Page 1

SEK Heat U8502000
3B Scientific GmbH • Rudorffweg 8 • 21031 Hamburg • Germany • www.3bscientific.com
Subject to technical amendments
© Copyright 2010 3B Scientific GmbH
Contents
1 1 Capillary tube with red alcohol filling
2 2 Thermometers
3 1 Capillary tube
4 1 Metal beaker, black
5 1 Metal beaker, aluminium
6 1 Calorimeter with heating filament
7 1 Holder for metal beaker
8 4 g of glycerine
9 5 ml of food colouring
10 10 g of table salt
11 2 Rubber stoppers with one hole
12 1 Rubber stopper with two holes
13 1 Test tube
14 1 Measuring cylinder
15 1 Hose
16 1 Conical flask
17 1 Beaker
18 1 Metal tube, short
19 2 Double clamps
20 1 Bimetal strip
21 1 Aluminium tube
22 1 Steel tube
23 1 Brass tube
24 Stand rod with internal and external threads
25 4 Wooden rods
26 1 Spirit burner
27 1 Pointer/hook
28 10 Sheets of thermal paper
29 1 Test tube holder
30 1 Stirrer
31 10 Round filters
32 3 Flow spirals
33 2 Round gaskets
34 1 Steel body and 1 lead body
35 1 10 g weight
36 1 Angle scale
37 10 Sheets of paper
38 5 Sheets of aluminium foil
Page 2
SEK Thermodynamics/Heat
Work sheet
1
K303 Specific heat capacity of a calorimeter
Exercise
x Determine by experiment the specific heat capacity C
Kal
of a calorimeter.
Equipment
From SEK Thermodynamics (U8502000)
1 Stand rod with internal and external threads
1 Double clamp
1 Spirit burner
1 Test tube holder
1 Conical flask
2 Thermometers
1 Calorimeter
Additionally required
1 SEK base plate (U8408035)
Water
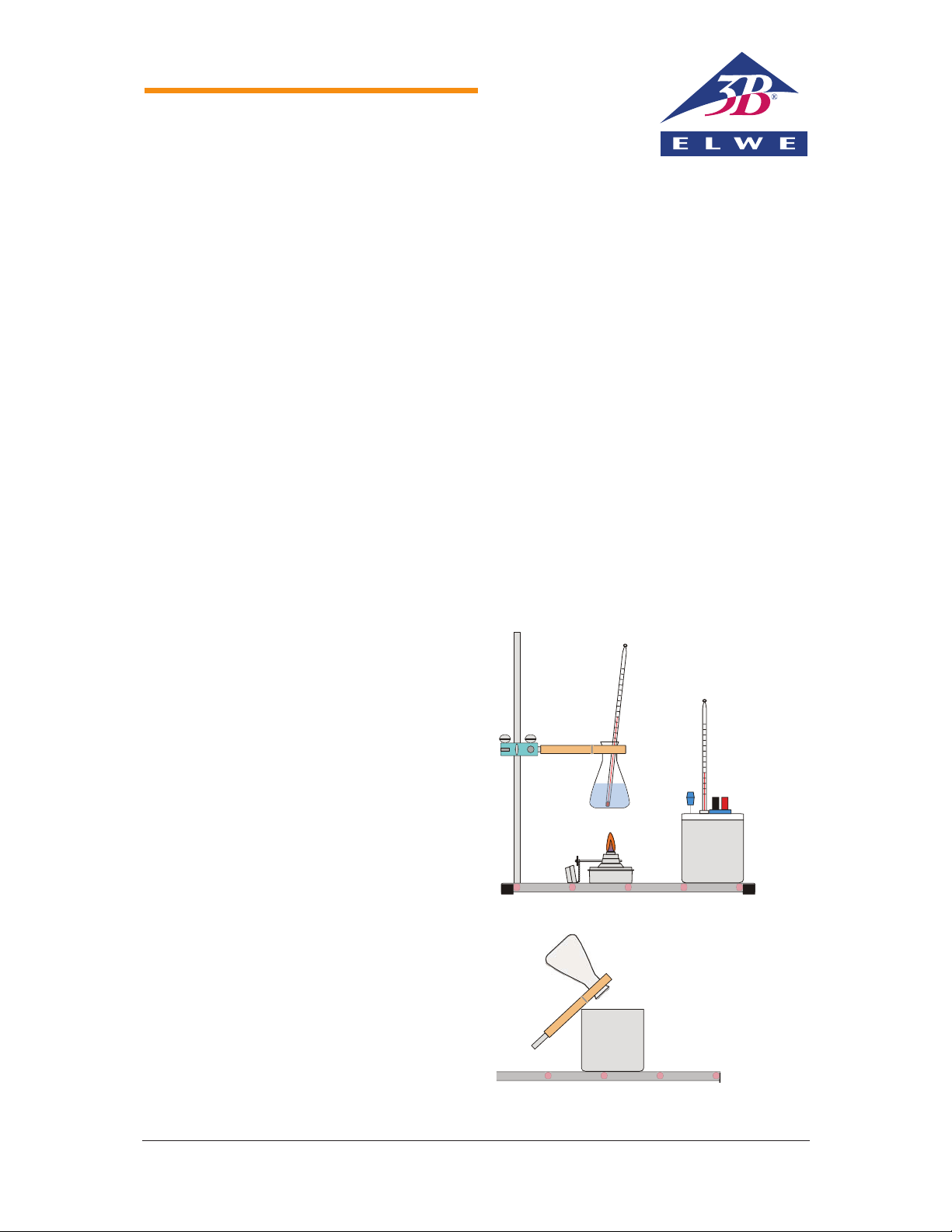
Set-up and procedure
1) Fill the metal beaker of the calorimeter with
50 ml of water and put the lid on it.
2) Push a thermometer through the rubber
stopper in the lid of the calorimeter so that
the tip of the thermometer is in the water but
does not touch the bottom of the vessel.
3) Measure the temperature of the water in the
calorimeter -
1
and enter the value into the
column Measurement 1 of the table.
4) Screw the stand rod with external and internal threads into the base plate (see Fig. 1).
5) Attach a double clamp to the rod at a height
of about 20 cm and clamp a test tube holder
into it.
6) Fill a conical flask with 50 ml of water, clamp
it into the test-tube holder and put a second
thermometer into it.
7) Put the spirit burner on the base plate and
move the double clamp holding the flask till
the flask is about 3 cm above the burner (see
Fig. 1).
8) Light the spirit burner and heat the water in
the flask till it reaches a temperature of
about 70°C.
9) Put out the flame once the experiment is
over by lowering the wick and putting the cap
over it.
10) Take the test tube holder out of the clamp
11) After about a minute, read off the temperature of the hot water -
2
and enter that value
into the table
12) Empty the water out of the conical flask into
the metal beaker of the calorimeter and close
the lid (see Fig. 2).
13) Stir the water well, measure the temperature
-
m
of the mixed water and enter the reading
into the table.
14) Now empty the water out of the metal beaker
back into the conical flask and briefly rinse
out the beaker with cold water.
15) Fill the beaker with a fresh 50 ml of water,
repeat the experiment and enter the results
in column Measurement 2 of the table.
Fig. 1
Fig. 2
Page 3

 Loading...
Loading...