Page 1
AERCO INTERNATIONAL, Inc., Northvale, New Jersey, 07647 USA
Instruction
No.
GF-127
Installation, Operation
& Maintenance Instructions
Benchmark 2.0LN
Dual-Fuel Series
Gas Fired
Boiler System
Natural Gas or Propane Fired
Condensing, Modulating,
Forced Draft, Hot Water Boiler
2,000,000 BTU/H Input
Appicable for Serial Numbers G-10-0631 and above
Printed in U.S.A. NOVEMBER 10, 2010
Page 2

Telephone Support
Direct to AERCO Technical Support
(8 am to 5 pm EST, Monday - Friday):
1-800-526-0288
AERCO International, Inc.
159 Paris Avenue
Northvale, NJ 07647-0128
www.aerco,com
© AERCO International, Inc., 2010
The information contained in this
installation, operation and maintenance manual is subject to change
without notice from AERCO International, Inc.
AERCO makes no warranty of any
kind with respect to this material,
including, but not limited to, implied
warranties of merchant-ability and
fitness for a particular application.
AERCO International is not liable for
errors appearing in this manual, nor
for incidental or consequential
damages occurring in connection
with the furnishing, performance, or
use of this material.
Page 3

FOREWORD
Foreword
The AERCO Benchmark 2.0LN Dual-Fuel, Low NOx Boiler is a modulating unit. It repr esents a
true industry advance that meets the needs of today's energy and environmental concerns.
Designed for application in any closed loop hydronic system, the Benchmark's modulating
capability relates energy input directly to fluctuat ing system loads. The Benchmark 2.0LN, with
its 20:1 turn down ratio and condensing capability, provides extremely high efficiencies and
makes it ideally suited for modern low temper ature, as well as, conventional heating systems.
The Benchmark 2.0 operates at inputs rang ing f rom 100,000 BT U/hr. to 2,000,000 BTU/ hr. The
output of the boiler is a f unction of the unit’s firing rate and return water temperat ure. Output
ranges from 99,000 BT U/hr. to 1,933,000 BTU/hr . , depending on operating conditions.
When installed and operated on natural gas in accordance with this Instruction Manual, the
Benchmark 2.0LN Boiler complies with the NOx emission standards outlined in:
• South Coast Air Quality Management District (SCAQMD), Rule 1146.2
Whether used in singular or m odular arrangement s, the Benchmark 2.0LN off ers the maximum
flexibility in venting with minimum installation space requirements. The Benchmark 's advanced
electronics are available in several selectable modes of operation offering the most efficient
operating methods and energy manag em ent system integration.
For service or parts, contact your local sales represent at ive or AERCO I NTERNATIONAL.
NAME:
ORGANIZATION:
ADDRESS:
TELEPHONE:
INSTALLATION DATE: _____________________________________________
A
Page 4

Page 5

CONTENTS
GF-127 - BENCHMARK 2.0 LN DUAL-FUEL GAS FIRED BOILER
Operating & Maintenance Instructions
FOREWORD A
Chapter 1 – SAFETY PRECAUTIONS 1-1
Para. Subject Page
1-1 Warnings & Cautions 1-1
1-2 Emergency Shutdown 1-2
Chapter 2 – INSTALLATION 2-1
Para. Subject Page
2.1 Introduction 2-1
2.2 Receiving the Unit 2-1
2.3 Unpacking 2-1
2.4 Site Preparation 2-1
2.5 Supply and Return Piping 2-3
2.6 Condensate Drain 2-3
2.7 Gas Supply Piping 2-4
2.8 AC Elec tric a l Po wer Wiring 2-5
Para. Subject Page
1-3 Prolonged Shutdown 1-2
Para. Subject Page
2.9 Modes of Operation and Field
Control Wiring
2.10 I/O Box Connections 2-8
2.11 Auxiliary Relay Contacts 2-10
2.12 Flue Gas Vent Installation 2-10
2.13 Combustion Air 2-10
2-6
Chapter 3 – CONTROL PANEL OPERATING PROCEDURES 3-1
Para. Subject Page
3.1 Introduction 3-1
3.2 Control Panel Description 3-1
3.3 Control Panel Menus 3-4
3.4 Operating Menu 3-5
3.5 Setup Menu 3-5
Para. Subject Page
3.6 Configuration Menu 3-6
3.7 Tuning Menu 3-7
3.8 Combustion Cal Menu 3-8
3.9 Start Sequence 3-9
3.10 Start/Stop Levels 3-11
Chapter 4 – INITIAL START-UP 4-1
Para. Subject Page
4.1 Initial Startup Requirements 4-1
4.2 Tools and Instruments for
Combustion Calibration
4.3 Natural Gas Combustion
Calibration
4-1
4-2
Para. Subject Page
4.4 Propane Combustion Calibration 4-6
4.5 Unit Reassembly
4.6 Over-Temperature Limit
Switches
4-9
4-9
i
Page 6

CONTENTS
Chapter 5 – MODE OF OPERATION 5-1
Para. Subject Page
5.1 Introduction 5-1
5.2 Indoor/Outdoor Reset Mode 5-1
5.3 Constant Setpoint Mode 5-2
5.4 Remote Setpoint Mode 5-2
5.5 Direct Drive Modes 5-3
Para. Subject Page
5.6 Boiler Management System
(BMS)
5.7 Combination Control System
(CCS)
5-4
5-5
Chapter 6 – SAFETY DEVICE TESTING PROCEDURES 6-1
Para. Subject Page
6.1 Testing of Safety Devices 6-1
6.2 Natural Gas Low Gas Pressure
Fault Test
6.3 Pr opa ne Lo w Gas Pres sur e
Fault Test
6.4 Natural Gas High Gas Pressure
Test
6.5 Propane High Gas Pressure
Test
6.6 Low Water Level Fault Test 6-3
6.7 Water Temperature Fault Test 6-3
6-1
6-2
6-2
6-2
Para. Subject Page
6.8 Interlock Tests 6-4
6.9 Flame Fault Test 6-4
6.10 Air Flow Fault Test 6-5
6.11 SSOV Proof of Closure Switch 6-6
6.12 Purge Switch Open During
Purge
6.13 Ignition Switch Open During
Ignition
6.14 Safety Pressure Relief Valve
Test
6-6
6-7
6-7
Chapter 7 – MAINTENANCE REQUIREMENTS 7-1
Para. Subject Page
7.1 Maintenance Schedule 7-1
7.2 Ignitor-Injector 7-2
7.3 Flame Detector 7-3
7.4 Combustion Calibration 7-3
7.5 Safety Device Testing 7-3
7.6 Burner Assembly Inspection 7-3
Para. Subject Page
7.7 Condensate Trap 7-5
7.8 Shutting the Boiler Down For An
Extended Period of Time
7.9 Placing The Boiler Back In
Service After A Prolong ed
Shutdown
7-6
7-6
Chapter 8 – TROUBLESHOOTING GUIDE 8-1
Para. Subject Page
8.1 Introduction 8-1
Para. Subject Page
ii
Page 7

CONTENTS
Chapter 9 - RS232 COMMUNICATION 9-1
Para. Subject Page
9.1 Introduction 9-1
9-2 RS232 Communication Setup 9-1
APPENDICES
App Subject Page
A Boiler Menu Item Descriptions A-1
B Startup, Status and Fault
Messages
C Temperature Sensor Resistance
Voltage Chart
D Indoor/Outdoor Reset Ratio
Charts
E Boiler Default Settings E-1
B-1
C-1
D-1
Para. Subject Page
9-3 Menu Processing Utilizing
RS232 Communication
9-4 Data Logging 9-2
App Subject Page
F Dimensionals and Parts Lists F-1
G Piping Diagrams G-1
H Wiring Schematics H-1
I Recommended Periodic Testing
Checklist
J Benchmark Control Panel Views J-1
K Benchmark 2.0LN Dual-Fuel
Switchover Instructions
L Recommended Spare Parts List L-1
9-1
I-1
K-1
WARRANTY W-1
iii
Page 8

Page 9
SAFETY PRECAUTIONS
CHAPTER 1 SAFETY PRECAUTIONS
1.1 WARNINGS & CAUTIONS
Installers and operat ing personnel MUST, at all
times, observe all safety regulations. The
following warnings an d cautions are gener al and
must be given the same attention as specific
precautions included in these instructions. In
addition to all the requirements included in this
AERCO Instruction Manual, the installation of
units MUST conform with local building codes,
or, in the absence of local codes, ANSI Z223.1
(National Fuel Gas Code Publ ication No. NFPA-
54). Where ASME CSD-1 is required by local
jurisdiction, the installation must conform to
CSD-1.
Where applicable, the equipment shall be
installed in accordance with the current
Installation Code for Gas Burning Appliances
and Equipment, CGA B149, and applicable
Provincial regulat io ns f or th e c las s; which should
be carefully followed in all cases. Authorities
having jurisdiction should be consulted before
installations are made.
IMPORTANT
This Instruction Manual is an integral
part of the product and must be
maintained in legible condition. It must
be given to the user by the installer
and kept in a safe place for future
reference.
WARNINGS!
MUST BE OBSERVED TO PREVENT
SERIOUS INJURY.
WARNING!
BEFORE ATTEMPTING TO PERFORM ANY MAINTENANCE ON THE
UNIT, SHUT OFF ALL GAS AND
ELECTRICAL INPUTS TO THE UNIT.
WARNING!
DO NOT USE MATCHES, CANDLES,
FLAMES, OR OTHER SOURCES OF
IGNITION TO CHECK FOR GAS
LEAKS.
WARNING!
FLUIDS UNDER PRESSURE MAY
CAUSE INJURY TO PERSONNEL
OR DAMAGE TO EQUIPMENT
WHEN RELEASED. BE SURE TO
SHUT OFF ALL INCOMING AND
OUTGOING WATER SHUTOFF
VALVES. CAREFULLY DECREASE
ALL TRAPPED PRESSURES TO
ZERO BEFORE PERFORMING
MAINTENANCE.
WARNING!
ELECTRICAL VOLTAGES UP TO
120 VAC ARE USED IN THIS
EQUIPMENT. THEREFORE THE
COVER ON THE UNIT’S POWER
BOX (LOCATED BEHIND THE
FRONT PANEL DOOR) MUST BE
INSTALLED AT ALL TIMES, EXCEPT
DURING MAINTENANCE AND SERVICING.
CAUTIONS!
Must be observed to prevent equipment damage or loss of operating
effectiveness.
CAUTION!
Many soaps used for gas pipe leak
testing are corrosive to metals. The
piping must
clean water after leak checks have
been completed.
be rinsed thoroughly with
WARNING!
THE EXHAUST VENT PIPE OF THE
UNIT OPERATES UNDER A
POSITIVE PRESSURE AND THEREFORE MUST BE COMPLETELY
SEALED TO PREVENT LEAKAGE
OF COMBUSTION PRODUCTS INTO
LIVING SPACES.
CAUTION!
DO NOT use this boiler if any part has
been under water. Call a qualified
service technician to inspect and
replace any part that has been under
water.
1-1
Page 10
SAFETY PRECAUTIONS
1.2 EMERGENCY SHUTDOWN
If overheating occurs or the gas supply fails to
shut off, close the manual gas shutoff valve
(Figure 1-1) located external to the unit.
IMPORTANT
The Installer must identify and indicate
the location of the emergency shutdown
manual gas valve to operating personnel.
1.3 PROLONGED SHUTDOWN
After prolonged shutdown, it is recommended
that the startup proce dures in Chapter 4 and the
safety device test procedures in Chapter 6 of
this manual be performed, to verify all systemoperating param eters. If ther e is an em ergenc y,
turn off the electrical power supply to the
AERCO boiler and close the manual gas valve
located upstream the unit. The installer must
identify the emergency shut-off device.
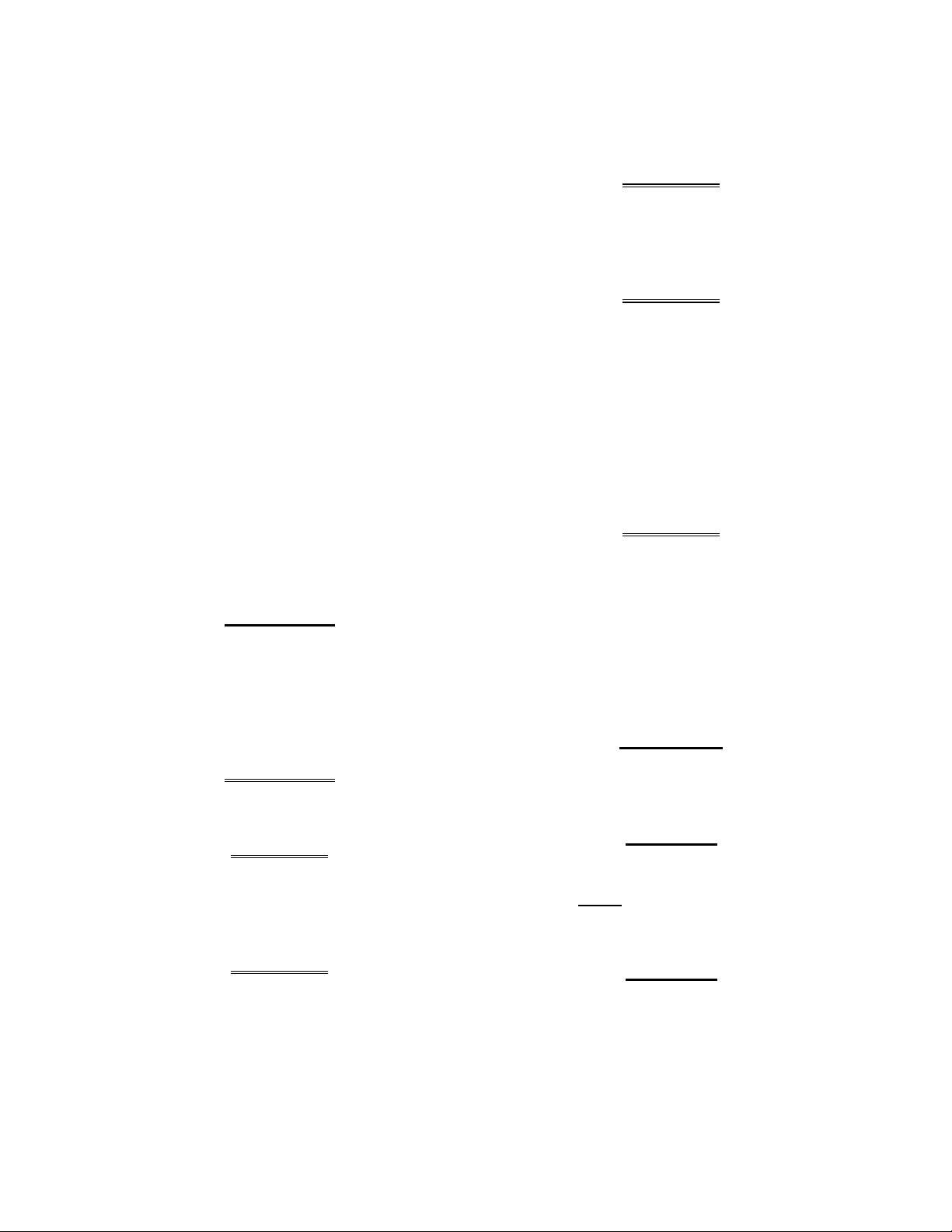
MANUAL GAS SHUTOFF VALVE
VALVE OPEN
Figure 1-1
Manual Gas Shutoff Valve
VALVE CLOSED
1-2
Page 11

INSTALLATION
CHAPTER 2 INSTALLATION
2.1 INTRODUCTION
This Chapter provides the descriptions and
procedures necessary to unpack, inspect and
install the AERCO Benc hmark 2.0LN Dual-Fuel
Boiler. Brief descriptions are also provided for
each available mode of operation. Detailed
procedures for implementing these modes are
provided in Chapter 5.
2.2 RECEIVING THE UNIT
Each Benchmark 2.0LN S ystem is shipped as a
single crated unit. The shipping weight is
approximately 1600 pounds. The unit must be
moved with the proper rigging equipment for
safety and to avoid equipment dam age. The unit
should be complete ly inspected for evidence of
shipping damage and ship ment com pleteness at
the time of receipt from the carrier and before
the bill of lading is signed.
NOTE
AERCO is not responsible for lost or
damaged freight.
Each unit has a Tip-N-Tell indicator on the
outside of the crate. T his indic ates if the un it has
been turned on its side during shipment. If the
Tip-N-Tell indicat or is trip ped, do not s ign for the
shipment. Note the information on the carrier’s
paperwork and request a freight claim and
inspection by a claims adjuster before
proceeding. Any other visual damage to the
packaging materials s hould also be made clear
to the delivering carrier.
2.3 UNPACKING
Carefully unpack the unit taking care not to
damage the unit enclosure when cutting away
packaging materials
A close inspection of the unit s hould be made to
ensure that there is no evidence of dam age not
indicated by the T ip-N-Tell indicator. The f reight
carrier should be notified immediately if any
damage is detected.
IMPORTANT
After unpacking, take off the unit top
panel and remove the strap and packing
material at the top of the h eat exchanger.
The packing material is located in the
area of the ignitor-injector and staged
ignition solenoid on the burner assembly.
The following accessories come standard with
each unit and are either packed separately
within the unit’s pack ing container or are fac tory
installed on the boiler:
• Pressure/Temperature Gauge
• Spare Spark Igniter
• Spare Flame Detector
• ASME Pressure Relief Valve
• Condensate Drain Trap
• 2” Gas Supply Shutoff Valve
When ordered, optional accessories may be
packed separately, packed within the boiler
shipping container, or may be installed on the
boiler. Any standard or optional accessories
shipped loose should b e identified and s tored in
a safe place until ready for installation or use.
2.4 SITE PREPARATION.
Ensure that the site selected for installation of
the Benchmark 2.0LN Boiler includes:
• Access to AC Input Power at 120 VAC,
Single-Phase, 60 Hz @ 20 A mps
• Access to Natural Gas line at a minimum
supply gas pressure of 8.5" W.C.
• Access to Propane l ine at a minimum supply
gas pressure of 8.5” W.C.
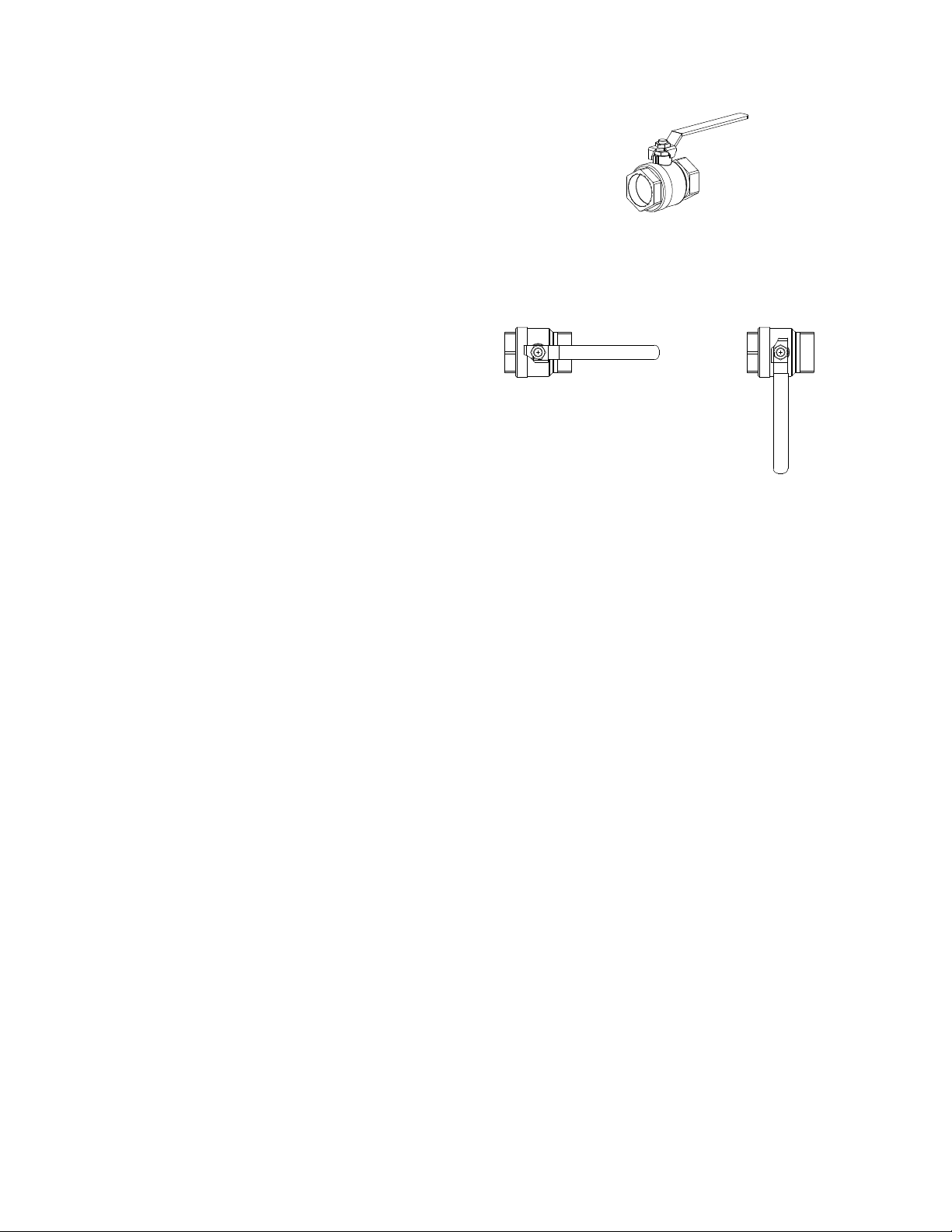
2.4.1 Installation Clearances
The unit must be installed with the prescribed
clearances for service as shown in Figure 2-1.
The minimum
AERCO, are listed below. However, if Local
Building Codes require additional clearances,
these codes shall supersede AERCO’s
requirements. Minimum acceptable clearances
required are:
• Sides: 24 inches
• Front : 24 inches
• Rear: 30 inches
• Top: 18 inches
All gas piping, water piping and el ec tric al c on du it
or cable must be arranged so that they do not
interfere with the removal of any panels, or
inhibit service or maintenance of the unit.
clearance dimens ions , requir ed by
2-1
Page 12
INSTALLATION
Figure 2-1 Benchmark 2.0LN Boiler Clearances
WARNING
KEEP THE UNIT AREA CLEAR AND
FREE FROM ALL COMBUSTIBLE
MATERIALS AND FLAMMABLE
VAPORS OR LIQUIDS
.
CAUTION
While packaged in the shipping
container, the boiler must be moved
by pallet jack or forklift from the
FRONT ONLY.
2.4.2 Setting the Unit
The unit must be installed on a 4 inch to 6 inch
housekeeping pad to e nsure proper conde nsate
drainage. If anchoring the unit, refer to the
dimensional drawings in Appendix F for anchor
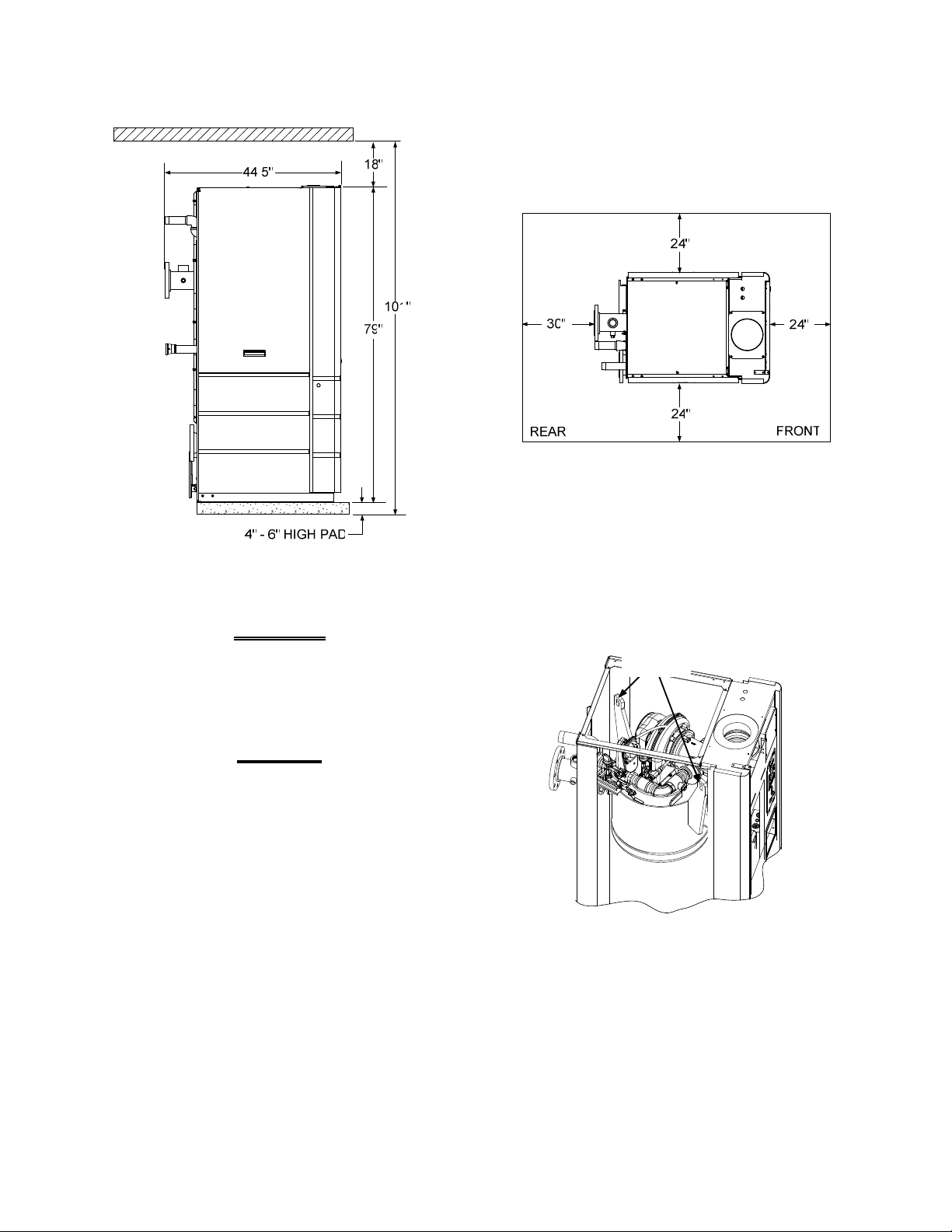
locations. Two lifting t abs ar e provided a t the top
of the heat exchanger as shown in Figure 2-2.
USE THE TABS SHOWN IN FIGURE 2-2 TO
LIFT AND MOVE THE UNIT. Remove the top
panel from the unit to provide access to the
lifting tabs. Remove the four (4) lag screws
securing the unit to the shipping skid. Lift the
unit off the shipping sk id and position it on the 4
inch to 6 inch housekeeping concrete pad
(required) in the desired location.
LIFTING
TABS (2)
Figure 2-2
View Showing Lifting Tab Locations
In multiple unit installations, it is important to
plan the position of each unit in advance.
Sufficient space for piping connections and
future service/maintenance requirements must
also be taken into cons ider ation. All pipin g m ust
include ample provisions for expansion.
2-2
Page 13
If installing a Combina tion Control Panel (CCP)
system, it is important to identify the
Combination Mode B oilers in adv ance and plac e
them in the proper physical location. Refer to
Chapter 5 for inform ation on Combination Mode
Boilers.
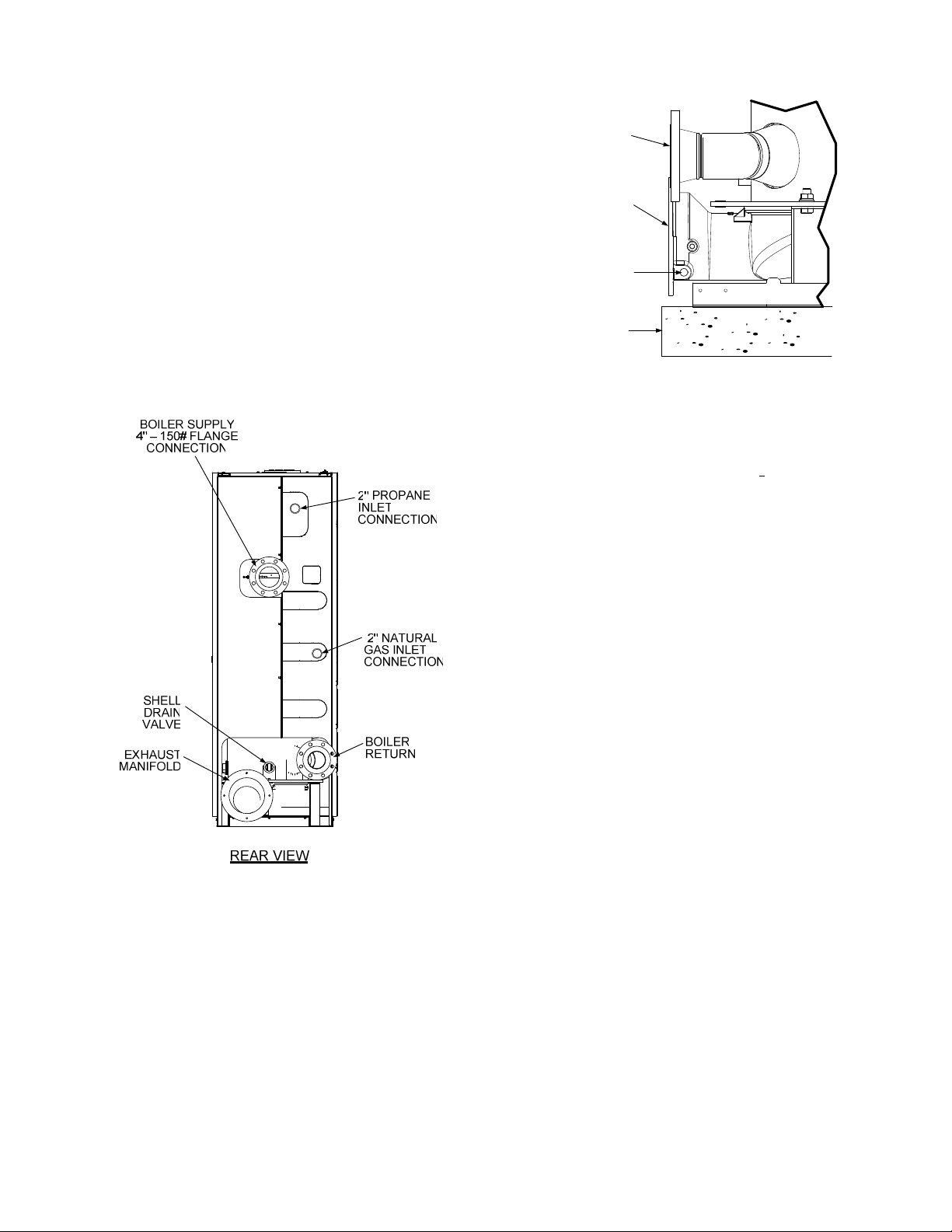
2.5 SUPPLY AND RETURN PIPING
The Benchmark 2.0LN Boiler utilizes 4” 150#
flanges for the water system supply and return
piping connectio ns. The physical location of the
supply and return p iping connections are on the
rear of the unit as shown in Figure 2-3. Ref er to
Appendix F, Drawing AP-A-798 for additional
dimensional data.
BOILER
RETURN
EXHAUST
MANIFOLD
1/2” NPT
CONDENSATE
DRAIN
CONNECTION
HOUSE-
KEEPING
PAD
INSTALLATION
Figure 2-4
Condensate Drain Connection Location
A condensate drain trap (part no. 24060) is
shipped loose and m ust be installed
of the unit. The trap inlet and outlet contain
tapped 3/4” NPT ports. The actual installation
details for the condensate trap will depend on
the available clearances, housekeeping pad
height/dimensions and other prevailing conditions at the site. However, the following
guidelines must be observed to ensure proper
condensate trap operation:
• The condensate trap inlet (Figure 2-5) must
be level with, or lower than the exhaust
manifold drain port.
at the rear
Figure 2-3
Supply and Return Locations
2.6 CONDENSATE DRAIN AND PIPING
The Boiler is designe d to condense water va por
from the flue produc ts. Therefore, the ins t al lat ion
must have provisions for suitable drainage or
collection. A 1/2” NPT drain connection is
provided on the exhaust manifold as shown in
Figure 2-4.
• The condensate trap must be supported to
ensure that its base is level (horizontal).
• The trap must be removable for routine
maintenance. AERCO recommends that a
union be utilized between the exhaust
manifold condensate drain port and the trap
inlet port.
1. While observing the above guidelines,
connect the condensate trap inlet to the
exhaust manifold dra in connection using th e
appropriate piping components (nipples,
reducers, elbows, etc.) for the boiler
installation site.
2. At the condensate trap outlet, install a 3/4”
NPT nipple.
3. Connect a length of 1” I.D polypropylene
hose to the trap outlet and secure with a
hose clamp.
4. Route the hose on the trap outlet to a
nearby floor drain.
2-3
Page 14
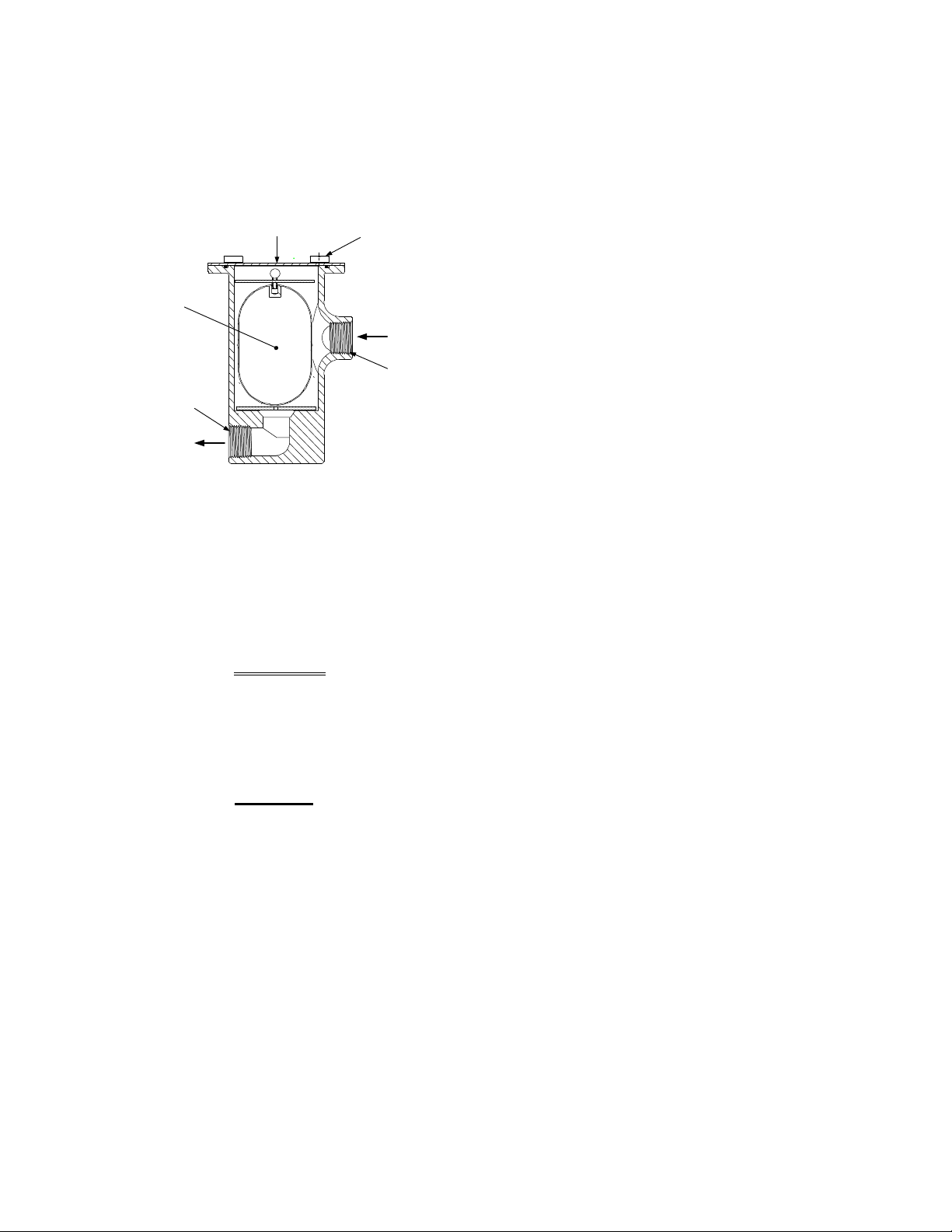
INSTALLATION
R
If a floor drain is not available, a condensate
pump can be used to remove the condens ate to
drain. The max imum condensate f low rate is 20
GPH. The condensate drain trap, associated
fittings and drain line must be removable for
routine maintenance.
FLOAT
3/4 NPT
PORT
OUTLET
COVE
THUMB
SCREWS
(4)
INLET
3/4 NPT
PORT
Figure 2-5
Condensate Trap Cut-Away View
2.7 GAS SUPPLY PIPING
The AERCO Benchmark 2.0LN Gas
Components and Supply Design Guide, GF2030LN must be consu lted prior to designing or
installing any gas supply piping.
WARNING
NEVER USE MATCHES, CANDLES,
FLAMES OR OTHER SOURCES OF
IGNITION TO CHECK FOR GAS
LEAKS
Many soaps used for gas pipe leak
testing are corrosive to metals. Therefore, piping must be rinsed thoroughly
with clean water after leak checks
have been completed.
All gas piping m ust be arranged so that it
does not interfere with removal of any
covers, inhibit service/maintenance, or
restrict access between the unit and
walls, or another unit.
.
CAUTION
NOTE
Benchmark 2.0LN Dual-F uel units contain t wo 2
inch gas inlet connectio ns on the rear of the unit
as shown in Figure 2-3.
Prior to installation, all pipes should be deburred and internall y cleared of any scale, m etal
chips or other foreign particles. Do Not install
any flexible connectors or unapproved gas
fittings. Piping must be s upported from the floor,
ceiling or walls onl y and must not be supported
by the unit.
A suitable piping compound, approved for use
with natural gas and/or propane, should be
used. Any excess m ust be wiped off to prevent
clogging of components.
To avoid unit damage whe n pres sur e tes ting gas
piping, isolate the unit from the gas supply
piping. At no time should the gas pressure
applied to the unit exceed 2 psi. Leak test all
external piping thoroughly using a soap and
water solution or suitable equivalent. The gas
piping used must meet all applicable codes.
2.7.1 Gas Supply Specifications.
The maximum static gas supply pressure to the
unit must not exceed 2 psi. The specifications
for natural gas and propane are as follows:
Natural Gas:
The gas supply pr essure to the unit m ust be
of sufficient capacity to provide 2000 cfh
while maintaining the gas pressure at 8.5"
W.C.
Propane:
The gas supply pr essure to the unit m ust be
of sufficient capacit y to provide 800 cfh while
maintaining the gas pressure at 8.5" W.C.
The maximum static pressure to the unit must
not exceed 2 psi. The minimum operating gas
pressure for natural gas and propane is 8.5
inches W.C. for both FM and IRI gas trains when
the unit is firing at maximum input.
2.7.2 Manual Gas Shutoff Valve
A manual shut-off valve must be installed in th e
gas supply line upstream of the Boiler as shown
in Figure 2-6. M aximum allowable gas pressure
to the Boiler is 2 psi.
2-4
Page 15
PROPANE
SUPPLY
NATURAL
GAS SUPPLY
2" MANUAL
SHUTOFF
VALVES
DIRT
TRAPS
Figure 2-6
Manual Gas ve Location
2
.7.3 IRI Gas Train Kit
The IRI gas train is an
configuration which is r e qui red i n s ome areas for
code compliance or for insurance purposes.
The IRI gas train is factor y pre-piped and wired.
See Appendix F, Drawing AP- A-843 for details.
Shut-Off Val
optional gas train
2.8 AC ELECTRICAL POWER WIRING
The AERCO Benchm ark 2.0LN Electr ical Powe
Wiring Guide, GF-2060LN, must be consulted
prior to connecting an y AC power wiring to the
unit. External AC power connections ar e made
to the unit inside the Power Box on the front
panel of the unit. Rem ove the front door of the
unit to access the Power Box mounted directly
above the Control Box. Loosen the four Power
Box cover screws and remove cover to access
the AC terminal connections inside the Power
Box (Figure 2-7).
r
INSTALLATION
TERMINAL BLOCK
UPPER RIGHT CORNER OF FRONT PANEL
Figure 2-7
AC Input Terminal Block Location
2.8.1 Electrical Power Requirements
The AERCO Benchmark 2.0LN Boiler accepts
120 VAC, single-phase, 60 Hz @ 20A. The
Power Box contains a ter minal block as shown
in Figure 2-8. In addition, a wiring diagram
showing the required AC power connections is
provided on the front cover of the Power Box.
Each Boiler must be connected to a dedicated
electrical circuit. NO OTHER DEVICES
SHOULD BE ON THE SAME ELECTRICAL
CIRCUIT AS THE BOILER. A means for
disconnecting AC po wer f rom the unit (such as a
service switch) must be installed near the unit
for normal operation and maintenance. All
electrical connections should be made in
accordance with the National Electrical Code
and/or with any applicable local codes.
For electrical power wiring diagrams, see the
AERCO Benchmark 2.0LN Electrical Power
Wiring Guide, (GF-2060LN).
NOTE
All elec rdware must
be installed so that it does not interfere
with the removal of any un it cover s, inh ibit
service/maintenance, or prevent access
between the unit and walls or another
unit.
trical conduit and ha
2-5
Page 16

INSTALLATION
120 VAC, 1 PHASE
GND
NEU
L1
Figure 2-8
AC Terminal Block Configurations
2.9 MODES OF OPERATION AN D FIELD CONTROL WIRING
The Benchmark 2.0LN Boiler is available in
several different modes of operation. While
each unit is fac tory configured and wired f or its
intended mode, som e additional field wiring may
be required to complete the installation. This
wiring is typicall y connected to the Input/Output
(I/O) Box located on the lower por tion of the unit
front panel (Figure 2-9) behind the removable
front door.
To access the I/O Box terminal strips shown in
Figure 2-9, loosen the four cover screws and
remove the cover. All field wiring is installed
from the rear of the panel by routing the wires
through one of the four bushings provided.
Refer to the wiring diagram provided on the
cover of the I/O Box (Figur e 2-10) when making
all wiring connections.
Brief descriptions of each mode of operation,
and their wiring requirements, are provided in
the following paragr aphs. Additional information
concerning field wiring is prov ided in paragr aphs
2.10.1 through 2.10.10. Refer to Chapter 5 for
detailed information on the available modes of
operation.
2.9.1 Constant Setpoint Mode
The Constant Setpoi nt Mode is used when it is
desired to have a fixed setpoint that does not
deviate. No wiring connections, other than AC
electrical power connections, are required for
this mode. However, if desired, fault monitor ing
or enable/disable in terlock wiring c an be utilized
(see paragraphs 2.10.9.1 and 2.10.10).
TERMINAL
STRIPS
LOWER RIGHT CORNER
OF FRONT PANEL
Figure 2-9.
Input/Output (I/O) Box Location
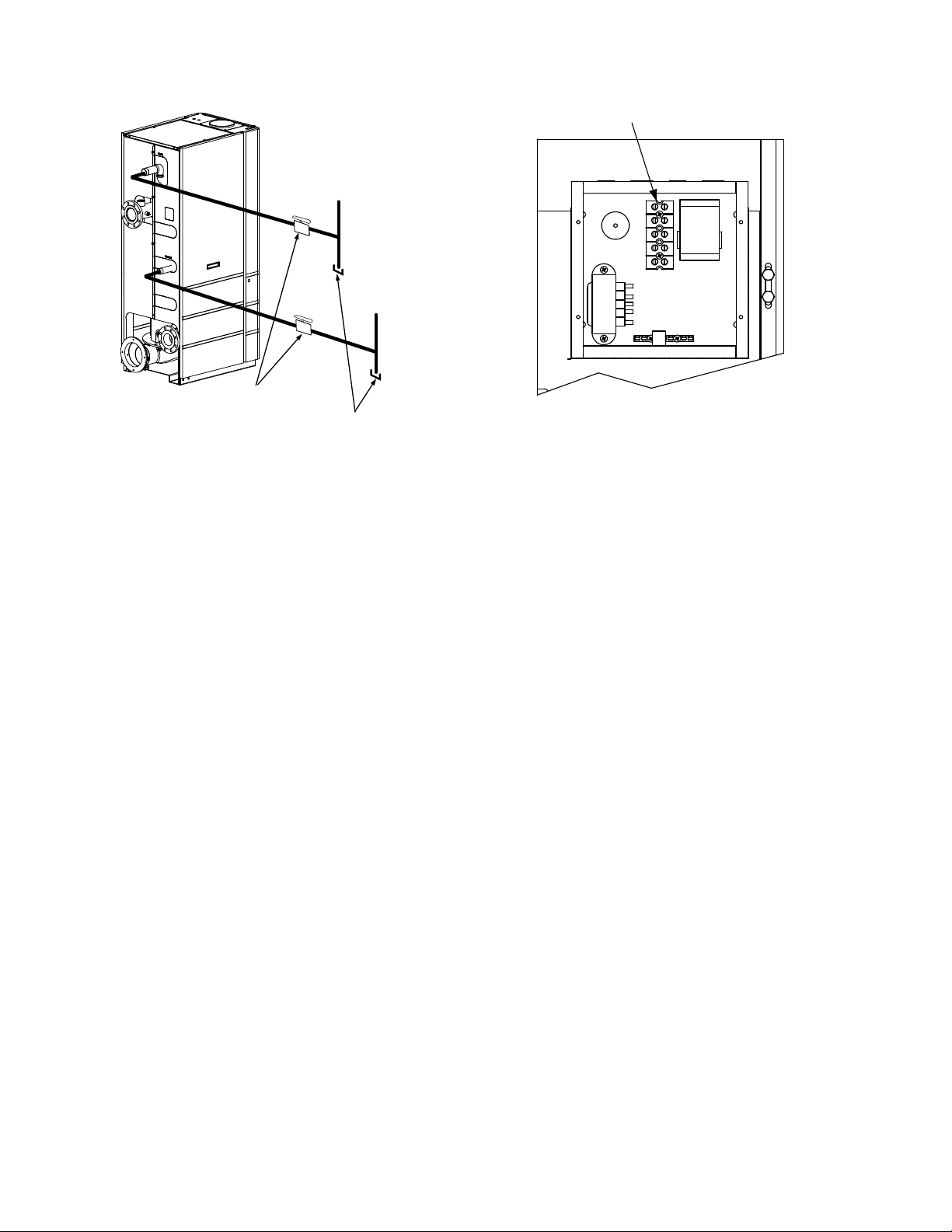
2.9.2 Indoor/Outdoor Reset Mode
This mode of operation increases supply water
temperature as outdoor te mperatures decrease.
An outside air temperatur e sensor (AERCO Part
No. 122790) is requ ired. The sensor MUST BE
wired to the I/O Box wiring term inals (see Figure
2-10). Refer to paragraph 2.10.1 for additional
information on outside air temperature sensor
installation.
2-6
Page 17
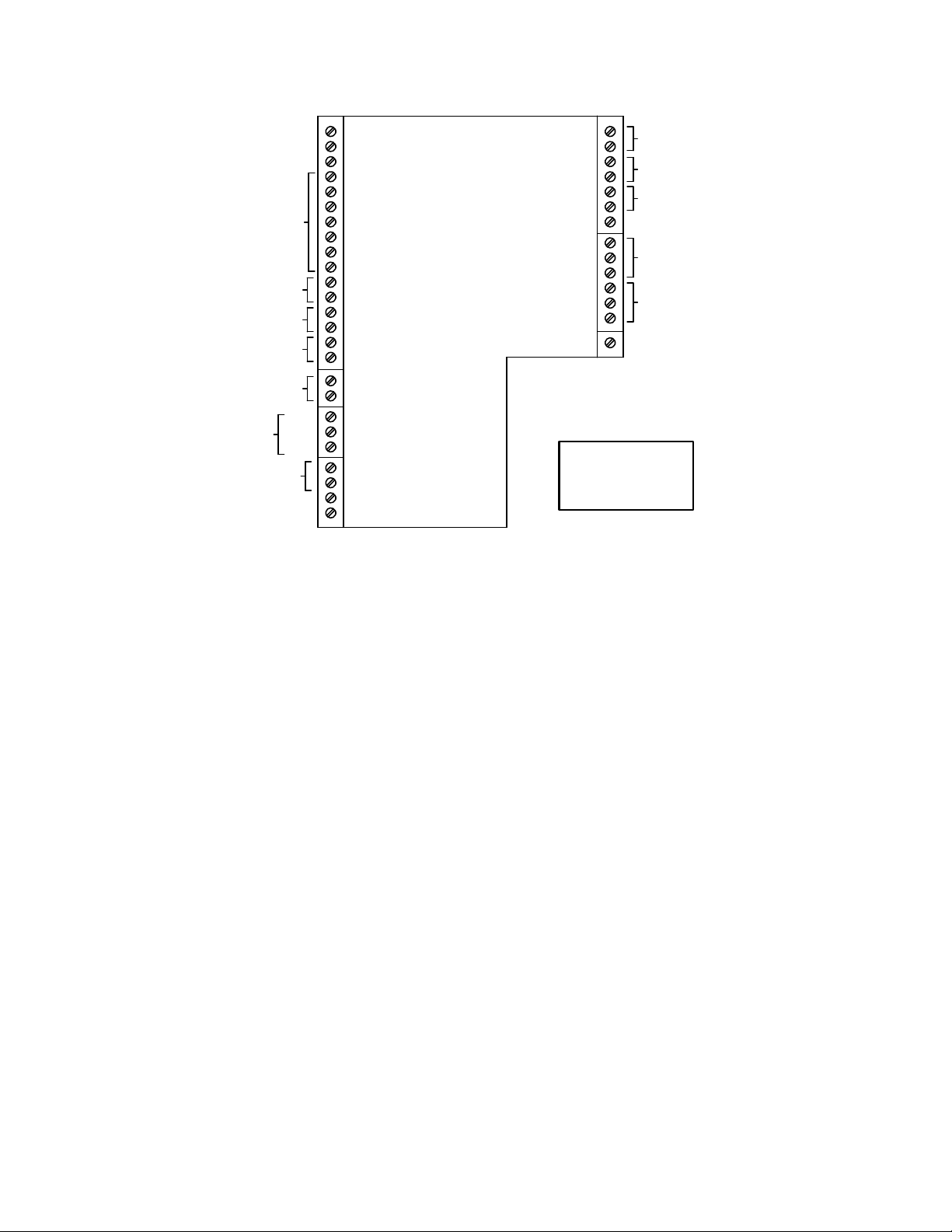
INSTALLATION
OUTDOOR SENSOR IN
SENSOR COMMON
(AIR) AUX SENSOR IN
B.M.S. (PWM) IN
NOT USED
ANALOG IN
SHIELD
mA OUT
RS-485
COMM.
NOT USED
0 – 10V
AGND
+
+
-
+
+
G
-
Figure 2-10. I/O Box Terminal Strip
REMOTE INTL'K IN
EXHAUST SWITCH IN
DELAYED INTL'K IN
NOT USED
NC
COM
NO
NC
COM
NO
NOT USED
RELAY CONTACTS:
120 VAC, 30 VDC
5 AMPS RESISTIVE
DANGER
120 VAC USED
IN THIS BOX
FAULT RELAY
120 VAC, 5A, RES
AUX RELAY
120 VAC, 5A, RES
2.9.3 Boiler Management System Mode NOTE
BMS Model 168 can utilize either pulse
width modulation (PWM) or RS485
Modbus signaling to the Boiler. BMS II
Model 5R5-384 can utilize only RS485
signaling to the Boiler.
When using an AERCO Boiler Management
System (BMS), the field wiring is connected
between the BMS Panel and each Boiler’s I/O
Box terminal strip (Figure 2-10). Twisted
shielded pair wire f rom 18 to 22 AWG must be
utilized for the connections. The BMS Mode can
utilize either pulse width modulation (PWM)
signaling, or RS485 Modbu s s ignaling. F or PWM
signaling, connections are made from the
AERCO Boiler Management System to the
B.M.S. (PWM) IN terminals on the I/O Box
terminal strip. For RS485 Modus signaling,
connections are made from the BMS to the
RS485 COMM term inals on the I/O Box ter minal
strip. Polarity m ust be maintain ed and the shie ld
must be connected only at the AERCO BMS.
The boiler end of the shield must be left floating.
For additional instructions, refer to Chapter 5,
paragraph 5.6 in this manual. Also, refer to
GF-108M (BMS Mode l 1 68 ) and G F- 1 24 ( BMS II
Model 5R5-384), BMS -Operations Guides.
2.9.4 Remote Setpoint and Direct Drive Modes
The boiler can accept several types of signal
formats from an Energy Management System
(EMS), Building Automation System (BAS) or
other source, to control either the setpoint
(Remote Setpoint Mode) or valve position
(Direct Drive Mode) of the Boi ler . T hes e f ormats
are:
• 4 to 20 mA/1 to 5 VDC
• 0 to 20 mA/0 to 5 VDC
• PWM – (Pulse W idth Modulated signal. See
para. 2.10.4)
• Network (RS485 Modbus. See para. 2.10.7)
While it is possible to c ontrol a boiler or boilers
using one of the previously described m odes of
operation, it ma y not be the method best suited
for the application. Prior to selecting one of
these modes of operation, it is recommended
that you consult with your local AERCO
representative or the factory for the mode of
operation that will work best with your
application. For m ore information on wir ing the
4 to 20 mA / 1 to 5VDC or the 0 to 20 mA / 0 to 5
VDC, see paragraph 2.9.3.
2-7
Page 18

INSTALLATION
2.9.5 Combination Mode NOTE
Only BMS Model 168 can be utilized for
the Combination Mode, not the BMS II
(Model 5R5-384).
With a Combination Mode unit, field wiring is
between the unit’s I/O Box wiring terminals, the
CCP (Combination Contr ol Panel), an d the BMS
(Boiler Management System). The wiring must
be accomplished using twisted-shielded pair
wire from 18 to 22 AWG. Polarity must be
maintained. For further instructions and wiring
diagrams, refer to the GF-108M Boiler
Management System Operations Guide and the
CCP-1 data sheet.
2.10 I/O BOX CONNECTIONS
The types of input and output signals and
devices to be connecte d to the I/O Box terminals
shown in Figure 2-10 are described in the
following paragraphs.
CAUTION
DO NOT make any connections to the
I/O Box terminals labeled “NOT
USED”. Attempting to do so may
cause equipment damage.
2.10.1 OUTDOOR SENSOR IN
An outdoor air temperature sensor (AERCO Part
No. 122790) will be required primarily for the
Indoor/Outdoor reset m ode of operation. It can
also be used with anoth er m ode if it is desired to
use the outdoor sensor enable/disable feature.
This feature allows the boiler to be enabled or
disabled based on the outdoor air temperature.
The factory default for the outdoor sensor is
DISABLED. To enable the sensor and/or select
an enable/disable o utdoor temperature, see the
Configuration menu in Chapter 3.
The outdoor sensor m ay be wired up t o 200 feet
from the boiler. It is connected to the OU T D OO R
SENSOR IN and SENSOR COMMON terminals
in the I/O Box (see Figures 2- 9 and 2-10). Wire
the sensor using a twisted shielded pair wire
from 18 to 22 AWG. There is no polarity to
observe when terminating these wires. The
shield is to be connected only to the terminals
labeled SHIELD in the I/O Box. The sensor end
of the shield must be left free and ungrounded.
When mounting the sensor, it must be located
on the North side of the building where an
average outside air temperature is expected.
The sensor must be shield ed f r om dir ect sunli ght
as well as impingement by the elements. If a
shield is used, it must allow for free air
circulation.
2.10.2 AIR SENSOR IN
The AIR SENSOR IN is connected to the AUX
SENSOR IN and SENSOR COMMON terminals
on the I/O board. The AIR SENSOR measures
the temperature of the air input to the Air/Fuel
Valve. This temperature reading is one of the
components used to calculate the rotational
speed of the blower used in the combustion
Calibration process (Chapter 4).
The AUX SENSOR IN terminals can b e used to
add an additional temperature sensor for
monitoring purposes. This input is always
enabled and is a view-only input that can be
seen in the Operating Menu. The sensor must
be wired to the AUX S ENSOR IN and SENSOR
COMMON terminals and must be similar to
AERCO BALCO wire se nsor Part No. 124 49. A
resistance chart for this sensor is provided in
Appendix C.
2.10.3 ANALOG IN
The ANALOG IN + and – terminals are used
when an external signal is used to drive the
air/fuel valve position (Direct Drive Mode) or
change the setpoint (R emote Setpoint Mode) of
the Boiler.
Either a 4 to 20 mA /1 to 5 VDC or a 0 to 20 mA/
0 to 5 VDC signal may be used to vary the
setpoint or valve position. The factory default
setting is for 4 to 20 mA / 1 to 5 VDC, however
this may be changed to 0 t o 20 mA / 0 to 5 VDC
using the Configuration Menu described in
Chapter 3. If voltage rather than current is
selected as the dr ive signal, a DIP switch mus t
be set on the PMC Board located inside the
Control Box. Contact the AERCO factory for
information on setting DIP switches.
All of the supplied signals must be floating
(ungrounded) signals . Connectio ns bet ween the
signal source and the Boiler’s I/O Box must be
made using twiste d shiel ded pa ir wire fr om 18 to
22 AWG, such as Belden 9841 (see Figure
2-10). Polarity mu st be maintained. The shi eld
must be connected only at the source end and
must be left floating (not connected) at the
Boiler’s I/O Box.
Regardless of whether volt age or curr ent is used
for the drive signal, the y are linearly mapped to
a 40°F to 240°F s etpoint or a 0% to 100% v alve
position. No scaling for these signals is provided
2-8
Page 19

INSTALLATION
2.10.4 B.M.S. (PWM) IN NOTE
Only BMS Model 168 can utilize Pulse
Width Modulation (PW M), not the BMS II
(Model 5R5-384).
These terminals are used to connect the
AERCO Boiler Management System (BMS) to
the unit. The BMS utilizes a 12 millisecond,
ON/OFF duty cycle. This duty cycle is Pulse
Width Modulated (PWM) to control the air/fuel
valve position. A 0% (open) air/fuel valve
position = a 5% ON pulse and a 100% open
valve position = a 95% ON pulse.
2.10.5 SHIELD
The SHIELD terminals are us ed to terminate any
shields used on sensor wires connected to the
unit. Only shields m ust be connected to these
terminals.
IMPORTANT
DO NOT USE the mA OUT output to
remotely monitor Set point, O utlet Tem p or
Fire Rate Out.
2.10.6 mA OUT
These terminals provide a 4 to 20 mA output to
a VFD (if so equipped) to control the rotationa l
speed of the blower. T his function is enable d in
the Configuration Menu (Chapter 3, Table 3-4).
2.10.7 0 – 10V OUT
These terminals provide a 0 to 10V output to
control the rotational speed of the blower. This
function is enabled in the Configuration Menu
(Chapter 3, Table 3-4).
2.10.8 RS-485 COMM
These terminals are used for RS-485 MODBUS
serial communication between the unit and an
external “Master” suc h as a Boiler Management
System (BMS), Energy Management System
(EMS), Building Automation System (BAS) or
other suitable device.
2.10.9 EXHAUST SWITCH IN
These terminals permit an external exhaust
switch to be connected to the exhaust manifold
of the boiler. The exhaust switch should be a
normally open t ype s witc h (such as AERCO Par t
No. 123463) that closes (trips) at 500°F.
2.10.10 INTERLOCKS
The unit offers two interlock circuits for
interfacing with Energy Management Systems
and auxiliary equipment such as pumps or
louvers. These interlock s are called the Rem ote
Interlock and Delayed Interlock (Figure 2-10).
The wiring terminals for these interlocks are
located inside the I/O Box on the unit front
panel. The I/O Box cover contains a wiring
diagram which s hows th e ter m inal str ip locat ions
for these interlocks (REMOTE INTL’K IN and
DELAYED INTL’K IN). Both interlocks,
described below, are fac tory wired in the closed
position.
NOTE
Both the Remote Interlock and Delayed
Interlock MUST be in the closed position
to allow the unit to fire.
2.10.10.1
The remote interlock circuit is provided to
remotely start (enable) and stop (disable) the
Boiler, if desired. T he circuit is labeled REMO TE
INTL’K IN and is located inside the I/O Box on
the front panel. The circuit is 24 VAC and is
factory pre-wired in the closed (jumpered)
position.
2.10.10.2
The delayed interlock is typically used in
conjunction with the aux iliary relay described in
paragraph 2.10. This interlock circuit is located
in the purge section of the start string. It can be
connected to the proving device (end switch,
flow switch etc.) of an auxiliary piece of
equipment started b y the Boiler’s a uxiliary rela y.
The delayed interlock must be closed for the
boiler to fire.
If the delayed interl ock is connec ted t o a pr oving
device that requir es tim e to clos e (mak e), a tim e
delay (Aux Start On Dly) that holds the start
sequence of the boiler lon g enoug h for a proving
switch to make can be progr amm ed. Should the
proving switch not prove within the programm ed
time frame, the boiler will shut down. The Aux
Start On Dly can be progr ammed from 0 to 120
seconds. This option is locate in the
Configuration Menu (Chapter 3, Table 3-4).
REMOTE INTERLOCK IN
DELAYED INTERLOCK IN
2-9
Page 20

INSTALLATION
2.10.11 FAULT RELAY
The fault relay is a single pole double throw
(SPDT) relay having a normally open and
normally closed set of relay contacts that are
rated for 5 amps at 12 0 VAC and 5 amps at 30
VDC. The relay energizes when any fault
condition occurs and remains energized until the
fault is cleared and the CLEAR button is
depressed. The fault relay connections are
shown in Figure 2-10.
2.11 AUXILI ARY RELAY CONTACTS
Each Boiler is equipped with a single pole
double throw (SPDT) relay that is energized
when there is a demand for heat and deenergized after the dem and for heat is satisf ied.
The relay is prov ided for the control of auxiliary
equipment, such as pumps and louvers, or can
be used as a Boiler status indictor (firing or n ot
firing). Its contacts are r ated for 120 VAC @ 5
amps. Refer to Figure 2- 10 to locate the AUX
RELAY terminals for wiring connections.
2.12 FLUE GAS VENT INSTALLATION
The minimum allowable vent diameter for a
single Benchmark 2.0LN Boiler is 8 inches.
The AERCO Benchmark Venting and
Combustion Air Guide, GF-2050, must be
consulted before any flue gas vent or inlet air
venting is designed or installed. U/L listed,
positive pressure, watertight vent materials as
specified in AERCO’s GF-2050, must be used
for safety and code com pliance. S ince the u nit is
capable of dischar ging low temperature ex haust
gases, horizontal sections of the flue vent
system must be pitched back to the unit a
minimum of 1/4 inch per foot to avoid
condensate pooling and allow for proper
drainage.
The combined pressure drop of vent and
combustion air systems must not exceed 140
equivalent feet of 8 inc h ducting. Fittings as we ll
as pipe lengths must be calculate d as part of the
equivalent length.
For a natural draf t installation the draf t must not
exceed ±0.25 inch W .C. These factors must be
planned into the vent installation. If the
maximum allowabl e equivalent lengt hs of piping
are exceeded, the unit will not operate properly
or reliably.
2.13 COMBUSTIO N AIR
The AERCO Benchmark Venting and
Combustion Air Guide, GF-2050 MUST be
consulted before any flue or com bustion supply
air venting is designed or implemented.
Combustion air supp ly is a direct r equirem ent of
ANSI 223.1, NFPA-54, and local codes. These
codes should be consulted before a permanent
design is determined.
The combustion air must be free of chlorine,
halogenated hydrocarbons, or other chemicals
that can become ha zardous when used in gasfired equipment. Common sources of these
compounds are swimming pools, degreasing
compounds, plastic proc essing and refrigerants.
Whenever the env ironment c ontains thes e t ypes
of chemicals, combustion air must be supplied
from a clean area outdoors for the protection
and longevity of the equipment.
The AERCO Benchmark 2.0LN Boiler is UL
listed for 100% sealed combustion. It can also
be installed us ing room air, provid ed there is an
adequate supply. (See para. 2.13.3 for more
information concerning sealed combustion air).
If the sealed com bustion air option is not be ing
used, an inlet screen will be attached at the air
inlet on the top of the unit
The more common methods of supplying
combustion air are outlined below. For more
information concerning combustion air, refer to
the AERCO Benchmark Venting and Combustion Air Guide, GF-2050.
2.13.1 Combustion Air From Outside the Building
Air supplied from outside the building must be
provided through two perm anent openings. Each
opening must have a free area of not less than
one square inch for each 4000 BTU/H boiler
input. The free area must take into account
restrictions such as louvers and bird screens.
2.13.2 Combustion Air From Inside the Building
When combustion air is provided f rom within the
building, it must be supplied through two
permanent openings in an interior wall. Each
opening must have a free area of not less than
one square inch per 1000 BTU/H of total boiler
input. The free area must take into ac count any
restrictions such as louvers.
2-10
Page 21

INSTALLATION
2.13.3 Sealed Combustion
The AERCO Benchmark 2.0LN Boiler is UL
listed for 100%-sealed combustion. For sealed
combustion installations, the screen on the air
inlet duct of the unit m ust be removed. T he inlet
air ductwork must then be attached directly to
the unit’s air inlet.
In a sealed combustion air application, the
combustion air ducting pre ssure losses must be
taken into account when calculating the total
maximum allowable venting run. See the
AERCO Benchmark Venting and Combustion
Air Guide, GF-20 50. When using the bo iler in a
sealed combustion air configuration, each unit
must have a minimum 8 inch diameter
connection at the unit.
2.13.4 Temporary Combustion Air
Filtering During Construction
When the AERCO Benchmark 2.0LN Boiler is
used to provide heat tem porarily during on going
building constructio n, accumulated drywall dust,
sawdust and similar par ticles can accumulate in
the unit’s combustion air intake filter and block
combustion air flow. In thes e situations, AERCO
recommends that a d isposable air intak e f ilter b e
installed, temporarily, above the boiler
combustion air inlet.
AERCO recommends that the temporary air filter
be cut from a McMaster- Carr part no. 2122K3 15
Polyester Air Filter Roll Tackfield, ½” thick, 16”
wide, or equivalent. Cov er the unit air inlet with
the blue side of the filter material fac ing outward
to hold the dust on the outside surface.
Maximize the surf ace area of the filter cover ing
the 8" diameter openin g by creating a dom e out
of the filter material.
Cover the flared duct op ening with the b lue side
facing outward. During construction check the
filter for dust accumulation and replace it when
the accumulation becomes noticeable.
2-11
Page 22

Page 23
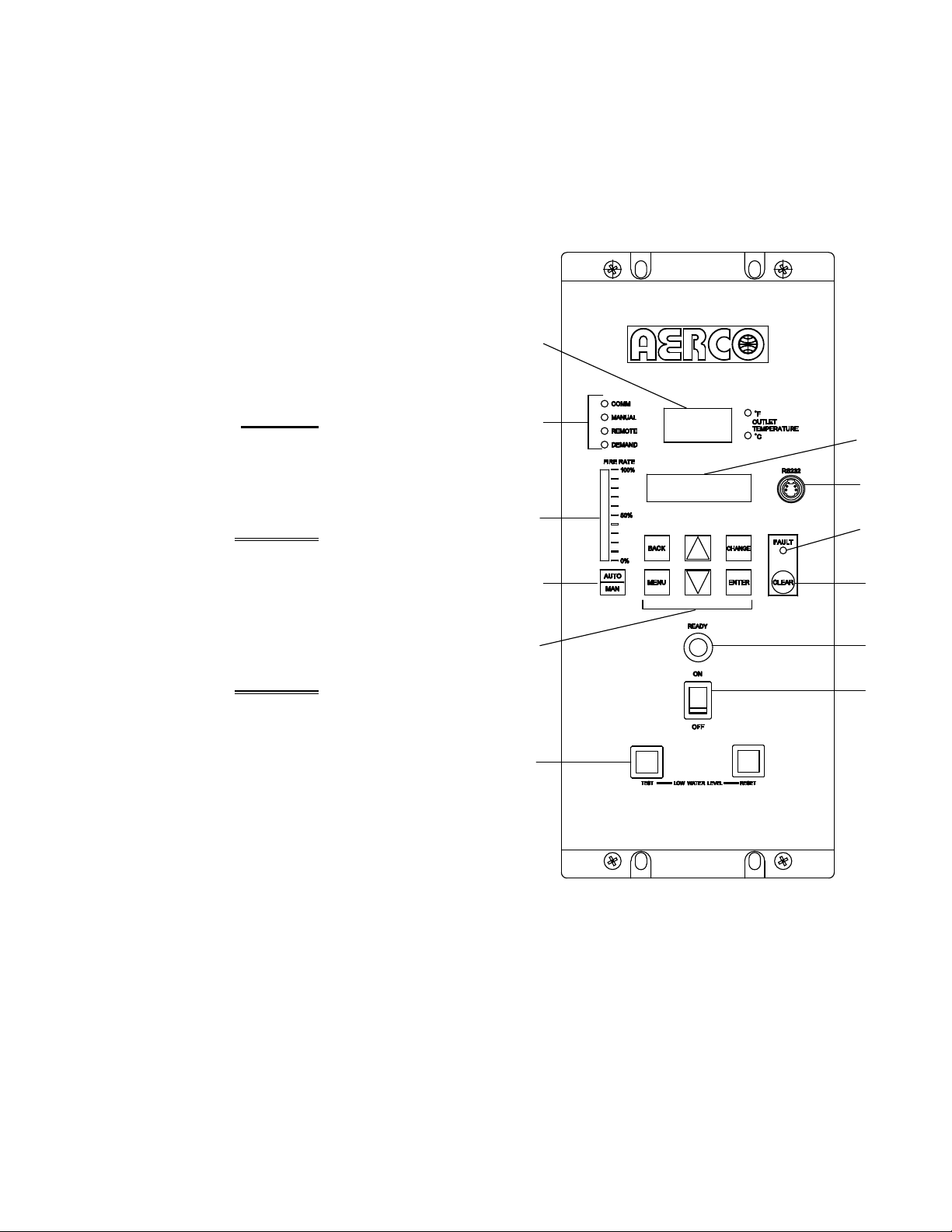
CONTROL PANEL OPERATING PROCEDURES
CHAPTER 3 CONTROL PANEL OPERATING PROCEDURES
3.1 INTRODUCTION
The information in this Chapter provides a guide
to the operation of the Benchmark 2.0LN Boiler
using the Control Panel mounted on the front of
the unit. It is imperative that the initial startup of
this unit be performed by factory trained
personnel. Operation prior to initial startup by
factory trained personnel will void the equipment
warranty. In addition, the following WARNINGS
and CAUTIONS must be observed at all times.
CAUTION
All of the installation procedures in
Chapter 2 must be completed before
attempting to start the unit.
WARNING
ELECTRICAL VOLTAGES IN THIS
SYSTEM MAY INCLUDE 460, 208
AND 24 VOLTS AC. IT MUST BE
SERVICED ONLY BY FACTORY
CERTIFIED SERVICE TECHNICIANS
2
1
3
4
12
11
10
5
6
7
WARNING
DO NOT ATTEMPT TO DRY FIRE
THE BOILER. STARTING THE UNIT
WITHOUT A FULL WATER LEVEL
CAN SERIOUSLY DAMAGE THE
UNIT AND MAY RESULT IN INJURY
TO PERSONNEL OR PROPERTY
DAMAGE. THIS SITUATION WILL
VOID ANY WARRANTY.
3.2 CONTROL PANEL DESCRIPTION
The Benchmark 2.0LN Control Panel shown in
Figure 3-1 contains all of the controls, indicators
and displays necessary to operate, adjust and
troubleshoot the Benchmark 2.0LN Boiler.
These operating controls, indicators and
displays are listed and described in Table 3-1.
Additional information on these items are
provided in the individual operating procedures
provided in this Chapter.
8
9
Figure 3-1.
Control Panel Front View
3-1
Page 24
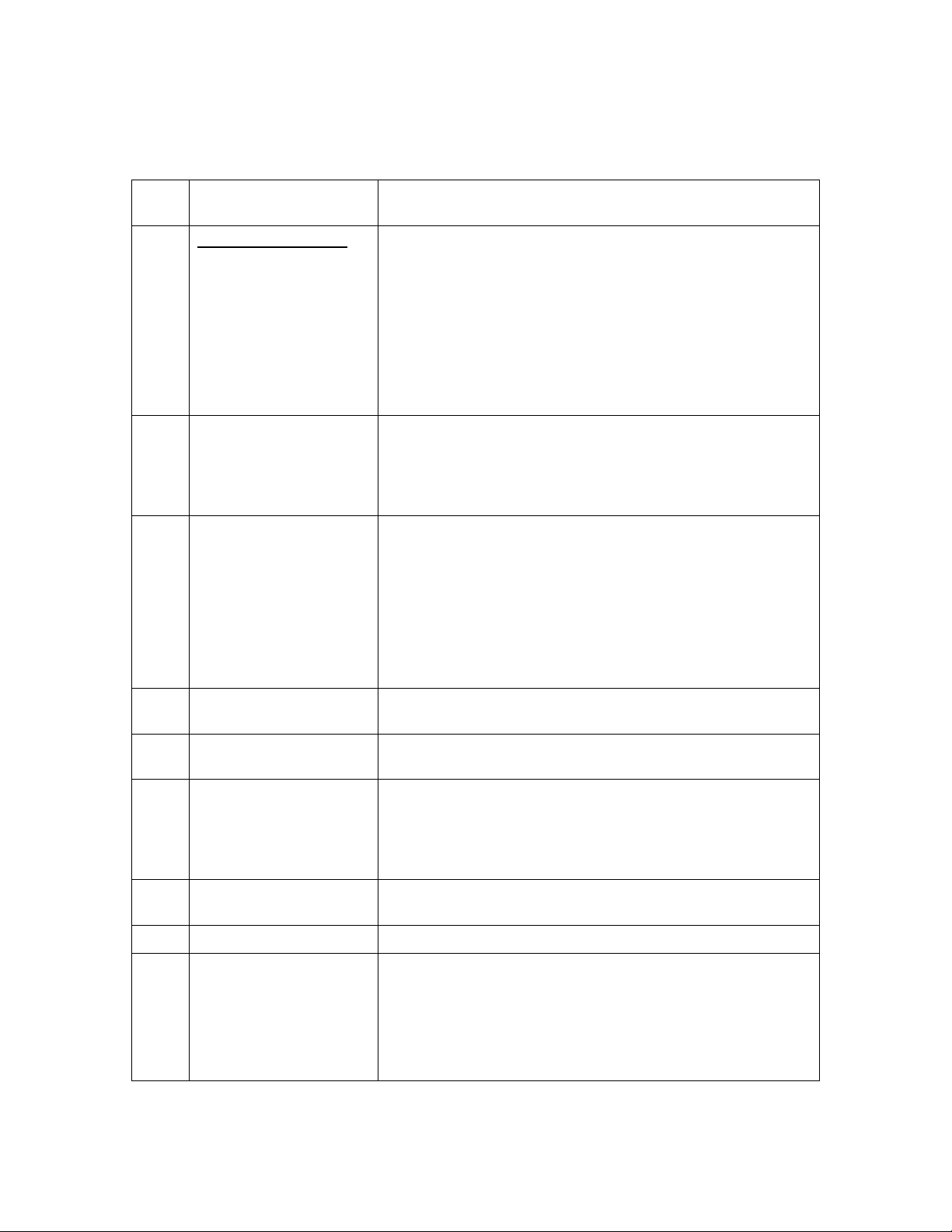
CONTROL PANEL OPERATING PROCEDURES
Table 3-1 Operating Controls, Indicators and Displays
ITEM
NO.
CONTROL, INDICATOR
OR DISPLAY
1 LED Status Indicators Four Status LEDs indicate the current operating status as
follows:
COMM
MANUAL
REMOTE
DEMAND
OUTLET
2
TEMPERATURE
Display
3 VFD Display Vacuum Fluorescent Display (VFD) consists of 2 lines each
Lights when RS-232 communication is occurring
Lights when the unit is being controlled using the front panel
keypad.
Lights when the unit is being controlled by an external signal
from an Energy Management System
Lights when there is a demand for heat.
3–Digit, 7–Segment LED display continuously displays the
outlet water temperature. The °F or °C LED next to the
display lights to indicate whether the displayed temperature is
in degrees Fahrenheit or degrees Celsius. The °F or °C blinks
when operating in the Deadband Mode.
capable of displaying up to 16 alphanumeric characters. The
information displayed includes:
Startup Messages
Fault Messages
FUNCTION
Operating Status Messages
Menu Selection
RS-232 Port
4
FAULT Indicator Red FAULT LED indicator lights when a boiler alarm
5
CLEAR Key Turns off the FAULT indicator and clears the alarm message
6
READY Indicator
7
ON/OFF Switch
8
LOW WATER LEVEL
9
TEST/RESET Switches
Port permits a Laptop Computer or External Modem to be
connected to the unit’s Control Panel.
condition occurs. An alarm message will appear in the VFD.
if the alarm is no longer valid. Lockout type alarms will be
latched and cannot be cleared by simply pressing this key.
Troubleshooting may be required to clear these types of
alarms.
Lights ON/OFF switch is set to ON and all Pre-Purge
conditions have been satisfied.
Enables and disables boiler operation.
Allows operator to test operation of the water level monitor.
Pressing TEST opens the water level probe circuit and
simulates a Low Water Level alarm.
Pressing RESET resets the water level monitor circuit.
Pressing the CLEAR key (item 6) resets the display.
3-2
Page 25
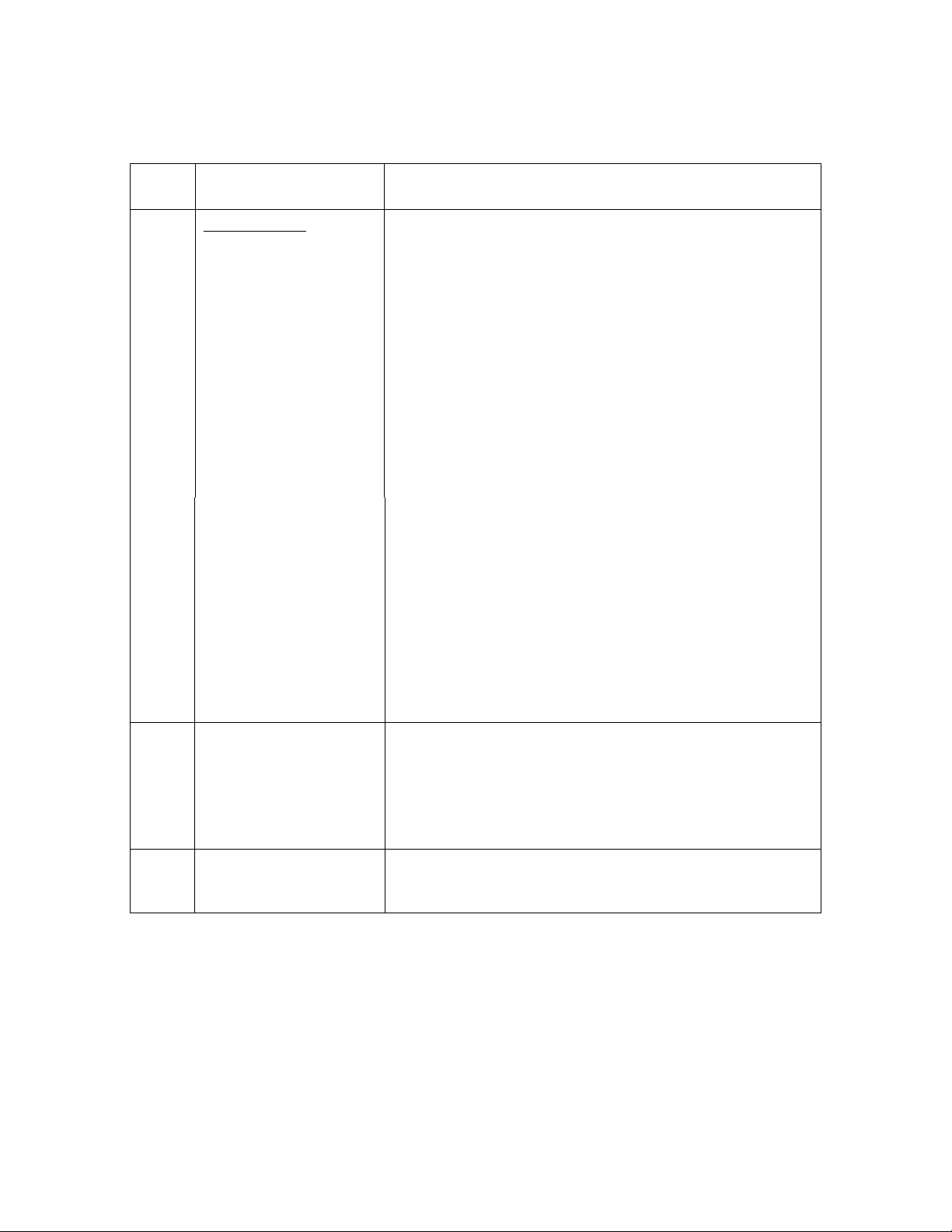
CONTROL PANEL OPERATING PROCEDURES
Table 3-1 Operating Controls, Indicators and Displays – Continued
ITEM
NO.
10 MENU Keypad Consists of 6 keys which provide the following functions for
CONTROL, INDICATOR
OR DISPLAY
the Control Panel Menus:
MENU
BACK
▲ (UP) Arrow When in one of the main menu categories (Figure 3-2),
▼ (DOWN) Arrow When in one of the main menu categories (Figure 3-2),
CHANGE
Steps through the main menu categories shown in Figure 3-
2. The Menu categories wrap around in the order shown.
Allows you to go back to the previous menu level without
changing any information. Continuously pressing this key
will bring you back to the default status display in the VFD.
Also, this key allows you to go back to the top of a main
menu category.
pressing the ▲ arrow key will select the displayed menu
category. If the CHANGE key was pressed and the menu
item is flashing, pressing the ▲ arrow key will increment the
selected setting.
pressing this key will select the displayed menu category. If
the CHANGE key was pressed and the menu item is
flashing, pressing the ▼ arrow key will decrement the
selected setting.
Permits a setting to be changed (edited). When the
CHANGE key is pressed, the displayed menu item will begin
to flash. Pressing the ▲ or ▼ arrow key when the item is
flashing will increment or decrement the displayed setting.
FUNCTION
11
12
ENTER
AUTO/MAN Switch
VALVE POSITION
Bargraph
Saves the modified menu settings in memory. The display
will stop flashing.
This switch toggles the boiler between the Automatic and
Manual modes of operation. When in the Manual (MAN)
mode, the front panel controls are enabled and the
MANUAL status LED lights.
When in the Automatic (AUTO) mode, the MANUAL status
LED will be off and the front panel controls disabled.
20 segment red LED bargraph continuously shows the
Air/Fuel Valve position in 5% increments from 0 to 100%
open.
3-3
Page 26
CONTROL PANEL OPERATING PROCEDURES
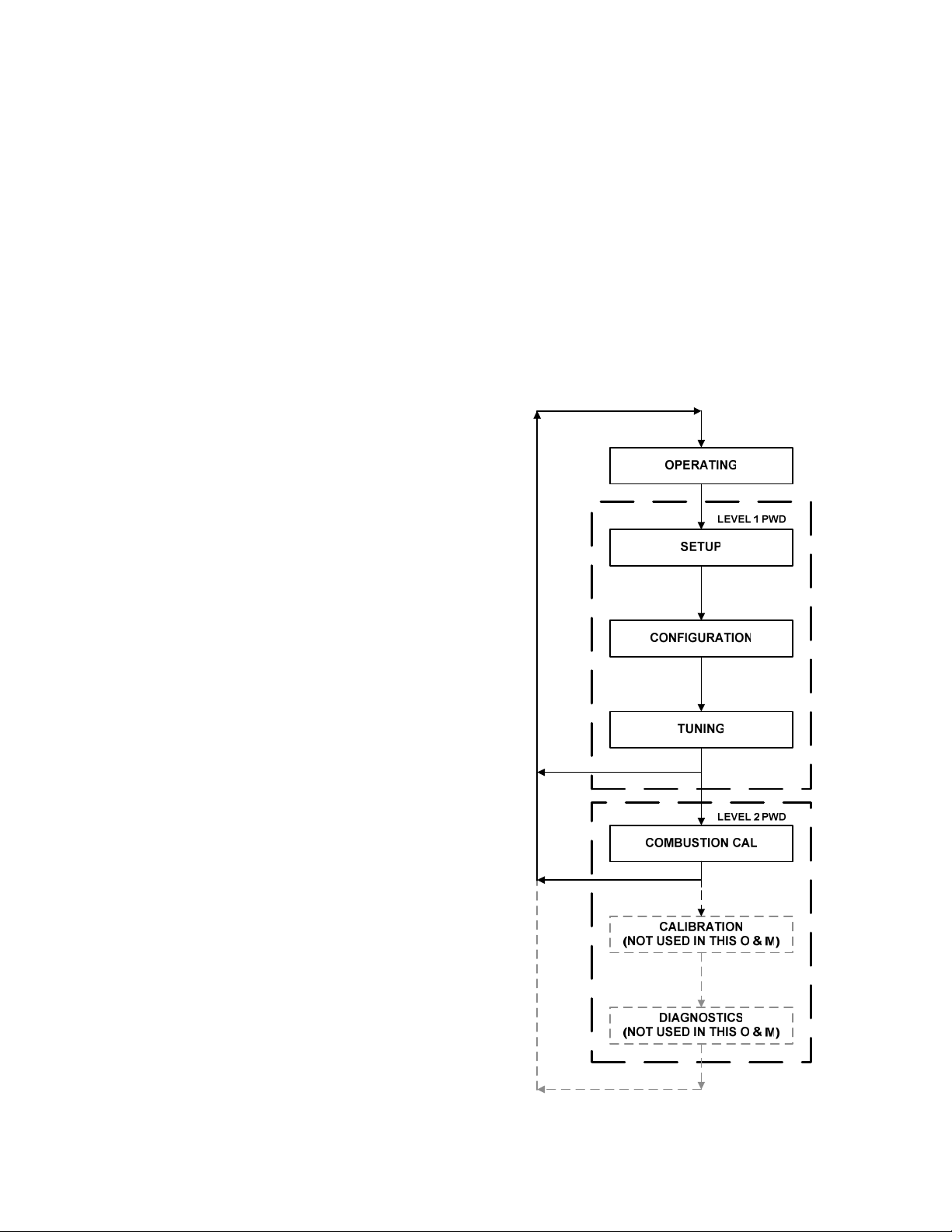
3.3 CONTROL PANEL MENUS
The Control Panel incorporates an extensive
menu structure which permits the operator to set
up, and configure the unit. The menu structure
consists of five major menu categories which are
applicable to this manual. These categories are
shown in Figure 3-2. Each of the menus shown,
contain options which permit operating
parameters to be viewed or changed. The
menus are protected by a password levels to
prevent unauthorized use.
Prior to entering the correct password, the
options contained in the Operation, Setup,
Configuration and Tuning Menu categories can
be viewed. However, with the exception of
Internal Setpoint Temperature (Configuration
Menu), none of the viewable menu options can
be changed.
Once the valid level 1 password (159) is
entered, the options listed in the Setup.
Configuration and Tuning Menus can be viewed
and changed, if desired. The Combustion Cal
Menu is protected by the level 2 password which
is used in Chapter 4 to perform combustion
calibration prior to service use.
available menu options in the Top-Down
sequence. Pressing the ▼ arrow key will
display the options in the Bottom-Up
sequence. The menu options will wraparound after the first or last available option
is reached.
6. To change the value or setting of a
displayed menu option, press the CHANGE
key. The displayed option will begin to flash.
Press the ▲ or ▼ arrow key to scroll
through the available menu option choices
for the option to be changed. The menu
option choices do not wrap around.
7. To select and store a changed menu item,
press the ENTER key.
3.3.1 Menu Processing Procedure
Accessing and initiating each menu and option
is accomplished using the Menu Keys shown in
Figure 3-1. Therefore, it is imperative that you
be thoroughly familiar with the following basic
steps before attempting to perform specific
menu procedures.
1. The Control Panel will normally be in the
Operating Menu and the VFD will display the
current unit status. Pressing the ▲ or ▼
arrow key will display the other available
data items in the Operating Menu.
2. Press the MENU key. The display will show
the Setup Menu, which is the next menu
category shown in Figure 3-2. This menu
contains the Password option which must be
entered if other menu options will be
changed.
3. Continue pressing the MENU key until the
desired menu is displayed.
4. With the desired menu displayed, press the
▲ or ▼ arrow key. The first option in the
selected menu will be displayed.
5. Continue to press the ▲ or ▼ arrow key
until the desired menu option is displayed.
Pressing the ▲ arrow key will display the
3-4
Figure 3-2. Menu Structure
Page 27
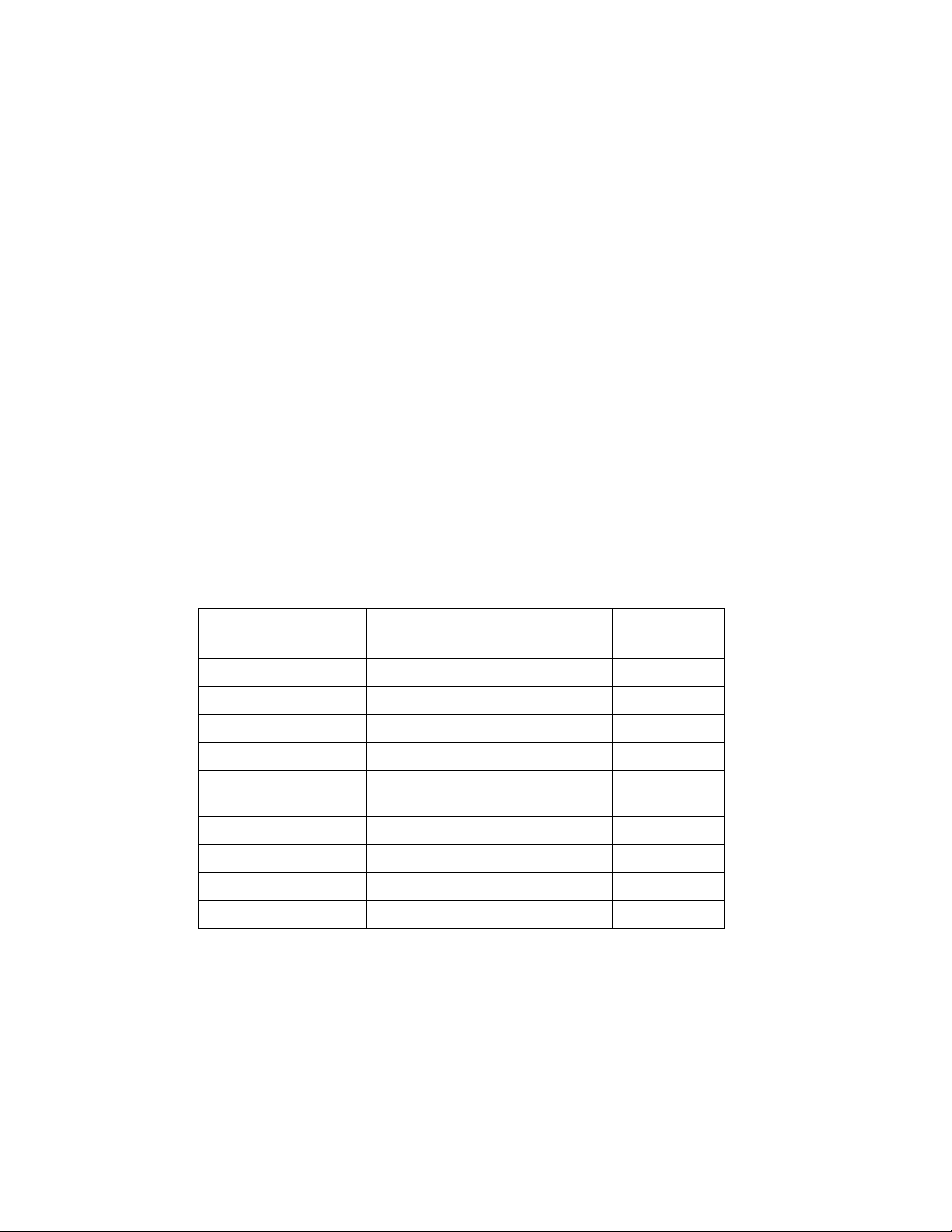
CONTROL PANEL OPERATING PROCEDURES
NOTE
The following paragraphs provide brief
descriptions of the options contained in each
menu. Refer to Appendix A for detailed
descriptions of each menu option. Refer to
Appendix B for listings and descriptions of
displayed startup, status and error
messages.
3.4 OPERATING MENU
The Operating Menu displays a number of key
operating parameters for the unit as listed in
Table 3-2. This menu is “Read-Only” and does
not allow personnel to change or adjust any
displayed items. Since this menu is “Read-Only”,
it can be viewed at any time without entering a
password. Pressing the ▲ arrow key to display
the menu items in the order listed (Top-Down).
Pressing the ▼ arrow key will display the menu
items in reverse order (Bottom-Up).
3.5 SETUP MENU
The Setup Menu (Table 3-3) permits the
operator to enter the unit password (159) which
is required to change the menu options. To
prevent unauthorized use, the password will
time-out after 1 hour. Therefore, the correct
password must be reentered when required. In
addition to permitting password entries, the
Setup Menu is also used to enter date and time,
units of temperature measurements and entries
required for external communication and control
of the unit via the RS-232 port. A view-only
software version display is also provided to
indicate the current Control Box software
version.
NOTE
The Outdoor Temp display item shown with
an asterisk in Table 3-2 will not be displayed
unless the Outdoor Sensor function has
been enabled in the Configuration Menu
(Table 3-4).
Table 3-2. Operating Menu
Available Choices or Limits
Menu Item Display Minimum Maximum Default
Status Message
Active Setpoint 40°F 240°F
AIR Temp -70°F 245°F
Outdoor Temp* -70°F 130°F
Valve Position In 0% 100% Valve
Position
Flame Strength 0% 100%
Run Cycles 0 999,999,999
Run Hours 0 999,999,999
Fault Log 0 19 0
3-5
Page 28
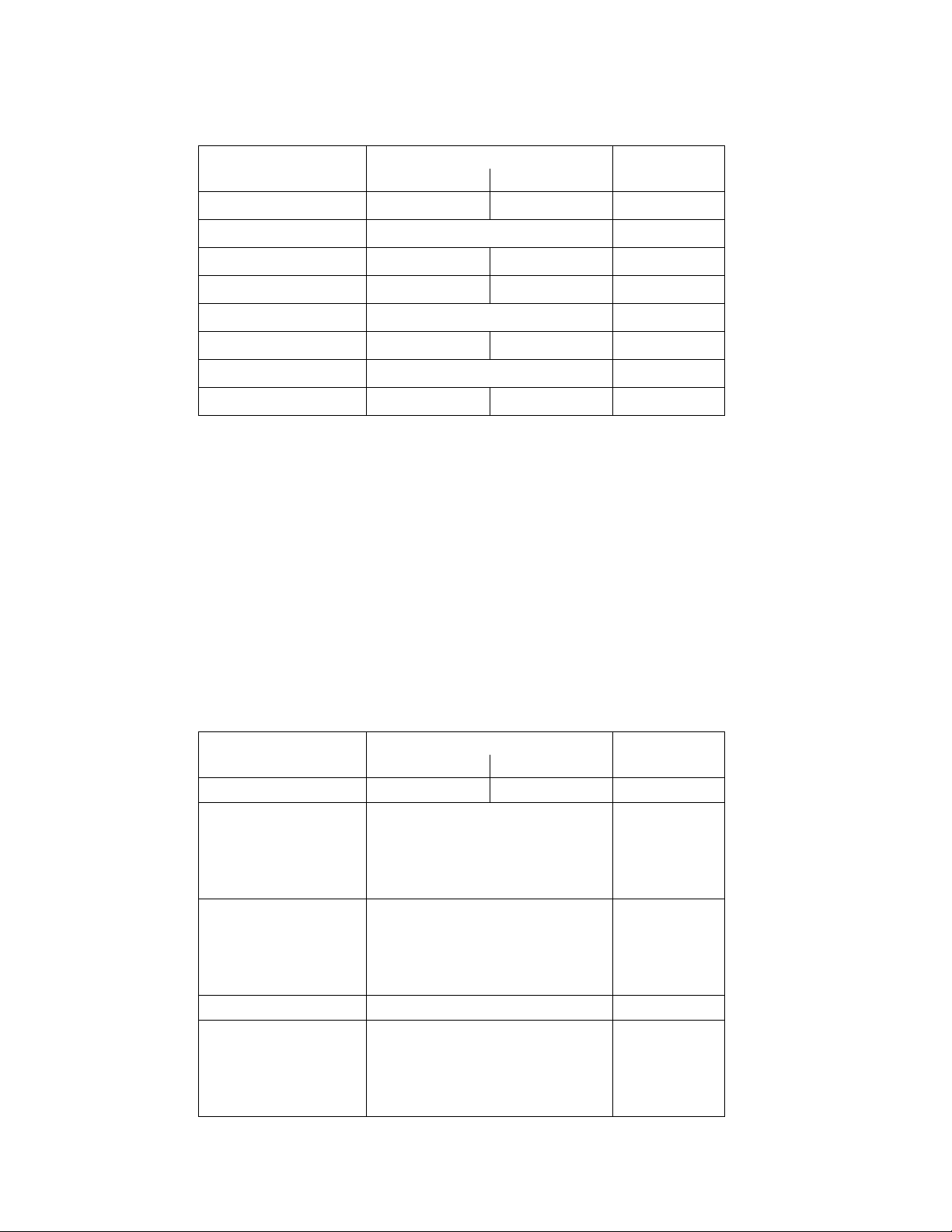
CONTROL PANEL OPERATING PROCEDURES
Table 3-3. Setup Menu
Available Choices or Limits
Menu Item Display Minimum Maximum Default
Passsword 0 9999 0
Language English English
Time 12:00 am 11:59 pm
Date 01/01/00 12/31/99
Unit of Temp Fahrenheit or Celsius Fahrenheit
Comm Address 0 127 0
Baud Rate 2400, 4800, 9600, 19.2K 9600
Software Ver 0.00 Ver 9.99
3.6 CONFIGURATION M ENU
The Configuration Menu shown in Table 3-4
permits adjustment of the Internal Setpoint
(Setpt) temperature regardless of whether the
valid password has been entered. Setpt is
required for operation in the Constant Setpoint
mode. The remaining options in this menu
require the valid password to be entered, prior to
changing existing entries. This menu contains a
number of other configuration settings which
may or may not be displayed, depending on the
current operating mode setting.
Table 3-4. Configuration Menu
Available Choices or Limits
Menu Item Display Minimum Maximum Default
Internal Setpt Lo Temp Limit Hi Temp Limit 130°F
Unit Type KC Boiler, KC Boiler LN,
BMK Boiler, BMK Boiler LN,
BMK Boiler Dual, KC Water
Heater, KC Water Heater LN,
Water Heater 2010
Unit Size 0.5 MBTU, 1.0 MBTU
1.5 MBTU, 2.0 MBTU
3.0 MBTU, 3.5 MBTU
4.0 MBTU, 5.0 MBTU
Fuel Type Natural Gas, Propane Natural Gas
Boiler Mode Constant Setpoint,
Remote Setpoint,
Combination
Outdoor Reset
NOTE
The Configuration Menu settings shown in
Table 3-4 are Factory-Set in accordance
with the requirements specified for each
individual order. Therefore, under normal
operating conditions, no changes will be
required.
BMK Boiler
LN
2.0 MBTU
6.0 MBTU
Constant
Setpoint
Direct Drive
3-6
Page 29
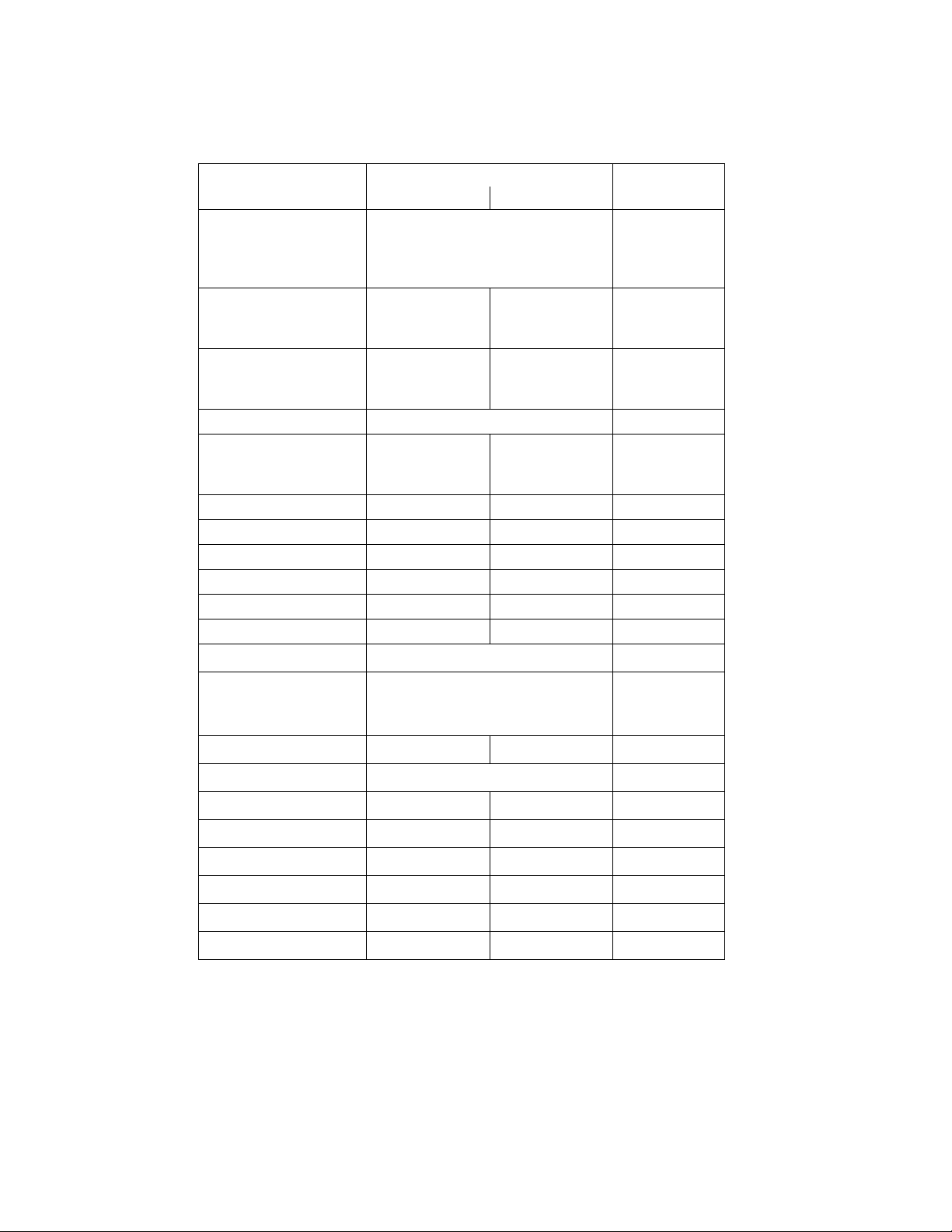
CONTROL PANEL OPERATING PROCEDURES
Table 3-4. Configuration Menu - Continued
Available Choices or Limits
Menu Item Display Minimum Maximum Default
Remote Signal
(If Mode = Remote
Setpoint, Direct Drive
or Combination)
Bldg Ref Temp
(If Mode = Outdoor
Reset)
Reset Ratio
(If Mode = Outdoor
Reset)
Outdoor Sensor Enabled or Disabled Disabled
System Start Tmp
(If Outdoor Sensor =
Enabled)
Setpt Lo Limit 40°F Setpt Hi Limit 60°F
Setpt Hi Limit Setpt Lo Limit 220°F 200°F
Temp Hi Limit 40°F 240°F 210°F
Max Valve Position 40% 100% 100%
Pump Delay Timer 0 min. 30 min. 0 min.
Aux Start On Dly 0 sec. 120 sec. 0 sec.
Failsafe Mode Shutdown or Constant Setpt Shutdown
4 – 20 mA/1 – 5V
0 -20 mA/0 – 5V
PWM Input (BMS)
Network
40°F 230°F 70°F
0.1 9.9 1.2
30°F 100°F 60°F
4 – 20 mA,
1-5V
*Analog Output
(See CAUTION at
end of Table 3-4 )
Low Fire Timer 2 sec. 600 sec. 2 sec.
Setpt Limiting Enabled or Disabled Disabled
Setpt Limit Band 0°F 10°F 5°F
Network Timeout 5 Sec 999 Sec 30 Sec
HI DB Setpt EN 0% 100% 30%
Demand Offsert 0 25 10
Deadband High 0 25 2
Deadband Low 0 25 2
*CAUTION:
DO NOT CHANGE the Analog Output Menu Item from its Default setting
(Valve Position 0-10V).
Off, Setpoint, Outlet Temp,
Valve Position 4-20 mA,
Valve Position 0-10V
*Valve
Position
0-10V
3-7
Page 30

CONTROL PANEL OPERATING PROCEDURES
3.7 TUNING MENU
The Tuning Menu items in Table 3-5 are Factory
set for each individual unit. Do not change
these menu entries unless specifically requested
to do so by Factory-Trained personnel.
3.8 COMBUSTION CAL MENU
The Combustion Cal (Calibration) Menu items in
Table 3-6 (Natural Gas) and Table 3-7
(Propane) are used to vary the speed of the
unit’s blower motor based on air temperature
Table 3-5. Tuning Menu
Available Choices or Limits
Menu Item Display Minimum Maximum Default
Prop Band 1°F 120°F 70°F
Integral Gain 0.00 2.00 1.00
Derivative Time 0.0 min 2.00 min 0.00 min
Reset Defaults? Yes, No, Are You Sure? No
Table 3-6. Combustion Cal Menu – Natural Gas (NEED DATA!)
and air density at prescribed Air/Fuel Valve
positions (% open). This is accomplished by
providing a DC drive voltage to the motor which
adjusts the rotational speed of the blower to
maximize combustion efficiency and ensure the
unit conforms to the Nitrogen Oxide (NOx) and
Carbon Monoxide (CO) emissions specified in
Chapter 4. The valve position (%) and default
drive voltages are listed in Tables 3-6 and 3-7..
Available Choices or Limits
Menu Item Display Minimum Maximum Default
CAL Voltage 20% .25 Vdc 10.0 Vdc 1.00 Vdc
CAL Voltage 30% .25 Vdc 10.0 Vdc 2.30 Vdc
CAL Voltage 45% .25 Vdc 10.0 Vdc 2.9 Vdc
CAL Voltage 60% .25 Vdc 10.0 Vdc 3.60 Vdc
CAL Voltage 80% .25 Vdc 10.0 Vdc 5.30 Vdc
CAL Voltage 100% .25 Vdc 10.0 Vdc 9.10 Vdc
SET Valve Position 0% 100% 0%
Blower Output Monitor Blower Output Voltage .00
Table 3-7. Combustion Cal Menu – Propane (NEED DATA!)
Available Choices or Limits
Menu Item Display Minimum Maximum Default
CAL Voltage 21% .25 Vdc 10.0 Vdc 1.10 Vdc
CAL Voltage 30% .25 Vdc 10.0 Vdc 1.95 Vdc
CAL Voltage 45% .25 Vdc 10.0 Vdc 3.00 Vdc
CAL Voltage 60% .25 Vdc 10.0 Vdc 3.00 Vdc
CAL Voltage 80% .25 Vdc 10.0 Vdc 4.45 Vdc
CAL Voltage 91% .25 Vdc 10.0 Vdc 8.20 Vdc
SET Valve Position 0% 91% 0%
Blower Output Monitor Blower Output Voltage .00
3-8
Page 31

CONTROL PANEL OPERATING PROCEDURES
3.9 START SEQUENCE
When the Control Box ON/OFF switch is set to
the ON position, it checks all pre-purge safety
switches to ensure they are closed. These
switches include:
• Safety Shut-Off Valve Proof of Closure
(POC) switch
• Low Water Level switch
• High Water Temperature switch
• High Gas Pressure switch
• Low Gas Pressure switch
• Blower Proof switch
If all of the above switches are closed, the
READY light above the ON/OFF switch will light
and the unit will be in the Standby mode.
When there is a demand for heat, the following
events will occur:
NOTE
If any of the Pre-Purge safety device
switches are open, the appropriate fault
message will be displayed. Also, the
appropriate fault messages will be displayed
throughout the start sequence, if the
required conditions are not observed.
1. The DEMAND LED status indicator will light.
2. The unit checks to ensure that the Proof of
Closure (POC) switch in the Safety Shut-Off
Valve (SSOV) is closed. Figure 3-3 shows
the Natural Gas SSOV location for a Factory
Mutual (FM) Gas Train.
PROPANE
SSOV
PROPANE
INLET
TO
AIR/FUEL
VALVE
NATURAL
GAS SSOV
NATURAL
GAS INLET
Figure 3-3.
FM Gas Train SSOV Locations
4. Next, the blower proof switch on the Air/Fuel
Valve (Figure 3-5) closes. The display will
show Purging and indicate the elapsed time
of the purge cycle in seconds. The normal
(default) time for the purge cycle is 12
seconds.
3. With all required safety device switches
closed, a purge cycle will be initiated and the
following events will occur:
(a) The Blower relay energizes and turns
on blower.
(b) The Air/Fuel Valve rotates to the full-
open purge position and closes purge
position switch. The dial on the Air/Fuel
Valve (Figure 3-4) will read 100 to
indicate that it is full-open (100%).
Figure 3-4.
Air/Fuel Valve In Purge Position
3-9
Page 32

CONTROL PANEL OPERATING PROCEDURES
Figure 3-5.
Blower Proof Switch
5. Upon completion of the purge cycle, the
Control Box initiates an ignition cycle and
the following events occur:
(a) The Air/Fuel Valve rotates to the low-
fire ignition position and closes the
ignition switch. The dial on the Air/Fuel
Valve (Figure 3-6) will read between 25
and 35 to indicate that the valve is in
the low-fire position.
(b) The igniter relay is activated and
provides ignition spark.
(c) The Safety Shut-Off Valve (SSOV) is
energized (opened) allowing gas to flow
into the Air/Fuel Valve.
6. Up to 7 seconds will be allowed for ignition
to be detected. The igniter relay will be
turned off one second after flame is
detected.
Air/Fuel Valve In Ignition Position
7. After 2 seconds of continuous flame, Flame
Proven will be displayed and the flame
strength will be indicated. After 5 seconds,
the current date and time will be displayed in
place of the flame strength.
8. With the unit firing properly, it will be
controlled by the temperature controller
circuitry. The boiler’s VALVE POSIT ION will
be continuously displayed on the front panel
bargraph.
Once the demand for heat has been satisfied,
the Control Box will turn off the SSOV gas valve.
The blower relay will be deactivated and the
Air/Fuel Valve will be closed. Standby will be
displayed.
Figure 3-6.
3-10
Page 33

CONTROL PANEL OPERATING PROCEDURES
3.10 START/STOP LEVELS
The start and stop levels are the Air/Fuel Valve
positions (% open) that start and stop the unit,
based on load. These levels are Factory preset
as follows:
Natural Gas
Start Level: 25% 25%
Stop Level: 20% 21%
Normally, these settings should not require
adjustment.
Propane
Note that the energy input of the boiler is not
linearly related to the Air/Fuel Valve position.
Refer to Table 3-8 for the relationship between
the energy input and valve open position (%) for
a unit running on natural gas.
Table 3-8.
Relationship Between Air/Fuel Valve Position and Energy Input For Unit Running On Natural Gas
Air/Fuel Valve Position
(% Open)
0 0 0
10% 0 0
20%
(Stop Level) 105,000
30% 325,000 16%
40% 590,000 30%
50% 830,000 42%
60% 1,030,000 52%
70% 1,210,000 61%
80% 1,440,000 72%
90% 1,750,000 88%
100% 2,000,000 100%
Energy Input
(BTU/Hr)
Boiler Energy Input
(% of Full Capacity)
5.0%
3-11
Page 34

Page 35

INITIAL START-UP
CHAPTER 4 INITIAL START-UP
4.1 INITIAL START-UP REQUIREMENTS
The requirements for the initial start-up of the
Benchmark 2.0 Low NOx (LN) Boiler consist of
the following:
• Complete installation
• Perform combustion calibration
• Set proper controls and limits
• Set up mode of operation (see Chapter 5)
• Test safety devices (see Chapter 6)
Installation should be fully completed before
performing initial start-up. The start-up must be
complete prior to putting the unit into service.
Starting a unit without the proper piping, venting,
or electrical systems can be dangerous and may
void the product warranty. The following start-up
instructions should be followed precisely in order
to operate the unit safely and at a high thermal
efficiency, with low flue gas emissions.
Initial unit start-up is to be performed ONLY by
AERCO factory trained start-up and service
personnel. After following the steps in this
chapter, it will be necessary to perform the Mode
of Operation settings in Chapter 5, and the
Safety Device Testing procedures in Chapter 6
to complete the initial unit start-up.
AERCO Gas Fired Startup Sheets, included with
each Benchmark Boiler, must be completed for
each unit for warranty validation and a copy
must be returned promptly to AERCO at:
AERCO International, Inc.
159 Paris Ave.
Northvale, NJ 07647
WARNING
DO NOT ATTEMPT TO DRY FIRE
THE BOILER. STARTING THE UNIT
WITHOUT A FULL WATER LEVEL
CAN SERIOUSLY DAMAGE THE
UNIT AND MAY RESULT IN INJURY
TO PERSONNEL OR PROPERTY
DAMAGE. THIS SITUATION WILL
VOID ANY WARRANTY.
CAUTION
All applicable installation procedures
in Chapter 2 must be completed
before attempting to start the unit.
4.2 TOOLS AND INSTRUMENTATION
FOR COMBUSTION CALIBRATION
To properly perform combustion calibration, the
proper instruments and tools must be used and
correctly attached to the unit. The following
paragraphs outline the necessary tools and
instrumentation as well as their installation.
4.2.1 Required Tools & Instrumentation
The following tools and instrumentation are
necessary to perform combustion calibration of
the unit:
• Digital Combustion Analyzer: Oxygen
accuracy to ± 0.4%; Carbon Monoxide
(CO) and Nitrogen Oxide (NOx) resolution
to 1PPM.
• 16 inch W.C. manometer or equivalent
gauge and plastic tubing.
• 1/8 inch NPT-to-barbed fittings for use with
gas supply manometer or gauge.
• Small and large flat blade screwdrivers.
• Tube of silicone adhesive
4.2.2 Installing Gas Supply Manometer
The gas supply manometer is installed in the
gas train as follows:
1. Close the main manual gas supply shut-off
valve upstream of the unit.
2. Remove the top panel and left or right side
panel from the boiler to access the gas train
components.
3. Remove the 1/8 inch NPT pipe plug from the
leak detection ball valve on the downstream
side of the Safety Shut Off Valve (SSOV) as
shown in Figure 4-1.
4-1
Page 36

INITIAL START-UP
4. Install a NPT-to-barbed fitting into the
tapped plug port.
5. Attach one end of the plastic tubing to the
barbed fitting and the other end to the 16
inch W.C. manometer.
PROPANE
INLET
PROPANE
LOW GAS
PRESSURE
SWITCH
1/8" NPT PLUG
(INSTALL
MANOMETER
HERE)
PROPANE
SSOV
LEAK
DETECTION
BALL VALVE
PROPANE PRESSURE
REGULATOR FEEDBACK
LINE
PROPANE HIGH
GAS PRESSURE
SWITCH
NAT. GAS HIGH
GAS PRESSURE
SWITCH
TO
AIR/FUEL
VALVE
NAT. GAS
PRESSURE
REGULATOR
FEEDBACK
LINE
NAT. GAS
LOW GAS
PRESSURE
SWITCH
BOILER
RETURN
EXHAUST
MANIFOLD
ANALYZER
PROBE PORT
1/2” NPT
CONDENSATE
DRAIN
CONNECTION
Figure 4-2
Analyzer Probe Port Location
IMPORTANT
For Dual Fuel units, perform the natural
gas combustion calibration procedures in
paragraph 4.3 before performing the
propane combustion calibration procedures in paragraph 4.4.
NATURAL
GAS INLET
BENCHMARK 2.0LN DUAL-FUEL FM GAS TRAIN
NATURAL GAS
SSOV
Figure 4-1.
1/8" NPT Plug Location On Leak
Detection Ball Valve
4.2.3 Accessing the Analyzer Probe Port
The unit contains NPT plugs on the left and right
side of the exhaust manifold at the rear of the
unit as shown in Figure 4-2. Prepare the port for
the combustion analyzer probe as follows:
1. Remove the plug from the probe port on the
right side of the exhaust manifold.
left or
2. If necessary, adjust the stop on the
combustion analyzer probe so that it will
extend mid-way into the flue gas flow. DO
NOT install the probe at this time.
Refer to Appendix K for switchover
instructions when changing from Natural
Gas to Propane or from Propane to
Natural Gas.
4.3 NATURAL GAS COMBUSTION CALIBRATION
The Benchmark 2.0LN Boiler is combustion
calibrated at the factory prior to shipping.
However, recalibration as part of initial start-up
is necessary due to changes in the local altitude,
gas BTU content, gas supply piping and supply
regulators. Factory Test Data sheets are
shipped with each unit. These sheets must be
filled out and returned to AERCO for proper
Warranty Validation.
It is important to perform the following procedure
as outlined. This will keep readjustments to a
minimum and provide optimum performance.
4-2
Page 37

INITIAL START-UP
1. Open the water supply and return valves to
the unit and ensure that the system pumps
are running.
2. Open the natural gas supply valve(s) to the
unit.
3. Set the control panel ON/OFF switch to the
OFF position.
4. Turn on external AC power to the unit. The
display will show LOSS OF POWER and the
time and date.
5. Set the unit to the Manual Mode by pressing
the AUTO/MAN key. A flashing Manual
Valve Position message will be displayed
with the present valve position in %. Also,
the MANUAL LED will light.
6. Adjust the air/fuel valve position to 0% by
pressing the ▼ arrow key.
7. Ensure that the leak detection ball valve
down-stream of the SSOV is open.
8. Ensure that the Fuel Selector Switch located
behind the front door of the unit (Figure 4-3)
is in the NATURAL GAS position.
Table 4-1
Combustion Oxygen Levels for a 100%
Valve Position
Inlet Air
Temp
>100°F 5.5 % <100 ppm <20 ppm
90°F 5.7 % <100 ppm <20 ppm
80°F 5.9 % <100 ppm <20 ppm
<70°F 6.0 % <100 ppm <20 ppm
Oxygen %
SEE
DETAIL “A”
± 0.2
Carbon
Monoxide NOx
9. Set the ON/OFF switch to the ON position.
10. Change the valve position to 34% using the
▲ arrow key. The unit should begin its start
sequence and fire.
11. Next, verify that the gas pressure
downstream of the SSOV is 7.3” W.C. for
both FM and IRI gas trains. If gas pressure
adjustment is required, remove the brass
hex nut on the Natural Gas SSOV actuator
containing the gas pressure regulator
(Figure 4-4). Make gas regulator
adjustments using a flat-tip screwdriver to
obtain 7.3” W.C.
12. Increase the valve position to 100% and
verify that the gas pressure downstream of
the SSOV remains at 7.2” W.C. Readjust
pressure if necessary.
13. With the valve position at 100%, insert the
combustion analyzer probe into the flue
probe opening and allow enough time for the
combustion analyzer to settle.
14. Compare the measured oxygen level to the
oxygen range for the inlet air temperature
shown in Table 4-1. Also, ensure that the
carbon monoxide (CO) and nitrogen oxide
(NOx) readings do not exceed the values
shown.
FRONT VIEW
ADJUSTABLE
TEMPERATURE
LIMIT SWITCH
RESET BUTTON
FOR MANUAL
TEMPERATURE
LIMIT SWITCH
DETAIL “A”
Figure 4-3
Front View With Door Removed
FUEL
SELECTOR
SWITCH
4-3
Page 38

INITIAL START-UP
BRASS HEX
HEAD CAP
(REMOVE TO
ACCESS GAS
PRESSURE
REGULATOR
ADJUSTMENT)
SSOV ACTUATOR WITH REGULATOR
Figure 4-4
Regulator Adjustment Screw Location
15. If necessary, adjust the iris air damper
shown in Figure 4-4 until the oxygen level is
within the range specified in Table 4-1.
AIR
INLET
NOTE
The remaining combustion calibration
steps are performed using the
Combustion Cal Menu included in the C-
More Control System. The combustion
calibration control functions will be used
to adjust the oxygen level (%) at valve
positions of 80%, 60%, 45%, 30% and
20% as described in the following steps.
These steps assume that the inlet air
temperature is within the range of 50°F to
100°F.
17. Press the MENU Key on the front panel of
the C-MORE and access the Setup menu.
Enter password 6817 and then press the
ENTER key.
18. Press the MENU Key on the front panel of
the C-MORE until Combustion Cal Menu
appears on the C-More display.
19. Press the ▲ arrow key until SET Valve
Position appears on the C-MORE display.
20. Press the CHANGE key. SET Valve will
begin to flash.
IRIS AIR
DAMPER
(SEE DETAIL “A”)
USE 1/2"
WRENCH TO
INCREASE (CW)
OR DECREASE
(CCW) INLET AIR
IRIS ADJUSTMENT
DETAIL “A”
Figure 4-4
Iris Air Damper Location/Adjustment
16. Once the oxygen level is within the specified
range at 100%, lower the valve position to
80%.
21. Press the ▲ arrow key until the SET Valve
Position reads 80%. Press the ENTER key.
22. Next, press the
CAL Voltage 80% is displayed.
down (▼) arrow key until
23. Press the CHANGE key and observe that
CAL Voltage 80% is flashing.
24. The oxygen level at the 80% valve position
should be as shown below. Also, ensure that
the carbon monoxide (CO) and nitrogen
oxide (NOx) readings do not exceed the
values shown.
Combustion Oxygen Level at
80% Valve Position
Oxygen %
± 0.2
6.0 % <100 ppm < 20 ppm
25. If the oxygen level is not within the specified
range, adjust the level using the ▲ and ▼
arrow keys. This will adjust the output
voltage to the blower motor as indicated on
the display. Pressing the ▲ arrow key
increases the oxygen level and pressing the
down ▼ arrow key decreases the oxygen
level.
Carbon
Monoxide
NOx
4-4
Page 39

INITIAL START-UP
26. Once the oxygen level is within the specified
range at 80%, press the ENTER key to store
the selected blower output voltage for 80%
valve position.
NOTE
The remaining steps basically repeat the
procedures in steps 19 through 26 for
valve positions of 60%, 45%, 30% and
20%. However, since oxygen levels vary,
these steps are repeated in their entirety.
When performing these steps, also
ensure that the carbon monoxide (CO)
and nitrogen oxide (NOx) readings do not
exceed the values shown for each valve
position.
27. Press the ▲ arrow key until SET Valve
Position appears on the C-MORE display.
28. Press the CHANGE key. SET Valve Position
will begin to flash.
29. Press the ▼ arrow key until the SET Valve
Position reads 60% and press the ENTER
key.
30. Press the
Voltage 60% is displayed.
down ▼ arrow key until CAL
31. Press the CHANGE key. CAL Voltage 60%
will begin to flash.
32. The oxygen level at the 60% valve position
should be as shown below. Also, ensure that
the carbon monoxide (CO) and nitrogen
oxide (NOx) readings do not exceed the
values shown.
Combustion Oxygen Level at
60% Valve Position
Oxygen %
± 0.2
6.0 % <100 ppm <20 ppm
33. If the oxygen level is not within the specified
range, adjust the level using the ▲ and ▼
arrow keys. This will adjust the output
voltage to the blower motor as indicated on
the display. Pressing the ▲ arrow key
increases the oxygen level and pressing the
▼ arrow key decreases the oxygen level.
34. Once the oxygen level is within the specified
range at 60%, press the ENTER key to store
the selected blower output voltage for 60%
valve position.
35. Press the ▲ arrow key until SET Valve
Position appears on the C-MORE display.
Carbon
Monoxide
NOx
36. Press the CHANGE key. SET Valve Position
will begin to flash.
37. Press the ▼ arrow key until the SET Valve
Position reads 45%, then press the ENTER
key.
38. Press the
45% is displayed.
▼ arrow key until CAL Voltage
39. Press the CHANGE key. CAL Voltage 45%
will begin to flash.
40. The oxygen level at the 45% valve position
should be as shown below. Also, ensure that
the carbon monoxide (CO) and nitrogen
oxide (NOx) readings do not exceed the
values shown.
Combustion Oxygen Level at
45% Valve Position
Oxygen %
± 0.2
6.4 % <50 ppm <20 ppm
41. If the oxygen level is not within the specified
range, adjust the level using the ▲ and ▼
arrow keys. This will adjust the output
voltage to the blower motor as indicated on
the display. Pressing the ▲ arrow key
increases the oxygen level and pressing the
▼ arrow key decreases the oxygen level.
42. Once the oxygen level is within the specified
range at 45%, press the ENTER key to store
the selected blower output voltage for the
45% valve position.
43. Press the ▲ arrow key until SET Valve
Position appears on the C-MORE display.
44. Press the CHANGE key. SET Valve Position
will begin to flash.
45. Press the ▼ arrow key until the SET Valve
Position reads 30%, then press the ENTER
key.
46. Press the
▼ arrow key until CAL Voltage
30% is displayed.
47. Press the CHANGE key. CAL Voltage 30%
will begin to flash.
48. The oxygen level at the 30% valve position
should be as shown below. Also, ensure that
the carbon monoxide (CO) and nitrogen
oxide (NOx) readings do not exceed the
values shown.
Carbon
Monoxide
NOx
4-5
Page 40

INITIAL START-UP
Combustion Oxygen Level at
30% Valve Position
Oxygen %
± 0.2
8.4 % <50 ppm <20 ppm
49. If the oxygen level is not within the specified
range, adjust the level using the ▲ and ▼
arrow keys. This will adjust the output
voltage to the blower motor as indicated on
the display. Pressing the ▲ arrow key
increases the oxygen level and pressing the
▼ arrow key decreases the oxygen level.
50. Once the oxygen level is within the specified
range at 30%, press the ENTER key to store
the selected blower output voltage for 30%
valve position.
51. Press the ▲ arrow key until SET Valve
Position appears on the C-MORE display.
52. Press the CHANGE key. SET Valve Position
will begin to flash.
53. Press the ▼ arrow key until the SET Valve
Position reads 20%, then press the ENTER
key.
54. Press the
▼ arrow key until CAL Voltage
18% is displayed.
55. Press the CHANGE key. CAL Voltage 20%
will begin to flash.
56. The oxygen level at the 20% valve position
should be as shown below. Also, ensure that
the carbon monoxide (CO) and nitrogen
oxide (NOx) readings do not exceed the
values shown.
Carbon
Monoxide
NOx
Combustion Oxygen Level at
20% Valve Position
Oxygen %
± 0.2
8.8 % <50 ppm <20 ppm
57. If the oxygen level is not within the specified
range, adjust the level using the ▲ and ▼
arrow keys. This will adjust the output
voltage to the blower motor as indicated on
the display. Pressing the ▲ arrow key
increases the oxygen level and pressing the
▼ arrow key decreases the oxygen level.
58. Once the oxygen level is within the specified
range at 20%, press the ENTER key to store
the selected blower output voltage for 20%
valve position.
Carbon
Monoxide
NOx
59. This completes the Natural Gas combustion
calibration procedure.
IMPORTANT
Refer to Appendix K for switchover
instructions when changing from Natural
Gas to Propane or from Propane to
Natural Gas.
4.4 PROPANE COMBUSTION
CALIBRATION
The Benchmark 2.0LN Dual-Fuel Boiler is
combustion calibrated at the factory prior to
shipping. However, recalibration as part of initial
start-up is necessary due to changes in the local
altitude, gas BTU content, gas supply piping and
supply regulators. Factory Test Data sheets are
shipped with each unit. These sheets must be
filled out and returned to AERCO for proper
Warranty Validation.
Prior to starting these procedures, ensure that
the Benchmark 2.0LN Dual-Fuel Boiler has been
set up as specified in paragraphs 4.2 through
4.2.3.
It is important to perform the following procedure
as outlined. This will keep readjustments to a
minimum and provide optimum performance.
1. Open the water supply and return valves to
the unit and ensure that the system pumps
are running.
2. Open the propane supply valve(s) to the
unit.
3. Set the control panel ON/OFF switch to the
OFF position.
4. Turn on external AC power to the unit. The
display will show LOSS OF POWER and the
time and date.
5. Set the unit to the Manual Mode by pressing
the AUTO/MAN key. A flashing Manual
Valve Position message will be displayed
with the present rate in %. Also, the
MANUAL LED will light.
6. Access the Control Panel Configuration
Menu and ensure that the Fuel Type is set
to Propane.
7. Adjust the valve position to 0% by pressing
the ▼ arrow key.
8. Ensure that the leak detection ball valve
(Figure 4-1) down-stream of the SSOV is
open.
4-6
Page 41

INITIAL START-UP
9. Set the Fuel Selector Switch (Figure 4-3) to
the PROPANE position.
10. Set the ON/OFF switch to the ON position.
11. Change the valve position to 34% using the
▲ arrow key. The unit should begin its start
sequence and fire.
12. Next, increase the valve position to 91%.
Verify that the gas pressure downstream of
the Propane SSOV is 2.8” W.C. for both FM
and IRI gas trains. If gas pressure
adjustment is required, remove the brass
hex nut on the Propane SSOV actuator
containing the gas pressure regulator (see
Figures 4-1 & 4-3). For IRI gas trains, the
regulator is on the downstream SSOV. Make
gas regulator adjustments using a flat-tip
screwdriver to obtain 2.8” W.C.
13. With the valve position at 91%, insert the
combustion analyzer probe into the flue
probe opening and allow enough time for the
combustion analyzer to settle.
14. Compare the measured oxygen % level to
the range shown below. Also, ensure that
the carbon monoxide (CO) and nitrogen
oxide (NOx) readings do not exceed the
values shown.
Combustion Oxygen Level for a 91%
Valve Position
Oxygen %
± 0.2
5.3 % <150 ppm <100 ppm
Carbon
Monoxide
NOx
15. If necessary, adjust the iris air damper
shown in Figure 4-4 until the oxygen level is
within the range specified above.
16. Once the oxygen level is within the specified
range at 91%, lower the valve position to
80%.
NOTE
The remaining combustion calibration
steps are performed using the
Combustion Cal Menu included in the C-
More Control System. The combustion
calibration control functions will be used
to adjust the oxygen level (%) at valve
positions of 80%, 60%, 45%, 30% and
21% as described in the following steps.
These steps assume that the inlet air
temperature is within the range of 50°F to
100°F.
17. Press the MENU Key on the front panel of
the C-MORE and access the Setup menu.
Enter password 6817 and then press the
ENTER key.
18. Press the MENU Key on the front panel of
the C-MORE until Combustion Cal Menu
appears on the C-More display.
19. Press the ▲ arrow key until SET Valve
Position appears on the C-MORE display.
20. Press the CHANGE key. SET Valve Position
will begin to flash.
21. Press the ▲ arrow key until the SET Valve
Position reads 80%. Press the ENTER key.
22. Next, press the
CAL Voltage 80% is displayed.
down (▼) arrow key until
23. Press the CHANGE key and observe that
CAL Voltage 80% is flashing.
24. The oxygen level at the 80% valve position
should be as shown below. Also, ensure that
the carbon monoxide (CO) and nitrogen
oxide (NOx) readings do not exceed the
values shown.
Combustion Oxygen Level at
80% Valve Position
Oxygen %
± 0.2
4.8 % <150 ppm <100 ppm
25. If the oxygen level is not within the specified
range, adjust the level using the ▲ and ▼
arrow keys. This will adjust the output
voltage to the blower motor as indicated on
the display. Pressing the ▲ arrow key
increases the oxygen level and pressing the
down ▼ arrow key decreases the oxygen
level.
26. Once the oxygen level is within the specified
range at 80%, press the ENTER key to store
the selected blower output voltage for 80%
valve position.
Carbon
Monoxide
NOx
NOTE
The remaining steps basically repeat the
procedures in steps 19 through 26 for
valve positions of 60%, 45%, 30% and
21%. However, since oxygen levels vary,
these steps are repeated in their entirety.
When performing these steps, also
ensure that the carbon monoxide (CO)
and nitrogen oxide (NOx) readings do not
exceed the values shown for each valve
position.
4-7
Page 42

INITIAL START-UP
27. Press the ▲ arrow key until SET Valve
Position appears on the C-MORE display.
28. Press the CHANGE key. SET Valve Position
will begin to flash.
29. Press the ▼ arrow key until the SET Valve
Position reads 60% and press the ENTER
key.
30. Press the
Voltage 60% is displayed.
down ▼ arrow key until CAL
31. Press the CHANGE key. CAL Voltage 60%
will begin to flash.
32. The oxygen level at the 60% valve position
should be as shown below. Also, ensure that
the carbon monoxide (CO) and nitrogen
oxide (NOx) readings do not exceed the
values shown.
Combustion Oxygen Level at
60% Valve Position
Oxygen %
± 0.2
5.0 % <150 ppm <100 ppm
33. If the oxygen level is not within the specified
range, adjust the level using the ▲ and ▼
arrow keys. This will adjust the output
voltage to the blower motor as indicated on
the display. Pressing the ▲ arrow key
increases the oxygen level and pressing the
▼ arrow key decreases the oxygen level.
34. Once the oxygen level is within the specified
range at 60%, press the ENTER key to store
the selected blower output voltage for the
60% valve position.
35. Press the ▲ arrow key until SET Valve
Position appears on the C-MORE display.
36. Press the CHANGE key. SET Valve Position
will begin to flash.
37. Press the ▼ arrow key until the SET Valve
Position reads 45%, then press the ENTER
key.
38. Press the
▼ arrow key until CAL Voltage
45% is displayed.
39. Press the CHANGE key. CAL Voltage 45%
will begin to flash.
40. The oxygen level at the 45% valve position
should be as shown below. Also, ensure that
the carbon monoxide (CO) and nitrogen
oxide (NOx) readings do not exceed the
values shown.
Carbon
Monoxide
NOx
Combustion Oxygen Level at
45% Valve Position
Oxygen %
± 0.2
7.0 % <100 ppm <100 ppm
41. If the oxygen level is not within the specified
range, adjust the level using the ▲ and ▼
arrow keys. This will adjust the output
voltage to the blower motor as indicated on
the display. Pressing the ▲ arrow key
increases the oxygen level and pressing the
▼ arrow key decreases the oxygen level.
42. Once the oxygen level is within the specified
range at 45%, press the ENTER key to store
the selected blower output voltage for the
45% valve position.
43. Press the ▲ arrow key until SET Valve
Position appears on the C-MORE display.
44. Press the CHANGE key. SET Valve Position
will begin to flash.
45. Press the ▼ arrow key until the SET Valve
Position reads 30%, then press the ENTER
key.
46. Press the
▼ arrow key until CAL Voltage
30% is displayed.
47. Press the CHANGE key. CAL Voltage 30%
will begin to flash.
48. The oxygen level at the 30% valve position
should be as shown below. Also, ensure that
the carbon monoxide (CO) and nitrogen
oxide (NOx) readings do not exceed the
values shown.
Carbon
Monoxide
NOx
Combustion Oxygen Level at
30% Valve Position
Oxygen %
± 0.2
7.9 % <100 ppm <100 ppm
49. If the oxygen level is not within the specified
range, adjust the level using the ▲ and ▼
arrow keys. This will adjust the output
voltage to the blower motor as indicated on
the display. Pressing the ▲ arrow key
increases the oxygen level and pressing the
▼ arrow key decreases the oxygen level.
50. Once the oxygen level is within the specified
range at 30%, press the ENTER key to store
the selected blower output voltage for the
30% valve position.
51. Press the ▲ arrow key until SET Valve
Position appears on the C-MORE display.
Carbon
Monoxide
NOx
4-8
Page 43

INITIAL START-UP
52. Press the CHANGE key. SET Valve Position
will begin to flash.
53. Press the ▼ arrow key until the SET Valve
Position reads 21%, then press the ENTER
key.
54. Press the
21% is displayed.
▼ arrow key until CAL Voltage
55. Press the CHANGE key. CAL Voltage 21%
will begin to flash.
56. The oxygen level at the 21% valve position
should be as shown below. Also, ensure that
the carbon monoxide (CO) and nitrogen
oxide (NOx) readings do not exceed the
values shown.
Combustion Oxygen Level at
21% Valve Position
Oxygen %
± 0.2
8.9 % <100 ppm <100 ppm
57. If the oxygen level is not within the specified
range, adjust the level using the ▲ and ▼
arrow keys. This will adjust the output
voltage to the blower motor as indicated on
the display. Pressing the ▲ arrow key
increases the oxygen level and pressing the
▼ arrow key decreases the oxygen level.
58. Once the oxygen level is within the specified
range at 21%, press the ENTER key to store
the selected blower output voltage for the
21% valve position.
59. This completes the Propane Combustion
Calibration procedure.
Carbon
Monoxide
NOx
4.5 UNIT REASSEMBLY
Once the combustion calibration adjustments in
paragraph 4.3 (natural gas) and 4.4 (propane)
are properly set, the unit can be reassembled for
service operation.
1. Set the ON/OFF switch in the OFF position.
2. Disconnect AC power from the unit.
3. Shut off the gas supply to the unit.
4. Remove the manometer and barbed fittings
and reinstall the NPT plug using a suitable
pipe thread compound.
5. Remove the combustion analyzer probe
from the vent hole. Replace the NPT plug in
the vent hole using a suitable pipe joint
compound.
6. Replace the unit’s side panels and front
door.
4.6 OVER-TEMPERATURE LIMIT
SWITCHES
The unit contains both automatic and manual
reset over-temperature limit switches. These
switches are mounted on a bracket located
behind the front door of the unit as shown in
Figure 4-3 (page 4-3). The manual reset switch
is not adjustable and is permanently fixed at
210°F. This switch will shut down and lock out
the boiler if the water temperature exceeds
210°F. Following an over-temperature condition,
it must be manually reset by pressing the
RESET button before the boiler can be
restarted. The automatic reset over-temperature
switch is adjustable and allows the boiler to
restart, once the temperature drops below its
temperature setting. Set the automatic overtemperature switch to the desired temperature
setting.
4-9
Page 44

Page 45

MODE OF OPERATION
CHAPTER 5 MODE OF OPERATION
5.1 INTRODUCTION
The boiler is capable of being operated in any
one of six different modes. The following
paragraphs in this Chapter provide descriptions
of each of these operating modes. Each boiler is
shipped from the factory tested and configured
for the ordered mode of operation. All
temperature related parameters are at their
factory default values which work well in most
applications. However, it may be necessary to
change certain parameters to customize the unit
to the system environment. A complete listing
and descriptions of the temperature related
parameters are included in Appendix A. Factory
defaults are listed in Appendix E. After reading
this chapter, parameters can be customized to
suit the needs of the specific application.
5.2 INDOOR/OUTDOOR RESET MODE
This mode of operation is based on outside air
temperatures. As the outside air temperature
decreases, the supply header temperature will
increase and vice versa. For this mode, it is
necessary to install an outside air sensor as well
as select a building reference temperature and a
reset ratio.
5.2.3 Outdoor Air Temperature Sensor
Installation
The outdoor air temperature sensor must be
mounted on the North side of the building in an
area where the average outside air temperature
is expected. The sensor must be shielded from
the sun's direct rays, as well as direct
impingement by the elements. If a cover or
shield is used, it must allow free air circulation.
The sensor may be mounted up to two hundred
feet from the unit. Sensor connections are
made at the Input/Output (I/O) Box on the front
of the boiler. Connections are made at the
terminals labeled OUTDOOR SENSOR IN and
SENSOR COMMON inside the I/O Box. Use
shielded 18 to 22 AWG wire for connections. A
wiring diagram is provided on the cover of the
I/O Box. Refer to Chapter 2, paragraph 2.9.1 for
additional wiring information.
5.2.4 Indoor/ Outdoor Startup
Startup in the Indoor/Outdoor Reset Mode is
accomplished as follows:
1. Refer to the Indoor/Outdoor reset ratio
charts in Appendix D.
5.2.1 Reset Ratio
Reset ratio is an adjustable number from 0.1 to
9.9. Once adjusted, the supply header
temperature will increase by that number for
each degree that the outside air temperature
decreases. For instance, if a reset ratio of 1.6 is
used, for each degree that outside air
temperature decreases the supply header
temperature will increase by 1.6 degrees.
5.2.2 Building Reference Temperature
This is a temperature from 40°F to 230°F. Once
selected, it is the temperature that the system
references to begin increasing its temperature.
For instance, if a reset ratio of 1.6 is used, and
we select a building reference temperature of
70°F, then at an outside temperature of 69°F,
the supply header temperature will increase by
1.6° to 71.6°F.
2. Choose the chart corresponding to the
desired Building Reference Temperature.
3. Go down the left column of the chart to the
coldest design outdoor air temperature
expected in your area.
NOTE
A design engineer typically provides
design outdoor air temperature and
header temperature data
supply
4. Once the design outdoor air temperature is
chosen, go across the chart to the desired
supply header temperature for the design
temperature chosen in step 3.
5. Next, go up that column to the Reset Ratio
row to find the corresponding reset ratio.
6. Access the Configuration Menu and scroll
through it until the display shows Bldg Ref
Temp. (Building Reference Temperature).
5-1
Page 46

MODE OF OPERATION
7. Press the CHANGE key. The display will
begin to flash.
8. Use the ▲ and ▼ arrow keys to select the
desired Building Reference Temperature.
9. Press ENTER to save any changes.
10. Next, scroll through the Configuration Menu
until the display shows Reset Ratio.
11. Press the CHANGE key. The display will
begin to flash.
12. Use the ▲ and ▼ arrow keys to select the
Reset Ratio determined in step 5.
13. Press ENTER to save the change.
Refer to paragraph 3.3 for detailed instructions
on menu changing.
5.3 CONSTANT SETPOINT MODE
The Constant Setpoint mode is used when a
fixed header temperature is desired. Common
uses of this mode of operation include water
source heat pump loops, and indirect heat
exchangers for potable hot water systems or
processes.
5.4 REMOTE SETPOINT MODES
The unit’s setpoint can be remotely controlled by
an Energy Management System (EMS) or
Building Automation System (BAS). The Remote
Setpoint can be driven by a current or voltage
signal within the following ranges:
4-20 mA/1-5 Vdc
0-20 mA/0-5 Vdc
The factory default setting for the Remote
Setpoint mode is 4 - 20 mA/1 - 5 Vdc. With this
setting, a 4 to 20 mA/1 to 5 Vdc signal, sent by
an EMS or BAS, is used to change the unit's
setpoint. The 4 mA/1V signal is equal to a 40°F
setpoint while a 20 mA /5V signal is equal to a
240°F setpoint. When a 0 to 20 mA/0 to 5 Vdc
signal is used, 0 mA is equal to a 40°F setpoint.
In addition to the current and voltage signals
described above, the Remote Setpoint mode
can also driven by a RS485 Modbus Network
signal from an EMS or BAS.
The Remote Setpoint modes of operation can be
used to drive single as well as multiple units.
No external sensors are required to operate in
this mode. While it is necessary to set the
desired setpoint temperature, it is not necessary
to change any other temperature-related
functions. The unit is factory preset with settings
that work well in most applications. Prior to
changing any temperature-related parameters,
other than the setpoint, it is suggested that an
AERCO representative be contacted. For
descriptions of temperature-related functions
and their factory defaults, see Appendices A and
E.
5.3.1 Setting the Setpoint
The setpoint temperature of the unit is
adjustable from 40°F to 240°F. To set the unit
for operation in the Constant Setpoint Mode, the
following menu settings must be made in the
Configuration Menu:
MENU OPTION SETTING
Boiler Mode Constant Setpoint
Internal Setpt Select desired setpoint
using ▲ and ▼ arrow
keys (40°F to 240°F)
NOTE
If a voltage, rather than current signal is
used to control the remote setpoint, a DIP
switch adjustment must be made on the
CPU Board located in the Control Panel
Assembly. Contact your local AERCO
representative for details.
In order to enable the Remote Setpoint Mode,
the following menu setting must be made in the
Configuration Menu:
MENU OPTION SETTING
Boiler Mode Remote Setpoint
Remote Signal 4-20mA/1-5V,
0-20mA/0-5V, or
Network
Refer to paragraph 3.3 for detailed instructions
on changing menu options.
Refer to paragraph 3.3 for detailed instructions
on changing menu options.
5-2
Page 47

MODE OF OPERATION
If the Network setting is selected for RS485
Modbus operation, a valid Comm Address must
be entered in the Setup Menu. Refer to Modbus
Communication Manual GF-114 for additional
information.
While it is possible to change the settings of
temperature related functions, the unit is factory
preset with settings that work well in most
applications. It is suggested that an AERCO
representative be contacted, prior to changing
any temperature related function settings. For
descriptions of temperature-related functions
and their factory defaults, refer to Appendices A
and E.
5.4.1 Remote Setpoint Field Wiring
The only wiring connections necessary for the
Remote Setpoint mode are connection of the
remote signal leads from the source to the unit’s
I/O Box. The I/O Box is located on the front
panel of the boiler. For either a 4-20mA/0-5V or
a 0-20mA/0-5V setting, the connections are
made at the ANALOG IN terminals in the I/O
Box. For a Network setting, the connections are
made at the RS-485 COMM terminals in the I/O
Box. The signal must be floating, (ungrounded)
at the I/O Box and the wire used must be a two
wire shielded pair from 18 to 22 AWG. Polarity
must be observed. The source end of the shield
must be connected at the source. When driving
multiple units, each unit’s wiring must conform to
the above.
5.4.2 Remote Setpoint Startup
Since this mode of operation is factory preset
and the setpoint is being externally controlled,
no startup instructions are necessary. In this
mode, the REMOTE LED will light when the
external signal is present.
To operate the unit in the Manual mode, press
the AUTO/MAN switch. The REMOTE LED will
go off and the MANUAL LED will light.
To change back to the Remote Setpoint mode,
simply press the AUTO/MAN switch. The
REMOTE LED will again light and the MANUAL
LED will go off.
5.5 DIRECT DRIVE MODES
The unit’s air/fuel valve position (% open) can be
changed by a remote signal which is typically
sent from an Energy Management System
(EMS) or from a Building Automation System
(BAS). The Direct Drive mode can be driven by
a current or voltage signal within the following
ranges:
4-20 mA/1-5 Vdc
0-20 mA/0-5 Vdc
The factory default setting for the Direct Drive
mode is 4-20 mA/1-5 Vdc. With this setting, a 4
to 20 mA signal, sent by an EMS or BAS is used
to change the unit’s valve position from 0% to
100%. A 4 mA/1V signal is equal to a 0% valve
position, while a 20 mA /5V signal is equal to a
100% valve position. When a 0-20 mA/0-5 Vdc
signal is used, zero is equal to a 0% valve
position.
In addition to the current and voltage signals
described above, the Direct Drive mode can also
driven by a RS485 Modbus Network signal from
an EMS or BAS.
When in a Direct Drive mode, the unit is a slave
to the EMS or BAS and does not have a role in
temperature control. Direct Drive can be used to
drive single, or multiple units.
NOTE
If a voltage, rather than current signal is
used to control the remote setpoint, a DIP
switch adjustment must be made on the
CPU Board located in the Control Box
Assembly. Contact your local AERCO
representative for details.
To enable the Direct Drive Mode, the following
menu setting must be made in the Configuration
Menu:
MENU OPTION SETTING
Boiler Mode Direct Drive
Remote Signal 4-20mA/1-5V,
0-20mA/0-5V, or
Network
Refer to paragraph 3.3 for instructions on
changing menu options.
5-3
Page 48

MODE OF OPERATION
If the Network setting is selected for RS485
Modbus operation, a valid Comm Address must
be entered in the Setup Menu. Refer to Modbus
Communication Manual GF-114 for additional
information.
5.5.1 Direct Drive Field Wiring
The only wiring connections necessary for Direct
Drive mode are connection of the remote signal
leads from the source to the unit’s I/O Box. For
either a 4-20mA/0-5V or a 0-20mA/0-5V setting,
the connections are made at the ANALOG IN
terminals in the I/O Box. For a Network setting,
the connections are made at the RS-485 COMM
terminals in the I/O Box. The signal must be
floating, (ungrounded) at the I/O Box and the
wire used must be a two wire shielded pair from
18 to 22 AWG. Polarity must be observed. The
source end of the shield must be connected at
the source. When driving multiple units, each
unit’s wiring must conform to the above.
5.5.2 Direct Drive Startup
Since this mode of operation is factory preset
and the valve position is being externally
controlled, no startup instructions are necessary.
In this mode, the REMOTE LED will light when
the signal is present.
To operate the unit in manual mode, press the
AUTO/MAN switch. The REMOTE LED will go
off and the MANUAL LED will light.
To change back to the Direct Drive mode, simply
press the AUTO/MAN switch. The REMOTE
LED will again light and the MANUAL LED will
go off.
5.6 BOILER MANAGEMENT SYSTEM
(BMS)
NOTE
BMS Model 168 can utilize either pulse
width modulation (PWM) or RS485
Modbus signaling to the Boiler. BMS II
Model 5R5-384 can utilize only RS485
signaling to the Boiler.
The BMS mode of operation is used in
conjunction with an AERCO Boiler Management
System. The BMS mode is used when it is
desired to operate multiple units in the most
efficient manner possible. For this mode of
operation, a BMS Header Sensor must be
installed between 2 and 10 feet downstream of
the LAST boiler in the boiler plant's supply water
header. The BMS can control up to 40 boilers; 8
via pulse width modulation (PWM) and up to 32
via Modbus (RS485) network communication.
For BMS programming, operation, and Header
Sensor installation details, see GF-108M (BMS
Model 168) and GF-124 (BMS II Model 5R5-
384), BMS Operations Guides. For operation via
an RS485 Modbus network, refer to Modbus
Communication Manual GF-114.
To enable the BMS Mode, the following menu
settings must be made in the Configuration
Menu:
MENU OPTION SETTING
Boiler Mode Direct Drive
Remote Signal BMS (PWM Input)
or
Network (RS485)
Refer to paragraph 3.3 for instructions on
changing menu options.
5.6.1 BMS External Field Wiring
Wiring connections for BMS control using PWM
signaling are made between connector JP2 on
the BMS panel (boilers 1 through 8), and the
B.M.S. (PWM) IN terminals in the I/O Box on the
front of the boilers. Refer to the wiring diagram
provided on the cover of the I/O Box.
Wiring connections for RS485 Modbus control
are made between connector JP11 on the BMS
(boilers 9 through 40) and the RS485 COMM
terminals in the I/O Box on the front of the
boilers.
Wire the units using shielded twisted pair wire
between 18 and 22 AWG. Observe the proper
polarity for the B.M.S. (PWM) IN and/or RS485
COMM wiring connections. Shields should be
terminated only at the BMS and the boiler end
must be left floating. Each unit’s wiring must
conform to the above.
5.6.2 BMS Setup and Startup
This mode of operation is factory preset and the
AERCO BMS controls the firing rate (air/fuel
valve % open position). There are no setup
instructions for each individual unit.
To operate the unit in manual mode, press the
AUTO/MAN switch. The REMOTE LED will go
off and the MANUAL LED will light
5-4
Page 49

MODE OF OPERATION
To change back to the BMS mode, simply press
the AUTO/MAN switch. The REMOTE LED will
again light and the MANUAL LED will go off.
5.7 COMBINATION CONTROL SYSTEM
(CCS)
NOTE
Only BMS Model 168 can be utilized for
the Combination Mode, not the BMS II
(Model 5R5-384).
A Combination Control System (CCS) is one
that uses multiple boilers to cover both spaceheating and domestic hot water needs. An
AERCO Boiler Management System (BMS)
Model 168 and a Combination Control Panel
(CCP) are necessary to configure this system.
Typically, an adequate number of boilers are
installed to cover the space-heating load on the
design day, however one or more units are used
for the domestic hot water load.
The theory behind this type of system is that the
maximum space-heating load and the maximum
domestic hot water load do not occur simultaneously.+ Therefore, boilers used for the
domestic hot water are capable of switching
between constant setpoint and BMS modes of
operation. These boilers are the combination
units and are referred to as the combo boilers.
The combo boilers heat water to a constant
setpoint temperature. That water is then
circulated through a heat exchanger in a
domestic hot water storage tank.
When the space-heating load is such that all the
space-heating boilers are at the 100% valve
position, the BMS will then ask the Combination
Control Panel for the domestic boilers to
become space-heating boilers. Provided the
domestic hot water load is satisfied, the combo
(hot water) boilers will then become spaceheating boilers. If the domestic hot water load is
not satisfied, the combo boiler(s) remain on the
domestic hot water load. If the combo boilers
switch over to space heating, but there is a call
for domestic hot water, the CCP switches the
combo units back to the domestic load.
When the combo units are satisfying the
domestic load they are in constant setpoint
mode of operation. When the combo units
switch over to space heating, their mode of
operation changes to the BMS mode. For more
information concerning the operation of the
Combination Control Panel see the AERCO
CCP-1 literature.
5.7.1 Combination Control System Field Wiring
Wiring for this system is between the BMS
Model 168 panel, the CCP and the B.M.S.
(PWM) IN terminals in the I/O Box. Wire the
units using a shielded twisted pair of 18 to 22
AWG wire. When wiring multiple units, each
unit’s wiring must conform to the above. For a
complete CCP system-wiring diagram see the
AERCO CCP-1 literature.
5.7.2 Combination Control System Setup and Startup
Setup for the Combination Mode requires entries
to be made in the Configuration Menu for boiler
mode, remote signal type and setpoint. The
setpoint is adjustable from 40°F to 240°F.
Enter the following settings in the Configuration
Menu:
MENU OPTION SETTING
Boiler Mode Combination
Remote Signal BMS (PWM Input)
Internal Setpt 40°F to 240°F
Refer to paragraph 3.3 for instructions on
changing menu options.
While it is possible to change other temperaturerelated functions for combination mode, thes
functions are preset to their factory default
values. These default settings work well in most
applications. It is suggested that AERCO be
contacted prior to changing settings other than
the unit’s setpoint. For a complete listing of
temperature related function defaults, see
Appendix E.
To set the unit to the manual mode, press the
AUTO/MAN switch. The MANUAL LED will
light.
To set the unit back to the auto mode, press the
AUTO/MAN switch. The MANUAL LED will go
off and the REMOTE LED will light.
When the boiler is switched to BMS mode, the
AERCO BMS controls the valve position. There
are no setup requirements to the boiler(s) in this
mode.
5-5
Page 50

Page 51

SAFETY DEVICE TESTING
G
CHAPTER 6 SAFETY DEVICE TESTING
6.1 TESTING OF SAFETY DEVICES
Periodic safety device testing is required to
ensure that the control system and safety
devices are operating properly. The Benchmark
1.5 Dual-Fuel control system comprehensively
monitors all combustion-related safety devices
before, during and after the start sequence. The
following tests check to ensure that the system
is operating as designed.
Operating controls and safety devices should be
tested on a regular basis or following service or
replacement. All testing must conform to local
codes such as ASME CSD-1.
NOTE
MANUAL and AUTO modes of operation
are required to perform the following
tests. For a complete explanation of these
modes, see Chapter 3.
NOTE
It will be necessary to remove the front
door and side panels from the unit to
perform the following tests.
WARNING
ELECTRICAL VOLTAGES IN THIS
SYSTEM MAY INCLUDE 120 AND 24
VOLTS AC. POWER MUST BE REMOVED PRIOR TO PERFORMING
WIRE REMOVAL OR OTHER TEST
PROCEDURES THAT CAN RESULT
IN ELECTRICAL SHOCK.
6.2 NATURAL GAS LOW GAS
PRESSURE FAULT TEST
Refer to Figure 6-1 and ensure that the leak
detection ball valve, located below the high gas
pressure switches, is closed.
4. Slowly open the ball valve near the natural
gas low gas pressure switch.
5. Place the unit in Manual Mode and adjust
the valve position to 34%.
6. While the unit is firing, slowly
external
manual gas shut-off valve.
close the
7. The unit should shut down and display a
LOW GAS PRESSURE fault message at
approximately 8.5” W.C. The FAULT indi-
cator should also start flashing.
8. Fully open the external manual gas shut-off
valve and press the CLEAR button on the
Control Box.
9. The fault message should clear and the
FAULT indicator should go off. The unit
should restart.
10. Upon test completion, close the ball valve
and remove the manometer. Replace the
1/8 “ plug removed in step 2.
PROPANE
PROPANE LOW
GAS PRESSURE
INLET
(INSTALL MANOMETER
HERE FOR PROPANE
LOW PRESSURE TEST)
PROPANE
SSOV
SWITCH
1/8" NPT PLU G
NATURAL GAS
PROPANE
HIGH GAS
PRESSURE
SWITCH
LOW GAS
PRESSURE
SWITCH
1/8" NPT PLUG
(INSTALL MANOM ETER
HERE FOR NAT.GAS
LOW PRESSURE TEST)
1/8" NPT PLU
(INSTALL
MANOMETER HERE
FOR HIGH
PRESSURE TESTS)
NAT. GAS
HIGH GAS
PRESSURE
SWITCH
LEAK
DETECTION
BALL VALVE
NATURAL
GAS SSOV
1. Ensure that the Fuel Selector Switch (Figure
4-3) is set to the NATURAL GAS position.
NATURAL
GAS INLET
2. Remove the 1/8“ plug from the ball valve at
the natural gas low gas pressure switch
shown in Figure 6-1.
3. Install a 0 – 16 “ W.C. manometer or a W.C.
gauge where the 1/8" plug was removed.
Figure 6-1
Low & High Gas Pressure Testing
6-1
Page 52

SAFETY DEVICE TESTING
6.3 PROPANE LOW GAS PRESSURE
FAULT TES T
Refer to Figure 6-1 and ensure that the leak
detection ball valve located at the high gas
pressure switch is closed.
1. Ensure that the Fuel Selector Switch (Figure
4-3) is set to the PROPANE position.
2. Remove the 1/8“ plug from the ball valve at
the propane low gas pressure switch shown
in the upper-left portion of Figure 6-1.
3. Install a 0 – 16 “ W.C. manometer or a W.C.
gauge where the 1/8" plug was removed.
4. Slowly open the ball valve near the propane
low gas pressure switch.
5. Place the unit in Manual Mode and adjust
the valve position to 34%.
6. While the unit is firing, slowly
external
7. The unit should shut down and display a
LOW GAS PRESSURE fault message at
approximately 8.5” W.C. The FAULT indi-
cator should also start flashing.
8. Fully open the external manual gas shut-off
valve and press the CLEAR button on the
Control Box.
9. The fault message should clear and the
FAULT indicator should go off. The unit
should restart.
10. Upon test completion, close the ball valve
and remove the manometer. Replace the
1/8“ plug removed in step 2.
manual gas shut-off valve.
close the
6.4 NATURAL GAS HIGH GAS
PRESSURE FAULT TEST
To simulate a natural gas high gas pressure
fault, refer to Figure 6-1 and proceed as follows:
1. Ensure that the Fuel Selector Switch (Figure
4-3) is set to the NATURAL GAS position.
2. Remove the 1/8“ plug from the leak
detection ball valve shown in Figure 6-1.
3. Install a 0 – 16” W.C. manometer (or W.C.
gauge) where the 1/8” plug was removed.
4. Slowly open the leak detection ball valve
5. Start the unit in Manual mode at a valve
position of 34%.
6. Slowly increase the gas pressure using the
regulator adjustment screw on the natural
gas SSOV.
7. The unit should shut down and display a
HIGH GAS PRESSURE fault message
when the gas pressure exceeds 10.5” W.C.
The FAULT indicator should also start
flashing.
8. Reduce the gas pressure back to 7.3” W.C.
9. Press the CLEAR button on the Control Box
to clear the fault.
10. The fault message should clear and the
FAULT indicator should go off. The unit
should restart.
11. Upon test completion, close the leak detection ball valve and remove the manometer.
Replace the 1/8“ plug removed in step 2.
6.5 PROPANE HIGH GAS PRESSURE
FAULT TES T
To simulate a propane high gas pressure fault,
refer to Figure 6-1 and proceed as follows:
1. Ensure that the Fuel Selector Switch (Figure
4-3) is set to the PROPANE position.
2. Remove the 1/8“ plug from the leak
detection ball valve shown in the upper
portion of Figure 6-1.
3. Install a 0 – 16” W.C. manometer (or W.C.
gauge) where the 1/8” plug was removed.
4. Slowly open the leak detection ball valve.
5. Start the unit in Manual mode at a valve
position of 34%.
6. Slowly increase the propane gas pressure
using the regulator adjustment screw on the
propane SSOV.
7. The unit should shut down and display a
HIGH GAS PRESSURE fault message
when the gas pressure exceeds 3.5” W.C.
The FAULT indicator should also start
flashing.
8. Reduce the gas pressure back to 2.8” W.C.
9. Press the CLEAR button on the Control Box
to clear the fault.
10. The fault message should clear and the
FAULT indicator should go off. The unit
should restart.
6-2
Page 53

SAFETY DEVICE TESTING
11. Upon test completion, close the ball valve
and remove the manometer. Replace the
1/8“ plug removed in step 2.
6.6 LOW WATER LEVEL FAU LT TEST
To simulate a low water level fault:
1. Set the ON/OFF switch to the OFF position
2. Close the water shut-off valves in the supply
and return piping to the unit.
3. Slowly open the drain valve on the rear of
the unit. If necessary the unit’s relief valve
may be opened to aid in draining.
4. Continue draining the unit until a LOW
WATER LEVEL fault message is displayed
and the FAULT indicator flashes.
5. Place the unit in the Manual Mode and raise
the valve position above 30%.
6. Set the ON/OFF switch to the ON position.
The READY light should remain off and the
unit should not start
shut the unit off immediately and refer fault
to qualified service personnel.
. If the unit does start,
7. Close the drain and pressure relief valve
used in draining the unit.
8. Open the water shut-off valve in the return
piping to the unit.
9. Open the water supply shut-off valve to the
unit to refill.
10. After the shell is full, press the LOW
WATER LEVEL RESET button to reset the
low water cutoff.
11. Press the CLEAR button to reset the
FAULT LED and clear the displayed error
message.
12. Set the ON/OFF switch to the ON position.
The unit is now ready for operation.
6.7 WATER TEMPERATURE FAULT
TEST
A high water temperature fault is simulated by
adjusting the automatic over-temperature switch.
This switch is accessible from the front of the
unit as shown in Figure 6-2.
Figure 6-2
Temperature Limit Switch Setting
1. Start the unit in the normal operating mode.
Allow the unit to stabilize at its setpoint.
2. Lower the adjustable over-temperature
switch setting to match the displayed
OUTLET TEMPERATURE.
3. Once the adjustable over-temperature
switch setting is approximately at, or just
below, the actual outlet water temperature,
the unit should shut down. The FAULT
indicator should start flashing and a HIGH
6-3
Page 54

SAFETY DEVICE TESTING
WATER TEMP SWITCH OPEN fault
message should be displayed. It should not
be possible to restart the unit.
4. Reset the adjustable over-temperature
switch to its original setting.
5. The unit should start once the adjustable
temperature limit switch setting is above the
actual outlet water temperature.
6.8 INTERLOCK TESTS
The unit is equipped with two interlock circuits
called the Remote Interlock and Delayed
Interlock. Terminal connections for these circuits
are located in the I/O Box (Figure 2-9) and are
labeled REMOTE INTL’K IN and DELAYED
INTL’K IN. These circuits can shut down the
unit in the event that an interlock is opened.
These interlocks are shipped from the factory
jumpered (closed). However, each of these
interlocks may be utilized in the field as a remote
stop and start, an emergency cut-off, or to prove
that a device such as a pump, gas booster, or
louver is operational.
6.8.1 REMOTE INTERLOCK
1. Remove the cover from the I/O Box and
locate the REMOTE INTL’K IN terminals.
2. Start the unit in the Manual Mode and set
the valve position to 34%.
3. If there is a jumper across the REMOTE
INTL’K IN terminals, remove one side of the
jumper. If the interlock is being controlled by
an external device, either open the interlock
via the external device or disconnect one of
the wires leading to the external device.
4. The unit should shut down and display
INTERLOCK OPEN.
5. Once the interlock connection is
reconnected, the INTERLOCK OPEN
message should automatically clear and the
unit should restart.
6.8.2 DELAYED INTERLOCK
1. Remove the cover from the I/O Box and
locate the DELAYED INTL’K IN terminals.
2. Start the unit in the Manual Mode at a valve
position between 25% and 30%.
3. If there is a jumper across the DELAYED
INTL’K IN terminals, remove one side of the
jumper. If the interlock is connected to a
proving switch of an external device,
disconnect one of the wires leading to the
proving switch.
4. The unit should shut down and display a
DELAYED INTERLOCK OPEN fault
message. The FAULT LED should be
flashing.
5. Reconnect the wire or jumper removed in
step 3 to restore the interlock.
6. Press the CLEAR button to reset the fault.
7. The unit should start.
6.9 FLAME FAULT TES TS
Flame faults can occur during ignition or while
the unit is already running. To simulate each of
these fault conditions, proceed as follows:
1. Set the ON/OFF switch to the OFF position.
2. Place the unit in the Manual Mode and set
the valve position to 34%.
3. Close the manual gas shutoff valve located
between the Safety Shut-Off Valves
(SSOVs) and the Air/Fuel Valve (see Figure
6-3).
4. Set the ON/OFF switch to the ON position to
start the unit.
5. The unit should shut down after reaching the
Ignition cycle and display FLAME LOSS
DURING IGN.
6. Open the valve previously closed in step 3
and press the CLEAR button.
7. Restart the unit and allow it to prove flame.
8. Once flame is proven, close the manual gas
valve located between the SSOV and the
Air/Fuel Valve.
9. The unit should shut down and execute an
IGNITION RETRY cycle by performing the
following steps:
(a) The unit will execute a shutdown purge
cycle for a period of 15 seconds and
display WAIT FAULT PURGE.
(b) The unit will execute a 30 second re-
ignition delay and display WAIT RETRY
PAUSE.
(c) The unit will then execute a standard
ignition sequence and display WAIT
IGNITION RETRY.
6-4
Page 55

SAFETY DEVICE TESTING
10. Since the manual gas shutoff valve is still
closed, the unit will shut down and display
FLAME LOSS DURING IGNITION following
the IGNITION RETRY cycle.
11. Open the valve previously closed in step 8.
12. Press the CLEAR button. The unit should
restart and fire.
3. The unit should shut down and execute an
IGNITION RETRY cycle by performing the
following steps:
(g) The unit will execute a 30 second re-
ignition delay and display WAIT RETRY
PAUSE.
(h) The unit will then execute a standard
ignition sequence and display WAIT
IGNITION RETRY.
4. The unit should perform two IGNITION
RETRY cycles and then shut down on the
third successive ignition attempt. The unit
will display AIRFLOW FAULT DURING
PURGE.
5. Re-enable the blower output drive voltage
by performing the following steps:
(i) Press the MENU key until CONFIGUR-
ATION MENU is displayed.
(j) Press the ▲ arrow key until the ANA-
LOG OUTPUT function is displayed,
then press the CHANGE key.
(k) Press the ▲ arrow key until VALVE
POSITION 0-10V is displayed, then
press the ENTER key.
Figure 6-3
Manual Gas Shut-Off Valve Location
6.10 AIR FLOW FAULT TESTS
These tests check the operation of the Blower
Proof Switch and Blocked Inlet Switch shown in
Figure 6-3.
1. Disable the blower output drive voltage as
follows:
(d) Press the MENU key until CONFIGUR-
ATION MENU is displayed.
(e) Press the ▲ arrow key until the ANA-
LOG OUTPUT function is displayed,
then press the CHANGE key.
(f) Press the ▼ arrow key until OFF is
displayed, then press the ENTER key.
2. Start the unit in the Manual Mode at a valve
position of 34%.
6. Once the unit has proved flame, turn off the
blower by going to the Configuration Menu,
Analog Output menu item and select OFF.
7. The Blower Proof Switch will open and the
blower should stop. The unit should shut
down and display AIRFLOW FAULT
DURING RUN.
8. Go to the Configuration Menu, Analog
Output item and select Valve Position 0-10v.
9. Press the CLEAR button. The unit should
restart.
10. Next, check the Blocked Inlet Switch by first
noting the current position of the Iris Air
Damper and then closing the Damper to
position 8.
11. The unit should shut down and again display
AIRFLOW FAULT DURING RUN.
12. Return the Iris Air Damper to its previous
setting.
13. Press the CLEAR button. The unit should
restart.
6-5
Page 56

SAFETY DEVICE TESTING
6.11 SSOV PROOF OF CLOSURE SWITCH
This test can be performed when the unit is set
up to run on either natural gas or propane fuel.
Both the Natural Gas and Propane SSOVs
contain proof of closure switches which are
wired in series.
1. Set the unit’s ON/OFF switch to the OFF
position.
2. Place the unit in Manual Mode and set the
valve position to 34%.
3. Refer to Figure 6-1 and locate the Natural
Gas SSOV.
4. Remove the cover from the SSOV by
loosening the screw shown in Figure 6-4. Lift
off the cover to access the terminal wiring
connections.
5. Disconnect wire #148 from the SSOV to
“open” the proof of closure switch circuit.
6. The unit should fault and display SSOV
SWITCH OPEN.
7. Replace wire #148 and press the CLEAR
button.
8. Set the ON/OFF switch to ON to restart the
unit.
9. Remove the wire again when the unit
reaches the purge cycle and PURGING is
displayed.
10. The unit should shut down and display
SSOV FAULT DURING PURGE.
11. Replace wire #148 on the SSOV and press
the CLEAR button. The unit should restart.
Figure 6-4
SSOV Actuator Cover Location
6.12 PURGE SWITCH OPEN DURING PURGE
The Purge Switch (and Ignition Switch) is
located on the Air/Fuel Valve. To check the
switch, proceed as follows:
1. Set the unit’s ON/OFF switch to the OFF
position. Place the unit in manual mode and
set the valve position to 34%.
2. Remove the Air/Fuel Valve cover by rotating
the cover counterclockwise to unlock it and
then remove the cover (see Figure 6-5).
3. Remove one of the two wires (#171 or #172)
from the Purge Switch (Figure 6-6).
4. Initiate a unit start sequence.
5. The unit should begin it’s start sequence,
then shut down and display PRG SWITCH
OPEN DURING PURGE.
6. Replace the wire on the Purge Switch and
depress the CLEAR button. The unit should
restart.
6-6
Page 57

SAFETY DEVICE TESTING
6.13 IGNITION SWITCH OPEN DURING
IGNITION
The Ignition Switch (and the Purge Switch) is
located on the Air/Fuel Valve. To check the
switch, proceed as follows:
1. Set the unit’s ON/OFF switch to the OFF
position.
2. Place the unit in Manual Mode and set the
valve position to 34%.
3. Remove the Air/Fuel Valve cover (Figure
6-5) by rotating the cover counterclockwise
to unlock and lift up to remove.
AIR/FUEL VALVE COVER
(ROTATE CCW TO REMOVE)
Figure 6-5
Air/Fuel Valve Cover Location
4. Remove one of the two wires (#169 or #170)
from the Ignition Switch (Figure 6-6).
5. Initiate a unit start sequence.
6. The unit should begin it’s start sequence
and then shut down and display IGN
SWITCH OPEN DURING IGNITION.
7. Replace the wire on the Ignition Switch and
press the CLEAR button. The unit should
restart.
6.14 SAFETY PRESSURE RELIEF
VALVE TEST
Test the Safety Pressure Relief Valve in
accordance with ASME Boiler and Pressure
Vessel Code, Section VI.
9
6
1
0
7
1
1
7
2
1
7
1
Figure 6-6
Air/Fuel Valve Purge and Ignition Switch
Locations
6-7
Page 58

Page 59

MAINTENANCE
CHAPTER 7 MAINTENANCE
7.1 MAINTENANCE SCHEDULE
The unit requires regular routine maintena nce to
keep up efficiency and reliability. For best
operation and life of the unit, the following
routine maintenance procedures should be
performed in the tim e periods specified in Table
7-1. See Appendix I for a complete CSD-1
inspection check list.
In order to perform the maintenance tasks
specified in Table 7-1, the following
maintenance kits are available through your
local AERCO Sales Representative:
• Annual Maintenance Kit, Part No. 58025-01
• 24-Month Waterside/Fireside Inspection Kit,
Part No. 58025-06 (See NOTE below)
NOTE
The 24-Month W aterside/Fireside Inspection Kit also includes the items contained
in the Annual Maintenance Kit. Therefore,
only Kit Part No. 58025-06 is required
when performing the waterside/fireside
inspections.
Appendix K contains recommended spare parts
lists for maintenance of the boiler.
WARNING
TO AVOID PERSONAL INJURY,
PRIOR TO SERVICING ENSURE
THAT THE FOLLOWING GUIDELINES ARE STRICTLY OBSERVED:
• DISCONNECT THE AC SUPPLY BY
TURNING OFF THE SERVICE
SWITCH AND AC SUPPLY CIRCUIT
BREAKER.
• SHUT OFF THE GAS SUPPLY AT
THE MANUAL SHUT-OFF VALVE
PROVIDED WITH THE U NIT
• ALLOW THE UNIT TO COOL TO A
SAFE WATER TEMPERATURE TO
PREVENT BURNING OR SCALDING
Table 7-1 - Maintenance Schedule
PARAGRAPH ITEM 6 Mos. 12 Mos. 24 Mos.
7.2
7.3
7.4
7.5
Ignitor-Injector
(58023)
Flame Detector
(66006)
Combustion
Calibration
Testing of
Safety Devices
*Inspect Inspect Replace 15 mins.
*Inspect Inspect Replace 15 mins.
*Check Check 1 hr.
See CSD-1
Chart in
20 mins.
Appendix I
7.6 Burner Inspect 2 hrs.
7.7
* Only performed after initial 6 month period after initial startup.
Condensate
Drain Trap
*Inspect
Inspect &
Clean
30 mins.
Labor
Time
7-1
Page 60

MAINTENANCE
7.2 IGNITOR-INJECTOR
The ignitor-injector ( part no . 58023) is loc a ted on
the burner plate at the top of the boiler. In
addition to providing the ignition spark required
to light the burner, the ignitor-injector also
contains a gas injector tube which connects to
the staged ignition assem bly. Figure 7-1 shows
the complete burner ass embly removed f r om the
boiler and indicates the location of the ignitorinjector flame detector and other related
components.
The ignitor-injector may be hot, therefore, care
should be exercised to a void burns. It is easier
to remove the ignitor-injec tor from the unit after
the unit has cooled to room temperature.
AIR/FUEL
BLOWER
VALVE
4. Refer to the partial ex ploded view in Figure
7-2. Using a 7/16” open-end wrench,
disconnect the compression nut securing the
gas injector tube of the ignitor- injector to th e
elbow of the staged ignition assembly.
Disconnect the staged ignition assembly
from the ignitor-injector.
IGNITOR-
INJECTOR
INDEXING
WASHERS
(QTY = 0-3
AS REQ’D)
COMPRESSION
FITTING & ELBOW
BURNER
PLATE
STAGED
IGNITION
ASSEMBLY
FLAME
DETECTOR
FLAME
DETECTOR
GASKET
Figure 7-2
IGNITOR-
INJECTOR
BURNER
PLATE
BURNER
FLAME
DETECTOR
STAGED
IGNITION
ASSEMBLY
Figure 7-1
Benchmark 2 ly
.0LN Burner Assemb
(Shown Removed from Boiler)
T
o inspect/replace the Igniter:
1. Set the ON/OFF switch on the control pa nel,
to the OFF position. Disconnect AC power
from the unit
2. Remove the
unit.
3. Disco
nnect the cable from the ignitor-
injector.
side and top panels from the
Ignitor-Injector & Flame Detector
Mounting Details
IMPORTANT
Prior to removing the ignitor-injector,
note the position of the gas injector
tube relative to the burner plate and
blower. This is necessary to ensure
that the ignitor injector is reinstalled in
the proper orientation when it is
reconnected to the staged ignition
assembly.
5. Next, lo osen and remove the ignitor-inj ector
from the burner plate using a 1" open-end
wrench.
6. Check the ignitor-injector for evidence of
erosion or carbon build-up. If there is
evidence of substantial erosion or carbon
build-up, the ignitor-injector should be
replaced. If carbon buil d-up is pres ent, clean
the component using fine emery cloth.
Repeated carbon build-up is an indication
that the combustion settings of the unit
should be checked. Refer to Chapter 4 for
combustion calibration procedures.
7. Prior to reinstalling the ignitor-injector, a high
temperature, conductive anti-seize compound must
be applied to the threads.
7-2
Page 61

NOTE
If a replacement ignitor-injector (part no.
58023) is being installed, a compression
nut containing a built-in ferrule will be
included with the replacement part. If
needed, 3 indexing washers are also
included These washers may be needed
to properly position the gas injector tube
of the ignitor-injector within the 120 ° angle
shown in Figure 7-3.
IGNITOR-
INJECTOR
BURNER
PLATE
BLOWER
0
2
1
GAS
INJECTOR
TUBE
Figure 7-3
MAINTENANCE
3. Disconnect the lead wire from the flame
detector.
4. Remove the two (2) screws securing the
flame detector to the plate (Figur e 7-2). The
flame detector is secured to the b urner plate
with one (1) #10-32 scre w and o ne (1) #8-3 2
screw.
5. Remove the flam e detector and gask et from
the burner plate.
6. Thoroughl y inspect the detector. If eroded,
the detector should be replac ed. Otherwise
clean the detector with a fine emery cloth.
7. Reinstall the flame detector and flame
detector gasket.
8. Reconnect the flame detector lead wire.
9. Reinstall the side and top panels on the unit.
7.4 COMBUSTION CALIBRATION
Combustion settings must be checked at the
intervals shown in Table 7-1 as part of the
maintenance requirem ents. Refer to Chapter 4
for combustion calibration instructions.
Ignitor-Injector Orientation
8. Reinstall the ignitor-injector in the burner
plate. Torque to 15 ft-lbs. Do not over
tighten.
9. Connect the staged ignit ion assembly to the
gas injector tube of the ignitor-injector by
securing the compression nut to the elbow
of the staged ignition assembly.
10. Reconnect the ignitor-injector cable.
11. Reinstall the side and top panels on the unit.
7.3 FLAME DETECTOR
The flame detector (part no. 66006) is located
on the burner plate at the top of the unit (see
Figures 7-1 and 7-2). T he f lame detector may be
hot. Allow the unit to cool sufficiently before
removing the flame detector.
To inspect or replace the flame detector:
1. Set the ON/OFF switch on the control pa nel,
to the OFF position. Disconnect AC power
from the unit.
2. Remove the side and top panels from the
unit.
7.5 SAFETY DEVICE TESTING
Systematic and thorough tests of the operating
and safety devices should be performed to
ensure that they are operating as designed.
Certain code requirements, such as ASME
CSD-1, require that t hese tests be perform ed on
a scheduled basis. Test schedules must
conform to local jurisdictions. The results of the
tests should be recorded in a log book. See
Chapter 6-Safety Device Testing Procedures.
7.6 BURNER ASSEMBLY INSPECTION
The burner assembly (part no. 24176-3) is
located at the top of the unit's hea t exchanger.
The burner assembly may be hot. Therefore,
allow the unit to cool s uf f ic ientl y bef or e removing
the burner assembly. It should be n oted that the
complete burner assembly also includes the
blower and air/fuel valve in addition to the
Benchmark 2.0 Low NOx burner.
The following parts will be necessary for
reassembly after inspection :
Part No.
81101 Burner Gaskets (2)
81048 Flame Detector Gasket
81068 Blower Gasket
Description
7-3
Page 62

MAINTENANCE
To inspect or replace the burner assembly:
1. Set the ON/OFF switch on the con trol pa nel,
to the OFF position. Disconnect AC power
from the unit and turn off the gas supply.
2. Remove the side and top panels from the
unit to provide access to the burner
assembly. See Figure 7-4.
3. Disconnect the lead wire from the flame
detector installed on t he bu rner plat e (Figur e
7-4).
4. Remove the two (2) screws securing the
flame detector to the plate. The flame
detector is secured to th e burner plate with
one (1) #10-32 screw and one (1) #8-32
screw.
5. Remove the flam e detector and gask et from
the burner plate.
6. Disconnect the cable from the ignitorinjector.
IGNITOR-
INJECTOR
STAGED
IGNITION
ASSEMBLY
FLAME
DETECTOR
NUTS (8)
3/8-16
BURNER
PLATE
GROUNDING
SCREW
(10-32 x 1/2" LG.)
BLOWER
AIR/FUEL
VALVE
7. Using a 7/16” ope n-end wrench, disconnect
the compression nut securing the gas
injector tube of the ignitor-injector to the
elbow of the staged ignition assembly (see
Figure 7-2). Disconnect the staged ignition
assembly from the ignitor-injector.
IMPORTANT
Prior to removing the ignitor-injector,
note the position of the gas injector
tube relative to the burner plate and
blower. This is necessary to ensure
that the ignitor injector is reinstalled in
the proper orientation when it is
reconnected to the staged ignition
assembly.
8. Next, lo osen and remove the ignitor-inj ector
from the burner plate using a 1" open-end
wrench.
9. Disconnect the unit wiring harness
connectors from the air/fuel valve and
blower motor.
10. Disconnect the wire leads connected to the
blower proof switch and b locked inlet switch
(Figure 7-5).
11. Remove the 10-32 x 1/2" long grounding
screw from the burner p late. Refer to Figure
7-4.
12. Disconnect the gas train from the air/fuel
valve flange b y removing the four 1/2” bo lts
and nuts (Figure 7-4).
13. Disconnect the inlet air flex hose from the
air/fuel valve by loosening the hose clamp.
1/2” BOLTS & NUTS (4)
CONNECT AIR/FUEL VALVE
TO GAS TRAIN
Burner Disassembly Diagram
7-4
14. Rem ove the six (6) 1/4-20 hex nuts and flat
washers securing the blower to the burner
plate (Figure 7-5).
Figure 7-4
Page 63

STAGED
IGNITION
ASSEMBLY
IGNITOR-
INJECTOR
BURNER
GASKET
BURNER
GASKET
BLOWER
BLOWER
GASKET
BLOWER
PROOF
SWITCH
BLOCKED
INLET
SWITCH
HEX NUTS &
WASHERS (6)
BURNER
PLATE
FLAME
DETECTOR
BURNER
AIR/FUEL
VAVLE
MAINTENANCE
19. Beginning with the burner assembly
removed in step 17, reinstall all the
components in the reverse order that they
were removed. During reassembly, replace
the gaskets for the blower and flame
detector with new parts.
20. Make sure to align the ignitor-injector and
flame detector tapped holes in the burner
plate with the heat exchanger top head.
21. Check to ensure that the ground ing screw is
reinstalled.
7.7 CONDENSATE TRAP
The Benchmark 2.0LN Boiler contains a
condensate trap as shown in Figure 2-5. The
trap is located external to t he unit and attached
to the condensate drain port on the exhaust
manifold. This trap should be inspected and, if
necessary, cleaned to e nsure proper operation.
To inspect and cle an the trap, refer to Figur e 7-6
and proceed as follows:
Figure 7-5
Burner Assembly Exploded View
15. Remove the blower and air/fuel valve from
the burner plate by lifting straight up. Also,
remove the blower gasket which will be
replaced with a new gasket.
16. Remove the eight (8) 3/8-16 nuts from the
burner flange (Figure 7-4) using a 9/16”
wrench.
NOTE
The burner assembly is heavy, weighing
approximately 30 pounds.
17. Remove the burner assembly from burner
flange by pulling straight up.
18. Remove and replace the two (2) burner
gaskets.
NOTE
During reassembly, apply high-temperature, anti-seize lu bricant to the threads of
the ignitor-injector and grounding screw.
Also, ensure that the ignitor-injector is
properly positioned as shown in Figure
7-3. Torque the ignitor-injector to 15 ft-lbs.
1. Disconnect the condensate trap by
loosening the connecti ons between the trap
and the exhaust manifold drain.
2. Remove the connections on the inlet and
outlet sides of the condensate trap (Figure
7-6).
O-RING
FLOAT
ORIFICE
GASKET
3/4 NPT
PORT
OUTLET
COVER
THUMB
SCREWS
(4)
INLET
3/4 NPT
PORT
Figure 7-6
Condensate Trap
3. Loosen the four (4) thumbscrews securing
the cover on the condensate trap. Remove
the cover.
7-5
Page 64

MAINTENANCE
4. Remove the float from the condensate trap.
5. Remove the orifice gasket from the trap.
6. Thoroughly clean t he trap and gasket. Also
inspect the drain piping for blockage. If the
trap cannot be thoroughly cleaned, replace
the trap.
7. After the above item s have been inspected
and thoroughly cleaned, replace the orifice
gasket and float in the condensat e trap and
replace the trap cover.
8. Reassemble all piping and hose connections
to the condensate trap inlet and outlet.
Reconnect trap to exhaust manifold drain.
7.8 SHUTTING THE BOILER DOWN FOR
AN EXTENDED PERIOD OF TIME
If the boiler is to be taken out of s ervice for an
extended period of tim e (one year or more), the
following instructions must be followed.
7.9 PLACING THE BOILER BACK IN SERVICE AFTER A PROLONGED SHUTDOWN
After a prolonged shutdo wn (one year or more),
the following procedures must be followed:
1. Rev iew installation req uirements include d in
Chapter 2.
2. Inspect all piping connections to the unit.
3. Inspect exhaust vent, air duct (if applicable).
4. Perform initial startup per Chapter 4.
5. Perform safety device testing and scheduled
maintenance per Chapters 6 and 7.
1. Set ON/OFF s witch on the f ront panel to the
OFF position to shut down the boiler’s
operating controls.
2. Dis c onnect AC po wer fr om the unit.
3. Close the water supply and return valves to
isolate boiler.
4. Close external gas supply valve.
5. O pen relief valve to vent water pressure.
7-6
Page 65

Chapter 8- TROUBLESHOOTING GUIDE
8.1 INTRODUCTION
This troubleshooting guide is intended to aid
service/maintenance personnel in isolating the
cause of a fault in a Benchm ark 2.0 Boiler. The
troubleshooting procedures contained her ein are
presented in tabular form on the f ollowing pages.
These tables are comprised of three columns
labeled: Fault Indication, Probable Cause and
Corrective Action. The numbered items in the
Probable Cause and Corrective Ac tion columns
correspond to each other. For example,
Probable Cause No. 1 corresponds to Corrective
Action No. 1, etc.
NOTE:
The front panel of the C-More Control Box
contains an RS232 port which can be interfaced
to a laptop computer or other suitable device.
This RS232 communication feature permits
service personnel to view menu item s and data
logs which can be useful in isolating faults. Refer
to Chapter 9 of this manual for detailed RS232
communication set-up and procedures.
TROUBLESHOOTING
When a fault occurs in the Benchmark Boiler,
proceed as follows to isolate and correct the
fault:
1. Observe the fault m essages dis played in the
Control Box display.
2. Refer to the Fault Indication column in
Troubleshooting Table 8-1 which f ollows and
locate the Fault that best describes the
existing conditions.
3. Pr oceed to the Probable Cause column and
start with the first item (1) lis ted for the Fault
Indication.
4. Perform the c hecks and procedures listed in
the Corrective Action column for the first
Probable Cause candidate.
5. Continue check ing each additional Probable
Cause for the existing fault until the fault is
corrected.
6. Paragraph 8.2 and Table 8-2 contain
additional troubleshooting information which
may apply when no fault message is
displayed.
7. If the fault cannot be corrected using the
information provided in the Troubleshooting
Tables, contact your local AERCO
Representative.
8-1
Page 66

current drain that may trip thermal or current overload devices.
leading up to the combustion blower for signs of blockage.
blockage, clean or replace as necessary.
1. Check combustion blower for signs of excessive heat or high
2. Inspect the inlet to the combustion blower including any ductwork
3. Remove the Blower proof switch and inspect for signs of
TABLE 8-1. BOILER TROUBLESHOOTING
or current overload
1. Blower stopped running due to thermal
2. Blocked Blower inlet or inlet ductwork
3. Blocked Blower proof switch
combustion blower running. If there is an erratic resistance
4. Measure the Blower proof switch for continuity with the
4. Defective Blower proof switch
positions, the position on the C-More barograph should match
reading or the resistance reading is greater than zero ohms,
replace the switch.
blockage, clean or replace as necessary.
combustion blower running. If there is an erratic resistance
reading or the resistance reading is greater than zero ohms,
replace the switch.
AUX input in the I/O Box. Verify that the voltage conforms to the
values shown in the tabular listing provided in Appendix C.
conforms to the values shown in Appendix C.
Motor.
equates to a 100% open Air/Fuel Valve position.
Menu. Valve Position 0-10V should be selected.
5. Remove the blocked air inlet switch and inspect for signs of
6. Measure the blocked-air inlet switch for continuity with the
5. Blockage in blocked-air inlet switch
6. Defective blocked air inlet switch
7. Check the actual inlet air temperature and measure voltage at
7. Loose temperature sensor to AUX
8. Refer to CORRECTIVE ACTION 7 and verify that the voltage
connection in I/O Box
8. Defective temperature sensor
9. Check wire connection from I/O Box 0-10V signal to the Blower
9. Loose wire connection between the
0-10V signal from I/O box to the
Blower Motor input
10. Measure voltage at the I/O box 0-10V output. A voltage of 9.1V
10. Defective I/O box
11. Check the Analog Out option on the C-More Configuration
control box
11. Wrong 0-10V output selection on the
the valve position.
12. Check Air/Fuel Valve position at 0%, 50% and 100% valve
12. Defective Air-Fuel Valve
potentiometer
AIRFLOW FAULT
DURING IGNITION
FAULT INDICATION PROBABLE CAUSES TROUBLESHOOTING/CORRECTIVE ACTION
TROUBLESHOOTING
8-2
Page 67

CORRECTIVE ACTION from 3 to 12 for AIRFLOW
TABLE 8-1. BOILER TROUBLESHOOTING – Continued
1. Star t the unit. If the blower does not run check the blower solid
1. Blower not running or running too slow
state relay for input and output voltage. If the relay is okay, check
the blower.
continuity. Replace the switch if there is no continuity.
clean or replace as necessary.
leading up to the combustion blower for signs of blockage.
switch to ground. If 24VAC is not present refer to qualified
2. Start the unit. If the blower runs, check the airflow switch for
3. Remove the air flow switch and inspect for signs of blockage,
4. Inspect the inlet to the combustion blower including any ductwork
5. Measure for 24 VAC during start sequence from eac h side of the
service personnel.
6. See
FAULT DURING IGNITION
current draw that may trip thermal or current overload devices.
1. Check combustion blower for signs of excessive heat or high
2. Inspect the inlet to the combustion blower including any ductwork
leading up to the combustion blower for signs of blockage.
3. Remove the airflow switch and inspect for signs of blockage,
clean or replace as necessary.
blower running. If there is an erratic resistance reading or the
resistance reading is greater than zero ohms, replace the switch.
4. Measure the airflow switch for continuity with the combustion
5. Run unit to full fire. If the unit rumbles or runs rough, perform
combustion calibration.
PROBABLE CAUSES from 3 to 16 for AIRFLOW FAULT
DURING IGNITION applies for this fault
6.
for AIRFLOW FAULT DURING
IGNITION applies for this fault
5. No voltage to switch from control box.
PROBABLE CAUSES from 3 to 12
6.
1. Blower stopped running due to thermal
or current overload
2. Blocked Blower inlet or inlet ductwork
3. Blocked airflow switch
4. Defective airflow switch
5. Combustion oscillations
2. Defective Air Flow Switch
3. Blocked Air flow Switch
4. Blocked Blower inlet or inlet ductwork.
for AIRFLOW FAULT DURING
IGNITION applies for this fault
PROBABLE CAUSES from 3 to 16
6.
DURING PURGE
AIRFLOW FAULT
DURING RUN
AIRFLOW FAULT
FAULT INDICATION PROBABLE CAUSES TROUBLESHOOTING/CORRECTIVE ACTION
TROUBLESHOOTING
8-3
Page 68

TABLE 8-1. BOILER TROUBLESHOOTING – Continued
1. Check for a jumper properly installed across the delayed
1. Delayed Interlock Jumper not
interlock terminals in the I/O box.
installed or removed.
an end switch for a device such as a pump, louver, etc. is tied
2. If there are 2 external wires on these terminals, check to see if
interlocks is not closed
2. Device proving switch hooked to
these interlocks. Ensure that the device and or its end switch
Hook up if not installed.
If installed, check polarity.
Measure signal level.
are functional. (jumper may be temporarily installed to test
interlock)
1. Check I/O Box to ensure signal is hooked up.
Not yet installed.
1. Direct drive signal is not present:
Check continuity of wiring between source and boiler.
Wrong polarity.
Signal defective at source.
Broken or loose wiring.
2. Check signal at source to ensure it is isolated.
3. Check DIP switch on PMC board to ensure it is set correctly for
2. Signal is not isolated (floating).
3. Control Box signal type selection
the type of signal being sent. Check control signal type set in
Configuration Menu.
1. Inspect and install/retighten Burner Ground Screw.
switches not set for correct signal
type (voltage or current).
1. Burner Ground Screw not installed
or loose.
Replace if necessary.
2. Remove and inspect the flame detector for signs of wear.
2. Worn flame detector
ignitor outside the unit.
ignition transformer during the ignition cycle.
3. Close the internal gas valve in the boiler. Install and arc a spark
4. If there is no spark, check for 120VAC at the primary side to the
3. No spark from Spark Plug 4. Defective Ignition Transformer 5. Defective Ignition/Stepper (IGST)
5. If 120VAC is not present, the IGST Board in the Control Box
may be defective. Refer fault to qualified service personnel.
6. While externally arcing the spark ignitor, observe the
Board
6. Defective SSOV
open/close indicator in the Safety Shut-Off Valve to ensure it is
opening. If the valve does not open, check for 120VAC at the
valves input terminals. If 120VAC is not present, the IGST
board in the Control Box may be defective. Refer fault to
qualified service personnel.
7. Check position of staged ignition manual ball valve (Fig. 8-1)
ignition line.
7. Closed manual valve in staged
DELAYED
DIRECT DRIVE
INTERLOCK OPEN
FAULT INDICATION PROBABLE CAUSES TROUBLESHOOTING/CORRECTIVE ACTION
TROUBLESHOOTING
SIGNAL FAULT
DURING IGN
FLAME LOSS
8-4
Page 69

maximum.
to 7.2” W.C. (for natural gas) or 2.7" W.C.(for propane), the
SSOV Actuator gas pressure adjustment mechanism may be
defective. [see para. 4.3, step 11 (natural gas), or 4.4, step 12
is opening.
8. When boiler goes to ignition, listen to solenoid valve to ensure it
9. Remove and inspect staged ignition piece for blockage. Remove the burner and inspect for any carbon or debris. Clean
and reinstall
cracked ceramic. Replace if necessary.
1. Remove and inspect the Flame Detector for signs of wear or
2. Check combustion calibration. Adjust as necessary.
and reinstall.
3. Remove the burner and inspect for any carbon or debris. Clean
4. Remove blockage in condensate drain.
replace Ignition/Stepper (IGST) Board.
1. Check to ensure gas pressure at inlet of SSOV is 2 psig
1. Pres s CLEAR button and restart the unit. If the fault persists,
2. Defective relay. Replace IGST Board.
2. If gas supply pressure downstream of SSOV cannot be lowered,
(propane)],
TABLE 8-1. BOILER TROUBLESHOOTING – Continued
valve.
(continued) 8. Defective staged ignition solenoid
9. Clogged staged ignition piece. 10. Carbon or other debris on burner
ceramic.
1. Worn Flame Detector or cracked
FLAME LOSS
DURING RUN
2. Poor combustion calibration.
3. Debris on burner. 4. Blocked condensate drain.
Ignition/Stepper board failed to
activate when commanded
1. The Heat Demand Relays on the
FAILURE
HEAT DEMAND
Demand
1. Incorrect supply gas pressure. 2. Defective gas pressure adjustment
2. Relay is activated when not in
HIGH GAS
in SSOV Actuator.
PRESSURE
FAULT INDICATION PROBABLE CAUSES TROUBLESHOOTING/CORRECTIVE ACTION
TROUBLESHOOTING
8-5
Page 70

TABLE 8-1. BOILER TROUBLESHOOTING – Continued
measure continuity across the common and normally closed
3. Remove the leads from the high gas pressure switch and
terminals with the unit not firing. Replace the switch if it does not
show continuity.
4. See Figure 8-1. Ensure that the gas pressure snubber is installed
4. Gas pressure snubber not installed. 5. Fluctuating supply gas pressure.
at the high gas pressure switch.
sudden changes (see Fig. 8-1).
temperature setting.
Appendix. If the settings have been changed, record the current
readings then reset them to the default values.
resistance of Shell sensor and BTU sensor at a known water
temperature.
5. Measure gas pressure upstream of SSOV and monitor for
1. Test the temperature switch to insure it trips at its actual water
2. Check PID settings against Menu Default settings in the
1. Faulty Water temperature switch. 2. Incorrect PID settings.
3. Using the resistance charts in the Appendix C, Measure the
3. Faulty shell temperature sensor.
Ensure that the temperature switch is set higher than the unit’s
setpoint.
necessary.
4. If unit is in Manual Mode switch to Auto Mode.
4. Unit in Manual mode
5. Check setpoint of unit and setpoint of Temperature Switch;
5. Unit setpoint is greater than Over
6. Check the BMS for changes to PID default values, correct as
Temperature Switch setpoint.
6. Boiler Management System PID or
other settings not correctly setup.
other than BMS or pumps are individually controlled by boiler,
check to see if there are flow switches interlocked to the BMS or
boiler.
changes to ensure that the rate of flow change is not faster than
what the boilers can respond to.
7. If system pump is controlled by Energy Management System
disable boiler(s) in event that system
7. No interlock to boiler or BMS to
pumps have failed.
8. If the system is a variable flow system, monitor system flow
8. System flow rate changes are
occurring faster than boilers can
respond.
1. See HIGH WATER TEMPERATURE SWITCH OPEN. 2. Check Temp HI Limit setting.
1. See HIGH WATER TEMPERATURE
SWITCH OPEN.
2. Temp HI Limit setting is too low.
1. Press CLEAR button and restart unit. If fault persists, contact
1. Communication fault has occurred
qualified Service Personnel.
between the PMC board and
Ignition/Stepper (IGST) board
(continued) 3. Defective High Gas Pressure Switch
SWITCH OPEN
FAULT INDICATION PROBABLE CAUSES TROUBLESHOOTING/CORRECTIVE ACTION
TROUBLESHOOTING
HIGH WATER TEMP
HIGH WATER
TEMPERATURE
IGN BOARD
COMM FAULT
8-6
Page 71

1. Start the unit. The Air/Fuel Valve should rotate to the purge
(open) position. If the valve does not rotate at all or does not
(open) position, then back to ignition position (towards closed)
during the ignition cycle. If the valve does not rotate back to the
ignition position, check the Air/Fuel Valve calibration. If
calibration is okay, the problem m ay be in the Air/Fuel Valve or
the Control Box. Refer fault to qualified service personnel.
ignition position switch for continuity between the N.O. and COM
terminals when in contact with the cam.
rotate fully open, check the Air/Fuel Valve calibration. If
calibration is okay, the problem may be in the Air-Fuel Valve or
the Control Box. Refer to qualified service personnel
switch for continuity between the N.O. and COM terminals. If the
switch shows continuity when not in contact with the cam replace
the switch.
numbers on the normally open terminals). If the switch is wired
correctly, replace the switch
steady ON, replace Power Supply Board.
every second. If not, replace IGST Board
2. . If the Air/Fuel Valve does rotate to purge, check the ignition
3. Check to ensure that the switch is wired correctly (correct wire
4. Check DS1 & DS2 LEDs on Power Supply Board. If they are not
1. Start the unit. The Air/Fuel Valve should rotate to the purge
5. Check “Heartbeat” LED DS1 and verify it is blinking ON & OFF
2. If the Air/Fuel Valve does rotate to the ignition position, check the
steady ON, replace Power Supply Board.
3. Check DS1 & DS2 LEDs on Power Supply Board. If they are not
4. Check “Heartbeat” LED DS1 and verify it is blinking ON & OFF
terminals in the I/O box
Energy Management system to see if they have the units
disabled (a jumper may be temporarily installed to see if the
interlock circuit is functioning).
every second. If not, replace IGST Board.
1. Check for a jumper properly installed across the interlock
2. If there are two external wires on these terminals check any
circuit is closing and that the device is operational.
3. Check that proving switch for any device hooked to the interlock
TROUBLESHOOTING
TABLE 8-1. BOILER TROUBLESHOOTING – Continued
FAULT INDICATION PROBABLE CAUSES TROUBLESHOOTING/CORRECTIVE ACTION
1. Air/Fuel Valve not rotating
DURING PURGE
IGN SWTCH CLOSED
2. Defective or shorted switch
fuse
3. Switch wired incorrectly
4. Defective Power Supply Board or
5. Defective IGST Board
position.
1. Air/Fuel Valve not rotating to ignition
DURING IGNITION
IGN SWTCH OPEN
fuse
2. Defective ignition switch
3. Defective Power Supply Board or
4. Defective IGST Board
removed
not have boiler enabled.
interlocks is not closed.
1. Interlock jumper not installed or
2. Energy Management System does
OPEN
INTERLOCK
3. Device proving switch hooked to
8-7
Page 72

reversed
1. Check hot and neutral in AC Power Box to ensure they are not
box transformer wiring diagram to ensure it is wired correctly
the unit firing. Refer to paragraph 2.7.1 to ensure that the gas
pressure is correct for the type of fuel and gas train being used.
pressure is 8.5” W.C. or higher, insure that continuity exists
across the switch terminals indicating the switch is closed. If the
pressure is 8.5” W.C. or higher and continuity does not exist
(switch open), replace the defective switch.
2. Check transformer wiring, in AC Power Box, against the power
1. Measure gas pressure upstream of the supply gas regulator with
2. Measure gas pressure at the low gas pressure switch. If the
1. Check system for sufficient water level.
2. Test water level circuitry using the Control Box front panel LOW
WATER TEST and RESET buttons. Replace water level
circuitry if it does not respond.
3. Check continuity of probe end to the shell, change probe if there
Service Personnel.
(open) position, then back to ignition position (towards closed)
during the ignition cycle. If the valve does not rotate back to the
ignition position, check the Air/Fuel Valve calibration. If
calibration is okay, the problem m ay be in the Air/Fuel Valve or
the Control Box. Refer fault to qualified service personnel.
purge switch for continuity between the N.O. and COM terminals.
If the switch shows c ontinuity when not in contact with the cam,
check to ensure that the switch is wired correctly (correct wire
is no continuity.
1. Check network connections. If fault persists, contact qualified
1. Start the unit. The Air/Fuel Valve should rotate to the purge
2. If the Air/Fuel Valve does rotate to the ignition position, check the
numbers on the normally open terminals).
3. If the switch is wired correctly, replace the switch.
4. Check DS1 & DS2 LEDs on Power Supply Board. If they are not
steady ON, replace Power Supply Board.
every second. If not, replace IGST Board.
5. Chec k “Heartbeat” LED DS1 and verify it is blinking ON & OFF
TROUBLESHOOTING
TABLE 8-1. BOILER TROUBLESHOOTING – Continued
FAULT INDICATION PROBABLE CAUSES TROUBLESHOOTING/CORRECTIVE ACTION
Power Box.
wiring.
1. Line and Neutral switched in AC
2. Incorrect power supply transformer
LINE VOLTAGE
OUT OF PHASE
1. Incorrect supply gas pressure.
LOW GAS
2. Defective Low Pressure Gas Switch
PRESSURE
did not rotate to ignition position
1. Insufficient water level in system
LEVEL
LOW WATER
2. Defective water level circuitry.
3. Defective water level probe.
Modbus network
1. A/F Valve rotated open to purge and
1. Boiler not seeing information from
FAULT
MODBUS COMM
DURING IGNITION
PRG SWTCH CLOSED
2. Defective or shorted switch.
fuse
3. Switch wired incorrectly.
4. Defective Power Supply Board or
5. Defective IGST Board
8-8
Page 73

continuity when closing. Replace switch if continuity does not
exist.
24VAC is not present, refer fault to qualified service personnel.
numbers on the normally open terminals).
1. If the air-fuel valve does rotate, check the purge switch for
2. Measur e for 24 VAC from each side of the s witch to ground. If
3. Check to ensure that the switch is wired correctly (correct wire
4. Check DS1 & DS2 LEDs on Power Supply Board. If they are not
specification.
steady ON, replace Power Supply Board.
every second. If not, replace IGST Board.
1. Inspect Outdoor Temperature sensor for loose or broken wiring.
5. Chec k “Heartbeat” LED DS1 and verify it is blinking ON & OFF
2. Check resistance of sensor to determine if it is within
3. Ensure that the correct sensor is installed.
Hook up if not installed.
1. Check I/O Box to ensure signal is hooked up.
If installed, check polarity.
Measure signal level.
Check continuity of wiring between source and boiler.
2. Check signal at source to ensure it is isolated. 3. Check DIP switch on PMC board to ensure it is set correctly for
the type of signal being sent. Check control signal type set in
Configuration Menu.
(SSOV) and ensure that the SSOV is fully closed. If not fully
1. Check open/close indicator window of Safety Shut-Off Valve
closed, replace the valve and or actuator. Close gas shut-off valve downstream of SSOV. Install a
manometer or gauge in a gas test port between the SSOV and
the gas shut off valve. If a gas pressure reading is observed
replace the SSOV valve and or actuator.
2. Replace Flame Detector.
TROUBLESHOOTING
TABLE 8-1. BOILER TROUBLESHOOTING – Continued
1. Defective purge switch.
DURING PURGE
PRG SWTCH OPEN
FAULT INDICATION PROBABLE CAUSES TROUBLESHOOTING/CORRECTIVE ACTION
2. No voltage present at switch. 3. Switch wired incorrectly.
fuse
1. Loose or broken wiring.
SENSOR FAULT
OUTDOOR TEMP
2. Defective Sensor. 3. Incorrect Sensor.
4. Defective Power Supply Board or
5. Defective IGST Board
1. Remote setpoint signal not present:
REMOTE SETPT
Not yet installed.
Wrong polarity.
SIGNAL FAULT
Signal defective at source.
Broken or loose wiring.
20 mA.
2. Signal is not isolated (floating) if 4 to
3. Control Box signal type selection
switches not set for correct signal
type (voltage or current).
1. SSOV not fully closed.
FLAME
RESIDUAL
2. Defective Flame Detector.
8-9
Page 74

TABLE 8-1. BOILER TROUBLESHOOTING – Continued
ensure stepper motor rotates properly between the 0% (fully
closed) and 100% (fully open) positions. Verify that the VALVE
POSITION bargraph and the dial on the Air/Fuel Valve track
each other to indicate proper operation. If operation is not
correct, perform the Stepper Feedback Calibration (GF-112,
persists, replace actuator.
Ignition/Stepper (IGST) Board.
and therefore there is a voltage measured between the two.
Normally this measurement should be near zero or no more than
a few millivolts.
1. Replace or adjust microswitch in SSOV actuator. If fault
1. Press CLEAR button and restart unit. If fault persists, replace
2. The Neutral and Earth Ground are not connected at the source
during run.
1. SSOV switch closed for 15 seconds
See SSOV SWITCH OPEN
1. SSOV relay failed on board. 2. Floating Neutral.
3. Check SSOV power wiring.
3. Hot and Neutral reversed at SSOV.
indicator on the Valve actuator and ensure that the valve is fully
1. Observe operation of the Safety Shut-Off Valve (SSOV) through
of gas valve
1. Actuator not allowing for full closure
and not partially closing.
2. If the SSOV never closes, it may be powered continuously. Close
2. SSOV powered when it should not be 3. Defective Switch or Actuator
the gas supply and remove power from the unit. Refer fault to
qualified service personnel.
3. Remove the electrical cover from the SSOV and check switch
continuity. If the switch does not show continuity with the gas
valve closed, either adjust or replace the switch or actuator.
1. Refer to GF-112 and perform Stepper Test (para. 6.3.5) to
4. Ensure that the SSOV Proof of Closure switch is correctly wired.
1. Air/Fuel Valve out of calibration.
4. Incorrectly wired switch.
para. 6.2.1).
and the wiring harness.
steady ON, replace Power Supply Board.
2. Check that the Air/Fuel Valve is connected to the Control Box.
3. .Inspect for loose connections between the Air/Fuel Valve motor
4. Replace stepper motor.
5. Check DS1 & DS2 LEDs on Power Supply Board. If they are not
stepper motor.
motor.
fuse
2. Air/Fuel Valve unplugged.
3. Loose wiring connection to the
4. Defective Air/Fuel Valve stepper
5. Defective Power Supply Board or
every second. If not, replace IGST Board.
6. Check “Heartbeat” LED DS1 and verify it is blinking ON & OFF
6. Defective IGST Board
SSOV
SWITCH OPEN
SSOV FAULT
SSOV FAULT
DURING RUN
DURING PURGE
FAILURE
SSOV RELAY
FAULT INDICATION PROBABLE CAUSES TROUBLESHOOTING/CORRECTIVE ACTION
TROUBLESHOOTING
FAILURE
STEPPER MOTOR
8-10
Page 75

being used is
downstream of the SSOV for the fuel source being used (natural
gas or propane) is open. Also, ensure that the 1/4” Ball Valve
downstream of the SSOV for the fuel source not
1. Refer to Appendix K and ensure that the 1/4” Ball Valve
being used.
closed. (See Figures 8-1, K-2 or K-3).
the fuel source that is not
damaged.
(Fig. 8-1). Start the unit and listen for a “clicking” sound that the
Staged Ignition Solenoid makes during Ignition Trial. If “clicking”
sound is not heard after 2 or 3 attempts, replace the Staged
Ignition Solenoid.
Building Supply Regulator.
SSOV Actuator shown in Figure 8-3. (For IRI Gas Trains, the
Damping Orifice is installed in the downstream SSOV Actuator).
Rev. E or higher.
2. Refer to Appendix K and close the Staged Ignition Ball Valve for
3. Remove and inspect Gas Injector to ensure it is not clogged or
4. Close the 2” and the 1/4” Ball Valves downstream of the SSOV
1. Stabilize gas pressure going into unit. If necessary, troubleshoot
2. Check to ensure that the Damping Orifice is installed in the
1. Check to ensure that the IGST and Power Supply Boards are
for the fuel source being used.
open.
(Figure 8-2).
2. Both Staged Ignition Ball Valves are
(Figure 8-2)
3. Clogged/damaged Gas Injector
4. Defective Staged Ignition Solenoid
fluctuating.
2. Damping Orifice not installed.
Control Box are outdated.
1. IGST and Power Supply Boards in
TABLE 8-2. BOILER TROUBLESHOOTING WITH NO FAULT MESSAGE DISPLAYED
Hard Light-Off 1. Staged Ignition Ball Valve is closed
OBSERVED INCIDENT PROBABLE CAUSES TROUBLESHOOTING/CORRECTIVE ACTION
TROUBLESHOOTING
8.2 ADDITIONAL FAULTS WITHOUT SPECIFIC FAULT MESSAGES
Refer to Table 8-2 to troubleshoot faults which may occur without a specific fault message being displayed.
Fluctuating Gas Pressure 1. Gas pressure going into unit is
Valve Position
Air/Fuel Valve “hunting” at 80%
8-11
Page 76

STAGED
T
IGNITION
ASSEMBLY
ORIFICE
DAMPING
NAT. GAS HIGH GAS
PROPANE HIGH GAS
PROPANE PRESSURE
REGULATOR FEEDBACK LINE
PRESSURE SWITCH
PRESSURE SWITCH
IGNITOR-
PLATE
BURNER
INJECTOR
TO
VALVE
AIR/FUEL
SNUBBERS
BURNER
NAT. GAS
Figure 8-2
PRESSURE
REGULATOR
NAT. GAS
FEEDBACK
LINE
Staged Ignition Solenoid Location
LOW GAS
PRESSURE
SWITCH
Figure 8-3
PRESSURE ADJUSTMEN
SSOV ACTUATOR WITH GAS
Damping Orifice Location
NAT. GAS SSOV
WITH REGULATOR
Figure 8-1
PROPANE SSOV
WITH REGULATOR
INLET
PROPANE
LOW GAS
PROPANE
PRESSURE
SWITCH
NATURAL
GAS INLET
High Pressure Gas Switch & Snubber Locat i ons
8-12
TROUBLESHOOTING
Page 77

CHAPTER 9 RS232 COMMUNICATION
9.1 INTRODUCTION
The RS232 port on the fron t panel of the C-More
Control Box (Figure 3-1) c an be interfaced to a
laptop computer or other suitable terminal using
a RS232 adapter cable. RS232 communication
can be accomplished using any “Dumb
Terminal” emulation, such as “Hyper Terminal”
which is included with Microsoft Windows. The
RS232 communication feature permits viewing
or changing of Control Panel menu optio ns and
also provides ac ces s to dat a lo gs s ho w ing E ven t
Time Line, Fault and Sensor log displays.
9.2 RS232 COMMUNICATION SETUP
Regardless of the terminal emulation utilized,
the following guidelines must be adhered to
when setting up the RS232 communication link:
1. Baud Rate – The baud rates which can be
used with the C-More Control Panel are:
2400
4800
9600 (Default)
19.2K
1. Data Form at – The program must be set for :
8 data bits, 1 stop bit, no parity and either
Xon/Xoff or No flow control.
9.3 MENU PROCESSING UTILIZING
RS232 COMMUNICATION
Viewing data logs and viewing or changing
Control Panel menu options using RS232
communication is accomplished as follows:
RS232 COMMUNICATION
M = Display next Menu
D = Display menu items
N = Display next menu items
Cxx = Change item xx
F = Fault log display
S = Sensor log display
T = Time line displa y
L = Log off
NOTE:
The Level 1 password (159) must be
entered to change options in the Setup,
Configuration and Tuning Menus. The
Level 2 password (6817) must be entered
to view or change options in the
Calibration and Diagnostics Menus.
With the exception of the password entry,
all other keyboard entries can be made
using either upper or lower case.
5. To view the availabl e menus in the top-do wn
sequence shown in Figure 3-2, enter M
<Rtn>. The Menu title and first 10 options
will be displayed.
6. When viewing menus containing more than
10 options, enter N <Rtn> to display the
remaining options.
7. Shortcut k e ys are a lso available to go d irec tly
to a specific menu. These shortcut keys are:
m0 Default (Operating) Menu
m1 Setup M enu
m2 Configuration Menu
m3 Tuning Menu
m4 Calibration Menu
m5 Diagnostic Menu
1. Start the emulator software program and
ensure that the specif ied baud rat e and data
formats have been entered.
2. Press the Enter key on the laptop. An
asterisk (*) prompt should appear.
3. At the prompt, enter the valid RS232
password (jaguar) in lower case letters and
press Enter.
4. “Welcom e to Aerco” will appear in the laptop
or “dumb terminal” display with a listing of
the following available entry cho ices :
8. To change a value or sett ing for a displa yed
menu option, proceed as follows:
(a) Enter C, followed by the number to the
right of the displayed option to be
changed, and then press <Rtn>.
(b) Enter the desired value or s etting f or the
option and press <Rtn>. Refer to
Chapter 3, Tables 3-2 through 3-5 for
allowable entry ranges and settings for
the Operating, Setup, Conf iguration and
Tuning Menus. (The Calibration and
Diagnostic Menus should only be used
by Factory-Trained service personnel).
9-1
Page 78

RS232 COMMUNICATION
(c) Menu changes will be stored in non-
volatile memory.
9. To redisplay the menu and view the option
which was just changed in step 5, enter D
and press <Rtn>.
10. T o display the Fault (F) Log, Se nsor (S) Log
or Time (T) Line Log, press F, S or T
followed by <Rtn>. Refer to paragr a ph 9.4 f or
descriptions and samples of these data logs.
11. To log off and terminate the RS232 communication link, press L followed by <Rtn>.
9.4 DATA LOGGING
During operation, the C-More Control Panel
continuously monitors and logs data associated
with operational events, faults and sensor
readings associated with the boiler or water
heater system. Descriptions of these data logs
are provided in the following paragraphs. The
basic procedure f or accessing each data log is
described in paragraph 9.3, step 7.
9.4.1 Fault Log
9.4.2 Operation Time Log
The Operation Time Log consists of a string of
ASCII records stored in non-volatile memory
within the C-More Control Panel. Events such
as power-up, ignition and turn-off are time
stamped. Data logged while the unit is running
are run-length encoded. Data is logged or the
run-length incremented every 30 seconds. For a
new run record to be logged, the fire rate or
flame strength must change by more than 5%,
or the run mode mus t change. At steady-state,
the run-length is allowed to reach a max imum of
30 minutes before the record is logged. This
means that no more than 3 0 minutes of data can
be lost if the unit loses po wer. Table 9-2 shows
a sample Operation Time Log for a boiler:
The Operation T ime Log can onl y be accessed
through the RS232 interface using a laptop or
other terminal device. Ten operation time
records are displayed for each T command
entry. The operation time log can be cleared
ONLY by factory authorize d personnel usin g the
Clear Log option in the Factory menu.
The C-More Control Pane l logs th e last 20 f aults
(0 – 19) starting with th e most recent (#0). T hey
can be viewed in the front panel display or via
the RS232 port. The Fault Log cannot be
cleared. If the Fault Log already contains 10
faults, the earliest fault is overwritten when a
new fault occurs. A sam ple Fault Log display is
shown in Table 9-1.
NOTE:
The Operation Time (T) Log can store
thousands of records. Therefore, to view
the most recently logged re cord, enter “T”
followed by 0 (zero) and press Enter
(i.e. T0 <Enter>). T o view earlier records
in reverse chronological order, enter T
and press Enter. To go ba ck 200 or 1000
records, enter T200 or T1000, etc. and
press Enter.
NOTE:
The Sensor (S) Log c an store up to 1 200
records. Therefore, to view the most
recently logged re cord, enter “S” foll owed
by 0 (zero) and then press Enter (i.e. S0
<Enter>). To view earlier records in
reverse chronological order, enter S and
press Enter. To go back 200 or 700
records, enter S200 or S700, etc. and
press Enter.
9.4.3 Sensor Log
The sensor values c an be logged at a different
rate if needed b y setting th e Sensor L og Inter val
in the Diagnostics Menu. The log interval can
vary from once ever y minute to once every day.
Table 9-3 shows a sample Sensor Log ever y 5
minutes for a boiler running in Constant Setp oint
mode.
9-2
Page 79

RS232 COMMUNICATION
Table 9-1. Sample Fault Log Display
No. Fault Message Cycle Date Time
0 Direct Drive Signal Fault 609 1/10/02 8:42am
1 Low Gas Pressure 366 7/04/01 5:29pm
2 Loss of Power 0 1/01/01 11:50am
Table 9-2. Sample Operation Time Log Display
Status Fire Rate Flame Run Length Date Time
Off, Direct Drive 0 0 8 1/15/02 2:35pm
Run, Direct Drive 38 100 34 1/15/02 2:27pm
Run, Direct Drive 31 100 30 1/15/02 1:53am
Run, Direct Drive 35 100 2 1/15/02 1:23pm
Run, Direct Drive 29 100 0 1/15/02 1:21pm
Ignition 0 0 0 1/15/02 1:20pm
Off, Switch 0 0 35 1/15/02 12:30pm
Run, Manual 40 100 0 1/15/02 11:55am
Ignition 0 0 0 1/15/02 11:55am
Power-up 0 0 0 1/15/02 11:50am
Table 9-3. Sample Sensor Log Display
Setpt Outlet Outdr FFWD Aux Inlet Exhst CO O2 Flow Date Time
130 181 OPEN OPEN OPEN OPEN OPEN 0 .0 0 1/15/02 5:51pm
130
130 180 OPEN OPEN OPEN OPEN OPEN 0 .0 0 1/15/02 5:41pm
130 179 OPEN OPEN OPEN OPEN OPEN 0 .0 0 1/15/02 5:36pm
130 180 OPEN OPEN OPEN OPEN OPEN 0 .0 0 1/15/02 5:31pm
130 180 OPEN OPEN OPEN OPEN OPEN 0 .0 0 1/15/02 5:26pm
130 180 OPEN OPEN OPEN OPEN OPEN 0 .0 0 1/15/02 5:21pm
130 180 OPEN OPEN OPEN OPEN OPEN 0 .0 0 1/15/02 5:16pm
130 179 OPEN OPEN OPEN OPEN OPEN 0 .0 0 1/15/02 5:11pm
130 180 OPEN OPEN OPEN OPEN OPEN 0 .0 0 1/15/02 5:06pm
180 OPEN OPEN OPEN OPEN OPEN 0 .0 0 1/15/02 5:46pm
9-3
Page 80

Page 81

APPENDIX A
APPENDIX A - BOILER MENU ITEM DESCRIPTIONS
MENU LEVEL & OPTION DESCRIPTION
OPERATING MENU
Active Setpoint This is the setpoint temperature to which the
control is set when operating in the Constant
Setpoint, Remote Setpoint or Outdoor Reset
Mode. When in the Constant Setpoint Mode, this
value is equal to the Internal Setpoint setting in the
Configuration Menu. When in the Remote
Setpoint Mode, this value is the setpoint equivalent
to the remote analog signal supplied to the unit.
When in the Outdoor Reset Mode, this is the
derived value from the charts in Appendix D.
Air Temp Air Temp is the air temperature at the input to the
Air/Fuel Valve. This reading is one of the
parameters used to control the Blower Motor
speed.
Outdoor Temp Displayed only if outdoor sensor is installed and
enabled.
Valve Position In Desired input valve position. This would normally
be the same as the fire valve position shown on
the bargraph (valve position out) when the boiler is
operating.
Flame Strength Displays flame strength from 0% to 100%.
Run Cycles Displays the total number of run cycles from 0 to
999,999.
Run Hours Displays total run time of unit in hours from 0 to
9,999,999.
Fault Log Displays information on the last 20 faults.
A-1
Page 82

APPENDIX A
APPENDIX A - BOILER MENU ITEM DESCRIPTIONS - CONTINUED
MENU LEVEL & OPTION DESCRIPTION
SETUP MENU
Password Allows password to be entered.
Language English only
Time Displays time from 12:00 am to 11:59 pm.
Date Displays dates from 01/01/00 to 12/31/99
Unit of Temp Permits selection of temperature displays in degrees
Comm Address For RS-485 communications (0 to 127). Default
Baud Rate Allows communications Baud Rate to be set (2400
Software Version Identifies the current software version of the control
Once the valid password (159) is entered, options in
the Setup, Configuration and Tuning Menus can be
modified.
Fahrenheit (°F) or degrees Celsius (°C). Default is
°F.
address is 0. RS-232 should have its own
(programmable) password.
to 19.2K). Default is 9600.
box (Ver 0.0 to Ver 9.9).
CONFIGURATION MENU
Internal Setpoint Allows internal setpoint to be set . Default is 130°F.
Unit Type Allows selection of KC Boiler, KC Boiler LN, BMK
Unit Size Sets unit size from 0.5 to 6.0 MBTUs. Default is 2.0
Fuel Type Allows selection of Natural Gas or Propane. Default
Boiler Mode It allows selection of: Constant Setpoint, Remote
Remote Signal Used to set the type of external signal which will be
Bldg Ref Temp
Boiler, BMK Boiler LN, BMK Boiler Dual, KC Water
Heater, KC Water Heater LN, Water Heater 2010
MBTU.
is Natural Gas.
Setpoint, Direct Drive, Combination, or Outdoor
Reset Mode. Default is Constant Setpoint Mode.
used when operating in the Remote Setpoint, Direct
Drive or Combination Mode. The factory default is
4-20 mA/1-5V.
Allows the building reference temperature to be set
when operating a boiler in the Outdoor Reset Mode.
Default is 70°F.
A-2
Page 83

APPENDIX A
APPENDIX A - BOILER MENU ITEM DESCRIPTIONS - Continued
MENU LEVEL & OPTION DESCRIPTION
CONFIGURATION MENU (Cont.)
Reset Ratio Permits setting of Reset Ratio when operating boiler
Outdoor Sensor Allows outdoor sensor function to be enabled or
System Start Tmp If outdoor sensor is enabled, this menu item allows
Setpoint Lo Limit Used to set the minimum allowable setpoint (40°F to
Setpoint Hi Limit Used to set the maximum allowable setpoint
Temp Hi Limit This is the maximum allowable outlet temperatur e
Max Valve Positon Sets the maximum allowable valve position for the
in the Outdoor Reset Mode. Reset Ratio is
adjustable from 0.1 to 9.9. Default is 1.2.
disabled. Default is disabled.
the system start temperature to be set from 30 to
100°F. Default is 60°F.
Setpoint Hi Limit). Default is 60°F
(Setpoint Lo Limit to 240°F). Default is 200°F.
(40 to 240°F). Any temperature above this setting
will turn off the unit. The temperature must then drop
5° below this setting to allow the unit to run. Default
Hi Limit is 210°F.
unit (40% to 100%). Default is 100%.
Pump Delay Timer Specifies the amount of time (0 to 30 min.) to keep
the pump running after the unit turns off. Default is
zero.
Aux Start On Dly Specif ies th e amount of time to wait (0 to 120 sec.)
between activating the Aux Relay (due to a demand)
and checking the pre-purge string to start the boiler.
Default is 0 sec.
Failsafe Mode Allows the Failsafe mode to be set to either
Constant Setpoint or Shutdown. Default is
Shutdown.
Analog Output Must be set to Valve Pos 0-10V for Benchmark
2.0LN.
Lo Fire Timer Specifies how long (2 to 600 sec.) to remain in the
low fire position after ignition, before going to the
desired output. Default is 2 sec.
Network Timeout Specifies the timeout value (seconds) before a
Modbus fault is declared. Available settings range
from 5 to 999 seconds. Default is 30 seconds.
A-3
Page 84

APPENDIX A
APPENDIX A - BOILER MENU ITEM DESCRIPTIONS - Continued
MENU LEVEL & OPTION DESCRIPTION
CONFIGURATION MENU (Cont.)
HI DB Setpt EN Operating at a Valve Position below this value will
Demand Offset This entry will reduce excessive ON/OFF cycling in
inhibit the DEADBAND feature. When operating at a
Valve Position below this value, the effective
Setpoint is equal to Active Setpoint + DEADBAND
HIGH.
Setting range is from 0 to 100. (Default is 30)
AUTO mode. When this entry is a non-zero value,
the unit will not turn on again until Valve Position In
reaches the Start Level value AND the Outlet
Temperature goes below the Active Setpoint –
Demand Offset. In addition, the boiler will fir e at the
29% Valve Position level or below for a period of
one minute.
When this entry is set to zero, the unit will turn on
again as soon as the Valve Position in reaches the
Start Level value. There will not be a one minute
delay when firing at the 34% Valve Position level.
Setting range is 0 to 25. (Default is 10)
Deadband High
Deadband Low
Deadband High and Deadband Low settings create
an “Outlet Temperature” Zone. In which no Valve
Position corrections will be attempted.
The Deadband ZONE is defined as operating with
an Outlet Temperature between Active Setpoint +
Deadband High and Active Setpoint – Deadband
Low.
When the Outlet Temperature reaches Active
Setpoint and remains there for a period of 15
seconds, the unit will go into a DEADBAND MODE
at which point no Valve Position corrections will be
attempted while the Outlet Temperature remains
anywhere within the Deadband ZONE. When the
unit is in the DEADBAND MODE, the °F or °C LED
will flash on and off. When the Outlet Temperature
drifts out of the Deadband ZONE, the DEADBAND
MODE will be terminated and the PID LOOP will
again attempt Valve Position corrections.
Setting range is 0 to 25. (Default is 2 for both
Deadband High and Deadband Low)
A-4
Page 85

APPENDIX A
MENU LEVEL & OPTION DESCRIPTION
TUNING MENU
Prop Band G ener ates a fire rate based on the error that exists
between the setpoint temperature and the actual
outlet temperature. If the actual error is less than
the proportional band setting (1 to 120°F), the fire
rate will be less than 100%. If the error is equal to
or greater than the proportional band setting, the fire
rate will be 100%.
Integral Gain This sets the fraction of the output, due to setpoint
error, to add or subtract from the output each minute
to move towards the setpoint. Gain is adjustable
from 0.00 to 1.00 (Default is 0.10).
Derivative Time T his value (0.0 to 20.0 min.) responds to the rate of
change of the setpoint error. This is the time that
this action advances the output.
Reset Defaults? Allows Tuning Menu options to be reset to their
Factory Default values.
A-5
Page 86

Page 87

APPENDIX B
APPENDIX B - STARTUP, STATUS AND FAULT MESSAGES
TABLE B-1 . STARTUP AND STAT US MES SAGES
MESSAGE DESCRIPTION
DEMAND DELAY
XX sec
DISABLED
HH:MM pm, pm
MM/DD/YY
FLAME PROVEN
IGNITION TR IAL
XX sec
PURGING
XX sec
STANDBY Displayed when ON/OFF switch is in the ON position, but
WAIT Prompts the operator to wait.
WARMUP
XX sec
Displayed if Demand Delay is active.
Displayed if ON/OFF switch is set to OFF. The display also
shows the time (am or pm) and date that the unit was
disabled.
Displayed after flame has been detected for a period of 2
seconds. Initially, the flame strength is shown in %. After 5
seconds has elapsed, the time and date are shown in place
of flame strength.
Displayed during ignition trial of startup sequence. The
duration of cycle counts up in seconds.
Displayed during the purge cycle during startup. The
duration of the purge cycle counts up in seconds.
there is no demand for heat. The time and date are also
displayed.
Displayed for 2 minutes during the initial warm-up only.
B-1
Page 88

APPENDIX B
FAULT MESSAGE FAULT DESCRIPTION
TABLE B-2. FAULT MESSAGES
AIRFLOW FAULT
DURING PURGE
AIRFLOW FAULT
DURING IGN
AIRFLOW FAULT
DURING RUN
DELAYED
INTERLOC K OPEN
DIRECT DRIVE
SIGNAL FAULT
FFWD TEMP
SENSOR FAULT
FLAME LOSS
DURING IGN
FLAME LOSS
DURING RUN
HEAT DEMAND
FAILURE
HIGH EXHAUST
TEMPERATURE
HIGH GAS
PRESSURE
HIGH WATER
TEMPERATURE
HIGH WATER TEMP
SWITCH OPEN
IGN BOARD
COMM FAULT
IGN SWTCH CLOSED
DURING PURGE
IGN SWTCH OPEN
DURING IGNITION
INTERLOCK
OPEN
LINE VOLTAGE
OUT OF PHASE
LOW GAS
PRESSURE
LOW WATER
LEVEL
NETWORK COMM
FAULT
The Blower Proof Switch opened during purge,
or air inlet is blocked.
The Blower Proof Switch opened during ignition.
The Blower Proof Switch opened during run.
The Delayed Interlock is open.
The direct drive signal is not present or is out of range.
The temperature measured by the Feed Forward (FFWD)
Sensor is out of range.
The Flame signal was not seen during ignition or lost within 5
seconds after ignition.
The Flame signal was lost during run.
The Heat Demand Relays on the Ignition board failed to
activate when commanded.
The High Exhaust Temperature Limit Switch is closed.
The High Gas Pressure Limit Switch is open.
The temperature measured by the Outlet Sensor exceeded
the Temp Hi Limit setting.
The High Water Temperature Limit Switch is open.
A communication fault has occurred between the PMC board
and Ignition board.
The Ignition Position Limit switch on the Air/Fuel Valve closed
during purge.
The Ignition Position Limit switch on the Air/Fuel Valve
opened during ignition.
The Remote Interlock is open.
The Line (Hot) and Neutral wires are reversed.
The Low Gas Pressure Limit Switch is open.
The Low Water Cutoff board is indicating low water level.
The RS-485 network information is not present or is
corrupted.
B-2
Page 89

FAULT MESSAGE FAULT DESCRIPTION
OUTDOOR TEMP
SENSOR FAULT
OUTLET TE MP
SENSOR FAULT
PRG SWTCH CLOSED
DURING IGNITION
PRG SWTCH OPEN
DURING PURGE
REMOTE SETPT
SIGNAL FAULT
RESIDUAL
FLAME
SSOV
SWITCH OPEN
SSOV FAULT
DURING PURGE
SSOV FAULT
DURING IGN
SSOV FAULT
DURING RUN
SSOV RELAY
FAILURE
STEPPER MOTOR
FAILURE
APPENDIX B
TABLE B-2. FAULT MESSAGES - Continued
The temperature measured by the Outdoor Air Sensor is out
of range.
The temperature measured by the Outlet Sensor is out of
range:
• OUTLET TEMPERATURE display = SHt Indicates sensor
is shorted
• OUTLET TEMPERATURE display = OPn indicates sensor
is open-circuited
The Purge Position Limit Switch on the Air/Fuel Valve closed
during ignition.
The Purge Position Limit Switch on the Air/Fuel Valve
opened during purge.
The Remote Setpoint signal is not present or is out of range.
The Flame signal was seen for more than 60 seconds during
standby.
The SSOV switch opened during standby.
The SSOV switch opened during purge.
The SSOV switch closed or failed to open during ignition.
The SSOV switch closed for more than 15 seconds during
run.
A failure has been detected in one of the relays that control
the SSOV.
The Stepper Motor failed to move the Air/Fuel Valve to the
desired position.
B-3
Page 90

Page 91

APPENDIX C
TEMPERATURE SENSOR RESISTANCE VOLTAGE CHART
(BALCO)
TEMP (°F) RES (OHMS) VOLTS*
-40
-30
-20
-10
0
10
20
30
40
50
60
70
80
90
100
110
120
130
140
150
160
170
180
190
200
210
220
230
240
250
*Voltage at AUX & Common terminals in the I/O Box
779.0
797.5
816.3
835.4
854.8
874.6
894.7
915.1
935.9
956.9
978.3
1000.0
1022.0
1044.4
1067.0
1090.0
1113.3
1137.0
1160.9
1185.2
1209.5
1234.7
1260.0
1285.6
1311.4
1337.7
1364.2
1391.0
1418.2
1445.7
1.93
1.96
1.99
2.02
2.05
2.07
2.10
2.12
2.15
2.17
2.20
2.23
2.25
2.27
2.30
2.32
2.34
2.36
2.39
2.41
2.43
2.45
2.47
2.50
2.52
2.54
2.56
2.58
C-1
Page 92

Page 93

Air
Temp
50F
45F
40F
35F
30F
25F
20F
15F
10F
5F
0F
-5F
-10F
-15F
-20F
Air
Temp
60F
55F
50F
45F
40F
35F
30F
25F
20F
15F
10F
5F
0F
-5F
-10F
-15F
-20F
APPENDIX D
APPENDIX D. - INDOOR/OUTDOOR RESET RATIO CHARTS
Table D-1. Header Temperature for a Building Reference Temperature of 50F
RESET RATIO
0.6 0.8 1.0 1.2 1.4 1.6 1.8 2.0 2.2 2.4
50 50 50 50 50 50 50 50 50 50
53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 60 62
56 58 60 62 64 66 68 70 72 74
59 62 65 68 71 74 77 80 83 86
62 66 70 74 78 82 86 90 94 98
65 70 75 80 85 90 95 100 105 110
68 74 80 86 92 98 104 110 116 122
71 78 85 92 99 106 113 120 127 134
74 82 90 98 106 114 122 130 138 146
77 86 95 104 113 122 131 140 149 158
80 90 100 110 120 130 140 150 160 170
83 94 105 116 127 138 149 160 171 182
86 98 110 122 134 146 158 170 182 194
89 102 115 128 141 154 167 180 193 206
92 106 120 134 148 162 176 190 204 218
Table D-2. Header Temperature for a Building Reference Temperatrure of 60F
RESET RATIO
0.6 0.8 1.0 1.2 1.4 1.6 1.8 2.0 2.2 2.4
60 60 60 60 60 60 60 60 60 60
63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72
66 68 70 72 74 76 78 80 82 84
69 72 75 78 81 84 87 90 93 96
72 76 80 84 88 92 96 100 104 108
75 80 85 90 95 100 105 110 115 120
78 84 90 96 102 108 114 120 126 132
81 88 95 102 109 116 123 130 137 144
84 92 100 108 116 124 132 140 148 156
87 96 105 114 123 132 141 150 159 168
90 100 110 120 130 140 150 160 170 180
93 104 115 126 137 148 159 170 181 192
96 108 120 132 144 156 168 180 192 204
99 112 125 138 151 164 177 190 203 216
102 116 130 144 158 172 186 200 214
105 120 135 150 165 180 195 210
108 124 140 156 172 188 204
D-1
Page 94

APPENDIX D
Table D-3. Header Temperature for a Building Reference Temperature of 65F
Air
Temp
65
60
55
50
45
40
35
30
25
20
15
10
5
0
-5
-10
-15
-20
Air
Temp
70F
65F
60F
55F
50F
45F
40F
35F
30F
25F
20F
15F
10F
5F
0F
-5F
-10F
-15F
-20F
0.6 0.8 1.0 1.2 1.4 1.6 1.8 2.0 2.2 2.4
65 65 65 65 65 65 65 65 65 65
68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77
71 73 75 77 79 81 83 85 87 89
74 77 80 83 86 89 92 95 98 101
77 81 85 89 93 97 101 105 109 113
80 85 90 95 100 105 110 115 120 125
83 89 95 101 107 113 119 125 131 137
86 93 100 107 114 121 128 135 142 149
89 97 105 113 121 129 137 145 153 161
92 101 110 119 128 137 146 155 164 173
95 105 115 125 135 145 155 165 175 185
98 109 120 131 142 153 164 175 186 197
101 113 125 137 149 161 173 185 197 209
104 117 130 143 156 169 182 195 208
107 121 135 149 163 177 191 205 219
110 125 140 155 170 185 200 215
113 129 145 161 177 193 209
116 133 150 167 201 218
Table D-4. Header Temperature for a Building Reference Temperature of 70F
0.6 0.8 1.0 1.2 1.4 1.6 1.8 2.0 2.2 2.4
70 70 70 70 70 70 70 70 70 70
73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82
76 78 80 82 84 86 88 90 92 94
79 82 85 88 91 94 97 100 103 106
82 86 90 94 98 102 106 110 114 118
85 90 95 100 105 110 115 120 125 130
88 94 100 106 112 118 124 130 136 142
91 98 105 112 119 126 133 140 147 154
94 102 110 118 126 134 142 150 158 166
97 106 115 124 133 142 151 160 169 178
100 110 120 130 140 150 160 170 180 190
103 114 125 136 147 158 169 180 191 202
106 118 130 142 154 166 178 190 202 214
109 122 135 148 161 174 187 200 213
112 126 140 154 168 182 196 210
115 130 145 160 175 190 205
118 134 150 166 182 198 214
121 138 155 172 189 206
124 142 160 178 196 214
RESET RATIO
RESET RATIO
D-2
Page 95

APPENDIX D
Table D-5. Header Temperature for a Building Reference Temperature of 75F
RESET RATIO
Air
Temp
75F
70F
65F
60F
55F
50F
45F
40F
35F
30F
25F
20F
15F
10F
5F
0F
-5F
-10F
-15F
Air
Temp
80F 80 80 80 80 80 80 80 80 80 80
75F 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92
70F 86 88 90 92 94 96 98 100 102 104
65F 89 92 95 98 101 104 107 110 113 116
60F 92 96 100 104 108 112 116 120 124 128
55F 95 100 105 110 115 120 125 130 135 140
50F 98 104 110 116 122 128 134 140 146 152
45F 101 108 115 122 129 136 143 150 157 164
40F 104 112 120 128 136 144 152 160 168 176
35F 107 116 125 134 143 152 161 170 179 188
30F 110 120 130 140 150 160 170 180 190 200
25F 113 124 135 146 157 168 174 190 201 212
20F 116 128 140 152 164 176 188 200 212
15F 119 132 145 158 171 184 197 210
10F 122 136 150 164 178 192 206
5F 125 140 155 170 185 200 215
0F 128 144 160 176 192 208
-5F 131 148 165 182 199 216
-10F 134 152 170 188 206
0.6 0.8 1.0 1.2 1.4 1.6 1.8 2.0 2.2 2.4
75 75 75 75 75 75 75 75 75 75
78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87
81 83 85 87 89 91 93 95 97 99
84 87 90 93 96 99 102 105 108 111
87 91 95 99 103 107 111 115 119 123
90 95 100 105 110 115 120 125 130 135
93 99 105 111 117 123 129 135 141 17
96 103 110 117 124 131 138 145 152 159
99 107 115 123 131 139 147 155 163 171
102 111 120 129 138 147 156 165 174 183
105 115 125 135 145 155 165 175 185 195
108 119 130 141 152 163 174 185 196 207
111 123 135 147 159 171 183 195 207 219
114 127 140 153 166 179 192 205 218
117 131 145 159 173 187 201 215
120 135 150 165 180 195 210
123 139 155 171 187 203 219
126 143 160 177 194 211
129 147 165 183 201 219
Table D-6. Header Temperature for a Building Reference Temperature of 80F
RESET RATIO
0.6 0.8 1.0 1.2 1.4 1.6 1.8 2.0 2.2 2.4
D-3
Page 96

APPENDIX D
Table D-7. Header Temperature for a Building Reference Temperature of 90F
RESET RATIO
Air
Temp
90F
85F
80F
75F
70F
65F
60F
55F
50F
45F
40F
35F
30F
25F
20F
15F
10F
5F
0F
0.6 0.8 1.0 1.2 1.4 1.6 1.8 2.0 2.2 2.4
90 90 90 90 90 90 90 90 90 90
93 94 95 96 97 98 99 100 101 102
96 98 100 102 104 106 108 110 112 114
99 102 105 108 111 114 117 120 123 126
102 106 110 114 118 122 126 130 134 138
105 110 115 120 125 130 135 140 145 150
108 114 120 126 132 138 144 150 156 162
111 118 125 132 139 146 153 160 167 174
114 122 130 138 146 154 162 170 178 186
117 126 135 144 153 162 171 180 189 198
120 130 140 150 160 170 180 190 200 210
123 134 145 156 167 178 189 200
126 138 150 162 174 186 198 210
129 142 155 168 181 194 207
132 146 160 174 188 202 216
135 150 165 180 195 210
138 154 170 186 202 218
141 158 175 192 209
144 162 180 198 216
D-4
Page 97

APPENDIX E
MENU & OPTION FACTORY DEFAULT
BOILER DEFAULT SETTINGS
Setup Menu
Password 0
Language English
Unit of Temp Fahrenheit
Comm Address 0
Baud Rate 9600
Configuration Menu
Internal Setpt 130°F
Unit Type BMK Boiler Dual
Unit Size 2.0 MBTU
Boiler Mode Constant Setpoint
Remote Signal
(If Mode = Remote Setpoint, Direct Drive or
Combination)
Bldg Ref Temp
(If Boiler Mode = Outdoor Reset)
4 – 20 mA / 1-5V
70°F
Reset Ratio
(If Boiler Mode = Outdoor Reset)
Outdoor Sensor Disabled
System Start Tmp
(If Outdoor Sensor = Enabled)
Setpt Lo Limit 60°F
Setpt Hi Limit 200°F
Temp Hi Limit
Max Valve Position 100% Natural Gas
Pump Delay Timer 0 min
Aux Start On Dly 0 sec
Failsafe Mode Shutdown
Analog Output Valve Position 0-10V
CAUTION: DO NOT Change
Lo Fire Timer 2 sec
Setpt Limit Band (If Setpt Limiting = Enabled) 5°F
1.2
60°F
215°F
91% Propane
E-1
Page 98

APPENDIX E
MENU & OPTION FACTORY DEFAULT
BOILER DEFAULT SETTINGS - Continued
Configuration Menu --Continued
Network Timeout 30 seconds
Hi DB Setpt En 30
Demand Offset 10
Deadband High 2
Deadband Low 2
Tuning Menu
Prop Band 70°F
Integral Gain 1.00
Derivative Time 0.0 min
E-2
Page 99

DIMENSIONALS & PARTS LISTS
APPENDIX F
F-1
Page 100

APPENDIX F
DIMENSIONALS & PARTS LISTS
B
REV
REAR
INTERNATIONAL, INC.
AERCO
NORTHVALE, NJ 07647
SD - A - 730
GAS FIRED BOILER
ANCHOR BOLT LOCATION
BENCHMARK 1.5 / 2.0 LOW NOx
*NOT TO SCALE*
DRWN BY: SJD
DATE: 10/12/07
F-2
FRONT
1) ALL HOLES ARE FLUSH WITH THE BOTTOM SURFACE OF THE FRAME
2) ALL DIMENSIONS SHOWN ARE IN INCHES (CENTIMETERS)
NOTES:
 Loading...
Loading...