100 Web interface and select Dashboard from the
System Settings tab.
The Dashboard Page is displayed. See Figure 3 on page 28.
All unsaved changes are discarded when you upgrade the software
on a switch. To save your changes to the startup configuration file,
click SAVE.
7. Select System Upgrade
at the bottom of the page.
The System Upgrade page is displayed. See Figure 22.
Figure 22. System Upgrade Page
8. Click Browse to select an image file.
9. Click Open to select the file that you downloaded in step 5.
10. Click Start Upgrade to begin the software upgrade or Cancel to
cancel the procedure.
The upgrade process takes approximately three minutes.
61
Page 62

Chapter 3: Basic Switch Parameters
Note
Upgrading the system software on the switch ends your current web
browser management session. To continue managing the switch,
you must login again.
62
Page 63

AlliedWare Plus Version 2.2.4 Management Software Web Browser User’s Guide
Returning the AlliedWare Plus Management Software to the Factory Default Values
To reset the AlliedWare Plus Management Software parameters to their
default values, you must use the Command Line Interface (CLI). You
cannot reset the management software to its factory settings in the web
interface. For instructions, see Chapter 7: Basic Switch Management in
the AlliedWare Plus Management Software Version 2.2.4 Command Line
Interface User’s Guide on our web site. To locate manuals online, see
“Downloading Management Software and Web-based Guides” on
page 17.
63
Page 64

Chapter 3: Basic Switch Parameters
Displaying System Information
To view basic information about the switch, select the System Tab.
The Dashboard Page is displayed as shown in Figure 3 on page 28.
The following fields are displayed:
Up Time— Indicates the length of time since the switch was last
reset or power cycled in days, hours, minutes and seconds.
The System section displays the following information:
MAC Address— Indicates the MAC address of the switch.
Contact— Displays the contact person for the switch. To specify
this field, see “Setting the Switch Information” on page 48.
Serial No.— Displays the unique serial number of the switch.
Location— Displays the location of the switch. To specify this
field, see “Setting the Switch Information” on page 48.
System Name— Indicates the name of the switch. To specify this
field, see “Setting the Switch Information” on page 48.
Version— Lists the software version number of the AlliedWare
Plus software.
The Services section displays the following information:
IPv6 Management— Indicates if IPv6 Management is enabled or
disabled on the switch.
Spanning Tree— Indicates if RSTP or STP is enabled on the
switch. The default setting is RSTP.
802.1x Port Authentication— Indicates if 802.1x Port
Authentication is enabled or disabled on the switch.
SNMP— Indicates the SNMP setting of the switch.
QoS— Indicates is QoS is enabled or disabled on the switch.
RIP— Indicates the HTTP setting of the switch
HTTP— Indicates the HTTP setting of the switch
LLDP— Indicates if LLDP is enabled or disabled on the switch.
Telnet— Indicates if Telnet is enabled or disabled on the switch.
SFLOW— Indicates is sFlow is enabled or disabled on the switch.
64
SSH— Indicates if SSH is enabled or disabled on the switch.
IGMP Snooping— Indicates if IGMP Snooping is enabled or
disabled on the switch.
Page 65

AlliedWare Plus Version 2.2.4 Management Software Web Browser User’s Guide
Remote Logging— Indicates if the remote log is enabled or
disabled on the switch.
IGMP Snooping Querier— Indicates if IGMP Snooping Querier is
enabled or disabled on the switch.
The Administration Options section displays the following information:
System Upgrade— Click this link to go to the System Upgrade
page to upgrade your system software. See “Upgrading the
Software” on page 60.
Reboot— Click this link to go to reboot the switch. For instructions,
see “Rebooting a Switch” on page 59.
65
Page 66

Chapter 3: Basic Switch Parameters
66
Page 67

Chapter 4
Setting Port Parameters
This chapter describes how to display and modify the port settings such as
back pressure and flow control. In addition, it provides procedures to
display and modify storm control settings.
This chapter contains the following sections:
“Port Numbers on the Switch” on page 68
“Displaying the Port Parameters” on page 69
“Changing the Port Settings” on page 72
“Displaying the Storm Control Settings” on page 76
“Modifying the Storm Control Settings” on page 78
For additional information about the port parameters and the storm control
feature, see the following chapters in the AlliedWare Plus Management
Software Version 2.2.4 Command Line Interface User’s Guide:
Port Parameters
Port Parameter Commands
67
Page 68

Chapter 4: Setting Port Parameters
Port Numbers on the Switch
The ports on the switch are identified in the format shown in Figure 23.
The variables in the parameter are defined here:
Switch ID: When the switch is a stand-alone switch, the Web interface
displays number 1 as the switch ID even though the stand-alone
switch displays number 0 on the Stack ID LED. The format of the port
for stand-alone AT-8100 Series switches is PORT1.0.n.
Figure 23. Port Number
When the switch is part of a hardware stack, the Web interface
displays the switch ID number that is displayed on the Stack ID LED.
Module Slot ID: This number is used to identify a slot in a modular
switch. This number should always be 0 for AT-8100 Series switches
because they are not modular switches.
Port number: This is the port number.
68
Page 69

Displaying the Port Parameters
To display the settings for all of the switch ports, do the following:
1. Select the Switching tab.
The Switching tab is displayed. See Figure 24.
AlliedWare Plus Version 2.2.4 Management Software Web Browser User’s Guide
Figure 24. Switching Tab with Port Tab
2. From the Switching tab, select Port.
The Port tab expands to the right.
3. From the Port tab, select Port Configuration.
The Port Configuration page is displayed. See Figure 25 on page 70.
69
Page 70

Chapter 4: Setting Port Parameters
Figure 25. Port Configuration Page
4. The following fields are displayed:
Interface— Indicates the port ID.
Type— Indicates the transmission speed and medium, copper or
fiber optic, of the port. For example, 1000Base-SX indicates that
the port is a fiber optic gigabit standard.
Status— Indicates if the port is enabled or disabled. The default
setting is “Enabled.” Disabling a port turns off its receiver and
transmitter so that the port cannot forward traffic.
Link— Indicates the port has successfully connected to a port on
another switch or unit.
Auto-Neg— Indicates Auto-Negotiation. The setting is “Auto” or
“Manual.” The default is “Auto.”
Speed— Indicates the speed of the port. The possible options are
“10” for 10Mbps, “100” for 100Mbps, and “1000” for 1000Mbps.
Duplex— Indicates the duplex mode of the twisted pair port. The
setting is “Half” or “Full.”
Polarity— Indicates the port’s wiring configuration is MDI (medium
dependent interface), MDI-X (medium dependent interface
crossover), or the auto setting. This setting only applies to a
twisted pair port that is operating at 10 or 100 Mbps.
70
Page 71

AlliedWare Plus Version 2.2.4 Management Software Web Browser User’s Guide
Back Pressure— Indicates if back pressure is enabled or disabled
on the port. Back pressure is used by a port during periods of
packet congestion to temporarily stop its network counterpart from
transmitting more packets. This prevents a buffer overrun and the
subsequent loss and retransmission of network packets. A port
initiates back pressure by transmitting on the shared link to cause a
data collision, which causes its link partner to cease transmission.
The default setting is “Disabled.”
Back Pressure Limit— Indicates the threshold level for back
pressure on the port. Specifies the number of cells for back
pressure. The default value is 7935 cells.
Flow Control— Indicates if flow control (send and receive) is
enabled or disabled on a port. If flow control is enabled, a port
sends pause packets when it reaches the point of packet
congestion. Also, the port stops transmitting packets when it
receives pause packets from its local or remote counterpart. When
flow control is disabled, the port sends pause packet regardless of
packet congestion. In addition the port continues transmitting
packets when it receives pause packets from its local or remote
counterpart. The default is “Disabled.”
Flow Control Limit— Indicates the threshold level for flow control
on a port. The default value is 7935.
Description— Indicates the description of a port. To specify this
field, see “Changing the Port Settings” on page 72.
71
Page 72

Chapter 4: Setting Port Parameters
Changing the Port Settings
You can change the settings of one port at a time. Use the following
procedure to change the port settings or reset a port to its default value,
To change the port settings, do the following:
1. Select the Switching tab.
The Switching tab is displayed. See Figure 24 on page 69.
2. From the Switching tab, select Port.
The Port tab expands to the right.
3. From the Port tab, select Port Configuration.
The Port Configuration page is displayed. See Figure 25 on page 70.
4. Click Edit
The Port Configuration Modify page is displayed. See Figure 26 on
page 73.
next to the port that you want to modify.
72
Page 73

AlliedWare Plus Version 2.2.4 Management Software Web Browser User’s Guide
Figure 26. Port Configuration Modify Page
5. Specify the following fields as needed:
Interface— Indicates the port ID.
Port Type— Indicates the transmission speed and medium,
copper or fiber, that the port supports.
Port Description— Enter a description of the port. You can enter
up to 80 alphanumeric characters; however, only 30 characters are
displayed in the Port Configuration List page. Spaces and special
characters are allowed.
Status— Select either “Enabled” or “Disabled.” The default setting
is enabled. Disabling a port turns off its receiver and transmitter so
that the port does not forward traffic. You may want to disable a
port if there is a problem with a cable or network device.
73
Page 74

Chapter 4: Setting Port Parameters
Note
Negotiation— Select the state of Auto Negotiation from the pull-
down menu. Setting “Auto” enables Auto Negotiation and setting
“Manual” disables Auto Negotiation. The default setting is “Auto.”
When the setting for this field is “Auto,” the Configure Speed and
Configure Duplex fields change from white to brown and you
cannot select them. To change the Configure Speed and
Configure Duplex fields, change the Negotiation setting to
“Manual.”
When the port type is 1000Base fiber optic, the Negotiation must be
“Auto” and you are not allowed to change the setting to “Manual.”
Current Speed— Displays the current speed of the port.
Current Duplex Mode— Displays the current duplex mode setting
of the port.
Configure Speed— Select a port speed from the pull-down menu.
For example, for a 10/100Base-T port, the options are 10 and 100.
For a 1000Base-SX/LX port, 1000 is the only option. You can enter
a value in this field when the Negotiation is set “Manual.”
Configure Duplex Mode— Select the duplex mode of the twisted
pair port. Choose from Half, Full, or Auto. A port operating in halfduplex mode can either receive or transmit packets, but not both at
the same time. Ports operating in full-duplex can both send and
receive packets, simultaneously.
Polarity— Select the wiring configuration of the twisted pair port.
When a port is operating at 1000 Mbps, the only option is “AUTO.”
When operating at 10 or 100 Mbps, in either half- or full-duplex
mode, the options are “AUTO,” “MDI,” and “MDI-X.”
To forward traffic, a port on the switch and a port on a network
device must have different settings. For instance, the wiring
configuration of a switch port has to be MDI if the wiring
configuration on a port on a network device is MDIX.
To set the polarity to either “MDI” or “MDI-X” on a port, the
Negotiation setting must be “Manual.” A port with the AutoNegotiation must set the polarity to “AUTO.”
Back Pressure Status— Enable or disable back pressure on a
port that is operating at 10 or 100 Mbps in half-duplex mode. Back
pressure is used by a port during periods of packet congestion to
temporarily stop their network counterparts from transmitting more
packets. This prevents a buffer overrun and the subsequent loss
and retransmission of network packets. A port initiates back
pressure by transmitting on the shared link to cause a data
collision, which causes its link partner to cease transmission.
74
Page 75

AlliedWare Plus Version 2.2.4 Management Software Web Browser User’s Guide
To enable and disable back pressure on a port, the speed and
duplex mode must be specified manually. You cannot set back
pressure on a port that is using Auto-Negotiation.
Back Pressure Limit (1 - 7935)— Enter a threshold level for back
pressure on the port. Enter the number of cells for back pressure.
A cell represents 128 bytes. The range is 1 to 7935 cells. The
default value is 7935 cells.
Flow Control Status— Enable or disable the flow control feature.
By default, flow control is disabled on the port.
Flow Control Limit (1 - 7935)— Set the threshold level for flow
control on the port. Enter the number of cells for flow control. A cell
represents 128 bytes. The range is 1 to 7935 cells. The default
value is 7935 cells.
6. To set the port to the default port value, click Default. Otherwise skip
this step.
7. Click Apply.
8. Click SAVE
to save your changes to the startup configuration file.
75
Page 76

Chapter 4: Setting Port Parameters
Displaying the Storm Control Settings
To display the storm control settings, do the following:
1. Select the Switching tab.
The Switching tab is displayed. See Figure 24 on page 69.
2. From the Switching tab, select Port.
The Port tab expands to the right.
3. From the Port tab, select Storm Control.
The Storm Control List page is displayed. See Figure 27.
76
Figure 27. Storm Control List Page
The following fields are displayed:
Interface— Indicates the port ID.
Broadcast— Indicates whether the Broadcast threshold setting is
enabled or disabled.
Broadcast Level— Indicates the maximum number of ingress
packets per second of broadcast packets the port receives.
Broadcast packets that exceed the threshold are discarded by the
port. The range is 0 to 33,554,431 packets. The default is
33,554,431 packets.
Page 77

AlliedWare Plus Version 2.2.4 Management Software Web Browser User’s Guide
Multicast— Indicates whether the Multicast threshold setting is
enabled or disabled.
Multicast Level— Indicates the maximum number of ingress
packets per second of multicast packets the port receives.
Multicast packets that exceed the threshold are discarded by the
port. The range is 0 to 33,554,431 packets. The default is
33,554,431 packets.
Dlf— Indicates whether the unknown unicast threshold setting is
enabled or disabled.
Dlf Level— Indicates the maximum number of ingress packets per
second of unknown unicast packets the port receives. Unknown
unicast packets that exceed the threshold are discarded by the
port. The range is 0 to 33,554,431 packets. The default is
33,554,431 packets.
77
Page 78

Chapter 4: Setting Port Parameters
Modifying the Storm Control Settings
To modify the storm control settings, do the following:
1. Select the Switching tab.
The Switching tab is displayed. See Figure 24 on page 69.
2. From the Switching tab, select Port.
The Port tab expands to the right.
3. From the Port tab, select Storm Control.
The Storm Control List page is displayed. See Figure 25 on page 70.
4. Click Edit
The Storm Control Settings page is displayed. See Figure 28.
on the port that you want to modify.
78
Figure 28. Storm Control Settings Page
Page 79

AlliedWare Plus Version 2.2.4 Management Software Web Browser User’s Guide
5. Change the following fields as needed:
Broadcast— Enable or disable the broadcast storm control
feature. When this feature is enabled, the port discards ingress
packets that exceed the specified level. This feature is disabled by
default.
Enter the Level— Enter the maximum number of ingress packets
per second of broadcast packets the port receives. Broadcast
packets that exceed this level are discarded when the feature is
enabled. The range is 0 to 33,554,431 packets. The default is
33,554,431 packets.
Multicast— Enable or disable the multicast storm control feature.
When this feature is enabled, the port discards ingress packets
that exceed the specified level. This feature is disabled by default.
Enter the Level— Enter the maximum number of ingress packets
per second of multicast packets the port receives. Multicast
packets that exceed this level are discarded when this feature is
enabled. The range is 0 to 33,554,431 packets. The default is
33,554,431 packets.
DLF— Enable or disable the unknown unicast storm control
feature. When this feature is enabled, the port discards ingress
packets that exceed the specified level.This feature is disabled by
default.
Enter the Level— Enter the maximum number of ingress packets
per second of unknown unicast packets the port receives.
Unknown unicast packets that exceed this level are discarded
when this feature is enabled. The range is 0 to 33,554,431 packets.
The default is 33,554,431 packets.
6. Click Apply.
7. Click SAVE
to save your changes to the startup configuration file.
79
Page 80

Chapter 4: Setting Port Parameters
80
Page 81

Chapter 5
Setting Port Statistics
This chapter describes how to display and clear port statistics. Within the
AlliedWare Plus™ software, you can display and clear transmit, receive,
and interface port statistics.
This chapter contains the following topics:
“Displaying Port Statistics” on page 82
“Clearing Port Statistics” on page 89
“Reloading Statistics” on page 90
For additional information about port statistics, see the following chapters
in the AlliedWare Plus Management Software Version 2.2.4 Command
Line Interface User’s Guide:
Port Parameters
Port Parameter Commands
81
Page 82

Chapter 5: Setting Port Statistics
Displaying Port Statistics
You can display several types of port statistics. See the following sections:
“Displaying Transmit and Receive Port Statistics” on page 82
“Displaying Receive Statistics” on page 83
“Displaying Transmit Statistics” on page 85
“Displaying Interface Statistics” on page 87
Displaying
Transmit and
Receive Port
Statistics
To display the transmit and receive statistics for all of the switch ports, do
the following:
1. Select the Switching tab.
The Switching tab is displayed. See Figure 24 on page 69.
2. From the Switching tab, select Port.
3. Move the cursor to the right and select Statistics.
The Port Statistics page is displayed with the Tx + Rx tab automatically
selected. See Figure 29.
82
Figure 29. Port Statistics Page with Tx + Rx Tab
Page 83

AlliedWare Plus Version 2.2.4 Management Software Web Browser User’s Guide
The following fields are displayed:
Interface— Indicates the port ID.
0-64 Byte Frames— Indicates the number of frames transmitted
by the port that contain 0 to 64 bytes.
65-127 Byte Frames— Indicates the number of frames transmitted
by the port that contain 65 to 127 bytes.
128-255 Byte Frames— Indicates the number of frames
transmitted by the port that contain 128 to 255 bytes.
256-511 Byte Frames— Indicates the number of frames
transmitted by the port that contain 256 to 511 bytes.
512-1023 Byte Frames— Indicates the number of frames
transmitted by the port that contain 512 to 1023 bytes.
1024-1518 Byte Frames— Indicates the number of frames
transmitted by the port that contain 1024 to 1518 bytes.
1519-1522 Byte Frames— Indicates the number of frames
transmitted by the port that contain 1519 to 1522 bytes.
Displaying
Receive Statistics
To display the statistics on the Receive Statistics tab, do the following:
1. Select the Switching tab.
The Switching tab is displayed. See Figure 24 on page 69.
2. From the Switching tab, select Port.
3. Move the cursor to the right and select Statistics.
The Port Statistics page with the Tx + Rx tab selected is displayed.
See Figure 29 on page 82.
4. Click on the Receive Tab.
The Port Statistics with the Receive tab selected is displayed. See
Figure 30 on page 84.
83
Page 84

Chapter 5: Setting Port Statistics
Figure 30. Port Statistics with the Receive Tab
The following fields are displayed:
Interface— Indicates the port ID.
Total Bytes— Indicates the number of received bytes.
Total Frames— Indicates the number of received frames.
Total Error Frames— Indicates the total number of received
frames with errors.
Multicast Frames— Indicates the number of received multicast
frames.
Broadcast Frames— Indicates the number of received broadcast
frames.
CRC Error Frames— Indicates the number of frames with a cyclic
redundancy check (CRC) error but with the proper length (64 1518 bytes) received by the port.
FSC Error Frames— Indicates the number of ingress frames that
had frame check sequence (FCS) errors.
Pause Frames— Indicates the number of received flow control
pause frames.
Oversized Frames— Indicates the number of received frames
that exceeded the maximum size as specified by IEEE 802.3 (1518
bytes including the CRC).
84
Fragmented Frames— Indicates the number of undersized
frames, frames with alignment errors, and frames with frame check
sequence (FCS) errors (CRC errors).
Page 85

AlliedWare Plus Version 2.2.4 Management Software Web Browser User’s Guide
Note
Jabber Frames— Indicates the number of occurrences of
corrupted data or useless signals the port has encountered.
The following fields are not displayed in Figure 30 on page 84.
Undersize Frames— Indicates the number of received frames that
were less than the minimum length as specified by IEEE 802.3 (64
bytes including the CRC).
Dropped Frames— Indicates the number of frames successfully
received and buffered by the port, but discarded and not
forwarded.
MTU Exceed Discarded Frames— Indicates the number of
received frames with an MTU that exceeds the MTU of the switch.
These frames are discarded.
MAC Error Frames— Indicates the number of Receive Error
events seen by the receive side of the MAC.
Displaying
Transmit
Statistics
To display the statistics on the Transmit Statistics tab, do the following:
1. Select the Switching tab.
The Switching tab is displayed. See Figure 24 on page 69.
2. From the Switching tab, select Port.
3. Move the cursor to the right and select Statistics.
The Port Statistics page with the Tx + Rx tab selected is displayed.
See Figure 29 on page 82.
4. Click the Transmit tab.
The Port Statistics with the Transmit tab selected is displayed. See
Figure 31 on page 86.
85
Page 86

Chapter 5: Setting Port Statistics
Figure 31. Port Statistics with the Transmit Tab
The following fields are displayed:
Interface— Indicates the port ID.
Total Bytes— Indicates the number of transmitted bytes.
Total Frames— Indicates the number of transmitted frames.
Total Error Frames— Indicates the number of transmitted frames
with errors.
Multicast Frames— Indicates the number of transmitted multicast
frames.
Broadcast Frames— Indicates the number of transmitted
broadcast frames.
Pause Frames Sent— Indicates the number of transmitted flow
control pause frames.
Deferred— Indicates the number of egress frames that the port
could not immediately transmit.
Single Collision— Indicates the number of frames that were
transmitted after at least one collision.
Multi Collision— Indicates the number of frames that were
transmitted after more than one collision.
86
Late Collision— Indicates the number of late collisions.
Excessive Collision— Indicates the number of excessive
collisions.
Page 87

AlliedWare Plus Version 2.2.4 Management Software Web Browser User’s Guide
Total Collision Frames— Indicates the total number of collisions
on the port.
MAC Error Frames— Indicates the number of frames not
transmitted correctly or dropped due to an internal MAC transmit
error.
Displaying
Interface
Statistics
To display the interface statistics, do the following:
1. Select the Switching tab.
The Switching tab is displayed. See Figure 24 on page 69.
2. From the Switching tab, select Port.
3. Move the cursor to the right and select Statistics.
The Port Statistics page with the Tx + Rx tab selected is displayed.
See Figure 29 on page 82.
4. Click the Interface tab.
The Port Statistics Page with the Interface tab selected is displayed.
See Figure 32.
Figure 32. Port Statistics Page with Interface Tab
The following fields are displayed:
Interface— Indicates the port ID.
Rx Unicast Packets— Indicates the number of ingress unicast
packets.
87
Page 88

Chapter 5: Setting Port Statistics
Rx Discard Packets— Indicates the number of ingress packets
that were discarded prior to transmission because of an error.
Rx IP Header Error Packets— Indicates the number of ingress
packets that were discarded because of a hardware error.
Tx Unicast Packets— Indicates the number of egress unicast
packets.
Tx Discard Packets— Indicates the number of egress packets
that were discarded prior to transmission because of an error.
Tx Error Packets— Indicates the number of egress error packets.
88
Page 89

Clearing Port Statistics
To clear the statistics for a port, do the following:
1. Select the Switching tab.
The Switching tab is displayed. See Figure 24 on page 69.
2. From the Switching tab, select Port.
3. Move the cursor to the right and select Statistics.
The Port Statistics Page with Tx + Rx tab selected is displayed. See
Figure 29 on page 82.
4. Select the desired Port Statistics tab. Choose from the following:
Tx+Rx— Displays the transmit and receive statistics.
Receive— Displays the receive statistics.
AlliedWare Plus Version 2.2.4 Management Software Web Browser User’s Guide
Transmit— Displays the transmit statistics.
Interface— Displays the interface statistics.
5. Click Clear
on the port that you want to clear.
89
Page 90

Chapter 5: Setting Port Statistics
Reloading Statistics
Port statistics are constantly counting and the values are changing so that
the data that is displayed in the Port Statistics pages is not the most
recent. To display the latest data possible, click on the Reload Page
button on a Port Statistics page.
Figure 33 shows the Reload Page button on Port Statistics page as an
example.
Figure 33. Port Statistics Page with the Reload Page Button
90
Page 91

Chapter 6
Port Mirroring
The port mirror is a management tool that allows you to monitor the traffic
on one or more ports on the switch. It works by copying the traffic from
source ports to a destination port where the traffic can be monitored with a
network analyzer. The port mirror can be used to troubleshoot network
problems or to investigate possible unauthorized network access. The
performance and speed of the switch is not affected by the port mirror.
This chapter provides a brief description of the port mirroring feature and
explains how to display and set port mirroring. See the following sections:
“Overview” on page 92
“Displaying Port Mirroring Settings” on page 93
“Assigning a Destination Port” on page 95
“Assigning Source Ports and Port Mirroring Values” on page 96
For more information about port mirroring, see the following chapters in the
AlliedWare Plus Management Software Version 2.2.4 Command Line
Interface User’s Guide:
Port Mirror
Port Mirror Commands
Page 92

Chapter 6: Port Mirroring
Overview
To use the port mirroring feature, you must designate one or more source
ports and one destination port. The source ports are the ports whose
packets are mirrored and monitored. The destination port is the port where
the packets from the source ports are copied and where the network
analyzer is connected. There can be only one destination port on the
switch.
Here are guidelines for setting the port mirroring feature:
The switch supports only one port mirror.
The port mirror can have one destination port.
The port mirror can have more than one source port. This allows you
to monitor the traffic on multiple ports at the same time. For example,
you may monitor the traffic on all the ports of a particular VLAN.
You can mirror the ingress traffic, the egress traffic, or both on the
source ports.
The destination port must not be a member of a static port trunk or an
LACP trunk.
92
Page 93

AlliedWare Plus Version 2.2.4 Management Software Web Browser User’s Guide
Displaying Port Mirroring Settings
To display the port mirroring assignments for all of the switch ports, do the
following:
1. Select the Switching tab.
The Switching tab is displayed. See Figure 24 on page 69.
2. From the Switching tab, select Port.
The Port tab is displayed.
3. From the Port tab, select Mirroring.
4. Move the cursor to the right and select Mirroring.
The Port Mirroring List page is displayed. See Figure 34.
Figure 34. Port Mirroring List Page
The following fields are displayed:
Destination Port— Use the pull-down menu to select the port
where the packets from the source ports are copied and where the
network analyzer is connected. You can assign only one
destination port to the switch. In Figure 34, the Destination Port is
port 1.
Interface— Indicates the port ID.
Mirror Transmit— Indicates a source port whose transmitted, or
egress, packets are mirrored and monitored. There can be multiple
source ports on the switch.
93
Page 94

Chapter 6: Port Mirroring
Mirror Receive— Indicates a source port whose received, or
ingress, packets are mirrored and monitored. There can be
multiple source ports on the switch.
94
Page 95

Assigning a Destination Port
You must assign the destination port before adding source ports. Also, you
are allowed to assign only one destination port to the switch.
To assign a destination port, do the following:
1. Select the Switching tab.
The Switching tab is displayed. See Figure 24 on page 69.
2. From the Switching tab, select Port.
The Port tab is displayed.
3. From the Port tab, select Mirroring.
The Port Mirroring List page is displayed. See Figure 34 on page 93.
4. Select the pull-down menu next to the Destination Port field at the top
of the page.
AlliedWare Plus Version 2.2.4 Management Software Web Browser User’s Guide
5. Click on the port that you want to designate as the destination port.
You can only assign one destination port to a switch.
6. Click Apply.
The Edit option is removed from the port. This indicates the
destination port for the switch.
7. Click SAVE
to save your changes to the startup configuration file.
95
Page 96

Chapter 6: Port Mirroring
Assigning Source Ports and Port Mirroring Values
To assign mirrored ports and mirroring ports, do the following:
1. Select the Switching tab.
The Switching tab is displayed. See Figure 24 on page 69.
2. From the Switching tab, select Port.
The Port tab is displayed.
3. From the Port tab, select Mirroring.
The Port Mirroring List page is displayed. See Figure 34 on page 93.
4. Click Edit
next to the port that you want to assign as a transmitting or
receiving port mirror.
The Modify Port Mirroring Page is displayed. See Figure 35.
96
Figure 35. Modify Port Mirroring Page
5. Select the type of mirroring for the port. The options are:
Transmit— Specifies the egress traffic on this port to be copied to
the destination port.
Page 97

AlliedWare Plus Version 2.2.4 Management Software Web Browser User’s Guide
Receive— Specifies the ingress traffic on this port to be copied to
the destination port.
Both— Specifies both the egress and ingress traffic on this port to
be copied to the destination port.
By default, there is no port assigned to port mirroring.
6. Click Apply.
7. Click SAVE
to save your changes to the startup configuration file.
97
Page 98

Chapter 6: Port Mirroring
Deleting Port Mirroring Settings
You have two ways to delete existing port mirroring settings. When you
assign a new port as the destination port, existing port mirroring settings
are removed because you can only assign one destination port to the
switch. Assigning the port to “None” deletes the existing port mirroring
settings as well.
To delete the existing port mirroring settings, assign the port to “None.”
To delete the port mirroring settings, do the following:
1. Display the port mirroring assignments. See “Displaying Port Mirroring
Settings” on page 93.
The Port Mirroring List page is displayed. See Figure 34 on page 93.
2. Select the pull-down menu next to the Destination Port field at the top
of the page.
3. Click on “None.”
4. Click Apply.
5. Click SAVE
to save your changes to the startup configuration file.
98
Page 99

Chapter 7
Note
Spanning Tree Protocol on a Port
The Spanning Tree Protocol (STP) and Rapid Spanning Tree Protocol
(RSTP) guard against the formation of loops in an Ethernet network
topology. A topology has a loop when two or more nodes can transmit
packets to each other over more than one data path. Packets can become
caught in repeating cycles, referred to as broadcast storms, that
AlliedWare Plus™ Version 2.2.4 needlessly consume network bandwidth
and that can significantly reduce network performance.
This chapter provides a brief description of the spanning tree protocols and
explains how to set spanning tree on a port. See the following sections:
“Overview” on page 100
“Displaying Port Spanning Tree Protocol Settings” on page 101
“Modifying Port Spanning Tree Protocol Settings” on page 103
For information about how to set a spanning tree protocol for the
switch, see Chapter 12, “Spanning Tree Protocols on the Switch” on
page 153.
For more information about the spanning tree protocols, see the following
chapters in the AlliedWare Plus Management Software Version 2.2.4
Command Line Interface User’s Guide:
Spanning Tree and Rapid Spanning Tree Protocols
Spanning Tree Protocol (STP)
STP Commands
Rapid Spanning Tree Protocol (RSTP)
RSTP Commands
99
Page 100

Chapter 7: Spanning Tree Protocol on a Port
Overview
STP and RSTP prevent loops from forming by ensuring that only one path
is available at a time between the switches in your network. Where
multiple paths exist, these spanning tree protocols place the extra paths in
a standby or blocking mode. In addition, these protocols can activate
redundant paths if primary paths go down. These protocols guard against
multiple links between segments and the risk of broadcast storms as well
as maintain network connectivity by activating backup redundant paths.
One of the primary differences between the STP and RTP protocols is in
the time each takes to complete the process referred to as convergence.
When a change is made to the network topology, such as the addition of a
new bridge, a spanning tree protocol determines whether there are
redundant paths that must be blocked to prevent data loops, or activated
to maintain communications between the various network segments. This
is the process of convergence.
With STP, convergence can take up to a minute to complete in a large
network. This can result in the loss of communication between various
parts of the network during the convergence process, and the subsequent
lost of data packets. RSTP is much faster than STP. It can complete a
convergence in seconds, and so greatly diminish the possible impact the
process can have on your network.
Only one spanning tree can be active on the switch at a time. The default
setting is RSTP.
100
 Loading...
Loading...