Page 1

Acronis Backup Advanced for
vCloud
Update 3
ADMINISTRATOR'S GUIDE
Page 2

Table of contents
1 Administrator's Guide ......................................................................................................4
1.1 About this document ................................................................................................................. 4
1.2 Introduction to Acronis Backup Advanced for vCloud ............................................................... 4
1.2.1 What's new in Update 3 ................................................................................................................................. 4
1.2.2 What's new in Update 1 ................................................................................................................................. 5
1.2.3 Software requirements ................................................................................................................................... 5
1.2.4 Acronis Backup Advanced for vCloud architecture ...................................................................................... 6
1.2.5 Planning hardware resources ......................................................................................................................... 8
1.3 Installing Acronis Backup Advanced for vCloud.......................................................................11
1.3.1 Preparation .................................................................................................................................................... 11
1.3.2 Installing and configuring RabbitMQ Server ............................................................................................... 12
1.3.3 Installing Acronis Backup Management Server .......................................................................................... 13
1.3.4 Using the management console .................................................................................................................. 17
1.3.5 Integrating the management server with vCenter Server ......................................................................... 17
1.3.6 Deploying Agent for VMware ....................................................................................................................... 18
1.3.7 Installing Acronis Backup Agent for vCloud ................................................................................................. 19
1.3.8 Configuring Acronis Backup Agent for vCloud ............................................................................................ 20
1.3.9 Checking network connections .................................................................................................................... 23
1.3.10 Updating to a new version ........................................................................................................................... 24
1.3.11 Uninstallation ................................................................................................................................................ 25
1.4 Logging in to the backup service .............................................................................................26
1.5 Administering organizations ....................................................................................................26
1.5.1 Monitoring organizations ............................................................................................................................. 26
1.5.2 Enabling backup for an organization ........................................................................................................... 27
1.5.3 Operating within an organization ................................................................................................................ 30
1.5.4 Enabling non-administrators to use the service ......................................................................................... 30
1.5.5 Disabling backup for an organization .......................................................................................................... 30
1.6 Configuring the backup service ...............................................................................................31
1.6.1 Managing system backup plans ................................................................................................................... 33
1.7 Generating usage reports ........................................................................................................34
1.8 Viewing audit logs ....................................................................................................................35
1.9 Collecting logs ..........................................................................................................................36
1.10 Advanced cases ........................................................................................................................36
1.10.1 Disaster recovery of physical machines to vCloud ..................................................................................... 36
1.10.2 Setting up deduplication ............................................................................................................................... 37
1.10.3 Changing the backup storage ....................................................................................................................... 37
1.10.4 Integration with third-party systems ........................................................................................................... 39
1.11 Security and customization......................................................................................................39
1.11.1 Changing the SSL certificate ......................................................................................................................... 39
1.11.2 Changing the logo and customizing the interface ...................................................................................... 40
2 User's Guide .................................................................................................................. 42
2.1 About the backup service ........................................................................................................42
2.2 Supported web browsers .........................................................................................................42
2.3 Installing VMware Tools ..........................................................................................................42
2.4 Basic operations .......................................................................................................................43
2.4.1 Logging in to the service ............................................................................................................................... 43
2 Copyright © Acronis International GmbH, 2002-2014
Page 3

2.4.2 Backing up virtual machines ......................................................................................................................... 43
2.4.3 Applying a backup plan ................................................................................................................................. 44
2.4.4 Overwriting a virtual machine with its backed-up version ........................................................................ 45
2.4.5 Recovering a virtual machine ....................................................................................................................... 46
2.4.6 Recovering files from a virtual machine backup ......................................................................................... 48
2.4.7 Monitoring protection statuses ................................................................................................................... 50
2.5 Operations with backups .........................................................................................................50
2.6 Operations with backup plans .................................................................................................51
2.6.1 Creating a backup plan ................................................................................................................................. 51
2.6.2 Editing a backup plan .................................................................................................................................... 55
2.6.3 Revoking a backup plan ................................................................................................................................ 55
2.6.4 Deleting a backup plan.................................................................................................................................. 55
2.7 Generating usage reports ........................................................................................................56
2.8 Enabling non-administrators to use the service ......................................................................57
2.8.1 Assigning a vCloud Director role to a user ................................................................................................... 57
2.9 Viewing audit logs ....................................................................................................................58
3 Terminology reference ................................................................................................... 59
3 Copyright © Acronis International GmbH, 2002-2014
Page 4

1 Administrator's Guide
1.1 About this document
This document is intended for system administrators of VMware vCloud Director who want to
provide a backup service to vCloud organizations by using Acronis Backup Advanced for vCloud.
The document explains how to:
Install Acronis Backup Advanced for vCloud
Configure it to work with vCloud Director
Enable the backup service for organizations
Administer the backup service (monitor the service status, configure backup and recovery
options, generate usage reports, and more)
For information about how to back up and recover virtual machines and administer an organization,
please refer to the Acronis Backup Advanced for vCloud User's Guide (p. 42).
Acronis Backup Advanced for vCloud belongs to the Acronis Backup Advanced suite of products.
Additional information about Acronis Backup can be found in the Acronis Backup Web Help:
http://www.acronis.com/en-us/support/documentation/AcronisBackup_11.5/
1.2 Introduction to Acronis Backup Advanced for vCloud
Acronis Backup Advanced for vCloud is a solution for backup and recovery of virtual machines
managed by VMware vCloud Director.
Acronis Backup Advanced for vCloud provides the backup service at a system administrator level and
organization user level. The backup service is available through a web interface. Users log in to the
service by using their vCloud Director credentials. The information that users see and operations they
can perform depend on the user rights in vCloud Director.
In order to deploy the backup service to your vCloud Director infrastructure, you need to install
Acronis Backup Advanced for vCloud components and integrate them with the vCloud Director
components.
Please review the topics in this section before starting with the installation.
1.2.1 What's new in Update 3
The updated version of the product includes the following new features:
Backup for non-administrative users (p. 30)
Administrators can enable non-administrative users to use the backup service.
Audit logs (p. 35)
System and organization administrators have a view into the log scoped to their area of control.
Hourly backup schedule (p. 52)
When creating a backup plan, you can choose to run backups on an hourly basis.
Quota for backed-up data (p. 31)
4 Copyright © Acronis International GmbH, 2002-2014
Page 5

System administrators can choose whether to set quotas for storage usage or for the amount of
backed-up data.
New "Over quota" column in the reports (p. 34)
System and organization administrators can see by how much an organization has exceeded its
quota.
For information about how to update the product, refer to "Updating to a new version" (p. 24).
1.2.2 What's new in Update 1
The product is renamed from Acronis Backup & Recovery for vCloud to Acronis Backup Advanced for
vCloud. Acronis Backup & Recovery 11.5 is renamed to Acronis Backup.
The updated version of the product includes the following new features:
File recovery
You can enable users to recover individual files and folders (p. 48) from backups of virtual
machines.
Applying a backup plan to a vApp
You can apply a backup plan (p. 44) to an entire vApp. The backup plan will be applied to all
virtual machines that are currently in the vApp and to any new machines that appear in it.
Setting up a default backup plan for an organization
When enabling backup for an organization (p. 27), you can select a system backup plan that will
be automatically applied to all current and future virtual machines in the organization.
Adding network adapters during recovery
Before recovering a virtual machine (p. 46), you can add or remove network adapters for the
machine and specify the settings for those adapters.
Recreating the original vApp during recovery
When recovering a virtual machine, (p. 46) you can automatically recreate the machine's original
vApp if that vApp is no longer present in the organization.
Improved security
Agent for vCloud stores the metadata of the backed-up virtual machines in a more secure,
password-protected database. A strong password is generated automatically during the upgrade.
You can change the password in the settings of Agent for vCloud (p. 20).
For information about how to update the product, refer to "Updating to a new version" (p. 24).
1.2.3 Software requirements
Supported VMware vCloud Director versions
VMware vCloud Director 1.5
VMware vCloud Director 5.0
VMware vCloud Director 5.1
VMware vCloud Director 5.5
Supported guest operating systems
Acronis Backup Advanced for vCloud supports a wide range of guest operating systems, including
Windows 8, Windows Server 2012, and all popular Linux distributions.
5 Copyright © Acronis International GmbH, 2002-2014
Page 6

Supported web browsers
Google Chrome 12 or later
Mozilla Firefox 12 or later
Windows Internet Explorer 9 or later
Safari 5 or later running in the Mac OS X and iOS operating systems
In other web browsers (including Safari browsers running in other operating systems), the user
interface might be displayed incorrectly, or all functions might not be available.
Make sure that JavaScript is enabled in the browser.
The screen resolution for displaying the graphical user interface must be 1024x768 or higher.
1.2.4 Acronis Backup Advanced for vCloud architecture
Acronis Backup Advanced for vCloud consists of multiple components that need to be installed on
separate machines.
Components of Acronis Backup Advanced for vCloud
A typical installation includes at least two virtual machines located in the vCloud management cluster
and a number of virtual appliances running in the vCloud resource group.
The following components run in the vCloud resource group:
Agents for VMware, formerly known as Agents for ESX(i), run as virtual appliances.
Agent for VMware performs backup and recovery of ESX(i) virtual machines without installing
agents into the guest systems.
The following components run in the management cluster:
Management Server needs to be installed on a virtual machine running Windows.
The management server integrates with vCenter Server (the one that is allocated for the
resource group), deploys Agents for VMware, and manages backup and recovery.
The management server stores its configuration, logs and statistics in Microsoft SQL databases.
The databases can be attached to the SQL Server Express instance that is installed by default with
the management server, or to any other SQL Server instance accessible by the management
server.
Agent for vCloud runs on a Linux virtual machine, which also serves as the web server. The agent
is delivered as an Open Virtualization Format (OVF) template.
Agent for vCloud provides a graphical user interface to the users. The agent queries vCloud
Director for the list of users who can log in to the service and the list of virtual machines. Based
on the users' choices, the agent instructs the management server when and how to back up the
selected virtual machines. The agent retrieves the protection statuses of virtual machines directly
from the management server database. The agent also generates reports about the backup
service usage.
Software that is necessary for using Acronis Backup Advanced for vCloud
vCloud users interact with Acronis Backup Advanced for vCloud by using a web browser. To log in to
the backup service, they use the same credentials as they use to log in to vCloud Director. The web
browser connects to the agent's web server and displays the information that the agent provides.
The amount of information depends on the user rights in vCloud Director.
6 Copyright © Acronis International GmbH, 2002-2014
Page 7

Acronis Backup Management Console enables you to connect directly to the management server.
This connection is required to integrate the management server with vCenter Server and to deploy
Agents for VMware. Once these operations are completed, the console is not necessary for
functioning of Acronis Backup Advanced for vCloud. However, you may need it for deploying
additional agents, for troubleshooting, and for other administrative tasks. The console can be
installed along with the management server or on any other machine that has network access to the
management server.
Agent for vCloud obtains events from vCloud Director via the RabbitMQ Server AMQP broker. If you
do not have RabbitMQ Server, add it to your vCloud infrastructure.
Installation example
The following diagram illustrates a typical installation and interaction of the components. In our
example, we assume that vCloud Director uses Microsoft SQL databases. Therefore, we can place the
management server databases on the same virtual machine with vCloud Director databases.
However, the management server databases must run on a separate SQL Server instance.
Acronis Backup Management Console is installed on the same virtual machine with the management
server.
7 Copyright © Acronis International GmbH, 2002-2014
Page 8

Virtual machines that run Acronis Backup Advanced for vCloud components are colored light blue.
Memory
Hard disk size
CPU number
Virtual machines that run VMware vCloud components are colored light green.
1.2.5 Planning hardware resources
Consider how much vSphere capacity you need for running Acronis Backup Advanced for vCloud and
where you will store the backups.
1.2.5.1 vSphere capacity requirements
Agent for VMware (Virtual Appliance)
Agents for VMware run as virtual appliances in the vCloud resource group. If a cluster contains a
large number of virtual machines to be backed up, you may want to deploy more than one agent to
this cluster.
The following table shows vSphere capacity requirements for Agent for VMware (Virtual Appliance).
8 Copyright © Acronis International GmbH, 2002-2014
Page 9

1 GB
6 GB (thick
provisioning)
2 (the default Virtual Appliance setting)
4-8 (recommended if backing up 5-10 VMs simultaneously)
Agent for vCloud
Memory
Hard disk size
CPU number
2 GB
8 GB (thin
provisioning)
1
Software installed on the machine
Memory
Hard disk size
CPU number
Management Server + Management Console
2 GB
min 20 GB (thick
provisioning)
1
Management Server + Management Console + Microsoft SQL
Server Express (installed by default with the management
server)
3 GB
min 30 GB (thick
provisioning)
2
Agent for vCloud needs to be imported from the OVF template to the management cluster.
The following table shows vSphere capacity requirements for Agent for vCloud.
Management Server
Acronis Backup Management Server needs to be installed in the management cluster on a virtual
machine running Windows.
The following table shows vSphere capacity requirements for a machine running Windows Server
2003/2008 R2 and the specified components.
1.2.5.2 Planning backup storages
Acronis Backup Advanced for vCloud stores backups in shared folders on the network.
Supported network protocols
The following network protocols are supported:
NFS
For information about how to prepare an NFS storage, see "Configuring an NFS storage" (p. 10).
SMB
BSP (protocol for accessing Acronis Backup Storage Node)
Acronis Backup Storage Node supports deduplication of the backed-up data. For information
about configuring a storage with deduplication, see "Setting up deduplication" (p. 37).
FTP
SFTP
Backup storages
A backup storage is a folder allocated for storing organization's backups. A path to a backup storage
should be specified in one of the following formats:
NFS
nfs://ServerX/ExportPath:/PathInExportFolder (for example:
nfs://Server/Backups/Organizations:/OrgName)
Note the colon after the export folder path. To specify the export folder without a subfolder, use
the following notation: nfs://ServerX/ExportPath:/
9 Copyright © Acronis International GmbH, 2002-2014
Page 10

BSP
bsp://ServerX/VaultName (for example: bsp://StorageNode/Backups)
SMB
smb://ServerX/.../FolderName (for example, smb://Server/Backups/Organizations/OrgName)
\\ServerX\ShareA\...\FolderName (for example, \\Server\Backups\Organizations\OrgName)
FTP
ftp://ServerX/.../FolderName (for example, ftp://Server/Backups/Organizations/OrgName)
SFTP
sftp://ServerX/.../FolderName (for example, sftp://Server/Backups/Organizations/OrgName)
For all storage types except Acronis Backup Storage Node, we strongly recommend that you create a
separate folder for each organization. If you allow multiple organizations to share a common backup
storage, every organization administrator will be able to see, delete, and even perform recovery from
other organization's backups.
On Acronis Backup Storage Node, create a single storage for all organizations, as described in
"Setting up deduplication" (p. 37).
Storage capacity requirements
The storage space required for an organization's backups depends on the amount of the backed-up
data, the backup schedule, retention rules, and other factors. As a rough estimate, you can expect
that the backups will occupy as much space as is allocated for the organization in vCloud Director.
Organizing a backup storage on a LUN device
You can use the NFS protocol to access logical unit number (LUN) devices in a Fibre-Channel or iSCSI
storage area network (SAN).
To organize an NFS folder on a LUN device
1. Install an NFS server on a machine running Linux.
2. Assign the LUN device to the machine so that the device appears as a local disk.
3. In the NFS server configuration, specify the LUN device as an NFS export folder.
Now you can create subfolders and specify their paths as described above for the NFS protocol.
Changing a backup storage
The organization's backup storage can be changed by a vCloud system administrator, if necessary.
For more information about how to do this, refer to "Changing the backup storage" (p. 37).
Configuring an NFS storage
If you chose to use an NFS storage, configure it as follows.
On the machine where Acronis Backup Management Server is installed
Install Microsoft Windows Services for NFS. For example, in Windows 7 or Windows 8, open Control
Panel, go to Programs and Features, click Turn Windows features on or off, and then select the
Services for NFS check box and its nested check boxes.
On the machine where the NFS server is installed
Make sure that the export folder is properly configured:
10 Copyright © Acronis International GmbH, 2002-2014
Page 11

a) The folder allows read/write access.
b) You have a user account that will act as the anonymous account, and you know the user ID and
group ID of this account.
To find out the user ID and group ID, run the id <User name> command.
c) All user accounts are mapped to the anonymous account.
To configure the folder this way, enable read/write access for it by using the chmod command, and
then specify the parameters in the /etc/exports configuration file for the folder, as follows:
/opt/backups *(rw,sync,all_squash,anonuid=65534,anongid=65534)
In this example, the folder name is /opt/backups, and the user ID and group ID of the anonymous
account are 65534 (this is the nfsnobody user account on the NFS server).
1.3 Installing Acronis Backup Advanced for vCloud
1.3.1 Preparation
Before starting the installation, please familiarize yourself with the Acronis Backup Advanced for
vCloud architecture (p. 6) and make sure that:
vCloud Director is installed and configured.
Sufficient vSphere resources are available to deploy Acronis Backup Advanced for vCloud.
Refer to the exact values in "vSphere capacity requirements" (p. 8).
You have a storage that supports any of the following network protocols: NFS, SMB, FTP, SFTP,
or BSP (protocol for accessing Acronis Backup Storage Node).
Refer to the exact requirements in "Planning backup storages" (p. 9).
You have license keys in a TXT file.
For multiple license keys, the text format is one line per key.
You have the Acronis Backup Advanced for vCloud installation package.
The package consists of:
Acronis Backup Advanced setup program.
Agent for vCloud OVF template.
The script enable_remote_sql_access.js.
You have a virtual machine to install the management server on.
The machine must run a Windows operating system (except for the Start, Home, and RT
editions).
The machine must have network access to the vCenter Server for the resource group and to
the resource group ESX(i) clusters.
The Windows time zone on the machine must be the same as in vCloud Director. (To find out
the vCloud Director time zone, run the date command on the vCloud Director machine.)
Host names in your network are correctly resolved by DNS to IP addresses.
Otherwise, the hosts that you specify during installation and configuration must use constant IP
addresses. Depending on which of the two requirements is met, you specify the hosts by host
names or by IP addresses.
11 Copyright © Acronis International GmbH, 2002-2014
Page 12

1.3.2 Installing and configuring RabbitMQ Server
Agent for vCloud obtains events from vCloud Director via the RabbitMQ Server AMQP broker.
If your vCloud Director already uses RabbitMQ Server, make sure that the exchange type is set to
topic, and continue to "Installing Acronis Backup Management Server" (p. 13).
If RabbitMQ Server is already installed, but not used by vCloud Director, skip to step 5 of the
following procedure.
To install and configure RabbitMQ Server
1. Download RabbitMQ Server from http://www.rabbitmq.com/download.html.
2. If you want to install RabbitMQ Server on a machine running Windows, download and run Erlang
Windows Binary File, which is available at http://www.erlang.org/download.html.
3. Follow the RabbitMQ installation instructions to install RabbitMQ on any convenient host. The
host must have network access to vCloud Director.
4. The RabbitMQ management plug-in is required so that you can configure RabbitMQ Server. Do
one of the following, depending on the operating system of the RabbitMQ Server host:
In Linux, run the following commands:
rabbitmq-plugins enable rabbitmq_management
service rabbitmq-server stop
service rabbitmq-server start
In Windows:
Go to Start > All programs > RabbitMQ Server > RabbitMQ Command Prompt.
Ensure that the command prompt shows the folder containing the RabbitMQ Server
executable files, such as C:\Program Files\RabbitMQ Server\rabbitmq_server-3.1.5\sbin.
If necessary, change the folder by using the cd command.
Run the following command: rabbitmq-plugins enable rabbitmq_management
Run Start > All programs > RabbitMQ Server > RabbitMQ Service - stop.
Run Start > All programs > RabbitMQ Server > RabbitMQ Service - start.
5. Run the following commands on the RabbitMQ Server host to create a new user account:
rabbitmqctl add_user <username> <password>
rabbitmqctl set_user_tags <username> management
rabbitmqctl set_permissions -p / <username> ".*" ".*" ".*"
Here, <username> and <password> are the name and password of the user account to create.
Note You can use an existing RabbitMQ Server user account with permissions equal to or higher than those
given by the commands above.
Acronis Backup Advanced for vCloud Agent for vCloud will use this account to receive event
notifications from vCloud Director. Remember the account credentials, as you will be asked for
them when configuring Agent for vCloud.
6. Open a web browser and go to the RabbitMQ Server Web UI located at: http://<server
name>:15672/. Here, <server name> is the address of the RabbitMQ Server host.
7. Provide the credentials of the RabbitMQ Server user created in step 5.
8. Click Exchanges.
9. Under Add a new exchange:
a. In Name, specify a name for a new exchange that will be used by Agent for vCloud. For
example, specify vcdExchange.
12 Copyright © Acronis International GmbH, 2002-2014
Page 13

b. In Type, select topic.
c. Leave the default values for all other settings.
d. Click Add exchange.
10. Log in as an administrator to vCloud Director.
11. Click Administration.
12. Under System settings, click Extensibility.
13. Under Notifications, select the Enable notifications check box.
14. Under AMQP Broker Settings:
a. In AMQP Host, specify the name or IP address of the RabbitMQ Server host.
b. In AMQP Port, type 5672.
c. In Exchange, specify the name of the new exchange that you created in step 9.
d. In vHost, type /.
e. In Prefix, type vcd.
f. In User Name and Password, type the credentials of the user account created in step 5.
15. Click Apply.
1.3.3 Installing Acronis Backup Management Server
Acronis Backup Management Server stores its configuration, logs, and statistics in Microsoft SQL
databases. There are two options for storing the databases:
Install and use SQL Server Express supplied with the management server. This option is available
through typical installation.
Use any existing SQL Server instance accessible by the management server. This option is
available through custom installation.
The custom installation method also enables you to specify other installation parameters.
Depending on where you want the management server to store its databases, follow one of the
procedures below.
1.3.3.1 Typical installation
1. On the machine that will act as the management server, log on as an administrator.
2. Start the Acronis Backup Advanced setup program.
3. Click Install Acronis Backup.
4. Accept the terms of the license agreement.
5. Select the Centrally monitor and configure backing up of physical and virtual machines check
box.
6. Provide the license for Acronis Backup Advanced for vCloud. Type all your license keys or import
them from a text file.
7. Choose whether the machine will participate in the Acronis Customer Experience Program (CEP).
8. Click Install to proceed with installation.
9. On successful installation, click Finish to close the wizard window.
10. Copy the script enable_remote_sql_access.js that is distributed with the product, to the
management server machine.
13 Copyright © Acronis International GmbH, 2002-2014
Page 14

Details. The script configures the SQL Server instance to be accessible to Agent for vCloud. It
creates a new SQL Server account that Agent for vCloud will use, configures the instance to listen
to a static port, and configures Windows Firewall to allow connections through that port.
11. Run the script in the following format:
cscript enable_remote_sql_access.js <new-user-name> <new-password> [-p <port>]
Where:
<new-user-name> and <new-password> are the user name and password for the new
account.
-p <port> is an optional parameter that enables you to specify the port to use.
For example:
C:\>cscript enable_remote_sql_access.js User 123 -p 3322
If you do not specify the port, it will be chosen automatically. Examine the port number that was
chosen by the script:
Port 1433 is picked
Important. Remember the credentials and the port number. You will be asked for them when configuring
Agent for vCloud.
1.3.3.2 Custom installation
Preparing SQL Server
Make sure that the SQL Server instance that will be used by the management server meets the
following requirements:
The instance uses the mixed authentication mode. This mode guarantees that Agent for vCloud
can also access the instance.
The TCP/IP protocol is enabled for the instance, the instance uses a static TCP port, you know the
port number, and your firewall allows connections through this port.
To change the authentication mode
1. Run Microsoft SQL Server Management Studio.
You can download Microsoft SQL Server Management Studio from
http://www.microsoft.com/en-us/download/details.aspx?id=7593
2. Right-click the instance, and then select Properties.
3. In Security, under Server authentication, select SQL Server and Windows Authentication mode.
4. Restart the service for the instance.
To set the required TCP/IP properties
1. In Microsoft SQL Server Configuration Manager, expand the SQL Server XXXX Network
Configuration node. (Here, XXXX is the version of SQL Server, such as 2008.)
2. Select the instance.
3. In the details pane, double-click TCP/IP.
4. On the Protocol tab, in Enabled, make sure that Yes is selected.
5. On the IP Addresses tab, under IPAll, do the following:
View or change the value in TCP Port.
14 Copyright © Acronis International GmbH, 2002-2014
Page 15

Make sure that the TCP Dynamic Ports field is blank.
6. If you made changes to the fields in the previous steps, restart the service for the instance.
Preparing SQL Server account for the management server
Decide whether the management server will use Windows Authentication or SQL Server
Authentication to connect to the SQL Server. Do one of the following, depending on your choice.
Windows Authentication
If Windows Authentication will be used, create local administrator accounts with the same user
name and password on the machine running SQL Server and the machine where the management
server will be installed.
After the installation, you can remove the account from the Administrators group on the SQL Server
machine. On the management server machine, the account must remain a local administrator.
SQL Server Authentication
If SQL Server Authentication will be used, create a SQL Server login account that is a member of the
sysadmin server role. When creating the account, clear the User must change password at next
login and Enforce password expiration check boxes.
During the installation, the account will become a member of the db_owner database role for the
management server databases (their names start with acronis). After the installation, you can
remove the account from the sysadmin server role.
15 Copyright © Acronis International GmbH, 2002-2014
Page 16

Installing the management server
1. On the machine that will act as the management server, log on as an administrator.
2. Start the Acronis Backup Advanced setup program.
3. Click Install Acronis Backup.
4. Accept the terms of the license agreement.
5. On the How do you want to use this machine page:
Select the Centrally monitor and configure backing up of physical and virtual machines
check box.
Select the I want to manually select the Acronis components and customize the installation
process check box.
6. [Optional] On the Select the components that you want to install page, clear the check box for
Components for Remote Installation. This will save about 900 MB of disk space.
7. Provide the license for Acronis Backup Advanced for vCloud. Type all your license keys or import
them from a text file.
8. Keep the default installation path.
9. Acronis Backup Management Server runs as a service. Specify the user account for running the
service in either of these ways:
[If you opted for Windows Authentication] Click Use an existing account, click Select, and
then specify the account of a local Windows administrator that you created in the "Preparing
user accounts" (p. 15) step. If prompted, confirm adding the additional user rights to the
account.
[If you opted for SQL Server Authentication] Keep the default setting to create a dedicated
user account for running the service.
10. Specify the Microsoft SQL Server instance for both Operational SQL Server and Reporting SQL
Server.
For each of the servers:
a. Click Change > Use existing SQL server. Specify the SQL Server instance in the <Host
name>\<Instance name> or <Host name>,<Instance port> format. For example:
dbserver\MyDatabases or dbserver,1433
b. Choose how the management server will connect to the SQL server:
[If you opted for Windows Authentication] Choose the Acronis Management Server
Service account option. The management server will connect using the account of the
management server service.
[If you opted for SQL Server Authentication] Choose the SQL Server Authentication
option. Specify the login name and password of the SQL server login account that you
chose in the "Preparing user accounts" (p. 15) step.
11. Do not enable the Management Server Web page.
12. Choose whether the machine will participate in the Acronis Customer Experience Program (CEP).
13. Click Install to proceed with installation.
14. On successful installation, click Finish to close the wizard window.
Preparing a SQL Server account for Agent for vCloud
Agent for vCloud can log in to the SQL Server instance by using either Windows Authentication or
SQL Server Authentication. To prepare an account for Agent for vCloud, follow these guidelines:
16 Copyright © Acronis International GmbH, 2002-2014
Page 17

If you chose SQL Server Authentication when installing the management server, use the SQL
Server login account that you specified for the management server (see step 10b in "Installing
the management server" (p. 16)).
If you chose Windows Authentication for the management server, use the user account that you
specified for the management server service (see step 9 in "Installing the management server" (p.
16)).
Alternatively, you can create a dedicated SQL Server account with minimal rights and a non-expiring
password.
To create a dedicated account for Agent for vCloud
1. Run Microsoft SQL Server Management Studio.
2. Expand the instance, expand Security, right-click Logins, and then click New Login.
3. In Login name, type the name of the account. For example: vCloudBackupUser
4. Select SQL Server authentication, and then type and confirm the password for the account.
5. Clear the User must change password at next login check box. We recommend that you also
clear the Enforce password expiration check box. Otherwise, you will have to change the Agent
for vCloud configuration every time the password expires.
6. On the User Mapping page, select the check boxes for all databases whose names start with
acronis (such as acronis_cms). For each of these databases, in Database role membership…,
select the db_datareader and public check boxes.
1.3.4 Using the management console
Acronis Backup Management Console enables you to connect directly to the management server.
The console can be installed along with the management server (by default) or on any other machine
that has network access to the management server.
To be able to connect the console to the management server, a user must be a member of the
Acronis Centralized Admins group on the management server machine.
If the console is installed on a different machine, the user must also be a member of the Acronis
Remote Users group on the management server machine.
Both groups are automatically created during the management server installation. Members of the
Administrators group are silently included in both groups.
To start the management console
Double-click the Acronis Backup icon on the desktop, or select from the Start menu: Acronis >
Acronis Backup Management Console > Acronis Backup.
To connect the console to the management server
1. Click Connect to a management server.
2. Specify the host name or IP address of the management server machine and the credentials of a
user account that has the rights described earlier in this topic.
1.3.5 Integrating the management server with vCenter Server
Acronis Backup Management Server has to be integrated with the vCenter Server for the resource
group.
To do this, use Acronis Backup Management Console. The console is automatically installed with the
management server.
17 Copyright © Acronis International GmbH, 2002-2014
Page 18

To integrate the management server with the vCenter Server
1. Connect the console to the management server as described in "Using the management console"
(p. 17).
2. In the Navigation tree, click Virtual machines and then click Configure VMware vCenter
integration.
3. Select the Enable integration with the following vCenter Server check box.
4. Specify the IP address or name of the vCenter Server for the resource group. Provide access
credentials for the server.
Details. This account will be used for deploying agents from the management server. This means
the account must have the necessary privileges for creating virtual machines on the vCenter
Server. We also recommend that the account have the necessary privileges for backup and
recovery, because the agents will use this account to connect to the vCenter Server by default.
For the exact list of the necessary privileges, refer to the "Privileges for VM backup and recovery"
section of the Acronis Backup built-in help.
5. If a DHCP server is present on the network, you may want to leave the Automatically deploy
Agent for VMware (Virtual Appliance) check box selected. When a backup is about to start, the
management server will automatically deploy Agent for VMware to every cluster that has virtual
machines to be backed up but does not have the agent yet.
If the network uses static IP addresses, or if you prefer to deploy the agents manually, or if the
automatic deployment fails, clear the Automatically deploy... check box. You will need to
perform a few additional steps described in "Deploying Agent for VMware" (p. 18).
6. Click OK to confirm the changes.
The virtual machines managed by the vCenter Server appear in the Virtual machines section of the
Navigation tree. The virtual machines are shown as grayed out because Agent for VMware has not
been deployed yet.
1.3.6 Deploying Agent for VMware
Agent for VMware (Virtual Appliance) will be deployed automatically as necessary, if this option was
enabled when integrating the management server with the vCenter Server (p. 17).
If you disabled the automatic deployment, deploy the agent to every ESX(i) cluster whose virtual
machines will be backed up.
If a cluster contains a large number of virtual machines, you may want to deploy additional agents to
this cluster, regardless of the automatic deployment setting.
To deploy Agent for VMware
1. Connect the console to the management server as described in "Using the management console"
(p. 17).
2. In the Navigation tree, expand Virtual machines, and then right-click the IP address or name of
the vCenter Server for the resource group.
3. Click Deploy Agent for VMware.
4. For each of the clusters whose virtual machine will be backed up, do the following:
a. Select a host to which you want to deploy the agent.
b. In Network interface, select the network interface that provides access to the management
server, the vCenter Server for the resource group, the cluster virtual machines, and the
backup storage.
18 Copyright © Acronis International GmbH, 2002-2014
Page 19

c. The Network configuration link enables you to select whether the agent will use a dynamic
(provided by a DHCP server) or a static IP address. If you want to leave the default setting of
using a dynamic address, skip this step.
If you want the agent to use a static IP address:
Click Network configuration.
Select Use the following network settings.
Specify the appropriate network settings for the agent, and then click OK.
Tip: You will be able to change the network settings after the agent is deployed. To do so, select the virtual
appliance in VMware vSphere inventory and go to the virtual appliance console. Under Agent options, click
the Change link next to the name of the network interface, such as eth0.
5. Click Deploy Agent for VMware.
The management server starts deploying Agent for VMware. The progress is shown at the bottom of
the window.
Once the agent is successfully deployed, the agent machine appears in the Machines with agents
view of the management server.
1.3.7 Installing Acronis Backup Agent for vCloud
Agent for vCloud is delivered as an OVF template.
To install the agent, deploy the OVF template to your management cluster. Map the network in the
OVF template to a network that provides access to the management cluster virtual machines, the
RabbitMQ Server host, and the SQL Server instance that stores the management server databases.
For general information about deploying an OVF template, refer to the following VMware knowledge
base article:
19 Copyright © Acronis International GmbH, 2002-2014
Page 20

http://pubs.vmware.com/vsphere-50/topic/com.vmware.vsphere.vm_admin.doc_50/GUID-6C847F7
7-8CB2-4187-BD7F-E7D3D5BD897B.html.
1.3.8 Configuring Acronis Backup Agent for vCloud
Before configuring Acronis Backup Agent for vCloud, make sure that Acronis Backup Management
Server is installed (p. 13) and configured (p. 17).
Logging in
Log in as a root user to the machine with Agent for vCloud. The default credentials are:
User name: root
Password: Default0 (case-sensitive)
Configuring the time zone
Set the time zone to that of the vCloud Director machine. This will enable Agent for vCloud to
convert time between user's and vCloud Director's time zones.
1. Find out the time zone of the vCloud Director machine. If you are not sure, log on to the machine
and run the date command. The output contains the time zone abbreviation. For example:
Mon Aug 26 23:00:00 EST 2013
EST stands for Eastern Standard Time. This time zone includes parts of the United States and
Canada, and some countries in South America. For more abbreviations see
http://www.timeanddate.com/library/abbreviations/timezones/.
2. On the machine with Agent for vCloud, in the /usr/share/zoneinfo directory, find the file that
corresponds to your region and time zone.
For example, for the Eastern Time Zone of the United States, the time zone file is:
/usr/share/zoneinfo/US/Eastern
3. Delete the old time zone settings:
rm -f /etc/localtime
4. Specify the new time zone settings:
ln -s <time_zone_file> /etc/localtime
For example:
ln -s /usr/share/zoneinfo/US/Eastern /etc/localtime
Configuring connection parameters
1. Go to the /opt/acronis/vcd-agent/bin folder and run the configure.sh command.
All available configuration scenarios are shown.
2. Choose the Initial agent configuration scenario.
3. Provide the vCloud Director connection parameters:
20 Copyright © Acronis International GmbH, 2002-2014
Page 21

vCloud Director host name or IP address
SQL Server Express installed by default
Another SQL Server
Host name/IP address:
Host name or IP address of the
management server.
Host name or IP address of the
machine with the SQL Server instance
used by the management server.
Port [1433]:
The port that was defined when running
the configuration script (p. 13) on the
management server.
If you do not remember the port number,
open SQL Server Configuration Manager
on the management server, select SQL
Server XXXX Network Configuration >
Protocols for ACRONIS, double-click
TCP/IP, and examine the TCP Port field.
The port that is used by the SQL
Server instance (p. 14).
User name:
Password:
The credentials you entered when running
the configuration script (p. 13) on the
management server.
The credentials of the SQL Server
login account you prepared for Agent
for vCloud (p. 16).
If you want to use Windows
Authentication for the agent, specify
the user account in the <Host
name>\\<User name> format (note
the double backslash). For example:
dbserver\\administrator
vCloud Director system administrator credentials
4. Provide the credentials of the RabbitMQ Server user that you created when configuring
RabbitMQ Server.
5. Provide the Acronis Backup Management Server connection parameters:
Host name or IP address of the management server machine
The user name and password of a user who is a member of the Acronis Centralized Admins
and Acronis Remote Users group on the management server machine
6. Provide the connection parameters for the SQL Server instance that stores the management
server databases.
7. To enable users to recover files from backups of virtual machines (p. 48), do the following:
At the Do you want to enable users to recover individual files… prompt, press y.
Specify the path to a network folder that will be used as the temporary storage for the
recovered files. The supported protocols are SMB and NFS.
A good idea is to use a shared folder on the management server's machine. Allow at least 20
GB of space for the temporary files. If necessary, add a separate disk to the machine and
create the folder on that disk.
When using the SMB protocol, specify the folder in the //Server/Share/Folder format (note
the forward slashes). Provide the user name and password for accessing the folder. If the
storage is located on a machine that is a member of an Active Directory domain, specify the
user name in the <Domain name>\\<User name> (note the double backslash) or <User
name>@<Domain name> format.
21 Copyright © Acronis International GmbH, 2002-2014
When using the NFS protocol, specify the folder in the
nfs://Server/ExportPath:/PathInExportFolder format (note the colon before the final slash).
Page 22

If necessary, provide the access credentials to the folder. Make sure that the export folder is
properly configured. For details, see "Configuring an NFS storage" (p. 10).
Configuring network settings
The machine with Agent for vCloud has two network adapters: eth0 for the internal network and
eth1 for the external network.
eth0 connects to the internal network where Acronis Backup Advanced for vCloud components
communicate with VMware vCloud components. It also accepts incoming connections from SSH
clients and web browsers in the internal network.
eth1 accepts incoming connections from web browsers in the external network. Make sure that your
firewall, NAT router, and other components of the network security system allow external
connection to this adapter through ports 80 and 443.
By default, both adapters take network settings from a DHCP server. You can assign a static IP
address to an adapter. For example, to ease port forwarding, you may want to assign a static IP
address to the external adapter.
To change Agent for vCloud network settings
1. Run the configure.sh command and choose the Change network settings scenario.
2. Specify network settings for the eth0 adapter.
To take the network settings from a DHCP server, press y.
To specify the network settings with a static IP address, press n, and then:
a. Specify the static IP address for the adapter, such as: 192.168.0.10
b. Specify the subnet mask for the adapter, such as: 255.255.0.0
c. Specify the IP address of the default gateway for the adapter, such as: 192.168.0.1
3. Specify network settings for the eth1 adapter.
To take the network settings from a DHCP server, press y.
To specify the network settings with a static IP address, press n, and then:
a. Specify the static IP address for the adapter, such as 10.0.0.10
b. Specify the subnet mask for the adapter, such as: 255.0.0.0
The command does not prompt for the default gateway, because the adapter is used only for
incoming connections.
4. If you configured both adapters to use static IP addresses, specify the following:
a. In DNS server 1, specify the IP address of the DNS server.
b. [Optional] In DNS server 2, specify the IP address of the secondary DNS server.
The DNS server settings apply to both adapters.
If one of the adapters uses a DHCP server, the DNS server settings for both adapters are taken
from that DHCP server.
If both adapters use DHCP servers, the settings for both adapters are taken from the DHCP server
for eth1 (provided that the list of DNS servers there is nonempty).
Other operations
To view the network settings
Run the configure.sh command and choose the Show network settings scenario.
To view the connection parameters
Run the configure.sh command and choose the Show agent configuration scenario.
22 Copyright © Acronis International GmbH, 2002-2014
Page 23
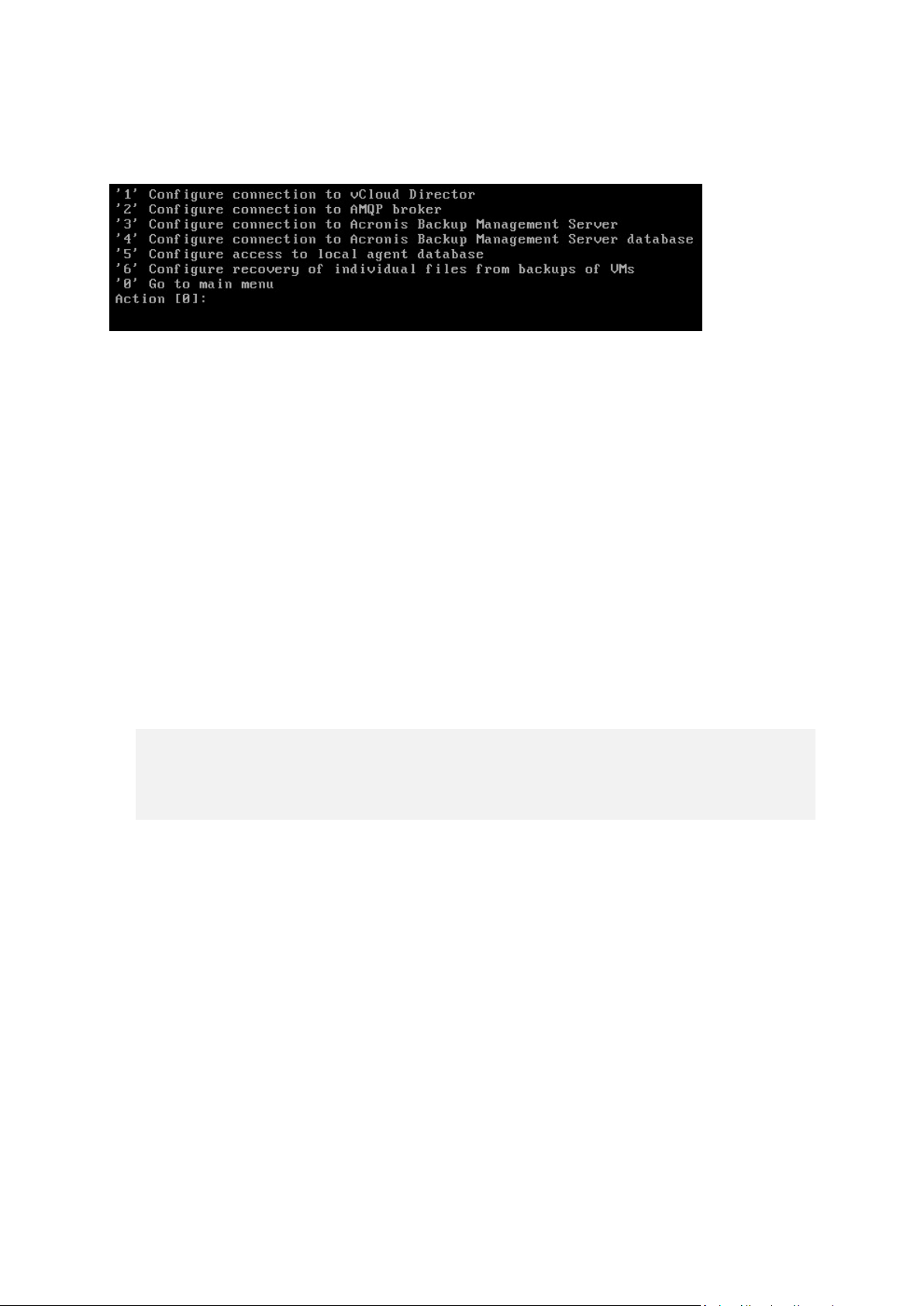
To change the connection parameters
Run the configure.sh command, choose the Change agent configuration scenario, and then
select the connection to change the configuration for.
To enable or disable recovering files from virtual machine backups
1. Run the configure.sh command and choose the Change agent configuration scenario.
2. Choose Configure recovery of individual files from backups of VMs.
3. Do one of the following:
To enable the setting, press y and specify the temporary storage for the recovered files, as
described in step 7 from "Configuring connection parameters" (see earlier in this section).
To disable this setting, press n. The recovered files that are currently stored in the temporary
storage will no longer be available to the users.
Password for accessing the database of Agent for vCloud
Agent for vCloud works with its database by using a database user account with a secure password.
The account name is vcda_db_user. The password is generated automatically.
Usually, changing the password is not needed. You may want to change the password if your security
policy prescribes regular password changes.
To change the password
1. On the machine with Agent for vCloud, run the following commands:
su postgres
psql
ALTER USER vcda_db_user WITH PASSWORD '<New password>';
\q
exit
2. Run the configure.sh command and choose the Change agent configuration scenario.
3. Choose Configure access to local agent database.
4. Specify the new password.
1.3.9 Checking network connections
Acronis Backup Advanced for vCloud components use TCP ports to communicate with VMware
vCloud components and with each other. Make sure that your firewalls and other components of
your network security system allow connections through these ports.
The diagram below illustrates the network connections that are necessary for the backup service to
function.
The arrow direction shows which component initiates a connection. The text shows the destination
port. The source port is taken from a standard range, depending on the operating system:
Agent for vCloud and Agent for VMware use the range 32768–61000.
23 Copyright © Acronis International GmbH, 2002-2014
Page 24

The management server and the external SQL Server use the range 1025–5000 (if installed in
Windows prior to Windows Vista) or 49152–65535 (if installed in Windows Vista and later).
Normally, the standard ranges are already open.
For the machine with Agent for vCloud, eth0 and eth1 show the network adapter through which the
connection is performed.
* The port is configurable. The diagram shows the default value.
1.3.10 Updating to a new version
Updating Acronis Backup Advanced for vCloud (formerly known as Acronis Backup & Recovery for
vCloud) to a new version includes updating the management server, Agents for VMware (formerly
known as Agents for ESX(i)), and Agent for vCloud.
The update preserves all settings, including the backup plans. Backup plans remain applied to the
corresponding virtual machines.
No additional licenses are required for the update.
Prerequisites
Before proceeding with the update, make sure that:
You have the setup program of the new version of Acronis Backup Advanced.
24 Copyright © Acronis International GmbH, 2002-2014
Page 25

You have the update script for Agent for vCloud. The name of the script file is updateX.sh, where
X is the product build number.
The machine with Agent for vCloud is connected to the Internet. The update script needs an
Internet connection to download additional packages from a Linux repository.
No backups will run during the update. To ensure this, you can disable backup (p. 30) for all
organizations for the time of the update.
Step 1: Updating the management server
1. On the machine where the management server is installed, log on as an administrator.
2. Start the setup program of the new version of Acronis Backup Advanced.
3. Click Install Acronis Backup.
4. Accept the terms of the license agreement.
5. Click Update.
6. Proceed with updating Acronis Backup.
Step 2: Updating the Agents for VMware
1. Connect the console to the management server as described in "Using the management console"
(p. 17).
2. In the Navigation tree, expand Virtual machines, and then right-click the IP address or name of
the vCenter Server for the resource group.
3. Click Update Agent for VMware.
4. Select all Agents for VMware in the list, and then click Update Agent for VMware.
Step 3: Updating Agent for vCloud
1. Log in to the machine with Agent for vCloud.
2. Copy the update script to the machine. Make sure to place the script file outside the /opt/acronis
folder. For example, place it in the /root folder.
3. Make the script file executable by running the following command:
chmod 755 updateX.sh
4. Run the update script.
Post-update actions
If you disabled backup for the time of the update, log in to the service and re-enable backup (p. 27).
1.3.11 Uninstallation
To uninstall Acronis Backup Advanced for vCloud
1. Log in to the service (p. 26).
2. Disable backup (p. 30) for every organization.
3. Delete all Agents for VMware.
a. Run Acronis Backup Management Console, and then click Connect to a management server.
b. Specify the host name or IP address of the current machine and credentials of a user account
that is a member of the Acronis Centralized Admins group on the machine.
c. In the Navigation tree, click Virtual machines.
d. On the toolbar, click Remove Agent for VMware.
e. Select all agents.
f. Click Remove Agent for VMware.
25 Copyright © Acronis International GmbH, 2002-2014
Page 26

The management server removes Agents for VMware. The progress is shown at the bottom
of the window.
g. Wait until all agents are removed.
4. Start the vSphere Client and log in to the vCenter Server for the management cluster.
5. Delete the Agent for vCloud virtual machine.
6. Delete the Acronis Backup Management Server virtual machine, or uninstall the management
server as follows:
a. Log in as an administrator on the machine.
b. Click Start -> All Programs -> Acronis -> Uninstall Acronis Backup.
c. [Optional] To delete the management server databases, select the Remove the product's log,
tasks, vaults and configuration settings check box.
d. Click Remove.
7. [Optional] Delete all backups from the backup storages.
1.4 Logging in to the backup service
You can log in to the backup service as an administrator under the following conditions:
Acronis Backup Advanced for vCloud is installed and configured.
You have a vCloud Director system administrator account.
To log in to the backup service
1. Go to the login page of the backup service. The address of the login page looks as follows:
https://<BackupServiceAddress>/.
When connecting from an internal network: <BackupServiceAddress> is the fully
qualified domain name, or the IP address of the Agent for vCloud host in this network.
For example, https://vcloudagent.vcloud.example.com/ or
https://10.200.200.10/
When connecting from an external network: <BackupServiceAddress> is the URL of
the backup service as it appears on the public side of a firewall, load balancer, NAT/reverse
proxy, and other network components that you may have in front of your infrastructure.
For example: https://backup.example.com/
2. Type the user name and password of your vCloud Director system administrator account.
3. Click Log in.
1.5 Administering organizations
1.5.1 Monitoring organizations
To access the following information about organizations, click the Organizations tab.
Backup enabled
Yes/No
Protection status
Not protected
None of the organization's virtual machines are protected. A virtual machine is considered
protected if a backup plan (p. 33) is applied to it.
Never backed up
26 Copyright © Acronis International GmbH, 2002-2014
Page 27

There are protected machines in the organization, but a backup has not run on any of them.
OK
The last backup was successful on all of the protected machines.
Error
The last backup of at least one protected machine in the organization failed.
To view status of a particular machine, switch to the organization administrator view (p. 30). The
statuses of a virtual machine are explained in "Monitoring protection statuses" (p. 50).
Backup storage
The backup storage assigned to the organization.
Quota
The storage quota for the organization.
If the quota is exceeded, the system administrators and the organization users see alerts in the
backup service interface. Restrictions on using the backup service are not applied unless a system
administrator does this manually.
To view the following information about an organization, select the organization in the list:
Number of vApps and Number of VMs
For those organizations where the backup service is enabled, the following information is also
displayed:
Login page
The address that the organization users use to log in to the service.
Backup storage
The path to the organization's backup storage, the storage quota for the organization, and the
space occupied by the organization backups.
System backup plans
The system backup plans (p. 33) available in the organization.
Privileges for organization users
The actions that the organization users are allowed to perform.
1.5.2 Enabling backup for an organization
Prerequisites
Make sure that the public URL for the backup service is specified, as described in "Public URL" in
"Configuring the backup service" (p. 31).
If the public URL is not specified, the users will not be able to log in to the backup service by using the
login page address that you provide.
To enable backup for an organization
1. Log in to the service.
2. Click the Organizations tab.
A list of organizations registered in vCloud Director is shown.
3. Select the organization to enable backup for.
27 Copyright © Acronis International GmbH, 2002-2014
Page 28

4. Click Configure.
5. On the Backup storage tab, do the following:
In Backup storage, specify the path to the shared folder allocated for storing organization's
backups. If authentication is required to access the folder, specify the credentials of a user
account that has read/write permissions for this folder.
We strongly recommend that each organization has a separate backup storage. You can
allow multiple organizations to share a common backup storage, but in this case every
organization administrator will be able to see, delete, and even perform recovery from other
organization's backups.
For information about the supported types of backup storage, see "Planning backup
storages" (p. 9).
[Optional] Specify the quota for the organization.
If the quota is exceeded, the system administrators and the organization users see alerts in
the backup service interface. Restrictions on using the backup service are not applied unless
a system administrator does this manually.
6. [Optional] On the System backup plans tab, specify which of the system backup plans (p. 33) will
be available in the organization. By default, all of the system backup plans will be available.
You can make one of these plans the default backup plan. To do so, specify the backup plan in
Default backup plan. This backup plan will be automatically applied to all future virtual machines
in the organization. To also apply this backup plan to all current virtual machines, select the
Apply to all vApps and VMs in the organization check box.
Users will be able to change the default backup plan on their machines, provided that they have
the privilege to apply backup plans (see step 7).
7. [Optional] On the User privileges tab, specify the actions that the organization users will be
allowed to perform. By default, the following actions are available to the users:
28 Copyright © Acronis International GmbH, 2002-2014
Page 29

Apply and revoke backup plans
Create, edit, and delete backup plans
Perform hourly backup
Perform backup on demand ('Back up now')
Recover virtual machines
Recover files from backups of virtual machines
Regardless of your selection, system administrators are allowed to perform all of these actions
within the organization.
If you clear the Log in to the backup service check box, only system administrators will be able to
use the backup service for this organization. For information about how to do this, refer to
"Operating within an organization" (p. 30).
8. Confirm the changes.
9. If this is the first time that a backup for this organization is being enabled, perform a test backup
to ensure that Agent for VMware is properly deployed to the organization's cluster.
a. Enter the organization (p. 30).
b. Back up a virtual machine (p. 43).
Depending on your decision in step 7, the backup service becomes available for either system
administrators only or for both system administrators and organization users.
If the backup service is available for organization users:
1. Inform organization administrators about the address of the login page for the organization. You
can see this address under Login page in the organization details area.
2. Inform organization users about the Help link and User's Guide.
29 Copyright © Acronis International GmbH, 2002-2014
Page 30

1.5.3 Operating within an organization
vCloud system administrators can perform any operation that organization administrators can
perform within an organization.
To administer an organization
1. Log in to the service.
2. Click the Organizations tab.
A list of organizations registered in vCloud Director is shown.
3. Select the organization to administer. The backup service must be already enabled for the
organization (p. 27).
4. Click Open.
You are now in the organization administrator's interface.
5. Depending on the operation you want to perform, refer to the corresponding section of the
Acronis Backup Advanced for vCloud User's Guide (p. 42).
1.5.4 Enabling non-administrators to use the service
System administrators and organization administrators can enable members of any vCloud Director
role to use the backup service.
You can either use an existing role or create a dedicated role for the backup service access. If you
want to use an existing role, skip the first procedure.
To create a new role in vCloud Director
1. Log in as an administrator to vCloud Director.
2. Click Administration > Roles.
3. Create a new role.
The simplest way to do this is to select the vApp User role and use the Copy to... action in the
context menu. You can choose any name for the new role, for example: Backup Administrator.
4. Notify organization administrators about this new role.
To enable members of a vCloud Director role to use the backup service
1. Enter the organization as described in "Operating within an organization" (p. 30).
2. For further steps, refer to the "Enabling non-administrators to use the service" (p. 57) section of
the Acronis Backup Advanced for vCloud User's Guide.
1.5.5 Disabling backup for an organization
To disable backup for an organization
1. Log in to the service.
2. Click the Organizations tab.
3. Select the organization to disable backup for.
4. Click Configure.
5. Clear the Enable backup for an organization check box.
6. Confirm the changes.
As a result:
The organization users will no longer be able to use the backup service.
30 Copyright © Acronis International GmbH, 2002-2014
Page 31

The organization's backup plans will be revoked from virtual machines, but will be preserved by
Agent for vCloud. If you re-enable backup, it will be enough to reapply the backup plans to the
machines so that the machines become protected again.
The existing backups will be kept. If the backups are no longer needed, you can manually delete
them from backup storages.
1.6 Configuring the backup service
To access these settings, click the Settings tab.
System backup plans
This setting is used for managing system backup plans (p. 33).
E-mail server settings
These settings are necessary for sending e-mail notifications to organization users. Unless the e-mail
server parameters are filled in, no notifications will be sent.
The subject can include ordinary text and variables. In the received e-mail messages, each variable
will be replaced by its value at the time of backup plan execution.
The default notification subject is:
[Backup service]: %Organization name% - %Backup plan name%
Where:
%Organization name% is the name of the organization.
%Backup plan name% is the name of the backup plan.
Other variables are not supported.
Tip E-mail notifications to a system administrator are configured on the management server. Go to Options >
Management server options, and then specify the e-mail server settings in E-mail settings. In Alert
notifications, you can select the specific alerts to send notifications about.
Backup and recovery options
Simultaneous backup
Specify how many virtual machines Agent for VMware may back up simultaneously. The default
value is 5. The maximum value is 10.
The value you specify is effective for a backup plan. If an agent runs more than one backup plan
simultaneously, the number of machines being backed up may exceed the setting, but it still
cannot exceed 10. A backup plan that requires to back up the 11th machine will not start until
one of the backup operations is finished.
Tip. Simultaneous backup of multiple virtual machines increases the amount of CPU resources
used by Agents for VMware. By default, Agent for VMware uses two virtual processors. If you
observe that CPU usage during backup approaches 100%, increase the number of virtual
processors in the virtual appliance settings. This may significantly increase the simultaneous
backup performance.
Network connection speed
Define the amount of network connection bandwidth allocated for transferring the backup data.
31 Copyright © Acronis International GmbH, 2002-2014
Page 32

By default the speed is set to maximum, so that the software uses all the network bandwidth
available when transferring the backup data. Use this option to reserve a part of the network
bandwidth for other network activities.
Error handling
Specify how to handle errors that might occur during backup or recovery.
When a recoverable error occurs, the program re-attempts to perform the unsuccessful
operation. You can set the time interval and the number of attempts. The attempts will stop as
soon as the operation succeeds OR the specified number of attempts are performed, depending
on which comes first.
For example, if Number of attempts is set to 30, Interval between attempts is set to 30 seconds,
and the backup destination on the network becomes unavailable or not reachable, the program
will attempt to reach the destination every 30 seconds, but no more than 30 times.
Usage report for Acronis
These settings are used when you send reports about using the backup service to Acronis.
Company name
Specify the name of your company. Acronis will use it to identify your usage reports.
Contact e-mail
Specify your e-mail address. Acronis will use this address to contact you, if needed.
If you want to automate sending the reports, select the Automatically send usage reports to Acronis
on the first day of each month check box.
For detailed information about usage reports, refer to "Generating usage reports" (p. 34).
Quota
This setting specifies which parameter will be used to determine the storage quota for an
organization. Choose one of the following:
Storage usage (default)
The quota will be based on the total size of all backups in the backup storage.
Backed-up data
The quota will be based on the total amount of data that was backed up. This setting is useful if
the backups are deduplicated.
Public URL
This setting is used to display an easily readable backup service address that you can provide to the
organization users. The address is displayed in the organization details under Login page.
By default, Agent for vCloud uses its IP address to construct the login page addresses. For example, if
the IP address is 10.200.200.10, after backup is enabled for an organization named MyOrganization,
the address under Login page in the organization details will be displayed as:
https://10.200.200.10/org/MyOrganization
In Public URL, specify how the URL of the backup service appears on the public side of a firewall, load
balancer, NAT/reverse proxy, and other network components that you may have in front of your
infrastructure. The URL must include either an external IP address or a valid DNS name that can be
resolved by the users' DNS servers.
For example: https://www.backup.example.com/
32 Copyright © Acronis International GmbH, 2002-2014
Page 33

After this public URL is specified, the backup service address for MyOrganization will look as follows:
Name
Schedule
Retention period
Daily
Every day at 22:00
1 week
Weekly
Every Friday at 22:00
4 weeks
Monthly
Every 4 weeks on Friday at 22:00
48 weeks
https://www.backup.example.com/org/MyOrganization
1.6.1 Managing system backup plans
What is a backup plan?
A backup plan is a set of rules that defines how to protect virtual machines. The rules include the
backup schedule, retention rules, and backup options such as protecting backups with a password.
The backup service users create backup plans and apply them to their virtual machines.
What is a system backup plan?
In order to assist the backup service users, a system administrator can create ready-to-use backup
plans, called system backup plans.
When enabling backup for an organization, the system administrator specifies which of the system
backup plans will be available to the organization users. The users can apply these backup plans to
their virtual machines but cannot delete them or change their schedule and retention rules.
The following table lists the system backup plans that are initially delivered with the software.
These backup plans start at 22:00 according to the time settings of Agent for VMware. The dates and
times shown to a user are adjusted to the time zone of the user's machine. Therefore, users located
in different time zones may see different times although the schedule is the same.
Operations with system backup plans
A system administrator can edit the system backup plans, create new ones, and delete existing
backup plans.
To create or edit a system backup plan
Important: Editing a system backup plan will affect all organizations for which you made this backup plan
available.
1. Log in to the service.
2. Click the Settings tab.
3. Click System backup plans.
4. Depending on what you want to do, click Create or select the backup plan to edit, and then click
Edit.
5. In Name, type the name of the backup plan. The name must differ from names of other backup
plans in the list.
6. Specify the schedule and retention rules (p. 52) for the backup plan.
Details. Because a system backup plan can be distributed across many organizations, you cannot
enable backup options (such as encryption or notifications) when creating or editing the plan.
Instead, you can enable different backup options in each organization where the plan is available.
33 Copyright © Acronis International GmbH, 2002-2014
Page 34

To enable backup options, switch to a specific organization (p. 30), select the plan in the list, and
then click Set options. Organization users can also enable or change these options.
7. Click OK.
To make a new system backup plan available for an organization
1. On the Organizations tab, select the organization, and then click Configure.
2. Click System backup plans.
3. Select the check box for the plan.
4. Click OK.
Clearing the check box for a system backup plan has the same effect as deleting a system backup
plan, but only within the selected organization.
To delete a system backup plan
Caution: As a result, backups will no longer run on the machines to which the backup plan was applied, until
users apply different backup plans to the machines.
1. Log in to the service.
2. Click the Settings tab.
3. Click System backup plans.
4. Select the backup plan to delete.
5. Click Delete.
6. Confirm your decision.
1.7 Generating usage reports
Usage reports provide historical data about using the backup service. The following reports are
available:
Selected organization
This report contains statistics for a given organization. It can be used to charge organizations for
the backup service.
All organizations
This report contains statistics for all organizations that used the backup service in the reporting
period (including organizations for which the backup service is currently disabled).
Report for Acronis
This report contains the same information as the report for all organizations with the addition of
your company name and contact e-mail.
Reporting parameters
The values of all parameters are checked every day at 23:55 according to the time settings of vCloud
Director. The report uses the values as they were at that time.
The report includes the following parameters for the organization:
Number of protected VMs: The total number of protected machines (that is, the machines to
which backup plans are applied), no matter whether backups of those machines exist
Storage usage: The total size of all backups in the backup storage (in gigabytes). This parameter
may be excluded from the report, depending on the backup service settings.
Backed-up data: The total amount of data that was backed up. This amount includes the initial
content of the virtual machine disks and the subsequent incremental changes to that content.
34 Copyright © Acronis International GmbH, 2002-2014
Page 35

Over quota: The amount of data that exceeds the quota set for the organization (in gigabytes)
Disk size of protected VMs: The total size of hard disks of the protected machines (in gigabytes),
regardless of the occupied space on those disks
RAM size of protected VMs: The total amount of memory of the protected machines (in
gigabytes)
CPU number of protected VMs: The total number of CPUs of the protected machines
To generate a usage report
1. Log in to the service.
2. Click the Organizations tab.
3. If you want to generate a report for an organization, select the organization. Otherwise, skip this
step.
4. Click Generate report, and then click Selected organization, All organizations or Report for
Acronis.
5. In Period, select the reporting period:
Current calendar month: The report will include data from the first day of the current month
up to the current day (when generating the report after 23:55) or up to the previous day
(when generating the report before 23:55).
Previous calendar month: The report will include data for the previous month. For example,
in April you will get a report for the time interval from March 1 through March 31.
Custom period: The report will include data for the time interval that you specify.
6. When generating a report for Acronis, skip this step. The report type will be set to Daily
statistics.
Otherwise, in Type, select the report type:
Daily statistics: The report will include the values of the reporting parameters for each day of
the reporting period. The report also includes the summary: the minimum, maximum, and
average values of each of the reporting parameters throughout the period.
Summary report: The Selected organization report will include only the summary (see the
previous option). The All organizations report will include average values throughout the
reporting period for each organization.
7. Click OK. The report will appear in a separate browser window or tab.
8. [Optional] To print the report, click Print. To save the report as a comma-separated values (.csv)
file, click Save as .csv file.
9. If you generated a report for Acronis and want to send it:
a. Click Send to Acronis.
b. If prompted, provide the name of your company and contact e-mail address.
Tip. The software can remember these settings so that you do not have to enter them every
time. Refer to "Usage report for Acronis" in "Configuring the backup service" (p. 31).
c. [Optional] If you want to automate sending the reports, select the Automatically send usage
reports to Acronis on the first day of each month check box.
1.8 Viewing audit logs
The backup service includes an audit log, which records operations performed by users.
System and organization administrators have a view into the log scoped to their area of control.
35 Copyright © Acronis International GmbH, 2002-2014
Page 36

To view the audit log
1. Log in to the service.
2. Click the Logs tab.
A system administrator can use the audit log for troubleshooting. They can also view details of a
failed task or collect the logs (p. 36), along with other Agent for vCloud information, and send those
for investigation to Acronis technical support.
1.9 Collecting logs
The log collection tool saves the log files of Agent for vCloud to a sysinfo.zip file. This file is
required when you contact Acronis technical support.
To collect logs by using the web interface
1. Log in to the service.
2. Click Help -> Collect logs.
3. If prompted by your web browser, specify where to save the file.
If you cannot log in to the service because of a web server problem, you can collect logs by using a
script.
To collect logs by using a script
1. Log in as a root user to the machine with Agent for vCloud. The default credentials are:
User name: root
Password: Default0 (case-sensitive)
2. Run the following command to start the log collection tool:
/opt/acronis/vcd-agent/bin/sysinfo.sh
3. Specify the user name and password of a vCloud Director system administrator.
4. Specify where to save the file.
5. After the file is saved, copy it from the agent machine to an appropriate location by using, for
example, the sftp tool.
1.10 Advanced cases
This section describes how you can use Acronis Backup Advanced for vCloud in more advanced cases.
1.10.1 Disaster recovery of physical machines to vCloud
If an organization backs up its physical machines by using Acronis Backup, you can allow the
organization to store the resulting backups in their Acronis Backup Advanced for vCloud backup
storage.
To do this, expose the backup storage as a network share and let the organization administrator do
any of the following:
1. Back up the physical machines directly to the backup storage.
2. Replicate or move backups of physical machines to the backup storage, as part of Acronis Backup
backup plans.
3. Export the backups from their original location to the backup storage.
36 Copyright © Acronis International GmbH, 2002-2014
Page 37

As a result, the organization administrator will see the backups of physical machines in the Acronis
Backup Advanced for vCloud interface. In case of a disaster, the organization administrator will be
able to recreate a physical server as a virtual machine in their vCloud organization.
1.10.2 Setting up deduplication
This section describes how to set up a storage in which data will be deduplicated across all
organizations, but users will see only backups from their organization.
Important Read the "Deduplication best practices" section of the Acronis Backup Help before setting up
deduplication.
Deduplication is supported by Acronis Backup Storage Node. The storage node requires a machine
with the following configuration:
Multi-core processor with at least 2.5 GHz clock rate
At least 32 GB of RAM
A 64-bit Windows operating system
When using deduplication, consider changing the quota setting (p. 31) from Storage usage to
Backed-up data, because the storage usage statistics for a single organization cannot be separated in
this case.
To set up deduplication
1. On the machine that will act as the storage node, run the setup program of Acronis Backup
Advanced.
2. Install the storage node as described in the "Getting started with a storage node" section of the
Acronis Backup Help.
3. Create a number of user accounts on the storage node, one account per organization. Make sure
that these accounts are not members of the Administrators group.
4. Create a single vault with deduplication, as described in the "Creating a managed centralized
vault" section of the Acronis Backup Help.
To specify the backup storage
When enabling backup for an organization (p. 27):
1. Specify the vault in the bsp://ServerX/VaultName format (for example:
bsp://StorageNode/Backups).
2. Specify the user account for that organization.
1.10.3 Changing the backup storage
vCloud system administrators can change the backup storage assigned to an organization.
If the storage device runs out of free space and cannot be upgraded, you may want to migrate some
or all of the backup storages to a new device. Besides changing the storage paths, you need to move
the previously created backups to the new location. Otherwise, these backups will not be available to
the organization users. While the backups are being moved, all operations that require access to the
backup storage must be disabled. Access to other backup storages located on the same device may
slow down. For these reasons, we recommend notifying the organization users about the upcoming
maintenance.
37 Copyright © Acronis International GmbH, 2002-2014
Page 38

The following steps are required to migrate backups storages to a new location. For easier access to
both the management server and the backup service interface, we recommend that you perform
these steps on the management server machine.
Disabling user access to the service
1. Log in to the service and click the Organizations tab.
2. Select the organization to change the backup storage for, and then click Configure.
3. On the User privileges tab, clear the Log in to the backup service check box. Click OK to confirm
the changes.
This will prevent the organization users from using the backup service while you are changing the
backup storage. (The currently logged-in users will remain logged in until they log out or until
their vCloud session is timed out.)
4. Repeat steps 2-3 for every organization for which the backup storage will be changed.
Disabling the backup plans
1. Connect the console to the management server (p. 17).
2. Click Backup plans and tasks.
3. Disable all backup plans that are applied to the organization's virtual machines by selecting each
of the backup plans and then clicking Disable.
Tip. A backup plan's name starts with the name of the organization. You can filter the backup
plans by typing their names in the field below the Name column's header.
The management server names backup plans by using the following
template: %OrgName%_%BackupPlanOwner%_%BackupPlanName%, where %OrgName% is the name of
an organization, %BackupPlanOwner% is the name of the backup plan owner as it is displayed in the
Acronis Backup Advanced for vCloud interface, and %BackupPlanName% is the name of the backup plan as
it is displayed in the Acronis Backup Advanced for vCloud interface. For example, MyOrg_OrgUser_Daily.
4. Repeat steps 2-3 for every organization for which the backup storage will be changed.
5. If any of the disabled backup plans are running, wait until all of them stop.
Tip. You can inspect backup plan's Execution state to see if it is currently running.
Moving the backups
1. Move an organization's backup storage to the new storage device.
Important. All of the folders and files in the backup storage must be moved. This operation may
be time consuming.
2. Repeat step 1 for every organization for which the backup storage will be changed.
Changing the backup storage
1. Log in to the service (if logged out) and click the Organizations tab.
2. Select the organization to change the backup storage for and then click Configure.
3. In Backup storage, specify the path to the new backup storage. If authentication is required to
access the folder, specify the credentials of a user account that has read/write permissions for
this folder.
4. Repeat steps 2-3 for every organization for which the backup storage will be changed.
Enabling the backup plans
1. Connect the console to the management server (p. 17) (if not connected).
2. Click Backup plans and tasks.
38 Copyright © Acronis International GmbH, 2002-2014
Page 39

3. Enable the previously disabled backup plans by selecting each of the backup plans and then
clicking Enable.
Enabling user access to the service
1. Log in to the service (if logged out) and click the Organizations tab.
2. Select the organization for which the backup storage has been changed and then click Configure.
3. On the User privileges tab, select the Log in to the backup service check box. Click OK to confirm
the changes.
4. Repeat steps 2-3 for every organization for which the backup storage has been changed.
1.10.4 Integration with third-party systems
The backup service can be integrated with third-party systems such as automation tools or
management portals by using Acronis Backup Agent for vCloud API. The API Reference Guide is
available by request.
1.11 Security and customization
This section describes how to change the security certificates that are used by the service, and how
to customize the user interface.
1.11.1 Changing the SSL certificate
Agent for vCloud uses a Secure Socket Layer (SSL) certificate to provide encryption for the web
interface. By default, the agent uses a self-signed certificate that is the same for all copies of Acronis
Backup Advanced for vCloud worldwide.
With the default certificate, users who log in to the service will see a security alert similar to the
following:
We recommend that you change the default certificate to your own certificate before you allow wide
use of the service.
To change the SSL certificate
1. Make sure that you have a .pem file with your certificate. You can buy a certificate from a
certificate authority (CA) or create a certificate by using a tool such as openssl.
2. Copy the .pem file to the machine with Agent for vCloud. You can place the file in the
/opt/keystore folder.
3. On the machine with Agent for vCloud, edit the /etc/lighttpd/conf.d/vcda_https.conf
configuration file and specify the file name of your certificate. For example, the configuration file
may look like:
39 Copyright © Acronis International GmbH, 2002-2014
Page 40

$SERVER["socket"] == ":443" {
Location
Format
Recommended size
Login page
PNG, JPG or GIF
160px x 72px
Main interface
PNG, JPG or GIF
160px x 72px
Browser tab (the
favicon)
ICO
16px x 16px
ssl.pemfile = "/opt/keystore/my_certificate.pem"
ssl.engine = "enable"
}
Depending on the certificate, you may need to specify other parameters in the configuration file.
For details about specifying SSL certificates, refer to the following Lighttpd Wiki article:
http://redmine.lighttpd.net/projects/1/wiki/Docs_SSL.
4. Restart the web server by running the following command:
service lighttpd restart
1.11.2 Changing the logo and customizing the interface
The look of the web interface is based on the Cascading Style Sheets (.css) files. By changing the
custom.css file, you can customize the interface appearance. For example, you can change the logo
or the colors of the background, text, and buttons.
This section describes how you can replace the Acronis logo with your company's logo.
Requirements for the logo files
To change the logo
1. Prepare the logo files according to the requirements above.
2. Copy the logo file (or files) to the machine with Agent for vCloud.
3. On the machine with Agent for vCloud, edit the
/opt/acronis/vcd-agent/client/custom/custom.css file as follows:
a. The .login-header-logo and .header-logo class selectors define the logo on the login page
and in the main interface, respectively. Replace the logo file paths in the background
property with the new paths.
b. If a logo size differs from the recommended values, do any the following:
Adjust its position by changing the values of the background properties.
40 Copyright © Acronis International GmbH, 2002-2014
Page 41

Adjust the position and the size of the container that stores the logo (by changing the
width, height, margin-left, and margin-top properties) in the corresponding class
selectors.
c. If necessary, you can align the product name with the logo by changing the margin-top and
padding-left property values in the .header-product-name class selector. To move the
product name further to the right, create a .login-header-text.prefix_2 class selector with the
padding-left property.
d. Save the file.
4. To change the image shown on the browser tab, replace the
/opt/acronis/vcd-agent/client/favicon.ico file with the new file.
No web server restart is needed for the changes to take effect. To see the changes in the currently
open webpages, press CTRL+F5 in the browser (or otherwise clear the browser cache).
41 Copyright © Acronis International GmbH, 2002-2014
Page 42

2 User's Guide
2.1 About the backup service
This service enables backup and recovery of virtual machines managed by VMware vCloud Director.
The service is available through a web interface. To log in to the backup service, use your vCloud
Director credentials.
What you can do after logging in depends on the settings made by a system administrator for your
organization. Due to these settings, some of the operations described in this guide may be not
available to you.
2.2 Supported web browsers
Google Chrome 12 or later
Mozilla Firefox 12 or later
Windows Internet Explorer 9 or later
Safari 5 or later running in the Mac OS X and iOS operating systems
In other web browsers (including Safari browsers running in other operating systems), the user
interface might be displayed incorrectly, or all functions might not be available.
Make sure that JavaScript is enabled in the browser.
The screen resolution for displaying the graphical user interface must be 1024x768 or higher.
2.3 Installing VMware Tools
We recommend installing VMware Tools on all virtual machines which you are planning to back up in
the powered-on state.
Installing VMware Tools is a common requirement for backing up at a hypervisor level. The backup
service uses VMware Tools to create a time-consistent backup of the machine. All data will be backed
up as it was at the moment when the backup started, even if the data changes while the backup is
running.
To install VMware Tools on a virtual machine
1. Log in to vCloud Director.
2. In the list of virtual machines, examine the VMware Tools column for the virtual machine. This
column is hidden by default.
3. If this column shows Not installed, install the most recent version as follows:
a. Power on the machine.
b. Right-click the machine and then click Install VMware Tools.
c. Follow the on-screen instructions.
For information about installing VMware Tools in a specific operating system, refer to the following
VMware knowledge base article:
http://pubs.vmware.com/vcd-51/topic/com.vmware.vcloud.users.doc_51/GUID-F0826E73-7F9F-489
C-B0DB-17C7D742B1AF.html.
42 Copyright © Acronis International GmbH, 2002-2014
Page 43

2.4 Basic operations
This section describes typical usage of the backup service.
2.4.1 Logging in to the service
You can log in to the backup service under the following conditions:
A system administrator has enabled use of the service for your organization.
[For non-administrative users] Your organization administrator has enabled use of the service for
your account.
To log in to the backup service
1. Go to the login page of the backup service. The URL of the login page looks like:
https://backup.example.com/org/<Organization name>
If you are unsure about the address of the login page, contact the system administrator or the
organization administrator.
2. Type the user name and password of your vCloud Director account.
3. Click Log in.
2.4.2 Backing up virtual machines
The virtual machines that you can back up are listed on the organization tab.
The vApps list shows all vApps that you own. The All virtual machines list shows all virtual machines
from those vApps. (An organization administrator sees all vApps and virtual machines in the
organization.)
Starting a backup
Select one or more virtual machines that you want to back up, and then click Back up now.
If you want backups to run on a schedule, apply a backup plan (p. 44) instead.
Monitoring a backup
A backup may start with a delay, depending on the backup service load.
43 Copyright © Acronis International GmbH, 2002-2014
Page 44

When the backup starts, you can see its progress in the machine details area on the right.
The number of machines that are backed up simultaneously and the order in which they are backed
up are defined by the backup service.
If you need to stop the backup on a specific machine, select the machine, and then click Stop backup
or click the stop button ( ) near the progress bar.
Viewing the result
Once a virtual machine is successfully backed up, the newly created backup appears in the Backups
column on the Backup storage tab.
2.4.3 Applying a backup plan
Applying a backup plan to a virtual machine enables you to automate creating and deleting the
machine's backups.
Depending on how the backup service is configured, you may be able to create your own backup
plans, apply backup plans shared by the system administrator, or both.
To apply a backup plan to virtual machines
1. Select one or more virtual machines in the All virtual machines list, or select an entire vApp in
the vApps list. If you select an entire vApp, the backup plan will be applied to all machines in the
vApp and to any new machines that appear in the future.
2. Click Apply backup plan.
44 Copyright © Acronis International GmbH, 2002-2014
Page 45

3. Select the backup plan that you want to apply to the machines. For example, select Daily.
A backup plan contains the following instructions for the backup service:
Schedule: When and how often to do backups.
Retention rules: How long to store the backups.
Backup options (p. 53).
4. Click OK.
The name of the applied backup plan appears in the Backup plan column. If another backup plan
was previously applied to the machine, that backup plan is revoked.
Tips on usage
The Protection status column shows whether the latest backup has completed successfully (OK)
or failed (Error).
Should you need to restart a failed backup, select a machine and click Back up now. The machine
will be backed up according to the backup plan settings. However, the retention rules will not be
applied this time.
Change a backup plan to one with a different Encryption setting (including different password)
only if it is really necessary. This operation is allowed, but it may cause some inconveniences. For
details, refer to "Consequences of changing encryption" in "Editing a backup plan" (p. 55).
2.4.4 Overwriting a virtual machine with its backed-up version
This recovery procedure can be easily run directly from the organization tab.
Overwriting a machine means that only the content of its original disks is overwritten. The content of
hard disks that were added after the backup will remain the same. The machine settings, such as CPU
and memory settings, and the MAC addresses (also known as physical addresses) of the network
adapters are also preserved.
A machine that was renamed or moved to a different vApp is considered a new machine. To
overwrite it, you need a backup that was created after renaming or moving the machine. If you need
to use an older backup, proceed as described in "Recovering a virtual machine" (p. 46).
45 Copyright © Acronis International GmbH, 2002-2014
Page 46

Setting up the recovery
1. On the organization tab, select the machine that you want to recover, and then click Recover.
2. In Recovery point, select the date and time to which the machine will be recovered. By default,
the latest recovery point will be used.
If the vApp no longer has one or more networks that were used by the backed-up machine, you
are prompted to map the network adapters of the virtual machine to the networks of the vApp.
3. [Optional] Select the Power on the virtual machine after recovery check box.
4. Click OK.
Monitoring the recovery progress
When the recovery starts, the machine will have the Recovering protection status. The progress of
recovery is shown in the machine details area on the right.
If you need to stop the recovery, click the Stop recovery button or the stop button ( ) near the
progress bar. The original machine will likely become corrupted.
After the recovery is completed, the information about its success or failure is shown in the machine
details area.
2.4.5 Recovering a virtual machine
This is a common recovery procedure. Unlike overwriting an existing virtual machine, this enables you
to recover a deleted virtual machine, create a new virtual machine by recovering it from a backup,
and change the machine's network settings.
46 Copyright © Acronis International GmbH, 2002-2014
Page 47

Setting up the recovery
1. Open the Backup storage tab.
2. In the list of backed-up machines, select the machine that you want to recover, and then click
Recover.
3. In Recovery point, select the date and time to which the machine will be recovered. By default,
the latest recovery point is selected.
4. In Target vApp, specify the vApp to which the machine will be recovered. By default, the original
vApp is selected.
If the original vApp no longer exists in the organization, you can recreate the original vApp and
recover the machine to it. To do so, select Recreate original vApp. The vApp will be created with
parameters that it had when the machine was backed up.
5. In Name of the recovered machine, type a name that the recovered machine will have in the
vApp. By default, the original machine's name is selected.
If a machine with the same name exists in this vApp, the software examines the machine's
unique identifier in vCloud Director. A machine with the same unique identifier will be
overwritten. If the machine has a different unique identifier, the software creates a new virtual
machine and adds a suffix like (1) to its name.
6. Under Show additional parameters, you can do any of the following:
In Computer name, change or specify the name that the machine will have on the network.
This is the name defined in the guest operating system (Control Panel > System > System
Properties > Computer Name).
Under Network adapters, change or specify the settings for the existing adapters, or add or
delete network adapters.
Details. To add a network adapter, click Add network adapter, and then specify the settings
for it. To delete a network adapter, click the Delete ( ) button next to it.
47 Copyright © Acronis International GmbH, 2002-2014
Page 48

In Preserve MAC addresses, specify whether the machine's network adapters (except the
newly added ones) will have the same MAC addresses as those of the original machine. To
prevent a MAC address conflict, avoid selecting this check box if the original machine exists
and will not be overwritten.
7. [Optional] Select the Power on the virtual machine after recovery check box.
8. Click OK.
Monitoring the recovery progress
The progress of recovery is shown in the machine details area on the right.
If you need to stop the recovery, click the Stop recovery button or the stop button ( ) near the
progress bar.
After the recovery is completed, the information about its success or failure is shown in the machine
details area.
2.4.6 Recovering files from a virtual machine backup
This procedure enables you to recover files and folders from a backup of a virtual machine without
recovering the virtual machine itself.
The files and folders that you select will be available for download as a .zip file.
You can recover files from volumes with the following file systems: FAT, FAT32, NTFS, Ext2, Ext3, and
Ext4. Regardless of the file system, you cannot recover files from volumes that are managed by Linux
Logical Volume Manager (LVM), also known as logical volumes; and from multiple-disk (MD) devices,
also known as Linux Software RAID.
To recover files of a virtual machine
1. Open the organization tab or the Backup storage tab.
2. Select the virtual machine whose files you want to recover, and then click Recover files.
3. In Recovery point, select the date and time that you want to recover the files to.
48 Copyright © Acronis International GmbH, 2002-2014
Page 49

The service shows the volumes, files, and folders that were present on the machine at that time.
Volumes that you cannot recover files from are not shown.
Select the files and folders that you want to recover, and then click OK.
After the recovery is completed, the link to download the .zip file appears on the Backup storage tab
in the machine details area on the right.
The link is valid for 24 hours. You can use the link only when you are logged in to the service.
The files are stored in the .zip file together with their entire folder structure. For example, the file
C:\Documents\Report.doc will be stored in the .zip file in the Drive(C)\Documents folder.
Recovering files to the original machine
To recover the files directly to the original virtual machine, use any of the following methods:
Extract the files to a system network share. After you download the .zip file to your machine,
power on the original virtual machine and extract the file to a network share such as
\\VM1\c$ (this network share corresponds to the C volume of the VM1 virtual machine). This
method of recovery works only for a virtual machine running Windows. You must provide the
credentials of a local administrator on that virtual machine.
Log in to the service on the virtual machine. Power on the virtual machine, start the browser,
log in to the service, and then download the .zip file and extract the files from it.
49 Copyright © Acronis International GmbH, 2002-2014
Page 50

2.4.7 Monitoring protection statuses
Status
Meaning
Not protected
No backup plan is applied to the machine.
Never backed up
A backup plan is applied to the machine, but no backup has been run.
OK
A backup plan is applied to the machine and the latest backup was completed
successfully.
Error
A backup plan is applied to the machine, and the latest backup failed.
The Protection status column on the organization tab indicates how well a virtual machine or a vApp
is protected.
Protection statuses of machines
The table below lists protection statuses of a machine by order of severity, from the least severe to
the most severe.
Instead of these statuses, the Backing up… or Recovering… status is shown when a backup operation
or a recovery operation is running.
Note The "Back up now" operation does not affect a protection status unless a backup plan is applied to the
machine.
Protection statuses of vApps
The protection status of a vApp is the most severe status among the machines in the vApp. This
status does not depend on whether a machine is currently being backed up or recovered.
2.5 Operations with backups
The Backup storage tab shows the list of backed-up virtual machines. Each of the machines has one
or more backups, also called recovery points. The backups are listed in the Backups area on the right.
Once you select a backup, the Machine details area shows the computer name, the guest operating
system, and the IP addresses for the machine at the time of backup.
The following operations with backups are available:
To recover a machine from a backup, select the machine and click Recover. Refer to "Recovering
a virtual machine" (p. 46).
To delete one or more backups of a machine, select the machine and click Delete. In the opened
window, select the backups that you want to delete and click Delete.
To delete all backups of two or more machines, select the machines and click Delete.
Storage usage/Backed-up data
This area contains information related to either the storage usage or the backed-up data, depending
on the backup service quota settings (p. 31).
This area is available only to administrators. It contains the following parameters:
The storage quota for the organization (if set by the system administrator).
The total size of backups stored in the backup storage or the total amount of data that was
backed up.
50 Copyright © Acronis International GmbH, 2002-2014
Page 51

The number of backed-up virtual machines.
The alerts about an almost-reached quota (80 percent or more is used) or an exceeded quota
(100 percent or more is used).
To see historical data on the storage usage, expand the area.
The column chart represents the service usage for the last 30 days. In the chart, red columns
show days when the storage quota was exceeded and orange columns show days when the
storage quota was almost reached.
To generate a comprehensive report on the service usage for a specific period, click Generate
usage report (p. 56).
2.6 Operations with backup plans
The Backup plans tab shows the backup plans that you can apply to your virtual machines.
The following backup plans are shown:
System backup plans ( ). System backup plans are shared with your organization by the
system administrator. Their schedule and retention rules can be changed only by using the
system administrator's interface. However, you can enable backup options for these plans, such
as encryption or notifications. To do so, click Set options. These options will be effective only
within your organization.
Backup plans created within the organization ( ). If you are an organization administrator,
you can perform any operations with these backup plans. Non-administrative users can perform
any operations with the backup plans they created. The Owner column shows who created the
backup plan. The owner of backup plans created by a system administrator is System.
2.6.1 Creating a backup plan
In addition to using existing backup plans, you can create your own backup plans.
To create a backup plan
1. Open the Backup plans tab.
2. Click Create.
3. Type the name of the backup plan. The name must differ from names of other backup plans in
the list of backup plans.
4. Specify the schedule type: Daily, Weekly, GFS (Grandfather-Father-Son), or Hourly.
5. On the Schedule and Retention rules tabs, specify the schedule and retention rules (p. 52) for
the backup plan.
6. On the Options tab, specify the backup options (p. 53).
7. Click OK.
After creating the backup plan, you can apply it to your virtual machines (p. 44).
51 Copyright © Acronis International GmbH, 2002-2014
Page 52

2.6.1.1 Schedule and retention rules
The backup operation runs according to the schedule you specify. The resulting backups are kept
according to the retention rules and then deleted.
The scheduled time is displayed according to the time zone set on the machine from which you are
logged in to the backup service. If you schedule backups to run, say, at 07:00, they will run when your
machine clock reaches 07:00, regardless of the time zone where the vCloud infrastructure is
physically located. If you change the time zone setting on the machine, the schedule will not change,
but you will see different start time.
The following schedule types and the corresponding retention rules are available:
Hourly backup
Schedule. Select the days of week to run backups and the time interval between the backups. In
From and To, specify the beginning and the end of the period when the backups will be run.
Retention rules. Specify how long you want to retain the backups.
By default, backups will run every four hours on workdays. The backups are retained for one week.
Daily backup
Schedule. Select the days of week and the time to run backups.
Retention rules. Specify how long you want to retain the backups.
By default, the backups will run Monday through Friday at 22:00. The resulting backups will be
retained for one week.
Weekly backup
With this schedule, the backups will run once in the specified number of weeks.
Schedule
1. Select the number of weeks.
2. Select the day of week and the time to run backups.
By default, the backups will run every week at 22:00, on the day of week on which the backup plan
was created.
Retention rules
Specify how long you want to retain the backups.
By default, the backups will be retained for four weeks.
GFS (Grandfather-Father-Son)
This schedule is useful for long-term storage of backups.
With this schedule, you have a single backup for each of the recent days and for each of the recent
weeks. For earlier periods of time, you have a single backup for each month.
Schedule
1. Select the days of week and the time when to run backups.
52 Copyright © Acronis International GmbH, 2002-2014
Page 53

2. Out of these days of week, choose the one to Do weekly/monthly backups on. Backups that are
Mon
Tue
Wed
Thu
Fri
Sat
Sun
March 1–7
D D D D W – –
March 8–14
D D D D W – –
March 15–21
D D D D W – –
March 22–28
D D D D M – –
March 29–April 4
D D D D W – –
April 5–11
D D D D W – –
April 12–18
D D D D W – –
April 19–25
D D D D W – –
April 26–May 2
D D D D M – –
performed on that day will be considered as weekly backups and monthly backups. Backups that
are performed on other days will be considered as daily backups.
By default, the backups will run Monday through Friday at 22:00. Friday is chosen for
Weekly/Monthly backups.
Retention rules
Specify how long you want to retain the daily, weekly, and monthly backups.
The default settings are the following:
Daily backups: 5 days (recommended minimum)
Weekly backups: 7 weeks
Monthly backups: 12 months
Example
Suppose that you use the default settings (run backups Monday through Friday, Weekly/Monthly
backups on Friday, the default retention rules) and apply the backup plan on Monday, March 1.
The following table shows which daily (D), weekly (W), and monthly (M) backups will remain on
Friday, April 30. Backups that are shown on the gray background will be deleted by that day.
2.6.1.2 Backup options
On the Options tab, configure the parameters of the backup operation.
Encryption
Specify the password to be used for encrypting the backups. The password prompt will appear when
someone tries to delete a backup or recover data from it.
The backups will be encrypted with the AES-256 encryption algorithm.
The password is not stored anywhere on the disk or in the backup file. Make sure you remember the
password. Recovering a lost password is not possible.
If you edit the backup plan (p. 55) and change or remove the password, the retention rules will no
longer apply to the backups with the old encryption setting. Also, separate entries will be shown in
53 Copyright © Acronis International GmbH, 2002-2014
Page 54

the backup storage for sets of backups with different encryption settings. During recovery, you will
need to select the correct entry and type the correct password.
Notifications
Specify whether to send e-mail notifications after a successful backup, after a failed backup, or both.
Specify the address to send the notifications. Separate multiple e-mail addresses with a semicolon.
For example: user1@example.com; user2@example.com
The notifications will be sent from the e-mail address specified by a system administrator.
Exclusions
Type one or more criteria. Files and folders that match any of the specified criteria will not be backed
up.
This option is effective only for files and folders that are stored on the following file systems:
FAT
NTFS
Ext3
Ext4
Regardless of the file system, this option is not effective for volumes that are managed by Linux
Logical Volume Manager (LVM), also known as logical volumes; and for multiple-disk (MD) devices,
also known as Linux Software RAID.
How to specify criteria
You can use the following criteria:
The full path to a file or folder, starting with the drive letter (when backing up Windows) or the
root directory (when backing up Linux).
Both in Windows and Linux, you can use a forward slash in the file or folder path (for example:
C:/Temp and C:/Temp/File.tmp). In Windows, you can also use the traditional backslash (for
example: C:\Temp and C:\Temp\File.tmp).
The name of a file or folder; for example: Document.txt. All files and folders with that name will
be excluded.
Separate multiple criteria with a semicolon (;).
The criteria are not case-sensitive. For example, if you choose to exclude all .tmp files and the
C:\Temp folder, also excluded will be all .Tmp files, all .TMP files, and the C:\TEMP folder.
Wildcard characters
You can use one or more wildcard characters * and ? in a criterion. These characters can be used
within the full path and in the file or folder name.
The asterisk (*) substitutes for zero or more characters in a file name. For example, the criterion
Doc*.txt covers files such as Doc.txt and Document.txt.
The question mark (?) substitutes for exactly one character in a file name. For example, the criterion
Doc?.txt covers files such as Doc1.txt and Docs.txt, but not the files Doc.txt or Doc11.txt.
54 Copyright © Acronis International GmbH, 2002-2014
Page 55

VSS
Specify whether to use Volume Shadow Copy Service (VSS) during backup.
This option is effective only for machines where VMware Tools is installed (p. 42).
This option ensures that the file system will be backed up in a consistent state. For machines running
Windows, this option also ensures the consistent state of all data that is used by VSS-aware
applications, such as by Microsoft SQL Server.
Without this option, the backup process is faster, but data consistency cannot be guaranteed.
2.6.2 Editing a backup plan
Important: The changes you make to a backup plan affect all virtual machines to which the backup plan is
applied, both your machines and other users' machines.
To edit a backup plan
1. Open the Backup plans tab.
2. Select the backup plan that you want to edit, and then click Edit.
3. View or change the name, schedule, retention rules (p. 52), and backup options (p. 53).
4. Click OK.
Consequences of changing encryption
If you need to change the Encryption setting (to enable or disable encryption or to change the
password), consider the following:
Retention rules will no longer apply to the backups with the old encryption setting. You can only
delete those backups manually (p. 55).
Separate entries will be shown in the backup storage for sets of backups with different
encryption settings. During recovery, you will need to select the correct entry and type the
correct password.
The same happens when you apply a backup plan to a machine where another backup plan with a
different Encryption setting is applied.
2.6.3 Revoking a backup plan
When you revoke a backup plan from a machine, a currently running backup (if any) is stopped. The
machine will no longer be backed up until a backup plan is applied again. Backups of the machine are
retained in the backup storage until you delete them manually (p. 50).
To revoke a backup plan
1. Open the tab with the organization name.
2. Select one or more machines from which you want to revoke backup plans.
3. Click Revoke backup plan.
2.6.4 Deleting a backup plan
When you delete a backup plan, it is revoked (p. 55) from all machines to which it is applied (both
your machines and other users' machines) and it is removed from the list of backup plans.
55 Copyright © Acronis International GmbH, 2002-2014
Page 56

To delete a backup plan
1. Open the Backup plans tab.
2. Select the backup plan that you want to delete, and then click Delete.
3. Confirm the deletion of the backup plan.
2.7 Generating usage reports
This functionality is available only to administrators.
Usage reports provide historical data about using the backup service in your organization. You may
need these reports to calculate how much your organization will be charged for the service.
Reporting parameters
The values of all parameters are checked every day at 23:55 according to the time settings of vCloud
Director. The report uses the values as they were at that time.
The report includes the following parameters for the organization:
Number of protected VMs: The total number of protected machines (that is, the machines to
which backup plans are applied), no matter whether backups of those machines exist
Storage usage: The total size of all backups in the backup storage (in gigabytes). This parameter
may be excluded from the report, depending on the backup service settings.
Backed-up data: The total amount of data that was backed up. This amount includes the initial
content of the virtual machine disks and the subsequent incremental changes to that content.
Over quota: The amount of data that exceeds the quota set for the organization (in gigabytes)
Disk size of protected VMs: The total size of hard disks of the protected machines (in gigabytes),
regardless of the occupied space on those disks
RAM size of protected VMs: The total amount of memory of the protected machines (in
gigabytes)
CPU number of protected VMs: The total number of CPUs of the protected machines
To generate a usage report
1. Open the Backup storage tab.
2. Expand the Storage usage area on the bottom, and then click Generate usage report.
3. In Period, select the reporting period:
Current calendar month: The report will include data from the first day of the current month
up to the current day (when generating the report after 23:55) or up to the previous day
(when generating the report before 23:55).
Previous calendar month: The report will include data from all days of the previous month.
For example, in April you will get a report for the time interval from March 1 through March
31.
Custom period: The report will include data from the interval that you specify.
4. In Type, select the report type:
Daily statistics: The report will include the values of the reporting parameters for each day of
the reporting period. The report also includes the summary: the minimum, maximum, and
average values of each of the reporting parameters throughout the period.
Summary report: The report will include only the summary (see the previous option).
5. Click OK. The report appears in a separate browser window or tab.
56 Copyright © Acronis International GmbH, 2002-2014
Page 57

6. [Optional] To print the report, click Print. To save the report as a comma-separated values (.csv)
file, click Save as .csv file.
2.8 Enabling non-administrators to use the service
Using the backup service includes logging in to it, performing backup and recovery, and managing
backups and backup plans. A system administrator may want to create a dedicated vCloud Director
role for the backup service access.
Organization administrators can enable members of any vCloud Director role to use the service.
To enable members of a vCloud Director role to use the service
1. Log in to the backup service.
2. Click the Settings tab.
The software displays a list of vCloud Director roles.
3. Select the Service enabled check box for the role.
Any member of this role will be able to use the backup service. If you need advice on how to assign a
vCloud Director role to a user, read the next section.
2.8.1 Assigning a vCloud Director role to a user
The following procedure is effective for both of the following types of users:
Local users: Users whose accounts were created in vCloud Director
LDAP users: Users whose accounts were imported to vCloud Director from a Lightweight
Directory Access Protocol (LDAP) directory, such as Active Directory
To assign a role to a user
1. Log in to vCloud Director.
2. Click Administration > Users.
3. Assign the role with the backup service access to the user.
The user can start using the service as soon as you have assigned the role.
Alternative method for LDAP users
If your organization has a large number of non-administrative LDAP users, you may want to follow a
different procedure to enable them to use the service.
To assign a role to an LDAP group
1. Log on to the LDAP server (such as an Active Directory domain controller), from which user
accounts are imported into vCloud Director.
2. Create a group in the LDAP directory (for example: vCloud Backup Service Users).
3. Add all users whom you want to access the service to the group created in step 2.
You can now log out from the LDAP server.
4. Log in to vCloud Director.
5. On the Groups page, find the group that you created in step 2.
6. Assign the role with the backup service access to the group.
By adding or removing group members on the LDAP server, you can change who can use the service.
57 Copyright © Acronis International GmbH, 2002-2014
Page 58

2.9 Viewing audit logs
The backup service includes an audit log, which records operations performed by users.
System and organization administrators have a view into the log scoped to their area of control.
To view the audit log
1. Log in to the service.
2. Click the Logs tab.
58 Copyright © Acronis International GmbH, 2002-2014
Page 59

3 Terminology reference
Agent for vCloud
The backup service infrastructure component that runs on a dedicated virtual machine within a
vCloud Director management cluster.
Backup (operation)
An operation that saves information about a virtual machine in a packaged form, for the purpose of
recovery.
Backup (recovery point)
The result of a single backup operation.
A backup represents a point in time to which a user can recover the virtual machine. The data that is
necessary for recovery is stored in two locations. The content of the virtual disks and the virtual
machine configuration are stored in the backup storage. The metadata that reflects the machine's
membership in vCloud (the virtual network adapters configuration, the computer name, the vApp
the machine is part of) is stored inside Agent for vCloud.
Backup plan
A set of rules that define how to protect virtual machines.
The rules include the backup schedule, retention rules and backup options such as protecting
backups with a password. For example: perform backup every day at midnight, delete backups that
are older than one month, and protect the backups with a password.
Backup plan owner
An organization user who created the backup plan.
The system backup plans have a special owner called System. The owner is also System for backup
plans created by the system administrator within the organization.
Backup storage
A folder allocated by a system administrator for storing an organization's backups.
Management cluster
An ESX(i) cluster that contains the vCloud Director infrastructure components.
Organization administrator
A user who has the Organization Administrator role in vCloud Director.
An organization administrator can back up and recover any virtual machine in the organization.
Protected machine
A virtual machine to which a backup plan is applied.
59 Copyright © Acronis International GmbH, 2002-2014
Page 60

Recovery
An operation that creates or overwrites a virtual machine by using the data that was earlier saved in
a backup. When you select for recovery the same machine that was backed up, it is overwritten.
Otherwise, a new virtual machine is created.
Resource group
One or more ESX(i) clusters that contain virtual machines of vCloud Director organizations.
Retention rules
A part of backup plan that specifies how long backups are kept.
Storage quota (quota)
The amount of storage space allocated for an organization.
If the quota is exceeded, the system administrator and the organization users see alerts in the
backup service interface. Restrictions on using the backup service are not applied unless the system
administrator does this manually.
System administrator
A user who has the System Administrator role in vCloud Director.
A system administrator can back up and recover any virtual machine in any organization. A system
administrator can allow organization users to back up virtual machines in their organization.
System backup plan
A ready-to-use backup plan predefined by the system administrator in order to make it available
across many organizations. Organization users can apply system backup plans to their virtual
machines.
Changes to the schedule or retention rules of a system backup plan affect all organizations to which
the plan was made available.
User
A person who has a user account in vCloud Director.
Depending on the permissions that are assigned to the user account in vCloud Director, a user can be
a system administrator, an organization administrator, or a non-administrative user in an
organization.
vApp
A set of virtual machines that is created in vCloud Director and that can be managed in vCloud
Director as a single entity.
60 Copyright © Acronis International GmbH, 2002-2014
Page 61

Copyright Statement
Copyright © Acronis International GmbH, 2002-2014. All rights reserved.
“Acronis” and “Acronis Secure Zone” are registered trademarks of Acronis International GmbH.
"Acronis Compute with Confidence", “Acronis Startup Recovery Manager”, “Acronis Active Restore”,
“Acronis Instant Restore” and the Acronis logo are trademarks of Acronis International GmbH.
Linux is a registered trademark of Linus Torvalds.
VMware and VMware Ready are trademarks and/or registered trademarks of VMware, Inc. in the
United States and/or other jurisdictions.
Windows and MS-DOS are registered trademarks of Microsoft Corporation.
All other trademarks and copyrights referred to are the property of their respective owners.
Distribution of substantively modified versions of this document is prohibited without the explicit
permission of the copyright holder.
Distribution of this work or derivative work in any standard (paper) book form for commercial
purposes is prohibited unless prior permission is obtained from the copyright holder.
DOCUMENTATION IS PROVIDED "AS IS" AND ALL EXPRESS OR IMPLIED CONDITIONS,
REPRESENTATIONS AND WARRANTIES, INCLUDING ANY IMPLIED WARRANTY OF MERCHANTABILITY,
FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE OR NON-INFRINGEMENT, ARE DISCLAIMED, EXCEPT TO THE
EXTENT THAT SUCH DISCLAIMERS ARE HELD TO BE LEGALLY INVALID.
Third party code may be provided with the Software and/or Service. The license terms for such
third-parties are detailed in the license.txt file located in the root installation directory. You can
always find the latest up-to-date list of the third party code and the associated license terms used
with the Software and/or Service at http://kb.acronis.com/content/7696
Acronis patented technologies
Technologies, used in this product, are covered and protected by one or more U.S. Patent Numbers:
7,047,380; 7,275,139; 7,281,104; 7,318,135; 7,353,355; 7,366,859; 7,475,282; 7,603,533; 7,636,824;
7,650,473; 7,721,138; 7,779,221; 7,831,789; 7,886,120; 7,895,403; 7,934,064; 7,937,612; 7,949,635;
7,953,948; 7,979,690; 8,005,797; 8,051,044; 8,069,320; 8,073,815; 8,074,035; 8,145,607; 8,180,984;
8,225,133; 8,261,035; 8,296,264; 8,312,259; 8,347,137; 8,484,427; 8,645,748; 8,732,121 and patent
pending applications.
61 Copyright © Acronis International GmbH, 2002-2014
 Loading...
Loading...