Page 1

IPitomy 1000 User Guide
Page 2

Page 3

Table of Contents
Introduction ..........................................................................................................................................1
About the IPitomy 1000 .....................................................................................................................1
Benefits of VoIP Technology ............................................................................................................. 1
How This Guide Works ....................................................................................................................... 2
Web-based System Setup.................................................................................................................2
The Installation Worksheet................................................................................................................ 2
Product Overview ................................................................................................................................ 3
IPitomy 1000 Components ................................................................................................................ 3
Powerful All-In-One Communications Platform............................................................................ 3
Entering System Information ............................................................................................................. 3
System Administration ....................................................................................................................... 4
System Overview ...............................................................................................................................5
Icon System .................................................................................................................................... 5
Extensions ...................................................................................................................................... 5
Groups ............................................................................................................................................5
Automated Attendant (Menu) ........................................................................................................5
Advanced Routing Functions ........................................................................................................5
Voicemail and Unified Messaging .................................................................................................5
Directory .......................................................................................................................................... 5
Direct Inward Dialing (DID) Numbers ........................................................................................... 6
Conferencing (Meet Me) ................................................................................................................ 6
Forwarding Gateway ......................................................................................................................6
Voicemail Gateway ........................................................................................................................6
Branch Offices ................................................................................................................................ 6
Supported IP Phone Sets .................................................................................................................. 6
Before Getting Started ........................................................................................................................7
Connecting the System .....................................................................................................................7
Hardware Setup.............................................................................................................................. 7
Connecting the Phone Lines and FAX Machines ........................................................................7
System Requirements ....................................................................................................................... 10
Network Requirements ....................................................................................................................10
IP Addresses ....................................................................................................................................10
Service Providers ............................................................................................................................. 10
System Administration .....................................................................................................................12
About the Administration Menu .......................................................................................................12
Log In ................................................................................................................................................13
Page 4

Networking ........................................................................................................................................ 13
TCP/IP Settings ............................................................................................................................14
DDNS ............................................................................................................................................18
MAC Clone....................................................................................................................................20
Routes ...........................................................................................................................................20
Security .........................................................................................................................................22
Application Forwarding ................................................................................................................27
Administration ...............................................................................................................................34
Analog Interface ...........................................................................................................................40
Providers...........................................................................................................................................45
CO Trunks.....................................................................................................................................45
SIP Providers................................................................................................................................46
Destinations ......................................................................................................................................50
Extensions .................................................................................................................................... 51
Groups ..........................................................................................................................................69
Menus............................................................................................................................................73
Meet-me Conferences ................................................................................................................. 77
Voicemail ...................................................................................................................................... 79
Schedules ..................................................................................................................................... 80
Branch Offices ..............................................................................................................................83
Call Routing ......................................................................................................................................85
Incoming Routing .........................................................................................................................85
Outgoing Routing .........................................................................................................................86
PBX Setup ........................................................................................................................................88
General .........................................................................................................................................88
Database....................................................................................................................................... 89
Voicemail ...................................................................................................................................... 90
Session Initiation Protocol (SIP) Settings ...................................................................................92
Prompts.........................................................................................................................................93
Music on Hold ...............................................................................................................................94
Feature Codes .............................................................................................................................. 96
Services ........................................................................................................................................96
Reports .............................................................................................................................................96
CDR Reports ................................................................................................................................96
Diagnostics ...................................................................................................................................97
Monitoring .....................................................................................................................................97
Appendices ......................................................................................................................................... 99
Page 5

Appendix 1: IP Telephones ............................................................................................................100
IPitomy 480i....................................................................................................................................100
IPitomy 9133i..................................................................................................................................100
IPitomy 9112i..................................................................................................................................100
IPitomy 480i CT..............................................................................................................................101
IPitomy 53i ......................................................................................................................................101
IPitomy 55i ......................................................................................................................................101
IPitomy 57i ......................................................................................................................................102
IPitomy 57i CT ................................................................................................................................102
IPitomy 536M .................................................................................................................................102
IPitomy 560M .................................................................................................................................103
CounterPath™ eyeBeam® 1.5 and X-Lite® 3.0 ............................................................................103
What is a Softphone?................................................................................................................. 103
X-Lite® 3.0 Free Softphone........................................................................................................103
eyeBeam® 1.5 (Pricing available at www.counterpath.com) ...................................................103
Appendix 2: Troubleshooting........................................................................................................108
Glossary ............................................................................................................................................109
Page 6

Introduction
About the IPitomy 1000
The IPitomy 1000 is a powerful business communications platform. It is a pure IP PBX designed
to use IP networks for voice calls. Engineered to support from 10 to 150 users, the system will
work with analog lines and T1 /PRI lines for traditional Public Switched Telephone Network
(PSTN) connectivity. In addition to traditional telephone lines, the IPitomy 1000 can use VoIP
service providers like IPitomy Exchange, replacing traditional PSTN lines with a broadband
connection.
Benefits of VoIP Technology
The IPitomy 1000 can support any or all of these connectivity methods simultaneously or in any
combination. Customers not quite ready to depend on VoIP providers for all of their business
communications can start at their own pace and gain a comfort level, shifting to VoIP broadband
providers at their own pace. Benefits of VoIP technology include:
One Wiring System The system uses a single wiring system for telephones and
dataall data and voice are on Local Area Network (LAN) Category 5 wiring.
Web-based Administration System administration is performed on the network
through a Web-based administration program.
Remote Users When calls are routed over the Internet, long distance charges can
be avoided. In businesses with remote workers, these employees can stay logged
into the office through a broadband connection at all times without incurring any
additional charges.
Centralized System Features Every extension that is logged into the system is
capable of receiving and originating calls. The use of system features such as
voicemail, automated attendant and email are all centralized simplifying all support
and maintenance.
Reduced Costs VoIP system users can reduce cost in many areas of a business.
VoIP telephony lowers the cost of support and maintenance costs, as well as,
reducing telephony line costs by up to 50%.
Simplifies Administration Moves, adds and changes are simple. The IPitomy
1000 provides enhanced capabilities for users to make changes without incurring a
service call.
Investment Protection VoIP, and in particular, Session Initiation Protocol (SIP)-
based VoIP products offer investment protection. The industry is rapidly moving
toward Internet Protocol (IP) communications technologies. Older digital and analog
technologies are becoming obsolete and are being replaced with IP-based products
that will be around for a long time.
Copyright IPitomy Communication, LLC 1 0007VRF
Page 7

How This Guide Works
Web-based System Setup
This is a Reference Guide designed to help you install and use the IPitomy 1000. Each section of
the guide provides easy-to-follow instructions regarding installation of the system. Within each
section of the Reference Guide you will find:
Step-by-Step Instructions – Use these easy-to-follow steps as part of any system
implementation.
Advanced Settings – These options are settings for handling some of the more
sophisticated capabilities of the IPitomy 1000.
Installation Notes – These business scenarios and tips describe applications where
or when a specific feature might be used.
Quick Reference – These are tips about completing fields throughout the
administration of the IPitomy 1000. Just move your mouse over the
description of the field pops up.
The Installation Worksheet
Use the IPitomy 1000 Installation Worksheet to make collecting information used in the
implementation of the system simple. This Worksheet can be downloaded from IPitomy.com in
the Dealer Section of the site.
and a brief
Copyright IPitomy Communication, LLC 2 0007VRF
Page 8

Product Overview
IPitomy 1000 Components
Understanding the IPitomy 1000’s architecture and how it works will make installing the system
simple.
Powerful All-In-One Communications Platform
The IPitomy 1000 IP PBX (Diagram 1) is an all-in-one business communications system.
This powerful system includes a complete suite of business communication applications
in one appliance:
Fully-featured Business Phone System
Automated Attendant and IVR
Enhanced Call Distribution
Enhanced Voice Messaging System with Unified Messaging
Meet-me Conference Application
Built-in Music on Hold
Call Queuing for Inbound Calls
Remote Extensions
Browser-based Administration
Branch Offices
Full Featured Router
Entering System Information
The system is configured by entering information into the appropriate fields on the menu screens.
External data sources such as CSV files or network scans can optionally be used to enter
extension data. Some fields are populated with data that is entered other fields are completed by
selecting from data presented in a drop-down menu. Drop-down menus are populated by
completing information in other sections of the system. To simplify system setup it is
recommended that information be entered in the following order:
Extensions
Groups
Menus
Providers
Entering information in this sequence will reduce the time it takes to up the system:
Extensions will be populated in the drop-down menus for creating groups.
Copyright IPitomy Communication, LLC 3 0007VRF
Page 9

Groups and extensions will be populated for creating automated attendant (menu)
routing.
Destinations will be populated for use in setting up providers and hardware trunks.
System Administration
IPitomy 1000’s administration menus are a series of Web pages accessible from a Web browser.
To the left of the Menu is a navigation bar that allows users to click on and administer each
section of the system. Administration of the IPitomy 1000 is simple and intuitive. The system is
designed with six primary areas of functionality.
System System setup consists of network configuration settings.
Providers Providers are sources of PSTN and VoIP connectivity. Providers are the
lines that handle all incoming and outgoing calls. All VoIP and traditional telephone
providers are setup here. DID numbers are also entered here.
Destinations Destinations are places where calls get routed in the system:
extensions, groups of extensions, automated attendants, conferences and voicemail.
Call Routing These settings route inbound calls to specific destinations within the
system, and send outbound calls over specific local, long distance, international and
emergency routes.
PBX Setup These settings globally configure PBX timers, voice messaging and
other system features.
Reports These reports display system usage, monitor activity and provide
diagnostic information.
Copyright IPitomy Communication, LLC 4 0007VRF
Page 10

System Overview
The system is designed to be quick to setup and install. Using the Installation Worksheet to
organize system information and plan the application in advance will reduce the time it takes to
install the system. Most businesses will have some common communication needs. The system
is organized based on these common needs.
Icon System
- Edit main settings. - Edit an extension’s phone settings.
- Delete an item from the system.
- Restore a file to the system.
- Download a file from the system.
Extensions
Extensions are telephones. A telephone can be an IP (SIP)-telephone or a Softphone.
Calls are routed to an extension where people answer them. In the IPitomy 1000, an
extension can be located in an office or outside the office when a broadband connection
is used.
Groups
Groups are a set of extensions. Once a group is created, extensions can be designated
members of the group. This is accomplished by selecting group members from a dropdown list. Calls can be routed to groups by using the Group function.
Automated Attendant (Menu)
To create an automated attendant use the system’s Menu function. The Menu function
routes calls to a destination in the system like a group, extension or another menu.
Destinations are selected from a drop-down list for each corresponding key-pad digit a
caller must select to get to their chosen destination. A Menu must have a Menu Prompt.
This is a recording that identifies for callers the destinations they may choose. For
example, a Menu Prompt might offer callers the option to press “1” for Sales, “2” for
Accounts Receivable or other digits for another department.
Advanced Routing Functions
When building an automated attendant (menu) all routable destinations in the system will
appear in the drop-down menu. In addition to the destinations that are created while
configuring the system, there are several advanced functions that can be used from the
drop-down list.
Voicemail and Unified Messaging
When an extension is created, a voicemail box for that extension is also created. A
voicemail box allows a caller to leave a message if a person is not available at the
extension. When dialing into a mailbox for the first time, a user must record their name
and a mailbox greeting. The name is used in the company’s dial-by-name directory when
selected from the auto attendant (menu). The greeting is played when they are not
available to take a call and a caller reaches their mailbox.
If an email address is included in the Extension page, a copy of the voicemail message
will be emailed as a .Wav file to the users email account. This message can then be
listened to on a PC.
Directory
The system has a dial-by-name directory. This option may be part of the automatedattendant. When this option is selected, a caller dials the first three letters of the last / first
Copyright IPitomy Communication, LLC 5 0007VRF
Page 11

name of the party they would like to reach. Names that match these three letters are
played and the caller selects the extension to which they want to be transferred. Names
are stated in the directory as they have been recorded by users in their voicemail box.
Direct Inward Dialing (DID) Numbers
A Direct Inward Dialed (DID) number is a telephone number assigned by a service
provider (i.e., T1 line, PRI or VoIP). DIDs allow direct routing of a call to a destination
within the system. This can be an individual extension, group, conference or menu.
Conferencing (Meet Me)
A Meet-me Conference is an extension on the system used for conference calls.
Participants of a conference can access a conference by dialing the designated Meet-me
Conference extension. Routing callers to a Meet-me Conference can be accomplished by
using a DID, a menu, or simply transferring callers to the conference extension.
Forwarding Gateway
Mobility has become a part of everyday life for most people. System users need to be
able to take calls anywhere. The IPitomy 1000 has the ability to forward calls. Users can
turn call forwarding “on” and “off” while in the office or away from the office by using a
touch-tone key pad. This is setup in the Extensions setup page, but can be modified from
any phone, including a cell phone. Modifying forward settings remotely requires the
automated attendant (menu) option to be programmed.
Voicemail Gateway
From the automated attendant (menu), users can call in from any telephone and check
messages. The voicemail gateway allows users to dial a pre-defined digit from a touchtone key pad on any phone to retrieve their messages.
Branch Offices
Branch offices can be created to allow multiple PBXs to route calls to each other. Branch
office extensions can be transferred to, or placed in ring groups, or selected as menu
destinations.
Supported IP Phone Sets
The IPitomy 1000 works with a variety of business-grade IP phone sets. See Appendix 1: IP
Telephones for a complete list.
Copyright IPitomy Communication, LLC 6 0007VRF
Page 12

Before Getting Started
Panning before getting started will make the setup and installation of the IPitomy 1000 simple.
IPitomy has created an Installation Worksheet to assist in recording business and system
information used in planning system setup and installation. This Checklist can be downloaded
from IPitomy.com in the Dealer Section of the Web site.
Connecting the System
Hardware Setup
The IPitomy 1000 comes assembled and ready to install. The system requires connection
to the PSTN for analog or T1 lines. It requires telephones to be connected to the local
area network (LAN). Broadband access must also be established for VoIP connectivity
(allowing remote extensions and remote management).
Connecting the Phone Lines and FAX Machines
The IP1000 is equipped to support analog, gateway or SIP connections. Analog lines are
connected with internal hardware resources. A gateway connects analog telephone lines
by registering itself as a SIP provider over the LAN. SIP providers create a direct
connection to the system.
Embedded Analog Phone Ports
The IP1000 has analog phone ports and analog line ports embedded on board:
Two Analog Phone Ports The IP1000 has two analog phone ports embedded on
board for connectivity to FAX machine, analog phones or cordless phones with FXS
interfaces.
Two Analog Line Ports The IP1000 has two analog line ports embedded on board
for PSTN connectivity.
Copyright IPitomy Communication, LLC 7 0007VRF
Page 13

Expandable Analog Line/Phone Card
The IP1000 equipped an expansion slot:
Analog Line Card This card supplies four analog lines to expand the PSTN
connectivity. The card supporting these connections is already installed and
completely configured. Simply connect the phone lines to the RJ11 jacks at the rear
of the IP1000 and start making calls. These connections are single pair; one line per
jack.
Connecting Using an External Gateway
PSTN lines are connected to a Gateway device. The gateway device is connected to the
LAN. The Gateway is then registered as a SIP provider in the system.
Connecting Using SIP Providers
Once connected to the LAN, the LAN's broadband connection provides a pathway for SIP
VoIP Providers. Use the SIP Provider pages to setup a connection.
Connecting Telephones
Copyright IPitomy Communication, LLC 8 0007VRF
Page 14

Connecting to a LAN
Copyright IPitomy Communication, LLC 9 0007VRF
Page 15

System Requirements
Network Requirements
Making preparations for the network in advance will assure there are no surprises. If you are
going to have remote extensions, you will need access to the router to setup a network address
translation (NAT) and port forwarding.
A LAN with a broadband connection is required for operation of the system. It is must be on fast
Ethernet (100baseT or better). The system must also use Ethernet data switches. The router
inside IP1000 can use DHCP or not, depending on preference. If IP1000 is connected to Internet
through broadband modem, use PPPoE for connection to Internet and use DHCP server for local
network is recommended.
IP Addresses
It is important to know the LAN configuration and IP addresses of the specific network the system
is becoming a part of to make installation of the IP1000 simple. The IP1000 is required to have a
fixed (static) IP address. To get the information about public IP check the network administrator.
By default, the IP address used by IP1000’s router for local network is 192.168.1.1. The devices
including PC, IP phones and other network devices will get IP address from IP1000’s DHCP
server and those IP addresses will be 192.168.1.xxx. To connect to IP1000 by PC in local
network for changing system settings or monitoring system’s status, login to IP1000 with IP
address 192.168.1.1. The public IP address used for IP1000 to connect to Internet can also be
viewed from IP1000’s web management pages.
Service Providers
In order to provision the IP1000 it is necessary to know the type of Service Providers being used.
Carrier and SIP are the most common service providers. Carriers provide Plain Old Telephone
Service (POTS). SIP Providers route voice calls over the Internet. This is called voice over
Internet protocol or VoIP.
Copyright IPitomy Communication, LLC 10 0007VRF
Page 16

As part of the installation it will be important to know the:
Name of Providers
Type of Service Provided (i.e., POTS or SIP)
Phone Numbers Associated with the Service
Password and Login Information for SIP Service
Record this information on the IP1000 Installation Worksheet.
Copyright IPitomy Communication, LLC 11 0007VRF
Page 17

System Administration
About the Administration Menu
IP1000’s online administration makes it simple to meet the demands of a frequently changing
business. It is also designed to be quick to setup and install. The Administration Menu is
located in the Navigation Bar to the left of the page. This menu contains the administration
pages used to configure the system. The Administration Menu is divided into six sections. To
navigate to an Administration Page click on the menu section and page to be changed.
Networking Networking setup consists of network configuration settings.
Providers Providers are sources of PSTN and VoIP connectivity. Providers are the
lines that handle all incoming and outgoing calls. All VoIP providers will be setup
here. DID numbers are also entered here.
Destinations Destinations are extensions, groups of extensions, automated
attendants (menus), conferences and voicemail. Destinations are places where calls
get routed to in the system.
Call Routing Routing sends callers to specific inbound destinations within the
system, and routing outbound callers over specific outbound routes like local, long
distance, international and emergency.
PBX Setup System settings allow global configuration settings for system
applications like PBX timers, voice messaging settings.
Reporting The system displays usage reports, diagnostic information and monitors
system activity.
Each Online Administration page also contains:
Title Bar – The Title Bar at the top of each page displays the name of the section of
the Administration Menu which is currently being edited.
Default Values – When the system is installed it automatically registers default
values in many of the administration fields. This simplifies the implementation
process.
Save Changes – Located in the bottom left corner of the screen, this button saves
changes to the page currently being administered. This button must be pressed
before leaving a page or changes will be lost.
Apply Changes – To apply changes to the system you must click the Apply
Changes button. Located in the top right corner of the screen, this button globally
applies changes to the system.
Edit – To make changes to an existing administration page click
Add New – The Add New button creates another destination, provider, route or
Copyright IPitomy Communication, LLC 12 0007VRF
Edit.
Page 18

schedule. For example, to add a new extension, click the Add New button on the
extension administration page.
Advanced – In several sections of the online administration there is an Advanced
button where the most sophisticated capabilities of the IPitomy 1000 can be
configured. The Advanced button is located on the lower left side of each page.
About Us – Located at the bottom left corner of each page, this link provides
additional information about IPitomy.
Contact Us – The IPitomy team is never more than a call or email away. To contact
an IPitomy team member, click on Contact Us in the lower left corner of the page.
Log In
User Name: pbxadmin
Password: ipitomy
Networking
The System Menu is for setting up network attributes. For example the IP address of the system
and router information.
Copyright IPitomy Communication, LLC 13 0007VRF
Page 19

TCP/IP Settings
The Networking Setup Menu defines the Internet Setup for the system’s hardware. Either
to get IP address through DHCP or PPPoE, or to be assigned by user, the system must
operate using an IP address. The TCP/IP Settings section configures the IP PBX for your
Internet connection type. This information can be obtained from the service provider.
Default values for the IP Address, Subnet Mask, Default Gateway and Static DNS will
appear in the Networking Setup Menu when this administration page is opened.
Copyright IPitomy Communication, LLC 14 0007VRF
Page 20

Setting Internet Connection Type
The IP1000 supports six connection types: Automatic Configuration – DHCP, Static IP,
PPPoE, PPTP, L2TP, and Telstra Cable. Each setup screen and available features will
differ depending on what kind of connection type you select.
Automatic Configuration (DHCP) – By default, the IP1000’s Internet Connection
Type is set to Automatic Configuration (DHCP), and it should be used only if your ISP
supports DHCP or you are connecting through a dynamic IP address.
Static IP – If a permanent IP address is provided then select Static IP. And
settings for following network attributes are required. Contact service provide or
the network administrator for any Information missed.
o Internet IP Address – Normally the static IP address is a public IP address
provided by service provider; it is used for connecting to Internet. If it is a local
IP address assigned by the network administrator; the router function in
IP1000 may need to be disabled.
o Subnet Mask – The subnet mask Information should be provided along
with IP address.
o Default Gateway – The IP address for the default network gateway, it is the
information service provider should provide.
o DNS 1-3 – Service provider will provide at least IP address for one DNS
(Domain Name System) server. At most three DNS servers can be set.
PPPoE –Some DSL service providers use PPPoE (Point-to-Point Protocol over
Copyright IPitomy Communication, LLC 15 0007VRF
Page 21

Ethernet) to establish Internet connections for end-users. If DSL connection to
Internet is using, check service provider for the connection provisioning type. Enable
it if PPPoE is used.
o User Name and Password – Enter the user name and password provided
by service provider. User name and password will be used for
authentication while establishing PPPoE connection.
o Max Idle Time and Connect on Demand – If the connection stay inactive for
over a specific period time (Max Idle Time) the PPPoE connection may be cut
off. Assign 0 to Max Idle Time field will always keep the connection no matter it
is active or not. If Internet connection has been terminated due to inactivity,
automatic re-establishment for Internet connection will be invoked by any
attempt of access to Internet if the Connect on Demand field is checked.
o Keep Alive and Redial Period – If Keep Alive is enabled, system will
periodically check the Internet connection. If the connection is down, then the
system will automatically re-establish the connection. To use this option, click
the radio button next to Keep Alive. The Redial Period is the time period to
trigger system to check the Internet connection; default Redial Period is 30
seconds.
PPTP – Point-to-Point Tunneling Protocol (PPTP) is a service that deployed in
Europe and Israel only.
o Internet IP Address – Normally the static IP address is a public IP address
provided by service provider; it is used for connecting to Internet. This IP
address must be assigned from IP provider.
o Subnet Mask – The subnet mask Information should be provided along
with IP address.
o Default Gateway – The IP address for the default network gateway, it is the
information service provider should provide.
o User Name and Password – Enter the user name and password provided
by service provider. User name and password will be used for
authentication while establishing PPTP connection.
o Max Idle Time – If the connection stay inactive for over a specific period time
(Max Idle Time) the Internet connection may be cut off. Assign 0 to Max Idle
Time field will always keep the connection no matter it is active or not.
o Connect on Demand – If Internet connection has been terminated due to
inactivity, automatic re-establishment for Internet connection will be invoked by
any attempt of access to Internet if the Connect on Demand field is checked.
o Keep Alive and Redial Period – If Keep Alive is enabled, system will
periodically check the Internet connection. If the connection is down, then the
system will automatically re-establish the connection. To use this option, click
the radio button next to Keep Alive. The Redial Period is the time period to
trigger system to check the Internet connection; default Redial Period is 30
seconds.
L2TP –Layer 2 Tunneling Protocol (L2TP) is a service that tunnels Point-to-Point
Protocol (PPP) across the Internet. It is used mostly in European countries. Check
with service provider for necessary setup information.
o Internet IP Address – Normally the static IP address is a public IP address
provided by service provider; it is used for connecting to Internet. This IP
address must be assigned from IP provider.
o User Name and Password – Enter the user name and password provided
Copyright IPitomy Communication, LLC 16 0007VRF
Page 22

by service provider. User name and password will be used for
authentication while establishing PPTP connection.
o Max Idle Time and Connect on Demand – If the connection stay inactive for
over a specific period time (Max Idle Time) the PPPoE connection may be cut
off. Assign 0 to Max Idle Time field will always keep the connection no matter it
is active or not. If Internet connection has been terminated due to inactivity,
automatic re-establishment for Internet connection will be invoked by any
attempt of access to Internet if the Connect on Demand field is checked.
o Keep Alive and Redial Period – If Keep Alive is enabled, system will
periodically check the Internet connection. If the connection is down, then the
system will automatically re-establish the connection. To use this option, click
the radio button next to Keep Alive. The Redial Period is the time period to
trigger system to check the Internet connection; default Redial Period is 30
seconds.
Telstra Cable –Telstra Cable is a service used in Australia only. Check with service
provider for necessary setup information.
o Server IP Address – Normal ly the static IP address is a public IP address
provided by service provider; it is used for connecting to Internet.
o User Name and Password – Enter the user name and password provided
by service provider. User name and password will be used for
authentication while establishing Telstra cable connection.
Optional Settings
Some server providers may require the following settings. Check with the service
provider before making any changes.
Host Name and Domain Name – Some service providers require these names as
identification. You may need to check with service provider to see if it is required. In
most cases, leaving these fields blank will work.
MTU – The MTU (Maximum Transmission Unit) setting specifies the largest packet
size permitted for network transmission. To manually set a value, select Manual and
enter the value desired in the Size field. MTU value should be in the range from 1200
to 1500. Normally the value 1492 is used. The default is Auto, which allows the
system to select the best MTU for your Internet connection.
Router IP
The local IP address and Subnet Mask are shown here. In most cases, keeping the
defaults is recommended.
IP Address – The default value is 192.168.1.1.
Subnet Mask – The default Subnet Mask is 255.255.255.0.
DHCP Server Setting
The IP1000 can be used as a Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP) server,
hence no router device is required. DHCP server automatically assigns an IP address to
each computer or network equipment in a local network. It is highly recommended to
utilize IP1000’s DHCP server function.
DHCP Server – By Factory default DHCP is enabled.
Start IP Address – Enter an initial IP address for the DHCP server to start with
when assigning IP addresses. Because the default local IP address for the IP1000 is
192.168.1.1, the Start IP Address must be one between 192.168.1.2 and
Copyright IPitomy Communication, LLC 17 0007VRF
Page 23

192.168.1.254. The default Start IP Address is 192.168.1.100
Minimum Number of Users – The maximum number of IP addresses that allow the
DHCP server to assign to. This number cannot exceed 253. The default number is
50.
Client Lease Time – The Client Lease Time is the amount of time a network device
will be allowed to use the dynamically assigned IP address by IP1000. After the
Client Lease Time expires the assigned IP address will be released and be assigned
with a new dynamic IP address. The default value is 0 minutes, which means one
day.
Static DNS 1-3 – The Domain Name System (DNS) is how the Internet translates
domain or website names into Internet addresses or URLs. Service providers should
provide at least one DNS Server IP Address to each user.
WINS – The Windows Internet Naming Service (WINS) converts NetBIOS names to
IP addresses. If a WINS server is used, enter the servers IP address here, otherwise
leave this field blank.
DDNS
The IP1000 offers a Dynamic Domain Name System (DDNS) feature. DDNS assigns a
fixed host name and a domain name to a dynamic Internet IP address. It is useful when
users are hosting their own website, FTP server, or other server behind the IP1000.
Before using this service, it is required to sign up DDNS service at one of two DDNS
service providers such as DynDNS.org or TZO.com. Default setting is Disabled.
DDNS Service
Select the DDNS service provider from the drop-down menu. There are two options in the
menu, DynDNS.org and TZO.com. The features available on the DDNS screen will vary
depending on which DDNS service provider is used.
Copyright IPitomy Communication, LLC 18 0007VRF
Page 24

DynDNS.org
o User Name, Password and Host Name – Enter the settings of the account
you set up with DynDNS.org.
o System – Select the DynDNS service you use: Dynamic, Static, or Custom.
o Mail Exchange – Enter the settings of the account set up with DynDNS.org.
o Backup MX – This feature allows the mail exchange server to be a backup.
By default, this feature is Enabled. To disable this feature, select Disabled.
o WildCard – This setting is for enabling or disabling wildcards. For example, if
your DDNS address is myplace.dyndns.org and you enable wildcards, then
x.myplace.dyndns.org will work as well (x is the wildcard). By default wildcards
is Enabled. To disable wildcards, select Disabled.
o Internet IP Address – The IP1000’s Internet IP address is displayed here.
o Status – The status of the DDNS service connection is displayed here.
o Update – To manually trigger an update, click this button.
TZO.com
Copyright IPitomy Communication, LLC 19 0007VRF
Page 25

o E-mail Address, TZO Password, and Domain Name – Enter the settings of
the account set up with TZO.
o Internet IP Address – The IP1000’s Internet IP address is displayed here.
o Status – The status of the DDNS service connection is displayed here.
o Update – To manually trigger an update, click this button.
MAC Clone
A MAC address is a 12-digit code assigned to a unique piece of hardware for
identification, like a social security number. Some ISPs will require you to register a MAC
address in order to access the Internet. If you do not wish to re-register the MAC address
with your ISP, you may assign the MAC address you have currently registered with your
ISP to the IP PBX with the MAC Address Clone feature.
MAC Address Clone
To use MAC address cloning, select Enabled. Otherwise, keep the default, Disabled.
MAC Address
Enter the MAC Address registered with service provider.
Clone My PC’s MAC
Click this button to clone the MAC address of the PC be currently using to configure the
IP1000. The IP1000 will automatically detect PC’s MAC address. It is recommended that
the PC registered to the service provider is used to open the MAC Address Clone screen.
Routes
The Routes screen allows user to configure the dynamic and static routing settings.
Copyright IPitomy Communication, LLC 20 0007VRF
Page 26

NAT
If IP1000 is hosting your network’s connection to the Internet, select Enabled. If another
Router exists in front of IP1000, select Disabled. When the NAT setting is disabled,
dynamic routing will be enabled.
Dynamic Routing (RIP)
This feature enables the IP1000 to automatically adjust to physical changes in the
network’s layout and exchange routing tables with the other router(s). The IP PBX
determines the network packets’ route based on the fewest number of hops between the
source and the destination locations. To use dynamic routing, select Enabled. Otherwise,
select Disabled. When the NAT setting is disabled, dynamic routing will be enabled.
Static Routing
A static route is a pre-determined pathway that network information must travel to reach a
specific host or network. Use this feature to set up a static route, alter the following
settings:
Route Entries – Select the number of the static route from the drop-down menu.
Enter Route Name – Enter a name for the static route, using a maximum of 25
alphanumeric characters.
Destination LAN IP – The Destination LAN IP Address is the address of the remote
network or host to which you want to assign a static route. Enter the IP address of the
host for which you wish to create a static route.
Subnet Mask – The Subnet Mask determines which portion of a Destination IP
address is the network portion, and which portion is the host portion.
Gateway – This is the IP address of the gateway device that allows for contact
between the IP PBX and the remote network or host.
Copyright IPitomy Communication, LLC 21 0007VRF
Page 27

Interface – Select LAN or WAN (Internet) depending on the location of the final
destination.
Delete This Entry
To delete a route, select its number from the drop-down menu, and click this button.
Show Routing Table
Click the Show Routing Table button to open a screen displaying how data is routed
through your local network. For each route, the Destination LAN IP address, Subnet
Mask, Gateway, and Interface are displayed. Click the Refresh button to update the
information. Click the Close button to exit this screen.
Security
Firewall
The Firewall screen offers a firewall and filters that block specific Internet data types.
Firewall
SPI Firewall Protection – A firewall enhances network security and use Stateful
Packet Inspection (SPI) or more detailed review of data packets entering your
network. Select Enabled to use a firewall, or Disabled to disable it.
Allow Remote SIP Clients – Enabling Allow Remote SIP Clients setting will allow
the SIP packets to pass through the firewall. This allows administrators to setup the
connection between this IP PBX and the external SIP phones or SIP trunks from the
Internet. To enable the communication with remote SIP devices, select Enabled.
Otherwise, select Disabled.
Copyright IPitomy Communication, LLC 22 0007VRF
Page 28

Allow Remote IAX Clients – Enabling Allow Remote IAX Clients setting will allow
the IAX packets to pass through the firewall. This will allow the IP1000 to setup a
peer-to-peer connection with another IP1000. To enable the IAX peer-to-peer
communication with remote IP PBX, select Enabled. Otherwise, select Disabled.
Internet Filter
Filter Anonymous Internet Requests – When enabled, this feature protects the
network behind IP1000 from being “pinged” or detected by other Internet users. It
also hides the used network ports. This filter is enabled by default. Click the check
box to enable or disable.
Filter Multicast – Multicasting allows for multiple transmissions to specific recipients
at the same time. If multicasting is permitted, then IP1000 will allow IP multicast
packets to be forwarded to the appropriate computers. Click the check box to enable
or disable.
Filter Internet NAT Redirection – This feature uses port forwarding to block access
to local servers from local network computers. Click the check box to enable or
disable.
Filter IDENT (Port 113) – This feature protects port 113 from being scanned by
devices outside of your local network. Click the check box to enable or disable.
Web Filter
Proxy – Use of WAN proxy servers may compromise the Gateway’s security.
Denying Filter Proxy will disable access to any WAN proxy servers. To enable proxy
filtering, click the checkbox.
Java – Java is a programming language for websites. If Java is filtered, it may fail to
access to Internet sites created by using Java. To enable Java filtering, click the
checkbox.
ActiveX – ActiveX is a programming language for websites. If ActiveX is filtered, it
may failed to access to Internet sites created by using ActiveX. To enable ActiveX
filtering, click the checkbox.
Cookies – A cookie is data stored on your computer and used by Internet sites when
you interact with them. To enable cookie filtering, click the checkbox.
VPN Passtrough
The VPN Passthrough allows VPN tunneling using IPSec, L2TP or PPTP protocols to
pass through the IP1000.
Copyright IPitomy Communication, LLC 23 0007VRF
Page 29

IPSec Passthrough – IPSec (Internet Protocol Security) is a suite of protocols used
to implement secure exchange of packets at the IP layer.
L2TP Passthrough – Layer 2 Tunneling Protocol is the method used to enable
Point-to-Point Protocol (PPP) to be tunneled through an IP network.
PPTP Passthrough – PPTP (Point-to-Point Tunneling Protocol) Passthrough allows
the Point-to-Point Protocol (PPP) to be tunneled through an IP network.
Copyright IPitomy Communication, LLC 24 0007VRF
Page 30

Access Restriction
Copyright IPitomy Communication, LLC 25 0007VRF
Page 31

Internet Access Policy
The Internet Access Policy screen allows you to block or allow specific kinds of Internet
applications and traffic such as Internet access, designated services, websites, and
inbound traffic during specific days and times.
Access Policy – Access can be managed by a policy by using the settings on this
screen to establish an access policy. Selecting a policy from the drop-down menu will
display that policy’s settings. To delete a policy, select that policy’s number and click
the Delete This Policy button. To view all the policies, click the Summary button.
Policy Table – On the Summary screen, the policies are listed with the following
information: No., Policy Name, Access, Days, Time, and status (Enabled). To enable
a policy, click the Enabled checkbox. To delete a policy, click its Delete button. Click
the Save Settings button to save your changes, or click the Cancel Changes button
to cancel your changes. To return to the Internet Access Policy screen, click the
Close button.
Status – Policies are disabled by default. To enable a policy, select the policy
number from the drop-down menu. And click the radio button beside Enabled.
To create a policy:
Select a number from the Access Policy drop-down menu.
Enter a Policy Name.
Enable this policy by checking the Enabled.
Click the Edit List button to select the PCs to be affected by the policy. The List of
PCs screen will appear. You can select a PC by MAC address or IP address. You
can also enter a range of IP addresses if you want this policy to affect a group of
PCs.
Select Deny or Allow to block or allow Internet access for the PCs you listed on the
screen.
Decide the days and times you want this policy to be enforced. Select the individual
days during which the policy will be in effect, or select Everyday.
Enter a range of hours and minutes during which the policy will be in effect, or select
24 Hours.
To block websites with specific URL addresses, enter URL address in a separate
field next to Website Blocking.
To block websites using specific keywords, enter each keyword in a separate field
next to Website Blocking.
To filter access to various services over the Internet, choose the access to be
blocked such as FTP or Telnet. Up to three kinds of access methods can be blocked
per each policy.
From the Applications list, select the applications to be blocked. Then click the >>
(move right) button to move it to the Blocked List. To remove an application from the
Blocked List, select it and click the << (move left) button.
To add an application to block or to edit a service’s settings, enter the application’s
name and its range in the Port Range fields, select its protocol from the Protocol
drop-down menu. Then click the Add button.
To modify a service, select it from the Application list. Then click the Delete button.
Click the Save Settings button to save the policy’s settings.
Copyright IPitomy Communication, LLC 26 0007VRF
Page 32

Application Forwarding
Single Port
On this screen, forwarding applications per port basis to specified network servers is
customized. Once configured, the requests received from Internet for the configured
application and through the specified port will be forwarded to the appropriate servers
(computers). Before using forwarding, static IP addresses should be assigned to the
designated servers (use the DHCP Reservation feature on the Networking/TCP/IP
Settings screen).
Single Port Forwarding
Common applications are available for the first five entries. Select the appropriate
application, then enter the IP address of the server that should receive these requests.
Click the Enabled checkbox to activate this entry.
For additional applications, complete the following fields:
Application Name – Enter the name of the application.
External Port – Enter the external port number used by the server or Internet
application. Check the Internet application documentation for more information.
Internal Port – Enter the internal port number used by the server or Internet
application. Check the Internet application documentation for more information.
Protocol – Select the protocol TCP or UDP, or select Both.
To IP Address – Enter the IP address of the server that should receive the requests.
Enabled – Click the Enabled checkbox to enable the applications you have defined.
Copyright IPitomy Communication, LLC 27 0007VRF
Page 33

Application
Application screen sets up public services on local network, such as web servers, ftp
servers, e-mail servers or other specialized Internet applications. (Specialized Internet
applications are any applications that use Internet access to perform functions such as
videoconferencing or online gaming. Some Internet applications may not require any
forwarding.)
When the types of requests for configured applications are received via Internet, IP1000
will forward those requests to the appropriate servers (computers). Before using
forwarding, assigning static IP addresses to the designated servers (use the DHCP
Reservation feature on the Networking/TCP/IP Settings screen) is recommended.
If you need to forward all ports to one PC, using DMZ is recommended.
Port Range Forwarding
To add an application, complete the following fields:
Application Name – Enter the name of the application
Start – End Port – Enter the number or range of port(s) used by the server or
Internet application. Check with the Internet application documentation for more
information.
Protocol – Select the protocol TCP or UDP, or select Both.
To IP Address – Enter the IP address of the server that allows Internet users to
access.
Enabled – Click the Enabled checkbox to enable the applications you have defined.
This is disabled (unchecked) by default.
Copyright IPitomy Communication, LLC 28 0007VRF
Page 34

Port Range
This screen instructs the IP1000 to watch outward data for specific port numbers. The IP
address of the computer that matched is remembered by IP1000, so that when the
requested data returns through the IP PBX, the data is sent to the proper computer by
way of IP address and port mapping rules.
To add an application, complete the following fields:
Application Name – Enter the name of the application
Triggered Range – Enter the range of port numbers. Check with the Internet
application documentation for the port number(s) needed.
Forwarded Range – Enter the range of the forwarded port numbers. Check with the
Internet application documentation for the port number(s) needed.
Enabled – Click the Enabled checkbox to enable the applications you have defined.
This is disabled (unchecked) by default.
Copyright IPitomy Communication, LLC 29 0007VRF
Page 35

DMZ
The DMZ screen allows one local user to be exposed to the Internet for use of a special
purpose service such as Internet gaming and videoconferencing. DMZ hosting forwards
all the ports at the same time to one PC. The Port Range Forwarding is more secure
because only the configured ports are opened. If DMZ hosting opens all the ports of one
computer, it exposes the computer to the Internet.
Any PC whose port is being forwarded must have its DHCP client function disabled and
should have a new static IP address assigned to it because its IP address may change
when using the DHCP function.
To use this feature, select Enabled. To disable DMZ hosting, select Disabled.
Source IP Address – If any IP address can be the source, select Any IP Address.
Want to specify an IP address or a range of IP addresses as the designated source,
click the second radio button and enter the IP address.
Destination – Want to specify the DMZ host by IP address, select IP Address and
enter the IP address. Or want to specify the DMZ host by MAC address, select MAC
Address and enter the MAC address. To retrieve this information, click the DHCP
Client Table button.
The DHCP Client Table lists computers and other devices that have been assigned IP
addresses by the IP1000. The Client table is sorted by Client Name, Interface, IP
Address, MAC Address and Expired Time (how much time is left for the current IP
address). To select a DHCP client, click the Select button. To retrieve the most up-to-
date information, click the Refresh button. To exit this screen and return to the DMZ
screen, click the Close button.
QoS
Quality of Service (QoS) ensures better service to high-priority types of network traffic,
which may involve demanding and real-time applications such as videoconferencing.
Copyright IPitomy Communication, LLC 30 0007VRF
Page 36

Internet Access Priority
Select Enabled to use the QoS policy and system will allow user to setup the QoS policy.
Administrators can choose to manually set the Internet bandwidth or let system to
determine it automatically.
Category
There are four categories available. Select one of the following: Applications, Online
Games, MAC Address, Ethernet Port, or Voice Device. In this section, you can select the
bandwidth priority for a variety of applications and devices. There are four levels priority:
High, Medium, Normal and Low. When setting priority do not set all applications to High,
because this will defeat the purpose of allocating the available bandwidth. Select Low for
those require normal bandwidth. A few attempts to establish the appropriate bandwidth
priority may be required. It depends on the application.
Applications
Applications – Select the appropriate application, If you select Add a New
Application – follow the Add a New Application Instructions.
Priority – Select the appropriate priority: High, Medium, Normal, or Low.
Add a New Application:
Copyright IPitomy Communication, LLC 31 0007VRF
Page 37

o Enter a Name – Enter any name to indicate the name of the entry.
o Port Range – Enter the port range that the application will use. For example, if
administrators want to allocate bandwidth for FTP, enter 21-21; if need services
for an application that uses from 1000 to 1250, then enter 1000-1250. There are
totally up to three ranges to define for this bandwidth allocation. Port numbers
can range from 1 to 65535. Check your application’s documentation for details on
the service ports used.
o Protocol – Select the protocol TCP or UDP, or select Both.
o Priority – Select the appropriate priority: High, Medium, Normal, or Low.
Online Games
Select a Game – Select the appropriate game.
Priority – Select the appropriate priority: High, Medium, Normal, or Low.
Click the Add button to save your changes. New entry will appear in the Summary
List
MAC Address
Enter a Name – Enter a name for your device.
Mac Address – Enter the MAC address of your device
Priority – Select the appropriate priority: High, Medium, Normal, or Low.
Click the Add button to save your changes. New entry will appear in the Summary
List
Ethernet Port
Ethernet – Select the appropriate Ethernet port.
Priority – Select the appropriate priority: High, Medium, Normal, or
Low.
Click the Add button to save your changes. New entry will appear in the Summary
List
Voice Device.
Enter a Name – Enter a name for voice device.
Mac Address – Enter the MAC address of your voice device.
Copyright IPitomy Communication, LLC 32 0007VRF
Page 38

Priority – Select the appropriate priority: High, Medium, Normal, or Low.
Click the Add button to save your changes. New entry will appear in the Summary
List
Summary
This lists the QoS entries you have created for your applications and devices
Priority – This displays the bandwidth priority of High, Medium, Normal, or Low.
Name – This displays the application, device, or port name.
Information – This displays the port range or MAC address entered for your entry. If
a pre-configured application or game was selected, there will be no valid entry shown
in this section.
Remove – Click this button to remove an entry.
Copyright IPitomy Communication, LLC 33 0007VRF
Page 39

Administration
Administration
The Administration screen allows user to change the IP PBX’s access settings and
configure the UPnP (Universal Plug and Play) features as well as to backup and restore
the IP PBX’s configuration data.
Web Access
Web Utility Access – HTTP (HyperText Transport Protocol) is the communications
protocol used to connect to servers on the World Wide Web. HTTPS uses SSL
(Secured Socket Layer) to encrypt transmitted data for higher security. IP1000
supports two types of protocols, HTTP or HTTPS, for web access.
Remote Access
Settings for this field can only be configured from LAN network.
Remote Management – If remote access to the IP1000 from outside the local
network is permitted, choose Enabled. Otherwise, keep the default setting,
Disabled.
Copyright IPitomy Communication, LLC 34 0007VRF
Page 40

Web Utility Access – HTTP (Hyper Text Transport Protocol) is the communications
protocol used to connect to servers on the World Wide Web. HTTPS uses SSL
(Secured Socket Layer) to encrypt transmitted data for higher security. IP1000
supports two types of protocols, HTTP or HTTPS, for web access.
Remote Upgrade – If remote upgrade from outside the local network is allowed,
select Enabled. (You must have the Remote Management feature enabled as well.)
Otherwise, keep the default setting, Disabled.
Allow Remote IP Address – If allow remote IP address from outside the local
network is allowed, select Any IP Address. If administrators want to specify an
external IP address or a range of IP addresses, then select the second option and
complete the fields provided.
Remote Management Port – Enter the port number that will be open to outside
access.
UPnP
Universal Plug and Play (UPnP) allows Windows system to automatically configure the IP
PBX for various Internet applications, such as gaming and videoconferencing.
UPnP – To use UPnP, keep the default setting, Enabled. Otherwise, select
Disabled.
Allow Users to Configure – Select Enabled if users are allowed to configure
manually while using the UPnP feature. Otherwise, keep the default setting,
Disabled.
Allow Users to Disable Internet Access – Select Enabled if users are allowed to
configure to prohibit all Internet connections. Otherwise, keep the default setting,
Disabled.
Backup and Restore
Backup Configurations – To back up the IP1000 network configuration settings,
click this button and follow the on-screen instructions.
Restore Configurations – To restore the IP1000 network configuration settings,
click this button and follow the on-screen instructions. (You must have previously
backed up the IP1000 network configuration settings.)
Voice Backup and Restore
Backup Configurations – To back up the IP1000 PBX configuration settings, click
this button and follow the on-screen instructions.
Restore Configurations – To restore the IP1000 PBX configuration settings for on-
board analog devices, click this button and follow the on-screen instructions. (You
must have previously backed up the IP1000 PBX configuration settings.)
Log
The Log screen provides you with a log of all incoming and outgoing URLs or IP
addresses for your Internet connection.
Copyright IPitomy Communication, LLC 35 0007VRF
Page 41

Log – To access activity logs, select the Enabled radio button. While logging is
enabled, users can choose to view temporary logs. Click the Disabled button to
disable this function
View Log – To view the logs, click View Log, a new screen will appear with logged
information shown on it. Four types of logging are supported, Incoming Log,
Outgoing Log, Security Log or DHCP Client Log, choose one from the Type dropdown menu.
o Incoming Log –The Incoming Log displays a temporary log of the source IP
addresses and destination port numbers for the incoming Internet traffic.
o Outgoing Log –The Outgoing Log displays a temporary log of the local IP
addresses, destination URLs/IP addresses, and service/port numbers for the
outgoing Internet traffic.
o Security Log –The Security log displays the login information for the Web-
based Utility.
o DHCP Client Log – The DHCP Client Log displays the LAN DHCP server
status information.
Click the Refresh button to update the log. Click the Clear Log button to clear all the
information that is displayed. Click the Close button to close the log window.
Diagnostics
The diagnostic tests (Ping and Traceroute) allow you to check the connections of your
network devices including the connection to the Internet.
Copyright IPitomy Communication, LLC 36 0007VRF
Page 42

Ping Test – The Ping test will check the status of a connection. Enter the IP address
or URL of the PC whose connection you wish to test, the packet size (default is 60
bytes), and how many times you wish to test it. Then, click the Start to Ping button.
The Ping screen will then display the test results. Click the Close button to return to
the Diagnostics screen.
Traceroute Test – To test the performance of a connection, enter the IP address or
URL of the PC whose connection and click the Start to Traceroute button. The
Traceroute screen will then display the test results. Click the Close button to return to
the Diagnostics screen.
Factory Defaults
Factory Defaults – The Factory Defaults screen allows administrators to restore the
IP PBX’s configuration to its factory default settings.
Restore Factory Defaults – To clear all of the IP PBX’s settings and reset them to
its factory defaults, click the Restore Factory Defaults button.
Firmware Upgrade
The Firmware Upgrade screen allows you to upgrade the IP1000’s firmware.
Please Select a File to Upgrade – Enter the name of the new firmware file, or click
the Browse button to find this file.
Start to Upgrade – After the appropriate file is selected, click this button and follow
the on-screen instructions to perform firmware upgrading
Status
The Status screen displays information about the Routing function in the IP1000 and its
current settings. The on-screen information will vary depending on the Internet
Connection Type selected on the TCP/IP Settings screen.
Copyright IPitomy Communication, LLC 37 0007VRF
Page 43
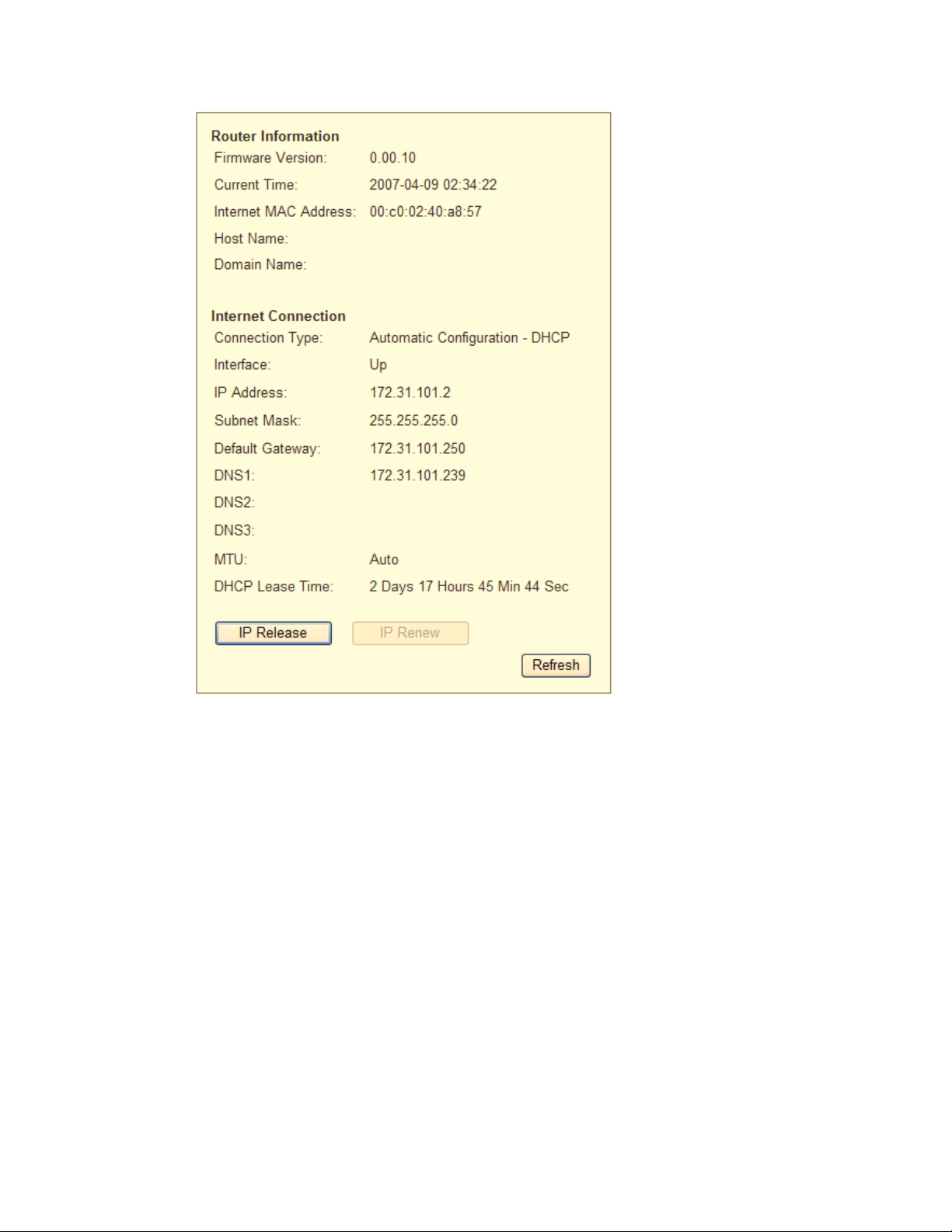
Router Information
Firmware Version – This shows version number of the IP1000’s firmware
Current Time – This shows the time set on the IP1000
Internet MAC Address – This is the IP1000’s MAC address.
Host Name – The Host Name entered when set TCP/IP Settings screen.
Domain Name – The Domain Name entered when set TCP/IP Settings screen
Internet Connection
Connection Type – This indicates the type of Internet connection you are using. For
dial-up style connections such as PPPoE or PPTP, there is a Connect button to reestablish the Internet connection if there is no connection.
Interface – This indicates the Internet connection of the IP PBX, up or down.
IP Address – Show IP1000’s Internet IP address.
Subnet Mask and Default Gateway – The IP PBX’s Subnet Mask and Default
Gateway address are displayed here for DHCP and static IP connections.
DNS1-3 – Show the DNS (Domain Name System) IP addresses currently used by
the IP1000.
Copyright IPitomy Communication, LLC 38 0007VRF
Page 44

MTU – Show the MTU (Maximum Transmission Unit) setting for the IP1000.
IP Release – It is available for a DHCP connection, click this button to release the
current IP address got from DHCP server.
IP Renew – It is available for a DHCP connection, click this button to release the
current IP address and get a new IP address from DHCP server.
Local Network
The local Network screen displays the information about the local network.
Local Network
Local MAC Address – The MAC Address of the IP1000 for local interface.
Router IP Address – This shows the IP address used by IP1000 for appearing on
local network.
Subnet Mask – The IP1000’s Subnet Mask is shown here.
DHCP Server
DHCP Server – Display the status of the IP1000 embedded DHCP server.
Start IP Address – The starting IP address of the range of IP addresses are used by
DHCP server for being assigned to devices on local network.
End IP Address –The ending IP address of the range of IP addresses are used by
DHCP server for being assigned to devices on local network.
DHCP Client Table
Click the DHCP Clients Table button to view the DHCP Client Table. It lists computers
and other devices that have been assigned IP addresses by the IP1000 embedded
DHCP server. Sorting by Client Name, Interface, IP Address, MAC Address or Expired
Time (how much time is left for the current IP address) is supported. To remove a DHCP
client, select it and click the Delete button. To retrieve the most up-to-date information,
click the Refresh button. To exit this screen and return to the Local Network screen, click
the Close button.
Copyright IPitomy Communication, LLC 39 0007VRF
Page 45

Analog Interface
The Analog Interface screen is used to configure the on-board analog ports. In IP1000, it
includes 2 FXS ports and 6 FXO ports. Each analog port uses SIP protocol to register to
the SIP proxy server embedded in IP1000
SIP Settings
This screen lets you configure the SIP server and the related parameters that the analog
ports will register to. The SIP server address is the same gateway address of IP PBX, so
you don’t need to specify the SIP server address.
Proxy Port – The port used for initiating connections to the SIP server, the default
port number is 5060
Regist Expire – It is a timer for monitoring the registration to embedded SIP proxy
server in IP1000. When connection is idle for over the Register Expire time, the
connection will be terminated automatically. The default value for this item is 120
seconds.
SIP Port – The UDP port number that the analog ports use for incoming call setup
request. The default value is 5060
RTP Port – The base UDP port that the analog ports uses for transmitting RTP and
RTCP packets. The analog ports use a block of port numbers for sending/receiving
RTP and RTCP packets from this port number. The default value is 10000.
SIP TOS – TOS field in IP header used in outgoing SIP packets. The default value is
7.
Voice TOS – TOS field in IP header used in outgoing RTP/RTCP packets. The
default value is 176.
Copyright IPitomy Communication, LLC 40 0007VRF
Page 46
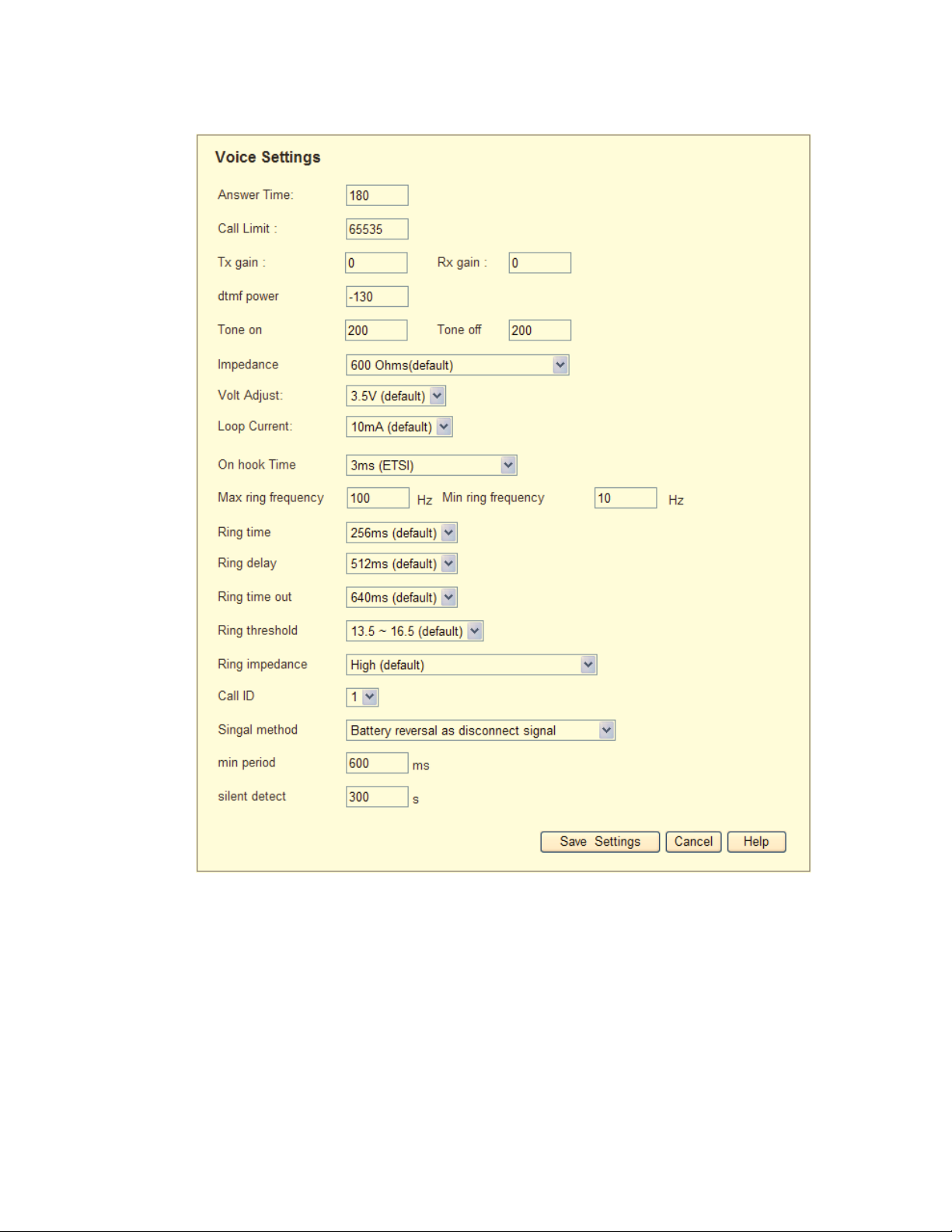
Voice
The Voice Settings screen is for selecting and configuring the FXO line settings.
Answer Time – Specify the time in seconds that the analog ports wait for the called
party to answer the call. If the called party does not answer the call within this time
period, the call is terminated automatically. The default value is 180 seconds.
Call Limit – Specify the maximum number of seconds for a call conversation. When
the duration of a call exceeds this value, the call is terminated automatically. The
default value is 65535 seconds.
Tx Gain – The FXO ports may increase or attenuate the power level before
transmitting to the telephony port, changing gain level manually may be required.
This field allows user to set the transmitter gain level in dB
Copyright IPitomy Communication, LLC 41 0007VRF
Page 47

Rx Gain –The FXO ports may increase or attenuate the power level of the telephony
port, changing gain level manually may be required. This field allows user to set the
receiver gain level in dB
DTMF Power – Enter the desired value for the DTMF power that FXO ports dial
toward PSTN. Each level for changing is 0.1dBm.The default value is -130*0.1 dB.
This setting will only affect the DTMF tones sent by SIP INFO.
Tone On – Specify the Tone-On time in millisecond for an out dialing DTMF digit.
The default value is 200 milliseconds. This setting will only affect the DTMF tones
sent by SIP INFO.
Tone Off – Specify the Tone-Off time in millisecond for an out dialing DTMF digit.
The default value is 200 milliseconds. This setting will only affect the DTMF tones
sent by SIP INFO.
Impedance – Select the impedance of the lines connecting to PSTN ports.
Volt Adjust – Select the TIP/RING voltage adjust value, low-voltage countries should
use a lower voltage.
Loop Current – Select the minimum operational loop current at which the FXO ports
will operate.
On Hook Time – Select the amount of time to wait for the FXO port to go on-hook
Min Ring Frequency – Enter the minimum ring frequency for the FXO port to detect.
The default minimum ring frequency is 10Hz
Max Ring Frequency – Enter the maximum ring frequency for the FXO port to
detect. The default maximum ring frequency is 100Hz
Ring Time – Select the amount of ringing time in millisecond that the FXO port
detects to be a valid ring time.
Ring Delay – Select the amount of time in millisecond as the duration starts when a
ring signal is validated and till a valid ring signal is confirmed.
Ring Time Out – Select the amount of time in millisecond for determining that ring
signal is stopped.
Ring Threshold – Select the minimum voltage level the incoming ringing signal must
be presented with for the FXO port to detect it.
Ring Impedance – Select the desired value to satisfy the maximum ringer
impedance specification.
Call ID – We don’t use this setting anymore, but still keep it in the configuration file
for compatibility issues.
Signal Method – Select the line disconnection signal method. Two options to be
selected::
o 1. Battery reversal as disconnect signal.
o 2. Loop period shut-down as disconnect signal.
Min Period – Enter the minimum period of time for the above hardware to receive a
disconnect signal. The default value is 600 milliseconds.
Silent Detect – The amount of time to wait for the FXO port to disconnect after not
receiving RTP packets on the port. The default value is 300 seconds.
Copyright IPitomy Communication, LLC 42 0007VRF
Page 48

Codec
This screen is for selecting and configuring the voice codec, voice parameters.
Codec
Prefer Type – Select this preferred voice codec that analog ports (FXO and FXS
ports) used to negotiate with SIP sever for determining the voice codec. Available
codecs are G.711u, G.711a, and G.729.
G711u_pkt – Select this packetization time for G.711u. The packetization time is the
duration that the analog port samples voice signal and compresses it into a packet
before sending to the remote SIP device.
G711u_vad – Select this button to enable or disable Voice Activity Detection for
G.711u. This should be disabled for Asterisk application requirements.
G711a_pkt – Select this packetization time for G.711a
G711a_vad – Select this button to enable or disable Voice Activity Detection for
G.711a. This should be disabled for Asterisk application requirements.
G729_pkt – Select this packetization time for G.729.
G729_vad – Select this button to enable or disable Voice Activity Detection for
G.729. This should be disabled for Asterisk application requirements.
FXO
This portion is for configuring the FXO dial in/out parameters
Answer_after – Input the number of rings that the FXO port will keep waiting before
answering the incoming calls. The default value is 2 rings.
Copyright IPitomy Communication, LLC 43 0007VRF
Page 49

Out_wait – Enter the time in milliseconds that the FXO port keeps waiting after
seizing a telephony port and before dialing out DTMF signals. The default value is
1000 millisecond.
Bat_vol – Before seizing a FXO port for dialing out, the FXO port detects voltage
level on the port to ensure that the port is connected and available. If the voltage
level is below this threshold level, the port is declared unavailable
Call Progress
This screen is for configuring the CP (Call Progress) tone detection for FXO port. For
normal application, it is not recommended to modify the default settings.
Tone Detection – This specifies the ON/OFF of CP tone (busy tone for general
case) cadence periods. For instance, On of Tone 1 is 500 and Off of Tone 1 is 500
means the cadence is ON for 500ms then OFF for 500ms. If more than one ON/OFF
cadence detections are required, for example, ON 300ms/OFF 400ms, then ON
500ms/OFF 600ms, then program On of Tone 1 to be 300, Off of Tone 1 to be 400,
On of Tone 2 to be 500, Off of Tone 2 to be 600.
Repeat Count – Input the minimum detection cycles for the above CP tone cadence.
Tone On Fraction – Input the CP tone sensitivity level. This parameter controls the
SNR and frequency offset. The default value is 50%.
Copyright IPitomy Communication, LLC 44 0007VRF
Page 50

High Cutoff Frequency – Input the high cut-off frequency that the CP tone detection
will take. The default value is 550 Hz
Low Cutoff Frequency – Input the low cut-off frequency that the CP tone detection
will take. The default value is 260 Hz.
Reset Analog
The Reset Analog button allows administrators to reset the analog ports including all
FXS and FXO ports. For some reason, the analog ports may lose their connection
with the SIP server, in this case, the user can reset the analog ports to recover the
connection.
Providers
Providers are telephone lines, VoIP providers and other telecommunication resources. This
section of the system’s online administration is where these provider resources are provisioned.
The system is equipped to handle two types of provider settings Hardware Trunks and SIP
Providers.
CO Trunks
Hardware trunks are associated with telephone lines that connect to the PSTN. These
lines process inbound and outbound communication traffic that flows over communication
channels.
Connecting Phone Lines
Before hardware trunks can be provisioned, they must be connected to the system.
Connecting Using Internal Analog Line Cards
The VB400 Analog Line Card (4 PSTN line connections) Connect the phone
lines to the RJ11 jacks at the rear of the IP1000 and start making calls. These
connections are single pair; one line per jack.
Provisioning a New Hardware Trunk
Provisioning a hardware trunk tells the system what phone numbers are associated with
the trunk. It also establishes rules for the system to follow when processing incoming and
outgoing calls through this physical network connection. To provision a hardware trunk:
Copyright IPitomy Communication, LLC 45 0007VRF
Page 51

SIP Providers
SIP Providers are VoIP service provider accounts or other SIP-based devices that
provide PSTN connectivity. SIP provider accounts can have multiple phone numbers or
Direct Inward Dialing numbers (DIDs). The individual numbers can be routed to different
destinations within the system just like a trunk (T1 or plain old telephone line).
SIP Provider settings vary widely. To simplify the provisioning process a list of SIP
providers and their settings are below. If the provider needed is not contained on this list,
contact an IPitomy Service Representative at (941) 306-2200.
Copyright IPitomy Communication, LLC 46 0007VRF
Page 52

Add a New SIP Provider
1. Click on Providers and SIP Providers. The SIP Providers landing page
will appear.
2. Click on Add Provider. The Edit SIP Providers page appears.
3. Assign a Name to the SIP Provider.
4. Select the User Type associated with the SIP Provider.
5. Select DTMF Mode associated with the SIP Provider.
Copyright IPitomy Communication, LLC 47 0007VRF
Page 53

6. For the Host enter the domain or IP address associated with the SIP
Provider.
7. Select the Register option needed for the SIP Provider.
Yes – automatically registers with provided settings.
No – Doesn’t register.
Custom – Allows for any special registration rules needed for the SIP
provider.
8. Select Authentication Mode for the SIP Provider.
Yes – automatically generates based upon provided settings.
No – Doesn’t use authentication for the SIP Provider.
Custom – Allows for any special authentication rules needed for the SIP
provider.
9. Enter User Name associated with the SIP Provider.
10. Enter the Secret “password” for the SIP Provider.
11. Set the Call Limit “number of lines” for the SIP Provider.
12. Set the Dial Prefix if it is required by the SIP Provider.
13. Set the Area Code for the SIP Provider.
14. Check Dial Area Code With Local Calls if the system should always
dial an area code with outbound 7 digit calls. In most cases it is best to
not check this box. See Implementation Note below.
15. Check Dial 1 With Area Code if the system should always dial “1” with
the area code when making outbound calls on both 7 and 10 digit routes.
In some cases it may be best NOT to check this box. See Installation
Note 1.
Installation Note 1
In some business locations it can be convenient to have the system add an area code and
a “1” when placing a local or long distance call. However, in locations where businesses
are close to several telecommunication transport areas it can be confusing. In these cases
it is best to not check the boxes next to Dial Area Code With Local Calls and Dial 1 With
Area Code. Example: Bradenton, Sarasota and Englewood Florida are all within 50 miles
of each other. A business located in Bradenton Florida makes local calls by dialing a
standard seven digit number (223-4567)*. Calls made from Bradenton to the neighboring
city of Sarasota require the use of the area code or a ten digit number (941-223-4567)*.
Calls made from Bradenton to Englewood require the use of a “1” in front of the ten digit
number (1-941-223-4567)*.
*These phone numbers are not real and are for demonstration purposes only.
16. Check Call Recording if users of this provider will be allowed to record
calls. In a standard business application this feature is typically not
needed.
17. Can Reinvite
Yes – select this if the phone type allows the re-invite feature.
No – select this if the phone type doesn’t allow the re-invite mechanism
Copyright IPitomy Communication, LLC 48 0007VRF
Page 54

for reconnecting the call mid stream.
18. Select Insecure option from provided drop down list. This specifies how
to handle connections with peers.
Port - ignore the port number where authentication came from. INVITE do not require initial invite to authenticate.
Port.Invite - do not require initial invite to authenticate and ignore the
port where the request came from.
Yes - To match a peer based by IP address only and not port.
Very - To allow registered hosts to call without re-authenticating.
19. Allow Codecs – encodes a stream or signal for transmission. Select
which codecs will be enabled for this provider.
20. Add custom dialing rules - These are numbers that should be passed
through to this provider when dialed by an end user – (e.g. 411, 1411).
21. Add the Phone Numbers associated with the provisioned trunk. Type the
phone number in the field provided and click Add. The phone number will
appear in the field to the right. To Remove a number from the list click
the Phone Number and the Remove button.
22. Define a Destination for the number by clicking it and selecting where it
is to be routed to from the drop-down menu. Destinations can be:
Locations in the business like Conference Rooms.
Extensions where specific people or departments can be reached.
Ring Groups through which groups of people respond to similar
types of calls.
Schedules that when applied route callers to different destinations or
people in the organization during specified times and dates.
Voicemail Boxes where callers can leave a message.
Menus through which callers can personally select from a variety of
destinations in the system.
Implementation Note 9
How Destinations Populate
The destinations dropdown list is populated as destinations are added to the
system. During system implementation these destinations can be populated first
and then the hardware provisioned or the hardware can be provisioned without
the destinations and set once they have been added to the system.
Assigning a Destination
Most often businesses assign phone numbers to a:
Main Menu destination where callers can select specific
people or departments within an organization.
Ring All destination where everyone in the business has
access to answering all calls.
Copyright IPitomy Communication, LLC 49 0007VRF
Page 55

23. Click the Save Changes button.
24. Click Apply Changes when ready to implement these changes to the
system.
Edit an Existing SIP Provider
1. Click on Providers and SIP Provider. The SIP Providers landing page
will appear.
2. Select a provider from the list in the SIP Provider Window on the landing
page.
3. Select a Provider by clicking on the Provider Name or Edit.
4. Make changes to the provider.
5. Click on Save Changes.
6. Click on Apply Changes when ready to implement these changes to the
system.
Delete a SIP Provider
1. Click on Providers and SIP Provider. The SIP Provider page will
appear.
2. Select a provider from the list in the SIP Provider Window on the landing
page.
3. Click on
Provider Window on the landing page.
Delete. The SIP provider will be removed from the SIP
Destinations
Destinations are the various places that a call can be routed to within the system. Destinations in
the IPitomy 1000 include:
Extensions are individual extensions with a telephone. When an extension is
created, a voicemail box is also created. This voicemail box is automatically the
destination for an extension call which exceeds its ring time.
Groups are groups of extensions that can have different ringing strategies and can
be routed from any trunk, another destination or dialed from an extension.
Menus are used for creating automated attendant menus to route callers to a
destination within the system. A voice recording can also be used to play a caller
information like driving directions.
Meet-me Conference Rooms are where callers can call into a conference call.
Callers can be routed in any way to a Meet-me Conference; direct dialed, through a
DID, using an automated attendant or transferred by a person.
Voicemail Boxes are where callers leave a message when someone is not available
at an extension. Voicemail boxes that are created separate from extensions can be
used to route callers after hours or as an overflow destination. Note that in the current
implementation Voicemail Boxes without an extension cannot be dialed with only the
voicemail box number. You can enter as one leaving a message by dialing *+ box
Copyright IPitomy Communication, LLC 50 0007VRF
Page 56

number or you can check the messages by going through the voicemail gateway or
dialing 924.
Schedules route callers to different destinations or people in the organization during
specified times and dates.
Branch Office connections provide broadband access to other branch locations by
dialing a short access code followed by the extension number. Branch Extensions
can also be defined as part of a branch office. These are remote extensions that can
be dialed directly as though they were local extensions on your PBX. Branch
Extensions also appear in drop down boxes for routing calls to specific destinations.
These system destinations (where and to whom calls will be routed) should be planned in
advance. In most cases, there will be a menu to setup for an automated attendant. There will also
be business hours to setup. The IPitomy 1000 Installation Worksheet helps organize
provisioning information prior to installation.
Extensions
Extensions define where specific people or departments can be reached in an
organization. They should be setup first in the system. Once extensions are setup then
the rest of the application can be provisioned.
Auto Discovery - This network discovery tool identifies phones and other devices
connected to the network and allows you to remotely configure networked phones.
CSV Upload – Easily upload one CSV file and auto create all extensions.
Add Range – This allows you to easily mass create extensions.
Phone Settings - This tool allows you to modify a phone’s keys. It includes support
for all Aastra model phones.
General Settings – Identifies the owner of the extension, email address, extension
and password information.
Forward Settings – Sets the forwarding behavior. Calls can be forwarded to local
destinations, PSTN and cell numbers.
Network Settings – These are extension authentication settings for SIP registration
with the IPitomy 1000. This is also where selecting the model of telephone for Auto
Configuration and changing button mapping is done.
CODEC Permissions – The quality of voice transmission and bandwidth utilization
Copyright IPitomy Communication, LLC 51 0007VRF
Page 57

are dictated by CODECs. Different CODECs compress voice packets differently.
G.711 is the most common and highest quality, but consumes the most bandwidth.
G.729 requires license fees to use in conjunction with the IPitomy 1000 services like
voicemail, conferencing and music on hold.
Voicemail Settings – Manages voicemail messaging and routing.
Calling Permissions – Defines types of calls that can be originated, received and
some advanced options like park and record calls.
Auto Discovery
This network discovery tool identifies phones and other devices connected to the network
and allows you to remotely configure networked phones.
Toolbar: Edit Selected
Button Function Commands Phone?
Create Create new extensions for
No
selected phones. You can
upload extension details in a
file or manually enter
information.
Copyright IPitomy Communication, LLC 52 0007VRF
Page 58
Assign Assign existing extensions
No
to selected phones.
Unassign Removes the configuration
No
file for the phone and all
association between the
extension and the phone.
Unassign & Default Same as Unassign but also
Yes
sends a Factory Default
instruction to the phone.
Toolbar: Command Selected
Button Function Commands Phone?
Factory Default Sends a Factory Default and
Yes
restarts the phone.
Restart Sends a Restart instruction
Yes
to the phone.
Configure & Restart Instructs phone to set TFTP
Yes
server to the Server
specified under Advanced
Settings. Then the phone is
commanded to restart.
Assign, Configure &
Restart
Combines the functions of
the Assign button with the
Yes
Configure & Restart button.
Toolbar: View
Button Function Commands Phone?
Select All, None,
Invert
Check or uncheck multiple
checkboxes with the click of
No
a button.
Refresh Scan the network for
No
devices. Scanning is done
using the settings in
Advanced Scan Settings.
The scan results displayed
depend on the active filters
(controlled via Advanced
Filter Settings).
Filter Only Displays results of the last
No
network scan after applying
the filters set in Advanced
Filter Settings.
Tip: You must check the checkbox beside each item you wish to modify before issuing
any commands.
Copyright IPitomy Communication, LLC 53 0007VRF
Page 59

List of Devices & Extensions
The list of discovered network devices uses two sources of information:
o Network
o PBX Database
Device column lists info about the device. Database info is preferred, so if a
device is set to a certain phone type in the database, this is listed instead of the
actual device type. The help/info question mark to the right can be hovered over
to get more specific info about the device.
Hover your cursor over the info icon to obtain details about the networked
device or phone. This can be an important source of information about which
phones are available for live configuration.
If you click refresh-view more than once in a short time period, the network is not
re-scanned. The minimum time period allowed between scans is indicated under
advanced scan settings (Min Refresh Interval).
Tip: The network is only scanned for new information when you click [Refresh].
Both Refresh & [Filter Only] apply whatever filters you have chosen to the
displayed list.
Advanced Filter Settings
Filtering does not change how the network scanning is performed. It only limits
the list of items displayed. This means that if you only want to change filters it is
not necessary to re-scan the network. All of the network information from the last
network scan is retained and used by filters.
Sort Order
Determine what order items are listed in. Hover your cursor over the help icon
next to the Sort Order fields for options.
Hide
You can hide different device types from view.
Filter Patterns
You can enter a partial MAC or IP here. The limitation is that the pattern must
match from the first character onward. i.e. “000D” would match “000DE” but not
“A000DE”.
More advanced pattern filtering:
Full Regular Expression Matching is supported when you enclose your search
pattern in double quotes.
Pattern Equivalent to
1.2.3 ^1\.2\.3
“1\.2\.3.*” 1\.2\.3.*
Copyright IPitomy Communication, LLC 54 0007VRF
Page 60

Filter by Type:
You can select multiple device types to filter for. Auto-Discovery is aware of MAC
address ranges used by many popular networked devices. Although this is not
the only way Auto-Discovery identifies devices, this allows the tool to identify and
filter devices by type.
Tip: Only Aastra phones are shown by default because they are set in the Filter
by Type.
Advanced Scan Settings
Changes to Scan Settings are kept when you click the GUI ‘Refresh’ button.
Clicking on your browser’s refresh button will discard changes.
The ‘Reset’ button will return all Scan Settings to original default values.
Advanced Scan Setting Description
Min Refresh Interval Minimum number of seconds required
between fresh network scans. If you
attempt to scan the network more often
than this you only get results stored from
a previous scan.
Maximum wait Maximum number of seconds to wait for
all packets to return.
Packet Count
Number of packets to send.
TX Interval Transmission interval between packets.
Only meaningful when Packet Count is
greater than 1. Minimum allowed value
is 0.2
Batch Size Divide scanning range into batch jobs.
Jobs are run sequentially. Each job will
have at most <Batch Size> pings
running in parallel at a time. The special
value 255 means run all pings as one
big job.
Network Network address with last octet reserved
for From and To range. Example:
192.168.1.x
From Start number for last octet of network
address.
To End number for last octet of network
address.
Send Wakeup ping before Survey
Ping if…
Some devices are slow to respond to the
first ping they receive but have faster
response times afterwards.
Copyright IPitomy Communication, LLC 55 0007VRF
Page 61

Port 80 Ping Wait Maximum seconds to wait for basic
phone web interface to signal that it is
alive. Rarely used.
Command Wait Maximum seconds to wait for most
commands.
User Password Phone’s Web User Name & Password
may have to be specified if the phone is
not using factory default settings for
these items. When these fields are blank
Auto-Discovery uses default settings.
Factory Default Wait Maximum seconds to wait for the phone
to signal completion of a Factory
Default.
Troubleshooting Network Scanning Problems
Scan settings have been tuned to work in a network environment with two
switches and a router between the PBX and the phone. More complicated
environments may require further tuning. The most useful setting is ‘Maximum
wait’. However noisy environments will require increasing the packet Count and
TX interval.
To tune scanning for your network:
1. Click on Advanced Scan Settings
2. Increase the ‘Maximum Wait’ setting by a few seconds.
3. Click the GUI ‘Refresh’ button.
More specific tuning will require a knowledge of your network and diagnostic
tools like Ping.
Tip: Phones do not show up as ‘online’ in a network scan if they are in the
process of restarting, turned off, or operating on a different network.
Example Workflow # 1 – Create, Assign & Configure phones.
This assumes that you have already Factory Defaulted the phones.
1. Go to the Extensions page. Click the “Create” button.
2. Enter the new extension information or upload a CSV file for the
extensions. You do not need to provide MAC addresses. Then Click the
“Create” button. If successful, Click “Return to Extensions”
3. Click the “Auto-Discovery” button.
4. Next to each phone you wish to configure, click the checkbox and use
the drop down
5. Assigned” list to select the extension you wish to assign to the phone.
6. Click the “Assign, Configure & Restart” button.
Example Workflow # 2 – Create, Factory Default, Assign & Configure phones.
1. Go to the Extensions page. Click the “Auto-Discovery” Button. This will
scan the network for phones and other devices.
2. Click the checkboxes next to phones you wish to configure. Then Click
the “Create” button. This takes you to the Extension Creation page.
Copyright IPitomy Communication, LLC 56 0007VRF
Page 62
3. Enter the new extension information or upload a CSV file for the
extensions. Then Click the “Create” button. If successful, Click the
“Return to Extensions” button.
4. Click the “Auto-Discovery” button.
5. All of the phones you are attempting to setup are highlighted. Click the
checkboxes next to these phones (verifying that you are only checking
the ones from step 2.).
6. Click the “Factory Default”. Wait long enough for the phones to default
and restart. This could be anywhere from 30 seconds to 2 minutes for
each phone, depending on the model.
7. Click the checkboxes next to the phones from step 2. Click the “Assign,
Configure, and Restart” button.
CSV Upload
Each line is a record consisting of 1-5 comma separated fields. The order of the fields
must be:
Name, Email, Number, Phone Type, MAC
o Number: the extension number.
o Phone Type: This should be spelled out in English. Example Aastra 480i
You may omit fields starting from the right hand side of a record but the order of the
remaining fields must match the file format above.
Comments may be placed in the CSV file by using ‘#’ marks. Comments must either be
at the start of a line or have only spaces in front of the mark. Comments must not be
placed on the same line as a record entry.
Add Range
1. Go to Destinations > Extensions.
2. Enter the number of extensions to be created in the provided text box.
3. Click the Add Range button.
4. Give the system a starting extension#.
Copyright IPitomy Communication, LLC 57 0007VRF
Page 63
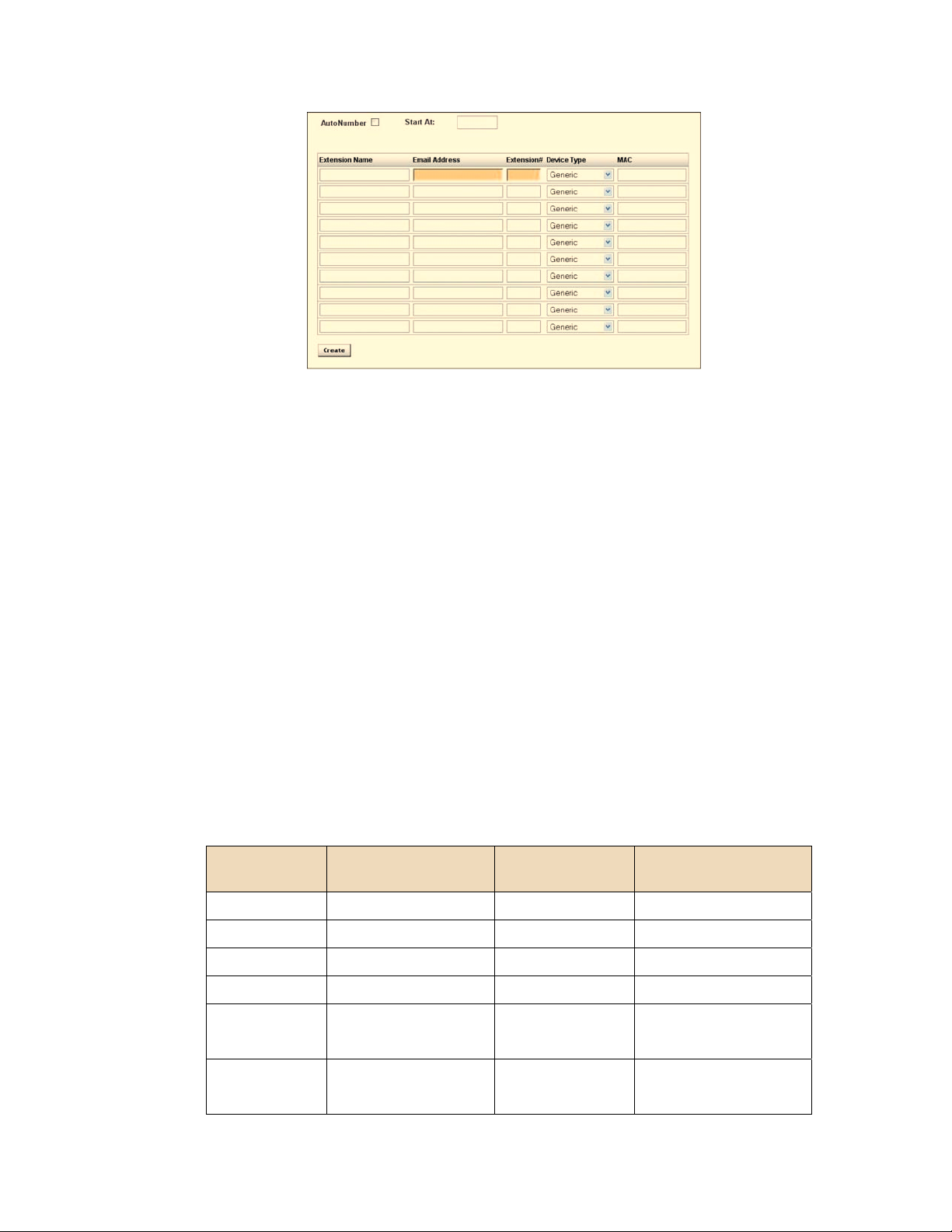
5. Check the Auto Number check box.
6. If Auto-Discovery is going to be used skip to Step7. If Auto Discovery is
not going to be used than fill in all the pertinent information for each
extension.
7. Click the Create button.
8. The screen that follows displays the results of each extension. If satisfied
with the results click “Return to Extensions”.
Phone Settings
This tool allows you to modify a phone’s keys. It includes support for all Aastra model
phones. It includes support for Aastra phones running firmware version 1.4.2.1081
Buttons:
[Save Changes] – Save changes but does not restart the phone.
[Save & Restart Phone] - Save changes and restart the phone. The phone is only
restarted if there have been changes.
[Exit] - Leave the Phone Settings page without modifying any phone settings.
Table of supported phones, and key counts.
Aastra Model Programmable Keys Top & Bottom
Key Sections?
Expansion Module
Support
9112i 2 No -
9113i 7 No -
480i & 480iCT 20 No -
53i 4 No -
55i 26
Yes 536EM & 560EM
(Add up to 180 keys)
57i 30 Yes 536EM & 560EM
(Add up to 180 keys)
Copyright IPitomy Communication, LLC 58 0007VRF
Page 64

Phones with top and bottom key areas will display shortcut links for Top &
Bottom.
The total number of keys displayed on the phone at any moment depends not
only on the display area available, but also on the state of the phone lines (see
Key State for more information). Expansion modules display a fixed number of
keys and are not limited by state.
Tip: Although the 9112i has many physical keys, most of them were never
supported by Aastra so they remain unusable.
A list of available keys fills most of the Phone Settings Page. Each row of the list
contains: Key Type, Label, Value, and States (if applicable).
Key Type
Key type determines what function a key performs. A dropdown list shows which
key types are available to the phone model you are working with. Here is a
complete list of programmable key types:
Key Type Additional Information
BLF
Speed Dial
DND
Blind Transfer
Call Pickup
Voicemail
Voicemail Gateway
Record
Fwd On
Fwd Off
Set Fwd
Busy Lamp Field
Do Not Disturb
Forwarding On
Forwarding Off
Set Forwarding Number
Fwd Gateway
Park Menu
Intercom
Directory
Callers
Services
Copyright IPitomy Communication, LLC 59 0007VRF
Page 65
Tip: Keys will only work if the System Administrator has configured the system for the
particular function.
Key Label
The label is the display name to use for the key. It is visible on the phone’s LCD
screen (except for models 9112i and 9113i).
Key Value
The value completes a key’s function. It may contain a number to dial special
codes or allow you to select an extension from a dropdown list. Most key types
do not require you to enter a value. For example, the Voicemail key does not
require a value because the System Administrator determines it for the end user.
Keys that require users to enter values:
o BLF
o Speed Dial
Key State
Generally, a key is only active when the current extension line status matches
the enabled states. Some special keys are always active, regardless of state.
When a key is active you can see the key’s label printed on the phone’s display
screen. When a key is inactive it is not displayed and cannot be used. Default
states for each key type will be automatically filled in for you.
Key State Description
Idle No current call activity.
Connected A call is connected.
Incoming A call is ringing the extension.
Outgoing A call is being placed from the extension.
To program a key’s state:
Check the desired boxes (any of: Idle, Connected, Incoming, Outgoing). If no
boxes are available for checking it means that the key will always be active.
Copyright IPitomy Communication, LLC 60 0007VRF
Page 66

Advanced Settings
Custom Sip Settings
Network *LAN
*WAN
*Custom
Server The IP address or name of the server to
use for the Network type selected. A user
must use the Custom Network type to set
a user defined Server.
Time Settings
Network *PBX
*Custom
Time Server The IP address or name of the server to
obtain time information from. A user must
use the Custom Network type to set a
user defined Time Server.
Time Zone *US-Eastern
*US-Central
*US-Mountain
*US-Pacific
*US-Alaska
*US-Aleutian
*US-Hawaii
Volume Controls
Headset Transmit Gain This is the audio volume level (dB)
transmitted by the PBX to the phone.
Headset Side Tone Gain This is the audio volume level (dB) of your
voice signal sent back into your ear so
you can hear yourself talk and know that
the line is not dead.
Handset Transmit Gain This is the audio volume level (dB)
transmitted by the PBX to the phone.
Handset Side Tone Gain This is the audio volume level (dB) of your
voice signal sent back into your ear so
you can hear yourself talk and know that
the line is not dead.
Hands free transmit Gain This is the audio volume level (dB)
transmitted by the PBX to the phone’s
speaker.
Microphone Mute Disable the phone’s microphone(s).
Copyright IPitomy Communication, LLC 61 0007VRF
Page 67

Aastra Expansion Modules
Module Type *None
*536 EM
*560 EM
Working with Expansion Modules
When a phone has a Module Type set you will see the Module Type name and
quick links to module keys at the top of the page.
The most advanced module is the 560 EM. Its LCD screen displays button
names in two columns. Each column can be given a name via Phone Settings.
Module Descriptions and Options:
o 560 Expansion Module -
This module has 60 keys. It has a LCD screen split into two columns.
There are 20 physical keys (10 per column) plus buttons to switch
screens. There are 3 screens, bringing the total number of
programmable keys to 60. You can Daisy Chain up to 3 modules to a
single phone.
o 536 Expansion Module -
This module has 36 physical keys. Each key has an indicator lamp. The
module requires printed labels to be inserted. You can Daisy Chain up to
3 modules to a single phone.
To Change Module Type
Warning: When changing module types, you will lose any existing module key
settings.
1. Click on “Advanced Settings”
2. Select the Module Type connected to the phone.
3. Configure the module keys as desired.
4. Click on Save & Restart to immediately update the phone.
To Add a Module of the Same Type
Do not change the module type. Support for up to three modules of the same
type is automatic. Simply go to the desired module via the quick links at the top
of the Phone Settings page. Modules are numbered from left to right so Module 1
is the first module, and Module 3 is the last one.
Copyright IPitomy Communication, LLC 62 0007VRF
Page 68

Add a New Extension
1. Click Destinations and Extensions in the navigation bar of the system’s
administration menu. The Extensions page will appear.
2. Click Add Extension. The Edit Extensions page will appear. Note that
each new extension added automatically has a voice mailbox created.
3. Insert the Name or department associated with the extension being
created.
4. Create an Extension Number for this person or department.
5. Populate the Email address for the person or extension. This will allow
the system to forward email messages to the address of the person at
the extension.
6. Select a status from the drop-down menu. An extension can be:
-Active – Currently in use.
-Disabled – Not currently in use.
7. Create a voicemail PIN for the extension. PIN numbers must be
between 3 and 4 characters long. The default setting is for the PIN to be
the extension number. Be sure to instruct users to change the PIN to
avoid unauthorized use.
8. Enter a Ring Time. This is the time in seconds that a call will ring before
it is considered unanswered. Ring time must be between 1 and 360
seconds in length.
9. Define a Call Limit. This is the number of concurrent calls allowable at
an extension. The Call Limit selected must be between 0 and 9. This limit
will depend on the phone being installed. Note that setting a call limit will
cause busy lamp fields for this extension to only light up when the call
limit is reached. Setting this to 0 is preferred because IP phones are
Copyright IPitomy Communication, LLC 63 0007VRF
Page 69

capable of rejecting calls when they reach their limits independent of this
setting.
10. Create a Call Group number. This number assigns this extension to a
group with a similar purpose (e.g., Sales or Customer Service). Multiple
call groups can be assigned to each extension by putting a comma
between the group numbers. The call groups also define which Pickup
Groups can answer calls to this extension.
11. Create a Pickup Group. This number must match the Call Group
number(s). It defines the Call Group Numbers this extension can pickup
remotely by pressing 99.
12. Click Apply Schedule. When an extension is created, a schedule
destination is created. This schedule is not activated until the Apply
Schedule box is selected. When it is selected, you can setup a schedule
for this extension by selecting Schedule under the Destinations Menu
and clicking on the schedule for that extension. Extension schedules will
appear with the name of the extension (e.g., Extension 123 would
appear as “ext_123”). See the Schedules section of this guide for more
information.
Forward Settings
The forwarding settings are made to be very user friendly. The settings may be modified
from the Smart Personal Console, changed from your telephone extension or changed
remotely from any telephone (including cell phones), using the touch-tone key pad.
Forward settings routes calls to a different destination. These settings can be:
Unconditional – Always route calls to a specific destination.
Busy – Route calls to a specific destination when the extension is in use or do not
disturb is selected.
No Answer – Route calls to a specific destination when a call is not answered.
Unavailable – Route calls to a specific destination when a phone is turned off, is not
registered with the system or has reached Its call limit (as set In the IPitomy 1000).
Changing Forward Settings
To enable or disable forward settings:
1. Pick the setting to be modified – Unconditional, Busy, No Answer or
Unavailable.
2. Select Enabled or Disabled. Disabled turns the forward setting off.
Enabled turns the forward setting on.
If the Forward setting is Enabled, you can choose to select a destination from the
drop-down list. The IPitomy 1000 allows calls to be forwarded to a public
switched telephone number (PSTN). Forwarding calls to a PSTN number by
entering it into the field provided. Calls can be forwarded to any destination from
the drop down list or any telephone number.
Changing a Forwarding Number from an Extension
Only unconditional forwarding can be changed from a touch-tone keypad.
o Dial *90 to disable forwarding.
o Dial *91 to enable forwarding.
o Dial *92 to set the forwarding number.
Copyright IPitomy Communication, LLC 64 0007VRF
Page 70

Changing a Forwarding Number from a PC
1. Browse to the Smart Personal Console page.
2. Login.
3. Select a Destination for the chosen forward type.
4. Enter the telephone number.
Changing a Forwarding Number While Away from an Extension
Only unconditional forwarding can be changed from a touch-tone keypad.
When it is necessary to modify the forwarding setting while away from the office,
the IPitomy 1000 has a forwarding application built into the system. It is
necessary to have an automated attendant menu accessible from outside the
system. The forwarding gateway is selectable as an option from the menu. When
away from the office, it is possible to call into the automated attendant, enter the
digit setup to be the forwarding gateway. Here users can turn forwarding “on” or
“off” and enter a different number to forward calls to.
1. Call into the Automated Attendant (menu).
2. Select the touch-tone digit that has been set for modifying forwarding
settings.
3. The system will prompt for an Extension Number and Password.
4. The system will indicate if extension forwarding is Enabled or Disabled.
5. Pressing “1” toggles between Enabled and Disabled.
6. Pressing “2” allows the forwarding destination to be modified.
Advanced Settings
Network Settings
Network settings automatically register in the extension through the system.
These settings represent registration and identification information. The system
(extension) defaults should not be changed without advanced knowledge of the
behaviors of the particular settings.
Copyright IPitomy Communication, LLC 65 0007VRF
Page 71

Copyright IPitomy Communication, LLC 66 0007VRF
Page 72

Phone Type
It is necessary to enter the MAC address of each telephone. The telephones
have a barcode with the MAC ID printed on them. The phone type is a drop down
list for selecting which IP phone hardware is being used on the extension.
IPitomy supports Aastra
and Polycom phones and will be adding additional
phone types in the future. When the phone type is selected, another
configuration option is available to program the button mapping of each
telephone model. The IPitomy 1000 supports a variety of pre-programmed
buttons like BLF, park, voicemail, as well as, speed dial buttons. Each phone can
be configured for its own unique set of buttons.
Phone MAC
All of the IP phones have a MAC Address. The MAC ID identifies the piece of
equipment for configuration. The auto configuration features of IPitomy rely on
the MAC address to load the proper configuration files into the telephone when
changes are made in the Web-based interface. The configuration files are stored
on the IPitomy 1000 and used when the phone powers back on after a power
down cycle. If the configuration files have been updated when the phone powers
back on, a new configuration is loaded into the phone. When the new
configuration file is loaded, the settings on the phone take priority and will be kept
in tact during the upgrade. Note that at this time only Aastra
phones require and
utilize the MAC address in the phone settings.
Copyright IPitomy Communication, LLC 67 0007VRF
Page 73

CODEC Permissions (Allow CODECs)
These transmission speeds are delivered by the service provider and
automatically register in the extension through the system. These extension
defaults should not be changed.
Voicemail Settings
These settings manage voicemail messaging and routing. When a voicemail box
is created with an extension, it is not possible to change the voicemail box in the
extension screen.
o Attach to Email – Send a voicemail message to an email address by
attaching it to an email message as an audio file (.Wav).
o Delete After Emailing – Delete the voicemail after it has been emailed
to the email address provided for the extension in General Settings.
o Turn Old After Emailing – Turns all voicemail in the voicemail box old
so the message waiting light will not be turned on.
o Say Caller ID – State Caller ID prior to playback of the message.
o Allow Re vie w – Allow callers to review a message after it has been
played.
o Allow Operator – Allow pressing “0” during the voicemail greeting to
reach the system-wide operator.
o Play Envelope Message – Play caller ID and time of call prior to audio
version of a message delivered through email.
o Delete Email After – Define the number of days in which voicemail
messages are to be automatically deleted from a mailbox.
Installation Note 3
Not applicable (NA) accepts the system-wide default set in the System Setup
section of the administration menu. If the global settings are acceptable, leave the
NA setting.
Calling Permissions
Calling permissions define the types of calls that can be sent and received from
an extension and the call actions this extension can take. This feature is useful if
there are certain permissions that an entire group needs to have, but extensions
within that group that need to be restricted. For example, a phone in the lobby of
a small business may be permitted to make local calls and dial extensions within
the business, but be prohibited from making long distance or international calls.
1. Check the permission box if an extension is to have the calling capability.
The following permissions can be set for an extension:
Local Calls – Permits calls that do not require a prefix or “1”
prior to dialing.
Long Distance Calls – Permits both calls that require a prefix
and calls requiring “1” and the prefix before the seven digit
number.
International Calls – Permits calls that begin with “010.”
Incoming Outside Calls – Permits calls made to the business
from people outside the business.
Internal Calls – Permits calls made from internal extensions.
Copyright IPitomy Communication, LLC 68 0007VRF
Page 74

Allow Incoming Intercom Paging – Permits a page to be heard
through this extension.
Allow Outgoing Intercom Paging – Permits a page to be made
through this extension.
Allow User to Forward Calls – Permits an extension to forward
a call or voicemail message to another extension on the system.
Allow User to Record Calls – Permits the extension to record
phone conversations.
Allow User to Monitor Calls – Permits a user to listen to
another extension’s (person’s) phone calls.
Allow Call Park – Permits extension to park a call.
3. Click on Save Changes.
4. Click on Apply Changes when ready to implement changes to the
system.
Edit an Existing Extension
1. Click on Destinations and Extensions. The Extensions page will
appear.
2. Select an extension from the Extension Window on the page.
3. Select an Extension by clicking on the Extension Name or Edit.
4. Make changes to the extension.
5. Click Save Changes.
6. Click Apply Changes when ready to implement changes to the system.
Delete an Extension
1. Click on Destinations and Extensions. The Extensions page will
appear.
2. Select an extension.
3. Click
Delete. The extension will be removed from the Extensions
Window on the page.
Groups
The Group function allows incoming calls to be distributed to a group of extensions rather
than just one extension. Within the Group function, different distributions strategies may
be selected based on the call coverage required by the application. Groups can be
intercom paging groups too. By dialing the intercom button or code followed by the group
number, the group will receive the page over the intercom. Groups are a set of
extensions that are related either because they:
Serve a similar business function.
Work within the same department.
Are located in proximity to each other.
For example, a business might create a group for Sales, Customer Service or
Engineering departments. Groups may also be created for people in similar locations like
a plant floor, the north section of a building or the front office. The goal of a group is to
ring telephones based on the incoming call DID, the Auto Attendant, or the choice
Copyright IPitomy Communication, LLC 69 0007VRF
Page 75
selected by the incoming caller or the time of day. Note that all calls to ring group
members from the ring group number or routed to the ring group will bypass forwarding
settings set on the PBX. The exception to this is that some phones have forwarding
settings which are independent of the PBX (not set through the PBX Web GUI). These
settings will still be applied.
Ring Group Examples
Ring groups define a set of extensions (people) that answer calls. Ring groups can be
created for departments (e.g., Sales or Engineering) or business regions (e.g., north,
south, etc.), or areas of a business (e.g., a warehouse or plant floor). These ring groups
can appear on an Automated Attendant (menu). When the group option is selected from
an Automated Attendant Menu, the call is routed to the group. Calls will be distributed to
the members in the group based upon the ring strategy for the group.
The ring strategy for the group can be set from the drop-down list. Available call
distribution options are:
Ring All
Round Robin
Round Robin (with memory)
Least Recent
Fewest Recent
Fewest Calls
Random
Ring group definitions can be found in the Add a New Ring Group section of this guide. If
a business has the following departments and people:
This business can setup the following ring groups supporting business operations.
Example Ring Group 1 – Departmental Grouping
Group 1 Sales Ext. Group 2 Customer
Service
Cathy Caldwell 123 Gretchen Goodall 134
David Dawson 124 Peter Polk 135
Susan Smith 125
Robert Reed 126
Ext.
Using this ring group scenario the Menu would look like:
Sales (Destination - Group 1).
Customer Service (Destination - Group 2).
Office Manager (Destination - Ext. 113).
The menu prompt for this menu and group arrangement would read as follows:
Thank you for calling ATI Connect a leading manufacturer of cable assemblies and wiring
harnesses. If you know the extension of the party you would like to reach you may dial it
at any time.
For Sales, press 1.
For Customer Service, press 2.
Copyright IPitomy Communication, LLC 70 0007VRF
Page 76

For Accounting, press 3.
Once a call is sent to Sales the ring group strategy might be to have calls answered
Round Robin or distributed to one Sales person after the other.
Example Ring Group 2 – Regional Sales Grouping
Group 1
East Coast Sales
Cathy Caldwell 123 Susan Smith 125 Gretchen Goodall 134
David Dawson 124 Robert Reed 126 Peter Polk 135
Ext. Group 2
West Coast
Sales
Ext. Group 3
Customer
Service
Ext.
Using this ring group scenario the Menu would look like:
East Coast Sales (Destination - Group 1).
West Coast Sales (Destination - Group 2).
Customer Service (Destination - Group 3).
Office Manager (Destination - Ext. 113).
The menu prompt for this menu and group arrangement would read as follows:
Thank you for calling ATI Connect a leading manufacturer of cable assemblies and wiring
harnesses. If you know the extension of the party you would like to reach you may dial it
at any time. For:
East Coast Sales, press 1.
West Coast Sales, press 2.
Customer Service, press 3.
Accounting, press 4.
Calls sent to these groups might use different ring strategies. The East Coast Sales
group might answer calls Round Robin, distributing the calls to each Sale Representative
consecutively. If a sales person is missing from the West Coast team this group might set
phones to Ring All in the group so that calls don’t get missed. The Customer Service
team may get high volumes of calls during a specified period of time in this group calls
may be set to ring Least Recent. Using this strategy the person having answered the
smallest number of recent calls would get the next incoming call.
Copyright IPitomy Communication, LLC 71 0007VRF
Page 77
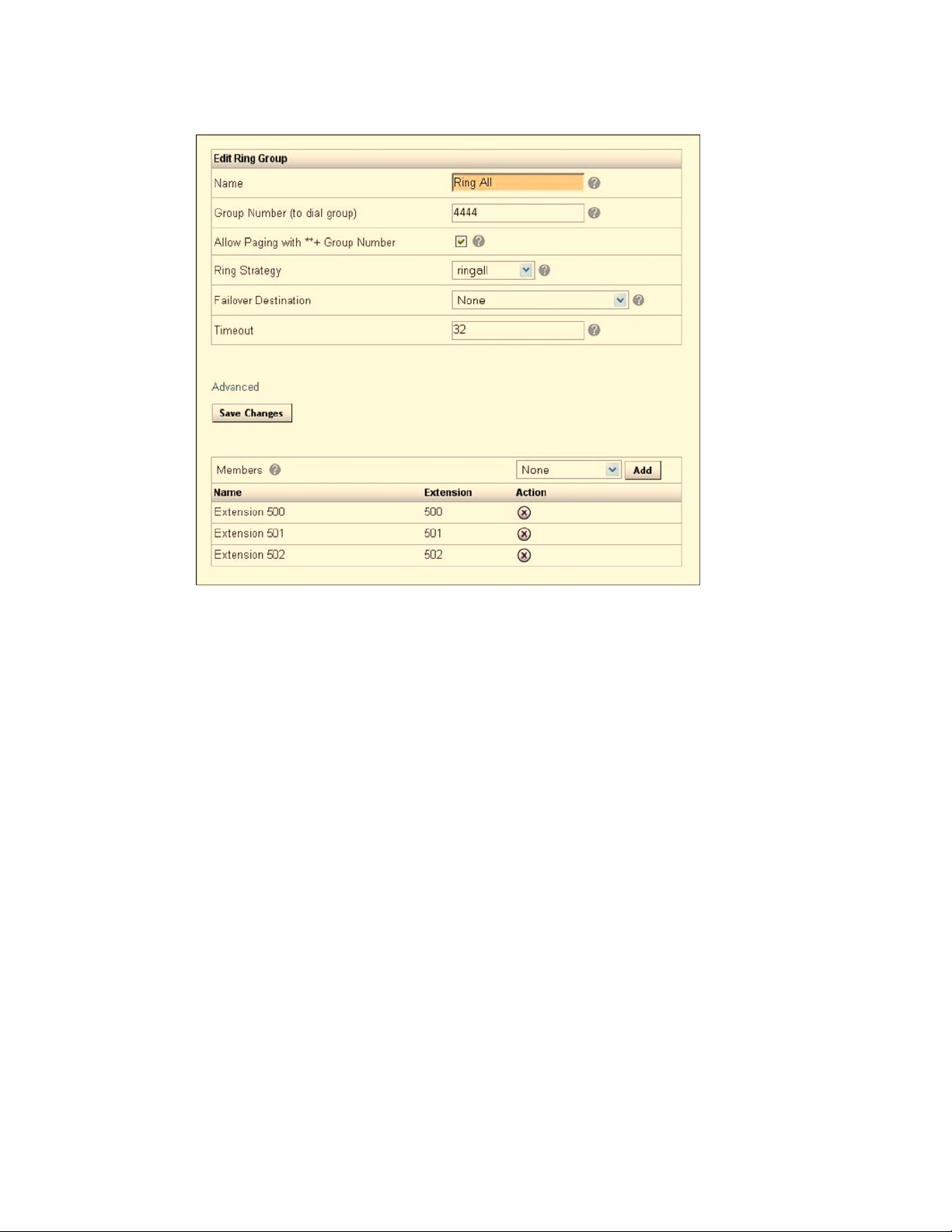
Add a New Group
1. Click Destinations and Groups. The Groups page will appear.
2. Click Add Group. The Edit Ring Group page will appear.
3. Enter a Name for the group.
4. Enter a Group Number. This number must be three or four digits in
length.
5. Check Allow Paging with ** + the Group Number if this group will need
to be paged. Note that only Aastra
phones support this off-hook paging
functionality at this point.
6. Define a Ring Strategy for the group by selecting it from the drop-down
menu. Calls can ring:
Ring All – Ring all phones in the group.
Round Robin – Distributes calls to extensions consecutively one
after the other. Delivers a new call to the first person in the group
only after the last person in the group has taken a call. If an
extension is busy the call will automatically be routed to the next
extension in the group.
Round Robin (with memory) – Distributes calls to extensions
consecutively one after the other. Delivers a new call to the first
person in the group only after the last person in the group has
taken a call. Remembers where the last call was taken and
distributes new calls to the next extension in the rotation.
Least Recent – Distributes a call to an extension in the group
with the longest time between calls.
Copyright IPitomy Communication, LLC 72 0007VRF
Page 78

Fewest Recent – Distributes a call to an extension in the group
that has taken the fewest recent calls.
Fewest Calls – Distributes a call to an extension in the group
that has taken the fewest total calls
Random – Distributes calls randomly to the group.
7. Choose a Fail over Destination for the group’s calls. If no one in the
group accepts the call this is the destination to which the call will be sent.
Destinations can be extensions, other ring groups, a menu or a voicemail
box. Selecting “None” will give the caller a fast busy.
8. Define the time in which calls will timeout, end the ring strategy and
be sent to the fail over destination. Timeout can be between 1 and 32
seconds.
9. Click Save Changes.
10. Click Apply Changes when ready to implement changes to the system.
Advanced Settings
Call Ring Settings
Caller Ring Settings – Defines what a caller will here while they are waiting for
someone to pick up a call from the call group. Callers can either hear:
o Ringing – The phone continues to ring while the caller is waiting.
o Music on Hold – The caller hears music while waiting for a group
member to pick up the call.
Queue Dial String
Queue Dial String is an advanced group setting reserved for IPitomy
administrative support. This field should not be populated.
Edit an Existing Group
1. Click on Destinations and Groups. The Groups page will appear.
2. Select a Group by clicking on the Group Name or Edit.
3. Make changes to the Group.
4. Click Save Changes.
5. Click Apply Changes when ready to implement changes to the system.
Delete a Group
1. Click on Destinations and Groups. The Groups page will appear.
2. Click
Delete. The Group will be removed.
Menus
Menus direct callers to destinations within a business. A menu can route a caller to a
destination once a number on a key-pad has been pressed. A menu prompt tells a caller
what number to press to get to a desired destination. Menus can also be used to provide
information to callers like driving directions etc.
Copyright IPitomy Communication, LLC 73 0007VRF
Page 79
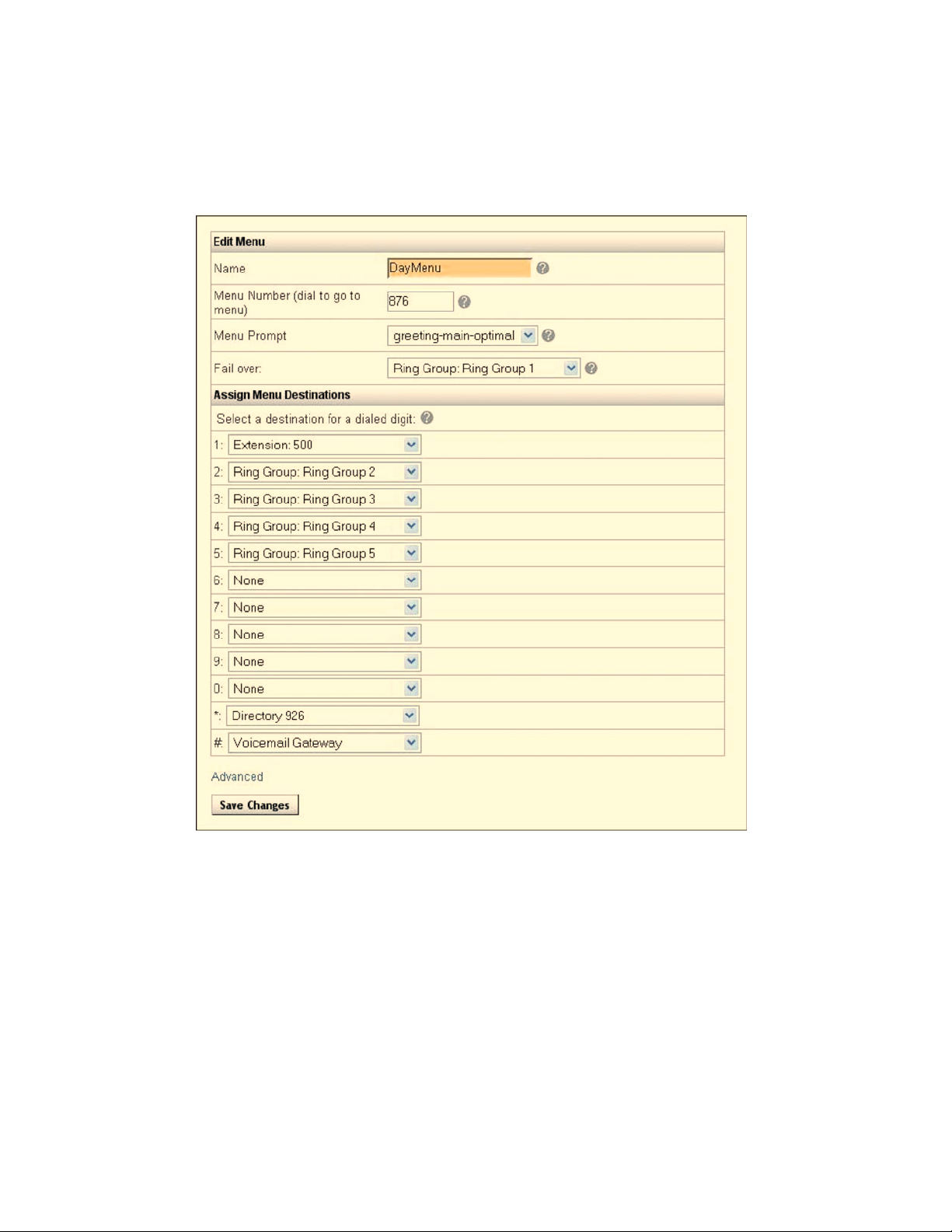
Menu Examples
A business can create a variety of different menus to direct calling traffic through a
business. Some common menu examples are defined for a business with the
departments and people listed below.
Menu Example 1 – Main Menu (Auto Attendant)
This menu example is used to automatically route callers to the destination (person or
group) they would like to speak to. The automated attendant helps minimize the number
of calls to the receptionist and frees up time for other tasks. A Main Menu for this
company might be listed as follows:
Sales (Destination - Group 1).
Customer Service (Destination - Group 2).
Office Manager (Destination - Ext. 113).
The menu prompt for this menu and group arrangement would read as follows:
Thank you for calling ATI Connect a leading manufacturer of cable assemblies and wiring
harnesses. If you know the extension of the party you would like to reach you may dial it
at any time. For:
Copyright IPitomy Communication, LLC 74 0007VRF
Page 80

Sales, press 1.
Customer Service, press 2.
Accounting, press 3.
Calls sent to the Sales department in this case might use a Round Robin ring strategy,
answering calls consecutively one after the other. The Sales team may have times during
the day that there are extremely high call volumes and the team might need to alleviate
the problem of loading one Representative with all of the calls. In this case the company
might set a Fewest Recent ring strategy, which sends a call to the Sales Representative
that has received the smallest number of recent calls. If the Customer Service team is
missing a team member their calls might be set to Ring All, so that the first available
Representative can take a call from a customer.
Menu Example 2 – Regional Sales
This menu example allows the business to direct callers to regional sales groups once
the Sales destination has been selected from the main menu. Then, through Menu 2,
routes callers to Representatives by the region of the country they are calling from:
Menu 1
Sales (Destination - Menu 2).
Customer Service (Destination - Group 2).
Office Manager (Destination - Ext. 113).
Menu 2
New York (Destination - Ext. 123, Cathy Caldwell).
Florida (Destination - Ext. 124, David Dawson).
California (Destination - Ext. 125, Susan Smith).
Arizona (Destination - Ext. 126, Robert Reed).
The menu prompt for this menu and group arrangement would read as follows:
Thank you for calling ATI Connect a leading manufacturer of cable assemblies and wiring
harnesses. If you know the extension of the party you would like to reach you may dial it
at any time. For:
Sales, press 1.
Customer Service, press 2.
Accounting, press 3.
When a caller pressed “1” they would hear a menu prompt for Menu 2:
For sales in:
New York, press 1.
Florida, press 2.
California, press 3.
Arizona, press 4.
In Menu 1 Customer Service might use a Ring All strategy, which would allow the first
available Customer Service Representative to pick up a call. In Menu 2 calls would be
directed to specific Representatives. The Company can set the fail over Destination to
Group 1 (Sales) and set the ring strategy for this group to Ring All. This would direct calls
to any available Sales Representative.
Copyright IPitomy Communication, LLC 75 0007VRF
Page 81

Menu Example 3 – After Hours Menu
This menu directs traffic when the office is closed. After hours calls would be routed
through a Schedule to the After Hours Menu which might be listed as follows for this
company:
1 – Sales (Destination - Sales General Mailbox).
2 – Customer Service (Destination - Customer Service General Mailbox).
3 – Office Manager (Ext. 113).
A menu prompt for this menu might read as follows:
Thank you for calling ATI Connect a leading manufacturer of cable assemblies and wiring
harnesses. We are closed right now, but will respond to your call on the next business
day. If you know the extension of the party you are calling you may dial it at any time. To
leave a message for:
Sales, press 1.
Customer Service, press 2.
All other callers press 3.
Add a New Menu
1. Click on Destinations and Menus. The Menus page will appear.
2. Click Add Menu. The Edit Menu page will appear.
3. Enter a Name for the menu.
4. Enter a Menu Number. This number must be three or four digits long.
5. Select a Greeting (Prompt) to be used for the Menu from the drop-down
box. If a greeting does not exist. Record one and apply it to the Menu
later in the system installation.
6. Select a Fail over Destination for the call. This is where the call will be
directed to if the caller does not select a menu option as directed by the
greeting (prompt).
Select a destination for the dialed digits from the drop-down menu. The system permits
twelve menu selections “0” through “9”, * and #. Destinations can be Groups, Extensions,
Locations in the Business (Conference Rooms), People, Voicemail Boxes, or Branch
Offices (other office locations).
Advanced Menu Settings
Advanced menu settings create rules by which the menu will operate. They also
permit other dialing options if callers do not want to use the menu to reach a
destination within the business.
Response Time Out
Enter the number of seconds the system will wait for a menu selection from the
caller after the greeting (prompt).
Digit Time Out
Enter the number of seconds the system will wait for a digit to be pressed by a
caller after the greeting (prompt).
Number of Times to Play the Greeting Before Time Out
Enter the number of times the greeting is to play before timing out. The minimum
Copyright IPitomy Communication, LLC 76 0007VRF
Page 82

number of times it will play is “1” and the maximum number of times it will play is
“10.”
Fail Over Caller Hears
Setting currently disabled – reserved for future use.
Local Exchange Dialing
This allows callers to dial the extension of the person they are trying to reach, if
they know it. Select “Yes” from the drop-down menu to activate this feature and
No if this is not a menu option.
Edit an Existing Menu
1. Click on Destinations and Menus. The Menus page will appear.
2. Select a Menu by clicking on the Menu Name or Edit.
3. Make changes to the Menu.
4. Click Save Changes.
5. Click Apply Changes when ready to implement changes to the system.
Delete a Menu
1. Click on Destinations and Menus. The Menus page will appear.
2. Click
Delete. The Menu will be removed.
The menu will be removed from the Menu Window on the page.
Meet-me Conferences
The IPitomy Meet-me Conference Bridge allows groups of callers (large and small) to dial
into a conference call. To gain access to the conference, participants dial into an
extension and are admitted to the conference room by entering a PIN number. A
conference call can also be established without a PIN. To reach the two pre-programmed
conference rooms from an extension dial:
Conference 1 – Dial, 901.
Conference 2 – Dial, 902.
The Administrator of the conference call is the person who establishes the call. This
person uses an Administrative Personal Identification Number (PIN). The administrator
can also control how callers enter the conference. If the “Announce on enter” checkbox is
checked, callers will be prompted to record their name as they enter the conference
room. The new participants name will be announced to other participants in the
conference. If the “Enter Muted” checkbox is checked, conference callers will enter the
conference with their phones muted. Users may press the (*1) to disable muting or
enable muting on their telephones during the conference call.
PINs are not permanent, which offers a business the security of knowing that the
conference extensions can be used multiple times without fear of interruption. By
providing a new Administrative and General PIN number each time the room is to be
used for a different purpose the business can prevent conference interruptions from
parties not participating in a call.
Copyright IPitomy Communication, LLC 77 0007VRF
Page 83

Setting Up a Conference
1. Click on Destinations and Conferences. The Conferences page will
appear.
2. Select a conference room.
3. Enter an Administrative PIN (Admin PIN). PIN numbers must be three
or four characters long.
4. Enter a General PIN.
5. Check “Announce on enter” if caller’s should announce their names to
other participants in the conference.
6. Check “Enter Muted” if callers should enter the conference with their
phones muted.
7. Click on Save Changes.
8. Click on Apply Changes when ready to implement the changes to the
system.
Meet-me Conferences Features
Conference Calling offers several features that are available to participants in the
conference. All features are invoked by participants pressing the star (*) key on their
telephone plus a feature code number.
Copyright IPitomy Communication, LLC 78 0007VRF
Page 84

*1 – Mutes and un-mutes your telephone.
*2 – Locks or un-locks the conference to additional participants. (Only available to the
conference administrator).
*3 – Ejects the last participant to enter the conference call. (Only available to the
conference administrator).
*4 – Decrease the Conference volume (voice volume from other participants).
*6 – Increase the Conference volume (voice volume from other participants).
*7 – Decrease User Volume (voice volume from your phone).
*9 – Increase User Volume (voice volume from your phone).
*8 – Exit Menu (terminate volume adjusting input)
Voicemail
There are two places in the system that will allow the management of a voicemail box.
Voicemail boxes associated with an extension are automatically created when an
extension is created and can be administered from the Advanced Settings section of the
Extension. Voicemail boxes that do not have an extension associated with them are
administered as a destination independently. Voicemail boxes not associated with an
extension can be used as a general mailbox for groups or for employees that do not have
extensions, but require a voicemail box.
Creating a Voicemail Box Without An Associated Extension
1. Click Destinations and Voicemail. The Voicemail page will appear with
any extensions that have already been created.
2. Click Add Mailbox. The Edit Voicemail page will appear.
3. Enter the Mailbox Number. Be sure to verify that the number you select
is not being used for a conference (extensions 901 and 902), a group or
an existing extension within the organization.
4. Enter the User’s Name of the Mailbox.
5. Enter a Password for the Mailbox.
6. Enter an Email Address for the Mailbox user.
7. Check Yes, No or Not Applicable (N/A) to the following:
Copyright IPitomy Communication, LLC 79 0007VRF
Page 85

Attach to E-mail – Send a voicemail message to an Email
address by attaching it to an email message as an audio file
(.Wav).
Delete After Email – Delete the voicemail after it has been
emailed to the address provided for the extension in General
Settings.
Turn Old After Emailing – Turn the message old after emailing.
Say Caller ID – State Caller ID prior to playback of the message.
Allow Review – Permits callers to review a voicemail message
after it has been recorded.
Allow Operator – Allows people calling this mailbox to press ‘0’
to go to the system operator destination.
Play Envelope Message – Plays caller ID and time of call prior
to audio version of a message delivered through Email.
Implementation Note 4
Not applicable (N/A) denotes that this mailbox should use the system wide
default settings for this setting.
8. Define the number of days in which voicemail messages are to be
automatically deleted from the mailbox. The minimum number of days is
1 and the maximum number of days is 365.
9. Click Save Changes.
10. Click Apply Changes when ready to implement changes to system.
Edit an Existing Voicemail Box
1. Click on Destinations and Voicemail. The Voicemail page will appear.
2. Select a Voicemail Box by clicking on the Voicemail Box Name or
Edit.
3. Make changes to the Voicemail Box.
4. Click Save Changes.
5. Click Apply Changes when ready to implement changes to the system.
Delete a Voicemail Box
1. Click on Destinations and Voicemail. The Menus page will appear.
2. Click
Delete. The Voicemail box will be removed.
Schedules
A schedule is a destination. A schedule defines the destination to which calls are to be
routed for a specified time period. A schedule can be used to define when a business,
department, group or extension is open, closed or out to lunch. The IPitomy 1000
automatically creates a schedule when an extension is provisioned in the system. These
schedules are very flexible. They are designed to accommodate even the most complex
business hour scenarios.
Copyright IPitomy Communication, LLC 80 0007VRF
Page 86

Multiple schedules can be created that account for different business, customer,
departmental or system user needs. Schedules do not need to be applied to an entire
company, they can be applied to individual destinations or routes based on the needs of
a business. This works well in businesses where departments have different business
hours, but are served by the same system.
Create A Schedule
1. Click on Destinations and Schedules. The Schedules page will appear.
2. Click Add Schedule. The Edit Schedules page will appear.
3. Enter a Name for the Schedule.
4. Define Hours of Operation for the schedule by selecting times from the
Start and Stop drop-down boxes for each day of the week.
5. Select a destination for calls that are In Hours. Destinations can be
Groups, Extensions, Locations in the Business (Conference Rooms),
People, Voicemail Boxes, or Branch Offices (other office locations).
6. Check Apply Forward Settings. This will apply the Forward Settings
established within each destination. Note there are only forwarding
settings on extensions currently, so this will not effect destinations that
do not have forwarding settings.
7. Select a destination for calls that are “Outside of Hours.”
8. Check Apply Forward Settings.
9. Define Lunch Hours for the schedule by selecting times from the Start
and Stop drop-down boxes for each day of the week. Lunch hours must
be within the hours of operation for the respective day.
10. Select a destination for calls during Lunch Hours.
Copyright IPitomy Communication, LLC 81 0007VRF
Page 87

11. Check Apply Forward Settings.
12. Click the “Save Changes” button to save the schedule data.
13. Creating Holiday Schedules:
Enter a Name the Holiday.
Clicking the “add” button to create the holiday, the Holiday name
appears in the Holiday list.
Highlight (Select) the new holiday in the Holiday list.
Enter a Start and End Date for the Holiday in the Month, Day
fields.
Enter a Start and End Time for the span.
Enter a destination for calls during the Holiday.
Click the “Set” button to save the holiday data.
Repeat this process for each Holiday observed.
Note that Holidays override the operating hours for the time frame specified.
This time is all inclusive, meaning it includes ALL times between the start and
the stop times.
14. Click Save Changes.
15. Click Apply Changes when ready to implement changes to the system.
Editing an Existing Schedule
1. Click on Destinations and Schedules. The Schedules page will appear.
2. Select a Schedule by clicking on the Schedule Name or Edit.
3. Make changes to the Schedule.
4. Click Save Changes.
5. Click Apply Changes when ready to implement changes to the system.
Deleting a Schedule
1. Click on Destinations and Schedules. The Schedules page will appear.
2. Click
Deleting a Holiday
1. Click on Destinations and Schedules. The Schedules page will appear.
2. Click the Schedule Name containing the Holiday to be deleted.
3. In the Holidays section, highlight the Holiday name you want to delete.
4. Click the “remove” button.
Delete. The Schedule will be removed.
5. Click the “Save Changes” button.
Copyright IPitomy Communication, LLC 82 0007VRF
Page 88

Branch Offices
Branch Offices is a powerful tool that is used to link up multiple PBX’s located in external
offices. By utilizing Branch Offices you are able to create direct extension dialing from
one office location to another with a simple dialing prefix.
Configuring Router
Please see Appendix on Router Configuration
Configuring Office 1
1. Click on Destinations and Branch Offices. The Branch Offices page
will appear.
2. Click on Add Office.
3. Give a unique name for the connection
4. Type dynamic for host.
5. Create a unique dialing prefix for the extensions connected to the Office
1 PBX.
6. Give a unique password for the connection.
7. Select No for register. (Note that registration is not required if host is
known).
8. Leave qualify at 30000.
9. Click Save Changes
10. Click Apply Changes
Configuring Office 2
1. Click on Destinations and Branch Offices. The Branch Offices page
will appear.
2. Click on Add Office.
3. Name should match that given to the Office 1 PBX. The name should
only contain alpha-numeric characters and no spaces.
Copyright IPitomy Communication, LLC 83 0007VRF
Page 89

4. Host needs to be the external IP address or domain corresponding to the
IP of the main office PBX.
5. Create a unique dialing prefix for the extensions connected to the Office
2 PBX.
6. Password needs to be the same as the one assigned in the Office 1
PBX.
7. Select Yes for register.
8. Leave qualify at 30000.
9. Click Save Changes
10. Click Apply Changes
To setup up multiple PBX’s just follow the above pattern linking each PBX to each other
and use a unique dialing prefix for each one.
To place a call from one Branch Office to another just dial the prefix that was assigned to
that locations PBX + the extension of the user trying to be reached at the other office.
This same easy concept works for transferring calls from one Branch Office to another.
Branch Extensions
Branch Extensions can also be added to a branch office. These extensions are created
through the add extension field at the bottom of the branch office edit page. Branch
extensions can be dialed directly without a prefix, provided that these extensions are
properly configured on the PBX for which the branch extensions are defined. Branch
extensions will appear in call routing drop down lists throughout the system after they are
created.
Configuring Office 2 with branch extensions
1. Click on Destinations and Branch Offices. The Branch Offices page
will appear.
2. Click on the branch office connection for Office 1
3. Assuming Office 1 has extensions 100-110. Enter 100-110 in the field
Copyright IPitomy Communication, LLC 84 0007VRF
Page 90

above the add button. You can also enter individual extension numbers.
These numbers are checked against existing system extensions to
insure conflicts are not created.
4. Click the Add button
5. Apply Changes
6. Verify dialing the new extensions from phones registered to Office 2.
Call Routing
Routing tells the system what destination to send calls to within the business. It also tells the
system what provider services to use when making outbound calls.
Incoming Routing
The Incoming Routing administration specifies system routing, the service provider and
DID level for incoming calls. The different levels may overlap at times so it is important to
understand their order of precedence:
Phone Number
Provider (how that phone number arrives at the system)
System Default
The system default destination is the weakest precedent. The provider levels and the
specific numbers being routed follow in precedent. When the stronger precedent is set to
default it will follow the weaker precedents. If the route is set to something other than
default it will override the weaker precedents.
For example, if a user selects default for a phone numbers incoming destination and the
provider of that phone number is a SIP provider, when that number is called from the
PSTN it will route to the default destination of the provider. If the provider destination is
set to default, the system will route calls to the system’s default incoming destination. If
the provider had a destination other than the system default, the call would route to that
destination rather than the system default. If the particular phone number is set to a
destination other than default, the system will route a call to that destination rather than
the provider or system defaults.
The IPitomy 1000 allows for flexible routing arrangements. Calls can initially be routed to
a Menu, Schedule, Extension or Group. Establishing Incoming Routing sets the default
destination for all calls.
Copyright IPitomy Communication, LLC 85 0007VRF
Page 91

Setting the Default Incoming Destination
To set the Default Incoming Destination:
1. Click on Call Routing and Incoming. The Incoming Call Routing page
will appear.
2. Select a Default Incoming Destination from the drop-down box.
3. Click the Set button.
4. Click the Save Changes button.
Defining the Service Provider Destination
A service provider destination can also be defined. The service provider destination acts
as the default incoming destination for a particular provider. To set the service provider
destination:
1. Select an Incoming Destination from the drop-down box.
2. Click on Save Changes button.
3. Click on Apply Changes when ready to implement these changes to the
system.
Outgoing Routing
Outgoing routing tells the system what service providers certain types of calls should use.
The IPitomy 1000 comes with common outgoing call routes already provisioned in the
system:
7 digit dialing
10 digit dialing
Copyright IPitomy Communication, LLC 86 0007VRF
Page 92

11 digit (1+ dialing)
International
Emergency Calls
Custom Dialing
These routes cannot be deleted from the system.
Adding A New Call Subroute
A sub route is a specific pattern within a route type that will be routed differently from
other routes. For instance, if you add 858 as a route to 10 digit or 11 digit dialing, you can
define the trunks that specifically route to that area code. If you do not add any trunks to
the newly created sub route, that dialing pattern is effectively blocked and users of the
phone system will hear “all outgoing lines are unavailable” when attempting to dial the
858 area code.
1. Click Call Routing and Outgoing. The Outgoing Call Routing page will
appear.
2. Click the Add Route button. The Edit New Outgoing Route page will
appear.
3. Enter a Route Name.
4. Select the Route Type the call is to take. This identifies the call as:
a) Local (7-digit)
b) 10 Digit
c) Long Distance (1+10 digit) dialing
d) International
5. Assign a routing Number.
Editing An Existing Route
To change a call route to a different service provider or to change the order in which calls
are routed over providers:
1. Click on Call Routing and Outgoing Routing. The Outgoing Routing
page will appear.
2. Select a Route in the Route Window to be changed.
3. Click Edit. The Edit Route page will appear.
4. Change the Route Name, Type and Number as needed.
5. Change the Trunk associated with the Route.
Changing the Order Service Providers are Selected
From the service providers available:
1. Click on the Name of a provider.
2. Click the Up or Down button to position the provider. Calls will be routed
in the order the service providers appear in the list.
3. Repeat this process until the providers are in the order calls should be
routed over the available service providers.
Copyright IPitomy Communication, LLC 87 0007VRF
Page 93
Adding a Service Provider
1. Select a service provider from the drop-down box to the left of the
Trunks list.
2. Click Add. The service provider will appear in the list.
3. Click on the Name of the provider.
4. Click the Up or Down button to position the service provider in the list in
the order calls are to be routed over this resource.
Deleting a Service Provider
1. Click on a Service Provider in the list.
2. Click Delete.
3. Click on Save Changes.
4. Click on Apply Changes when ready to implement these changes to the
system.
Implementation Note 5
Default Settings For Existing Routes
The Outgoing Call Routes already in the IPitomy 1000 ha ve the following default
settings Route Type and route Number. These default settings cannot be
changed. The Name of the route, service provider associated with the route and
the order in which service providers are selected for the route can be changed.
PBX Setup
PBX setup is used by a System Administrator to manage system-specific and system-wide
capabilities of the IPitomy1000.
General
General setup manages the Administrative Settings for the system: User Name,
Password and Time Zone.
Edit General Settings
1. Click on PBX Setup and General. The General System Setup page will
appear.
2. Enter an Administrative User Name.
3. Enter an Administrative Password.
4. Re-enter the Password.
5. Select a Time Zone from the drop-down box provided.
6. Select a System Operator Destination. This is the destination that
people will go to when pressing ‘0’ while in a voicemail box, if Allow
Operator is enabled on a voicemail box.
Copyright IPitomy Communication, LLC 88 0007VRF
Page 94

7. Select Mailbox Exit destination – this is the destination calls will be
routed to when leaving a voicemail box.
8. Select Directory Type – this is the type of directory to use for the
Directory destination.
9. Click on Save Changes.
10. Click on Apply Changes when ready to implement changes to the
system.
Database
The IPitomy 1000 is like a computer, in that; information can be stored in the system or
backed up in case it goes down. For additional protection, the system also allows a copy
of the system setup to be stored in an external source like a computer or CD. The
Database section of online administration manages the process of downloading and
storing copies of the system setup to the system itself or an external source.
Backing Up a Copy of the System’s Setup
The system can be backed up to an internal database or to an external source like a
computer or CD.
1. Click on PBX Setup and Database. The Database Setup page will
appear.
2. To back up a copy of the System’s Setup to the internal database,
click the Backup button. The backup version of the file will appear in the
Databases Window with the Date, Time and Version of the backup.
3. To back up a copy of the System’s Setup to an external source like a
computer or CD, click on
Download button. Give the file a name
and store it in a place that is easily accessible.
Restoring a Copy of System’s Setup
The system can be restored from a copy of the System’s Setup in the internal database
or from a copy on an external source.
1. Click on PBX Setup and Database. The Database Setup page will
appear.
2. To restore a copy of the System’s Setup using the internal database,
select the Backup version to be restored from the Database Window
and click the
Restore button. This will restore the version of the
System’s Setup selected.
2. To restore a copy of the System’s Setup using an external source,
Browse for the file in the external source (click Open from the operating
system for the file to appear in the Browse Window) and click Send File.
The Backup file will appear in the Database Window. Click Restore.
3. Click on Apply Changes when ready to implement these changes to the
system.
Copyright IPitomy Communication, LLC 89 0007VRF
Page 95

Deleting a Backup Version from the System
1. Click on PBX Setup and Database. The Database Setup page will
appear.
2. To delete a copy of the System’s Setup from the internal database,
select the Backup version to be deleted from the Database Window
and click the
Delete button. This will delete the version of the
System’s Setup selected.
3. To delete a copy of the System’s Setup from an external source, use
the delete function of the operating system or throw away the CD that
contains the Backup file.
Voicemail
System-wide voicemail defaults define the rules by which voicemail boxes operate. In the
IPitomy 1000 General, Menu and Email settings can be set for voicemail boxes systemwide.
General
General settings relate to the capacity (storage time and message length) of a voicemail
box. To define the General Settings:
1. Click on PBX Setup and Voicemail. The Voicemail Settings page will
appear. Within this page are the General Settings.
2. Enter the following General Settings:
Maximum Number of Messages – This is the greatest number
of voicemail messages a box can hold. The system limit is 300.
Maximum Message Length – This is the longest duration of
time allowable for each message. The system limit is 10 minutes.
Minimum Message Length – This is the shortest duration of
time allowable for each message. The system minimum is 2
seconds.
Maximum Greeting Length – This is the longest duration of
time allowable for a voicemail greeting. The system maximum is
30 seconds.
Maximum Seconds of Silence – This is the longest duration of
time a caller can be silent before the system considers the call
complete. Setting this to zero will end the voicemail recording
when the caller terminates the call or connection. The system
maximum is 20 seconds.
Silence Threshold – This is the amount of time that the system
will wait for a response from a caller leaving a message.
3. Click Save Changes.
4. Click on Apply Changes when ready to implement these changes to the
system.
Copyright IPitomy Communication, LLC 90 0007VRF
Page 96

Voicemail Settings
1. Select and enter Voicemail Menu settings:
Play the Envelope Message – This is the Time and Date of the
call.
Say Caller ID – This plays the caller’s phone number when
available.
Skip MS on Playback – This is the interval (in Milliseconds) that
voicemail will skip forward or backward on playback. This
number must be between 1 and 4.
Maximum Failed Login Attempts – This is the maximum
number of times a user may try to login to a voicemail box before
the system disconnects the call. This number must be between 3
and 5.
On Delete, Play Next Message – This tells the system to play
the next message in queue when a message has been deleted.
2. Click Save Changes.
3. Click on Apply Changes when ready to implement these changes to the
system.
Email Settings
1. Select Yes or No to allowing voicemail messages to be attached as an
2. Set the from address for the email address you would like the attached
3. Voicemail Server can either be Loc (local) or Ext (External).
4. Authentication Required can either be Yes or No
5. User Name – user name required for authentication
6. Password – password for authentication that is associated with the
7. Click on Save Changes.
8. Click on Apply Changes when ready to implement the changes to the
audio file (.Wav) to the email address associated with the voicemail box.
voicemail to be sent from.
Local – internal PBX mail server
External – an external mail server such as (smtp.ipitomy.com)
Yes – authentication is required for this mail server
No – authentication is not required for this mail server
above user name.
system.
* For external mail servers please check with your ISP or hosting
provider for their required settings.
Copyright IPitomy Communication, LLC 91 0007VRF
Page 97

* There is no guarantee that an external mail server will work, some
ISP’s or hosts may have mail filters and could block a message.
Advanced Settings
Allow Review – Allows users to review a message after it has been played.
Allow Operator – Allows people calling this mailbox to press ‘0’ to go to the system
operator destination.
Voicemail Archive
Download
Creates a backup of all user Voicemail messages, message envelopes and
greeting files. The backup file is downloaded to your computer.
Erase
Deletes all user Voicemail data on the PBX, including personal greetings.
Upload
Restores a previously made backup.
Tip: Voicemail recordings may contain sensitive information. You should only
store Voicemail archives in a secure location.
Session Initiation Protocol (SIP) Settings
These settings tell the system the IP address of calls coming into the system and the
local network. In addition, they define to which communication traffic the system is to
listen. To provision SIP settings enter the:
External IP – This is the IP address of the ISP and can be obtained from the network
router. The external IP address can also be obtained online at whatismyip.com
the address in a Web browser click Enter and the external IP address will appear on
a page.
Local Network – This is the default IP address of the router with the last digit
replaced by a zero. In most cases the default router address will be 192.168.1.1. By
replacing the last digit (1) with a zero this indicates that the local network (traffic
addressed to 192.168.1) includes any variation of the fourth number in the IP
address. This means that the local network includes traffic addressed to:
192.168.1.1, 192.168.1.2, 192.168.1.3 etc.
Subnet Mask – Leave the default setting for the Subnet Mask as is (255.255.255.0).
Provided by the router, this mask tells the network what communication traffic to
listen to. For example, the setting 255.255.255.0 tells the system to listen to
communication traffic sent to “192.168.1” for any variation of the fourth number
(designate by the zero at the end).
Implementation Note 6
For the Loca l Network and Subnet Mask to work correctly the fourth digit in
both numbers must be a “0.” The zero in the Subnet Mask indicates that the network is
. Type
to listen to traffic addressed to any IP address within the Local Network. The Zero in the
Local Network indicates that the Local Network can include an IP address with any
variation of the fourth number.
Copyright IPitomy Communication, LLC 92 0007VRF
Page 98

Advanced Settings
Advanced SIP settings define in more detail the management of network traffic.
These settings are automatically provisioned when the system registers with the
router. In most business implementations it is not necessary to make changes to
these settings.
Prompts
A prompt or greeting can welcome a caller to the business, direct them to a destination,
provide instructions or deliver information. The IPitomy 1000 makes managing prompts
easy.
Upload Voice Prompt
1. Click PBX Setup and Prompts. The Edit Prompts page will appear.
2. Select Browse and locate the prompt file to be uploaded.
3. Open the file using the operating system. The file will appear in the
File Name Window.
4. Enter a Name for the File in the Description field.
5. Click on Upload File. The file will appear in the Prompt Files on Server
Window. It will display the File Name, Description and Size.
6. Click on Save Changes.
7. Click on Apply Changes when ready to implement these changes to the
system.
Record New Voice Prompt
1. Click PBX Setup and Prompts. The Edit Prompts page will appear.
2. Define a Prompt Name and Description.
3. Assign an Extension to the prompt.
4. Click Record. The system will dial the extension assigned to the prompt.
A message screen will appear on the computer indicating that the
system is trying to reach the extension.
5. Answer the call from the system and record the prompt.
6. Click the Continue button on the message screen. The new prompt will
appear in the Prompt Files on Server Window. It will display the File
Name, Description and Size.
7. Click on Save Changes.
8. Click on Apply Changes when ready to implement these changes to the
system.
Copyright IPitomy Communication, LLC 93 0007VRF
Page 99

Download a Prompt
1. Click PBX Setup and Prompts. The Edit Prompts page will appear.
2. Select a prompt from the Prompt Files on Server Window.
3. Click
Download. The prompt will download.
Delete a Prompt
1. Click PBX Setup and Prompts. The Edit Prompts page will appear.
2. Select a prompt from the Prompt Files on Server Window.
3. Click Delete. The prompt will be deleted from the list.
4. Click Save Changes.
5. Click Apply Changes when ready to implement these changes to the
system.
Music on Hold
In a busy business it is sometimes necessary to place callers on hold. Playing music
while a caller waits can make this time more pleasant. Music files must be in .MP3
format.
Add New Music Files
1. Click PBX Setup and Music on Hold. The Music on Hold page will
appear.
2. Click Add New. The Edit Music on Hold Page will appear.
3. Name the music play list.
2. Set Random to Yes or No. If the music file is to play randomly, select
Yes. If it is to play sequentially with files that already exist, then select
No.
Copyright IPitomy Communication, LLC 94 0007VRF
Page 100

3. Click Save Changes.
4. Select Browse and locate the music file to be uploaded.
5. Open the file using the operating system. The file will appear in the
Load This Music File Window.
6. Click on Upload File. The file will appear under the play list of which it
was uploaded too.
Edit Existing Music Files
1. Click PBX Setup and Music on Hold. The Music on Hold page will
appear.
2. Select a music file from the Music on Hold Main page.
3. Select a play list by clicking on the play list Name or Edit.
4. Change the Name, Random Setting, Load a New File, or Delete the
existing files.
5. Click Save Changes.
6. Click Apply Changes.
Delete a Play list
1. Click PBX Setup and Music on Hold. The Music on Hold page will
appear.
2. Select a Music on Hold play list.
3. Click
Delete. The play list will be deleted from the list.
* Note if the individual music files aren’t deleted from inside the play list, the music files
will be generated inside the next play list created.
Setting Music on Hold
1. Click PBX Setup and Music on Hold. The Music on Hold page will
appear.
2. Select your default Music on Hold play list from the dropdown menu.
3. Click Set System Default.
4. Click Apply Changes.
Copyright IPitomy Communication, LLC 95 0007VRF
 Loading...
Loading...