Page 1
& K DSWHU
System Board
The V56LA is a high-performance system board with a 64-bit
architecture. It supports the Intel P54C and P55C CPUs running at
100/120/133/150/166/200 MHz. It also supports 6x86/6x86L
Cyrix/IBM and AMD K5/K6 CPUs. The system board utilizes the
Peripheral Component Interconnect (PCI) local bus architecture that
maximizes the system performance by enabling high-speed
peripherals to match the speed of the microproces sor with its 120 MB
or 132 MB per second transfer rate in burst mode.
A 1-MB or 2-MB SGRAM comes mounted onboard. Two DRAM
banks composed of four 72-pin sockets come with the board to
support single- and double-density SIMMs for a maximum system
memory of 128 MB. The SIMM sockets accommodate both the
standard page mode and extended data output (EDO) type SIMMs.
The board supports a 256-KB or 512-KB pipeline burst second-level
cache.
The system board includes a 188-pin connector f or the slot board that
contains the PCI and ISA bus slots. The two onboard PCI- enhanced
IDE interfaces with a zero-wait state and 16.6 MB per second transfer
rate support up to four IDE devices. Onboar d I/O interfaces c omprise
of two UART 16550 serial ports, a parallel port with ECP/EPP feature,
and PS/2 keyboard and mouse ports.
As added enhancements, the board also incorporates a Sound Blaster
Pro-compatible audio subsystem plus plug-and-play (PnP), power
management, and software shutdown features.
System Board 1-1
Page 2

1.1 Major Components
The system board has the following major components:
A zero-insertion force (ZIF) socket for Intel Pentium and
•
Pentium/MMX, 6x86/6x86L Cyrix/IBM, and AMD K5/K6
Two DRAM banks composed of four 72-pin SIMM sockets that
•
support 4/8/16/32-MB 60/70ns SIMMs
256/512-KB write-back pipeline burst second-level cache
•
128/256-KB boot block mode Flash RO M for system BIOS, VGA
•
BIOS, and PnP ESCD
Two PCI-enhanced IDE interfaces that support up to four IDE
•
devices
System clock/calendar with 256-byte CMOS RAM
•
Standard 1-MB SGRAM onboard
•
188-pin connector for PCI/ISA slot board
•
Feature socket for multimedia or Ethernet solution
•
168-pin cache module socket for cache upgrade
•
External ports:
•
PS/2 keyboard and mouse ports
•
Two buffered high-speed serial ports
•
One ECP/EPP high-speed parallel port
•
Video port
•
RJ-45 connector (optional)
•
1-2 User’s Guide
Page 3
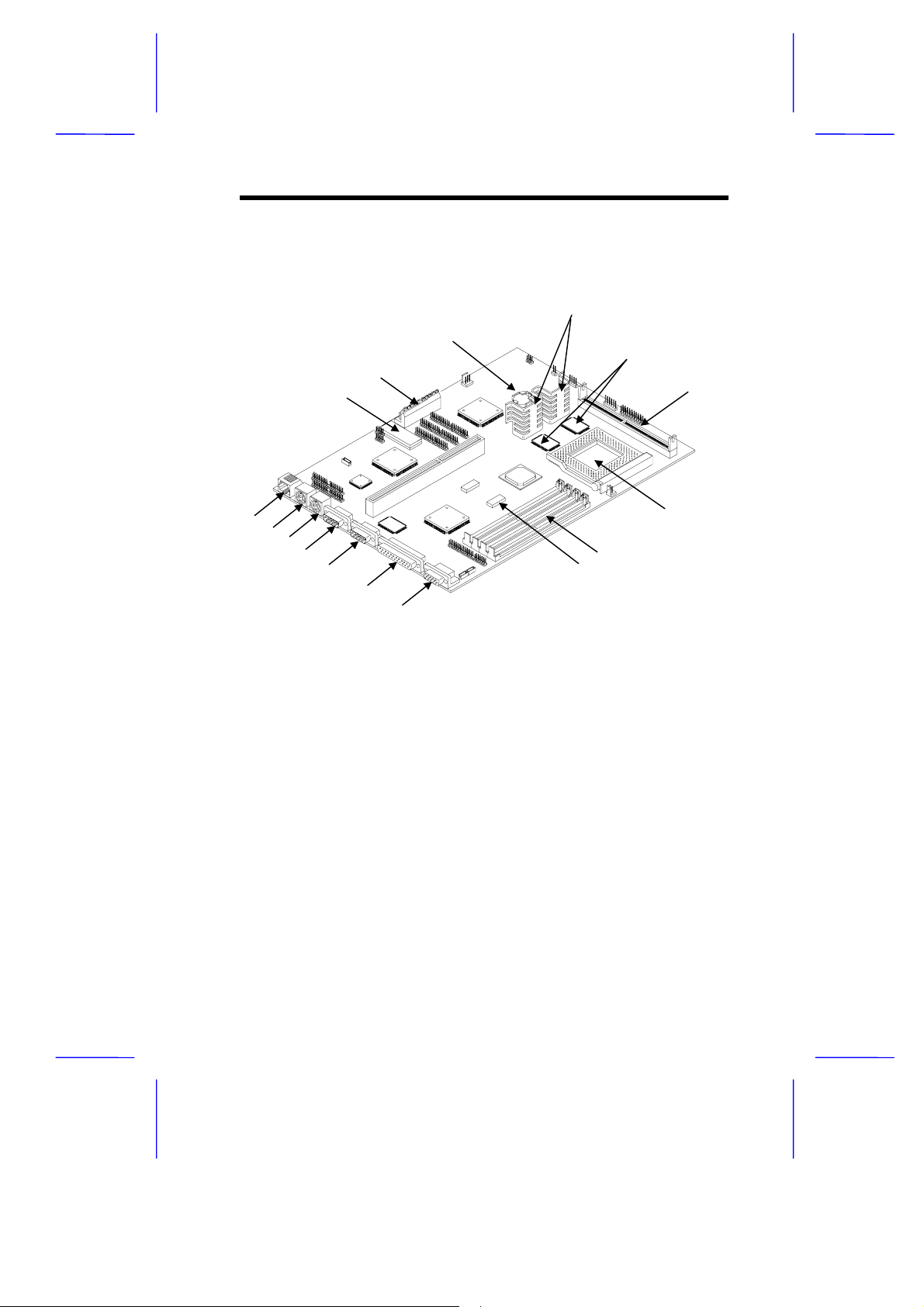
1.1.1 System Board
23456
715
6
4
Figure 1-1 shows the locations of the system board major
components.
13
1
12
1
1
1 RJ-45 connector (optional)
2 Keyboard port
3 Mouse port
4 Serial port 1
5 Serial port 2
6 Parallel port
7 Video port
8 Tag SRAM
9 SIMM sockets
Figure 1-1 System Board Layout
10
9
8
10 CPU socket
11 Pipeline burst second-level
cache upgrade socket (optional)
12 Second-level cache onboard
13 CPU voltage regulators
14 Battery
15 Power connector
16 BIOS
11
System Board 1-3
Page 4
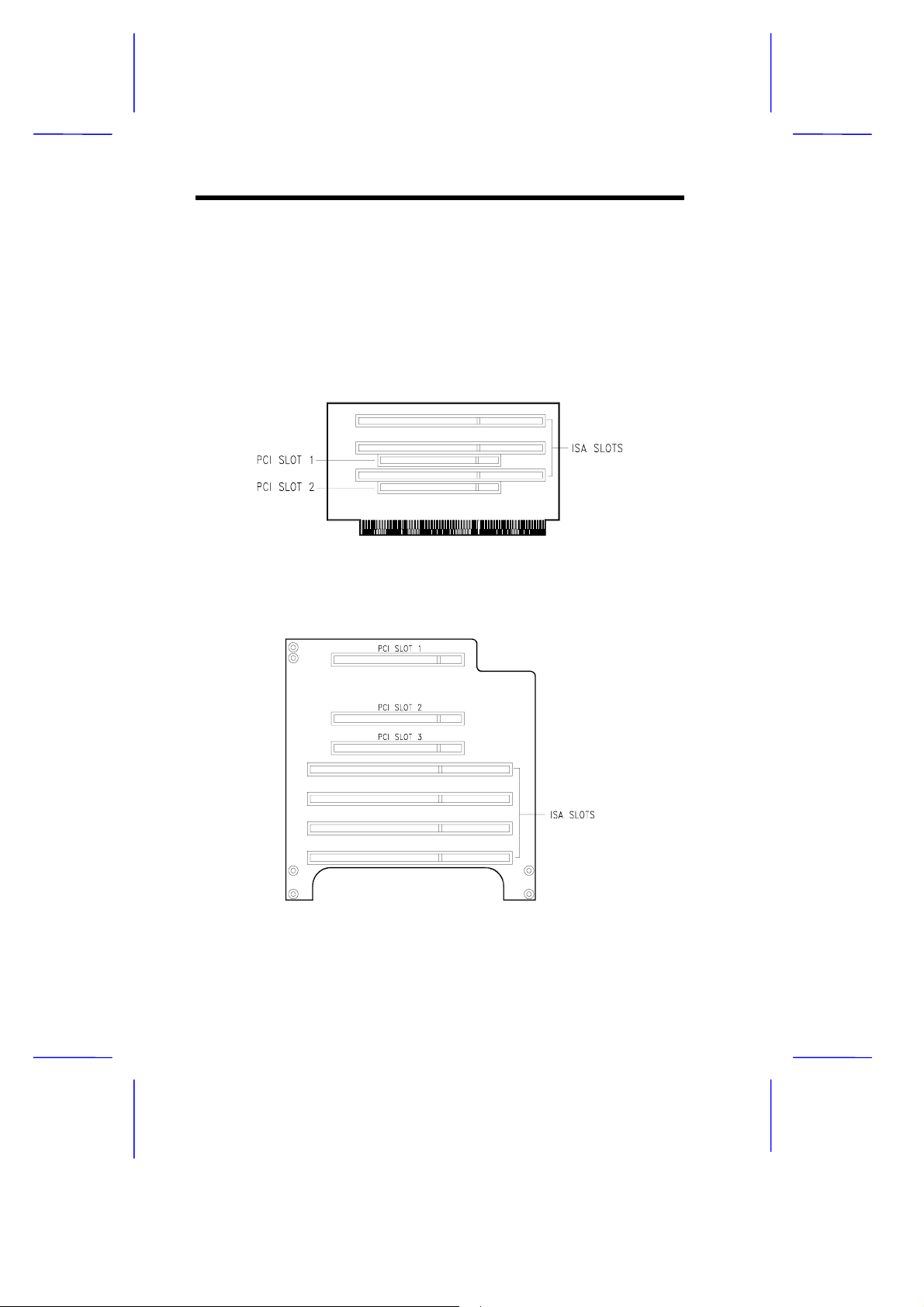
1.1.2 Slot Boards
The system board comes with a slot board already installed. The slot
board carries the PCI and ISA bus slots for system enhanc ements and
future expansion.
The slot board may vary in size and layout depending on your system
housing. Figures 1-2 to 1-6 show the slot board types.
Figure 1-2 2 -PCI/3-ISA Slot Board (for desktop systems)
Figure 1-3 3-PCI/4-ISA Slot Board (for minitower systems)
1-4 User’s Guide
Page 5

Figure 1-4 2 -PCI/3-ISA Slot Board (for Aspire desktop systems)
Figure 1-5 3-PCI/4-ISA Slot Board
(for Aspire minitower systems)
System Board 1-5
Page 6
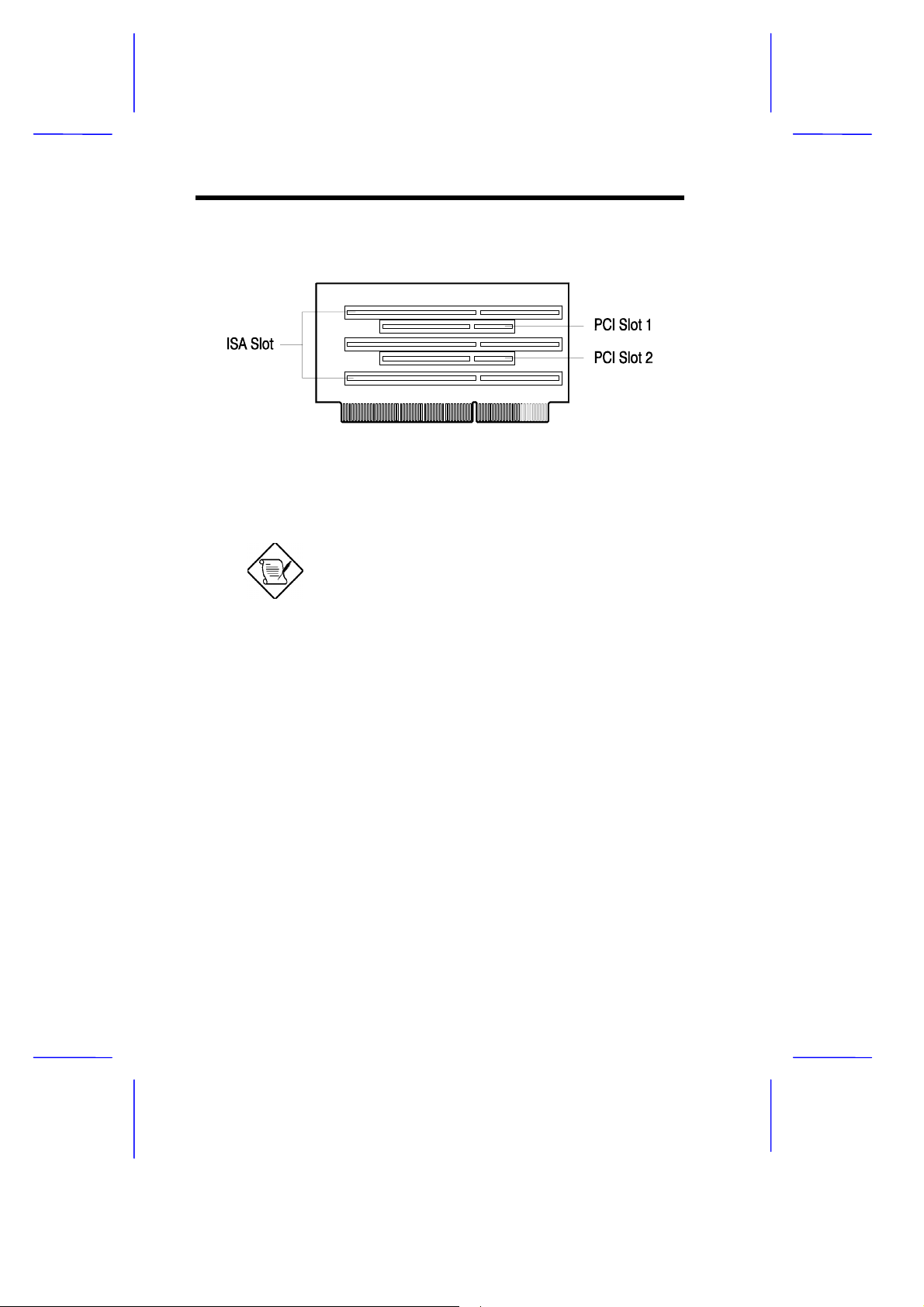
Figure 1-6 3-ISA Slot Board (for AcerBasic system)
Refer to the corresponding housing manual
for slot board installation instructions.
1-6 User’s Guide
Page 7
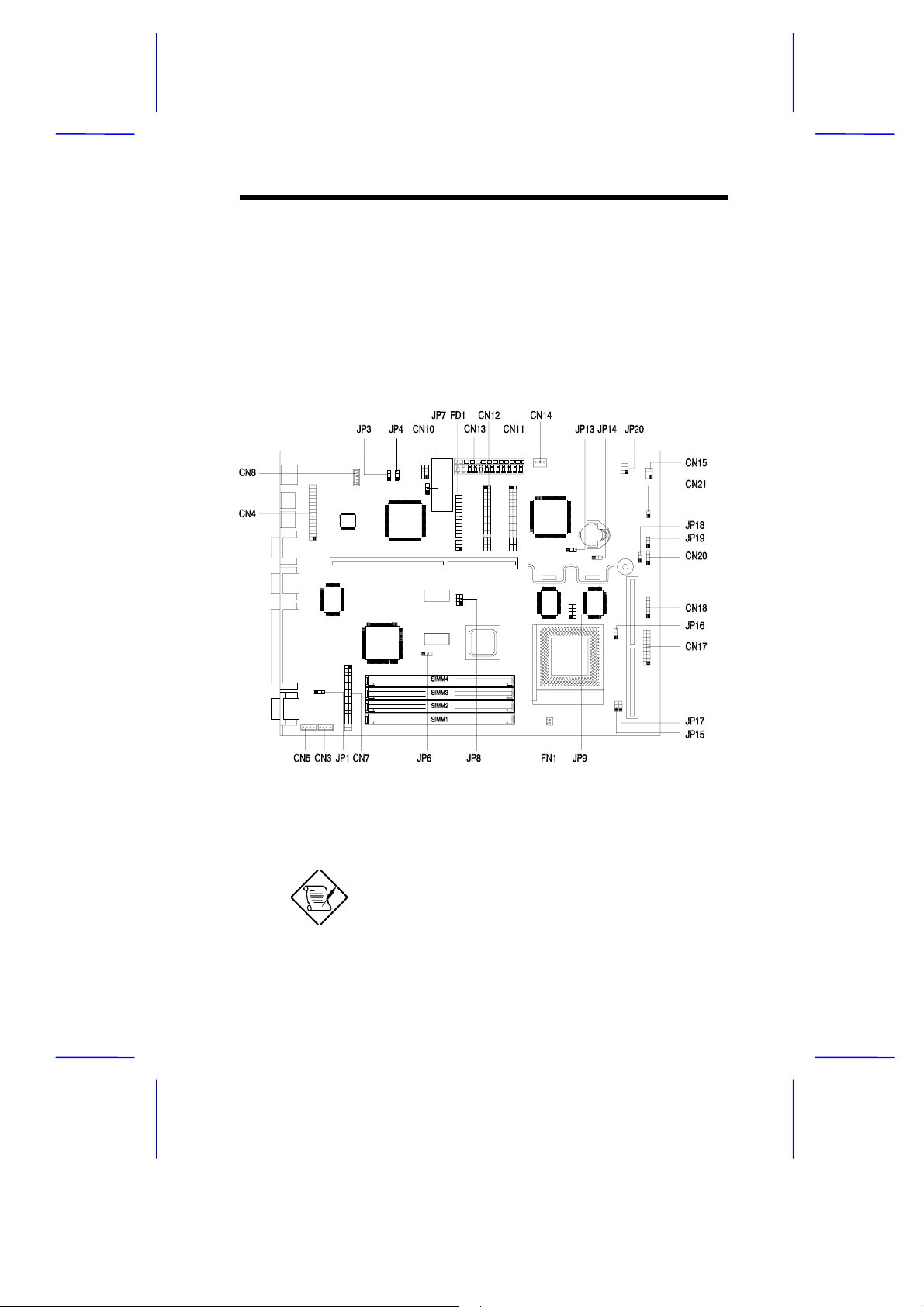
1.2 Jumpers and Connectors
1.2.1 Jumper and Connector Locations
Figure 1-7 shows the jumper and connector locations on the s yst em
board.
Figure 1-7 System Board Jumper and Connector Locations
The blackened pin of a jumper represents
pin 1.
System Board 1-7
Page 8
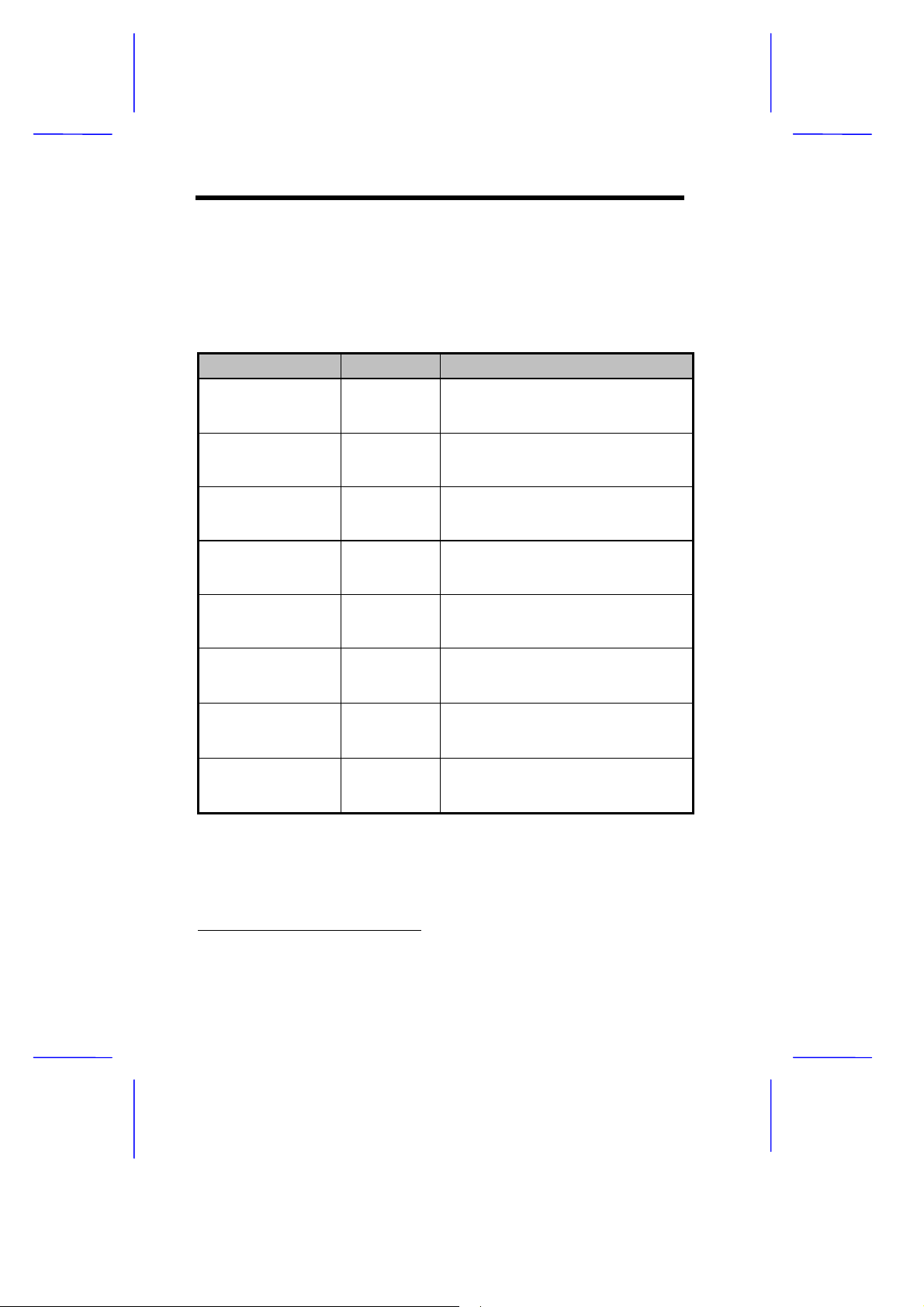
1.2.2 Jumper Settings
Table 1-1 lists the system board jumpers with their corresponding
settings and functions.
Table 1-1 System Board Jumper Settings
Jumper Setting Function
JP1 1-2
*
2-3
JP3 1-2*
2-3
JP4 1-2
2-3*
JP6 1-2*
2-3
JP7 1-2*
2-3
JP18 1-2
2-3*
JP19 1-2*
2-3
JP20 1-2 and 4-5*
2-3 and 5-6
Onboard VGA
Disabled
Enabled
BIOS Type
Acer BIOS
OEM BIOS
Password Security
Check password
Bypass password
Cache Size
256 KB
512 KB
BIOS ROM Type
Block ROM (2 Mbit)
Flash ROM (Intel 28F001)
LED Functions
IDE and FDD LED
IDE LED only
External Switch
Suspend button
Reset button
Software Shutdown
Software shutdown
Appears off
See Table 1-2 for the specif ic settings of j umpers JP8-J P15 and JP17
when selecting the CPU type and speed.
*
Default setting
1-8 User’s Guide
Page 9
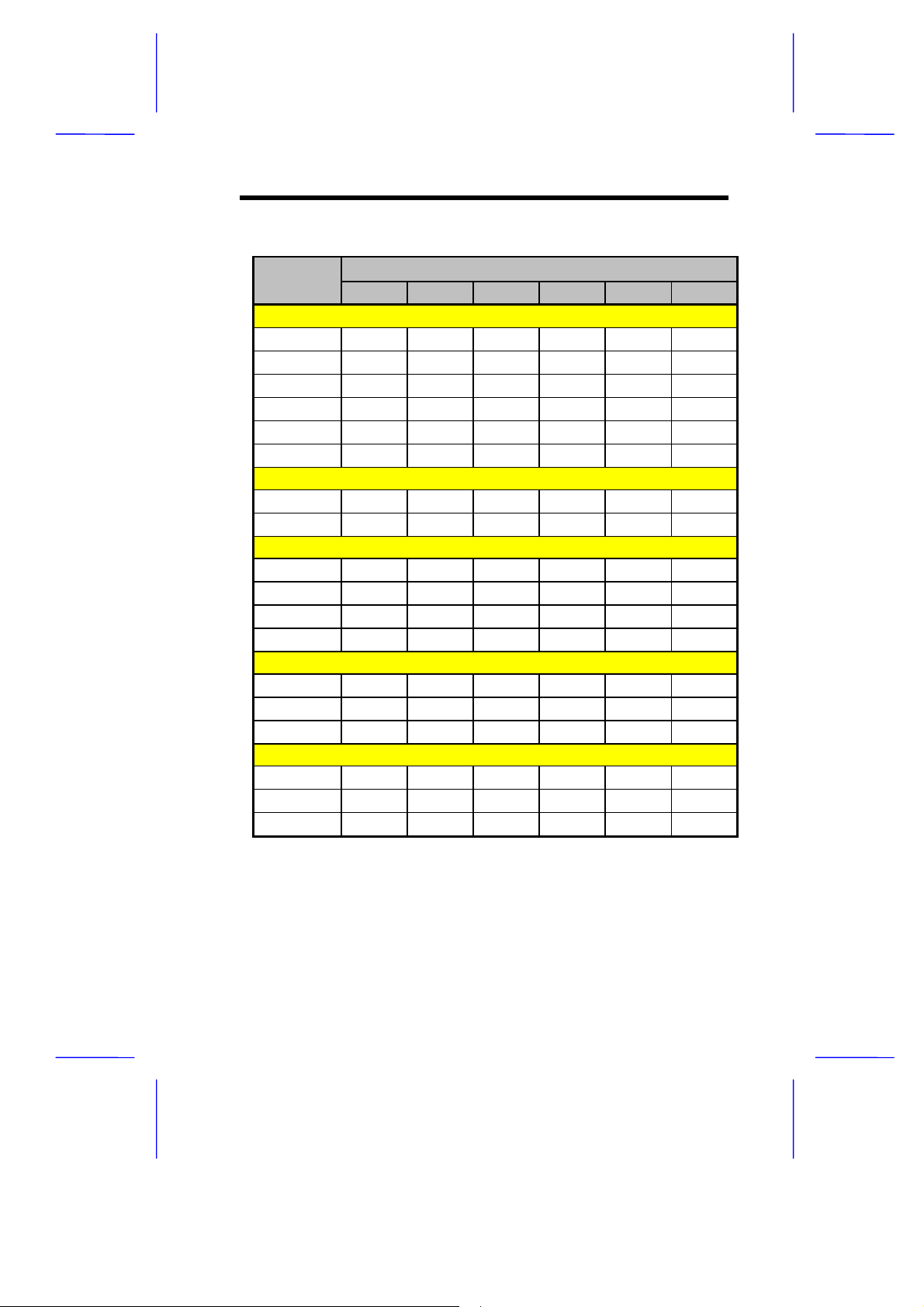
Table 1-2 CPU Type Selection
Jumper
CPU
Pentium
P-100 3-6 ON 1-2 1-2 1-2 1-2
P-120 2-5 ON 1-2 1-2 1-2 2-3
P-133 3-6 ON 1-2 1-2 1-2 2-3
P-150 2-5 ON 1-2 1-2 2-3 2-3
P-166 3-6 ON 1-2 1-2 2-3 2-3
P-200 3-6 ON 1-2 1-2 2-3 1-2
Pentium ODP/MMX
166 3-6 OFF 1-2 1-2 2-3 2-3
200 3-6 OFF 1-2 1-2 2-3 1-2
AMD K5
PR120 2-5 ON 1-2 1-2 1-2 1-2
PR133 3-6 ON 1-2 1-2 1-2 1-2
PR150 2-5 ON 1-2 1-2 1-2 2-3
PR166 3-6 ON 1-2 1-2 1-2 2-3
Cyrix/IBM 6x86
P120+ 1-4 ON 1-2 1-2 1-2 2-3
P150+ 2-5 ON 1-2 1-2 1-2 2-3
P166+ 3-6 ON 1-2 1-2 1-2 2-3
Cyrix/IBM 6x86L
P120+ 1-4 OFF 1-2 1-2 1-2 2-3
P150+ 2-5 OFF 1-2 1-2 1-2 2-3
P166+ 3-6 OFF 1-2 1-2 1-2 2-3
JP8 JP9 JP13 JP14 JP15 JP17
System Board 1-9
Page 10

1.2.3 Connector Functions
Table 1-3 lists the differ ent connectors on the system board and their
respective functions.
Table 1-3 Connector Functions
Connector Function
CN1 Video port
CN3 Fax/modem/voice-in connector
CN4 Audio I/O board connector
CN5 Line-in for AMC connector
CN6 Slot board connector
CN7 ATI media connector
CN8 CD-in connector
CN10 WaveTable connector
CN11 IDE 1 connector
CN12 IDE 2 connector
CN13 Power connector
CN14 Software shutdown connector
CN15 Active/LED connector
CN17 Reset/LED connector
CN18 IrDA connector (optional)
CN20 FDD/HDD LED connector
CN21 Power switch connector
FD1 Diskette drive connector
FN1 CPU fan connector
1-10 User’s Guide
Page 11

Figure 1-8 shows the cables you can connect to the multifunction
connector CN17.
Suspend Switch
Power LED
Figure 1-8 20-pin Reset/LED Connector (CN17)
1.3 ESD Precautions
Always observe the following electrostatic discharge (ESD)
precautions before installing a system component:
1. Do not remove a component from its antistatic packaging until
you are ready to install it.
2. Wear a wrist grounding strap before handling electronic
components. Wrist grounding straps are available at most
electronic component stores.
Do not attempt the procedures described in
the following sections unless you are a
qualified technician.
System Board 1-11
Page 12

1.4 Memory Upgrade
The system board comes with four 72-pin SIMM soc kets that support
4-MB and 16-MB single-density SIMMs and 8-MB and 32-MB doubledensity SIMMs. Table 1-4 lists the possible 64-bit memory
configurations.
Table 1-4 Memory Configurations (64-bit)
Bank 0 Bank 1 Total
SIMM-1 SIMM-2 SIMM-3 SIMM-4 Memory
4 MB 4 MB 8 MB
4 MB 4 MB 8 MB
8 MB 8 MB 16 MB
8 MB 8 MB 16 MB
4 MB 4 MB 4 MB 4 MB 16 MB
4 MB 4 MB 8 MB 8 MB 24 MB
8 MB 8 MB 4 MB 4 MB 24 MB
8 MB 8 MB 8 MB 8 MB 32 MB
16 MB 16 MB 32 MB
16 MB 16 MB 32 MB
4 MB 4 MB 16 MB 16 MB 40 MB
16 MB 16 MB 4 MB 4 MB 40 MB
8 MB 8 MB 16 MB 16 MB 48 MB
16 MB 16 MB 8 MB 8 MB 48 MB
16 MB 16 MB 16 MB 16 MB 64 MB
32 MB 32 MB 64 MB
32 MB 32 MB 64 MB
4 MB 4 MB 32 MB 32 MB 72 MB
32 MB 32 MB 4 MB 4 MB 72 MB
8 MB 8 MB 32 MB 32 MB 80 MB
32 MB 32 MB 8 MB 8 MB 80 MB
16 MB 16 MB 32 MB 32 MB 96 MB
32 MB 32 MB 16 MB 16 MB 96 MB
32 MB 32 MB 32 MB 32 MB 128 MB
1-12 User’s Guide
Page 13

The system also supports 32-bit m emory configurations . This feature
allows you to install only one SIMM in a bank or in a configuration.
Table 1-5 shows the 32-bit configurations.
Table 1-5 Memory Configurations (32-bit)
Bank 0 Bank 1 Total
SIMM-1 SIMM-2 SIMM-3 SIMM-4 Memory
*
4 MB
4 MB 4 MB 4 MB 12 MB
4 MB 4 MB 8 MB 16 MB
4 MB 4 MB 16 MB 24 MB
4 MB 4 MB 32 MB 40 MB
8 MB* 8 MB
8 MB 8 MB 4 MB 20 MB
8 MB 8 MB 8 MB 24 MB
8 MB 8 MB 16 MB 32 MB
8 MB 8 MB 32 MB 48 MB
16 MB* 16 MB
16 MB 16 MB 4 MB 36 MB
16 MB 16 MB 8 MB 40 MB
16 MB 16 MB 16 MB 48 MB
16 MB 16 MB 32 MB 64 MB
32 MB* 32 MB
32 MB 32 MB 4 MB 68 MB
32 MB 32 MB 8 MB 72 MB
32 MB 32 MB 16 MB 80 MB
32 MB 32 MB 32 MB 96 MB
4 MB
*
May also be installed in SIMM-2, SI MM-3, or SIMM-4.
System Board 1-13
Page 14

1.4.1 Installing a SIMM
Follow these steps to install a SIMM:
1. Carefully slip a SIMM at a 45° angle into a socket making sure
that the curved edge indicating the pin 1 of the SIMM matches
pin 1 of the socket.
A SIMM fits only in one direction. If you slip
in a SIMM but would not completely fit, you
may have inserted it the wrong way. Reverse
the orientation of the SIMM.
2. Gently push the SIMM to a vertical position until the pegs of the
socket slip into the holes on the SIMM, and the holding clips lock
the SIMM into position. The SIMM should be at a 90° angle when
installed.
1
Pin 1 Indicator
(curved edge)
Figure 1-8 Installing a SIMM
1-14 User’s Guide
2
Peg
Hole
Page 15

1.4.2 Removing a SIMM
Follow these steps to remove a SIMM:
1. Press the holding clips on both sides of the SIMM outward to
release it.
2. Move the SIMM to a 45° angle.
3. Pull the SIMM out of the socket.
Holding Clip
1
3
2
Figure 1-9 Removing a SIMM
Always remove SIMMs from the socket
labeled SIMM-4, then SIMM-3, and so on.
System Board 1-15
Page 16

1.4.3 SIMM Type Selection
When selecting SIMMs to install, mak e sure to take note of the height
limitations of the slot board installed in the system.
Table 1-6 shows the SIMM height limitations for the different slot
boards.
Table 1-6 SIMM Height Limitations
Slot Board SIMM Height Limit
Aspire Desktop and AcerBasic 23.3 mm
Aspire Minitower 28.8 mm
ID2PN and ID2M 21.8 mm
IDABN 26.8 mm
1-16 User’s Guide
Page 17

1.4.4 Reconfiguring the System
You must enter Setup after installing or removing SIMMs to
reconfigure the system.
Follow these steps to reconfigure the system:
1. Turn the system on. A memory error message appears,
indicating that the total memory does not match the value stored
in CMOS.
2. Press
appears indicating an incorrect memory configuration.
3. Press
The system boots with the new memory configuration.
+ + to enter Setup. A warning message
twice to exit and reboot the system.
1.5 IDE Hard Disk Support
The system board supports four IDE hard disks, or any other IDE
devices, through the two onboard PCI IDE interfaces. See Figure 1-1
for the location.
Follow the instructions in the housing installation manual on how to
install a hard disk in the system. Connect the c ables according to the
IDE hard disk configuration in Table 1-7.
Table 1-7 IDE Hard Disk Configuration
IDE Connector Master Slave
Channel 1 Hard disk 0 Hard disk 1
Channel 2 Hard disk 2 Hard disk 3
System Board 1-17
Page 18

1.6 CPU Installation
The system board com es with a zero-insertion for ce ( ZIF) CPU s ock et
for easy installation.
Follow these steps to install a Pentium CPU:
1. Lift up the socket lever.
2. Insert the CPU to the socket. Mak e sure that the notched corner
of the CPU matches the pin 1 indicator on the socket.
Be careful not to bend any pins.
3. Pull down the socket lever.
STEP 1
Notched Corner
STEP 2
STEP 3
Pin 1 Indicator
Figure 1-10 Installing a Pentium CPU
4. Set the CPU jumpers accordingly. Refer to Table 1-1.
1-18 User’s Guide
Page 19

1.7 Video Memory Upgrade
Larger video memory allows you to display higher resolutions and
more colors. The system board comes with a 1-MB video memory
onboard upgradable to 2 MB.
1.8 Second-level Cache Configuration
The system board supports 256-KB or 512-KB pipeline bur st secondlevel cache. Table 1-8 shows the sec ond-level cache configurations.
Note that the cache is mounted onboard and not user-upgradable.
Table 1-8 Second-level Cache Configurations
Cache Size Data SRAM Type Tag SRAM Type
256 KB onboard 7 ns 32K * 32 x 2 15 ns 32K * 32 x 1
512 KB onboard 7 ns 32K * 32 x 2 15 ns * 8K 15 ns x 1
System Board 1-19
Page 20

1.9 Audio Features
4
The system board supports a audio features compatible with Sound
Blaster, Sound Blaster Pro, and Windows Sound System. It has
connectors onboard to accommodate the audio-I/O board,
WaveTable, CD-ROM, and fax-voice modem.
You may disable the audio feature in the
BIOS Utility.
1.9.1 Installing the Audio-I/O Board
The connector CN4 on the system board acc ommodates the audio- I/O
board. Figure 1-11 shows how to install the board.
CN
Figure 1-11 Installing the Audio-I/O Board
1-20 User’s Guide
Page 21

1.9.2 Audio-I/O Board Features
The audio-I/O board consists of microphone port, line-in port, line-out
port, and MIDI/game port. These ports accommodate the external
audio devices.
Microphone Port
Line-in Port
Line-out Port
MIDI/Game Port
Figure 1-12 Audio-I/O Board
The internal connectors on the audio-I/O boar d are useful for s ystem
housings with built-in speakers, microphone, amplifier, or auxiliary
devices. With the internal audio c onnectors func tioning exactly as the
external audio ports, you can utilize all the sound features supported
by the system board.
Since external speakers, microphone, and other audio devices give
better sound quality, the external audio ports take higher priority than
the internal connectors. When you attach external audio devices to
the ports, the internal audio devices are automatically disabled.
System Board 1-21
Page 22

1.9.3 WaveTable Daughterboard (Optional)
4
0
The system board supports a WableTable
daughterboard as option. The WaveTable
does not come with the basic system.
The WaveTable daughterboard supports the same external
connectors as the audio-I/O board but comes with enhanced audio
features. It bundles chipsets that work together to produce better
sound quality.
Figure 1-13 shows the WaveTable installation.
CN1
CN
Figure 1-13 WaveTable Daughterboard
1-22 User’s Guide
Page 23

1.9.4 Audio-I/O Devices
Figure 1-14 shows the various devices that you can connect to the
audio-I/O board.
Joystick
Synthesizer
MIDI Adapter
Speakers
Microphone
Figure 1-14 Audio I/O External Devices
Head phones
Stereo Amplifier
CD Player
System Board 1-23
Page 24

1.10 QuickStart Power Saving Feature
(for Aspire models only)
The system board supports a special power saving feature called
QuickStart mode. QuickStart turns off the hard disk, monitor,
keyboard, and mouse once you press the power switch for less than
four seconds while the system is on.
This feature requires the Power Saving
Operation Mode parameter in the BIOS to be
QuickStart
set to
information on the setting description.
1.10.1 QuickStart Mode Operation
At any time while the system is running, enter the Quick Start mode by
simply pressing the power switch for less the four seconds. This
action causes the system to rest ( Quick Start state 1) by turning off the
keyboard, mouse, and monitor. After the specified time in the
QuickStart State Timer parameter in BIOS, the system sleeps
(QuickStart state 2) and turns off the hard disk.
Once the system enters Quick Star t mode, the hard disk/m es sage LED
and keyboard LED go off, while the power and monitor LEDs start
blinking.
. See Chapter 2 for more
When a mess age comes, the hard disk/message LED star ts blinking
orange, then green when the hard disk reads the message. After
getting the message, the hard disk and the LED go off again.
Press the power switch again for less than f our seconds to return to
the normal mode.
To enter or exit the QuickStart mode, make
sure to press the power switch within four
seconds. Pressing it for more than four
seconds turns off the system.
1-24 User’s Guide
Page 25

1.11 Installing ISA Cards
Both PnP and non-PnP ISA cards require specific IRQs. When
installing ISA cards, mak e sure that the IRQs required by these c ards
are not previously assigned to PCI devices to avoid resource conflicts.
Follow these steps when installing ISA cards:
1. Remove all PnP cards installed in the system, if any.
2. Install non-PnP ISA cards.
3. Turn on the system.
4. Use Windows 95 or ICU to m anually assign the appropriate IRQs
to the cards. This ensures that BIOS will not use the resources
assigned to the non-PnP ISA cards.
BIOS detects and configures only PnP cards.
5. Turn off the system.
6. Install PnP ISA and PCI cards.
7. Turn on the system. This time PnP BIOS automatically configures
the PnP ISA and PCI cards with the remaining free IRQs.
System Board 1-25
Page 26

1.12 Error Messages
Do not continue using the computer if you receive an error m es sage of
any type. Note the message and take corrective action. This sec tion
explains the different types of error messages and corresponding
corrective measures.
There are two general types of error messages:
Software
•
System
•
1.12.1 Software Error Messages
Software error messages are returned by your operating system or
application. These messages typically occur after you boot the
operating system or when you run your applications. If you receive
this type of message, consult your application or operating system
manual for help.
1.12.2 System Error Messages
A system error message indicates a pr oblem with the computer itself .
A message of this type normally appears during the power-on self-test,
before the operating system prompt appears.
Table 1-9 lists the system error messages.
1-26 User’s Guide
Page 27

Table 1-9 System Error Messages
Message Action
CMOS Battery Error Replace the RTC chip or
contact your dealer.
CMOS Checksum Error Check the RTC chip and the
necessary jumper. If the
battery is still good, run Setup.
Display Card Mismatch Run Setup
Diskette Drive Controller Error
or Not Installed
Diskette Drive Error Diskette may be defective. If
Diskette Drive A Type
Mismatch
Diskette Drive B Type
Mismatch
Equipment Configuration Error Modify the memory
Hard disk Controller Error Run Setup.
Hard disk 0 Error Check all cable connections.
Hard disk 1 Error Check all cable connections.
Keyboard Error or No
Keyboard Connected
Keyboard Interface Error Replace the keyboard or
Check and connect the control
cable to the diskette
controller.
not, replace the diskette drive.
Run Setup and select the
proper drive type.
Run Setup and select the
proper drive type.
configuration to agree with
one of the options in Tables
1-3 or 1-4.
Replace hard disk.
Replace hard disk.
Check and connect the
keyboard to the system unit.
contact your dealer.
System Board 1-27
Page 28

Table 1-9 System Error Messages (continued)
Message Action
Memory Error at:
MMMM:SSSS:OOO
(W:XXXX, R:YYYY)
where:
M: MB, S: Segment,
O: Offset, X/Y: write/read
pattern
CPU Clock Mismatch Run Setup. Check if the CPU
Onboard Serial Port 1
Conflict
Onboard Serial Port 2
Conflict
Onboard Parallel Port Conflict Run Setup and disable the
Pointing Device Error Check and connect pointing
Pointing Device Interface
Error
Press key to continue or
+ + for Setup
Real Time Clock Error Check the RTC chip. If it is still
Check SIMMs on the system
board. Contact your dealer.
clock is correct. If correct, exit
Setup and reboot the system.
If the error message reappears,
ask for technical assistance.
Run Setup and disable the
port.
Run Setup and disable the
port.
port.
device.
Replace the pointing device or
contact your dealer.
Press
to enter Setup.
good, run Setup. If not, replace
the RTC chip.
or + +
1-28 User’s Guide
Page 29

1.12.3 Correcting Error Conditions
As a general rule, if an error message says "Press F1 to continue," it is
caused by a configuration problem, which can be easily corrected. An
equipment malfunction is more likely to cause a fatal error, i.e., an
error that causes complete system failure.
Here are some corrective measures for error conditions:
1. Run Setup. You must know the correct configuration values for
your system before you enter Setup, which is why you should
write them down when the system is correctly configured. An
incorrect configuration is a major cause of power-on error
messages, especially for a new system.
2. Remove the system unit cover. Check that the jumpers on the
system board and any expansion boards are set correctly.
3. If you cannot access a new disk, it m ay be because your disk is
not properly formatted. Format the disk fir st using the FDISK and
FORMAT commands.
4. Check that all connectors and boards are securely plugged in.
If you go through the corrective steps above and still receive an error
message, the cause may be an equipment malfunction.
If you are sure that your configuration values are correct and your
battery is in good condition, the problem may lie in a damaged or
defective chip.
In both cases, contact an authorized service center for assistance.
System Board 1-29
 Loading...
Loading...