Page 1

LEA-19A08G
Page 2

SAFETY
SAFETY
SAFETY
SAFETY PRECAUTIONS
PRECAUTIONS
PRECAUTIONS
PRECAUTIONS
IMPORTANT
IMPORTANT
IMPORTANT
IMPORTANT SAFETY
Many electrical and mechanical parts in this chassis have special safety-related characteristics. These parts are identified by
in the Schematic Diagram and Replacement Parts List.
It is essential that these special safety parts should be replaced with the same components as recommended in this manual to
prevent Shock, Fire, or other Hazards.
Do not modify the original design without permission of manufacturer.
General
General
General
General Guidance
AC power line. Use a transformer of adequate power rating as this protects the technician from accidents resulting in personal
injury from electrical shocks.
inadvertently introduced during the service operation.
If any fuse (or Fusible Resistor) in this TV receiver is blown,replace it with the specified.
Before returning the receiver to the customer, always perform an AC leakage current check on the exposed metallic parts of the
cabinet, such as antennas, terminals, etc., to be sure the set is safe to operate without damage of electrical shock.
Guidance
Guidance
Guidance
An isolation Transformer should always be used during the servicing of a receiver whose chassis is not isolated from the
It will also protect the receiver and it's components from being damaged by accidental shorts of the circuitry that may be
When replacing a high wattage resistor (Oxide Metal Film Resistor, over 1W), keep the resistor 10mm away from PCB.
Keep wires away from high voltage or high temperature parts.
SAFETY
SAFETY
SAFETY NOTICE
NOTICE
NOTICE
NOTICE
Leakage
Leakage
Leakage
Leakage Current
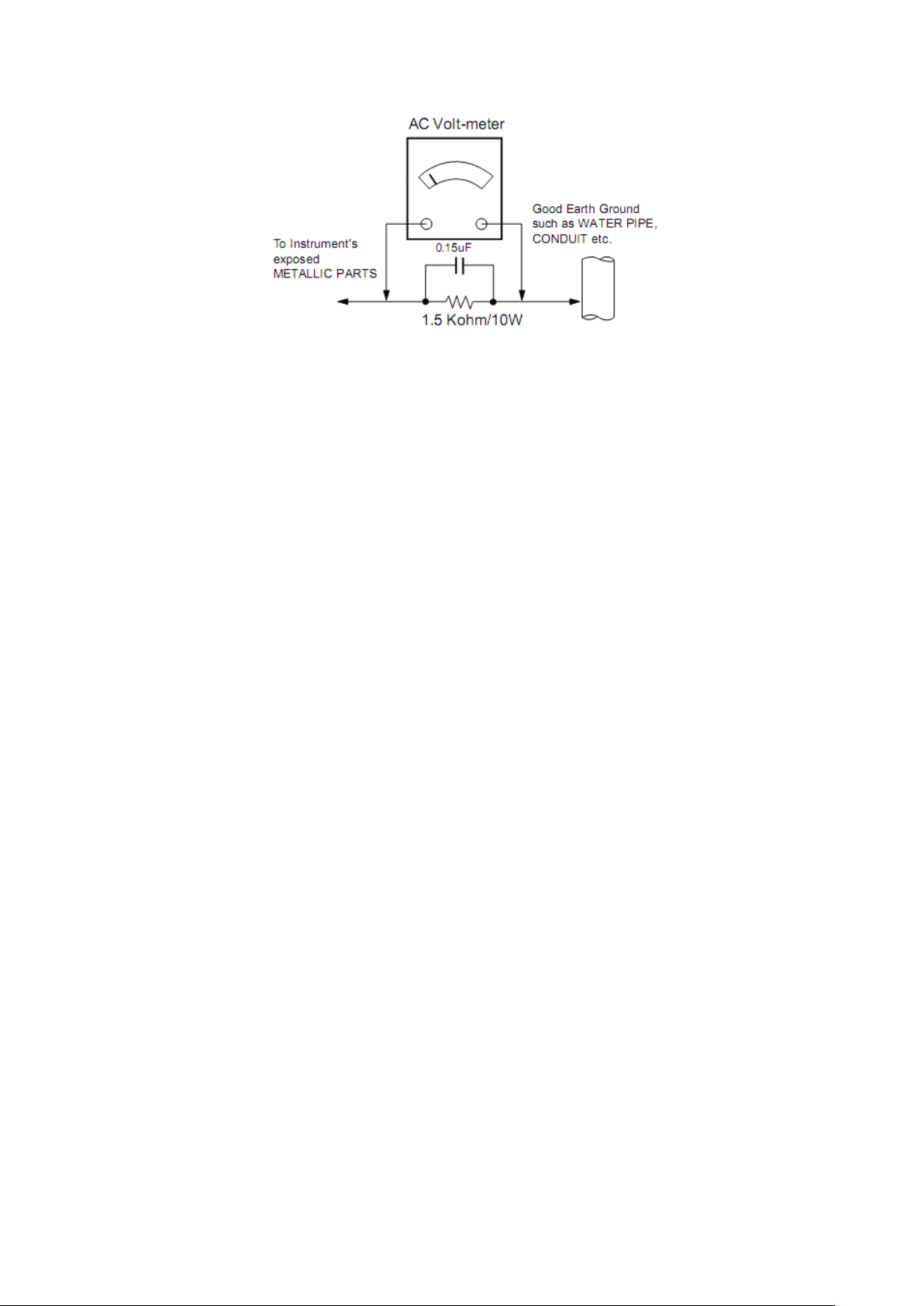
With the instrument AC plug removed from AC source, connect an electrical jumper across the two AC plug prongs. Place the
AC switch in the on position, connect one lead of ohm-meter to the AC plug prongs tied together and touch other ohm-meter lead
in turn to each exposed metallic parts such as antenna terminals, phone jacks, etc.
If the exposed metallic part has a return path to the chassis, the measured resistance should be between 1M Ω and 5.2M Ω .
When the exposed metal has no return path to the chassis the reading must be infinite.
An other abnormality exists that must be corrected before the receiver is returned to the customer.
Leakage
Leakage
Plug the AC cord directly into the AC outlet.
capacitor between a known good earth ground (Water Pipe, Conduit, etc.) and the exposed metallic parts.
voltage measured must not exceed 0.75 volt RMS which is corresponds to 0.5mA.
In case any measurement is out of the limits specified, there is possibility of shock hazard and the set must be checked and
repaired before it is returned to the customer.
Current
Current
Current Cold
Leakage
Leakage Current
Do not use a line Isolation Transformer during this check. Connect 1.5K/10watt resistor in parallel with a 0.15uF
Measure the AC voltage across the resistor using AC voltmeter with 1000 ohms/volt or more sensitivity.
Reverse plug the AC cord into the AC outlet and repeat AC voltage measurements for each exposed metallic part. Any
Cold
Cold
Cold Check(Antenna
Current
Current
Current Hot
Hot
Hot
Hot Check
Check(Antenna
Check(Antenna
Check(Antenna Cold
Check
Check
Check (See
(See
(See
(See below
Cold
Cold
Cold Check
below
below
below Figure)
Check
Check
Check
Figure)
Figure)
Figure)
Page 3
Leakage
Leakage
Leakage
Leakage Current
Current
Current
Current Hot
Hot
Check
Hot
Check
Hot Check
Check circuit
circuit
circuit
circuit
SERVICING
SERVICING
SERVICING
SERVICING PRECAUTIONS
CAUTION
CAUTION
CAUTION
CAUTION : Before servicing receivers covered by this service manual and its supplements and addenda, read and follow
SAFETY PRECAUTIONS on page 3 of this publication.
NOTE:
NOTE:
NOTE:
NOTE: If unforeseen circumstances create conflict between the following servicing precautions and any of the safety
precautions on page 3 of this publication, always follow the safety precautions. Remember: Safety First.
General
General
General
General Servicing
1. Always unplug the receiver AC power cord from the AC power source before;
a. Removing or reinstalling any component, circuit board module or any other receiver assembly.
b. Disconnecting or reconnecting any receiver electrical plug or other electrical connection.
c. Connecting a test substitute in parallel with an electrolytic capacitor in the receiver.
CAUTION
CAUTION
CAUTION
CAUTION : A wrong part substitution or incorrect polarity installation of electrolytic capacitors may result in an
explosion hazard.
2. Test high voltage only by measuring it with an appropriate high voltage meter or other voltage measuring device (DVM,
FETVOM , etc) equipped with a suitable high voltage probe. Do not test high voltage by "drawing an arc".
3. Do not spray chemicals on or near this receiver or any of its assemblies.
4. Unless specified otherwise in this service manual, clean electrical contacts only by applying the following mixture to the
contacts with a pipe cleaner, cotton-tipped stick or comparable non-abrasive applicator; 10% (by volume) Acetone and 90%
(by volume) isopropyl alcohol (90%-99% strength)
CAUTION
CAUTION
CAUTION
CAUTION : This is a flammable mixture.
Unless specified otherwise in this service manual, lubrication of contacts in not required.
5. Do not defeat any plug/socket B+ voltage interlocks with which receivers covered by this service manual might be
equipped.
6. Do not apply AC power to this instrument and/or any of its electrical assemblies unless all solid-state device heat sinks ar
correctly installed.
7. Always connect the test receiver ground lead to the receiver chassis ground before connecting the test receiver positive
lead.
Always remove the test receiver ground lead last.
8. Use with this receiver only the test fixtures specified in this service manual.
CAUTION:
CAUTION:
CAUTION:
CAUTION: Do not connect the test fixture ground strap to any heat sink in this receiver.
Servicing
Servicing
Servicing Precautions
Precautions
Precautions
Precautions
PRECAUTIONS
PRECAUTIONS
PRECAUTIONS
Electrostatically Sensitive (ES) Devices
Some semiconductor (solid-state) devices can be damaged easily by static electricity. Such components commonly are called
Electrostatically Sensitive (ES) Devices. Examples of typical ES devices are integrated circuits and some field-effect
transistors and semiconductor "chip" components. The following techniques should be used to help reduce the incidence of
component damage caused by static by static electricity.
Page 4

1. Immediately before handling any semiconductor component or semiconductor-equipped assembly, drain off any
electrostatic charge on your body by touching a known earth ground. Alternatively, obtain and wear a commercially available
discharging wrist strap device, which should be removed to prevent potential shock reasons prior to applying power to the unit
under test.
2. After removing an electrical assembly equipped with ES devices, place the assembly on a conductive surface such as
aluminum foil, to prevent electrostatic charge buildup or exposure of the assembly
3. Use only a grounded-tip soldering iron to solder or unsolder ES devices.
4. Use only an anti-static type solder removal device. Some solder removal devices not classified as "anti-static" can
generate electrical charges sufficient to damage ES devices.
5. Do not use freon-propelled chemicals. These can generate electrical charges sufficient to damage ES devices.
6. Do not remove a replacement ES device from its protective package until immediately before you are ready to install it.
(Most replacement ES devices are packaged with leads electrically shorted together by conductive foam, aluminum foil or
comparable conductive material).
7. Immediately before removing the protective material from the leads of a replacement ES device, touch the protective
material to the chassis or circuit assembly into which the device will be installed.
CAUTION
CAUTION
CAUTION
CAUTION : Be sure no power is applied to the chassis or circuit, and observe all other safety precautions.
8. Minimize bodily motions when handling unpackaged replacement ES devices. (Otherwise harmless motion such as the
brushing together of your clothes fabric or the lifting of your foot from a carpeted floor can generate static electricity sufficient
to damage an ES device.)
General
General
General
General Soldering
1. Use a grounded-tip, low-wattage soldering iron and appropriate tip size and shape that will maintain tip temperature within
the range or 500 ° F to 600 °
2. Use an appropriate gauge of RMA resin-core solder composed of 60 parts tin/40 parts lead.
3. Keep the soldering iron tip clean and well tinned.
4. Thoroughly clean the surfaces to be soldered. Use a mall wire-bristle (0.5 inch, or 1.25cm) brush with a metal handle.
Do not use freon-propelled spray-on cleaners.
5. Use the following unsoldering technique
a. Allow the soldering iron tip to reach normal temperature. (500 ° F to 600 ° F)
b. Heat the component lead until the solder melts.
c. Quickly draw the melted solder with an anti-static, suction-type solder removal device or with solder braid.
CAUTION
CAUTION
CAUTION
CAUTION : Work quickly to avoid overheating the circuit board printed foil.
6. Use the following soldering technique.
a. Allow the soldering iron tip to reach a normal temperature (500 ° F to 600 ° F)
b. First, hold the soldering iron tip and solder the strand against the component lead until the solder melts.
c. Quickly move the soldering iron tip to the junction of the component lead and the printed circuit foil, and hold it there only
until the solder flows onto and around both the component lead and the foil.
CAUTION
CAUTION
CAUTION
CAUTION : Work quickly to avoid overheating the circuit board printed foil.
d. Closely inspect the solder area and remove any excess or splashed solder with a small wire-bristle brush.
Soldering
Soldering
Soldering Guidelines
Guidelines
Guidelines
Guidelines
F.
IC
Remove/Replacement
IC
Remove/Replacement
IC
IC Remove/Replacement
Remove/Replacement
Some chassis circuit boards have slotted holes (oblong) through which the IC leads are inserted and then bent flat against the
circuit foil. When holes are the slotted type, the following technique should be used to remove and replace the IC. When working
with boards using the familiar round hole, use the standard technique as outlined in paragraphs 5 and 6 above.
Removal
Removal
Removal
Removal
1. Desolder and straighten each IC lead in one operation by gently prying up on the lead with the soldering iron tip as the solder
melts.
2. Draw away the melted solder with an anti-static suction-type solder removal device (or with solder braid) before removing the
IC.
Page 5

Replacement
Replacement
Replacement
Replacement
1. Carefully insert the replacement IC in the circuit board.
2. Carefully bend each IC lead against the circuit foil pad and solder it.
3. Clean the soldered areas with a small wire-bristle brush. (It is not necessary to reapply acrylic coating to the areas).
"Small-Signal" Discrete Transistor
Removal/Replacement
Removal/Replacement
Removal/Replacement
Removal/Replacement
1. Remove the defective transistor by clipping its leads as close as possible to the component body.
2. Bend into a "U" shape the end of each of three leads remaining on the circuit board.
3. Bend into a "U" shape the replacement transistor leads.
4. Connect the replacement transistor leads to the corresponding leads extending from the circuit board and crimp the "U" with
long nose pliers to insure metal to metal contact then solder each connection.
Power
Power
Power
Power Output,
Removal/Replacement
Removal/Replacement
Removal/Replacement
Removal/Replacement
1. Heat and remove all solder from around the transistor leads.
2. Remove the heat sink mounting screw (if so equipped).
3. Carefully remove the transistor from the heat sink of the circuit board.
4. Insert new transistor in the circuit board.
5. Solder each transistor lead, and clip off excess lead.
6. Replace heat sink.
Diode
Diode
Diode
Diode Removal/Replacement
1. Remove defective diode by clipping its leads as close as possible to diode body.
2. Bend the two remaining leads perpendicular y to the circuit board.
3. Observing diode polarity, wrap each lead of the new diode around the corresponding lead on the circuit board.
4. Securely crimp each connection and solder it.
5. Inspect (on the circuit board copper side) the solder joints of the two "original" leads. If they are not shiny, reheat them and if
necessary, apply additional solder.
Fuse
Fuse
Fuse
Fuse and
Removal/Replacement
Removal/Replacement
Removal/Replacement
Removal/Replacement
1. Clip each fuse or resistor lead at top of the circuit board hollow stake.
2. Securely crimp the leads of replacement component around notch at stake top.
3. Solder the connections.
CAUTION:
CAUTION:
CAUTION:
CAUTION: Maintain original spacing between the replaced component and adjacent components and the circuit board to
prevent excessive component temperatures.
Output,
Output,
Output, Transistor
Removal/Replacement
Removal/Replacement
Removal/Replacement
and
and
and Conventional
Transistor
Transistor
Transistor Device
Conventional
Conventional
Conventional Resistor
Device
Device
Device
Resistor
Resistor
Resistor
Circuit
Circuit
Circuit
Circuit Board
Excessive heat applied to the copper foil of any printed circuit board will weaken the adhesive that bonds the foil to the circuit
board causing the foil to separate from or "lift-off" the board. The following guidelines and procedures should be followed
whenever this condition is encountered.
At
At
At
At IC
To repair a defective copper pattern at IC connections use the following procedure to install a jumper wire on the copper pattern
side of the circuit board. (Use this technique only on IC connections).
1. Carefully remove the damaged copper pattern with a sharp knife. (Remove only as much copper as absolutely necessary).
2. carefully scratch away the solder resist and acrylic coating (if used) from the end of the remaining copper pattern.
3. Bend a small "U" in one end of a small gauge jumper wire and carefully crimp it around the IC pin. Solder the IC connection.
4. Route the jumper wire along the path of the out-away copper pattern and let it overlap the previously scraped end of the good
Board
Board
Board Foil
IC
Connections
IC
Connections
IC Connections
Connections
Foil
Foil
Foil Repair
Repair
Repair
Repair
Page 6

copper pattern. Solder the overlapped area and clip off any excess jumper wire.
At
Other
At
At
At Other
Use the following technique to repair the defective copper patternat connections other than IC Pins. This technique involves the
nstallation of a jumper wire on the component side of the circuit board.
1. Remove the defective copper pattern with a sharp knife. Remove at least 1/4 inch of copper, to ensure that a hazardous
condition will not exist if the jumper wire opens.
2. Trace along the copper pattern from both sides of the pattern break and locate the nearest component that is directly
connected to the affected copper pattern.
3. Connect insulated 20-gauge jumper wire from the lead of the nearest component on one side of the pattern break to the lead
of the nearest component on the other side. Carefully crimp and solder the connections.
CAUTION
CAUTION
CAUTION
CAUTION : Be sure the insulated jumper wire is dressed so the it does not touch components or sharp edges.
NOTE
NOTE
NOTE
NOTE : Specifications and others are subject to change without notice for improvement.
1. Application range
This specification is applied to the LCD TV used AS-MST6M181VS-LE1 chassis.
2. Requirement for Test
Each part is tested as below without special appointment.
1) Temperature : 25 ± 5 º C (77 ± 9 º F), CST : 40 ± 5 º C
2) Relative Humidity : 65 ± 10%
3) Power Voltage : Standard input voltage(100-240V~, 50/60Hz)
* Standard Voltage of each products is marked by models.
4) Specification and performance of each parts are followed each drawing and specification by part number in accordance with
BOM.
5) The receiver must be operated for about 20 minutes prior to the adjustment.
3. Test method
1) Performance: TV test method followed
2) Demanded other specification
- Safety: CB specification
- EMC: CISPR 13 specification
4.
4.
4.
4. General
Connections
Other
Connections
Other Connections
Connections
General
General
General specification
specification
specification
specification
SPECIFICATION
SPECIFICATION
SPECIFICATION
SPECIFICATION
Item Specification Remark
Broadcasting system PAL-BG
1) VHF : 00 ~ 12
Available Channel
Tuner IF
Input V oltage 100 - 240V~, 50/60Hz Mark : 240V, 50Hz
Screen Size 18.5 inch Wide (1366 x 768) LC185EXN-SCA1
Aspect Ratio 16:9
Module LC185EXN-SCA1 LC185EXN-SCA1
Operating Environment
Storage Environment
2) UHF : 20 ~ 75
3) CATV : 02 ~ 44
1)
PAL
: 38.90MHz(Picture)
34.40MHz(Sound)
1) Temp : 0 ~ 40 deg
2) Humidity : ~ 80 %
1) Temp : -20 ~ 60 deg
2) Humidity : ~ 85 %
Spec
Page 7
5.
Chrominance
5.
Chrominance
5.
5. Chrominance
Chrominance &
No Item Min Typ Max Unit Remark
1
White peak brightness
2 Contrast ratio cd/m2 N/A
3 Brightness uniformity 70 % Full white
4 Color coordinate
5 Color coordinate uniformity N/A
6 Color Gamut 68 %
7 Color Temperature 10000 K
6.
Component
6.
Component
6.
6. Component
Component Video
No
1 720x480 15.73 59.94 SDTV,DVD 480i
2 720x480 15.75 60 SDTV, DVD 480i
3 720x480 31.47 59.94 SDTV 480p
4 720X480 31.5 60 SDTV 480p
5 720x576 15.625 50 SDTV, DVD 576i
6 720x576 31.25 50 SDTV 576p
7 1280x720 44.96 59.94 HDTV 720p
8 1280x720 45 60.36 HDTV 720p
9 1280x720 37.5 50 HDTV 720p
10 1920x1080 28.125 50 HDTV 1080i
11 1920x1080 33.75 60 HDTV 1080i
12 1920x1080 33.72 59.94 HDTV 1080i
13 1920x1080 56.25 50 HDTV 1080p
14 1920x1080 67.433 59.94 HDTV 1080p
15 1920x1080 67.5 60 HDTV 1080p
7.
RGB
PC
7.
RGB
7.
7. RGB
RGB PC
No Resolution H-freq(kHz) V-freq.(Hz) Pixel clock(MHz) Proposed Remark
1 720*400 31.468 70.08 28.321
2
3
4 1024*768
5 1280*768 47.78 59.87 79.5 WXGA
6 1360*768 47.72 59.8 84.75 WXGA
INPUT
PC
INPUT
PC INPUT
INPUT Mode
640*480 31.469 59.94 25.17 VESA Input 848*480 60Hz,
852*480 37.684 75.00 31.50 --> 640*480 60Hz Display
800*600
&
Luminance
&
Luminance
& Luminance
Luminance Specification
Video
Input
Video
Input
Video Input
Input
Mode
Mode
Mode
Specification
Specification
Specification
240 300 cd/m2
RED
GREEN
BLUE
WHITE
(Y,
PB,
(Y,
(Y,
(Y,
37.879 60.31 40.00 VESA
46.875 75.00 49.50
48.363 60.00 65.00 VESA(XGA)
56.470 70.00 75.00
60.123 75.029 78.75
PR)
PB,
PR)
PB,
PB, PR)
PR)
Resolution H-freq(kHz) V-freq(Hz)
X
Y 0.344
X 0.327
Y 0.626
X 0.155
Y 0.042
X 0.279
Y 0.292
Typ..
-0.03
Specification
0.620
Typ..
+0.03
LC185EXN-SCA1
LC185EXN-SCA1
Remark
Page 8

7 1366*768 47.56 59.6 84.75 WXGA
8 1280*1024 63.595 60.0 108.875 SXGA
9 1920*1080 66.647 59.988 138.625 WUXGA
8.
HDMI
8.
HDMI
8.
8. HDMI
HDMI Input
No Resolution H-freq(kHz) V -freq.(Hz) Pixel clock(MHz) Proposed Remark
PC
PC
PC
PC
1 720*400 31.468 70.08 28.321 HDCP
2 640*480 31.469 59.94 25.17 VESA HDCP
3 800*600 37.879 60.31 40.00 VESA HDCP
4 1024*768
5 1280*768 47.78 59.87 79.5 WXGA HDCP
6 1360*768 47.72 59.8 84.75 WXGA HDCP
7 1366*768 47.56 59.6 84.75 WXGA HDCP
8 1280*1024 63.595 60.0 108.875 SXGA
9 1920*1080 66.647 59.988 138.625 WUXGA
DTV
DTV
DTV
DTV
10 720*480 31.47 59.94 27.00 SDTV 480P(4:3)
11 720*480 31.50 60 27.027 SDTV 480P(4:3)
12 720*480 31.47 59.94 27.000 SDTV 480P(16:9)
13 720*480 31.50 60.00 27.027 SDTV 480P(16:9)
14 720*576 31.25 50.00 27.000 SDTV 576P
15 1280*720 37.50 50.00 74.176 HDTV 720P HDCP
16 1280*720 44.96 59.94 74.176 HDTV 720P HDCP
17 1280*720 45.00 60.00 74.250 HDTV 720P
18 1920*1080 33.72 59.94 74.176 HDTV 1080I HDCP
19 1920*1080 33.75 60.00 74.250 HDTV 1080I HDCP
20 1920*1080 28.125 50.00 74.250 HDTV 1080I 50Hz HDCP
21 1920*1080 27.000 24.00 74.250 HDTV 1080P 24Hz HDCP
22 1920*1080 56.250 50 148.500 HDTV 1080P 50Hz HDCP
23 1920*1080 67.433 59.94 148.352 HDTV 1080P HDCP
24 1920*1080 67.500 60 148.500 HDTV 1080P HDCP
Input
(PC/DTV)
Input
(PC/DTV)
Input (PC/DTV)
(PC/DTV)
48.363 60.00 65.00 VESA(XGA) HDCP
56.470 70.00 75.00
Software
Software
Software
Software upgrade
1.
Application
1.
Application
1.
1. Application
Application Range
This specification sheet is applied to all of the LCD TV with AS-MST6M181VS-LE1 chassis.
2.
Designation
2.
Designation
2.
2. Designation
Designation
1) The adjustment is according to the order which is designated and which must be followed, according to the plan which can be
changed only on agreeing.
2) Power Adjustment: Free Voltage
3) Magnetic Field Condition: Nil.
4) Input signal Unit: Product Specification Standard
5) Reserve after operation: Above 5 Minutes (Heat Run)
Temperature : at 25 ± 5 º C
Relative humidity : 65 ± 10%
Input voltage : 220V , 60Hz
Range
Range
Range
upgrade
upgrade
upgrade
Page 9

* Download
1) Execute ISP program “ Mstar ISP Utility ” and then click “ Config ” tab.
2) Set as below, and then click “ Auto Detect ” and check “ OK ” message. If display “ Error ” , Check connect computer, jig,
and set.
3) Click “ Connect ” tab. If display “ Can ’ t ” , Check connect computer, jig, and set.
4) Click “ Read ” tab, and then load download file(XXXX.bin) by clicking “ Read ” .
5. Click “ Auto ” tab and set as below
6. Click “ Run ” .
7. After downloading, check “ OK ” message.
Page 10

Service Mode
How to enter into Service Mode.
The way to the factory mode menu:
Step 1: Enter to AV1 mode, using the Source button
Step 2: Press MENU button
Step 2: Input 710
Step 3: Press “OK”
System will be into the factory mode menu.
Page 11

1.
TV/CATV
1.
TV/CATV
1.
1. TV/CATV
TV/CATV doesn
Check TU1 Pin1 0,Pin11 (V IF ),
Can you see the normal signal?
doesn
doesn
doesn
YES
’
TROUBLESHOOTING
TROUBLESHOOTING
TROUBLESHOOTING
TROUBLESHOOTING
t
display
t
display
t
t display
display
You
should replace TUNER.
NO
Could you measure voltage of TU1 & IIC lines?
Are they all normal?
YES NO
You
should check power line & IIC lines.
Check the output of L32 .
Can you see the normal waveform?
YES
Check the output of Main IC( U12 ).
Especially you should check
The VIF and IIC.
Can you see the normal waveform?
YES
This board has big problem because Main
IC( U12 ) have some troubles.
After checking thoroughly all path once
again,
You
should decide to replace Main Board
or not.
NO
NO
You
should replace TUNER.
After checking the Power of Main IC( U12 )
you should decide to replace Main IC or
not.
Page 12

2.
AV
2.
2.
2.
doesn
AV
doesn
AV
AV
doesn
doesn
Check CN9,CN28 Can you see the normal
waveform?
t
display
t
display
t
t display
display
’
YES
NO
CN9,CN28 may have problem.
Replace this Jack .
Check the input of Main IC(U12)
Can you see the normal waveform?
YES
Check the output of Main IC(I U12 ).
Especially you should check
Can you see the normal waveform?
YES
This board has big problem because Main
IC( U12 ) have some troubles.
After checking thoroughly all path once
again,
You
should decide to replace Main
Board or not.
NO
NO
After checking the Power of Main
IC(U12)
After checking the Power of Main IC( U12 )
you should decide to replace Main IC or
not.
Page 13

3.
Component
3.
Component
3.
3. Component
Component doesn
doesn
doesn
doesn
t
display
t
display
t
t display
display
’
Check CN24 .
Can you see the normal waveform?
YES
Check the output of Main IC( U12 ).
Especially you should check
The H,V sync and clock. Can you see the
normal waveform?
YES
This board has big problem because Main
IC( U12 ) have some troubles.
After checking thoroughly all path once
again,
You
should decide to replace Main
Board or not.
NO
NO
CN24 may have problem. Replace this
Jack.
After checking the Power of Main IC( U12 )
you should decide to replace Main IC or
not.
Page 14

4.
RGB
4.
RGB
4.
4. RGB
RGB PC
PC
doesn
PC
doesn
PC doesn
doesn
t
display
t
display
t
t display
display
’
Check CN7 ,
Can you see the normal waveform?
YES
Check the input of RGB Video
switch( U10 ) ,Can you see the normal
waveform?
YES
Check the input of RGB switch( U10 ) ,Can
you see the normal waveform?
YES
NO
NO
NO
CN7 may have problem. Replace this
Jack.
After checking the Power of RGB Video
switch, you should decide to replace RGB
Video switch or not.
After checking the Power of RGB
switch you should decide to replace RGB
Audio switch or not.
Check the output of RGB
switch( U10 ) ,Can you see the normal
waveform?
YES
Check the output of Main IC( U10 ).
Especially you should check The H,V
sync and clock.
Can you see the normal waveform?
YES
This board has big problem because Main
IC( U12 ) have some troubles.
After checking thoroughly all path once
again,
You
should decide to replace Main
Board or not.
NO
NO
After checking the Power of RGB switch
you should decide to replace RGB Audio
switch or not.
After checking the Power of Main IC( U10 )
you should decide to replace Main IC or
not.
Page 15

5.
HDMI
5.
HDMI
5.
5. HDMI
HDMI doesn
doesn
doesn
doesn
t
display
t
display
t
t display
display
’
Check input connect CN4
Can you see the normal waveform?
YES
Check DDC communication lines( CN4 ,
Pin 15,16 )
YES
Check HDCP communication lines( U12 )
YES
Check the output of Main IC( U12 ).
Especially you should check The sync and
clock.Can you see the normal waveform?
NO
NO
NO
NO
CN4
may have problem. Replace this Jack.
After checking the Power of this chip, you
should decide to replace this or not.
After checking the Power of this chip, you
should decide to replace this or not.
After checking the Power of Main IC( U12 )
you should decide to replace Main IC or
not.
YES
This board has big problem because Main
IC( U12 ) have some troubles.
After checking thoroughly all path once
again,
You
should decide to replace Main
Board or not.
Page 16

SCHEMATIC
C96100PF
L129 FB/0603
VDDC-PIN86
R127 NC/0R
C2490.1uF/50V
+12V_PWR
L124FB/0603
C1310.1u
C3974.7u
C1350.1u
C1340.1u
C1360.1u
VDD33
C1420.1u
AVDD_PLL
AU33
350mA
Normal Pow er 3.3 V
Normal Pow er 3.3 V
Normal Pow er 3.3 V
Normal Pow er 3.3 V
C1230.1u
C4004.7u
C1520.1u
C1240.1u C 1530.1u
C1290.1u C 1490.1u
C1550.1u
C1500.1u
C1250.1u
C39810u
C1280.1u
C1560.1u
C1540.1u
C1510.1uC1220.1u
AVDD_DDR_2.5V
C40410u
C1270.1u
+2.5V_Normal
AVDD_DDR1_2.5V
STANDBY
C1160.1u
C1150.1u
L123 FB/0603
C1170.1u
C1300.1u
C4014.7u
AVDD_DMPLL
AVDD_DVI
C3964.7u
AVDD_ADC
+3.3V_Standby
STANDBY
C1090.1u
L119 FB/0603
C1030.1u
L127 FB/0603
L128 FB/0603
AU25
C1050.1u
AVDD25_DEMODADC2P5
C38110uF
ADJ
OUT
IN
OUT
U04 BM1117-3.3
321
4
100mA
+5V_Normal
400mA
ADJ
OUT
IN
OUT
U05 BM1117
321
4
R61470
C680.1u
C740.1u
R64470
C3924.7u
BL-ON/OFF
BL-ADJUST
+
CA16470uF/10V
+5V_Normal
DDR Power 2.5V
DDR Power 2.5V
DDR Power 2.5V
DDR Power 2.5V
L120FB/0603
L118 FB/0603
+2.5V_PGA
C1010.1u
U01 BM9435
S1
1
S2
2
S3
3
G2
4
D1
8
D1
7
D2
6
D2
5
+5V_Standby
C3884.7u
+
CA105100uF
C3854.7u
C510.1u
R343 1K
R274.7K
R341 2.7K
Q38
3904
1
2 3
PANEL-ON/OFF
R342 1K
PANEL-ON/OFF
R344 1K
+5V_Standby
PWR-ON/OFF
R304.7K
Q39
3904
1
2 3
AVSS_PGA
Standby Po wer 3. 3V
Standby Po wer 3. 3V
Standby Po wer 3. 3V
Standby Po wer 3. 3V
AVSS_PGA
C540. 1uF
ADJ
OUT
IN
OUT
U06 BM1117-3.3
321
4
C590. 1uF
C470. 1uF
C3862.2u C 3914.7u
C2470.1uF/50V
R309 0
+5V_Standby
R363100K
D6733V
33V
Tuner+40V_PWM2
+5V_Normal
+3.3V_Normal
WARNING !!!
WARNING !!!
WARNING !!!
WARNING !!!
R310 4.7K
D31 1N4148R65 10R
+
CA25NC/2.2uF/50V
40V
L115 220uH
Q44
2SC1815
+12V_NORMAL
C197 0.1uF
C183 0.1uF
C185 0.1uF
+5V_Standby
C186NC R177 NC
+
CA47 470uF
R181 36K R244 10K
+
CA19 470uF/10V
C187 0.1uF
C188 0.1uF
C275 0.01uF
C189 NC
U03FR9888
BS
1
VI
2
SW
3
G
4
FB5COMP6EN7N/C
8
R245 100K
+12V_PWR
L33 18uH/4A
1 2
R248 12K/1%
DC TO DC
DC TO DC
DC TO DC
DC TO DC
L117 FB/0603
C3994.7u
C990.1u
C3954. 7u
C98100PF
C91100PF
C90100PF
C95100PF
VDDC
AVDD1P2
DVDD_DDR_1.2V
L121 FB/0603
AVDD2P5_MOD
C1020.1u
C1100.1u
Normal Pow er 1.2 V
Normal Pow er 1.2 V
Normal Pow er 1.2 V
Normal Pow er 1.2 V
L4018or10uH/2A
12
C1580.1u
R104 12K_1%
R10215K_1%
+
CA103100uF
+
CA104470uF/10V
R118 100K
+5V_Normal
U02 FP6161
IN
4
GND2FB
5
SW
3
EN
1
+1.2V_VDDC
600mA
STANDBY
CN15 12p/2.0
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
BL-ADJUST
BL-ON/OFF
STANDBY
R106 1K
R128 750K
R107 1K
R130100K
R131 100K
C40. 1uF
R13247K
Q4
3904
1
2 3
C51u
Q50 AO3401A
+12V_NORMAL
+12V_PWR
Q3
3904
1
2 3
+5V_Normal+5V_Standby
C2480.1uF/50V
SCHEMATIC
SCHEMATIC
SCHEMATIC DIAGRAM
DIAGRAM
DIAGRAM
DIAGRAM
Page 17

VIFP
VIFM
AV-AUOUTL3
RGB0_Pb+
RGB0_Pr+
RGB0_Y+
RGB0_Y-SOG
VGA_HS
VGA_VS
VGA_HS
VGA_VS
RGB0_Pb+
RGB0_Y-SOG
RGB0_Y+
RGB0_Pr+
AMP-MUTE
PC-Rin
PC-Lin
AV3-in
AV2-in
PC-Lin
CVBS_OUT0
CVBS_OUT0
AV2-in
PC-Rin
AV3-in
IRIN
AV2_Rin
AV2_Lin
AV3_Lin
AV3_Rin
AV2_Rin
AV2_Lin
AV3_Lin
AV3_Rin
AV1-Lin
AV1-Rin
AV1-Lin
AV1-Rin
USB2_DM
A-MADR0
A-MADR1
A-MADR2
A-MADR3
A-MADR4
A-MADR5
A-MADR6
A-MADR7
A-MADR8
A-MADR9
A-MADR11
A-MADR12A_MAD R12
A-MADR12
A-MADR10
WEZM0
UDM0A_MD QMU
UDQSA_MDQSU
LDM0A_MDQML
LDQSA_MDQSL
A-MADR7A_MAD R7
MBA0A-MBADR0
A-MADR5A_MAD R5
A-MADR6A_MAD R6
A-MADR1A_MAD R1
A-MADR3A_MAD R3
A-MADR4A_MAD R4
A-MADR8A_MAD R8
A-MADR2A_MAD R2
A-MADR9A_MAD R9
WEZM0A-MW EZ
CASZM0A-MCASZ
A-MADR0A_MAD R0
A-MADR11A_MAD R11
RASZM0A-MRASZ
CASZM0
A-MADR10A_MAD R10
MBA1A-MBADR1
RASZM0
MBA0
UART-TX
LDQS
LDM0
UDM0
UDQS
UART-RX
MBA1
UART-TX
UART-RX
AV_AUOUTL3
AV_AUOUTR3
AV2_Rin
LED
AUR4
AV2_Lin AUL4
TUNER_SCL
RXE0+
RXOC-
RXO2+
RXO3-
RXOC+
RXO3+
RXE0-
RXO2-
RXO0+
RXO0-
RXO1+
RXO1-
HDMI1-CLKN
HDMI1-CLKP
HDMI1-SCL
HDMI1-RX1N
HDMI1-RX1P
HDMI1-RX2N
HDMI1-RX2P
HDMI1-RX0N
HDMI1-RX0P
HDMI1-SDA
AMP-AUOUTR0
XTALO
XTALI
AUBCK_OUT
AV3_Lin
SPDIF_OUT
PANEL_ON/O FF
PANEL_ON/O FF
HD-SW
Tuner+40V_PWM3
HD-SW
SPDIF_OUT
Tuner+40V_PWM2
XTALI
XTALO
AUMCK_OUT
AUBCK_OUT
DVD_ON/OFF
USB2_DP
AVSS_PGA
AVSS_PGA
PC-Lin
PC-Rin AUR0
AUL0
AUR1
AUL1
AV-AUOUTR3
AMP-AUOUTR0
AMP-AUOUTL0
AV-AUOUTL3
AUMCK_OUT
AV2-in
AV3-in
AV1-in
CVBS1P
CVBS2P
VCOM0
CVBS0P
C1191u
C761u
BRI_ADJ-PWM 0
BRI_ADJ-PWM 0
AMP-AUOUTL0
FLASH_CS0N
FLASH_WP0N
SPI_Flash-SDI
SPI_Flash-SDO
AMP_AUOUTR0
AV3_Rin
SPI_Flash-SCK
SPDIF_OUT
HDMI_HP1
KEY0-SAR0
KEY1-SAR1
KEY0-SAR0
KEY1-SAR1
LED
IRIN
LED
IRIN
PANEL_ON/OFF
AGC
CFG-PWM 1
BRI_ADJ-PWM 0
AV_AUOUTR3
AV_AUOUTL3
AMP_AUOUTR0
AMP_AUOUTL0
AV_AUOUTL3
AMP_AUOUTR0
AMP_AUOUTL0
AV_AUOUTR3
DVD_IR
ARC
CFG-PWM 1
AMP_AUOUTL0
R108200 K
C2122 . 2u
R121 68R
C10422n
C71 47n
C1660. 1u
C75 1n
R205 4.7 K
C147 33p
R83 4.7K
TAGC
TAGC
Q17
3906
1
3 2
R89 68R C56 47n
C85 47n
R29710K
C82 47n
C84 47n
R124200 K
C1000. 1u
R122 68R
R2074.7K
R92 4.7K
C53 2.2u
C1110 . 1u
R1714.7K
C80 47n
C83 47n/NC
C50 47n
C73 47n
R20422K
R1634.7K
4'h0
4'h0
4'h0
4'h0
4'h3
4'h3
4'h3
4'h3
4'h7
4'h7
4'h7
4'h7
R459100
R1594.7K
C37910u
C79 47n
R45768R
R11510K
HDMI-CEC
UART-RX
RXO0RXO1-
SC_FS
RXO2RXOCRXO3RXE0-
C1121u
R28 1K
RXE1RXE2RXECRXE3RXO0+
RXO1+
SPI-SCK SPI_Flash-SCK
PWR-ON/OFF
SPI_WP0N
SPI-CS0N SPI_ CS0N
SPI-SDI SPI_Flash-SD I
RXO2+
RXOC+
RXO3+
RXE0+
UART-TX
KEY0-SAR0
KEY1-SAR1
SPI-SDO SPI_Flash-SD O
RXE1+
RXE2+
RXEC+
RXE3+
RXO0RXO1RXO2-
R1704.7K
R153NC/10K
RXOCRXO3RXE0-
RXE3-
C1591n
RXEC-
RXE2-
RXE1-
RXE3+
R1160 4.7K
RXE2+
RXEC+
RXE0+
RXE1+
RXOC+
RXO3+
RXO0+
RXO1+
RXO2+
Close to IC
Close to IC
Close to IC
Close to IC
with width trace
with width trace
with width trace
with width trace
C1650. 1u
AUVRP
AUVAG
AUVRM
C55 1n
R33200K
C86 47n
C87 47n
C38010u
Y124MHz
1 2
3
R29 NC/33R
C48220 p C45220p
R1574.7K
C52 47n
D54
BAV99
3
2
1
C401u
C391u
C70220 p
C351u
RGB0_Pb+
C381u
RGB0_Y+
RGB0_Y-SOG
RGB0_Pr+
R45868R
BIN0
GIN0M
GIN0P
SOGIN0
VGA_HS
VGA_VS
RIN0
MST6M181 VS
MST6M181 VS
MST6M181 VS
MST6M181 VS
U12
RESET
3
HOTPLUGA
4
RXCN
5
RXCP
6
RX0N
7
RX0P
8
AVDD_DVI_3.3V
9
RX1N
10
RX1P
11
DDCDA_DA
12
RX2N
13
RX2P
14
DDCDA_CK
15
ARC
16
NC
17
NC
18
NC
19
NC
20
NC
21
NC
22
NC
23
VDDC
24
HSYNC0
25
BIN0P
26
SOGIN0
27
GIN0P
28
GIN0M
29
RIN0P
30
VSYNC0
31
AVDD1P2
32
AVDD2P5_ADC
33
BIN1P
34
SOGIN1
35
GIN1P
36
GIN1M
37
RIN1P
38
AVDD3P3_ADC
39
CVBS4
40
CVBS3
41
CVBS2
42
CVBS1
43
CVBS0
44
VCOM
45
CVBS_OUT1
46
LINEIN_L0
47
LINEIN_R 0
48
LINEIN_L1
49
LINEIN_R 1
50
VRM
51
VRP
52
VAG
53
AVDD_AU25
54
LINEIN_L355LINEIN_R356LINEIN_L457LINEIN_R458LINEIN_L559LINEIN_R560AVDD_AU3361LINEOUT_L362LINEOUT_R363LINEOUT_L064LINEOUT_R065NC66NC67NC68XTAL_IN69XTAL_OUT70AVDD_DMPLL71AVDD25_REF72AVSS_PGA73VIFM74VIFP75AVDD25_PGA76SIFP77SIFM78TAGC79GPIO22/I2S_OUT_WS/RX280GPIO23/I2S_OUT_SD/TX281GPIO24/TUNER_SCL82GPIO25/TUNER_SDA83GPIO26/SPDIF_IN/RX1/PWM384GPIO27/SPDIF_OUT85VDDC86VDDP_187GPIO2888GPIO30/I2S_OUT_MCK89GPIO32/I2S_OUT_BCK90GPIO3691GPIO3792GPIO3893GPIO4594GPIO4795GPIO4996NC97B_ODD0/RXE4+98B_ODD1/RXE4-99B_ODD2/RXE3+
100
B_ODD3/RXE3-
101
B_ODD4/RXEC+
102
B_ODD5/RXEC-
103
B_ODD6/RXE2+
104
B_ODD7/RXE2-
105
G_ODD0 /RXE1+
106
G_ODD1 /RXE1-
107
AVDD2P5_MOD
108
G_ODD2/R XE0+
109
G_ODD3/R XE0-
110
G_ODD4/R XO4+
111
G_ODD5/R XO4-
112
G_ODD6/R XO3+
113
G_ODD7/R XO3-
114
R_ODD0/RXOC+
115
R_ODD1/RXOC-
116
R_ODD2/RXO2+
117
R_ODD3/RXO2-
118
R_ODD4/RXO1+
119
R_ODD5/RXO1-
120
R_ODD6/RXO0+
121
R_ODD7/RXO0-
122
VDDC
123
AVDD2P5_MOD
124
AVDD_LPLL
125
GPIO74/I2S_IN _WS/PWM4/R X3/LCK
126
GPIO75/I2S_IN _SD/PWM5/TX3/LD E
127
GPIO76/I2S_IN _BCK/PWM2/LHSYNC
128
GPIO77/I2S_OUT_M UTE/PWM3/LVSYNC
129
VDDP_2
130
GPIO20/PWM0
131
GPIO21/PWM1
132
VDDC
133
NC
134
NC
135
A_DDR1_A3
136
A_DDR1_A2
137
A_DDR1_A1
138
A_DDR1_A0
139
A_DDR1_A10
140
A_DDR1_BA1
141
AVDDIO_2.5V
142
A_DDR1_BA0
143
A_DDR1_RAS
144
A_DDR1_CAS
145
A_DDR1_WEZ
146
A_DDR1_DQ0
147
AVDDIO_2.5V
148
A_DDR1_DQ1
149
A_DDR1_DQ2
150
A_DDR1_DQ3
151
A_DDR1_DQ4
152
AVDDIO_2.5V
153
A_DDR1_DQ5
154
A_DDR1_DQ6
155
A_DDR1_DQ7
156
NC
157
NC
158
AVDDIO_2.5V
159
LDQS0
160
LDQM0
161
DVDD_DDR_1.2V
162
AVDD_PLL
163
UDQM0
164
UDQS0
165
A_DDR1_DQ8
166
A_DDR1_DQ9
167
AVDDIO_2.5V
168
A_DDR1_DQ1 0
169
A_DDR1_DQ1 1
170
A_DDR1_DQ1 2
171
A_DDR1_DQ1 3
172
A_MVREF
173
A_DDR1_DQ1 4
174
AVDDIO_2.5V
175
A_DDR1_DQ1 5
176
A_DDR1_MCL KZ
177
AVDDIO_2.5V
178
A_DDR1_MCL K
179
NC
180
A_DDR1_CKE
181
A_DDR1_A12
182
A_DDR1_A11
183
A_DDR1_A9
184
AVDDIO_2.5V
185
A_DDR1_A8
186
A_DDR1_A7
187
A_DDR1_A6
188
A_DDR1_A5
189
A_DDR1_A4
190
VDDC
191
DDCR_DA
192
VDDP_3
193
DDCR_CK
194
TESTPIN
195
DM_P0
196
DP_P0
197
AVDD_NODIE
200
DVDD_NODIE
201
GND_EFUSE
202
SPI_CK
203
SPI_DI
204
SPI_DO
205
SPI_CZ
206
GPIO11/SAR0
207
GPIO12/SAR1
208
GPIO13/SAR2
209
GPIO10/PMGPIO
210
DDCA_CK
211
DDCA_DA
212
GPIO6/PM1/TX
213
GPIO7/PM4/POWER_ON
214
GPIO8/PM5/RX
215
GPIO9/PM6/CS1
216
IRIN
1
CEC
2
E-pad
217
DP_P1
199
DM_P1
198
C2132. 2u
C57 47n
SPI_WP0N
R261M
R59200K
R15510K
R1161 4.7K
U08
EN25Q32_100 HIP
CE#
1
SO
2
WP#
3
VSS4SI
5
SCK
6
HOLD#
7
VDD
8
R1841M
FB6FB/0603
C691u
C1181u
DVD_ON/OFF
C77220p
R1561K
BRI_ADJ-PWM 0
CVBS3P
CVBS4P
C721u
C144 33p
R1494.7K
A_MDQSL
A_MDQML
A-MCASZ
A_MADR2
A_MADR0
A_MADR10
VIFM
VIFP
VIFM
A_MADR1
A_MADR3
A_MDATA4
A_MDATA1
AVSS_PGA
+3.3V_Standby
+5V_Standby
VIFP
A_MDATA0
A_MDATA5
A_MDATA3
A_MDATA2
A_MDATA7
+5V_Normal
+5V_Standby
A_MDATA6
A-MWEZ
A-MRASZ
A-MBADR0
A-MBADR1
+5V_Normal
AU25
AU33
AGC
AVDD_DDR_2.5V
AVDD_DDR_2.5V
AVDD_DDR_2.5V
DVDD_DDR_1.2V
AVDD_DDR_2.5V
AVDD_DDR_2.5V
AVDD_DDR_2.5V
AVDD_DDR_2.5V
AVDD_DDR_2.5V
AVDD_PLL
AVDD_DVI
VDDC
AVDD1P2
AVDD_ADC
ADC2P5
AVDD2P5_MOD
AVDD25_DEMOD
VDDC-PIN86
+2.5V_PGA
VDD33
AVDD_DMPLL
VDDC
UART-RX
UART-TX
VDD33
AVDD2P5_MOD
AVDD_PLL
VDDC
VDD33
VDDC
AVDD_DVI
+3.3V_Norm al
System-RST
USB0_DM
USB0_DP
Tuner+40V_PWM2
DVD_IR
DVD_ON/OFF
DVD_IR
TUNER_SDA
TUNER_SCL
DVD_ON/OFF
TUNER_SDA
TUNER_SCL
TUNER_SDA
AV1-in
RGB2-HDTV_BIN
RGB2-HDTV_SOGIN
RGB2-HDTV_GIN
RGB2-HDTV_RIN
RGB2-HDTV_SOGIN
RGB2-HDTV_GIN
RGB2-HDTV_RIN
RGB2-HDTV_BIN
AV1-in
System-RST
AV-AUOUTR3
RGB2-HDTV_SOGIN
RGB2-HDTV_GIN
RGB2-HDTV_RIN
A_MCLK
A_MCLKZ
A_MDQMU
A_MDQSU
A_MADR5
A_MDATA8
A_MADR7
A_MADR11
A_MADR9
A_MADR8
A_MADR6
A_MDATA9
A_MDATA11
A_MDATA10
A_MDATA12
RGB2-HDTV_BIN
RIN2
A_MDATA13
A_MDATA14
A_MDATA15
A_MADR12
A-MCKE
SOGIN2
GIN2P
GIN2M
BIN2
A_MADR4
{I2S_OU T_BCK , I2S_O UT_MC K, PAD_P WM1, PAD_P WM0}
{I2S_OU T_BCK , I2S_O UT_MC K, PAD_P WM1, PAD_P WM0}
{I2S_OU T_BCK , I2S_O UT_MC K, PAD_P WM1, PAD_P WM0}
{I2S_OU T_BCK , I2S_O UT_MC K, PAD_P WM1, PAD_P WM0}
B51_no_ EJ
B51_no_ EJ
B51_no_ EJ
B51_no_ EJ
B51_Sec ure_n o_scram ble
B51_Sec ure_n o_scram ble
B51_Sec ure_n o_scram ble
B51_Sec ure_n o_scram ble
B51_Sec ure_s cramble
B51_Sec ure_s cramble
B51_Sec ure_s cramble
B51_Sec ure_s cramble
A_MCLKZC LKN0
A_MCLKCLK0
A-MCKE
A_MDATA2
DVD_IR
A_MDATA3
A_MDATA4
A_MDATA5
A_MDATA6
A_MDATA7
A_MDATA8
A_MDATA9
A_MDATA10
A_MDATA11
A_MDATA12
A_MDATA13
A_MDATA14
A_MDATA15
A-MVREF
A_MCLKZ
A_MCLK
A_MDATA3DATA3
A_MDATA2DATA2
A_MDATA1DATA1
A_MDATA7DATA7
A_MDATA0DATA0
A_MDATA6DATA6
A_MDATA5DATA5
A_MDATA4DATA4
A-MVREF
A_MDATA8DATA8
A_MDATA12DATA12
A_MDATA15DATA15
A_MDATA14DATA14
A_MDATA13DATA13
A_MDATA11DATA11
A_MDATA10DATA10
A_MDATA9DATA9
A-MCKE
A_MDATA0
A_MDATA1
SPI_CS0N
TAGC
CVBS_OUT0
AMP-MUTE
USB2_DM
USB2_DP
AV1-Lin
SC_FS
PWR-ON / OFF
VBL_CTRL
USB2_D+
AV1-Rin
USB0_DP
USB0_DM
USB2_DUSB1_D+
USB1_D-
VBL_CTRL
AMP-MUTE
PWR-ON / OFF
SC_FS
RXEC-
RXE3+
RXE1-
RXE2-
RXEC+
RXE1+
RXE2+
RXE3-
TUNER_SCL
TUNER_SDA
HDMI1-CLKN
HDMI1-CLKP
HDMI1-SCL
HDMI1-RX1N
HDMI1-RX1P
HDMI1-RX2N
HDMI1-RX2P
HDMI1-RX0N
HDMI1-RX0P
HDMI1-SDA
HDMI_HP1
ARC
HDMI-CEC
HDMI-CEC
HDMI1-RX2P
HDMI1-RX2N
HDMI1-RX1P
HDMI1-RX1N
HDMI1-RX0P
HDMI1-RX0N
HDMI1-CLKP
HDMI1-CLKN
HDMI1-SCL
HDMI1-SDA
HDMI_HP1
ARC
HD-SW
VBL_CTRL
Page 18

+5V_USB1
+5V_USB1
+5V_USB1
USB1_DUSB1_D+
USB2_DUSB2_D+
+5V_USB1
NC/100uF
C92
CN5
1
1 VCC
2
2 D-
3
3 D+
4
4 GND
5
SHIELD
6
SHIELD
USB_4P
CN6
1
1
2
2
3
3
4
4
4p/2.0
USB1_DUSB1_D+
USB2_DUSB2_D+
DDR-SDRAM DATA[15:0]
DDR-SDRAM DATA[15:0]
DDR-SDRAM DATA[15:0]
DDR-SDRAM DATA[15:0]
A-MAD R0A_MADR0
A-MAD R1A_MADR1
A-MAD R2A_MADR2
A-MAD R3A_MADR3
A-MAD R4A_MADR4
A-MAD R5A_MADR5
A-MAD R6A_MADR6
A-MAD R7A_MADR7
A-MAD R8A_MADR8
A-MAD R9A_MADR9
A-MAD R11A_MADR11
A-MAD R12A_MADR12
A-MAD R10A_MADR10
WEZM0A-MWEZ
CASZM0A-MCA SZ
RASZM0A-MRA SZ
MBA0A-MBA DR0
LDQSA_MD QSL
LDM0A_MDQ ML
UDM0A_MDQMU
UDQSA_MDQ SU
MBA1A-MBA DR1
A-MAD R0A_MADR0
A-MAD R1A_MADR1
A-MAD R2A_MADR2
A-MAD R3A_MADR3
A-MAD R4A_MADR4
A-MAD R5A_MADR5
A-MAD R6A_MADR6
A-MAD R7A_MADR7
A-MAD R8A_MADR8
A-MAD R9A_MADR9
A-MAD R11A_MADR11
A-MAD R12A_MADR12
A-MAD R10A_MADR10
WEZM0A-MWEZ
CASZM0A-MCA SZ
RASZM0A-MRA SZ
MBA0A-MBA DR0
LDQSA_MD QSL
LDM0A_MDQ ML
UDM0A_MDQMU
UDQSA_MDQ SU
MBA1A-MBA DR1
U09
29
A0
30
A1
31
A2
32
A3
35
A4
36
A5
37
A6
38
A7
39
A8
40
A9
41
A11
42
A12
28
A10/AP
21
WE
22
CAS
23
RAS
26
BA0
16
LDQS
20
LDM
47
UDM
51
UDQS
27
BA1
24
CS
14
NC
17
NC
34
VSS
48
VSS
66
VSS
6
VSSQ
12
VSSQ
52
VSSQ
58
VSSQ
64
VSSQ
4M X 16bit X 4BK
4M X 16bit X 4BK
4M X 16bit X 4BK
4M X 16bit X 4BK
ESMT-M13 S2561616A-4TG
NAYAN NT 5DS16M16DS -4T
NAYAN NT 5DS16M16DS -4T
NAYAN NT 5DS16M16DS -4T
NAYAN NT 5DS16M16DS -4T
A-MAD R0
A-MAD R1
A-MAD R2
A-MAD R3
A-MAD R4
A-MAD R5
A-MAD R6
A-MAD R7
A-MAD R8
A-MAD R9
A-MAD R11
A-MAD R12
A-MAD R10
WEZM0
CASZM0
RASZM0
MBA0
LDQS
LDM0
UDM0
UDQS
MBA1
2
DQ0
4
DQ1
5
DQ2
7
DQ3
8
DQ4
10
DQ5
11
DQ6
13
DQ7
54
DQ8
56
DQ9
57
DQ10
59
DQ11
60
DQ12
62
DQ13
63
DQ14
65
DQ15
49
VREF
46
CLK
45
CLK
44
CKE
19
NC
25
NC
43
NC
50
NC
53
NC
1
MVDD
18
MVDD
33
MVDD
3
VDDQ
9
VDDQ
15
VDDQ
55
VDDQ
61
VDDQ
A-MVR EF
A-MCK E
A_MDATA0 DATA 0
A_MDATA1 DATA 1
A_MDATA2 DATA 2
A_MDATA3 DATA 3
A_MDATA4 DATA 4
A_MDATA5 DATA 5
A_MDATA6 DATA 6
A_MDATA7 DATA 7
A_MDATA8 DATA 8
A_MDATA9 DATA 9
A_MDATA1 0 DAT A10
A_MDATA1 1 DAT A11
A_MDATA1 2 DAT A12
A_MDATA1 3 DAT A13
A_MDATA1 4 DAT A14
A_MDATA1 5 DAT A15
A-MVR EF
A_MCLK ZCLKN0
MCKE
R1156 0R
R1162 220
A_MCLKCLK0
A-MCK EMCKE
USE NANYA NT5D S16M16DS-4T:R1 156 NC,R1162 2 00ohm.
USE other DDR: R1156 0ohm,R11 62 NC.
AVDD_DDR 1_2.5V
A_MDATA0 DATA 0
A_MDATA1 DATA 1
A_MDATA2 DATA 2
A_MDATA3 DATA 3
A_MDATA4 DATA 4
A_MDATA5 DATA 5
A_MDATA6 DATA 6
A_MDATA7 DATA 7
A_MDATA8 DATA 8
A_MDATA9 DATA 9
A_MDATA1 0 DAT A10
A_MDATA1 1 DAT A11
A_MDATA1 2 DAT A12
A_MDATA1 3 DAT A13
A_MDATA1 4 DAT A14
A_MDATA1 5 DAT A15
A_MCLK Z CLKN 0
A_MCLKCLK0
A_MDATA0
A_MDATA1
A_MDATA2
A_MDATA3
A_MDATA4
A_MDATA5
A_MDATA6
A_MDATA7
A_MDATA8
A_MDATA9
A_MDATA1 0
A_MDATA1 1
A_MDATA1 2
A_MDATA1 3
A_MDATA1 4
A_MDATA1 5
A-MVR EF
A_MCLK Z
A_MCLK
A-MCK E
AVDD_DDR 1_2.5V
R1981K_1 %
A-MVR EF
R2021K_1%
AVDD_DDR 1_2.5V
C1480.1u
+5V_Normal
+5V_Normal
+5V_Normal
+5V_Normal
USB1_D1-_i n
USB1_D1+_in
USB2_D1-_i n
USB2_D1+_in
+5V_USB1
D139NC
1 2
D141NC
1 2
+5V_USB1
1 2
1 2
L21 R56
R38 5.1R
R39 5.1R
D140NC
R36 5.1R
R37 5.1R
D142NC
USB2_D1-_i n
USB2_D1+_in
C93 10u
USB1_D1+_in
USB1_D1-_i n
TU1
ET-6N1E-CF101R
AGC1NC12AS3SCL4SDA55VA65VB7NC3833V9NC410IFout
AS
R306
TUAGC
TU_SCL
TU_SDA
68R
TU3
GND
GND
GND
GND
NC
VCC
SCL
SDA
GND
CLK_OUT
IF_OUT
IF_OUT
IF_AGC
14
GND1
15
GND4
13
GND2
12
GND3
11
IF-IN-
C3570.1u
C355 33R
C369 51R
L32100nH_10%_Q>15
C359220p
C358 0.1u
Q :15(MIN)
VIFM
VIFM
C350=220P,FOR 38.9MHZ OR 38MHZ(PAL)
IF-IN+
IF-IN-
33V
+5V_Tuner
BPF_IN
BPF_IN
BPF_IN
BPF_IN
IF-IN+
C3650.1u
C361 33R
BPF FOR 3 8.9MHz OR 38MHZ
TUNER AGC,Close TUNER
TUAGC TAGC
TU_SDA TUNER_SDA
TU_SCL
13
12
11
10
9
8
TU_SCL
7
TU_SDA
6
5
4
IF-IN-
3
IF-IN+
2
TUAGC
1
+5V_Tuner
+5V_Normal
U24 N C/BM1117-3.3
IN
321
C2454.7u
R291 100R
R299 68R
R307 68R
C23933p
C23733p
C2400.1u
OUT
OUT
ADJ
4
+
C2430.1u
C2440.1u
CA21470uF/10V
TUNER_SCL
+5V_Tuner
TAGC
TUNER_SDA
TUNER_SCL
+12V_NORMAL
+5V_Normal
C359=120P,FOR 45.75MHZ(NTSC)
C366 51R
L116 N C/100uH
C363 0.1u
U13
BM78M05
IN
VIFP
GND
OUT
+5V_Tuner
231
C2420.1u
VIFP
NC/CDT-3NP3I1-00
Page 19

HDMI1-RX2HDMI1-RX1+
HDMI1-RX1+
HDMI1-RX2-
HDMI1-SCL
HDMI1-RX1-
HDMI1-RX0+
HDMI1-RX0-
HDMI1-RXC+
HDMI1-RXC-
HDMI_HP1
HDMI1-DDC-SDA HDMI1-SDA
HDMI1-DDC-SCL
HDMI_HP1
HDMI1-RX1-
HDMI-CECCEC
HDMI1-RX1P
HDMI1-RX2N
HDMI1-RX1N
HDMI1-RX0P
HDMI1-RX0N
HDMI1-CLKP
HDMI1-CLKN
HDMI1-RX2P
HDMI1-HPD
HDMI1-RX2+
HDMI1-RX0+
CEC
HDMI1-RX0HDMI1-RXC+
HDMI1-RXC-
ARC
ARC
HDMI1-SCL
HDMI1-SDA
R674 220R
R94 22R
R675 10R
R8110K
C89 47n
Q29
3904
1
2 3
R8510K
R8410K
R109 4.7K
R110 22R
R676 10R
R861K
CN4
HDMI_J
DATA2+
1
DATA2 SHIELD
2
DATA2-
3
DATA1+
4
DATA1 SHIELD
5
DAT1A-
6
DATA0+
7
8
DATA0 SHIELD
DATA0-
9
CLK+
10
CLK SHIELD
11
CLK-
12
CEC
13
NC
14
SCL
15
SDA
16
DDC/CEC GND
17
+5V POWER
18
HOT PLUG
19
20
GND1
21
GND2
22
GND3
23
GND4
HDMI1/5V
R677 10R
HDMI1-RX2P
HDMI1-RX2N
HDMI1-RX1P
HDMI1-RX1N
HDMI1-RX0P
HDMI1-RX0N
HDMI1-CLKP
HDMI1-CLKN
HDMI-CEC
R678 10R
HDMI_HP1
HDMI1-SCL
HDMI1-SDA
ARC
R679 10R
R680 10R
R681 10R
R682 10R
HDMI1-RX2+
+5V_Normal
HDMI1/5V
C780.1uF
D19
BAT54C
D13 5NC
1 2
D13 6NC
1 2
D13 7NC
1 2
R396 10K
R29 412 K
R29 512 K
CN7
VGA-SMALL
5
10
4
9
3
8
2
7
1
15
14
13
12
11
6
16
17
R11 675 R
R397 10K
R21 7
10 K
R142 68R
R28 575 R
CN8
PHONEJACK
2
3
5
1
4
R283 68R
R11 975 R
R22 910 K
PC-Lin
PC-Rin
VGA_HS
VGA_VSin
UART-TX
UART-RX
PC-L
PC-Rin
PC-Lin
VGA-SCL UART-RX
UART-TXVGA-SDA
VGA-Bin
VGA_VSin
VGA_HS
C82 9NC/33p
PC-R
C83 0NC/33p
+5V_Normal
R12 010 0K R12 310 0K
C145 4.7UF
VGA-Rin
VGA-Gin
VGA-B
VGA-G
VGA-R
VGA-VS
VGA-HS
Page 20

AV_R OUT
AV2_L
SCAR T-Bin
AV2_V
AV_V OUT
AV2_R
SCAR T-Rin
SCAR T-Gin
SC_F S
AV_LO UT
Blanki ng I/O
Switch
R 23 275 R
D 12 7N C
1 2
R 23 12.7 K
CN1 3
SCAR T/NG
2
4
6
8
10
12
14
16
18
20
1
3
5
7
9
11
13
15
17
19
21
23
22
R230 10 K
CN1 0
1P-RC A
12
3
+5V_N ormal
AV2_R in
AV2-i n
AV3_R in
AV3-i n
AV3_L in
R378 10 K
R377 10 K
R280 33R
R 28 175 RR 2 8 41 2 KR2 2 412 K
D 14 4N C
1 2
D 14 7N C
1 2
SPDI F_OUT
SPDI F_OUT
HD_ Y
VGA _VS
VGA -G
HD-S W
R434 47 0
R432 NC/ 0
R215 1K
+5V_N ormal
SCAR T-G
C 14 10. 1u
+3.3V _Normal
SCAR T-Rin
SCAR T-Bin
+5V_N ormal
SC_F B
U10
NC/BA T3257
S1A
2
S1B
5
S1C
11
S1D
14
S2A
3
S2B
6
S2C
10
S2D
13
IN
1
DA
4
DB
7
DC
9
DD
12
VCC
16
GND
8
EN
15
+3.3V _Normal
R216 4. 7K
D 14 8N C
1 2
SCAR T-Rin
SCAR T-Bin
SCAR T-Gin
AV2_L
AV2_R
CN2 8 6P RCA I NPUT
778
8
445
5
2
2
1
1
3
3
6
6
9
9
10
10
11
11
12
12
131314
14
AV2_V
HD_ Pb
HD_ Y
HD_ Pr
CN2 7
NC/6P/ 2.0
5
4
3
2
1
6
D 13 3N C
1 2
D 14 5N C
1 2
C 17 4N C /3 3 p
AV_A UOUTL3
AV3_R
AV3_L
AV3_V
CN1 1
5p/2.0
5
4
3
2
1
EXTERN AV
EXTERN AV
EXTERN AV
EXTERN AV
C 17 5NC / 56 0 p
C 17 1N C /3 3 p
AV1-R in
AV1-R in
AV1-i n
AV1-Li n
AV1-i n
AV1-Li n
AV_A UOUTR3
C 16 1NC / 56 0 p
SC_F S 2
SC_F S
C 17 2N C /3 3 p
AV1_R
AV1_V
C227 47n
CN9
3P RCA INPUT
552
2
334
4
6
6
1
1
AV1_L
R226 33 R
D 14 6N C
1 2
R228 33 R C231 47 n
AV1_L
YPBPR and
YPBPR and
YPBPR and
YPBPR and
AV input
AV input
AV input
AV input
C 17 3N C /3 3 p
AV2_V
SCART INPUT
SCART INPUT
SCART INPUT
SCART INPUT
R206 0R
R98 0R
R96 0R
R 24 07 5R
C 82 4N C /5 6 0p
R 34 910 0 K
R375 10 K
D 13 4N C
1 2
R 14 175 R
R275 33 R
R374 10 K
R376 10 K
R278 33 R
R 22 212 K R2 7 675 R
C296 2.2u
R 27 9
75 R
D 13 1N C
1 2
C295 2.2u
R373 10 K
R686 47R
R685 47R
R 27 712 K
R 22 312 K
R 23 812 K
RGB0_ Y-SOG
RGB0_ Pb+
VGA _VS
RGB0_ Pr+
VGA _VS
C 82 5N C /5 6 0p
HD-S W
RGB0_ Pr+
RGB0_ Y+
HD-S W
RGB0_ Y-SOG
RGB0_ Y+
RGB0_ Pb+
R348
100K
R208 0R
AV_LO UT
D 14 3N C
1 2
AV2_L in
D 13 2N C
1 2
CLOSED TO MST 6M18 1CS
R82150
HD_ Pb
HD_ Y
CN2 4PJ
5
3
2
1
4
67
DD3 1
NC/ES D-0402
R 15 815 0
SPDI F_OUT
HD_ Pr
AV2-i n
AV2_L in
AV2_L in
AV2-i n
SC_F B
AV3_R
AV3_L
AV3_V
C 16 4NC / 56 0 p
C 15 70. 1u
R433 75 0K
Q47 A O3401A
DVD _IR
IR
5V
CN1 2
NC/3P/ 2.0
1
2
3
Q28
3904
1
2 3
R431 10 0
R49
4.7K
R 24
47 K
DVD _ON/OFF
DVD _ON/OFF
SCAR T-Gin
AV1_R
AV2_R
RGB2- HDTV_BI N
CVBS _OUT0
CVBS _OUT0
C 16 0N C /3 3 p
CN1 4
1P-RC A
12
3
R 14 775 R
D 12 9N C
1 2
AV_A UOUTL3
AV_A UOUTL3
SCAR T-Bin
C223 47n
C222 1nR220 33 R
R221 33 R
RGB2- HDTV_SO GIN
RGB2- HDTV_GI N
VGA -B
VGA _VSin
VGA -R
VGA -G
VGA -R
VGA -G
VGA -B
VGA _VSin
CVBS _OUT0
R 28 77 5R
Q32
3904
1
2 3
R288
220R
R 29 212 K
Q33
3906
1
3 2
C 82 3N C / 33 p
DVD _ON/OFF
DVD _ON/OFF
C 21 10. 1u
R 29 3
22 K
R282
75R
R 28 622 0R
+5V_N ormal
C383
10u
AV_A UOUTR3
AV_A UOUTR3
R 23 47 5R
VGA -R
R125 10 0K
R126 10 0K
VGA -B
VGA _VSin
C146 4.7u
SPDI F
R 23 97 5R
RGB2- HDTV_R IN
D 13 0N C
1 2
HD_ Pb
HD_ Pr
SCAR T-Rin
AV_R OUT
AV2_L
SCAR T-G
AV1_V
AV1_L
AV1_R
CN1 6
NC/5p/ 2.0
5
4
3
2
1
R 12 975 R
D 12 8N C
1 2
AV1-R in
AV1_V AV 1-in
AV1-Li n
HD_ Pr
AV3-i n
AV3_L in
AV3-i n
AV3_L in
AV3_R in
AV3_R in
RGB2- HDTV_BI N
RGB2- HDTV_GI N
RGB2- HDTV_SO GIN
RGB2- HDTV_BI N
RGB2- HDTV_R IN
RGB2- HDTV_GI N
RGB2- HDTV_SO GIN
RGB2- HDTV_R IN
AV_V OUT
R95 33 R
R203 33 R
R97 33 R
R114 33 R
RGB0_ Pr+
RGB0_ Pb+
RGB0_ Y-SOG
RGB0_ Y+
SPDI F
AV2_R in
AV2_R in
Page 21

AMP_AUOUTL0
AMP_AUOUTR0
+12V_NORMAL
AMP-EN
AUDIO Pre AMP 4W/4ohm
AUDIO Pre AMP 4W/4ohm
AUDIO Pre AMP 4W/4ohm
AUDIO Pre AMP 4W/4ohm
AMP_AUOUTL0
AMP_AUOUTR0
C190 2.2u
C191 2.2u
+12V_NORMAL
+
R25510K
CA37 470uF
R256 1K
R2576.8K
R247 10K
R258 10K
C192NC/0.1uF
C193 47uF
U11
18
1
INV1
9
INV2
7
VP
8
M/SS
3
SVRR
GND
GND
GND10GND11GND12GND13GND14GND15GND
2
5
+
CA35100 uF
4
16
TDA1715P
6
CA33 470uF
+
CA34 470uF
+
SP_L
SP_R
SP_R
SP_L+
SP_R+
R3041K/0603
R3051K/0603
R-R
1 2
1 2
SP_R+
SP_L+
L-R
SP_L
L-R
R-R
OUT1
GND17GND
OUT2
4P/2.5
4
4
3
3
2
2
1
1
CN18
1
5
6
4
7
3
2
CN26
1
5
6
4
7
3
2
HP-JACK
CN20
8P/2.0
KEYBOARD
+5V_Standby
8
7
6
5
4
3
2
1
+12V_NORMAL
IR-in
LED_R
LED_G
KEY1-in
KEY0-in
+5V_Standby
Mute-VCC
R316 100R
3
BAV99
1
R318 470RR319 47K
+
CA82 100uF
AMP-MUTE
R709 10K
IR-in
R710 68R
VD99NC
1 2
R711 10K
C903
10n
R739 10K
R737 100
R712 100
C904
10n
KEY0-in
KEY1-in
VD98NC
VD100NC
1 2
1 2
C194 4.7u
Q37
1
3906
R320 1K
3 2
R30822K
AMP-MUTE
+5V_Standby
1
Q13
3904
IRIN
C905
33p
+3.3V_Standby
KEY0-SAR0
KEY1-SAR1
2
D70
+5V_Standby
AMP-EN
R3304.7K
2 3
R325
R708 4.7K
LED
R354 1 K
R351 4 .7K
Q14
1
1K
3904
2 3
+5V_Standby+3.3V_Standby
Q22
1
+5V_Standby
Q18
1
KEY0-SAR0
KEY1-SAR1
LED
IRIN
RXO0RXO1-
R3534.7K
LED_RLED_R
3904
2 3
R3522.7K
LED_G
3904
2 3
RXO2RXOCRXO3RXE0RXE1RXE2RXECRXE3-
RXO0+
RXO1+
RXO2+
RXOC+
RXO3+
RXE0+
RXE1+
RXE2+
RXEC+
RXE3+
PANEL_ON/OFF
PANEL-ON/OFF
VBL_CTRL
BRI_ADJ-PWM0
KEY0-SAR0
KEY1-SAR1
LED
IRIN
RXO0RXO1RXO2RXOCRXO3RXE0RXE1RXE2RXECRXE3-
RXO0+
RXO1+
RXO2+
RXOC+
RXO3+
RXE0+
RXE1+
RXE2+
RXEC+
RXE3+
PANEL_ON/OFF
PANEL-ON/OFF
VBL_CTRL
BRI_ADJ-PWM0
6
5
4
3
2
1
BL-ADJUST
6
5
4
3
2
1
6p/2.0
BL-ON/OFF
CN21
BL-ON/OFF
BL-ADJUST
C49
10u
+12V_PWR
R5310K
BL-ON/OFF
BL-ADJUST
NC/1K
R62
Q31
R57
3904
NC/10K
+5V_Normal
R58
10K
Q30
3904
2 3
R4 0/0603
CN23 NC/3*2.5*1
+3.3V_Normal
+5V_Normal
+12V_NORMAL
+3.3V_Standby
3
2
1
CN25 NC/3*2.5*1
3
2
1
R210K
C20.22u F
R52
R544.7K
R55
10K
R514.7K
VBL_CTRL
BRI_ADJ-PWM0
1K
1
1
2 3
PANEL-ON/OFF
PANEL_ON/OFF
R17 4.7K
IO ,
R111
10K
R3 10K
Q1
1
3904
2 3
Q48AO 3401A
RXO0RXO1RXO2-
RXOCRXO3RXE0RXE1RXE2-
RXECRXE3-
VCC-Panel
CN22
1
3
5
7
9
11
13
15
17
19
21
23
25
27
29
HEADER_15*2
C30.1uF
C6NC
1
3
5
7
9
11
13
15
17
19
21
23
25
27
29
2
2
4
4
6
6
8
10
12
14
16
18
20
22
24
26
28
30
RXO0+
8
RXO1+
10
RXO2+
12
14
RXOC+
16
RXO3+
18
RXE0+
20
RXE1+
22
RXE2+
24
26
RXEC+
28
RXE3+
30
 Loading...
Loading...