ZyXEL Communications NWA5112-NI, NWA5123-NI, NWA5123-AC, NWA5123-AC HD, NWA5301-NJ User Manual
...Page 1

Default Login Details
User’s Guide
NWA/WAC Series
802.11 a/b/g/n/ac Unified Access Point
LAN IP Address DHCP-assigned
OR
http://192.168.1.2
User Name admin
Password 1234
Version 5.10 Edition 1, 09/2017
Copyright © 2017 Zyxel Communications Corporation
Page 2

IMPORTANT!
READ CAREFULLY BEFORE USE.
KEEP THIS GUIDE FOR FUTURE REFERENCE.
This is a User’s Guide for a series of products. Not all products support all firmware features. Screenshots
and graphics in this book may differ slightly from your product due to differences in your product
firmware or your computer operating system. Every effort has been made to ensure that the information
in this manual is accurate.
Related Documentation
•Quick Start Guide
The Quick Start Guide shows how to connect the NWA/WAC and access the Web Configurator.
•CLI Reference Guide
The CLI Reference Guide explains how to use the Command-Line Interface (CLI) and CLI commands
to configure the NWA/WAC.
Note: It is recommended you use the Web Configurator to configure the NWA/WAC.
• Web Configurator Online Help
Click the help icon in any screen for help in configuring that screen and supplementary information.
•More Information
Go to support.zyxel.com to find other information on the NWA/WAC
.
NWA / WAC Series User’s Guide
2
Page 3
Document Conventions
Warnings and Notes
These are how warnings and notes are shown in this guide.
Warnings tell you about things that could harm you or your device.
Note: Notes tell you other important information (for example, other things you may need to
configure or helpful tips) or recommendations.
Syntax Conventions
• All models in this series may be referred to as the “NWA/WAC” in this guide.
• Product labels, screen names, field labels and field choices are all in bold font.
• A right angle bracket ( > ) within a screen name denotes a mouse click. For example, Configuration >
Network > IP Setting means you first click Configuration in the navigation panel, then the Network sub
menu and finally the IP Setting tab to get to that screen.
Icons Used in Figures
Figures in this guide may use the following generic icons. The NWA/WAC icon is not an exact
representation of your device.
NWA/WAC Router Switch Internet
Server Desktop Laptop AP Controller
NWA / WAC Series User’s Guide
3
Page 4

Contents Overview
Contents Overview
User’s Guide ......................................................................................................................................12
Introduction ........................................................................................................................................... 13
The Web Configurator ......................................................................................................................... 35
Setup Wizard ......................................................................................................................................... 47
Technical Reference ........................................................................................................................53
Dashboard ............................................................................................................................................ 54
Monitor ................................................................................................................................................... 60
Network ................................................................................................................................................. 75
Wireless ................................................................................................................................................... 84
Bluetooth ............................................................................................................................................... 97
User ....................................................................................................................................................... 100
AP Profile .............................................................................................................................................. 107
MON Profile ......................................................................................................................................... 126
WDS Profile ........................................................................................................................................... 130
Certificates .......................................................................................................................................... 132
System .................................................................................................................................................. 148
Log and Report ................................................................................................................................... 173
File Manager ....................................................................................................................................... 185
Diagnostics .......................................................................................................................................... 196
LEDs ...................................................................................................................................................... 198
Antenna Switch .................................................................................................................................. 200
Reboot ................................................................................................................................................. 202
Shutdown ............................................................................................................................................. 203
Troubleshooting .................................................................................................................................. 204
NWA / WAC Series User’s Guide
4
Page 5

Table of Contents
Table of Contents
Document Conventions ... .... .... ............................................ ... .... .... ....................................................3
Contents Overview .............................................................................................................................4
Table of Contents.................................................................................................................................5
Part I: User’s Guide.......................................................................................... 12
Chapter 1
Introduction ........................................................................................................................................13
1.1 Overview ........................................................................................................................................ 13
1.1.1 Management Mode ............................................................................................................. 17
1.1.2 MBSSID .................................................................................................................................... 18
1.1.3 Dual-Radio ............................................................................................................................. 19
1.1.4 Root AP ................................................................................................................................... 19
1.1.5 Repeater ................................................................................................................................ 20
1.2 Ways to Manage the NWA/WAC .................................................................................................21
1.3 Good Habits for Managing the NWA/WAC ................................................................................ 22
1.4 Hardware Connections ................................................................................................................. 22
1.5 NWA5301-NJ Hardware ................................................................................................................. 22
1.5.1 110 Punch-Down Block ......................................................................................................... 22
1.5.2 Phone Port ............................................................................................................................. 24
1.5.3 Console Port .......................................................................................................................... 24
1.6 LEDs .................................................................................................................................................. 25
1.6.1 WAC6502D-E, WAC6502D-S, and WAC6503D-S ................................................................ 25
1.6.2 NWA1123-AC PRO and WAC6103D-I ................................................................................. 27
1.6.3 NWA5301-NJ .......................................................................................................................... 29
1.6.4 NWA1123-ACv2, NWA5121-N, NWA5121-NI, NWA5123-AC and NWA5123-NI .............. 30
1.6.5 WAC5302D-S .......................................................................................................................... 31
1.6.6 NWA1123-AC HD, NWA5123-AC HD and WAC6303D-S ................................................... 32
1.7 Starting and Stopping the NWA/WAC ......................................................................................... 33
Chapter 2
The Web Configurator........................................................................................................................35
2.1 Overview ......................................................................................................................................... 35
2.2 Accessing the Web Configurator ................................................................................................. 35
2.3 Navigating the Web Configurator ............................................................................................... 36
2.3.1 Title Bar ................................................................................................................................... 37
NWA / WAC Series User’s Guide
5
Page 6

Table of Contents
2.3.2 Navigation Panel .................................................................................................................. 40
2.3.3 Warning Messages ................................................................................................................ 43
2.3.4 Tables and Lists ...................................................................................................................... 43
Chapter 3
Setup Wizard.......................................................................................................................................47
3.1 Accessing the Wizard ..................................................................................................................... 47
3.2 Using the Wizard ............................................................................................................................. 47
3.2.1 Country Code ....................................................................................................................... 47
3.2.2 Time Zone ............................................................................................................................... 48
3.2.3 Uplink ...................................................................................................................................... 48
3.2.4 Radio ..................................................................................................................................... 49
3.2.5 SSID ........................................................................................................................................ 50
3.2.6 Summary ............................................................................................................................... 52
Part II: Technical Reference........................................................................... 53
Chapter 4
Dashboard..........................................................................................................................................54
4.1 Overview ......................................................................................................................................... 54
4.1.1 What You Can Do in this Chapter ....................................................................................... 54
4.2 Dashboard ...................................................................................................................................... 54
4.2.1 CPU Usage ............................................................................................................................. 58
4.2.2 Memory Usage ...................................................................................................................... 59
Chapter 5
Monitor................................................................................................................................................60
5.1 Overview ......................................................................................................................................... 60
5.1.1 What You Can Do in this Chapter ....................................................................................... 60
5.2 What You Need to Know ............................................................................................................... 60
5.3 Network Status ................................................................................................................................ 61
5.3.1 Port Statistics Graph .............................................................................................................. 63
5.4 Radio List ........................................................................................................................................ 64
5.4.1 AP Mode Radio Information ................................................................................................65
5.5 Station List ....................................................................................................................................... 67
5.6 WDS Link Info ................................................................................................................................... 68
5.7 Detected Device ........................................................................................................................... 69
5.8 View Log .......................................................................................................................................... 72
Chapter 6
Network...............................................................................................................................................75
NWA / WAC Series User’s Guide
6
Page 7

Table of Contents
6.1 Overview ......................................................................................................................................... 75
6.1.1 Management Mode ............................................................................................................. 75
6.1.2 What You Can Do in this Chapter ....................................................................................... 77
6.2 IP Setting ......................................................................................................................................... 78
6.3 VLAN ................................................................................................................................................ 79
6.4 AC (AP Controller) Discovery ........................................................................................................ 82
Chapter 7
Wireless...............................................................................................................................................84
7.1 Overview ......................................................................................................................................... 84
7.1.1 What You Can Do in this Chapter ....................................................................................... 84
7.1.2 What You Need to Know ..................................................................................................... 85
7.2 AP Management ............................................................................................................................ 85
7.3 Rogue AP ......................................................................................................................................... 88
7.3.1 Add/Edit Rogue/Friendly List ................................................................................................ 90
7.4 Load Balancing .............................................................................................................................. 91
7.4.1 Disassociating and Delaying Connections ........................................................................ 93
7.5 DCS .................................................................................................................................................. 94
7.6 Technical Reference ...................................................................................................................... 94
Chapter 8
Bluetooth.............................................................................................................................................97
8.1 Overview ......................................................................................................................................... 97
8.1.1 What You Need To Know ..................................................................................................... 97
8.2 Bluetooth Advertising Settings ....................................................................................................... 97
8.2.1 Edit Advertising Settings ....................................................................................................... 98
Chapter 9
User....................................................................................................................................................100
9.1 Overview ....................................................................................................................................... 100
9.1.1 What You Can Do in this Chapter ..................................................................................... 100
9.1.2 What You Need To Know ................................................................................................... 100
9.2 User Summary ................................................................................................................................ 101
9.2.1 Add/Edit User ....................................................................................................................... 101
9.3 Setting ........................................................................................................................................... 103
9.3.1 Edit User Authentication Timeout Settings ........................................................................ 105
Chapter 10
AP Profile...........................................................................................................................................107
10.1 Overview ..................................................................................................................................... 107
10.1.1 What You Can Do in this Chapter ................................................................................... 107
10.1.2 What You Need To Know ................................................................................................. 107
10.2 Radio ............................................................................................................................................ 108
NWA / WAC Series User’s Guide
7
Page 8

Table of Contents
10.2.1 Add/Edit Radio Profile ...................................................................................................... 109
10.3 SSID .............................................................................................................................................. 114
10.3.1 SSID List ............................................................................................................................... 114
10.3.2 Add/Edit SSID Profile ......................................................................................................... 115
10.4 Security List .................................................................................................................................. 118
10.4.1 Add/Edit Security Profile ................................................................................................... 118
10.5 MAC Filter List .............................................................................................................................. 121
10.5.1 Add/Edit MAC Filter Profile ............................................................................................... 122
10.6 Layer-2 Isolation List .................................................................................................................... 123
10.6.1 Add/Edit Layer-2 Isolation Profile .................................................................................... 124
Chapter 11
MON Profile.......................................................................................................................................126
11.1 Overview ..................................................................................................................................... 126
11.1.1 What You Can Do in this Chapter ................................................................................... 126
11.2 MON Profile ................................................................................................................................. 126
11.2.1 Add/Edit MON Profile ....................................................................................................... 127
11.3 Technical Reference .................................................................................................................. 128
Chapter 12
WDS Profile........................................................................................................................................130
12.1 Overview ..................................................................................................................................... 130
12.1.1 What You Can Do in this Chapter ................................................................................... 130
12.2 WDS Profile ................................................................................................................................... 130
12.2.1 Add/Edit WDS Profile ........................................................................................................ 131
Chapter 13
Certificates .......................................................................................................................................132
13.1 Overview ..................................................................................................................................... 132
13.1.1 What You Can Do in this Chapter ................................................................................... 132
13.1.2 What You Need to Know ................................................................................................. 132
13.1.3 Verifying a Certificate ...................................................................................................... 134
13.2 My Certificates ........................................................................................................................... 135
13.2.1 Add My Certificates .......................................................................................................... 136
13.2.2 Edit My Certificates ........................................................................................................... 138
13.2.3 Import Certificates ........................................................................................................... 141
13.3 Trusted Certificates ..................................................................................................................... 142
13.3.1 Edit Trusted Certificates .................................................................................................... 143
13.3.2 Import Trusted Certificates ............................................................................................... 146
13.4 Technical Reference .................................................................................................................. 147
Chapter 14
System...............................................................................................................................................148
NWA / WAC Series User’s Guide
8
Page 9

Table of Contents
14.1 Overview ..................................................................................................................................... 148
14.1.1 What You Can Do in this Chapter ................................................................................... 148
14.2 Host Name ................................................................................................................................... 148
14.3 Date and Time ........................................................................................................................... 149
14.3.1 Pre-defined NTP Time Servers List ..................................................................................... 152
14.3.2 Time Server Synchronization ............................................................................................ 152
14.4 WWW Overview .......................................................................................................................... 153
14.4.1 Service Access Limitations ............................................................................................... 153
14.4.2 System Timeout .................................................................................................................. 153
14.4.3 HTTPS ................................................................................................................................... 154
14.4.4 Configuring WWW Service Control ................................................................................. 154
14.4.5 HTTPS Example ................................................................................................................... 155
14.5 SSH ............................................................................................................................................. 163
14.5.1 How SSH Works .................................................................................................................. 163
14.5.2 SSH Implementation on the NWA/WAC ......................................................................... 164
14.5.3 Requirements for Using SSH ..............................................................................................165
14.5.4 Configuring SSH ................................................................................................................. 165
14.5.5 Examples of Secure Telnet Using SSH .............................................................................. 165
14.6 Telnet ........................................................................................................................................... 167
14.7 FTP ................................................................................................................................................ 167
14.8 SNMP ........................................................................................................................................... 168
14.8.1 Supported MIBs ................................................................................................................. 169
14.8.2 SNMP Traps ......................................................................................................................... 170
14.8.3 Configuring SNMP ............................................................................................................. 170
14.8.4 Adding or Editing an SNMPv3 User Profile ...................................................................... 171
Chapter 15
Log and Report....... .... ... ............................................. ... .... ............................................ ...................173
15.1 Overview ..................................................................................................................................... 173
15.1.1 What You Can Do In this Chapter .................................................................................. 173
15.2 Email Daily Report ....................................................................................................................... 173
15.3 Log Setting .................................................................................................................................. 175
15.3.1 Log Setting Screen ............................................................................................................ 176
15.3.2 Edit System Log Settings .................................................................................................. 177
15.3.3 Edit Remote Server ........................................................................................................... 181
15.3.4 Active Log Summary ....................................................................................................... 182
Chapter 16
File Manager ....................................................................................................................................185
16.1 Overview ..................................................................................................................................... 185
16.1.1 What You Can Do in this Chapter ................................................................................... 185
16.1.2 What you Need to Know .................................................................................................. 185
16.2 Configuration File ....................................................................................................................... 186
NWA / WAC Series User’s Guide
9
Page 10

Table of Contents
16.2.1 Example of Configuration File Download Using FTP ...................................................... 190
16.3 Firmware Package .................................................................................................................... 191
16.3.1 Example of Firmware Upload Using FTP .......................................................................... 192
16.4 Shell Script ................................................................................................................................... 193
Chapter 17
Diagnostics.......................................................................................................................................196
17.1 Overview ..................................................................................................................................... 196
17.1.1 What You Can Do in this Chapter ................................................................................... 196
17.2 Diagnostics .................................................................................................................................. 196
Chapter 18
LEDs ...................................................................................................................................................198
18.1 Overview ..................................................................................................................................... 198
18.1.1 What You Can Do in this Chapter ................................................................................... 198
18.2 Suppression Screen .................................................................................................................. 198
18.3 Locator Screen .......................................................................................................................... 199
Chapter 19
Antenna Switch................................................................................................................................200
19.1 Overview ..................................................................................................................................... 200
19.1.1 What You Need To Know ................................................................................................. 200
19.2 Antenna Switch Screen ............................................................................................................. 200
Chapter 20
Reboot...............................................................................................................................................202
20.1 Overview ..................................................................................................................................... 202
20.1.1 What You Need To Know ................................................................................................. 202
20.2 Reboot ......................................................................................................................................... 202
Chapter 21
Shutdown..........................................................................................................................................203
21.1 Overview ..................................................................................................................................... 203
21.1.1 What You Need To Know ................................................................................................. 203
21.2 Shutdown ..................................................................................................................................... 203
Chapter 22
Troubleshooting................................................................................................................................204
22.1 Overview ..................................................................................................................................... 204
22.2 Power, Hardware Connections, and LED ................................................................................ 204
22.3 NWA/WAC Access and Login ................................................................................................... 205
22.4 Internet Access ........................................................................................................................... 206
22.5 Wireless Connections ................................................................................................................. 207
NWA / WAC Series User’s Guide
10
Page 11

Table of Contents
22.6 Resetting the NWA/WAC ........................................................................................................... 212
22.7 Getting More Troubleshooting Help .........................................................................................213
Appendix A Importing Certificates ............................................................................................... 214
Appendix B IPv6............................................................................................................................... 227
Appendix C Customer Support ..................................................................................................... 235
Appendix D Legal Information ...................................................................................................... 241
Index.................................................................................................................................................254
NWA / WAC Series User’s Guide
11
Page 12

PART I
User’s Guide
12
Page 13
1.1 Overview
This User’s Guide covers the following models: NWA1123-ACv2, NWA1123-AC PRO, NWA1123-AC HD,
NWA5121-N, NWA5121-NI, NWA5123-AC, NWA5123-AC HD, NWA5123-NI, NWA5301-NJ, WAC5302D-S,
WAC6103D-I, WAC6303D-S, WAC6502D-E, WAC6502D-S, WAC6503D-S, and WAC6553D-E. Your NWA/
WAC is a wireless AP (Access Point). It extends the range of your existing wired network without
additional wiring, providing easy network access to mobile users.
Table 1 NWA1123 Series Comparison Table
FEATURES NWA1123-ACV2 NWA1123-AC PRO NWA1123-AC HD
Supported Wireless
Standards
Supported Frequency
Bands
Available Security
Modes
Number of SSID
Profiles
Number of Wireless
Radios
Monitor Mode &
Rogue APs
Containment
Rogue APs Detection Yes Yes Yes
WDS (Wireless
Distribution System) Root AP & Repeater
Modes
Tunnel Forwarding
Mode
Layer-2 Isolation Yes Yes Yes
Power Detection No No No
External Antennas No No No
Internal Antennas Yes Yes Yes
Antenna Switch No Yes No
LED Locator No Yes Yes
CHAPTER 1
Introduction
IEEE 802.11a
IEEE 802.11b
IEEE 802.11g
IEEE 802.11n
IEEE 802.11ac
2.4 GHz
5 GHz
None
WEP
WPA2
WPA2-MIX
WPA2-PSK
WPA2-PSK-MIX
64 64 64
222
Yes Yes No
Yes Yes No
No No No
IEEE 802.11a
IEEE 802.11b
IEEE 802.11g
IEEE 802.11n
IEEE 802.11ac
2.4 GHz
5 GHz
None
WEP
WPA2
WPA2-MIX
WPA2-PSK
WPA2-PSK-MIX
IEEE 802.11a
IEEE 802.11b
IEEE 802.11g
IEEE 802.11n
IEEE 802.11ac
2.4 GHz
5 GHz
None
WEP
WPA2
WPA2-MIX
WPA2-PSK
WPA2-PSK-MIX
NWA / WAC Series User’s Guide
13
Page 14
Chapter 1 Introduction
Table 1 NWA1123 Series Comparison Table
FEATURES NWA1123-ACV2 NWA1123-AC PRO NWA1123-AC HD
CAPWAP Managed
AP Mode
AC (AP Controller)
Discovery
802.11r Fast Roaming
Support in Managed
AP Mode
Bluetooth Low Energy
(BLE)
Maximum number of
log messages
No No No
No No No
No No No
No No No
512 event logs or 1024 debug logs
Table 2 NWA5000 Series Comparison Table
FEATURES NWA5121-N
Supported Wireless
Standards
Supported Frequency
Bands
Available Security
Modes
Number of SSID
Profiles
Number of Wireless
Radios
Monitor Mode &
Rogue APs
Containment
Rogue APs Detection Yes Yes Yes Yes Yes Yes
WDS (Wireless
Distribution System) Root AP & Repeater
Modes
Tunnel Forwarding
Mode
Layer-2 Isolation Yes Yes Yes Yes Yes Yes
Power Detection NoNoNo NoNoNo
External Antennas Yes No No No No No
Internal Antennas No Yes Yes Yes Yes Yes
Antenna Switch No No No No No No
LED Locator No No No Yes No No
CAPWAP Managed
AP Mode
IEEE 802.11b
IEEE 802.11g
IEEE 802.11n
2.4 GHz 2.4 GHz
None
WEP
WPA2
WPA2-MIX
WPA2-PSK
WPA2-PSK-
MIX
64 64 64 64 64 64
112 221
Yes Yes Yes No Yes No
Yes Yes Yes No Yes Yes
No No No No No No
Yes Yes Yes Yes Yes Yes
NWA5121-NINWA5123-ACNWA5123-
AC HD
IEEE 802.11b
IEEE 802.11g
IEEE 802.11n
None
WEP
WPA2
WPA2-MIX
WPA2-PSK
WPA2-PSK-
MIX
IEEE 802.11a
IEEE 802.11b
IEEE 802.11g
IEEE 802.11n
IEEE 802.11ac
2.4 GHz
5 GHz
None
WEP
WPA2
WPA2-MIX
WPA2-PSK
WPA2-PSK-
MIX
IEEE 802.11a
IEEE 802.11b
IEEE 802.11g
IEEE 802.11n
IEEE 802.11ac
2.4 GHz
5 GHz
None
WEP
WPA2
WPA2-MIX
WPA2-PSK
WPA2-PSK-
MIX
NWA5123-NINWA5301-
NJ
IEEE 802.11a
IEEE 802.11b
IEEE 802.11g
IEEE 802.11n
2.4 GHz
5 GHz
None
WEP
WPA2
WPA2-MIX
WPA2-PSK
WPA2-PSK-
MIX
IEEE 802.11b
IEEE 802.11g
IEEE 802.11n
2.4 GHz
None
WEP
WPA2
WPA2-MIX
WPA2-PSK
WPA2-PSK-
MIX
NWA / WAC Series User’s Guide
14
Page 15
Chapter 1 Introduction
Table 2 NWA5000 Series Comparison Table
FEATURES NWA5121-N
AC (AP Controller)
Discovery
802.11r Fast Roaming
Support in Managed
AP Mode
Bluetooth Low Energy
(BLE)
Maximum number of
log messages
Yes Yes Yes Yes Yes Yes
Yes Yes Yes Yes Yes Yes
No No No No No No
256 event
logs or 1
debug logs
NWA5121-NINWA5123-ACNWA5123-
256 event
logs or 1
debug logs
512 event
logs or 1024
debug logs
512 event
logs or 1024
debug logs
Table 3 WAC5000/6000 Series Comparison Table
FEATURES WAC5302D-S WAC6103D-I WAC6303D-S
Supported Wireless
Standards
Supported Frequency
Bands
Available Security
Modes
Number of SSID Profiles 64 64 64
Number of Wireless
Radios
Monitor Mode & Rogue
APs Containment
Rogue APs Detection Yes Yes Yes
WDS (Wireless
Distribution System) Root AP & Repeater
Modes
Tunnel Forwarding
Mode
Layer-2 Isolation Yes Yes Yes
Power Detection Yes No Yes
External Antennas No No No
Internal Antennas Yes Yes Yes
Antenna Switch No Yes No
LED Locator No Yes Yes
CAPWAP Managed AP
Mode
AC (AP Controller)
Discovery
IEEE 802.11a
IEEE 802.11b
IEEE 802.11g
IEEE 802.11n
IEEE 802.11ac
2.4 GHz
5 GHz
None
WEP
WPA2
WPA2-MIX
WPA2-PSK
WPA2-PSK-MIX
222
No Yes No
No Yes Yes
No Yes Yes
Yes Yes Yes
Yes Yes Yes
IEEE 802.11a
IEEE 802.11b
IEEE 802.11g
IEEE 802.11n
IEEE 802.11ac
2.4 GHz
5 GHz
None
WEP
WPA2
WPA2-MIX
WPA2-PSK
WPA2-PSK-MIX
IEEE 802.11a
IEEE 802.11b
IEEE 802.11g
IEEE 802.11n
IEEE 802.11ac
2.4 GHz
5 GHz
None
WEP
WPA2
WPA2-MIX
WPA2-PSK
WPA2-PSK-MIX
AC HD
NWA5123-NINWA5301-
NJ
256 event
logs or 1
debug logs
256 event
logs or 1
debug logs
NWA / WAC Series User’s Guide
15
Page 16
Chapter 1 Introduction
Table 3 WAC5000/6000 Series Comparison Table
FEATURES WAC5302D-S WAC6103D-I WAC6303D-S
802.11r Fast Roaming
Support in Managed AP
Mode
Bluetooth Low Energy
(BLE)
Maximum number of
log messages
No Yes Yes
Yes No Yes
256 event logs
or 1 debug logs
512 event logs
or 1024 debug
logs
512 event logs
or 1024 debug
logs
Table 4 WAC6500 Series Comparison Table
FEATURES WAC6502D-E WAC6502D-S WAC6503D-S WAC6553D-E
Supported Wireless
Standards
Supported Frequency
Bands
Available Security
Modes
Number of SSID Profiles 64 64 64 64
Number of Wireless
Radios
Monitor Mode & Rogue
APs Containment
Rogue APs Detection Yes Yes Yes Yes
WDS (Wireless
Distribution System) Root AP & Repeater
Modes
Tunnel Forwarding
Mode
Layer-2 Isolation Yes Yes Yes Yes
Power Detection Yes Yes Yes Yes
External Antennas Yes No No Yes
Internal Antennas No Yes Yes No
Antenna Switch No No No No
LED Locator Yes Yes Yes Yes
CAPWAP Managed AP
Mode
AC (AP Controller)
Discovery
802.11r Fast Roaming
Support in Managed AP
Mode
IEEE 802.11a
IEEE 802.11b
IEEE 802.11g
IEEE 802.11n
IEEE 802.11ac
2.4 GHz
5 GHz
None
WEP
WPA2
WPA2-MIX
WPA2-PSK
WPA2-PSK-MIX
2222
YesYesYesYes
YesYesYesYes
YesYesYesYes
YesYesYesYes
YesYesYesYes
YesYesYesYes
IEEE 802.11a
IEEE 802.11b
IEEE 802.11g
IEEE 802.11n
IEEE 802.11ac
2.4 GHz
5 GHz
None
WEP
WPA2
WPA2-MIX
WPA2-PSK
WPA2-PSK-MIX
IEEE 802.11a
IEEE 802.11b
IEEE 802.11g
IEEE 802.11n
IEEE 802.11ac
2.4 GHz
5 GHz
None
WEP
WPA2
WPA2-MIX
WPA2-PSK
WPA2-PSK-MIX
IEEE 802.11a
IEEE 802.11b
IEEE 802.11g
IEEE 802.11n
IEEE 802.11ac
2.4 GHz
5 GHz
None
WEP
WPA2
WPA2-MIX
WPA2-PSK
WPA2-PSK-MIX
NWA / WAC Series User’s Guide
16
Page 17
Chapter 1 Introduction
Table 4 WAC6500 Series Comparison Table
FEATURES WAC6502D-E WAC6502D-S WAC6503D-S WAC6553D-E
Bluetooth Low Energy
(BLE)
Maximum number of
log messages
No No No No
512 event logs or 1024 debug logs
You can set the NWA/WAC to operate in either standalone AP or managed AP mode. When the NWA/
WAC is in standalone AP mode, it can serve as a normal AP, as an RF monitor to search for rouge APs to
help eliminate network threats (if it supports monitor mode and rogue APs detection/containment), or
even as a root AP or a wireless repeater to establish wireless links with other APs in a WDS (Wireless
Distribution System). A WDS is a wireless connection between two or more APs.
Your NWA/WAC’s business-class reliability, SMB features, and centralized wireless management make it
ideally suited for advanced service delivery in mission-critical networks. It uses Multiple BSSID and VLAN
to provide simultaneous independent virtual APs. Additionally, innovations in roaming technology and
QoS features eliminate voice call disruptions.
The NWA/WAC controls network access with Media Access Control (MAC) address filtering, and rogue
Access Point (AP) detection. It also provides a high level of network traffic security, supporting IEEE
802.1x, Wi-Fi Protected Access 2 and Wired Equivalent Privacy (WEP) data encryption.
Your NWA/WAC is easy to install, configure and use. The embedded Web-based configurator enables
simple, straightforward management and maintenance. See the Quick Start Guide for how to make
hardware connections.
1.1.1 Management Mode
The NWA/WAC is a unified AP and can work either in standalone AP mode or in managed AP mode. If
the NWA/WAC and a Zyxel AP controller, such as the NXC2500 or NXC5500, are in the same subnet, it will
be managed by the controller automatically.
An AP controller uses Control And Provisioning of Wireless Access Points (CAPWAP, see RFC 5415) to
discover and configure multiple managed APs.
To set the NWA/WAC to be managed by an AP controller in a different subnet or change between
management modes, use the AC (AP Controller) Discovery screen (see Section 6.4 on page 82).
Table 5 NWA/WAC Management Mode Comparison
MANAGEMENT MODE DEFAULT IP ADDRESS UPLOAD FIRMWARE VIA
Standalone AP
Managed AP Dynamic CAPWAP or FTP
When the NWA/WAC is in standalone AP mode and connects to a DHCP server, it uses the IP address
assigned by the DHCP server. Otherwise, the NWA/WAC uses the default static management IP address
(192.168.1.2). You can use the AC Discovery screen to have the NWA/WAC work as a managed AP.
Dynamic or
Static (192.168.1.2)
Web Configurator or FTP
When the NWA/WAC is in managed AP mode, it acts as a DHCP client and obtains an IP address from
the AP controller. It can be configured ONLY by the AP controller. To change the NWA/WAC back to
standalone AP mode, use the Reset button to restore the default configuration. Alternatively, you need
to check the AP controller for the NWA/WAC’s IP address and use FTP to upload the default
configuration file at conf/system-default.conf to the NWA/WAC and reboot the device.
NWA / WAC Series User’s Guide
17
Page 18
1.1.2 MBSSID
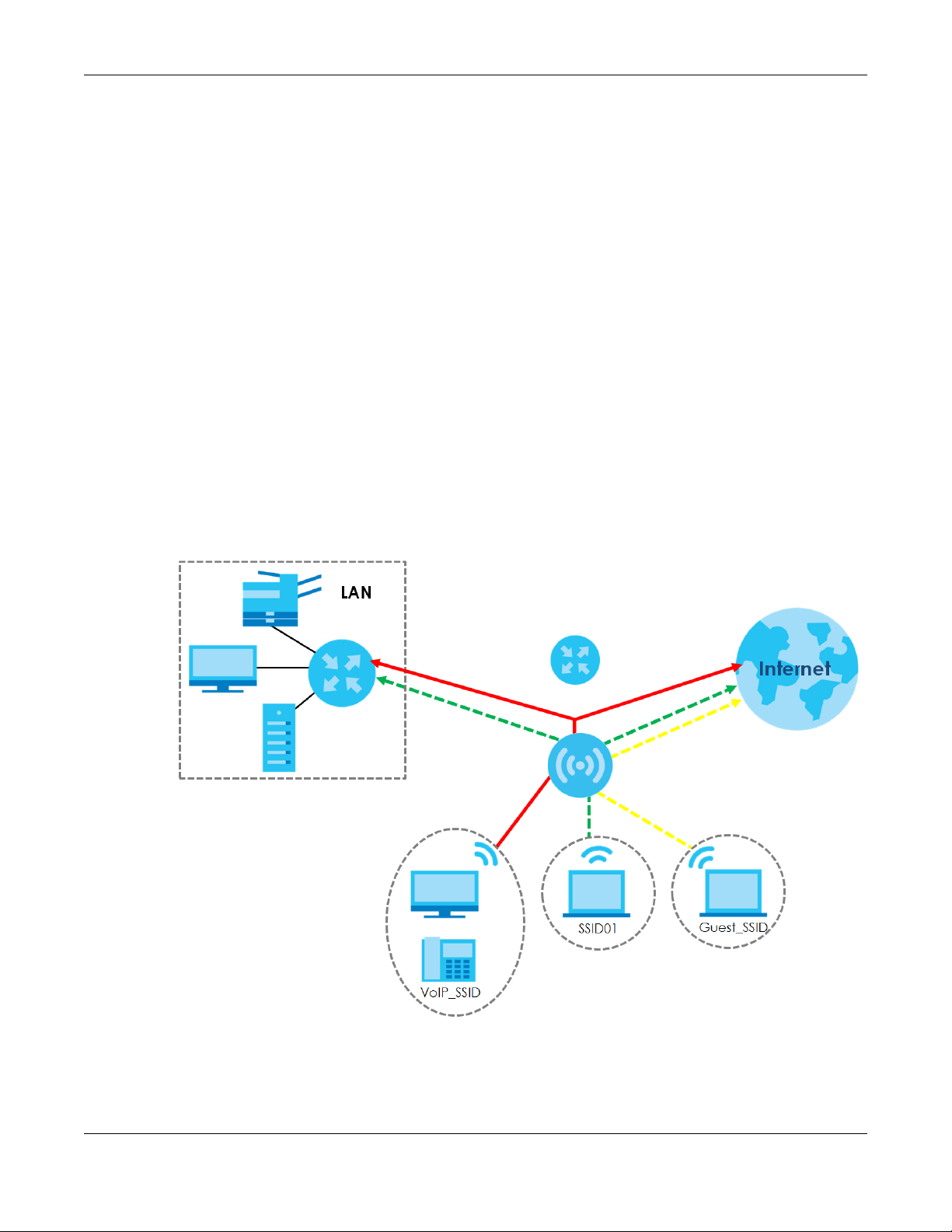
A Basic Service Set (BSS) is the set of devices forming a single wireless network (usually an access point
and one or more wireless clients). The Service Set IDentifier (SSID) is the name of a BSS. In Multiple BSS
(MBSSID) mode, the NWA/WAC provides multiple virtual APs, each forming its own BSS and using its own
individual SSID profile.
You can configure multiple SSID profiles, and have all of them active at any one time.
You can assign different wireless and security settings to each SSID profile. This allows you to
compartmentalize groups of users, set varying access privileges, and prioritize network traffic to and
from certain BSSs.
To the wireless clients in the network, each SSID appears to be a different access point. As in any wireless
network, clients can associate only with the SSIDs for which they have the correct security settings.
For example, you might want to set up a wireless network in your office where Internet telephony (VoIP)
users have priority. You also want a regular wireless network for standard users, as well as a ‘guest’
wireless network for visitors. In the following figure, VoIP_SSID users have QoS priority, SSID01 is the wireless
network for standard users, and Guest_SSID is the wireless network for guest users. In this example, the
guest user is forbidden access to the wired Land Area Network (LAN) behind the AP and can access
only the Internet.
Chapter 1 Introduction
Figure 1 Multiple BSSs
NWA / WAC Series User’s Guide
18
Page 19
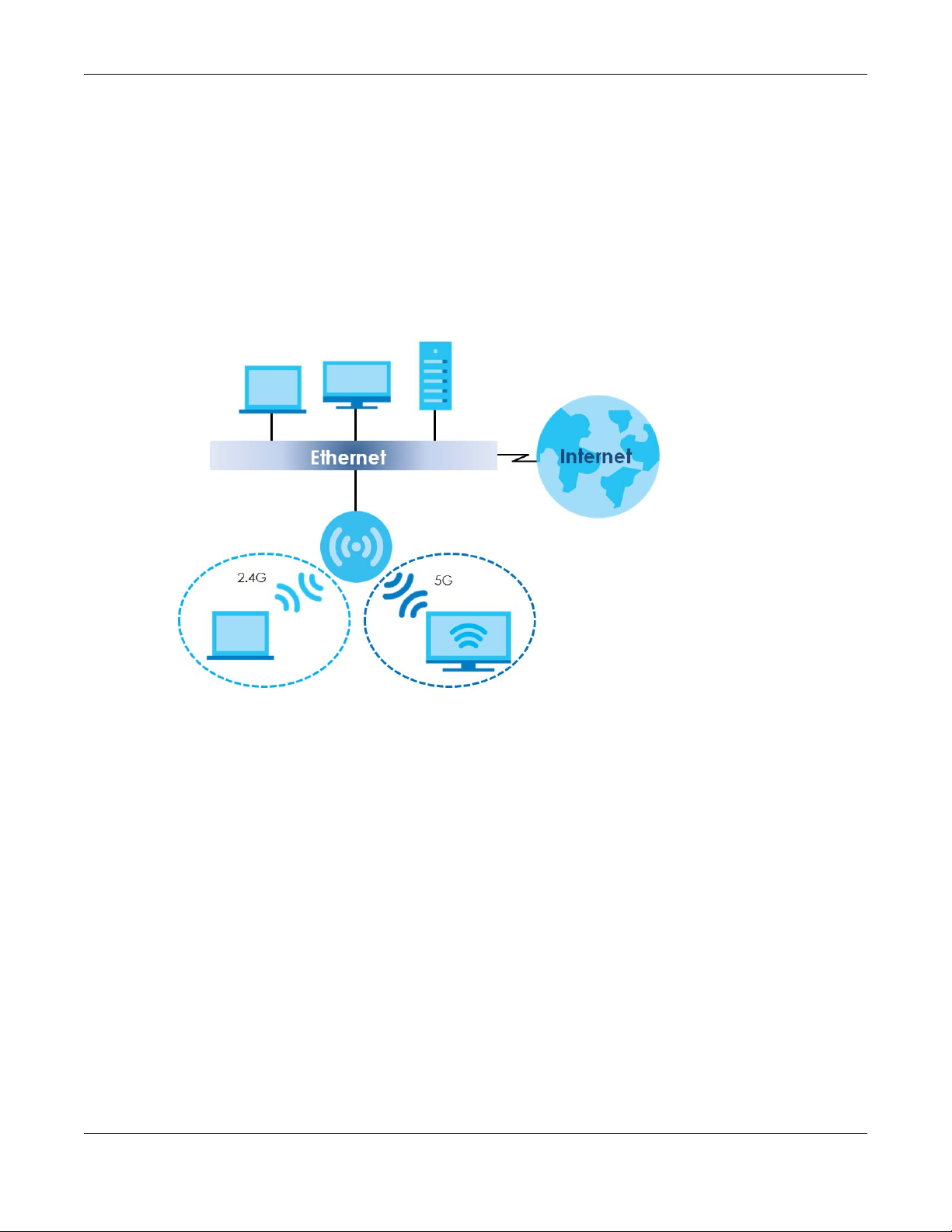
1.1.3 Dual-Radio
Some of the NWA/WAC models are equipped with dual wireless radios. This means you can configure
two different wireless networks to operate simultaneously.
Note: A different channel should be configured for each WLAN interface to reduce the
effects of radio interference.
You could use the 2.4 GHz band for regular Internet surfing and downloading while using the 5 GHz
band for time sensitive traffic like high-definition video, music, and gaming.
Figure 2 Dual-Radio Application
Chapter 1 Introduction
1.1.4 Root AP
In Root AP mode, the NWA/WAC (Z) can act as the root AP in a wireless network and also allow
repeaters (X and Y) to extend the range of its wireless network at the same time. In the figure below,
both clients A, B and C can access the wired network through the root AP.
NWA / WAC Series User’s Guide
19
Page 20
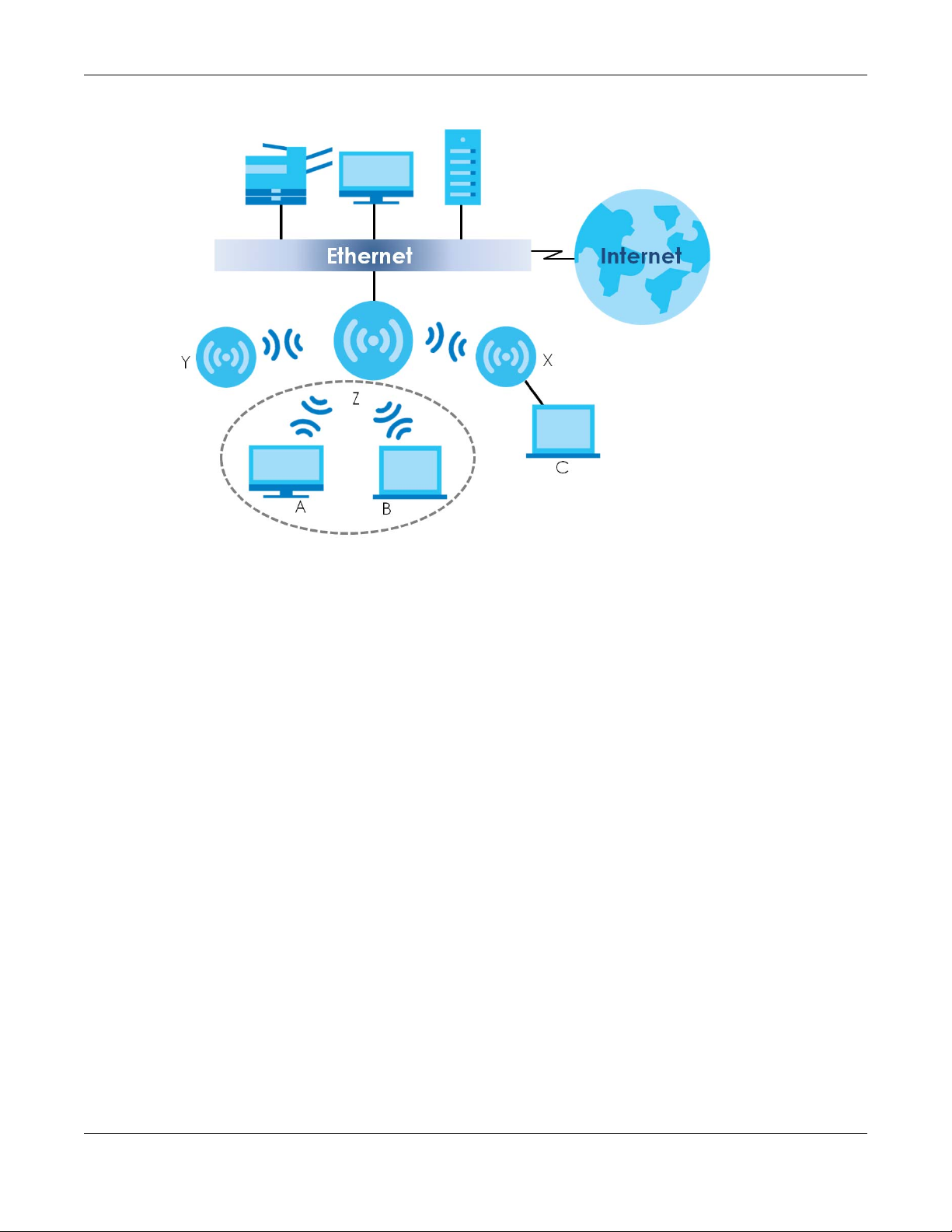
Figure 3 Root AP Application
Chapter 1 Introduction
On the NWA/WAC in Root AP mode, you can have multiple SSIDs active for regular wireless connections
and one SSID for the connection with a repeater (repeater SSID). Wireless clients can use either SSID to
associate with the NWA/WAC in Root AP mode. A repeater must use the repeater SSID to connect to
the NWA/WAC in Root AP mode.
When the NWA/WAC is in Root AP mode, repeater security between the NWA/WAC and other repeater
is independent of the security between the wireless clients and the AP or repeater. When repeater
security is enabled, both APs and repeaters must use the same pre-shared key. See Section 7.2 on page
85 and Section 12.2 on page 130 for more details.
Unless specified, the term “security settings” refers to the traffic between the wireless clients and the AP.
At the time of writing, repeater security is compatible with the NWA/WAC only.
1.1.5 Repeater
The NWA/WAC can act as a wireless network repeater to extend a root AP’s wireless network range,
and also establish wireless connections with wireless clients.
Using Repeater mode, your NWA/WAC can extend the range of the WLAN. In the figure below, the
NWA/WAC in Repeater mode (Z) has a wireless connection to the NWA/WAC in Root AP mode (X)
which is connected to a wired network and also has a wireless connection to another NWA/WAC in
Repeater mode (Y) at the same time. Z and Y act as repeaters that forward traffic between associated
wireless clients and the wired LAN. Clients A and B access the AP and the wired network behind the AP
through repeaters Z and Y.
NWA / WAC Series User’s Guide
20
Page 21
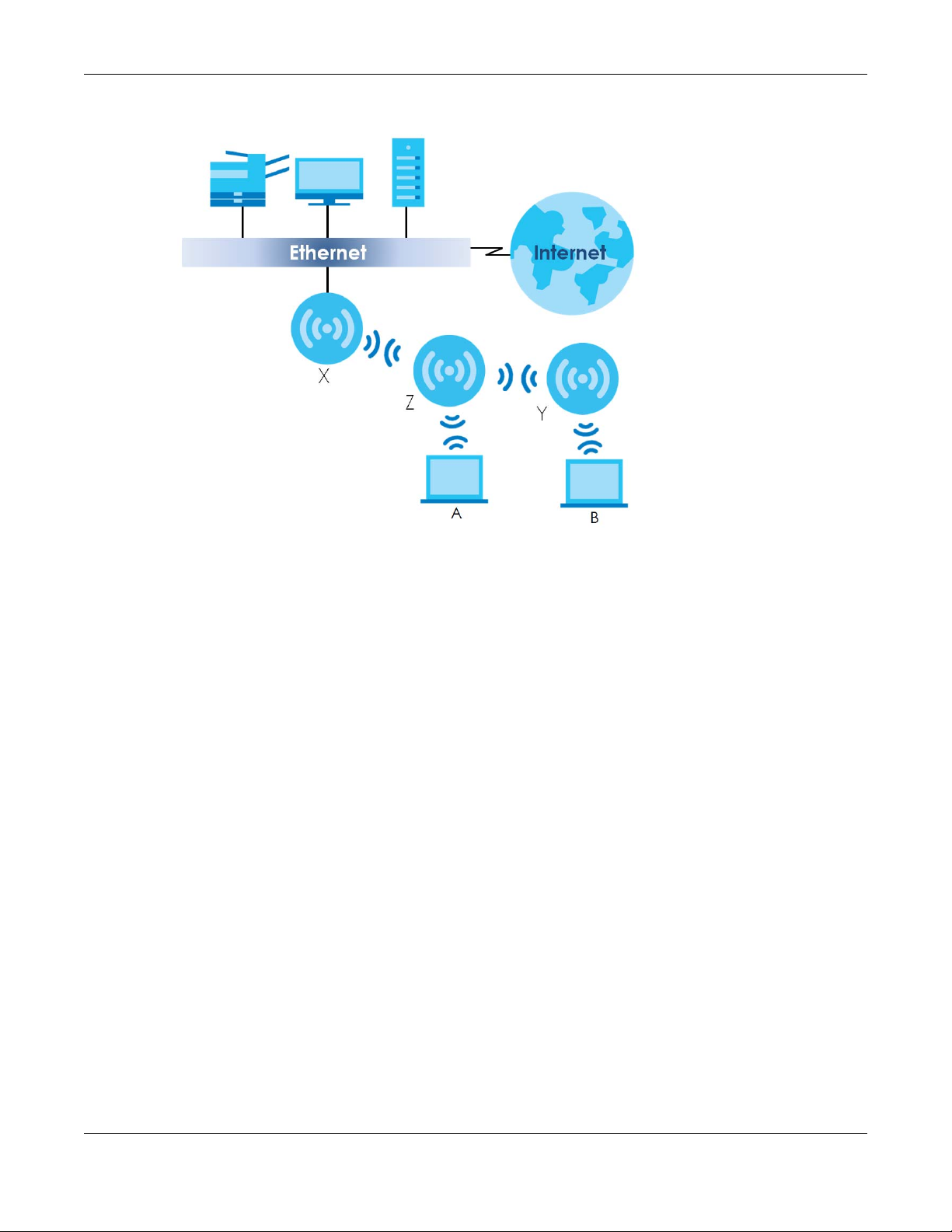
Figure 4 Repeater Application
Chapter 1 Introduction
When the NWA/WAC is in Repeater mode, repeater security between the NWA/WAC and other
repeater is independent of the security between the wireless clients and the AP or repeater. When
repeater security is enabled, both APs and repeaters must use the same pre-shared key. See Section 7.2
on page 85 and Section 12.2 on page 130 for more details.
Once the security settings of peer sides match one another, the connection between devices is made.
At the time of writing, repeater security is compatible with the NWA/WAC only.
1.2 Ways to Manage the NWA/WAC
You can use the following ways to manage the NWA/WAC.
Web Configurator
The Web Configurator allows easy NWA/WAC setup and management using an Internet browser. This
User’s Guide provides information about the Web Configurator.
Command-Line Interface (CLI)
The CLI allows you to use text-based commands to configure the NWA/WAC. You can access it using
remote management (for example, SSH or Telnet). See the Command Reference Guide for more
information.
File Transfer Protocol (FTP)
This protocol can be used for firmware upgrades and configuration backup and restore.
NWA / WAC Series User’s Guide
21
Page 22

Chapter 1 Introduction
Simple Network Management Protocol (SNMP)
The NWA/WAC can be monitored by an SNMP manager. See the SNMP chapter in this User’s Guide.
1.3 Good Habits for Managing the NWA/WAC
Do the following things regularly to make the NWA/WAC more secure and to manage it more
effectively.
• Change the password often. Use a password that’s not easy to guess and that consists of different
types of characters, such as numbers and letters.
• Write down the password and put it in a safe place.
• Back up the configuration (and make sure you know how to restore it). Restoring an earlier working
configuration may be useful if the device becomes unstable or even crashes. If you forget your
password, you will have to reset the NWA/WAC to its factory default settings. If you backed up an
earlier configuration file, you won’t have to totally re-configure the NWA/WAC; you can simply restore
your last configuration.
1.4 Hardware Connections
See your Quick Start Guide for information on making hardware connections.
1.5 NWA5301-NJ Hardware
1.5.1 110 Punch-Down Block
This section shows you how to use a punch-down tool to seat an 8-wire Ethernet cable to the 110 punchdown block. You can connect a PoE switch to the 110 punch-down block to provide power and
Internet access to the NWA through this connection. An 8-pin Ethernet cable has four pairs of color
coded wires.
1 Cut out one and a half inches of the jacket from the Ethernet cable to expose the wires.
2 Untwist the wire pairs no more than one inch.
3 Match each wire to the correct slot according to the color codes for wiring shown below.
NWA / WAC Series User’s Guide
22
Page 23
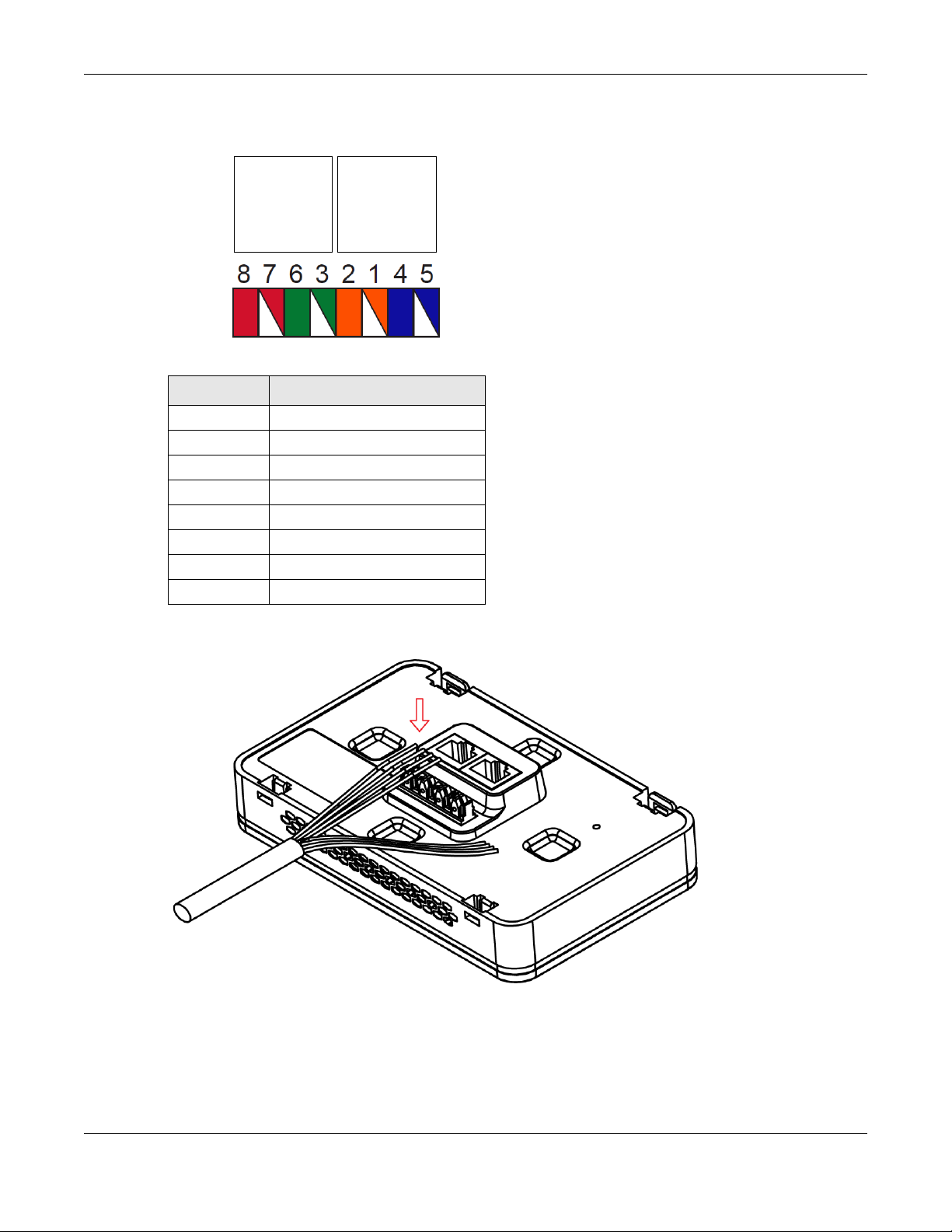
Chapter 1 Introduction
PIN#
PHONE
PORT
UPLINK
PORT
NWA Rear Panel
Table 6 Color Codes for 110 Punch Down Block Wiring
PIN# WIRE COLOR
1White/Orange
2Orange
3 White/Green
4Blue
5White/Blue
6 Green
7White/Brown
8Brown
4 Use a punch-down tool to seat the wires down properly into the slot.
5 Trim any excess wires. Place the dust caps over the terminated wires.
NWA / WAC Series User’s Guide
23
Page 24
1.5.2 Phone Port
Chapter 1 Introduction
Connect a digital telephone to the RJ-45 PHONE port at the bottom of the NWA to forward voice traffic
to/from the telephone switchboard that is connected to the RJ-45 PHONE port on the back of the NWA.
The NWA does not support VoIP (Voice over Internet Protocol) and the PHONE port is NOT for making
calls over the regular networking network (PSTN), either.
1.5.3 Console Port
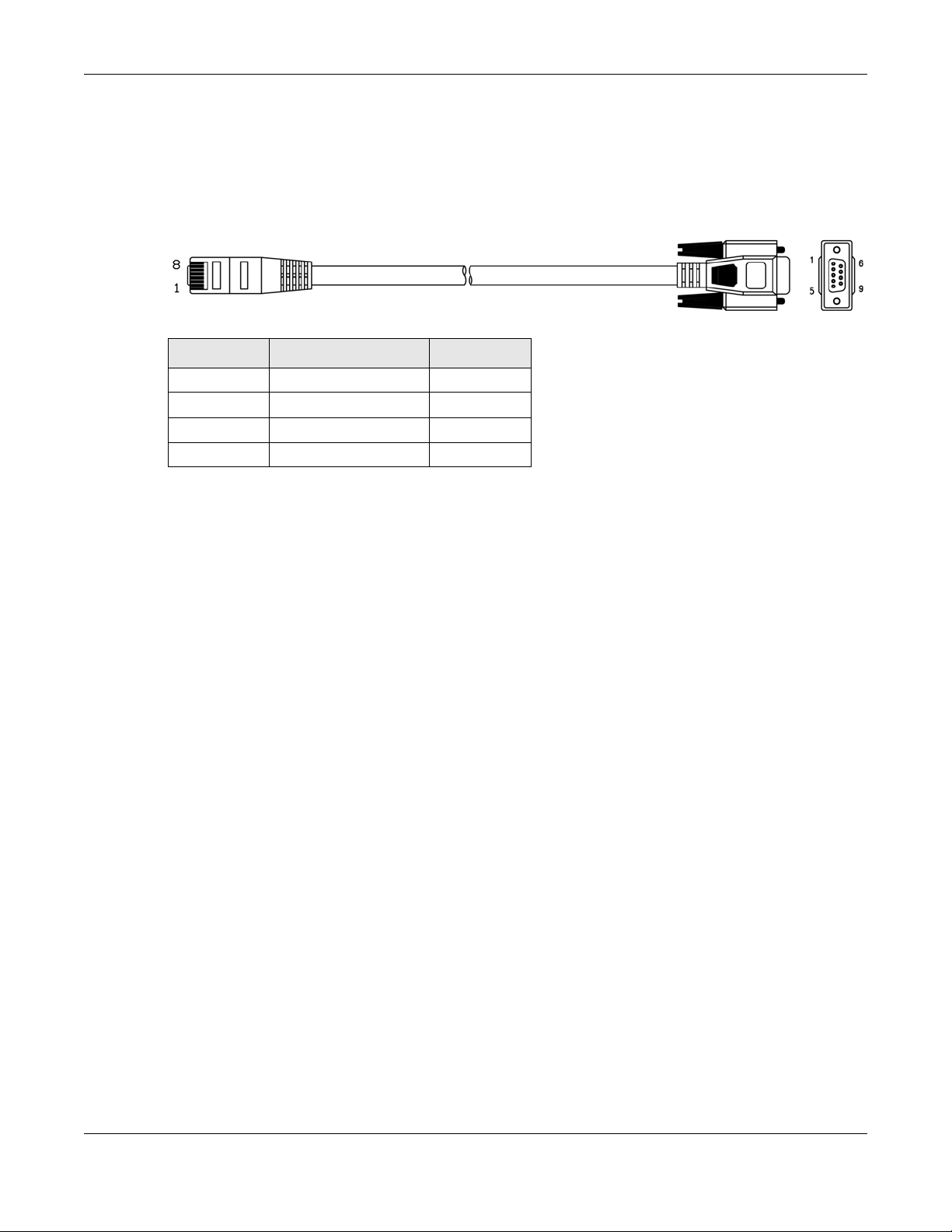
To use the CLI commands to configure the NWA, connect an RJ-45-to-DB-9 cable to the PHONE port at
the bottom of the NWA.
For local management, you can use a computer with terminal emulation software configured to the
following parameters:
• VT100 terminal emulation
NWA / WAC Series User’s Guide
24
Page 25
Chapter 1 Introduction
• 115200 bps
• No parity, 8 data bits, 1 stop bit
• No flow control
The following table shows you the wire color codes and pin assignment for the console cable.
Table 7 RJ45-to-DB-9 Console Cable Color Codes
RJ45 PIN# WIRE COLOR DB-9 PIN#
1Black 1
7Brown 2
2Blue 3
8Purple 5
1.6 LEDs
The LEDs of your WAC6500 and NWA5301 can be controlled by using the Suppression feature such that
the LEDs stay lit (ON) or OFF after the device is ready.
The WAC6500 also features Locator LED which allows you to see the actual location of the WAC6500
between several devices in the network.
Following are LED descriptions for the NWA/WAC series models.
1.6.1 WAC6502D-E, WAC6502D-S, and WAC6503D-S
The LEDs will stay ON when the WAC6500 Series is ready. You can change this setting in the Maintenance
> LEDs > Suppression screen.
NWA / WAC Series User’s Guide
25
Page 26
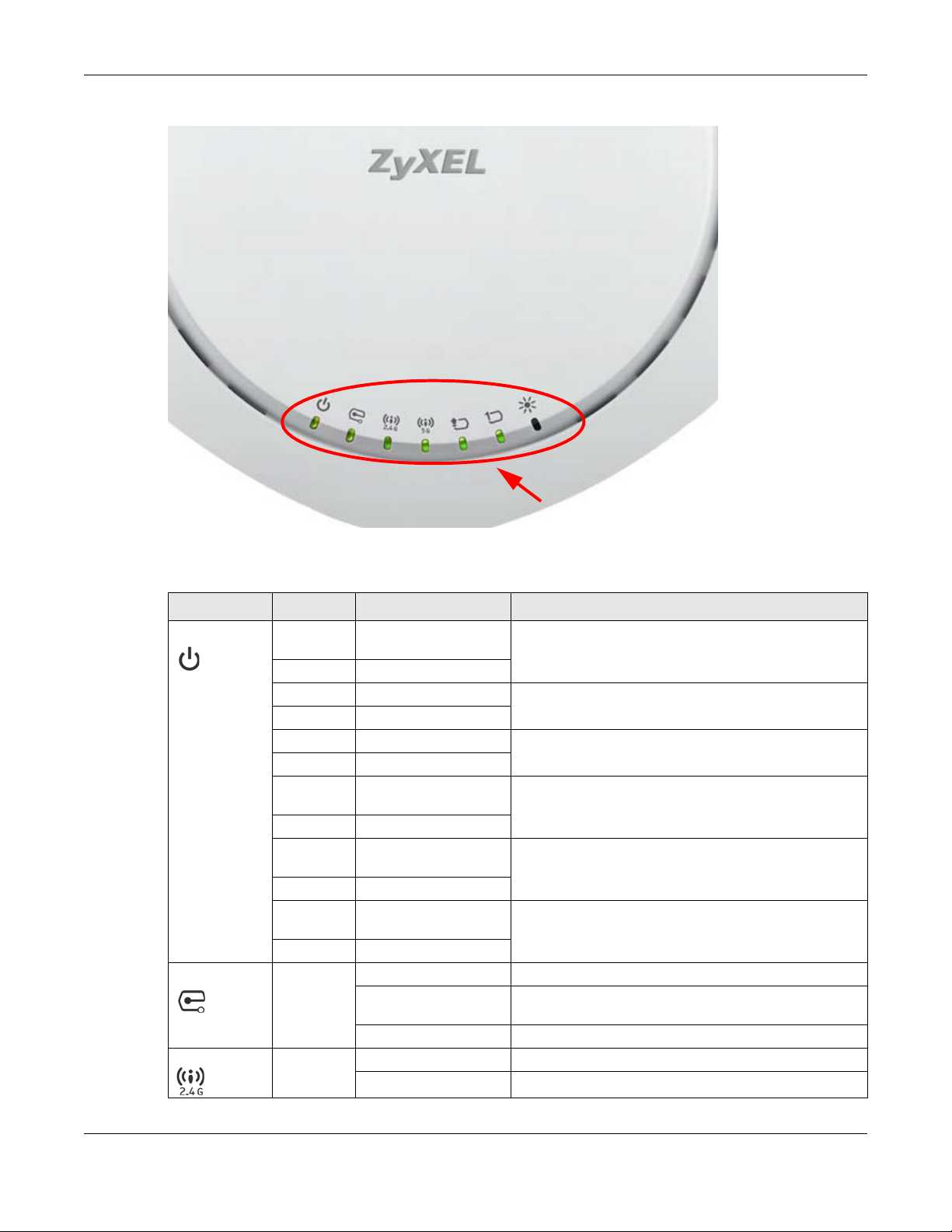
Figure 5 WAC6500 Series LEDs
Chapter 1 Introduction
The following table describes the LEDs.
Table 8 WAC6500 Series LEDs
LED COLOR STATUS DESCRIPTION
PWR/SYS Red Slow Blinking (On for 1s,
Off for 1s)
Green On
Red Off The WAC is ready for use.
Green On
Red On There is system error and the WAC cannot boot up, or the
Green Off
Red Fast Blinking (on for
50ms, Off for 50ms)
Green Off
Red Slow Blinking (blink for 3
times, Off for 3s)
Green Off
Red Slow Blinking (blink for 2
times, Off for 3s)
Green Off
Management Green On The WAC AP is managed by a controller.
Slow Blinking (blink for 3
times, Off for 3s)
Off The WAC AP is in standalone mode.
WLAN Green On The 2.4 GHz WLAN is active.
Off The 2.4 GHz WLAN is not active.
The WAC is booting up.
WAC suffered a system failure.
The WAC is doing firmware upgrade.
The Uplink port is disconnected.
The wireless module of the WAC is disabled or failed.
The WAC AP is searching (discovery) for a controller.
NWA / WAC Series User’s Guide
26
Page 27
Chapter 1 Introduction
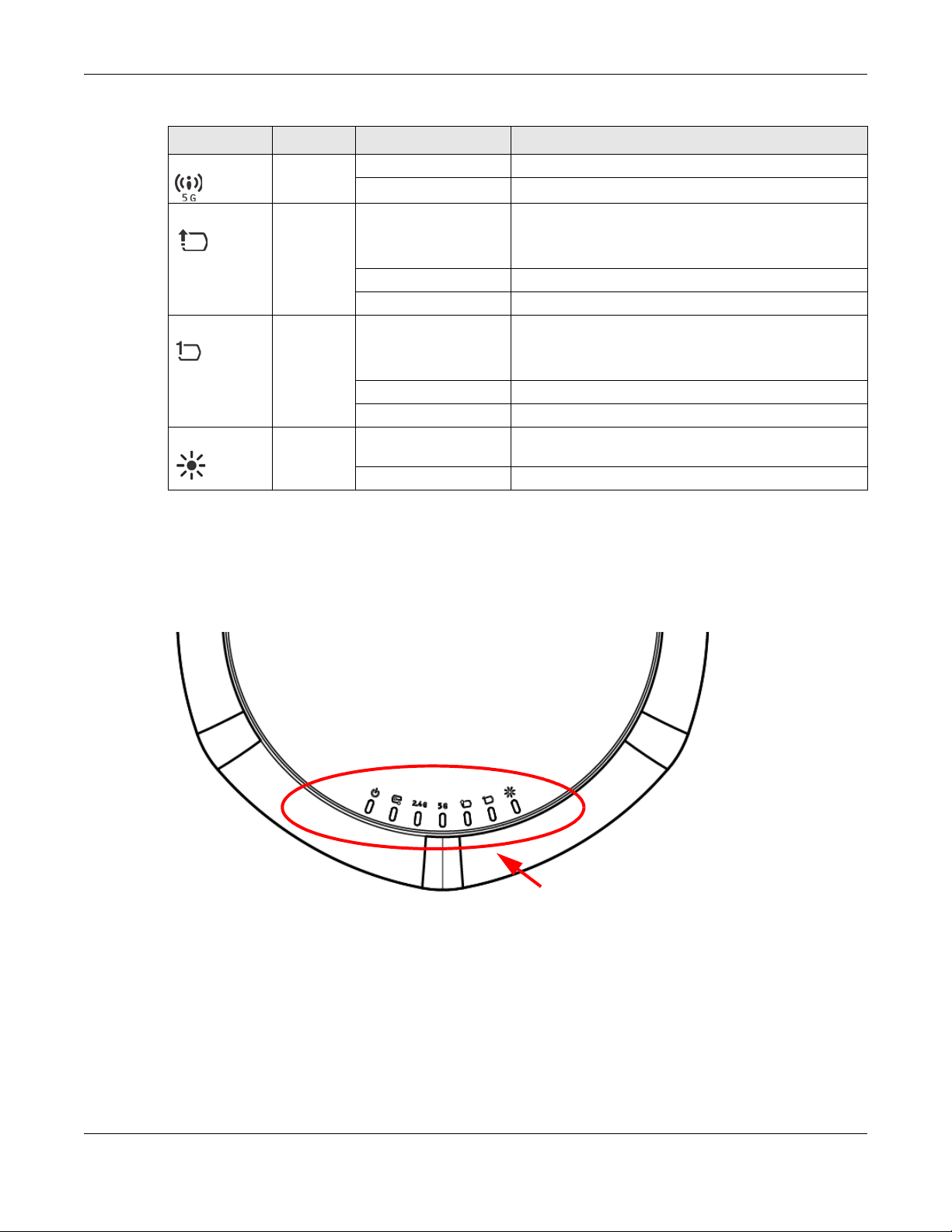
Table 8 WAC6500 Series LEDs (continued)
LED COLOR STATUS DESCRIPTION
WLAN Green On The 5 GHz WLAN is active.
Off The 5 GHz WLAN is not active.
UPLINK Amber/
Green
LAN Amber/
Green
Locator White Blinking The Locator is activated and will show the actual location
On Amber - The port is operating as a 100-Mbps connection.
Blinking The WAC is sending/receiving data through the port.
Off The port is not connected.
On Amber - The port is operating as a 100-Mbps connection.
Blinking The LAN port is sending/receiving data through the port.
Off The LAN port is not connected.
Off The Locator function is off.
1.6.2 NWA1123-AC PRO and WAC6103D-I
The LEDs will stay ON when the NWA1123-AC PRO or WAC6103D-I is ready. You can change this setting
in the Maintenance > LEDs > Suppression screen.
Figure 6 NWA1123-AC PRO and WAC6103D-I LEDs
Green - The port is operating as a Gigabit connection
(1000 Mbps).
Green - The port is operating as a Gigabit connection
(1000 Mbps).
of the WAC between several devices in the network.
NWA / WAC Series User’s Guide
27
Page 28
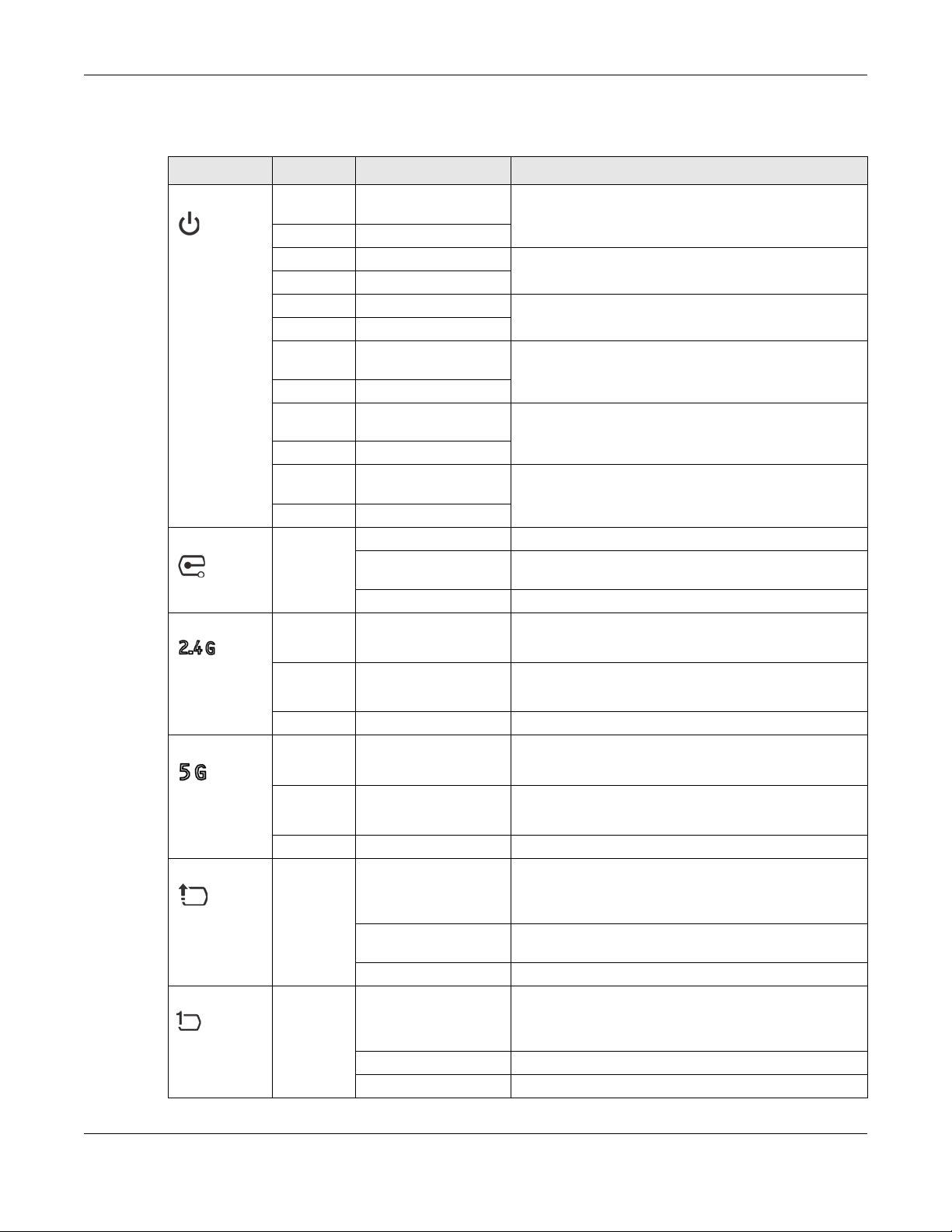
Chapter 1 Introduction
The following table describes the LEDs.
Table 9 NWA1123-AC PRO and WAC6103D-I LEDs
LED COLOR STATUS DESCRIPTION
PWR/SYS Red Slow Blinking (On for 1s,
Off for 1s)
Green On
Red Off The NWA/WAC is ready for use.
Green On
Red On There is system error and the NWA/WAC cannot boot up,
Green Off
Red Fast Blinking (on for
50ms, Off for 50ms)
Green Off
Red Slow Blinking (blink for 3
times, Off for 3s)
Green Off
Red Slow Blinking (blink for 2
times, Off for 3s)
Green Off
Management Green On The NWA/WAC is managed by a controller.
Slow Blinking (blink for 3
times, Off for 3s)
Off The NWA/WAC is in standalone mode.
WLAN Green On The antenna switch is set to “Ceiling” for the radio.
The NWA/WAC is booting up.
or the NWA/WAC suffered a system failure.
The NWA/WAC is doing firmware upgrade.
The Uplink port is disconnected.
The wireless module of the NWA/WAC is disabled or
failed.
The NWA/WAC is searching (discovery) for a controller.
The 2.4 GHz WLAN is active.
Amber On The antenna switch is set to “Wall” for the radio.
The 2.4 GHz WLAN is active.
Off The 2.4 GHz WLAN is not active.
WLAN Green On The antenna switch is set to “Ceiling” for the radio.
The 5 GHz WLAN is active.
Amber On The antenna switch is set to “Wall” for the radio.
The 5 GHz WLAN is active.
Off The 5 GHz WLAN is not active.
UPLINK Amber/
Green
LAN Amber/
Green
On Amber - The port is operating as a 100-Mbps connection.
Green - The port is operating as a Gigabit connection
(1000 Mbps).
Blinking The NWA/WAC is sending/receiving data through the
port.
Off The port is not connected.
On Amber - The port is operating as a 100-Mbps connection.
Green - The port is operating as a Gigabit connection
(1000 Mbps).
Blinking The LAN port is sending/receiving data through the port.
Off The LAN port is not connected.
NWA / WAC Series User’s Guide
28
Page 29
Table 9 NWA1123-AC PRO and WAC6103D-I LEDs (continued)
LED COLOR STATUS DESCRIPTION
Locator White Blinking The Locator is activated and will show the actual location
1.6.3 NWA5301-NJ
The LEDs automatically turn off when the NWA5301-NJ is ready. You can press the LED ON button for one
second to turn on the LEDs again. The LEDs will blink and turn off after two minutes.
Figure 7 NWA5301-NJ LEDs
Chapter 1 Introduction
of the NWA/WAC between several devices in the
network.
Off The Locator function is off.
The following are the LED descriptions for your NWA5301-NJ.
Table 10 NWA5301-NJ LEDs
LABEL COLOR STATUS DESCRIPTION
PWR/SYS Amber Slow Blinking (On for 1s,
Off for 1s)
Green On
Amber Off The NWA is ready for use.
Green On
Amber Slow Blinking (blink for 3
times, Off for 3s)
Green On
Amber On The NWA failed to boot up or is experiencing system
Green Off
Amber Fast Blinking (On for
50ms times, Off for
50ms)
Green Off
Amber Slow Blinking (blink for 3
times, Off for 3s)
Green Off
Amber Slow Blinking (blink for 2
times, Off for 3s)
Green Off
PoE Green On Power is supplied to the yellow PoE Ethernet port (LAN1).
Off There is no power supply.
The NWA is booting up.
The NWA is discovering an AP controller
failure.
The NWA is undergoing firmware upgrade.
The Uplink port is disconnected.
The wireless module of the WAC is disabled or failed.
NWA / WAC Series User’s Guide
29
Page 30
Chapter 1 Introduction
Table 10 NWA5301-NJ LEDs (continued)
LABEL COLOR STATUS DESCRIPTION
WLAN Green On The WLAN is active.
Off The WLAN is not active.
UPLINK Green On The port is connected.
Blinking The NWA is sending/receiving data through the port.
Off The port is not connected.
LAN1-3 Green On The port is connected.
Blinking The NWA is sending/receiving data through the port.
Off The port is not connected.
1.6.4 NWA1123-ACv2, NWA5121-N, NWA5121-NI, NWA5123-AC and NWA5123-NI
The following are the LED descriptions for your NWA1123/5120 series.
Figure 8 NWA1123/5120 Series LED
The following are the LED descriptions for your NWA1123/5120 series.
Table 11 NWA1123/5120 Series LED
COLOR STATUS DESCRIPTION
Amber Slow Blinking (On for 1s,
Off for 1s)
Green On
NWA / WAC Series User’s Guide
The NWA is booting up.
30
Page 31

Chapter 1 Introduction
Table 11 NWA1123/5120 Series LED (continued)
COLOR STATUS DESCRIPTION
Amber Off The NWA is ready for use.
Green On
Amber Off The NWA’s wireless interface is activated.
Green On
Amber Slow Blinking (blink for 3
times, Off for 3s)
Green On
Amber On The NWA failed to boot up or is experience system failure.
Green Off
Amber Fast Blinking (On for
50ms, Off for 50ms)
Green Off
Amber Slow Blinking (blink for 3
times, Off for 3s)
Green Off
Amber Slow Blinking (blink for 2
times, Off for 3s)
Green Off
The NWA is discovering an AP controller.
The NWA is undergoing firmware upgrade.
The Uplink port is disconnected.
The wireless LAN is disabled or fails.
1.6.5 WAC5302D-S
The LEDs automatically turn off when the WAC5302D-S is ready. You can press the LED ON button for one
second to turn on the LEDs again. The LEDs will blink and turn off after two minutes.
Figure 9 WAC5302D-S LEDs
NWA / WAC Series User’s Guide
31
Page 32

Chapter 1 Introduction
The following table describes the LEDs.
Table 12 WAC5302D-S LEDs
LED COLOR STATUS DESCRIPTION
PWR/SYS Red Slow Blinking (On for 1s,
Green On
Red Off The WAC is ready for use.
Green On
Red On There is system error and the WAC cannot boot up, or the
Green Off
Red Fast Blinking (on for
Green Off
Red Slow Blinking (blink for 3
Green Off
Red Slow Blinking (blink for 2
Green Off
Management Green On The WAC AP is managed by a controller.
UPLINK Amber/
Green
WLAN Green On The 2.4 GHz WLAN is active.
WLAN Green On The 5 GHz WLAN is active.
Off for 1s)
50ms, Off for 50ms)
times, Off for 3s)
times, Off for 3s)
Slow Blinking (blink for 3
times, Off for 3s)
Off The WAC AP is in standalone mode.
On Amber - The port is operating as a 10/100-Mbps
Blinking The WAC is sending/receiving data through the port.
Off The port is not connected.
Off The 2.4 GHz WLAN is not active.
Off The 5 GHz WLAN is not active.
The WAC is booting up.
WAC suffered a system failure.
The WAC is doing firmware upgrade.
The Uplink port is disconnected.
The wireless module of the WAC is disabled or failed.
The WAC AP is searching (discovery) for a controller.
connection.
Green - The port is operating as a Gigabit connection
(1000 Mbps).
LAN Amber/
Green
On Amber - The port is operating as a 10/100-Mbps
connection.
Green - The port is operating as a Gigabit connection
(1000 Mbps).
Blinking The LAN port is sending/receiving data through the port.
Off The LAN port is not connected.
1.6.6 NWA1123-AC HD, NWA5123-AC HD and WAC6303D-S
The following are the LED descriptions for your NWA/WAC.
NWA / WAC Series User’s Guide
32
Page 33

Chapter 1 Introduction
Figure 10 NWA1123-AC HD, NWA5123-AC HD and WAC6303D-S LED
The following are the LED descriptions for your NWA/WAC.
Table 13 NWA1123-AC HD, NWA5123-AC HD and WAC6303D-S LED
COLOR STATUS DESCRIPTION
Amber Slow Blinking (On for 1s,
Off for 1s)
Green On
Amber Slow Blinking (blink for 3
times, Off for 3s)
Green On
Green On The NWA/WAC is ready for use, the NWA/WAC’s wireless interface is
Bright Blue On The NWA/WAC’s wireless interface is activated, but there are no wireless
Red On The NWA/WAC failed to boot up or is experience system failure.
Red Fast Blinking (On for
50ms, Off for 50ms)
Red Slow Blinking (blink for 3
times, Off for 3s)
Green Slow Blinking (blink for 1
time, Off for 1s)
Blue Slow Blinking (blink for 1
time, Off for 1s)
The NWA/WAC is booting up.
The NWA/WAC is discovering an AP controller.
activated, and/or wireless clients are connected to the NWA/WAC.
clients connected.
The NWA/WAC is undergoing firmware upgrade.
The Uplink port is disconnected.
The wireless LAN is disabled or fails.
The NWA/WAC is checking for an available 5GHz channel.
1.7 Starting and Stopping the NWA/WAC
Here are some of the ways to start and stop the NWA/WAC.
NWA / WAC Series User’s Guide
33
Page 34

Chapter 1 Introduction
Always use Maintenance > Shutdown or the shutdown command
before you turn off the NWA/WAC or remove the power. Not doing so
can cause the firmware to become corrupt.
Table 14 Starting and Stopping the NWA/WAC
METHOD DESCRIPTION
Turning on the power A cold start occurs when you turn on the power to the NWA/WAC. The NWA/WAC
powers up, checks the hardware, and starts the system processes.
Rebooting the NWA/
WAC
Using the RESET button If you press the RESET button on the back of the NWA/WAC, the NWA/WAC sets the
Clicking Maintenance
> Shutdown >
Shutdown or using the
shutdown command
Disconnecting the
power
A warm start (without powering down and powering up again) occurs when you use the
Reboot button in the Reboot screen or when you use the reboot command. The NWA/
WAC writes all cached data to the local storage, stops the system processes, and then
does a warm start.
configuration to its default values and then reboots. See Section 22.6 on page 212 for
more information.
Clicking Maintenance > Shutdown > Shutdown or using the shutdown command writes all
cached data to the local storage and stops the system processes. Wait for the device to
shut down and then manually turn off or remove the power. It does not turn off the
power.
Power off occurs when you turn off the power to the NWA/WAC. The NWA/WAC simply
turns off. It does not stop the system processes or write cached data to local storage.
The NWA/WAC does not stop or start the system processes when you apply configuration files or run shell
scripts although you may temporarily lose access to network resources.
NWA / WAC Series User’s Guide
34
Page 35

The Web Configurator
2.1 Overview
The NWA/WAC Web Configurator allows easy management using an Internet browser. Browsers
supported are:
• Firefox 36.0.1 or later
• Chrome 41.0 or later
• IE 10 or later
The recommended screen resolution is 1024 x 768 pixels and higher.
2.2 Accessing the Web Configurator
CHAPTER 2
1 Make sure your NWA/WAC is working in standalone AP mode (see Section 1.1.1 on page 17) and
hardware is properly connected. See the Quick Start Guide.
2 If the NWA/WAC and your computer are not connected to a DHCP server, make sure your computer’s
IP address is in the range between "192.168.1.3" and "192.168.1.254".
3 Browse to the NWA/WAC’s DHCP-assigned IP address or http://192.168.1.2. The Login screen appears.
4 Enter the user name (default: “admin”) and password (default: “1234”). Click Login.
NWA / WAC Series User’s Guide
35
Page 36

Chapter 2 The Web Configurator
5 If you logged in using the default user name and password, the Update Admin Info screen appears.
Otherwise, the dashboard appears.
The Update Admin Info screen appears every time you log in using the default user name and default
password. If you change the password for the default user account, this screen does not appear
anymore.
2.3 Navigating the Web Configurator
The following summarizes how to navigate the web configurator from the Dashboard screen. This guide
uses the NWA1123-ACv2 screens as an example. The screens may vary slightly for different models.
NWA / WAC Series User’s Guide
36
Page 37

Chapter 2 The Web Configurator
A
C
B
Figure 11 The Web Configurator’s Main Screen
The Web Configurator’s main screen is divided into these parts:
• A - Title Bar
• B - Navigation Panel
• C - Main Window
2.3.1 Title Bar
The title bar provides some useful links that always appear over the screens below, regardless of how
deep into the Web Configurator you navigate.
Figure 12 Title Bar
The icons provide the following functions.
Table 15 Title Bar: Web Configurator Icons
LABEL DESCRIPTION
Logout Click this to log out of the Web Configurator.
Wizard Click this to open the wizard. See Chapter 3 on page 47 for more information.
Help Click this to open the help page for the current screen.
NWA / WAC Series User’s Guide
37
Page 38

Chapter 2 The Web Configurator
Table 15 Title Bar: Web Configurator Icons (continued)
LABEL DESCRIPTION
About Click this to display basic information about the NWA/WAC.
Site Map Click this to see an overview of links to the Web Configurator screens.
Object
Reference
CLI Click this to open a popup window that displays the CLI commands sent by the Web
Click this to open a screen where you can check which configuration items reference an
object.
Configurator.
About
Click About to display basic information about the NWA/WAC.
Figure 13 About
The following table describes labels that can appear in this screen.
Table 16 About
LABEL DESCRIPTION
Boot Module This shows the version number of the software that handles the booting process of the NWA/
WAC.
Current Version This shows the firmware version of the NWA/WAC.
Released Date This shows the date (yyyy-mm-dd) and time (hh:mm:ss) when the firmware is released.
OK Click this to close the screen.
Site Map
Click Site MAP to see an overview of links to the Web Configurator screens. Click a screen’s link to go to
that screen.
NWA / WAC Series User’s Guide
38
Page 39

Figure 14 Site Map
Object Reference
Chapter 2 The Web Configurator
Click Object Reference to open the Object Reference screen. Select the type of object and the
individual object and click Refresh to show which configuration settings reference the object.
Figure 15 Object Reference
The fields vary with the type of object. The following table describes labels that can appear in this
screen.
Table 17 Object References
LABEL DESCRIPTION
Object Name This identifies the object for which the configuration settings that use it are displayed. Click the
object’s name to display the object’s configuration screen in the main window.
# This field is a sequential value, and it is not associated with any entry.
Service This is the type of setting that references the selected object. Click a service’s name to display
the service’s configuration screen in the main window.
NWA / WAC Series User’s Guide
39
Page 40

Chapter 2 The Web Configurator
Table 17 Object References (continued)
LABEL DESCRIPTION
Priority If it is applicable, this field lists the referencing configuration item’s position in its list, otherwise
N/A displays.
Name This field identifies the configuration item that references the object.
Description If the referencing configuration item has a description configured, it displays here.
Refresh Click this to update the information in this screen.
Cancel Click Cancel to close the screen.
CLI Messages
Click CLI to look at the CLI commands sent by the Web Configurator. These commands appear in a
popup window, such as the following.
Figure 16 CLI Messages
Click Clear to remove the currently displayed information.
Note: See the Command Reference Guide for information about the commands.
2.3.2 Navigation Panel
Use the menu items on the navigation panel to open screens to configure NWA/WAC features. Click the
arrow in the middle of the right edge of the navigation panel to hide the navigation panel menus or
drag it to resize them. The following sections introduce the NWA/WAC’s navigation panel menus and
their screens.
NWA / WAC Series User’s Guide
40
Page 41

Chapter 2 The Web Configurator
Figure 17 Navigation Panel
Dashboard
The dashboard displays general device information, system status, system resource usage, and
interface status in widgets that you can re-arrange to suit your needs.
For details on the Dashboard’s features, see Chapter 4 on page 54.
Monitor Menu
The monitor menu screens display status and statistics information.
Table 18 Monitor Menu Screens Summary
FOLDER OR LINK TAB FUNCTION
Network Status Network
Status
Wireless
AP Information Radio List Display information about the radios of the connected APs.
Station Info Station List Display information about the connected stations.
WDS Link Info WDS Link Info Display statistics about the NWA/WAC’s WDS (Wireless Disctribution
Detected Device Detected
Device
Log View Log Display log entries for the NWA/WAC.
Display general LAN interface information and packet statistics.
System) connections.
Display information about suspected rogue APs.
Configuration Menu
Use the configuration menu screens to configure the NWA/WAC’s features.
Table 19 Configuration Menu Screens Summary
FOLDER OR LINK TAB FUNCTION
Network IP Setting Configure the IP address for the NWA/WAC Ethernet interface.
VLAN Manage the Ethernet interface VLAN settings.
AC Discovery Configures the NWA/WAC’s AP Controller settings.
NWA / WAC Series User’s Guide
41
Page 42

Chapter 2 The Web Configurator
Table 19 Configuration Menu Screens Summary (continued)
FOLDER OR LINK TAB FUNCTION
Wireless
AP
Management
Rogue AP Rogue/Friendly AP
Load Balancing Load Balancing Configure load balancing for traffic moving to and from wireless
DCS DCS Configure dynamic wireless channel selection.
Bluetooth Advertising Settings Configure the beacon ID(s) to be included in the Bluetooth
Object
User User Create and manage users.
AP Profile Radio Create and manage wireless radio settings files that can be
MON Profile MON Profile Create and manage rogue AP monitoring files that can be
WDS Profile WDS Create and manage WDS profiles that can be used to connect to
Certificate My Certificates Create and manage th e NWA/WAC’s certificates.
System
Host Name Host Name Configure the system and domain name for the NWA/WAC.
Date/Time Date/Time Configure the current date, time, and time zone in the NWA/WAC.
WWW Service Control Configure HTTP, HTTPS, and general authentication.
SSH SSH Configure SSH server and SSH service settings.
TELNET TELNET Configure telnet server settings for the NWA/WAC.
FTP FTP Configure FTP server settings.
SNMP SNMP Configure SNMP communities and services.
Log & Report
Email Daily
Report
Log Setting Log Setting Configure the system log, e-mail logs, and remote syslog servers.
WLAN Setting Manage the NWA/WAC’s general wireless settings.
Configure how the NWA/WAC monitors for rogue APs.
List
clients.
advertising packet.
Setting Manage default settings for all users, general settings for user sessions,
and rules to force user authentication.
associated with different APs.
SSID Create and manage wireless SSID, security, MAC filtering, and layer-2
isolation files that can be associated with different APs.
associated with different APs.
different APs in WDS.
Trusted Certificates Import and manage certificates from trusted sources.
Email Daily Report Configure where and how to send daily reports and what reports to
send.
NWA / WAC Series User’s Guide
42
Page 43

Maintenance Menu
Use the maintenance menu screens to manage configuration and firmware files, run diagnostics, and
reboot or shut down the NWA/WAC.
Table 20 Maintenance Menu Screens Summary
FOLDER OR LINK TAB FUNCTION
File Manager Configuration File Manage and upload configuration files for the NWA/WAC.
Firmware Package View the current firmware version and to upload firmware.
Shell Script Manage and run shell script files for the NWA/WAC.
Diagnostics Diagnostics Collect diagnostic information.
LEDs Suppression Enable this feature to keep the LEDs off after the NWA/WAC starts.
Locator Enable this feature to see the actual location of the NWA/WAC
Antenna Antenna Switch Change antenna orientation for the radios.
Reboot Reboot Restart the NWA/WAC.
Shutdown Shutdown Turn off the NWA/WAC.
2.3.3 Warning Messages
Chapter 2 The Web Configurator
between several devices in the network.
Warning messages, such as those resulting from misconfiguration, display in a pop up window.
Figure 18 Warning Message
2.3.4 Tables and Lists
The Web Configurator tables and lists are quite flexible and provide several options for how to display
their entries.
2.3.4.1 Manipulating Table Display
Here are some of the ways you can manipulate the Web Configurator tables.
NWA / WAC Series User’s Guide
43
Page 44

Chapter 2 The Web Configurator
1 Click a column heading to sort the table’s entries according to that column’s criteria.
2 Click the down arrow next to a column heading for more options about how to display the entries. The
options available vary depending on the type of fields in the column. Here are some examples of what
you can do:
• Sort in ascending alphabetical order
• Sort in descending (reverse) alphabetical order
• Select which columns to display
•Group entries by field
•Show entries in groups
• Filter by mathematical operators (<, >, or =) or searching for text.
3 Select a column heading cell’s right border and drag to re-size the column.
NWA / WAC Series User’s Guide
44
Page 45

Chapter 2 The Web Configurator
4 Select a column heading and drag and drop it to change the column order. A green check mark
displays next to the column’s title when you drag the column to a valid new location.
5 Use the icons and fields at the bottom of the table to navigate to different pages of entries and control
how many entries display at a time.
2.3.4.2 Working with Table Entries
The tables have icons for working with table entries. A sample is shown next. You can often use the [Shift]
or [Ctrl] key to select multiple entries to remove, activate, or deactivate.
Table 21 Common Table Icons
Here are descriptions for the most common table icons.
Table 22 Common Table Icons
LABEL DESCRIPTION
Add Click this to create a new entry. For features where the entry’s position in the numbered list is
important (features where the NWA/WAC applies the table’s entries in order like the firewall
for example), you can select an entry and click Add to create a new entry after the
selected entry.
Edit Double-click an entry or select it and click Edit to open a screen where you can modify the
entry’s settings. In some tables you can just click a table entry and edit it directly in the
table. For those types of tables small red triangles display for table entries with changes that
you have not yet applied.
NWA / WAC Series User’s Guide
45
Page 46

Chapter 2 The Web Configurator
Table 22 Common Table Icons (continued)
LABEL DESCRIPTION
Remove To remove an entry, select it and click Remove. The NWA/WAC confirms you want to
remove it before doing so.
Activate To turn on an entry, select it and click Activate.
Inactivate To turn off an entry, select it and click Inactivate.
Object Reference Select an entry and click Object Reference to open a screen that shows which settings use
the entry.
NWA / WAC Series User’s Guide
46
Page 47

3.1 Accessing the Wizard
When you log into the Web Configurator for the first time or when you reset the NWA/WAC to its default
configuration, the wizard screen displays.
Note: If you have already configured the wizard screens and want to open it again, click the
Wizard icon on the upper right corner of any Web Configurator screen.
3.2 Using the Wizard
This wizard helps you configure the NWA/WAC IP address, change time zone, daylight saving and radio
settings, and edit an SSID profile to change general wireless and wireless security settings.
CHAPTER 3
Setup Wizard
3.2.1 Country Code
The welcome screen displays. Select the country where the NWA/WAC is located and click Next.
Note: You cannot change the country code if the NWA/WAC products comply with the U.S.
laws, policies and regulations and are to be sold to the U.S. market.
Figure 19 Wizard: Country Code
NWA / WAC Series User’s Guide
47
Page 48

3.2.2 Time Zone
Use this screen to configure the NWA/WAC’s time zone and daylight saving time.
• Time Zone: Select the time zone of your location. This will set the time difference between your time
zone and Greenwich Mean Time (GMT).
• Enable Daylight Saving: Select the option if you use Daylight Saving Time. Configure the day and time
when Daylight Saving Time starts and ends.
• Offset allows you to specify how much the clock changes when daylight saving begins and ends.
Enter a number from 1 to 5.5 (by 0.5 increments).
Click Prev to return to the previous screen. Click Next to proceed. Click Cancel to close the wizard
without saving.
Figure 20 Wizard: Time Zone
Chapter 3 Setup Wizard
3.2.3 Uplink
Use this screen to configure the NWA/WAC’s IP address.
Uplink Connection: Select Auto (DHCP) if the NWA/WAC is connected to a router with the DHCP server
enabled. You then need to check the router for the IP address assigned to the NWA/WAC in order to
access the NWA/WAC’s web configurator again.
Otherwise, select Static IP when the NWA/WAC is NOT connected to a router or you want to assign it a
fixed IP address. You will need to manually enter:
• the NWA/WAC’s IP address and subnet mask.
• the IP address of the router that helps forward traffic.
• a DNS server's IP address. The Domain Name System (DNS) maps a domain name to an IP address
and vice versa. The DNS server is extremely important because without it, you must know the IP
address of a computer before you can access it.
NWA / WAC Series User’s Guide
48
Page 49

Chapter 3 Setup Wizard
Click Prev to return to the previous screen. Click Next to proceed. Click Cancel to close the wizard
without saving.
Figure 21 Wizard: Uplink
3.2.4 Radio
Use this screen to configure the NWA/WAC’s radio transmitter(s).
• Channel Selection: Select Auto to have the NWA/WAC automatically choose a radio channel that
has least interference. Otherwise, select Manual and specify a channel the NWA/WAC will use in the
2.4GHz or 5GHz wireless LAN. The options vary depending on the frequency band and the country
you are in.
• Maximum Output Power: Enter the maximum output power of the NWA/WAC. If there is a high density
of APs in an area, decrease the output power of the NWA/WAC to reduce interference with other
APs.
Note: Reducing the output power also reduces the NWA/WAC’s effective broadcast radius.
Click Prev to return to the previous screen. Click Next to proceed. Click Cancel to close the wizard
without saving.
NWA / WAC Series User’s Guide
49
Page 50

Figure 22 Wizard: Radio
3.2.5 SSID
Chapter 3 Setup Wizard
Use this screen to enable, disable or edit an SSID profile.
Select an SSID profile and click the Activate icon to turn it on or click the Inactivate icon to turn it off. To
change an SSID profile’s settings, such as the SSID (WiFi network name) and WiFi password, select the
SSID profile from the list and click the Edit icon. See Section 3.2.5.1 on page 50 for more information.
Note: You cannot add or remove an SSID profile after running the setup wizard.
Figure 23 Wizard: SSID
3.2.5.1 Edit SSID Profile
Use this screen to configure an SSID profile.
NWA / WAC Series User’s Guide
50
Page 51

Chapter 3 Setup Wizard
The screen varies depending on the security type you selected.
• SSID - Enter a descriptive name of up to 32 printable characters for the wireless LAN.
• VLAN ID: Enter a VLAN ID for the NWA/WAC to use to tag traffic originating from this SSID.
• Band Mode: Select the wireless band which this profile should use. 2.4 GHz is the frequency used by
IEEE 802.11b/g/n wireless clients. 5 GHz is the frequency used by IEEE 802.11ac/a/n wireless clients.
Not all NWA/WACs support both 2.4 GHz and 5 GHz frequency bands.
• Security Type: Select WPA2 to add security on this wireless network. Otherwise, select OPEN to allow
any wireless client to associate this network without authentication.
• PSK (Pre-shared Key): If you set Security Type to wpa2 and select PSK, enter a pre-shared key of
between 8 and 63 case-sensitive ASCII characters (including spaces and symbols) or 64 hexadecimal
characters.
• 802.1x: Select 802.1x and the Primary / Secondary Radius Server check box to have the NWA/WAC
use the specified RADIUS server. You have to enter the IP address, port number and shared secret
password of the RADIUS server to be used for authentication.
Click OK to proceed. Click Cancel to close the screen without saving.
Figure 24 Wizard: SSID: Edit (WPA2)
NWA / WAC Series User’s Guide
51
Page 52

Chapter 3 Setup Wizard
Figure 25 Wizard: SSID: Edit (802.1x)
3.2.6 Summary
Use this screen to check whether what you have configured is correct. Click Save to apply your settings
and complete the wizard setup. Otherwise, click Prev to return to the previous screen or click Cancel to
close the wizard without saving.
Figure 26 Wizard: Summary
NWA / WAC Series User’s Guide
52
Page 53

PART II
Technical Reference
53
Page 54

4.1 Overview
Use the Dashboard screens to check status information about the NWA/WAC.
4.1.1 What You Can Do in this Chapter
• The main Dashboard screen (Section 4.2 on page 54) displays the NWA/WAC’s general device
information, system status, system resource usage, and interface status. You can also display other
status screens for more information.
4.2 Dashboard
CHAPTER 4
Dashboard
This screen is the first thing you see when you log into the NWA/WAC. It also appears every time you click
the Dashboard icon in the navigation panel. The Dashboard displays general device information, system
status, system resource usage, and interface status in widgets that you can re-arrange to suit your
needs. You can also collapse, refresh, and close individual widgets.
NWA / WAC Series User’s Guide
54
Page 55

Figure 27 Dashboard
B
C
D
A
Chapter 4 Dashboard
The following table describes the labels in this screen.
Table 23 Dashboard
LABEL DESCRIPTION
Widget Settings (A) Use this link to re-open closed widgets. Widgets that are already open appear grayed out.
Refresh Time Setting
(B)
Refresh Now (C) Click this to update the widget’s information immediately.
Close Widget (D) Click this to close the widget. Use Widget Settings to re-open it.
Device Information
System Name This field displays the name used to identify the NWA/WAC on any network. Click the icon to
System Location This field displays the location of the NWA/WAC. Click the icon to open the screen where
Model Name This field displays the model name of this NWA/WAC.
Serial Number This field displays the serial number of this NWA/WAC.
MAC Address
Range
Firmware Version This field displays the version number and date of the firmware the NWA/WAC is currently
Last Firmware
Upgrade Status
Set the interval for refreshing the information displayed in the widget.
open the screen where you can change it.
you can change it.
This field displays the MAC addresses used by the NWA/WAC. Each physical port or wireless
radio has one MAC address. The first MAC address is assigned to the Ethernet LAN port, the
second MAC address is assigned to the first radio, and so on.
running. Click the icon to open the screen where you can upload firmware.
This field displays whether the latest firmware update was successfully completed.
NWA / WAC Series User’s Guide
55
Page 56

Chapter 4 Dashboard
Table 23 Dashboard (continued)
LABEL DESCRIPTION
Last Firmware
Upgrade
System Resources
CPU Usage This field displays what percentage of the NWA/WAC’s processing capability is currently
Memory Usage This field displays what percentage of the NWA/WAC’s RAM is currently being used. Hover
Flash Usage This field displays what percentage of the NWA/WAC’s onboard flash memory is currently
Ethernet Neighbor
Local Port
(Description)
Model Name This field displays the model name of the discovered device.
System Name This field displays the system name of the discovered device.
FW Version This field displays the firmware version of the discovered device.
Port (Description) This field displays the discovered device’s port which is connected to the NWA/WAC.
IP This field displays the IP address of the discovered device. Click the IP address to access
MAC This field displays the MAC address of the discovered device.
WDS (Wireless Distribution System) Uplink/Downlink Status
MAC Address This field displays the MAC address of the root AP or repeater to which the NWA/WAC is
Radio This field displays the radio number on the root AP or repeater to which the NWA/WAC is
Channel This field displays the channel number on the root AP or repeater to which the NWA/WAC is
SSID This field displays the name of the wireless network to which the NWA/WAC is connected
Security Mode This field displays which secure encryption methods is being used by the NWA/WAC to
Link Status This field displays the RSSI (Received Signal Strength Indicator) and transmission/reception
System Status
System Uptime This field displays how long the NWA/WAC has been running since it last restarted or was
Current Date/
Time
Current Login
User
This field displays the date and time when the last firmware update was made.
being used. Hover your cursor over this field to display the Show CPU Usage icon that takes
you to a chart of the NWA/WAC’s recent CPU usage.
your cursor over this field to display the Show Memory Usage icon that takes you to a chart
of the NWA/WAC’s recent memory usage.
being used.
This field displays the port of the NWA/WAC, on which the neighboring device is discovered.
and manage the discovered device using its web configurator.
connected using WDS.
connected using WDS.
connected using WDS.
using WDS.
connect to the root AP or repeater using WDS.
rate of the wireless connection in WDS.
turned on.
This field displays the current date and time in the NWA/WAC. The format is yyyy-mm-dd
hh:mm:ss.
This field displays the user name used to log in to the current session, the amount of
reauthentication time remaining, and the amount of lease time remaining.
NWA / WAC Series User’s Guide
56
Page 57

Chapter 4 Dashboard
Table 23 Dashboard (continued)
LABEL DESCRIPTION
Boot Status This field displays details about the NWA/WAC’s startup state.
OK - The NWA/WAC started up successfully.
Firmware update OK - A firmware update was successful.
Problematic configuration after firmware update - The application of the configuration
failed after a firmware upgrade.
System default configuration - The NWA/WAC successfully applied the system default
configuration. This occurs when the NWA/WAC starts for the first time or you intentionally
reset the NWA/WAC to the system default settings.
Fallback to lastgood configuration - The NWA/WAC was unable to apply the startupconfig.conf configuration file and fell back to the lastgood.conf configuration file.
Fallback to system default configuration - The NWA/WAC was unable to apply the
lastgood.conf configuration file and fell back to the system default configuration file
(system-default.conf).
Booting in progress - The NWA/WAC is still applying the system configuration.
Management
Mode
Power Mode This displays the NWA/WAC’s power status.
This shows whether the NWA/WAC is set to work as a stand alone AP.
Full - the NWA/WAC receives power using a power adaptor and/or through a PoE switch/
injector using IEEE 802.3at PoE plus.
Limited - the NWA/WAC receives power through a PoE switch/injector using IEEE 802.3af PoE
even when it is also connected to a power source using a power adaptor.
When the NWA/WAC is in limited power mode, the NWA/WAC throughput decreases and
has just one transmitting radio chain.
It always shows Full if the NWA/WAC does not support power detection. At the time of
writing, only the WAC6500 series APs support the power detection feature.
Interface Status
Summary
Name This field displays the name of each interface.
Status This field displays the current status of each interface. The possible values depend on what
VID This field displays the VLAN ID to which the interface belongs.
IP Addr/Netmask This field displays the current IP address and subnet mask assigned to the interface. If the IP
IP Assignment This field displays how the interface gets its IP address.
If an Ethernet interface does not have any physical ports associated with it, its entry is
displayed in light gray text. Click the Detail icon to go to a (more detailed) summary screen
of interface statistics.
type of interface it is.
Inactive - The Ethernet interface is disabled.
Down - The Ethernet interface is enabled but not connected.
Speed / Duplex - The Ethernet interface is enabled and connected. This field displays the
port speed and duplex setting (Full or Half).
address is 0.0.0.0, the interface is disabled or did not receive an IP address and subnet mask
via DHCP.
Static - This interface has a static IP address.
DHCP Client - This interface gets its IP address from a DHCP server.
Action If the interface has a static IP address, this shows n/a.
If the interface has a dynamic IP address, use this field to get or to update the IP address for
the interface. Click Renew to send a new DHCP request to a DHCP server.
NWA / WAC Series User’s Guide
57
Page 58

Chapter 4 Dashboard
Table 23 Dashboard (continued)
LABEL DESCRIPTION
WLAN Interface
Status Summary
Status This displays whether or not the WLAN interface is activated.
MAC Address This displays the MAC address of the radio.
Radio This indicates the radio number on the NWA/WAC.
Band This indicates the wireless frequency band currently being used by the radio.
OP Mode This indicates the radio’s operating mode. Operating modes are AP (MBSSID), MON
Channel This indicates the channel number the radio is using.
Antenna This indicates the antenna orientation for the radio (Wall or Ceiling).
Station This displays the number of wireless clients connected to the NWA/WAC.
AP Information This shows a summary of connected wireless Access Points (APs).
All Sensed Device This sections displays a summary of all wireless devices detected by the network. Click the
Un-Classified AP This displays the number of detected unclassified APs.
Rogue AP This displays the number of detected rogue APs.
Friendly AP This displays the number of detected friendly APs.
This displays status information for the WLAN interface.
This shows - when the radio is in monitor mode.
(monitor), Root AP or Repeater.
This field is not available if the NWA/WAC does not allow you to adjust antenna orientation
for each radio using the web configurator or a physical switch. Refer to Table 1 on page 13
and Table 3 on page 15 to see if your NWA/WAC has an antenna switch.
link to go to the Monitor > Wireless > Detected Device screen.
4.2.1 CPU Usage
Use this screen to look at a chart of the NWA/WAC’s recent CPU usage. To access this screen, click CPU
Usage in the dashboard.
Figure 28 Dashboard > CPU Usage
NWA / WAC Series User’s Guide
58
Page 59

The following table describes the labels in this screen.
Table 24 Dashboard > CPU Usage
LABEL DESCRIPTION
% The y-axis represents the percentage of CPU usage.
time The x-axis shows the time period over which the CPU usage occurred
Refresh Interval Enter how often you want this window to be automatically updated.
Refresh Now Click this to update the information in the window right away.
4.2.2 Memory Usage
Use this screen to look at a chart of the NWA/WAC’s recent memory (RAM) usage. To access this screen,
click Memory Usage in the dashboard.
Figure 29 Dashboard > Memory Usage
Chapter 4 Dashboard
The following table describes the labels in this screen.
Table 25 Dashboard > Memory Usage
LABEL DESCRIPTION
% The y-axis represents the percentage of RAM usage.
time The x-axis shows the time period over which the RAM usage occurred
Refresh Interval Enter how often you want this window to be automatically updated.
Refresh Now Click this to update the information in the window right away.
NWA / WAC Series User’s Guide
59
Page 60

5.1 Overview
Use the Monitor screens to check status and statistics information.
5.1.1 What You Can Do in this Chapter
• The Network Status screen (Section 5.3 on page 61) displays general LAN interface information and
packet statistics.
• The AP Information > Radio List screen (Section 5.4 on page 64) displays statistics about the wireless
radio transmitters in the NWA/WAC.
• The Station Info screen (Section 5.5 on page 67) displays statistics pertaining to the associated
stations.
• The WDS Link Info screen (Section 5.6 on page 68) displays statistics about the NWA/WAC’s WDS
(Wireless Distribution System) connections.
• The Detected Device screen (Section 5.7 on page 69) displays information about suspected rogue
APs.
• The View Log screen (Section 5.8 on page 72) displays the NWA/WAC’s current log messages. You
can change the way the log is displayed, you can e-mail the log, and you can also clear the log in
this screen.
CHAPTER 5
Monitor
5.2 What You Need to Know
The following terms and concepts may help as you read through the chapter.
Rogue AP
Rogue APs are wireless access points operating in a network’s coverage area that are not under the
control of the network’s administrators, and can open up holes in a network’s security. See Chapter 11
on page 126 for details.
Friendly AP
Friendly APs are other wireless access points that are detected in your network, as well as any others that
you know are not a threat (those from neighboring networks, for example). See Chapter 11 on page 126
for details.
NWA / WAC Series User’s Guide
60
Page 61

5.3 Network Status
Use this screen to look at general Ethernet interface information and packet statistics. To access this
screen, click Monitor > Network Status. The screen varies depending on whether the NWA/WAC has an
extra Ethernet port (except the uplink port).
Figure 30 Monitor > Network Status (for NWA/WAC with one Ethernet port)
Chapter 5 Monitor
Figure 31 Monitor > Network Status (for NWA/WAC with multiple Ethernet ports)
NWA / WAC Series User’s Guide
61
Page 62

Chapter 5 Monitor
The following table describes the labels in this screen.
Table 26 Monitor > Network Status
LABEL DESCRIPTION
Interface
Summary
IPv6 Interface
Summary
Name This field displays the name of the physical Ethernet port on the NWA/WAC.
Status This field displays the current status of each physical port on the NWA/WAC.
VID This field displays the VLAN ID to which the port belongs.
IP Addr/Netmask
IP Address
IP Assignment This field displays how the interface gets its IPv4 address.
Use the Interface Summary section for IPv4 network settings. Use the IPv6 Interface Summary
section for IPv6 network settings if you connect your NWA/WAC to an IPv6 network. Both
sections have similar fields as described below.
Down - The port is not connected.
Speed / Duplex - The port is connected. This field displays the port speed and duplex setting
(Full or Half).
This field displays the current IP address (and subnet mask) of the interface. If the IP address is
0.0.0.0 (in the IPv4 network) or :: (in the IPv6 network), the interface does not have an IP address
yet.
Static - This interface has a static IPv4 address.
DHCP Client - This interface gets its IPv4 address from a DHCP server.
Action Use this field to get or to update the IP address for the interface. Click Renew to send a new
DHCP request to a DHCP server. If the interface cannot use one of these ways to get or to
update its IP address, this field displays n/a.
Port Statistics
Table
Poll Interval Enter how often you want this window to be updated automatically, and click Set Interval.
Set Interval Click this to set the Poll Interval the screen uses.
Stop Click this to stop the window from updating automatically. You can start it again by setting the
Poll Interval and clicking Set Interval.
Switch to Graphic
View
Name This field displays the name of the interface.
Status This field displays the current status of the physical port.
TxPkts This field displays the number of packets transmitted from the NWA/WAC on the physical port
RxPkts This field displays the number of packets received by the NWA/WAC on the physical port since
Tx Bcast This field displays the number of broadcast packets transmitted from the NWA/WAC on the
Rx Bcast This field displays the number of broadcast packets received by the NWA/WAC on the physical
Collisions This field displays the number of collisions on the physical port since it was last connected.
Tx This field displays the transmission speed, in bytes per second, on the physical port in the one-
Click this to display the port statistics as a line graph.
Down - The physical port is not connected.
Speed / Duplex - The physical port is connected. This field displays the port speed and duplex
setting (Full or Half).
since it was last connected.
it was last connected.
physical port since it was last connected.
port since it was last connected.
second interval before the screen updated.
NWA / WAC Series User’s Guide
62
Page 63

Table 26 Monitor > Network Status (continued)
LABEL DESCRIPTION
Rx This field displays the reception speed, in bytes per second, on the physical port in the one-
second interval before the screen updated.
Up Time This field displays how long the physical port has been connected.
System Up Time This field displays how long the NWA/WAC has been running since it last restarted or was turned
on.
5.3.1 Port Statistics Graph
Use the port statistics graph to look at a line graph of packet statistics for the Ethernet port. To view, click
Monitor > Network Status and then the Switch to Graphic View button.
This screen is NOT available on the NWA/WAC that has an extra Ethernet port (except the uplink port).
Figure 32 Monitor > Network Status > Switch to Graphic View
Chapter 5 Monitor
The following table describes the labels in this screen.
Table 27 Monitor > Network Status > Switch to Graphic View
LABEL DESCRIPTION
Refresh Interval Enter how often you want this window to be automatically updated.
Refresh Now Click this to update the information in the window right away.
Switch to Grid
View
Kbps/Mbps The y-axis represents the speed of transmission or reception.
Time The x-axis shows the time period over which the transmission or reception occurred.
TX This line represents traffic transmitted from the NWA/WAC on the physical port since it was last
Click this to display the port statistics as a table.
connected.
NWA / WAC Series User’s Guide
63
Page 64

Table 27 Monitor > Network Status > Switch to Graphic View (continued)
LABEL DESCRIPTION
RX This line represents the traffic received by the NWA/WAC on the physical port since it was last
Last Update This field displays the date and time the information in the window was last updated.
5.4 Radio List
Use this screen to view statistics for the NWA/WAC’s wireless radio transmitters. To access this screen,
click Monitor > Wireless > AP Information > Radio List.
Figure 33 Monitor > Wireless > AP Information > Radio List (for NWA/WAC that supports WDS)
Chapter 5 Monitor
connected.
Figure 34 Monitor > Wireless > AP Information > Radio List (for NWA/WAC that doesn’t support WDS)
The following table describes the labels in this screen.
Table 28 Monitor > Wireless > AP Information > Radio List
LABEL DESCRIPTION
More Information Click this to view additional information about the selected radio’s wireless traffic and station
Status This displays whether or not the radio is enabled.
count. Information spans a 24 hour period.
NWA / WAC Series User’s Guide
64
Page 65

Chapter 5 Monitor
Table 28 Monitor > Wireless > AP Information > Radio List (continued)
LABEL DESCRIPTION
Loading This indicates the AP’s load balance status (UnderLoad or OverLoad) when load balancing is
enabled on the NWA/WAC. Otherwise, it shows - when load balancing is disabled or the radio
is in monitor mode.
MAC Address This displays the MAC address of the radio.
Radio This indicates the radio number on the NWA/WAC to which it belongs.
OP Mode This indicates the radio’s operating mode. Operating modes are AP (MBSSID), MONITOR, Root
AP/WDS Profile This indicates the AP profile name and WDS profile name to which the radio belongs.
Profile This indicates the AP profile name to which the radio belongs.
Frequency Band This indicates the wireless frequency band currently being used by the radio.
Channel This indicates the radio’s channel ID.
Tx Power This displays the output power of the radio.
Station This displays the number of wireless clients connected to this radio on the NWA/WAC.
Rx This displays the total number of packets received by the radio.
Tx This displays the total number of packets transmitted by the radio.
AP or Repeater
This field is available only on the NWA/WAC that supports WDS.
This field is available only on the NWA/WAC that doesn’t support WDS.
This shows - when the radio is in monitor mode.
5.4.1 AP Mode Radio Information
This screen allows you to view a selected radio’s SSID details, wireless traffic statistics and station count
for the preceding 24 hours. To access this window, select a radio and click the More Information button
in the Radio List screen.
NWA / WAC Series User’s Guide
65
Page 66

Chapter 5 Monitor
Figure 35 Monitor > Wireless > AP Information > Radio List > More Information
The following table describes the labels in this screen.
Table 29 Monitor > Wireless > AP Information > Radio List > More Information
LABEL DESCRIPTION
SSID Detail This list shows information about all the wireless clients that have connected to the specified
# This is the items sequential number in the list. It has no bearing on the actual data in this list.
radio over the preceding 24 hours.
NWA / WAC Series User’s Guide
66
Page 67

Chapter 5 Monitor
Table 29 Monitor > Wireless > AP Information > Radio List > More Information (continued)
LABEL DESCRIPTION
SSID Name This displays an SSID associated with this radio. There can be up to eight maximum.
BSSID This displays a BSSID associated with this radio. The BSSID is tied to the SSID.
Security
Mode
VLAN This displays the VLAN ID associated with the SSID.
Traffic Statistics This graph displays the overall traffic information of the radio over the preceding 24 hours.
Kbps/Mbps This y-axis represents the amount of data moved across this radio in megabytes per second.
Time This x-axis represents the amount of time over which the data moved across this radio.
Station Count This graph displays the connected station information of the radio over the preceding 24 hours
Stations The y-axis represents the number of connected stations.
Time The x-axis shows the time period over which a station was connected.
Last Update This field displays the date and time the information in the window was last updated.
OK Click this to close this window.
Cancel Click this to close this window.
This displays the security mode in which the SSID is operating.
5.5 Station List
Use this screen to view statistics pertaining to the associated stations (or “wireless clients”). Click Monitor
> Wireless > Station Info to access this screen.
Figure 36 Monitor > Wireless > Station Info
The following table describes the labels in this screen.
Table 30 Monitor > Wireless > Station Info
LABEL DESCRIPTION
# This is the station’s index number in this list.
IP Address This is the station’s IP address.
MAC Address This is the station’s MAC address.
Radio This is the radio number on the NWA/WAC to which the station is connected.
Capability This displays the supported standard currently being used by the station or the standards
supported by the station.
NWA / WAC Series User’s Guide
67
Page 68

Table 30 Monitor > Wireless > Station Info (continued)
LABEL DESCRIPTION
SSID Name This indicates the name of the wireless network to which the station is connected. A single AP
can have multiple SSIDs or networks.
Security Mode This indicates which secure encryption methods is being used by the station to connect to the
network.
Signal Strength This is the RSSI (Received Signal Strength Indicator) of the station’s wireless connection.
Tx Rate This is the maximum transmission rate of the station.
Rx Rate This is the maximum reception rate of the station.
Association Time This displays the time the station first associated with the NWA/WAC’s wireless network.
Refresh Click this to refresh the items displayed on this page.
5.6 WDS Link Info
Use this screen to view the WDS traffic statistics between the NWA/WAC and a root AP or repeaters.
Click Monitor > Wireless > WDS Link Info to access this screen.
Chapter 5 Monitor
Figure 37 Monitor > Wireless > WDS Link Info
The following table describes the labels in this screen.
Table 31 Monitor > Wireless > WDS Link Info
LABEL DESCRIPTION
WDS Uplink Info
WDS Downlink
Info
# This is the index number of the root AP or repeater in this list.
Uplink refers to the WDS link from the repeaters to the root AP.
Downlink refers to the WDS link from the root AP to the repeaters.
When the NWA/WAC is in root AP mode and connected to a repeater, only the downlink
information is displayed.
When the NWA/WAC is in repeater mode and connected to a root AP directly or via another
repeater, the uplink information is displayed.
When the NWA/WAC is in repeater mode and connected to a root AP and other repeater(s),
both the uplink and downlink information would be displayed.
NWA / WAC Series User’s Guide
68
Page 69

Chapter 5 Monitor
Table 31 Monitor > Wireless > WDS Link Info (continued)
LABEL DESCRIPTION
MAC Address This is the MAC address of the root AP or repeater to which the NWA/WAC is connected using
WDS.
Radio This is the radio number on the root AP or repeater to which the NWA/WAC is connected using
WDS.
SSID Name This indicates the name of the wireless network to which the NWA/WAC is connected using
Security Mode This indicates which secure encryption methods is being used by the NWA/WAC to connect to
Signal Strength This is the RSSI (Received Signal Strength Indicator) of the wireless connection in WDS.
Tx Rate This is the maximum transmission rate of the root AP or repeater to which the NWA/WAC is
Rx Rate This is the maximum reception rate of the root AP or repeater to which the NWA/WAC is
Association Time This displays the time the NWA/WAC first associated with the wireless network using WDS.
Refresh Click this to refresh the items displayed on this page.
WDS.
the root AP or repeater using WDS.
connected using WDS.
connected using WDS.
5.7 Detected Device
Use this screen to view information about suspected rogue APs. Click Monitor > Wireless > Detected
Device to access this screen. Not all NWA/WACs support monitor mode.
Note: If the NWA/WAC supports monitor mode, the radio or at least one of the NWA/WAC’s
radio must be set to monitor mode (in the Wireless > AP Management screen) in order
to detect other wireless devices in its vicinity.
If the NWA/WAC doesn’t support monitor mode, turn on rogue AP detection in the
Configuration > Wireless > Rogue AP screen to detect rogue APs.
NWA / WAC Series User’s Guide
69
Page 70

Chapter 5 Monitor
Figure 38 Monitor > Wireless > Detected Device (for NWA/WAC that supports Monitor mode)
NWA / WAC Series User’s Guide
70
Page 71

Chapter 5 Monitor
Figure 39 Monitor > Wireless > Detected Device (for NWA/WAC that doesn’t support Monitor mode)
The following table describes the labels in this screen.
Table 32 Monitor > Wireless > Detected Device
LABEL DESCRIPTION
Discovered APs
Rogue AP This shows how many devices are detected as rogue APs.
Suspected rogue APThis shows how many devices are detected as possible rogue APs by classification rule.
Friendly AP This shows how many devices are detected as friendly APs.
Un-classified AP This shows how many devices are detected, but have not been classified by the NWA/WAC.
Detect Now Click this button for the NWA/WAC to scan for APs in the network.
Detected Device
NWA / WAC Series User’s Guide
71
Page 72

Chapter 5 Monitor
Table 32 Monitor > Wireless > Detected Device (continued)
LABEL DESCRIPTION
Mark as Rogue APClick this button to mark the selected AP as a rogue AP. A rogue AP can be contained in the
Configuration > Wireless > Rogue AP screen (Section 7.3 on page 88).
Mark as Friendly APClick this button to mark the selected AP as a friendly AP. For more on managing friendly APs,
see the Configuration > Wireless > Rogue AP screen (Section 7.3 on page 88).
# This is the detected device’s index number in this list.
Status This indicates the detected device’s status.
Device This indicates the type of device detected.
Role This indicates the detected device’s role (such as friendly or rogue).
Classified by This indicates the detected device’s classification rule.
MAC Address This indicates the detected device’s MAC address.
SSID Name This indicates the detected device’s SSID.
Channel ID This indicates the detected device’s channel ID.
802.11 Mode This indicates the 802.11 mode (a/b/g/n) transmitted by the detected device.
Security This indicates the encryption method (if any) used by the detected device.
Description This displays the detected device’s description. For more on managing friendly and rogue APs,
Last Seen This indicates the last time the device was detected by the NWA/WAC.
Refresh Click this to refresh the items displayed on this page.
see the Configuration > Wireless > Rogue AP screen (Section 7.3 on page 88).
5.8 View Log
Log messages are stored in two separate logs, one for regular log messages and one for debugging
messages. In the regular log, you can look at all the log messages by selecting All Logs, or you can
select a specific category of log messages (for example, user). You can also look at the debugging log
by selecting Debug Log. All debugging messages have the same priority.
To access this screen, click Monitor > Log. The log is displayed in the following screen.
Note: When a log reaches the maximum number of log messages, new log messages
automatically overwrite existing log messages, starting with the oldest existing log
message first.
Events that generate an alert (as well as a log message) display in red. Regular logs display in black.
Click a column’s heading cell to sort the table entries by that column’s criteria. Click the heading cell
again to reverse the sort order.
NWA / WAC Series User’s Guide
72
Page 73

Figure 40 Monitor > Log > View Log
Chapter 5 Monitor
The following table describes the labels in this screen.
Table 33 Monitor > Log > View Log
LABEL DESCRIPTION
Show Filter / Hide
Filter
Display Select the category of log message(s) you want to view. You can also view All Logs at one
Priority This displays when you show the filter. Select the priority of log messages to display. The log
Source Address This displays when you show the filter. Type the source IP address of the incoming packet that
Click this button to show or hide the filter settings.
If the filter settings are hidden, the Display, Email Log Now, Refresh, and Clear Log fields are
available.
If the filter settings are shown, the Display, Priority, Source Address, Destination Address, Source
Interface, Destination Interface, Protocol, Keyword, and Search fields are available.
time, or you can view the Debug Log.
displays the log messages with this priority or higher. Choices are: any, emerg, alert, crit, error,
warn, notice, and info, from highest priority to lowest priority. This field is read-only if the
Category is Debug Log.
generated the log message. Do not include the port in this filter.
NWA / WAC Series User’s Guide
73
Page 74

Chapter 5 Monitor
Table 33 Monitor > Log > View Log (continued)
LABEL DESCRIPTION
Destination
Address
Source Interface This displays when you show the filter. Select the source interface of the packet that generated
Destination
Interface
Protocol This displays when you show the filter. Select a service protocol whose log messages you would
Keyword This displays when you show the filter. Type a keyword to look for in the Message, Source,
Search This displays when you show the filter. Click this button to update the log using the current filter
Email Log Now Click this button to send log messages to the Active e-mail addresses specified in the Send Log
Refresh Click this to update the list of logs.
Clear Log Click this button to clear the whole log, regardless of what is currently displayed on the screen.
# This field is a sequential value, and it is not associated with a specific log message.
Time This field displays the time the log message was recorded.
Priority This field displays the priority of the log message. It has the same range of values as the Priority
Category This field displays the log that generated the log message. It is the same value used in the
Message This field displays the reason the log message was generated. The text “[count=x]”, where x is a
Source This field displays the source IP address and the port number in the event that generated the
Source Interface This field displays the source interface of the packet that generated the log message.
Destination This field displays the destination IP address and the port number of the event that generated
Destination
Interface
Protocol This field displays the service protocol in the event that generated the log message.
Note This field displays any additional information about the log message.
This displays when you show the filter. Type the IP address of the destination of the incoming
packet when the log message was generated. Do not include the port in this filter.
the log message.
This displays when you show the filter. Select the destination interface of the packet that
generated the log message.
like to see.
Destination and Note fields. If a match is found in any field, the log message is displayed. You
can use up to 63 alphanumeric characters and the underscore, as well as punctuation marks
()’ ,:;?! +-*/= #$% @ ; the period, double quotes, and brackets are not allowed.
settings.
To field on the Configuration > Log & Report > Log Settings screen.
field above.
Display and (other) Category fields.
number, appears at the end of the Message field if log consolidation is turned on and multiple
entries were aggregated to generate into this one.
log message.
the log message.
This field displays the destination interface of the packet that generated the log message.
The Web Configurator saves the filter settings if you leave the View Log screen and return to it later.
NWA / WAC Series User’s Guide
74
Page 75

6.1 Overview
This chapter describes how you can configure the management IP address and VLAN settings of your
NWA/WAC.
The Internet Protocol (IP) address identifies a device on a network. Every networking device (including
computers, servers, routers, printers, etc.) needs an IP address to communicate across the network.
These networking devices are also known as hosts.
Figure 41 IP Setup
CHAPTER 6
Network
The figure above illustrates one possible setup of your NWA/WAC. The gateway IP address is 192.168.1.1
and the managed IP address of the NWA/WAC is 192.168.1.2 (default), but if the NWA/WAC is assigned
an IP address by a DHCP server, the default (192.168.1.2) will not be used. The gateway and the NWA/
WAC must belong in the same IP subnet to be able to communicate with each other.
6.1.1 Management Mode
This discusses using the NWA/WAC in management mode, which determines whether the NWA/WAC is
used in its standalone mode, or as part of a Control And Provisioning of Wireless Access Points (CAPWAP)
network.
About CAPWAP
The NWA/WAC supports CAPWAP. This is Zyxel’s implementation of the CAPWAP protocol (RFC 5415).
The CAPWAP data flow is protected by Datagram Transport Layer Security (DTLS).
The following figure illustrates a CAPWAP wireless network. You (U) configure the AP controller (C), which
then automatically updates the configurations of the managed APs (M1 ~ M4).
NWA / WAC Series User’s Guide
75
Page 76

Chapter 6 Network
Figure 42 CAPWAP Network Example
Note: The NWA/WAC can be a standalone AP (default), or a CAPWAP managed AP.
CAPWAP Discovery and Management
The link between CAPWAP-enabled access points proceeds as follows:
1 An AP in managed AP mode joins a wired network (receives a dynamic IP address).
2 The AP sends out a discovery request, looking for a CAPWAP AP controller.
3 If there is an AP controller on the network, it receives the discovery request. If the AP controller is in
Manual mode it adds the details of the AP to its Unmanaged Access Points list, and you decide which
available APs to manage. If the AP controller is in Always Accept mode, it automatically adds the AP to
its Managed Access Points list and provides the managed AP with default configuration information, as
well as securely transmitting the DTLS pre-shared key. The managed AP is ready for association with
wireless clients.
Managed AP Finds the Controller
A managed NWA/WAC can find the controller in one of the following ways:
• Manually specify the controller’s IP address in the Web Configurator’s AC (AP Controller) Discovery
screen.
• Get the controller’s IP address from a DHCP server with the controller’s IP address configured as
option 138.
• Get the controller’s IP address from a DNS server SRV (Service) record.
NWA / WAC Series User’s Guide
76
Page 77

Chapter 6 Network
• Broadcasting to discover the controller within the broadcast domain.
Note: The AP controller needs to have a static IP address. If it is a DHCP client, set the DHCP
server to reserve an IP address for the AP controller.
CAPWAP and IP Subnets
By default, CAPWAP works only between devices with IP addresses in the same subnet.
However, you can configure CAPWAP to operate between devices with IP addresses in different
subnets by doing the following.
• Activate DHCP. Your network’s DHCP server must support option 138 defined in RFC 5415.
• Configure DHCP option 138 with the IP address of the CAPWAP AP controller on your network.
DHCP Option 138 allows the CAPWAP management request (from the AP in managed AP mode) to
reach the AP controller in a different subnet, as shown in the following figure.
Figure 43 CAPWAP and DHCP Option 138
Notes on CAPWAP
This section lists some additional features of Zyxel’s implementation of the CAPWAP protocol.
• When the AP controller uses its internal Remote Authentication Dial In User Service (RADIUS) server,
managed APs also use the AP controller’s authentication server to authenticate wireless clients.
• If a managed AP’s link to the AP controller is broken, the managed AP continues to use the wireless
settings with which it was last provided.
6.1.2 What You Can Do in this Chapter
• The IP Setting screen (Section 6.2 on page 78) configures the NWA/WAC’s LAN IP address.
• The VLAN screen (Section 6.3 on page 79) configures the NWA/WAC’s VLAN settings.
• The AC (AP Controller) Discovery screen (Section 6.3 on page 79) configures the NWA/WAC’s AP
Controller settings.
NWA / WAC Series User’s Guide
77
Page 78

6.2 IP Setting
Use this screen to configure the IP address for your NWA/WAC. To access this screen, click Configuration
> Network > IP Setting.
Figure 44 Configuration > Network > IP Setting
Chapter 6 Network
Each field is described in the following table.
Table 34 Configuration > Network > IP Setting
LABEL DESCRIPTION
IP Address
Assignment
Get
Automatically
Use Fixed IP
Address
IP Address Enter the IP address for this interface.
Subnet Mask Enter the subnet mask of this interface in dot decimal notation. The subnet mask indicates
Gateway Enter the IP address of the gateway. The NWA/WAC sends packets to the gateway when it
DNS Server IP
Address
Select this to make the interface a DHCP client and automatically get the IP address,
subnet mask, and gateway address from a DHCP server.
Select this if you want to specify the IP address, subnet mask, and gateway manually.
what part of the IP address is the same for all computers in the network.
does not know how to route the packet to its destination. The gateway should be on the
same network as the interface.
Enter the IP address of the DNS server.
NWA / WAC Series User’s Guide
78
Page 79

Chapter 6 Network
Table 34 Configuration > Network > IP Setting (continued)
LABEL DESCRIPTION
IPv6 Address
Assignment
Enable Stateless
Address Autoconfiguration
(SLAAC)
Link-Local
Address
IPv6 Address/
Prefix Length
Gateway Enter the IPv6 address of the default outgoing gateway using colon (:) hexadecimal
Metric Enter the priority of the gateway (if any) on the LAN interface. The NWA/WAC decides
DHCPv6 Client Select this option to set the NWA/WAC to act as a DHCPv6 client.
DUID This field displays the DHCP Unique IDentifier (DUID) of the NWA/WAC, which is unique and
Request Address Select this option to get an IPv6 address from the DHCPv6 server.
DHCPv6 Request
Options
DNS Server Select this option to obtain the IP address of the DNS server.
NTP Server Select this option to obtain the IP address of the NTP server.
Apply Click Apply to save your changes back to the NWA/WAC.
Reset Click Reset to return the screen to its last-saved settings.
Select this to enable IPv6 stateless auto-configuration on the NWA/WAC. The NWA/WAC will
generate an IPv6 address itself from a prefix obtained from an IPv6 router in the network.
This displays the IPv6 link-local address and the network prefix that the NWA/WAC
generates itself for the LAN interface.
Enter the IPv6 address and the prefix length for the LAN interface if you want to use a static
IP address. This field is optional.
The prefix length indicates what the left-most part of the IP address is the same for all
computers in the network, that is, the network address.
notation.
which gateway to use based on this priority. The lower the number, the higher the priority. If
two or more gateways have the same priority, the NWA/WAC uses the one that was
configured first. Enter zero to set the metric to 1024 for IPv6.
used for identification purposes when the NWA/WAC is exchanging DHCPv6 messages with
others. See Appendix B on page 227 for more information.
Select this option to determine what additional information to get from the DHCPv6 server.
6.3 VLAN
This section discusses how to configure the NWA/WAC’s VLAN settings.
NWA / WAC Series User’s Guide
79
Page 80

Chapter 6 Network
Figure 45 Management VLAN Setup
In the figure above, to access and manage the NWA/WAC from computer A, the NWA/WAC and
switch B’s ports to which computer A and the NWA/WAC are connected should be in the same VLAN.
A Virtual Local Area Network (VLAN) allows a physical network to be partitioned into multiple logical
networks. Devices on a logical network belong to one group. A device can belong to more than one
group. With VLAN, a device cannot directly talk to or hear from devices that are not in the same
group(s); the traffic must first go through a router.
VLAN also increases network performance by limiting broadcasts to a smaller and more manageable
logical broadcast domain. In traditional switched environments, all broadcast packets go to each and
every individual port. With VLAN, all broadcasts are confined to a specific broadcast domain.
IEEE 802.1Q Tag
The IEEE 802.1Q standard defines an explicit VLAN tag in the MAC header to identify the VLAN
membership of a frame across bridges. A VLAN tag includes the 12-bit VLAN ID and 3-bit user priority.
The VLAN ID associates a frame with a specific VLAN and provides the information that devices need to
process the frame across the network.
Use this screen to configure the VLAN settings for your NWA/WAC. To access this screen, click
Configuration > Network > VLAN.
The screen varies depending on whether the NWA/WAC has an extra Ethernet port (except the uplink
port).
NWA / WAC Series User’s Guide
80
Page 81

Chapter 6 Network
Figure 46 Configuration > Network > VLAN (for NWA/WAC with multiple Ethernet ports)
Figure 47 Configuration > Network > VLAN (for NWA/WAC with one Ethernet port)
Each field is described in the following table.
Table 35 Configuration > Network > VLAN
LABEL DESCRIPTION
VLAN Settings
Management
VLAN ID
As Native VLAN Select this option to treat this VLAN ID as a VLAN created on the NWA/WAC and not one
LAN Setting
Port Setting
Edit Double-click an entry or select it and click Edit to open a screen where you can modify the
Activate/
Inactivate
# This is the index number of the port.
Enter a VLAN ID for the NWA/WAC.
assigned to it from outside the network.
entry’s settings. In some tables you can just click a table entry and edit it directly in the
table. For those types of tables small red triangles display for table entries with changes that
you have not yet applied.
To turn on an entry, select it and click Activate. To turn off an entry, select it and click
Inactivate.
NWA / WAC Series User’s Guide
81
Page 82

Chapter 6 Network
Table 35 Configuration > Network > VLAN (continued)
LABEL DESCRIPTION
Status This field indicates whether the port is enabled (a yellow bulb) or not (a gray bulb).
Port This field displays the name of the port.
PVID This field displays the port number of the VLAN ID.
VLAN Configuration
Add Click this to create a new entry. For features where the entry’s position in the numbered list is
important (features where the NWA/WAC applies the table’s entries in order like the SSID for
example), you can select an entry and click Add to create a new entry after the selected
entry.
Edit Double-click an entry or select it and click Edit to open a screen where you can modify the
entry’s settings. In some tables you can just click a table entry and edit it directly in the
table. For those types of tables small red triangles display for table entries with changes that
you have not yet applied.
Remove To remove an entry, select it and click Remove. The NWA/WAC confirms you want to
remove it before doing so.
Activate/
Inactivate
# This is the index number of the VLAN ID
Status This field indicates whether the VLAN is enabled (a yellow bulb) or not (a gray bulb).
Name This field displays the name of each VLAN.
VID This field displays the VLAN ID.
Member This field displays the VLAN membership to which the port belongs.
Apply Click Apply to save your changes back to the NWA/WAC.
Reset Click Reset to return the screen to its last-saved settings.
To turn on an entry, select it and click Activate. To turn off an entry, select it and click
Inactivate.
6.4 AC (AP Controller) Discovery
This section discusses how to configure the NWA/WAC’s AC (AP Controller) Discovery settings. You can
have the NWA/WAC managed by an AP controller on your network. When you do this, the NWA/WAC
can be configured ONLY by the AP controller. See Section 6.1.1 on page 75 for more information on
management mode and AP Controller.
Note: The AC (AP Controller) Discovery settings are not available in all NWA/WACs. See
Section 1.1 on page 13 for more information.
If you want to return the NWA/WAC to standalone AP mode, you can do one of the two following
options:
• Press the Reset button.
• Check the AP controller for the NWA/WAC’s IP address and use FTP to upload the default
configuration file to the NWA/WAC. You can get the configuration file at conf/system-default.conf.
You must reboot the device after uploading the configuration file.
To access the Controller Discover screen, click Configuration > Network > AC Discovery.
NWA / WAC Series User’s Guide
82
Page 83

Chapter 6 Network
Figure 48 Configuration > Network > AC Discovery
Each field is described in the following table.
Table 36 Configuration > Network > AC Discovery
LABEL DESCRIPTION
Discovery Setting
Auto Select this option to use DHCP option 138/DNS SRV record/Broadcast to get the AP
controller’s IP address. If the NWA/WAC and a Zyxel AP controller, such as the NXC2500
or NXC5500, are in the same subnet, it will be managed by the controller automatically.
Manual Select this option and enter the IP address of the AP controller manually. This is
necessary when the AP Controller is not in the same subnet and you want it to manage
the NWA/WAC.
Primary / Secondary
Static AC IP
Disable Select this to manage the NWA/WAC using its own web configurator, neither managing
Apply Click Apply to save the information entered in this screen.
Reset Click Reset to return the screen to its last-saved settings.
Specify the primary and secondary IP address of the AP controller to which the NWA/
WAC connects.
nor managed by other devices. Please note if an AP Controller is in the same subnet,
you will need to click Disable if you do not want the NWA/WAC to be managed.
If you select Auto or Manual, the AP controller uploads the firmware package for
managed AP mode to the NWA/WAC and you cannot log in as the web configurator is
disabled; you must manage the NWA/WAC through the AP controller on your network.
NWA / WAC Series User’s Guide
83
Page 84

7.1 Overview
This chapter discusses how to configure the wireless network settings in your NWA/WAC.
The following figure provides an example of a wireless network.
Figure 49 Example of a Wireless Network
CHAPTER 7
Wireless
The wireless network is the part in the blue circle. In this wireless network, devices A and B are called
wireless clients. The wireless clients use the access point (AP) to interact with other devices (such as the
printer) or with the Internet. Your NWA/WAC is the AP.
7.1.1 What You Can Do in this Chapter
• The AP Management screen (Section 7.2 on page 85) manages the NWA/WAC’s general wireless
settings.
• The Rogue AP screen (Section 7.3 on page 88) allows you to assign APs either to the rogue AP list or
the friendly AP list.
• The Load Balancing screen (Section 7.4 on page 91) configures network traffic load balancing
between the APs and the NWA/WAC.
• The DCS screen (Section 7.5 on page 94) configures dynamic radio channel selection.
NWA / WAC Series User’s Guide
84
Page 85

7.1.2 What You Need to Know
The following terms and concepts may help as you read this chapter.
Station / Wireless Client
A station or wireless client is any wireless-capable device that can connect to an AP using a wireless
signal.
Dynamic Channel Selection (DCS)
Dynamic Channel Selection (DCS) is a feature that allows an AP to automatically select the radio
channel upon which it broadcasts by scanning the area around it and determining what channels are
currently being used by other devices.
Load Balancing (Wireless)
Wireless load balancing is the process where you limit the number of connections allowed on an wireless
access point (AP) or you limit the amount of wireless traffic transmitted and received on it so the AP
does not become overloaded.
Chapter 7 Wireless
7.2 AP Management
Use this screen to manage the NWA/WAC’s general wireless settings. Click Configuration > Wireless > AP
Management to access this screen.
NWA / WAC Series User’s Guide
85
Page 86

Chapter 7 Wireless
Figure 50 Configuration > Wireless > AP Management
Each field is described in the following table.
Table 37 Configuration > Wireless > AP Management
LABEL DESCRIPTION
Radio 1 Setting
Radio 1 Activate Select the check box to enable the NWA/WAC’s first (default) radio.
NWA / WAC Series User’s Guide
86
Page 87

Chapter 7 Wireless
Table 37 Configuration > Wireless > AP Management (continued)
LABEL DESCRIPTION
Radio 1 OP Mode Select the operating mode for radio 1.
AP Mode means the radio can receive connections from wireless clients and pass their data
traffic through to the NWA/WAC to be managed (or subsequently passed on to an
upstream gateway for managing).
MON Mode means the radio monitors the broadcast area for other APs, then passes their
information on to the NWA/WAC where it can be determined if those APs are friendly or
rogue. If a radio is set to this mode it cannot receive connections from wireless clients.
Root AP means the radio acts as an AP and also supports the wireless connections with
other APs (in repeater mode) to form a WDS (Wireless Distribution System) to extend its
wireless network.
Repeater means the radio can establish a wireless connection with other APs (in either root
AP or repeater mode) to form a WDS.
Radio 1 Profile Select the radio profile the radio uses.
Note: You can only apply a 2.4G AP radio profile to radio 1. Otherwise, the first
radio will not be working.
Radio 1 WDS Profile This field is available only when the radio is in Root AP or Repeater mode.
Select the WDS profile the radio uses to connect to a root AP or repeater.
Uplink Selection
Mode
Max Output Power Enter the maximum output power (between 0 to 30 dBm) of the NWA/WAC in this field. If
This field is available only when the radio is in Repeater mode.
Select AUTO to have the NWA/WAC automatically use the settings in the applied WDS
profile to connect to a root AP or repeater.
Select Manual to have the NWA/WAC connect to the root AP or repeater with the MAC
address specified in the Radio 1 Uplink MAC Address field.
there is a high density of APs in an area, decrease the output power of the NWA/WAC to
reduce interference with other APs.
Note: Reducing the output power also reduces the NWA/WAC’s effective
broadcast radius.
MBSSID Settings
Edit Double-click an entry or select it and click Edit to open a screen where you can modify the
entry’s settings. In some tables you can just click a table entry and edit it directly in the
table. For those types of tables small red triangles display for table entries with changes that
you have not yet applied.
# This field shows the index number of the SSID
SSID Profile This field displays the SSID profile that is associated with the radio profile.
Radio 2 Setting
Radio 2 Activate This displays if the NWA/WAC has a second radio.
Select the check box to enable the NWA/WAC’s second radio.
NWA / WAC Series User’s Guide
87
Page 88

Chapter 7 Wireless
Table 37 Configuration > Wireless > AP Management (continued)
LABEL DESCRIPTION
Radio 2 OP Mode This displays if the NWA/WAC has a second radio. Select the operating mode for radio 2.
AP Mode means the radio can receive connections from wireless clients and pass their data
traffic through to the NWA/WAC to be managed (or subsequently passed on to an
upstream gateway for managing).
MON Mode means the radio monitors the broadcast area for other APs, then passes their
information on to the NWA/WAC where it can be determined if those APs are friendly or
rogue. If a radio is set to this mode it cannot receive connections from wireless clients.
Root AP means the radio acts as an AP and also supports the wireless connections with
other APs (in repeater mode) to form a WDS to extend its wireless network.
Repeater means the radio can establish a wireless connection with other APs (in either root
AP or repeater mode) to form a WDS.
Radio 2 Profile This displays if the NWA/WAC has a second radio. Select the radio profile the radio uses.
Note: You can only apply a 5G AP radio profile to radio 2. Otherwise, the second
radio will not be working.
Radio 2 WDS Profile This field is available only when the radio is in Root AP or Repeater mode.
Select the WDS profile the radio uses to connect to a root AP or repeater.
Uplink Selection
Mode
This field is available only when the radio is in Repeater mode.
Select AUTO to have the NWA/WAC automatically use the settings in the applied WDS
profile to connect to a root AP or repeater.
Max Output Power Enter the maximum output power (between 0 to 30 dBm) of the NWA/WAC in this field. If
MBSSID Settings
Edit Double-click an entry or select it and click Edit to open a screen where you can modify the
# This field shows the index number of the SSID
SSID Profile This field shows the SSID profile that is associated with the radio profile.
Apply Click Apply to save your changes back to the NWA/WAC.
Reset Click Reset to return the screen to its last-saved settings.
7.3 Rogue AP
Use this screen to assign APs either to the rogue AP list or the friendly AP list. A rogue AP is a wireless
access point operating in a network’s coverage area that is not under the control of the network
administrator, and which can potentially open up holes in a network’s security.
Select Manual to have the NWA/WAC connect to the root AP or repeater with tbe MAC
address specified in the Radio 2 Uplink MAC Address field.
there is a high density of APs in an area, decrease the output power of the NWA/WAC to
reduce interference with other APs.
Note: Reducing the output power also reduces the NWA/WAC’s effective
broadcast radius.
entry’s settings. In some tables you can just click a table entry and edit it directly in the
table. For those types of tables small red triangles display for table entries with changes that
you have not yet applied.
Click Configuration > Wireless > Rogue AP to access this screen.
NWA / WAC Series User’s Guide
88
Page 89

Chapter 7 Wireless
Figure 51 Configuration > Wireless > Rogue AP (for NWA/WAC that supports Monitor mode)
Figure 52 Configuration > Wireless > Rogue AP (for NWA/WAC that doesn’t support Monitor mode)
NWA / WAC Series User’s Guide
89
Page 90

Chapter 7 Wireless
Each field is described in the following table.
Table 38 Configuration > Wireless > Rogue AP
LABEL DESCRIPTION
Rogue AP Detection
Setting
Enable Rogue AP
Detection
Suspected Rogue AP
Classification Rule
Add Click this to add an SSID Keyword.
Edit Select an SSID Keyword and click this button to modify it.
Remove Select an existing SSID keyword and click this button to delete it.
# This is the SSID Keyword’s index number in this list.
SSID Keyword This field displays the SSID Keyword.
Rogue/Friendly AP List
Add Click this button to add an AP to the list and assign it either friendly or rogue status.
Edit Select an AP in the list to edit and reassign its status.
Remove Select an AP in the list to remove.
# This field is a sequential value, and it is not associated with any interface.
Role This field indicates whether the selected AP is a rogue-ap or a friendly-ap. To change
MAC Address This field indicates the AP’s radio MAC address.
Description This field displays the AP’s description. You can modify this by clicking the Edit button.
Rogue/Friendly AP List
Importing/Exporting
File Path / Browse /
Importing
Select this option to detect Rogue APs in the network.
Click the check boxes (Weak Security (Open, WEP, WPA-PSK), Hidden SSID, SSID
Keyword) of the characteristics an AP should have for the NWA/WAC to rule it as a
Rogue AP.
the AP’s role, click the Edit button.
These controls allow you to export the current list of rogue and friendly APs or import
existing lists.
Enter the file name and path of the list you want to import or click the Browse button
to locate it. Once the File Path field has been populated, click Importing to bring the
list into the NWA/WAC.
You need to wait a while for the importing process to finish.
Exporting Click this button to export the current list of either rogue APs or friendly APS.
Apply Click Apply to save your changes back to the NWA/WAC.
Reset Click Reset to return the screen to its last-saved settings.
7.3.1 Add/Edit Rogue/Friendly List
Click Add or select an AP and click the Edit button in the Configuration > Wireless > Rogue AP table to
display this screen.
NWA / WAC Series User’s Guide
90
Page 91

Chapter 7 Wireless
Figure 53 Configuration > Wireless > Rogue AP > Add/Edit Rogue/Friendly AP List
Each field is described in the following table.
Table 39 Configuration > Wireless > Rogue AP > Add/Edit Rogue/Friendly AP List
LABEL DESCRIPTION
MAC Enter the MAC address of the AP you want to add to the list. A MAC address is a unique
Description Enter up to 60 characters for the AP’s description. Spaces and underscores are allowed.
Role Select either Rogue AP or Friendly AP for the AP’s role.
OK Click OK to save your changes back to the NWA/WAC.
Cancel Click Cancel to close the window with changes unsaved.
hardware identifier in the following hexadecimal format: xx:xx:xx:xx:xx:xx where xx is a
hexadecimal number separated by colons.
7.4 Load Balancing
Use this screen to configure wireless network traffic load balancing between the APs on your network.
Click Configuration > Wireless > Load Balancing to access this screen.
Figure 54 Configuration > Wireless > Load Balancing
NWA / WAC Series User’s Guide
91
Page 92

Chapter 7 Wireless
Each field is described in the following table.
Table 40 Configuration > Wireless > Load Balancing
LABEL DESCRIPTION
Enable Load
Balancing
Mode Select a mode by which load balancing is carried out.
Max Station
Number
Traffic Level Select the threshold traffic level at which the NWA/WAC begins load balancing its
Disassociate
station when
overloaded
Select this to enable load balancing on the NWA/WAC.
Use this section to configure wireless network traffic load balancing between the managed
APs in this group.
Select By Station Number to balance network traffic based on the number of specified
stations connected to the NWA/WAC.
Select By Traffic Level to balance network traffic based on the volume generated by the
stations connected to the NWA/WAC.
Select By Smart Classroom to balance network traffic based on the number of specified
stations connected to the NWA/WAC. The NWA/WAC ignores association request and
authentication request packets from any new station when the maximum number of
stations is reached.
If you select By Station Number or By Traffic Level, once the threshold is crossed (either the
maximum station numbers or with network traffic), the NWA/WAC delays association
request and authentication request packets from any new station that attempts to make a
connection. This allows the station to automatically attempt to connect to another, less
burdened AP if one is available.
Enter the threshold number of stations at which the NWA/WAC begins load balancing its
connections.
connections (Low, Medium, High).
The maximum bandwidth allowed for each level is:
• Low - 11 Mbps,
• Medium - 23 Mbps
• High - 35M bps
This function is enabled by default and the disassociation priority is always Signal Strength
when you set Mode to By Smart Classroom.
Select this option to disassociate wireless clients connected to the AP when it becomes
overloaded. If you do not enable this option, then the AP simply delays the connection until
it can afford the bandwidth it requires, or it transfers the connection to another AP within its
broadcast radius.
The disassociation priority is determined automatically by the NWA/WAC and is as follows:
• Idle Timeout - Devices that have been idle the longest will be kicked first. If none of the
connected devices are idle, then the priority shifts to Signal Strength.
• Signal Strength - Devices with the weakest signal strength will be kicked first.
Note: If you enable this function, you should ensure that there are multiple APs
within the broadcast radius that can accept any rejected or kicked
wireless clients; otherwise, a wireless client attempting to connect to an
overloaded AP will be disassociated permanently and never be allowed to
connect.
Apply Click Apply to save your changes back to the NWA/WAC.
Reset Click Reset to return the screen to its last-saved settings.
NWA / WAC Series User’s Guide
92
Page 93

Chapter 7 Wireless
7.4.1 Disassociating and Delaying Connections
When your AP becomes overloaded, there are two basic responses it can take. The first one is to
“delay” a client connection. This means that the AP withholds the connection until the data transfer
throughput is lowered or the client connection is picked up by another AP. If the client is picked up by
another AP then the original AP cannot resume the connection.
For example, here the AP has a balanced bandwidth allotment of 6 Mbps. If laptop R connects and it
pushes the AP over its allotment, say to 7 Mbps, then the AP delays the red laptop’s connection until it
can afford the bandwidth or the laptop is picked up by a different AP with bandwidth to spare.
Figure 55 Delaying a Connection
The second response your AP can take is to kick the connections that are pushing it over its balanced
bandwidth allotment.
Figure 56 Kicking a Connection
NWA / WAC Series User’s Guide
93
Page 94

Connections are kicked based on either idle timeout or signal strength. The NWA/WAC first looks to see
which devices have been idle the longest, then starts kicking them in order of highest idle time. If no
connections are idle, the next criteria the NWA/WAC analyzes is signal strength. Devices with the
weakest signal strength are kicked first.
7.5 DCS
Use this screen to configure dynamic radio channel selection. Click Configuration > Wireless > DCS to
access this screen.
Figure 57 Configuration > Wireless > DCS
Chapter 7 Wireless
Each field is described in the following table.
Table 41 Configuration > Wireless > DCS
LABEL DESCRIPTION
Select Now Click this to have the NWA/WAC scan for and select an available channel immediately.
Apply Click Apply to save your changes back to the NWA/WAC.
Reset Click Reset to return the screen to its last-saved settings.
7.6 Technical Reference
The following section contains additional technical information about the features described in this
chapter.
Dynamic Channel Selection
When numerous APs broadcast within a given area, they introduce the possibility of heightened radio
interference, especially if some or all of them are broadcasting on the same radio channel. If the
interference becomes too great, then the network administrator must open his AP configuration options
and manually change the channel to one that no other AP is using (or at least a channel that has a
lower level of interference) in order to give the connected stations a minimum degree of interference.
Dynamic channel selection frees the network administrator from this task by letting the AP do it
automatically. The AP can scan the area around it looking for the channel with the least amount of
interference.
In the 2.4 GHz spectrum, each channel from 1 to 13 is broken up into discrete 22 MHz segments that are
spaced 5 MHz apart. Channel 1 is centered on 2.412 GHz while channel 13 is centered on 2.472 GHz.
NWA / WAC Series User’s Guide
94
Page 95

Chapter 7 Wireless
Figure 58 An Example Three-Channel Deployment
Three channels are situated in such a way as to create almost no interference with one another if used
exclusively: 1, 6 and 11. When an AP broadcasts on any of these three channels, it should not interfere
with neighboring APs as long as they are also limited to same trio.
Figure 59 An Example Four-Channel Deployment
However, some regions require the use of other channels and often use a safety scheme with the
following four channels: 1, 4, 7 and 11. While they are situated sufficiently close to both each other and
the three so-called “safe” channels (1,6 and 11) that interference becomes inevitable, the severity of it is
dependent upon other factors: proximity to the affected AP, signal strength, activity, and so on.
Finally, there is an alternative four channel scheme for ETSI, consisting of channels 1, 5, 9, 13. This offers
significantly less overlap that the other one.
Figure 60 An Alternative Four-Channel Deployment
Load Balancing
Because there is a hard upper limit on an AP’s wireless bandwidth, load balancing can be crucial in
areas crowded with wireless users. Rather than let every user connect and subsequently dilute the
NWA / WAC Series User’s Guide
95
Page 96

Chapter 7 Wireless
available bandwidth to the point where each connecting device receives a meager trickle, the load
balanced AP instead limits the incoming connections as a means to maintain bandwidth integrity.
There are three kinds of wireless load balancing available on the NWA/WAC:
Load balancing by station number limits the number of devices allowed to connect to your AP. If you
know exactly how many stations you want to let connect, choose this option.
For example, if your company’s graphic design team has their own AP and they have 10 computers,
you can load balance for 10. Later, if someone from the sales department visits the graphic design
team’s offices for a meeting and he tries to access the network, his computer’s connection is delayed,
giving it the opportunity to connect to a different, neighboring AP. If he still connects to the AP
regardless of the delay, then the AP may boot other people who are already connected in order to
associate with the new connection.
Load balancing by smart classroom also limits the number of devices allowed to connect to your AP.
But any new connections will be just rejected when the AP is overloaded.
Load balancing by traffic level limits the number of connections to the AP based on maximum
bandwidth available. If you are uncertain as to the exact number of wireless connections you will have
then choose this option. By setting a maximum bandwidth cap, you allow any number of devices to
connect as long as their total bandwidth usage does not exceed the configured bandwidth cap
associated with this setting. Once the cap is hit, any new connections are rejected or delayed provided
that there are other APs in range.
Imagine a coffee shop in a crowded business district that offers free wireless connectivity to its
customers. The coffee shop owner can’t possibly know how many connections his AP will have at any
given moment. As such, he decides to put a limit on the bandwidth that is available to his customers but
not on the actual number of connections he allows. This means anyone can connect to his wireless
network as long as the AP has the bandwidth to spare. If too many people connect and the AP hits its
bandwidth cap then all new connections must basically wait for their turn or get shunted to the nearest
identical AP.
NWA / WAC Series User’s Guide
96
Page 97

8.1 Overview
Use this screen to configure the Bluetooth advertising settings for the NWA/WAC that supports Bluetooth
Low Energy (BLE). Bluetooth Low Energy, which is also known as Bluetooth Smart, transmits less data over
a shorter distance and consumes less power than classic Bluetooth.
8.1.1 What You Need To Know
iBeacon is Apple’s communication protocol on top of Bluetooth Low Energy wireless technology.
Beacons (Bluetooth radio transmitters) or BLE enabled devices broadcast packets to every device
around it to announce their presence. Advertising packets contain their iBeacon ID which mainly
consists of the UUID, major number, minor number and TX (transmit) power. The ID is used to distinguish
beacons in your network.
CHAPTER 8
Bluetooth
The universally unique identifier (UUID) is a 128-bit (16-byte) number which can be used to identify a
service, a device, a manufacturer or an owner. The 2-byte major number is to identify and distinguish a
group, and the 2-byte minor number is to identify and distinguish an individual.
For example, you can set all the beacons in one network to share the same UUID, the beacons in a
particular room to use the same major number, and each beacon in the room can have its own minor
number.
NETWORK A
ROOM X ROOM Y
BEACON 1 BEACON 2 BEACON 3
UUID EBAECFAF-DFE0-4039-BE5A-F030EED4303C
Major 10 10 20
Minor 121
8.2 Bluetooth Advertising Settings
The NWA/WAC communicates with another BLE enabled device using advertisements. Use this screen
to configure the beacon ID(s) to be included in the advertising packet. You can have up to five
combinations of the UUID, Major and Minor parameters.
To access this screen, click Configuration > Bluetooth > Advertising Settings.
NWA / WAC Series User’s Guide
97
Page 98

Chapter 8 Bluetooth
Figure 61 Configuration > Bluetooth > Advertising Settings
The following table describes the labels in this screen.
Table 42 Configuration > Bluetooth > Advertising Settings
LABEL DESCRIPTION
Edit Click this to edit the selected entry.
Activate To turn on an entry, select it and click Activate.
Inactivate To turn off an entry, select it and click Inactivate.
# This field is a sequential value, and it is not associated with a specific entry.
Status This field shows whether or not the entry is activated.
A yellow bulb signifies that this rule is active. A gray bulb signifies that this rule is not active.
UUID This field indicates the UUID to be included in the Bluetooth advertising packets.
Major This field indicates the major number to be included in the Bluetooth advertising packets.
Minor This field indicates the minor number to be included in the Bluetooth advertising packets.
8.2.1 Edit Advertising Settings
Select an entry in the Configuration > Bluetooth > Advertising Settings screen and click the Edit icon to
open the Edit Advertising screen. Use this screen to configure the beacon ID in the Bluetooth advertising
packets.
Figure 62 Configuration > Bluetooth > Advertising Settings > Edit
NWA / WAC Series User’s Guide
98
Page 99

Chapter 8 Bluetooth
The following table describes the labels in this screen.
Table 43 Configuration > Bluetooth > Advertising Settings > Edit
LABEL DESCRIPTION
Activate Select this option to enable the advertising settings.
UUID To specify a UUID of the NWA/WAC’s beacon ID, enter 32 hexadecimal digits in the range of
Generate new
UUID
Major Enter an integer from 0 to 65535 as the major value to identify the beacon.
Minor Enter an integer from 0 to 65535 as the minor value to identify the beacon.
OK
Cancel Click Cancel to exit this screen without saving your changes.
“A-F”, “a-f” and “0-9”, split into five groups separated by hyphens (-). The UUID format is as
follows: xxxxxxxx-xxxx-xxxx-xxxx-xxxxxxxxxxxx (8-4-4-4-12)
Click this button to have the NWA/WAC generate a UUID automatically.
Click OK to save your changes back to the NWA/WAC.
NWA / WAC Series User’s Guide
99
Page 100

9.1 Overview
This chapter describes how to set up user accounts and user settings for the NWA/WAC.
9.1.1 What You Can Do in this Chapter
• The User screen (see Section 9.2 on page 101) provides a summary of all user accounts.
•The Setting screen (see Section 9.3 on page 103) controls default settings, login settings, lockout
settings, and other user settings for the NWA/WAC.
9.1.2 What You Need To Know
The following terms and concepts may help as you read this chapter.
CHAPTER 9
User
User Account
A user account defines the privileges of a user logged into the NWA/WAC. User accounts are used in
controlling access to configuration and services in the NWA/WAC.
User Types
These are the types of user accounts the NWA/WAC uses.
Table 44 Types of User Accounts
TYPE ABILITIES LOGIN METHOD(S)
Admin Users
admin Change NWA/WAC configuration (web, CLI) WWW, TELNET, SSH, FTP
limited-admin Look at NWA/WAC configuration (web, CLI)
Perform basic diagnostics (CLI)
Access Users
user Used for the embedded RADIUS server and
SNMPv3 user access
Browse user-mode commands (CLI)
Note: The default admin account is always authenticated locally, regardless of the
authentication method setting.
WWW, TELNET, SSH
NWA / WAC Series User’s Guide
100
 Loading...
Loading...