
GPC and Agilent PolarGel-M
Columns for the True Representation
of Novolac Resins
Application Note
Authors
Greg Saunders, Ben MacCreath
Agilent Technologies, Inc.
Introduction
Novolac resins are thermoplastic materials made with an excess of phenol in an
acid catalyzed reaction with formaldehyde. Novolacs are commonly employed as
photoresists (light-sensitive materials used to form patterned surface coatings) and
in varnishes. They have higher heat distortion temperatures and tend to be more
expensive than regular epoxy resins.
GPC Analysis
Results
PolarGel-M GPC columns are packed with low swell,
macroporous copolymer beads that have a surface of
balanced polarity, comprizing hydrophobic and hydrophilic
components. These allow PolarGel-M to be used in the
analysis of high polarity polymers that are insoluble in water
to give a more accurate representation of the molecular
weight distribution of the polymer. If these polar polymers
were to be analyzed with traditional styrene/divinyl benzene
columns, interactions would cause artifacts in the peak
shape and longer retention times, which would translate into
apparently much lower molecular weight averages.
Sample Preparation
Two novolac resins were analyzed to obtain an indication of
differences in molecular weight, if any. The samples were
made up at 0.2 % (w/v) in DMSO, with 0.1 % LiBr added to
reduce sample aggregation, and injected without further
treatment.
Conditions
Columns: 2 x PolarGel-M, 300 x 7.5 mm (p/n PL1117-6800)
Eluent: DMSO & 0.1 % LiBr
Flow Rate: 1.0 mL/min
Injection Volume: 100 µL
Temperature: 50 ºC
Detectors: Agilent PL-GPC 50, RI
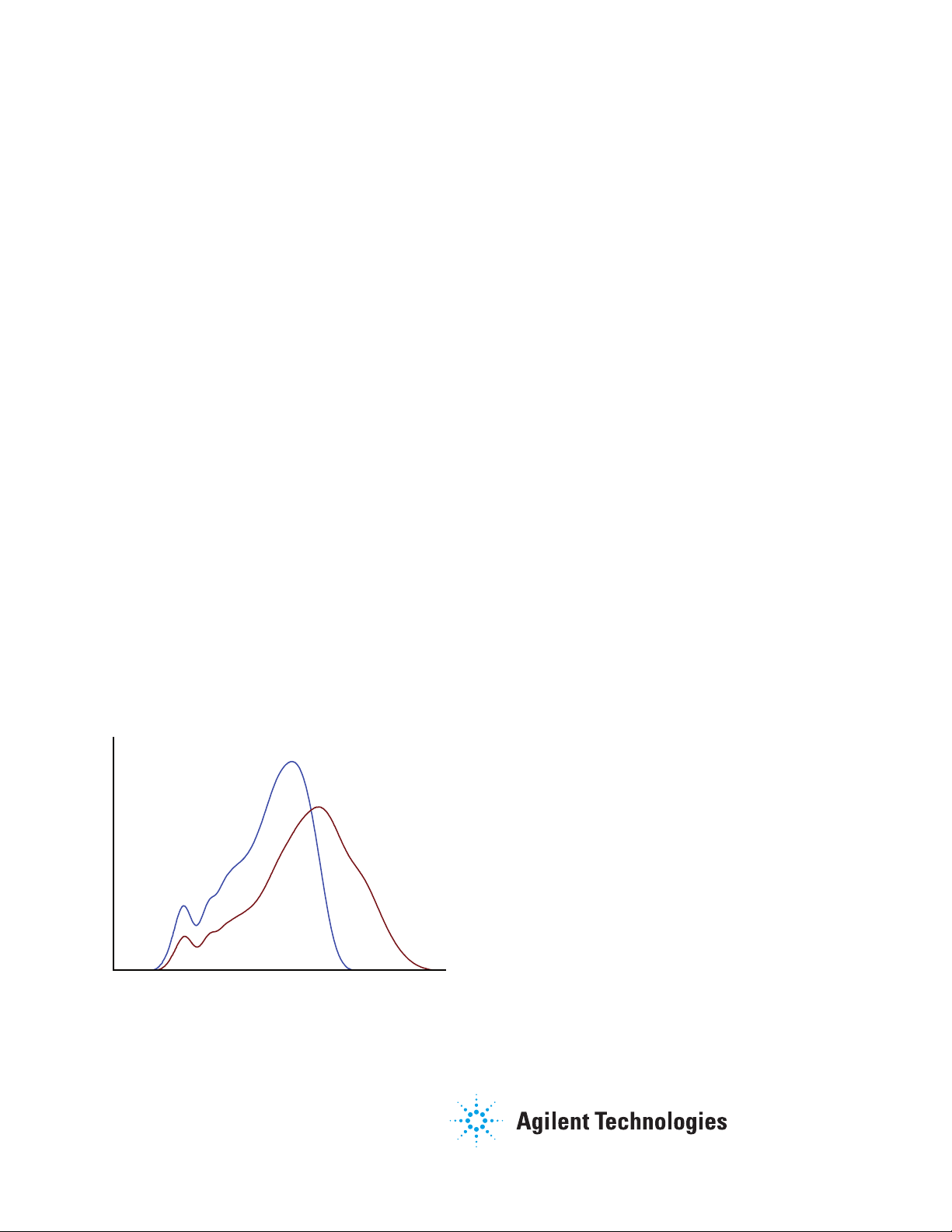
Figure 1 shows the overlaid molecular weight distributions of
two novolac resins.
Conclusion
GPC with PolarGel-M columns allows for the artifact,
interaction free calculation of the composition and molecular
weight distributions of novolac resins that are difcult to
analyze on traditional, organic (PS/DVB) GPC columns.
1
dw/dlogM
0
1
Figure 1. Overlaid molecular weight distributions of two novolac resins
A
B
logM
www.agilent.com/chem
This information is subject to change without notice.
© Agilent Technologies, Inc. 2010
Published in UK, September 2, 2010
SI-00948
5
 Loading...
Loading...