Page 1

P-870HW -51a v2
802.11bg Wireless VDSL2 4-Port Gateway
User’s Guide
Version 1.00
11/2008
Edition 1
www.zyxel.com
Page 2

Page 3

About This User's Guide
About This User's Guide
Intended Audience
This manual is intended for people who want to configure the ZyXEL Device using the web
configurator. You should have at least a basic knowledge of TCP/IP networking concepts and
topology.
Related Documentation
• Quick Start Guide
The Quick Start Guide is designed to help you get up and running right away. It contains
information on setting up your network and configuring for Internet access.
• Web Configurator Online Help
Embedded web help for descriptions of individual screens and supplementary
information.
" It is recommended you use the web configurator to configure the ZyXEL
Device.
• Supporting Disk
Refer to the included CD for support documents.
• ZyXEL Web Site
Please refer to www.zyxel.com
certifications.
User Guide Feedback
Help us help you. Send all User Guide-related comments, questions or suggestions for
improvement to the following address, or use e-mail instead. Thank you!
The Technical Writing Team,
ZyXEL Communications Corp.,
6 Innovation Road II,
Science-Based Industrial Park,
Hsinchu, 300, Taiwan.
E-mail: techwriters@zyxel.com.tw
for additional support documentation and product
P-870HW-51a v2 User’s Guide
3
Page 4
Document Conventions
Document Conventions
Warnings and Notes
These are how warnings and notes are shown in this User’s Guide.
1 Warnings tell you about things that could harm you or your device.
" Notes tell you other important information (for example, other things you may
need to configure or helpful tips) or recommendations.
Syntax Conventions
•The P-870HW-51a v2 may be referred to as the “ZyXEL Device”, the “device”, the
“system” or the “product” in this User’s Guide.
• Product labels, screen names, field labels and field choices are all in bold font.
• A key stroke is denoted by square brackets and uppercase text, for example, [ENTER]
means the “enter” or “return” key on your keyboard.
• “Enter” means for you to type one or more characters and then press the [ENTER] key.
“Select” or “choose” means for you to use one of the predefined choices.
• A right angle bracket ( > ) within a screen name denotes a mouse click. For example,
Maintenance > Log > Log Setting means you first click Maintenance in the navigation
panel, then the Log sub menu and finally the Log Setting tab to get to that screen.
• Units of measurement may denote the “metric” value or the “scientific” value. For
example, “k” for kilo may denote “1000” or “1024”, “M” for mega may denote “1000000”
or “1048576” and so on.
• “e.g.,” is a shorthand for “for instance”, and “i.e.,” means “that is” or “in other words”.
4
P-870HW-51a v2 User’s Guide
Page 5

Document Conventions
Icons Used in Figures
Figures in this User’s Guide may use the following generic icons. The ZyXEL Device icon is
not an exact representation of your device.
ZyXEL Device Computer Notebook computer
Server DSLAM Firewall
Telephone Switch Router
P-870HW-51a v2 User’s Guide
5
Page 6

Safety Warnings
Safety Warnings
1 For your safety, be sure to read and follow all warning notices and instructions.
• Do NOT use this product near water, for example, in a wet basement or near a swimming
pool.
• Do NOT expose your device to dampness, dust or corrosive liquids.
• Do NOT store things on the device.
• Do NOT install, use, or service this device during a thunderstorm. There is a remote risk
of electric shock from lightning.
• Connect ONLY suitable accessories to the device.
• Do NOT open the device or unit. Opening or removing covers can expose you to
dangerous high voltage points or other risks. ONLY qualified service personnel should
service or disassemble this device. Please contact your vendor for further information.
• Make sure to connect the cables to the correct ports.
• Place connecting cables carefully so that no one will step on them or stumble over them.
• Always disconnect all cables from this device before servicing or disassembling.
• Use ONLY an appropriate power adaptor or cord for your device.
• Connect the power adaptor or cord to the right supply voltage (for example, 110V AC in
North America or 230V AC in Europe).
• Do NOT allow anything to rest on the power adaptor or cord and do NOT place the
product where anyone can walk on the power adaptor or cord.
• Do NOT use the device if the power adaptor or cord is damaged as it might cause
electrocution.
• If the power adaptor or cord is damaged, remove it from the device and the power source.
• Do NOT attempt to repair the power adaptor or cord. Contact your local vendor to order a
new one.
• Do not use the device outside, and make sure all the connections are indoors. There is a
remote risk of electric shock from lightning.
• Do NOT obstruct the device ventilation slots, as insufficient airflow may harm your
device.
• Use only No. 26 AWG (American Wire Gauge) or larger telecommunication line cord.
• Antenna Warning! This device meets ETSI and FCC certification requirements when
using the included antenna(s). Only use the included antenna(s).
• If you wall mount your device, make sure that no electrical lines, gas or water pipes will
be damaged.
6
P-870HW-51a v2 User’s Guide
Page 7
This product is recyclable. Dispose of it properly.
Safety Warnings
P-870HW-51a v2 User’s Guide
7
Page 8

Safety Warnings
8
P-870HW-51a v2 User’s Guide
Page 9

Contents Overview
Contents Overview
Introduction ............................................................................................................................23
Introducing the ZyXEL Device ...................................................................................................25
Tutorials .....................................................................................................................................31
Introducing the Web Configurator .............................................................................................. 39
Status Screens .......................................................................................................................... 43
Network ...................................................................................................................................51
WAN Setup ................................................................................................ ... ... ... .... ... ................53
LAN Setup ................................................................................................................................. 67
Wireless LAN ......................................... ... ... ........................................................... ... ... .............75
Network Address Translation (NAT) .......................................................................................... 99
Security .................................................................................................................................105
IP Filter ..................... ... ... .... ... ... .......................................................... ... .... ... ... ... .....................107
Advanced .............................................................................................................................. 111
Static Route ..............................................................................................................................113
Quality of Service (QoS) ..................................................................................................... ......117
Dynamic DNS Setup ................................................................................................................ 127
Remote Management ..............................................................................................................129
Universal Plug-and-Play (UPnP) ............................................................................................. 131
Maintenance, Troubleshooting and Specifications ..........................................................141
System Settings ........... .......................................................... .... ... ... ... ... .................................. 143
Logs ........................................................................................................................................ 147
Tools ........................................................................................................................................149
Diagnostic .................................... ....................................................... ..................................... 155
Troubleshooting ..................................................... .................................................................. 159
Product Specifications ............................................................................................................. 165
Appendices and Index .........................................................................................................171
P-870HW-51a v2 User’s Guide
9
Page 10

Contents Overview
10
P-870HW-51a v2 User’s Guide
Page 11

Table of Contents
Table of Contents
About This User's Guide..........................................................................................................3
Document Conventions............................................................................................................4
Safety Warnings ........................................................................................................................6
Contents Overview ...................................................................................................................9
Table of Contents....................................................................................................................11
List of Figures.........................................................................................................................17
List of Tables...........................................................................................................................21
Part I: Introduction................................................................................. 23
Chapter 1
Introducing the ZyXEL Device...............................................................................................25
1.1 Overview ............. .......................................................... ... .... ... ... ... ....................................... 25
1.2 Ways to Manage the ZyXEL Device ................................ .... ... ... ... ... .... ................................ 25
1.3 Good Habits for Managing the ZyXEL Device ..................................................................... 25
1.4 Applications for the ZyXEL Device ...................................................................................... 26
1.4.1 Internet Access ................................................ ... ... .... ................................................26
1.5 LEDs (Lights) ...................................... ... .... .......................................................... ... .............26
1.6 The RESET Button ... .... ... ... ... .... .......................................................... ... ... ... .... ... ................28
1.6.1 Using the Reset Button .................................................................................... ... .... ... 28
1.7 The WPS WLAN Button ...................................................................................................... 28
1.7.1 Turn the Wireless LAN Off or On ...............................................................................28
1.7.2 Activate WPS ...................... ... ... .......................................................... .... ...................28
Chapter 2
Tutorials...................................................................................................................................31
2.1 How to Set up a Wireless Network ...................................................................................... 31
2.1.1 Example Parameters ........................... ... ... .... ... ... ... .... ... ............................................. 31
2.1.2 Configuring the AP .................... ... .... ... ... ... .......................................................... .... ... 31
2.1.3 Configuring the Wireless Client .................................................................................. 33
Chapter 3
Introducing the Web Configurator ........................................................................................39
P-870HW-51a v2 User’s Guide
11
Page 12

Table of Contents
3.1 Web Configurator Overview .................................................................................................39
3.1.1 Accessing the Web Configurator ................................................................................ 39
3.2 Web Configurator Main Screen ........................................................................................... 40
3.2.1 Title Bar ...................................................................................................... ... .............40
3.2.2 Navigation Panel ....................... ... .... ..........................................................................41
3.2.3 Main Window .......................... ... .......................................................... .... ... ... ... ... .......42
3.2.4 Status Bar ............................................... ... .................................................................42
Chapter 4
Status Screens........................................................................................................................43
4.1 Status Screen ..... ... ... .... ... ... ... .... ... .......................................................... ... ... .... ... ... .............43
4.1.1 WAN Service Statistics ...............................................................................................46
4.1.2 Route Info ..................... .... ... ... ... ... .... .......................................................... ... ... ... ....... 47
4.1.3 WLAN Station List ............ ... .......................................................... ... .......................... 47
4.1.4 LAN Statistics ......................................... ... .... ... .......................................................... 48
4.1.5 Client List ......................................................................................................... ... ....... 50
Part II: Network....................................................................................... 51
Chapter 5
WAN Setup...............................................................................................................................53
5.1 Overview ............. .......................................................... ... .... ... ... ... ....................................... 53
5.1.1 What Yo u Can Do in this Chapter ..............................................................................53
5.2 What You Need to Know ......................................... ... ... .......................................................54
5.3 Before You Begin .......... ... .......................................................... ... ... .... ... ... ... .... ... ... .............54
5.4 The Internet Connection Screen .......................................................................................... 54
5.4.1 Advanced Internet Connection Setup ........................................................................ 56
5.5 The More Connections Screen ...........................................................................................58
5.5.1 More Connections Edit .............................................. ... ... ... ... .... ... ............................. 59
5.5.2 Configuring More Connections Advanced Setup ....................... ................................ 61
5.6 Te chnical R eference .................. ... ... ... ... .... ... ... ... .... ... .......................................................... 62
Chapter 6
LAN Setup................................................................................................................................67
6.1 Overview ............. .......................................................... ... .... ... ... ... ....................................... 67
6.1.1 What Yo u Can Do in this Chapter ..............................................................................67
6.2 What You Need To Know ................................. ... .... ... ... ... .... ................................................ 67
6.3 Before You Begin .......... ... .......................................................... ... ... .... ... ... ... .... ... ... .............68
6.4 The LAN IP Screen .............................................................................................................. 68
6.5 The Client List Screen ......................................................................................................... 70
6.6 The IP Alias Screen ................................................ ............................................................. 70
12
P-870HW-51a v2 User’s Guide
Page 13

Table of Contents
6.6.1 Configuring the LAN IP Alias Screen ......................................................................... 71
6.7 Te chnical R eference .................. ... ... ... ... .... ... ... ... .... ... .......................................................... 72
Chapter 7
Wireless LAN...........................................................................................................................75
7.1 Overview ............. .......................................................... ... .... ... ... ... ....................................... 75
7.1.1 What Yo u Can Do in this Chapter ..............................................................................75
7.2 What You Need to Know ......................................... ... ... .......................................................76
7.3 Before You Begin .......... ... .......................................................... ... ... .... ... ... ... .... ... ... .............77
7.4 The General Screen ........................................................................................................... 78
7.4.1 No Security .......................... ... .......................................................... ... .... ... ... ... ..........79
7.4.2 WEP Encryption .................. ... ... ... .... .......................................................... ... ... ... .... ... 80
7.4.3 WPA(2)-PSK .............................................................................................................. 81
7.4.4 WPA(2) Authentication ........................................... .... ... ... ... ... .... ... ... .......................... 82
7.5 The WPS Screen ............................................ ... .... ... ... ... .................................................... 84
7.6 The WPS Station Screen ....................................................................................................85
7.7 The MAC Filter Screen ................................................................................................... 86
7.8 The Advanced Setup Screen .............................................................................................. 87
7.9 Te chnical R eference .................. ... ... ... ... .... ... ... ... .... ... .......................................................... 88
7.9.1 Wireless Network Overview ................... ... .... ... ... ....................................................... 88
7.9.2 Additional Wireless Terms .......................................................................................... 90
7.9.3 Wireless Security Overview ....................................................................................... 90
7.9.4 WiFi Protected Setup ................................................................................................. 92
Chapter 8
Network Address Translation (NAT)......................................................................................99
8.1 Overview ............... .......................................................... .... ... ... ... ... .................................... 99
8.1.1 What Yo u Can Do in this Chapter ..............................................................................99
8.2 What You Need to Know ......................................... ... ... .......................................................99
8.3 The Port Forwarding Screen ...............................................................................................99
8.3.1 The Port Forwarding Edit Screen ............................................................................ 101
8.4 Te chnical R eference .................. ... ... ... ... .... ... ... ... .... ... ........................................................ 103
Part III: Security.................................................................................... 105
Chapter 9
IP Filter...................................................................................................................................107
9.1 Overview ............... .......................................................... .... ... ... ... ... .................................. 107
9.1.1 What Yo u Can Do in this Chapter ............................................................................107
9.2 What You Need to Know ......................................... ... ... ..................................................... 107
9.3 The Incoming IP Filtering Screen ...................................................................................... 108
P-870HW-51a v2 User’s Guide
13
Page 14

Table of Contents
9.3.1 Creating Incoming Filtering Rules .......................................................................... 109
Part IV: Advanced .................................................................................111
Chapter 10
Static Route...........................................................................................................................113
10.1 Overview ........................................................................................................................113
10.1.1 What You Can Do in this Chapter ...........................................................................113
10.2 The Static Route Screen ...................................................................................................114
10.2.1 Static Route Edit ....................................................................................................114
Chapter 11
Quality of Service (QoS).......................................................................................................117
11.1 Overview ..........................................................................................................................117
11.1.1 What You Can Do in this Chapter ...................................... ... .... ... ... ... .... ..................117
11.2 What You Need to Know ...................................................................................................118
11.3 The Quality of Service Screen .........................................................................................118
11.4 The Queue Setup Screen .................................................................................................119
11.4.1 Adding a QoS Queue ............................................................................................120
11.5 The Class Setup Screen ................................................................................................120
11.5.1 QoS Class Edit ......................................................................................................122
11.6 Technical Reference ........................................................................................................124
Chapter 12
Dynamic DNS Setup .............................................................................................................127
12.1 Overview ......................................................................................................................... 127
12.1.1 What You Can Do in this Chapter .......................................................................... 127
12.2 What You Need To Know ................................................................................................. 127
12.3 The Dynamic DNS Screen ................................................ ... ... ... ... .... ... ... ... .... ... ... ...........127
Chapter 13
Remote Management............................................................................................................129
13.1 Overview .......................................................................................................................... 129
13.1.1 What You Can Do in this Chapter .......................................................................... 129
13.2 The TR-069 Screen .........................................................................................................129
Chapter 14
Universal Plug-and-Play (UPnP)..........................................................................................131
14.1 Overview ......................................................................................................................... 131
14.1.1 What You Can Do in this Chapter .......................................................................... 131
14.2 What You Need to Know ..................................................................................................131
14
P-870HW-51a v2 User’s Guide
Page 15

Table of Contents
14.3 The UPnP Screen ............................................................................................................ 132
14.4 Installing UPnP in Windows Example ..............................................................................132
14.5 Using UPnP in Windows XP Example .............................................................................135
Part V: Maintenance, Troubleshooting and Specifications.............. 141
Chapter 15
System Settings....................................................................................................................143
15.1 Overview .......................................................................................................................... 143
15.1.1 What You Can Do in this Chapter .......................................................................... 143
15.1.2 What You Need to Know ........................................................................................ 143
15.2 The General Screen ........................................................................................................143
15.3 The Time Setting Screen ................................................................................................144
Chapter 16
Logs ......................................................................................................................................147
16.1 Overview ......................................................................................................................... 147
16.1.1 What You Can Do in this Chapter .......................................................................... 147
16.2 The View Log Screen ...................................................................................................... 147
16.3 The Log Settings Screen ..................... .... ........................................................................148
Chapter 17
Tools.......................................................................................................................................149
17.1 Overview .......................................................................................................................... 149
17.1.1 What You Can Do in this Chapter .......................................................................... 149
17.2 The Firmware Upgrade Screen ....................................................................................... 150
17.3 The Configuration Screen ................................................................................................ 151
17.4 The Restart Screen .........................................................................................................154
Chapter 18
Diagnostic..............................................................................................................................155
18.1 Overview .......................................................................................................................... 155
18.1.1 What You Can Do in this Chapter .......................................................................... 155
18.2 What You Need to Know ..................................................................................................155
18.3 The 802.1ag Screen ........................................................................................................156
Chapter 19
Troubleshooting....................................................................................................................159
19.1 Power, Hardware Connections, and LEDs .... ... .... ... ... ... .... ... ... ........................................ 1 59
19.2 ZyXEL Device Access and Login .................................................................................... 160
19.3 Internet Access ................................................................................................................161
P-870HW-51a v2 User’s Guide
15
Page 16

Table of Contents
Chapter 20
Product Specifications.........................................................................................................165
20.1 Hardware Specifications ..................................................................................................165
20.2 Firmware Specifications ...................................................................................................165
20.3 Wireless Features ............................................................................................................ 167
Part VI: Appendices and Index ........................................................... 171
Appendix A Setting Up Your Computer’s IP Address...........................................................173
Appendix B Pop-up Windows, JavaScripts and Java Permissions......................................197
Appendix C IP Addresses and Subnetting ...........................................................................205
Appendix D Wireless LANs ..................................................................................................215
Appendix E Common Services.............................................................................................229
Appendix F Legal Information ..............................................................................................233
Appendix G Customer Support ............................................................................................237
Index.......................................................................................................................................243
16
P-870HW-51a v2 User’s Guide
Page 17

List of Figures
List of Figures
Figure 1 ZyXEL Device’s Router Features ............................................................................................. 26
Figure 2 LEDs on the Top of the Device ................................................................................................. 27
Figure 3 AP: Wireless LAN ....................................................................................................................32
Figure 4 AP: Wireless LAN > Advanced Setup ...................................................................................... 32
Figure 5 AP: Status .................................................................................................................................33
Figure 6 AP: Status: WLAN Station List .................................................................................................33
Figure 7 ZyXEL Utility: Site Survey ....................................................................................................... 34
Figure 8 ZyXEL Utility: Security Settings ............................................................................................... 35
Figure 9 ZyXEL Utility: Confirm Save ..................................................................................................... 35
Figure 10 ZyXEL Utility: Link Info ............................ .... ... .......................................................................35
Figure 11 ZyXEL Utility: Profile ............................................................................................................... 36
Figure 12 ZyXEL Utility: Add New Profile ............................................................................................... 36
Figure 13 ZyXEL Utility: Profile Security ................... .................... ................... .................... ................... 37
Figure 14 ZyXEL Utility: Profile Encryption ...................... ....................... ................... .............................37
Figure 15 Profile: Wireless Protocol Settings. . ... ... ... .... ... .......................................................... ... .......... 37
Figure 16 Profile: Confirm Save .............................................................................................................38
Figure 17 Profile: Activate ......................................................................................................................38
Figure 18 Password Screen ................................................................................................................... 40
Figure 19 Main Screen ........................................................................................................................... 40
Figure 20 Status Screen .........................................................................................................................43
Figure 21 Status > WAN Service Statistics ............................................................................................ 46
Figure 22 Status > Route Info ................................................................................................................ 47
Figure 23 Status > WLAN Station List .................................................................................................... 48
Figure 24 Status > LAN Statistics ..........................................................................................................49
Figure 25 Status > Client List .................................................................. ... ... ... ... .................................... 50
Figure 26 LAN and WAN ........................................................................................................................ 53
Figure 27 WAN > Internet Connection (PPPoE) ..................................................................................... 55
Figure 28 WAN > Internet Connection: Advanced Setup ....................................................................... 57
Figure 29 WAN > More Connections ...................................................................................................... 58
Figure 30 WAN > More Connections: Edit ..............................................................................................59
Figure 31 WAN > More Connections: Edit: Advanced Setup ................................................................. 61
Figure 32 Full Cone NAT Example ......................................................................................................... 64
Figure 33 Symmetric NAT ............................................ ... ... ....................................................................64
Figure 34 LAN > IP ................................................................................................................................. 69
Figure 35 LAN > Client List .......................................... ... ... ....................................................................70
Figure 36 Physical Network & Partitioned Logical Networks .................................................................. 71
Figure 37 Network > LAN > IP Alias .......................................................................................................71
Figure 38 LAN and WAN IP Addresses .................................................................................................. 72
P-870HW-51a v2 User’s Guide
17
Page 18

List of Figures
Figure 39 Network > Wireless LAN > General ...................................................................................... 78
Figure 40 Wireless LAN > General: No Security ............................. ... .... ................................................ 80
Figure 41 Wireless LAN > General: Static WEP Encryption ...................................................................81
Figure 42 Wireless LAN > General: WPA(2)-PSK ..................................................................................82
Figure 43 Wireless LAN > General: WPA(2) ...................... ... .... ... ... ... .... ................................................ 83
Figure 44 Network > Wireless LAN > WPS ............................................................................................ 84
Figure 45 Network > Wireless LAN > WPS Station ................................................................................85
Figure 46 Wireless LAN > MAC Filter .....................................................................................................86
Figure 47 Wireless LAN > Advanced Setup ...........................................................................................87
Figure 48 Example of a Wireless Network ............................................................................................. 89
Figure 49 Example WPS Process: PIN Method .....................................................................................94
Figure 50 How WPS works ..................................................................................................................... 95
Figure 51 WPS: Example Network Step 1 .............................................................................................. 96
Figure 52 WPS: Example Network Step 2 .............................................................................................. 96
Figure 53 WPS: Example Network Step 3 .............................................................................................. 97
Figure 54 NAT Port Forwarding ........................................................................................................... 100
Figure 55 Port Forwarding Edit ............................................................................................................ 102
Figure 56 Multiple Servers Behind NAT Example ................................................................................103
Figure 57 Incoming IP Filter .................................................................................................................108
Figure 58 Incoming IP Filtering: Add ....................................................................................................109
Figure 59 Example of Static Routing Topology ......................................................................................113
Figure 60 Advanced > Static Route .......................................................................................................114
Figure 61 Static Route: Add ..................................................................................................................115
Figure 62 QoS ......................................................................................................................................118
Figure 63 QoS Queue Setup ................................................................................................................119
Figure 64 QoS Queue Setup: Add .......................................................................................................120
Figure 65 QoS Class Setup .................................................................................................................121
Figure 66 QoS Class Setup: Add .........................................................................................................122
Figure 67 Advanced > Dynamic DNS ................................................................................................... 128
Figure 68 TR-069 ................................................................................................................................130
Figure 69 Advanced > UPnP ............................................................................................................... 132
Figure 70 Add/Remove Programs: Windows Setup: Communication ..................................................133
Figure 71 Add/Remove Programs: Windows Setup: Communication: Components ............................ 133
Figure 72 Network Connections ........................................................................................................... 134
Figure 73 Windows Optional Networking Components Wizard ........................................... ... ... ... ... .... . 134
Figure 74 Networking Services ............................................................................................................. 135
Figure 75 Network Connections .................................................................................................
Figure 76 Internet Connection Properties ............................................................................................136
Figure 77 Internet Connection Properties: Advanced Settings ........ ... .... ... ... ... ... .... ... ... ... .....................137
Figure 78 Internet Connection Properties: Advanced Settings: Add ............... ... .... ... ... ... .... .................137
Figure 79 System Tray Icon ..................................................................................................................138
Figure 80 Internet Connection Status ................................................................................................... 138
Figure 81 Network Connections ........................................................................................................... 139
.......... 136
18
P-870HW-51a v2 User’s Guide
Page 19

List of Figures
Figure 82 Network Connections: My Network Places ............................................ ... ... ... .... ... ..............140
Figure 83 Network Connections: My Network Places: Properties: Example ........................................140
Figure 84 Maintenance > System > General ........................................................................................144
Figure 85 Maintenance > System > Time Setting ............................................................ .... ... ... ...........145
Figure 86 Maintenance > Logs > View Log ............................... ... ... ... .... ... ... ... ... .... ... ... ... .... ... ... ... ... .....147
Figure 87 Maintenance > Logs > Log Settings ... ..................................................................................148
Figure 88 Maintenance > Tools > Firmware ......................................................................................... 150
Figure 89 Firmware Upload In Progress ............................................................................................... 151
Figure 90 Network Temporarily Disconnected ...................................................................................... 151
Figure 91 Error Message ......................................................................................................................151
Figure 92 Maintenance > Tools > Configuration ................................................. .................................. 152
Figure 93 Configuration Upload Successful .........................................................................................153
Figure 94 Network Temporarily Disconnected ...................................................................................... 153
Figure 95 Configuration Upload Error ...................................................................................................153
Figure 96 Reset Warning Message ...................................................................................................... 153
Figure 97 Maintenance > Tools >Restart .............................................................................................154
Figure 98 802.1ag ...............................................................................................................................156
Figure 99 Windows XP: Start Menu ................. .....................................................................................174
Figure 100 Windows XP: Control Panel ...............................................................................................174
Figure 101 Windows XP: Control Panel > Network Connections > Properties ......................... ... ... .... . 175
Figure 102 Windows XP: Local Area Connection Properties ............................................................... 175
Figure 103 Windows XP: Internet Protocol (TCP/IP) Properties ........ .... ... ... ... ... .................................. 176
Figure 104 Windows Vista: Start Menu ................................................................................................. 177
Figure 105 Windows Vista: Control Panel ............................................................................................ 177
Figure 106 Windows Vista: Network And Internet ................................................................................ 177
Figure 107 Windows Vista: Network and Sharing Center ..................................................................... 178
Figure 108 Windows Vista: Network and Sharing Center ..................................................................... 178
Figure 109 Windows Vista: Local Area Connection Properties ............................................................ 179
Figure 110 Windows Vista: Internet Protocol Version 4 (TCP/IPv4) Properties ....................................180
Figure 111 Mac OS X 10.4: Apple Menu .............................................................................................. 181
Figure 112 Mac OS X 10.4: System Preferences ................................................................................. 181
Figure 113 Mac OS X 10.4: Network Preferences ................................................................................ 182
Figure 114 Mac OS X 10.4: Network Preferences > TCP/IP Tab. ........................................................ 182
Figure 115 Mac OS X 10.4: Network Preferences > Ethernet ..............................................................183
Figure 116 Mac OS X 10.4: Network Utility .......................................................................................... 183
Figure 117 Mac OS X 10.5: Apple Menu .............................................................................................. 184
Figure 118 Mac OS X 10.5: Systems Preferences ............................................................................... 184
Figure 119 Mac OS X 10.5: Network Preferences > Ethernet ..............................................................185
Figure 120 Mac OS X 10.5: Network Preferences > Ethernet ................ ................................... ........... 186
Figure 121 Mac OS X 10.5: Network Utility .......................................................................................... 186
Figure 122 Ubuntu 8: System > Administration Menu ..........................................................................187
Figure 123 Ubuntu 8: Network Settings > Connections ...................... .... .............................................. 187
Figure 124 Ubuntu 8: Administrator Account Authentication ................................................................ 188
P-870HW-51a v2 User’s Guide
19
Page 20

List of Figures
Figure 125 Ubuntu 8: Network Settings > Connections ...................... .... .............................................. 188
Figure 126 Ubuntu 8: Network Settings > Properties ........................................................................... 189
Figure 127 Ubuntu 8: Network Settings > DNS ...................................................................................189
Figure 128 Ubuntu 8: Network Tools .................................................................................................... 190
Figure 129 openSUSE 10.3: K Menu > Computer Menu .....................................................................191
Figure 130 openSUSE 10.3: K Menu > Computer Menu .....................................................................191
Figure 131 openSUSE 10.3: YaST Control Center ..............................................................................192
Figure 132 openSUSE 10.3: Network Settings .................................................................................... 192
Figure 133 openSUSE 10.3: Network Card Setup ...............................................................................193
Figure 134 openSUSE 10.3: Network Settings .................................................................................... 194
Figure 135 openSUSE 10.3: KNetwork Manager ................................................................................. 195
Figure 136 openSUSE: Connection Status - KNetwork Manager ........................................................ 195
Figure 137 Pop-up Blocker ...................................................................................................................197
Figure 138 Internet Options: Privacy .................................................................................................... 198
Figure 139 Internet Options: Privacy .................................................................................................... 199
Figure 140 Pop-up Blocker Settings .....................................................................................................199
Figure 141 Internet Options: Security ................................................................................................... 200
Figure 142 Security Settings - Java Scripting ....................................................................................... 201
Figure 143 Security Settings - Java ...................................................................................................... 201
Figure 144 Java (Sun) .......................................................................................................................... 202
Figure 145 Mozilla Firefox: Tools > Options .................... ... ... .... ... ... ... .... ... ........................................... 203
Figure 146 Mozilla Firefox Content Security .........................................................................................203
Figure 147 Network Number and Host ID ............................................................................................ 206
Figure 148 Subnetting Example: Before Subnetting ....................................... ... .... ... ... ... .....................208
Figure 149 Subnetting Example: After Subnetting ....................................... ... ... .... ... ... ... .....................209
Figure 150 Conflicting Computer IP Addresses Example .................................................................... 213
Figure 151 Conflicting Computer IP Addresses Example .................................................................... 213
Figure 152 Conflicting Computer and Router IP Addresses Example .................................................. 214
Figure 153 Peer-to-Peer Communication in an Ad-hoc Network ......................................................... 215
Figure 154 Basic Service Set ............................................................................................................... 216
Figure 155 Infrastructure WLAN ............................... ................................................. ........................... 217
Figure 156 RTS/CTS ........................................................................................................................... 218
Figure 157 WPA(2) with RADIUS Application Example ....................................................................... 225
Figure 158 WPA(2)-PSK Authentication ............................................................................................... 226
20
P-870HW-51a v2 User’s Guide
Page 21

List of Tables
List of Tables
Table 1 LED Descriptions ......................................................................................................................27
Table 2 Web Configurator Icon in the Title Bar ...................................................................................... 41
Table 3 Navigation Panel Summary ...................................................................................................... 41
Table 4 Status Screen ............................................................................................................................ 43
Table 5 Status > WAN Service Statistics ............................................................................................... 46
Table 6 Status > Route Info ................................................................................................................... 47
Table 7 Status > WLAN Station List ....................................................................................................... 48
Table 8 Status > LAN Statistics .............................................................................................................. 49
Table 9 Status > Client List .................................................................................................................... 50
Table 10 WAN > Internet Connection .................................................................................................... 55
Table 11 WAN > Internet Connection: Advanced Setup ........................................................................ 57
Table 12 W AN > More Connections ......................................................................................................58
Table 13 W AN > More Connections: Edit .............................................................................................. 59
Table 14 WAN > More Connections: Edit: Advanced Setup ........................... ... .... ... ... ... .... ... ................61
Table 15 LAN > IP ................................................................................................................................. 69
Table 16 LA N > Client List .............. ... ... .......................................................... ... .... ... ... ... .... ...................70
Table 17 Network > LAN > IP Alias ....................................................................................................... 71
Table 18 Network > Wireless LAN > General ........................................................................................79
Table 19 Wireless LAN > General: No Security ..................................................................................... 80
Table 20 Network > Wireless LAN > General: St atic WEP Encryption ........................................ ... .... ... 81
Table 21 Wireless LAN > General: WPA(2)-PSK ...................................................................................82
Table 22 Wireless LAN > General: WPA(2) ........................................................................................... 83
Table 23 Network > Wireless LAN > WPS .............................................................................................85
Table 24 Network > Wireless LAN > WPS Station .................................................................................86
Table 25 Wireless LAN > MAC Filter ..................................................................................................... 87
Table 26 Wireless LAN > Advanced Set up .................................. ... ... .... ... ... ... ... .... ... ... ... .... ... ... ... ... ....... 88
Table 27 Additional Wireless Terms ....................................................................................................... 90
Table 28 Types of Encryption for Each Type of Authentication ............................................................. 91
Table 29 NAT Port Forwarding ............................................................................................................ 100
Table 30 Port Forwarding Edit .............................................................................................................102
Table 31 Services and Port Numbers ............................. ... ... .... ... ... ... .... ... ... ... ... .................................. 103
Table 32 Common IP Ports ..................................................................................................................107
Table 33 Incoming IP Filtering ............................................................................................................. 108
Table 34 Incoming IP Filtering: Add ...................... ... .... ... ... ... ............................................................... 109
Table 35 Advanced > Static Route ........................................................................................................114
Table 36 Static Route: Add ...................................................................................................................115
Table 37 QoS ........................................................................................................................................118
Table 38 QoS Queue Setup ..................................................................................................................119
P-870HW-51a v2 User’s Guide
21
Page 22

List of Tables
Table 39 QoS Queue Setup: Add ........................................................................................................ 120
Table 40 QoS Class Setup .................................................................................................................. 121
Table 41 QoS Class Configuration ...................................................................................................... 123
Table 42 IEEE 802.1p Priority Level and Traffic Type ......................................................................... 124
Table 43 Advanced > Dynamic DNS ...................................................................................................128
Table 44 TR-069 Client ........................................................................................................................ 130
Table 45 Advanced > UPnP ................................................................................................................132
Table 46 Maintenance > System > Genera ........................................................... ... ... ... .... ... ... ... ... ..... 144
Table 47 Maintenance > System > Time Setting ................................................................................. 145
Table 48 Maintenance > Logs > View Log ...........................................................................................148
Table 49 Maintenance > Logs > Log Settings .....................................................................................148
Table 50 Maintenance > Tools > Firmware ..........................................................................................150
Table 51 Restore Configuration ...........................................................................................................152
Table 52 802.1ag ................................................................................................................................. 156
Table 53 Hardware Specifications ....................................................................................................... 165
Table 54 Firmware Specifications ........................................................................................................ 165
Table 55 Wireless Features ............................... ... ... .... ... ... .................................................................. 167
Table 56 Standards Supported ............................................................................................................168
Table 57 IP Address Network Number and Host ID Example ........................... .... ...... ... .... ... ... ... ... .... . 206
Table 58 Subnet Masks .......................................................................................................................207
Table 59 Maximum Host Numbers .................... ... ... .... ... ... ... .... ... ... ... .... ... ... ... ... .... ... ... ... .... ... ... ... ........207
Table 60 Alternative Subnet Mask Notation ......................................................................................... 207
Table 61 Subnet 1 ................................................................................................................................209
Table 62 Subnet 2 ................................................................................................................................210
Table 63 Subnet 3 ................................................................................................................................210
Table 64 Subnet 4 ................................................................................................................................210
Table 65 Eight Subnets ................................................... ... ... .... ... ........................................................ 210
Table 66 24-bit Network Number Subnet Planning ...................................................... ... .... ... ... ... ... ......211
Table 67 16-bit Network Number Subnet Planning ...................................................... ... .... ... ... ... ... ......211
Table 68 IEEE 802.11g ........................................................................................................................219
Table 69 Wireless Security Levels ....................................................................................................... 220
Table 70 Comparison of EAP Authentication Types ............................................................................ 223
Table 71 Wireless Security Relational Matrix ......................................................................................226
Table 72 Commonly Used Services .....................................................................................................229
22
P-870HW-51a v2 User’s Guide
Page 23

PART I
Introduction
Introducing the ZyXEL Device (25)
Tutorials (31)
Introducing the Web Configurator (39)
Status Screens (43)
23
Page 24

24
Page 25
CHAPTER 1
Introducing the ZyXEL Device
This chapter introduces the main applications and features of the ZyXEL Device. It also
introduces the ways you can manage the ZyXEL Device.
1.1 Overview
The P-870HW-51a v2 is a VDSL2 gateway that allows super-fast, secure Internet access over
analog (POTS) telephone lines.
you can use Quality of Service (QoS) to efficiently manage traffic on your network by giving
priority to certain types of traffic and/or to particular computers.
Please refer to the following description of the product name format.
• “H” denotes an integrated 4-port hub (switch).
• “W” denotes wireless functionality. There is an embedded mini-PCI module for IEEE
802.11g wireless LAN connectivity.
1 Only use firmware for your ZyXEL Device’s specific model. Refer to the label
on the bottom of your ZyXEL Device.
See Chapter 20 on page 165 for a full list of features.
1.2 Ways to Manage the ZyXEL Device
Use any of the following methods to manage the ZyXEL Device.
• Web Configurator. This is recommended for everyday management of the ZyXEL Device
using a (supported) web browser.
• TR-069. This is an auto-configuration server used to remotely configure your device.
1.3 Good Habits for Managing the ZyXEL Device
Do the following things regularly to make the ZyXEL Device more secure and to manage the
ZyXEL Device more effectively.
P-870HW-51a v2 User’s Guide
25
Page 26
Chapter 1 Introducing the ZyXEL Device
• Change the password. Use a password that’s not easy to guess and that consists of
different types of characters, such as numbers and letters.
• Write down the password and put it in a safe place.
• Back up the configuration (and make sure you know how to restore it). Restoring an
earlier working configuration may be useful if the device becomes unstable or even
crashes. If you forget your password, you will have to reset the ZyXEL Device to its
factory default settings. If you backed up an earlier configuration file, you would not have
to totally re-configure the ZyXEL Device. You could simply restore your last
configuration.
1.4 Applications for the ZyXEL Device
Here are some example uses for which the ZyXEL Device is well suited.
1.4.1 Internet Access
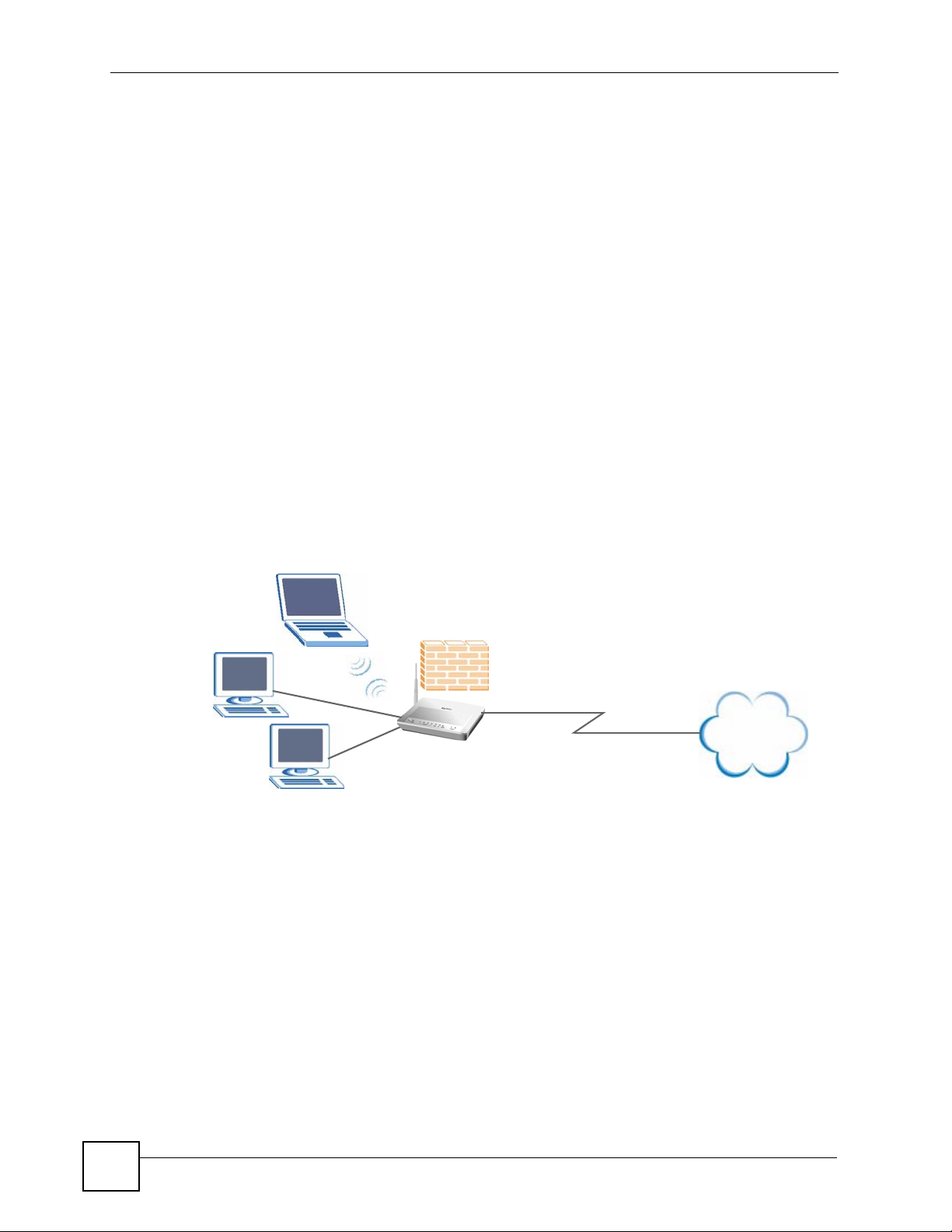
Your ZyXEL Device provides shared Internet access by connecting the DSL port to the DSL
or MODEM jack on a splitter or your telephone jack. Computers can connect to the ZyXEL
Device’s LAN por ts (or wirelessly).
Figure 1 ZyXEL Device’s Router Features
LAN
You can also configure IP filtering on the ZyXEL Device for secure Internet access. When the
IP filter is on, all incoming traffic from the Internet to your network is blocked by default
unless it is initiated from your network. This means that probes from the outside to your
network are not allowed, but you can safely browse the Internet and download files.
1.5 LEDs (Lights)
The following graphic displays the labels of the LEDs.
DSL
Internet
26
P-870HW-51a v2 User’s Guide
Page 27
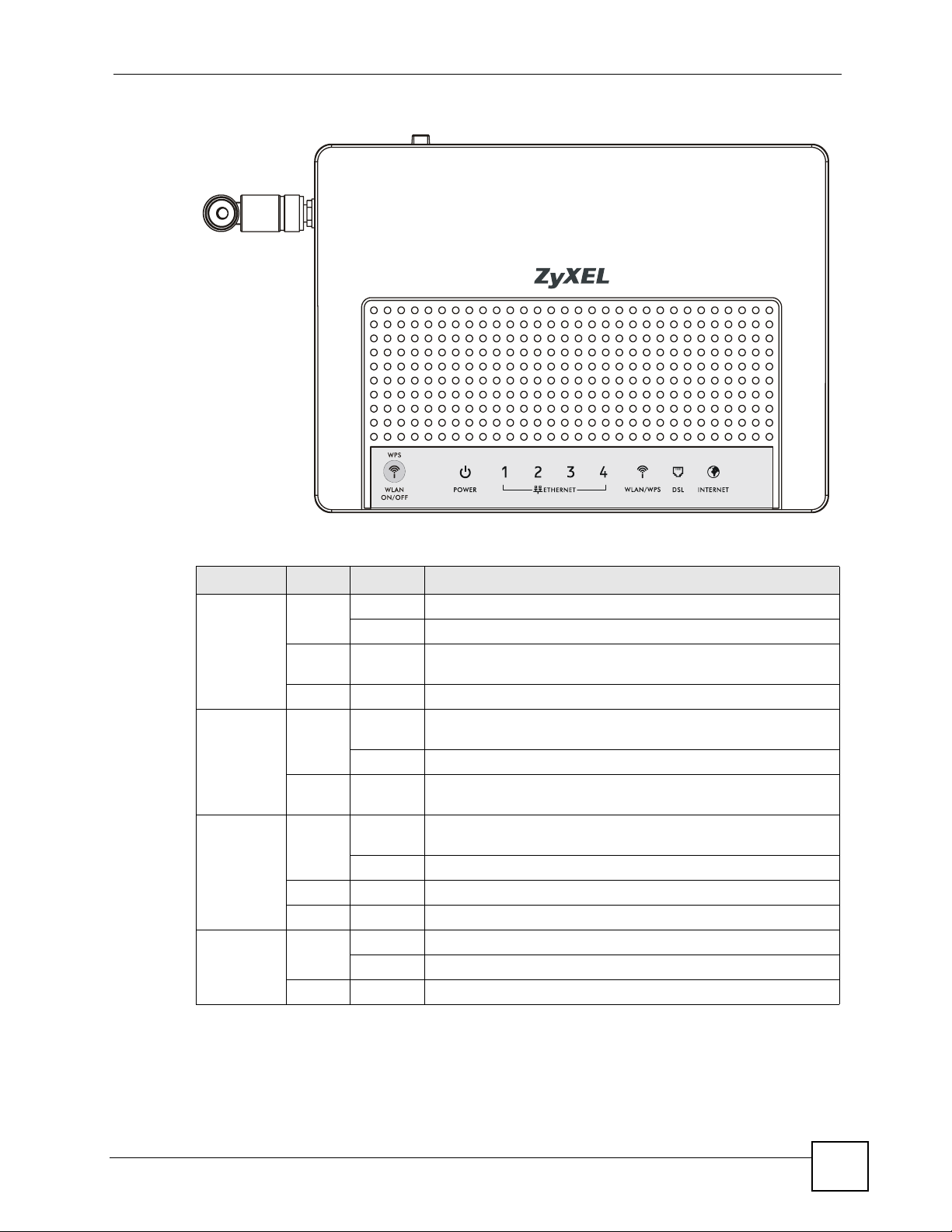
Figure 2 LEDs on the Top of the Device
Chapter 1 Introducing the ZyXEL Device
None of the LEDs are on if the ZyXEL Device is not receiving power.
Table 1 LED Descriptions
LED COLOR STATUS DESCRIPTION
POWER Green On The ZyXEL Device is receiving power and ready for use.
Blinking The ZyXEL Device is self-testing.
Red On The ZyXEL Device detected an error while self-testing, or there is
a device malfunction.
Off The ZyXEL Device is not receiving power.
ETHERNET
1-4
WLAN/WPS Green On The wireless network is activated and is operating in IEEE
DSL Green On The DSL line is up.
Green On The ZyXEL Device has an Ethernet connection with a device on
the Local Area Network (LAN).
Blinking The ZyXEL Device is sending/receiving data to /from the LAN.
Off The ZyXEL Device does not have an Ethernet connection with
the LAN.
802.1 1b/g mode.
Blinking The ZyXEL Device is communicating with other wireless clients.
Orange Blinking The ZyXEL Device is setting up a WPS connection.
Off The wireless network is not activated.
Blinking The ZyXEL Device is initializing the DSL line.
Off The DSL line is down.
P-870HW-51a v2 User’s Guide
27
Page 28
Chapter 1 Introducing the ZyXEL Device
Table 1 LED Descriptions
LED COLOR STATUS DESCRIPTION
INTERNET Green On The ZyXEL Device has an IP connection but no traffic.
Blinking The ZyXEL Device is sending or receiving IP traffic.
Red On The ZyXEL Device attempted to make an IP connection but
Off The ZyXEL Device does not have an IP connection.
Refer to the Quick Start Guide for information on hardware connections.
1.6 The RESET Button
If you forget your password or cannot access the web configurator, you will need to use the
RESET button at the back of the device to reload the factory-default configuration file. This
means that you will lose all configurations that you had previously and the password will be
reset to “1234”. You can also use the
Y our device has a W AN IP address (either static or assigned by a
DHCP server), PPP negotiation was successfully completed (if
used) and the DSL connection is up.
failed. Possible causes are no response from a DHCP server, no
PPPoE response, PPPoE authentication failed.
1.6.1 Using the Reset Button
1 Make sure the POWER LED is on (not blinking).
2 To set the device back to the factory default settings, press the RESET button for ten
seconds or until the POWER LED begins to blink and then release it. When the
POWER LED begins to blink, the defaults have been restored and the device restarts.
1.7 The WPS WLAN Button
You can use the WPS WLAN ON/OFF button ( ) on the top of the device to turn the
wireless LAN off or on. You can also use it to activate WPS in order to quickly set up a
wireless network with strong security.
1.7.1 Turn the Wireless LAN Off or On
1 Make sure the POWER LED is on (not blinking).
2 Press the WPS WLAN ON/OFF button for one second and release it. The WLAN/
WPS LED should change from on to off or vice versa.
1.7.2 Activate WPS
28
1 Make sure the POWER LED is on (not blinking).
2 Press the WPS WLAN ON/OFF button for more than five seconds and release it. Press
the WPS button on another WPS -enabled device within range of the ZyXEL Device.
P-870HW-51a v2 User’s Guide
Page 29

Chapter 1 Introducing the ZyXEL Device
The WLAN/WPS L ED should flash whi le the ZyXEL Device sets up a WPS connection
with the wireless device.
" You must activate WPS in the ZyXEL Device and in another wireless device
within two minutes of each other. See Section 7.9.4 on page 92 for more
information.
P-870HW-51a v2 User’s Guide
29
Page 30

Chapter 1 Introducing the ZyXEL Device
30
P-870HW-51a v2 User’s Guide
Page 31

CHAPTER 2
Tutorials
This chapter describes how to set up a wireless network.
2.1 How to Set up a Wireless Network
This tutorial gives you examples of how to set up an access point and wireless client for
wireless communication using the following parameters. The wireless clients can access the
Internet through an AP wirelessly.
2.1.1 Example Parameters
SSID SSID_Example3
Security WPA-PSK
(Pre-Shared Key: ThisismyWPA-PSKpre-sharedkey)
802.11 mode IEEE 802.11b/g
An access point (AP) or wireless router is referred to as “AP” and a computer with a wireless
network card or USB/PCI adapter is referred to as “wireless client” here.
We use the ZyXEL Device web screens and M-302 utility screens as an example. The screens
may vary slightly for different models.
2.1.2 Configuring the AP
Follow the steps below to configure the wireless settings on your AP.
1 Open the Network > Wireless LAN screen in the AP’s web configurator.
P-870HW-51a v2 User’s Guide
31
Page 32

Chapter 2 Tutorials
Figure 3 AP: Wireless LAN
2 Make sure the Active Wireless LAN check box is selected.
3 Enter “SSID_Example3” as the SSID and select a channel which is not used by another
AP.
4 Set security mode to WPA-PSK and enter “ThisismyWPA-PSKpre-sharedkey” in the
Pre-Shared Key field. Click Apply.
5 Click the Advanced Setup tab and select 54g Auto in the 54g
TM
Mode field. Click
Apply.
Figure 4 AP: Wireless LAN > Advanced Setup
32
6 Open the Status screen.Verify your wireless and wireless security settings under Device
Information and check if the WLAN connection is up under Interface Status.
P-870HW-51a v2 User’s Guide
Page 33

Figure 5 AP: Status
Chapter 2 Tutorials
7 Click the WLAN Station List hyperlink in the AP’s Status screen. You can see if any
wireless client has connected to the AP.
Figure 6 AP: Status: WLAN Station List
2.1.3 Configuring the Wireless Client
This section describes how to connect the wireless client to a network.
P-870HW-51a v2 User’s Guide
33
Page 34

Chapter 2 Tutorials
2.1.3.1 Connecting to a Wireless LAN
The following sections show you how to join a wireless network using the ZyXEL utility , as in
the following diagram. The wireless client is labeled C and the access point is labeled AP.
Internet
C
There are three ways to connect the client to an access point.
• Configure nothing and leave the wireless client to automatically scan for and connect to
any available network that has no wireless security configured.
• Manually connect to a network.
• Configure a profile to have the wireless client automatically connect to a specific network
or peer computer.
This example illustrates how to manually connect your wireless client to an access point (AP)
which is configured for WPA-PSK security and connected to the Internet. Before you connect
to the access point, you must know its Service Set IDentity (SSID) and WPA-PSK pre-shared
key. In this example, the SSID is “SSID_Example3” and the pre-shared key is
“ThisismyWPA-PSKpre-sharedkey”.
After you install the ZyXEL utility and then insert the wireless client, follow the steps below
to connect to a network using the Site Survey screen.
1 Open the ZyXEL utility and click the Site Survey tab to open the screen shown next.
Figure 7 ZyXEL Utility: Site Survey
AP
34
2 The wireless client automatically searches for available wireless networks. Click Scan if
you want to search again. If no entry displays in the Available Network List, that means
there is no wireless network available within range. Make sure the AP or peer computer
is turned on or move the wireless client closer to the AP or peer computer.
3 When you try to connect to an AP with security configured, a window will pop up
prompting you to specify the security settings. Enter the pre-shared key and leave the
encryption type at the default setting.
P-870HW-51a v2 User’s Guide
Page 35

Chapter 2 Tutorials
Use the Next button to move on to the next screen. You can use the Back button at any
time to return to the previous screen, or the Exit button to return to the Site Survey
screen.
Figure 8 ZyXEL Utility: Security Settings
4 The Confirm Save window appears. Check your settings and click Save to continue.
Figure 9 ZyXEL Utility: Confirm Save
5 The ZyXEL utility returns to the Link Info screen while it connects to the wireless
network using your settings. When the wireless link is established, the ZyXEL utility
icon in the system tray turns green and the Link Info screen displays details of the active
connection. Check the network information in the Link Info screen to verify that you
have successfully connected to the selected network. If the wireless client is not
connected to a network, the fields in this screen remain blank.
Figure 10 ZyXEL Utility: Link Info
P-870HW-51a v2 User’s Guide
35
Page 36

Chapter 2 Tutorials
6 Open your Internet browser and enter http://www.zyxel.com or the URL of any other
web site in the address bar. If you are able to access the web site, your wireless
connection is successfully configured.
If you cannot access the web site, try changing the encryption type in the Security
Settings screen, check the Troubleshooting section of this User's Guide or contact your
network administrator.
2.1.3.2 Creating and Using a Profile
A profile lets you automatically connect to the same wireless network every time you use the
wireless client. You can also configure different profiles for different networks, for example if
you connect a notebook computer to wireless networks at home and at work.
This example illustrates how to set up a profile and connect the wireless client to an access
point configured for WPA-PSK security. In this example, the SSID is “SSID_Example3”, the
profile name is “PN_Example3” and the pre-shared key is “ThisismyWPA-PSKpresharedkey”. You have chosen the profile name “PN_Example3”.
1 Open the ZyXEL utility and click the Profile tab to open the screen shown next. Click
Add to configure a new profile.
Figure 11 ZyXEL Utility: Profile
36
2 The Add New Profile screen appears. The wireless client automatically searches for
available wireless networks, which are displayed in the Scan Info box. Click on Scan if
you want to search again. You can also configure your profile for a wireless network that
is not in the list.
Figure 12 ZyXEL Utility: Add New Profile
P-870HW-51a v2 User’s Guide
Page 37

Chapter 2 Tutorials
3 Give the profile a descriptive name (of up to 32 printable ASCII characters). Select
Infrastructure and either manually enter or select the AP's SSID in the Scan Info table
and click Select.
4 Choose the same encryption method as the AP to which you want to connect (In this
example, WPA-PSK).
Figure 13 ZyXEL Utility: Profile Security
5 This screen varies depending on the encryption method you selected in the previous
screen. Enter the pre-shared key and leave the encryption type at the default setting.
Figure 14 ZyXEL Utility: Profile Encryption
6 In the next screen, leave both boxes checked.
Figure 15 Profile: Wireless Protocol Settings.
7 Verify the profile settings in the read-only screen. Click Save to save and go to the next
screen.
P-870HW-51a v2 User’s Guide
37
Page 38

Chapter 2 Tutorials
Figure 16 Profile: Confirm Save
8 Click Activate Now to use the new profile immediately. Otherwise, click the Activate
Later button.
If you clicked Activate Later, you can select the profile from the list in the Profile
screen and click Connect to activate it.
" Only one profile can be activated and used at any given time.
Figure 17 Profile: Activate
9 When you activate the new profile, the ZyXEL utility returns to the Link Info screen
while it connects to the AP using your settings. When the wireless link is established, the
ZyXEL utility icon in the system tray turns green and the Link Info screen displays
details of the active connection.
10Open your Internet browser, enter http://www.zyxel.com or the URL of any other web
site in the address bar and press ENTER. If you are able to access the web site, your new
profile is successfully configured.
11 If you cannot access the Internet go back to the Profile screen, select the profile you are
using and click Edit. Check the details you entered previously. Also, refer to the
Troubleshooting section of this User's Guide or contact your network administrator if
necessary.
38
P-870HW-51a v2 User’s Guide
Page 39

CHAPTER 3
Introducing the Web
Configurator
This chapter describes how to access and navigate the web configurator.
3.1 Web Configurator Overview
The web configurator is an HTML-based management interface that allows easy device setup
and management via Internet browser. Use Internet Explorer 6.0 and later or Netscape
Navigator 7.0 and later versions. The recommended screen resolution is 1024 by 768 pixels.
In order to use the web configurator you need to allow:
• Web browser pop-up windows from your device. Web pop-up blocking is enabled by
default in Windows XP SP (Service Pack) 2.
• JavaScripts (enabled by default).
• Java permissions (enabled by default).
See Appendix B on page 197 if you need to make sure these functions are allowed in Internet
Explorer.
3.1.1 Accessing the Web Configurator
1 Make sure your ZyXEL Device hardware is properly connected (refer to the Quick Start
Guide).
2 Launch your web browser.
3 Type "192.168.1.1" as the URL.
4 A password screen displays. Enter the default user name 1234 and default password
1234.The password displays in non-readable characters. If you have changed the
password, enter your password and click Login. Click Cancel to revert to the default
password in the password field.
P-870HW-51a v2 User’s Guide
39
Page 40

Chapter 3 Introducing the Web Configurator
A
Figure 18 Password Screen
3.2 Web Configurator Main Screen
Figure 19 Main Screen
B
As illustrated above, the main screen is divided into these parts:
• A - title bar
• B - navigation panel
• C - main window
• D - status bar
3.2.1 Title Bar
The title bar allows you to change the language and provides an icon in the upper right corner.
D
C
40
P-870HW-51a v2 User’s Guide
Page 41

Chapter 3 Introducing the Web Configurator
The icon provides the following function.
Table 2 Web Configurator Icon in the Title Bar
ICON DESCRIPTION
Help: Click this icon to open up help screens.
3.2.2 Navigation Panel
Use the menu items on the navigation panel to open screens to configure ZyXEL Device
features. The following tables describe each menu item.
Table 3 Navigation Panel Summary
LINK TAB FUNCTION
Status This screen shows the ZyXEL Device’s general device and network status
information. Use this screen to access the statistics and client list.
Network
WAN Internet
Connection
More
Connections
LAN IP Use this screen to configure LAN TCP/IP DHCP settings.
Client List Use this screen to view current DHCP client information and to always
IP Alias Use this screen to partition your LAN interface into subnets.
Wireless LAN General Use this screen to configure the wireless LAN settings and WLAN
WPS Use this screen to enable WPS (Wi-Fi Protected Setup) and view the WPS
WPS Station Use this screen to use WPS to set up your wireless network.
MAC Filter Use this screen to configure the ZyXEL Device to give exclusive access to
Advanced Setup Use this screen to configure the advanced wireless LAN settings.
NAT Port Forwarding Use this screen to make your local servers visible to the outside world.
Security
IP Filter Incoming This screen shows a summary of the IP filtering rules, and allows you to
Advanced
Static Route IP Static Route Use this screen to configure IP static routes to tell your device about
QoS General Use this screen to enable QoS.
Queue Setup
Class Setup Use this screen to define a classifier.
Dynamic DNS This screen allows you to use a static hostname alias for a dynamic IP
Use this screen to configure ISP parameters, WAN IP address assignment,
DNS servers and other advanced properties.
Use this screen to configure additional WAN connections.
assign specific IP addresses to individual MAC addresses (and host
names).
authentication/security settings.
status.
specific wireless clients or exclude specific wireless clients from accessing
the ZyXEL Device.
add or remove an incoming IP filtering rule that allows incoming traffic from
the WAN.
networks beyond the directly connected remote nodes.
Use this screen to configure QoS queues.
address.
P-870HW-51a v2 User’s Guide
41
Page 42

Chapter 3 Introducing the Web Configurator
Table 3 Navigation Panel Summary
LINK TAB FUNCTION
Remote MGMT TR069 Use this screen to configure the ZyXEL Device to be managed by an ACS
(Auto Configuration Server).
UPnP General Use this screen to turn UPnP on or off.
Maintenance
System General Use this screen to configure your device’s name, domain name,
management inactivity timeout and password.
Time Setting Use this screen to change your ZyXEL Device’s time and date.
Logs View Log Use this screen to view the logs for the level that you selected.
Log Settings Use this screen to change your ZyXEL Device’s log settings.
Tools Firmware Use this screen to upload firmware to your device.
Configuration Use this screen to backup and restore your device’s configuration (settings)
or reset the factory default settings.
Restart This screen allows you to reboot the ZyXEL Device without turning the
power off.
Diagnostic 802.1ag Use this screen to configure CFM (Connectivity Fault Management) and
perform connectivity tests and view test reports.
3.2.3 Main Window
The main window displays information and configuration fields. It is discussed in the rest of
this document.
Right after you log in, the Status screen is displayed. See Chapter 4 on page 43 for more
information about the Status screen.
3.2.4 Status Bar
Check the status bar when you click Apply or OK to verify that the configuration has been
updated.
42
P-870HW-51a v2 User’s Guide
Page 43

CHAPTER 4
Status Screens
Use the Status screens to look at the current status of the device, system resources and
interfaces (LAN and W AN). The Status screen also provides detailed information from DHCP
and statistics from traffic.
4.1 Status Screen
Click Status to open this screen.
Figure 20 Status Screen
Each field is described in the following table.
Table 4 Status Screen
LABEL DESCRIPTION
Refresh Interval Enter how often you want the ZyXEL Device to update this screen.
Apply Click this to update this screen immediately.
Device
Information
P-870HW-51a v2 User’s Guide
43
Page 44

Chapter 4 Status Screens
Table 4 Status Screen
LABEL DESCRIPTION
Host Name This field displays the ZyXEL Device system name. It is used for identification.
Model
Number
MAC Address This is the MAC (Media Access Control) or Ethernet address unique to your
ZyNOS
Firmware
Version
DSL Firmware
Version
WAN Information
Mode This is the method of encapsulation used by your ISP.
IP Address This field displays the current IP address of the ZyXEL Device in the WAN. Click
IP Subnet
Mask
LAN Information
IP Address This field displays the current IP address of the ZyXEL Device in the LAN. Click
IP Subnet
Mask
DHCP This field displays what DHCP services the ZyXEL Device is providing to the LAN.
WLAN
Information
ESSID This is the descriptive name used to identify the ZyXEL Device in the wireless
Channel This is the channel number used by the ZyXEL Device now.
WPS This field displays the status of WPS (Wi-Fi Protected Setup). Click this to go to
System Status
System
Uptime
Current Date/
Time
System Mode This displays whether the ZyXEL Device is functioning as a router or a bridge.
CPU Usage This field displays what percentage of the ZyXEL Device’s processing ability is
Click this to go to the screen where you can change it.
This is the model name of your device.
ZyXEL Device.
This field displays the current version of the firmware inside the device. It also
shows the date the firmware version was created. Click this to go to the screen
where you can change it.
This field displays the current version of the device’s DSL modem code.
this to go to the screen where you can change it.
This field displays the current subnet mask in the WAN.
this to go to the screen where you can change it.
This field displays the current subnet mask in the LAN.
Choices are:
Server - The ZyXEL Device is a DHCP server in the LAN. It assigns IP addresses
to other computers in the LAN.
None - The ZyXEL Device is not providing any DHCP services to the LAN.
Click this to go to the screen where you can change it.
LAN. Click this to go to the screen where you can change it.
the screen where you can change it.
This field displays how long the ZyXEL Device has been running since it last
started up. The ZyXEL Device starts up when you plug it in, when you restart it
(Maintenance > Tools > Restart), or when you reset it (see Section 1.6 on page
28).
This field displays the current date and time in the ZyXEL Device. You can change
this in Maintenance > System > Time Setting.
currently used. When this percentage is close to 100%, the ZyXEL Device is
running at full load, and the throughput is not going to improve anymore. If you
want some applications to have more throughput, you should turn off other
applications (for example, using QoS; see Chapter 11 on page 117).
44
P-870HW-51a v2 User’s Guide
Page 45

Chapter 4 Status Screens
Table 4 Status Screen
LABEL DESCRIPTION
Memory
Usage
Interface Status
Interface This column displays each interface the ZyXEL Device has.
Status This field indicates whether or not the ZyXEL Device is using the interface.
Rate For the LAN interface, this displays the port speed and duplex setting.
More Status
WAN Service
Statistics
Route Info Click this link to view the internal routing table on the ZyXEL Device. See Section
WLAN Station
List
LAN Statistics Click this link to view packet specific sta ti s ti cs on th e LAN an d WLAN in terfaces.
Client List Click this link to view current DHCP client information. See Section 4.1.5 on page
This field displays what percentage of the ZyXEL Device’s memory is currently
used. Usually, this percentage should not increase much. If memory usage does
get close to 100%, the ZyXEL Device is probably becoming unstable, and you
should restart the device. See Section 17.4 on page 154, or turn off the device
(unplug the power) for a few seconds.
For the DSL interface, this field displays NoSignal (line is down) or Up (line is up
or connected).
For the LAN interface, this field displays Up when the ZyXEL Device is using the
interface and Disabled when the ZyXEL Device is not using the interface.
For the WLAN interface, it displays Up when WLAN is enabled or Disabled when
WLAN is not active.
For the DSL interface, it displays the downstream and upstream transmission rate.
For the WLAN interface, it displays the maximum transmission rate.
Click this link to view packet specific statistics of the WAN connection(s). See
Section 4.1.1 on page 46.
4.1.2 on page 47.
Click this link to display the MAC address(es) of the wireless stations that are
currently associating with the ZyXEL Device. See Section 4.1.3 on page 47.
See Section 4.1.4 on page 48.
50.
P-870HW-51a v2 User’s Guide
45
Page 46

Chapter 4 Status Screens
4.1.1 WAN Service Statistics
Click Status > WLAN Service Statistics to access this screen. Use this screen to view the
WAN statistics.
Figure 21 Status > WAN Service Statistics
The following table describes the labels in this screen.
Table 5 Status > WAN Service Statistics
LABEL DESCRIPTION
Interface T his shows the name of the WAN interface used by this connection.
The default name ptm0 indicates the DSL port. The last number represents the
index number of connections over the same PVC or the VLAN ID number assigned
to traffic sent through this connection.
Description This shows the descriptive name of this connection.
Received
Bytes This indicates the number of bytes received on this interface.
Pkts This indicates the number of transmitted packets on this interface.
Errs This indicates th e number of frames with errors received on this interface.
Drops This indicates the number of received packets dropped on this interface.
Transmitted
Bytes This indicates the number of bytes transmitted on this interface.
Pkts This indicates the number of transmitted packets on this interface.
Errs This indicates th e number of frames with errors transmitted on this interface.
Drops This indicates the number of outgoing packets dropped on this interface.
Refresh Interval Enter the time interval for refreshing statistics in this field.
Set Interval Click this button to apply the new poll interval you entered in the Refresh Interval
field.
Stop Click Stop to stop refreshing statistics.
46
P-870HW-51a v2 User’s Guide
Page 47

4.1.2 Route Info
Routing is based on the destination address only and the ZyXEL Device takes the shortest path
to forward a packet. Click Status > Route Info to access this screen. Use this screen to view
the internal routing table on the ZyXEL Device.
Figure 22 Status > Route Info
The following table describes the labels in this screen.
Table 6 Status > Route Info
LABEL DESCRIPTION
Destination This indicates the destination IP address of this route.
Gateway This indicates the IP address of the gateway that helps forward this route’s traffic.
Subnet Mask This indicates the destination subnet mask of this route.
Flag This indicates the route status.
Metric The metric represents the "cost of transmission". A router determines the best route
Service This indicate s th e na me of th e se rvi ce used to forward the route.
Interface This indicates the name of the interface through wh ich the route is forwarded.
Chapter 4 Status Screens
Up: The route is up.
Reject: The route is blocked and will force a route lookup to fail.
Gateway: The route uses a gateway to forward traffic.
Host: The target of the route is a hos t.
Reinstate: The route is reinstated for dynamic routing.
Dynamic (redirect): The route is dynamically installed by a routing daemon or redirect
Modified (redirect): The route is modified from a routing daemon or rederict.
for transmission by choosing a path with the lowest "cost". The smaller the number,
the lower the "cost".
4.1.3 WLAN Station List
Click Status > WLAN Station List to access this screen. Use this screen to view the wireless
stations that are currently associated to the ZyXEL Device.
P-870HW-51a v2 User’s Guide
47
Page 48

Chapter 4 Status Screens
Figure 23 Status > WLAN Station List
The following table describes the labels in this screen.
Table 7 Status > WLAN Station List
LABEL DESCRIPTION
MAC Address This field shows the MAC (Media Access Control) address of an associated wireless
Associated This field shows whether the wireless station is currently associated to the ZyXEL
Authorized This field shows whether the wireless station is allowed to access network resources
SSID This field shows the SSID to which the wireless station is connected.
Interface This field shows the wireless interface to which the wireless station is connected.
Refresh
Interval
Set Interval Click this button to apply the new poll interval you entered in the Refresh Interval
Stop Click Stop to stop refreshing statistics.
4.1.4 LAN Statistics
Click Status > LAN Statistics to access this screen. Use this screen to view the LAN statistics.
station.
Device (Yes) or not (No).
behind the ZyXEL Device (Yes) or not (No).
Enter the time interval for refreshing statistics in this field.
field.
48
P-870HW-51a v2 User’s Guide
Page 49

Figure 24 Status > LAN Statistics
Chapter 4 Status Screens
The following table describes the labels in this screen.
Table 8 Status > LAN Statistics
LABEL DESCRIPTION
Interface T his shows the LAN or WLAN interface. eth0~3 represent the physical Ethernet
ports 1~ 4.
Received
Bytes This indicates the number of bytes received on this interface.
Pkts This indicates the number of transmitted packets on this interface.
Errs This indicates th e number of frames with errors received on this interface.
Drops This indicates the number of received packets dropped on this interface.
Transmitted
Bytes This indicates the number of bytes transmitted on this interface.
Pkts This indicates the number of transmitted packets on this interface.
Errs This indicates th e number of frames with errors transmitted on this interface.
Drops This indicates the number of outgoing packets dropped on this interface.
Refresh Interval Enter the time interval for refreshing statistics in this field.
Set Interval Click this button to apply the new poll interval you entered in the Refresh Interval
field.
Stop Click Stop to stop refreshing statistics.
P-870HW-51a v2 User’s Guide
49
Page 50

Chapter 4 Status Screens
4.1.5 Client List
DHCP (Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol, RFC 2131 and RFC 2132) allows individual
clients to obtain TCP/IP configuration at start-up from a server. You can configure the ZyXEL
Device as a DHCP server or disable it. When configured as a server, the ZyXEL Device
provides the TCP/IP configuration for the clients. If DHCP service is disabled, you must have
another DHCP server on your LAN, or else the computer must be manually configured.
Click Status > Client List to open the following screen. The read-only DHCP table shows
current DHCP client information (including IP Address, Host Name and MAC Address) of
all network clients using the ZyXEL Device’s DHCP server.
Figure 25 Status > Client List
The following table describes the labels in this screen.
Table 9 Status > Client List
LABEL DESCRIPTION
Host Name This indicates the computer host name.
MAC Address Every Ethernet device has a unique MAC (Media Access Control) address. The
IP Address This indicates the IP address assigned to this client computer.
MAC address is assigned at the factory and consists of six pairs of hexadecimal
characters, for example, 00:A0:C5:00:00:02.
This indicates the MAC address of the client computer.
50
P-870HW-51a v2 User’s Guide
Page 51

PART II
Network
WAN Setup (53)
LAN Setup (67)
Wireless LAN (75)
Network Address Translation (NAT) (99)
51
Page 52

52
Page 53

CHAPTER 5
WAN Setup
5.1 Overview
This chapter discusses the ZyXEL Device’s WAN screens. Use these screens to configure your
ZyXEL Device for Internet access.
A WAN (Wide Area Network) connection is an outside connection to another network or the
Internet. It connects your private networks (such as a LAN (Local Area Network) and other
networks, so that a computer in one location can communicate with computers in other
locations.
Figure 26 LAN and WAN
LAN
• See Section 5.6 on page 62 for advanced technical information on WAN.
• See Chapter 2 on page 31 for WAN tutorials.
5.1.1 What You Can Do in this Chapter
•The Internet Connection screen lets you configure the WAN settings on the ZyXEL
Device for Internet access (Section 5.4 on page 54).
•The More Connections screen lets you set up additional Internet access connections
(Section 5.5 on page 58).
WAN
Internet
P-870HW-51a v2 User’s Guide
53
Page 54

Chapter 5 WAN Setup
5.2 What You Need to Know
Encapsulation Method
Encapsulation is used to include data from an upper layer protocol into a lower layer protocol.
To set up a WAN connection to the Internet, you need to use the same encapsulation method
used by your ISP (Internet Service Provider). If your ISP offers a dial-up Internet connection
using PPPoE (PPP over Ethernet) or PPPoA, they should also provide a username and
password (and service name) for user authentication.
WAN IP Address
The WAN IP address is an IP address for the ZyXEL Device, which makes it accessible from
an outside network. It is used by the ZyXEL Device to communicate with other devices in
other networks. It can be static (fixed) or dynamically assigned by the ISP each time the
ZyXEL Device tries to access the Internet.
If your ISP assigns you a static WAN IP address, they should also assign you the subnet mask
and DNS server IP address(es) (and a gateway IP address if you use the Ethernet or ENET
ENCAP encapsulation method).
PTM
Packet Transfer Mode (PTM) is packet-oriented and supported by the VDSL2 standard. In
PTM, packets are encapsulated directly in the High-level Data Link Control (HDLC) frames.
It is designed to provide a low-overhead, transparent way of transporting packets over DSL
links, as an alternative to ATM.
5.3 Before You Begin
You need to know your Internet access settings suc h as encapsulation and WAN IP address.
Get this information from your ISP.
5.4 The Internet Connection Screen
Use this screen to change your ZyXEL Device’s WAN settings. Click Network > WAN >
Internet Connection. The screen differs by the mode you select.
54
P-870HW-51a v2 User’s Guide
Page 55

Figure 27 WAN > Internet Connection (PPPoE)
Chapter 5 WAN Setup
The following table describes the labels in this screen.
Table 10 WAN > Internet Connection
LABEL DESCRIPTION
General
Name Specify a name for this connection. You can use up to 32 letters, numerals and
Mode The ZyXEL Device is in routing mode by default. This allows multiple computers
User Name (PPPoE encapsulation only) Enter the user name exactly as your ISP assigned.
Password (PPPoE encapsulation only) Enter the password associated with the user name
P-870HW-51a v2 User’s Guide
any printable character found on a typical English language keyboard.
to share an Internet account. Select the method of encapsulation (ENET
ENCAP or PPPoE) used by your ISP from the drop-down list box.
Otherwise, select Bridge when your ISP provides you more than one IP address
and you want the connected computers to get individual IP address from ISP’s
DHCP server directly. If you select Bridge, you cannot use IP filter, DHCP
server and NAT on the ZyXEL Device.
If assigned a name in the form user@domain where domain identifies a service
name, then enter both components exactly as given.
above.
55
Page 56

Chapter 5 WAN Setup
Table 10 WAN > Internet Connection (continued)
LABEL DESCRIPTION
Service Name (PPPoE encapsulation only) Type the name of your PPPoE service here.
IP Address A st atic IP address is a fixed IP that your ISP gives you. A dynamic IP address is
IP Address Enter the IP address assigned by your ISP if you select Static IP Address.
Subnet Mask Enter a subnet mask in dotted decimal notation when you select ENET ENCAP
Gateway IP
address
Connection
(PPPoE only)
Nailed-Up
Connection
Connect on
Demand
Max Idle Time Specify an idle time-out in the Max Idle Time field when you select Connect on
NAT
Active NAT Select this check box to enable NAT on this connection.
Symmetric Select this option to enable symmetric NAT on this connection.
Fullcone Select this option to enable full cone NAT on this connection.
DNS Servers Select From ISP if your ISP dynamically assigns DNS server information (and
First DNS Server
Second DNS Server
Apply Click this to save the changes.
Reset Click this to begin configuring this screen afresh.
Advanced Setup Click this button to display the Advanced WAN Setup screen and edit more
not fixed; the ISP assigns you a different one each time you connect to the
Internet.
Select Obtain an IP Address Automatically if you have a dynamic IP address;
otherwise select Static IP Address and type your ISP assigned IP address in
the IP Address field below.
in the Mode field.
You must specify a gateway IP address (supplied by your ISP) when you select
ENET ENCAP in the Mode field.
Select Nailed-Up Connection when you want your connection up all the time.
The ZyXEL Device will try to bring up the connection automatically if it is
disconnected.
Select Connect on Demand when you don't want the connection up all the time
and specify an idle time-out in the Max Idle Time field.
Demand. The default setting is 0, which means the Internet session will not
timeout.
This field is available only when you select Active NAT.
This field is available only when you select Active NAT.
the ZyXEL Device's WAN IP address).
Select Static IP if you have the IP address of a DNS server.
If you select Static IP, enter the DNS server's IP address in the field to the right.
details of your WAN setup.
5.4.1 Advanced Internet Connection Setup
Use this screen to edit your ZyXEL Device's advanced WAN settings. Click the Advanced
Setup button in the Internet Connection screen. The screen appears as shown.
56
P-870HW-51a v2 User’s Guide
Page 57

Chapter 5 WAN Setup
Figure 28 WAN > Internet Connection: Advanced Setup
The following table describes the labels in this screen.
Table 11 WAN > Internet Connection: Advanced Setup
LABEL DESCRIPTION
RIP & Multicast
Setup
RIP Version RIP (Routing Information Protocol) allows a router to exchange routing information
RIP
Operation
IGMP
Multicast
PPPoE
Passthrough
(PPPoE
encapsulation
only)
IP Filter This section is not available when you configure the ZyXEL Device to be in bridge
IP Filter
Active
VLAN
This section is not available when you configure the ZyXEL Device to be in bridge
mode.
with other routers.
This field is available only when you select ENET ENCAP.
This shows the RIP version used for this WAN connection.
This field is available only when you select ENET ENCAP.
This shows whether RIP is enabled (Active) or not (Disable) on this WAN
connection.
Multicast packets are sent to a group of computers on the LAN and are an
alternative to unicast packets (packets sent to one computer) and broadcast
packets (packets sent to every computer).
IGMP (Internet Group Multicast Protocol) is a network-layer protocol used to
establish membership in a multicast group. The ZyXEL Device supports both IGMP
version 1 and version 2. Select Enable to turn on IGMP. Otherwise, select Disable.
This field is available when you select PPPoE encapsulation.
In addition to the ZyXEL Device's built-in PPPoE client, you can enable PPPoE
pass through to allow up to ten hosts on the LAN to use PPPoE client software on
their computers to connect to the ISP via the ZyXEL Device. Each host can have a
separate account and a public WAN IP address.
PPPoE pass through is an alternative to NAT for application where NAT is not
appropriate.
Disable PPPoE pass through if you do not need to allow hosts on the LAN to use
PPPoE client software on their computers to connect to the ISP.
mode.
Select this option to enable IP filtering on this connection.
P-870HW-51a v2 User’s Guide
57
Page 58

Chapter 5 WAN Setup
Table 11 WAN > Internet Connection: Advanced Setup (continued)
LABEL DESCRIPTION
VLAN Active Select this option to enable VLAN multiplexing of multiple protocols over a single
VLAN ID Enter a VLAN ID number for traffic that goes through this connection.
Priority Enter a priority level for traffic that goes through this connection.
Back Click this to return to the previous screen.
Apply Click this to save the changes.
Reset Click this to restore your last-saved settings.
virtual circuit. You need to assign a VLAN ID and priority level to traffic through
each WAN connection. All WAN connections share one MAC address. This allows
the backbone switch to classify and service traffic based on the VLAN tag, instead
of the MAC address.
Otherwise, disable VLAN multiplexing and each WAN connection has its own MAC
address.
Note: This field is only configurable for the first WAN connection.
When you change the setting here, all existing WAN
connections will be removed except for the first WAN
connection.
5.5 The More Connections Screen
The ZyXEL Device allows you to configure more than one Internet access connection. To
configure additional Internet access connections click Network > WAN > More
Connections. The screen differs by the encapsulation you select. When you use the WAN >
Internet Connection screen to set up Internet access, you are configuring the first WAN
connection.
Figure 29 WAN > More Connections
The following table describes the labels in this screen.
Table 12 WAN > More Connections
LABEL DESCRIPTION
# This is an index number indicating the number of the corresponding connecti on.
Name This is the name you gave to the Internet connection.
VLAN ID/Priority This field shows the VLAN ID number and priority configured for this WAN
connection when VLAN multiplexing is enabled. Otherwise, it shows disable.
Encapsulation This field indicates the encapsulation method of the Internet connection.
58
P-870HW-51a v2 User’s Guide
Page 59

Table 12 WAN > More Connections (continued)
LABEL DESCRIPTION
Modify The first (ISP) connection is read-only in this screen. Use the WAN > Internet
Connection screen to edit it.
Click the edit icon to edit the Internet connection settings. Click this icon on an
empty configuration to add a new Internet access setup.
Click the remove icon to delete the Internet access setup from your connection list.
Add Click this to add a new connection.
5.5.1 More Connections Edit
Click the edit icon or Add button in the More Connections screen to configure a connection.
Figure 30 WAN > More Connections: Edit
Chapter 5 WAN Setup
The following table describes the labels in this screen.
Table 13 WAN > More Connections: Edit
LABEL DESCRIPTION
General
Active Select the check box to activate or clear the check box to deactivate this
P-870HW-51a v2 User’s Guide
connection.
59
Page 60

Chapter 5 WAN Setup
Table 13 WAN > More Connections: Edit (continued)
LABEL DESCRIPTION
Name Specify a name for this connection. You can use up to 32 letters, numerals and
Mode The ZyXEL Device is in routing mode by default. This allows multiple computers
User Name (PPPoE encapsulation only) Enter the user name exactly as your ISP assigned.
Password (PPPoE encapsulation only) Enter the password associated with the user name
Service Name (PPPoE encapsulation only) Type the name of your PPPoE service here.
IP Address A st atic IP address is a fixed IP that your ISP gives you. A dynamic IP address is
IP Address Enter the IP address assigned by your ISP if you select Static IP Address.
Subnet Mask Enter a subnet mask in dotted decimal notation when you select ENET ENCAP
Gateway IP
address
Connection
(PPPoE only)
Nailed-Up
Connection
Connect on
Demand
Max Idle Time Specify an idle time-out in the Max Idle Time field when you select Connect on
NAT
Active NAT Select this check box to enable NAT on this connection.
Symmetric Select this option to enable symmetric NAT on this connection.
Fullcone Select this option to enable full cone NAT on this connection.
DNS Servers Select
First DNS Server
Second DNS Server
Back Click this to return to the More Connections screen with saving your changes.
any printable character found on a typical English language keyboard.
to share an Internet account. Select the method of encapsulation (ENET
ENCAP or PPPoE) used by your ISP from the drop-down list box.
Otherwise, select Bridge when your ISP provides you more than one IP address
and you want the connected computers to get individual IP address from ISP’s
DHCP server directly. If you select Bridge, you cannot use IP filter, DHCP
server and NAT on the ZyXEL Device.
If assigned a name in the form user@domain where domain identifies a service
name, then enter both components exactly as given.
above.
not fixed; the ISP assigns you a different one each time you connect to the
Internet.
Select Obtain an IP Address Automatically if you have a dynamic IP address;
otherwise select Static IP Address and type your ISP assigned IP address in
the IP Address field below.
in the Mode field.
You must specify a gateway IP address (supplied by your ISP) when you select
ENET ENCAP in the Mode field.
Select Nailed-Up Connection when you want your connection up all the time.
The ZyXEL Device will try to bring up the connection automatically if it is
disconnected.
Select Connect on Demand when you don't want the connection up all the time
and specify an idle time-out in the Max Idle Time field.
Demand. The default setting is 0, which means the Internet session will not
timeout.
This field is available only when you select Active NAT.
This field is available only when you select Active NAT.
From ISP if your ISP dynamically assigns DNS server information (and
the ZyXEL Device's WAN IP address).
Select Static IP if you have the IP address of a DNS server.
If you select Static IP, enter the DNS server's IP address in the field to the right.
60
P-870HW-51a v2 User’s Guide
Page 61

Table 13 WAN > More Connections: Edit (continued)
LABEL DESCRIPTION
Apply Click this to save the changes.
Reset Click this to begin configuring this screen afresh.
Advanced Setup Click this button to display the More Connections Advanced Setup screen and
edit more details of your WAN setup.
5.5.2 Configuring More Connections Advanced Setup
To edit your ZyXEL Device's advanced WAN settings, click the Advanced Setup button in
the More Connections Edit screen. The screen appears as shown.
Figure 31 WAN > More Connections: Edit: Advanced Setup
Chapter 5 WAN Setup
The following table describes the labels in this screen.
Table 14 WAN > More Connectio ns: Edit: Advanced Setup
LABEL DESCRIPTION
RIP & Multicast
Setup
RIP Version RIP (Routing Information Protocol) allows a router to exchange routing information
RIP
Operation
P-870HW-51a v2 User’s Guide
This section is not available when you configure the ZyXEL Device to be in bridge
mode.
with other routers. The version field controls the format and the broadcasting
method of the RIP packets that the ZyXEL Device sends (it recognizes both
formats when receiving). RIP-1 is universally supported; but RIP-2 carries more
information. RIP-1 is probably adequate for most networks, unless you have an
unusual network topology
This field is available only when you select ENET ENCAP.
Select the RIP version from RIPv1, RIPv2 and RIPv1v2.
This field is available only when you select ENET ENCAP.
Select Active to enable RIP. Othe rwise, select Disable.
61
Page 62

Chapter 5 WAN Setup
Table 14 WAN > More Connections: Edit: Advanced Setup (continued)
LABEL DESCRIPTION
IGMP
Multicast
PPPoE
Passthrough
(PPPoE
encapsulation
only)
IP Filter This section is not available when you configure the ZyXEL Device to be in bridge
IP Filter
Active
VLAN
VLAN Active Select this option to enable VLAN multiplexing of multiple protocols over a single
Multicast packets are sent to a group of computers on the LAN and are an
alternative to unicast packets (packets sent to one computer) and broadcast
packets (packets sent to every computer).
IGMP (Internet Group Multicast Protocol) is a network-layer protocol used to
establish membership in a multicast group. The ZyXEL Device supports both IGMP
version 1 and version 2. Select Enable to turn on IGMP. Otherwise, select Disable.
This field is available when you select PPPoE encapsulation.
In addition to the ZyXEL Device's built-in PPPoE client, you can enable PPPoE
pass through to allow up to ten hosts on the LAN to use PPPoE client software on
their computers to connect to the ISP via the ZyXEL Device. Each host can have a
separate account and a public WAN IP address.
PPPoE pass through is an alternative to NAT for application where NAT is not
appropriate.
Disable PPPoE pass through if you do not need to allow hosts on the LAN to use
PPPoE client software on their computers to connect to the ISP.
mode.
Select this option to enable IP filtering on this connection.
virtual circuit. You need to assign a VLAN ID and priority level to traffic through
each WAN connection. All WAN connections share one MAC address. This allows
the backbone switch to classify and service traffic based on the VLAN tag.
Otherwise, disable VLAN multiplexing and each WAN connection has its own MAC
address.
Note: This field is only configurable for the first WAN connection.
When you change the setting here, all existing WAN
connections will be removed except for the first WAN
connection.
VLAN ID Enter a VLAN ID number for traffic that goes through this connection.
Priority Enter a priority level for traffic that goes through this connection.
Back Click this to return to the previous screen.
Apply Click this to save the changes.
Reset Click this to restore your last-saved settings.
5.6 Technical Reference
The following section contains additional technical information about the ZyXEL Device
features described in this chapter.
Encapsulation
Be sure to use the encapsulation method required by your ISP . The ZyXEL Device can work in
bridge mode or routing mode. When the ZyXEL Device is in routing mode, it supports the
following methods.
62
P-870HW-51a v2 User’s Guide
Page 63

Chapter 5 WAN Setup
ENET ENCAP
The MAC Encapsulated Routing Link Protocol (ENET ENCAP) is only implemented with the
IP network protocol. IP packets are routed between the Ethernet interface and the WAN
interface and then formatted so that they can be understood in a bridged environment. For
instance, it encapsulates routed Ethernet frames into bridged ATM cells.
PPP over Ethernet
Point-to-Point Protocol over Ethernet (PPPoE) provides access control and billing
functionality in a manner similar to dial-up services using PPP. PPPoE is an IETF standard
(RFC 2516) specifying how a personal computer (PC) interacts with a broadband mod em
(DSL, cable, wireless, etc.) connection.
For the service provider, PPPoE offers an access and authentication method that works with
existing access control systems (for example RADIUS).
One of the benefits of PPPoE is the ability to let you access one of multiple network services,
a function known as dynamic service selection. This enables the service provider to easily
create and offer new IP services for individuals.
Operationally , PPPoE saves significant effort for both you and the ISP or carrier, as it requires
no specific configuration of the broadband modem at the customer site.
By implementing PPPoE directly on the ZyXEL Device (rather than individual computers),
the computers on the LAN do not need PPPoE software installed, since the ZyXEL Device
does that part of the task. Furthermore, with NAT, all of the LANs’ computers will have
access.
IP Address Assignment
A static IP is a fixed IP that your ISP gives you. A dynamic IP is not fixed; the ISP assigns you
a different one each time. The Single User Account feature can be enabled or disabled if you
have either a dynamic or static IP. However the encapsulation method assigned influences
your choices for IP address and default gateway.
Full Cone NAT
In full cone NAT, the NAT router maps all outgoing packets from an internal IP address and
port to a single IP address and port on the external network. The NAT router also maps packets
coming to that external IP address and port to the internal IP address and port.
In the following example, the ZyXEL Device maps the source address of all packets sent from
the internal IP address 1 and port A to IP address 2 and port B on the external network. The
ZyXEL Device also performs NAT on all incoming packets sent to IP address 2 and port B and
forwards them to IP address 1, port A.
P-870HW-51a v2 User’s Guide
63
Page 64

Chapter 5 WAN Setup
Figure 32 Full Cone NAT Example
1, A
Symmetric NAT
The full, restricted and port restricted cone NAT types use the same mapping for an outgoing
packet’s source address regardless of the destination IP address and port. In symmetric NAT,
the mapping of an outgoing packet’s source address to a source address in another network is
different for each different destination IP address and port.
In the following example, the ZyXEL Device maps the source address IP address 1 and port A
to IP address 2 and port B on the external network for packets sent to IP address 3 and port C.
The ZyXEL Device uses a different mapping (IP address 2 and port M) for packets sent to IP
address 4 and port D.
A host on the external network (IP address 3 and port C for example) can only send packets to
the internal host via the external IP address and port that the NAT router used in sending a
packet to the external host’s IP address and port. So in the example, only 3, C is allowed to
send packets to 2, B and only 4, D is allowed to send packets to 2, M.
Figure 33 Symmetric NAT
2, B
3, C
64
2, B
1, A
Introduction to VLANs
A Virtual Local Area Network (VLAN) allows a physical network to be partitioned into
multiple logical networks. Devices on a logical network belong to one group. A device can
belong to more than one group. With VLAN, a device cannot directly talk to or hear from
devices that are not in the same group(s); the traffic must first go through a router.
2, M
5, B
P-870HW-51a v2 User’s Guide
4, D
4, E
Page 65

Chapter 5 WAN Setup
In Multi-Tenant Unit (MTU) applications, VLAN is vital in providing isolation and security
among the subscribers. When properly configured, VLAN prevents one subscriber from
accessing the network resources of another on the same LAN, thus a user will not see the
printers and hard disks of another user in the same building.
VLAN also increases network performance by limiting broadcasts to a smaller and more
manageable logical broadcast domain. In traditional switched environments, all broadcast
packets go to each and every individual port. With VLAN, all broadcasts are confined to a
specific broadcast domain.
Introduction to IEEE 802.1Q Tagged VLAN
A tagged VLAN uses an explicit tag (VLAN ID) in the MAC header to identify the VLAN
membership of a frame across bridges - they are not confined to the switch on which they were
created. The VLANs can be created statically by hand or dynamically through GVRP. The
VLAN ID associates a frame with a specific VLAN and provides the information that switches
need to process the frame across the network. A tagged frame is four bytes longer than an
untagged frame and contains two bytes of TPID (Tag Protocol Identifier), residing within the
type/length field of the Ethernet frame) and two bytes of TCI (Tag Control Information), star ts
after the source address field of the Ethernet frame).
The CFI (Canonical Format Indicator) is a single-bit flag, always set to zero for Ethernet
switches. If a frame received at an Ethernet port has a CFI set to 1, then that frame should not
be forwarded as it is to an untagged port. The remaining twelve bits define the VLAN ID,
giving a possible maximum number of 4,096 VLANs. Note that user priority and VLAN ID
are independent of each other. A frame with VID (VLAN Identifier) of null (0) is called a
priority frame, meaning that only the priority level is significant and the default VID of the
ingress port is given as the VID of the frame. Of the 4096 possible VIDs, a VID of 0 is used to
identify priority frames and value 4095 (FFF) is reserved, so the maximum possible VLAN
configurations are 4,094.
TPID
2 Bytes
User Priority
3 Bits
CFI
1 Bit
VLAN ID
12 Bits
Multicast
IP packets are transmitted in either one of two ways - Unicast (1 sender - 1 recipient) or
Broadcast (1 sender - everybody on the network). Multicast delivers IP packets to a group of
hosts on the network - not everybody and not just 1.
Internet Group Multicast Protocol (IGMP) is a network-layer protocol used to establish
membership in a Multicast group - it is not used to carry user data. IGMP version 2 (RFC
2236) is an improvement over version 1 (RFC 11 12) but IGMP versi on 1 is still in wide use. If
you would like to read more detailed information about interoperability between IGMP
version 2 and version 1, please see sections 4 and 5 of RFC 2236. The class D IP address is
used to identify host groups and can be in the range 224.0.0.0 to 239 .255.255.255. The addr ess
224.0.0.0 is not assigned to any group and is used by IP multicast computers. The address
224.0.0.1 is used for query messages and is assigned to the permanent group of all IP hosts
(including gateways). All hosts must join the 224.0.0.1 group in order to participate in IGMP.
The address 224.0.0.2 is assigned to the multicast routers group.
At start up, the ZyXEL Device queries all directly connected networks to gather group
membership. After that, the ZyXEL Device periodically updates this information.
P-870HW-51a v2 User’s Guide
65
Page 66

Chapter 5 WAN Setup
DNS Server Address Assignment
Use Domain Name System (DNS) to map a domain name to its corresponding IP address and
vice versa, for instance, the IP address of www.zyxel.com is 204.217.0.2. The DNS server is
extremely important because without it, you must know the IP address of a computer before
you can access it.
The ZyXEL Device can get the DNS server addresses in the following ways.
1 The ISP tells you the DNS server addresses, usually in the form of an information sheet,
when you sign up. If your ISP gives you DNS server addresses, manually enter them in
the DNS server fields.
2 If your ISP dynamically assigns the DNS server IP addresses (along with the ZyXEL
Device’s WAN IP address), set the DNS server fields to get the DNS server address from
the ISP.
66
P-870HW-51a v2 User’s Guide
Page 67

CHAPTER 6
LAN Setup
6.1 Overview
A Local Area Network (LAN) is a shared communication system to which many computers
are attached. A LAN is usually located in one immediate area such as a building or floor of a
building.
The LAN screens can help you configure a LAN DHCP server and manage IP addresses.
LAN
DSL
• See Section 6.7 on page 72 for more information on LANs.
• See Appendix D on page 215 for more information on IP addresses and subnetting.
6.1.1 What You Can Do in this Chapter
•The LAN IP screen lets you set the LAN IP address and subnet mask of your ZyXEL
device and configure the ZyXEL Device’s DHCP settings (Section 6.4 on page 68).
•The Client List screen lets you assign IP addresses on the LAN to specific individual
computers based on their MAC Addresses (Section 6.5 on page 70).
•The IP Alias screen lets you change your ZyXEL Device’s IP alias settings (Section 6.6
on page 70).
6.2 What You Need To Know
IP Address
Similar to the way houses on a street share a common street name, so too do computers on a
LAN share one common network number. This is known as an Internet Protocol address.
Internet
P-870HW-51a v2 User’s Guide
67
Page 68

Chapter 6 LAN Setup
Subnet Mask
The subnet mask specifies the network number portion of an IP address. Your ZyXEL Device
will compute the subnet mask automatically based on the IP address that you entered. You
don't need to change the subnet mask computed by the ZyXEL Device unless you are
instructed to do otherwise.
DHCP
DHCP (Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol) allows clients to obtain TCP/IP configuration
at start-up from a server. This ZyXEL Device has a built-in DHCP server capability that
assigns IP addresses and DNS servers to systems that support DHCP client capability.
RIP
RIP (Routing Information Protocol) allows a router to exchange routing information with
other routers.
Multicast and IGMP
Traditionally, IP packets are transmitted in one of either two ways - Unicast (1 sender - 1
recipient) or Broadcast (1 sender - everybody on the network). Multicast delivers IP packets to
a group of hosts on the network - not everybody and not just 1.
IGMP (Internet Group Multicast Protocol) is a network-layer protocol used to establish
membership in a Multicast group - it is not used to carry user data. There are two versions 1
and 2. IGMP version 2 is an improvement over version 1 but IGMP version 1 is still in wide
use.
DNS
DNS (Domain Name System) maps a domain name to its corresponding IP address and vice
versa. The DNS server is extremely important because without it, you must know the IP
address of a computer before you can access it. The DNS server addresses you enter when you
set up DHCP are passed to the client machines along with the assigned IP address and subnet
mask.
6.3 Before You Begin
Find out the MAC addresses of your network devices if you intend to add them to the DHCP
Client List screen.
6.4 The LAN IP Screen
Click Network > LAN to open the IP screen. See Section 6.7 on page 72 for background
information. Use this screen to set the Local Area Network IP address and subnet mask of your
ZyXEL Device.
68
Follow these steps to configure your LAN settings.
1 Enter an IP address into the IP Address field. The IP address must be in dotted decimal
notation. This will become the IP address of your ZyXEL Device.
P-870HW-51a v2 User’s Guide
Page 69

Chapter 6 LAN Setup
2 Enter the IP subnet mask into the IP Subnet Mask field. Unless instructed otherwise it
is best to leave this alone, the configurator will automatically compute a subnet mask
based upon the IP address you entered.
3 Click Apply to save your settings.
Figure 34 LAN > IP
The following table describes the fields in this screen.
Table 15 LAN > IP
LABEL DESCRIPTION
LAN TCP/IP
IP Address Enter the LAN IP address you want to assign to your ZyXEL Device in dotted
decimal notation, for example, 192.168.1.1 (factory default).
IP Subnet Mask Type the subnet mask of your network in dotted decimal notation, for example
255.255.255.0 (factory default).
DHCP Setup
Active DHCP
Server
IP Pool Starting
Address
Pool Size This field specifies the size, or count of the IP address pool.
IGMP Snooping
Active IGMP
Snooping
Apply Click Apply to save your changes back to the ZyXEL Device.
Select this option to have the ZyXEL Device assign IP addresses and provide
subnet mask, gateway, and DNS server information to the network. The ZyXEL
Device is the DHCP server for the network.
Otherwise, deselect this to not have the ZyXEL Device provide any DHCP
services. The DHCP server will be disabled.
When the ZyXEL Device acts as a DHCP server, the following items need to be
set:
This field specifies the first of the contiguous addresses in the IP address pool.
Select this option to enable IGMP snooping. This allows the ZyXEL Device to
passively learn multicast group.
P-870HW-51a v2 User’s Guide
69
Page 70

Chapter 6 LAN Setup
6.5 The Client List Screen
This table allows you to assign IP addresses on the LAN to specific individual computers
based on their MAC Addresses.
Every Ethernet device has a unique MAC (Media Access Control) address. The MAC address
is assigned at the factory and consists of six pairs of hexadecimal characters, for example,
00:A0:C5:00:00:02.
Click Network > LAN > Client List to open the following screen. Use this screen to change
your ZyXEL Device’s static DHCP settings.
Figure 35 LAN > Client List
The following table describes the labels in this screen.
Table 16 LAN > Client List
LABEL DESCRIPTION
IP Address Enter the IP address that you want to assign to the computer on your LAN with
the MAC address that you will also specify.
MAC Address Enter the MAC address of a computer on your LAN.
Add Entries Click this to add a static DHCP entry.
# This is the index number of the static IP table entry (row).
IP Address This field displays the IP address relative to the # field listed above.
MAC Address The MAC (Media Access Control) or Ethernet address on a LAN (Local Area
Network) is unique to your computer (six pairs of hexadecimal notation).
A network interface card such as an Ethernet adapter has a hardwired address
that is assigned at the factory. This address follows an industry standard that
ensures no other adapter has a similar address.
Remove Click this to delete a static DHCP entry. You cannot delete a dynamic DHCP entry.
Apply Click this to save your changes back to the ZyXEL Device.
6.6 The IP Alias Screen
IP alias allows you to partition a physical network into different logical networks over the
same Ethernet interface. The ZyXEL Device supports three logical LAN interfaces via its
single physical Ethernet interface with the ZyXEL Device itself as the gateway for each LAN
network.
70
When you use IP alias, you can also configure firewall rules to control access between the
LAN's logical networks (subnets).
P-870HW-51a v2 User’s Guide
Page 71

Chapter 6 LAN Setup
" Make sure that the subnets of the logical networks do not overlap.
The following figure shows a LAN divided into subnets A and B.
Figure 36 Physical Network & Partitioned Logical Networks
A: 192.168.1.1 - 192.168.1.24
Ethernet
Interface
B: 192.168.2.1 - 192.168.2.24
6.6.1 Configuring the LAN IP Alias Screen
Click Network > LAN > IP Alias to open the following screen. Use this screen to change
your ZyXEL Device’s IP alias settings.
Figure 37 Network > LAN > IP Alias
The following table describes the labels in this screen.
Table 17 Network > LAN > IP Alias
LABEL DESCRIPTION
Active IP Alias Select the check box to configure another LAN network for the ZyXEL Device.
IP Address Enter the IP address of your ZyXEL Device in dotted decimal notation.
IP Subnet Mask Type the subnet mask of your network in dotted decimal notation, for example
Apply Click this to save your changes back to the ZyXEL Device.
255.255.255.0 (factory default).
P-870HW-51a v2 User’s Guide
71
Page 72

Chapter 6 LAN Setup
6.7 Technical Reference
The following section contains additional technical information about the ZyXEL Device
features described in this chapter.
LANs, WANs and the ZyXEL Device
The actual physical connection determines wh ether the ZyXEL Device ports are LAN or
WAN ports. There are two separate IP networks, one inside the LAN network and the other
outside the WAN ne twork as shown next.
Figure 38 LAN and WAN IP Addresses
LAN
WAN
Internet
DHCP Setup
DHCP (Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol, RFC 2131 and RFC 2132) allows individual
clients to obtain TCP/IP configuration at start-up from a server. You can configure the ZyXEL
Device as a DHCP server or disable it. When configured as a server, the ZyXEL Device
provides the TCP/IP configuration for the clients. If you turn DHCP service off, you must
have another DHCP server on your LAN, or else the computer must be manually configured.
IP Pool Setup
The ZyXEL Device is pre-configured with a pool of IP addresses for the DHCP clients (DHCP
Pool). See the product specifications in the appendices. Do not assign static IP addresses from
the DHCP pool to your LAN computers.
72
LAN TCP/IP
The ZyXEL Device has built-in DHCP server capability that assigns IP addresses and DNS
servers to systems that support DHCP client capability.
IP Address and Subnet Mask
Similar to the way houses on a street share a common street name, so too do computers on a
LAN share one common network number.
Where you obtain your network number depends on your particular situation. If the ISP or
your network administrator assigns you a block of registered IP addresses, follow their
instructions in selecting the IP addresses and the subnet mask.
P-870HW-51a v2 User’s Guide
Page 73

Chapter 6 LAN Setup
If the ISP did not explicitly give you an IP network number, then most likely you have a single
user account and the ISP will assign you a dynamic IP address when the connection is
established. If this is the case, it is recommended that you select a network number from
192.168.0.0 to 192.168.255.0 and you must enable the Network Address Translation (NAT)
feature of the ZyXEL Device. The Internet Assigned Number Authority (IANA) reserved this
block of addresses specifically for private use; please do not use any other number unless you
are told otherwise. Let's say you select 192.168.1.0 as the network number; which covers 254
individual addresses, from 192.168.1.1 to 192.168.1.254 (zero and 255 are reserved). In other
words, the first three numbers specify the network number while the last number identifies an
individual computer on that network.
Once you have decided on the network number, pick an IP address that is easy to remember,
for instance, 192.168.1.1, for your ZyXEL Device, but make sure that no other device on your
network is using that IP address.
The subnet mask specifies the network number portion of an IP address. Your ZyXEL Device
will compute the subnet mask automatically based on the IP address that you entered. You
don't need to change the subnet mask computed by the ZyXEL Device unless you are
instructed to do otherwise.
Private IP Addresses
Every machine on the Internet must have a unique address. If your networks are isolated from
the Internet, for example, only between your two branch offices, you can assign any IP
addresses to the hosts without problems. However, the Internet Assigned Numbers Authority
(IANA) has reserved the following three blocks of IP addresses specifically for private
networks:
• 10.0.0.0 — 10.255.255.255
• 172.16.0.0 — 172.31.255.255
• 192.168.0.0 — 192.168.255.255
You can obtain your IP address from the IANA, from an ISP or it can be assigned from a
private network. If you belong to a small organization and your Internet access is through an
ISP, the ISP can provide you with the Internet addresses for your local networks. On the other
hand, if you are part of a much larger organization, you should consult your network
administrator for the appropriate IP addresses.
" Regardless of your particular situation, do not create an arbitrary IP address;
always follow the guidelines above. For more information on address
assignment, please refer to RFC 1597, “Address Allocation for Private
Internets” and RFC 1466, “Guidelines for Management of IP Address S pace”.
Multicast
Traditionally, IP packets are transmitted in one of either two ways - Unicast (1 sender - 1
recipient) or Broadcast (1 sender - everybody on the network). Multicast delivers IP packets to
a group of hosts on the network - not everybody and not just 1.
P-870HW-51a v2 User’s Guide
73
Page 74

Chapter 6 LAN Setup
IGMP (Internet Group Multicast Protocol) is a network-layer protocol used to establish
membership in a Multicast group - it is not used to carry user data. IGMP version 2 (RFC
2236) is an improvement over version 1 (RFC 11 12) but IGMP versi on 1 is still in wide use. If
you would like to read more detailed information about interoperability between IGMP
version 2 and version 1, please see sections 4 and 5 of RFC 2236. The class D IP address is
used to identify host groups and can be in the range 224.0.0.0 to 239 .255.255.255. The addr ess
224.0.0.0 is not assigned to any group and is used by IP multicast computers. The address
224.0.0.1 is used for query messages and is assigned to the permanent group of all IP hosts
(including gateways). All hosts must join the 224.0.0.1 group in order to participate in IGMP.
The address 224.0.0.2 is assigned to the multicast routers group.
The ZyXEL Device supports both IGMP version 1 (IGMP-v1) and IGMP version 2 (IGMP-
v2). At start up, the ZyXEL Device queries all directly connected networks to gather group
membership. After that, the ZyXEL Device periodically updates this information. IP
multicasting can be enabled/disabled on the ZyXEL Device LAN and/or WAN interfaces in
the web configurator (LAN; WAN). Select None to disable IP multicasting on these
interfaces.
74
P-870HW-51a v2 User’s Guide
Page 75

CHAPTER 7
Wireless LAN
7.1 Overview
This chapter describes how to perform tasks related to setting up and optimizing your wireless
network, including the following.
• Turning the wireless connection on or off.
• Configuring a name, wireless channel and security for the network.
• Using WiFi Protected Setup (WPS) to configure your wireless network.
• Using a MAC (Media Access Control) address filter to restrict access to the wireless
network.
See Chapter 2 on page 31 for a tutorial showing how to set up your wireless connection in an
example scenario.
See Section 7.9 on page 88 for advanced technical information on wireless networks.
7.1.1 What You Can Do in this Chapter
This chapter describes the ZyXEL Device’s Network > Wireless LAN screens. Use these
screens to set up your ZyXEL Device’s wireless connection.
•The General screen lets you turn the wireless connection on or off, set up wireless
security and make other basic configuration changes (Section 7.4 on page 78).
• Use the WPS screen and the WPS Station screen to use WiFi Protected Setup (WPS).
WPS lets you set up a secure network quickly, when connecting to other WPS-enabled
devices.
Use the WPS screen (see Section 7.5 on page 84) to enable or disable WPS, generate a
security PIN (Personal Identification Number) and see information about the ZyXEL
Device’s WPS status.
Use the WPS Station (see Section 7.6 on page 85) screen to set up WPS by pressing a
button or using a PIN.
•The MAC Filter screen lets you configure the MAC filter to allow or block access to the
ZyXEL Device based on the MAC addresses of the wireless stations (Section 7.7 on page
86).
•The Advanced Setup screen lets you change the wireless mode, and make other advanced
wireless configuration changes (Section 7.8 on page 87).
You don’t necessarily need to use all these screens to set up your wireless connection. For
example, you may just want to set up a network name, a wireless radio channel and some
security in the General screen.
P-870HW-51a v2 User’s Guide
75
Page 76

Chapter 7 Wireless LAN
7.2 What You Need to Know
Wireless Basics
“Wireless” is essentially radio communication. In the same way that walkie-talkie radios send
and receive information over the airwaves, wireless networking devices exchange information
with one another. A wireless networking device is just like a radio that lets your computer
exchange information with radios attached to other computers. Like walkie-talkies, most
wireless networking devices operate at radio frequency b ands that are open to the public and
do not require a license to use. However, wireless networking is different from that of most
traditional radio communications in that there a number of wireless networking standards
available with different methods of data encryption.
Wireless Network Construction
Wireless networks consist of wireless clients, access points and bridges.
• A wireless client is a radio connected to a user’s computer.
• An access point is a radio with a wired connection to a network, which can connect with
numerous wireless clients and let them access the network.
• A bridge is a radio that relays communications between access points and wireless clients,
extending a network’s range.
Traditionally, a wireless network operates in one of two ways.
• An “infrastructure” type of network has one or more access points and one or more
wireless clients. The wireless clients connect to the access points.
• An “ad-hoc” type of network is one in which there is no access point. Wireless clients
connect to one another in order to exchange information.
Network Names
Each network must have a name, referred to as the SSID - “Service Set IDentifier”. The
“service set” is the network, so the “service set identifier” is the network’s name. This helps
you identify your wireless network when wireless networks’ coverage areas overlap and you
have a variety of networks to choose from.
Radio Channels
In the radio spectrum, there are certain frequency bands allocated for unlicensed, civilian use.
For the purposes of wireless networking, these bands are divided into numerous channels. This
allows a variety of networks to exist in the same place without interfering with one another.
When you create a network, you must select a channel to use.
Since the available unlicensed spectrum varies from one country to another, the number of
available channels also varies.
76
P-870HW-51a v2 User’s Guide
Page 77

Chapter 7 Wireless LAN
Wireless Security
By their nature, radio communications are simple to intercept. For wireless data networks, this
means that anyone within range of a wireless network without security can not only read the
data passing over the airwaves, but also join the network. Once an unauthorized person has
access to the network s/he can either steal information or introduce malware (malicious
software) intended to compromise the network. For these reasons, a variety of security
systems have been developed to ensure that only authorized people can use a wireless data
network, or understand the data carried on it.
These security standards do two things. First, they authenticate. This means that only people
presenting the right credentials (often a username and password, or a “key” phrase) can access
the network. Second, they encrypt. This means that the information sent over the air is
encoded. Only people with the code key can understand the information, and only peopl e who
have been authenticated are given the code key.
These security standards vary in effectiveness. Some can be broken, such as the old Wired
Equivalent Protocol (WEP). Using WEP is better than using no security at all, but it will not
keep a determined attacker out. Other security standards are secure in themselves but can be
broken if a user does not use them properly. For example, the WPA-PSK security standard is
perfectly secure if you use a long key which is difficult for an attacker’s software to guess - for
example, a twenty-letter long string of apparently random numbers and letters - but it is not
very secure if you use a short key which is very easy to guess - for example, a three-letter word
from the dictionary.
Because of the damage that can be done by a malicious attacker, it’s not just people who have
sensitive information on their network who should use security. Everybody who uses any
wireless network should ensure that effective security is in place.
A good way to come up with effective security keys, passwords and so on is to use obscure
information that you personally will easily remember, and to enter it in a way that appears
random and does not include real words. For example, if your mother owns a 1970 Dodge
Challenger and her favorite movie is Vanishing Point (which you know was made in 1971)
you could use “70dodchal71vanpoi” as your security key.
Signal Problems
Because wireless networks are radio networks, their signals are subject to limitations of
distance, interference and absorption.
Problems with distance occur when the two radios are too far apart. Problems with
interference occur when other radio waves interrupt the data signal. Interference may come
from other radio transmissions, such as military or air traffic control communications, or from
machines that are coincidental emitters such as electric motors or microwaves. Problems with
absorption occur when physical objects (such as thick walls) are between the two radios,
muffling the signal.
7.3 Before You Begin
Before you start using these screens, ask yourself the following questions. See Section 7.2 on
page 76 if some of the terms used here do not make sense to you.
P-870HW-51a v2 User’s Guide
77
Page 78

Chapter 7 Wireless LAN
• What wireless standards do the other wireless devices support (IEEE 802.11g, for
example)? What is the most appropriate standard to use?
• What security options do the other wireless devices support (WPA-PSK, for example)?
What is the best one to use?
• Do the other wireless devices support WPS (Wi-Fi Protected Setup)? If so, you can set up
a well-secured network very easily.
Even if some of your devices support WPS and some do not, you can use WPS to set up
your network and then add the non-WPS devices manually, although this is somewhat
more complicated to do.
• What advanced options do you want to configure, if any? If you want to configure
advanced options, ensure that you know precisely what you want to do. If you do not want
to configure advanced options, leave them alone.
7.4 The General Screen
" If you are configuring the ZyXEL Device from a computer connected to the
wireless LAN and you change the ZyXEL Device’s SSID or security settings,
you will lose your wireless connection when you press Apply to confirm. You
must then change the wireless settings of your computer to match the ZyXEL
Device’s new settings.
Click Network > Wireless LAN to open the General screen.
Figure 39 Network > Wireless LAN > General
78
P-870HW-51a v2 User’s Guide
Page 79

The following table describes the labels in this screen.
Table 18 Network > Wireless LAN > General
LABEL DESCRIPTION
Active Wireless
LAN
Network Name
(SSID)
Click the check box to activate wireless LAN.
The SSID (Service Set IDentity) identifies the service set with which a wireless device
is associated. Wireless devices associating to the access point (AP) must have the
same SSID. Enter a descriptive name (up to 32 printable 7-bit ASCII characters) for
the wireless LAN.
Note: If you are configuring the ZyXEL Device from a computer
connected to the wireless LAN and you change the ZyXEL
Device’s SSID or WEP settings, you will lose your wireless
connection when you press Apply to confirm. You must then
change the wireless settings of your computer to match the
ZyXEL Device’s new settings.
Hide Network
Name (SSID)
Channel
Selection
Security Mode See the following sections for more details about this field.
Apply Click this to save your changes back to the ZyXEL Device.
Reset Click this to reload the previous configuration for this screen.
Select this check box to hide the SSID in the outgoing beacon frame so a station
cannot obtain the SSID through scanning using a site survey tool.
Set the operating frequency/channel depending on your particular region.
Select a channel from the drop-down list box.
Chapter 7 Wireless LAN
7.4.1 No Security
Select No Security to allow wireless devices to communicate with the access points without
any data encryption or authentication.
" If you do not enable any wireless security on your ZyXEL Device, your network
is accessible to any wireless networking device that is within range.
P-870HW-51a v2 User’s Guide
79
Page 80

Chapter 7 Wireless LAN
Figure 40 Wireless LAN > General: No Security
The following table describes the labels in this screen.
Table 19 Wireless LAN > General: No Security
LABEL DESCRIPTION
Security Mode Choose No Security from the drop-down list box.
7.4.2 WEP Encryption
In order to configure and enable WEP encryption; click Network > Wireless LAN to display
the General screen. Select WEP from the Security Mode list.
80
P-870HW-51a v2 User’s Guide
Page 81

Figure 41 Wireless LAN > General: Static WEP Encryption
Chapter 7 Wireless LAN
The following table describes the wireless LAN security labels in this screen.
Table 20 Network > Wireless LAN > General: Static WEP Encryption
LABEL DESCRIPTION
Security Mode Choose Static WEP from the drop-down list box.
WEP
Encryption
Key 1 to Key 4 If you chose 64-bit WEP in the WEP Encryption field, then enter any 5 characters
7.4.3 WPA(2)-PSK
In order to configure and enable WPA(2)-PSK authentication; click Network > Wireless
LAN to display the General screen. Select WPA-PSK or WPA2-PSK from the Security
Mode list.
WEP (Wired Equivalent Privacy) provides data encryption to prevent unauthorized
wireless stations from accessing data transmitted over the wireless network.
Select 64-bit WEP or 128-bit WEP to enable data encryption.
(ASCII string) or 10 hexadecimal characters ("0-9", "A-F") preceded by 0x for each
key.
If you chose 128-bit WEP in the WEP Encryption field, then enter 13 characters
(ASCII string) or 26 hexadecimal characters ("0-9", "A-F") preceded by 0x for each
key.
There are four data encryption keys to secure your data from eavesdropping by
unauthorized wireless users. Both the ZyXEL Device and the wireless stations must
use the same WEP key for data transmission.
P-870HW-51a v2 User’s Guide
81
Page 82

Chapter 7 Wireless LAN
Figure 42 Wireless LAN > General: WPA(2)-PSK
The following table describes the wireless LAN security labels in this screen.
Table 21 Wireless LAN > General: WPA(2)-PSK
LABEL DESCRIPTION
Security Mode Choose WPA-PSK or WPA2-PSK from the drop-down list box.
Active Compatible This field is only available for WP A2-PSK. Select this if you want the ZyXEL
Pre-Shared Key The encryption mechanisms used for WPA(2) and WPA(2)-PSK are the same.
(WPA) Group Key
Update Timer
WPA Encryption Select the encryption type (TKIP or AES) for data encryption.
Device to support WPA-PSK and WPA2-PSK simultaneously.
The only difference between the two is that WPA(2)-PSK uses a simple common
password, instead of user-specific credentials.
Type a pre-shared key from 8 to 63 case-sensitive ASCII characters (including
spaces and symbols).
The (WPA) Group Key Update Timer is the rate at which the AP (if using
WPA(2)-PSK key management) or RADIUS server (if using WPAWPA(2) key
management) sends a new group key out to all clients. The re-keying process is
the WPA(2) equivalent of automatically changing the WEP key for an AP and all
stations in a WLAN on a periodic basis. Setting of the (WPA) Group Key Update
Timer is also supported in WPA(2)-PSK mode. The ZyXEL Device default is 1800
seconds (30 minutes).
7.4.4 WPA(2) Authentication
Use this screen to configure and enable WPA or WPA2 authentication; click the Wireless
LAN link under Network to display the General screen. Select WPA or WPA2 from the
Security Mode list.
82
P-870HW-51a v2 User’s Guide
Page 83

Figure 43 Wireless LAN > General: WPA(2)
Chapter 7 Wireless LAN
The following table describes the wireless LAN security labels in this screen.
Table 22 Wireless LAN > General: WPA(2)
LABEL DESCRIPTION
Security Mode Choose WPA or WPA2 from the drop-down list box.
Active Compatible This field is only available for WPA2. Select this if you want the ZyXEL Device to
support WPA and WPA2 simultaneously.
WPA Encryption Select the encryption type (TKIP or AES) for data encryption.
WPA2
Preauthentication
ReAuthentication
Timer
This field is available only when you select WPA2.
Pre-authentication enables fast roaming by allowing the wireless client (already
connecting to an AP) to perform IEEE 802.1x authentication with another AP
before connecting to it. Select Enabled to turn on preauthentication in WAP2.
Otherwise, select Disabled.
This field is available only when you select WPA2.
Specify how often wireless stations have to resend usernames and passwords in
order to stay connected. Enter a time interval between 10 and 9999 seconds.
The default time interval is 1800 seconds (30 minutes).
Note: If wireless station authentication is done using a RADIUS
server, the reauthentication timer on the RADIUS server
has priority.
Idle Timeout The ZyXEL Device automatically disconnects a wireless station from the wired
network after a period of inactivity. The wireless station needs to enter the
username and password again before access to the wired network is allowed.
The default time interval is 3600 seconds (or 1 hour).
P-870HW-51a v2 User’s Guide
83
Page 84

Chapter 7 Wireless LAN
Table 22 Wireless LAN > General: WPA(2)
LABEL DESCRIPTION
Group Key Update
Timer
Authentication Server
IP Address Enter the IP address of the external authentication server in dotted decimal
Port Number Enter the port number of the external authentication server. The default port
Shared Secret Enter a password (up to 31 alphanumeric characters) as the key to be shared
This field is available only when you select WPA.
The Group Key Update T i mer is the rate at which the AP (if using WPA(2)-PSK
key management) or RADIUS server (if using WPA(2) key management) sends
a new group key out to all clients. The re-keying process is the WPA(2)
equivalent of automatically changing the WEP key for an AP and all stations in a
WLAN on a periodic basis. Setting of the Group Key Update Timer is also
supported in WPA(2)-PSK mode. The ZyXEL Device default is 1800 seconds (30
minutes).
notation.
number is 1812.
You need not change this value unless your network administrator instructs you
to do so with additional information.
between the external authentication server and the ZyXEL Device.
The key must be the same on the external authentication server and your ZyXEL
Device. The key is not sent over the network.
7.5 The WPS Screen
Use this screen to configure WiFi Protected Setup (WPS) on your ZyXEL Device.
WPS allows you to quickly set up a wireless network with strong security, without having to
configure security settings manually . Set up each WPS connection between t wo devices. Both
devices must support WPS.
Click Network > Wireless LAN >WPS. The following screen displays.
Figure 44 Network > Wireless LAN > WPS
84
P-870HW-51a v2 User’s Guide
Page 85

Chapter 7 Wireless LAN
The following table describes the labels in this screen.
Table 23 Network > Wireless LAN > WPS
LABEL DESCRIPTION
WPS Setup
Enable WPS Select the check box to activate WPS on the ZyXEL Device.
PIN Number This shows the PIN (Personal Identification Number) of the ZyXEL Device. Enter
this PIN in the configuration utility of the device you want to connect to using WPS.
The PIN is not necessary when you use WPS push-button method.
Generate Click this button to have the ZyXEL Device create a new PIN.
WPS Status This displays Configured when the ZyXEL Device has connected to a wireless
network using WPS or Enable WPS is selected and wireless or wireless security
settings have been changed. The current wireless and wireless security settings
also appear in the screen.
This displays Unconfigured if WPS is disabled and there is no wireless or wireless
security changes on the ZyXEL Device or you click Release_Configuration to
remove the configured wireless and wireless security settings.
Release_Con
figuration
Apply Click Apply to save your changes back to the ZyXEL Device.
Refresh Click Refresh to reload the previous configuration for this screen.
This button is available when the WPS status is Configured.
Click this button to remove all configured wireless and wireless security settings for
WPS connections on the ZyXEL Device.
7.6 The WPS Station Screen
Use this screen to set up a WPS wireless network using either Push Button Configuration
(PBC) or PIN Configuration.
Click Network > Wireless LAN > WPS Station. The following screen displays.
Figure 45 Network > Wireless LAN > WPS Station
P-870HW-51a v2 User’s Guide
85
Page 86

Chapter 7 Wireless LAN
The following table describes the labels in this screen.
Table 24 Network > Wireless LAN > WPS Station
LABEL DESCRIPTION
Push Button Click this button to add another WPS-enabled wireless device (within wireless
range of the ZyXEL Device) to your wireless network. This button may either be a
physical button on the outside of device, or a menu button similar to the Push
Button on this screen.
Note: You must press the other wireless device’s WPS button within
two minutes of pressing this button.
Or input station's
PIN number
Enter the PIN of the device that you are setting up a WPS connection with and click
Start to authenticate and add the wireless device to your wireless network.
Y ou can find the PIN either on the outside of the device, or by checkin g the device’ s
settings.
Note: Y ou must also act ivate WPS on that device within two minutes
to have it present its PIN to the ZyXEL Device.
7.7 The MAC Filter Screen
This screen allows you to configure the ZyXEL Device to give exclusive access to specific
devices (Allow) or exclude specific devices from accessing the ZyXEL Device (Deny). Every
Ethernet device has a unique MAC (Media Access Control) address. The MAC address is
assigned at the factory and consists of six pairs of hexadecimal characters, for example,
00:A0:C5:00:00:02. You need to know the MAC addresses of the devices to configure this
screen.
Use this screen to change your ZyXEL Device’s MAC filter settings.Click Network >
Wireless LAN > MAC Filter. The following screen displays.
Figure 46 Wireless LAN > MAC Filter
86
P-870HW-51a v2 User’s Guide
Page 87

Chapter 7 Wireless LAN
The following table describes the labels in this screen.
Table 25 Wireless LAN > MAC Filter
LABEL DESCRIPTION
Active MAC
Filter
MAC Restrict
Mode
MAC
Address
Add Entries Click this to save and insert the entry to the table below.
Set
MAC
Address
Remove Select the entry(ies) that you want to delete in the Remove column, then click the
Apply Click this to save your changes back to the ZyXEL Device.
Remove Click this to delete the selected entry(ies).
Select the check box to enable MAC address filtering.
Define the filter action for the list of MAC addresses in the table below.
Select Allow to permit access to the ZyXEL Device, MAC addresses not listed will be
denied access to the ZyXEL Device.
Select Deny to block access to the ZyXEL Device, MAC addresses not listed will be
allowed to access the ZyXEL Device
Enter the MAC addresses of the wireless devices that are allowed or denied access to
the ZyXEL Device in these address fields. Enter the MAC addresses in a valid MAC
address format, that is, six hexadecimal character pairs, for example,
12:34:56:78:9a:bc.
This is the index number of the MAC address.
This is the MAC addresses of the wireless devices that are allowed or denied access to
the ZyXEL Device.
Remove button.
7.8 The Advanced Setup Screen
T o configure advanced wireless settings, click Network > Wir eless LAN > Advanced Setup.
The screen appears as shown.
Figure 47 Wireless LAN > Advanced Setup
P-870HW-51a v2 User’s Guide
87
Page 88

Chapter 7 Wireless LAN
The following table describes the labels in this screen.
Table 26 Wireless LAN > Advanced Setup
LABEL DESCRIPTION
RTS/CTS
Threshold
Fragmentation
Threshold
Number of
Wireless
Stations
Allowed
Output Power Set the output power of the ZyXEL Device. If there is a high density of APs in an area,
54gTM Mode Select 54g Auto to allow either IEEE 802.11b or IEEE 802.11g compliant WLAN
54gTM
Protection
Preamble Select a preamble type from the drop-down list menu. Choices are Long or Short.
Apply Click this to save your changes back to the ZyXEL Device.
Reset Click this to reload the previous configura tio n for this screen.
Enter a value between 0 and 2432.
This is the maximum data fragment size that can be sent. Enter a value between 256
and 2432.
Specify the maximum number of the wireless stations that may connect to the ZyXEL
Device.
decrease the output power to reduce interference with other APs. Se lect one of the
following 20%, 40%, 60%, 80% or 100%.
devices to associate with the ZyXEL Device. The ZyXEL Device adjusts the
transmission rate automatically according to the wireless standard supported by the
wireless devices.
Select 54g Performance to allow only IEEE 802.11b compliant WLAN devices to
associate with the ZyXEL Device.
Select 802.11b Only to allow either IEEE 802.11b or IEEE 802.11g compliant WLAN
devices to associate with the ZyXEL Device. In this mode, all wireless devices can
only transmit at the data rates supported by IEEE 802.11b.
Enabling this feature can help prevent collisions in mixed-mode networks (networks
with both IEEE 802.11b and IEEE 802.11g traffic).
Select Auto to have the wireless devices transmit data after a RTS/CTS handshake.
This helps improve IEEE 802.11g performance.
Select Off to disable 54g protection. The transmission rate of your ZyXEL Device
might be reduced in a mixed-mode network.
The default setting is Long. See the appendix for more information.
7.9 Technical Reference
This section discusses wireless LANs in depth. For more information, see the appendix.
7.9.1 Wireless Network Overview
The following figure provides an example of a wireless network.
88
P-870HW-51a v2 User’s Guide
Page 89

Figure 48 Example of a Wireless Network
Chapter 7 Wireless LAN
AP
A
The wireless network is the part in the blue circle. In this wireless network, devices A and B
use the access point (AP) to interact with the other devices (such as the printer) or with the
Internet. Your ZyXEL Device is the AP.
Every wireless network must follow these basic guidelines.
• Every device in the same wireless network must use the same SSID.
The SSID is the name of the wireless network. It stands for Service Set IDentity.
• If two wireless networks overlap, they should use a different channel.
Like radio stations or television channels, each wireless network uses a specific channel,
or frequency, to send and receive information.
• Every device in the same wireless network must use security compatible with the AP.
Security stops unauthorized devices from using the wireless network. It can also protect
the information that is sent in the wireless network.
B
P-870HW-51a v2 User’s Guide
89
Page 90

Chapter 7 Wireless LAN
7.9.2 Additional Wireless Terms
The following table describes some wireless network terms and acronyms used in the ZyXEL
Device’s Web Configurator.
Table 27 Additional Wireless Terms
TERM DESCRIPTION
RTS/CTS Threshold In a wireless network which covers a large area, wireless devices are
Preamble A preamble affects the timing in your wireless network. There are two
Authentication The process of verifying whether a wireless device is allowed to use the
Fragmentation
Threshold
sometimes not aware of each other’s presence. This may cause them to send
information to the AP at the same time and result in information colliding and
not getting through.
By setting this value lower than the default value, the wireless devices must
sometimes get permission to send information to the ZyXEL Device. The
lower the value, the more often the devices must get permission.
If this value is greater than the fragmentation threshold value (see below),
then wireless devices never have to get permission to send information to the
ZyXEL Device.
preamble modes: long and short. If a device uses a different preamble mode
than the ZyXEL Device does, it cannot communicate with the ZyXEL Device.
wireless network.
A small fragmentation threshold is recommended for busy networks, while a
larger threshold provides faster performance if the network is not very busy.
7.9.3 Wireless Security Overview
The following sections introduce different types of wireless security you can set up in the
wireless network.
7.9.3.1 SSID
Normally , the ZyXEL Device acts like a beacon and regularly broadcasts the SSID in the area.
You can hide the SSID instead, in which case the ZyXEL Device does not broadcast the SSID.
In addition, you should change the default SSID to something that is difficult to guess.
This type of security is fairly weak, however, because there are ways for unauthorized wireless
devices to get the SSID. In addition, unauthorized wireless devices can still see the
information that is sent in the wireless network.
7.9.3.2 MAC Address Filter
Every device that can use a wireless network has a unique identificatio n number, called a
MAC address.
example, 00A0C5000002 or 00:A0:C5:00:00:02. To get the MAC address for each device in
the wireless network, see the device’s User’s Guide or other documentation.
You can use the MAC address filter to tell the ZyXEL Device which devices are allowed or
not allowed to use the wireless network. If a device is allowed to use the wireless network, it
still has to have the correct information (SSID, channel, and security). If a device is not
allowed to use the wireless network, it does not matter if it has the correct information.
1
A MAC address is usually written using twelve hexadecimal characters2; for
90
1. Some wireless devices, such as scanners, can detect wireless networks but cannot use wireless networks.
These kinds of wireless devices might not have MAC addresses.
2. Hexadecimal characters are 0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, A, B, C, D, E, and F.
P-870HW-51a v2 User’s Guide
Page 91

This type of security does not protect the information that is sent in the wireless network.
Furthermore, there are ways for unauthorized wireless devices to get the MAC address of an
authorized device. Then, they can use that MAC address to use the wireless network.
7.9.3.3 User Authentication
Authentication is the process of verifying whether a wireless device is allowed to use the
wireless network. You can make every user log in to the wireless network before they can use
it. However, every device in the wireless network has to support IEEE 802.1x to do this.
For wireless networks, you can store the user names and passwords for each user in a RADIUS
server. This is a server used in businesses more than in homes. If you do not have a RADIUS
server, you cannot set up user names and passwords for your users.
Unauthorized wireless devices can still see the information that is sent in the wireless network,
even if they cannot use the wireless network. Furthermore, there are ways for unauthorized
wireless users to get a valid user name and password. Then, they can use that user name and
password to use the wireless network.
7.9.3.4 Encryption
Wireless networks can use encryption to protect the information that is sent in the wireless
network. Encryption is like a secret code. If you do not know the secret code, you cannot
understand the message.
Chapter 7 Wireless LAN
The types of encryption you can choose depend on the type of authentication. (See Section
7.9.3.3 on page 91 for information about this.)
Table 28 Types of Encryption for Each Type of Authentication
NO AUTHENTICATION RADIUS SERVER
Weakest No Security
Static WE P
WPA-PSK
Strongest WPA2-PSK WPA2
For example, if the wireless network has a RADIUS server, you can choose WPA or WPA2. If
users do not log in to the wireless network, you can choose no encryption, Static WEP, WPA-
PSK, or WPA2-PSK.
Usually, you should set up the strongest encryption that every device in the wireless network
supports. For example, suppose you have a wireless network with the ZyXEL Device and you
do not have a RADIUS server. Therefore, there is no authentication. Suppose the wireless
network has two devices. Device A only supports WEP, and device B supports WEP and
WPA. Therefore, you should set up Static WEP in the wireless network.
WPA
" It is recommended that wireless networks use WPA-PSK, WPA, or stronger
encryption. The other types of encryption are better than none at all, but it is
still possible for unauthorized wireless devices to figure out the original
information pretty quickly.
P-870HW-51a v2 User’s Guide
91
Page 92

Chapter 7 Wireless LAN
When you select WPA2 or WPA2-PSK in your ZyXEL Device, you can also select an option
(WPA compatible) to support WPA as well. In this case, if some of the devices support WPA
and some support WPA2, you should set up WPA2-PSK or WPA2 (depending on the type of
wireless network login) and select the WPA compatible option in the ZyXEL Device.
Many types of encryption use a key to protect the information in the wireless network. The
longer the key, the stronger the encryption. Every device in the wireless network must have the
same key.
7.9.4 WiFi Protected Setup
Your ZyXEL Device supports WiFi Protected Setup (WPS), which is an easy way to set up a
secure wireless network. WPS is an industry standard specification, defined by the WiFi
Alliance.
WPS allows you to quickly set up a wireless network with strong security, without having to
configure security settings manually. Each WPS connection works between two devices. Both
devices must support WPS (check each device’s documentation to make sure).
Depending on the devices you have, you can either press a button (on the device itself, or in its
configuration utility) or enter a PIN (a unique Personal Identification Number that allows one
device to authenticate the other) in each of the two devices. When WPS is activated on a
device, it has two minutes to find another device that also has WPS activated. Then, the two
devices connect and set up a secure network by themselves.
7.9.4.1 Push Button Configuration
WPS Push Button Configuration (PBC) is initiated by pressing a button on each WPS-enabled
device, and allowing them to connect automatically. You do not need to enter any information.
Not every WPS-enabled device has a physical WPS button. Some may have a WPS PBC
button in their configuration utilities instead of or in addition to the physical button.
Take the following steps to set up WPS using the button.
1 Ensure that the two devices you want to set up are within wireless range of one another.
2 Look for a WPS button on each device. If the device does not have one, log into its
configuration utility and locate the button (see the device’s User’s Guide for how to do
this - for the ZyXEL Device, see Section 7.6 on page 85).
3 Press the button on one of the devices (it doesn’t matter which). For the ZyXEL Device
you must press the WPS button for more than three seconds.
4 W ithin two minutes, press the button on the other device. The registrar sends the network
name (SSID) and security key through an secure connection to the enrollee.
If you need to make sure that WPS worked, check the list of associated wireless clients in the
AP’s configuration utility. If you see the wireless client in the list, WPS was successful.
7.9.4.2 PIN Configuration
Each WPS-enabled device has its own PIN (Personal Identification Number). This may either
be static (it cannot be changed) or dynamic (in some devices you can generate a new PIN by
clicking on a button in the configuration interface).
92
P-870HW-51a v2 User’s Guide
Page 93

Chapter 7 Wireless LAN
Use the PIN method instead of the push-button configuration (PBC) method if you want to
ensure that the connection is established between the devices you specify, not just the first two
devices to activate WPS in range of each other. However, you need to log into the
configuration interfaces of both devices to use the PIN method.
When you use the PIN method, you must enter the PIN from one device (usually the wireless
client) into the second device (usually the Access Point or wireless router). Then, when WPS
is activated on the first device, it presents its PIN to the second device. If the PIN matches, one
device sends the network and security information to the other, allowing it to join the network.
Take the following steps to set up a WPS connection between an access point or wireless
router (referred to here as the AP) and a client device using the PIN method.
1 Ensure WPS is enabled on both devices.
2 Access the WPS section of the AP’s configuration interface. See the device’s User’s
Guide for how to do this.
3 Look for the client’s WPS PIN; it will be displayed either on the device, or in the WPS
section of the client’s configuration interface (see the device’s User’s Guide for how to
find the WPS PIN - for the ZyXEL Device, see Section 7.5 on page 84).
4 Enter the client’s PIN in the AP’s configuration interface.
" If the client device’s configuration interface has an area for entering another
device’s PIN, you can either enter the client’s PIN in the AP, or enter the AP’s
PIN in the client - it does not matter which.
5 Start WPS on both devices within two minutes.
" Use the configuration utility to activate WPS, not the push-button on the device
itself.
6 On a computer connected to the wireless client, try to connect to the Internet. If you can
connect, WPS was successful.
If you cannot connect, check the list of associated wireless clients in the AP’s
configuration utility. If you see the wireless client in the list, WPS was successful.
The following figure shows a WPS-enabled wireless client (installed in a notebook computer)
connecting to the WPS-enabled AP via the PIN method.
P-870HW-51a v2 User’s Guide
93
Page 94

Chapter 7 Wireless LAN
Figure 49 Example WPS Process: PIN Method
ENROLLEE
REGISTRAR
WPS
This device’s
WPS PIN: 123456
WPS
Enter WPS PIN
from other device:
7.9.4.3 How WPS Works
When two WPS-enabled devices connect, each device must assume a specific role. One device
acts as the registrar (the device that supplies network and security settings) and the other
device acts as the enrollee (the device that receives network and security settings. The registrar
creates a secure EAP (Extensible Authentication Protocol) tunnel and sends the network name
(SSID) and the WPA-PSK or WPA2-PSK pre-shared key to the enrollee. Whether WPA-PSK
or WPA2-PSK is used depends on the standards supported by the devices. If the registrar is
already part of a network, it sends the existing information. If not, it generates the SSID and
WPA(2)-PSK randomly.
WPS
START
WITHIN 2 MINUTES
SECURE EAP TUNNEL
SSID
WPA(2)-PSK
COMMUNICATION
WPS
START
94
The following figure shows a WPS-enabled client (installed in a notebook computer)
connecting to a WPS-enabled access point.
P-870HW-51a v2 User’s Guide
Page 95

Figure 50 How WPS works
Chapter 7 Wireless LAN
ACTIVATE
WPS
WITHIN 2 MINUTES
WPS HANDSHAKE
SECURE TUNNEL
SECURITY INFO
COMMUNICATION
ACTIVATE
WPS
REGISTRARENROLLEE
The roles of registrar and enrollee last only as long as the WPS setup process is active (two
minutes). The next time you use WPS, a different device can be the registrar if necessary.
The WPS connection process is like a handshake; only two devices participate in each WPS
transaction. If you want to add more devices you should repeat the process with one of the
existing networked devices and the new device.
Note that the access point (AP) is not always the registrar, and the wireless client is not always
the enrollee. All WPS-certified APs can be a registrar, and so can some WPS-enabled wireless
clients.
By default, a WPS devices is “unconfigured”. This means that it is not part of an existing
network and can act as either enrollee or registrar (if it supports both functions). If the registrar
is unconfigured, the security settings it transmits to the enrollee are randomly-generated. Once
a WPS-enabled device has connected to another device using WPS, it becomes “configured”.
A configured wireless client can still act as enrollee or registrar in subsequent WPS
connections, but a configured access point can no longer act as enrollee. It will be the registrar
in all subsequent WPS connections in which it is involved. If you want a configured AP to act
as an enrollee, you must reset it to its factory defaults.
7.9.4.4 Example WPS Network Setup
This section shows how security settings are distributed in an example WPS setup.
The following figure shows an example network. In step 1, both AP1 and Client 1 are
unconfigured. When WPS is activated on both, they perform the handshake. In this example,
AP1 is the registrar, and Client 1 is the enrollee. The registrar randomly generates the security
information to set up the network, since it is unconfigured and has no existing information.
P-870HW-51a v2 User’s Guide
95
Page 96

Chapter 7 Wireless LAN
Figure 51 WPS: Example Network Step 1
CLIENT 1
In step 2, you add another wireless client to the network. You know that Client 1 supports
registrar mode, but it is better to use AP1 for the WPS handshake with the new client since
you must connect to the access point anyway in order to use the network. In this case, AP1
must be the registrar, since it is configured (it already has security information for the
network). AP1 supplies the existing security information to Client 2.
Figure 52 WPS: Example Network Step 2
REGISTRARENROLLEE
SECURITY INFO
AP1
REGISTRAR
EXISTING CONNECTION
CLIENT 1
ENROLLEE
O
F
N
I
Y
T
I
R
U
C
E
S
AP1
CLIENT 2
In step 3, you add another access point (AP2) to your network. AP2 is out of range of AP1, so
you cannot use AP1 for the WPS handshake with the new access point. However, you know
that Client 2 supports the registrar function, so you use it to perform the WPS handshake
instead.
96
P-870HW-51a v2 User’s Guide
Page 97

Figure 53 WPS: Example Network Step 3
EXISTING CONNECTION
CLIENT 1
G
N
I
T
S
I
X
E
REGISTRAR
Chapter 7 Wireless LAN
N
O
I
T
C
E
N
N
O
C
AP1
CLIENT 2
7.9.4.5 Limitations of WPS
WPS has some limitations of which you should be aware.
• WPS works in Infrastructure networks only (where an AP and a wireless client
communicate). It does not work in Ad-Hoc networks (where there is no AP).
• When you use WPS, it works between two devices only. You cannot enroll multiple
devices simultaneously, you must enroll one after the other.
For instance, if you have two enrollees and one registrar you must set up the first enrollee
(by pressing the WPS button on the registrar and the first enrollee, for example), then
check that it successfully enrolled, then set up the second device in the same way.
• WPS works only with other WPS-enabled devices. However, you can still add non-WPS
devices to a network you already set up using WPS.
WPS works by automatically issuing a randomly-generated WPA-PSK or WPA2-PSK
pre-shared key from the registrar device to the enrollee devices. Whether the network uses
WPA-PSK or WPA2-PSK depends on the device. You can check the configuration
interface of the registrar device to discover the key the network is using (if the device
supports this feature). Then, you can enter the key into the non-WPS device and join the
network as normal (the non-WPS device must also support WPA-PSK or WPA2-PSK).
• When you use the PBC method, there is a short period (from the moment you press the
button on one device to the moment you press the button on the other device) when any
WPS-enabled device could join the network. This is because the registrar has no way of
identifying the “correct” enrollee, and cannot differentiate between your enrollee and a
rogue device. This is a possible way for a hacker to gain access to a network.
S
E
C
U
R
I
T
Y
I
N
F
O
ENROLLEE
AP2
P-870HW-51a v2 User’s Guide
97
Page 98

Chapter 7 Wireless LAN
You can easily check to see if this has happened. WPS works between only two devices
simultaneously , so if another device has enrolled your device will be unable to enroll, and
will not have access to the network. If this happens, open the access point’s configuration
interface and look at the list of associated clients (usually displayed by MAC address). It
does not matter if the access point is the WPS registrar, the enrollee, or was not involved
in the WPS handshake; a rogue device must still associate with the access point to gain
access to the network. Check the MAC addresses of your wireless clients (usually printed
on a label on the bottom of the device). If there is an unknown MAC address you can
remove it or reset the AP.
98
P-870HW-51a v2 User’s Guide
Page 99

CHAPTER 8
Network Address Translation
(NAT)
8.1 Overview
This chapter discusses how to configure NAT on the ZyXEL Device.
Network Address Translation (NAT, RFC 1631) is the translation of the IP address of a host in
a packet, for example, the source address of an outgoing packet, used within one network to a
different IP address known within another network.
8.1.1 What You Can Do in this Chapter
The Port Forwarding screen lets you configure forward incoming service requests to the
server(s) on your local network (Section 8.3 on page 99).
8.2 What You Need to Know
The following terms and concepts may help as you read through this chapter.
NAT
In the simplest form, NAT changes the source IP address in a packet received from a
subscriber (the inside local address) to another (the inside global address) before forwarding
the packet to the WAN side. When the response comes back, NAT translates the destination
address (the inside global address) back to the inside local address before forwarding it to the
original inside host.
Port Forwarding
A port forwarding set is a list of inside (behind NAT on the LAN) servers, for example, web or
FTP, that you can make visible to the outside world even though NAT makes your whole
inside network appear as a single computer to the outside world.
8.3 The Port Forwarding Screen
This summary screen provides a summary of all port forwarding rules and their configuration.
In addition, this screen allows you to create new port forwarding rules and delete existing
rules.
P-870HW-51a v2 User’s Guide
99
Page 100

Chapter 8 Network Address Translation (NAT )
You may enter a single port number or a range of port numbers to be forwarded, and the local
IP address of the desired server. The port number identifies a service; for example, web service
is on port 80 and FTP on port 21. In some cases, such as for unknown services or where one
server can support more than one service (for example both FTP and web service), it might be
better to specify a range of port numbers. Y ou can allocate a server IP address that corresponds
to a port or a range of ports.
" Many residential broadband ISP accounts do not allow you to run any server
processes (such as a Web or FTP server) from your location. Your ISP may
periodically check for servers and may suspend your account if it discovers
any active services at your location. If you are unsure, refer to your ISP.
To access this screen, click Network > NAT. The following screen appears.
Figure 54 NAT Port Forwarding
The following table describes the labels in this screen.
Table 29 NAT Port Forwarding
LABEL DESCRIPTION
Service Name Select a pre-defined service from the drop-down list box. The pre-defined service
WAN Interface Select the WAN interface through which the service is forwarded.
Server IP
Address
External Port
Start
External Port
End
port number(s) and protocol will display in the External port, Internal port and
Protocol fields.
Otherwise, select User Define to open the Rule Setup screen where you can
manually enter the port number(s) and select the IP protocol.
Enter the IP address of the server for the specified service.
Enter the original destination port for the packets.
To forward only one port, enter the port number again in the External Port End
field.
To forward a series of ports, enter the start port number here and the end port
number in the External Port End field.
Enter the last port of the original destination port range.
To forward only one port, enter the port number in the External Port Start field
above and then enter it again in this field.
To forward a series of ports, enter the last port number in a series that begins with
the port number in the External Port Start field above.
100
P-870HW-51a v2 User’s Guide
 Loading...
Loading...