Page 1

EDGE User Manual
Firmware Version 4.5
Ag Leader PN 4002086 Rev. F
Page 2

Page 3

Table of Contents
General
Introduction and Company Profile .........................................................................1
ABOUT US..................................................................................................................1
INNOVATION..............................................................................................................1
COMPATIBILITY.........................................................................................................1
QUALITY AND SUPPORT..........................................................................................1
WE WANT TO HEAR FROM YOU! ............................................................................1
About the Display........................................................................................................1
SERVICE ....................................................................................................................2
SYSTEM USES...........................................................................................................2
SYSTEM FEATURES.................................................................................................2
DATA CARD USAGE..................................................................................................3
COLOR TOUCH SCREEN..........................................................................................3
CAN-BUS TECHNOLOGY..........................................................................................3
TECHNICAL SPECIFICATIONS.................................................................................3
SYSTEM UPGRADES................................................................................................3
Conventions Used in this Manual................................................................................4
Cautions and Warnings .........................................................................................4
Cross-References and Web Links.........................................................................4
Viewing this Manual Online ...................................................................................4
How to Find Information You’re Looking For.........................................................5
Display Hardware ..................................................................................................5
Installation Instructions..........................................................................................5
Mounting the Display........................................................................................6
Mounting Components.....................................................................................6
Fuse Installation and Replacement..................................................................7
Screen Icon Conventions.......................................................................................7
TABLE OF CONTENTS
Setup
System Functionality...................................................................................................9
Home Screen..............................................................................................................9
Setup Screen ............................................................................................................10
Management.............................................................................................................10
Grower Management Tab....................................................................................10
Importing an .MSF File...................................................................................11
Season Management Tab ...................................................................................11
Field Management Tab........................................................................................12
Import and Export Boundaries........................................................................12
Boundary Import .......................................................................................13
Boundary Export.......................................................................................13
Console.....................................................................................................................13
General Tab.........................................................................................................13
Memory Tab.........................................................................................................14
Features Tab .......................................................................................................15
Advanced Tab......................................................................................................15
iii
Page 4

Module Firmware Management..................................................................... 15
Field Notes ............................................................................................................... 16
Start Field Operation ................................................................................................ 17
Run Time Environment: Map Screen.................................................................. 18
Title Bar ......................................................................................................... 18
Task Bar Buttons........................................................................................... 18
Map Screen Icons.......................................................................................... 19
Map Screen Status Items .............................................................................. 21
Edit Legend .............................................................................................................. 21
Create a Boundary ................................................................................................... 22
Start Boundary............................................................................................... 22
Pause Boundary.................................................................................................. 22
View Boundary.................................................................................................... 23
View Map Markers .............................................................................................. 23
Summary.................................................................................................................. 23
Select Summary ............................................................................................ 24
Diagnostics............................................................................................................... 24
Device Information.............................................................................................. 24
Memory............................................................................................................... 24
Display ................................................................................................................ 25
GPS
GPS General Tab..................................................................................................... 27
OmniSTAR Settings ................................................................................................. 28
Serial Port Settings................................................................................................... 28
OmniSTAR Settings — GPS 2500........................................................................... 29
GPS Port Setup - GPS 2500.................................................................................... 30
GPS Diagnostics ...................................................................................................... 31
GPS Information - First Screen........................................................................... 31
GPS Information - Second Screen ..................................................................... 32
GPS Information - Third Screen.......................................................................... 32
OnTrac2 Information........................................................................................... 33
ParaDyme Information........................................................................................ 33
NTRIP Information .............................................................................................. 33
Guidance
GPS Guidance Tab .................................................................................................. 35
Guidance Control........................................................................................... 35
Pattern Files................................................................................................... 35
Lightbar Settings................................................................................................. 36
Guidance Functions.................................................................................................. 36
On-Screen Lightbar............................................................................................. 36
Guidance Screen ................................................................................................ 37
New AB Pattern............................................................................................. 38
SmartPath ..................................................................................................... 40
Creating a SmartPath Pattern.................................................................. 40
SmartPathNotes:...................................................................................................... 41
Select a Previous SmartPath Pass .......................................................... 41
iv
Page 5

Create an AB Line Within a SmartPath Pass............................................41
Choose Existing Lines Within SmartPath .................................................42
SmartPath Guidance Options...................................................................42
Save Pattern...................................................................................................43
Reset Pattern .................................................................................................43
Load Pattern...................................................................................................43
About Guidance Patterns.....................................................................................44
A+ Pattern ......................................................................................................44
Pivot ...............................................................................................................45
Adaptive Curve...............................................................................................46
Identical Curve ...............................................................................................46
Guidance Options................................................................................................47
Pause.............................................................................................................47
Remark A .......................................................................................................47
Shift................................................................................................................47
Adaptive Curve...............................................................................................47
Nudge..................................................................................................................48
OnTrac2....................................................................................................................48
OnTrac2 Setup Tasks..........................................................................................49
Vehicle Configuration...........................................................................................49
Edit Vehicle Settings............................................................................................50
OnTrac2 Tools Tab..............................................................................................51
Calibrating OnTrac2.......................................................................................52
OnTrac2 Steering Diagnostics .......................................................................53
Steering.....................................................................................................53
Drive Unit..................................................................................................54
Status........................................................................................................54
Adjust Disengage Sensitivity..........................................................................54
Minimum Output.............................................................................................54
OnTrac2 Advanced Tab.......................................................................................55
Vehicle Database......................................................................................55
Log Files ...................................................................................................55
OnTrac2 Run Time Environment.........................................................................55
Steering Adjustment.......................................................................................55
Tuning ............................................................................................................56
How the OnTrac2 System works....................................................................57
Steering.....................................................................................................58
Heading.....................................................................................................58
Cross Track...............................................................................................59
TABLE OF CONTENTS
Tillage
Run Time Environment: Map Screen........................................................................61
Create a Tillage Configuration ..................................................................................61
Create a Configuration...................................................................................61
Configuration Notes..................................................................................62
GPS Offsets..............................................................................................................62
Antenna Offsets...................................................................................................62
Hitch Tab Settings ...............................................................................................63
v
Page 6

Implement Offsets .................................................................................................... 63
Planting
Run Time Environment: Map Screen ....................................................................... 65
Map Screen: Zoom to Extent .............................................................................. 65
Map Screen: Zoom Detail ................................................................................... 65
Planting Map Screen Items................................................................................. 66
Planting Setup Tabs................................................................................................. 66
Create a Planting Configuration ............................................................................... 67
Configuration Settings.............................................................................................. 68
Configuration Settings: Equipment Configuration............................................... 69
Equipment Configuration Settings - SeedCommand................................ 69
Speed Input Settings........................................................................................... 69
Calibrate Distance ......................................................................................... 69
Auxiliary Input Settings (Switch Mapping)........................................................... 70
Add Auxiliary Input Settings ..................................................................... 70
AutoSwath........................................................................................................... 71
AutoSwath Notes........................................................................................... 72
Fixing Overplanting and Underplanting in AutoSwath................................... 72
Vehicle Tab............................................................................................................... 72
GPS Offsets........................................................................................................ 72
Antenna Tab.................................................................................................. 73
Hitch Tab ....................................................................................................... 73
Implement Tab.......................................................................................................... 74
Implement Offsets............................................................................................... 74
Section Offsets .............................................................................................. 74
Controller Tab........................................................................................................... 74
Controller Settings (SeedCommand).................................................................. 75
Product Tab.............................................................................................................. 75
Product Options .................................................................................................. 76
Add Product................................................................................................... 76
Import Product............................................................................................... 76
Product Settings.................................................................................................. 77
Planting: SeedCommand™ Machine-Specific Setup............................................... 77
Map Screen: Zoom to Extent .............................................................................. 78
Map Screen: Zoom Detail ................................................................................... 78
Planting Map Screen Items................................................................................. 79
Run Time Environment: Rate Screen....................................................................... 79
Planting Rate Control Configuration Screen....................................................... 80
Loading Prescriptions.................................................................................... 80
Row Shutoff.............................................................................................................. 81
Row Shutoff Configuration.................................................................................. 81
Row Shutoff Look-Ahead Numbers..................................................................... 83
Checking AutoSwath Performance for Row Shutoff ........................................... 83
Hydraulic Seed Rate Control.................................................................................... 84
Hydraulic Seed Rate Control Configuration........................................................ 84
Controller Settings for Hydraulic Seed Rate Motor Drives.................................. 85
Channel Tabs ................................................................................................ 85
vi
Page 7

Control Valve Settings - PWM ..................................................................86
Control Valve Settings - Servo..................................................................86
Auxiliary Tab...................................................................................................86
Hydraulic Seed Controller Settings for Specific Planter.................................87
John Deere Planters.................................................................................87
White Planters...........................................................................................87
Case IH Planters.......................................................................................87
Hydraulic Seed Meter Calibration Numbers...................................................87
Stepper Seed Rate Control.......................................................................................89
Stepper Seed Rate Control Configuration...........................................................89
Controller Settings for Stepper Seed Rate Motor Drives.....................................90
Channel Tabs.................................................................................................90
Auxiliary Tab...................................................................................................90
Gear Ratio Calculations for Seed Rate Motors....................................................91
Gear Ratio Drawing - For Single Motor Drive.................................................91
Gear Ratio Drawing - For Multiple Drive Combinations .................................92
Seed Ratio Calculation Example Procedure..................................................92
Gear Ratio Drawing - For John Deere Pro-Shaft™ Drives.............................93
Priming Seed Rate Meters...................................................................................94
Calibrating Seed Rate Meters..............................................................................94
Troubleshooting ........................................................................................................95
Zero Flow Offset Variation...................................................................................95
Hydraulic Seed Control: Zero Flow Offset Variation............................................96
Stepper Seed Control Meter Alarms....................................................................96
Diagnostics................................................................................................................97
Clutch Diagnostics (for Row Shutoff)...................................................................97
Input Diagnostics.................................................................................................97
TABLE OF CONTENTS
Application
Run Time Environment: Map Screen........................................................................99
Map Screen - Zoom to Extent..............................................................................99
Map Screen: Zoom Detail....................................................................................99
Application Map Screen Items...........................................................................100
Application Setup Tabs...........................................................................................100
Create an Application Configuration .......................................................................101
Configuration Settings.............................................................................................103
Configuration Settings: Equipment Configuration..............................................103
Configuration Settings - Area Logging....................................................103
Edit Configuration Settings - Area Logging.............................................103
Configuration Settings - DirectCommand.....................................................104
Configuration Settings - DirectCommand ...............................................104
Speed Input Settings .........................................................................................104
Calibrate Distance........................................................................................104
Auxiliary Input Settings......................................................................................105
Add Auxiliary Input Settings....................................................................106
Fence Row Nozzle Indicators.................................................................106
AutoSwath .........................................................................................................107
AutoSwath Notes..........................................................................................108
vii
Page 8

Vehicle Tab............................................................................................................. 108
GPS Offsets...................................................................................................... 109
Antenna Tab................................................................................................ 109
Mount Tab.................................................................................................... 109
Hitch Tab ..................................................................................................... 109
Implement Tab........................................................................................................ 110
Implement Offsets............................................................................................. 110
Section Offsets ............................................................................................ 110
Controller Tab......................................................................................................... 111
Controller Settings (DirectCommand)............................................................... 111
Product Tab............................................................................................................ 112
Product Screen ................................................................................................. 112
Product Settings .......................................................................................... 113
Product Options ................................................................................................ 113
Tank Mix Setup................................................................................................. 114
Dry (Granular) Fertilizer Blend Setup................................................................ 114
Miscellaneous Items............................................................................................... 115
Fertilizer Default Product Settings..................................................................... 115
John Deere Specific Instructions....................................................................... 116
MASTER SWITCH INPUT...................................................................................... 116
MASTER SWITCH USAGE.................................................................................... 116
TARGET RATE ...................................................................................................... 117
DATA COLLECTION.............................................................................................. 117
AUTOSWATH BOOM SECTION CONTROL......................................................... 117
SPRAY STAR APPLICATION RATE ..................................................................... 117
SPRAY STAR RINSE CYCLE................................................................................ 117
Control Valve Settings............................................................................................ 117
Liquid Product Control Valve Configuration...................................................... 117
Servo Control Valve Settings (By Manufacturer) .............................................. 119
Control Valve Settings for Self-Propelled Sprayers .......................................... 121
Liquid Servo Settings Description..................................................................... 124
Liquid PWM Control Valve Settings Description............................................... 125
Spinner Spreader Servo Settings Description................................................... 125
Spinner Spreader PWM Control Valve Settings Description............................. 126
Spinner Speed PWM Valve Settings Description.............................................. 126
Dickey John NH3 Conversions ......................................................................... 127
Conversion Formulas............................................................................. 127
Application: DirectCommand™ Machine-Specific Setup........................................ 127
Map Screen: Zoom to Extent.................................................................................. 128
Map Screen: Zoom Detail....................................................................................... 128
Application Map Screen Items .......................................................................... 129
Run Time Environment: Rate Screen..................................................................... 129
Target Rate.................................................................................................. 129
Rate Screen: Container Level........................................................................... 130
Tank Fill....................................................................................................... 130
Tank Empty.................................................................................................. 131
Tank Partial Fill............................................................................................ 131
Adjust Container Amount ....................................................................... 131
Tank Alarms................................................................................................. 131
viii
Page 9

Container Alarm Screen..........................................................................131
Rate Screen: Liquid Flow/Pressure...................................................................132
Rate Screen: Spinner Spreader Settings...........................................................132
Spinner Spreader Product Settings..............................................................132
Spreader Control..........................................................................................133
Application Rate Control Configuration Screen.................................................134
Loading Prescriptions...................................................................................134
Shape File Conversion............................................................................................135
Liquid Application Control .......................................................................................136
Liquid Application Control Configuration............................................................136
Liquid Application Controller Settings................................................................139
Controller Settings - PWM ......................................................................139
Controller Settings - Servo, Calibrated Reflow or Ramsey Valve...........140
Rate Error Alarm Threshold...............................................................................140
Direct Injection ........................................................................................................141
Direct Injection Configuration Setup..................................................................141
Direct Injection Controller Settings ....................................................................143
Priming an Injection Pump.................................................................................144
Calibrating an Injection Pump............................................................................144
Injection Diagnostics..........................................................................................146
Spinner Spreader Granular Control ........................................................................147
Spinner Spreader Control Configuration............................................................147
Spinner Spreader Controller Settings................................................................148
Controller Settings - Spinner Spreader ........................................................148
Controller Settings - PWM ......................................................................149
Controller Settings - Servo......................................................................149
Fan Settings.................................................................................................150
Conveyor Rate and Product Density Look-Up...................................................150
NORAC UC5 Setup.................................................................................................151
Norac UC5 Setup Screen..................................................................................151
Automatic Setup...........................................................................................151
Retune..........................................................................................................152
Minimum Height Settings .............................................................................152
Norac UC5 Run Time Environment...................................................................153
Boom Height Screen....................................................................................153
Engage button.........................................................................................154
Boom Height Control Options.......................................................................154
Troubleshooting ......................................................................................................154
Troubleshooting DirectCommand Liquid Applications.......................................154
Troubleshooting Direct Injection Configurations................................................157
Direct Injection: Pump Doesn’t Run .............................................................157
Battery Power Pin-Outs...........................................................................................158
Direct Injection: Pump Runs Full Speed.......................................................158
Direct Injection: Application Error.................................................................159
Direct Injection: Discharge Flow Sensor Error .............................................159
Discharge Flow Sensor Pin Outs............................................................................160
Direct Injection: Inlet Restriction...................................................................160
VACUUM SWITCH PIN OUTS ...............................................................................160
Troubleshooting DirectCommand Granular Applications...................................160
TABLE OF CONTENTS
ix
Page 10

Troubleshooting Serial Control Applications (Liquid and Granular).................. 161
Troubleshooting Serial Control Applications (Liquid Only)................................ 162
Troubleshooting Serial Control Applications (Granular Only) ........................... 162
Miscellaneous......................................................................................................... 162
Glossary of Application Settings ....................................................................... 162
Configuration Settings ................................................................................. 162
Speed Input Settings ................................................................................... 162
Automatic Swath Control Settings............................................................... 163
Auxiliary Input Settings................................................................................ 163
Controller Settings....................................................................................... 163
Controller Settings: Direct Injection Pump Calibration................................. 164
Pump Calibration Setting........................................................................ 164
Rate Response Warning........................................................................ 164
Flow Monitor Warning ............................................................................ 164
Run Screen.................................................................................................. 165
Diagnostics............................................................................................................. 165
Input Diagnostics............................................................................................... 165
Harvest
Run Time Environment: Map Screen ..................................................................... 167
Map Screen: Zoom to Extent ............................................................................ 167
Map Screen: Zoom Detail ................................................................................. 167
Harvest Button on Task Bar......................................................................... 168
Map Screen: Flow Delay................................................................................... 168
Run Time Environment: Harvest Screen................................................................ 169
Harvest Screen Display Items........................................................................... 169
Harvest Screen - Active Display Items.............................................................. 170
Harvest Setup Tabs................................................................................................ 171
Create a Harvest Configuration.............................................................................. 171
Configuration Settings....................................................................................... 172
Primary and Backup Speed Source............................................................. 172
Calibrate Distance ....................................................................................... 172
Combine Tab.......................................................................................................... 173
Combine Settings.............................................................................................. 173
Advanced Combine Settings ....................................................................... 173
Map Delays.................................................................................................. 173
GPS Offsets................................................................................................. 174
Antenna Offsets...................................................................................... 174
Head Offset............................................................................................ 174
Header Tab............................................................................................................. 174
Header Settings ................................................................................................ 175
Calibrate Header Sensor................................................................................... 175
Header Offset.................................................................................................... 176
Crops Tab............................................................................................................... 176
Crop Settings .................................................................................................... 177
Calibration Tab....................................................................................................... 177
Pre-Harvest Checklist ....................................................................................... 178
Calibration Sequence .................................................................................. 178
x
Page 11

Vibration Calibration.....................................................................................178
Temperature Calibration...............................................................................179
Moisture Calibration .....................................................................................179
Grain Weight Calibration..............................................................................179
Adding a New Calibration..................................................................................182
Diagnostics..............................................................................................................184
Appendix
“Company Warranty Statement” on page 186System Diagrams Reference ..........185
File Formats............................................................................................................185
Prescription Map File Types..............................................................................185
Boundary and Guideline File Types...................................................................185
System File Types.............................................................................................185
Module LED Diagnostic States ...............................................................................186
LED display........................................................................................................186
Company Warranty Statement................................................................................186
WARRANTY............................................................................................................186
PROPRIETARY TECHNOLOGY NOTICE............................................................................................... 186
COPYRIGHT NOTICE............................................................................................186
SERVICE AND SUPPORT .....................................................................................187
TABLE OF CONTENTS
xi
Page 12

xii
Page 13

GENERAL
GENERAL
INTRODUCTION AND COMPANY PROFILE
ABOUT US
Welcome to the Ag Leader Technology family. Ag Leader Technology, Inc. is the global leader in yield
monitor and precision farming systems and is committed to meeting the present and future needs of the
agriculture industry by providing high quality products and first class customer support.
INNOVATION
Ag Leader Technology manufactures and sells products which support a wide array of precision farming
practices. These include grain and cotton yield monitoring, application rate control and monitoring,
variable rate fertilizer application, site-verification, GPS guidance and interface to Autosteer
technologies.
COMPATIBILITY
GENERAL
Ag Leader Technology offers compatibility and supports integration of many different types and brands
of equipment used for precision farming. The latest equipment available is supported as well as older
series of combines, planters, sprayers, tillage equipment, etc.
QUALITY AND SUPPORT
Ag Leader Technology continues to provide the best customer support in the industry. Precision farming
doesn't come without questions. Ag Leader is committed to providing the most responsive,
knowledgeable and friendly technical support available. Our technical support team is available sevendays-a-week during peak seasons to answer your questions on the operation of Ag Leader products.
WE WANT TO HEAR FROM YOU!
Feel free to call and discuss:
• Operational questions about the display
• Features you would like to see implemented to improve the system or features you would like to see
added to the system to increase functionality
ABOUT THE DISPLAY
This display provides an entry-level precision farming solution to meet the year round needs of today’s
precision farming operation. It combines a greater level of simplicity with SeedCommand™,
DirectCommand™ and yield monitoring capabilities to meet the year-round needs of today’s precision
farming operation.
1
Page 14

The display is a GPS-compatible universal monitor/controller for use in crop production and protection. It
can easily be transferred between multiple vehicles through out the growing season to maximize your
return on investment cost.
The display features a 6.5-inch color touchscreen in which users will find a greater level of simplicity
combined with SeedCommand, DirectCommand and yield monitoring capabilities. The display is ideal
for operations just getting started in precision farming, but also fits operations requiring multiple displays.
Support for the AutoSwath feature makes the display a great investment for any operation looking for an
easy-to-use, input-cost saving solution.
The display has its own internal memory for recording GPS and logging all information collected during
various field activities. No external data card is needed for in-field data collection.
The display has been built to withstand the harsh environment associated with today's agricultural
industry. The weather-tight enclosure is designed to seal out any dirt and moisture that is encountered
during normal operating conditions.
Note: The card door slot must be fully closed for the display to remain weather-tight.
SERVICE
There are no user-serviceable parts inside the display. Ag Leader Technical Support ph: (515) 232-5363
fax: (515) 232-3595
e-mail: support@agleader.com
CAUTION: This display has an internal lithium coin cell battery and an internal nickel metal hydride battery.
There is a risk of explosion if either battery is replaced by an incorrect type. Dispose of used batteries
according to the battery manufacturer’s instructions.
SYSTEM USES
• Grain yield monitoring
• Variety logging
• Liquid spray system control
• NH3 application control
• Granular and liquid fertilizer application
• Mapping tillage operations
• Mapping and logging product application
• Mapping of all field boundaries, sub-boundaries, waterways and terraces
SYSTEM FEATURES
• 6.5" color display
• Sunlight-readable screen
• Large internal memory
• Rugged sealed enclosure
2
Page 15

• Compatible with most NMEA GPS receivers
• DirectCommand product control using industry standard CAN-bus interface
• Adjustable volume control
DATA CARD USAGE
The display uses a compact flash card for transferring data in and out of the display. The system is
compatible with all current card sizes; 64 MB is the minimum recommended size for use with the system.
COLOR TOUCH SCREEN
The display features a 6.5-inch color touch screen display. The touch screen allows easy and intuitive
navigation through the screens on the display without the need for any external keypad or mouse
devices. Here are a few key things to remember if you are new to using a touch screen device.
• Do not use any sharp objects for running the touch screen device, this could result in damage to the
display. Using the tip of a finger is the recommended method of operating the display touch screen.
• Do not use any harsh chemicals to clean the touch screen. Using a damp soft cloth or an anti-static wipe
made specifically for cleaning computer displays is the correct way to clean the screen and the display
enclosure.
• The touch screen requires only a gentle touch of about half-second in duration to operate correctly. A
common mistake new users make is to try to navigate too quickly through the system using firm taps
instead of gentle presses on the display screen.
GENERAL
CAN-BUS TECHNOLOGY
The display uses Controller Area Network (CAN) technology. CAN systems are comprised of individual
modules, each with their own high speed processor, connected through a high-speed communications
cable. CAN has many benefits, including greater ability to configure and expand the system,
compatibility, simpler installs with less wiring, and increased system dependability.
TECHNICAL SPECIFICATIONS
Do not exceed the specifications below:
• Storage Temperature: -30°C to +70°C.
• Operating Temperature: -10°C to +65°C
• Operating Input Voltage: 9 –16 V DC
CAUTION: Exceeding these specifications may result in degraded operation and/or damage to the display.
SYSTEM UPGRADES
Ag Leader Technology will periodically provide operating program updates that will improve the
performance of your display. Required software updates will be available free of charge for download
from
www.agleader.com. On occasion, major releases will be made available that have significant product
feature additions or enhancements. These optional software updates may have an additional fee
associated with them.
3
Page 16

When registering your Ag Leader Technology products by one of the following methods, you can elect to
receive notice of any new product updates or features.
Register by mail: Ag Leader Technology
2202 South Riverside Dr.
P.O. Box 2348
Ames, IA 50010
Register by Fax: 515-232-3595
Register at the Ag Leader Web site at
http://www.agleader.com
CONVENTIONS USED IN THIS MANUAL
CAUTIONS AND WARNINGS
The user manual uses the following text formatting schemes to call attention to information related to
simplifying system operation and proper operating practices to prevent accidental data loss. If in doubt
about the results of performing an action or deleting an item from the system, back up all system files to
the external storage card prior to proceeding with the action.
Note: Provides informative tips to assist with system setup, calibration, and operation.
CAUTION: Indicates specific settings, calibrations, and procedures that must be followed for proper system
performance and operation.
WARNING: Indicates specific instructions to avoid accidental loss of data and system configurations
settings.
CROSS-REFERENCES AND WEB LINKS
Throughout this manual, numerous cross-references are provided to other pages or sections. These
cross-references are always shown in blue, italic text; and list the title and page number If you are
viewing this manual in a .PDF format, you can click on this blue text and go directly to the link.
Links to web sites are shown in blue, italicized, and underlined text, as in the following example: To see
the web site, go to:
www.agleader.com.
VIEWING THIS MANUAL ONLINE
This user manual can be viewed online at Ag Leader’s Web site. To view an online version, go to the Ag
Leader Web site, and click the Support link. You should see a page titled “Manuals and Quick Reference
Sheets.”
To view and/or print the display’s User Manual online, you will need the Adobe Acrobat or Adobe Reader
.pdf file format. The Adobe Reader software comes pre-installed on most personal computers. If Adobe
Reader is not installed on your computer the program is available for download at no charge. A link to
the Adobe download site is located at the Ag Leader Web site.
4
Page 17

HOW TO FIND INFORMATION YOU’RE LOOKING FOR
What do you do if you cannot find the information that you’re looking for? There are three different ways
at your disposal to find specific information quickly. These steps can include:
1. Look up the information in the Table of Contents.
2. Look up the information in the section indexes that are located at the end of each manual section
(Planting, Tillage, Application, and Harvest).
3. Use the Adobe Reader’s search function. While viewing this manual online in PDF format, press the
CTRL+F buttons on your keyboard. A search menu should appear, and from here, you may enter in a
search term.
DISPLAY HARDWARE
GENERAL
Front Back
• (A) Compact Flash Card Slot
The compact flash card slot has a sensor that allows the display to know when the door is open or closed.
If the door is opened when a card is in the display, an on-screen warning will appear indicating when the
card can safely be removed. The display comes with a compact flash card. The compact flash card will be
required to transfer files from the display to a desktop computer.
• (B) RAM Mount
For more information, see
• (C) 28-Pin Connector
The 28-Pin round connector contains CAN, RS-232 serial, and system power and ground connections.
• (D) Speaker
The built-in speaker is used for audible warnings. The speaker volume can be adjusted through the display
setup routine.
• (E) Power/Reset Switch
The Power/Reset switch is used for turning the display on and off in installations where the system is
connected to a continuous power supply. If the display ever stops responding, the manual power switch
may be held in for five seconds to restart the system. Only do this as a last resort, data loss could occur
during times of improper shutdown.
“Mounting the Display” on page 6.
INSTALLATION INSTRUCTIONS
All machine installation and mounting kits are shipped with instructions specific to that kit. Instructions
include special details relating to mounting, wiring and display configuration.
5
Page 18

Mounting the Display
Mount the display to a secure support inside the vehicle cab. The following must be considered when
choosing a mounting location.
• The display must be readily accessible to the machine operator.
• The display must not obstruct the machine operator's normal driving view.
• The display must not interfere with or limit access to any of the existing machine controls.
• The display CAN system cabling be routed and secured without interfering with existing machine controls.
WARNING: If drilling holes is required during the mounting process, care must be taken to insure that
damage is not done to existing vehicle wiring, mechanical, or cab structure. Refer to vehicle manufacturer
documentation for specific details on your equipment. Follow all OEM instructions, cautions, and warnings
when working around equipment.
Mounting Components
1. RAM Base, PN 4000280
2. RAM Arm - 5”, PN 4000279
3. 2”X6” Base, PN 400187
6
Page 19

Fuse Installation and Replacement
GENERAL
CAUTION: The fuse is to be placed in the fuse holder in-line with the battery power cable and used with
display only.
SCREEN ICON CONVENTIONS
The following control buttons are made available for entering names and calibration values into the
display.
7
Page 20

An on-screen Keyboard is made available when appropriate
for use during all setup processes. Press the keyboard
button to access the on-screen text entry screen.
An on-screen Numeric Keypad is made available for
changing configuration settings and calibration numbers.
Press the keypad button to access the on-screen numeric
entry screen.
8
Page 21

SETUP
SETUP
SYSTEM FUNCTIONALITY
Prior to setup, most of the functionality of the display is not
available until the basic setup process is completed, and the
Home screen will look like the picture below. The Run Time
Environment is not accessible, because the Map button does
not appear on the task bar at bottom.
You must complete these initial configuration steps for the Run
Time Environment to be active:
1. Grower, Farm, and Field management.
For more information, see
2. Equipment Operating Configuration.
For more information, see the configuration information described in each Operations chapter (for example,
Planting, Application, Tillage, etc.).
3. Product setup.
For more information, see the configuration information described in each Operations chapter.
“Management” on page 10.
SETUP
4. Start Field Operation.
For more information, see
“Start Field Operation” on page 17.
HOME SCREEN
After a Grower, Farm and Field has been selected, the Home
screen will appear as shown. Specific functions available at the
Home screen are described in the table below.
• Diagnostics button
Opens screens that display Device Information, Memory, Display, and module diagnostics.
For more information, see
The Start Field Operation button, the top center button which shows the Grower Farm and Field, opens
the Field Operation Wizard where you can enter information relating to your Growing Season, Grower,
Farm, Field, Crop Type and Product. For more information, see
“Diagnostics” on page 24.
“Field Notes” on page 16.
• Setup (wrench) button
Opens the Setup screen. For more information, see
“Setup Screen” on page 10.
9
Page 22

• View Operation Summary button
Opens the Select Summary screen, where you can select different configuration settings for
Seasons, Grower, Farm, Field, Operations, and Product. For more information, see
on page 23.
SETUP SCREEN
The Setup Screen is where you can access management information, adjust display and
GPS settings, and specify field operations. Begin by going to the Home Screen, and pressing
the Setup (wrench) tool. The Setup Screen appears, as shown.
“Summary”
Press the Management button, and the Management tabs
appear. These are described on the following pages.
MANAGEMENT
The Management tabs, which are accessible from the Management button on the Setup
screen, include Grower, Season and Field.
• For information on the Season Tab, see
• For information on the Field Tab, see
“Field Management Tab” on page 12.
GROWER MANAGEMENT TAB
The Grower is a global setting that refers to the business or
person the system is in operation for. Contact information can
be added for each grower. The Grower information will be
passed into mapping software for automatic Grower setup
within desktop software.
• Press the Add (plus sign) button to add a Grower.
• Press the Delete (minus sign) button to delete a Grower.
• You may edit an existing name of a Grower by highlighting that name and pressing the on-screen
keyboard.
“Season Management Tab” on page 11
.
• Press the Wrench Button to add or edit information for a Contact Person, Business Phone, Mobile
Phone, or import an .msf file. For more information on adding an .msf file, see
on page 11.
10
“Importing an .MSF File”
Page 23

Importing an .MSF File
A Management Setup File (.msf) is a file format that allows the display to import Grower and Field
information from desktop software via a Compact Flash Card. Follow the process outlined below to
import desktop software information from your Compact Flash Card.
Note: When importing management items from an .MSF setup file, the imported data will always update or
be added to existing management data and will not overwrite it.
1. In the Grower Tab, press the Wrench Button. A screen opens, showing the name of that
Grower in the Title Bar, as shown.
2. Press the Import MSF button, and the File Selection screen
appears. (Be sure that your Compact Flash Card is already
placed in the display)
3. Open this folder by pressing the Plus sign to the left of the
folder. Highlight the desired .msf file and press the checkmark
box.
SETUP
4. The .msf file now appears under the Grower Tab on the
Grower list.
SEASON MANAGEMENT TAB
A season is defined as the calendar year that the crop will be
harvested. Creating a season and setting it to active is
required prior to the system logging any data.
The seasons are displayed in lists, with the Active season
displayed in bold face type. All new data is logged to the active
season; therefore a season must be set as Active before you
can log any new data to it.
• Press the Add (plus sign) button to add a Season.
• Press the Delete (minus sign) button to delete a Season.
• You may edit an existing name of a Season by highlighting that name and pressing the on-screen
keyboard.
• Press the Set Active button to set the season selected in the Summary list box to the active season.
• Press the Season Reminder button to set the date that the system will prompt the user to create a new
season.
11
Page 24

FIELD MANAGEMENT TAB
A field consists of one or more outer boundaries. Each outer boundary can contain one or more inner
boundaries used to define any combination of roadways, waterways, building sites, or bodies of water. If
the display will be used for multiple Growers, enter each Grower business name and associate the field
names with the correct grower when the fields are setup within the system.
In the Field Tab, select a Grower underneath the drop-down
menu at the top. Each farm of that particular grower is shown
in a list, with the fields within that farm as subcomponents
within that list.
• Press the Add (plus sign) button to add a Field.
• Press the Delete (minus sign) button to delete a Field.
• You may edit an existing name of a Field by highlighting that
name and pressing the on-screen keyboard.
• Press the Wrench Button to add or edit information regarding that field and its boundary. The Field
Information screen opens, showing the name of that field in the Title Bar.
The example shows the “160” Field of the “Home” Farm.
• Farm
Name of farm.
• Area
Total acres of farm.
• Clear bounds
Press the Clear Bounds button to center the map on the current
GPS position. This is particularly useful if you have flyer points or
have logged a point outside the mappable range of your current location.
• FSA Number
The U.S. Farm Service Agency’s four-digit number assigned to every farm.
• FSA Area
Tillable acres as established by the FSA.
• Boundary
Press the Boundary button to import and export boundaries. A detailed explanation is described on the
following pages.
Import and Export Boundaries
Boundaries can be created with the display or imported from
desktop GIS software. For more information on creating
boundaries, see
files present in the display can also be exported for use in
desktop mapping software. Begin by pressing the Boundary
button on the Field Information screen, which can be viewed
after pressing the Field Tab’s Wrench Button button. The View
Boundary screen appears.
“Create a Boundary” on page 22. Any boundary
12
Page 25

Boundary Import
Boundary Export
SETUP
1. To import a boundary from the external data card, press
Import. The File Selection screen appears, as shown.
2. Select the desired file to import.
3. Press the checkmark box on the File Selection screen to
complete the import process.
1. To export a boundary to the external data card, press
Export.
2. A screen appears, telling you that the boundary was
exported successfully. Press the checkmark box.
3. Press the checkmark box on the View Boundary screen.
CONSOLE
The Console screen contains settings related to Time, Date, display console screen
settings, operating units and external card information. To go to the Console screen, press
the Console button on the Setup screen. The Console screen consists of four tabs: General,
GENERAL TAB
Note: The display will then shut down immediately. If you do not want to shut the monitor down, press the
Close (Red X) button.
• Brightness and volume percentages
To change these, press the Brightness/Volume button and use the up and down arrow buttons to change
the percentage of the Display Brightness and Speaker Volume.
Memory, Features and Advanced.
The General Tab consists of the following items:
• Time and Date settings
To change these, press on this button and use the up and down
arrow keys to adjust the hours, minutes, A.M./P.M. settings, month,
date and year. To make these changes effective, press the
checkmark/ Shutdown button.
• Calibrate Touchscreen
Press this to launch the Touch Screen Calibration wizard. Calibrate the touch screen by following the onscreen instructions.
13
Page 26

• Time Zone
Use the drop-down menu to select your time zone.
• Country/Language Selection
Use the drop-down menu to select the language.
• Operating Units
Select either Imperial or Metric.
MEMORY TAB
The Memory Tab displays the used and free space available
on the external data card, as well as the percentage of memory
used on that card.
The Memory Tab also includes the following items:
• Create Backup
Press to create a backup file of all configuration settings, products, and Grower-Field Management data
structure on the external memory card. Backup files are stored using the .ibk file format.
• Restore Backup
Press to restore a backup file from the external data card to the internal memory of the display.
• Copy to Card
Copies files which have not yet been copied to the external storage card. (Log files are stored using the .ilf
file format).
• Upgrade
Press to load program upgrade files from the external storage card in order to upgrade the display and
modules.
• Browse Files
Press to view all files on the external memory card.
• Clear Internal Memory
Press this button to clear the internal memory of the monitor. The system will present a warning dialog box
and ask if you would like to create a backup file prior to clearing the memory.
CAUTION: The display will be returned to a “new out-of-box” un-configured state when the memory is
cleared.
14
Page 27
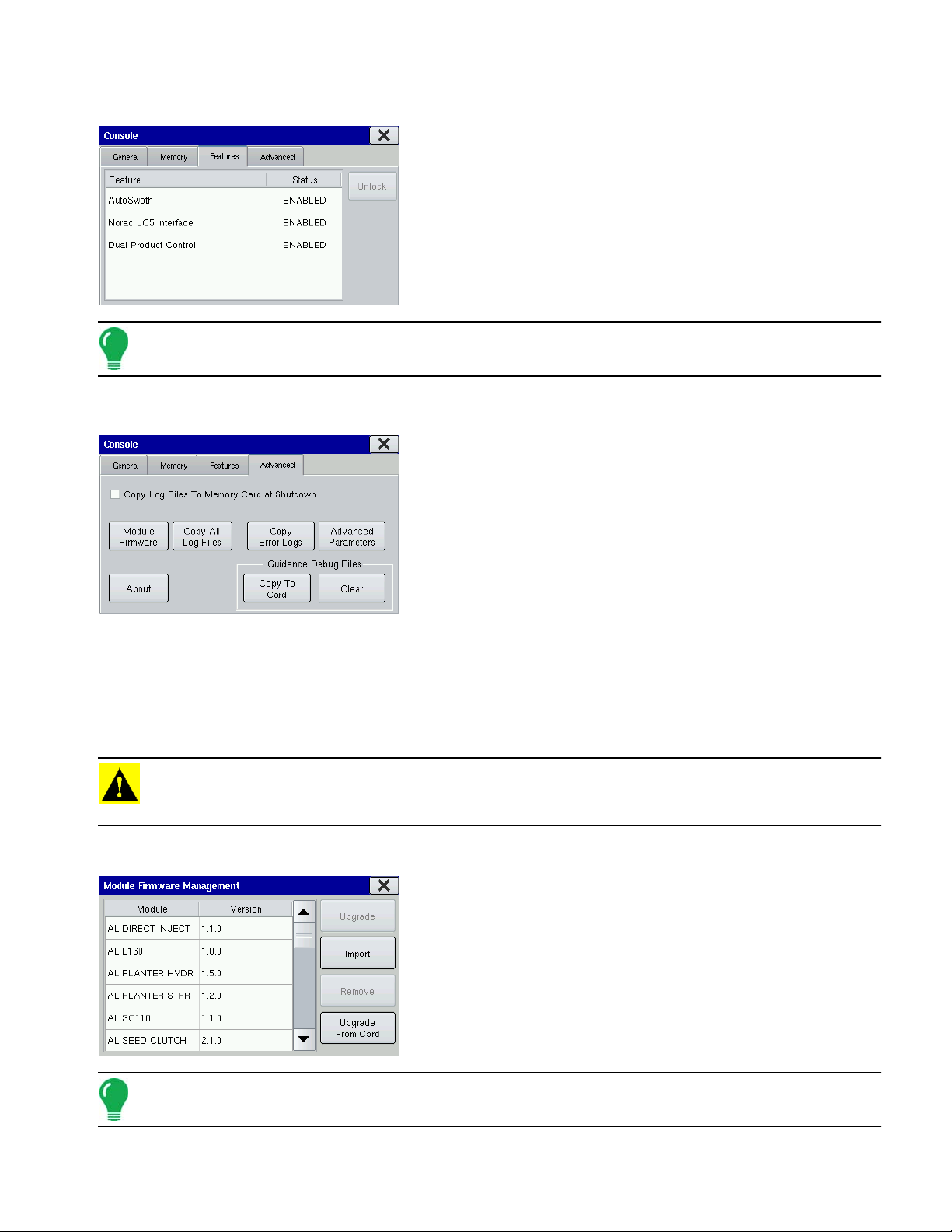
FEATURES TAB
Unlock codes are unique to the serial number of each display
and the feature registration number. You must supply these
numbers to your dealer when purchasing any unlock codes.
Press the Unlock button, and the Feature Registration box
appears. Use the on-screen keyboard to enter the unlock code
and press the checkmark box to enable the feature. This
feature then appears and the status is shown as “Enabled”.
Note: Once a feature is unlocked, that feature remains with that display and cannot be transferred to another.
ADVANCED TAB
The Advanced Tab contains the following functions of interest
to most users:
• Copy Log Files to Memory Card at Shutdown
Checking this checkbox will copy all log files to the external
memory card when the display is turned off.
SETUP
• Copy All Log Files
Press to copy all logged data in the display to the external storage
card.
• About
Displays product licensing information and copyright information.
• Module Firmware Management
Displays a list of all firmware modules and firmware versions that are available for the display. For more
information, see
CAUTION: The Advanced Parameters, Copy Error Logs, Guidance Debug Files (Copy to Card, and Clear)
functionality is reserved for use by the manufacturer. Do not change any of these settings without specific
instruction from Technical Support.
“Module Firmware Management” on page 15
.
Module Firmware Management
The Module Firmware Management screen displays a list of all
firmware modules and firmware versions that are available for
the display.
Note: The Module Firmware Management list includes module firmware that you may not be running.
15
Page 28

• Upgrade
Makes necessary upgrades to all the modules’ firmware while the display’s firmware is upgraded.
• Import
Imports any firmware stored on the Compact Flash Card into the display memory.
• Remove
Removes unwanted module firmware from the Module Firmware Management list.
Note: Pressing the Remove button does not remove firmware from the module itself. It merely removes the
upgrade file from the display.
• Upgrade from Card
Upgrades an individual module directly from the Compact Flash Card.
FIELD NOTES
Markers are a collection of point objects shown as icons on the Map Screen. As the name suggests,
markers allow the operator to mark mapping points “on the go” and thus identify specific features within
a field.
You can create markers by pressing the Field Notes button on the Setup screen. The Field
Notes screen opens.
• Add
Press the Add button to add a Field Note. This marker then
appears on Map Options at the Map screen. For an
example, see
• Keyboard button
Press the on-screen keyboard button to edit the marker
name.
• Up and down arrow buttons
Press the up and down arrow buttons to rearrange the
order of the map icons.
• Change Icon button
Opens the Icon Selection screen, as shown, where you can change the appearance of a map icon.
“View Map Markers” on page 23.
Note: For information on viewing the Field Notes on the Map Screen, see “View Map Markers” on page 23.
16
Page 29
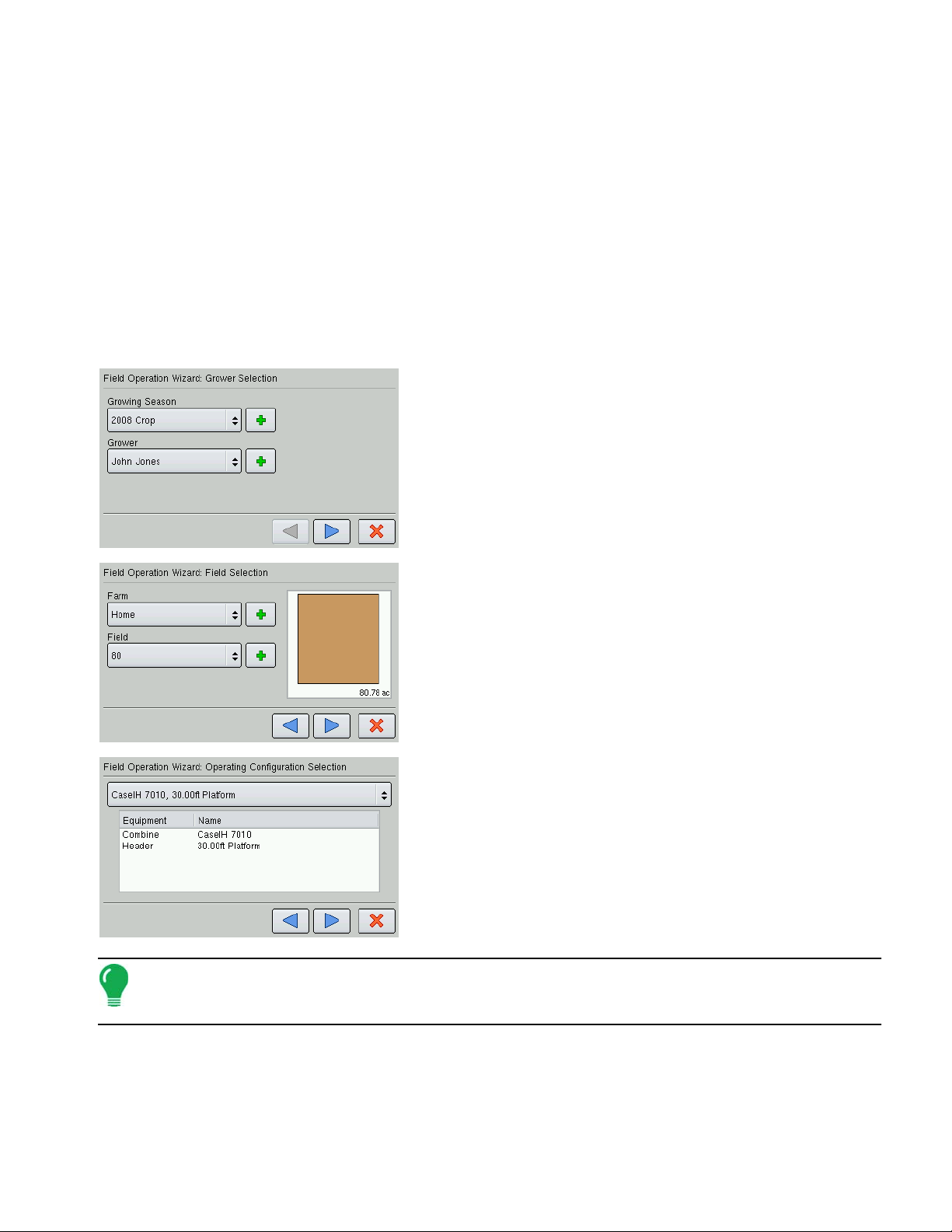
START FIELD OPERATION
You can start field operations after setting up a Grower, Farm and Field; and then creating an operating
configuration.
SETUP
• To set up a Planting Operating Configuration, see
• To set up a Tillage Operating Configuration, see
• To set up an Application Operating Configuration, see
• To set up a Harvest Operating Configuration, see
After creating an operating configuration, begin by returning to the Home screen. To Start Field
Operations, press the Start Field Operation button. The Field Operation Wizard appears. Follow the
steps in the Wizard to select an operating configuration.
1. Grower Selection
Enter a Growing Season and Grower either by using the drop-down
arrows to select existing ones, or by pressing on the Add (plus sign)
arrow to create new ones. Press the blue right-arrow key at the
bottom of the screen to proceed to the next step.
2. Field Selection
Add a Farm and Field either by using the drop-down arrows to
select existing ones, or by pressing on the Add (plus sign) arrow to
create new ones. Press the blue right-arrow key at the bottom of
the screen to proceed to the next step.
“Create a Planting Configuration” on page 67.
“Create a Tillage Configuration” on page 61.
“Create an Application Configuration” on page 101.
“Create a Harvest Configuration” on page 171.
3. Operating Configuration Selection
Use the drop-down arrow to select a configuration. Press the blue
right-arrow button to continue.
4. Product Selection
Users creating Field Operating Configuration in either Planting or
Application must select a product from the drop-down list. Press
the blue right-arrow button to continue. At the Options screen, enter
in a Controlling Product and Units.
Note: If you are selecting an Application product, you may check the box marked Show Only Tank Mixes
and Blends at the Product Selection Screen. If this box is checked, the display will only allow the selection of
tank mixes that were previously set up.
5. When you complete the steps in the Wizard, you will return to the Home Screen.
17
Page 30

RUN TIME ENVIRONMENT: MAP SCREEN
The appearance of the map screen varies, depending upon which operation you are performing. As
examples, typical map screens for Tillage and Harvest are shown. Data shown at the Title Bar at the top
of the Map Screen show speed and distance logged. Icons on the Map Screen itself indicate features
pertaining to the specific operation you are viewing at the map screen. Buttons on the Task Bar at the
bottom of the map screen show all operations that you are currently performing.
• Map Screen - Tillage (Zoom Detail)
• (A) Title bar
• (B) Map Screen Icons
• (C) Task bar
• Map Screen - Harvest (Zoom to Extent)
• (A) Legend
• (B) Status Item
Title Bar
The Title Bar shows current speed in miles per hour (kilometers per hour) and area logged.
Task Bar Buttons
The task bar displays buttons relating to various functions of the display. These buttons include Home,
Mapping, Liquid Rate Control, Planting Rate Control, Harvest, Autoswath, and Logging. These buttons
are shown in front of a green background when you are at that screen; otherwise they are shown in front
of a blue background.
Home Button. Pressing the Home button takes you to the Home screen.
Map Button. Pressing the Map button takes you to the Map screen. Pressing it more than once cycles
the Map screen to zoom in and out.
ZOOM DETAILS ZOOM TO EXTENT PERSPECTIVE VIEW
Note: The Perspective View is only available when guidance is active.
AutoSwath Button. Pressing this button turns the AutoSwath feature on and off. When AutoSwath is
on, the icon is green; when it is off the icon is white.
18
Page 31

AutoSwath - ON AutoSwath - OFF
Area Logging Status Button. This button appears for configurations that do not use rate control, such
as Tillage, Harvest, Planting operations that do not use SeedCommand, and Application operations that
do not use DirectCommand. Pressing this button turns logging on and off.
ON OFF
Rate Control Button. Pressing this button takes you to the Rate Control screen, which is
shown for both Planting and Application.
The NORAC Engage button enables boom height control. This button can toggle back and forth
between Automatic Mode and Manual Mode.
• NORAC Engage - Enabled
When you enable Automatic Mode, this button turns green and an arrow appears above the
triangle. At the same time, the display beeps three times.
SETUP
• NORAC Engage - Disabled
When you disable Automatic Mode on any part of the boom and the display switches to
Manual Mode, this button turns grey and the display beeps twice. If less than the full boom
remains in Manual Mode, the display will continue beeping twice every three seconds.
The Master Switch Indicator, shown for SeedCommand or DirectCommand functions, shows if the
master switch is on (green) or off (red). The master switch is shown in the F1 position on the Auxiliary
Input Settings screen.
Master Switch - ON Master Switch - OFF
Map Screen Icons
The GPS button in the upper left-hand corner of the Map screen, displays the following colors:
• Differential GPS
Green if you are receiving a differential GPS signal
• GPS - No differential
Yellow if you are receiving GPS, but no differential signal
• No GPS
Grey if you are receiving no GPS signal.
19
Page 32

The Engage icon shows that the OnTrac2 autosteer system is on, off, or off but ready to engage. The
appearance of this icon displays the following:
• Engage - On Green
autosteer system is on.
• Engage - Ready Grey
autosteer system off but ready to engage.
• Engage - Off Grey with a red circle and slash
autosteer system is off and unable to engage.
For more information, see the Guidance chapter at
“Guidance” on page 35.
The Map Options icon is used for numerous purposes. With this button, you can create
boundaries or place Field Markers. For more information, see
“Create a Boundary” on page 22
and “View Map Markers” on page 23.
Display Legend Icon - Off
Display Legend Icon - On
The Display Legend icon shows the Rate Display.
• If off, the Display Legend icon appears with the arrow pointing to the top and a grid within its border.
• If on, the Display Legend icon appears with the button pointing down and no grid within its border.
Vehicle Icon - Zoom to Extent
The Vehicle Icon is shown by an arrow inside a circle if the Map Screen is viewed in Zoom to
Extent.
The vehicle appears as a gold-colored triangle if the Map Screen is viewed in Zoom Detail. The
appearance of the zoomed-in icon changes depending upon the data being logged in the field. The
Zoom Detail changes the Map Screen’s appearance so that the vehicle icon is always shown pointed to
the top.
20
• Vehicle Icon - Logging
If the vehicle is logging, the implement icon appears as a green bar behind it, as shown
at far left.
• Vehicle Icon - with sections
If the vehicle is logging data from an implement split into sections, (for instance during
a planting or application operation), then these sections appear in the implement icon.
For an example, see the middle picture.
• Vehicle Icon - Not logging
If the vehicle is not logging data, then the implement icon appears as a grey bar, as shown
at the picture at right
Page 33

Press the center of the Map Screen, and four arrow icons appears around the vehicle icon. An
example of one of these arrow buttons is shown at left. Pressing these arrow icons will move
the center of the Map Screen in the direction of the arrow button.
• Zoom tools
The Zoom Tool icons, which resemble a magnifying glass, are shown at the
bottom right-hand side of the Map Screen. Pressing the zoom tool with the plus
sign increases the scale of the Map Screen; pressing the zoom tool with the
minus sign decreases the scale of the Map Screen.
Map Screen Status Items
The Legend is shown on the left-hand side of the Map Screen. This legend is shown
for Application, Planting and Harvest operations.
The colors and rate increments of the Legend can be adjusted. For more
information, see “Edit Legend” on page 21.
SETUP
EDIT LEGEND
By pressing on the Legend, the Legend Settings screen
appears, as shown. The Legend Settings screen allows you to
change the default legend for the rate applied.
Note: Legend settings changes that are made at this screen will affect all regions.
• Attribute
Attributes shown for Harvest include Yield and Moisture. The Rate attribute is shown for Planting and
Application operations.
• Average
The Average button changes the average rate for the legend.
• Spacing
The range Spacing button changes the difference between the rates in one color range.
• Ranges
The Ranges up and down arrow buttons change the number of range increments displayed in the legend.
21
Page 34

• Color Scheme
The color scheme can be modified by using the drop down list.
• Reset Legend
Resets the legend to the default settings.
• Automatic Legend
If the Automatic Legend checkbox is selected, the average automatically sets itself to the field average and
updates as the field average changes
• Save as Product Legend
Select the Save as Product Legend checkbox if you wish to set the current legend as the default legend for
all regions of the same product.
CREATE A BOUNDARY
To begin creating a Map boundary, press the Map Options icon on the Map Screen. The
Boundary Creation screen appears, as shown.
Press the Start button to start creating a boundary. The
Start Boundary screen appears, as shown.
• (A) View Guidance
• (B) View Boundary
• (C) View Map Markers
Start Boundary
1. You can create two types of Map Screen boundaries in the
display: Outer boundaries delineate the borders of an entire
field; inner boundaries mark specific features within that field,
such as waterways or buildings. Choose whether to create
either an Outer boundary or Inner boundary by pressing one of
the two Boundary Type buttons.
2. If you are creating an Inner Boundary, choose either
Roadway, Body of Water, Waterway, Buildings or
Undefined.
3. The Boundary Offset feature enables mapping a boundary at a user-defined distance to the left or right
of the GPS antenna centerline. If desired, specify a Boundary Offset distance by choosing a direction and
distance from the GPS antenna centerline.
4. Press the checkmark box to start the boundary.
PAUSE BOUNDARY
When creating a boundary, you can use the Pause Boundary button to create a straight line between
two points. To do this, drive the vehicle to a point, press the Pause Boundary button, then drive to the
second point. When you resume boundary creation, a straight line is created between your current point
and your pause location.
22
Page 35

VIEW BOUNDARY
At the Boundary Creation screen, you can press the View button to open the File Selection screen,
where you can view all field boundary information.
VIEW MAP MARKERS
Pressing on the View Map Markers button on the Create Boundary screen cycles this screen
to the Map Markers screen, as shown.
The Map Markers screen shows all of the Markers that you
created in
Note: If all of the Markers that you created are not immediately visible in this screen, use the up and down
arrows on the right-hand side to view more markers that you created.
“Field Notes” on page 16.
SETUP
• Press an individual marker to indicate a Field Note on the Map Screen.
• Press Clear Map to permanently remove all logged data from the active field operation.
• Press Clear Marks to permanently removes all mapped marks from the active field.
Note: For an explanation of the View Guidance screen, see “Guidance Functions” on page 36.
SUMMARY
Press the Summary button at the bottom of the Home Screen to view a summary information,
which shows you field totals and averages for a specific field.
If you have performed only one instance in a specific field, the
Summary Screen appears. Use the bottom scroll bar to view
all data for a particular field.
23
Page 36

Select Summary
If you have performed more than one operation for a field, the
Select Summary Screen appears. Use the center-right dropdown menu to choose the Operation that you wish to view.
Press the View Map button (A) to view a Summary Map.
Press the Summary Screen button (B) at bottom right to view
the Summary Screen.
DIAGNOSTICS
Pressing on the Diagnostics button on the Home Screen summons the Diagnostics screens
that pertain to your configuration. Technical support may request that you look at these
screens for help in diagnosing a problem. Three screens that appear for all configurations
include Device Information, Memory and Display, which are described in the following
section. Additional screens, appropriate to the connected modules, are present as needed.
Note: GPS Diagnostic information can be found at “GPS Diagnostics” on page 31.
DEVICE INFORMATION
MEMORY
The Device Information screen shows generalized diagnostic
information, including Firmware information, Hardware
information, Serial Number, Revision Number, Run Time, and
Boot Counter.
Additionally, the CAN Device List on the left-hand side of this
screen displays the modules that are connected to the CAN
Bus. Select a device to display specific details in the Firmware
and Hardware Information frames of the CAN tab. Check the
CAN device list to ensure that all modules appear there.
The Memory screen shows information about memory usage,
both for the display as well as an external memory card.
24
Page 37

DISPLAY
SETUP
The Display screen shows generalized diagnostic information
about the display, including display temperature, as well as
display and CAN Bus voltage.
25
Page 38

26
Page 39

GPS
GPS
During your field operation, the GPS icon/button in the upper left-hand side of the Map
Screen should appear as green, which means you are receiving a differential GPS
signal. If this icon appears yellow, you are still receiving GPS but are not receiving a
differential signal. If it appears gray then you have lost GPS. In either case, you should
check your GPS settings.
GPS GENERAL TAB
At the Home screen, press the Wrench Button to go to the Setup Screen. Press the GPS
button, and the GPS General Tab appears, as shown.
- If using a GPS 2500 receiver, see“OmniSTAR Settings — GPS 2500” on page 29.
GPS
• Differential Source
Select choice of WAAS/EGNOS, Satellite (OmniSTAR®) or
Beacon (Coast Guard) differential sources.
• Wrench button
Pressing the Wrench button opens different settings screens,
depending on whether you are using OmniSTAR®, Beacon, or
WAAS.
• If using OmniSTAR
see
“OmniSTAR Settings” on page 28
• GPS Rate (Hz)
The GPS Position Rate drop-down menu represents the cycles per second that the display receives
guidance information from the GPS receiver. Select one of the available Hz rates from the drop-down menu.
• Age of Differential
Displays the elapsed time since reception of last differential correction signal. The Age of Differential button
is only functional when GPS is connected.
• Port Settings button
Displays the Serial Port Settings screen, where you can adjust GPS output. For more information, see
“Serial Port Settings” on page 28.
• Force TSIP Connection button
Forcibly connects to TSIP GPS receiver. Pressing this button will force the port to TSIP communication.
Note: This button is functional only if the TSIP GPS receiver is physically connected.
• Reset to Defaults button
Press this button to restore receiver settings to the factory default. This will remove all custom settings.
.
Note: Differential settings and NMEA messages will need to be configured for the system to function properly
after resetting factory defaults.
27
Page 40

• Ignore NMEA Checksum
Check this to ignore intermittent GPS message errors.
OMNISTAR SETTINGS
Pressing the Wrench button on the GPS General Tab opens the OmniSTAR® Settings
screen, as shown, where you can view differential source and frequency settings.
Serial Number/OmniSTAR User ID
This box shows the serial number of your receiver. It may also
display your OmniSTAR User ID.
• Differential Source
The choices include VBS, HP/XP, and HP/XP with VBS backup.
Note: The use of OmniSTAR® differential requires purchase of a subscription from OmniSTAR. Settings
related to using satellite differential correction vary based upon your geographic location. Setup details are
explained below. More specific information can be obtained by contacting OmniSTAR.
Note: You will need to know this number when contacting OmniSTAR in order to set up the receiver.
SERIAL PORT SETTINGS
A Serial Port Settings screen, where you can adjust GPS output, is shown for both Port A and Port B. To
go to this screen, first go to the Home screen, press the Wrench button and go to the Setup Screen.
Press the GPS button, and at the GPS General Tab appears, press the Port Settings button. The Serial
Port Settings screen appears, as shown. The appearance of this screen is the same for Port B.
• Output Type
Displays what type of protocol the receiver is using. (NMEA or
TSIP).
• Output Baud Rate
Displays the speed at which the receiver communicates with the
display. For optimal performance, the GPS baud rate should be set
at 192000 or higher.
• Output Parity
Displays either Odd or None.
- If using TSIP, this setting should be Odd.
- If using NMEA, this setting should be None.
Note: Parity refers to a technique for checking data integrity after transmission.
28
Page 41

• GPS Pos. Rate (Hz)
Represents the cycles per second (shown in Hz) that the display receives position information from the
receiver. (This is the same number as shown on GPS Rate (Hz) drop-down list menu located on the
General Tab).
• Output Rate (Hz)
Represents the cyclical rate (in Hz) at which the receiver sends information to the display. This field shows
a value of either 1 or ASAP.
- The default rate is 1 Hz.
- ASAP represents a Hz value of more than 1. (TSIP only)
• NMEA Messages
These check boxes represent various communication protocols or formats that have been set by the
National Marine Electronics Association (NMEA), and used in information “strings” or sentences output by
the GPS Receiver. At present, the display only uses two NMEA Message formats: GGA and VTG.
- GGA: This NMEA message format is the data fix that establishes your position in longitude and
latitude.
- VTG: This NMEA message format stands for ground speed (velocity) in area over distance
- GLL, GSV, GSA, ZDA, RMC, MSS: Leave these other NMEA message formats unchecked, unless you
are connected to a third-party monitor and have been directed to do so.
OMNISTAR SETTINGS — GPS 2500
GPS
At the Home screen, press the Wrench Button to go to the Setup Screen. Press the GPS button, and the
GPS General Tab appears, as shown.
When connected to a GPS 2500 receiver, the setup screen will
appear as shown to the left. To access the setup screen from
the home screen press the setup button (wrench) and then the
receiver button:
From this screen, you can view differential source and
frequency settings.
• Differential Source
Select choice of WAAS/EGNOS, Satellite (OmniSTAR®), or e-Dif.
• Wrench button
Pressing the Wrench button opens the OmniSTAR® setup screens.
• Age of Differential
Displays the elapsed time since reception of last differential correction signal. The Age of Differential button
is only functional when GPS is connected.
• Port Settings
Displays the Serial Port Settings screen, where you can adjust GPS output.
Note: This button is functional only if the TSIP GPS receiver is physically connected.
29
Page 42

• Reset to Defaults
Press the Reset button to restore the receiver settings to the factory default. This will remove all custom
settings.
Note: Differential settings and NMEA messages will need to be configured for the system to function properly
after resetting factory defaults.
• Ignore NMEA Checksum
Check this to ignore intermittent GPS message errors.
Pressing the Wrench button on the GPS/Guidance - GPS 2500 screen opens the
OmniSTAR® Setup screen, shown.
The General tab shows:
• OmniSTAR User ID
This box displays the receiver’s OmniSTAR User ID.
• Differential Source
The choices include VBS, HP/XP, and HP/XP with VBS backup.
The Provider tab shows:
• Frequency
Select the correct frequency for your area or contact OmniSTAR
support for help.
• Custom Frequency
Use only if directed to by OmniSTAR support or Technical Support.
• Baud Rate
Displays the speed at which the receiver communicates with the
display. For optimal performance, the GPS baud rate should be set at 192000 or higher.
• Differential Threshold
Is the limit at which the receiver will provide differential correction.
• AutoTune Frequency check box
Receiver will automatically select the strongest frequency.
• Fast Restart (AutoSeed)
Allows the receiver to get a converged position faster, on startup, if the vehicle has not moved since it was
powered down.
• GGA (GLONASS)
Checking this box allows the additional GLONASS satellites to be displayed in the GGA message.
GPS PORT SETUP - GPS 2500
To access the GPS Port Setup screen, press the Port Settings button, on the General tab of the GPS
Setup Screen.
30
Page 43

From this screen the user can adjust GPS output. The screen
is the same for both Port A and Port B.
• Output Baud Rate
Displays the speed at which the receiver communicates with the
display. For optimal performance, the GPS baud rate should be set
at 192000 or higher.
• GPS Rate (Hz)
Represents the cycles per second (shown in Hz) that the display
receives position information from the receiver. (This is the same
number as shown on GPS Rate (Hz) drop-down list menu located on the General Tab).
• NMEA Messages
These check boxes represent various communication protocols or formats that have been set by the
National Marine Electronics Association (NMEA), and used in information “strings” or sentences output by
the GPS Receiver. At present, the display only uses two NMEA Message formats: GGA and VTG.
- GGA: This NMEA message format is the data fix that establishes your position in longitude and
latitude.
- VTG: This NMEA message format stands for ground speed (velocity) in area over distance
- GLL, GSV, GSA, ZDA, RMC, MSS: Leave these other NMEA message formats unchecked, unless you
are connected to a third-party monitor and have been directed to do so.
GPS
GPS DIAGNOSTICS
To access Diagnostic information about the GPS signal, press the Satellite icon that appears
in the top-left corner of the Map Screen. GPS Information then appears on three different
GPS Information screens. You can cycle through these screens by pressing the blue rightarrow button.
GPS INFORMATION - FIRST SCREEN
• Latitude, Longitude, Elevation
Displays current position (in longitude and latitude) and elevation.
• Heading
Displays degree heading of travel.
• Differential
If a TSIP receiver is being used, the differential status will display
the differential source,(i.e. WAAS, Beacon or OmniSTAR). This
message field will display either Diff On or Diff Off.
- Diff On: Indicates the receiver is receiving a differential GPS signal.
- Diff Off: Indicates the receiver is not receiving a differential GPS signal.
• View Messages
To view the NMEA or TSIP messages coming from the receiver, press the View Messages button.
31
Page 44

GPS INFORMATION - SECOND SCREEN
• UTC Time
UTC is an acronym for Coordinated Universal Time, a highprecision atomic time standard that defines local time throughout
the world. Different versions of universal time use atomic clocks to
correct for irregularities in the Earth's rotation and orbit. UTC is
used in navigation, astronomy, aviation, Internet broadcasts, and
amateur radio. If you are receiving information from the satellite,
then the UTC Time should automatically update.
• HDOP
Horizontal Dilution of Precision (HDOP) indicates the quality of the horizontal GPS position. Lower HDOP
numbers are optimal, higher numbers are undesirable.
• PDOP
Position Dilution of Precision (PDOP) is a unitless measure indicating when the satellite geometry can
provide the most accurate results. When satellites are spread around the sky, the PDOP value is low and
the computed position is more accurate. When satellites are grouped close together, the PDOP is high and
the positions are less accurate. Lower PDOP numbers are optimal, higher numbers are undesirable.
• Port
The connection between the display and the GPS as established at a message format and baud rate.
• Frequency
The Correction Frequency indicates the GPS satellite frequency used by the receiver.
Note: The Correction Frequency diagnostic does not show for WAAS connections.
• SNR
If your receiver is using Beacon differential corrections, the frequency and signal to noise ratio (SNR) will
be displayed. Signal-to-Noise Ratio (SNR) indicates the strength of the differential correction signal in
relation to the amount of background noise that can interfere with signal reception.
• GPS Speed (mph)
The speed of the vehicle.
• GPS Rate
The update rate from the GPS receiver, shown in Hz.
GPS INFORMATION - THIRD SCREEN
• Receiver ID
• Firmware Version
• Serial Number
32
• Receiver Voltage
• Fast Update Rate
The Fast Update Rate indicates whether your receiver is capable
of outputting an update rate faster than 1 Hz per second.
Page 45

- If the Fast Update Rate is ON, then your receiver is capable of outputting an update rate faster than 1
Hz per second.
- If the Fast Update Rate is OFF, then currently your receiver is only capable of an update rate of 1 Hz
per second. Contact Technical Support to see if your receiver can be upgraded to a faster update rate.
Note: The settings shown on this GPS Information screen varies, depending upon your model of GPS
receiver.
Fast Update Rate and Everest Multipath are only available with TSIP receivers.
ONTRAC2 INFORMATION
Users of the OnTrac2 guidance system can also view the
OnTrac2 Information screen below, in addition to the GPS
Information screens discussed previously.
• OnTrac2 Vehicle
Displays active vehicle profile.
• ESC Firmware Version and ECU Firmware Version
Displays current firmware versions for OnTrac2.
• Steering Status
Displays either Good or Bad. If the MDU does not have power, it will display a message stating MDU Power
Error.
GPS
PARADYME INFORMATION
Displays current steering profile.
• Steering Status
Displays either Good or lists system errors.
NTRIP INFORMATION
Users of the ParaDyme guidance system can also view the
ParaDyme Information screen (shown at the left) in addition to
the GPS Information screens discussed previously.
• Firmware Version
Displays ParaDyme firmware version.
• Serial Number
Displays ParaDyme serial number.
• Active Vehicle
Users of the NTRIP guidance system can also view the NTRIP
Information screen below, in addition to the GPS Information
screens discussed previously
• Connect
Connects the display to the NTRIP correction source.
• NTRIP Stream
Network mount point.
33
Page 46

• NTRIP Status
Displays NTRIP connection; either Connected or Disconnected.
• Cellular Status
Displays status of ParaDyme cellular modem; either Connected or Disconnected.
• Cellular Signal Strength (%)
Displays a number between 0 and 100%.
• WiFi Status
Displays status of WiFi router; either Connected or Disconnected.
• WiFi Signal Strength
Displays a number between 0 and 100%.
Note: This screen is only available with the Paradyme receiver.
34
Page 47

GUIDANCE
GUIDANCE
The Guidance Tab, located on the GPS screen, includes some general settings for the onscreen lightbar and L160 External Lightbar features.
Note: In order to use guidance with the display, you must have a GPS receiver capable of a GPS output rate
of 5 Hz or more.
GPS GUIDANCE TAB
Guidance Control
The Guidance Controls area of the Guidance Tab includes
information specific to lightbar and guidance features.
• Manual Guidance
Select this to adjust lightbar settings. For more information, see
“Lightbar Settings” on page 36.
GUIDANCE
• OnTrac2 Steering
Select this for the OnTrac2 feature. For more information, see
“OnTrac2” on page 48.
• ParaDyme Steering
Select this for the ParaDyme feature. For more information, consult the ParaDyme Insert, PN 4002139 Rev.
C.
• Required Differential Correction for Guidance
When un-checked allows guidance to operate without differential correction.
• Lightbar Settings
Opens the Lightbar Settings screen. For more information, see
• Operator Presence Alarm
Available for OnTrac2 and ParaDyme users. The Operator Presence Alarm disengages guidance control if
the operator does not have any interaction with the display for a specified period of time. Use the drop-down
menu to specify the period of time before guidance is automatically disengaged.
Pressing the Wrench Button on the Guidance Tab opens the guidance system settings for
the selected guidance system.
“Lightbar Settings” on page 36.
Pattern Files
The Pattern Files area of the Guidance Tab Imports guidance pattern files from the compact flash card.
For more information, see
• Import
Imports guidance pattern files from the compact flash card.
• Export
Exports guidance pattern files from the display to the compact flash card.
“Guidance Screen” on page 37.
35
Page 48

• Remove All
This will remove all guidance pattern files from the display’s internal memory.
LIGHTBAR SETTINGS
To adjust lightbar settings, press the Lightbar Settings button on the Manual Guidance screen. The Lightbar Settings screen appears, as shown.
• LED Spacing
Enter in an amount specifying the distance represented by each
square of the lightbar. You can enter in a number ranging between
6 and 72 inches.
• Mode
This determines which method to use the GPS information
provided on the display's Map screen to center the vehicle on the AB Line. Select either Chase or Pull.
- If you select Chase, then in order to center the vehicle on the AB Line, you must follow the indicator
lights on the lightbar.
- If you select Pull, then in order to center the vehicle on the AB Line, you must turn the vehicle in the
opposite direction of the indicator lights on the lightbar.
• External Lightbar LED Brightness
If applicable, use the up and down arrows to enter in a number specifying the brightness of the LED lights
on the L160 lightbar. The number 1 is the dimmest setting and 10 is the brightest; the default setting is 5.
GUIDANCE FUNCTIONS
Display users can use either Manual Guidance, OnTrac2, or ParaDyme for guidance operations. The
setup procedures and use are explained below. Lightbar operation and pattern information applies to
users of the Manual Guidance, OnTrac2 and ParaDyme features.
ON-SCREEN LIGHTBAR
The on-screen lightbar is an option for users who have not
purchased an external lightbar. This on-screen lightbar will not
appear if you are using an external lightbar.
• (A) Cross-Track Error
The Cross-Track Error indicates your vehicle's distance from the
AB Line. This distance from AB Line number shows the length
between the location of your vehicle's GPS antenna and the
nearest point on the closest pass.
• (B) Guidance Lights
The guidance lights indicate directional changes as you steer the
vehicle right or left. You can specify the distance each guidance
light indicates (for example, 6 inches or 1 foot).
• (C) Pass Number
The number of passes (either right or left) from the AB Line.
36
Page 49

• (D) Map Icon (Perspective View)
• AB Line
The AB Line is a line that runs between Point A and Point B.In most cases, the AB Line is the reference line
for subsequent swaths. When you press the Set A button on your display, the "A" point will appear on your
display's screen. When you press the Set B button, the "B" point will also appear on the screen, and the
line between the two points serves as your AB Line.
Note: You do not have to set a B point for an A+ Pattern.
Note: In order for the lightbar to appear, you must first create a new pattern. For more information, see “New
AB Pattern” on page 38.
GUIDANCE SCREEN
The Guidance Screen is where you can create a new pattern, load an existing pattern, or adjust
Guidance Options and Guidance Settings. At the Map Screen, press the Map Options button.
If the Guidance Screen does not automatically appear, press the Guidance button and go to the
Guidance Screen. The Guidance Screen appears, as shown. After you have created an AB line,
the appearance of the Guidance Screen changes and different options are available.
GUIDANCE
• Save Pattern
For more information, see
“Save Pattern” on page 43.
• Options
For more information, see
“Guidance Options” on page 47.
• Adjust Steering
For more information, see
“Steering Adjustment” on page 55.
• A-B
For more information, see
Lines Within SmartPath” on page 42.
“Create an AB Line Within a SmartPath Pass” on page 41
• Nudge settings
For more information, see
“Nudge” on page 48.
The Guidance Screen includes the following
• New Pattern
For more information, see
Guidance Patterns” on page 44.
“New AB Pattern” on page 38
• Load Pattern
For more information, see
“Load Pattern” on page 43.
• Reset
For more information, see
“Reset Pattern” on page 43.
and
and
“About
“Choose Existing
37
Page 50

New AB Pattern
Use the following procedure to create a new pattern. The following example explains how to create an
AB line.
Note: Pattern options other than SmartPath and Straight AB are explained in full detail on “About Guidance
Patterns” on page 44.
1. Press New Pattern
At the Guidance screen, press the New Pattern button.
2. Select Pattern
The New Pattern Screen appears.
Select from the following available guidance patterns:
• SmartPath
• Adaptive Curve
For more information, see
For more information, see
• Straight AB
• Pivot
For more information, see
“Adaptive Curve” on page 46
and
“Adaptive Curve” on page 47
“SmartPath” on page 40.
“Pivot” on page 45.
.
• Identical Curve
For more information, see
Note: If you would like to use an A+ Heading pattern option, check the Use A+ Heading check box and use
the number pad to enter in the heading (in degrees). For more information, see “A+ Pattern” on page 44.
“Identical Curve” on page 46.
3. Change Guidance Width (optional)
In addition to these Guidance Options, a default Guidance Width is shown, based on the Implement Width
that you specified in Implement Configuration. If you wish to change this Guidance Width, enter the new
number using the numeric keypad. Press the green check mark box when finished.
Note: Guidance Width allows you to use guidance lines independent of implement width.
4. Mark the A Point
The Map Screen appears, with a point marker box in the center
marked A, as shown. Press the Set A button when you wish to mark
your A point.
5. Drive distance of AB Line
The place where you marked your A point now appears with a
green ball.
38
Page 51

Additionally, the point marker box changes its appearance, so
that the letter changes from Set A to Set B, however the Set B
button appears as greyed out. You must drive a minimum of
100 feet (30 meters) before marking the B point.
Note: If you are creating a Pivot pattern, you must drive a minimum of 160 yards (49 meters) before marking
the B point.
6. Mark B Point
After you have driven the appropriate distance, the Set B button
appears as a solid text, after which time you can mark a B point.
GUIDANCE
7. AB Line appears
When you have marked the B point, the AB line appears on the
Map screen as shown. The end of the AB line is marked with a red
point.
8. Create next pass
Turn left or right for the next swath. The next pass is automatically generated. Steer the vehicle so that you
center the green lights on the lightbar as you drive forward along the swath.
Note: On straight AB lines, if you complete a swath that is longer than the previous one, the display
automatically extends the guidance path for the following swaths.
39
Page 52

SmartPath
The SmartPath pattern is designed to give guidance
from any previously-driven pass. This is used in
irregular-shaped and terraced fields where you cannot
run all passes parallel to the previous pass. Instead, the
SmartPath guidance allows you to move to a different
area of the field, and then resume a previous guidance
pattern later. Moreover, you can use SmartPath to
create straight AB patterns within the SmartPath
pattern and cycle between any available pattern within
SmartPath to choose the appropriate one.
Creating a SmartPath Pattern
1. Press New Pattern
At the Guidance Screen, press the New Pattern button.
2. Select Pattern
The New Pattern Screen appears.
3. Select SmartPath
Select SmartPath from the drop-down list of available guidance
patterns.
4. Change Guidance Width (optional)
In addition to these Guidance Options, a default Guidance Width is shown, based on the Implement Width
that you specified in Implement Configuration. If you wish to change this Guidance Width, enter the new
number using the numeric keypad. Press the green check mark box when finished.
Note: Guidance Width allows you to use guidance lines independent of implement width.
5. Drive the SmartPath
The Map Screen changes its appearance to Perspective View, and the Active Line Cycle button appears
on the Map Screen.
40
Page 53

6. Turn Around.
After you turn around on your first pass, the system
guidance will follow a maroon-colored line parallel to
your previously-driven pass. An example is shown in
the picture below.
As you continue using the SmartPath, the map
screen will display three lines:
• (A) Base Path
Appears as a black line, is the initial SmartPath that
you created on the first pass.
• (B) Followed Path
Appears as a maroon-colored line, is the path that your vehicle is currently using.
• (C) Projected Path
Appears as a blue-colored line on the opposite side of the Base Path, is an alternate path parallel to the
Base Path. The system guidance created this path when you created the Base Path. This is the path that
your vehicle would have taken if you had turned it in the opposite direction.
• (D) Active Line Cycle
SMARTPATHNOTES:
GUIDANCE
• The Projected Path and Base Path both remain in display memory, unless you press the Reset All button
without saving the SmartPath pattern.
• Pressing the Save Pattern button saves all the SmartPath passes within the display’s memory for future
use.
• If you drive your vehicle onto the Projected Path, the system guidance uses this as the Followed Path.
Select a Previous SmartPath Pass
If you have specified SmartPath as your desired pattern, but you are not following an active guidance
pattern, the Guidance System automatically begins searching for SmartPath patterns for your use.
If you wish to use a previously-created SmartPath pattern, you can do so by pressing on the
Active Line Cycle button. This button allows you to cycle between available SmartPath
patterns.
Notes:
• When the guidance system looks for other available SmartPath patterns, it first displays the nearestavailable pass.
• You can adjust the available area in which the Guidance System searches for previously-created
SmartPath passes. To do this, adjust the Heading Threshold settings on the Smart Tab of the Guidance
Options screen. For more information, see
“SmartPath Guidance Options” on page 42.
Create an AB Line Within a SmartPath Pass
In addition to creating irregular curved passes within SmartPath, you can also create straight AB lines to
be used in conjunction with the curved passes. By doing this, you can switch back and forth between a
SmartPath and a Straight AB pattern.
As you are using a SmartPath pattern, go to the Guidance Screen and press the A-B button. Follow the
instructions on creating an AB line as explained in
“New AB Pattern” on page 38.
41
Page 54

Once the AB line is created you can switch between the AB line and SmartPath patterns by pressing the
AB/SmartPath toggle.
A-B/SmartPath Toggle
• Curved Lines
• Straight AB Line
After the Guidance System has switched over to a different
path, the name of the currently-followed pattern is shown
within a black box on the Map Screen.
Choose Existing Lines Within SmartPath
You can create up to 10 different AB lines within SmartPath. Select the desired AB line by
pressing the A-B button on the Guidance Screen. The AB Manager Screen appears, which
shows all AB lines created within a particular field. An example is shown.
• Highlight the desired AB line, then press the green check
mark button to close the screen.
• Press the New button to add an AB line.
• Press the Load button to load an AB line.
• Press the Edit button to edit the name of an AB line.
• Press the Remove button to remove an AB line.
SmartPath Guidance Options
SmartPath only creates a SmartPath pass when you are logging data in the field. However, you have the
option of using it to create SmartPath passes continually during all field operations.
To adjust this setting, press the Options button on the Guidance screen. At the Guidance Options
screen, press the Smart button. The SmartPath Options screen appears, as shown.
Notes:
• The default setting is Logged Area. This setting only creates
passes when you are logging field data.
• By selecting All Area Covered, you can create SmartPath
passes even when not logging field data.
42
• The Heading Threshold setting is the available area that the
Guidance System uses to search for previously-created SmartPath
passes. The default setting is 20 degrees.
Page 55

Save Pattern
You can save a pattern (.pat file) to the display's internal memory to the current field by using the
following procedure.
1. Press Save Pattern
The Save Pattern screen appears, as shown.
Note: The Save Pattern button will appear when there is an active pattern.
2. Name the pattern
Press the keyboard button and enter a unique pattern name. When finished, press the green check mark
box.
Notes:
GUIDANCE
• To verify that the pattern is saved, you can open the Save Pattern screen again by pressing the Save
Pattern button. Your newly-saved or named pattern should now appear in the Save Pattern screen.
• You may remove all of the patterns by pressing the Remove All button. A warning appears, stating “All
guidance patterns will be permanently erased from memory.” If you wish to do this, press the green
check mark box to continue.
Reset Pattern
If you have been using an already-saved pattern, and wish to
switch over to a different pattern in the same field, you can use
the Reset Pattern feature by following the steps below.
1. Press Reset
Press the Reset button on the Guidance screen.
2. Confirm Reset
The Guidance screen appears, asking you to reset the current
guidance pattern. Press the green check mark box to continue.
3. Create new pattern (optional)
The pattern is now reset. You may now create a new pattern, if desired.
Load Pattern
You can load a pattern from the display's internal memory to the current field by using the following
procedure.
1. Press Load Pattern
Press the Load Pattern button on the Guidance screen.
43
Page 56

2. Select a Pattern
The Load Pattern screen appears, as shown. Select and highlight
the desired pattern. If the pattern you selected was an AB Line, that
pattern now appears on the Map screen. Press the green check
mark box to continue.
3. (Optional) Enter Guidance Width
The Shift Pattern screen appears. The default Guidance Width is
shown, based on the Implement Width that you specified in
Implement Configuration. If you wish to change this Guidance
Width, enter the new number using the numeric keypad. Press the blue right-arrow button to continue.
4. Select Shift Pattern
The Shift Pattern screen appears.
• If you have chosen the Shift by Distance option, use the numeric
keypads to select the distance, in feet and inches, that you wish to
shift the pattern. Use the bottom drop-down menu to enter the
direction, (either left or right), which you wish to shift the pattern
relative to the AB Line. When finished, press the green check mark
box.
• If you have chosen the Shift by Rows option, use the first
numeric keypad to select the number of rows you wish to shift. Next, use the second numeric keypad to
select the row spacing in inches that you wish to shift the pattern. Use the bottom drop-down menu to
enter the direction, (either left or right), which you wish to shift the pattern relative to the AB Line. When
finished, press the green check mark box
ABOUT GUIDANCE PATTERNS
The following pages define available guidance pattern other than a SmartPath or Straight AB Line.
• For a description of a Straight AB line, see
• For a description of SmartPath, see
“SmartPath” on page 40.
A+ Pattern
Similar to an AB line, an A+ line is also a straight line. It is defined by a
single point on the line (the A point) and the heading of the line. Use this
pattern when you wish to make a straight line based on a compass
heading. The A+ line extends 1 mi (1.6 km) before and after the A point.
1. At the Guidance Screen, press the New Pattern button. Choose
Straight AB, and enter a swath width. Press the Use A+ Heading check
mark box and enter in a degree number. Press the green check mark box
when finished. You will automatically return to the Map screen.
2. To map the start of the first swath, map Point A. The heading of the
AB line equals either the previous AB heading of the manually-entered
heading (if the current vehicle is within plus or minus 90 degrees of the
AB heading). Otherwise, the A+ heading is in the opposite direction.
3. Follow the AB line for guidance down the first swath.
4. Turn left or right for the next swath. The next swath is automatically selected.
“New AB Pattern” on page 38.
5. Steer the vehicle so that you center the green lights in the lightbar as you drive forward along the swath.
44
Page 57

Pivot
Use the Pivot pattern for a field that is irrigated using a center-pivot.
With this pattern, you can drive concentric circles around the centerpivot. The display will calculate the center point based on where you
have driven. Otherwise, you can enter in the latitude and longitude of
the center point, if known.
1. At the Guidance Screen, press the New Pattern button. Choose
Pivot, and enter a swath width. Press the green check mark box when
finished. You will automatically return to the Map screen.
2. Position one wheel of the vehicle in a pivot wheel rut, with the rear of
the vehicle to the pivot arm.
3. To start the pivot, set Point A.
4. Drive around the field. Keep the vehicle wheel in the rut. The lightbar
does not yet provide guidance.
5. When you are almost back to the pivot arm or the edge of the field, set Point B.
6. A screen appears. It states: “Please wait while the Pivot Center is
calculated”.
GUIDANCE
Next, you must set the Field Edge. You may do this
when the Pivot Field Edge screen appears on your display, as
shown left. From here, you may choose one of three options:
• Shift By Distance - This sets the field edge as the distance and direction
in relation to the AB Line created. In the Pivot Field Edge Distance portion
of the screen, enter the distance in feet and inches.
• Shift By Rows - This sets the field edge as the number of crop rows
multiplied by the number of spacing. In the Pivot Field Edge Distance
portion of the screen, enter the Number of Rows and Row Spacing. In
the example shown at bottom left, if you entered 3 rows and 30 inchspacing, the field edge would equal 90 inches.
• Close (red X)- The vehicle uses the driven pass as the AB Line.
Use the numeric keypads to enter the Number of Rows and Row
Spacing. Choose the direction relative to the AB Line (either
Outward or Inward), and press the green check mark box.
7. Turn left or right for the next swath. The next swath is automatically selected.
8. Steer the vehicle so that you center the green lights in the lightbar as you drive forward along the path.
To work from the center of the field outwards, the initial pivot must have:
45
Page 58

- A radius of at least two swath widths.
- An arc length of at least two swath widths.
• You can shift to the nearest row by going to the Guidance Screen and pressing Options.
At the Guidance Options screen, press the Nearest Row button.
The Shift to Nearest Row screen appears, as shown at left. Use the
numeric keypad to enter in Row Spacing, and then press the
Calculate Shift button in order to enter in the amount of distance to
shift. Press the green check mark box when finished.
Adaptive Curve
Use the Adaptive Curve pattern to follow gentle contours in the field, or
when you need to avoid obstacles. This pattern provides guidance
based on the last curve driven.
1. At the Guidance Screen, press the New Pattern button. Choose
Adaptive Curve, and enter a swath width. Press the green check mark
box when finished. You will automatically return to the Map screen.
2. At the start of the first swath, map Point A.
3. Drive the initial curve. At the other end of the first swath, map Point B.
4. Turn left or right for the next swath. The next swath is automatically
selected.
5. Steer the vehicle so that you center the green lights in the lightbar as you drive forward along the swath.
Notes:
• Guidance extends beyond the end of curved swaths. This makes it possible to get LED guidance back onto
the swath if the vehicle drives past the end of a swath. The extended swath lines do not appear on screen.
• You can adjust the degree heading at which the system generates the next pass by doing the following: Go to
the Guidance screen and press the Options button. The Guidance Options screen appears; press the
Adaptive Curve button. At the New Pass drop-down menu, select Heading Change, then use the numeric
keypad to enter in the degree number of your Heading Threshold.
Identical Curve
Use the Identical Curve pattern when you want to work the field with
gentle curves. This pattern provides guidance based on the initial
curve. It ignores any deviation around an obstacle.
1. At the Guidance Screen, press the New Pattern button. Choose
Identical Curve, and enter a swath width. Press the green check mark
box when finished. You will automatically return to the Map screen.
2. At the start of the first swath, map Point A.
3. Drive the initial curve. At the other end of the first swath, map Point
B.
4. Turn left or right for the next swath. The next swath is automatically
selected.
5. Steer the vehicle so that you center the green lights in the lightbar as you drive forward along the swath.
46
Page 59

Note: Guidance extends beyond the end of curved swaths. This makes it possible to get LED guidance back
onto the swath if the vehicle drives past the end of a swath. The extended swath lines do not appear on screen.
GUIDANCE OPTIONS
The Options button on the Guidance Screen becomes active after you have set an AB line. The
Options button opens the Guidance Options screen. The appearance of the Guidance Options screen
varies, depending upon the pattern type you have selected. Three Guidance Options features described
here and on the following page include Pause, Remark A and Shift.
Pause
The Pause button allows your display to stop logging points along an AB Line. Once this button is
pressed, a Resume button will take its place until you press this button and Pause reappears.
Note: If you are using the display to follow a set AB Line and wish to temporarily deviate from this line, you
can use the Pause button to pause the display's logging activity. This feature could be used, for example, by
a vehicle operator who must refill a sprayer. When paused, the display will continue to give the distance back
to the original pause point position.
1. Press Pause button
Press the Pause button on the Guidance screen. When you do so, the place where you paused appears
on the Map screen as a yellow ball.
GUIDANCE
Note: You can pause a pattern even if you have not set the "B" point yet. If you do so, the message in the
lightbar will read "Need B." If you pause the pattern after you have set your AB Line, then the lightbar will
indicate the distance your vehicle must travel to return to the pause point.
2. Press Resume button
To resume your pattern, press the Resume button to resume logging on your AB line.
Note: If you press the Resume button before you have returned to the original AB Line, your display will
select the closest AB Line to your vehicle.
Remark A
If you chose Straight AB or A+ Heading as your pattern option at the New Pattern screen, the Remark
A button appears on the Guidance Options screen. The Remark A button "re-marks" the A point by
moving it to the current position while maintaining the same heading. A brief message appears in the onscreen lightbar, stating "Point A Remarked."
Shift
For an explanation of the Shift Pattern feature, see “Load Pattern” on page 43.
Adaptive Curve
If you chose Adaptive Curve as your pattern option at the New Pattern screen, see “New AB Pattern” on
page 38 and “Adaptive Curve” on page 46. The Adaptive Curve button appears on the Guidance Options
screen. This button opens the Adaptive Pattern Options screen. At this screen, you can choose pattern
options that tell the system where to log a new pass. These options include:
• New Pass.
This sets the conditions for the display to log a new pass. Select either Area Count or Heading Change.
47
Page 60

- Area Count generates the next pass, based on coverage area of the previous pass. The display must
be logging coverage data in order to generate the next pass.
- Heading Change logs the next pass when the vehicle turns past the heading threshold.
• Heading Threshold.
Enter in the degree of turning angle that your vehicle will need to make before creating another pass.
Note: You should always set the Heading Threshold number past 90 degrees. The default number is 110
degrees.
NUDGE
You can adjust Nudge settings at the Guidance Screen,
shown. The blue double arrows allow you to adjust the AB Line
by the specified distance left or right.
Note: The Nudge setting is only available with SmartPath, AB, A+ and Pivot patterns.
Pressing the Options button opens the Guidance Options
screen, which is discussed at
Pressing the Nudge button on the Guidance Options screen
opens the Nudge screen, as shown.
• Use the numeric keypad to enter a distance to move the swaths.
• To clear out the adjustment and go to the original position, press
Clear Nudge.
ONTRAC2
Access the OnTrac2 guidance feature by pressing the Setup button (wrench) on the home
screen
Then press the GPS button on the Setup Screen.
Then the Guidance tab will appear.
From the Guidance/Steering Type menu, select OnTrac2 Steering.
“Guidance Options” on page 47.
Acknowledge the Automatic Steering Liability Notice by pressing Accept, and wait for the steering
software to initialize.
48
Page 61

ONTRAC2 SETUP TASKS
Upon installation of the OnTrac2 hardware, you must set up a new configuration using the OnTrac2
guidance feature, by performing the following tasks:
• Configure a vehicle on the OnTrac2 Configuration Tab
For more information, see
• Calibrate OnTrac2
For more information, see
included with this calibration procedure.
• Perform a Steering Diagnostics Check
For more information, see
• Adjust the tuning parameters
For more information, see
• Adjust the Response Rate and Line Acquisition Rate settings as necessary
These improve how the vehicle acquires and holds the AB line. For more information, see
Adjustment” on page 55.
“Vehicle Configuration” on page 49.
“Calibrating OnTrac2” on page 52.
“OnTrac2 Steering Diagnostics” on page 53.
“Tuning” on page 56.
Adjusting the Disengage Sensitivity should be
“Steering
VEHICLE CONFIGURATION
Press the Setup (wrench) tool and go to the OnTrac2 Vehicle Configuration Tab. Create an
OnTrac2 vehicle configuration.
GUIDANCE
Note: Even if you already performed a vehicle configuration in Setup, you must still perform a vehicle
configuration at the OnTrac2 Tab. The two vehicle configurations - in Setup and OnTrac2 - are independent
of each other.
1. Press the Add button
2. Choose Vehicle Style
Enter the type of your vehicle. Press the blue right-arrow button to continue.
3. Enter the Wheel Base
Use the numeric keypad to enter the vehicle wheel base. Press the
blue right-arrow button to continue.
49
Page 62

4. Enter Antenna Forward/Behind Offset
Use the numeric keypad to enter the antenna Forward/Behind
position. Press the blue right-arrow button to continue.
Note: Forward indicates the antenna is located in front of the vehicle’s control point. Behind indicates the
antenna is located behind the vehicle’s control point. Be sure to select the appropriate offset for your
configuration.
Note: The Control Point of a vehicle varies, depending upon the type of vehicle. These variations are as
follows:
• Standard Wheeled Vehicle, Sprayer, and Floater - Rear Axle
• Track Vehicle - Center of tracks
• Articulated Tractor - Pivot point of vehicle
• Combine/Swather - Front Axle
5. Enter Antenna Height
Use the numeric keypad to enter the Antenna Height position.
Press the blue right-arrow button to continue.
Note: Antenna height is measured from the base of the antenna to the ground.
6. Enter Vehicle Name
Use the on-screen keyboard to enter in a vehicle name. Press the blue right-arrow button to continue.
7. Acknowledge the Confirmation
The Confirmation screen shows your vehicle name and settings. Press the green check mark box to finish
the configuration. The newly-configured vehicle will now appear in the list underneath the Vehicle Tab.
EDIT VEHICLE SETTINGS
1. Open Vehicle Settings Screen
At the OnTrac2 Vehicle Tab, press the Setup (wrench) tool. At the Vehicle Tab, highlight the vehicle
and press the Setup (wrench) tool at this screen. The Vehicle Settings screen appears, as shown.
50
Page 63

ONTRAC2 TOOLS TAB
2. Press Edit
Press the Edit button, and a second Vehicle Settings screen
appears, as shown.
3. Adjust Settings, if necessary
At the Vehicle Settings screen, you can adjust the following
settings:
• Wheel Base
• Antenna Forward/Behind Offset
• Antenna Height
Press the green check mark box when finished.
The OnTrac2 Tools Tab is where you can calibrate OnTrac2,
perform a Vehicle Steering Diagnostics check, perform a
Steering Tuning Adjustment, enable a Remote Engage Switch,
and upgrade ESC firmware.
GUIDANCE
• Calibrate
Starts the procedure to calibrate OnTrac2. For more information,
see
“Calibrating OnTrac2” on page 52.
• Steering Diagnostics
Performs a Vehicle Steering Diagnostics check. For more
information, see
• Disengage Sensitivity
The Disengage Sensitivity adjusts how hard you have to turn the wheel to get the OnTrac2 guidance to
disengage and return to manual steering. For more information, see
page 54.
• Enable Remote Switch check box
Enables the OnTrac2 operation to use a Remote Engage Switch.
• Minimum Output
Allows the operator to adjust how aggressively OnTrac2 will turn the wheel when it engages. See
Output” on page 54.
• Upgrade
Upgrades the ECU firmware.
Note: The Remote Engage Switch is an optional feature. Contact a sales representative for details.
“OnTrac2 Steering Diagnostics” on page 53.
“Adjust Disengage Sensitivity” on
“Minimum
51
Page 64

Calibrating OnTrac2
Calibration of the OnTrac2 should be performed after you install it on your vehicle. This calibration
procedure consists of four main tasks: Selecting the Electronic Control Unit (ECU) orientation,
Calibrating the Tilt Sensor, Adjusting the minimum output for the Motor Drive Unit, and Adjusting the
Disengage Sensitivity.
1. Open Calibration Screen
At the GPS Guidance Tab, press the Setup (wrench) tool. Go to the OnTrac2 Tools Tab. Press the
Calibrate button, and the Calibration screen opens.
2. Read Calibration Instructions
Read the calibration instructions and press the blue right-arrow button to continue.
3. Select ECU Orientation
Select one of the four buttons (pictures) that accurately represents
the direction that the cable connectors on the ECU are facing.
Press the blue right-arrow button to continue.
Note: Mount the ECU so that is lies flat. Do not install it on its side or at an angle that is diagonal to the vehicle
direction.
4. Calibrate Tilt Sensor
Place the vehicle in Park on a flat, level surface. Press the blue
right-arrow button to continue. The Calibration in Progress
messages display and a countdown simultaneously takes place.
Note: The vehicle must be sitting on a flat, level location and must not move while the ECU Orientation takes
place.
5. Begin Minimum Output Calibration
The Minimum Output Calibration screen appears. Calculating the
minimum output tells the ECU how much electrical current is
needed to make steering adjustments. Drive your vehicle forward
in a straight line between 0.05—3.0 mph (0.8—4.8 km/h).
52
Page 65

Notes:
6. Wheel Rotating
As you drive forward, your wheel will begin to rotate. Press the
Wheel Rotating button when this happens. The Disengage Test
message then displays. Press the blue right-arrow button to
continue.
- If you run out of space in the field at any time during the Calibration procedure, you can manually
reposition the vehicle by pressing the Pause and Resume buttons.
- The default Disengage value should be adequate. However, if the system disengages too easily during
normal field operations, see “Adjust Disengage Sensitivity” on page 54 to adjust the Disengage value
to a setting that works.
7. Calibration Complete
Press the green check mark box to accept the calibration.
GUIDANCE
OnTrac2 Steering Diagnostics
Perform a Vehicle Steering Diagnostics check after a new vehicle installation. This verifies that the MDU
and the OnTrac2 System are operating correctly, adjusts the Disengage Sensitivity, and (for those who
wish to use a Foot Pedal) enables Remote Engage/Disengage.
To begin the diagnostics check, go to the OnTrac2 Tools tab and press the Steering Diagnostics
button. The Steering Tab displays, as shown. Use the buttons to send the specified command to the
motor. Observe that the wheel behaves according to the specified command.
Steering
• Hard Left, Hard Right buttons
Turns the wheel left or right 100 percent.
• % Left, % Right buttons
Turns the wheels left or right in the percentage amount specified by
the Command Percent slider bar at the bottom of the screen.
• 0% button
The Zero Percent button stops the steering wheel’s turning motion.
• Stop button
Ends the Vehicle Steering Diagnostics procedure.
• Command Percent slider
Controls the percentage of directional change on intermediate left and right turns.
53
Page 66

Drive Unit
The Drive Unit Tab displays the following information:
Status
• Engaged
Shows the OnTrac2 system is actively attempting to turn the
steering wheel.
• MDU Power
Shows the MDU Power Switch is set to On.
• Remote Engage
Flashes green when the remote switch is pressed.
• ECU Communication
Fast blinking green indicates normal operation.
Adjust Disengage Sensitivity
The Disengage Sensitivity adjusts how hard you have to turn
the wheel to get the OnTrac2 guidance to disengage and
return to manual steering.
Press the GO button and the steering wheel will begin to move
clockwise.
- If steering disengages too easily, press Increase.
- If steering does not disengage easily, press Decrease.
Other Notes:
- If the limit is set too low the system will disengage under normal conditions.
- On some vehicles, disengaging steering is easier through the use of the Remote Engage Switch
instead of grabbing the steering wheel.
The Remote Engage Switch is optional. Contact a sales representative for details.
Minimum Output
The initial Minimum Output is determined during the calibration
process which calculates how much electrical current is
needed to make steering adjustments. Minimum Output can
also be adjusted manually on the Minimum Output screen. It
can be adjusted up if sluggish or down if too aggressive.
54
Page 67

ONTRAC2 ADVANCED TAB
The Advanced Tab is where you can back up and restore all of
your OnTrac2 data.
Note: OnTrac2 data is stored in internal memory independently of other data. Thus the backup and restore
procedures described in this section both save different data than the data described in the Console Memory
Tab in “Memory Tab” on page 14. Back up both the display data as well as OnTrac2 data.
Vehicle Database
• Backup
This backs up all of your OnTrac2 data in a folder, named ontrac2, on the external card.
• Restore
This takes the backup you made on your external card and restores it onto the display
GUIDANCE
Note: Any settings changes (including new vehicles) that you made since your last backup will be deleted
when you restore your data.
• Reset to Defaults
This deletes all created vehicles and restores settings to defaults.
Log Files
• Copy Logs to Card
Copies steering logs into the OnTrac2 folder on the external card.
• Clear
Clears all steering logs.
ONTRAC2 RUN TIME ENVIRONMENT
Steering Adjustment
The Steering Adjustment screen is where you can adjust Tuning settings as well as the Line
Acquisition Rate and Steering Response. To go to the Steering Adjustment screen, first go
to the Map screen and press the Map Options icon. At the Guidance Screen, press the Adjust
Steering button. The Steering Adjustment screen opens as shown
Note: Adjust Tuning before adjusting the Line Acquisition and Steering Response. For more information, see
“Tuning” on page 56.
55
Page 68

• Tuning
The Tuning process is where you can adjust individual settings for
Steering, Heading and Cross-Track Error. For more information,
see “Tuning” on page 56.
• Line Acquisition
Controls the aggressiveness that a vehicle acquires an AB line.
Increasing this value will cause the vehicle to take a sharper angle
toward the AB line. Decreasing this value will cause the vehicle to
approach the AB line at a more gradual angle. The default of this
setting is 10; it should remain at 10 before adjusting Tuning settings.
• Steering Response
Controls how well the vehicle holds the AB line. Increasing or decreasing this rate adjusts all three tuning
parameters (Motor Aggressiveness, Heading Aggressiveness and Cross-Track Error) simultaneously.
Increasing this rate may allow the vehicle to hold the AB line closer; but if adjusted too far it could cause
the vehicle to oscillate across the line. Hence, use this adjustment only after the OnTrac2 tuning parameters
have been adjusted to their correct values. The default of this setting is 10; it should remain at 10 before
adjusting Tuning settings.
Note: You can use this adjustment to account for different implements (as some pull harder than others),
ground conditions (more or less slippage) or increases and decreases in vehicle speed.
Tuning
The Tuning process is where you can adjust individual settings for Motor Aggressiveness, Heading
Aggressiveness and Cross-Track Error. Adjust the tuning parameters in the following order:
1. Set AB Line.
2. Adjust Motor Aggressiveness.
3. Adjust Heading Aggressiveness.
4. Adjust Cross Track Error.
5. Readjust tuning parameters as needed.
Note: To get an idea of how a parameter will affect how the vehicle drives, set the parameter at a very low
value, such as 3 or 4; and then at a very high value, such as 15 or 16. This will give a good indication of how
each tuning parameter affects performance.
• Motor Aggressiveness
How quickly or aggressively the OnTrac2 Mechanical Drive Unit motor moves the steering wheel. The
higher the Motor Aggressiveness Value the more responsive or aggressive the OnTrac2 Mechanical Drive
Unit will move the steering wheel. This value is limited by the maximum speed and torque output of the
OnTrac2 Mechanical Drive Unit.
Note: Set this value as high as possible, but if set too high it could cause the steering wheel to oscillate.
56
Page 69

• Heading Aggressiveness
How accurately the OnTrac2 system’s will control the heading or the direction of the vehicle when on the
AB line. The higher the Heading Aggressiveness Value the more accurately the system will try to control
the actual heading of the vehicle. Heading Aggressiveness should be set as high as possible. If it is set too
high, the OnTrac2 system will try and control the vehicle’s heading too accurately, and will oscillate across
the AB line of the OnTrac2 Mechanical Drive Unit.
Note: Heading is very important to the vehicle’s ability to maintain an AB line, as it adjusts the vehicle’s
direction and future location.
• Cross-Track Error
Cross Track Error adjusts how close the vehicle holds to the AB line. Increasing Cross Track Error will
improve or decrease the amount a vehicle is off the AB line. If it is set too high, the OnTrac2 system will
oscillate across the AB line.
How the OnTrac2 System works
Imagine three men in a special tractor cab, called Steering, Heading and Cross Track. The cab on the
tractor is special because none of the three men can see outside the windows of the cab. Inside the cab,
each man has a unique job and end goal:
• Steering
Steers the tractor left and right.
GUIDANCE
• Heading’
Uses a compass and measure the difference between the tractor’s heading and the AB line heading.
• Cross Track
Uses a measuring tape and to measure how far offline the tractor is from the AB line.
These three men interact with each other to steer the tractor in the following way, keeping in mind they
cannot see their steered wheels or where they are headed.
• Steering listens to Heading and Heading listens to Cross Track, which issue commands on how far left
or right to steer the tractor so that it stays on the AB line.
- Steering’s goal: To steer the tractor in a responsive manner, but not in a jerky or lazy way.
• Heading tells Steering how to steer the tractor left and right in order to minimize the difference between
the tractor’s heading and the AB Line heading.
- Heading’s goal: To minimize the difference in the tractor’s heading and the AB Line heading.
• Cross Track also tells Heading which in turn tells Steering how much to steer the tractor left and right in
order to minimize the tractor’s distance from the AB Line, or its offline distance.
- Cross Track’s goal: To minimize the distance between the tractor and the AB Line.
• Line Acquisition Mode is the mode in which the steering controller is in when the OnTrac2 system is
driving on the AB Line. The OnTrac2 system comes out of Line Acquisition Mode when the vehicle Cross
Track Error is approximately less than six inches for approximately two or more seconds
Note: During Line Acquisition (when the vehicle is acquiring the AB line), Steering ignores Cross Track Error,
so only Steering and Heading are responsible for getting a vehicle to the AB Line.
Note: Because of the sequential nature of the 3 men, Cross Track talks to Heading which talks to Steering,
in is very important to adjust them in order, Steering first, Heading next and then Cross Track.
57
Page 70

Steering
Motor Aggressiveness adjusts how
aggressively Steering turns the steering wheel
left and right. The higher Motor Aggressiveness
is set, the quicker and more responsive Steering
turns the steering wheel. The lower the Motor
Aggressiveness is set, the more lazily Steering
turns the steering wheel. Motor Aggressiveness
should be set as high as possible so that the
steered wheels move quickly, but not so quickly
that the wheels are jittery.
• Steering’s Simple Analogy: Motor Aggressiveness is a setting which varies how responsive or reactive
Steering is at turning the steering wheel.
- Too High: If Steering is responsive but jittery or jumpy at turning the steering wheel, Motor
Aggressiveness is too high and should be reduced.
- Ideal: If Steering is responsive and not jittery or jumpy at turning the steering wheel, Motor
Aggressiveness is set correctly.
- Too Low: If Steering is lazy or not very responsive at turning the steering wheel, Motor
Aggressiveness is too low and should be increased.
Heading
Heading Aggressiveness does two things:
- First, it adjusts how loudly that Heading gives commands
to Steering.
- Second, it tightens the tolerance which Heading tries to
keep the tractor’s heading within.
The higher Heading Aggressiveness is set, the
louder Heading talks to Steering and the tighter it
tries to keep the tractor’s heading tolerance. Lowering
Heading Aggressiveness lowers the volume at which
Heading talks to Steering and loosens the tractor’s
heading tolerance. Heading Aggressiveness should
be set as high as possible so that the tractor does not
oscillate or wander across the AB Line.
• Heading’s Simple Analogy: The Heading Aggressiveness setting could be viewed as the volume at
which Heading speaks to Steering.
- Too High: If Heading speaks “too loudly” to Steering, Steering over responds to Heading’s
commands and the tractor oscillates across the AB Line. Heading Aggressiveness is set too high
and should be lowered.
- Ideal: If Heading speaks at the “ideal volume” to Steering, Steering responds just right to Heading’s
commands, and the tractor does not oscillate or wander across the AB Line. Heading
Aggressiveness is set correctly.
- Too Low: If Heading speaks “too softly” to Steering, Steering is not responsive enough to Heading’s
command and the tractor wanders across the AB Line. Heading Aggressiveness is set too low and
should be increased.
58
Page 71

Cross Track
Cross Track Error also does two things:
- First, it adjusts the volume at which Cross Track talks
to Steering.
- Second, it adjusts the offline tolerance at which Cross
Track tries to hold the tractor on the AB Line.
The higher Cross Track Error is set, the louder
Cross Track talks to Steering; and the tighter
Cross Track tries to hold the tractor to the AB
Line. The lower Cross Track Error is set, the
softer Cross Track talks to Steering; and the
more relaxed Cross Track is at holding the tractor
to the AB Line. Cross Track Error should be set
as high as possible so that the tractor stays close
to the AB Line, but does not oscillate or wander
across the AB Line.
Cross Track’s Simple Analogy: Cross Track Error could be viewed as the volume at which Cross
Track talks to Steering.
- Too High: If Cross Track speaks “too loudly” to Steering, Steering over responds to Cross Track’s
commands and the tractor oscillates across the AB Line. Cross Track Error is set too high and
should be lowered.
- Ideal: If Cross Track speaks at the “ideal volume” to Steering, Steering responds just right and the
tractor does not oscillate or wander across the AB Line. Cross Track Error is set correctly.
- Too Low: If Cross Track speaks “too softly” to Steering, Steering is not responsive enough to Cross
Track and the tractor wanders across the AB Line. Cross Track Error is set too low and should be
increased.
GUIDANCE
59
Page 72

60
Page 73

TILLAGE
TILLAGE
RUN TIME ENVIRONMENT: MAP SCREEN
The screen shown is for a Tillage configuration. In order for you to view the Map screen, you must first
set up a Grower, Farm and Field at the Start Field Operation portion of the Home screen.
• (A) Total Field Acres
• (B) GPS Status
• (C) Map Options
• (D) Home button
• (E) Map View button
• (F) Vehicle icon
• (G) Implement icon
• (H) Logging Status button
• (I) Ground Speed
TILLAGE
For more information, see
View button appears at the bottom of the Home screen.
Press the Map View button, and the map screen appears, as shown.
Note: Pressing the Map View button will cycle between the available map screen views, and the appearance
of the Map View button changes. For information on Map Screen items that are standard for all operations,
see “Run Time Environment: Map Screen” on page 18.
“Management” on page 10. Once a configuration has been completed, the Map
CREATE A TILLAGE CONFIGURATION
To set up a Tillage configuration, you must first set up Vehicle and Implement with the following
procedures.
Create a Configuration
1. At the Setup screen, press the Tillage icon.
2. The Tillage Configuration Tab opens.
61
Page 74

3. Press the Add button.
4. The Operating Configuration Wizard appears. Follow the
wizard’s instructions to complete the configuration.
Configuration Notes
If you are not using GPS for ground speed, then the ground speed sensor input must be calibrated for
accurate speed and area calculations.
GPS OFFSETS
After completing the process of setting up a Vehicle, you must configure GPS Offsets. The GPS Offsets
define where the machine’s rear axle and hitch is in relation to the GPS antenna. These settings are
used by mapping.
To configure the GPS Offsets, you must first press the Tillage button and go to the Vehicle
Tab. Press on the vehicle name to highlight it, then press the Wrench Button.
ANTENNA OFFSETS
The Make/Model/Type screen opens.
Press the GPS Offsets button, and the GPS Offsets screen
appears, which has two tabs: Antenna and Hitch.
The Antenna Tab is shown. This tab contains three different
settings:
• Measure and enter the horizontal distance from the rear axle to
the position of the GPS antenna. Select IN FRONT or BEHIND to
indicate the position of the antenna in relation to the rear axle.
• Measure and enter the horizontal distance from the centerline of
the vehicle to the position of the GPS antenna. Select LEFT or
RIGHT to indicate the position from the vehicle centerline.
62
• Measure and enter the vertical height of the antenna above the
ground.
Page 75

Note: Accuracy when measuring for a specific setting is essential to ensure proper machine performance.
HITCH TAB SETTINGS
The Hitch Tab is shown.
The Hitch Tab allows you to enter in the distance from four
different mounting positions on the tractor to the rear axle. Use
the number pads to enter these values in if using the hitch
point.
Note: Accuracy when measuring for a specific setting is essential to ensure proper machine performance.
IMPLEMENT OFFSETS
TILLAGE
After completing the initial process of configuring an implement, you must enter accurate values in the
Implement Offsets screen.
To configure the Implement Offsets, you must first go to the Setup screen, press the Tillage
button and go to the Implement Tab. Highlight the implement that you wish to configure,
press the Wrench Button.
The Implement Information screen opens.
Press the Swath Section Offsets button, and the Implement
Offsets screen appears, as shown.
• Use the first numeric keypad to enter the distance from the midpoint of the swath section to the machine’s centerline. Select to the
left/to the right to indicate the direction the swath section is located
from the vehicle centerline.
• Use the second numeric keypad to enter the distance that the swath section is located from the hitch point.
Press the check mark button when finished.
Note: Accuracy when measuring and entering implement offsets is required to ensure proper machine
performance.
63
Page 76

64
Page 77

PLANTING
PLANTING
RUN TIME ENVIRONMENT: MAP SCREEN
The screens shown in this section are for a Planting configuration. In order for you to view the Map
Screen, you must first select a Grower, Farm and Field at the Start Field Operation portion of the Home
Screen.
For more information, see “Management” on page 10.
Once a configuration has been completed, the Map View button appears at the bottom of the
Home Screen. Press the Map View button, and the Map Screen appears.
MAP SCREEN: ZOOM TO EXTENT
The map shows a Planting Area Logging configuration, displayed in Zoom to Extent view
• (A) Total Acres
• (B) GPS Status
PLANTING
• (C) Map Options
• (D) Display Legend button
• (E) Home
• (F) Map View
• (G) Vehicle icon
• (H) Ground Speed
• (I) Logging Status (shown for area logging Planting Configuration)
Note: Pressing the Map View button will cycle between the available map screen views, and the appearance
of the Map View button changes.
MAP SCREEN: ZOOM DETAIL
When the Map Screen is shown in Zoom Detail,
the Vehicle Icon appears as a gold triangle, rather
than an arrow.
65
Page 78

• (A) Total Acres
• (B) GPS Status
• (C) Map Options
• (D) Home
• (E) Map View
• (F) Vehicle Icon
• (G) Implement Icon
• (H) Ground Speed
(I) Logging Status (shown for area logging Planting Configuration)
The map is shown for a typical Planting Configuration which does not include any Rate Control or Row
Shutoff features. This planter includes two sections, and these sections are shown as individual boxes
on the Implement Icon behind the Vehicle Icon.
Note: For information on Map Screen items that are standard for all operations, see “Run Time Environment:
Map Screen” on page 18.
PLANTING MAP SCREEN ITEMS
The following Planting Map Screen Items are available at the Map Screen:
• Legend
During Planting operations, the Map Screen displays three types of items in the Legend: Rate, Varieties
and Prescription (Rx). The Legend is only accessible in the Zoom to Extent view. For more information
about the Display Legend, see
• Display Legend icon
The Display Legend icon makes the Legend appear. When the Legend appears, the arrow points down;
when it is turned off the arrow points up. As with the Legend, the Display Legend icon is only accessible in
the Zoom to Extent view.
• Vehicle and Implement Icon
The vehicle icon shows the vehicle, while the Implement Icon shows the number of sections on the planting
implement, as well as the implement’s logging status. This item only appears in the Zoom Detail view.
• Logging Status Button
This button shows for Planting Operations that are configured for Area Count.
“Edit Legend” on page 21.
PLANTING SETUP TABS
Pressing the Planting button at the Setup Screen takes you to the Planting Configuration
Tab.
66
Page 79

This Tab is shown in front of four other tabs: Vehicle,
Implement, Controller and Product.
• Configuration Tab
The Configuration Tab is where you can add and edit operating
configurations. For more information, see
Configuration” on page 67 and “Configuration Settings” on page 68.
• Vehicle Tab
The Vehicle Tab is where you can add and edit vehicles. For more
information, see
• Implement Tab
The Implement Tab is where you can add and edit implements. For more information, see
on page 74.
• Controller Tab
The Controller Tab is where you can add and edit controllers for use during planting. For more information,
see
“Controller Tab” on page 74.
• Product Tab
The Product Tab is where you can add new products or edit existing products for planting. For more
information, see
“Product Tab” on page 75.
“Vehicle Tab” on page 72.
“Create a Planting
“Implement Tab”
PLANTING
CREATE A PLANTING CONFIGURATION
To set up a Planting configuration, you must set up Vehicle, Implement, Controller and Products with the
procedure described on this and following pages.
1. At the Setup screen, press the Planting button.
2. The Configuration Tab opens, as shown.
3. Press the Add button.
67
Page 80

4. The Operating Configuration Wizard appears, as shown.
From here, follow the Wizard’s instructions to create a
configuration that includes Vehicle, Implement, and Controller
settings
Note: From the Configuration Tab, you can also:
• Press the on-screen keyboard to edit or rename existing configurations.
• Press the Wrench button to access Configuration Settings. For more information see “Configuration
Settings” on page 68.
• Press the Remove button to remove a configuration. Caution: When deleting a configuration all data logged
with that configuration will be deleted.
CONFIGURATION SETTINGS
By highlighting a configuration and pressing the Wrench button on the Configuration Tab, you
can summon the Configuration Settings screen, where you can edit Configuration Settings,
Speed Input Settings, Auxiliary Input Settings and AutoSwath Settings.
Press to display and edit planting/seeding settings specific to a
vehicle, implement and controller combination. For more
information, see
on page 69.
“Configuration Settings: Equipment Configuration”
• Speed Input
Press to select speed input device. For more information, see
“Speed Input Settings” on page 69.
• Aux Input
Press to display Auxiliary Input settings. For more information, see
“Auxiliary Input Settings (Switch Mapping)” on page 70.
• AutoSwath
Press to display and edit automatic swath control settings. For more information, see
page 71.
Note: You must have an unlock code to activate the AutoSwath feature. If you have been using AutoSwath
with the DirectCommand™ system, the feature is already activated and ready to use. If you have not unlocked
the AutoSwath feature yet, the code can be purchased through your local dealer.
“AutoSwath” on
68
Page 81

CONFIGURATION SETTINGS: EQUIPMENT CONFIGURATION
The Equipment Configuration screen displays the Implement
and Controller information. The appearance of this screen may
vary, depending upon your particular planting configuration. To
edit equipment configuration settings, highlight a configuration
and press Edit.
Equipment Configuration Settings - SeedCommand
Users of the Hydraulic Drive and Stepper Seed Meter planting configurations may adjust the following
settings at this screen:
• The Rate Outside of Field selection
determines product control channel behavior when the field boundary is exited. The drop-down menu
includes the following options:
- Zero: Product application will turn off.
- Last Good: Product application will continue at the last value used by the control system.
- Rx Default: Product will be applied at the default rate setting
PLANTING
• The Rate Display Smoothing check box
determines how the feedback from the control channel rate sensor will be displayed on the Map screen.
When de-selected, the system will display raw feedback from the rate sensor. When checked, the system
will display the target rate when the actual rate is within +/- 10% of the target rate setting.
• The Controller Time Delay setting
compensates for any latency in the control system when changing between different product flow rates
during variable rate application. A typical setting range for this 0-1 seconds.
SPEED INPUT SETTINGS
The Speed Input Settings screen is where you can calibrate the ground speed input for accurate speed
and area calculations. If you are not using GPS for ground speed, then after you have created a
configuration you must calibrate the ground speed input. If you are using GPS, it is recommended to
calibrate distance in the event of GPS loss.
Calibrate Distance
1. Open Configuration Information screen
On the Configuration Tab, press on the configuration name to highlight it, then press the Wrench
Button, and the Configuration Settings screen appears.
2. Press Speed Input, and the Speed Input screen appears as
shown.
3. Press the Calibrate Distance button, and the Speed Sensor
Calibration wizard appears, as shown.
69
Page 82

4. From here, follow the on-screen wizard’s instructions to
complete the distance calibration procedure.
AUXILIARY INPUT SETTINGS (SWITCH MAPPING)
To view Auxiliary Input Settings, go to the Planting
Configuration Tab, highlight the desired configuration and
press the Wrench button. At the Configuration Settings screen,
press the Aux Input button, and the Auxiliary Input Settings
screen appears, as shown.
This Switch Mapping function is active only for users with
DirectCommand or SeedCommand features. The Auxiliary
Input Settings screen displays settings for the Master Switch
and other switches on a SeedCommand Switch Box.
The Master Source drop down menu controls the master switch for your entire configuration. You may
see the following options underneath this menu:
• Switch
Controls the master switch.
• External 2
This setting can control an optional, floor-mounted master switch.
• External 1, 3 & 4
Not used at this time.
The F1-F11 cells can be assigned to any implement sections. You can use these to choose the switches
that control a particular section or controller planting clutch. From here, you can also make the following
changes to the switch settings.
• Add a switch setting. For more information, see
• Remove a switch setting.
• Reset All. This resets the settings to defaults.
“Add Auxiliary Input Settings” on page 70.
Add Auxiliary Input Settings
If you wish to add a switch setting, press the Add button on the Auxiliary Input Settings Screen, and a
second Auxiliary Input Settings screen appears, as shown. This screen shows the following drop down
menus:
70
Page 83

• Control Module
Specifies the function of your DirectCommand or Planting Row
Shutoff.(For example, Seed Clutch).
• Channel
Select the channel to control.
• F2 Switch 1
Selects the section to turn on and off.
AUTOSWATH
The Automatic Swath Control feature turns sections off and on automatically based upon the following
conditions:
• Entering and exiting internal and outer field boundaries.
• Entering and exiting previously-applied areas within a field.
To access the Automatic Swath Control settings, go to the Configuration Tab, highlight a configuration and press the Wrench button. Once the Configuration Settings Screen appears, press the AutoSwath button. The Automatic Swath Control screen appears, as shown. This screen displays Automatic Swath Control settings that are specific to that operation.
PLANTING
Note: The Automatic Swath Control functionality is an optional feature of both the DirectCommand and
SeedCommand Systems. An unlock code must be purchased and installed to enable this feature. Call your
local dealer for details and pricing.
• Turn-On Look Ahead
This setting determines how far ahead the system looks to turn the
sections back on. This setting compensates for delay in the
planting control system when the implement sections are turned
on.
• Turn-Off Look Ahead
This setting determines how far ahead the system looks to turn the
sections off. This setting compensates for delay in the product
control system when the sections are turned off. To see what these
numbers should look like for Row Shutoff Modules, see
“Row Shutoff Look-Ahead Numbers” on page 83
• Outside Boundary Option
Select one of the two options to determine system behavior when a section exits a field boundary.
• Coverage Option
In the Coverage Option area, you must choose between three options:
- The Minimize Skip option turns off the implement section after the entire section is fully inside your
coverage area. This prevents the possibility of skips.
- The Minimize Overlap option turns off the implement section when that section first enters your
coverage area. This prevents the possibility of overlaps.
- The User Defined option allows you to choose what percentage of the implement section is within the
coverage area before that section turns off. For example, if you choose 70%, then the section will
switch off when half of it is within your coverage area.
.
71
Page 84

AutoSwath Notes
To use AutoSwath for planting operations, you are required to use a 5 Hz or higher GPS output rate.
AutoSwath control will not allow sections to be turned on until the master and planting section switches
are on. If you have less than a 5 Hz GPS output rate and you select AutoSwath, a warning appears,
telling you that AutoSwath Control is not available at less than 5 Hz.
Fixing Overplanting and Underplanting in AutoSwath
Turn Off Look-Ahead
Overplanting
Increase look-ahead number
The AutoSwath anticipates headlands sooner and turns the planter off sooner.
Underplanting
Decrease look-ahead number
The AutoSwath anticipates headlands later and turns the planter off later.
Turn On Look-Ahead
Overplanting
Decrease look-ahead number
The AutoSwath anticipates headlands later and turns the planter on later.
Underplanting
Increase look-ahead number
The AutoSwath anticipates headlands sooner and turns the planter on sooner.
VEHICLE TAB
The Vehicle Tab provides functionality for setting up and
configuring vehicles. The vehicle list will show any vehicles
that have already been created.
• Add
The Add button allows you to add a new vehicle. A wizard will walk
you through the vehicle setup process.
• Keyboard Button
The Keyboard button allows you to edit the name of a vehicle in the
list. To edit, highlight the name of a vehicle in the list and then press
this button.
• Wrench Button
The Wrench Button button opens the Vehicle Settings Screen, where you can configure GPS Offsets. For
more information, see
• Remove
The Remove button allows you to remove a vehicle.
Note: If a vehicle is deleted, all data in the regions and configurations using it will be deleted.
“GPS Offsets” on page 72.
GPS OFFSETS
After completing the process of setting up a Vehicle, you must also configure GPS Offsets. The GPS
Offsets define where machine rear axle, hitch, and product placement is in relation to the GPS antenna.
72
Page 85

These settings are used by mapping, product control, and Automatic Swath Control.
Press the GPS Offsets button to view Antenna and Hitch Tab
GPS settings. More information can be found at
on page 73 and “Hitch Tab” on page 73.
Antenna Tab
The Antenna Tab contains three different settings.
• Measure and enter the horizontal distance from the rear axle to
the position of the GPS antenna. Select IN FRONT or BEHIND
from the list box to indicate the position of the antenna in relation to
the rear axle.
• Measure and enter the horizontal distance from the centerline of
the vehicle to the position of the GPS antenna. Select LEFT or
RIGHT to indicate the position from the vehicle centerline.
PLANTING
“Antenna Tab”
• Measure and enter the vertical height of the antenna above the
ground.
Note: Accuracy when measuring for a specific setting is essential to ensure proper machine performance.
Hitch Tab
The Hitch Tab allows you to enter in the distance from one of
four different mounting positions on the tractor to the rear axle.
Use the Number Pads to enter a value in for the respective
hitch point.
Note: Accuracy when measuring for a specific setting is essential to ensure proper machine performance.
73
Page 86

IMPLEMENT TAB
Individual implements are set up and configured from the
Implement Tab. The Implement List displays all previouslyconfigured implements that are available for use.
• Add
Press to add a new implement. A wizard will walk you through
setting up the implement.
• Keyboard Button
Press to edit the name of a selected implement from the list.
• Wrench Button
Press to edit the Swath Section Offsets. For more information, see
• Remove
Press to remove a selected implement.
Note: When deleting an implement all data in the regions and configurations using it will be deleted!
IMPLEMENT OFFSETS
“Implement Offsets” on page 74.
After you complete the initial process of configuring an Implement, you must enter accurate values in the
Section Offsets to ensure proper machine performance. Section Offsets are configured as outlined in the
following steps.
Section Offsets
1. Press Wrench Button
On the Implement Tab, highlight the Implement Configuration,
press the Wrench Button, and the Implement Offsets screen
appears.
2. Enter left or right distance from hitch point
Use the numeric keypad to enter the distance of the midpoint of the
swath section from the machine centerline. Select Left or Right to
indicate the direction the swath section is located from the vehicle
centerline.
3. Enter Forward or Backward Distance from Hitch Point
Use the numeric keypad to enter the distance from the front or back of the hitch point. Press the checkmark
box when complete.
CONTROLLER TAB
Use the Controller Tab to add and configure SeedCommand controllers for use during SeedCommand
planting operations.
Note: No settings are available under the Controller Tab that pertain to Area Logging (non-SeedCommand)
planting operations.
74
Page 87

• Add
Press to add a new controller. A wizard will walk you through
setting up the controller.
• Keyboard Button
Press to edit the name of a selected controller from the list.
• Wrench Button
Press to edit Controller Settings, including tabs for Channel 1, 2 &
3 settings, and also Auxiliary settings. For more information, see
“Controller Settings (SeedCommand)” on page 75.
• Remove
Press to remove a controller.
Note: When deleting a controller all data in the regions and configurations using it will be deleted.
CONTROLLER SETTINGS (SEEDCOMMAND)
To view Controller Settings, go to the Planting Controller Tab, highlight the controller, press the Wrench
Button, and the Controller Settings screen shows as appears below. The current Device and Serial
Number of that Device is displayed.
PLANTING
Press the Controller Settings button and another Controller
Settings screen opens, where you can view controller settings.
The appearance of this Controller Setting screen varies,
depending upon your SeedCommand configuration.
PRODUCT TAB
The Product Tab allows you to add new products or edit existing products for planting and seeding.
• Add
The Add button summons the Product Options screen, where you
can add or import a product. For more information, see
Options” on page 76.
• Keyboard Button
Press to edit the name of a selected product from the list.
• Wrench Button
Press to view product manufacturer, edit product type, edit product
color or edit map legend. For more information, see
“Product Settings” on page 77.
“Product
• Remove
The Remove button allows you to remove a product.
75
Page 88

Note: When deleting a product all data using it will be deleted.
PRODUCT OPTIONS
To add or import a product, press the Add button located on the Product Tab. The Product Options
screen appears, as shown.
• Add Product
The Add Product button summons the Variety Setup Wizard. For
more information, see
• Import Product
The Import Product button summons the Product Import Wizard,
For more information, see
Add Product
To add a new product, press the Add Product button on the Product Options screen. The Variety Setup
Wizard appears, as shown.
1. Select Crop Type
Select a Crop Type and the Units As Planted from the drop down
menus.
“Add Product” on page 76.
“Import Product” on page 76.
2. Enter Variety Information
Use the on-screen keyboards to enter the manufacturer name and
the variety or hybrid. Only the variety or hybrid name is required.
Press the checkmark box when complete.
Import Product
Note: To import a product from a desktop .msf file, you must first have created an .msf file that includes
Grower, Farm and Field information. To do this, see “Importing an .MSF File” on page 11.
To import a product from a desktop .msf file, go to the Product Tab and press the Wrench button. When
the Product Options screen appears, press the Import Product button. The Product Import Wizard
appears, as shown.
76
Page 89

PRODUCT SETTINGS
The Product Settings screen is where you can edit product information, add a color or edit
the legend. To view the Product Settings screen, go to the Product Tab and press the
Wrench button.
1. Select Product and Type
Select the Product and Type from the drop-down menus.
2. Select Units
Select the units of the product.
3. Follow the steps in the Wizard to complete the procedure.
PLANTING
• Edit Info
The Edit Info button summons a second Product Settings screen,
where you can specify or change the manufacturer of a specific
variety.
• Edit Color
The Edit Color button summons the Color Selection screen, where
you can change the color associated with a product.
• Edit Legend
The Edit Legend button allows you to change the map legend associated with a specific product.
PLANTING: SEEDCOMMAND™ MACHINE-SPECIFIC SETUP
SeedCommand is a planter control system that automatically turns individual planter sections on and off,
based on a coverage map. The display includes options for four separate SeedCommand features:
AutoSwath, Planter Row Shutoff, Hydraulic Seed Rate Control and Stepper Seed Rate Control. This
subsection describes the following features:
• Map Screen functions
beginning on
“Map Screen: Zoom to Extent” on page 78
• Rate Screen functions
beginning on
“Run Time Environment: Rate Screen” on page 79
.
77
Page 90

• Planter Row Shutoff functions
beginning on
“Row Shutoff” on page 81
• Hydraulic Seed Rate Control functions
beginning on
“Hydraulic Seed Rate Control” on page 84
.
• Stepper Seed Rate Control functions
beginning on
Note: For information on AutoSwath functionality, see the pages beginning at “AutoSwath” on page 71 of the
Planting section.
Note: Additionally, consult “Auxiliary Input Settings (Switch Mapping)” on page 70 of the Planting section for
information on the Auxiliary Input Settings (Switch Mapping) feature.
“Stepper Seed Rate Control” on page 89
.
MAP SCREEN: ZOOM TO EXTENT
The map is shown for a SeedCommand configuration running a Row Shutoff Module and Planter
Hydraulic Drive Control.
• (A) Total Acres
• (B) Legend
• (C) Display Legend Button
• (D) Home
• (E) Map View
• (F) Rate button (Only appears on hydraulic
drive configuration)
• (G) Vehicle Icon
• (H) Ground Speed
(I) Logging Status (shown for Clutch Control and Hydraulic Drive Configuration)
MAP SCREEN: ZOOM DETAIL
The map is shown for a Planter with SeedCommand features. This planter includes 12 sections, and
these sections are shown as individual boxes on the Implement Icon behind the Vehicle Icon.
78
Page 91

• (A) Total Acres
• (B) GPS Status
• (C) Map Options
• (D) Home
• (E) Map View
• (F) Rate Button
• (G) Vehicle Icon
• (H) Implement Icon
• (I) Ground Speed
• (J) Status Items: Target Rate + Actual Rate
• (K) AutoSwath
PLANTING MAP SCREEN ITEMS
The following Planting Map Screen Items are available for SeedCommand users at the Map Screen:
• Status Items: Target Rate and Actual Rate
Target Rate (A) and Actual Rate (B), appear in the Status Items box at the
top right-hand corner of the Map Screen. As with the Legend, the Status
Items are only accessible in the Zoom to Extent view.
PLANTING
• Rate Button
This only appears on Hydraulic Drive configurations. For more information, see
Rate Screen” on page 79.
• AutoSwath Button
This button appears for all SeedCommand configurations, including Row Shutoff and Hydraulic Drive
configurations. For more information, see
Note: For an explanation of display items not listed above, see “Map Screen Icons” on page 19.
“Run Time Environment: Rate Screen” on page 79.
“Run Time Environment:
RUN TIME ENVIRONMENT: RATE SCREEN
You can view the Rate screen by pressing the Rate button, as shown at left.
The Target Rate screen will appear for all target rates
being applied. Items that appear on this screen are
explained on this and the following pages.
• Target Rate
The Target Rate is the amount of seeds that you wish to
plant.
• Actual Rate
The Flow Sensor returns the actual rate of the seeds that
you are planting.
79
Page 92

• (A) Active Rate
Note: In some conditions, the Actual Rate may increment slower than the Target Rate, or its numeric values
may vary before matching the Target Rate.
• Meter RPM
The Meter RPM button, as shown at left, displays the number of hydraulic motors and their
speed, shown in Revolutions Per Minute (RPM). Pressing the Meter RPM button summons
the Seed Rate Planter Control Screen, where you can calibrate and prime the seed meters. For more
information, see
• Rate 1 and Rate 2 Settings
The Rate 1 and Rate 2 settings represent preset planting rates that allow operators to quickly change
between desired planting rates for each individual product. The active rate button appears with a gray
background behind it.
• Manual Valve Control
“Priming Seed Rate Meters” on page 94
The Manual Valve Control button (shown at left) The Manual Valve Control button allows
operators to specify the position of the control valve. Operators use this option to prime the
system before application or clean out equipment at the end of the day.
and
“Calibrating Seed Rate Meters” on page 94
PLANTING RATE CONTROL CONFIGURATION SCREEN
• Planting Rate Control Configuration Button
The Planting Control Configuration button, which appears on the Rate Screen as shown at left,
summons the Planting Rate Control Configuration, shown.
.
• Rate 1 & Rate 2
The Rate 1 and Rate 2 settings represent preset application rates
that allow operators to quickly change between desired target rates
for each individual product. Use the numeric keypad to enter the
desired amount.
• Increment
The Increment button allows operators to specify the increase or
decrease amounts used when Rate 1 or Rate 2 is selected. Use the
numeric keypad to enter the desired increment.
• Prescription
To load a map-based prescription file, press the Prescription button. For more information, see
Prescriptions” on page 80.
“Loading
Loading Prescriptions
To load a map-based prescription file, go to the Rate Screen, press the Planting Configuration button
and the Planting Rate Control Configuration screen appears.
1. Press the Prescription button, as shown at left. The File Selection screen opens, as shown.
80
Page 93

ROW SHUTOFF
2. Choose an .irx (prescription) file from the names list. Press
the checkmark box when complete.
3. Once selected, the Prescription button on the Planting
Rate Control Configuration Screen will change its
appearance to the Remove Prescription button, which
appears as a minus sign. This will allow you to clear out
the selected prescription. (For an example, see below).
• (A) Default Prescription Rate
• (B) Remove Prescription button
PLANTING
By configuring your display with Row Shutoff, you can start and stop seed flow and control planter
sections row-by-row, allowing AutoSwath Control to automatically turn planter row units on and off based
on your planting map.
ROW SHUTOFF CONFIGURATION
Press the Planting button at the Setup Screen and go to the Planting Configuration Tab.
1. Create or add a vehicle
Follow the on-screen wizard to set up a vehicle.
2. Add Implement
After you have completed the vehicle configuration, the Implement Attachment Wizard appears. Add a new
implement, and select the implement attachment method.
3. Select Implement Options
Use the drop-down menu to select the planter or seeder type, and press the blue right-arrow button to
continue. Check the Planter Section Row Shutoff check box to enable Row Shutoff functionality.
4. Enter Number of Rows and Spacing
Use the up and down arrows to enter the number of rows and spacing, and press the blue right-arrow button
to continue.
81
Page 94

5. Enter Number of Implement Sections
Use the up and down arrows to enter the number of clutch sections,
and press the blue right-arrow button to continue.
Note: Do not enter the number of individual rows. Enter the number of swath sections that can be
independently turned on and off.
6. Enter Section Widths from Left to Right
The Enter Section Widths from Left to Right screen appears. This screen shows the number of sections
and number of rows in your configuration. From here you can:
- Press Next, or
- Highlight the section number, and use the numeric keypad to change the section row numbers; then
press the blue right-arrow button to continue.
Note: The implement is divided up into equal section sizes by default. To modify the sections, press the
keypad button for each section that needs to be changed.
7. Enter Distance from Hitch to Application Point
Use the numeric keypad to enter the distance from the implement hitch to the application point (from front
to back). When finished, press the blue right-arrow button to continue.
8. Enter Implement Name
Use the numeric keypad to enter a name for the implement, and press the check mark box.
9. Enable Seed Row Shutoff
On the Implement Tab, first highlight the desired implement from the Implement List, then check the Enable
Seed Row Shutoff check box. Next, press the Configure Clutch Modules button.
Note: You must have the Enable Row Shutoff Module check box selected in order to have the Configure
Row Shutoff button enabled.
10. Enter number of clutch sections
Once you have pressed the Configure Clutch Modules button, the Clutch Module Configuration box
appears. Enter the same number of clutch sections that you specified in Step 5; then press the checkmark
box.
11. Configuration Complete
The configuration appears, as shown.
82
Page 95

Note: The Clutch Module Configuration must match the actual number of clutch sections on the planter.
Otherwise, you will see a message stating that “The number of detected module outputs does not equal the
number of planter sections.” (This message may also appear if you have not connected the clutches to the
module).
ROW SHUTOFF LOOK-AHEAD NUMBERS
This table references the Turn-On Look-Ahead and Turn-Off Look-Ahead numbers for both Electric
Clutch and Air Row Shutoff Modules.
Planter Unit Seed Meter Type On/Off Electric Clutch Air Clutch
Turn On 0.9 1.1
Finger Units
Turn Off 0.3 0.3
Turn On 0.9 1.1
Vacuum
Turn Off 0.4 0.4
Note: Using the above settings will produce accurate field results. However, always take the time to check
for proper seed placement in the field and make system setting adjustments as needed. Do not rely solely
upon the appearance of the On-Screen map. The on screen map will not show gaps and overlaps caused by
incorrect GPS Offsets or AutoSwath Look-Ahead settings.
PLANTING
CHECKING AUTOSWATH PERFORMANCE FOR ROW SHUTOFF
The settings given in the above AutoSwath look-ahead table shown previously have been tested with
each clutch and seed meter combination to work for your planter. However, always take the time to
check for proper seed placement in the field and make system setting adjustments as needed. Do not
rely solely upon the appearance of the On-Screen map. The on screen map will not show gaps and
overlaps caused by incorrect GPS Offsets or AutoSwath Look-Ahead settings. Verify settings with the
following procedure:
1. Stop the planter within 20 feet of the planted headland.
2. Select one row unit from each planter swath section to observe.
3. Remove the down pressure from the closing wheel of each selected row unit.
4. Hold the closing wheels off the ground by attaching a chain or strap from the hopper support panel to
the closing wheel arm. (This prevents the closing wheels from closing the seed trench).
Securing these closing wheels up allows you to observe the planted seed in the trench so that you can
observe when the display is turned off and on during the seed application.
5. Resume planting in your normal fashion, then stop when you are 20 feet out of the headland of the
next pass.
6. Stop the planter and observe the AutoSwath shutting off and turning on to see if the results are
acceptable.
• If the results are correct, then return the closing wheels to their previous operational state. Close the seed
trench on the observed rows and return to planting.
83
Page 96

• If you suspect the results are incorrect, then adjust the appropriate look-ahead setting one-tenth (.1)
second per trial. When making changes to the look-ahead settings, make sure to adjust these settings
only one-tenth (.1) second per trial. Larger adjustments can cause unintentional large changes in the
AutoSwath’s performance. When adjusting the look-ahead numbers from the suggested settings, it is
recommended that you observe multiple trials to confirm the operations’ accuracy.
• If you encounter overplanting or underplanting problems, see
AutoSwath” on page 72.
“Fixing Overplanting and Underplanting in
HYDRAULIC SEED RATE CONTROL
The Hydraulic Seed Control Module is a SeedCommand™ product that allows users to control up to
three hydraulic motor drives via the display. Configure the Hydraulic Seed Rate Control module in the
following order.
1. Configure Hydraulic Seed Rate Control module
See
“Hydraulic Seed Rate Control Configuration” on page 84
2. Enter Controller Settings
Included the Max Meter Speed, Gear Ratio and Minimum Allowable Ground Speed. See
for Hydraulic Seed Rate Motor Drives” on page 85
3. Prime the Hydraulic Seed Meter
This fills the seed meter with seed, and thus allows you to avoid skips in your field. See
Meters” on page 94
4.
- a. Enter Meter Calibration Number. This number, representing seeds per revolution, is set according
to the number of seed dropped per one revolution of the seed meter. For more information,
“Calibrating Seed Rate Meters” on page 94.
- b. Perform a Seed Meter Calibration (not always required). A new calibration should be performed if
your as-applied seed rate does not match the actual population planted. For more information,
“Calibrating Seed Rate Meters” on page 94.
.
.
“Controller Settings
“Priming Seed Rate
HYDRAULIC SEED RATE CONTROL CONFIGURATION
Press the Planting button at the Setup Screen and go to the Planting Configuration Tab.
1. Create or add a vehicle
Follow the on-screen wizard to set up a vehicle.
2. Add Implement
After you have completed the vehicle configuration, the Implement Attachment Wizard appears. Add a new
implement, and select the implement attachment method.
3. Select Implement
Using the drop-down box, select the implement you would like to use in this configuration. If there are no
implements in the list, press the New button.
4. Select Operation Type
Select the Rate Logging/Control operation type. Press the blue right-arrow button to continue.
84
Page 97

5. Select Controller
Select an existing controller from the drop-down menu, or press the New button and use the Controller
Setup Wizard to create a controller.
6. Select Device and Seed Command Type
After pressing the New button, the Controller Setup Wizard appears. Use the drop-down menus to select
SeedCommand as your device. Use the bottom drop-down menu to select Hydraulic Seed Control as the
SeedCommand Type. Press the blue right-arrow button to continue.
7. Enter number of drives
Use the up and down arrows to enter in the number of hydraulic drives on your planter. Press the blue rightarrow button to continue.
8. Enter suggested controller name
A suggested controller name appears. If necessary, use the on-screen keyboard to edit the name of the
controller.
9. Select Ground Speed Source
Select a Primary and Backup Ground Speed Source, (such as GPS, Wheels, Track or Radar). Press the
blue right-arrow button to continue.
10. Enter Suggested Name for Configuration
Use the keyboard button to enter a name for the configuration. Press the checkmark box when complete.
PLANTING
CONTROLLER SETTINGS FOR HYDRAULIC SEED RATE MOTOR DRIVES
Channel Tabs
• Shaft Speed Cal
Calibration number representing the pulses that equal one
revolution of the hydraulic motor.
• Max Meter Speed
Setting determines the maximum RPM of the seed meter, and is
specified by the manufacturer. A warning informs you if this
threshold is exceeded.
• Gear Ratio
Ratio of the revolutions of the hydraulic drive as compared to the revolutions of the seed meter.
• Allowable Error
Determines the percent of error that is allowed prior to the product control system making any flow rate
changes.
• Control Valve Settings
This button summons the Control Valve Settings screen. If your planting configuration uses a PWM valve,
see
“Control Valve Settings - PWM” on page 86
“Control Valve Settings - Servo” on page 86.
. If your planting configuration uses a Servo valve, see
85
Page 98

Control Valve Settings - PWM
• Control Valve
Setting determines the type of control valve being used for the
hydraulic motor. Choices include PWM or Servo.
• PWM Frequency
The frequency that the PWM control valve is pulsed at. Settings
can be found from the manufacturer of the valve. Typical settings
range from 100-125 Hz.
• PWM Gain
Determines how aggressively the control valve responds when making rate change adjustments. The
higher the value the more aggressive the system response is.
• Zero Flow Offset
Represents the maximum duty cycle that is sent to the control valve without producing any hydraulic flow
from the PWM valve. Using too high of a Zero Flow Offset value can cause the product control system to
not properly control low rates. See the PWM valve manufacturer’s information for recommended settings.
Control Valve Settings - Servo
• Control Valve
Setting determines the type of control valve being used for the
hydraulic motor. Choices include PWM or Servo.
• Valve Response 1
Determines the speed of the servo valve when product control error
exceeds the Response Threshold setting.
• Valve Response 2
Determines the speed of the servo valve when product control error
is less than the Response Threshold setting.
• Response Threshold
Determines the system responsiveness to rate change.
Auxiliary Tab
The Auxiliary Tab of the Controller Settings screen adjusts the minimum speed, threshold and rate time
of the motion detection sensor that turns the Hydraulic Drive on.
• Minimum Ground Speed
The Minimum Ground Speed performs two functions: It determines
the speed at which the motion detection sensor disengages and
actual ground speed is used for rate control; and also determines
the minimum seed meter RPM when the motion detection sensor
is active.
• Rate Not Responding Threshold
The percentage of seed rate error that triggers the alarms.
• Rate Not Responding Time
The amount of time that the error occurs before the alarm sounds.
86
Page 99

Hydraulic Seed Controller Settings for Specific Planter
John Deere Planters
• Control Valve Configuration — PWM
• PWM Frequency — 175
• PWM Gain — 110
• Zero Flow Offset — 40
• Gear Ratio
- (chain drive) — 2.374
- (ProShaft) — 2.417
• Pulses/Rev. —360
White Planters
• Control Valve Configuration — PWM
• PWM Frequency — 200
• PWM Gain — 90
• Zero Flow Offset — 30
• Gear Ratio — 5.5
PLANTING
• Pulses/Rev. — 360
Case IH Planters
• Control Valve Configuration — PWM
• PWM Frequency — 100
• PWM Gain — 95
• Zero Flow Offset — 40
• Gear Ratio — 6.803
• Pulses/Rev. — 360
Hydraulic Seed Meter Calibration Numbers
Prior to calibrating the Hydraulic Seed Meter, the numbers that appear in the Meter Calibration box in the
Planter Control window should be similar to the numbers that appear below. If they are not, then your
seed meter may be working incorrectly, or you may have set the Gear Ratio incorrectly. In these cases,
contact Technical Support for further assistance.
87
Page 100

Cotton
Planter brand and type Corn Soybeans
Standard
Sorghum
Rate
John Deere
Vacuum: Standard 30 108 64 45
Vacuum: ProMax™ 40
Vacuum: Precision Planting eSet® 30
Vacuum: VenHuizen AccuVac Kit 40
Mechanical: Finger 12
Mechanical: Brush Meter 56
Case IH
Vacuum 48 60 80 80
Cyclo[ 36 240
KINZE
EdgeVac® 39 60 54 60
Mechanical:Finger 12 56 48 60
White
30 60
Great Plains
Mechanical Standard 12 110 120 102
Mechanical: Twin Row 6 100 135
Note: Check your operator’s manual for more specific information on other seed disk options.
Note: If you are encountering a problem with skips in the field or if the hydraulic drive is not shutting off
properly, you may need to adjust the Zero Flow Offset settings. For more information, see “Zero Flow Offset
Variation” on page 95.
88
 Loading...
Loading...