
User’s Guide
Layer 2
Ethernet Switch
AT-8000S Series

Table of Contents
Table of Contents
Preface.................................................................................................................................... 6
Web Browser Interface User’s Guide Overview ..............................................................................7
Intended Audience...........................................................................................................................7
Document Conventions ...................................................................................................................8
Contacting Allied Telesis .................................................................................................................8
Getting Started...................................................................................................................... 10
Starting the Application..................................................................................................................10
Using the Web Browser Interface..................................................................................................12
Viewing the Device Representation.........................................................................................................12
User Interface Components.....................................................................................................................13
Using the Management Buttons ..............................................................................................................14
Adding, Modifying and Deleting Information............................................................................................15
Saving Configurations..............................................................................................................................16
Logging Out...................................................................................................................................16
Resetting the Device .............................. ... ... .................................................................................17
Defining System Information.................................................................................................18
Configuring System Time...................................................................................................... 20
Setting the System Clock ....................... ... ... .... .......................................... ... ... ... .... ... ...................22
Configuring SNTP..........................................................................................................................23
Polling for Unicast Time Information........................................................................................................23
Polling for Anycast Time Information.......................................................................................................23
Broadcast Time Information.....................................................................................................................23
Configuring Daylight Saving Time .................................................................................................24
Configuring Device Security..................................................................................................26
Configuring Management Security ................................................................................................27
Defining Access Profiles..........................................................................................................................28
Defining Profile Rules......................................... ... ... .................................... ...........................................31
Defining Authentication Profiles.................................................................. .............................................34
Mapping Authentication Profiles............................................. ... ..............................................................37
Configuring Server Based Authentication................................................................................................38
Configuring TACACS+ ............................................................................................................................38
Configuring RADIUS................................................................................................................................41
Configuring Local Users ..........................................................................................................................43
Configuring Network Security........................................................................................................45
Network Security Overview......................................................................... .. ...........................................46
Managing Port Security ...........................................................................................................................46
Defining 802.1x Port Access....................................................................................................................49
Enabling Storm Control............................................................................................................................52
Page 1

Allied Telesis AT-8000S Switch
Web Browser Interface User’s Guide
Configuring Ports.................................................................................................................. 54
Defining Port Settings ................................................................................................................... 55
Configuring Port Mirroring............................................................................................................. 59
Aggregating Ports ......................................................................................................................... 62
Defining Trunk Settings............................................................................. ... ........................................... 63
Defining Port Trunking.......................................... .................................... .............................................. 67
Configuring LACP...................................................................................................................................69
Configuring Interfaces........................................................................................................... 70
Defining MAC Addresses.............................................................................................................. 71
Configuring VLANs........................................................................................................................ 74
Defining VLAN Properties.......................................................................................... ... ... ....................... 75
Defining VLAN Interface Settings ...........................................................................................................77
Defining GVRP........................................ .................................... ..................................... ....................... 79
Configuring System Logs......................................................................................................82
Defining Log Settings.................................................................................................................... 83
Clearing Event Logs...................................................................................................................... 85
Configuring Log Servers ............................................................................................................... 85
Setting System Log Display.................... ... ... ... ... .......................................... .... ... ... ... .... ... ... ... ...... 86
Viewing Flash Logs....................................................................................................................... 87
Configuring Spanning Tree................................................................................................... 88
Configuring Classic Spanning Tree...............................................................................................89
Defining STP Properties ..................................................... ... .................................... ... .......................... 89
Defining STP Interfaces......................................................... .................................... ... .......................... 91
Configuring Rapid Spanning Tree.................................................................................................94
Configuring Multiple Spanning Tree..............................................................................................96
Defining MSTP Properties ................ ... .................................... ... ..................................... .. .....................97
Defining MSTP Interfaces.......................................................................................... ... ... ....................... 98
Defining MSTP Instances ...................................................... .. ..................................... ... .....................100
Configuring Multicast Forwarding ....................................................................................... 102
Configuring IGMP Snooping .......................................................................................................103
Defining Multicast Bridging Groups............................................................................................. 105
Defining Multicast Forward All Settings....................................................................................... 107
Configuring SNMP.............................................................................................................. 110
SNMP Overview.......................................................................................................................... 111
Enabling SNMP........................................................................................................................... 112
Defining SNMP Communities...................................................................................................... 114
Defining SNMP Groups............................................................................................................... 116
Defining SNMP Users................................................................................................................. 118
Defining SNMP Views................................................................................................................. 120
Page 2

Table of Contents
Configuring SNMP Notifications ..................................................................................................122
Defining Notification Recipients.............................................................................................................122
Defining Notification Filters....................................................................................................................124
Configuring Power Over Ethernet.......................................................................................126
Enabling PoE and Setting the Power Threshold .........................................................................127
Defining PoE Settings..................................................................................................................128
Configuring Services...........................................................................................................132
Enabling Class of Service (CoS) .................................................................................................133
Configuring CoS Priorities ...........................................................................................................135
Mapping Queues .........................................................................................................................136
Mapping CoS Values to Queues ........................ ... ................................................................................136
Mapping DSCP Values to Queues ..................... ..................................... ... ...........................................137
Configuring Bandwidth QoS ........................................................................................................138
Managing System Files....................................................................................................... 140
Restoring the Default Configuration ............................................................................................141
Defining TFTP File Uploads and Downloads...............................................................................142
Viewing Integrated Cable Tests...................................................................................................145
Viewing Optical Transceivers ......................................................................................................147
Resetting the Device .............................. ... ... ...............................................................................148
Viewing Statistics................................................................................................................150
Viewing Interface Statistics..........................................................................................................151
Viewing Interface Statistics....................................................................................................................151
Viewing Etherlike Statistics............................................................................................... ... ..................153
Managing RMON Statistics .................... ... ... .... ... ... ... .......................................... .... ... ... ... ... .... ....155
Viewing RMON Statistics.............................................................. .................................... ... ..................155
Configuring RMON History....................................................................................................................157
Configuring RMON Events ....................................................................................................................161
Defining RMON Alarms .........................................................................................................................164
Managing Stacking .............................................................................................................168
Stacking Overview.......................................................................................................................169
Stacking Ring Topology.........................................................................................................................169
Stacking Chain Topology.......................................................................................................................169
Stacking Members and Unit ID....................................................... ... ..................................... ... ............170
Removing and Replacing Stacking Members........................................................................................170
Exchanging Stacking Members.............................................................................................................171
Configuring Stacking Management .............................................................................................172
Connecting a Terminal...................... ... .......................................... ... ... .... ... ... ...........................174
Initial Configuration ...................................................................................................................174
Configuration175
Static IP Address and Subnet Mask175
User Name176
Page 3

Allied Telesis AT-8000S Switch
Web Browser Interface User’s Guide
Downloading Software.............................................................................................................. 176
Standalone Device Software Download176
Stacking Member Software Download177
RS-232 Port Settings................................................................................................................ 181
Port Defaults......................................... ... ... .......................................... ... ... .............................. 181
Configuration Defaults...... ... .......................................... .... ... ... ... .... .......................................... 181
Security Defaults ...................................................................................................................... 181
System Time Defaults .............................................................................................................. 182
Spanning Tree Defaults............................................................................................................ 182
Address Table Defaults............................................................................................................ 182
VLAN Default............................................................................................................................ 183
Trunking Defaults ..................................................................................................................... 183
Multicast Defaults..................................................................................................................... 183
Page 4

Table of Contents
Page 5

Allied Telesis AT-8000S Switch
Web Browser Interface User’s Guide
Preface
This guide contains instructions on how to configure an AT -8000S Series Layer 2+ Fast Ethernet Switch using the
interface in the Embedded Management System (EWS).
The Embedded Management System enables configuring, monitoring, and troubleshooting of ne twork devices
remotely via a web browser. The web pages are easy-to-use and easy-to-navigate.
This preface provides an overview of the Web Browser Interface User’s Guide, and includes the following
sections:
• Web Browser Interface User’s Guide Overview
• Intended Audience
Page 6

Preface
Web Browser Interface User’s Guide Overview
Web Browser Interface User’s Guide Overview
The Web Browser Interface User’s Guide provides the following sections:
• Section 1,“Getting Started” — Provides information for using the Embedded Web Management System,
including adding, editing, and deleting configurations.
• Section 2, “Defining System Information” — Provides information for defining basic device information.
• Section 3, “Configuring System Time” — Provides information for configuring Daylight Savings Time and
Simple Network Time Protocol (SNTP).
• Section 4, “Configuring Device Security” — Provides information for configuring both system and network
security, including traffic control, and switch access methods.
• Section 5, “Configuring Ports” — Provides information for configuring ports, port aggregation, port
mirroring and LACP.
• Section 6, “Configuring Interfaces” — Provides information for defining ports, LAGs, and VLANs.
• Section 7, “Configuring System Logs” — Provides information for setting up and viewing system logs, and
configuring switch log servers.
• Section 8, “Configuring Spanning Tree” — Provides information for configuring Classic, Rapid, and
Multiple Spanning Tree.
• Section 9, “Configuring Multicast Forwarding” — Provides information for configuring both the static and
dynamic forwarding databases.
• Section 10, “Configuring SNMP” — Provides information for configuring SNMP access and management.
• Section 11, “Configuring Power Over Ethernet” — Provides information for configuring Power over
Ethernet (PoE) on the device.
• Section 12, “Configuring Services” — Provides information for configuring Quality of Service CoS
parameters.
• Section 13, “Managing System Files” — Provides information for managing system files.
• Section 14, “Viewing Statistics” — Provides information about viewing device statistics, including Remote
Monitoring On Network (RMON) statistics, and device history events.
• Section 15, “Managing Stacking” — Provides information for stacking, including a stacking overview.
Intended Audience
This guide is intended for network administrators familiar with IT concepts and terminology.
Page 7
Page 7
Allied Telesis AT-8000S Switch
Web Browser Interface User’s Guide
Document Conventions
This document uses the following conventions:
Note
Provides related information or information of special importance.
Caution
Indicates potential damage to hardware or software, or loss of data.
Warning
Indicates a risk of personal injury.
Contacting Allied Telesis
This section provides Allied Telesis contact information for technical support as well as sales or corporate
information.
Online Support
Email and Telephone
Support
Returning Products
For Sales or
Corporate
Information
Management
Software Updates
You can request technical support online by accessing the Allied Telesis Knowledge Base
from the following web site: www.alliedtelesis.com/kb. You can use the Knowledge Base
to submit questions to our technical support staff and review answers to previously asked
questions.
For Technical Support via email or telephone, refer to the Support & Services section of
the Allied Telesis web site: www.alliedtelesiselesis.com.
Products for return or repair must first be assigned a Return Materials Authorization (RMA)
number. A product sent to Allied Telesis without a RMA number will be returned to the
sender at the sender’s expense.
To obtain a RMA number, contact Allied Telesis’s Technical Support at our web site:
www.alliedtelesiselesis.com.
You can contact Allied Telesis for sales or corporate information at our web site:
www.alliedtelesis.com. To find the contact information for your country , select Cont act Us
-> Worldwide Contacts.
You can download new releases of management software for our managed products from
either of the following Internet sites:
• Allied Telesis web site: www.alliedtelesis.com
• Allied Telesis FTP server: ftp://ftp.alliedtelesis.com
To download new software from the Allied Telesis FTP server using your workstation’s
command prompt, you need FTP client software and you must log in to the server. Enter
“anonymous” as the user name and your email address for the password.
Page 8

Preface
Contacting Allied Telesis
Page 9
Page 9

Allied Telesis AT-8000S Switch
Web Browser Interface User’s Guide
Section 1. Getting Started
This section provides an introduction to the Web Browser Interface, and includes the following topics:
• Starting the Application
• User Interface Components
• Resetting the Device
• Starting the Application
Starting the Application
This section contains information for starting the application. The login information is configured with a default user
name and password. The default password is friend; the default user name is manager. Passwords are both case
sensitive and alphanumeric. Additional user names can be added.
To open the application:
1. Open a web browser.
2. Enter the device IP address in the address bar and press <Enter>. The Login Page opens:
Figure 1: Login Page
3. Enter the user name and password.
4. Click Login. The Embedded Web System Home Page opens:
Page 10
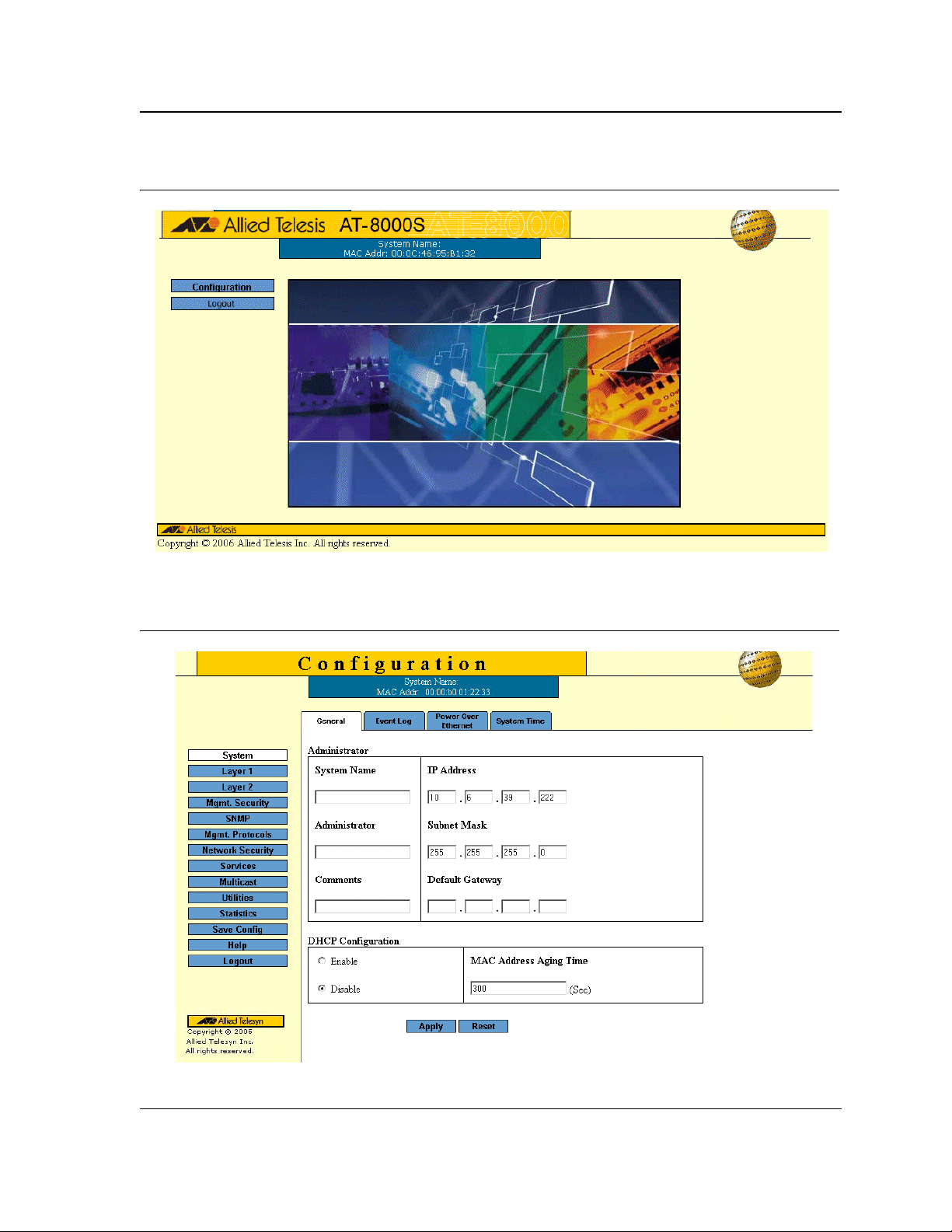
Figure 2: Embedded Web System Home Page
Getting Started
Starting the Application
5. Click Configuration. The System General Page opens:
Figure 3: System General Page
Page 11
Allied Telesis AT-8000S Switch
Web Browser Interface User’s Guide
Using the Web Browser Interface
This section provides general information about the interface, and describes the following topics:
• Viewing the Device Representation
• User Interface Components
• Using the Management Buttons
• Using the Management Buttons
• Adding, Modifying and Deleting Information
Viewing the Device Representation
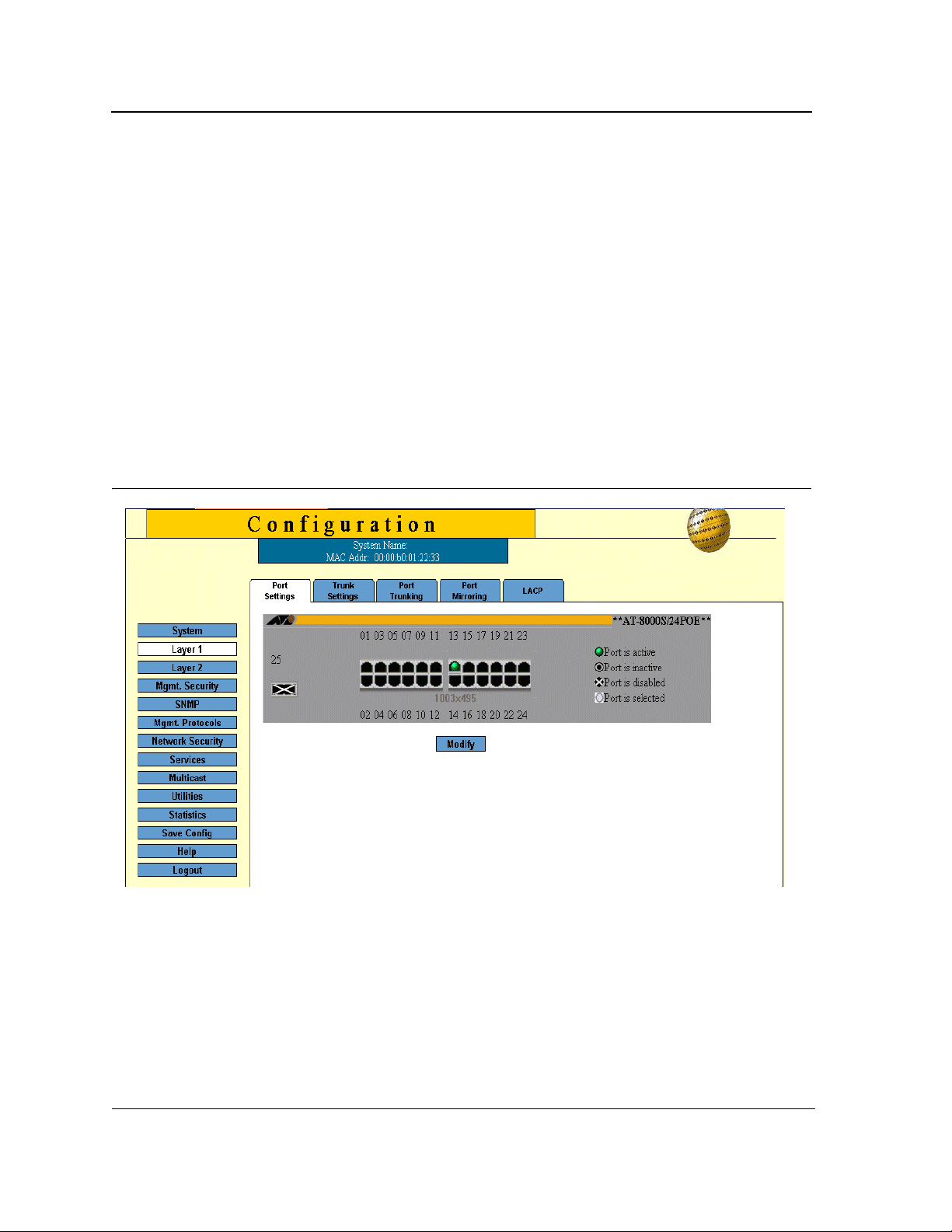
Zoom Views provide a graphical representation of the device ports. The Port Settings Page displays an example
of the Zoom View with a detailed graphical representation of the device ports.
To open a zoom view of device ports:
• Click Layer 1 > Port Settings. The Port Settings Page opens:
Figure 4: Port Settings Page
The port status indicators vary with context, for example the general port status indicators are as in the figure
above while port mirror indicators are different. Indicator legend descriptions are provided with each context of the
specific Zoom View.
Page 12

User Interface Components
The System General Page example shows the interface components.
Figure 5: System General Page
Getting Started
Using the Web Browser Interface
The following table lists the interface components with their corresponding numbers:
Table 1: Interface Components
Component Description
1 Menu The Menu provides easy navigation through the main management software
features. In addition, the Menu provides general navigation options.
2 Tabs Provide navigation to configurable device sub-features.
3 Management Buttons Enable configuring parameters and navigation to other pages, see Using the
Management Buttons.
Page 13

Allied Telesis AT-8000S Switch
Web Browser Interface User’s Guide
Using the Management Buttons
Management buttons provide an easy method of configuring device information, and include the following:
Table 2: Configuration Management Buttons
Button Button Name Description
Add Opens a page which creates new configuration entries.
Create Opens a page which creates new configuration entries.
Modify Modifies the configuration settings. The configuration change is
saved to the Running Configuration file and is maintained until
reset or power-up.
Apply Saves configuration changes to the device. The configu r ation
change is saved to the Running Configuration file and is
maintained until reset or power-up.
Configure Opens a page which creates or modifies configuration entries.
Delete Deletes the selected table and configuration entries.
View Displays detailed information for the current page/configuration.
Refresh Refreshes information displayed on the current page.
Reset Device reset. Resets the device information for all device
parameters according to current configuration.
Defaults Configuration reset. Resets the information for all parameters in
the current context (page/tab) to predefined defaults.
Test Performs a diagnostic test.
Clear All Counters Removes all counters.
The application menu includes the following general purpose buttons:
Configuration Opens the default configuration page (System General).
Login Signs the user into the WBI, starts the management session.
Logout Signs the user out of the WBI, ending the management session.
Help Opens the online help page.
Exit Help Closes the online help page.
Save Config Used when configuration changes to the device need to be saved
as permanent. The configuration is saved as permanent by
copying the current Running Configuration file to the Startup
Configuration file.
Page 14
Getting Started
Using the Web Browser Interface
Adding, Modifying and Deleting Information
The WBI contains and tables for configuring devices. User-defined information can be added, modified or deleted
in specific WBI pages.
To add information to tables or WBI pages:
1. Open a WBI page.
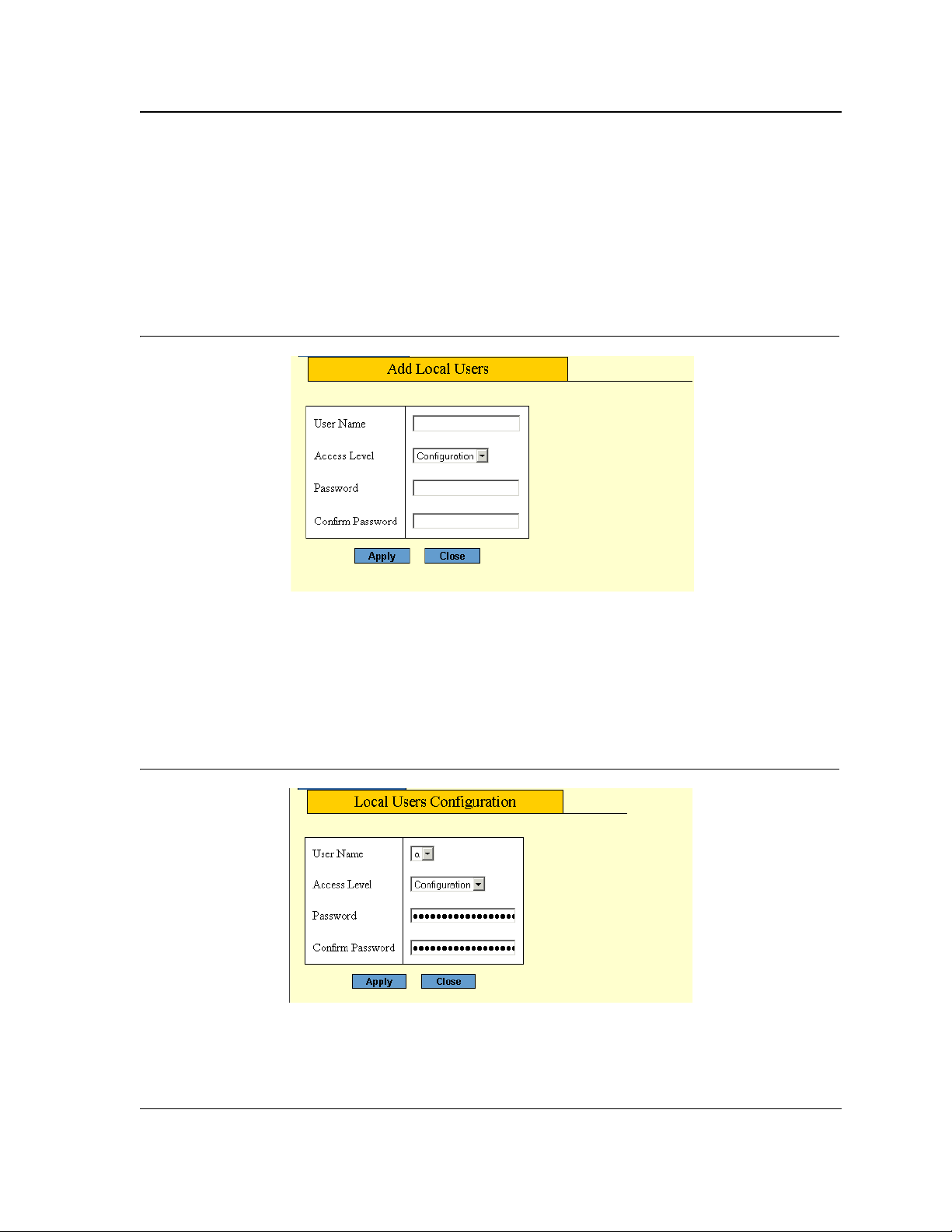
2. Click Add. An Add page opens, for example, the Add Local User Page:
Figure 6: Add Local User Page
3. Define the fields.
4. Click Apply. The configuration information is saved, and the device is updated.
To modify information in tables or WBI pages:
1. Open a WBI page.
2. Select a table entry.
3. Click Modify. A Modify (or Settings) page opens, for example, the Local User Settings Page:
Figure 7: Local User Setting s Page
4. Define the fields.
5. Click Apply. The fields are modified, and the information is saved to the device.
Page 15

Allied Telesis AT-8000S Switch
Web Browser Interface User’s Guide
To delete information in tables or WBI pages:
1. Open the WBI page.
2. Select a table row.
3. Click Delete. The information is deleted, and the device is updated.
Saving Configurations
User-defined information can be saved for permanent use or until next update, not just for the current session.
A configuration is saved as permanent by copying the current Running Configuration file to the Startup
Configuration file.
To save changes permanently:
• Click Save Config on the menu.
Logging Out
The Logout option enables the user to log out of the device thereby terminating the running session.
To log out:
• In any page, click Logout on the menu. The current management session is ended and the Login Page
opens:
Figure 8: Login Page
For more information about login, refer to Starting the Application.
Page 16

Getting Started
Resetting the Device
Resetting the Device
The Reset option enables resetting the device from a remote location.
Note
Save all changes to the Running Configuration file before resetting the device. This prevents the current
device configuration from being lost. See also "Managing System Files".
To reset the device:
1. In the System General Page, click Reset. You are prompted to confirm.
2. Click OK. The device is reset. Resetting the device ends the web browser management session. You must
restart the session to continue managing the device. After the device is reset, a prompt for a user name and
password displays.
3. Enter a user name and password to reconnect to the Web Interface.
To reset the device to the predefined default configuration:
• In the System General Page, click Defaults. The default settings are restored and the device is reset.
Page 17
Allied Telesis AT-8000S Switch
Web Browser Interface User’s Guide
Section 2. Defining System Information
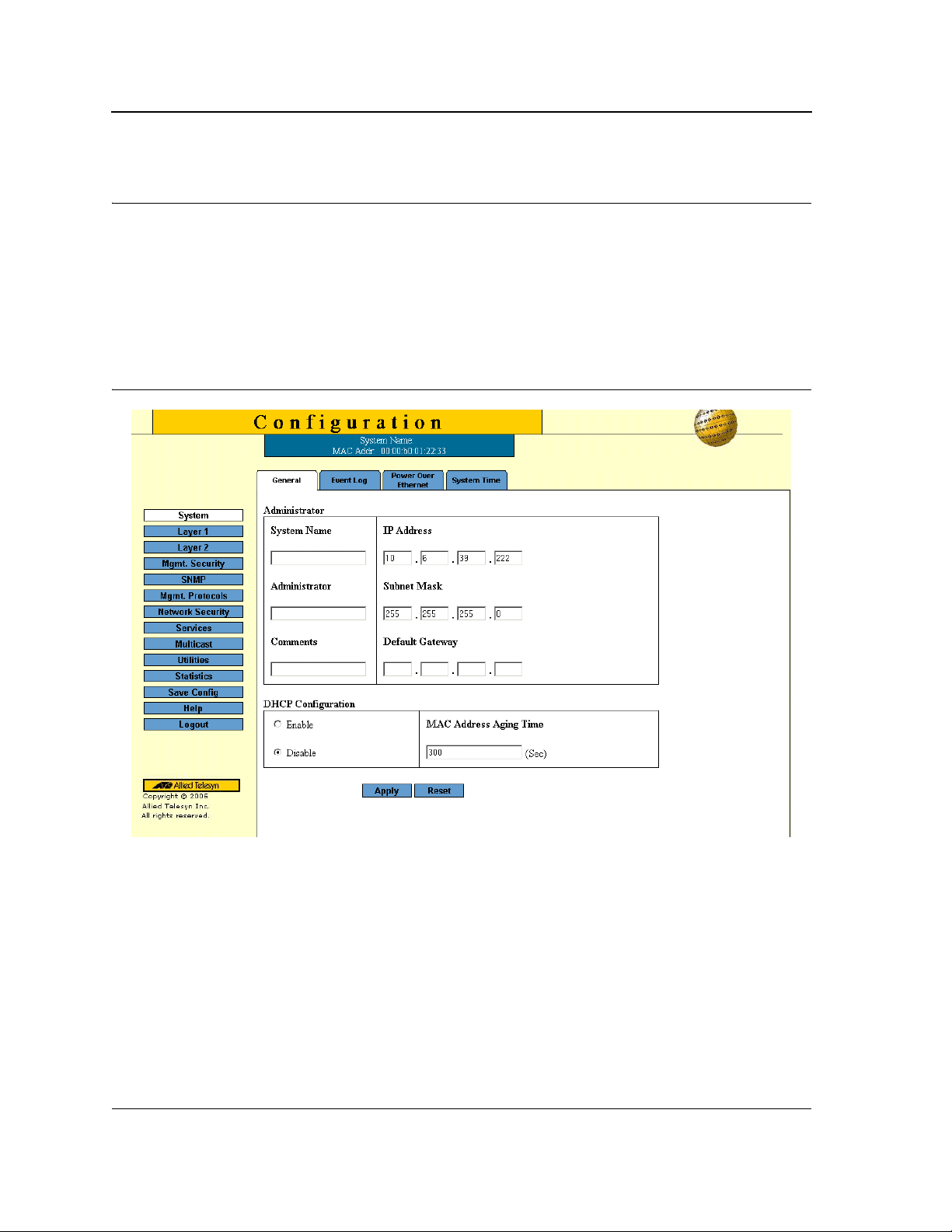
The System General Page contains general device information, including system name and its IP addressing,
administrator and passwords information, Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP) configuration and MAC
Address Aging Time.
To define the general system information:
1. Click System > General. The System General Page opens:
Figure 9: System General Page
The System General Page comprises two sections: Administration and DHCP Configuration.
The Administration section of the System General Page contains the following fields:
• System Name — Indicates the user-defined name of the device. This is a required field.
The field range is 0-159 characters.
• Administrator — Indicates the name of the administrator responsible for managing the device. The field
range is 0-159 characters.
• Comments — (Optional) The user can add any comments about the device in this field, for example, fill in
the location of the device.
• IP Address — Indicates the device’s IP address.
• Subnet Mask — Indicates the device’s subnet mask.
Page 18

Defining System Information
• Default Gateway — The IP address of a router for remote management of the device. The address must be
entered in the format: xxx.xxx.xxx.xxx. The default value is 0.0.0.0.
Note
Packets are forwarded to the default IP when frames are sent to a remote network via the default gateway.
The configured IP address must belong to the same subnet as one of the IP interfaces.
The DHCP Configuration section of the System General Page contains the following fields:
• DHCP — Indicates if the Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP) is enabled.
– Enable — DHCP dynamically assigns IP addresses to devices on a network. With dynamic addressing,
a device can have a different IP address every time it connects to the network. If the DHCP client
software is activated, the device immediately begins to query the network for a DHCP server. The device
continues to query the network for its IP configuration until it receives a response. If the device and IP
address are manually assigned, that address is deleted and replaced by the IP address received from
the DHCP server.
– Disable — Disables DHCP on the device.
• Mac Address Aging Time — The time interval an inactive dynamic MAC address can remain in the MAC
address table before it is deleted. The default time is 300 seconds, and the range is 0-300.
2. Define the administration, passwords and DHCP configuration fields.
3. Click Apply. The system general information is defined and the device is updated.
4. Click Save Config on the menu to save the changes permanently.
Page 19

Allied Telesis AT-8000S Switch
Web Browser Interface User’s Guide
Section 3. Configuring System Time
This section provides information for configuring system time parameters, including:
• Setting the System Clock
• Configuring SNTP
• Configuring Daylight Saving Time
The following is a list of Daylight Savings Time start and end dates by country:
• Albania — From the last weekend of March until the last weekend of October.
• Australia — From the end of October until the end of March.
• Australia - Tasmania — From the beginning of October until the end of March.
• Armenia — From the last weekend of March until the last weekend of October.
• Austria — From the last weekend of March until the last weekend of October.
• Bahamas — From April to October, in conjunction with Daylight Savings Time in the United States.
• Belarus — From the last weekend of March until the last weekend of October.
• Belgium — From the last weekend of March until the last weekend of October.
• Brazil — From the third Sunday in October until the third Saturday in March. During the period of Daylight
Saving Time, Brazilian clocks go forward one hour in most of the Brazilian southeast.
• Chile — In Easter Island, from March 9 until October 12. In the rest of the country, from the first Sunday in
March or after 9th March.
• China — China does not use Daylight Saving Time.
• Canada — From the first Sunday in April until the last Sunday of October. Daylight Saving Time is usually
regulated by provincial and territorial governments. Exceptions may exist in certain municipalities.
• Cuba — From the last Sunday of March to the last Sunday of October.
• Cyprus — From the last weekend of March until the last weekend of October.
• Denmark — From the last weekend of March until the last weekend of October.
• Egypt — From the last Friday in April until the last Thursday in September.
• Estonia — From the last weekend of March until the last weekend of October.
• Finland — From the last weekend of March until the last weekend of October.
• France — From the last weekend of March until the last weekend of October.
• Germany — From the last weekend of March until the last weekend of October.
• Greece — From the last weekend of March until the last weekend of October.
• Hungary — From the last weekend of March until the last weekend of October.
• India — India does not use Daylight Saving Time.
• Iran — From Farvardin 1 until Mehr 1.
• Iraq — From April 1 until October 1.
• Ireland — From the last weekend of March until the last weekend of October.
• Israel — Varies year-to-year.
• Italy — From the last weekend of March until the last weekend of October.
• Japan — Japan does not use Daylight Saving Time.
• Jordan — From the last weekend of March until the last weekend of October.
• Latvia — From the last weekend of March until the last weekend of October.
• Lebanon — From the last weekend of March until the last weekend of October.
Page 20

Configuring System Time
• Lithuania — From the last weekend of March until the last weekend of October.
• Luxembourg — From the last weekend of March until the last weekend of October.
• Macedonia — From the last weekend of March until the last weekend of October.
• Mexico — From the first Sunday in April at 02:00 to the last Sunday in October at 02:00.
• Moldova — From the last weekend of March until the last weekend of October.
• Montenegro — From the last weekend of March until the last weekend of October.
• Netherlands — From the last weekend of March until the last weekend of October.
• New Zealand — From the first Sunday in October until the first Sunday on or after March 15.
• Norway — From the last weekend of March until the last weekend of October.
• Paraguay — From April 6 until September 7.
• Poland — From the last weekend of March until the last weekend of October.
• Portugal — From the last weekend of March until the last weekend of October.
• Romania — From the last weekend of March until the last weekend of October.
• Russia — From the last weekend of March until the last weekend of October.
• Serbia — From the last weekend of March until the last weekend of October.
• Slovak Republic - From the last weekend of March until the last weekend of October.
• South Africa — South Africa does not use Daylight Saving Time.
• Spain — From the last weekend of March until the last weekend of October.
• Sweden — From the last weekend of March until the last weekend of October.
• Switzerland — From the last weekend of March until the last weekend of October.
• Syria — From March 31 until October 30.
• Taiwan — T aiwan does not use Daylight Saving Time.
• Turkey — From the last weekend of March until the last weekend of October.
• United Kingdom — From the last weekend of March until the last weekend of October.
• United States of America — From the first Sunday in April at 02:00 to the last Sunday in October at 02:00.
Page 21

Allied Telesis AT-8000S Switch
Web Browser Interface User’s Guide
Setting the System Clock
The System Time Page contains fields for defining system time parameters for both the local hardware clock and
the external SNTP clock. If the system time is kept using an external SNTP clock, and the external SNTP clock
fails, the system time reverts to the local hardware clock. Daylight Savings Time can be enabled on the device.
To configure the system clock time:
1. Click System > System Time. The System Time Page opens:
Figure 10: System Time Page
The Clock Source and System Time sections of the System Time Page contains the following fields:
• Clock Source — The source used to set the system clock. The possible field values are:
– Use Local Settings — Indicates that the clock is set locally.
– Use SNTP Server — Indicates that the system time is set via an SNTP server.
• System Time — Sets the local clock time. The field format is HH:MM:SS. For example: 21:15:03.
• System Date — Sets the system date. The field format is Day/Month/Year. For example: 04/May/50 (May 4,
2050).
• Time Zone Offset — The difference between Greenwich Mean Time (GMT) and local time. For example, the
Time Zone Offset for Paris is GMT +1, while the Time Zone Offset for New York is GMT –5.
To set the system clock:
2. Select the system time mode.
3. Define the System Date, System Time and Time Zone Offset fields.
4. Click Apply in each section. The local system clock settings are saved, and the device is updated.
5. Click Save Config on the menu to save the changes permanently.
Page 22

Configuring System Time
Configuring SNTP
Configuring SNTP
The device supports the Simple Network Time Protocol (SNTP). SNTP assures acc urate network device clock
time synchronization up to the millisecond. Time synchronization is performed by a network SNTP server. The
device operates only as an SNTP client, and cannot provide time services to other systems. The device can poll
the following server types for the server time:
• Unicast
• Anycast
• Broadcast
Time sources are established by stratums. Stratums define the accuracy of the reference clock. The higher the
stratum (where zero is the highest), the more accurate the clock. The device receives time from stratum 1 and
above. The following is an example of stratums:
Stratum 0 — A real time clock (such as a GPS system) is used as the time source.
Stratum 1 — A server that is directly linked to a Stratum 0 time source is used. Stratum 1 time servers provide
primary network time standards.
Stratum 2 — The time source is distanced from the Stratum 1 server over a network path. For example, a Stratum
2 server receives the time over a network link, via NTP, from a Stratum 1 server.
Polling for Unicast Time Information
Polling for Unicast information is used for polling a server for which the IP address is known. T1 - T4 are used to
determine the server time. This is the preferred method for synchronizing device time.
Polling for Anycast Time Information
Polling for Anycast information is used when the SNTP server IP address is unknown. The first Anycast server to
return a response is used to set the time value. Time levels T3 and T4 are used to determine the server time.
Using Anycast time information for synchronizing device time is preferred to using Broadcast time information.
Broadcast Time Information
Broadcast information is used when the server IP address is unknown. When a broadcast message is sent from
an SNTP server, the SNTP client listens for the response. The SNTP client neither sends time information
requests nor receives responses from the Broadcast server.
Message Digest 5 (MD5) Authentication safeguards device synchronization paths to SNTP servers. MD5 is an
algorithm that produces a 128-bit hash. MD5 is a variation of MD4, and increases MD4 security. MD5 verifies the
integrity of the communication, authenticates the origin of the communication.
To define SNTP global parameters:
1. Click System > System Time. The System Time Page opens.
The SNTP Settings section of the System Time Page contains the following fields:
• Status — Indicates if SNTP is enabled on the device. The possible field values are:
– Disabled — Indicates that SNTP is disabled.
– Enabled — Indicates that SNTP is enabled.
• Server IP Address — Displays a user-defined SNTP server IP address.
• Poll Interval — Defines the interval (in seconds) at which the SNTP server is polled for Unicast information.
The Poll Interval default is 1024 seconds.
2. Select the SNTP Status.
Page 23

Allied Telesis AT-8000S Switch
Web Browser Interface User’s Guide
3. Define the Server IP Address and the Poll Interval fields.
4. Click Apply. The SNTP global settings are defined, and the device is updated.
5. Click Save Config on the menu to save the changes permanently.
Configuring Daylight Saving Time
To configure DST:
1. Click System > System Time. The System Time Page opens:
The Additional Time Parameters section of the System Time Page contains the following fields:
• Daylight Saving — Enables automatic Daylight Saving Time (DST) on the device based on the device’s
location. There are two types of daylight settings, either by a specific date in a particular year or a recurring
setting irrespective of the year. For a specific setting in a particular year complete the Daylight Savings area,
and for a recurring setting, complete the Recurring area. The possible field values are:
– USA — The device devices to DST at 2:00 a.m. on the first Sunday of April, and reverts to standard time
at 2:00 a.m. on the last Sunday of October.
– European — The device devices to DST at 1:00 am on the last Sunday in March and reverts to standard
time at 1:00 am on the last Sunday in October. The European option applies to EU members, and other
European countries using the EU standard.
– Custom — The DST definitions are user-defined based on the device locality. If Custom is selected, the
From and To fields must be defined.
• Time Set Offset — Used for non-USA and European countries to set the amount of time for DST
(in minutes). The default time is 60 minutes. The range is 1-1440 minutes.
• From — Indicates the time that DST begins in countries other than the USA and Europe, in the format Day/
Month/Year in one field and HH:MM in another. For example, if DST begins on October 25, 2007 at 5:00 am,
the two fields should be set to 25/Oct./07 and 05:00. The possible field values are:
– Date — The date on which DST begins. The possible field range is 1-31.
– Month — The month of the year in which DST begins. The possible field range is Jan.-Dec.
– Year — The year in which the configured DST begins.
– Time — The time at which DST begins. The field format is HH:MM. For example: 05:30.
• To — Indicates the time that DST ends in countries other than the USA and Europe, in the format Day/Month/
Year in one field and HH:MM in another. For example, if DST ends on March 23, 2008 at midnight, the two
fields should be 23/Mar/08 and 00:00. The possible field values are:
– Date — The date on which DST ends. The possible field range is 1-31.
– Month — The month of the year in which DST ends. The possible field range is Jan-Dec.
– Year— The year in which the configured DST ends.
– Time — The time at which DST starts. The field format is HH:MM. For example: 05:30.
• Recurring — Enables user-defined DST for countries in which DST is constant from year to year, other than
the USA and Europe.
• From — The time that DST begins each year. In the example, DST begins locally every first Sunday in April
at midnight. The possible field values are:
– Day — The day of the week from which DST begins every year. The possible field range is Sunday-
Saturday.
– Week — The week within the month from which DST begins every year. The possible field range is 1-5.
– Month — The month of the year in which DST begins every year. The possible field range is Jan.-Dec.
Page 24

Configuring System Time
Configuring Daylight Saving Time
– Time — The time at which DST begins every year. The field format is Hour:Minute. For example: 02:10.
• To — The time that DST ends each year. In the example, DST ends locally every first Sunday in October at
midnight. The possible field values are:
– Day — The day of the week at which DST ends every year. The possible field range is Sunday-Saturday.
– Week — The week within the month at which DST ends every year. The possible field range is 1-5.
– Month — The month of the year in which DST ends every year. The possible field range is Jan.-Dec.
– Time — The time at which DST ends every year. The field format is HH:MM. For example: 05:30.
2. To configure the device to automatically switch to DST, select Daylight Savings and select either USA,
European, or Other. If you select Other, you must define it s From and To fields. To configure DST parameters
that will recur every year, select Recurring and define its From and To fields.
3. Click Apply. The DST settings are saved, and the device is updated.
4. Click Save Config on the menu to save the changes permanently.
Page 25

Allied Telesis AT-8000S Switch
Web Browser Interface User’s Guide
Section 4. Configuring Device Security
This section describes setting security parameters for ports, device management methods, users, and servers.
This section contains the following topics:
• Configuring Management Security
• Configuring Network Security
Page 26

Configuring Device Security
Configuring Management Security
Configuring Management Security
This section provides information for configuring device management security: device authentication methods,
users and passwords.
This section includes the following topics:
• Defining Access Profiles
• Defining Profile Rules
• Defining Authentication Profiles
• Mapping Authentication Profiles
• Configuring Server Based Authentication
• Configuring TACACS+
• Configuring RADIUS
• Configuring Local Users
Page 27
Allied Telesis AT-8000S Switch
Web Browser Interface User’s Guide
Defining Access Profiles
Access profiles are profiles and rules for accessing the device. Access to management functions can be limited to
user groups. User groups are defined for interfaces according to IP addresses or IP subnets. Access profiles
contain management methods for accessing and managing the device. The device ma nagement methods
include:
• All
• Telnet
• Secure Telnet (SSH)
• HTTP
Management access to different management methods may differ between user groups. For example, User
Group 1 can access the device module only via an HTTPS session, while User Group 2 can access the device
module via both HTTPS and Telnet sessions. The Access Profile Page contains the currently configured access
profiles and their activity status.
Assigning an access profile to an interface denies access via other interfaces. If an access profile is assigned to
any interface, the device can be accessed by all interfaces.
To define access profiles:
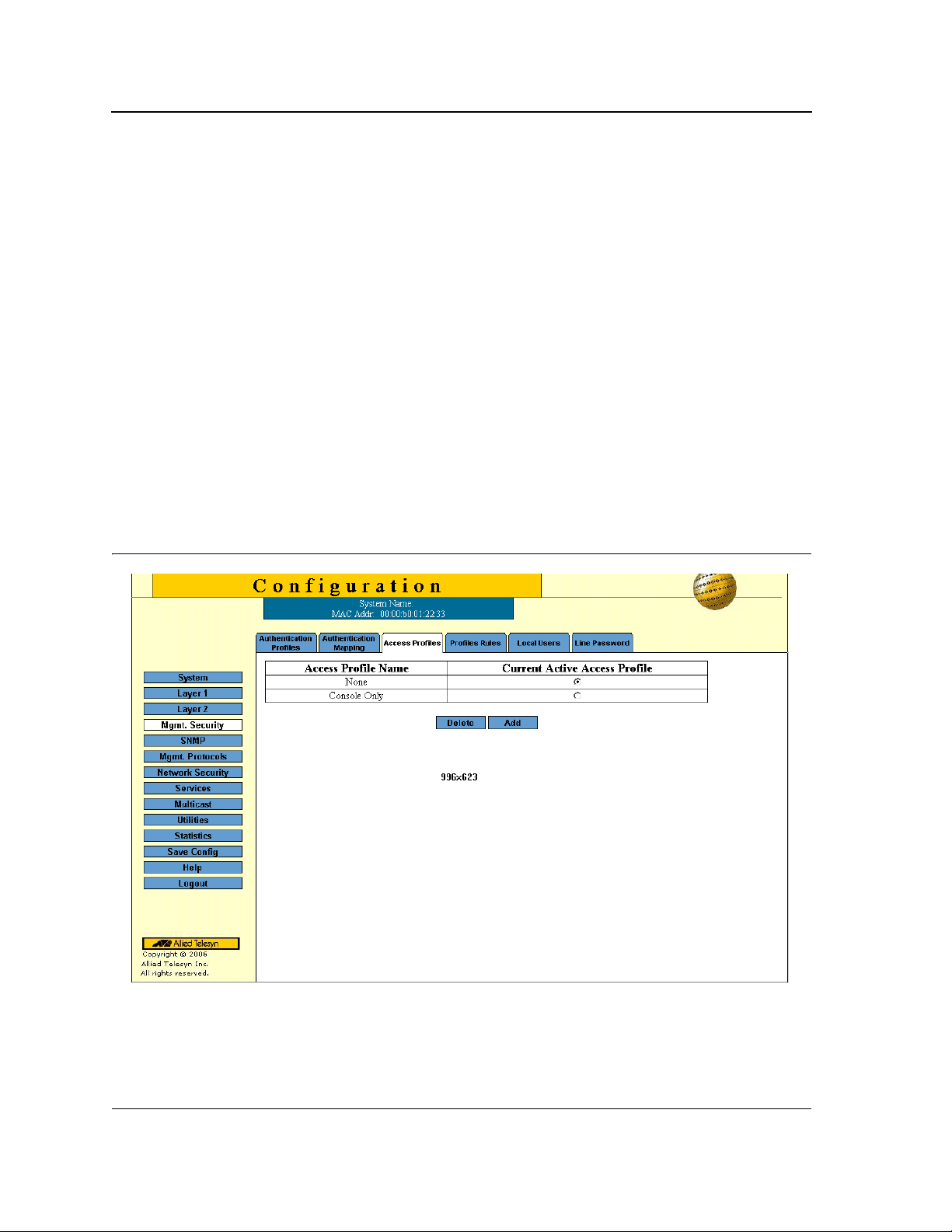
1. Click Mgmt. Security > Access Profile. The Access Profile Page opens:
Figure 11: Access Profile Page
The Access Profile Page contains a table listing the currently defined profiles and their active status:
• Access Profile Name — The name of the profile. The access profile name can contain up to 32 characters.
• Current Active Access Profile — Indicates if the profile is currently active . The possible field values are:
Page 28

Configuring Device Security
Configuring Management Security
– Checked — The access profile is currently active. Access Profiles cannot be deleted when acti ve.
– Unchecked — Disables the active access profile.
2. Click Add. The Add Access Profile Page opens:
Figure 12: Add Access Profile Page
The Add Access Profile Page contains the following fields:
• Access Profile Name — Defines the name of a new access profile.
• Rule Priority — Defines the rule priority. When the packet is matched to a rule, user groups are either
granted permission or denied device management access. The rule number is essential to matching packets
to rules, as packets are matched on a first-fit basis. The rule priorities are assigned in the Profile Rules Page.
• Management Method — Defines the management method for which the rule is defined. Users with this
access profile can access the device using the management method selected. The possible field values are:
– All — Assigns all management methods to the rule.
– Telnet — Assigns Te lnet access to the rule. If selected, users accessing the device using Telnet meeting
access profile criteria are permitted or denied access to the device.
– Secure Telnet (SSH) — Assigns SSH access to the rule. If selected, users accessing the device using
Telnet meeting access profile criteria are permitted or denied access to the device.
– HTTP — Assigns HTTP access to the rule. If selected, users accessing the device using HTTP meeting
access profile criteria are permitted or denied access to the device.
– Secure HTTP (HTTPS) — Assigns HTTPS access to the rule. If selected, users accessing the device
using HTTPS meeting access profile criteria are permitted or denied access to the device.
– SNMP — Assigns SNMP access to the rule. If selected, users accessing the device using SNMP
meeting access profile criteria are permitted or denied access to the device.
• Interface — Defines the interface on which the access profile is defined. The possible field values are:
– Port — Specifies the port on which the access profile is defined.
– LAG — Specifies the LAG on which the access profile is defined.
– VLAN — Specifies the VLAN on which the access profile is defined.
• Source IP Address — Defines the interface source IP address to which the access profile applies.
The Source IP Address field is valid for a subnetwork.
Page 29

Allied Telesis AT-8000S Switch
Web Browser Interface User’s Guide
– Network Mask — Defines the network mask of the source IP address.
– Prefix Length — Defines the number of bits that comprise the source IP address prefix, or the network
mask of the source IP address.
• Action — Defines the action attached to the access rule. The possible field values are:
– Permit — Permits access to the device.
– Deny — Denies access to the device. This is the default.
3. Define the fields.
4. Click Apply. The access profile is saved and the device is updated.
5. Click Save Config on the menu to save the changes permanently.
Page 30

Configuring Device Security
Configuring Management Security
Defining Profile Rules
Access profiles can contain up to 128 rules that determine which users can manage the device module, and by
which methods. Users can also be blocked from accessing the device. Rules are composed of filters including:
• Rule Priority
• Interface
• Management Method
• IP Address
• Prefix Length
• Forwarding Action
To define profile rules:
1. Click Mgmt. Security > Profile Rules: The Profile Rules Page opens:
Figure 13: Profile Rules Page
•
Access Profile Name — Displays the access profile to which the rule is attached.
• Priority — Defines the rule priority. When the packet is matched to a rule, user groups are either granted
permission or denied device management access. The rule number is essential to matching packets to rules,
as packets are matched on a first-fit basis.
• Interface — Indicates the interface type to which the rule applies. The possible field val ues are:
– Port — Attaches the rule to the selected port.
– LAG — Attaches the rule to the selected LAG.
– VLAN — Attaches the rule to the selected VLAN.
Page 31

Allied Telesis AT-8000S Switch
Web Browser Interface User’s Guide
• Management Method — Defines the management method for which the rule is defined. Users with this
access profile can access the device using the management method selected. The possible field values are:
– All — Assigns all management methods to the rule.
– Telnet — Assigns Te lnet access to the rule. If selected, users accessing the device using Telnet meeting
access profile criteria are permitted or denied access to the device.
– Secure Telnet (SSH) — Assigns SSH access to the rule. If selected, users accessing the device using
Telnet meeting access profile criteria are permitted or denied access to the device.
– HTTP — Assigns HTTP access to the rule. If selected, users accessing the device using HTTP meeting
access profile criteria are permitted or denied access to the device.
– Secure HTTP (HTTPS) — Assigns HTTPS access to the rule. If selected, users accessing the device
using HTTPS meeting access profile criteria are permitted or denied access to the device.
– SNMP — Assigns SNMP access to the rule. If selected, users accessing the device using SNMP
meeting access profile criteria are permitted or denied access to the device.
• Source IP Address — Defines the interface source IP address to which the rule applies.
• Prefix Length — Defines the number of bits that com prise the source IP address prefix, or the network mask
of the source IP address.
• Action — Defines the action attached to the rule. The possible field values are:
– Permit — Permits access to the device.
– Deny — Denies access to the device. This is the default.
2. Click Add. The Add Profile Rule Page opens:
Figure 14: Add Profile Rule Page
3. Define the fields.
4. Click Apply. The profile rule is added to the access profile, and the device is updated.
5. Click Save Config on the menu to save the changes permanently.
Page 32

To modify an access rule:
1. Click Mgmt. Security > Profile Rule: The Profile Rules Page opens.
2. Click Modify. The Profiles Rules Configuration Page opens:
Figure 15: Profiles Rules Configuration Page
Configuring Device Security
Configuring Management Security
3. Define the fields.
4. Click Apply. The profile rule is saved, and the device is updated.
Page 33
Allied Telesis AT-8000S Switch
Web Browser Interface User’s Guide
Defining Authentication Profiles
Authentication profiles allow network administrators to assign authentication methods for user authentication.
User authentication can be performed either locally or on an external server. User authentication occurs in the
order the methods are selected. If the first authentication method is not available, the next selected method is
used. For example, if the selected authentication methods are RADIUS and Local, and the RADIUS server is not
available, then the user is authenticated locally.
To define Authentication profiles:
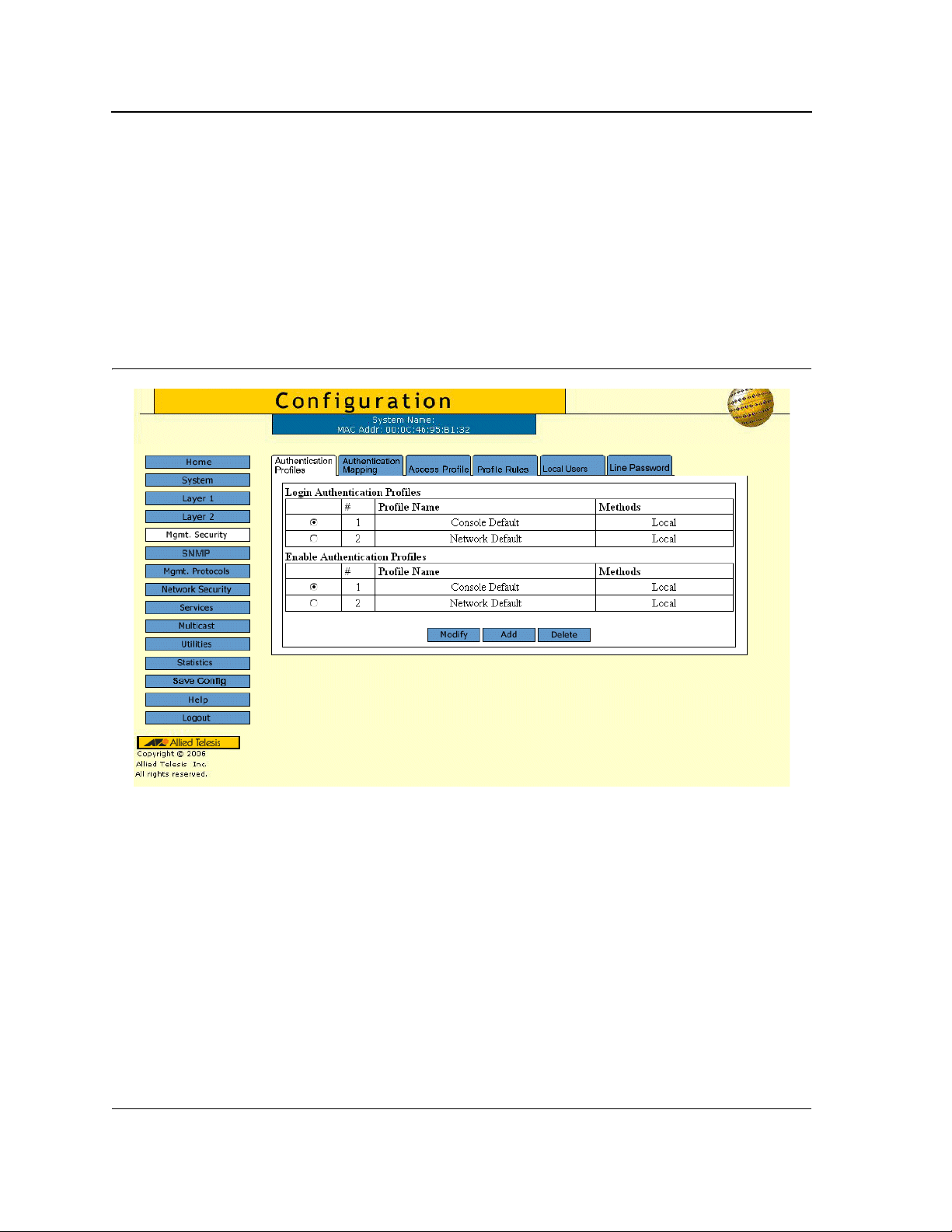
1. Click Mgmt. Security > Authentication Profiles. The Authentication Profiles Page opens:
Figure 16: Authentication Profiles Page
The Authentication Profiles Page contains two tables which display the currently defined profiles:
• Login Authentication Profiles — Provides the method by which system users logon to the device.
• Enable Authentication Profiles — Provides user authentication levels for users accessing the device.
Each table contains the following fields:
• Profile Name — Contains a list of user-defined authentication profile lists to which user-defined
authentication profiles are added. The default configuration displays as: Console Default, and Network
Default.
• Methods — Indicates the authentication method for the selected authentication profile. The possible
authentication methods are:
– None — Assigns no authentication method to the authentication profile.
– Line — Indicates that authentication uses a line p a ssw ord .
– Enable — Indicates that authentication uses an Enable password.
Page 34

Configuring Device Security
Configuring Management Security
– Local — Authenticates the user at the device level. The device checks the user name and password for
authentication.
– RADIUS — Authenticates the user at the RADIUS server. For more information, see Defining RADIUS
Server Settings.
– TACACS+ — Authenticates the user at the TACACS+ server. For more information, see Defining
T ACACS+ Host Settings.
– Local, RADIUS — Indicates that authentication first occurs locally. If authentication cannot be verified
locally, the RADIUS server authenticates the management method. If the RADIUS server cannot
authenticate the management method, the session is blocked.
– RADIUS, Local — Indicates that authentication first occurs at the RADIUS server. If authentication
cannot be verified at the RADIUS server, the session is authenticated locally. If the session cannot be
authenticated locally, the session is blocked.
– Local, RADIUS, None — Indicates that authentication first occurs locally. If authentication cannot be
verified locally, the RADIUS server authenticates the management method. If the RADIUS server cannot
authenticate the management method, the session is permitted.
– RADIUS, Local, None — Indicates that Authentication first occurs at the RADIUS server. If authentication
cannot be verified at the RADIUS server, the session is authenticated locally. If the session cannot be
authenticated locally, the session is permitted.
– Local, TACACS+ — Indicates that Authentication first occurs locally. If authentication cannot be verified
locally, the TACACS+ server authenticates the management method. If the TACACS+ server cannot
authenticate the management method, the session is blocked.
– TACACS+, Local — Indicates that authentication first occurs at the TACACS+ server. If authentication
cannot be verified at the TACACS+ server, the session is authenticated locally. If the sessi on cannot be
authenticated locally, the session is blocked.
– Local, TACACS+, None — Indicates that authentication first occurs locally. If authentication cannot be
verified locally, the TACACS+ server authenticates the management method. If the TACACS+ server
cannot authenticate the management method, the session is permitted.
– TACACS+, Local, None — Indicates that authentication first occurs at the TACACS+ server. If
authentication cannot be verified at the TACACS+ server, the session is authenticated locally. If the
session cannot be authenticated locally, the session is permitted.
2. Click Add. The Add Authentication Profile Page opens:
Page 35

Allied Telesis AT-8000S Switch
Web Browser Interface User’s Guide
Figure 17: Add Authentication Profile Page
3. Select the type of function to configure for the profile: Method or Login.
4. Enter the Profile Name.
5. Using the arrows, move the method(s) from the Optional Method list to the Selected Method list.
6. Click Apply. The authentication profile is defined . The profile is added to the profiles table and the device is
updated.
To modify the authentication profile settings:
1. Click Mgmt. Security > Authentication Profiles. The Authentication Profiles Page opens.
2. Click Modify. The Authentication Profile Configuration Page opens:
Figure 18: Authentication Profile Configuration Page
3. Select the Profile Name from the list.
4. Using the arrows, move the method(s) from the Optional Method list to the Selected Method list.
5. Click Apply. The profile settings are saved and the device is updated.
Page 36

Configuring Device Security
Configuring Management Security
Mapping Authentication Profiles
After authentication profiles are defined, they can be applied to management access methods. For example,
console users can be authenticated by Authentication Profile List 1, while Telnet users are authenticated by
Authentication Profile List 2. Authentication methods are selected using arrows. The order in which the methods
are selected is the order by which the authentication methods are used.
To map authentication methods:
1. Click Mgmt. Security > Authentication Mapping. The Authentication Mapping Page opens:
Figure 19: Authentication Mapping Page
The Authentication Mapping Page comprises three sections:
• Authentication Login and Enable
• Secure HTTP
• HTTP
The Authentication Mapping Page contains the following fields:
• Console — Indicates that authentication profiles are used to authenticate console users.
• Telnet — Indicates that authentication profiles are used to authenticate Telnet users.
• Secure Telnet (SSH) — Indicates that authentication profiles are used to authenticate Secure Shell (SSH)
users. SSH provides clients secure and encrypted remote connections to a device.
• Secure HTTP — Indicates that authentication methods are used for secure HTTP access. The possible
methods are:
– Local — Authentication occurs locally.
– RADIUS — Authenticates the user at the RADIUS server.
– TACACS+ — Authenticates the user at the TACACS+ server.
Page 37

Allied Telesis AT-8000S Switch
Web Browser Interface User’s Guide
– None — Indicates that no authentication method is used for access.
• HTTP — Indicates that authentication methods are used for HTTP access. Possible methods are:
– Local — Authentication occurs locally.
– RADIUS — Authenticates the user at the RADIUS server.
– TACACS+ — Authenticates the user at the TACACS+ server.
– None — Indicates that no authentication method is used for access.
2. Define the Console, Telnet, and Secure Telnet (SSH) fields.
3. Map the authentication method(s) in the Secure HTTP selection box using the arrow.
4. Map the authentication method(s) in the HTTP selection box.
5. Click Save Config on the menu to save the changes permanently.
Configuring Server Based Authentication
Network administrators assign authentication methods for user authentication. User authentication can be
performed locally, or on an external server . User authentication occurs in the order the methods are selected.
If the first authentication method is not available, the next selected method is used.
Configuring TACACS+
Terminal Access Controller Access Control System (T ACACS+) provides centralized security user access
validation. The system supports up-to 4 TACACS+ servers. TACACS+ provides a centralized user management
system, while still retaining consistency with RADIUS and other authentication processes. TACACS+ provides the
following services:
• Authentication — Performed at login and via user names and user-defined passwords.
• Authorization — Performed at login. Once the authentication session is completed, an authorization session
starts using the authenticated user name.
The TACACS+ protocol ensures network integrity through encrypted protocol exchanges between the client and
T ACACS+ server.
To define TACACS+ security settings:
1. Click Mgmt. Protocols > TACACS+. The TACACS+ Configuration Page opens.
Page 38

Figure 20: TACACS+ Configuration Page
Configuring Device Security
Configuring Management Security
The TACACS+ Configuration Page contains the following fields:
• Timeout for Reply — Defines the time interval in seconds that passes before the connection between the
device and the TACACS+ server times out. The field range is 1-60 seconds and the default is 10 seconds.
• Key String — Defines the default key string.
• Server # — Displays the server number.
• Host IP Address — Displays the TACACS+ server IP address.
• Priority — Defines the order in which the TACACS+ servers are used. The field range is 0-65535. The
default is 0.
• Authorization Port — Identifies the authentication port. The authentication port is used to verify the
T ACACS+ server authentication.
• Timeout for Reply — Defines the time interval in seconds that passes before the connection between the
device and the TACACS+ server times out. The field range is 1-60 seconds and the default is 10 seconds.
• Single Connection — Maintains a single open connection between the device and the TACACS+ server.
The possible field values are:
– Checked — Enables a single connection.
– Unchecked — Disables a single connection.
• Status — Indicates the connection status between the device and the TACACS+ server. The possible field
values are:
– Connected — Indicates there is currently a connection between the device and the T AC A C S+ serve r.
– Not Connected — Indicates there is not currently a connection between the device and the TACACS+
server.
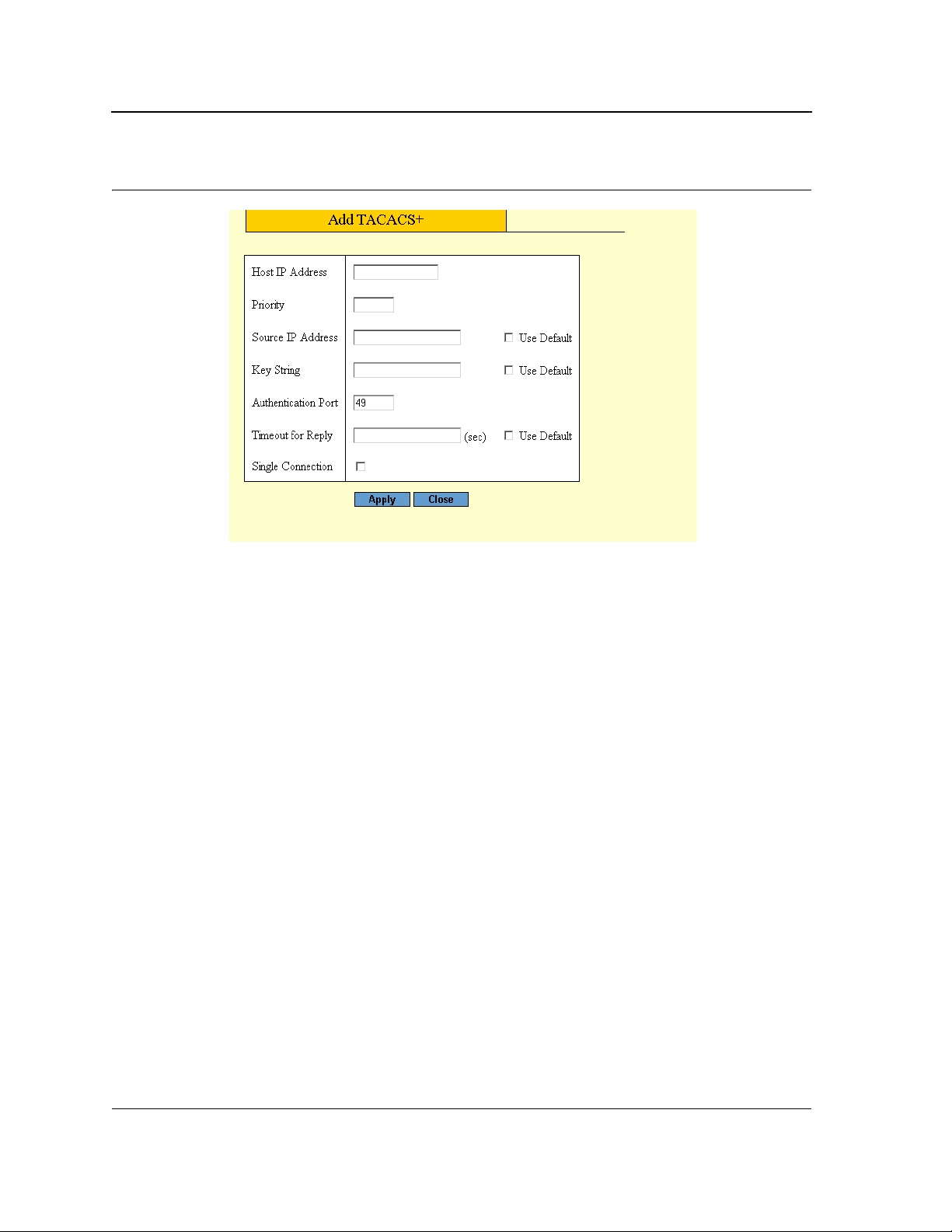
2. Click Create. The Add TACACS+ Page opens.
Page 39
Allied Telesis AT-8000S Switch
Web Browser Interface User’s Guide
Figure 21: Add TACACS+ Page
3. Define the fields.
4. Click Apply. The TACACS+ profile is saved, and the device is updated.
Page 40

Configuring Device Security
Configuring Management Security
Configuring RADIUS
Remote Authorization Dial-In User Service (RADIUS) servers provide additional security for networks. RADIUS
servers provide a centralized authentication method for web access. To configure RADIUS security settings:
1. Click Mgmt. Protocols > RADIUS. The RADIUS Configuration Page opens:
Figure 22: RADIUS Configuration Page
The RADIUS Configuration Page contains the following fields:
• Default Retries — Defines the default number of transmitted requests sent to the RADIUS server before a
failure occurs. Possible field values are 1-10.
• Default Timeout for Reply — Defines the default time interval in seconds that passes before the connection
between the device and the TACACS+ server times out. The field range is 1-60 seconds and the default is 10
seconds.
• Default Dead Time — Defines the default amount of time (in minutes) that a RADIUS server is bypassed for
service requests. The range is 0-2000.
• Server # — Displays the RADIUS server number.
• IP Address — Displays the RADIUS server IP address.
• Priority — Displays the RADIUS server priority. The possible values are 1-65535, where 1 is the highest
value. The RADIUS server priority is used to configure the server query order.
• Authorization Port — Identifies the authentication port. The authentication port is used to verify the RADIUS
server authentication. The authenticated port default is 1812.
• Number of Retries — Defines the number of transmitted requests sent to the RADIUS server before a failure
occurs. Possible field values are 1-10.
Page 41
Allied Telesis AT-8000S Switch
Web Browser Interface User’s Guide
• Timeout for Reply — Defines the time interval in seconds that passes before the connection between the
device and the RADUIUS server times out. The field range is 1-60 seconds and the default is 10 seconds.
• Dead Time — Defines the amount of time (in minutes) that a RADIUS server is bypassed for service
requests. The range is 0-2000. The default is 0 minutes.
• Key String — Defines the default key string used for authenticating and encrypting all RADIUS-
communications between the device and the RADIUS server. This key must match the RADIUS encryption.
• Usage Type— Specifies the RADIUS server authentication type. The default value is All. The possible field
values are:
– Log in — Indicates the RADIUS server is used for authenticating user name and passwords.
– 802.1X — Indicates the RADIUS server is used for 802.1X authentication.
– All — Indicates the RADIUS server is used for authenticating user names and passwords, and 802.1X
port authentication.
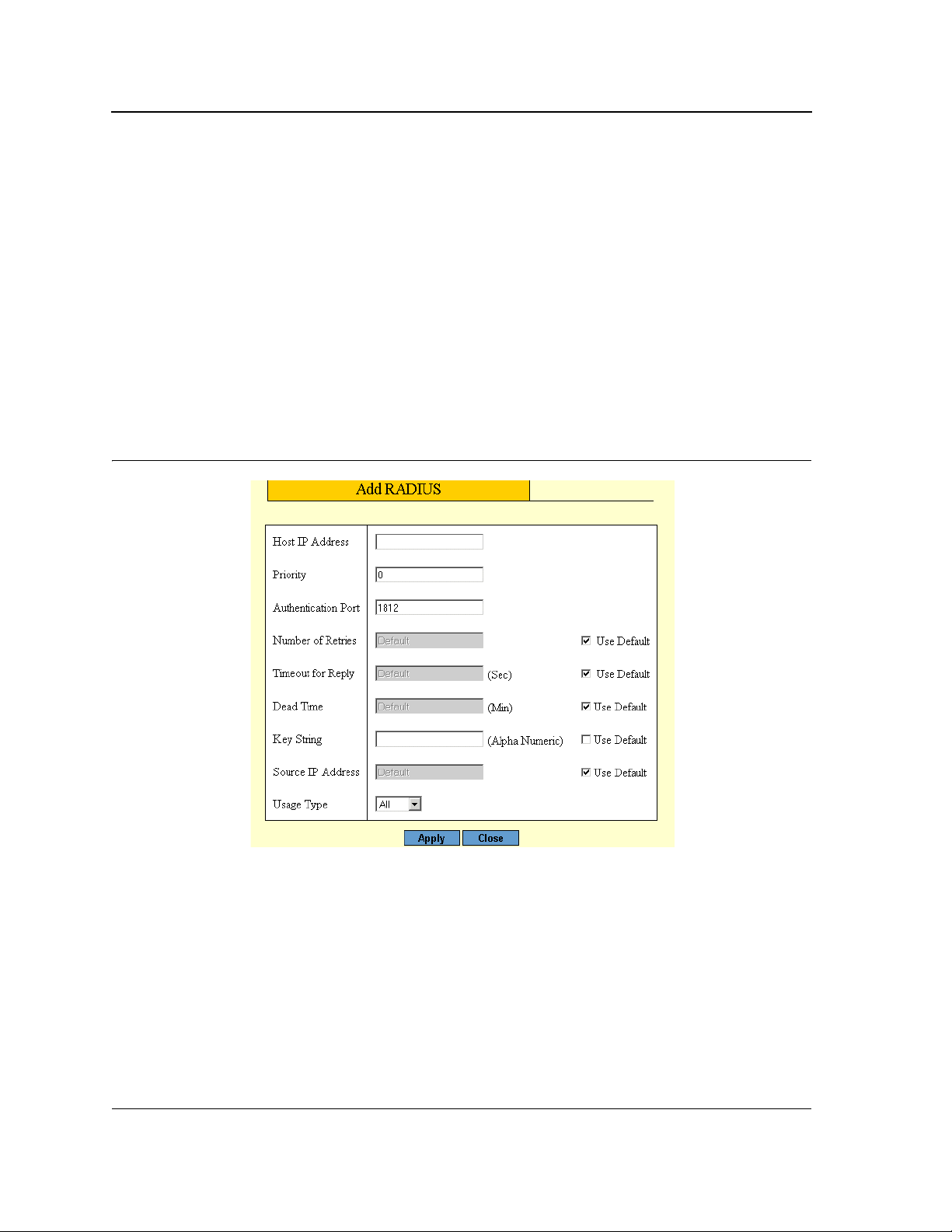
2. Click Create. The Add RADIUS Page opens.
Figure 23: Add RADIUS Page
3. Define the fields.
4. Click Apply. The RADIUS profile is saved, and the device is updated.
Page 42

Configuring Device Security
Configuring Management Security
Configuring Local Users
Network administrators can define users, passwords, and access levels for users using the Local Users Page.
To configure local users and passwords:
1. Click Mgmt. Security > Local Users. The Local Users Page opens:
Figure 24: Local Users Page
The Local Users Page displays the list of currently defined local users and contains the following fields:
• User Name — Displays the user’s name.
• Access Level — Displays the user access level. The lowest user access level is 1 and the highest is 15.
Users assigned access level 1 have read/write access to the device. User assigned a access level of 15 have
read-only access. The possible field values are:
– Configuration — Provides configuration device privileges.
– Monitoring — Provides device Read and Read/Write privileges.
Page 43

Allied Telesis AT-8000S Switch
Web Browser Interface User’s Guide
2. Click Create. The Add Local User Page opens:
Figure 25: Add Local User Page
In addition to the fields in the Local Users Page, the Add Local User Page contains the following fields:
• Password — Defines the local user password. Local user passwords can contain up to 159 characters.
• Confirm Password — Verifies the password.
3. Define the fields.
4. Click Apply. The user is added to the Local Users table and the device is updated.
To modify local users:
1. Click Mgmt. Security > Local Users. The Local Users Page opens.
2. Click Modify. The Local User Configuration Page opens:
Figure 26: Local User Configuration Page
3. Define the User Name, Access Level, Password, and Confirm Password fields.
4. Click Apply. The local user settings are defined, and the device is updated.
Page 44

Configuring Device Security
Configuring Network Security
Network security manages locked ports. This section contains the following topics:
• Network Security Overview
• Managing Port Security
• Defining 802.1x Port Access
• Enabling Storm Control
Configuring Network Security
Page 45

Allied Telesis AT-8000S Switch
Web Browser Interface User’s Guide
Network Security Overview
Port-based authentication provides traditional 802.1x support, as well as, Guest VLANs. Guest VLANs limited
network access to authorized ports. If a port is denied network access via port-based authorization, but the Guest
VLAN is enabled, the port receives limited network access. For example, a network administrator can use Guest
VLANs to deny network access via port-based authentication, but grant Internet access to unauthorized users.
Managing Port Security
Network security can be increased by limiting access on a specific port only to users with specific MAC addresses.
The MAC addresses can be dynamically learned or statically configured. Locked port security monitors both
received and learned packets that are received on specific ports. Access to the locked port is limited to users with
specific MAC addresses. These addresses are either manually defined on the port, or learned on that port up to
the point when it is locked. When a packet is received on a locked port, and the packet D-Link source MAC
address is not tied to that port (either it was learned on a different port, or it is unknown to the system), the
protection mechanism is invoked, and can provide various options. Unauthorized packets arriving at a locked port
are either:
• Forwarded
• Discarded with no trap
• Discarded with a trap
• Shuts down the port.
Locked port security also enables storing a list of MAC addresses in the configuration file. The MAC address list
can be restored after the device has been reset. Disabled ports are activated from the Port Security Page. To
define port security
The Port Security Page enhances network security by providing port locking management to network
administrators.
To configure secure ports:
1. Click Network Security > Port Security. The Port Security Page opens:
Page 46
Figure 27: Port Security Page
Configuring Device Security
Configuring Network Security
The Port Security Page displays the Zoom View of device ports. The possible port indicators are:
Port is not selected — Indicates that security is currently not enabled on the port.
Port is selected — Indicates that security is currently enabled on the port.
2. Select the ports to lock. The port indicator changes to selected.
3. Click Modify. The Port Security Configuration Page opens:
Page 47

Allied Telesis AT-8000S Switch
Web Browser Interface User’s Guide
Figure 28: Port Security Configuration Page
The Port Security Configuration Page contains the following fields:
• Unit Number — Defines the unit number.
• Interface — Displays the port or LAG name.
• Learning Mode — Defines the locked port type. The Learning Mode field is enabled only if Locked is
selected in the Set Port field.The possible field values are:
– Classic Lock — Locks the port using the classic lock mechanism. The port is immediately locked,
regardless of the number of addresses that have already been learned.
– Limited Dynamic Lock — Locks the port by deleting the current dynamic MAC addresses associated with
the port. The port learns up to the maximum addresses allowed on the port. Both relearning and aging
MAC addresses are enabled.
• Enable Trap — Indicates if the SNMP trap generated if there is a violation. The possible values are:
– Yes — Trap is generated.
– No — No trap is generated.
• Trap Frequency — The time interval (in seconds) between traps. The possible field range is 1-1,000,000
seconds, and the default is 10 seconds.
• Action On Violation— Indicates the intruder action defined for the port. Indicates the action to be applied to
packets arriving on a locked port. The possible values are:
– Forward — Forwards packets from an unknown source without learning the MAC address.
– Discard — Discards packets from any unlearned source. This is the default value.
– Shutdown — Discards packets from any unlearned source and shuts down the port. The port remains
shut down until reactivated, or until the device is reset.
• Max Entries — Specifies the number of MAC addresses that can be learned on the port before the port is
locked. The field range is 1-128. The default is 1.
• Lock Interface —Locks the interface.
4. Select the security mode for the selected port(s).
5. Click Apply. The port security settings are saved and the device is updated.
Page 48

Configuring Device Security
Configuring Network Security
6. Click Save Config on the menu to save the changes permanently.
Defining 802.1x Port Access
The 802.1x Port Access Page allows enabling port access globally, defining the authentication method, and
configuration of port roles and settings.
To configure 802.1x port access parameters:
1. Click Network Security > 802.1x Port Access. The 802.1x Port Access Page opens:
Figure 29: 802.1x Port Access Page
The 802.1x Port Access Page contains the following fields:
• Enable Port Access — Enables the 802.1x port access globally. The possible values are:
– Checked — Enables the 802.1x port access on the device.
– Unchecked — Disables the 802.1x port access on the device. This is the default value.
• Authentication Method — Displays the method by which the last session was authenticated. The possible
field values are:
– None — Indicates that no authentication method is used to authenticate the port.
– RADIUS — Provides port authentication using the RADIUS server.
– RADIUS, None — Provides port authentication, first using the RADIUS server. If the port is not
authenticated, then no authentication method is used, and the session is permitted.
• Guest VLAN —Provides limited network access to authorized ports. If a port is denied network access via
port-based authorization, but the Guest VLAN field is enabled, the port receives limited network access.
Page 49

Allied Telesis AT-8000S Switch
Web Browser Interface User’s Guide
For example, a network administrator can use Guest VLANs to deny network access via port-based
authentication, but grant Internet access to unauthorized users. The possible field values are:
– Enable — Enables Guest VLANs.
– Disable — Disables Guest VLANs.
• Guest VLAN ID — Lists the currently defined VLANs.
2. Click Enable Port Access.
3. Select the Authentication Method.
4. Define the VLAN fields
5. Click Apply. The 802.1x access is configured globally and device information is updated.
To modify port based authentication settings:
1. Click Settings. The Port Authentication Settings Page opens:
Figure 30: Port Authentication Settings Page
The Port Authentication Settings Page contains the following port authentication parameters:
• Port — Displays a list of interfaces on which port-based authentication is enabled.
• User Name — Displays the supplicant user name.
• Current Port Control — Displays the current port authorization state. The possible field values are:
Page 50

Configuring Device Security
Configuring Network Security
– Auto — Enables port-based authentication on the device. The interface moves between an authorized or
unauthorized state based on the authentication exchange be tween the device and the client.
– Authorized — Indicates the interface is in an authorized state without being authenticated. The interface
re-sends and receives normal traffic without client port-based authentication.
– Unauthorized — Denies the selected interface system access by moving the interface into unauthorized
state. The device cannot provide authentication services to the client through the interface.
• Admin Port Control — Indicates the port state. The possible field values are:
– Auto —Enables port-based authentication on the device. The interface moves between an authorized or
unauthorized state based on the authentication exchange be tween the device and the client.
– ForceAuthorized — Indicates the interface is in an authorized state without being authenticated. The
interface re-sends and receives normal traffic without client port-based authentication.
– ForceUnauthorized — Denies the selected interface system access by moving the interface into
unauthorized state. The device cannot provide authentication services to the client through the interface.
• Enble Guest VLAN — Indicates if the Guest VLAN is enabled. The possible field values are:
– Checked — Enables the Guest VLAN.
– Unchecked — Disables the Guest VLAN. This is the default value.
• Enable Periodic Reauthentication — Permits immediate port reauthentication. The possible field
values are:
– Enable — Enables immediate port reauthentication. This is the default value.
– Disable — Disables port reauthentication.
• Reauthentication Period — Displays the time span (in seconds) in which the selected port is
reauthenticated. The field default is 3600 seconds.
• Reauthenticate Now — Reauthenticates the port immediately.
• Authenticator State — Displays the current authenticator state (as defined in Admin Port Control).
• Quiet Period — Displays the number of seconds that the device remains in the quiet state following a failed
authentication exchange. The possible field range is 0-65535. The field default is 60 seconds.
• Resending EAP — Defines the amount of time (in seconds) that lapses before EAP requests are resent.
The field default is 30 seconds.
• Max EAP Requests — Displays the total amount of EAP requests sent. If a response is not received after the
defined period, the authentication process is restarted. The field default is 2 retries.
• Supplicant Timeout — Displays the amount of time (in seconds) that lapses before EAP requests are resent
to the supplicant. The field default is 30 seconds.
• Server Timeout — Displays the amount of time (in seconds) that lapses before the device re-sends
a request to the authentication server. The field default is 30 seconds.
• Termination Cause — Indicates the reason for which the port authentication was terminated.
2. Click Apply. The port authentication configuration is saved and the device is updated.
3. Click Save Config on the menu to save the changes permanently.
Page 51

Allied Telesis AT-8000S Switch
Web Browser Interface User’s Guide
Enabling Storm Control
Storm control limits the amount of unknown Unicast, Multicast and Broadcast frames accepted and forwarded by
the device. When Layer 2 frames are forwarded, Broadcast, and Multicast frames are flooded to all ports on the
relevant VLAN. This occupies bandwidth, and loads all nodes on all ports.
A Broadcast Storm is a result of an excessive amount of broadcast messages simultaneously transmitted across a
network by a single port. Forwarded message responses are heaped onto the network, straining network
resources or causing the network to time out.
Storm control is enabled for all ports by defining the packet type and the rate the packets are transmitted. The
system measures the incoming Broadcast and Multicast frame rates separately on each port, and discards the
frames when the rate exceeds a user-defined rate. The Storm Control Page provides fields for configuring
broadcast storm control.
To enable storm control:
1. Click Network Security > Storm Control. The Storm Control Page opens:
Figure 31: Storm Control Page
The Storm Control Page displays the Zoom View of device ports.
2. Select a port to configure. The port indicator changes to Port is selected (white).
3. Click Modify. The Storm Control Configuration Page opens:
Page 52

Configuring Device Security
Configuring Network Security
Figure 32: Storm Control Configuration Page
The Storm Control Configuration Page contains the following fields:
• Port — Indicates the port from which storm control is enabled.
• Enable Broadcast Control — Indicates if forwarding Broadcast packet types is enabled on the port.
The field values are:
– Enabled — Enables storm control on the selected port.
– Disabled — Disables storm control on the selected port.
• Broadcast Mode — Specifies the Broadcast mode currently enabled on the device.The possible field
values are:
– Multicast & Broadcast — Counts both Broadcast and Multicast traffic together.
– Broadcast Only — Counts only the Broadcast traffic.
• Broadcast Rate Threshold — Indicates the maximum rate (kilobits per second) at which unknown packets
are forwarded. The range is 70-100,000. The default value is 2500. The range for Giga ports is 3500-100,000.
4. Select the Port Storm Control Settings.
5. Click Enable Broadcast Control, and define the Rate Threshold.
6. Click Apply. Storm control is enabled on the device for the selected port.
7. Click Save Config on the menu to save the changes permanently.
Page 53

Allied Telesis AT-8000S Switch
Web Browser Interface User’s Guide
Section 5. Configuring Ports
This section contains the procedures for configuring ports on the device.
This section contains the following topics:
• Defining Port Settings
• Configuring Port Mirroring
• Aggregating Ports
• Configuring LACP
Page 54

Defining Port Settings
The Port Settings Page contains fields for defining port parameters.
To define port general settings:
1. Click Layer 1 > Port Settings. The Port Settings Page opens:
Figure 33: Port Settings Page
Configuring Ports
Defining Port Settings
The Port Settings Page contains the Zoom View of the device ports. The possible port settings are:
Port is active — Indicates the port is linked.
Port is inactive — Indicates the port is not linked.
Port is disabled — Indicates that the port is disabled.
Port is selected — Indicates that the port is selected for modification.
2. Select the port(s). Clicking a port toggles it through the possible settings.
3. Click Modify. The Modify Port Settings Page opens:
Page 55

Allied Telesis AT-8000S Switch
Web Browser Interface User’s Guide
Figure 34: Modify Port Settings Page
The Modify Port Settings Page contains the following fields:
• Port— Lists the names of configured ports.
• Description — Provides a user-defined port description.
• Port Type — Indicates the type of port.
• Admin Status — Displays the link operational status. Changes to the port state are active only after the
device is reset. The possible field values are:
– Up — Indicates that the port is currently operating.
– Down — Indicates that the port is currently not operating.
• Current Port Status — Indicates whether the port is currently operational or non-operational. The possible
field values are:
– Up — Indicates the port is currently operating.
Page 56

Configuring Ports
Defining Port Settings
– Down — Indicates the port is currently not operating.
• Reactivate Suspended — Reactivates suspended ports. The possible field values are:
– Checked — Reactivates the selected suspended port.
– Unchecked — Maintains the port status. This is the default value.
• Operational Status — Indicates the port operational status. Possible field values are:
– Suspended — The port is currently active, and is not receiving or transmitting traffic.
– Active — Indicates the port is currently active and is receiving and transmitting traffic.
– Disable — Indicates the port is currently disabled, and is not receiving or transmitting traffic.
• Admin Speed — Indicates the configured rate for the port. The port type determines what speed setting
options are available. Admin speed can only be designated when the port is disabled.
• Current Port Speed — Displays the configured rate for the port. The port type determines the speed settings
available. Port speeds can only be configured when auto-negotiation is disabled. The possible field values
are:
– 10 — Indicates the port is currently operating at 10 Mbps.
– 100 — Indicates the port is currently operating at 100 Mbps.
– 1000 — Indicates the port is currently operating at 1000 Mbps.
• Duplex Mode — Displays the port duplex mode. This field is configurable only when auto negotiation is
disabled, and the port speed is set to 10M or 100M. This field cannot be configured on LAGs. The possible
field values are:
– Full — The interface supports transmission between the device and its link partner in both directions
– simultaneously.
– Half — The interface supports transmission between the device and the client in only one direction at a
time.
• Auto Negotiation — Displays the auto negotiation status on the port. Auto negotiation is a protocol between
two link partners that enables a port to advertise its transmission rate, duplex mode, and flow control abilities
to its partner.
• Current Auto Negotiation — Displays the current Auto Negotiation setting.
• Current Advertisement — Indicates the port advertises its speed to its neighbor port to start the negotiation
process. The possible field values are th ose specified in the Admin Advertisement field .
• Neighbor Advertisement — Indicates the neighboring port’s advertisement settings. The field values are
identical to the Admin Advertisement field values.
• Advertisement — Defines the auto negotiation setting the port advertises. The possible field values are:
– Max Capability — Indicates that all port speeds and duplex mode settings are accepted.
– 10 Half — Indicates that the port advertises for a 10 Mbps speed port and half duplex mode setting.
– 10 Full — Indicates that the port advertises for a 10 Mbps speed port and full duplex mode setting.
– 100 Half — Indicates that the port advertises for a 100 Mbps speed port and half duplex mode setting.
– 100 Full — Indicates that the port advertises for a 100 Mbps speed port and full duplex mode setting.
– 1000 Full — Indicates that the port advertises for a 1000 Mbps speed port and full duplex mode setting.
• Back Pressure — Displays the back pressure mode on the port. Back pressure mode is used with half
duplex mode to disable ports from receiving messages.
• Flow Control — Displays the flow control status on the port. Operates when the port is in full duplex mode.
– Enable — Indicates that flow control is currently enabled for the selected port. This is the default value.
Page 57

Allied Telesis AT-8000S Switch
Web Browser Interface User’s Guide
– Disable — Indicates that flow control is currently disabled for the selected port.
• MDI/MDIX — Displays the MDI/MDIX status on the port. Hubs and switches are deliberately wired opposite
the way end stations are wired, so that when a hub or switch is connected to an end station, a straight through
Ethernet cable can be used, and the pairs are matched up properly. When two hubs or switches are
connected to each other, or two end stations are connected to each other, a crossover cable is used to ensure
that the correct pairs are connected. The possible field values are:
– Auto — Use to automatically detect the cable type.
– MDI (Media Dependent Interface) — Use for end stations.
– MDIX (Media Dependent Interface with Crossover) — Use for hubs and switches.
4. Define the fields.
5. Click Apply. The port settings are saved and the device is updated. The Port Settings Page is displayed.
6. Click Save Config on the menu to permanently save the change.
Page 58

Configuring Ports
Configuring Port Mirroring
Configuring Port Mirroring
Port mirroring monitors and mirrors network traffic by forwarding copies of incoming and outgoing packets from
one port to a monitoring port. Port mirroring can be used as a diagnostic tool as well as a debugging feature. Port
mirroring also enables device performance monitoring.
Network administrators can configure port mirroring by selecting a specific port from which to copy all packets,
and other ports to which the packets copied. Any number of ports on the device can be mirrors, except the
destination port.
To define port mirroring:
1. Click Layer 1 > Port Mirroring. The Port Mirroring Page opens:
Figure 35: Port Mirroring Page
The Port Mirroring Page contains information about all port mirrors currently defined on the device. The following
information is displayed:
• Port Destination — Defines the port number to which port traffic is copied. Note that this port has to be
detached from its VLAN before mirroring is configured
indicates that port mirroring is not enabled.
. Only one destination port can be defined. A zero value
• Source Port — Indicates the port from which the packets are mirrored.
• Type — Indicates the port mode configuration for port mirroring. The possible field values are:
– RX — Defines the port mirroring on receiving ports.
– TX — Defines the port mirroring on transmitting ports.
– Both — Defines the port mirroring on both receiving and transmitting ports. This is the default value.
• Status — Indicates if the port is currently monitored. The possible field values are:
Page 59

Allied Telesis AT-8000S Switch
Web Browser Interface User’s Guide
– Active — Indicates the port is currently monitored.
– Ready — Indicates the port is not currently monitored.
2. Click Modify. The Modify Mirror Page opens:
Figure 36: Modify Mirror Page
The Modify Mirror Page contains the following fields:
• Unit Number— Displays the stacking member for which the port is defined.
• Zoom View - Port Mirror — Displays the status of mirror ports and enables port selection. The possible
values are:
Mirror to Port — Indicates the destination (mirror) port. There can be only one destination port.
Mirror Ingress Port — Indicates that the port is currently defined as
traffic is mirrored to the destination port.
Mirror Egress Port — Indicates that the port is currently defined as source port. The port’s egress traffic
is mirrored to the destination port.
Mirror Ingress/Egress Port — Indicates that the port is currently defined as sourc e po rt . The port’s
ingress and egress traffic is mirrored to the destination port.
3. Click the ports to mirror. Clicking a port toggles it through the possible settings.
4. Click Enable Mirror.
5. Click Apply. The port mirror status indicators are updated.
6. Click Refresh in the Port Mirroring Page. Port mirroring information is updated. The port mirror is now active
on the device. You can connect a data analyzer to the destination port to monitor the traffic on the source
ports.
7. Click Save Config on the menu to permanently save the change.
source port. The port’s ingress
Page 60

Configuring Ports
Configuring Port Mirroring
To modify or delete a port mirror:
1. Click Layer 1 > Port Mirroring. The Port Mirroring Page opens.
2. Click Modify. The Modify Mirror Page opens.
3. Click the checked Enable Mirror to disable the option.
4. Modify the mirror settings on the port(s) by toggling the port until the required mirror indicator is displayed. To
delete the port mirror, toggle a port to its original (black) state.
5. Click Enable Mirror to enable the mirror again.
6. Click Apply. The destination port is modified. If indicated as black, the port is deleted from port mirrors list
and is available for normal network operations.
7. Click Save Config on the menu to permanently save the change.
Page 61

Allied Telesis AT-8000S Switch
Web Browser Interface User’s Guide
Aggregating Ports
Link Aggregation optimizes port usage by linking a group of ports together to form a single LAG . Aggregating ports
multiplies the bandwidth between the devices, increases port flexibility, and provides link redundancy. The device
supports both static LAGs and Link Aggregation Control Protocol (LACP) LAGs. LACP LAGs negotiate
aggregating port links with other LACP ports located on a different device. If the other device ports are also LACP
ports, the devices establish a LAG between them.
Ensure the following:
• All ports within a LAG must be the same media type.
• A VLAN is not configured on the port.
• The port is not assigned to a different LAG.
• Auto-negotiation mode is not configured on the port.
• The port is in full-duplex mode.
• All ports in the LAG have the same ingress filtering and tagged modes.
• All ports in the LAG have the same back pressure and flow control modes.
• All ports in the LAG have the same priority.
• All ports in the LAG have the same transceiver type.
• The device supports up to eight LAGs, and eight ports in each LAG.
• Ports can be configured as LACP ports only if the ports are not part of a previously configured LAG.
• Ports added to a LAG lose their individual port configuration. When ports are removed from the LAG, the
original port configuration is applied to the ports.
This section contains the procedures for configuring static port trunks on the device.
• Defining Trunk Settings
• Defining Port Trunking
• Configuring LACP
Page 62

Defining Trunk Settings
The Trunk Settings Page contains parameters for defining Trunks. To define a port trunk:
1. Click Layer 1 > Port Trunking. The Trunk Settings Page opens:
Figure 37: Trunk Settings Page
Configuring Ports
Aggregating Ports
The Trunk Settings Page displays information about the currently defined trunks and contains the following fields:
• Trunk — Displays the trunk name.
• Description — Displays the user-defined trunk name and/or description.
• Type — Indicates the type of LAG defin ed by the first port assigned to the trunk. For example, 100-Copper,
or 100-Fiber.
• Status — Indicates if the LAG is currently linked. The possible field values are:
– Up — Indicates the LAG is currently linked, and is forwarding or receiving traffic.
– Down — Indicates the LAG is not currently linked, and is not forwarding or receiving traffic.
• Speed — Displays the configured aggregated rate for the trunk. The possible field values are:
– 10 — Indicates the port is currently operating at 10 Mbps.
– 100 — Indicates the port is currently operating at 100 Mbps.
– 1000 — Indicates the port is currently operating at 1000 Mbps.
• Auto Negotiation — Displays the auto negotiation status of the trunk. Auto negotiation is a protocol between
two link partners that enables a port to advertise its transmission rate, duplex mode, and flow control abilities
to its partner.
Page 63

Allied Telesis AT-8000S Switch
Web Browser Interface User’s Guide
• Flow Control — Displays the flow control status of the trunk.
• LACP — Indicates if LACP is enabled on the trunk. The possible values are:
– Enable — LACP is enabled on the trunk.
– Disable — LACP is disabled on the trunk.
2. Click Modify. The Trunk Settings Page opens:
Figure 38: Trunk Configuration Settings Page
The Trunk Settings Page contains the following fields:
• Trunk— Lists the names of configured trunks.
• Description — Provides a user-defined trunk description.
• Type — Indicates the type of trunk.
• Admin Status — Displays the link operational status. Changes to the trunk state are active only after the
device is reset. The possible field values are:
– Up — Indicates that the trunk is currently operating.
Page 64

Configuring Ports
Aggregating Ports
– Down — Indicates that the trunk is currently not operating.
• Current Trunk Status — Indicates whether the trunk is currently operational or non-operational. The
possible field values are:
– Up — Indicates the trunk is currently operating.
– Down — Indicates the trunk is currently not operating.
• Reactivate Suspended — Reactivates suspended trunks. The possible field values are:
– Checked — Reactivates the selected suspended trunk.
– Unchecked — Maintains the trunk status. This is the default value.
• Operational Status — Indicates the trunk operational status. Possible field values are:
– Suspended — The trunk is currently active, and is not receiving or transmitting traffic.
– Active — Indicates the trunk is currently active and is receiving and transmitting traffic.
– Disable — Indicates the trunk is currently disabled, and is not receiving or transmitting traffic.
• Admin Speed — Indicates the configured rate for the trunk. The trunk type determines what speed setting
options are available. Admin speed can only be designated when the trunk is disabled.
• Current Trunk Speed — Displays the configured rate for the trunk. The trunk type determines the speed
settings available. trunk speeds can only be configured when auto-negotiation is disabled. The possible field
values are:
– 10 — Indicates the trunk is currently operating at 10 Mbps.
– 100 — Indicates the trunk is currently operating at 100 Mbps.
– 1000 — Indicates the trunk is currently operating at 1000 Mbps.
• Duplex Mode — Displays the trunk duplex mode. This field is configurable only when auto negotiation is
disabled, and the trunk speed is set to 10M or 100M. This field cannot be configured on LAGs. The possible
field values are:
– Full — The interface supports transmission between the device and its link partner in both directions
– simultaneously.
– Half — The interface supports transmission between the device and the client in only one direction at a
time.
• Auto Negotiation — Displays the auto negotiation status on the trunk. Auto negotiation is a protocol
between two link partners that enables a trunk to advertise its transmission rate, duplex mode, and flow
control abilities to its partner.
• Current Auto Negotiation — Displays the current Auto Negotiation setting.
• Current Advertisement — Indicates the trunk advertises its speed to its neighbor trunk to start the
negotiation process. The possible field values are those specified in the Admin Advertisement field.
• Neighbor Advertisement — Indicates the neighboring trunk’s advertisement settings. The field values are
identical to the Admin Advertisement field values.
• Advertisement — Defines the auto negotiation setting the trunk advertises. The possible field values are:
– Max Capability — Indicates that all trunk speeds and duplex mode settings are accepted.
– 10 Half — Indicates that the trunk advertises for a 10 Mbps speed trunk and half duplex mode setting.
– 10 Full — Indicates that the trunk advertises for a 10 Mbps speed trunk and full duplex mode setting.
– 100 Half — Indicates that the trunk advertises for a 100 Mbps speed trunk and half duplex mode setting.
– 100 Full — Indicates that the trunk advertises for a 100 Mbps speed trunk and full duplex mode setting.
Page 65

Allied Telesis AT-8000S Switch
Web Browser Interface User’s Guide
– 1000 Full — Indicates that the trunk advertises for a 1000 Mbps speed trunk and full duplex mode
setting.
• Back Pressure — Displays the back pressure mode on the trunk. Back pressure mode is used with half
duplex mode to disable trunks from receiving messages.
• Flow Control — Displays the flow control status on the trunk. Operates when the trunk is in full duplex mode.
– Enable — Indicates that flow control is currently enabled for the selected trunk. This is the default value.
– Disable — Indicates that flow control is currently disabled for the selected trunk.
• MDI/MDIX — Displays the MDI/MDIX status on the trunk. Hubs and switches are deliberately wired opposite
the way end stations are wired, so that when a hub or switch is connected to an end station, a straight through
Ethernet cable can be used, and the pairs are matched up properly. When two hubs or switches are
connected to each other, or two end stations are connected to each other, a crossover cable is used to ensure
that the correct pairs are connected. The possible field values are:
– Auto — Use to automatically detect the cable type.
– MDI (Media Dependent Interface) — Use for end stations.
– MDIX (Media Dependent Interface with Crossover) — Use for hubs and switches.
3. Modify the fields.
4. Click Apply. The Trunk settings are saved and the device is updated.
Page 66

Defining Port Trunking
The Port Trunking Page displays information about the defined trunks.
To modify Port Trunking settings:
1. Click Layer 1 > Port Trunking. The Trunk Settings Page opens:
Figure 39: Port Trunking Page
Configuring Ports
Aggregating Ports
The Port Trunking Page contains information about all port trunks currently defined on the device. The following
information is displayed:
• Trunk — Displays the ID number of the trunk.
• Name — Displays the name of the trunk. The name can be up to sixteen alphanumeric characters. No
spaces or special characters, such as asterisks and exclamation points, are allowed. Each trunk must be
given a unique name.
• Link State —Indicates the current link status.
• Members — Indicates the ports which are defined for the trunk.
2. Select the trunk to modify.
3. Click Modify. The Modify Trunk Page opens:
Page 67

Allied Telesis AT-8000S Switch
Web Browser Interface User’s Guide
Figure 40: Modify Trunk Page
In addition to the fields in the The Port Trunking Page , the Modify Trunk Page contians the following additional
field:
• LACP — Indicates if LACP is enabled on the trunk. The possible field values are:
– Checked — Enables LACP on the trunk.
– Unchecked — Disables LACP on the trunk. This is the default value.
4. Modify the Trunk ID, LACP, Unit Number, and Trunk(LAG) Name fields.
5. Select the ports for the trunk from the Port List using the arrow. The selected ports are displayed as
Trunk Members.
6. Click Apply. Trunking information is modified and the device is updated.
7. Click Save Config in the Trunk Settings Page menu to permanently save the changes.
Page 68
Configuring Ports
Aggregating Ports
Configuring LACP
LAG ports can contain different media types if the ports are operating at the same speed. Aggregated links can be
set up manually or automatically established by enabling Lin k Aggregation Control Protocol (LACP) on the
relevant links. Aggregate ports can be linked into link-aggregation port-groups. Each group is comprised of ports
with the same speed. The LACP Page contains fields for configuring LACP LAGs.
To configure LACP for LAGs:
1. Click Layer 1 > LACP. The LACP Page opens:
Figure 41: LACP Page
The LACP Page contains the following fields:
• LACP System Priority — Specifies system priority value. The field range is 1-65535. The field default is 1.
• Unit Number — Displays the stacking member for which the LAG parameters are defined.
• Port — Displays the port number to which timeout and priority values are assigned.
• Port Priority — Displays the LACP priority value for the port. The field range is 1-65535.
• LACP Timeout — Displays the administrative LACP timeout.
2. Click Modify. the Modify LACP Settings Page opens:
3. Define the fields.
4. Click Apply. The LACP settings are saved and the device is updated.
Page 69

Allied Telesis AT-8000S Switch
Web Browser Interface User’s Guide
Section 6. Configuring Interfaces
This section contains information on configuring the interfaces of the device.
This section describes the following topics:
• Defining MAC Addresses
• Configuring VLANs
Page 70

Configuring Interfaces
Defining MAC Addresses
Defining MAC Addresses
The MAC Address Page contains parameters for querying information in the Static Mac Address Table and the
Dynamic MAC Address Table. The MAC Address tables contain address parameters by which packets are directly
forwarded to the ports and can be sorted by interface, VLAN, and MAC Address.
To configure MAC addresses:
1. Click Layer 2 > MAC Address. The MAC Address Page opens:
Figure 42: MAC Address Page
The MAC Address Page contains the following sections:
• View/Add Unicast MAC Addresses — Enables viewing and configuring Unicast addresses.
• View/Add Multicast MAC Addresses — Enables viewing and configuring Multicast addresses.
The fields in both page sections are the same. Only one page can be selected at a time. The default
selection is the View All option for Multicast MAC addresses.
Page 71

Allied Telesis AT-8000S Switch
Web Browser Interface User’s Guide
The MAC Address Page contains the following fields:
• View All — Displays all dynamic addresses learned on the ports of the device and all static addresses that
have been assigned to the ports.
• View Static — Displays the static addresses assigned to the ports on the device.
• View Dyn amic — Displays the dynamic addresses learned on the ports on the device.
• View MAC Addresses on Port — Displays the dynamic and static MAC addresses of a port. You can specify
more than one port at a time.
• View MAC Addresses for VLAN — Displays the static and dynamic addresses learned on the tagged and
untagged ports of a specific VLAN. You specify the VLAN by entering the VLAN ID. Only one VLAN can be
defined at a time.
• View MAC Address — Displays the number of the port on which a MAC address was assigned or learned.
To find out on which port a particular MAC address was learned, even if the device is part of a large network,
you can just specify the MAC address. The system automatically locates the port on the device where the
device is connected.
2. Define the fields for the Unicast or Multicast MAC addresses to add.
3. Click Add. The Add MAC Address Page opens:
Figure 43: Add MAC Address Page
The Add MAC Address Page contains the following fields:
• MAC Address —Defines the static or dynamic Unicast MAC address.
• Port Number —Indicates the port on which the address was learned or assigned. The MAC address with
port “CPU” is the address of the device.
• VLAN ID — Displays the VLAN ID number to which the entry refers.
• Status — Indicates the current status of the address. The possible values are:
– Permanent — The MAC address is permanent.
– Delete on Reset — The MAC address is deleted when the device is reset.
– Delete on Timeout — The MAC address is deleted when a timeout occurs.
– Secure Options — The MAC Address is defined for locked ports.
Note
When viewed, the information also includes the Type of the address: static or dynamic.
Page 72
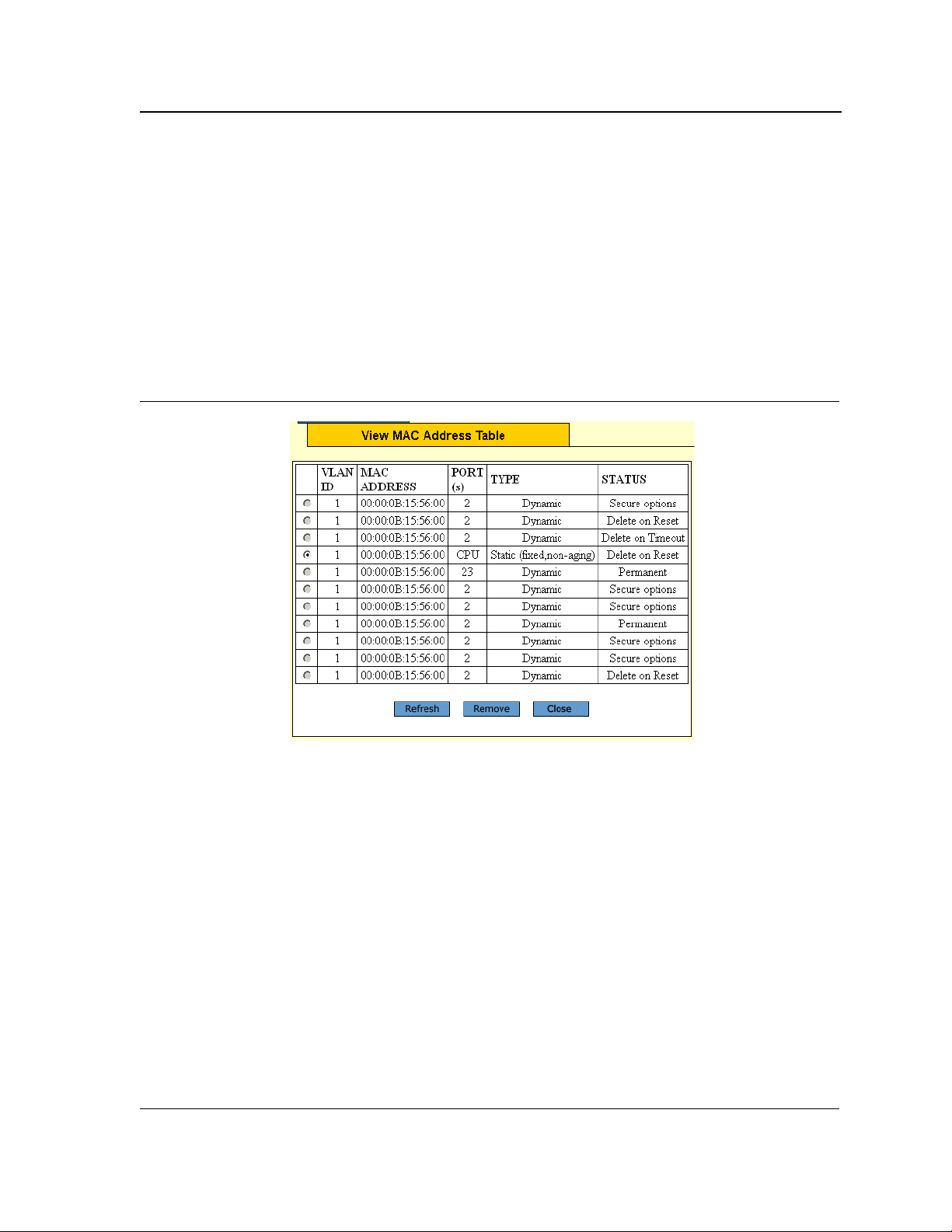
Configuring Interfaces
Defining MAC Addresses
4. Click Apply. The new MAC address is added to the addresses table and the device information is updated.
To delete all MAC addresses:
1. Click Layer 2 > MAC Address. The MAC Address Page opens.
2. Click Delete in the Delete All MAC Addresses section of the MAC Address Page. All addresses are cleared
from the Dynamic MAC Address T able and the device begins to learn new addresses as packets arrive on the
ports.
To view or remove MAC addresses:
1. Click Layer 2 > MAC Address. The MAC Address Page opens.
2. Click View in either View/Add Unicast MAC Addresses section or the View/Add Multicast MAC Addresses
section. The View MAC Address Table Page opens:
Figure 44: View MAC Address Table Page
The View MAC Address Table Page displays all MAC addresses of the selected type (Unicast or Multicast).
3. Click the radio button to select a VLAN ID.
4. Click Remove. The MAC Address is deleted from the list.
5. Click Refresh. The Mac Addresses information is updated.
6. Click Close. The View MAC Address Table Page is displayed.
Page 73

Allied Telesis AT-8000S Switch
Web Browser Interface User’s Guide
Configuring VLANs
This section describes how to create an d configure Virtual LANs (VLANs).
VLANs are logical subgroups with a Local Area Network (LAN) which combine user stations and network devices
into a single unit, regardless of the physical LAN segment to which they are attached. VLANs allow network traffic
to flow more efficiently within subgroups. VLANs use software to reduce the amount of time it takes for network
changes, additions, and moves to be implemented.
VLANs have no minimum number of ports, and can be created per unit, per device, or through any other logical
connection combination, since they are software-based and not defined by physical attributes.
VLANs function at Layer 2. Since VLANs isolate traffic within the VLAN, a Layer 3 router working at a protocol
level is required to allow traffic flow between VLANs. Layer 3 routers identify segments and coordinate with
VLANs. VLANs are Broadcast and Multicast domains. Broadcast and Multicast traffic is transmitted only in the
VLAN in which the traffic is generated. VLAN tagging provides a method of transferring VLAN information between
VLAN groups. VLAN tagging attaches a 4-byte tag to packet headers. The VLAN tag indicates to which VLAN the
packets belong. VLAN tags are attached to the VLAN by either the end station or the network device. VLAN tags
also contain VLAN network priority information.
Combining VLANs and Generic Attribute Registration Protocol (GARP) allows network managers to define
network nodes into Broadcast domains.
When configuring VLANs ensure the following:
• When using this feature, the management VLAN must exist on each 8000S Series device that you want to
manage.
• All of the devices in an enhanced stack must use the same management VLAN. Consequently, you must use
the following procedure to specify the management VLAN on each slave and master device of an enhanced
stack.
• The uplink and downlink ports on each device that are functioning as the tagged or untagged data links
between the devices must be either tagged or untagged members of the management VLAN.
• The port on the device to which the management station is connected must be a member of the management
VLAN.
This section contains the following topics:
• Defining VLAN Properties
• Defining VLAN Interface Settings
• Defining GVRP
Page 74

Configuring Interfaces
Configuring VLANs
Defining VLAN Properties
The VLAN Page provides information and global parameters for configuring and working with VLANs.
To configure a VLAN:
1. Click Layer 2 > VLAN. The VLAN Page opens:
Figure 45: VLAN Page
The VLAN Page contains the following fields:
• Select VLAN ID — Contains a drop-down list of the currently configured VLAN IDs.
• Show All — Displays all currently configured VLANs.
• VLAN ID — Displays the VLAN ID.
• VLAN Name — Displays the user-defined VLAN name. This is a required field.
• VLAN Type — Displays the VLAN type. The possible field values are:
– Dynamic — Indicates the VLAN was dynamically created through GARP.
– Static — Indicates the VLAN is user-defined.
– Default — Indicates the VLAN is the default VLAN.
• Authentication — Indicates whether unauthorized users can access a Guest VLAN. The possible field
values are:
– Enable — Enables unauthorized users to use the Guest VLAN.
– Disable — Disables unauthorized users from using the Guest VLAN.
Page 75

Allied Telesis AT-8000S Switch
Web Browser Interface User’s Guide
The Zoom View shows port representation on the device and enables selecting ports for the VLAN. The Zoom
View of VLAN ports includes the following indicators:
• I — Include — Indicates that the port is included in the VLAN.
• E — Exclude — Indicates that the port is excluded from the VLAN.
• F — Forbidden — Indicates that the port cannot be included in the VLAN.
Page 76
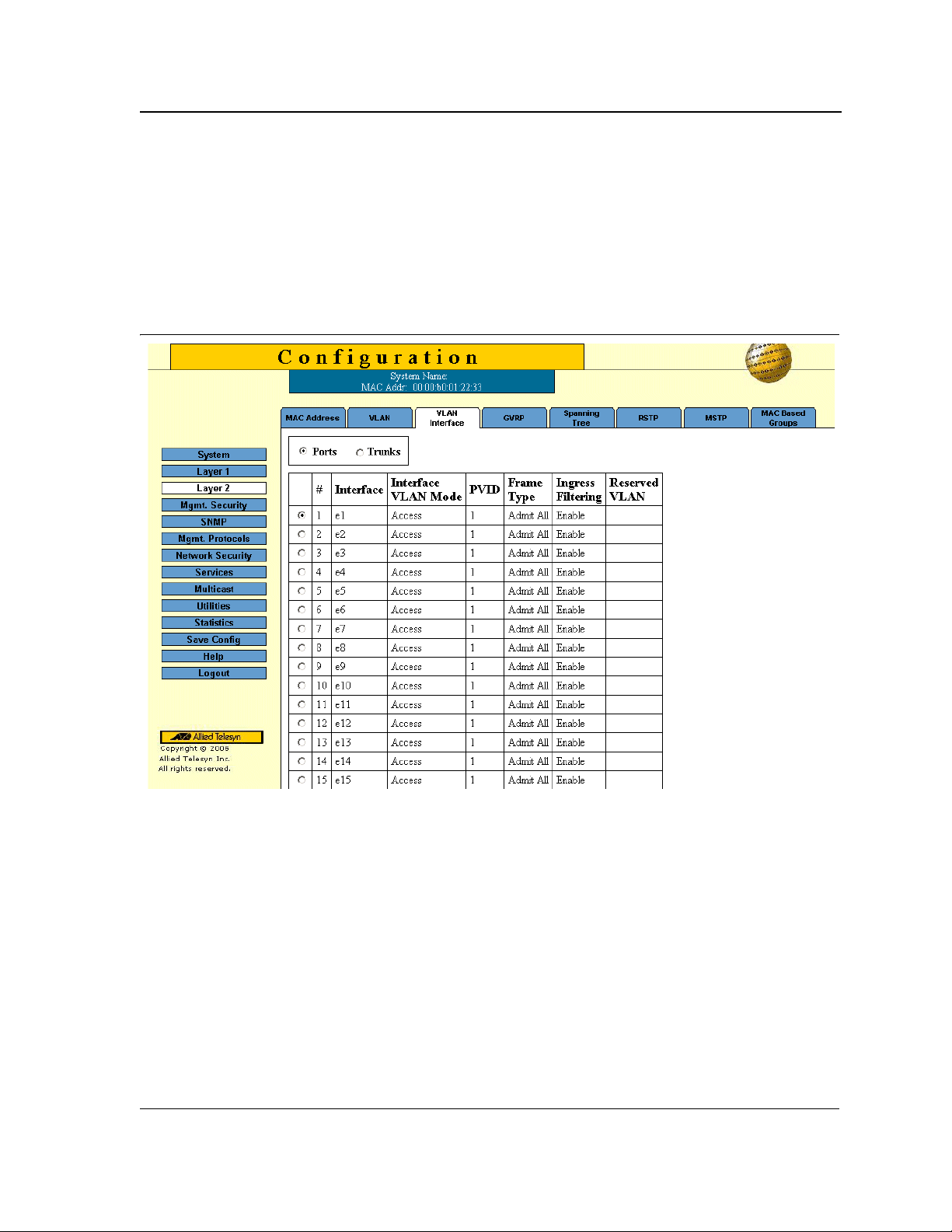
Configuring Interfaces
Configuring VLANs
Defining VLAN Interface Settings
The VLAN Member Interface Settings Page contains fields for managing ports that are part of a VLAN. The Port
Default VLAN ID (PVID) is configured on the Modify Interface Configuration Page. All untagged packets arriving at
the device are tagged with the port PVID.
To define VLAN interface.
1. Click Layer 2 > VLAN Interface. The VLAN Interface Page opens:
Figure 46: VLAN Interface Page
The VLAN Interface Page displays the VLAN interface information for a selected Port/Unit or Trunk:
• Port Interface — Displays the port number included in the VLAN.
• PVID — Assigns a VLAN ID to untagged packets. The possible values are 1-4094. VLAN 4095 is defined as
per standard and industry practice as the Discard VLAN. Packets classified to the Discard VLAN are dropped.
• Ingress Filtering — Indicates whether ingress filtering is enabled on the port. The possible field values are:
– Enable — Enables ingress filtering on the device. Ingress filtering discards packets that are defined to
VLANs of which the specific port is not a member.
– Disable — Disables ingress filtering on the device.
• Reserve VLAN for Internal Use — Indicates which VLAN is reserved for internal use by the system. One
VLAN must be reserved.
• Port VLAN Mode — Displays the port mode. The possible values are:
Page 77
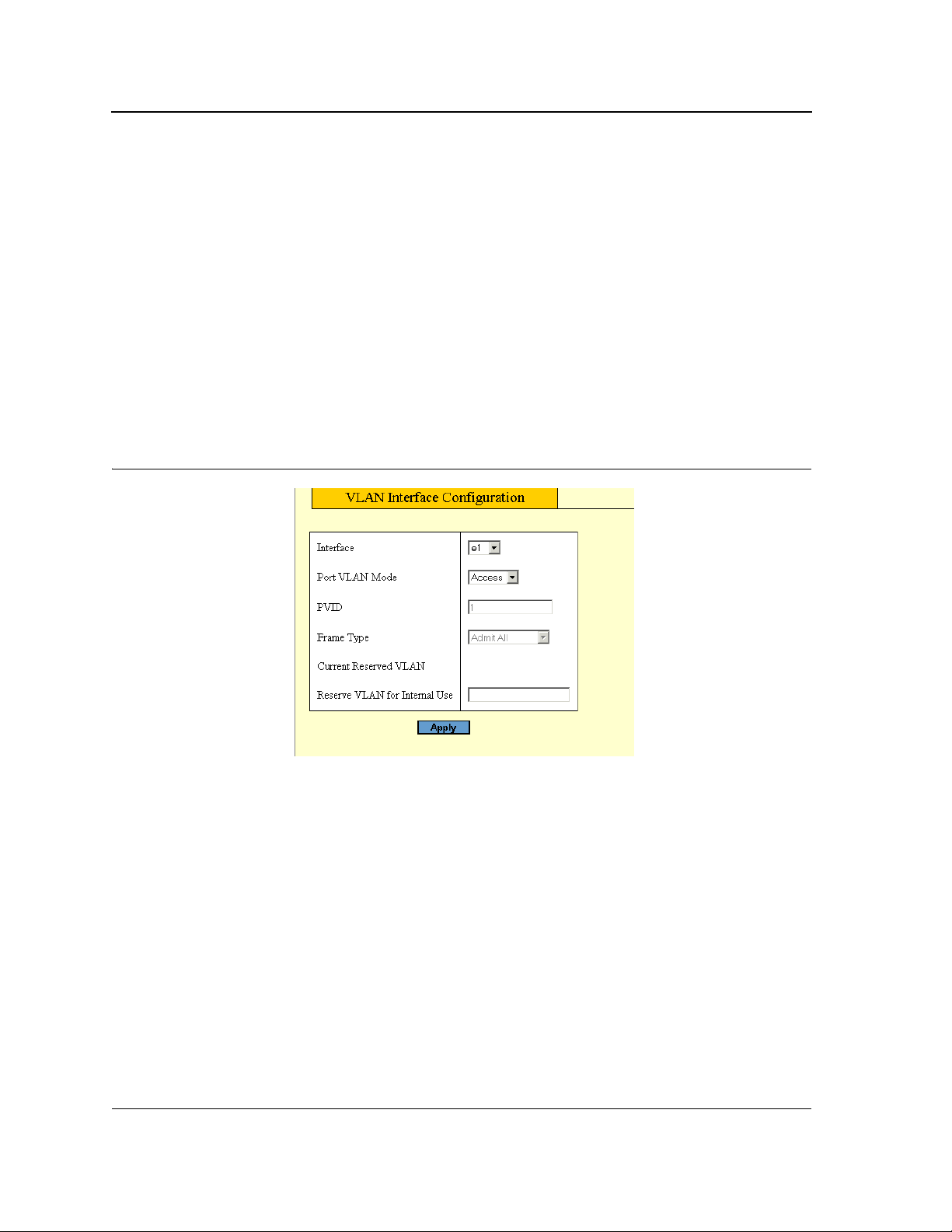
Allied Telesis AT-8000S Switch
Web Browser Interface User’s Guide
– General — Indicates the port belongs to VLANs, and each VLAN is user-defined as tagged or untagged
(full IEEE802.1q mode).
– Access — Indicates a port belongs to a single untagged VLAN. When a port is in Access mode, the
packet types which are accepted on the port cannot be designated. Ingress filtering cannot be enabled or
disabled on an access port.
– Trunk — Indicates the port belongs to VLANs in which all ports are tagged, except for one port that can
be untagged.
• Frame Type — Specifies the packet type accepted on the port. The possible fi eld values are:
– Admit Ta g Only — Only tagged packets are accepted on the port.
– Admit All — Both tagged and untagged packets are accepted on the port.
• Current Reserved VLAN — Indicates that the VLAN selected by the user is reserved, if not in use by the
system.
2. Click Modify. The Modify Interface Configuration Page opens:
Figure 47: Modify Interface Configuration Page
3. Define the fields.
4. Click Apply. The VLAN interface configuration is saved and the device is updated.
Page 78

Configuring Interfaces
Configuring VLANs
Defining GVRP
This section explains how to configure GVRP on the device. GARP VLAN Registration Protocol (GVRP) is
specifically provided for automatic distribution of VLAN membership information among VLAN-aware bridges.
GVRP allows VLAN-aware bridges to automatically learn VLANs to bridge ports mapping, without having to
individually configure each bridge and register VLAN membership. This section describes the following topics:
• Configuring GVRP
• Enabling/Disabling GVRP on a Port
Notes
• GVRP cannot be configured if MSTP is enabled on the device.
• The Default button returns all GVRP parameter settings to their default values.
Caution
The settings for the three GVRP timers must be the same on all GVRP-active devices in your network.
Configuring GVRP
To define GVRP on the device:
1. Click Layer 2 > GVRP. The GVRP Page opens:
Figure 48: GVRP Page
The GVRP Page contains the following fields:
• GVRP Global Status — Indicates if GVRP is enabled on the device. The possible field values are:
Page 79

Allied Telesis AT-8000S Switch
Web Browser Interface User’s Guide
– Enable — Enables GVRP on the selected device.
– Disable — Disables GVRP on the selected device.
• Port — Displays the ports table.
• Trunk — Displays the trunks table.
• Interface — Displays the port or trunk on which GVRP is enabled. The possible field values are:
– Port — Indicates the port number on which GVRP is enabled.
– Trunk — Indicates the LAG number on which GVRP is enabled.
• GVRP State — Indicates if GVRP is enabled on the port. The possible field values are:
– Enable — Enables GVRP on the selected port.
– Disable — Disables GVRP on the selected port.
• Dynamic VLAN Creation — Indicates if Dynamic VLAN creation is enabled on the interface. The possible
field values are:
– Enable — Enables Dynamic VLAN creation on the interface.
– Disable — Disables Dynamic VLAN creation on the interface.
• GVRP Registration — Indicates if VLAN registration through GVRP is enabled on the device. The possible
field values are:
– Enable — Enables GVRP registration on the device.
– Disable — Disables GVRP registration on the device.
2. Select Enable GVRP.
3. Define the GVRP parameters.
4. Click Apply. The global GVRP parameters are saved and the device is updated.
5. Click Save Config on the menu to permanently save the change.
6. Select Port and Unit or Trunk.
7. Click Modify. The GVRP Port Configuration Page opens:
Page 80

Enabling/Disabling GVRP on a Port
To modify the GVRP ports:
1. Click Layer 2 > GVRP. The GVRP Page opens.
2. Select Port and Unit or Trunk in the GVRP Port Configuration section.
3. Click Modify. The GVRP Port Configuration Page opens:
Figure 49: GVRP Port Configuration Page
Configuring Interfaces
Configuring VLANs
•
Unit Number — The stacking member for which the GVRP parameters are displayed.
• Interface — Displays the port on which GVRP is enabled. The possible field values are:
– Port — Indicates the port number on which GVRP is enabled.
– LAG — Indicates the LAG number on which GVRP is enabled.
• GVRP State — Indicates if GVRP is enabled on the port. The possible field values are:
– Enabled — Enables GVRP on the selected port.
– Disabled — Disables GVRP on the selected port.
• Dynamic VLAN Creation — Indicates if Dynamic VLAN creation is enabled on the interfa ce . Th e possible
field values are:
– Enabled — Enables Dynamic VLAN creation on the interface.
– Disabled — Disables Dynamic VLAN creation on the interface.
• GVRP Registration — Indicates if VLAN registration through GVRP is enabled on the device. The possible
field values are:
– Enabled — Enables GVRP registration on the device.
– Disabled — Disables GVRP registration on the device.
4. Select the interface (Port or Trunk).
5. Define the GVRP State and GVRP Registration fields.
6. Click Apply. The change to the GVRP mode is activated on the selected interface.
Page 81

Allied Telesis AT-8000S Switch
Web Browser Interface User’s Guide
Section 7. Configuring System Logs
This section provides information for managing system logs. System logs enable viewing device events in real
time and recording the events for later usage. System Logs record and manage events, and report errors and
informational messages.
This section includes the following topics:
• Defining Log Settings
• Configuring Log Servers
• Setting System Log Display
• Clearing Event Logs
• Viewing Flash Logs
Page 82

Configuring System Logs
Defining Log Settings
Defining Log Settings
Event messages have a unique format, which is the Syslog protocols recommended message format for all error
reporting. For example, Syslog and local device reporting messages are assigned a severity code and include a
message mnemonic which identifies the source application generating the message. This allows messages to be
filtered based on their urgency or relevancy. The message severity determines the set of event logging devices
that are sent for each event message. The default severity for all logs is Informational, with the exception of logs in
the Remote Log Server, which are Error.
The following table lists the available system log severity levels and the corresponding messages:
Table 3: System Log Severity Levels
Severity Level Description Message
Emergency 0 The highest warning level. If the
device is down or not functioning
properly, an emergency log message
is saved to the specified logging
location.
Alert 1 The second highest warning level. An
alert log is saved if there is a serious
device malfunction. For example, all
device features are down.
Critical 2 The third highest warning level.
A critical log is saved if a critical
device malfunction occurs. For
example, two device ports are no t
functioning, while the rest of the
device ports remain functional
Error 3 A device error has occurred. For
example, a single port is offline.
The system is not functioning.
The system needs immediate attention.
The system is in a critical state.
A system error has occurred.
Warning 4 The lowest level of a device warning.
The device is functioning, but an
operational problem has occurred.
Notice 5 The system is functioning properly,
but a system notice has occurred.
Informational 6 Provides device information. Provides device information.
Debug 7 Provides detailed information about
the log. If a Debug error occurs,
contact Customer Tech Support.
The Event Log Page page contains fields for defining which events are recorded to which logs. It contains fields
for enabling logs globally and parameters for defining logs.
Page 83
A system warning has occurred.
The system is functioning properly, but a
system notice has occurred.
Provides detailed information about the
log. If a Debug error occurs, contact
Customer Tech Support.

Allied Telesis AT-8000S Switch
Web Browser Interface User’s Guide
To define system log parameters:
1. Click System > Event Log. The Event Log Page opens:
Figure 50: Event Log Page
The Event Log Page contains the following fields:
• Minimum Severity — Indicates the minimum severity level to be included in the log output. All logs that have
the severity higher than the minimum severity are also included in the output. When the minimum severity
level is defined, logs of all higher severity levels are selected automatically.
– Disable — Disables minimum severity.
– Enable — Enables minimum severity.
The Log Outputs table displays the following log information:
• Type — Indicates the log type included in the output. The possible values are:
– Console — Indicates that the output is of a console log.
– Temporary — Indicates that the output is of the temporary memory log.
– Syslog — Indicates that the output is of a a system log.
– Flash — Indicates that the output is of a Flash memory log.
• IP Address — Displays the defined IP address of the syslog server.
• Minimum Severity — Indicates the defined minimum severity level.
Page 84

Configuring System Logs
Clearing Event Logs
• Description — Provides additional information about the syslog server.
2. Define the Minimum Severity for the log.
3. Click Apply. Logging is enabled on the device.
Clearing Event Logs
To clear all events from the log:
1. Click System > Event Log. The Event Log Page opens:
2. Click Clear Logs. The stored logs are cleared. If logging is enabled, the system begins to log new events.
Configuring Log Servers
To add a log server:
1. Click System > Event Log. The Event Log Page opens.
2. Select a Log Type in the Configure Log Outputs table’
3. Click Create. The Add Syslog Server Page opens:
Figure 51: Add Syslog Server Page
The Add Syslog Server Page contains the following fields:
• Log Server IP Address — Defines the IP address of the syslog server.
• UDP Port — Defines the UDP port to which the server logs are sent. The possible range is 1-65535.
The default value is 514.
• Facility — Defines an application from which system logs are sent to the remote server. Only one facility can
be assigned to a single server. If a second facility level is assigned, the first facility is overridden. All
applications defined for a device utilize the same facility on a server. The field default is Local 7. The possible
field values are Local 0 - Local 7.
• Description — Provides any additional information about the syslog server, for example its location.
• Minimum Severity — Indicates the minimum severity level to be included in the log output. All logs that have
the severity higher than the minimum severity are also included in the output. When the minimum severity
level is defined, logs of all higher severity levels are selected automatically.
4. Define the IP Address, UDP Port, Facility, Description, and Minimum Severity fields.
5. Click Apply. The Log server is defined and the device is updated.
Page 85

Allied Telesis AT-8000S Switch
Web Browser Interface User’s Guide
Setting System Log Display
The Modify Event Log Output Page contains options to set output parameters for system logs.
To configure log output properti es:
1. Click System > Event Log. The Event Log Page opens.
2. Select a Log Type in the Configure Log Outputs table.
3. Click Modify. The Modify Event Log Output Page opens:
Figure 52: Modify Event Log Output Page
The following fields are displayed in the Modify Event Log Output Page:
• Enable Logging — Defines if logging is enabled. Possible values are:
– Checked — Logging is enabled on the device.
– Unchecked — Logging is disabled on the device.
• Severity — Indicates the event severity to trigger a log. Log severities are listed from highest to lowest
severity. See Table 3, “System Log Severity Levels,” on page 83.
• Console — Indicates that the output is of a Console log.
• Memory Logs — Indicates that the output is of a Memory log.
• Log Flash — Indicates that the output is of a Flash log.
4. Check the Enable Logging option.
5. Map the log output severities to log types in the Console, Memory Logs and Log Flash columns. Checking all
Includes all severity levels in the log
6. Click Apply. The output settings are saved and the device is updated.
7. Click Save Config in the Event Log Page menu to save the changes permanently.
Page 86

Configuring System Logs
Viewing Flash Logs
Viewing Flash Logs
The Syslog Flash Page contains information about log entries saved to the log file in Flash, including the time the
log was generated, the log severity, and a description of the log message. The message log is available after
reboot.
To display Flash logs:
1. Click System > Event Log. The Event Log Page opens:
2. Click View Flash. The Flash Log Page opens:
Figure 53: Flash Log Page
The Flash Log Page lists the following information:
• Log Index — Lists the log index number.
• Log Time — Lists the date and time that the log was entered.
• Severity — Lists the severity of the event for which the log was created in Flash memory.
• Description — Lists the event details.
To clear Flash memory logs:
1. Click Clear Logs. Logs are removed from the table.
2. Click Close. The Event Log Page is displayed.
Page 87

Allied Telesis AT-8000S Switch
Web Browser Interface User’s Guide
Section 8. Configuring Spanning Tree
Spanning Tree Protocol (STP) provides tree topography for any arrangement of bridges. STP also provides a
single path between end stations on a network, eliminating loops.
Loops occur when alternate routes exist between hosts. Loops in an extended network can cause bridges to
forward traffic indefinitely, resulting in increased traffic and reducing network efficiency.
The device supports the following STP versions:
• Classic STP — Provides a single path between end stations, avoiding and eliminating loops. For more
information on configuring Classic STP , see Configuring Classic Spanning Tree.
• Rapid STP — Detects and uses network topologies that provide faster convergence of the spanning tree,
without creating forwarding loops. For more information on configuring Rapid STP, see Configuri ng Rapid
Spanning Tree.
• Multiple STP — Provides various load balancing scenarios. For example, if port A is blocked in one STP
instance, the same port can be placed in the Forwarding State in another STP instance. For more information
on configuring Multiple STP, see Configuring Multiple Spanning Tree.
This section contains the following topics:
• Configuring Classic Spanning Tree
• Defining STP Interfaces
• Configuring Rapid Spanning Tree
• Configuring Multiple Spanning Tree
Page 88

Configuring Spanning Tree
Configuring Classic Spanning Tree
Configuring Classic Spanning Tree
This section contains the following topics:
• Defining STP Properties
• Defining STP Interfaces
Defining STP Properties
The Spanning Tree Page contains parameters for enabling and configuring STP on the device.
To enable STP on the device:
1. Click Layer 2 > Spanning Tree (STP). The Spanning Tree Page opens:
Figure 54: Spanning Tree Page
The STP General section of the Spanning Tree Page contains the following fields:
• Spanning Tree State — Indicates whether STP is enabled on the device. The possible field values are:
– Enable — Enables STP on the device.
– Disable — Disables STP on the device.
• STP Operation Mode — Specifies the STP mode that is enabled on the device.
The possible field values are:
– Classic STP — Enables Classic STP on the device. This is the default value.
– Rapid STP — Enables Rapid STP on the device.
Page 89

Allied Telesis AT-8000S Switch
Web Browser Interface User’s Guide
– Multiple STP — Enables Multiple STP on the device.
• BPDU Handling — Determines how BPDU packets are managed when STP is disabled on the port or
device. BPDUs are used to transmit spanning tree information. The possible field values are:
– Filtering — Filters BPDU packets when spanning tree is disabled on an interface.
– Flooding — Floods BPDU packets when spanning tree is disabled on an interface. This is the default
value.
• Path Cost Default Values — Specifies the method used to assign default path cost to STP ports. The
possible field values are:
– Short — Specifies 1 through 65,535 range for port path cost.
– Long — Specifies 1 through 200,000,000 range for port path cost. This is the default value.
The Bridge Settings section of the Spanning Tree Page contains the following fields:
• Priority — Specifies the bridge priority value. When switches or bridges are running STP, each is assigned a
priority. After exchanging BPDUs, the device with the lowest priority value becomes the Root Bridge. The
default value is 32768. The port priority value is provided in increments of 4096; the value range is 0-65535.
• Hello Time — Specifies the device Hello Time, in seconds. The Hello Time is the time interval during which a
Root Bridge waits between configuration messages. The value range is 1-10 seconds; the default value is
2 seconds.
• Max Age — Specifies the device Maximum Age Time, in seconds. The Maximum Age Time is the time
interval during which a bridge waits before sending configuration messages. The value range is 6-40
seconds; the default value is 20 seconds.
• Forward Delay — Specifies the device Forward Delay Time, in seconds. The Forward Delay T ime is the time
interval during which a bridge remains in the listening-and-learning state before forwarding packets.
The value range is 4-30 seconds; the default value is 15 seconds.
The Designated Root section of the Spanning Tree Page contains the following fields:
• Bridge ID — Identifies the Bridge priority and MAC address.
• Root Bridge ID — Identifies the Root Bridge priority and MAC address.
• Root Port — Indicates the port number that offers the lowest cost path from this bridge to the Root Bridge.
This field is significant when the bridge is not the Root Bridge. The default is zero.
• Root Path Cost — The cost of the path from this bridge to the Root Bridge.
• Topology Changes Counts — Specifies the total amount of STP state changes that have occurred.
• Last Topology Change — Indicates the time interval that has elapsed since the bridge was initialized or
reset, and the last topographic change that occurred. The time is displayed in a day-hour-minute-second
format, such as 2 days 5 hours 10 minutes and 4 seconds.
2. Complete the Spanning Tree State and Bridge Settings fields.
3. Click Apply. The new STP definition is added and device information is updated.
4. Click Save Config on the menu to save the settings permanently.
Page 90
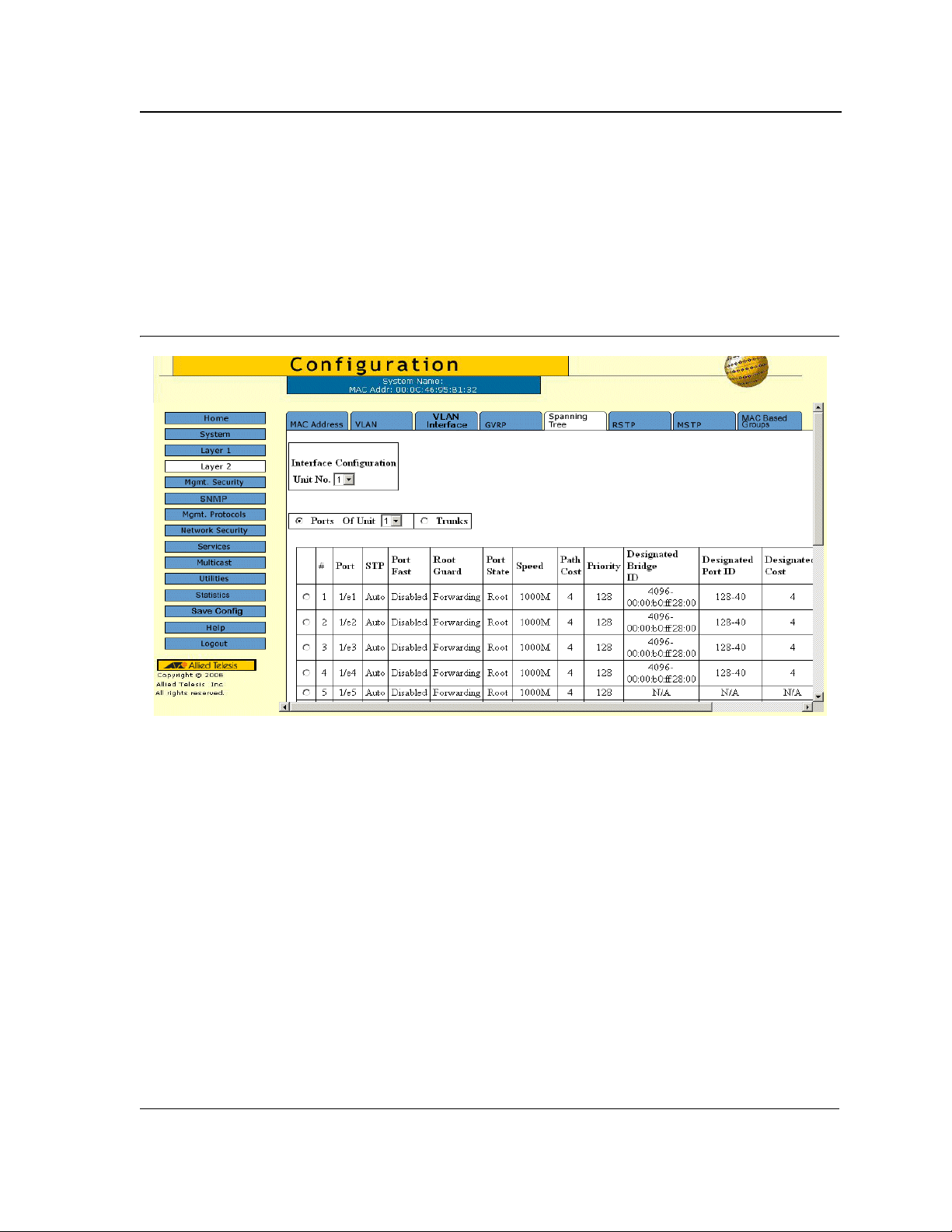
Configuring Spanning Tree
Configuring Classic Spanning Tree
Defining STP Interfaces
Network administrators can assign STP settings to a specific interface (port or LAG) using the STP Interface
Configuration Page. The Global LAGs section displays the STP information for Link Aggregated Groups.
To assign STP settings to an interface (port or LAG):
1. Click Layer 2 > Spanning Tree. The Spanning Tree Page opens.
2. Click Configure. The STP Interface Configuration Page opens:
Figure 55: STP Interface Configuration Page
The STP Interface Configuration Page contains the following sections:
• Interface Configuration
• STP Port Parameters table
• Global System LAGs table
The parameters listed in both tables are identical.
The STP Interface Configuration Page contains the following fields:
• Unit Number — Indicates the stacking member for which the STP information is displayed.
• Port — Displays the port or LAG on which STP is enabled.
• STP Status — Indicates if STP is enabled on the port. The possible field values are:
– Enabled — Indicates that STP is enabled on the port.
– Disabled — Indicates that STP is disabled on the port.
• Port Fast — Indicates if Fast Link is enabled on the port. If Fast Link mode is enabled for a port, the Port
State is automatically placed in the Forwarding state when the port link is up. Fast Link optimizes the STP
protocol convergence. STP convergence can take 30-60 seconds in large networks.
• Root Guard — Prevents devices outside the network core from being assigned the spanning tree root.
• Port State — Displays the current STP state of a port. If enabled, the port state determines what forwarding
Page 91

Allied Telesis AT-8000S Switch
Web Browser Interface User’s Guide
action is taken on traffic. Possible port states are:
– Disabled — Indicates that STP is currently disabled on the port. The port forwards traffic while learning
MAC addresses.
– Blocking — Indicates that the port is currently blocked and cannot forward traffic or learn MAC
addresses. Blocking is displayed when Classic STP is enabled.
• Speed — Indicates the speed at which the port is operating.
• Path Cost — Indicates the port contribution to the root path cost. The path cost is adjusted to a higher or
lower value, and is used to forward traffic when a path is rerouted.
• Priority — Indicates the priority value of the port. The priority value influences the port choice when a bridge
has two ports connected in a loop. The priority value is between 0-240. The priority value is determined in
increments of 16.
• Designated Bridge ID — Indicates the bridge priority and the MAC Address of the designated bridge.
• Designated Port ID — Indicates the selected port priority and interface.
• Designated Cost — Indicates the cost of the port participating in the STP topology. Ports with a lower cost
are less likely to be blocked if STP detects loops.
• Forward Transitions — Indicates the number of times the port has changed from Forwarding state to
Blocking state.
• LAG — Indicates the LAG to which the port belongs.
3. Select the Unit, in the STP Interface Configuration section.
4. Click Modify. The STP Modify Interface Configuration Page opens:
Page 92
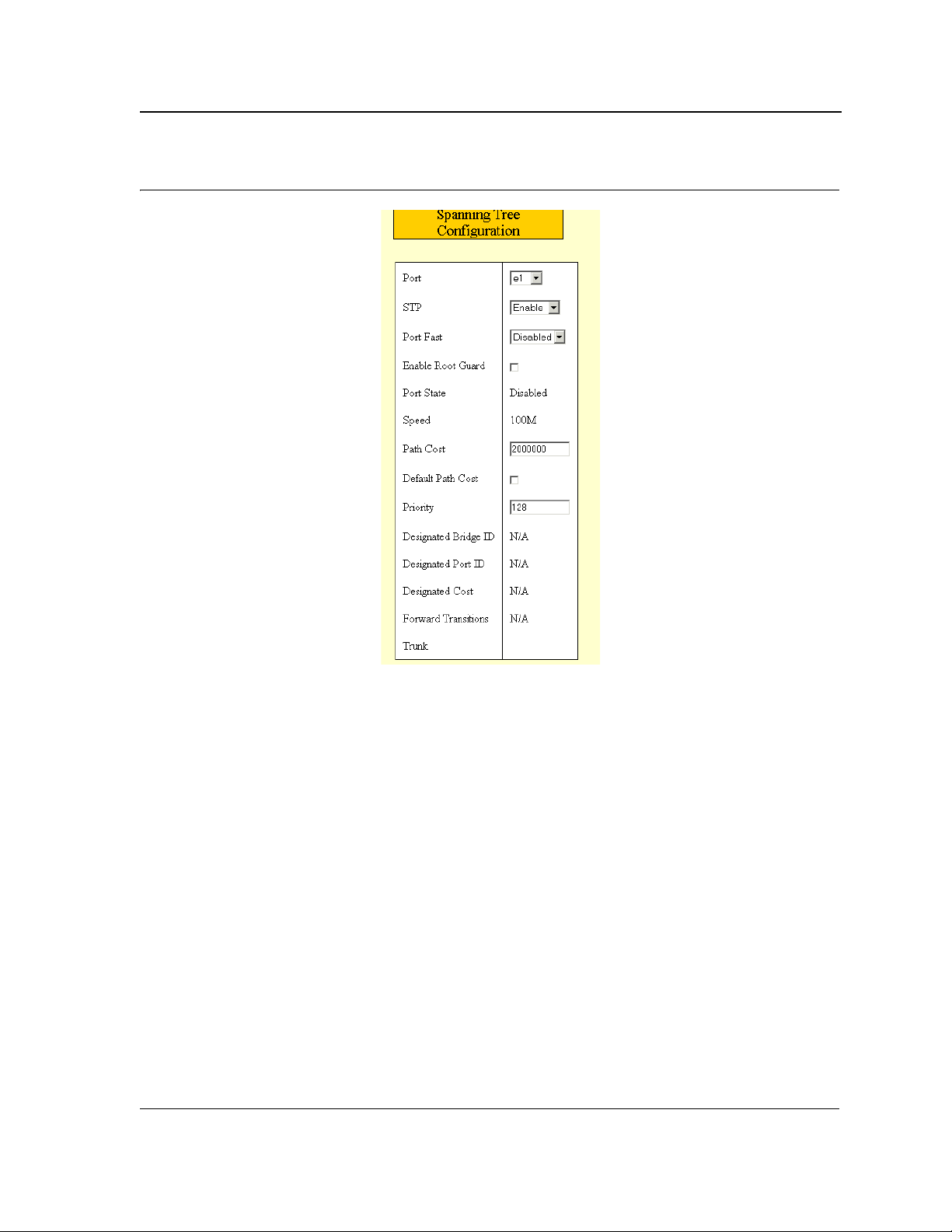
Figure 56: STP Modify Interface Configuration Page
Configuring Spanning Tree
Configuring Classic Spanning Tree
5. Select Enable in the STP field.
6. Define the Port Fast, Enable Root Guard, Path Cost, Default Path Cost, and Priority fields.
7. Click Apply. STP is enabled on the interface, and the device is updated.
Page 93
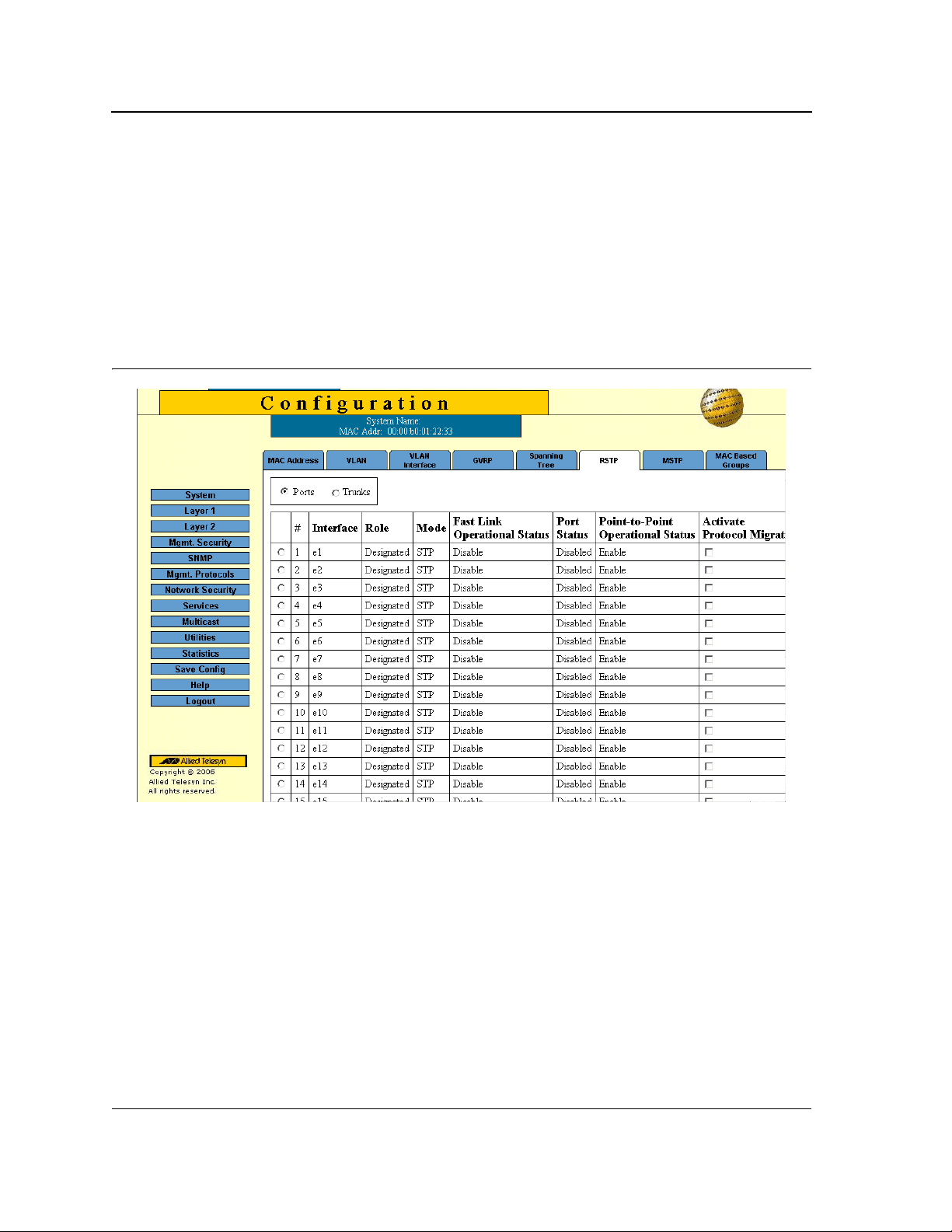
Allied Telesis AT-8000S Switch
Web Browser Interface User’s Guide
Configuring Rapid Spanning Tree
While Classic STP prevents Layer 2 forwarding loops in a general network topology, convergence can take
between 30-60 seconds. This time may delay detecting possible loops and propagating status topology changes.
Rapid Spanning Tree Protocol (RSTP) detects and uses network topologies that allow a faster STP convergence
without creating forwarding loops. The Global System LAG information displays the same field information as the
ports, but represent the LAG RSTP information.
To define RSTP on the device:
1. Click Layer 2 > RSTP. The RSTP Page opens:
Figure 57: RSTP Page
The RSTP Page contains the following fields:
• Unit Number — Indicates the stacking member for which the Rapid STP information is displayed.
• Interface — Displays the port or LAG on which Rapid STP is enabled.
• State — Indicates if
• Role — Displays the port role assigned by the STP algorithm to provide to STP paths. The possible field
values are:
– Root — Provides the lowest cost path to forward packets to the root switch.
– Designated — The port or LAG through which the desig nated switch is attached to the LAN.
– Alternate — Provides an alternate path to the root switch from the root interface.
Page 94

Configuring Spanning Tree
Configuring Rapid Spanning Tree
– Backup — Provides a backup path to the designated port path toward the Spanning Tree leaves. Backup
ports occur only when two ports are connected in a loop by a point-to-point link, or when a LAN has two
or more connections to a shared segment.
– Disabled — The port is not participating in the Spanning Tree.
• Mode — Displays the current STP mode. The STP mode is selected in the Spanning Tree Page.
The possible field values are:
– STP — Classic STP is enabled on the device.
– Rapid STP — Rapid STP is enabled on the device.
– Multiple STP — Multiple STP is enabled on the device.
• Fast Link Operational Status — Indicates whether Fast Link is enabled or disabled for the port or LAG.
If Fast Link is enabled for a port, the port is automatically placed in the forwarding state.
• Point-to-Point Admin Status — Indicates whether a point-to-point link is established, or if the device is
permitted to establish a point-to-point link. The possible field values are:
– Enable — The device is permitted to establish a point-to-point link, or is configured to automatically
establish a point-to-point link. To establish communications over a point-to-point link, the originating PPP
first sends Link Control Protocol (LCP) packets to configure and test the data link. After a link is
established and optional facilities are negotiated as needed by the LCP, the originating PPP sends
Network Control Protocol (NCP) packets to select and configure one or more network layer protocols.
When each of the chosen network layer protocols has been configured, packets from each network layer
protocol can be sent over the link. The link remains configured for communications until explicit LCP or
NCP packets close the link, or until some external event occurs. This is the actual switch port link type.
It may differ from the administrative state.
– Disable — Disables point-to-point link.
• Point-to-Point Operational Status — Displays the point-to-point operating state.
2. Click Modify. The Modify RSTP Page opens:
Figure 58: Modify RSTP Page
Page 95

Allied Telesis AT-8000S Switch
Web Browser Interface User’s Guide
3. Define the STP, Fast Link, Enable Root Guard, Port State Path Cost, Default Path Cost and Priority fields.
4. Click Apply. RSTP is defined for the selected interface, and the device is updated.
5. Click Save Config on the menu, to save changes permanently.
Configuring Multiple Spanning Tree
Multiple Spanning Tree Protocol (MSTP) provides differing load balancing scenarios. For example, while port A is
blocked in one STP instance, the same port can be placed in the Forwarding state in another STP instance.
The MSTP Page contains information for defining global MSTP settings, including region names, MSTP revisions,
and maximum hops.
This section contains the following topics:
• Defining MSTP Properties
• Defining MSTP Interfaces
• Defining MSTP Instances
Page 96

Defining MSTP Properties
To define MSTP:
1. Click Layer 2 > MSTP. The MSTP Page opens:
Figure 59: MSTP Page
Configuring Spanning Tree
Configuring Multiple Spanning Tree
The MSTP Page contains the following fields:
• Region Name — User-defined STP region name.
• Revision — An unsigned 16-bit number that identifies the revision of the current MSTP configuration. The
revision number is required as part of the MSTP configuration. The possible field range is 0-65535.
• Max Hops — S pecifies the total number of hops that occur in a specific region before the BPDU is discarded.
Once the BPDU is discarded, the port information is aged out. The possible field range is 1-40. The field
default is 20 hops.
• IST Master
2. Define the Region Name, Revision, and Max Hops fields.
3. Click Apply. The MSTP properties are defined, and the device is updated.
—
Identifies the Spanning Tree Master instance. The IST Master is the specified instance root.
Page 97

Allied Telesis AT-8000S Switch
Web Browser Interface User’s Guide
Defining MSTP Interfaces
Network administrators can assign MSTP settings to a specific interface (port or LAG) using the MSTP Interface
Settings Page.
To define MSTP interface settings:
1. Click Layer 2 > MSTP. The MSTP Page opens.
2. Click Configure next to the Configure Interface Settings option. The MSTP Interface Settings Page opens:
Figure 60: MSTP Interface Settings Page
The MSTP Interface Settings Page
contains the following fields:
• Instance ID — Lists the MSTP instances configured on the device. The possible field range is 0-7.
• Interface Priority — Defines the interface priority for the specified instance. The default value is 128.
• Interface — Displays the interface for which the MSTP settings are displayed. The possible field values are:
– Port of Unit — Specifies the port for which the MSTP settings are displayed.
– LAG — Specifies the LAG for which the MSTP settings are displayed.
• Path Cost — Indicates the port contribution to the Spanning Tree instance. The field range is 1-200,000,000.
• MSTP — Specifies whether or not MSTP is enabled on the interface. The possible field values are:
– Enable — Enables MSTP on the interface.
– Disable — Disables MSTP on the interface.
• Port State — Indicates whether the port is enabled for the specific instance. The possible field values are:
– Enable — Enables the port for the specific instance.
Page 98

Configuring Spanning Tree
Configuring Multiple Spanning Tree
– Disable — Disables the port for the specific instance.
• Type — Indicates whether the port is a Boundary or Master port. The possible field values are:
– Boundary Port — Indicates that the port is a Boundary port. A Boundary port attaches MST bridges to
LANs in an outlying region. If the port is a Boundary port, this field also indicates whether the device on
the other side of the link is working in RSTP or STP mode.
– Master Port — Indicates the port is a master port. A Master port provides connectivity from an MSTP
region to the outlying CIST root.
• Role — Indicates the port role assigned by the STP algorithm to provide to STP paths. The possible field
values are:
– Root — Provides the lowest cost path to forward packets to the root device.
– Designated — Indicates the port or LAG through which the designated device is attached to the LAN.
– Alternate — Provides an alternate path to the root device from the root interface.
– Backup — Provides a backup path to the designated port path toward the Spanning Tree leaves. Backup
ports occur only when two ports are connected in a loop by a point-to-point link or when a LAN has two or
more connections to a shared segment.
– Disabled — Indicates the port is not participating in the Spanning Tree.
• Mode — Indicates the STP mode by which STP is enabled on the device. The possible field values are:
– Classic STP — Classic STP is enabled on the device. This is the default value.
– Rapid STP — Rapid STP is enabled on the device.
– Multiple STP — Multiple STP is enabled on the device.
• Designated Bridge ID — Displays the ID of the bridge that connects the link or shared LAN to the root.
• Designated Port ID — Displays the ID of the port on the designated bridge that connects the link or the
shared LAN to the root.
• Designated Cost — Indicates that the default path cost is assigned according to the method selected on the
Spanning Tree Global Settings.
• Forward Transitions — Indicates the number of times the LAG State has changed from a Forwarding state
to a Blocking state.
• Remain Hops — Indicates the hops remaining to the next destination.
3. Define the fields.
4. Click Apply. MSTP is defined for the selected interface, and the device is updated. The MSTP Page is
displayed.
5. Click Save Config on the menu, to save changes permanently.
Page 99
 Loading...
Loading...