3B SCIENTIFIC® PHYSICS
Apparatur zum Boyle-Mariotte Gesetz U30046
Bedienungsanleitung
11/08 ALF
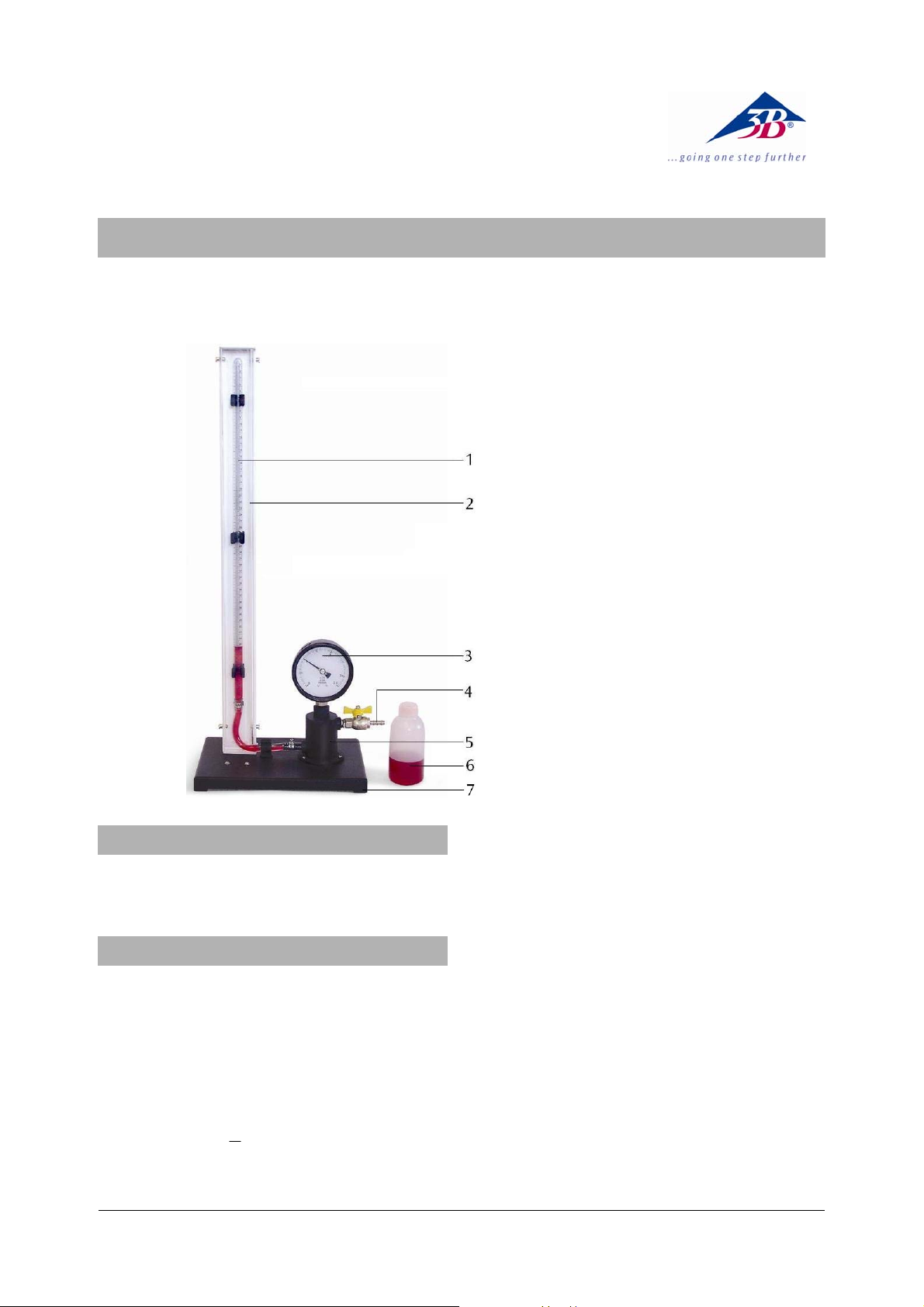
1 Glasrohr
2 Metallplatte
3 Manometer
4 Hahn mit Pumpenanschluss
5 Öl-Vorratsbehälter
6 Ersatzöl
7 Grundplatte
1. Sicherheitshinweise
• Druck nicht über den Messbereich des
Manometers erhöhen.
2. Beschreibung
Die Apparatur zum Boyle-Mariotte Gesetz dient zur
experimentellen Bestimmung der Abhängigkeit von
Gasvolumen (Luft) und Druck bei konstanter
Temperatur (Gesetz von Boyle-Mariotte).
Das Gesetz von Boyle-Mariotte besagt, dass bei einer
gegebenen Gasmenge bei gleichbleibender
Temperatur das Produkt aus dem Volumen V und
dem Druck p konstant ist:
kVP =⋅ ⇒
kp1⋅=
V
1
Die Apparatur besteht aus einem mit Luft gefüllten,
extra starken Glasrohr mit Graduierung montiert auf
einer weißen Metallplatte. Aus Sicherheitsgründen ist
das Glasrohr von einer zusätzlichen
Plastikabschirmung umgeben. Das Glasrohr ist
verbunden mit einem Öl-Vorratsbehälter, auf den ein
Manometer aufgesetzt ist. Über eine Handpumpe wird
rotes Öl aus dem Vorratsbehälter in das Glasrohr
gepumpt und so die eingeschlossene Luft
komprimiert. Das Volumen der eingeschlossenen Luft
ist leicht an einer Skala am Glasrohr ablesbar,
während der Druck am Manometer in Pa x 10
angezeigt wird (Normaldruck = 1,01325 x 10
Das Manometer ist mit einer durchsichtigen Rückseite
ausgestattet, so dass seine Funktionsweise beobachtet
werden kann.
5
Pa).
5
3. Technische Daten
Pumpenanschluss: 10 mm Ø
Max. Druck: 3,4 x 10
5
Pa
Abmessungen: ca. 350 x 200 x 760 mm³
4. Zusätzlich erforderliche Geräte
1 Hand Vakuumpumpe U20500
5. Bedienung
5.1 Aufbau
• Glasrohr vorsichtig in die Klemmen auf der
Metallplatte einschieben und auf der Grundplatte
aufbauen.
• Hahn öffnen und Öl-Vorratsbehälter so weit
auffüllen, dass bei normalem Luftdruck das Öl
den unteren Bereich der Skala erreicht. Dabei
darauf achten, dass nicht zuviel Öl eingefüllt wird,
da es sonst durch den Pumpenanschluss in die
Pumpe gelangen kann.
• Manometer vorsichtig aufschrauben.
• Handpumpe anschließen.
5.2 Durchführung
• Anfangsvolumen der Luft und angezeigten Druck
in einer Tabelle notieren (siehe Tabelle 1).
• Mittels der Pumpe Druck etwas erhöhen, dann ca.
1 Minute warten, bis die Apparatur wieder Raumtemperatur erreicht hat.
• Druck und Volumen in die Tabelle eintragen.
• Schritte wiederholen, bis genügend Messwerte
vorhanden sind.
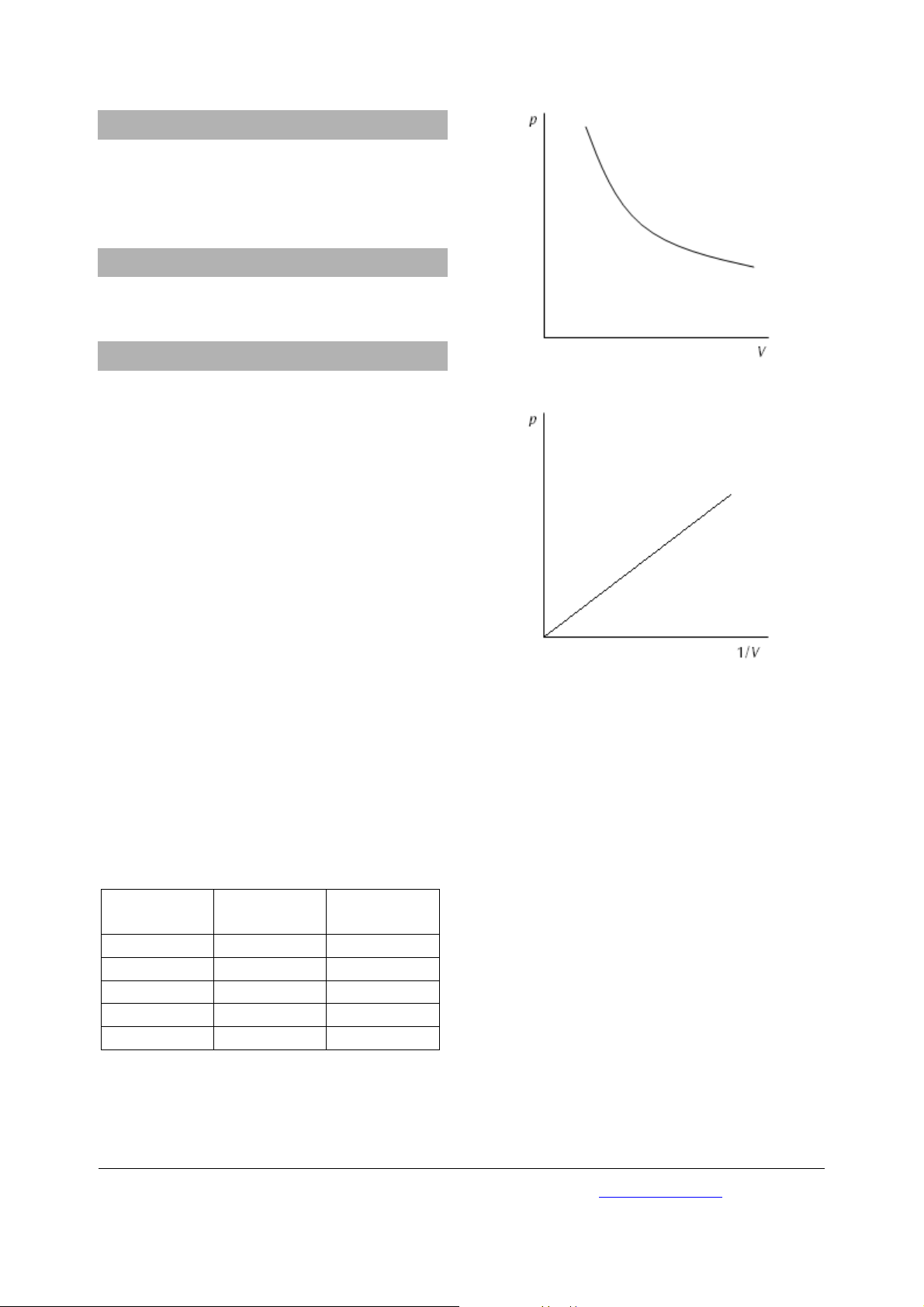
• Druck in Abhängigkeit des Volumens und in
Abhängigkeit von 1/V graphisch darstellen (siehe
Fig. 1 und 2).
Volumen der
Luft V, (ml)
Druck p
(Pa x 105)
1/V (ml
-1
)
Tab. 1 Messwerte
Fig. 1 Druck in Abhängigkeit des Volumens
Fig. 2 Druck in Abhängigkeit von 1/V
3B Scientific GmbH • Rudorffweg 8 • 21031 Hamburg • Deutschland • www.3bscientific.com
Technische Änderungen vorbehalten
© Copyright 2008 3B Scientific GmbH
3B SCIENTIFIC® PHYSICS
Boyle’s Law Apparatus U30046
Instruction Sheet
11/08 ALF
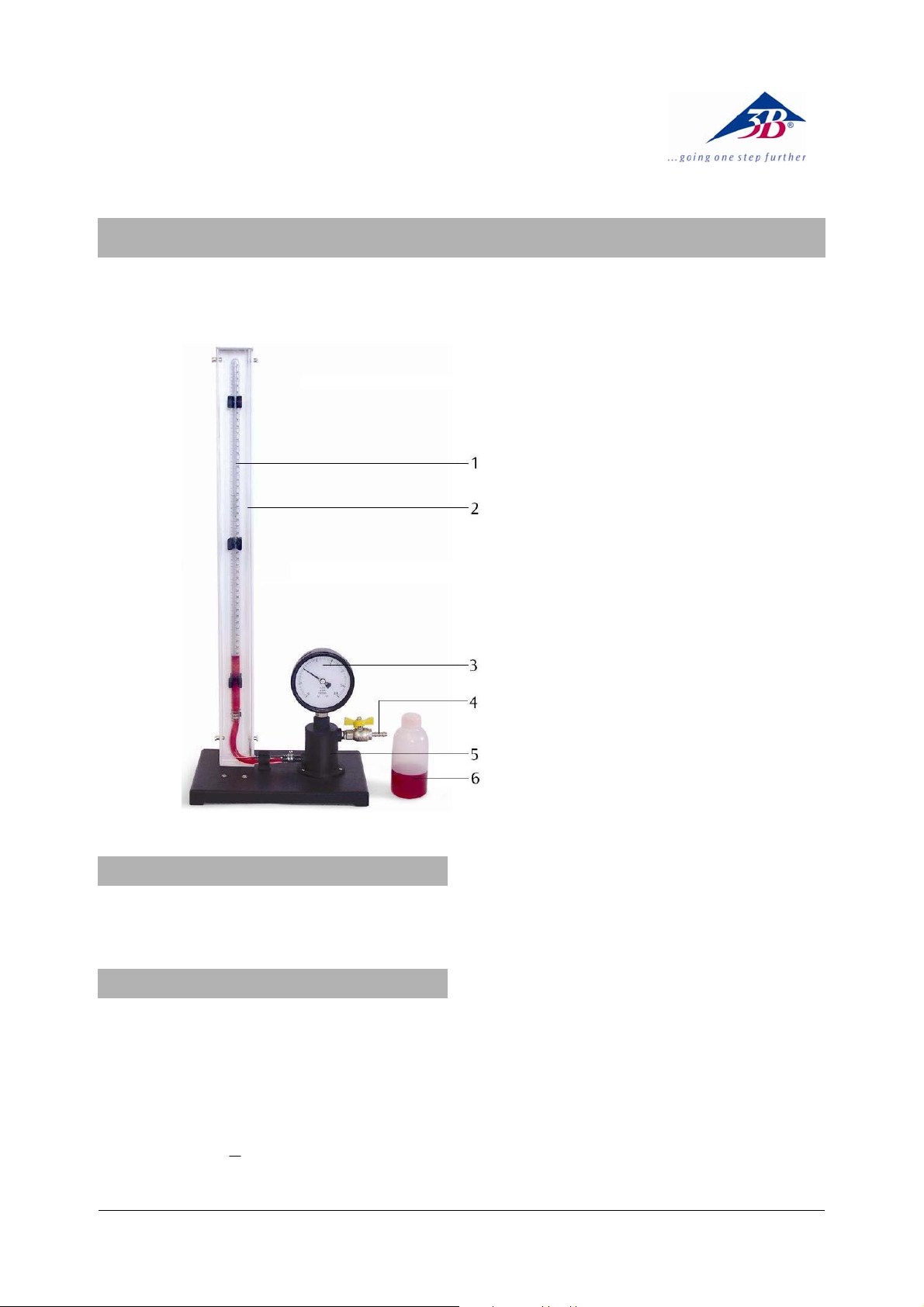
1 Spare oil
2 Oil reservoir
3 Hose connection
4 Bourdon gauge
5 Plastic safety screen
6 Calibrated glass tube
7 Metal plate
1. Safety instructions
• Avoid going beyond range on pressure meter.
2. Description
Boyle’s Law apparatus is used for the experimentbased determination of the relationship between the
volume and the pressure of a gas (air) at constant
temperature (Boyle’s Law).
Boyle’s law states that for a given mass of gas (air) at a
constant temperature the product made up of the
volume V and the pressure p is constant:
kVP =⋅ ⇒
kp1⋅=
V
The apparatus is essentially a calibrated glass tube
mounted on a white metal plate. The glass tube is
extra strong and additionally protected by a plastic
safety screen. It is connected to an oil reservoir on
which a Bourdon gauge is fitted. By means of a hand
pump coloured oil is gradually pumped from the oil
reservoir into the tube creating over pressure. Whilst
the volume of the trapped is read from a scale clearly
visible at the tube, pressure is measured by a Bourdon
gauge, which reads in Pa x 10
1.01325 x 10
transparent plastic back to allow students to see its
working parts.
1
5
Pa). The Bourdon gauge is fitted with a
5
. (Standard pressure =
3. Technical data
Hose nipple: 10 mm dia.
Pressure max.: 3.4 x 10
5
Pa
Dimensions: approx. 350 x 200 x 760 mm³
4. Additionally required equipment
1 Vacuum hand pump U20500
5. Operation
5.1 Assembly and set up
• Insert the glass tube carefully into the clamps on
the metal plate and mount it on to the base plate.
• Open the stop cock and fill up the oil reservoir so
that at normal atmospheric pressure the oil just
reaches the bottom calibration on the tube. Be
careful not to fill in too much oil, because
otherwise it might flow out through the hose
connection into the pump.
• Screw on the Bourdon gauge carefully.
• Attach the hand pump.
5.2 Experiment procedure
• Record the reading on the tube (the volume) and
the reading on the manometer in a table (refer to
table 1).
• Use the pump to increase the pressure slightly,
and then allow a minute for the apparatus to
return to room temperature.
• Repeat the readings of pressure and volume.
• Repeat this process until you have sufficient
readings.
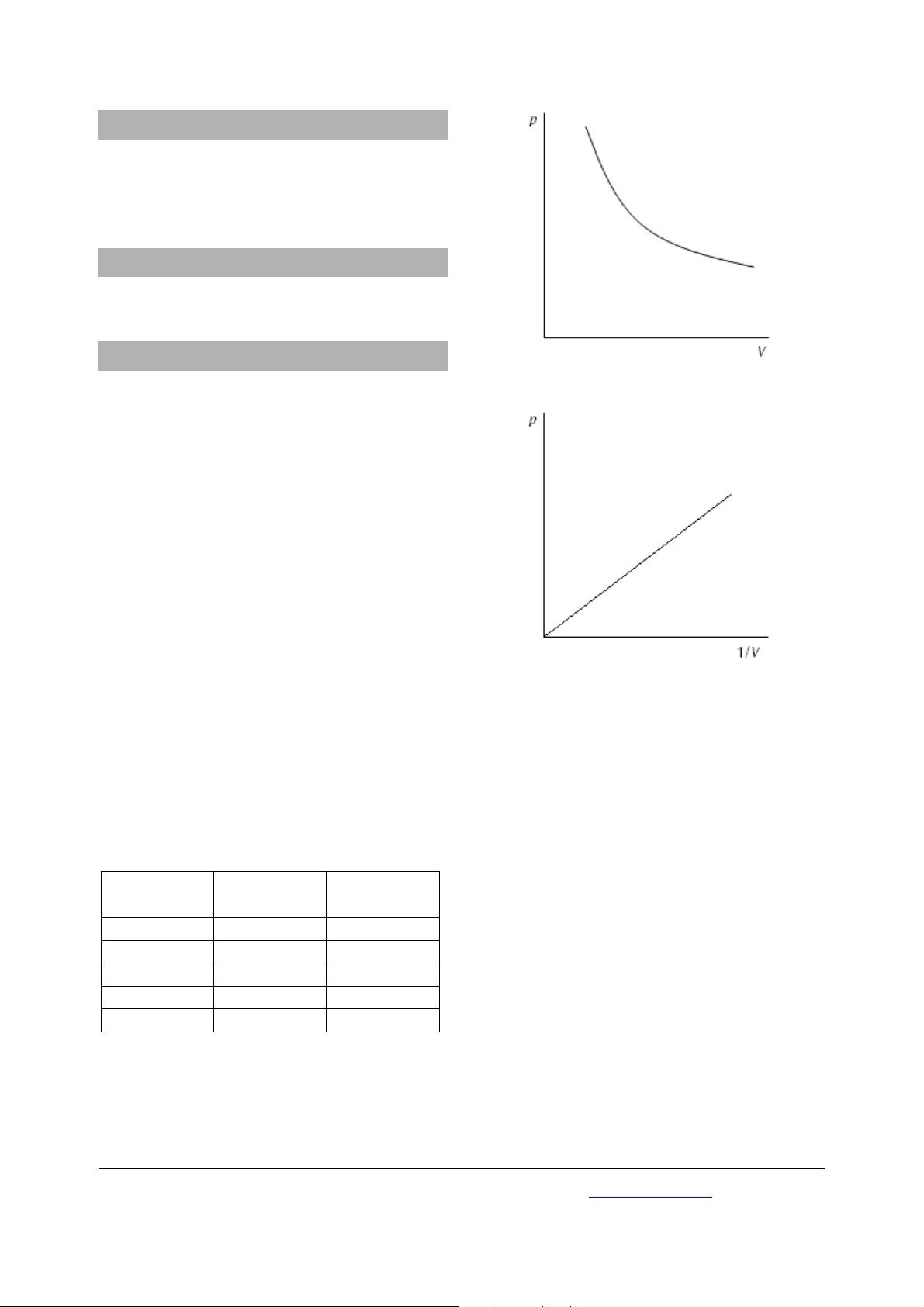
• Plot the values in a graph of p against V and p
against 1/V (refer to fig. 1 and 2).
Volume of air,
(V /ml)
Pressure p
(Pa x 105)
1/V (ml
-1
)
Table 1 Measuring values
Fig. 1 Graph of pressure against volume
Fig. 2 Graph of pressure against 1/V
3B Scientific GmbH • Rudorffweg 8 • 21031 Hamburg • Germany • www.3bscientific.com
Subject to technical amendment
© Copyright 2008 3B Scientific GmbH
 Loading...
Loading...