Page 1

TOTAL ACCESS 544R
System Manual
4200704L2#ATM Total Access 544R ATM
1200704L3 Total Access 544R without Power Cord
4200704L8 Total Access 544R with Euro Power Cord
4200704L9 Total Access 544R Total Access 544R with UK Power Cord
4200704L10 Total Access 544R with Australian Power Cord
4200704L11 Total Access 544R with US Power Cord
61200704L2-1B
July 2003
Page 2

Trademarks Total Access 544R System Manual
Trademarks
Any brand names and product names included in this manual are trademarks, registered trademarks, or
trade names of their respective holders.
To the Holder of the Manual
The contents of this manual are current as of the date of publication. ADTRAN reserves the right to change
the contents without prior notice.
In no event will ADTRAN be liable for any special, incidental, or consequential damages or for
commercial losses even if ADTRAN has been advised thereof as a result of issue of this publication.
About this Manual
This manual provides a complete description of the Total Access 544R system and system software. The
purpose of this manual is to provide the technician, system administrator, and manager with general and
specific information related to the planning, installation, operation, and maintenance of the Total Access
544R. This manual is arranged so that needed information can be quickly and easily found.
901 Explorer Boulevard
P.O. Box 140000
Huntsville, AL 35814-4000
Phone: (256) 963-8000
© 2003 ADTRAN, Inc.
All Rights Reserved.
Printed in U.S.A.
2 © 2003 ADTRAN, Inc. 61200704L2-1B
Page 3

Total Access 544R System Manual Revision History
Revision History
This is the second issue of this manual.
Conventions
Notes provide additional useful information.
Cautions signify information that could prevent service interruption.
Warnings provide information that could prevent damage to the equipment or
endangerment to human life.
61200704L2-1B © 2003 ADTRAN, Inc. 3
Page 4

Safety Instructions Total Access 544R System Manual
Safety Instructions
When using your telephone equipment, please follow these basic safety precautions to reduce the risk of
fire, electrical shock, or personal injury:
1. Do not use this product near water, such as a bathtub, wash bowl, kitchen sink, laundry tub, in a
wet basement, or near a swimming pool.
2. Avoid using a telephone (other than a cordless-type) during an electrical storm. There is a remote
risk of shock from lightning.
3. Do not use the telephone to report a gas leak in the vicinity of the leak.
4. Use only the power cord, power supply, and/or batteries indicated in the manual. Do not dispose of
batteries in a fire. They may explode. Check with local codes for special disposal instructions.
Save These Important Safety Instructions
4 © 2003 ADTRAN, Inc. 61200704L2-1B
Page 5

Total Access 544R System Manual Save These Important Safety Instructions
Federal Communications Commission Radio Frequency Interference Statement
This equipment has been tested and found to comply with the limits for a Class A digital device, pursuant
to Part 15 of the FCC Rules. These limits are designed to provide reasonable protection against harmful
interference when the equipment is operated in a commercial environment. This equipment generates,
uses, and can radiate radio frequency energy and, if not installed and used in accordance with the
instruction manual, may cause harmful interference to radio frequencies. Operation of this equipment in a
residential area is likely to cause harmful interference in which case the user will be required to correct the
interference at his own expense.
Shielded cables must be used with this unit to ensure compliance with Class A FCC limits.
Changes or modifications to this unit not expressly approved by the party responsible
for compliance could void the user’s authority to operate the equipment.
61200704L2-1B © 2003 ADTRAN, Inc. 5
Page 6

Affidavit Requirements for Connection to Digital Services Total Access 544R System Manual
Affidavit Requirements for Connection to Digital Services
• An affidavit is required to be given to the telephone company whenever digital terminal equipment
without encoded analog content and billing protection is used to transmit digital signals containing
encoded analog content which are intended for eventual conversion into voiceband analog signals and
transmitted on the network.
• The affidavit shall affirm that either no encoded analog content or billing information is being
transmitted or that the output of the device meets Part 68 encoded analog content or billing protection
specifications.
• End user/customer will be responsible for filing an affidavit with the local exchange carrier when
connecting unprotected customer premise equipment (CPE) to 1.544 Mbps or subrate digital services.
• Until such time as subrate digital terminal equipment is registered for voice applications, the affidavit
requirement for subrate services is waived.
6 © 2003 ADTRAN, Inc. 61200704L2-1B
Page 7

Total Access 544R System Manual Affidavit Requirements for Connection to Digital Services
Affidavit for Connection of Customer Premises Equipment to 1.544 Mbps and/or Subrate Digital
Services
For the work to be performed in the certified territory of ___________________ (telco name)
State of ________________
County of ________________
I, _______________________ (name), ____________________________________ (business address),
____________________ (telephone number) being duly sworn, state:
I have responsibility for the operation and maintenance of the terminal equipment to be connected
to 1.544 Mbps and/or ________ subrate digital services. The terminal equipment to be connected
complies with Part 68 of the FCC rules except for the encoded analog content and billing protection
specifications. With respect to encoded analog content and billing protection:
I attest that all operations associated with the establishment, maintenance, and adjustment of the
digital CPE with respect to analog content and encoded billing protection information continuously
complies with Part 68 of the FCC Rules and Regulations.
The digital CPE does not transmit digital signals containing encoded analog content or billing
information which is intended to be decoded within the telecommunications network.
The encoded analog content and billing protection is factory set and is not under the control of the
customer.
I attest that the operator(s)/maintainer(s) of the digital CPE responsible for the establishment,
maintenance, and adjustment of the encoded analog content and billing information has (have) been
trained to perform these functions by successfully having completed one of the following (check
appropriate blocks):
A training course provided by the manufacturer/grantee of the equipment used to encode analog
signals; or
A training course provided by the customer or authorized representative, using training materials
and instructions provided by the manufacturer/grantee of the equipment used to encode analog
signals; or
An independent training course (e.g., trade school or technical institution) recognized by the
manufacturer/grantee of the equipment used to encode analog signals; or
In lieu of the preceding training requirements, the operator(s)/maintainer(s) is (are) under the
control of a supervisor trained in accordance with _________ (circle one) above.
I agree to provide ______________________ (telco’s name) with proper documentation to
demonstrate compliance with the information as provided in the preceding paragraph, if so
requested.
_________________________________Signature
_________________________________Title
_________________________________ Date
Transcribed and sworn to before me
61200704L2-1B © 2003 ADTRAN, Inc. 7
Page 8

Affidavit Requirements for Connection to Digital Services Total Access 544R System Manual
This ________ day of _______________, _______
_________________________________
Notary Public
My commission expires:
_________________________________
8 © 2003 ADTRAN, Inc. 61200704L2-1B
Page 9

Total Access 544R System Manual Industry Canada Compliance Information
Industry Canada Compliance Information
Notice: The Industry Canada label applied to the product (identified by the Industry Canada logo or the
“IC:” in front of the certification/registration number) signifies that the Industry Canada technical
specifications were met.
Notice: The Ringer Equivalence Number (REN) for this terminal equipment is supplied in the
documentation or on the product labeling/markings. The REN assigned to each terminal device indicates
the maximum number of terminals that can be connected to a telephone interface. The termination on an
interface may consist of any combination of devices subject only to the requirement that the sum of the
RENs of all the devices should not exceed five (5).
Canadian Emissions Requirements
This digital apparatus does not exceed the Class A limits for radio noise emissions from digital apparatus
as set out in the interference-causing equipment standard entitled “Digital Apparatus,” ICES-003 of the
Department of Communications.
Cet appareil numérique respecte les limites de bruits radioelectriques applicables aux appareils numériques
de Class A prescrites dans la norme sur le materiel brouilleur: “Appareils Numériques,” NMB-003 edictee
par le ministre des Communications.
61200704L2-1B © 2003 ADTRAN, Inc. 9
Page 10

Product Warranty Total Access 544R System Manual
Product Warranty
ADTRAN will replace or repair this product within the warranty period if it does not meet its published
specifications or fails while in service. Warranty information can be found at www.adtran.com/warranty.
Product Registration
Registering your product helps ensure complete customer satisfaction. Please take time to register your
products on line at www.adtran.com
. Click Service and Support on the top of the page, and then click
Product Registration under Support.
Customer Service, Product Support Information, and Training
ADTRAN will replace or repair this product within the warranty period if it does not meet its published
specifications or fails while in service. Warranty information can be found at www.adtran.com/warranty.
A return material authorization (RMA) is required prior to returning equipment to ADTRAN. For service,
RMA requests, training, or more information, use the contact information given below.
Repair and Return
If you determine that a repair is needed, please contact our Customer and Product Service (CAPS)
department to have an RMA number issued. CAPS should also be contacted to obtain information
regarding equipment currently in house or possible fees associated with repair.
CaPS Department (256) 963-8722
Identify the RMA number clearly on the package (below address), and return to the following address:
ADTRAN Customer and Product Service
901 Explorer Blvd. (East Tower)
Huntsville, Alabama 35806
RMA # _____________
Pre-Sales Inquiries and Applications Support
Your reseller should serve as the first point of contact for support. If additional pre-sales support is needed,
the ADTRAN Support web site provides a variety of support services such as a searchable knowledge
base, latest product documentation, application briefs, case studies, and a link to submit a question to an
Applications Engineer. All of this, and more, is available at:
http://support.adtran.com
When needed, further pre-sales assistance is available by calling our Applications Engineering
Department.
Applications Engineering (800) 615-1176
10 © 2003 ADTRAN, Inc. 61200704L2-1B
Page 11

Total Access 544R System Manual Customer Service, Product Support Information, and Training
Post-Sale Support
Your reseller should serve as the first point of contact for support. If additional support is needed, the
ADTRAN Support web site provides a variety of support services such as a searchable knowledge base,
updated firmware releases, latest product documentation, service request ticket generation and
trouble-shooting tools. All of this, and more, is available at:
http://support.adtran.com
When needed, further post-sales assistance is available by calling our Technical Support Center. Please
have your unit serial number available when you call.
Technical Support (888) 4ADTRAN
Installation and Maintenance Support
The ADTRAN Custom Extended Services (ACES) program offers multiple types and levels of installation
and maintenance services which allow you to choose the kind of assistance you need. This support is
available at:
http://www.adtran.com/aces
For questions, call the ACES Help Desk.
ACES Help Desk (888) 874-ACES (2237)
Training
The Enterprise Network (EN) Technical Training Department offers training on our most popular products.
These courses include overviews on product features and functions while covering applications of
ADTRAN's product lines. ADTRAN provides a variety of training options, including customized training
and courses taught at our facilities or at your site. For more information about training, please contact your
Territory Manager or the Enterprise Training Coordinator.
Training Phone (800) 615-1176, ext. 7500
Training Fax (256) 963-6700
Training Email training@adtran.com
61200704L2-1B © 2003 ADTRAN, Inc. 11
Page 12

Customer Service, Product Support Information, and Training Total Access 544R System Manual
12 © 2003 ADTRAN, Inc. 61200704L2-1B
Page 13

Table of Contents
Section 1 System Description . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 15
This section of ADTRAN’s Product System Manual is designed for use by network engineers,
planners, and designers for overview information about the Product.
It contains general information and describes the L2 protocol support, routing capability, security, and testing features. This section should be used in conjunction with Section 2, Engineering
Guidelines, of this System Manual.
Section 2 Engineering Guidelines . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 19
Provides equipment dimensions, power requirements, front panel design, rear panel design,
LEDs, and at-a-glance specifications.
Section 3 Network Turnup Procedure. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 25
Provides shipment contents list, grounding instructions, mounting options, and specifics of supplying power to the unit.
Section 4 SHDSL RCU ATM User Interface Guide . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 29
The SHDSL RCU ATM User Interface Guide is designed for use by network administrators and
others who will configure and provision the system. This section provides details unique to the
SHDSL RCU ATM firmware. It contains an overview, application details, configuration information, and menu
Section 5 Detail Level Procedures. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 95
DLP-1 Connecting the Terminal or PC to the CRAFT Port . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 97
DLP-2 Logging in to the System . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 101
DLP-3 Adding/Removing Telnet Users and Changing Password Security Levels . . . . . . . . 105
DLP-4 Setting Ethernet IP Parameters . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 109
DLP-5 Verifying Communications Over an IP LAN . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 111
DLP-6 Telnetting to the Unit . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 115
DLP-7 Upgrading the Firmware Using XMODEM . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 119
DLP-8 Upgrading the Firmware Using TFTP . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 121
DLP-9 Saving the Current Configuration Using TFTP . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 125
DLP-10 Loading the Current Configuration Using TFTP . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 129
DLP-11 Saving the Current Configuration Using XMODEM . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 133
DLP-12 Loading the Current Configuration Using XMODEM . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 135
DLP-13 Saving and Loading Text Configuration Using the Terminal Command Line. . . . . . 137
DLP-14 Unit Installation Using The Auto-Config Feature. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 141
DLP-15 A.03 to A.04 Firmware Upgrade. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 145
Section 6 ADTRAN Utilities . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 149
Provides instructions for configuring and using the ADTRAN Utilities software programs including Telnet, VT100, Syslog, and TFTP.
Section 7 MIBs. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 159
Provides a listing of SNMP Management Information Bases (MIBs) supported by the Total Access 544R. Traps supported for each MIB are also listed.
61200704L2-1B © 2003 ADTRAN, Inc. 13
Page 14

Table of Contents Total Access 544R System Manual
14 © 2003 ADTRAN, Inc. 61200704L2-1B
Page 15

SYSTEM DESCRIPTION
This section of ADTRAN’s Product System Manual is designed for use by network engineers, planners,
and designers for overview information about the Product.
It contains general information and describes the L2 protocol support, routing capability, security, and
testing features. This section should be used in conjunction with Section 2, Engineering Guidelines, of this
System Manual.
CONTENTS
Firmware Updates. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 16
Terminal Menu . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 16
Features and Benefits . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 16
Configuration and Management . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 16
Software Upgradeable . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 17
Network Interface . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 17
LAN Interface . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 17
Protocol Support . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 17
ATM Support . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 18
PPP. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 18
Routing Capability . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 18
Security . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 18
Integrated Components. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 18
61200704L2-1B © 2003 ADTRAN, Inc. 15
Page 16

Section 1 System Description Total Access 544R System Manual
1. SYSTEM OVERVIEW
The Total Access 544R is a cost-effective SHDSL access router designed for small and medium
businesses, branch offices and campuses. The unit provides up to 2312 kbps for dedicated Internet access
or remote office connectivity. With its integrated CSU/DSU, the Total Access 544R provides wide area
network access over a standard SHDSL or fractional SHDSL circuit.
Multiple users can share network access over a single SHDSL connection. For simultaneous access to
both a corporate network and the public Internet, the unit offers the ability to configure multiple PVCs. In
addition, the unit includes NAT/NAPT and IP filtering which provides security from unauthorized access
to the user's network.
The Total Access 544R also provides a cost-effective campus connectivity solution. When used with
private dry copper, the unit delivers up to 2.3 Mbps to cross-campus network elements. This solution is
ideal for extending LAN segments to other buildings.
Other features include a DHCP server, TELNET support, SNMP support, ping utility, and software
upgrades via TFTP and XMODEM.
Until now, the Total Access 544R unit has been running firmware version A.00.XX. Recently, D.04.XX
has been released. The development of D.04.XX code is a significant step in the evolution of the Total
Access product line, as it allows all Total Access family members to share the same base code. This means
that features and fixes are more easily implemented and are propagated across the product line. Section 4,
SHDSL ATM User Interface Guide, of this manual represents the D.04 firmware.
Firmware Updates
Firmware can be updated by using XMODEM transfer protocol via the unit’s CRAFT port or by using
TFTP from a network server.
Terminal Menu
The terminal menu is the access point to all other operations. Each terminal menu item has several
functions and submenus that identify and provide access to specific operations and parameters. These
menu selections are described later in this System Manual.
2. FEATURES AND BENEFITS
Below is a list of unit features and benefits.
Configuration and Management
• VT100 emulation via the CRAFT port
•Telnet
•SNMP
• LAN and WAN status LEDs
• Text-based configuration file support
• Syslog client
16 © 2003 ADTRAN, Inc. 61200704L2-1B
Page 17

Total Access 544R System Manual Section 1 System Description
• ICMP Ping utility
• Trace route utility
Software Upgradeable
• TFTP download
• XMODEM via CRAFT port
Network Interface
G.shdsl: (ITU G.991.2 Compliant)
• Line Rate: 200- 2312 kbps (3-36 DS0s)
• Physical Interface: RJ-48C
• Rate Adaptive
• Improved Spectral Compatibility
• Echo Cancellation
LAN Interface
• 10/100 BaseT
• Half or Full Duplex
•RJ-45
• Secondary IP address
• DHCP server
• IEEE 802.3
Protocol Support
•IP
• DNS
•TCP
• RIP V1, V2 and static routes
• UDP, UDP Relay
•ICMP
•ARP
•PPP
•Frame Relay
61200704L2-1B © 2003 ADTRAN, Inc. 17
Page 18

Section 1 System Description Total Access 544R System Manual
ATM Support
•6 PVCs
• IP over ATM (RFC 1483)
• RFC 1483 (Multiprotocol Encapsulation over ATM), PPPoA (RFC 2364)
• Full Traffic Shaping and QoS Support
• VBR-rt and UBR Support
• F5 OAM Loopback Capability
PPP
• LCP, IPCP, BCP, CCP
• Van Jacobson (VJ) header compression
Routing Capability
• Ethernet: 10/100BaseT (RJ-45)
• IEEE 802.3 and 802.1D (MAC Bridging)
• IP Support: TCP, RIP V1, RIP V2, UDP, ICMP, ARP, UDP Relay, SYSLOG
• PPP Support: LCP, IPCP, BCP
• DHCP Server to LAN, DHCP from network (NAT)
Security
• PAP, CHAP, EAP, and Radius
• NAT/NAPT
• Packet filtering by source and destination IP address, source and destination port number, MAC
address, protocol or pattern
• Multi-layer Password protection
• Telnet security: Access list and password protection
Integrated Components
•IP router
• Network connection
• 10/100BaseT connection
• CRAFT port
18 © 2003 ADTRAN, Inc. 61200704L2-1B
Page 19

ENGINEERING GUIDELINES
Provides equipment dimensions, power requirements, front panel design, rear panel design, LEDs, and
at-a-glance specifications.
CONTENTS
Reviewing the Front Panel Design . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 20
Front Panel LEDs . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 20
Reviewing the Rear Panel Design . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 21
NTWK Connection (RJ-48C). . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 21
CRAFT Port (RJ-48C) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 21
10/100BASET Connection (RJ-48C). . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 22
AC Power Connection. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 22
DB-9 to RJ Adapter . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 23
FIGURES
Figure 1. Total Access 544R Front Panel Layout . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 20
Figure 2. Total Access 544R Rear Panel . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 21
TABLES
Table 1. Total Access 544R Front Panel LEDs . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 20
Table 2. SHDSL NTWK Connection Pinout . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 21
Table 3. CRAFT Pinout . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 22
Table 4. 10/100BASET Pinout . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .22
Table 5. DB-9 to RJ Adapter Pinout . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .23
EQUIPMENT DIMENSIONS
The Total Access 544R measures 11.25” W, 7.5” D, and 2” H and comes equipped for table top or wall
mount use.
61200704L2-1B © 2003 ADTRAN, Inc. 19
Page 20
Section 2 Engineering Guidelines Total Access 544R System Manual
1. POWER REQUIREMENTS
The Total Access 544R operates with 240 VAC, 50 Hz and a maximum current drain of 300 mA. The Total
Access 544R maximum power consumption shall not exceed 10 Watts.
2. REVIEWING THE FRONT PANEL DESIGN
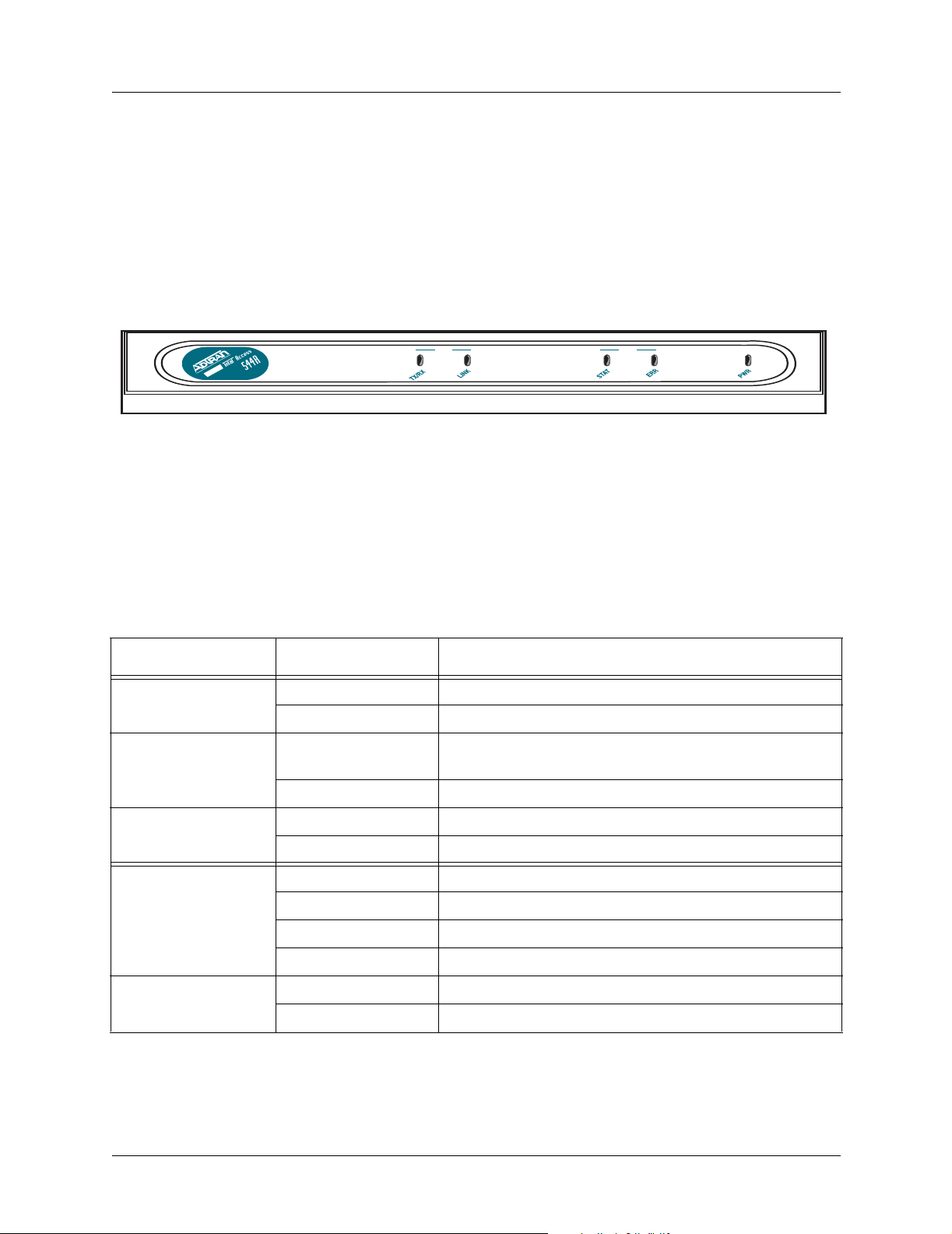
Figure 1. shows the front panel of the Total Access 544R which contains the LAN, WAN, and power
LEDs. These LEDs and their functions are described in Table 1.
.
LAN WAN
Figure 1. Total Access 544R Front Panel Layout
Front Panel LEDs
The front panel provides five status LEDs to monitor operation and activity. The following table provides
LED activity explanations.
Table 1. Total Access 544R Front Panel LEDs
For these LEDs... This color light... Indicates that...
LAN TX/RX Off there is no data traffic on the LAN.
Green (blinking) there is data traffic on the LAN.
LAN LINK
Off
Green (solid) there is link integrity on the LAN (physical link is up).
WAN STAT Red (solid) the SHDSL is shut down.
Green (solid) the SHDSL is up.
WAN ERR Red (flashing) the SHDSL is down.
Yellow (solid) errors are present on the WAN link.
Red (solid) severe errors are present on the WAN link.
Off the WAN link is up and error-free.
PWR Green (solid) power is supplied to the unit.
the physical link is down; there is no Ethernet
connection.
Off power is not supplied to the unit.
20 © 2003 ADTRAN, Inc. 61200704L2-1B
Page 21

Total Access 544R System Manual Section 2 Engineering Guidelines
3. REVIEWING THE REAR PANEL DESIGN
The Total Access 544R rear panel is shown in Figure 2..
Figure 2. Total Access 544R Rear Panel
NTWK Connection (RJ-48C)
The NTWK connection pinout is an SHDSL connection. Table 1 shows the pinout for this connection.
Connector type RJ-48C
Table 2. SHDSL NTWK Connection Pinout
PIN DESCRIPTION
1-3 Not Used
4 Ring
5 Tip
6-8 Not Used
CRAFT Port (RJ-48C)
The CRAFT port connects to a computer or modem. The CRAFT port input provides the following
functions:
• Accepts input from a PC or a modem for controlling the unit.
• Operates at 300, 1200, 2400, 4800, 9600, 19200, 38400, 57600, and 115200 bps.
• Acts as input for either VT100 or PC control.
• Acts as an interface for flash memory software downloads using XMODEM.
Table 3 shows the
CRAFT port pinout.
61200704L2-1B © 2003 ADTRAN, Inc. 21
Page 22
Section 2 Engineering Guidelines Total Access 544R System Manual
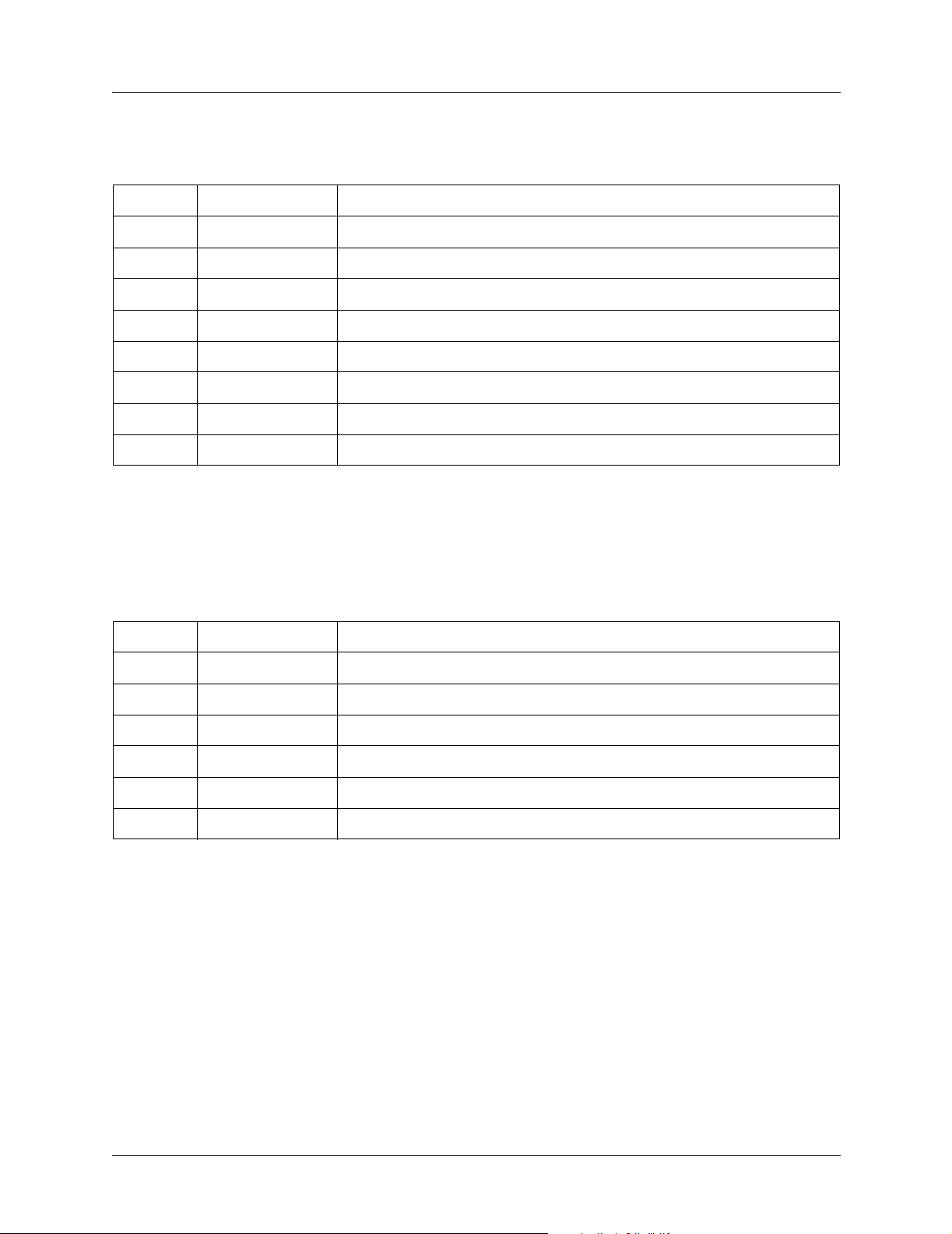
Table 3. CRAFT Pinout
PIN NAME DESCRIPTION
1 GND Ground - connected to unit chassis
2 RTS Request to send - flow control
3 RXDATA Data received by the unit.
4 DTR Data terminal ready
5 TXDATA Data transmitted by the unit.
6 CD Carrier detect
7 UNUSED —
8 CTS Clear to send - flow control
10/100BASET Connection (RJ-48C)
The 10/100BASET port (RJ-48C) provides a 10/100BaseT Ethernet LAN connection, which is used for IP
Routing, TFTP, SNMP, and Telnet connections. Table 4 shows the
Table 4. 10/100BASET Pinout
PIN NAME DESCRIPTION
1 TX1 Transmit Positive
2 TX2 Transmit Negative
3 RX1 Receive Positive
4, 5 UNUSED —
6 RX2 Receive Negative
7, 8 UNUSED —
10/100BASET port pinout.
AC Power Connection
Each unit includes an auto ranging 100-250 VAC, 50/60 Hz power supply with a 3-prong removable cable.
Connect the power supply to a standard 120 VAC, 60 Hz electrical outlet for proper operation.
22 © 2003 ADTRAN, Inc. 61200704L2-1B
Page 23
Total Access 544R System Manual Section 2 Engineering Guidelines
4. DB-9 TO RJ ADAPTER
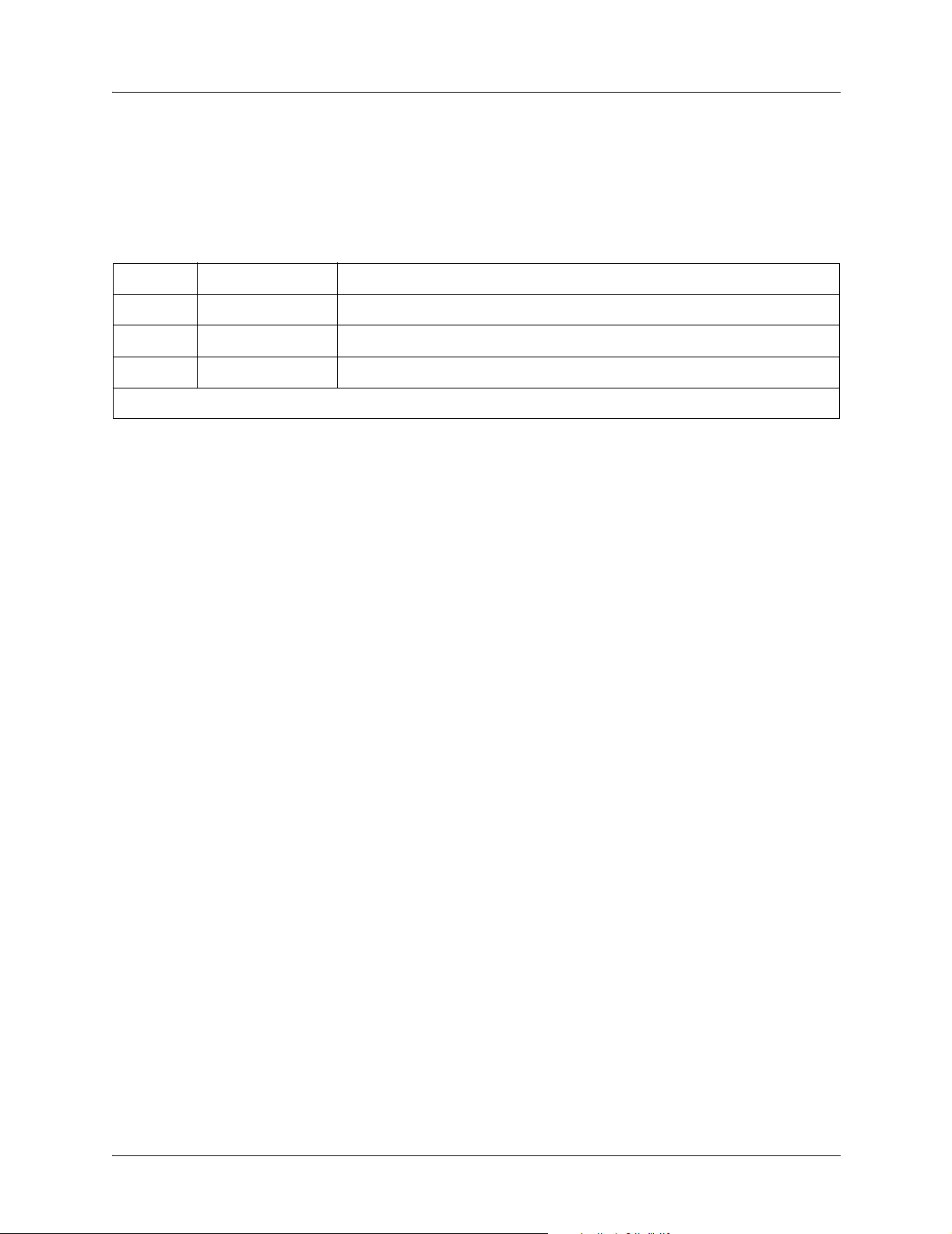
The DB-9 to RJ adapter is used to connect a PC or VT100 terminal to the CRAFT port. The adapter pinout
is shown in Table 5.
Table 5. DB-9 to RJ Adapter Pinout
DB-9 RJ-45 DESCRIPTION
25 TX Data
33 RX Data
51 GND
Note: All other pins are unused.
61200704L2-1B © 2003 ADTRAN, Inc. 23
Page 24

Section 2 Engineering Guidelines Total Access 544R System Manual
24 © 2003 ADTRAN, Inc. 61200704L2-1B
Page 25

NETWORK TURNUP PROCEDURE
Provides shipment contents list, grounding instructions, mounting options, and specifics of supplying
power to the unit.
CONTENTS
Tools Required . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 26
Unpack and Inspect the System . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 26
Contents of ADTRAN Shipment . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 26
Grounding Instructions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 27
Supplying Power to the Unit . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 28
Mounting Options . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 28
61200704L2-1B © 2003 ADTRAN, Inc. 25
Page 26

Section 3 Network Turnup Procedure Total Access 544R System Manual
1. INTRODUCTION
This section discusses the unit installation process.
2. TOOLS REQUIRED
The tools required for unit installation are:
• Screws (customer-provided for wallmount installation)
• Screwdriver (for wall or rackmount installation)
To prevent electrical shock, do not install equipment in a wet location or during a
lightning storm.
During installation, power should be the last connection made.
Electronic modules can be damaged by static electrical discharge. Before handling
modules, wear an antistatic discharge wrist strap to prevent damage to electrical
components. Place modules in antistatic packing material when transporting or storing.
When working on modules, always place them on an approved antistatic mat that is
electrically grounded.
3. UNPACK AND INSPECT THE SYSTEM
Each unit is shipped in its own cardboard shipping carton. Open each carton carefully and avoid deep
penetration into the carton with sharp objects.
After unpacking the unit, inspect it for possible shipping damage. If the equipment has been damaged in
transit, immediately file a claim with the carrier, and then contact ADTRAN Customer Service (see the
contact information in the front of this manual).
Contents of ADTRAN Shipment
Your ADTRAN shipment of the Total Access 544R includes the following items:
• Mounting Instructions (P/N 64200600L1#T-19A)
•CD
• Cable Tie (P/N 3292032)
• Silver Satin Cable (P/N 3127004)
• Four Rubber Feet (P/N 3270BF003)
• Power Cord (P/N 3127009)
• 2 Mounting Brackets (P/N 3265421@C)
26 © 2003 ADTRAN, Inc. 61200704L2-1B
Page 27

Total Access 544R System Manual Section 3 Network Turnup Procedure
• 4 Screws (P/N 3276003003)
• RJ-45 to DB-9 Adapter (P/N 3196ADPT001)
• The Total Access 544R base unit
Customers must supply the Ethernet cable.
4. GROUNDING INSTRUCTIONS
The following provides grounding instruction information from the Underwriters’ Laboratory UL60950
Standard for Safety of Information Technology Equipment Including Electrical Business Equipment, Third
Edition, of December 1, 2000.
An equipment grounding conductor that is not smaller in size than the ungrounded branch-circuit supply
conductors is to be installed as part of the circuit that supplies the product or system. Bare, covered, or
insulated grounding conductors are acceptable. Individually covered or insulated equipment grounding
conductors shall have a continuous outer finish that is either green, or green with one or more yellow
stripes. The equipment grounding conductor is to be connected to ground at the service equipment.
The attachment-plug receptacles in the vicinity of the product or system are all to be of a grounding type,
and the equipment grounding conductors serving these receptacles are to be connected to earth ground at
the service equipment.
A supplementary equipment grounding conductor shall be installed between the product or system and
ground that is in addition to the equipment grounding conductor in the power supply cord.
The supplementary equipment grounding conductor shall not be smaller in size than the ungrounded
branch-circuit supply conductors. The supplementary equipment grounding conductor shall be connected
to the product at the terminal provided, and shall be connected to ground in a manner that will retain the
ground connection when the product is unplugged from the receptacle. The connection to ground of the
supplementary equipment grounding conductor shall be in compliance with the rules for terminating
bonding jumpers at Part K or Article 250 of the National Electrical Code, ANSI/NFPA 70. Termination of
the supplementary equipment grounding conductor is permitted to be made to building steel, to a metal
electrical raceway system, or to any grounded item that is permanently and reliably connected to the
electrical service equipment ground.
The supplemental grounding conductor shall be connected to the equipment using a number 8 ring terminal
and should be fastened to the grounding lug provided on the rear panel of the equipment. The ring terminal
should be installed using the appropriate crimping tool (AMP P/N 59250 T-EAD Crimping Tool or
equivalent).
• This unit shall be installed in accordance with Article 400 and 364.8 of the NEC NFPA
70 when installed outside of a Restricted Access Location (i.e., central office, behind a
locked door, service personnel only area).
• Power to the unit’s AC system must be from a grounded 100-250 VAC, 50/60 Hz source.
• The power receptacle uses double-pole, neutral fusing.
• Maximum recommended ambient operating temperature is 45 ºC.
61200704L2-1B © 2003 ADTRAN, Inc. 27
Page 28

Section 3 Network Turnup Procedure Total Access 544R System Manual
5. SUPPLYING POWER TO THE UNIT
The AC powered unit comes equipped with a detachable power cord with a 3-prong plug for connecting to
a grounded power receptacle. As shipped, the unit is set to factory default conditions. After installing the
chassis, the unit is ready for power-up. To power-up the unit, ensure that the unit is properly connected to
an appropriate power source.
6. MOUNTING OPTIONS
The Total Access 544R comes equipped for table top or wallmount use. The unit is shipped with two
wall-mount brackets (P/N 326542@C) and four screws (P/N 3276003003) which the customer must attach
to the base unit for wallmount use.
If wallmounted, the Total Access 544R must be mounted with the LEDs pointing
down or sideways as shown in the mounting instructions (P/N 64200600L1#T-19A).
28 © 2003 ADTRAN, Inc. 61200704L2-1B
Page 29

SHDSL RCU ATM USER INTERFACE GUIDE
The SHDSL RCU ATM User Interface Guide is designed for use by network administrators and others who
will configure and provision the system. This section provides details unique to the SHDSL RCU ATM
firmware. It contains an overview, application details, configuration information, and menu
CONTENTS
System Info . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 30
System Config. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 32
System Utility . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 46
Interfaces (SHDSL) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 53
Interfaces (ETH) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 55
L2 Protocol . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 56
L2 Protocol (SHDSL). . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 56
L2 Protocol (ETH) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 63
Bridge . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 65
Router . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 67
Security . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 83
FIGURES
Figure 1. System Info Menu . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 30
Figure 2. System Config Menu . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 32
Figure 3. System Utility Menu . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 46
Figure 4. Interfaces Menu . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 53
Figure 5. L2 Protocol Menu . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 56
Figure 6. Bridge Menu . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 66
Figure 7. Router Menu . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 68
Figure 8. Security Menu . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 83
Figure 9. Application Diagrams . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 90
TABLES
Table 1. Instructions for Changing Passwords . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 33
Table 2. Telnet Security Levels . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 35
61200704L2-1B © 2003 ADTRAN, Inc. 29
Page 30
Section 4 SHDSL RCU ATM User Interface Guide Total Access 544R System Manual
1. SYSTEM INFO
The System Info menu provides basic information about the unit as well as data fields for editing
information. Figure 1 displays the submenus that are available when you select this menu item.
Figure 1. System Info Menu
SYSTEM INFO > SYSTEM NAME
Provides a user-configurable text string for the name of the unit. This name can help you distinguish
between different installations. You can enter up to 31 alpha-numeric characters in this field, including
spaces and special characters (such as an underscore). This name will appear on the top line of all screens.
This field is blank by default.
SYSTEM INFO > SYSTEM LOCATION
Provides a user-configurable text string for the location of the unit. This field is to help you keep track of
the actual physical location of the unit. You can enter up to 31 alphanumeric characters in this field,
including spaces and special characters (such as an underscore). This field is blank by default.
SYSTEM INFO > SYSTEM CONTACT
Provides a user-configurable text string for a contact name. You can use this field to enter the name, phone
number, or E-mail address of a person responsible for the unit. You can enter up to 31 alpha-numeric
characters in this field, including spaces and special characters (such as an underscore). The factory default
is to have no entry in the system contact field
30 © 2003 ADTRAN, Inc. 61200704L2-1B
Page 31

Total Access 544R System Manual Section 4 SHDSL RCU ATM User Interface Guide
SYSTEM INFO > UNIT NAME
Product-specific name for the unit.
SYSTEM INFO > CLEI CODE
The CLEI code for the unit.
SYSTEM INFO > PART NUMBER
ADTRAN part number for the unit.
SYSTEM INFO > SERIAL NUMBER
The serial number field will reflect serial number located on bottom of the unit’s chassis.
SYSTEM INFO > FIRMWARE REVISION
Displays the current firmware revision level of the unit.
SYSTEM INFO > BOOTCODE REVISION
Displays the bootcode revision.
SYSTEM INFO > SYSTEM UPTIME
Displays the length of time since the last reboot of the unit.
Each time you reset the system, this value resets to 0 days, 0 hours, 0 min. and 0 secs.
SYSTEM INFO > DATE/TIME
Displays the current date and time, including seconds. This field can be edited. Enter the time in 24-hour
format (such as 23:00:00 for 11:00 pm). Enter the date in mm-dd-yyyy format (for example, 10-30-1998).
61200704L2-1B © 2003 ADTRAN, Inc. 31
Page 32

Section 4 SHDSL RCU ATM User Interface Guide Total Access 544R System Manual
SYSTEM CONFIG
Set up the unit’s operational configuration from the SYSTEM CONFIG menu. Figure 3 shows the items
included in this menu.
Figure 2. System Config Menu
SYSTEM CONFIG > MANAGEMENT
Set up the CRAFT PORT, TELNET ACCESS, SNMP MANAGEMENT, and FDL MANAGEMENT from this menu.
SYSTEM CONFIG > MANAGEMENT > CRAFT PORT
Set up the CRAFT PORT parameters from this menu.
SYSTEM CONFIG > MANAGEMENT > CRAFT PORT > PASSWORD PROTECT
The unit’s VT100 CRAFT port can be accessed via an RJ-48C connector located on the rear of the unit, or
the DB-9 connector on the front of the unit.
PASSWORD PROTECT is set to NO, the CRAFT port is not password protected. When YES (def), the
When
unit will prompt for a password upon startup.
SYSTEM CONFIG > MANAGEMENT > CRAFT PORT > PASSWORD
This is the text string that is used for comparison when password protecting the CRAFT port. By default,
no password is entered. You can enter up to 30 characters in this field. Table 1 provides instructions for
changing the password.
32 © 2003 ADTRAN, Inc. 61200704L2-1B
Page 33

Total Access 544R System Manual Section 4 SHDSL RCU ATM User Interface Guide
The security level for the CRAFT port is always set to FULL. This gives full access to all
menus.
Passwords are case-sensitive and can contain up to 30 alphanumeric characters
(including spaces and special characters).
Table 1. Instructions for Changing Passwords
Step Action
1
2 Type the new password in the ENTER field.
3 Type the new password again in the CONFIRM field.
Select the PASSWORD field—a new PASSWORD field displays.
SYSTEM CONFIG > MANAGEMENT > CRAFT PORT > IDLE TIME
This option defines the amount of time in minutes user may stay connected without any activity on the
CRAFT port before the user is automatically logged out of the system. A value of 0 disables this inactivity
timer function enabling users to stay connected until manually logged out. The value range is
255 (min).
0 (def) to
SYSTEM CONFIG > MANAGEMENT > CRAFT PORT > BAUD RATE
This is the asynchronous rate that the CRAFT port will run. The possible values are 300, 1200, 2400, 4800,
9600, 19200, 38400, 57600, and 115200. The default value is 9600.
SYSTEM CONFIG > MANAGEMENT > CRAFT PORT > DATA BITS
This is the asynchronous bit rate that the CRAFT port will run. The possible values are 7 or 8 (def) bits.
SYSTEM CONFIG > MANAGEMENT > CRAFT PORT > PARITY
This is the asynchronous parity that the CRAFT port will run. The possible values are NONE (def), ODD, or
EVEN.
SYSTEM CONFIG > MANAGEMENT > CRAFT PORT > STOP BITS
This is the number of stop bits used for the CRAFT port. The possible values are 1 (def), 1.5 or 2.
SYSTEM CONFIG > MANAGEMENT > TELNET ACCESS
Activate the Telnet access and set up the various telnet parameters from this menu.
61200704L2-1B © 2003 ADTRAN, Inc. 33
Page 34

Section 4 SHDSL RCU ATM User Interface Guide Total Access 544R System Manual
SYSTEM CONFIG > MANAGEMENT > TELNET ACCESS > ACCESS
Sets ACCESS to ON or OFF. The factory default value for this parameter is ON.
SYSTEM CONFIG > MANAGEMENT > TELNET ACCESS > AUTHEN METHOD
Set up the telnet authentication method from this menu. The choices are PASSWORD, RADIUS,
PASSWORD/RADIUS, and RADIUS/PASSWORD. PASSWORD/RADIUS indicates that the unit will try Password
Authentication first and if that fails, it will try Radius Authentication.
RADIUS/PASSWORD indicates that the
unit will try Radius authentication first and if that fails, it will try Password authentication. The default is
PASSWORD.
SYSTEM CONFIG > MANAGEMENT > TELNET ACCESS > USER LIST
Add telnet users and control the telnet access conditions through this menu.
#
Display the index number of the telnet users. Up to four users can be configured for access to the
unit. Each user can be assigned a security level and idle time.
NAME
The name is a text string of the user name for this session. You can enter up to 15 characters in this
field. The factory default is no entry in the
PASSWORD
NAME field
When the authenticating method is password, or password radius, this text string is used for the
password. You can enter up to 30 characters in this field. The factory default is no entry in this field.
IDLE TIME (MINS)
This sets the amount of time in minutes you can be idle before you are automatically logged off. The
factory default is
LEVEL
10 MINUTES. The range is 1-255 minutes.
This is the security level granted to the user. Table 2 gives a brief description of each level. The
factory default is
FULL.
34 © 2003 ADTRAN, Inc. 61200704L2-1B
Page 35

Total Access 544R System Manual Section 4 SHDSL RCU ATM User Interface Guide
Table 2. Telnet Security Levels
Security
Description
Level
Full The user has all access to view and configure all menus (same as logging in to
the CRAFT port)
Support The user has read only access to view the SYSTEM INFO menu. The user has
privileges to view and change everything under the S
YSTEM CONFIG menu
except for the CRAFT port settings, telnet access lists, and the SNMP
management communities. The user has full access to the S
YSTEM UTILITY
menu, including the ability to upgrade firmware and reset the unit. The user has
full access to the I
The user does not have the ability to set R
S
ECURITY menu.
NTERFACES, L2 PROTOCOL, BRIDGE, ROUTER, and DS0 menus.
ADIUS SERVER settings under the
Config The same privileges as support, except that the user does not have privileges to
download firmware or configuration from the S
YSTEM UTILITY menu. The user
additionally does not have the privilege to reset the unit remotely, or enter the
terminal menu.
Router The user has read only privileges for the SYSTEM INFO menu. There is no access
to the S
the S
status from the I
R
YSTEM CONFIG menu. The user has PING and TRACEROUTE access from
YSTEM UTILITY menu. The user is limited to ethernet configuration and
NTERFACES menu. The user has full access to the BRIDGE and
OUTER menus. Access is limited to filters only from the SECURITY menu.
Voice The user has read only privileges for the SYSTEM INFO menu. The user has
access to the P
The user has full access to the FXS module from the I
ING and TRACEROUTE utilities from the SYSTEM UTILITIES menu.
NTERFACES menu.
Status The user has read access of all menus except for the following: SYSTEM
C
ONFIG/CRAFT PORT, SYSTEM CONFIG/TELNET ACCESS, SYSTEM CONFIG/SNMP
M
ANAGEMENT, and SECURITY/ RADIUS SERVER. The user does not have access
to U
PGRADE FIRMWARE, UPGRADE CONFIG, PING, or TRACEROUTE menus. The
user cannot reset the unit or enter terminal mode.
SYSTEM CONFIG > MANAGEMENT > TELNET ACCESS > IP ACCESS LIST
Set up the list of allowed telnet managers.
NETWORK ADDRESS AND MASK
Enter a network address and subnet mask from which telnet access to the unit is allowed. When a
remote unit requests telnet access to the unit, if the access list is empty or the remote’s IP address
matches a list entry, remote access is granted. A subnet mask of 0.0.0.0 will allow any host telnet
access, regardless of the network address. A network address of 0.0.0.0 with corresponding netmask
255.255.255.255 will not allow any host telnet access.
The factory default is
0.0.0.0. for both parameters, which will allow all users telnet IP access.
61200704L2-1B © 2003 ADTRAN, Inc. 35
Page 36

Section 4 SHDSL RCU ATM User Interface Guide Total Access 544R System Manual
SYSTEM CONFIG > MANAGEMENT > SNMP MANAGEMENT
Access the SNMP management and configure the SNMP communities and traps from this menu.
SYSTEM CONFIG > MANAGEMENT > SNMP MANAGEMENT > ACCESS
When set to OFF, SNMP access is denied. When set to ON, the unit will respond to SNMP managers based
on the configuration. The factory default is
ON.
SYSTEM CONFIG > MANAGEMENT > SNMP MANAGEMENT >TRAP DELAY
Time in seconds that represents the delay inserted between the trap creation and trap transmission. The
range is 0 to 600 seconds. The factory default is
0 SEC.
SYSTEM CONFIG > MANAGEMENT > SNMP MANAGEMENT > COMMUNITIES
Set up the SNMP communities parameters from this menu.
#
Displays the index number of the SNMP Communities.
This list is used to set up to 8 SNMP communities that the unit will allow.
NAME
This is the text string used to identify the SNMP community. This field is blank by default.
PRIVILEGE
The access for this manager can be assigned three levels. The factory default is NONE.
NONE
GET
GET/SET
MANAGER IP
No access is allowed for this community or manager.
Manager can only read items.
Manager can read and set items.
This may be used in conjunction with the Netmask field to define a range of manager IPs. A netmask
of 255.255.255.255 defines a single IP as the manager host IP. The default value is
0.0.0.0.
36 © 2003 ADTRAN, Inc. 61200704L2-1B
Page 37

Total Access 544R System Manual Section 4 SHDSL RCU ATM User Interface Guide
NETMASK
The mask is used to determine which bits of the MANAGER IP are significant. A "0" bit means "don't
care." A "1" bit means that the corresponding address bits in the incoming SNMP packet must match
the address bit in the defined
the manager host IP. The default value is
MANAGER IP. The netmask of 255.255.255.255 defines a single IP as
0.0.0.0.
SYSTEM CONFIG > MANAGEMENT > SNMP MANAGEMENT > TRAPS
Sets up the trap manager name and IP from this menu.
#
Displays the index number in the SNMP traps table.
This list allows up to 20 managers to be listed to receive traps.
MANAGER NAME is the text string describing the name of the entry. It is intended for easy reference
and has no bearing on the SNMP trap function. You can enter up to 31 characters in this field. The
factory default is no entry in the manager name field.
MANAGER IP
This is the IP address of the manager that is to receive the traps. The factory default is 0.0.0.0.
SYSTEM CONFIG > MANAGEMENT > FDL MANAGEMENT
Enables the FDL management and configures mode and IP addresses from this menu.
SYSTEM CONFIG > MANAGEMENT > FDL MANAGEMENT > MODE
This enables the FDL (only in ESF mode) to be used for management. Learning mode can also be enabled
so the unit can "learn" its IP configuration to be used for its FDL management. Once it learns this
information from, for example a Total Access 4303, the configuration items populate. The factory default
is
ON.
SYSTEM CONFIG > MANAGEMENT > FDL MANAGEMENT > LINK IP ADDRESS
This is the local IP address used for FDL management. The FDL uses a separate IP network for
communication, distinct from the customer data that is configured under the Router menus. The factory
default is
0.0.0.0.
SYSTEM CONFIG > MANAGEMENT > FDL MANAGEMENT > IP NETMASK
This is the subnet mask defining the IP network used for FDL management. The factory default is 0.0.0.0.
61200704L2-1B © 2003 ADTRAN, Inc. 37
Page 38

Section 4 SHDSL RCU ATM User Interface Guide Total Access 544R System Manual
SYSTEM CONFIG > MANAGEMENT > FDL MANAGEMENT > FAR-END IP ADDRESS
This is the far-end IP address used for the FDL management. The FDL is a separate IP network from the
customer data that is configured under the Router menus. The factory default is
0.0.0.0.
SYSTEM CONFIG > MANAGEMENT > FDL MANAGEMENT > LEARN ADDRESS
When set to ON, the destination address on each received packet is assumed to be the FDL interface
address. A 255.255.255.252 netmask is used, which determines the far-side address as well (since there can
be only two addresses on a subnet with that netmask). When set to
assigned to the FDL interface. Default is
ON.
OFF, the user must input the IP address
SYSTEM CONFIG > MANAGEMENT > FDL MANAGEMENT > ACCEPT ALL SNMP
When set to ON, SNMP gets/sets received over the FDL link are always accepted regardless of the
community table. When set to
SNMP traffic is rejected if a match is not found. Default is
OFF, the community table is searched for valid manager IP addresses and the
ON.
SYSTEM CONFIG > MANAGEMENT > FDL MANAGEMENT > MTU
Maximum Transmit Unit allows the user to set the largest acceptable IP packets that will be transmitted
before configuration takes place. The range is 64 to 256 kbps. The default is
256 KBPS.
SYSTEM CONFIG > SYSLOG
Configure the unit Syslog client for use with a Syslog server (supplied with ADTRAN Utilities or available
on most Unix platforms) from this menu.
For additional information, reference RFC3164: The BSD Syslog Protocol.
SYSTEM CONFIG > SYSLOG > SYSLOG IP
IP address of the syslog daemon to which log message should be sent. The values must be dotted decimal
notation.
SYSTEM CONFIG > SYSLOG > SYSLOG FORMAT
The SYSLOG FORMAT is the format of log messages. "ADTRAN" uses a format that is compatible with
Adtran Utilities and forces the Syslog Facility to LOCAL0.
reports at the configured facility level.
UNIX uses the traditional Unix format and
Adtran Utilities may malfunction if messages are received in the Unix format.
38 © 2003 ADTRAN, Inc. 61200704L2-1B
Page 39

Total Access 544R System Manual Section 4 SHDSL RCU ATM User Interface Guide
SYSTEM CONFIG > SYSLOG > SYSLOG FACILITY
The choices are: LOCAL0, LOCAL1, LOCAL2, LOCAL3, LOCAL4, LOCAL5, LOCAL6, LOCAL7. SYSLOG FACILITY
is the facility level for all messages forwarded from the unit to the syslog server. This allows all messages
received from the IAD to be filtered by facility level. See RFC3164: The BSD Syslog Protocol.
This does not have to correspond to the facility level shown in the terminal mode option.
See SYSLOG Facility using Terminal Mode on page 40.
The remaining Syslog parameters have the following level choices:
FATAL (Highest priority)
ALERT
CRITICAL
ERROR
WA R NI N G
NOTICE
INFO
DEBUG (Lowest priority)
Every log message generated by the IAD has a reporting level priority. If the message priority is lower than
the configured priority for the destination log, the message is not forwarded to the syslog daemon. See
RFC3164: The BSD Syslog Protocol. The lower the log level, the more messages that will be generated.
Setting reporting levels to DEBUG may negatively affect the performance of the IAD, including causing
the IAD to reset.
ADTRAN recommends using DEBUG for only short periods of time for debug purposes
only.
61200704L2-1B © 2003 ADTRAN, Inc. 39
Page 40

Section 4 SHDSL RCU ATM User Interface Guide Total Access 544R System Manual
SYSLOG using Terminal Mode
Another option for configuring syslog is using the terminal mode command log dump <logname>. The
logname must be all CAPS and be one of the following names:
FATAL
ALERT
CRITICAL
ERROR
WA R NI N G
NOTICE
INFO
DEBUG
The command will dump all messages for the indicated log (
the internal log buffer to the command line display.
ALL LEVEL shows all log messages) stored in
SYSTEM CONFIG > SYSLOG > ALL LEVEL
This entry allows setting the default reporting level for all log entries. If ALL LEVEL is a lower priority than
the individual log entry level,
ALL LEVEL overrides the individual log reporting level.
SYSTEM CONFIG > SYSLOG > KERNEL LEVEL
Minimum required level for sending KERNEL log messages.
SYSTEM CONFIG > SYSLOG > DHCP LEVEL
Minimum required level for sending DHCP log messages.
SYSTEM CONFIG > SYSLOG > NTP LEVEL
Minimum required level for sending NTP log messages.
SYSTEM CONFIG > SYSLOG > TFTP LEVEL
Minimum required level for sending TFTP log messages.
SYSTEM CONFIG > SYSLOG > TELNET LEVEL
Minimum required level for sending TELNET log messages.
SYSTEM CONFIG > SYSLOG > IP LEVEL
Minimum required level for sending IP log messages.
40 © 2003 ADTRAN, Inc. 61200704L2-1B
Page 41

Total Access 544R System Manual Section 4 SHDSL RCU ATM User Interface Guide
SYSTEM CONFIG > SYSLOG > PPP LEVEL
Minimum required level for sending PPP log messages.
SYSTEM CONFIG > SYSLOG > NAT LEVEL
Minimum required level for sending NAT log messages.
SYSTEM CONFIG > SYSLOG > ARP LEVEL
Minimum required level for sending ARP log messages.
SYSTEM CONFIG > SYSLOG > UDP LEVEL
Minimum required level for sending UDP log messages.
SYSTEM CONFIG > SYSLOG > NETWRITE LEVEL
This parameter is for ADTRAN internal use only.
SYSTEM CONFIG > SYSLOG > TCP LEVEL
Minimum required level for sending TCP log messages.
SYSTEM CONFIG > SYSLOG > COMPSYS LEVEL
This parameter is for ADTRAN internal use only.
SYSTEM CONFIG > SYSLOG > CONSOLE LEVEL
This parameter is for ADTRAN internal use only.
SYSTEM CONFIG > SYSLOG > CFGXFER LEVEL
Minimum required level for sending configuration transfer log messages.
SYSTEM CONFIG > SYSLOG > ROUTER LEVEL
Minimum required level for sending router log messages.
SYSTEM CONFIG > SYSLOG > NONVOL LEVEL
Minimum required level for sending nonvolatile memory log messages.
61200704L2-1B © 2003 ADTRAN, Inc. 41
Page 42

Section 4 SHDSL RCU ATM User Interface Guide Total Access 544R System Manual
SYSTEM CONFIG > SYSLOG > NOKIA LEVEL
Minimum required level for sending log messages about communication with the Nokia DSLAM.
Messages are only generated for products with an SHDSL WAN interface.
SYSTEM CONFIG > SYSLOG > AUTOBAUD LEVEL
Minimum required level for sending log messages about communication with the Lucent Stinger DSLAM.
Messages are only generated for products with an SHDSL WAN interface.
SYSTEM CONFIG > SYSLOG > TOLLBRG LEVEL
Minimum required level for sending log messages about communication with the Tollbridge Voice
Gateway. Messages are only generated for ATM products.
SYSTEM CONFIG > SYSLOG > CMCP LEVEL
Minimum required level for sending log messages about communication with the CopperMountain
DSLAM. Messages are only generated for ATM products.
SYSTEM CONFIG > SYSLOG > SHDSL LEVEL
This parameter is for ADTRAN internal use only.
SYSTEM CONFIG > SYSLOG > L1 LEVEL
Minimum required level for sending log messages about WAN physical or Layer 1 connection.
SYSTEM CONFIG > SYSLOG > ETH LEVEL
Minimum required level for sending log messages about Ethernet physical connection.
SYSTEM CONFIG > SYSLOG > ICMP LEVEL
Minimum required level for sending ICMP log messages.
SYSTEM CONFIG > SYSLOG > CONFIG LEVEL
This parameter is for ADTRAN internal use only.
SYSTEM CONFIG > SYSLOG >DS0 LEVEL
Minimum required level for sending log messages about DSO mapping.
SYSTEM CONFIG > SYSLOG > SELFTEST LEVEL
Minimum required level for sending log messages about selftest.
42 © 2003 ADTRAN, Inc. 61200704L2-1B
Page 43

Total Access 544R System Manual Section 4 SHDSL RCU ATM User Interface Guide
SYSTEM CONFIG > SYSLOG > VOICE LEVEL
Minimum required level for sending log messages about AAL2 voices services.
Messages are only generated for ATM products.
SYSTEM CONFIG > SYSLOG > JETSTREAM LEVEL
Minimum required level for sending log messages about communication with the JetStream Voice
Gateway. Messages are only generated for ATM products.
SYSTEM CONFIG > SYSLOG > POTS LEVEL
Minimum required level for sending log messages about POTS line cards and services.
SYSTEM CONFIG > SYSLOG > LESCAS LEVEL
Minimum required level for sending messages about communication with LESCAS compatible Voice
Gateways. Messages are only generated for ATM products.
SYSTEM CONFIG > SYSLOG > ATM LEVEL
Minimum required level for sending ATM log messages. Messages are only generated for ATM products.
SYSTEM CONFIG > SYSLOG > COPPERCOM LEVEL
Minimum required level for sending log messages about communication with the CopperCom Voice
Gateway. Messages are only generated for ATM products.
SYSTEM CONFIG > SYSLOG > VOFR LEVEL
Minimum required level for sending voice-over-frame-relay log messages about communication with the
CopperMountain DSLAM. Messages are only generated for ATM products.
SYSTEM CONFIG > SYSLOG > XMODEM LEVEL
Minimum required level for sending XMODEM log messages for firmware and configuration transfers.
SYSTEM CONFIG > SYSLOG > EMWEB LEVEL
This parameter is for ADTRAN internal use only.
SYSTEM CONFIG > SYSLOG > FRELAY LEVEL
Minimum required level for sending frame relay log messages.
61200704L2-1B © 2003 ADTRAN, Inc. 43
Page 44

Section 4 SHDSL RCU ATM User Interface Guide Total Access 544R System Manual
SYSTEM CONFIG > SYSLOG > BRIDGE LEVEL
Minimum required level for sending bridge mode log messages.
SYSTEM CONFIG > SYSLOG > MAINT LEVEL
Minimum required level for sending CRAFT port log messages.
SYSTEM CONFIG > SYSLOG > HDLC LEVEL
Minimum required level for sending low level HDLC log messages.
SYSTEM CONFIG > SYSLOG > VOATM LEVEL
Minimum required level for sending Voice-over-ATM log messages.
SYSTEM CONFIG > SYSLOG > PPPOA LEVEL
Minimum required level for sending PPP-over-ATM log messages.
SYSTEM CONFIG > SYSLOG > FDL LEVEL
Minimum required level for sending FDL log messages.
SYSTEM CONFIG > NETWORK TIME
Activate the network time and configure the server type, time zone and various other network time
parameters from this menu.
SYSTEM CONFIG > NETWORK TIME > SERVER TYPE
The unit time can be entered manually from the SYSTEM INFO menu, or the unit can receive time from an
NTP/SNTP server. The
communicates with the time server.
The server type defines the port on which the unit will listen to receive timing information from the time
server. The choices are
server running SNTP software on its TIME port. When set to
an SNTP server. The factory default is
NETWORK TIME menu includes all parameters relating to how the unit
NT TIME and SNTP. When set to NT TIME, the unit will receive time from an NT
SNTP, the unit will receive time directly from
SNTP.
SYSTEM CONFIG > NETWORK TIME > ACTIVE
This network timing feature can be turned on and off. It determines whether the unit will request and
receive time from a time server. The factory default is
NO.
44 © 2003 ADTRAN, Inc. 61200704L2-1B
Page 45

Total Access 544R System Manual Section 4 SHDSL RCU ATM User Interface Guide
SYSTEM CONFIG > NETWORK TIME > TIME ZONE
All time zones are based off of Greenwich Mean Time (GMT). The choices are listed below
•GMT
• GMT -5 (E
• GMT -6 (C
• GMT -7 (M
• GMT -8 (P
• GMT -9 (A
• GMT -10 (H
ASTERN)
ENTRAL)
OUNTAIN)
ACIFIC)
LASKA)
AWAII)
The factory default is GMT-6 (CENTRAL).
SYSTEM CONFIG > NETWORK TIME > ADJUST FOR DAYLIGHT SAVING
Since some areas of the world use Daylight Savings Time, the unit is designed to adjust the time on the
first Sunday in April and the last Sunday in October accordingly if this option is turned on. The factory
default is
YES.
SYSTEM CONFIG > NETWORK TIME > HOST ADDRESS
This is the IP address of the time server that the unit will request and receive time from. The factory default
is no entry in the host address field.
SYSTEM CONFIG > NETWORK TIME > REFRESH
This is the interval of time between each request the unit sends out to the time server. A smaller refresh
time guarantees that the unit receives the correct time from the server and corrects possible errors more
quickly. This may be more taxing on the machine. A range of refresh times is available for the user to
decide which is best for their unit. Choices include
MINS, 40 MINS, 45 MINS, 50 MINS, 55 MINS, and 60 MINS. The factory default is 60 MINS.
5 MINS, 10 MINS, 15 MINS, 20 MINS, 25 MINS, 30 MINS, 35
SYSTEM CONFIG > NETWORK TIME > STATUS
This displays the current status of the time negotiation process. If an error is displayed, check all
connections and configurations to try to resolve the problem.
61200704L2-1B © 2003 ADTRAN, Inc. 45
Page 46

Section 4 SHDSL RCU ATM User Interface Guide Total Access 544R System Manual
SYSTEM UTILITY
Use the SYSTEM UTILITY menu to view and set the system parameters shown in Figure 4.
Figure 3. System Utility Menu
SYSTEM UTILITY > UPGRADE FIRMWARE
Select the firmware upgrade method and perform upgrade from this menu.
SYSTEM UTILITY > UPGRADE FIRMWARE > TRANSFER METHOD
The customer can update firmware when unit enhancements are released.
The two methods for upgrading are
information.)
TFTP requires a TFTP server running on the network. The unit starts a TFTP client function
which gets the upgrade code from the TFTP server. Selecting
through the
TFTP.
CRAFT port using any PC terminal emulator with XMODEM capability. The factory default is
XMODEM and TFTP. (See the DLP section of this manual for more
XMODEM will load the upgrade code
SYSTEM UTILITY > UPGRADE FIRMWARE > TFTP SERVER ADDRESS
This is required when the transfer method is TFTP. It is the IP address or domain name (if DNS is
configured) of the TFTP server. The factory default is no entry in the TFTP server address field.
46 © 2003 ADTRAN, Inc. 61200704L2-1B
Page 47

Total Access 544R System Manual Section 4 SHDSL RCU ATM User Interface Guide
SYSTEM UTILITY > UPGRADE FIRMWARE > TFTP SERVER FILENAME
This is required when the transfer method is TFTP. It is the case-sensitive file name which contains the
upgrade code. The factory default is no entry in the
TFTP SERVER FILENAME field.
SYSTEM UTILITY > UPGRADE FIRMWARE > TRANSFER STATUS
This appears when TFTP is used. It displays the status of the transfer as it happens. Any error or success
message will be displayed here.
SYSTEM UTILITY > UPGRADE FIRMWARE > START TRANSFER
This activator is used when the configurable items in this menu are complete. This will initiate the transfer
for either TFTP or XMODEM upgrades.
Before using START TRANSFER, the unit should have a valid IP address, subnet mask, and
default gateway (if required). See DLP-2, Setting IP Parameters for the Total Access 544R
for more information.
SYSTEM UTILITY > UPGRADE FIRMWARE > ABORT TRANSFER
Use this activator to cancel any TFTP transfer in progress.
SYSTEM UTILITY > CONFIG TRANSFER
Select the config transfer method and perform the transfer from this menu.
SYSTEM UTILITY > CONFIG TRANSFER > TRANSFER METHOD
Sends a file containing the unit configuration to a PC connected to the CRAFT port using XMODEM
protocol or to a file on a TFTP server using the TFTP protocol.
CONFIG TRANSFER also lets you save the unit configuration as a backup file, so you can use the same
configuration with multiple units. In addition,
TFTP server.
To support these transfers, ADTRAN delivers a TFTP program with the unit called TFTP Server. You can
configure any PC running Microsoft Windows with this software, and store a configuration file.
Before using Start Transfer, the unit should have a valid IP address, subnet mask, and
default gateway (if required). See DLP-2, Setting IP Parameters for the Total Access 544R
for more information.
CONFIG TRANSFER can retrieve a configuration file from a
Only one configuration transfer session (upload or download) can be active at a time.
XMODEM and TFTP
are supported.
61200704L2-1B © 2003 ADTRAN, Inc. 47
Page 48

Section 4 SHDSL RCU ATM User Interface Guide Total Access 544R System Manual
SYSTEM UTILITY > CONFIG TRANSFER > TFTP SERVER IP ADDRESS
Specifies the IP address of the TFTP server. Get this number from your system administrator. If using the
ADTRAN Utilities TFTP server, this number appears in the TFTP server status window. The factory
default value is
0.0.0.0.
SYSTEM UTILITY > CONFIG TRANSFER > TFTP SERVER FILENAME
Defines the name of the configuration file that you transfer to or retrieve from the TFTP server. The default
name is
ta_iad.cfg, but you can edit this name.
SYSTEM UTILITY > CONFIG TRANSFER > CURRENT TRANSFER STATUS
Indicates the current status of the update.
SYSTEM UTILITY > CONFIG TRANSFER > PREVIOUS TRANSFER STATUS
Indicates the status of the previous update.
SYSTEM UTILITY > CONFIG TRANSFER > LOAD AND USE CONFIG
Retrieves the configuration file specified in the TFTP Server Filename field from the server. To start this
command, enter
Y to begin or enter N to cancel.
If you execute this command, the unit retrieves the configuration file, reboots, then restarts
using the new configuration
SYSTEM UTILITY > CONFIG TRANSFER > SAVE CONFIG REMOTELY
Saves the configuration file specified in TFTP Server Filename to the server identified in TFTP Server IP
Address. To start this command, enter
Y to begin or enter N to cancel.
Before using this command, you must have identified a valid TFTP server in TFTP SERVER
IP A
DDRESS.
SYSTEM UTILITY > SYSTEM UTILIZATION
View the CPU utilization stats from this menu.
SYSTEM UTILITY > SYSTEM UTILIZATION > PERFORMANCE
Clear the system utilization stats and view the total and current CPU utilization stats from this menu.
48 © 2003 ADTRAN, Inc. 61200704L2-1B
Page 49

Total Access 544R System Manual Section 4 SHDSL RCU ATM User Interface Guide
SYSTEM UTILITY > SYSTEM UTILIZATION > PERFORMANCE > TOTAL AVG CPU UTILIZATION
TOTAL AVG CPU UTILIZATION is a running total of CPU utilization since the last reset.
SYSTEM UTILITY > SYSTEM UTILIZATION > PERFORMANCE > CURRENT AVG CPU UTILIZATION
CURRENT AVG CPU UTILIZATION is the running total of CPU utilization since the last clear.
SYSTEM UTILITY > SYSTEM UTILIZATION > PERFORMANCE >TOTAL AVG ISR UTILIZATION
The Total Avg ISR Utilization is a running total average of the ISR Utilization.
SYSTEM UTILITY > SYSTEM UTILIZATION > PERFORMANCE > CLEAR STATS
This activator will clear all the system utilization performance stats.
SYSTEM UTILITY > PING
Activate the ping test and define the ping packet characteristics from this menu.
SYSTEM UTILITY > PING > START/STOP
Activator to start and cancel a ping test.
Only one ping session can be active at a time.
Diagnostic features such as ping, extended ping, traceroute, extended traceroute, and
telnet client can also be performed via
TERMINAL MODE (see page 40).
SYSTEM UTILITY > PING > HOST ADDRESS
IP address or domain name (if DNS is configured) of device to receive the ping. This field is left blank by
default.
SYSTEM UTILITY > PING > SIZE (40-1500)
Total size of the ping to send. Range is 40 to 1500 bytes. The default is 64.
SYSTEM UTILITY > PING > # OF PACKETS
Total packets to send every 2 seconds. Setting this to 0 allows the client to ping continuously. The default is
5.
61200704L2-1B © 2003 ADTRAN, Inc. 49
Page 50

Section 4 SHDSL RCU ATM User Interface Guide Total Access 544R System Manual
SYSTEM UTILITY > PING > # TRANSMITS
Total packets sent (read only).
SYSTEM UTILITY > PING > # RECEIVES
Total packets received (read only).
SYSTEM UTILITY > PING > % LOSS
Percentage loss based on ping returned from host (read only).
SYSTEM UTILITY > TRACEROUTE
Utility program used to trace a data path to a final destination.
SYSTEM UTILITY > TRACEROUTE > TRACE TARGET
Specifies the IP address of the remote system to trace the routes to.
SYSTEM UTILITY > TRACEROUTE > MAXIMUM HOPS
Specifies the maximum number of router exchanges allowed when traveling to the final destination
(specified using the
TRACE TARGET field) Range is 1 to 30. Default is 30.
SYSTEM UTILITY > TRACEROUTE > TIMEOUT (IN SECS)
Specifies the maximum delay (in milliseconds) given to a host (along a path to the final destination) to
respond to the probe datagram sent before considering the packet a failure.
SYSTEM UTILITY > TRACEROUTE > RETRIES
Specifies the number of times the probe datagram is sent to each host (along the path to the final
destination).
SYSTEM UTILITY > TRACEROUTE > BEGIN TRACEROUTE
Activates the traceroute process by sending a probe datagram with a Time To Live (TTL) value of 1.
SYSTEM UTILITY > RESET UNIT
Selecting this activator will power reset the unit.
50 © 2003 ADTRAN, Inc. 61200704L2-1B
Page 51

Total Access 544R System Manual Section 4 SHDSL RCU ATM User Interface Guide
SYSTEM UTILITY > TERMINAL MODE
Selecting the terminal mode gives the user a command-line prompt to perform utilities such as pings,
traceroutes, resets, firmware updates, configuration, and more.
using the shortcut keys
CNTRL T from other menu screens. From this command-line prompt, you can:
• Perform a reset with the command "reset"
• Perform a factory restore with the command "factory_reset"
• Configure the unit. The unit has the ability to download a text file which contains the configuration of
the entire unit. This configuration may then be altered in a text editor, and then uploaded to a unit.
• Debug and troubleshoot. This function would be carried out with the assistance of ADTRAN Technical
Support.
• Start and stop the fail-safe timer for the auto-config feature.
• Perform a firmware upgrade via TFTP.
upgrade_firmware hostname filename
• Use the save command to write the entire configuration to flash.
• Display the unit’s MAC address with the command mac
• Perform a ping or extended ping. Syntax is:
TERMINAL MODE can also be accessed by
ping hostname/address [repeat xx] [size xx] [timeout xx] [source xx] [noNat]
Options:
repeat <repeat count> Number of pings to send (default 5)
size (datagram size) Range is 40-1500
timeout (seconds) Timeout in seconds (range 1-10)
source (address or name) Source address or interface name to use
noNat Do not NAT the ping packet
Options may be entered in any order and may be truncated.
Valid interface names are eth0, fdl0, ppp0, fr0, fr1, etc.
Example usage: ping 10.0.0.5 r si 1500 so eth0 n
This will ping with a repeat count of 10. The datagram size is 1500 bytes, and the source address
used in the ping packet will be the ethernet IP address. The “noNat” option has been specified, so
if NAT is enabled, this packet will NOT be translated.
• Perform a traceroute or extended traceroute. Syntax is:
traceroute hostname/address [hops xx] [timeout xx] [retries xx] [source xx] [noNat]
Options:
hops <hops count> Max number of hops (default 30)
timeout <seconds> Timeout in seconds (default 3)
retries <seconds> Number of retries per hop (default 3)
source <address or name> Source address or interface name to use
61200704L2-1B © 2003 ADTRAN, Inc. 51
Page 52

Section 4 SHDSL RCU ATM User Interface Guide Total Access 544R System Manual
noNat Do not NAT the trace packets
Options may be entered in any order and may be truncated.
Valid interface names are eth0, fdl0, ppp0, fr0, fr1, etc.
Example usage: trace 10.0.0.5 h 20 t 1 r 1 so eth0
This will perform a trace to 10.0.0.5 with a max hop count of 20. The timeout for each hop is 1
second, and the retry count per hop is 1. The ethernet IP will be used as the source address, and the
packet WILL go through NAT if NAT is enabled, meaning that the packet will be translated and
the source address will be replaced by the NAPT address.
• Use the telnet client feature to telnet to a remote host. Syntax is:
telnet hostname/address [port xx]
Default port is 23 (TELNET).
• To exit terminal mode, type exit or !exit,
exit - if any configuration have been made, you will be prompted whether or not to save these
changes. If no changes were made then the terminal session will exit without the confirm message.
!exit - exit without saving or applying any configuration changes.
Extended ping, extended traceroute, and telnet client are new features initially available in
D.04.14. These functions may be performed simultaneously from multiple user sessions.
52 © 2003 ADTRAN, Inc. 61200704L2-1B
Page 53

Total Access 544R System Manual Section 4 SHDSL RCU ATM User Interface Guide
INTERFACES (SHDSL)
View the SHDSL interface status and configure SHDSL parameters from this menu.
Figure 4. Interfaces Menu
INTERFACES (SHDSL) > CONFIG > ANNEX = A/B
Select the maintenance or signaling protocol used over the network port. The signaling types supported are
ANNEX A, ANNEX B, and ANNEX A AND B. The default is ANNEX A, which is the ITU-T adopted interface
standard for international frame relay applications.
INTERFACES (SHSDL) > CONFIG > ITU-T/GSPAN V1.2
Select ITU-T or GLOBESPAN V1.2. The factory default setting is ITU-T.
INTERFACES (SHSDL) > CONFIG > RADSL (AUTO/FIXED)
Rate Adaptive Digital Subscriber Line. Set the speed transmission type for the RADSL.
INTERFACES (SHDSL) > STATUS > SHDSL STATS > TRAINING STATS
This field is for internal ADTRAN use only.
INTERFACES (SHDSL) > STATUS > SHDSL STATS > DATA RATE
Displays the data rate of the SHDSL network connection.
61200704L2-1B © 2003 ADTRAN, Inc. 53
Page 54

Section 4 SHDSL RCU ATM User Interface Guide Total Access 544R System Manual
INTERFACES (SHDSL) > STATUS > SHDSL STATS > FRAME MODE
Displays the type of framing (either SHDSL Framed or SHDSL Framed Plesio w/bit stuffing).
INTERFACES (SHDSL) > STATUS > SHDSL STATS > G.HS EVENT
This field is for internal ADTRAN use only.
INTERFACES (SHDSL) > STATUS > SHDSL STATS > ANNEX
Displays the Annex type set in the SHDSL config.
INTERFACES (SHDSL) > STATUS > EOC STATS > SHDSL VERSION
ITU-T G.991.2 version supported by remote unit.
INTERFACES (SHDSL) > STATUS > EOC STATS > VENDOR LIST NUMBER
List number of remote unit.
INTERFACES (SHDSL) > STATUS > EOC STATS > VENDOR ISSUE NUMBER
Issue number of remote unit.
INTERFACES (SHDSL) > STATUS > EOC STATS > CLEI CODE
CLEI code of remote unit.
INTERFACES (SHDSL) > STATUS > EOC STATS > VENDOR ID
Vendor ID of remote unit.
INTERFACES (SHDSL) > STATUS > EOC STATS > MANUFACTURE DATE
Manufacture date of remote unit.
INTERFACES (SHDSL) > STATUS > EOC STATS > PROM CHECKSUM
PROM checksum of remote.
INTERFACES (SHDSL) > STATUS > EOC STATS > VENDOR MODEL NUMBER
Model number of remote unit.
54 © 2003 ADTRAN, Inc. 61200704L2-1B
Page 55

Total Access 544R System Manual Section 4 SHDSL RCU ATM User Interface Guide
INTERFACES (SHDSL) > STATUS > EOC STATS > VENDOR SERIAL NUMBER
Serial number of remote unit.
INTERFACES (SHDSL) > STATUS > EOC STATS > VENDOR SOFTWARE VERSION
Software version of remote unit.
INTERFACES (SHDSL) > STATUS > PERFORMANCE MONITORING > SNR MARGIN (DB)
Signal-to-voice ration margin on SHDSL line.
INTERFACES (SHDSL) > STATUS > PERFORMANCE MONITORING > LOOP ATTENUATION
Loop attenuation on SHDSL line
INTERFACES (SHDSL) > STATUS > PERFORMANCE MONITORING > ERRORED SECONDS
Number of errored seconds on SHDSL line.
INTERFACES (SHDSL) > STATUS > PERFORMANCE MONITORING > SEVERELY ERRORED
SECONDS
Number of severely errored seconds on SHDSL line.
INTERFACES (SHDSL) > STATUS > PERFORMANCE MONITORING > UNAVAILABLE SECONDS
Number of unavailable seconds on SHDSL line.
INTERFACES (SHDSL) > STATUS > PERFORMANCE MONITORING > CODE VIOLATIONS COUNT
Number of code violations on SHDSL line.
INTERFACES (SHDSL) > STATUS > PERFORMANCE MONITORING > LOSS OF SYNC WORD
ECONDS
S
Number of seconds of sync loss on SHDSL line.
INTERFACES (ETH)
NTERFACES (ETH) > CONFIG > AUTONEGOTIATION
I
Set the Ethernet rate to automatically negotiate the speed or option to set manually. Select ON or OFF. The
default is
61200704L2-1B © 2003 ADTRAN, Inc. 55
ON.
Page 56

Section 4 SHDSL RCU ATM User Interface Guide Total Access 544R System Manual
INTERFACES > STATUS > MAC ADDRESS
This is a read-only field which displays the unique MAC address programmed at ADTRAN.
INTERFACES > STATUS > DATA LINK
Displays the data link layer protocol status.
L2 PROTOCOL
Use the L2 protocol menu to select the L2 protocol, configure the protocol specific parameters and view
the status as shown in Figure 5.
Figure 5. L2 Protocol Menu
L2 PROTOCOL (SHDSL)
Configure the L2 Protocol parameters and view the status of the SHDSL interface using ATM protocol
from this menu.
L2 PROTOCOL (SHDSL) > PROTOCOL
Select the L2 protocol mode. The default is ATM.
56 © 2003 ADTRAN, Inc. 61200704L2-1B
Page 57

Total Access 544R System Manual Section 4 SHDSL RCU ATM User Interface Guide
L2 PROTOCOL (SHDSL) > PROTOCOL> ATM
Asynchronous Transfer Mode allocates bandwidth on demand, automatically adjusting the network
capacity to meet the system needs. Fixed-length cells (53 octet) require lower processing overhead and
allow higher transmission speeds than traditional packet switching methods. ATM uses five octet headers
in each fifty-three octet cell to match cells with specific virtual channels to which they belong.
L2 PROTOCOL (SHDSL - ATM) > CONFIG
Configure the L2 Protocol parameters for the SHDSL interface using ATM protocol.
L2 PROTOCOL (SHDSL - ATM) > CONFIG > ATM CONFIG
Use the ATM config menu to set the parameters listed below.
L2 PROTOCOL (SHDSL - ATM) > CONFIG > ATM CONFIG > IDLE CELLS
The Idle Cells format must be configured for either ATM F ORUM (UNASSIGNED) or ITU (IDLE). Configuring
this setting incorrectly for a particular circuit will cause poor performance at the ATM Layer. The default is
ATM FORUM (UNASSIGNED).
L2 PROTOCOL (SHDSL - ATM) > CONFIG > ATM CONFIG > DATA SCRAMBLING
DATA SCRAMBLING can be ENABLED or DISABLED for cell traffic. Configuring this setting incorrectly for a
particular circuit will cause poor performance at the ATM Layer.
The setting must match the configuration setting of the ATM switch or DSLAM at the other
end of the circuit.
L2 PROTOCOL (SHDSL - ATM) > CONFIG > ATM CONFIG > HEC COSET
Header Error Control is located in the last (5th) byte of the ATM cell header that checks for cell integrity
only. The Coset polynomial is applied to the received HEC for comparison with the HEC generated
internally. HEC errors may be detected after synchronization any bit errors detected will prompt that cell
be dropped. The choice are
ENABLED or DISABLED. The default is ENABLED.
L2 PROTOCOL (SHDSL - ATM) > CONFIG > PVC CONFIG
Configure up to six ATM PVCs from this menu.
L2 PROTOCOL (SHDSL - ATM) > CONFIG > PVC CONFIG > NUM
Displays the index number for the PVC entry.
61200704L2-1B © 2003 ADTRAN, Inc. 57
Page 58

Section 4 SHDSL RCU ATM User Interface Guide Total Access 544R System Manual
L2 PROTOCOL (SHDSL - ATM) > CONFIG > PVC CONFIG > ACTIVE
Activates the ATM PVC. The choices are YES or NO. Default is NO.
L2 PROTOCOL (SHDSL - ATM) > CONFIG > PVC CONFIG > SUB-INTERFACE
The SHDSL Sub-Interface is ATM that represents the SHDSL physical and logical ports respectively. This
is a read-only field.
L2 PROTOCOL (SHDSL - ATM) > CONFIG > PVC CONFIG > VPI
ATM Virtual Path Identifier located in the ATM cell header identifies the virtual path over which this port
is running. The range is
0-256. The default is 0.
L2 PROTOCOL (SHDSL - ATM) > CONFIG > PVC CONFIG > VCI
This is the ATM Virtual Channel Identifier that serves as an address for the virtual channel cell
transmissions between two devices. The range is
0-6535. The default setting is 38.
L2 PROTOCOL (SHDSL - ATM) > CONFIG> PVC CONFIG > CONNECTION
Select the physical and logical method of data transfer over the virtual path.
L2 PROTOCOL (SHDSL - ATM) > CONFIG > PVC CONFIG > CONNECTION [ROUTER] > SETUP
> PROTOCOL
Select the data-link protocol for the PVC. The choices are IP or PPP. The default is IP.
The following PPP SETUP menu options only appear when the Protocol is set to PPP.
L2 Protocol > Config > PVC Config > Setup > PPP Setup.
AUTHENTICATION [+]
The AUTHENTICATION menu contains the required parameters for the authentication of the PPP peer
and for being authenticated by the PPP peer. Authentication is applied between the unit and the PPP
peer as described in the
AUTHENTICATION submenus.
TX METHOD
This parameter specifies how the unit is to be authenticated by the PPP peer. There are four possible
selections. Default it
58 © 2003 ADTRAN, Inc. 61200704L2-1B
NONE.
Page 59

Total Access 544R System Manual Section 4 SHDSL RCU ATM User Interface Guide
NONE
PAP, CHAP, OR EAP
CHAP OR EAP
EAP ONLY
PAP ONLY
RX METHOD
The connection will not allow the PPP peer to authenticate it.
The unit will ask for EAP during the first PPP LCP negotiation and
allow the PPP peer to negotiate down to
CHAP or PAP.
The unit will ask for EAP during the first PPP LCP negotiation and
allow the PPP peer to negotiate down to
CHAP but not PAP.
The unit will only allow EAP to be negotiated. If the PPP peer is not
capable of doing
EAP, then the connection will not succeed.
The unit will only allow PAP to be negotiated. If the PPP peer is not
capable of doing
PAP, then the connection will not succeed.
This parameter specified how the unit is to be authenticated by the PPP peer. There are four possible
selections. Default is
NONE
PAP, CHAP, OR EAP
NONE.
The connection will not allow the PPP peer to authenticate it.
The unit will ask for EAP during the first PPP LCP negotiation and
allow the PPP peer to negotiate down to
CHAP or PAP.
CHAP OR EAP
EAP
PPP
The unit will ask for EAP during the first PPP LCP negotiation and
allow the PPP peer to negotiate down to
CHAP but not PAP.
The unit will only allow EAP to be negotiated. If the PPP peer is not
capable of doing
EAP, then the connection will not succeed.
Configure the PPP specific parameters such as MAX CONFIG, MAX TIMER, MAX FAILURE, and FORCE
PEER IP ADDRESS from this menu.
MAX CONFIG
This value is the number of unanswered configuration-requests that should be transmitted before
resetting PPP negotiations. the possible values are
MAX TIMER (SEC)
5, 10, 15, and 20 (default).
This value is the number of seconds to wait between unanswered configuration-requests. The
possible values are
1 SEC, 2 SECS, 3 SECS (DEFAULT), 5 SECS, and 10 SECS.
61200704L2-1B © 2003 ADTRAN, Inc. 59
Page 60

Section 4 SHDSL RCU ATM User Interface Guide Total Access 544R System Manual
MAX FAILURE
Due to the nature of PPP, configuration option may not be agreed upon between two PPP peers. This
value is the number of configuration-naks that should occur before an option is
configuration-rejected. The possible values are
FORCE PEER IP ADDRESS
5 (DEFAULT), 10, 15, and 20.
This option forces the PPP to negotiate the IP address entered instead of allowing another address to
be assigned by the remote end. The default is
KEEPALIVE PERIOD
NO.
This option allows the user to generate PPP keepalive packets that can be sent every 1 minute, 2
minutes, or every
The default is
PPP ENCAPSULATION
5 minutes. A value of 0 (OFF) disables the PPP keepalive packet generating feature.
0 (OFF).
This option allows the user to set the encapsulation modes for PPP over ATM. LLC has an
encapsulation header in the AAL5 frame indicating it is encapsulating PPP. VC-Mux does not have a
header, and is therefor dedicated to using PPP. The choices are
VC-MUX.
LLC or VC-MUX. The default is
L2 PROTOCOL (SHDSL - ATM) > CONFIG > PVC CONFIG > CONNECTION [ROUTER] > SETUP
> MODE
This mode identifies how the data will be transferred. The choices are:
ROUTE IP
BRIDGE ALL
ROUTE IP/BRIDGE
O
THER
The default is
ROUTE IP.
All IP data for this PVC will be routed.
All data for this PVC will bridged.
All IP data will be routed. All other data will be bridged.
L2 PROTOCOL (SHDSL - ATM) > STATUS > ATM STATUS
AP: TX CELLS
This is the number of cells transmitted.
60 © 2003 ADTRAN, Inc. 61200704L2-1B
Page 61

Total Access 544R System Manual Section 4 SHDSL RCU ATM User Interface Guide
AP: RX CELLS
This is the number of cells received.
AP: RX OAM CELLS
This is the number of OAM cells received
AP: RECEIVE CELLS DISCARDED
This is the number of cells received and discarded. An incrementing count in this field could indicate a
configuration problem with the ATM layer.
AP: RECEIVE CELL ERRORS
This is the number of cells received with an HEC error.
AP: SYNC
This indicates cell delineation at the ATM layer.
AP: OUT OF CELL DELINEATION
This indicates loss of cell delineation at the ATM layer.
AAL5: TRANSMIT FRAMES
This is the number of AAL5 frames transmitted.
AAL5: RECEIVE FRAMES
This is the number of AAL5 frames received.
AAL5: TRANSMIT DISCARDED FRAMES
This is the number of AAL5 frames discarded.
AAL5: RECEIVE ERRORS
This is the number of AAL5 errors received.
AAL5: RECEIVE DISCARDED FRAMES
This is the number of AAL5 frames received from the network that have been discarded.
61200704L2-1B © 2003 ADTRAN, Inc. 61
Page 62

Section 4 SHDSL RCU ATM User Interface Guide Total Access 544R System Manual
AAL5: NO ATM FRAMES
This is for internal use only.
AAL5: NO DATA PACKETS
This is for internal use only.
CLEAR STATS
This is used to clear the counters on this menu screen.
L2 PROTOCOL (SHDSL - ATM) > STATUS > PVC STATUS
View the ATM PVC statistics from this menu.
L2 PROTOCOL (SHDSL - ATM) > STATUS > PVC STATUS > NUM
Displays the index number in the PVC Status menu.
L2 PROTOCOL (SHDSL - ATM) > STATUS > PVC STATUS > SUB-INTERFACE
The SHDSL SUB-INTERFACE is ATM that represents the SHDSL physical and logical ports respectively.
This is a read-only field.
L2 PROTOCOL (SHDSL - ATM) > STATUS > PVC STATUS > AAL STATS
Shows the statistics of ATM Adaptation Layer frames.
MAX PDU SIZE
TX DATA BYTES
TX FRAMES
TX CELLS (ALL TYPES)
TX OAM CELLS
TX RM CELLS
TX EFCI=1 CELLS
TX CLPI=1 CELLS
Maximum Protocol Data Unit size for the ATM AAL5 frame.
Number of AAL5 data bytes transmitted.
Number of AAL5 frames transmitted.
Total number of AAL5 cells transmitted (all types).
Number of AAL5 Operations, Administration, and cells
transmitted.
Number of AAL5 RM cells transmitted.
Number of AAL5 EFCI=1 cells transmitted.
Number of AAL5 CLPI=1 transmitted.
RX DATA BYTES
RX FRAMES
62 © 2003 ADTRAN, Inc. 61200704L2-1B
Number of AAL5 data bytes received.
Number of AAL5 frames received
Page 63

Total Access 544R System Manual Section 4 SHDSL RCU ATM User Interface Guide
RX USER CELLS
RX OAM CELLS
RX BAD OAM CELLS
RX RM CELLS
RX BAD RM CELLS
RX EFCI=1 CELLS
RX CLPI=1 CELLS
DISCARD RX CELLS
DISCARD RX FRAMES
DISCARD TX FRAMES
TX QUEUE OVERFLOW
TX OUT OF CELLS
TX INACTIVE
Number of AAL5 user cells received
Number of AAL5 OAM cells received
Number of AAL5 Bad OAM cells received
Number of AAL5 RM cells received
Number of AAL5 Bad RM cells received
Number of AAL5 EFCI=1 cells received.
Number of AAL5 CLPI=1 cells received.
Number of AAL5 RX cells which were discarded.
Number of AAL5 RX frames which were discarded.
Number of AAL5 TX frames which were discarded.
Number of cells discarded due to queue overflow.
Number of AAL5 TX Out of Cells.
Number of TX frames discarded while PVC is inactive.
RX INACTIVE
CRC ERRORS
REASSEMBLY TIMEOUTS
TOO LONG FRAMES
CLEAR COUNTS
Number of RX frames discarded while PVC is inactive.
Number of AAL5 CRC Errors.
Number of AAL5 Reassembly Timeouts.
Number of AAL5 Too Long Frames.
Select to clear counters.
L2 PROTOCOL (SHDSL - ATM) > STATUS > PVC STATUS > PROTOCOL STATUS
Use these menus to view the PROTOCOL STATS and to CLEAR STATS for the PVC Protocol.
CLEAR STATS
The Clear Stats option is used to clear the statistic counters.
L2 PROTOCOL (ETH)
Configure the L2 PROTOCOL parameters and view the status of the Ethernet interface from this menu.
61200704L2-1B © 2003 ADTRAN, Inc. 63
Page 64

Section 4 SHDSL RCU ATM User Interface Guide Total Access 544R System Manual
L2 PROTOCOL (ETH) > INTERFACE
Displays the interface type.
L2 PROTOCOL (ETH) > PROTOCOL
Displays the L2 protocol for the 10/100BaseT Ethernet port. Currently only 802.3 is supported.
L2 PROTOCOL (ETH) > CONFIG
Configure the mode for this 10/100BaseT Ethernet port from this menu.
L2 PROTOCOL (ETH) > CONFIG > MODE
The mode identifies how the data will be forwarded. The choices are:
ROUTE IP
BRIDGE ALL
ROUTE IP/BRIDGE
OTHER
The default is ROUTE IP.
All IP data will be routed
All data will be bridged
All IP data will be routed. All other data will be bridged.
L2 PROTOCOL (ETH) > STATUS
View the L2 protocol statistics for the 10/100BASET Ethernet port from this menu.
L2 PROTOCOL (ETH) > STATUS > TX PACKETS
Total number of packets transmitted out the Ethernet port.
L2 PROTOCOL (ETH) > STATUS > RX PACKETS
Total number of packets received from the Ethernet port.
L2 PROTOCOL (ETH) > STATUS > TX ERRORS
Total number of transmit errors encountered on Ethernet port.
L2 PROTOCOL (ETH) > STATUS > SINGLE COLLISIONS
Total number of single collisions before successful transmission.
L2 PROTOCOL (ETH) > STATUS > MULTIPLE COLLISIONS
Total number of multiple collisions before successful transmission.
64 © 2003 ADTRAN, Inc. 61200704L2-1B
Page 65

Total Access 544R System Manual Section 4 SHDSL RCU ATM User Interface Guide
L2 PROTOCOL (ETH) > STATUS > EXCESSIVE COLLISIONS
Total number of collisions that resulted in packet being dropped.
L2 PROTOCOL (ETH) > STATUS > DEFERRED TRANSMISSIONS
Total number of packets deferred due to collisions.
L2 PROTOCOL (ETH) > STATUS > CARRIER SENSE ERRORS
Total number of carrier sense errors encountered (no link integrity).
L2 PROTOCOL (ETH) > STATUS > RX ERRORS
Number of packets received in error and dropped.
L2 PROTOCOL (ETH) > STATUS > CRCS
Number of packets detected with CRC errors.
L2 PROTOCOL (ETH) > STATUS > RX COLLISIONS
Number of collisions which occurred during reception.
L2 PROTOCOL (ETH) > STATUS > NON-ALIGNED
The Non-Aligned parameter is set when the number of bits received is not divisible by 8.
L2 PROTOCOL (ETH) > STATUS > CLEAR COUNTS
Selecting this activator clears all the Ethernet stats.
BRIDGE
Configure the bridge parameters and view bridging statistics from this menu as shown in Figure 6.
61200704L2-1B © 2003 ADTRAN, Inc. 65
Page 66

Section 4 SHDSL RCU ATM User Interface Guide Total Access 544R System Manual
Figure 6. Bridge Menu
BRIDGE > CONFIG
Configure the interfaces and bridge table parameters from this menu.
BRIDGE > CONFIG > INTERFACES
Configure the SHDSL interface bridging parameters from this menu.
BRIDGE > CONFIG > INTERFACES > NUM
Displays the index number fro the INTERFACE menu entries.
BRIDGE > CONFIG > INTERFACES > INTERFACE
This is a read-only field that displays the interface.
BRIDGE > CONFIG > INTERFACES > SUB-INTERFACE
This is a read-only field that displays the sub-interface.
BRIDGE > CONFIG > BRIDGE TABLE
Configure the bridge table parameters from this menu.
66 © 2003 ADTRAN, Inc. 61200704L2-1B
Page 67

Total Access 544R System Manual Section 4 SHDSL RCU ATM User Interface Guide
BRIDGE > CONFIG > BRIDGE TABLE > BRIDGE TABLE AGING (0-65535)
BRIDGE TABLE AGING is how soon an entry ages out of the Bridge table (in minutes). Default is 5.
BRIDGE > STATUS
View the bridging statistics from this menu.
BRIDGE > STATUS > BRIDGE TABLE
View the bridge table status from this menu.
BRIDGE > STATUS > BRIDGE TABLE > MAC ADDRESS
Ethernet address for device learned. This is a read-only field.
BRIDGE > STATUS > BRIDGE TABLE > LOCATION
Location indicates if it is LAN or WAN. This is a read-only field.
BRIDGE > STATUS > BRIDGE TABLE > TTL
Time to Live (TTL) is the number of seconds until the address is removed from the table. This is a read
only field.
ROUTER
Configure the router parameters and view routing statistics from this menu as shown in Figure 7.
61200704L2-1B © 2003 ADTRAN, Inc. 67
Page 68

Section 4 SHDSL RCU ATM User Interface Guide Total Access 544R System Manual
Figure 7. Router Menu
ROUTER > CONFIG
Configure the interfaces, routes, DHCP Server, and UDP Relay options from this menu.
ROUTER > CONFIG > INTERFACES
Configure the layer 3 options for the Ethernet and SHDSL interfaces from this menu.
ROUTER > CONFIG > INTERFACES (ETH)
Configure the layer 3 options for the Ethernet parameters from this menu.
The Ethernet port will always appear in the ROUTER > CONFIG > INTERFACES table
regardless of the L2 protocol mode setting.
ROUTER > CONFIG > INTERFACES (ETH) > SUB-INTERFACE
The Ethernet sub-interface is 802.3. This is a read-only field.
68 © 2003 ADTRAN, Inc. 61200704L2-1B
Page 69

Total Access 544R System Manual Section 4 SHDSL RCU ATM User Interface Guide
ROUTER > CONFIG > INTERFACES (ETH)> SETUP
Configure the Ethernet addressing, RIP, and Proxy ARP from this menu.
PRIMARY IP
This is used to setup the IP addresses for the LAN on the unit.
IP ADDRESS
The IP address assigned to the unit's Ethernet port is set here. This address must be unique within
the network. Default is
SUBNET MASK
This is the IP network mask that is to be applied to the unit's Ethernet port. Default is
255.255.255.0.
RIP
10.0.0.1.
Use this menu to enable RIP on the LAN interface.
VERSION
Enables or disables RIP and specifies the RIP protocol. Choices are; OFF (which disables
V1 (RIP Version 1) or V2 (RIP Version 2). The default is OFF.
RIP),
METHOD
Specifies the way the RIP protocol sends out its advertisements. The following options are
available:
SPLIT HORIZON (DEF)
POISON REVERSE
Only routes not learned from this circuit are advertised.
All routes are advertised, but the routes learned from this port
are “poisoned” with an infinite metric. The default is Split
Horizon.
DIRECTION
Allows the direction at which RIP advertisements are sent and received to be specified.
TX AND RX (DEF)
RIP advertisements are periodically transmitted and are listened
to on this port.
TX ONLY
RIP advertisements are periodically transmitted but are not
listened to on this port.
RX ONLY
RIP advertisements are listened to on this port, but are not
transmitted on this port.
61200704L2-1B © 2003 ADTRAN, Inc. 69
Page 70

Section 4 SHDSL RCU ATM User Interface Guide Total Access 544R System Manual
V2 SECRET
Enter the secret used by RIP version 2 here.
PROXY ARP
This feature allows the network portion of a group of addresses to be shared among several
physical network segments. The ARP protocol provides a way for devices to create a mapping
between physical addresses and logical IP addresses. Proxy ARP makes use of this mapping
feature by instructing a router to answer ARP requests as a "proxy" for the IP addresses behind
one of its ports. The device which sent the ARP request will then correctly assume that it can
reach the requested IP address by sending packets to the physical address that was returned. This
technique effectively hides the fact that a network has been (further) subnetted. If this option is
set to
YES, when an ARP request is received on the Ethernet port the address is looked up in the
IP routing table. If the forwarding port is not on the Ethernet port and the route is not the default
route, the unit will answer the request with its own hardware address. Default is
SECONDARY IPS
NO.
This allows the unit to specify additional IP addresses and networks on its Ethernet. The maximum
number of entries is 5.
NUM
Displays the index number in the secondary IP list.
IP ADDRESS
This is the second IP address the unit will respond to on the Ethernet. Default is 0.0.0.0.
SUBNET MASK
This is the mask for the network. Default is 255.255.255.255.
NAT MODE
This mode specifies whether Network Address Translation (NAT) should be use on this
interface. When this mode is set to
interface. The other choice is
PRIVATE (def) NAT is automatically specified on this
PUBLIC which specifies not going through NAT.
ROUTER > CONFIG > INTERFACES (ETH) > SUB-INTERFACE
The Ethernet sub-interface is ATM[0.1]. The [0.1] represents the ATM physical and logical ports, when 0
is the physical port and 1 is the logical port assigned to the ATM interface. This a read-only field.
70 © 2003 ADTRAN, Inc. 61200704L2-1B
Page 71

Total Access 544R System Manual Section 4 SHDSL RCU ATM User Interface Guide
ROUTER > CONFIG > ROUTES
Configures the default gateway and static routes from this menu.
ROUTER > CONFIG > ROUTES > DEFAULT GATEWAY
The default gateway is used by the unit to send IP packets whose destination addresses are not found in the
route table. Default is
0.0.0.0.
ROUTER > CONFIG > ROUTES > STATIC ROUTES
Use this menu to enter static routes to other networks.
NUM
Displays the index number in the static route table.
ACTIVE
Adds this static route entry to the IP routing table when set to YES and removes it (if it was previously
added) if set to
IP ADDRESS
NO. Default is NO.
The IP address of the host or network address of the device being routed to. Default is 0.0.0.0.
SUBNET MASK
Determines the bits in the previous IP address that are used. If this is to be a host route, it must be set
to all ones (255.255.255.255). Default is
GATEWAY
0.0.0.0.
The IP address of the router to receive the forwarded IP packet. Default is 0.0.0.0.
HOPS
The number of router hops required to get to the network or host. Maximum distance is 16 hops.
Default is
PRIVATE
1.
When set to NO, the unit will advertise this static route using RIP. Setting to YES means that the route
is kept private. Default is
NO.
ROUTER > CONFIG > DHCP SERVER
Use this menu to set up the DHCP server.
61200704L2-1B © 2003 ADTRAN, Inc. 71
Page 72

Section 4 SHDSL RCU ATM User Interface Guide Total Access 544R System Manual
ROUTER > CONFIG > DHCP SERVER > DHCP MODE
When set to ON, the unit acts as a DHCP server and will dynamically assign IP, network mask, default
gateway, and DNS addresses to any device which transmits a broadcast DHCP request. The addresses
assigned are based on the unit’s own IP address and will be within the same network. Default is
OFF.
ROUTER > CONFIG > DHCP SERVER > DHCP RENEWAL TIME (HOURS)
The number of hours that the DHCP server should allow the device to keep its previous IP assignment,
before it is required to send a new DHCP request. The default is
0 HOURS which represents an infinite
lease.
ROUTER > CONFIG > DHCP SERVER > DOMAIN NAME
Text string used to represent the domain name used by the unit.
ROUTER > CONFIG > DHCP SERVER > PRIMARY DNS
First server to which domain name requests are sent.
Default is
0.0.0.0.
ROUTER > CONFIG > DHCP SERVER > SECONDARY DNS
Server used as a backup, in case the primary address does not respond to the request.
Default is
0.0.0.0.
ROUTER > CONFIG > DHCP SERVER > PRIMARY NBNS/WINS
Primary address of the NBNS/WINS server.
Default is
0.0.0.0.
ROUTER > CONFIG > DHCP SERVER > SECONDARY NBNS/WINS
Secondary address of the NBNS/WINS server.
Default is
0.0.0.0.
ROUTER > CONFIG > UDP RELAY
This menu configures the unit to act as a UDP relay agent for applications requiring a response from UDP
hosts that are not on the same network segment as their clients.
ROUTER > CONFIG > UDP RELAY > MODE
When this option is set to ON, the unit will act as a relay agent. Default is OFF.
72 © 2003 ADTRAN, Inc. 61200704L2-1B
Page 73

Total Access 544R System Manual Section 4 SHDSL RCU ATM User Interface Guide
ROUTER > CONFIG > UDP RELAY > UDP RELAY LIST
Up to four relay destination servers can be specified in this list.
#
Indicates the entry number in the UDP Relay List table.
RELAY ADDRESS
This is the IP address of the server that will receive the relay packet. Default is 0.0.0.0.
UDP PORT TYPE
The choices are STANDARD (def) and SPECIFIED. The following standard UDP protocols are relayed
when set: DHCP, TFTP, DNS, NTP (Network Time Protocol, port 123), NBNS (NetBios Name
Server, port 137), NBDG (NetBIOS Datagram, port 138), and BootP. When
UDP port (1 to 65535) can be specified in the UDP Port columns (up to three per server).
SPECIFIED is set, the
UDP PORT 1, 2, 3
Used for specifying UDP ports to be relayed. These fields only apply when UDP PORT TYPE is set to
SPECIFIED. Default is 0.
ROUTER > STATUS
View t h e IP ROUTES, IP STATS, and ARP CACHE statistics from this menu.
ROUTER > STATUS > IP ROUTES
This lists the contents of the unit’s IP route table.
ROUTER > STATUS > IP ROUTES > IP ADDRESS
Network or host destination address.
ROUTER > STATUS > IP ROUTES > NETMASK
Network mask applied to the destination address.
ROUTER > STATUS > IP ROUTES > GATEWAY
Host or router to receive this packet.
ROUTER > STATUS > IP ROUTES > PORT
Port gateway is located on:
61200704L2-1B © 2003 ADTRAN, Inc. 73
Page 74

Section 4 SHDSL RCU ATM User Interface Guide Total Access 544R System Manual
LOCAL
ETH0
WAN0
FR 0 . . . FR 9
Sent directly to the unit’s router
The unit’s Ethernet port
The unit’s first PPP bundle
The unit is connected up to 10 DLCIs
ROUTER > STATUS > IP ROUTES > USE
Number of times the unit has referenced the route.
ROUTER > STATUS > IP ROUTES > FLAGS
Important tags associated with this route entry
H
G
S
R1
R2
I
C
P
T
U
route is a host route
route is a gateway route
static route, or learned via IPCP, IARP, DHCP
learned from RIP Version 1
learned from RIP Version 2
route learned from an ICMP redirect
directly connected interface
route is private and is not advertised with RIP
route is to a triggered port (updates only when table changes)
learned by unknown method
ROUTER > STATUS > IP ROUTES > HOPS
Number of routers that must go through to get to destination. Ranges from 0-15 or 16 for infinite (can’t get
there from here).
ROUTER > STATUS > IP ROUTES > TTL
Seconds until address is removed from table. Value of 999 means route is static.
74 © 2003 ADTRAN, Inc. 61200704L2-1B
Page 75

Total Access 544R System Manual Section 4 SHDSL RCU ATM User Interface Guide
ROUTER > STATUS > IP STATS
This section describes the following Statistics submenus (and see the tables on the pages following):
•IP
•ICMP
•TCP
• UDP
All of these statistics are taken from the MIB-II variables in RFC 1156. To clear the accumulated statistics,
press the
<Enter> key on CLEAR COUNTS.
ROUTER > STATUS > IP STATS > IP
View the IP statistics from this menu.
DEFAULT TTL
The default value inserted into the Time-To-Live field of the IP header of datagrams originated at this
unit, whenever a TTL value is not supplied by the transport layer protocol.
IP DATAGRAMS RECEIVED
The total number of input datagrams received from interfaces, including those received in error.
BAD HEADER PACKETS
The number of input datagrams discarded due to errors in their IP headers, including bad check sums,
version number mismatch, other format errors, time-to-live exceeded, errors discovered in
processing their IP options, etc.
BAD IP ADDRESSES
The number of input datagrams discarded because the IP address in their IP header's destination field
was not a valid address to be received at this unit. This count includes invalid addresses (e.g., 0.0.0.0)
and addresses of unsupported Classes (e.g., Class E). For entities which are not IP Gateways and
therefore do not forward datagrams, this counter includes datagrams discarded because the
destination address was not a local address.
TOTAL FORWARDED DATAGRAMS
The number of input datagrams for which this unit was not their final IP destination, as a result of
which an attempt was made to find a route to forward them to that final destination. In entities which
do not act as IP Gateways, this counter will include only those packets which were Source-Routed
via this unit, and the Source-Route option processing was successful.
61200704L2-1B © 2003 ADTRAN, Inc. 75
Page 76

Section 4 SHDSL RCU ATM User Interface Guide Total Access 544R System Manual
BAD PROTOCOL DISCARDS
The number of locally-addressed datagrams received successfully but discarded because of an
unknown or unsupported protocol.
DATAGRAMS DISCARDED
The number of input IP datagrams for which no problems were encountered to prevent their
continued processing, but which were discarded (e.g., for lack of buffer space). Note that this counter
does not include any datagrams discarded while awaiting re-assembly.
SENT DATAGRAMS TO UPPER LAYERS
The total number of input datagrams successfully delivered to IP user-protocols (including ICMP).
IP DATAGRAMS SENT
IP packets from the unit's IP stack.
ERRORFREE DISCARDS
The number of output IP datagrams for which no problem was encountered to prevent their
transmission to their destination, but which were discarded (e.g., for lack of buffer space). Note that
this counter would include datagrams counted in
TOTAL FORWARDED DATAGRAMS if any such packets
met this (discretionary) discard criterion.
ROUTELESS DISCARDS
The number of IP datagrams discarded because no route could be found to transmit them to their
destination. Note that this counter includes any packets counted in
TOTAL FORWARDED DATAGRAMS
which meet this “no-route” criterion. Note also that this includes any datagrams which a host cannot
route because all of its default gateways are down.
IP REASSEMBLY TIMEOUT
The maximum number of seconds received fragments are held while awaiting reassembly at this unit.
DISASSEMBLED FRAGMENTS
The number of IP fragments received which needed to be reassembled at this unit.
IP DATAGRAMS REASSEMBLED
The number of IP datagrams successfully reassembled.
76 © 2003 ADTRAN, Inc. 61200704L2-1B
Page 77

Total Access 544R System Manual Section 4 SHDSL RCU ATM User Interface Guide
IP REASSEMBLY FAILURES
The number of failures detected by the IP reassembly algorithm (for whatever reason: timed out,
errors, etc.). Note that this is not necessarily a count of discarded IP fragments since some algorithms
(notably RFC 815s) can lose track of the number of fragments by combining them as they are
received.
SUCCESSFUL FRAGMENTS
The number of IP datagrams that have been successfully fragmented at this unit.
FAILED FRAGMENTS
The number of IP datagrams that have been discarded because they needed to be fragmented at this
unit but could not be e.g., because their “Don't Fragment” flag was set.
TOTAL IP FRAGMENTS
The number of IP datagram fragments that have been generated as a result of fragmentation at this
unit.
DISCARDED ROUTING ENTRIES
A packet the unit couldn't route.
CLEAR COUNTS
Setting this activator clears the IP Statistics.
ROUTER > STATUS > IP STATS > ICMP
ICMP MESSAGES RECEIVED
The total number of ICMP messages the unit received. Note that this counter includes all those
counted by
ICMP SPECIFIC ERRORS
The number of ICMP messages the unit received but determined as having errors (bad ICMP
checksums, bad length, etc.)
ICMP DEST. UNREACHABLE MSGS RCVD
The number of ICMP Destination Unreachable messages received.
ICMP SPECIFIC ERRORS.
61200704L2-1B © 2003 ADTRAN, Inc. 77
Page 78

Section 4 SHDSL RCU ATM User Interface Guide Total Access 544R System Manual
ICMP TIMEOUTS RECEIVED
The number of ICMP Time Exceeded messages received.
ICMP PARAMETER PROBLEM MSGS RCVD
The number of ICMP Parameter Problem messages received.
ICMP SOURCE QUENCH MSGS RCVD
The number of ICMP Source Quench messages received.
ICMP REDIRECTED MESSAGES RCVD
The number of ICMP Redirect messages received.
ICMP ECHO REQUEST MSGS RCVD
The number of ICMP Echo (request) messages received.
ICMP ECHO REPLY MSGS RCVD
The number of ICMP Echo Reply messages received.
ICMP TIMESTAMP REQUEST MSGS RCVD
The number of ICMP Timestamp request messages received.
ICMP TIMESTAMP REPLY MSGS RCVD
The number of ICMP Timestamp Reply messages received.
ICMP ADDRESS MASK REQUEST MSGS RCVD
The number of ICMP Address Mask Request messages received.
ICMP ADDRESS MASK REPLY MSGS RCVD
The number of ICMP Address Mask Reply messages received.
ICMP MESSAGES SENT
The total number of ICMP messages this unit attempted to send. Note that this counter includes all
those counted by
78 © 2003 ADTRAN, Inc. 61200704L2-1B
ICMP PACKET ERRORS.
Page 79

Total Access 544R System Manual Section 4 SHDSL RCU ATM User Interface Guide
ICMP PACKET ERRORS
this unit did not send due to problems discovered within ICMP such as a lack of buffers. This value
should not include errors discovered outside the ICMP layer such as the inability of IP to route the
resultant datagram. In some implementations there may be no types of error which contribute to this
counter's value.
ICMP DEST. UNREACHABLE MSGS SENT
The number of ICMP Destination Unreachable messages sent.
ICMP TIME ECEEDED MSGS SENT
The number of ICMP Time Exceeded messages sent.
ICMP PARAMETER PROBLEM MSGS SENT
The number of ICMP Parameter Problem messages sent.
ICMP SOURCE QUENCH MSGS SENT
The number of ICMP Source Quench messages sent.
ICMP REDIRECT MSGS SENT
The number of ICMP Redirect messages sent.
ICMP ECHO REQUEST MSGS SENT
The number of ICMP Echo Request messages sent.
ICMP ECHO REPLY MSGS SENT
The number of ICMP Echo Reply messages sent.
ICMP TIMESTAMP REQUEST MSGS SENT
The number of ICMP Timestamp (request) messages sent.
ICMP TIMESTAMP REPLY MSGS SENT
The number of ICMP Timestamp Reply messages sent.
ICMP ADDR MASK REQUEST MSGS SENT
The number of ICMP Address Mask Request messages sent.
61200704L2-1B © 2003 ADTRAN, Inc. 79
Page 80

Section 4 SHDSL RCU ATM User Interface Guide Total Access 544R System Manual
ICMP ADDR MASK REPLY MSGS SENT
The number of ICMP Address Mask Reply messages sent.
CLEAR COUNTS
Selecting this activator will clear the ICMP statistics.
ROUTER > STATUS > IP STATS > UDP
View the UDP statistics from this menu.
UDP DATAGRAMS RECEIVED
The total number of UDP datagrams delivered to UDP users.
NO APPLICATION AT DEST. PORT
The total number of received UDP datagrams for which there was no application at the destination
port.
UDP BAD PACKETS
The number of received UDP datagrams that could not be delivered for reasons other than the lack of
an application at the destination port.
UDP DATAGRAMS SENT
The total number of UDP datagrams sent from this unit.
CLEAR COUNTS
Selecting this activator clears the UDP statistics.
ROUTER > STATUS > IP STATS > UDP TABLE
View the UDP table statistics from this menu.
LOCAL IP ADDRESS
The destination IP address of the packet
PORT
The destination UDP port of the packet.
80 © 2003 ADTRAN, Inc. 61200704L2-1B
Page 81

Total Access 544R System Manual Section 4 SHDSL RCU ATM User Interface Guide
ROUTER > STATUS > IP STATS > TCP
View the TCP statistics from this menu.
RETRANSMISSION TIMEOUT ALGORITHM
The algorithm used to determine the timeout value used for retransmitting unacknowledged octets.
MIN RETRANSMISSION TIMEOUT (MS)
The minimum value permitted by a TCP implementation for the retransmission timeout, measured in
milliseconds. More refined semantics for objects of this type depend upon the algorithm used to
determine the retransmission timeout. In particular, when the timeout algorithm is rsre(3), an object
of this type has the semantics of the
MAX RETRANSMISSION TIMEOUT (MS)
The maximum value permitted by a TCP implementation for the retransmission timeout, measured in
milliseconds. More refined semantics for objects of this type depend upon the algorithm used to
determine the retransmission timeout. In particular, when the timeout algorithm is rsre(3), an object
of this type has the semantics of the
LBOUND quantity described in RFC 793.
UNBOUND quantity described in RFC 793.
MAX TCP CONNECTIONS
The limit on the total number of TCP connections the unit can support. In entities where the
maximum number of connections is dynamic, this object should contain the value -1.
ACTIVE TCP CONNECTIONS
The number of times TCP connections have made a direct transition to the SYN-SENT state from the
CLOSED state.
TCP PASSIVE CONNECTIONS
The number of times TCP connections have made a direct transition to the SYN-RCVD state from the
LISTEN state.
TCP FAILED ATTEMPTS
The number of times TCP connections have made a direct transition to the CLOSED state from either
SYN-SENT state or the SYN-RCVD state, plus the number of times TCP connections have made a
the
direct transition to the
TOTAL TCP RESETS
LISTEN state from the SYN-RCVD state.
The number of times TCP connections have made a direct transition to the CLOSED state from either
the
ESTABLISHED state or the CLOSE-WAIT state.
61200704L2-1B © 2003 ADTRAN, Inc. 81
Page 82

Section 4 SHDSL RCU ATM User Interface Guide Total Access 544R System Manual
TCP CURRENT CONNECTIONS
The number of TCP connections for which the current state is either ESTABLISHED or CLOSE-WAIT.
TCP SEGMENTS RECEIVED
The total number of segments received, including those received in error. This count includes
segments received on currently established connections.
TCP SEGMENTS SENT
The total number of segments sent, including those on current connections but excluding those
containing only retransmitted octets.
TOTAL TCP RETRANSMITS
The total number of segments retransmitted – that is, the number of TCP segments transmitted
containing one or more previously transmitted octets.
CLEAR COUNTS
Selecting this activator clears the TCP statistics.
ROUTER > STATUS > IP STATS > TCP CONNS
View the TCP Conns Statistics from this menu. This table shows the different states of each TCP
connection.
STATE
The possible states are FREE, CLOSED, LISTEN, SYNC SENT, SYNC RECEIVED, ESTABLISHED, FINWAIT1,
F
INWAIT2, CLOSEWAIT, LASTACK, CLOSING, and TIMEWAIT.
LOCAL IP ADDRESS
Local IP address of the TCP connection.
LOCAL PORT
Local port of the TCP connection.
REMOTE IP ADDRESS
Remote IP address of the TCP connection.
82 © 2003 ADTRAN, Inc. 61200704L2-1B
Page 83

Total Access 544R System Manual Section 4 SHDSL RCU ATM User Interface Guide
REMOTE PORT
Remote port of the TPC connection.
ROUTER > STATUS > IP STATS > ARP CACHE
This lists the contents of the units’s ARP table. All resolved cache entries time out after 20 minutes.
Unresolved entries time out in 3 minutes. The ARP cache can be cleared by pressing
menu or by pressing <d> on the individual number for that entry.
IP ADDRESS
IP address used for resolving MAC address.
MAC ADDRESS
Ethernet address resolved (0=no resolution).
<f> while on the
TIME
Minutes since entry was first entered.
SECURITY
Configure the SECURITY FILTERS and RADIUS SERVER parameters from this menu as shown in Figure 8.
Figure 8. Security Menu
61200704L2-1B © 2003 ADTRAN, Inc. 83
Page 84

Section 4 SHDSL RCU ATM User Interface Guide Total Access 544R System Manual
SECURITY > FILTERS
Configure the filter characteristics from this menu.
SECURITY > FILTERS > FILTER DEFINES
The unit can filter packets based on certain parameters within the packet. The method used by the unit
allows the highest flexibility for defining filters and assigning them to a PVC or PPP link. The filters are
set up in two steps: (1) defining the filter types, and (2) applying them to a list under the PVC or PPP
configuration. This menu is used to define the individual filter defines based on packet type.
The Filter Defines option works for Frame Relay and PPP.
SECURITY > FILTERS > FILTER DEFINES > MAC FILTER DEFINES
The MAC filter is applied to bridge packets only. Bridge packets which are forwarded by the bridge
functionality of the unit are defined here. Up to 32 MAC defines can be specified.
NUM
Indicates the entry number in the MAC Filter Defines table.
NAME
Identifies the filter entry. Default is no entry in NAME field.
SRC ADDR
48-bit MAC source address used for comparison. Values are in hexadecimal format. Default is
00:00:00:00:00:00.
SRC MASK
Bits in the MAC source address which are compared. Values are in hexadecimal format. Default is
00:00:00:00:00:00.
DEST ADDR
48-bit MAC destination address used for comparison. Values are in hexadecimal format. Default is
00:00:00:00:00:00.
DEST MASK
Bits in the MAC destination address used for comparison. Values are in hexadecimal format. Default
is
00:00:00:00:00:00.
84 © 2003 ADTRAN, Inc. 61200704L2-1B
Page 85

Total Access 544R System Manual Section 4 SHDSL RCU ATM User Interface Guide
TYPE
16-bit type field used for comparison. Values are in hexadecimal format. Default is 00:00.
TYPE MASK
Bits in the type field used for comparison. Values are in hexadecimal format. Default is 00:00.
SECURITY > FILTERS > FILTER DEFINES > PATTERN FILTER DEFINES
The pattern filter is applied to bridge packets only. That is any packet which is forwarded by the bridge
functionality of the unit. Up to 32 pattern defines can be specified.
NUM
Indicates the entry number in the Pattern Filter Defines table.
NAME
Identifies the filter entry. Default is no entry in NAME field.
OFFSET
Offset from beginning of packet of where to start the pattern comparison. Default is 0.
PATTERN
64 bits used for comparison. Values are in hexadecimal format. Default is 00:00:00:00:00:00:00:00.
MASK
Bits in the pattern to be compared. Values are in hexadecimal format. Default is
00:00:00:00:00:00:00:00.
SECURITY > FILTERS > FILTER DEFINES > IP FILTER DEFINES
The IP filter defines apply to any IP packet, whether it is routed or bridged. Up to 32 IP defines can be
specified.
NUM
Indicates the entry number in the IP Filter Defines table.
NAME
Identifies the filter entry. Default is no entry in name field.
61200704L2-1B © 2003 ADTRAN, Inc. 85
Page 86

Section 4 SHDSL RCU ATM User Interface Guide Total Access 544R System Manual
SRC ADDR
IP address compared to the source address. Value is in dotted decimal format. Default is 0.0.0.0.
SRC MASK
Bits which are used in the source comparison. Value is in dotted decimal format. Default is 0.0.0.0.
DEST ADDR
IP address compared to the destination address. Value is in dotted decimal format. Default is 0.0.0.0.
DEST MASK
Bits which are used in the destination comparison. Value is in dotted decimal format. Default is
0.0.0.0.
SRC PORT
IP source port number used for comparison. Value is in decimal format. Range: 0 TO 65535. Default
is
0.
SRC PORT COMP
Type of comparison that is performed. Default is NONE.
= means ports equal to
NOT = means port not equal to
> means port greater than
< means port less than
NONE - means the source port is not compared
DEST PORT
IP destination port number used for comparison. Value is in decimal format. Range: 0 TO 65535.
Default is
0.
86 © 2003 ADTRAN, Inc. 61200704L2-1B
Page 87

Total Access 544R System Manual Section 4 SHDSL RCU ATM User Interface Guide
DEST PORT COMP
Type of comparison that is performed. Default is NONE.
= means ports equal to
NOT = means port not equal to
> means port greater than
< means port less than
NONE - means the source port is not compared
PROTO PORT
Protocol used for comparison. Value is in decimal format. Range: 0 to 255. Default is 0.
PROTO PORT COMP
Type of comparison that is performed. Default is NONE.
= means ports equal to
NOT = means port not equal to
> means port greater than
< means port less than
NONE - means the source port is not compared
TCP ESTAB
YES - only when TCP established
NO - only when TCP not established
IGNORE - ignore TCP flags (default)
SECURITY > RADIUS SERVER
The parameters for the Radius Server are configured in this menu.
Telnet radius is only available in C.04 firmware or later.
SECURITY > RADIUS SERVER > SERVER 1
This is the IP address of the first RADIUS SERVER that the unit should attempt to communicate with when
authenticating a telnet session. Default is
61200704L2-1B © 2003 ADTRAN, Inc. 87
0.0.0.0.
Page 88

Section 4 SHDSL RCU ATM User Interface Guide Total Access 544R System Manual
SECURITY > RADIUS SERVER > SERVER 2
This is the IP address of the second RADIUS SERVER that the unit should attempt to communicate with
when the primary server does not respond. Default is 0
.0.0.0.
SECURITY > RADIUS SERVER > SERVER 3
This is the IP address of the third RADIUS SERVER that the unit should attempt to communicate with when
authenticating a Telnet session. Default is
0.0.0.0.
88 © 2003 ADTRAN, Inc. 61200704L2-1B
Page 89

Total Access 544R System Manual Section 4 SHDSL RCU ATM User Interface Guide
SECURITY > RADIUS SERVER > UDP PORT
This is the UDP port the unit should use when communicating with the RADIUS SERVER. The default is
1812, which is the commonly used port.
SECURITY > RADIUS SERVER > SECRET
The RADIUS SERVER and unit share this text string. It is used by the RADIUS SERVER to authenticate the
unit, the RADIUS client. The factory default is not to use a secret.
SECURITY > RADIUS SERVER > RETRY COUNT (1-10)
The is the number of times the unit should send a request packet to the RADIUS SERVER without a response
before giving up. If the number of attempts to communicate with the primary server is equal to the retry
count, the second server (if defined) is tried. If the second server does not respond within the retry count
the third sever (if defined) is tried. If the third server does not respond with the retry count, the Telnet
session is not authenticated and is dropped. The default is
5.
61200704L2-1B © 2003 ADTRAN, Inc. 89
Page 90

Section 4 SHDSL RCU ATM User Interface Guide Total Access 544R System Manual
Appendix A. RFC1483 Quick Start (IP Routing)
The Total Access 544R allows for complete integration of data delivery from one compact platform (see
Figure 9).
Multiple users can share network access over a single SHDSL connection. For simultaneous access to
both a corporate network and the public Internet, the unit offers the ability to configure multiple PVCs. In
addition, the unit includes NAT/NAPT and IP filtering which provides security from unauthorized access
to the user's network.
The Total Access 544R also provides a cost-effective campus connectivity solution. When used with
private dry copper, the unit delivers up to 2.3 Mbps to cross-campus network elements. This solution is
ideal for extending LAN segments to other buildings.
Total Access 3000
Total Access 544R
10/100BaseT
ATM
LAN WAN
SHDSL
Total Access 544R Total Access 544R
LAN WANLAN WAN
SHDSL
Twisted Copper pair
Figure 9. Application Diagrams
To configure a Total Access 544R for IP routing, you need to know the VPI and VCI values for the data
circuit on your network. You also need the IP address of the next hop router in the circuit.
The table on the next page shows how to configure the Total Access 544R for IP Routing.
90 © 2003 ADTRAN, Inc. 61200704L2-1B
Page 91

Total Access 544R System Manual Section 4 SHDSL RCU ATM User Interface Guide
.
IP Routing
Step Action
1.
From the Total Access 544R main menu, select the L2 PROTOCOL >
I
NTERFACES menu. Set up the ATM network here.
2. Select the ATM CONFIG menu located under the main CONFIG field.
3. Enter the IDLE CELLS format for your network.
4. Set DATA SCRAMBLING appropriately for your network.
5.
Back all the way out to the top level Total Access 544R menu, and then
select the R
OUTER menu.
From the CONFIG menu, you will set up addresses for your LAN and
6.
WAN.
For basic IP routing, use all the default values.
7.
Select the INTERFACE > SETUP menu, enter the IP menu to enter your
LAN configuration under P
RIMARY IP.
Enter your LAN IP ADDRESS and SUBNET MASK information.
8.
For this example, the IP ADDRESS is 192.168.1.2, the SUBNET MASK is
255.255.255.0. Enter the Default Gateway under R
R
OUTES.
OUTER > CONFIG >
Arrow back to the main menu, and select the L2 Protocol Interfaces
9.
menu and then the Config > PCV Config menu. Enter your data PVC
information here.
10.
11.
12.
Create a new PVC by entering the menu and press <i> under NUM
field. Enter your VPI and VCI values.
From the Main Router > Config > Interfaces (SHDSL) > Setup menu,
enter your LAN information.
For this example, the FAR END IP ADDRESS is 10.25.4.9, the IP
N
ETMASK is 255.255.255.252, and the LOCAL IP ADDRESS is 10.25.4.10.
Arrow back to the top level Total Access 544R menu to activate your
changes.
61200704L2-1B © 2003 ADTRAN, Inc. 91
Page 92

Section 4 SHDSL RCU ATM User Interface Guide Total Access 544R System Manual
Appendix B. RFC1483 Quick Start (IP Routing with NAT)
To illustrate the use of NAT, consider the example from Appendix B. To set up a single public address that
will be used to access the public network, you will use the NAT menu.
IP Routing with NAT
Step Action
1.
2.
The NAT menu is found under ROUTER > CONFIG > INTERFACES (ETH) >
S
ETUP > SECONDARY IPS > NAT MODE.
This mode specifies whether NETWORK ADDRESS TRANSLATION (NAT) should
be use on this interface. When this mode is set to P
automatically specified on this interface. The other choice is P
RIVATE (def) NAT is
UBLIC which
specifies not going through NAT.
92 © 2003 ADTRAN, Inc. 61200704L2-1B
Page 93

Total Access 544R System Manual Section 4 SHDSL RCU ATM User Interface Guide
Appendix C. RFC 1483 Quick Start (Bridging)
The Total Access 544R allows for complete integration of data delivery from one compact platform.
To configure a Total Access 544R for Bridging, you need to know the VPI values for the data circuit on
your network.
Bridging
Step Action
1.
From the Total Access 544R main menu, select the L2 PROTOCOL >
I
NTERFACES menu. (Here you set up the ATM network.)
2. Select the ATM C ONFIG menu located under the main CONFIG field.
3. Enter the IDLE CELLS format for your network.
4. Set DATA SCRAMBLING appropriately for your network.
5.
Back all the way out to the top level Total Access 544R menu, and then
select the L2 P
ROTOCOL > CONFIG for the ETH menu.
6. From the CONFIG menu, you will set the MODE to BRIDGE ALL.
7.
Select the ROUTER > CONFIG > INTERFACE > SETUP (ETH) menu, enter
your LAN configuration under P
RIMARY IP.
Enter your LAN IP ADDRESS and SUBNET MASK information.
8.
For this example, the IP ADDRESS is 192.168.1.2, the SUBNET MASK is
255.255.255.0.
Arrow back to the main menu, and select the L2 Protocol Interfaces
9.
menu and then the Config > PCV Config menu. Enter your data PVC
information here.
10.
Create a new PVC by entering the menu and press <i> under NUM field.
Enter your VPI and VCI values.
11.
61200704L2-1B © 2003 ADTRAN, Inc. 93
Arrow back to the top level Total Access 544R menu to activate your
changes.
Page 94

Section 4 SHDSL RCU ATM User Interface Guide Total Access 544R System Manual
94 © 2003 ADTRAN, Inc. 61200704L2-1B
Page 95

DETAIL LEVEL PROCEDURES
DLP-1 Connecting the Terminal or PC to the CRAFT Port . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 97
DLP-2 Logging in to the System . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 101
DLP-3 Adding/Removing Telnet Users and Changing Password Security Levels . . . . . . . . . . . . . 105
DLP-4 Setting Ethernet IP Parameters . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 109
DLP-5 Verifying Communications Over an IP LAN . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 111
DLP-6 Telnetting to the Unit . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 115
DLP-7 Upgrading the Firmware Using XMODEM . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 119
DLP-8 Upgrading the Firmware Using TFTP . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 121
DLP-9 Saving the Current Configuration Using TFTP. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 125
DLP-10 Loading the Current Configuration Using TFTP. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 129
DLP-11 Saving the Current Configuration Using XMODEM . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 133
DLP-12 Loading the Current Configuration Using XMODEM . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 135
DLP-13 Saving and Loading Text Configuration Using the Terminal Command Line . . . . . . . . . . . 137
DLP-14 Unit Installation Using The Auto-Config Feature . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 141
DLP-15 A.03 to A.04 Firmware Upgrade. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 145
61200704L2-1B © 2003 ADTRAN, Inc. 95
Page 96

Section 5 Detail Level Procedures Total Access 544R System Manual
96 © 2003 ADTRAN, Inc. 61200704L2-1B
Page 97
DLP-1 Connecting the Terminal or PC to the CRAFT Port
Introduction
Provisioning is facilitated by a series of intuitive menus that are accessible on a computer screen.
Connecting either a VT100 terminal or a PC emulating a VT100 terminal to the
the unit allows access to the menus and management features of the unit. This section specifies how to
connect the VT100 terminal or PC to the unit.
CRAFT port on the rear of
Access to the unit is through the port labeled
ADTRAN adapter is required for access to this port.
CRAFT, an RJ-45 connector on the back of the unit. A special
Prerequisite Procedures
The unit must be powered for terminal communication to function.
Tools and Materials Required
• VT100 compatible terminal or computer with terminal emulation software
• Appropriate cable to connect terminal to the unit (customer-provided)
• DB-9 female to RJ-45 female adapter for connecting to the CRAFT port on the rear of the unit. This
adapter is ADTRAN-proprietary and is provided with the unit.
To prevent electrical shock, do not install equipment in a wet location or during a
lightning storm.
61200704L2-1B © 2003 ADTRAN, Inc. 97
Page 98

Section 5 DLP-1 Total Access 544R System Manual
Perform Steps Below in the Order Listed
1. Connect a VT100 terminal to the unit.
2. Connect a PC emulating a VT100 terminal to the unit.
• Set the parameters of the VT100 terminal to:
– 9600 baud rate
– 8 data bits
– No parity
– 1 stop bit
– No flow control
• If the terminal has a parallel setting, disable it and use serial port.
• Plug the RJ-45 male end of the data cable into the CRAFT port on the rear of the unit by
using the ADTRAN-proprietary DB-9 to RJ-45 adapter. Make the connection to the VT100
terminal as appropriate for your equipment.
3. Most personal computers or laptops can run communications software that will emulate a VT100
©
terminal. Windows programs such as Terminal
or Hyperterminal© are two such examples in the
Windows format. However, there are many other adequate, commercially available software packages
which will allow your PC or laptop to emulate a VT100 terminal. Certain configuration items must be
set on a PC or laptop for it to act as a VT100 terminal for the unit.
• Set the PC for direct connect on the appropriate com port (instead of dial-up connection).
• Set the parameters of the communications software to:
– 9600 baud rate
– 8 data bits
– No parity
– 1 stop bit
– No flow control
• Plug the RJ-45 male end of the data cable into the CRAFT port on the rear of the unit by
using the ADTRAN-proprietary DB-9 to RJ-45 adapter. Make connection to the PC or laptop
as appropriate for your equipment.
4. Press <Enter> or <Ctrl + R> until the Login menu appears on screen.
You are now ready to log in to the unit, as described in DLP-2, Logging in to the System.
A VT100 terminal program is provided with the ADTRAN Utilities.
98 © 2003 ADTRAN, Inc. 61200704L2-1B
Page 99

Total Access 544R System Manual Section 5 DLP-1
Follow-up Procedures
Once this procedure is complete, return to the procedure which referred you to this DLP and continue with
the tasks indicated there.
61200704L2-1B © 2003 ADTRAN, Inc. 99
Page 100

Section 5 DLP-1 Total Access 544R System Manual
100 © 2003 ADTRAN, Inc. 61200704L2-1B
 Loading...
Loading...