Page 1

NuDAM
®
NuDAM-6000 User’s Guide
Recycled Paper
Page 2

© Copyright 1999~2001 ADLINK Technology Inc.
All Rights Reserved.
Manual Rev. 3.00: March 16, 2001
The information in this document is subject to change without prior notice in
order to improve reliability, design and function and does not represent a
commitment on the part of the manufacturer.
In no event will the manufacturer be liable for direct, indirect, special, incidental,
or consequential damages arising out of the use or inability to use the product or
documentation, even if advised of the possibility of such damages.
This document contains proprietary information protected by copyright. All rights
are reserved. No part of this manual may be reproduced by any mechanical,
electronic, or other means in any form without prior written permission of the
manufacturer.
Trademarks
Nudam is registered trademarks of ADLINK Technology Inc.,
Other product names mentioned herein are used for identification purposes only
and may be trademarks and/or registered trademarks of their respective
companies.
Page 3

Table of Contents
INTRODUCTION .............................................................................................. 11
1.1 WHAT IS NUDAM ?............................................................................. 11
1.2 OUTSTANDING FEATURES OF NUDAM ................................................ 12
1.3 NUDAM-6000 SERIES PRODUCTS OVERVIEW ...................................... 13
1.4 EIA RS-485 STANDARD ...................................................................... 14
1.5 RS-485 ON NUDAM ........................................................................... 14
1.6 NUDAM RS-485 NETWORK CONFIGURATIONS ................................... 15
1.7 CONSTRUCTING A NUDAM NETWORK ................................................ 18
1.8 TERMINATION BUS .............................................................................. 18
1.9. SHIELDING ........................................................................................... 19
COMMUNICATION MODULE ....................................................................... 20
2.1 OVERVIEW OF NUDAM-6520 ............................................................. 20
2.1.1 Features of NuDAM-6520 ................................................................. 20
2.1.2 Specifications of NuDAM-6520 ......................................................... 21
2.1.3 A Look at NuDAM-6520 & Pin Assignment ...................................... 22
2.1.4 Pin Definition of NuDAM-6520 ......................................................... 23
2.1.5 NuDAM-6520 Functional Block Diagram ......................................... 25
2.1.6 Setup .................................................................................................. 26
2.1.7 Installation ......................................................................................... 27
2.1.8 Programming ..................................................................................... 27
2.2 OVERVIEW OF NUDAM-6510 ............................................................. 28
2.2.1 Features of NuDAM-6510 ................................................................. 28
2.2.2 Specifications of NuDAM-6510 ......................................................... 28
2.2.3 A Look at NuDAM-6510 & Pin Assignment ...................................... 30
2.2.4 Pin Definition of NuDAM-6510 ......................................................... 31
2.2.5 NuDAM-6510 Functional Block Diagram ......................................... 31
2.2.6 Setup .................................................................................................. 32
2.2.7 Installation ......................................................................................... 33
2.2.8 Programming ..................................................................................... 34
2.3 OVERVIEW OF NUDAM-6530 ............................................................. 35
2.3.1 Features of NuDAM-6530 ................................................................. 35
2.3.2 Specifications of NuDAM-6530 ......................................................... 36
2.3.3 A Look at NuDAM-6530 & Pin Assignment ...................................... 37
2.3.4 Pin Definition of NuDAM-6530 ......................................................... 38
2.3.5 NuDAM-6530 Functional Block Diagram ......................................... 38
Table of Concents • i
Page 4

2.3.6 Setup .................................................................................................. 40
2.3.7 Installation ......................................................................................... 41
2.3.8 Programming ..................................................................................... 43
2.4 OVERVIEW OF NUDAM-6531 ............................................................. 44
2.4.1 Features of NuDAM-6531 ................................................................. 44
2.4.2 Specifications of NuDAM-6531 ......................................................... 45
2.4.3 A Look at NuDAM-6531 & Pin Assignment ...................................... 46
2.4.4 Pin Definition of NuDAM-6531 ......................................................... 47
2.4.5 NuDAM-6531 Functional Block Diagram ......................................... 48
2.4.6 Initialation & Installation .................................................................. 49
2.4.7 Install a New NuDAM-6531 to a Existing Network ........................... 51
ANALOG INPUT MODULES .......................................................................... 53
3.1 OVERVIEW OF NUDAM-6013 ............................................................. 53
3.1.1 Features of NuDAM-6013 ................................................................. 53
3.1.2 Specifications of NuDAM-6013 ......................................................... 53
3.1.3 A Look at NuDAM-6013 & Pin Assignment ...................................... 55
3.1.4 Pin Definition of NuDAM-6013 ......................................................... 56
3.1.5 NuDAM-6013 Functional Block Diagram ......................................... 56
3.2 OVERVIEW OF NUDAM-6017 ............................................................. 57
3.2.1 Features of NuDAM-6017 ................................................................. 57
3.2.2 Specifications of NuDAM-6017 ......................................................... 57
3.2.3 A Look at NuDAM-6017 & Pin Assignment ...................................... 59
3.2.4 Pin Definition of NuDAM-6017 ......................................................... 60
3.2.5 NuDAM6017 Functional Block Diagram .......................................... 60
3.3 OVERVIEW OF NUDAM-6018 ............................................................. 61
3.3.1 Features of NuDAM-6018 ................................................................. 61
3.3.2 Specifications of NuDAM-6018 ......................................................... 61
3.3.3 A Look at NuDAM-6018 & Pin Assignment ...................................... 63
3.3.4 Pin Definition of NuDAM-6018 ......................................................... 64
3.3.5 NuDAM-6018 Functional Block Diagram ......................................... 64
ANALOG OUTPUT MODULES ...................................................................... 65
4.1 OVERVIEW OF NUDAM-6021 ............................................................. 65
4.1.1 Features of NuDAM-6021 ................................................................. 65
4.1.2 Specifications of NuDAM-6021 ......................................................... 66
4.1.3 A Look at NuDAM-6021 & Pin Assignment ...................................... 67
4.1.4 Pin Definition of NuDAM-6021 ......................................................... 68
4.1.5 NuDAM-6021 Functional Block Diagram ......................................... 68
4.2 OVERVIEW OF NUDAM-6024 ............................................................. 69
ii • Table of Contents
Page 5

4.2.1 Features of NuDAM-6024 ................................................................. 69
4.2.2 Specifications of NuDAM-6024 ......................................................... 69
4.2.3 A Look at NuDAM-6024 & Pin Assignment ...................................... 71
4.2.4 Pin Definitions of NuDAM-6024 ....................................................... 72
4.2.5 NuDAM-6024 Functional Block Diagram ......................................... 73
DIGITAL I/O MODULES ................................................................................. 74
ABOUT THE NUDAM DIO MODULES .............................................................. 74
5.1 OVERVIEW OF NUDAM-6050 ............................................................. 75
5.1.1 Features of NuDAM-6050 ................................................................. 75
5.1.2 Specifications of NuDAM-6050 ......................................................... 75
5.1.3 A Look at NuDAM-6050 & Pin Assignment ...................................... 77
5.1.4 Pin Definitions of NuDAM-6050 ....................................................... 78
5.1.5 NuDAM-6050 Functional Block Diagram ......................................... 79
5.2 OVERVIEW OF NUDAM-6052 ............................................................. 80
5.2.1 Features of NuDAM-6052 ................................................................. 80
5.2.2 Specifications of NuDAM-6052 ......................................................... 80
5.2.3 A Look at NuDAM-6052 & Pin Assignment ...................................... 81
5.2.4 Pin Definitions of NuDAM-6052 ....................................................... 82
5.2.5 NuDAM-6052 Functional Block Diagram ......................................... 83
5.3 OVERVIEW OF NUDAM-6053 ............................................................. 84
5.3.1 Features of NuDAM-6053 ................................................................. 84
5.3.2 Specifications of NuDAM-6053 ......................................................... 84
5.3.3 A Look at NuDAM-6053 & Pin Assignment ...................................... 85
5.3.4 Pin Definitions of NuDAM-6053 ....................................................... 86
5.3.5 NuDAM-6053 Functional Block Diagram ......................................... 87
5.4 OVERVIEW OF NUDAM-6054 ............................................................. 88
5.4.1 Features of NuDAM-6054 ................................................................. 88
5.4.2 Specifications of NuDAM-6054 ......................................................... 88
5.4.3 A Look at NuDAM-6054 & Pin Assignment ...................................... 90
5.4.4 Pin Definitions of NuDAM-6054 ....................................................... 91
5.4.5 NuDAM-6054 Functional Block Diagram ......................................... 92
5.5 OVERVIEW OF NUDAM-6056 ............................................................. 93
5.5.1 Features of NuDAM-6056 ................................................................. 93
5.5.2 Specifications of NuDAM-6056 ......................................................... 93
5.5.3 A Look at NuDAM-6056 & Pin Assignment ...................................... 95
5.5.4 Pin Definitions of NuDAM-6056 ....................................................... 96
5.5.5 NuDAM-6056 Functional Block Diagram ......................................... 97
5.6 OVERVIEW OF NUDAM-6058 ............................................................. 98
5.6.1 Features of NuDAM-6058 ................................................................. 98
Table of Concents • iii
Page 6

5.6.2 Specifications of NuDAM-6058 ......................................................... 99
5.6.3 A Look at NuDAM-6058 & Pin Assignment .................................... 100
5.6.4 Pin Definitions of NuDAM-6058 ..................................................... 101
5.6.5 NuDAM-6058 Functional Block Diagram ....................................... 102
5.7 OVERVIEW OF NUDAM-6060 ........................................................... 103
5.7.1 Features of NuDAM-6060 ............................................................... 103
5.7.2 Specifications of NuDAM-6060 ....................................................... 103
5.7.3 A Look at NuDAM-6060 & Pin Assignment .................................... 105
5.7.4 Pin Definitions of NuDAM-6060 ..................................................... 106
5.7.5 NuDAM-6060 Functional Block Diagram ....................................... 107
5.8 OVERVIEW OF NUDAM-6063 ........................................................... 108
5.8.1 Features of NuDAM-6063 ............................................................... 108
5.8.2 Specifications of NuDAM-6063 ....................................................... 108
5.8.3 A Look at NuDAM-6063 & Pin Assignment .................................... 110
5.8.4 Pin Definitions of NuDAM-6063 ..................................................... 111
5.8.5 NuDAM-6063 Functional Block Diagram ....................................... 112
5.9 OVERVIEW OF NUDAM-6067 ........................................................... 113
5.9.1 Features of NuDAM-6067 ............................................................... 113
5.9.2 Specifications of NuDAM-6067 ....................................................... 113
5.9.3 A Look at NuDAM-6067 & Pin Assignment .................................... 115
5.9.4 Pin Definitions of NuDAM-6067 ..................................................... 116
5.9.5 NuDAM-6067 Functional Block Diagram ....................................... 117
5.10 OVERVIEW OF NUDAM-6080 ........................................................... 118
5.10.1 Features of NuDAM-6080 ............................................................. 119
5.10.2 Specifications of NuDAM-6080 ..................................................... 119
5.10.3
5.10.4 Pin Definitions of NuDAM-6080 ................................................... 122
5.10.5 NuDAM-6080 Functional Block Diagram ..................................... 123
A Look at NuDAM-6080 & Pin Assignment ............................... 121
COMMAND SET ............................................................................................. 124
6.1 COMMAND AND RESPONSE ................................................................ 124
6.1.1 Introduction ..................................................................................... 124
6.1.2 Format of NuDAM Commands ........................................................ 125
6.1.3 Response of NuDAM Commands ..................................................... 127
6.2 SUMMARY OF COMMAND SET ............................................................ 128
6.2.1 Set Configuration ............................................................................. 133
6.2.2 Read Configuration ......................................................................... 143
6.2.3 Read Module Name .......................................................................... 146
6.2.4 Read Firmware Version ................................................................... 147
iv • Table of Contents
Page 7

6.2.5 Reset Status ...................................................................................... 148
6.2.6 Soft Reset ......................................................................................... 149
6.3.1 Read Analog Data............................................................................ 150
6.3.2 Offset Calibration to each Channel ................................................. 151
6.3.3 Span Calibration to each Channel................................................... 152
6.3.4 Read Analog Data From Channel N................................................ 153
6.3.5 Read All Analog Data Channel ....................................................... 154
6.3.6 Enable/Disable channels for Multiplexing ...................................... 155
6.3.7 Read Channel Status ........................................................................ 156
6.3.8 Read CJC Status .............................................................................. 157
6.3.9 Enable/Disable CJC ........................................................................ 158
6.3.10 Read enable/disable CJC Status .................................................... 159
6.3.11 CJC Offset Calibration .................................................................. 160
6.3.12 Span Calibration ............................................................................ 161
6.3.13 Offset Calibration .......................................................................... 162
6.4.1 Synchronized Sampling .................................................................... 163
6.4.2 Read Synchronized Data .................................................................. 164
6.4.3 Digital Input..................................................................................... 165
6.4.4 Analog Data Output ......................................................................... 166
6.4.5 4mA Offset Calibration .................................................................... 168
6.4.6 20mA Calibration ............................................................................ 169
6.4.7 Trim Calibration .............................................................................. 170
6.4.8 Last Value Readback ....................................................................... 171
6.4.9 Current Readback ............................................................................ 172
6.4.10 Save Power On Analog Output Value ............................................ 173
6.5.1 Synchronized Sampling .................................................................... 174
6.5.2 Read Synchronized Data .................................................................. 175
6.5.3 Digital Output .................................................................................. 178
6.5.4 Digital Input..................................................................................... 182
6.5.5 Programmable I/O Mode Setting ..................................................... 185
6.6.1 Set RTS Status .................................................................................. 187
6.6.2 Read RTS Status ............................................................................... 188
6.6.3 Read CTS Status .............................................................................. 189
6.6.4 Set Device ID ................................................................................... 190
6.6.5 Read Device ID ................................................................................ 191
6.6.6 Set Delimiter .................................................................................... 192
6.6.7 Read Delimiter ................................................................................. 193
6.6.8 Data Pass ......................................................................................... 194
6.6.9 Open/Close Data Gate ..................................................................... 195
6.7.1 Set Input Mode ................................................................................. 196
Table of Concents • v
Page 8

6.7.2 Read Input Mode.............................................................................. 197
6.7.3 Read Counter/Frequency Value in HEX Format ............................. 198
6.7.4 Read Counter/Frequency Value in DEC Format ............................. 199
6.7.5 Set Gate Mode .................................................................................. 200
6.7.6 Read Gate Mode .............................................................................. 201
6.7.7 Set Maximum Counter Value ........................................................... 202
6.7.8 Read Maximum Counter Value ........................................................ 203
6.7.9 Set Initial Count Value ..................................................................... 204
6.7.10 Read Initial Count Value ............................................................... 205
6.7.11 Start/Stop Counter ......................................................................... 206
6.7.12 Read Start/Stop Counter Status ..................................................... 207
6.7.13 Clear Counter ................................................................................ 208
6.7.14 Read then Clear Overflow Flag ..................................................... 209
6.7.15 Enable/Disable Digital Filter ........................................................ 210
6.7.16 Read Filter Status .......................................................................... 211
6.7.17 Set Minimum Input Signal Width at High Level ............................ 212
6.7.18 Read Minimum Input Signal Width at High Level ......................... 213
6.7.19 Set Minimum Input Signal Width at Low Level ............................. 214
6.7.20 Read Minimum Input Signal Width at Low Level .......................... 215
6.7.21 Set TTL Input High Trigger Level .................................................. 216
6.7.22 Read TTL Input High Trigger Level .............................................. 217
6.7.23 Set TTL Input Low Trigger Level ................................................... 218
6.7.24 Read TTL Input Low Trigger Level ............................................... 219
6.7.25 Enable Alarm ................................................................................. 220
6.7.26 Disable Alarm ................................................................................ 221
6.7.27 Set Alarm Limit Value of Counter 0 ............................................... 222
6.7.28 Set Alarm Limit Value of Counter 1 ............................................... 223
6.7.29 Read Alarm Limit Value of Counter 0 ........................................... 224
6.7.30 Read Alarm Limit Value of Counter 1 ........................................... 225
6.7.31 Set Digital Output Values .............................................................. 226
6.7.32 Read Digital Output and Alarm Status .......................................... 227
6.8.1 Read Command Leading Code Setting ............................................ 229
6.8.2 Change Command Leading Code Setting ........................................ 230
6.8.3 Set Host Watchdog Timer & Safety Value ....................................... 232
6.8.4 Read Host Watchdog Timer & Safety Value .................................... 236
6.8.5 Change Polarity ............................................................................... 240
6.8.6 Read Polarity ................................................................................... 241
6.8.7 Host is OK........................................................................................ 242
INITIALIZATION & INSTALLATION ..................................................... 243
vi • Table of Contents
Page 9

7.1 SOFTWARE INSTALLATION ................................................................. 243
7.2 INITIALIZING A BRAND-NEW MODULE .............................................. 243
Objective of Initializing a Brand-New NuDAM ........................................ 243
Default State ............................................................................................. 244
Initialization Equipments .......................................................................... 244
Initialization Procedure ............................................................................ 245
Initialization Wiring .................................................................................. 245
7.3 INSTALL A NEW NUDAM TO A EXISTING NETWORK ......................... 245
Equipments for Install a New Module ...................................................... 245
Installing Procedures ................................................................................ 245
7.4 APPLICATION WIRING FOR NUDAM ................................................. 246
7.4.1 Differential Voltage Input ................................................................ 246
7.4.2 Single Ended Voltage Input ............................................................. 247
7.4.3 Current Measurement ...................................................................... 247
7.4.4 Differential Current Outpu .............................................................. 247
7.4.5 RTD Input ........................................................................................ 248
7.4.6 Differential Voltage Output ............................................................. 249
7.4.7 Digital Input onnect with TTL Signal .............................................. 249
7.4.8 Digital Input Connect with Switch or Push Button .......................... 249
7.4.9 Digital Output Connect with Power Loading .................................. 250
7.4.10 Isolated Differential Input ............................................................. 250
7.4.11 Isolated Single Ended Input ........................................................... 250
7.4.12 Wet Contact Input .......................................................................... 251
7.4.13 Contact Closure Input .................................................................... 251
7.4.14 Isolated Differential Input with External 24V power..................... 251
7.4.15 Isolated Common Ground Output ................................................. 252
7.4.16Thermocouple Input Measurement ................................................. 252
7.4.17 Form C Relay Output ..................................................................... 252
7.4.18 Form A Relay Output ..................................................................... 253
7.4.19 Discrete Input: Contact Mode ....................................................... 253
7.4.20 Discrete Input: Transistor Mode ................................................... 253
ANALOG MODULES DATA FORMAT ..................................................... 254
UNIT CONVERSION ........................................................................................ 254
8.1 Engineering Units ............................................................................... 254
8.2 Percent of FSR (Full Scale Range) ..................................................... 258
8.3 Hexadecimal or Two’s Complement Hexadecimal ............................. 261
8.4 Ohm .................................................................................................... 263
CALIBRATION .............................................................................................. 264
Table of Concents • vii
Page 10

9.1 HOW TO CALIBRATE THE ANALOG INPUT MODULES ? ....................... 264
Calibration Procedure for ND-6017 ........................................................ 264
Calibration Procedure for ND-6013 Firmware Rev A3.05 ...................... 265
Calibration Procedure for ND-6013 Firmware Rev C4.60 ...................... 266
Calibration Procedure for ND-6018 Firmware Rev B1.10 ...................... 266
Calibration Procedure for ND-6018 Firmware Rev E1.00 ...................... 266
CJC Calibration Procedure ...................................................................... 267
Analog Input Module‘s Calibration Voltages ........................................... 268
9.2 HOW TO CALIBRATE THE ANALOG OUTPUT MODULES ? ................... 270
APPENDIX...................................................................................................... 272
APPLICATION NOTE ....................................................................................... 272
SOFTWARE UTILITY ....................................................................................... 274
1.Software Installation .............................................................................. 274
2.How to Execute the NuDAM Administration ......................................... 274
3.NuDAM Administration Function Overview ......................................... 274
3.1 Change RS-232 Communication Port Setting. ................................... 275
3.2 Search all exist Nudam modules ......................................................... 276
3.3 Using Operations ................................................................................ 277
3.4 Save and Print Nudam modules’ information ..................................... 281
3.5 Version Information ............................................................................ 282
PRODUCT WARRANTY/SERVICE ........................................................... 283
viii • Table of Contents
Page 11

Table of Figure
Figure 1-1 Simple Topology ...................................................................... 15
Figure 1-2 Branch Topology ..................................................................... 16
Figure 1-3 Free Topology ......................................................................... 17
Figure 1-4 Terminator Connection ........................................................... 18
Figure 2-1 NuDAM-6520 profile .............................................................. 22
Figure 2-2 Connection Between Host and NuDAM-6520......................... 24
Figure 2-3 RS-422 Application Wiring ..................................................... 24
Figure 2-4 RS-485 Application Wiring ..................................................... 25
Figure 2-6 NuDAM-6510 profile .............................................................. 30
Figure 2-7 Block Diagram of NuDAM-6510 ............................................ 31
Figure 2-8 NuDAM-6530 profile .............................................................. 37
Figure 2-9 Block Diagram of NuDAM-6530 ............................................ 38
Figure 2-10 NuDAM-6531 profile ............................................................ 46
Figure 2-11 Block Diagram of NuDAM-6531 .......................................... 48
Figure 3-1 NuDAM-6013 profile .............................................................. 55
Figure 3-2 Block Diagram of NuDAM-6013 ............................................ 56
Figure 3-3 NuDAM-6017 profile .............................................................. 59
Figure 3-4 Block Diagram of NuDAM-6017 ............................................ 60
Figure 3-5 NuDAM-6018 profile .............................................................. 63
Figure 3-6 Block Diagram of NuDAM-6018 ............................................ 64
Figure 4-1 NuDAM-6021 profile .............................................................. 67
Figure 4-2 Block Diagram of NuDAM-6021 ............................................ 68
Figure 4-3 NuDAM-6024 profile .............................................................. 71
Figure 4-4 Block Diagram of NuDAM-6024 ............................................ 73
Figure 5-1 NuDAM-6050 profile .............................................................. 77
Figure 5-2 Block Diagram of NuDAM-6050 ............................................ 79
Figure 5-3 NuDAM-6052 profile .............................................................. 81
Figure 5-4 Block Diagram of NuDAM-6052 ............................................ 83
Figure 5-5 NuDAM-6053 profile .............................................................. 85
Figure 5-6 Block Diagram of NuDAM-6053 ............................................ 87
Figure 5-7 NuDAM-6054 profile .............................................................. 90
Figure 5-8 Block Diagram of NuDAM-6054 ............................................ 92
Figure 5-9 NuDAM-6056 profile .............................................................. 95
Table of Concents • ix
Page 12

Figure 5-10 Block Diagram of NuDAM-6056 .......................................... 97
Figure 5-11 NuDAM-6058 profile .......................................................... 100
Figure 5-12 Block Diagram of NuDAM-6058 ........................................ 102
Figure 5-13 ND-6060 profile .................................................................. 105
Figure 5-14 Block Diagram of NuDAM-6060 ........................................ 107
Figure 5-15 NuDAM-6063 profile .......................................................... 110
Figure 5-16 Block Diagram of NuDAM-6063 ........................................ 112
Figure 5-17 NuDAM-6067 profile .......................................................... 115
Figure 5-18 Block Diagram of NuDAM-6067 ........................................ 117
Figure 5-19 NuDAM-6080 profile .......................................................... 121
Figure 5-20 Block Diagram of NuDAM-6080 ........................................ 123
Figure 6-1 Data Format Setting of ND-601x .......................................... 139
Figure 6-2 Data format of ND-602x ....................................................... 140
Figure 6-3 Check sum flag setting of 605x ............................................. 141
Figure 6-4 Check sum flag setting of 6080 ............................................. 141
Figure 6-5 Response of check sum flag ................................................... 145
Figure 7-1 Layout for Initialization the NuDAM module ...................... 245
Figure A-1. ND-60xx Default Setting External Connection .................... 273
Figure A-2 Terminator Connection......................................................... 273
x • Table of Contents
Page 13

1
Introduction
1.1 What is NuDAM ?
NuDAM is a series of data acquisition modules.
the data acquisition network and control system. You can remotely control up to
256 NuDAM modules on RS-485 netowrk. All you need is to use a host computer,
like PC (Personal Computer), with one RS-232 serial port for controlling the
whole system. The maximum communication distance is 4000 feet from the
host computer.
NuDAM is based on the RS-485 multi-drop network system, each module has an
unique address ID. Using simple ASCII command & response protocol through
standard RS-485 interface can control all the NuDAM modules in the RS-485
network.
The NuDAM modules provide direct linkage to a wide variety of sensors and
perform all signal conditioning, scaling, linearization and conversion. The
modules can be used to measure temperature, pressure, flow, voltage, current
and numerous types of digital signals.
11
It provides a total solution of
Page 14

1.2 Outstanding Features of NuDAM
Industry standard networking
z
All NuDAM modules use the RS-485 communication protocol for transmitting
and receiving at high rates and over long distance.
Two-wire and multi-drop communication
z
A single twisted pair of wires is used to transmit and receive data between
modules. Multi-drop capability makes system configuration more flexible and
easy set-up of a network.
High transfer speed
z
NuDAM modules provide up to 115.2K bps data / command transfer rate. It can
promote system bandwidth.
Simple command / response protocol
z
All communications are performed with printable ASCII characters. This allows
the information to be processed with string functions common to the most
high-level languages.
Industrial design
z
The screw terminal plug connectors on every NuDAM module ensures simple
installation and easy modification. The compact size allows the modules to be
mounted on DIN rail, back-panel wall-mount, etc.
Watch-dog supervisory
z
NuDAM contains a watch-dog supervisory circuitry that will automatically reset
the module when the system fails. In addition, a user-programmable software
timer provides a ‘safe’ output signal in the event of host computer failure.
High isolation voltage
z
NuDAM provides photo-isolators, which ensure high isolation voltage, between
the data acquisition circuits and the communication port. The fatal
electric-shock won‘t go through and damage all the modules on the network.
Noise immunity
z
The NuDAM provide extra noise immunity capability. An electrode, which is
coated inside the ABS case, can reduce electro-magnetic interference (EMI)
and noise.
12
Page 15

Harsh environmental protection
z
A surface coating covers on the PCB and electronic components of the NuDAM.
It allows superior resistance to harsh environment such as humidity, salt spry
and most harsh chemicals.
1.3 NuDAM-6000 series products overview
The NuDAM-6000 series provides the complete sets of data acquisition modules,
including the communication modules, the analog input modules, the analog
output modules, and the digital I/O modules.
Communication Module
♦ ND-6510 : RS-422/RS-485 Repeater
♦ ND-6520 : RS-232 to RS-422/RS-485 Converter
♦ ND-6530 : USB to RS-422/RS-485 Converter
♦ ND-6531 : Addressable RS-422/RS-485 to RS-232 Converter
Analog Input Modules
♦ ND-6013 : 3-channel RTD Input Module
♦ ND-6017 : 8-channel Analog Input Module
♦ ND-6018 : 8-channel Thermocouple Input Module
Analog Output Modules
♦ ND-6021 : Single Channel Analog Output Module
♦ ND-6024 : 4-channel Analog Output Module with 7 DI channels
Digital I/O Modules
♦ ND-6050 : Module with 7 DI channels and 8 DO channels
♦ ND-6052 : 8-channel Isolated Input Module
♦ ND-6053 : 16-channel Digital Input Module
♦ ND-6054 : 15-channel Isolated Input Module
♦ ND-6056 : 15-channel Isolated Output Module
♦ ND-6058 : 28-channel Programable Digital I/O Module
♦ ND-6060 : 4-channel Relay Output & Isolated Input Module
♦ ND-6063 : 8-channel Relay Output Module
♦ ND-6067 : 8-channel AC Relay Output Module
♦ ND-6080 : 2-channel Counter/Frequency Input Module
13
Page 16

1.4 EIA RS-485 Standard
The EIA RS-485 interface is a communication standard developed for
multi-dropped systems that can communicate at high rate over long distance.
The standard RS-485 can operate at speed up to 10 M bps over cable length up
to 4000 feet.
The RS-485 interface can support up to 32 drivers / receivers on the same line.
This allows actual networking applications on a parity line system (sometimes
called multi-drop).
The RS-485 uses differential transmission on a balance line. Its easy wiring
make it popular to use in industrial applications.
1.5 RS-485 on NuDAM
The NuDAM improves the RS-485 capability for minimizing the user‘s cost. On
each NuDAM module, a half-duplex RS-485 transceiver is used to communicate
with other modules. A single twisted pair of wires, which provides standard
differential transmission, is used to transmit and receive data between modules.
The high input impedance of each NuDAM receiver allows up to 128 NuDAM
modules on the same RS-485 bus without using a signal repeater.
The maximum transfer rate of NuDAM is 115.2Kbps which is lower than the
maximum speed of the RS-485 standard. The slew-rate limiter on every RS-485
transceiver of NuDAM is very useful for transmitting error-free data, minimizing
EMI, and reducing reflections caused by improperly terminated cables.
The NuDAM on a network may not use the same power supply. Therefore, the
voltage difference between ground of the modules may exist.
Excessive output current and power dissipation caused by faults or by bus
contention are prevented by the current limiter and the thermal shutdown
circuitry inside the NuDAM.
14
Page 17
T
r
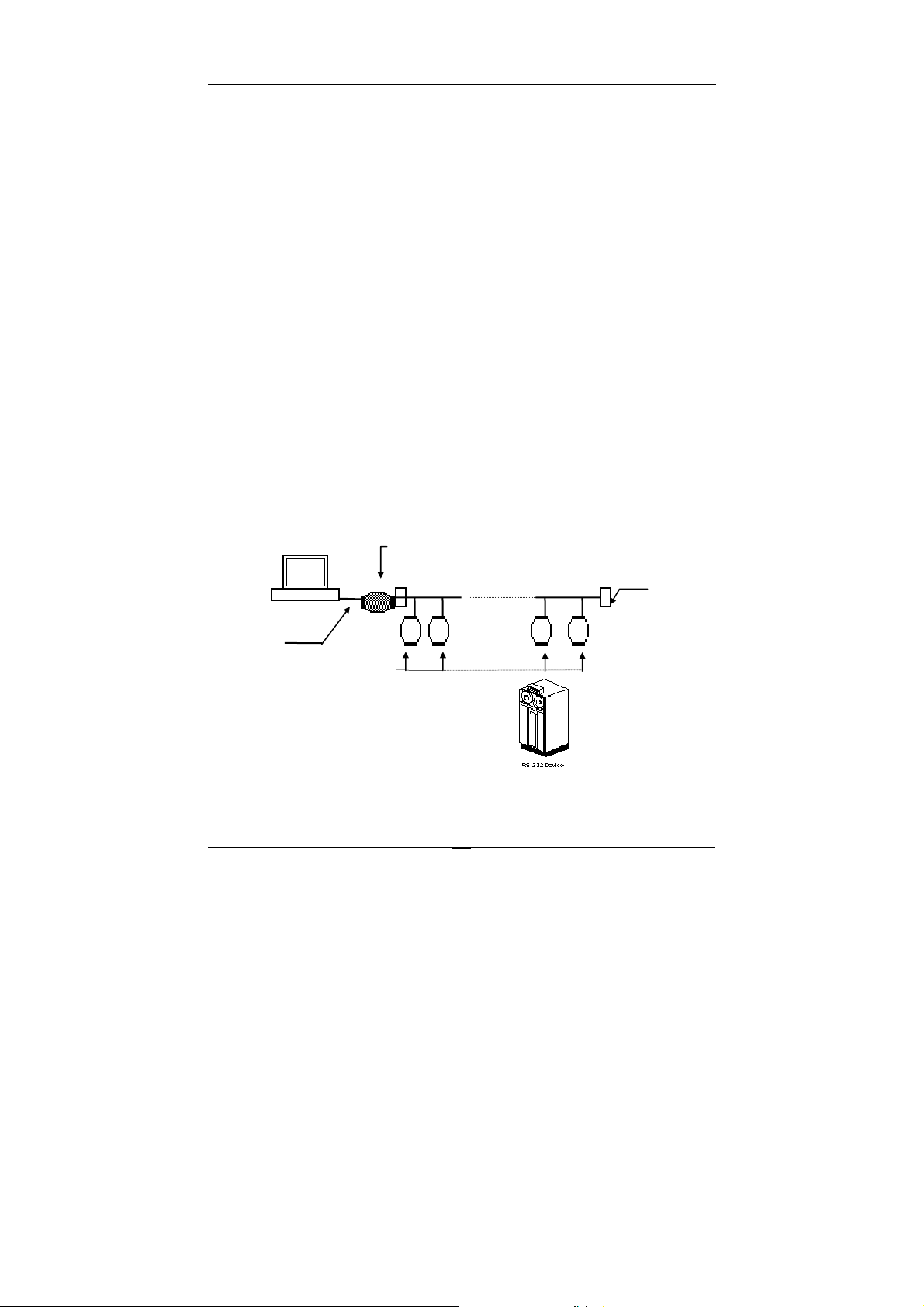
1.6 NuDAM RS-485 Network Configurations
NuDAM-6000 series is designed under RS-485 multi-drop network architecture.
256
Up to
of 256 is due to command code. The network can be connected by simple
topology (Figure 1-1) or branch topology (Figure 1-2) or free topology (Figure
1-3).
The ND-6520 and ND-6510 are the two basic communication modules to
construct a RS-485 network. The ND-6520 is a RS-232 to RS-485/RS-422
converter. The ND-6520 is used to build a RS-485 port for the host computer by
converting standard RS-232 signal into RS-485 signal.
The ND-6510 is the RS-485 signal repeater which is used to extend or to
lengthen the network distance. A NuDAM bus can connect up to
each segment is up to 128 modules. Whenever the numbers of the modules
excess 128, the repeater should be used. In addition, the length of a standard
RS-485 bus is up to 4000 feet, the repeater should be used whenever the length
of a signal bus is more than 4000 feet.
The ND-6530 is the USB to RS-485/RS-422/RS-232 converter, and it is used to
build the USB signal into RS-485/RS-422/RS-232 signal.
The ND-6531 is an addressable RS-485/RS-422 to RS-232 converter, it allows
the RS-232 devices easily link to Host by the RS-485/422 bus.
NuDAM modules can be controlled in a multi-drop network. The limit
256
modules,
Host
RS-232
ND-6520/ND-6530
RS-485 bus
NuDAM Modules
ND-6531
erminato
Figure 1-1 Simple Topology
15
Page 18
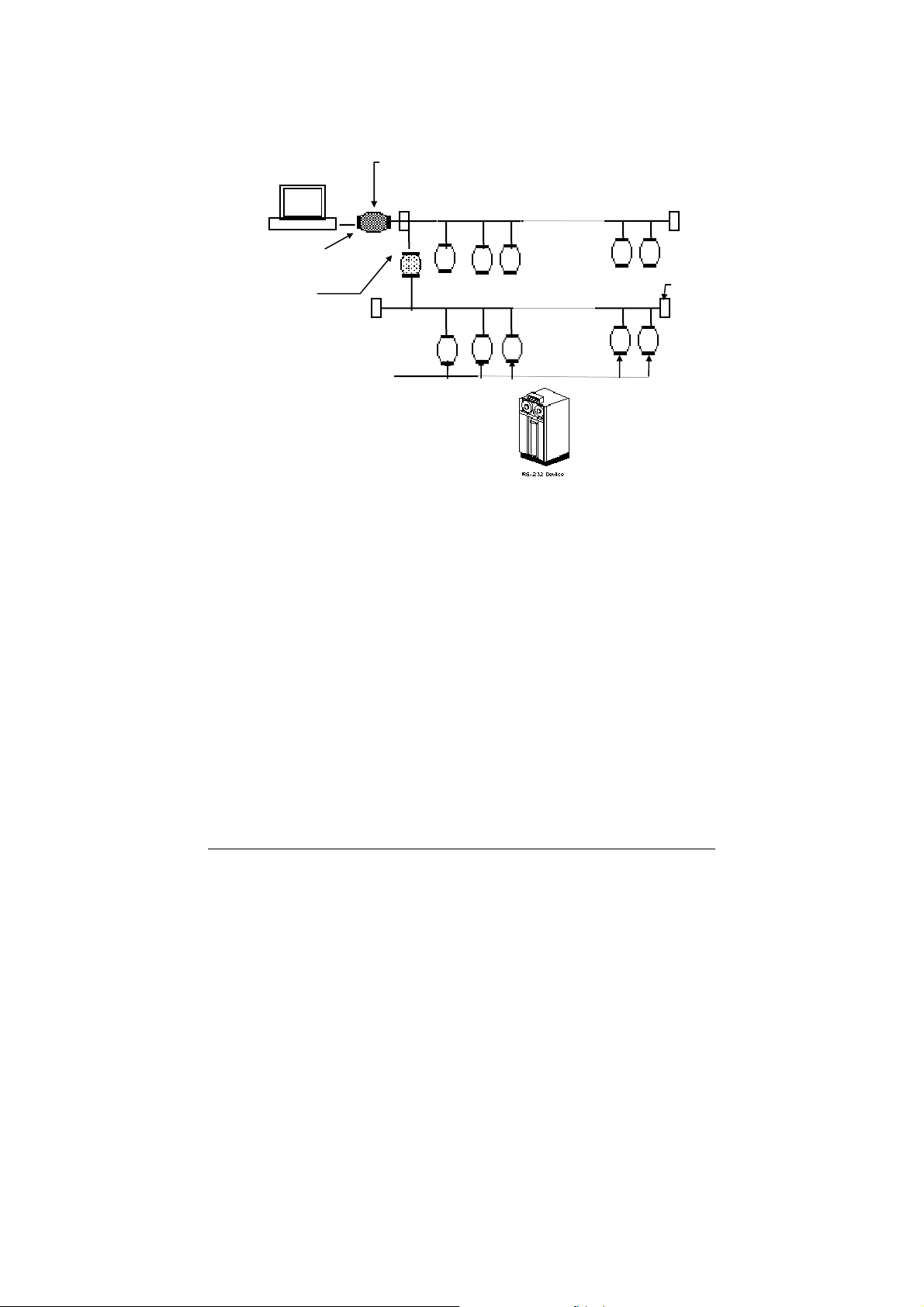
T
r
Host
RS-232
ND-6510
Repeater
NuDAM Modules
ND-6520/ND-6530
RS-485 bus
RS-485 bus
ND-6521
erminato
Figure 1-2 Branch Topology
16
Page 19
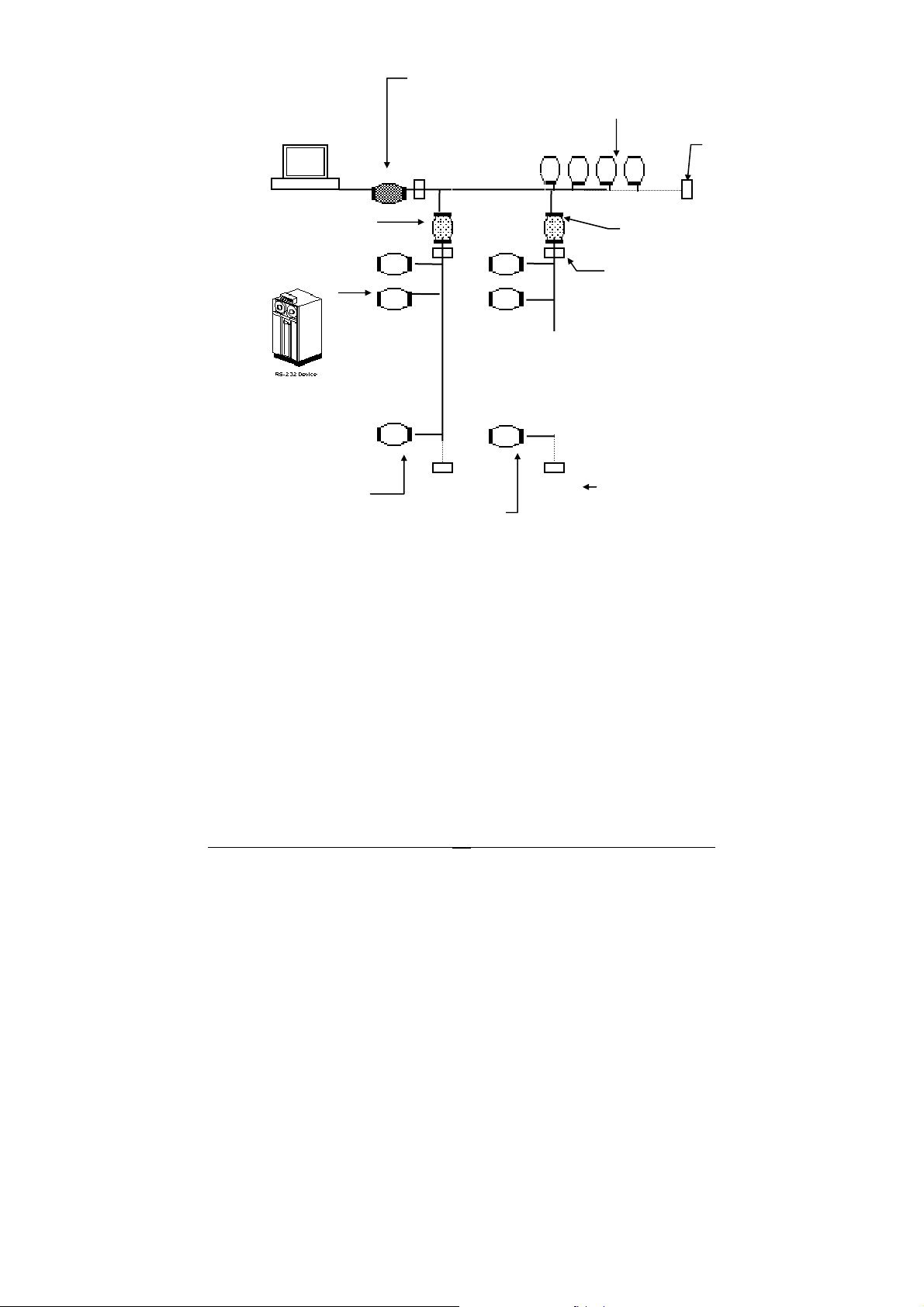
T
r
T
r
T
r
ND-6520/ND-6530
Host
ND-6510
Repeater
ND-6531
RS-485 bus
NuDAM Modules
ND-6510
Repeater
erminato
erminato
NuDAM I/O
modules
NuDAM I/O modules
Figure 1-3 Free Topology
erminato
17
Page 20
1.7 Constructing a NuDAM Network
Go through the following steps, the user can construct a NuDAM network easily.
1. Setup a ND-6520 or ND-6530.
2. Connect the host computer with the ND-6520 or ND-6530.
3. Setup one or more ND-6510 if necessary.
4. Connect the ND-6510 to extend to RS-485 bus if necessary.
5. Install the NuDAM utility software or ND-6530 driver from disk.
6. Initialize the brand-new NuDAM modules.
7. Add the new NuDAM modules into RS-485 network.
1.8 Termination Bus
In order to avoid signal reflections on the bus, each bus segment has to be
blanked off at its physical beginning and at its end with the characteristic
impedance. An termination resister ( Rt) is intalled for this purpose. The Rt value
120Ω ± 2%
from the “Terminator Connection” diagram below.
is recommended, and the detailed connection of Rt can be referred
Host
Data+
120 ohms
Data-
Terminator Connec tion
Data+
120 ohms
Data-
Figure 1-4 Terminator Connection
18
Page 21
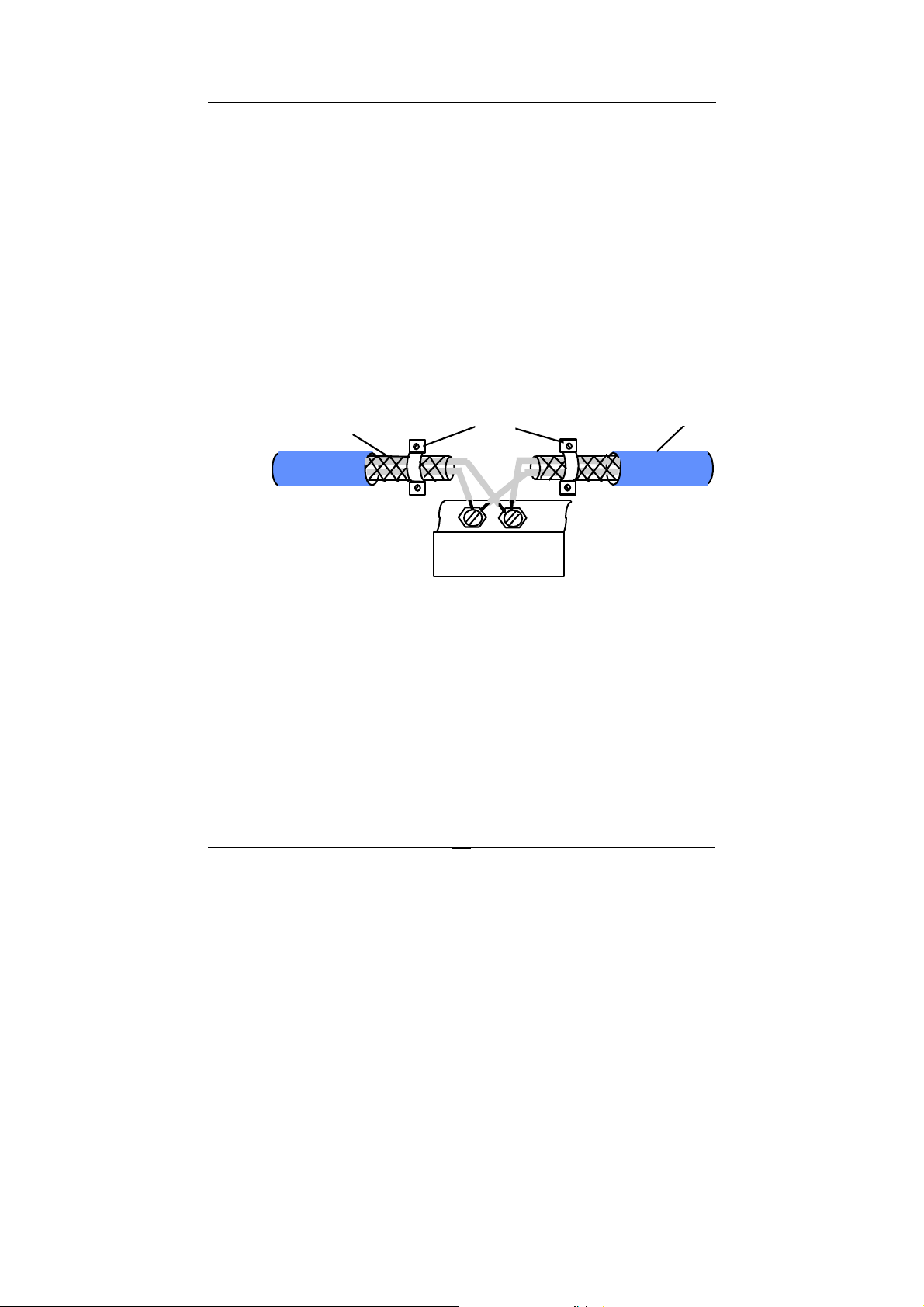
1.9. Shielding
In case of increased interference, a shielded bus cables is recommended to use
for wiring between module and modules. In addition, a shielding also should be
done for the cable of power supply and for the signal cables.
Some experiences and recommendations are concerning for shield connection.
1. The shield should be connected with protective earthing at each bus
connection.
2. The shield should be applied additionally several times along the course of the
cable.
3. The Computer should be applied the shield directly to the appliance or to
separate shield rails.
braided shield
Earthing Point
Isolation
RS-485 Connection Cable
DATA+
DATA -
NuDAM Module
19
Page 22

2
Communication Module
2.1 Overview of ND-6520
ND-6520 is a RS-232 to RS-422/RS-485 converter, it converts the RS-232
signal to the RS-422/RS-485 signals. The ND-6520 can be considered as an
extension RS-422/RS-485 serial port for the host computer. A standard 9-pin
D-type connector is used to connect the host computer and the ND-6520.
Hence, the ND-6520 can connect with all kinds the PC, IPC or Notebook PC,
which install a standard RS-232 interface.
2.1.1 Features of ND-6520
RS-422/RS-485 transceiver
z
Differenial 4-wire full-duplex RS-422
z
Differenial 2-wire half-duplex RS-485
z
Easily setup and installation
z
Auto direction flow control
z
Maximum 128 modules on a bus without using repeaters
z
Maximum 256 addressable modules.
z
High transfer speed
z
20
Page 23

High isolation voltage
z
Lower power consumption
z
2.1.2 Specifications of ND-6520
Input
♦ Interface : standard RS-232 9 pin female D-type connector
♦ Speed (bps) : 1200, 2400, 4800, 9600, 19.2K, 38.4K, 57.6K, 115.2K
♦ Data Format
Data bits : 5 bits, 6 bits, 7 bits, or 8 bits
Stop bits: 1, 2
Parity type: None, Even, Odd
Output
* :
♦ Interface :RS-485, differential, 2 half-duplex wires RS-422, differential,
4 full-duplex wires
♦ Speed (bps) : The same with input speed.
♦ Max RS-485 network bus distance : 4000 feet. (1200 meter)
Isolation
♦ Isolation voltage : 2500 Vrms(between RS-422/RS-485 network and
host computer)
Bus
♦ Max loading : 128 modules on a RS-485 network
♦ Max modules : 256 modules with one ND-6510 repeater
Power
♦ Power Supply : +10V to +30V
♦ Power Consumption : 0.912 W
Note* : It supports auto baudrate and parity, data bits adjustment.
21
Page 24

N
(
)
2.1.3 A Look at ND-6520 & Pin Assignment
(RS-232 IN)
RS-232 to RS-485
D-6520
/RS-422Converter
DATA+
Y
(G)DATA-
TX-
TX+
RX+
TX-
(B)GND
(R)+Vs
Figure 2-1 ND-6520 profile
22
Page 25

2.1.4 Pin Definition of ND-6520
Pin # Signal Name Description
1 (Y)DATA+ RS-485 transmission line, positive
2 (G)DATA- RS-485 transmission line, negative
4 TX+ RS-422 transmission line, positive
5 TX- RS-422 transmission line, negative
6 RX+ RS-422 receiving line, positive
7 RX- RS-422 receiving line, negative
9 (R)+VS NuDAM power supply, +10V~+30V
10 (B)GND NuDAM Ground
D type 9 Pin Connecter Definition of ND-6520
Pin # Signal Name Description
2 RXD RS-232 receiving line
3 TXD RS-232 transmission line
5 GND RS-232 Common Ground
23
Page 26
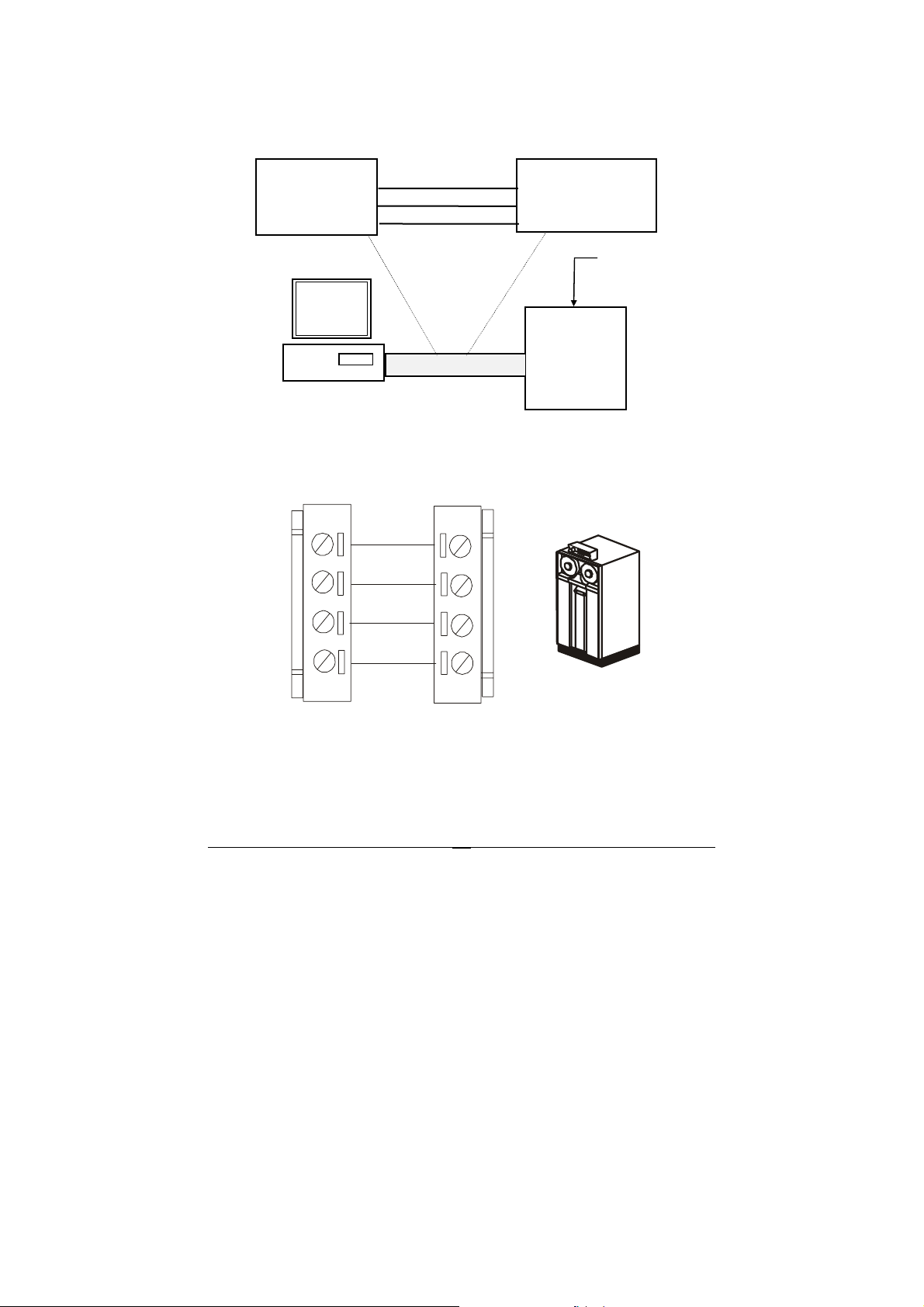
r
Connection Between Host and ND-6520
Host RS-232
GND r
TXD p
RXD o
Host
Computer
RS-232
Figure 2-2 Connection Between Host and ND-6520
RS-422 Application Wiring
ND-6520 RS-232
rGND
pTXD
oRXD
DATA +
DATA -
+Vs GND
ND-6520
RS-232 to RS-485/
RS-422 converte
TX+
TX-
RX+
RX-
Figure 2-3 RS-422 Application Wiring
24
RX+
RX-
TX+
TX-
RS-422 Device
Page 27
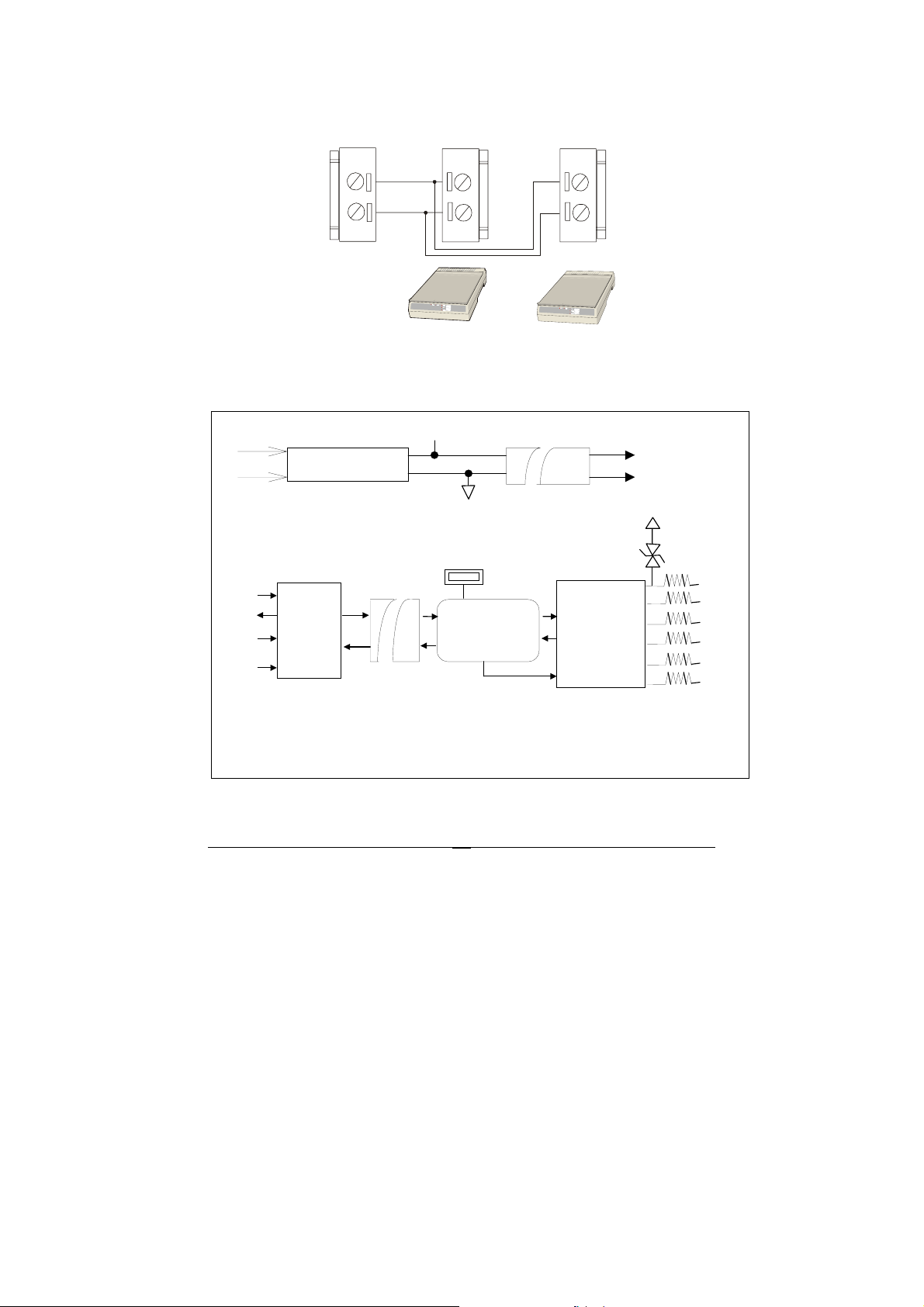
p
VS
RS-485 Application Wiring
DATA+
DATA-
RS-485 Device
DATA+
DATA-
Figure 2-4 RS-485 Application Wiring
2.1.5 ND-6520 Functional Block Diagram
+5V
Power Regulator
& Filter
Power Input
+10V ~ +30V
GND
DC to DC
Converter
SW1
TXD
RXD
RTS
RS-232
Receiver
/ Driver
Communication
Switchin g
Controller
GND
Opto-Isolation
Communication
Direction Control
.....
RS-485 Device
RS-422/RS-485
Receiver/Driver
DATA+
.....
DATA-
Isolation +5V
Isolation GND
T
PTC
Data+
Data-
Rx+
RxTx+
Tx-
TVS : Transient Voltage Suppresser
PTC : Positive Tem
erature Coefficie nt
Figure 2-5 Block Diagram of ND-6520
25
Page 28

2.1.6 Setup
Objective of Setup
In normal condition, it is not necessary to setup the ND-6520. The default
configuration of this communication module is 9600 bps and data format of 8
data bits with 1 start bit, 1 stop bit, and no parity check. Note that the data format
is reserved to be compatible with other brand‘s communication port, it should not
be modified if only NuDAM is used in a system. The baud rate can be
configured according applications’ requirement.
Setup Equipments
Only screw driver is used to open the case. Software, power supply, and wiring
are not necessary.
Setup Procedure
Only hardware switch setting can be setup in ND-6520. The user can set the
speed of the serial interface ( RS-232 and RS-422/RS-485 ), and the serial data
format. The speed and the data format on the whole RS-485 network must be
identical otherwise the communication will be not correct.
To setup the ND-6520, using the screw driver to open the case, then change the
switch setting. The new setting is valid after power on. The case must be put
back and locked carefully. Be careful not to scratch the surface of the circuit
while setting up, the surface coating or even the circuits will be damaged.
Default Setting
♦ 9600 baud rate
♦ 10 bits series data format : one start bit, eight data bits, one stop bit, no
parity check
26
Page 29
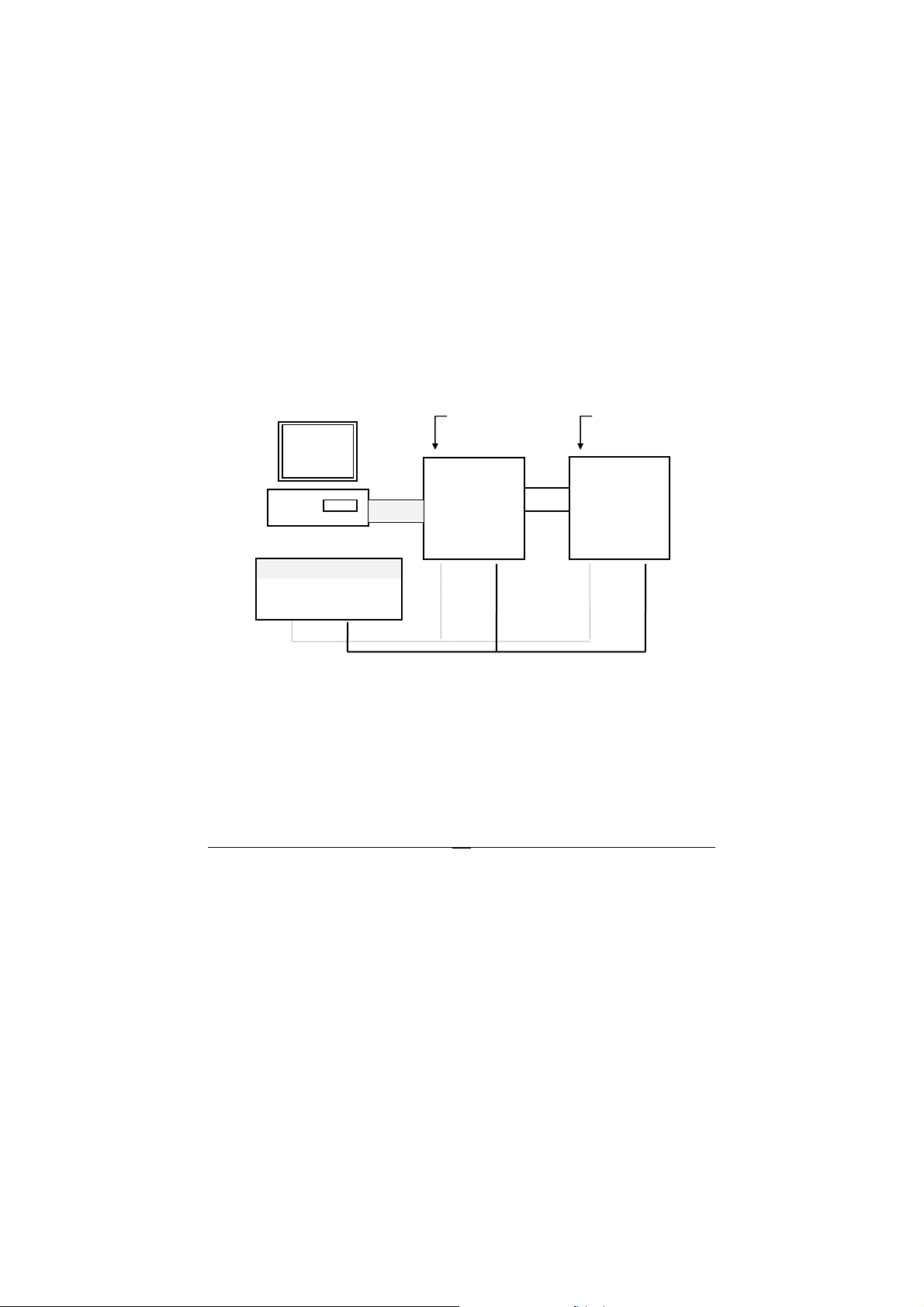
r
2.1.7 Installation
Software Utility
Software is not necessary for this module.
Equipments for Installation
A host computer with RS-232 port
RS-232 cable (DB-9 female)
DC Power supply (+10V~+30V)
Wires (shielded and grounded is recommended)
Installation Procedure
1. Make sure the host computer is power off.
2. Use RS-232 cable to connect ND-6520 with host computer.
3. Wire the power supply to NuDAMs.Note that the power supply should meet
the specification.
4. Wire other NuDAMs.
Application Wiring
Host
Computer
RS-232
ND-6520
RS-232 to RS-485/
RS-422 converte
DATA +
DATA -
+Vs GND
NuDAM
module
+ DATA
- DATA
+Vs GND
Local Power Supply
+10 V to +30 V
+Vs GND
Figure 2-6 Application wiring of NuDAM-6520
2.1.8 Programming
The ND-6520 is a communication module, it is not necessary to do any
programming.
27
Page 30

2.2 Overview of ND-6510
The ND-6510 is the RS-422/RS-485 signal repeater which is used to extend or
to lengthen the network distance. A NuDAM bus can connect up to 128 modules.
The repeater should be used when the numbers of the modules exceed 128. In
addition, the repeater should also be used when the length of a signal bus is
more than 4000 feet.
2.2.1 Features of ND-6510
z RS-422/RS-485 signal transceiver & repeater
z Bi-directions signal transmission for both RS-422/RS-485 ports
z Automatic transmission direction control
z Easy setup and installation
z Maximum 128 modules on a bus
z Maximum 256 addressable modules
z High transfer speed
z Surge protection
z Lower power consumption
2.2.2 Specifications of ND-6510
Input / Output
♦ Interface : RS-485, differential, 2 half-duplex wires.
RS-422, differential, 4 full-duplex wires
♦ Speed (bps) : 1200, 2400, 4800, 9600, 19.2K, 38.4K, 57.6K, 115.2K
♦ Data Format* :
Data bits : 5 bits, 6 bits, 7 bits, or 8 bits
Stop bits: 1, 2
Parity type: None, Even, Odd
♦ Max RS-485 network bus distance : 4000 feet. (1200 meter)
Note*: It is auto baudrate and parity, data bits adjust.
Bus
28
Page 31

♦ Max Loading : 128 NuDAMs on a bus
Power
♦ DC Power Supply : +10V to +30V
♦ Power Consumption : 1.104W
29
Page 32

N
1
10
r
2.2.3 A Look at ND-6510 & Pin Assignment
20
DATA+ (Y)
DATA- (G)
D-6510
Tx-
Tx+
Rx+
RS-422/RS-485
Repeapte
11
Rx-
RX-
(Y)DATA+
(G)DATA-
Tx+
Rx+
Tx-
(R)+Vs
(B)GND
Figure 2-6 ND-6510 profile
30
Page 33

g
p
VS
g
2.2.4 Pin Definition of ND-6510
Pin # Signal Name Description
1 (Y)DATA+ RS-485 transmission line, positive
2 (G)DATA- RS-485 transmission line, negative
4 TXIN+ RS-422 transmission input line, positive
5 TXIN- RS-422 transmission input line, negative
6 RXOUT+ RS-422 receiving output line, positive
7 RXOUT- RS-422 receiving output line, negative
9 (R)+VS NuDAM power supply, +10V~+30V
10 (B)GND NuDAM ground
Pin # Signal Name Description
14 RXIN- RS-422 receiving input line, negative
15 RXIN+ RS-422 receiving input line, positive
16 TXOUT- RS-422 transmission output line, negative
17 TXOUT+ RS-422 transmission output line, positive
19 (G)DATA- RS-485 transmission line, negative
20 (Y)DATA+ RS-485 transmission line, positive
2.2.5 ND-6510 Functional Block Diagram
+5V
Pow er Input
+10V ~ +30V
Power Regulator
& Filte r
GND
Data+
DataRx+
RxTx+
Tx-
RS-422/RS-485
Receiver/Driver
SW1
Communicatio
Switchin
Controller
n
Comm unication
T
RS-422/RS-485
Receiver/Driver
PTC
Data+
DataRx+
RxTx+
Tx-
Direction
Control
TVS : Tran sien t Volta
PTC : P o sitive Tem
e Suppresser
erature Coefficient
Figure 2-7 Block Diagram of ND-6510
31
Page 34

2.2.6 Setup
Objective of Setup
In normal condition, you only need to configure the ND-6510 when the NuDAM
bus with more than 128 modules or the distance exceeds 4000 feet long. The
default configuration of this communication module is 9600 bps, data format of 8
data bits with 1 start bit, 1 stop bit, and no parity check. Note that the data format
is reserved to be compatible with other brand‘s communication port, it should not
be modified if only NuDAM is used in a system. The baud rate can be
configured according user’s requirement.
Setup Equipments
Only screw driver is used to open the case. Software, power supply, and wiring
are not necessary.
Setup Procedure
Only hardware switch setting can be setup in ND-6510. The user can set the
speed and the data format of the RS-422/RS-485 interface. The speed and the
data format on the whole network must be identical otherwise the
communication may be not correct.
To setup the ND-6510, use the screw driver to open the case, then change the
switch setting. The new setting is valid after power on. The case must be put
back and locked carefully. Note that do not scratch the surface of the circuit
while setting up, otherwise the surface coating or even the circuits will be
damaged.
Default Setting
♦ 9600 Baud rate
♦ 10 bits serial data format : one start bit, eight data bits, one stop bit, no
parity check
32
Page 35

2.2.7 Installation
Software Utility
Software is not necessary.
Equipments for Installation
A 2-wire RS-485 network or 4-wire RS-422 network.
DC Power supply (+10V~+30V)
Wires
Installation Procedure
1. Make sure the original RS-422/RS-485 network is power off.
2. Wire the power supply to ND-6510. Note that the power supply should meet
the specification.
3. Wire other NuDAMs to the extend RS-485 bus
33
Page 36

Application Wiring
ND-6520
DATA +
DATA -
+Vs GND
+DATA DATA+
-DATA DATA-
+Vs GND
Local Power Supply
+10 V to +30 V
+Vs GND
Figure 3-1 ND-6510 wiring.
ND-6510
Repeater
NuDAM
module
+ DATA
- DATA
+Vs GND
2.2.8 Programming
The ND-6510 is a communication module, it is not necessary to do any
programming
34
Page 37

2.3 Overview of ND-6530
Universal Serial Bus (USB) is an open, royalty free, Plug and Play standard for
PC peripheral connectivity, supported by leading computer, telecommunications
and software company. It behaves in a similar fashion to conventional bus
technology (serial, parallel, ISA…), but is a faster, no extra slots or IRQ required
manner.
The ND-6530 takes advantages of the USB technology, and for the convenience
to the users of numerous PC, IPC, notebooks, laptops and handheld PC, it
provides an easy way to link with industry standard buses interface of
RS-232/422/485.
2.3.1 Features of ND-6530
z USB Specification 1.1 Compliant
z Plug and Play Installation
z Self power(by USB power)
z RS-232 support RTS, CTS handshake signal
z Full-Duplex RS-422 support
z Half-Duplex RS-485 support
z Up to 128 RS-485 devices on the bus
z Auto direction flow control on RS-485
z High transfer Speed up to 115.2Kbps
z High isolation voltage up to 2500Vrms
z Surge protection on RS-232/422/485 lines
z Driver support for Windows 2000/98/XP/Vista/Linux
z Low power consumption
z Easy setup and installation
35
Page 38

2.3.2 Specifications of ND-6530
USB controller:
♦ USB Spec. 1.1 compliant
I/O Interface:
♦ RS-232/422/485 DIP switch selectable
♦ RS-232 support RXD, TXD, RTS, CTS, FGND signals
♦ RS-422 support TX+, TX-, RX+, RX- 4 wires full-duplex signals
♦ RS-485 support DATA+, DATA- signals with auto direction control
♦ Selectable transfer speed with 1200, 2400, 4800, 9600, 19200, 38400,
57600, 115200 bps
♦ 2500Vrms isolation
♦ Surge protection on all signal lines
Connector:
♦ USB type B
♦ 10 pin screw terminal block
LED Indicator:
♦ ON: Receiving USB power
♦ Flashing: Data transfer
♦ OFF: No power applied
Cable: Type A to type B
Storage Temperature Range: -25 to 80 °C
Operating Temperature Range: -10 to 70 °C
Power Requirement: USB bus power
Power Consumption: 0.795W
Case: ABS with captive mounting hardware
CE Class A Conformity
36
Page 39

N
2.3.3 A Look at NuDAM-6530 & Pin Assignment
USB to RS-232/422/485
D-6530
Converter
FGND
TX+/D+
RX-
RX+
TX-/D-
TX
RX
CTS
RTS
Figure 2-8 ND-6530 profile
37
Page 40

2.3.4 Pin Definition of ND-6530
Pin # Signal Name Description
1 TX+/D+ RS-422 or RS-485 transmission line, positive
2 TX-/D- RS-422 or RS-485 transmission line, negative
3 RX+ RS-422 receive line, positive
4 RX- RS-422 receive line, negative
5 NC No connection
6 TX RS-232 transmission line
7 RX RS-232 receive line
8 RTS Request to send
9 CTS Clear to send
10 F.GND Ground
USB type B Connecter Definition of ND-6530
Pin # Signal Name Description
1 +5V USB +5V bus power
2 Data- USB data line, negative
3 Data+ USB data line, positive
4 Ground USB bus power ground
2.3.5 ND-6530 Functional Block Diagram
Figure 2-9 Block Diagram of ND-6530
38
Page 41

DIP Switch Setting (Convertion protocol)
RS-485 Mode(Default)
RS-422 Mode
RS-232 Mode
39
Page 42

2.3.6 Setup
Objective of Setup
In normal condition, it is not necessary to setup the ND-6520. The default
configuration of this communication module is in RS-485 mode and support
baudrate from 1200 to 115200, with data bit including 5, 6, 7 or 8 bits, and its
stop bit support 1, 1.5 or 2 bits, parity types are None, Odd, Even. Note that the
data format is reserved to be compatible with other brand‘s communication port,
it should not be modified if only NuDAM is used in a system. The baud rate is
not necessary to config.
Setup Equipments
Only screw driver is used on the dip switch beside the USB connector to select
the protocal type.
Setup Procedure
Only hardware switch setting can be setup in ND-6530. The user can select the
protocol types in RS-422, RS-485 or RS-232 interface. The speed and the data
format on the whole network must be identical otherwise the communication may
be not correct.
To setup the ND-6530, use the screw driver to adjust the dip switch beside the
USB connector to select the protocal type. The new setting is valid even the
power is on. The case will not be open.
40
Page 43

2.3.7 Installation
Application Wiring
RS-485
ND-6530
For RS-485 Transmission Distance Up to 1,200m (4,000 ft.)
Load more than 128 NuDAM I/O modules or more than 32
others RS-485 devices
DATA+
DATA-
RS-485 Device
DATA+
DATA-
DATA+
DATA-
DATA+
DATA-
.....
DATA+
DATA-
.....
41
Page 44

RS-422
For RS-422 Transmission Distance Up to 1,200m (4,000 ft.)
TXTX+
RXRX+
RS-232
TX+
ND-6530
TX-
RX+
RX-
RX+
RX-
TX+
TX-
RS-232 Device
TX
ND-6530
RX
RTS
CTS
FGND
1
6
TXD
2
CTS
7
RXD
3
8
RTS
4
9
5
GND
42
Page 45

2.3.8 Programming
The ND-6530 is a communication module, it is not necessary to do any
programming
43
Page 46

2.4 Overview of ND-6531
ND-6531 is a RS-422/485 to RS-232 converter. it converts the RS-422/485
communication signal to the RS-232 signals which makes your RS-232 devices
easily link up to RS-422/485 multi-drop network.
2.4.1 Features of ND-6531
z RS-422/RS-485 transceiver
z RS-232 support RTS CTS handshake signal
z RS-232 and RS-422/485 can be different baud rate
z Full-Duplex RS-422 support
z Half-Duplex RS-485 support
z Up to 128 RS-485 devices on the bus
z Auto direction flow control on RS-485
z Addressable and non-addressable mode configurable
z High transfer Speed up to 115.2Kbps
z High isolation voltage up to 2500Vrms
z Surge protection on RS-422/485 lines
z Low power consumption
z Easy setup and installation
44
Page 47

2.4.2 Specifications of ND-6531
Transmission Speed (bps): 1,200 ~ 115,200 (RS-422/485 and RS-232
can be set to different baud rate)
Data Format: RS-232 (RS-422/485 is fixed to 1 stop bit, non-parity, 8
data bits format)
♦ Stop bits: 1, 2
♦ Parity type: None, Even, Odd
♦ Data bits: 5, 6, 7, 8
RS-232:
♦ 9 pin D-sub female connector
♦ Support RXD, TXD, RTS, CTS signals
RS-422:
♦ Differential 4 full duplex wires
♦ Support TX+, TX-, RX+, RX- signals
♦ Surge protection on signal pins
RS-485:
♦ Differential 2 half duplex wires
♦ Support DATA+, DATA- signals
♦ Surge protection on signal pins
Isolation Voltage: 1000 V
Storage Temperature Range: -25 to 80 °C
DC
Operating Temperature Range: -10 to 70 °C
Power Requirement: +10V to +30V
reversal
Unregulated with against power
DC
♦ Power Consumption: 1.008W
Case: ABS with captive mounting hardware
CE Class A Conformity
45
Page 48

N
(
)
2.4.3 A Look at NuDAM-6531 & Pin Assignment
(RS-232 )
Addressable RS-422/485
To RS-232 Converter
D-6531
DATA+
Y
(G)DATA-
TX-
TX+
DEFAULT*
RX+
X-
(R)+Vs
FGND
Figure 2-10 NuDAM-6531 profile
(B)GND
46
Page 49

2.4.4 Pin Definition of ND-6531
Pin # Signal Name Description
1 (Y)DATA+ RS-485 transmission line, positive
2 (G)DATA- RS-485 transmission line, negative
3 DEFAULT* Initial state setting
4 TX+ RS-422 transmission line, positive
5 TX- RS-422 transmission line, negative
6 RX+ RS-422 receiving line, positive
7 RX- RS-422 receiving line, negative
8 FGND Field ground
9 (R)+VS Power supply, +10V~+30V
10 (B)GND Ground
D type 9 Pin Connecter Definition of ND-6531
Pin # Signal Name Description
2 TXD RS-232 transmission line
3 RXD RS-232 receiving line
5 GND RS-232 Signal Common Ground
7 CTS RS-232 Clear to Send
8 RTS RS-232 Ready to Send
Note* : The module is in DEFAULT mode when DEFAULT* pin connected to
GND while applying power on the module.
Note* : Do not apply any power signal to DEFAULT* pin, just left it open or
connected it to GND.
47
Page 50

2.4.5 ND-6531 Functional Block Diagram
+5V
Power Regulator
& Filter
Power Input
+10V ~ +30V
GND
DC to DC
Converter
Isolation +5V
Isolation GND
TXD
RXD
RTS
RS-232
Receiver
/ Driver
GND
Opto-Isolation
TVS : Transient Voltage Suppresser
PTC : Positive Tem perature Coefficient
Figure 2-11 Block Diagram of ND-6531
SW1
Communication
Switching
Controller
Communication
Direction Control
TVS
RS-422/RS-485
Receiver/Drive
PTC
Data+
Data-
Rx+
RxTx+
Tx-
48
Page 51

2.4.6 Initialation & Installation
Software Installation
1. If you have already installed “NuDAM Administration” then skip other steps.
2. Backup your software diskette
3. Insert “NuDAM Administration” disc into CD-ROM:
4. Change drive to the path of CD-ROM. For example, your drive of CD-ROM is
F:, then change the drive to F:
5. Find the setup of NuDAM Administration and run it.
6. Please follow the steps of setup program then you can successful to install the
nudism Administration.
Objective of Initializing a Brand-New ND-6531
All NuDAM modules. except ND-6520, ND-6510, and ND-6530, in a RS-485
network must have an unique address ID, however, every brand-new ND-6531
has a factory default setting as following:
♦ Address ID is 01.
♦ Baud rate is 9600 bps
♦ RS-485 Interface
♦ Host Watchdog timer is disable
Therefore, to configure the brand-new NuDAM before using is necessary,
otherwise the address ID will conflict with other modules if the ID of new module
is identical to any of the existing one. The baud rate may also be changed
according to user‘s requirement.
Default State
The NuDAM I/O modules must be set at Default State when you want to change
the default settings, such as the ID address, baud rate, check-sum status etc.
All NuDAM I/O modules have a special pin labeled as
will be in Default State if the
ON. Under this state, the default configuration is set as following:
DEFAULT*
pin is shorted to ground when power
DEFAULT*
. The module
♦ Address ID is 00.
♦ Baud rate is 9600 bps.
♦ RS-485 Interface
♦ 8 Data bits,1 Start bit,1 Stop bit and none parity check.
49
Page 52

Therefore, the communication between the host and the module can be easily
set up as the same configuration, the initialization of a module is possible no
matter what configuration is set under operating state
Initialization Equipments
♦ Host computer with a RS-232 port.
♦ An installed RS-485 module (ND-6520 or ND-6530) with 9600 baud rate.
♦ The brand new ND-6531
♦ Power supply (+10 to +30 V
) for NuDAM modules
DC
♦ Administration utility software
Note : Never Connect the DRFAULT* pin to Vs or power source just left it
open or wired to GND.
Initialization Procedure
1. Power off the host computer and the installed ND-6520 or ND-6530. Be sure
that the baud rate of the ND-6520 or ND-6530 is 9600 bps.
2. Connect a brand new NuDAM module with the RS-485. Set the module in
Default State by shorting the
wiring.
DEFAULT*
pin. Refer to Figure 2-12 for detailed
3. Power on the host computer.
4. Power on the power supply for NuDAM modules.
5. Use the NuDAM Administrating utility to configure the address ID, Baud rate
and check-sum status of the module.
50
Page 53

Figure 2-12 Wiring for NuDAM be in default state
2.4.7 Install a New ND-6531 to a Existing Network
Equipments for Install a New Module
♦ A existing NuDAM network
♦ New NuDAM modules.
♦ Power supply (+10 to +30 V
Installation Procedure
1. Configure the new NuDAM module according to the initialization procedure in
section 2.1.6.
2. The baud rate and check-sum status of the new module must be identical with
the existing RS-485 network. The address ID must not conflict with other
NuDAM modules on the network.
3. Power off the NuDAM power supply of the existing RS-485 network.
4. Power off the host computer.
5. Wire the power lines for the new NuDAM with the existing netw ork. Be careful
about the signal polarity when wiring.
6. Wire the RS-485 data lines for the new NuDAM with the existing netw ork. Be
careful about the signal polarity as wiring.
7. Wire to the input or output devices.
8. Power on the host computer.
9. Power on the NuDAM local power supply.
10. Use the NuDAM administration utility to check entire network.
DC
).
51
Page 54

Application Wiring
Host with RS-422/485 I/F
DATA+
DATA-
RX+
RX-
TX+
TX-
TX+
TX-
RX+
RX-
DATA+
DATA-
ND-6521
1
6
TXD
2
CTS
7
RXD
3
RTS
8
4
9
5
GND
RTS
CTS
1
6
2
7
3
8
4
9
5
RS-232 Device
RXD
TXD
GND
52
Page 55

3
Analog Input Modules
3.1 Overview of ND-6013
ND-6013 is a RTD input module with 3 input channels. It supports 2, 3 or 4 wires
RTD input devices
3.1.1 Features of ND-6013
z 3 RTD input channels
z 2, 3 or 4 wire RTD input support
z Programmable RTD input range
z Internal watchdog timer for device failure protection
z Easy programming by software
z Easy installation and wiring
.
3.1.2 Specifications of ND-6013
Interface
♦ Interface: RS-485, 2 wires
♦ Speed (bps): 1200, 2400, 4800, 9600, 19.2K, 38.4K ,57.6K ,115.2K
RTD Input
♦ Input type: Pt or Ni input, 2, 3 or 4 wires
♦ Channels Numbers: 3
♦ Resolution: 16 bits
♦ Sampling Rate:10 sample/sec
53
Page 56

♦ Unit Conversion: °C or Ohm
♦ Temperature Range: Programmable 5 levels, ±100°C, 0~100°C,
♦ Accuracy: ±0.1%
Power
♦ Power supply: +10V to +30V
♦ Current consumption: 0.696 W
0~200°C, 0~600°C, 0~60 Ohms
54
Page 57

N
3.1.3 A Look at ND-6013 & Pin Assignment
20
IEXC 1+
IEXC 1-
SENSE 1+
SENSE 1-
IEXC 2+
AGND 1
3-CH RTD Input
SENSE 2+
SENSE 2-
11
IEXC 2-
AGND 2
D-6013
α=0.00385 α=0.003916
Code Input Range Code Input Range
20 Pt.-100°C~+100°C 24 Pt.-100°C~+100°C
21 Pt. 0°C~+100°C 25 Pt. 0°C~+100°C
22 Pt. 0°C~+200°C 26 Pt. 0°C~+200°C
23 Pt. 0°C~+100°C 27 Pt. 0°C~+100°C
28 Ni-1000°C~+100°C29Ni-
SENSE 0+
IEXC 0+
1
SENSE 0-
IEXC 0-
AGND 0
1200°C~+100°C
DEFAULT*
DATA +
+Vs
GND
10
DATA -
Figure 3-1 ND-6013 profile
55
Page 58

g
p
r
3.1.4 Pin Definition of ND-6013
Pin # Signal Name Description
1 +IEXC0 Current source of CH0
2 +SENSE0 Differential positive input of CH0
3 -SENSE0 Differential negative input of CH0
4 -IEXC0 Current source of CH0
5 AGND0 Analog signal ground of CH0
6 DEFAULT* Initial state setting
7 (Y) DATA+ RS-485 series signal, positive
8 (G) DATA- RS-485 series signal, negative
9 (R) +Vs Power supply, +10V~+30V
10 (B) GND Ground
11 AGND2 Analog signal ground of CH2
12 -IEXC2 Current source of CH2
13 -SENSE2 Differential negative input of CH2
14 +SENSE2 Differential positive input of CH2
15 +IEXC2 Current source of CH2
16 AGND1 Analog signal ground of CH1
17 -IEXC1 Current source of CH1
18 -SENSE1 Differential negative input of CH1
19 +SENSE1 Differential positive input of CH1
20 +IEXC1 Current source of CH1
3.1.5 ND-6013 Functional Block Diagram
Data +
Data -
Power Input
+10V ~ +30V
Watchdog/Power
Failure Su
RS-485
Rec/Drv
EEPROM
Config Data
+ 5V
Power
Regulator & Filter
GND
erviso
Micro
Processor
ADC
Di
Mux
1-bit
ital Input
3
RTD
Input
Default*
Pin
Figure 3-2 Block Diagram of NuDAM-6013
56
+IEXC
+SENSE
-SENSE
-IEXC
GND
2, 3, 4
Page 59

3.2 Overview of ND-6017
ND-6017 is an analog input module with 8 input channels. Six of the eight
channels are differential type and the other two are single ended type.
3.2.1 Features of ND-6017
• 8 analog input channels
• 6 differential inputs and 2 single ended inputs
• Programmable input voltage range
• Programmable host watchdog timer for host failure protection
• 5000 Vrms isolation voltage
• Internal watchdog timer for device failure protection
• Easy programming by software
• Easy installation and wiring
3.2.2 Specifications of ND-6017
Interface
♦ Interface: RS-485, 2 wires
♦ Speed (bps): 1200, 2400, 4800, 9600, 19.2K, 38.4K , 57.6K, 115.2K
Analog Input *
♦ Input type: Differential input
♦ Channels Numbers: 8
♦ Resolution: 16 bits
♦ Sampling Rate:10 sample/sec
♦ Unit Conversion: mV, V, or mA
♦ Voltage Range: Programmable 5 levels , ±10V, ±5V, ±1V, ±500mV,
±150mV
♦ Current Measurement: 0~20mA (with external 125Ω resistor)
♦ Accuracy: ±0.1%
Power
♦ Power supply: +10V to +30V
♦ Current consumption: 1.2 W
57
Page 60

Note *: The maximum input voltage shall not exceed to ±30V with reference
to AGND. Otherwise, they may cause an unrecoverable damage to
the hardware component.
58
Page 61

3.2.3 A Look at ND-6017 & Pin Assignment
20
Vin 4-
Vin 4+
ND-6017
Vin 3-
CODE
08
09
0A
0B
0C
0D
Vin 3+
Vin 2-
8-CH Analog Input
Vin 2+
mV/mA
10V
5 V
1 V
500 mV
150 mV
100 mV
0 - 20 mA
11
Vin 0+
Vin 1+
Vin 1-
Vin 0-
1
Vin 5+
Vin 5-
Vin 6+
AGND
Vin 7+
DEFAULT*
(Y)DATA+
(G)DATA-
10
(R)+Vs
(B)GND
Figure 3-3 ND-6017 profile
59
Page 62

g
p
r
3.2.4 Pin Definition of ND-6017
Pin # Signal Name Description
1 Vin5+ Differential positive input channel 5
2 Vin5- Differential negative input channel 5
3 Vin6+ Single-ended voltage input channel 6
4 AGND Analog signal ground of CH6 & 7
5 Vin7+ Single-ended voltage input channel 7
6 DEFAULT* Initial state setting
7 (Y) DATA+ RS-485 series signal, positive
8 (G) DATA- RS-485 series signal, negative
9 (R) +Vs Power supply, +10V~+30V
10 (B) GND Ground
11 Vin0+ Differential positive input channel 0
12 Vin0- Differential negative input channel 0
13 Vin1+ Differential positive input channel 1
14 Vin1- Differential negative input channel 1
15 Vin2+ Differential positive input channel 2
16 Vin2- Differential negative input channel 2
17 Vin3+ Differential positive input channel 3
18 Vin3- Differential negative input channel 3
19 Vin4+ Differential positive input channel 4
20 Vin4- Differential negative input channel 4
3.2.5 ND-6017 Functional Block Diagram
Power
Power Input
+10V ~ +30V
Regulator & Filter
Watchdog/Power Failure
Data +
Data -
RS-485
Rec/Drv
Su
erviso
Processor
Micro
EEPROM
Config Data
Safe Value
Figure 3-4 Block Diagram of ND-6017
ADC
Di
+ 5V
GND
Mux
1-bit
ital Input
8
Analog
Input
Default*
Pin
60
Page 63

3.3 Overview of ND-6018
ND-6018 is a thermocouple input module with 8 input channels. Six of the eight
channels are differential type and the other two are single ended type.
3.3.1 Features of ND-6018
• 8 analog input channels
• 6 differential inputs and 2 single ended inputs
• Programmable input voltage range
• Programmable host watchdog timer for host failure protection
• On board CJC for temperature measurement
• 2500 Vrms isolation voltage
• Internal watchdog timer for device failure protection
• Easy programming by software
• Easy installation and wiring
• Wiring open detection
3.3.2 Specifications of ND-6018
Interface
♦ Interface: RS-485, 2 wires
♦ Speed (bps): 1200, 2400, 4800, 9600, 19.2K, 38.4K , 57.6K, 115.2K
Analog Input
♦ Input type: Differential input
♦ Channels Numbers: 8
♦ Resolution: 16 bits
♦ Sampling Rate:3 sample/sec
♦ Unit Conversion: Thermocouple, mV, V or mA
♦ Thermocouple Type: J, K, T, E, R, S, B, N, C
♦ J: 0°C~760°C K: 0°C~1370°C
♦ T: -100°C~400°C E: 0°C~1000°C
♦ R: 500°C~1750°C S: 500°C~1750°C
♦ B: 500°C~1800°C N: -270°C~1300°C
♦ C: 0°C~2320°C
♦ Voltage Range: Programmable 6 levels ±2.5V, ±1V, ±500mV,
♦ Current Measurement: 0~20mA (with external 125Ω resistor)
Power
*
±100mV, ±50mV, ±15mV
61
Page 64

♦ Power supply: +10V to +30V
♦ Current consumption: 0.96 W
Note *: The maximum input voltage shall not exceed to ±30V with
reference to AGND otherwise, they may cause an
unrecoverable damage to the hardware component.
62
Page 65

N
06±20
ype
3.3.3 A Look at ND-6018 & Pin Assignment
20
Vin 4+
Vin 4-
ND-6017
Code mV/mA Code T/C
00 ±15mV 0E J Type
01 ±50mV 0F K Type
02 ±100mV 10 T Type
03 ±500mV 11 E Type
04 ±1V 12 R Type
05 ±2.5V 13 S Type
Vin 3-
D-6018
CODE
08
09
0A
0B
0C
0D
Vin 3+
Vin 2-
Vin 2+
Multiple
8-CH Analog Input
Analog Input
mV/mA
10V
5 V
1 V
500 mV
100 mV
mA 14 B T
0 - 20 mA
11
Vin 0+
Vin 1+
Vin 1-
Vin 0-
1
Vin 5+
Vin 5-
Vin 6+
AGND
Vin 7+
DEFAULT*
(Y)DATA+
(G)DATA-
10
(R)+Vs
(B)GND
Figure 3-5 ND-6018 profile
63
Page 66

3.3.4 Pin Definition of ND-6018
Pin # Signal Name Description
1 Vin5+ Differential positive input channel 5
2 Vin5- Differential negative input channel 5
3 Vin6+ Single-ended voltage input channel 6
4 AGND Analog signal ground of CH6 & 7
5 Vin7+ Single-ended voltage input channel 7
6 DEFAULT* Initial state setting
7 (Y) DATA+ RS-485 series signal, positive
8 (G) DATA- RS-485 series signal, negative
9 (R) +Vs Power supply, +10V~+30V
10 (B) GND Ground
11 Vin0+ Differential positive input channel 0
12 Vin0- Differential negative input channel 0
13 Vin1+ Differential positive input channel 1
14 Vin1- Differential negative input channel 1
15 Vin2+ Differential positive input channel 2
16 Vin2- Differential negative input channel 2
17 Vin3+ Differential positive input channel 3
18 Vin3- Differential negative input channel 3
19 Vin4+ Differential positive input channel 4
20 Vin4- Differential negative input channel 4
3.3.5 ND-6018 Functional Block Diagram
Power Input
+10V ~ +30V
Data+
Data -
Config Data
Safe Value
Watchdog/Power Failure
RS-485
Rec/Drv
EEPROM
Figure 3-6 Block Diagram of ND-6018
Power
Regulator & Filter
Micro
Processor
+ 5V
ADC
GND
Mux
8
Thermo-
couple
Input
channels
1-bit
Default*
Pin
64
Page 67

4
Analog Output Modules
4.1 Overview of ND-6021
ND-6021 is an analog signal output module. It receives the digital command
from host computer through RS-485 network. The format of the digital value can
be engineering units, hexdecimal format or percentage of full-scale range(FSR).
A microprocessor is used to convert the digital command to digital value to send
to DAC. The DAC converts the digital value into analog form. The analog output
can be either voltage or current output.
The ND-6021 is designed for safety. It provides many safety functions such as
isolation, watchdog, and power on safe value. The opto-isolators provide
5000Vrms isolation voltage to isolate the digital section and the remote
controlled analog equipments. The damage of power surges is avoided.
Another safety fucntion is the watchdog. Whenever the host is loss contact with
the remoted NuDAM module, or the micro-processor is down, the module will
reset itself and send the safety value to the analog output therefore the industry
safety is guarantee. The safety value / power-up value can be set by
configuration software.
The analog output can be readback through the module‘s ADC. which can
monitor the ’real‘ output of the device. The host can check the digital command
and the real output to avoid short circuits. The slew rate of the output signal is
also controllable by software.
4.1.1 Features of ND-6021
65
Page 68

z One uni-polar analog output channel
z Two sets of differential current and voltage output terminals
z Versatile digital signal format
z Programmable host watchdog timer for host failure protection
z Internal watchdog timer for device failure protection
z Easy programming by software
z Easy installation and wiring
4.1.2 Specifications of ND-6021
Interface
♦ Interface : RS-485, 2 wires
♦ Speed (bps) : 1200, 2400, 4800, 9600, 19.2K, 38.4K, 57.6K, 115.2K
Analog Output
♦ Singal Output type: Differential type
♦ Resolution: 12 bits
♦ Accuracy: ±0.1% of FSR for current output
♦ Accuracy: ±0.2% of FSR for voltage output
♦ Unit Convertion: V or mA
♦ Voltage output range: 0 to 10 V (uni-polar)
♦ Current output range: 0 to 20 mA, 4 to 20 mA
♦ Maximum Sampling Rate: 100 samples /sec
♦ Slew rate of Voltage output: 0.0625 to 64 V/sec
♦ Slew reate of Current output: 0.125 to 128 mA/sec
♦ Internal Current Load Resistor: 500Ω (%1)
Isolation
♦ Isolation voltage: 5000 Vrms
Watchdog Function
♦ Module internal watchdog timer : 150 ms
♦ Power failure threshold : 4.65 V
♦ Host programmable watchdog : 100 ms ~ 25.500 sec
Power
♦ Power supply : +10V to +30V
♦ Power consumption : 1.32W
66
Page 69

4.1.3 A Look at ND-6021 & Pin Assignment
20
Analog Output
ND-6021
Code Output Range
30
31
32
(Current/Voltage)
1
+VOUT
-IOUT
+IOUT
-VOUT
Figure 4-1 ND-6021 profile
DEFAULT*
0 ~20 mA
4 ~ 20 mA
0 ~ 10V
(G)DATA-
(Y)DATA+
11
10
(R)+Vs
(B)GND
67
Page 70

4.1.4 Pin Definition of ND-6021
Pin # Signal Name Descriptio n
1 +IOUT Positive Current Output Terminal
2 -IOUT Negative Current OutputTerminal
3 + VOUT Positive Voltage Output Terminal
4 -VOUT Negative Voltage Output Terminal
6 Default* Initial state setting
7 (Y) DATA+ RS-485 series signal, positive
8 (G) DATA- RS-485 series signal, negative
9 (R) +Vs Power supply, +10V~+30V
10 (B) GND Ground
4.1.5 ND-6021 Functional Block Diagram
Data+
RS-485
Rec/DRv
Data-
RS-485
Terminator
Watchdog / Power Failure
Supervisor
EEPROM
Micro
Processor
Photo
Isolators
(12 bits)
*Defalut Setting
(1 bit Digital In)
DAC
Voltage Output
V to I
Current Output
VOUT +
VOUT -
IOUT +
IOUT -
+10V ~ +30 V
GND
Regulator
Power
+5V
GND
DC to DC
Convertor
Isolated Power
Isolated Ground
Figure 4-2 Block Diagram of ND-6021
68
Page 71

4.2 Overview of ND-6024
ND-6024 is a 4 channel bipolar analog signal output module. It receives the
digital command from host computer through RS-485 network. A
microprocessor is used to convert the digital command to digital value to send to
DAC. The DAC converts the digital value into analog form.
The ND-6024 is designed for safety. It provides many safety functions such as
isolation, watchdog, and power on safe value. The opto-isolators provide
5000Vrms isolation voltage to isolate the digital section and the remote
controlled analog equipments. The damage of power surges is avoided.
Another safety fucntion is the watchdog. Whenever the host is loss contact with
the remoted NuDAM module, or the micro-processor is down, the module will
reset itself and send the safety value to the analog output therefore the industry
safety is guarantee. The safety value/power-up value can be set by
configuration software.
4.2.1 Features of ND-6024
z 4 channel bipolar analog output
z Programmable host watchdog timer for host failure protection
z Internal watchdog timer for device failure protection
z Easy programming by software
z Easy installation and wiring
4.2.2 Specifications of ND-6024
Interface
♦ Interface : RS-485, 2 wires
♦ Speed (bps) : 1200, 2400, 4800, 9600, 19.2K, 38.4K, 57.6K, 115.2K
Analog Output
♦ Channel number : 4
♦ Singal Output type: Differential output
69
Page 72

Voltage Output: ±10V
♦ Resolution: 12 bits resolution
♦ Accuracy: +/-0.02% of FSR(max.)
Digital Input
♦ Channel numbers : 7
♦ Switching Level :TTL
Isolation
♦ Isolation voltage: 5000 Vrms
Power
♦ Power supply : +10V to +30V
♦ Power consumption : 1.848W
70
Page 73

4.2.3 A Look at ND-6024 & Pin Assignment
DI5
DI6
DGND
VOUTD+
CGND
VOUTC+
ND-6024 4-CH
Analog Output
Code Signal
33
10V
±
BGND
VOUTB+
AGND
VOUTA+
DI4
DI3
DI2
DI1
DI0
DEFAULT*
(Y)DAT A+
(G)DAT A-
(R)+Vs
(B)GND
Figure 4-3 ND-6024 profile
71
Page 74

4.2.4 Pin Definitions of ND-6024
Pin # Sig n al Description
1 DI4 Digital input channel 4
2 DI3 Digital input channel 3
3 DI2 Digital input channel 2
4 DI1 Digital input channel 1
5 DI0 Digital input channel 0
6 Default* Initial state setting
7 (Y) DATA+ RS-485 series signal, positive
8 (G) DATA- RS-485 series signal, negative
9 (R) +Vs Power supply, +10V~+30V
10 (B) GND Ground
11 VOUTA+ Positive Voltage Output A Terminal
12 AGND Negative Voltage Output A Terminal
13 VOUTB+ Positive Voltage Output B Terminal
14 BGND Negative Voltage Output B Terminal
15 VOUTC+ Positive Voltage Output C Terminal
16 CGND Negative Voltage Output C Terminal
17 VOUTD+ Positive Voltage Output D Terminal
18 DGND Negative Voltage Output D Terminal
19 DI6 Digital input channel 6
20 DI5 Digital input channel 5
72
Page 75

4.2.5 ND-6024 Functional Block Diagram
Data+
RS-485
Rec/DRv
Data-
RS-485
Terminator
Watchdog / Power Failure
Supervisor
+10V ~ +30 V
GND
EEPROM
Micro
Processor
Photo
Isolators
*DefalutSetting
(1 bit Digital In)
DIØ…… D I6
Power
Regulator
+5V
GND
DC to DC
Convertor
Figure 4-4 Block Diagram of ND-6024
DAC
(12 bits)
Voltage Output
Isolated Power
Isolated Ground
•VOUTA+
AGND
•VOUTB+
BGND
•VOUTC+
CGND
•VOUTD+
DGND
73
Page 76

5
Digital I/O Modules
About the NuDAM DIO Modules
The NuDAM provides a series of digital input or output (DIO) modules to
sense the digital signal or to control the remote devices.
The specified features of each module are shown here.
z ND-6050 : Digital I/O module
z ND-6052 : Isolated digital input module
z ND-6053 : 16-channel digital input module
z ND-6054 : 15-channel isolated digital input module
z ND-6056 : 15-channel isolated digital output module
z ND-6058 : 28 programmable digital I/O module
z ND-6060 : relay output and isolated digital input module
z ND-6063 : 8-channel relay output module
z ND-6067 : 8-channel AC relay output module
74
Page 77

5.1 Overview of ND-6050
ND-6050 is a digital input and output module. The digital input channels can
monitor active TTL signals, and sense passive switch on/off signal because
of the internal pull high resistors. The convenient open collector output
channels can sink up to 50 mA current. Combining with the relay devices, it
is possible to control the high power devices by programming output channel
of the ND-6050.
5.1.1 Features of ND-6050
z 7 channels digital input
z 8 channels open collector digital output
z Programmable host watchdog timer for host failure protection
z Internal watchdog timer for device failure protection
z Easy programming by software
z Easy installation and wiring
5.1.2 Specifications of ND-6050
Interface
♦ Interface : RS-485, 2 wires
♦ Speed (bps) : 1200, 2400, 4800, 9600, 19.2K, 38.4K, 57.6K,
115.2K
Digital Input
♦ Channel numbers : 7
♦ Switching Level :TTL
♦ Pull up resister : 10KΩ
♦ Maximum current : 0.5mA
75
Page 78

Digital Output
♦ Channel number : 8
♦ Output characteristic : open collector transistor
♦ Maximum current sink : 50mA
♦ Max. power dissipation : 300mW
Watchdog Function
♦ Module internal watchdog timer: 150 ms
♦ Power failure threshold : 4.65 V
♦ Safety value : 8 output channels
♦ Host programmable watchdog :
♦ 100 ms ~ 25.500 sec
Power
♦ Power supply : +10V to +30V
♦ Current consumption : 0.336W
76
Page 79

5.1.3 A Look at ND-6050 & Pin Assignment
DI 6
20
DI 4
DI 5
DI 1
DI 3
DI 2
DI 0
ND-6050
I/O Type
Digital Output
Digital Input
Digital
Input/Output
Signal
Bit 0-7
Bit 0-6
1
DO 5
DO 7
DO 6
DO 4
DO 3
DEFAULT*
(Y)DATA+
Figure 5-1 ND-6050 profile
DO 0
(G)DATA-
DO 1
DO 2
11
10
(R)+Vs
(B)GND
77
Page 80

5.1.4 Pin Definitions of ND-6050
Pin # Signal Name Description
1 DO 7 Digital output channel 7
2 DO 6 Digital output channel 6
3 DO 5 Digital output channel 5
4 DO 4 Digital output channel 4
5 DO 3 Digital output channel 3
6 Default* Initial state setting
7 (Y) DATA+ RS-485 series signal, positive
8 (G) DATA- RS-485 series signal, negative
9 (R) +Vs Power supply, +10V~+30V
10 (B) GND Ground
11 DO 2 Digital output channel 2
12 DO 1 Digital output channel 1
13 DO 0 Digital output channel 0
14 DI 0 Digital input channel 0
15 DI 1 Digital input channel 1
16 DI 2 Digital input channel 2
17 DI 3 Digital input channel 3
18 DI 4 Digital input channel 4
19 DI 5 Digital input channel 5
20 DI 6 Digital input channel 6
78
Page 81

5.1.5 ND-6050 Functional Block Diagram
Power Input
+10V ~ +30V
Data +
Data -
Regulator & Filter
Watchdog/Power Failure
Supervisor
RS-485
Rec/Drv
Processor
EEPROM
Config Data
Safe Value
Figure 5-2 Block Diagram of ND-6050
Power
Micro
+
8-bit
Digital/Output
7-bit
Digital/Input
1-bit
Digital/Input
DO7
DI6
Default*
Pin
79
Page 82

5.2 Overview of ND-6052
ND-6052 provides 8 isolated digital input channels. Six of the input channels
are differential type and two of them are single-ended with common ground.
The isolation voltage is up to 5000 Vrms. It is suitable to use ND-6052 in
industrial environment with high voltage electric shock.
5.2.1 Features of ND-6052
z 8 bits isolated input
z 5000 Vrms isolation voltage
z Programmable host watchdog timer for host failure protection
z Internal watchdog timer for device failure protection
z Easy programming by software
z Easy installation and wiring
5.2.2 Specifications of ND-6052
Interface
♦ Interface : RS-485, 2 wires
♦ Speed (bps) : 1200, 2400, 4800, 9600, 19.2K, 38.4K, 57.6K,
115.2K
Input
♦ Channel number : 6 differential channels, 2 single ended
♦ Logical level 0 : +1V Max.
♦ Logical level 1: +3.5V ~ +24V
Watchdog Function
♦ Module internal watchdog timer : 150ms
♦ Power failure threshold : 4.65 V
♦ Safe value : 8 output channels
♦ Host programmable watchdog :100 ms ~ 25.5 sec
Power
♦ Power supply : +10V to +30V
♦ Current consumption : 0.264 W
80
Page 83

5.2.3 A Look at ND-6052 & Pin Assignment
DI 1-
DI 4-
20
DI 3-
DI 4+
ND-6052
Input Type
Diffential
Single Ended
DI 3+
DI 2+
DI 2-
Isolated
Digital Input
Channels
6
2
DI 0-
DI 1+
DI 0+
11
1
DI 5-
DI 5+
D.GND
DI 6+
DI 7+
DEFAULT*
(Y)DATA+
(G)DATA-
10
(R)+Vs
(B)GND
Figure 5-3 ND-6052 profile
81
Page 84

5.2.4 Pin Definitions of ND-6052
Pin # Signal Name Description
1 DI5+ Digital Input Channel 5+
2 DI5 - Digital Input Channel 5 -
3 DI6+ Digital Input Channel 6+
4 D.GND Digital Input Ground
5 DI7+ Digital Input Channel 7+
6 Default* Initial state setting
7 (Y) DATA+ RS-485 series signal, positive
8 (G) DATA- RS-485 series signal, negative
9 (R) +VS Power supply, +10V~+30V
10 (B) GND Ground
11 DI0+ Digital Input Channel 0+
12 DI0 - Digital Input Channel 0 13 DI1+ Digital Input Channel 1+
14 DI1 - Digital Input Channel 1 15 DI2+ Digital Input Channel 2+
16 DI2 - Digital Input Channel 2 17 DI3+ Digital Input Channel 3+
18 DI3 - Digital Input Channel 3 19 DI4+ Digital Input Channel 4+
20 DI4 - Digital Input Channel 4 -
82
Page 85

5.2.5 ND-6052 Functional Block Diagram
Power Input
+10V ~ +30V
Regulator & Filter
Power
+5V
+5V
Watchdog/Power Failure
Supervisor
Data +
Data -
RS-485
Rec/Drv
EEPROM
Config Data
Safe Value
Micro
Processor
Figure 5-4 Block Diagram of ND-6052
DI0+
DI0-
DI0+
DI0-
DI5+
DI5-
DI6+
D.GND
DI7+
D.GND
83
Page 86

5.3 Overview of ND-6053
ND-6053 provides 16 digital input channels for dry contact or wet contact
signals. The effective distance from DI to contact point is up to 500 meter for
dry contact input.
5.3.1 Features of ND-6053
z 16 bits digital input
z Programmable host watchdog timer for host failure protection
z Internal watchdog timer for device failure protection
z Easy programming by software
z Easy installation and wiring
5.3.2 Specifications of ND-6053
Interface
♦ Interface : RS-485, 2 wires
♦ Speed (bps) : 1200, 2400, 4800, 9600, 19.2K, 38.4K, 57.6K,
115.2K
Input
♦ Channel numbers : 16
♦ Dry Contact:
♦ Logical level 0 : close to GND
♦ Logical level 1 : open
♦ Wet Contact :
♦ Switching Level :TTL
♦ Maximum current sink : 50mA
Watchdog Function
♦ Module internal watchdog timer : 150ms
♦ Power failure threshold : 4.65 V
♦ Host programmable watchdog : 100 ms ~ 25.5 sec
Power
♦ Power supply : +10V to +30V
♦ Current consumption : 0.408 W
84
Page 87

N
(
)
5.3.3 A Look at ND-6053 & Pin Assignment
DI 9
20
DI 8
DI 7
DI 6
DI 5
DI 4
DI 3 DI 2
D-6053
Input Type
Digital Input
16-CH
Digital
Channels
16
1
DI 10
DI 12 DI 13 DI 14
DI 11
DEFAULT
DATAG
(Y)DATA+
Figure 5-5 ND-6053 profile
DI 0
DI 1
11
10
(B)GND
(R)+Vs
85
Page 88

5.3.4 Pin Definitions of ND-6053
Pin # Signal Name Description
1 DI10 Digital Input Channel 10
2 DI11 Digital Input Channel 11
3 DI12 Digital Input Channel 12
4 DI13 Digital Input Channel 13
5 DI14 Digital Input Channel 14
6 Default*/DI15 Initial state setting/ Digital Input Channel 15
7 (Y) DATA+ RS-485 series signal, positive
8 (G) DATA- RS-485 series signal, negative
9 (R) +VS Power supply, +10V~+30V
10 (B) GND Ground
11 DI0 Digital Input Channel 0
12 DI1 Digital Input Channel 1
13 DI2 Digital Input Channel 2
14 DI3 Digital Input Channel 3
15 DI4 Digital Input Channel 4
16 DI5 Digital Input Channel 5
17 DI6 Digital Input Channel 6
18 DI7 Digital Input Channel 7
19 DI8 Digital Input Channel 8
20 DI9 Digital Input Channel 9
86
Page 89

5.3.5 ND-6053 Functional Block Diagram
Power Input
+10V ~ +30V
Power
Regulator & Filter
Watchdog/Power Failure
Supervisor
Data +
Data -
RS-485
Rec/Drv
Micro
Processor
EEPROM
Config Data
Safe Value
Figure 5-6 Block Diagram of ND-6053
+ 5V
15-bit
Digital/Input
1-bit
Digital/Input
DI0
DI14
Default*
Pin/DI15
87
Page 90

5.4 Overview of ND-6054
ND-6054 provides 15 isolated digital input channels. All of the input
channels are common power type and one of them is using the same pin
with default (use jumper to choose). The isolation voltage is up to 5000
Vrms. It is suitable to use ND-6054 in industrial environment with high
voltage electric shock.
5.4.1 Features of ND-6054
z 15 channels digital inputs with isolation protection and common power
z 5000 Vrms isolation voltage
z Programmable host watchdog timer for host failure protection
z Internal watchdog timer for device failure protection
z Easy programming by software
z Easy installation and wiring
5.4.2 Specifications of ND-6054
Interface
♦ Interface : RS-485, 2 wires
♦ Speed (bps) : 1200, 2400, 4800, 9600, 19.2K, 38.4K, 57.6K,
115.2K
Input
♦ Channel numbers : 15 isolation common power input channels
(the fifteenth channel is the same with default pin,
but can use jumper to choose)
♦ Logical level 0 : +1V Max.
♦ Logical level 1: +3.5V ~ +24V
♦ Effective distance: 500 meter
♦ Common external voltage: 24V
Watchdog Function
88
Page 91

♦ Module internal watchdog timer : 150msec
♦ Power failure threshold : 4.65 V
♦ Host programmable watchdog :100 ms ~ 25.5 sec
Power
♦ Power supply : +10V to +30V
♦ Power consumption : 0.216 W
89
Page 92

N
5.4.3 A Look at ND-6054 & Pin Assignment
DI5
DI3
DI2
DI0
20
DI1
D-6054
DI4
15-CH Isolated
Digital Input
Input Type
DI
DI6
Channels
15
DI7
DI8
DI9
11
*
DI11
DI10
DI13
DI12
Ext24V
DEFAULT/DI14
(G)DATA-
(Y)DATA+
10
(R)+Vs
(B)GND
Figure 5-7 ND-6054 profile
90
Page 93

5.4.4 Pin Definitions of ND-6054
Pin #
Signal Name Description
1 DI10 Digital input channel 10
2 DI11 Digital input channel 11
3 DI12 Digital input channel 12
4 DI13 Digital input channel 13
5 Ext24V External common +24V
6 Default*/DI14 Initial state setting or digital input channel 14
7 (Y) DATA+ RS-485 series signal, positive
8 (G) DATA- RS-485 series signal, negative
9 (R) +VS Power supply, +10V~+30V
10 (B) GND Ground
11 DI9 Digital input channel 9
12 DI8 Digital input channel 8
13 DI7 Digital input channel 7
14 DI6 Digital input channel 6
15 DI5 Digital input channel 5
16 DI4 Digital input channel 4
17 DI3 Digital input channel 3
18 DI2 Digital input channel 2
19 DI1 Digital input channel 1
20 DI0 Digital input channel 0
91
Page 94

5.4.5 ND-6054 Functional Block Diagram
Power Input
+10V ~ +30V
Power
Regulator & Filter
+5V
Watchdog/Power Failure
Supervisor
Data +
RS-485
Rec/Drv
Micro
Processor
Data -
EEPROM
Config Data
Safe Value
Figure 5-8 Block Diagram of ND-6054
+5V
+24V
DI0
+24V
DI1
+24V
DI12
+24V
DI13
+24V
DI14
92
Page 95

5.5 Overview of NuDAM-6056
What is NuDAM-6056 ?
NuDAM-6056 provides 15 isolated digital output channels. All of the output
channels are common ground type and one of them is use the same pin with
default (use jumper to choose). The isolation voltage is up to 5000 Vrms. It
is suitable to use NuDAM-6056 in industrial environment with high voltage
electric shock.
5.5.1 Features of NuDAM-6056
z 15 bits digital open collector output with isolation protection and
common ground
z 5000 Vrms isolation voltage
z Programmable host watchdog timer for host failure protection
z Internal watchdog timer for device failure protection
z Easy programming by software
z Easy installation and wiring
5.5.2 Specifications of NuDAM-6056
Interface
♦ Interface : RS-485, 2 wires
♦ Speed (bps) : 1200, 2400, 4800, 9600, 19.2K, 38.4K, 57.6K,
115.2K (115.2K is only for firmware reversion
above A4.00)
Digital Output
♦ Channel numbers : 15 isolation common ground output
channels(the fifteenth channel is the same with
default pin,but could use jumper to choose).
♦ Output characteristic:open collector transistor
♦ Maximum current sink:50mA(300mA for Hardware Reversion.A2)
♦ Max.power dissiation:200mW(3W for Hardware Reversion.A2)
♦ Isolation Voltage:5000Vrms
Watchdog Function
93
Page 96

Power
♦ Module internal watchdog timer : 150msec
♦ Power failure threshold : 4.65 V
♦ Safe value : 15 output channels
♦ Host programmable watchdog :100 ms ~ 25.5 sec
♦ Power supply : +10V to +30V
♦ Current consumption :1.32W
94
Page 97

N
g
5.5.3 A Look at NuDAM-6056 & Pin Assignment
DO9
20
DO8
DO7
DO6
DO5
DO4
DO3
DO2
D-6056
Output Type
DO
15-CH Isolated
Di
ital Output
Channels
15
1
DO10
DO11
DO12
DO13
Ext.GND
DEFAUL T
(G)DATA-
(Y)DATA+
Figure 5-9 NuDAM-6056 profile
DO1
(R)+Vs
DO0
11
10
(B)GND
95
Page 98

5.5.4 Pin Definitions of NuDAM-6056
Pin # Signal Name Description
1 DO10 Digital output channel 10
2 DO11 Digital output channel 11
3 DO12 Digital output channel 12
4 DO13 Digital output channel 13
5 ExtGND External Ground
6 Default*/DO14 Initial state setting or Digital output channel 14
7 (Y) DATA+ RS-485 series signal, positive
8 (G) DATA- RS-485 series signal, negative
9 (R) +VS Power supply, +10V~+30V
10 (B) GND Ground
11 DO0 Digital output channel 0
12 DO1 Digital output channel 1
13 DO2 Digital output channel 2
14 DO3 Digital output channel 3
15 DO4 Digital output channel 4
16 DO5 Digital output channel 5
17 DO6 Digital output channel 6
18 DO7 Digital output channel 7
19 DO8 Digital output channel 8
20 DO9 Digital output channel 9
96
Page 99

G
5.5.5 NuDAM-6056 Functional Block Diagram
Power Input
+10V ~
Watchdog/Power Failure
Supervisor
Data +
RS-485
Rec/Drv
Data -
EEPROM
Config Data
Safe Value
Figure 5-10 Block Diagram of NuDAM-6056
Power
Regulator & Filter
Micro
Processor
+5V
ND
+V
DO0
COM
DO1
COM
DO12
COM
DO13
COM
DO14
COM
97
Page 100

5.6 Overview of NuDAM-6058
What is NuDAM-6058 ?
NuDAM-6058 provides 28 digital I/O channels. It emulates industry
standard mode zero configuration of 8255 programmable peripheral
interface (PPI) chip. The PPI offers 3 ports A, B and C, the C port can also be
subdivided into 2 nibble-wide (4-bit) port – C upper and C lower. A 50 pin
SCSI connector equipped with ND-6058 which is corresponding to PPI chip
with 24 DIO points.
5.6.1 Features of NuDAM-6058
z Industry standard 8255 programmable peripheral interface mode 0
emulation
z 24 Programmable I/O channels
z 4 dedicated input channels
z Completely TTL compatible I/O lines
z Status read-back capability
z Direct bit set/reset capability
z Buffered circuits for higher driving capability
z Direct interface with OPTO-22 compatible I/O module
z Programmable host watchdog timer for host failure protection
z Internal watchdog timer for device failure protection
z On board resetable fuse to protect power supply form external devices
z Easy programming by software
z Easy installation and wiring
98
 Loading...
Loading...