Page 1

ZyXEL AG-225H User’s Guide
ZyXEL AG-225H
802.11a/b/g Wi-Fi Finder & USB Adapter
User's Guide
Version 2.1
September 2005
Page 2

ZyXEL AG-225H User’s Guide
Copyright
Copyright ©2005 by ZyXEL Communications Corporation
The contents of this publication may not be reproduced in any part or as a whole, transcribed, stored in a
retrieval system, translated into any language, or transmitted in any form or by any means, electronic,
mechanical, magnetic, optical, chemical, photocopying, manual, or otherwise, without the prior written
permission of ZyXEL Communications Corporati on.
Published by ZyXEL Communications Corporation. All rights reserved.
Disclaimer
ZyXEL does not assume any liability arising out of the application or use of any products, or software
described herein. Neither does it convey any license under its patent rights nor the patents' rights of others.
ZyXEL further reserves the right to make changes in any products described herein without notice. This
publication is subject to change without notice.
Trademarks
Trademarks mentioned in this publication are used for identification purposes only and may be properties
of their respective owners.
ii Copyright
Page 3

ZyXEL Limited Warranty
ZyXEL warrants to the original end user (purchaser) that this product is free from any defects in materials
or workmanship for a period of up to one (2) years from the date of purchase. During the warranty period
and upon proof of purchase, should the product have indications of failure due to faulty workmanship
and/or materials, ZyXEL will, at its discretion, repair or replace the defective products or com ponents
without charge for either parts or labor and to whatever extent it shall deem necessary to restore the product
or components to proper operating condition. Any replacement will consist of a new or re-manufactured
functionally equivalent product of equal value, and will be solely at the discretion of ZyXEL. This warranty
shall not apply if the product is modified, misused, tampered with, damaged by an act of God, or subjected
to abnormal working conditions.
NOTE
Repair or replacement, as provided under this warranty, is the exclusive remedy of the purchaser. This
warranty is in lieu of all other warranties, express or implied, including any implied warranty of
merchantability or fitness for a particular use or purpose. ZyXEL shall in no event be held liable for
indirect or consequential damages of any kind of character to the purchaser.
To obtain the services of this warranty, contact ZyXEL's Service Center for your Return Material
Authorization (RMA) number. Products must be returned Postage Prepaid. It is recommended that the unit
be insured when shipped. Any returned products without proof of purchase or those with an out-dated
warranty will be repaired or replaced (at the discretion of ZyXEL) and the customer will be billed for parts
and labor. All repaired or replaced products will be shipped by ZyXEL to the corresponding return address,
Postage Paid. This warranty gives you specific legal rights, and you may also have other rights that vary
from country to country.
Online Registration
-Please click “Product Registration” in the installation program of your support CD for the online
registration.
-Register online at www.zyxel.com
for free future product updates and information.
ZyXEL Limited Warranty iii
Page 4

ZyXEL AG-225H User’s Guide
Federal Communications Commission (FCC)
Interference Statement
This equipment has been tested and found to comply with the limits for a Class B digital device, pursuant to
Part 15 of the FCC Rules. These limits are designed to provide reasonable protection against harmful
interference in a residential installation. This equipment generates, uses and can radiate radio frequency
energy and, if not installed and used in accordance with the instructions, may cause harmful interference to
radio communications. However, there is no guarantee that interference will not occur in a particular
installation. If this equipment does cause harmful interference to radio or television reception, which can be
determined by turning the equipment off and on, the user is encouraged to try to correct the interference by
one of the following measures:
- Reorient or relocate the receiving antenna.
- Increase the separation between the equipment and receiver.
- Connect the equipment into an outlet on a circuit different from that to which the receiver is
connected.
- Consult the dealer or an experienced radio/TV technician for help.
This device complies with Part 15 of the FCC Rules. Operation is subject to the following two conditions: (1)
This device may not cause harmful interference, and (2) this device must accept any interference received,
including interference that may cause undesired operati on.
FCC Caution: Any changes or modifications not expressly approved by the party responsible for compliance
could void the user's authority to operate this equipment.
IMPORTANT NOTE:
FCC Radiation Exposure Statement:
This equipment complies with FCC radiation exposure limits set forth for an uncontrolled enviro nment. This
equipment should be installed and operated with minimum distance 20cm between the radiator & your body.
If this device is going to be operated in 5.15 ~ 5.25GHz frequency range, then it is restricted in indoor
environment only.
This transmitter must not be co-located or operating in conjunction with any other antenna or transmitter.
iv FCC Statement
Page 5

Customer Support
When contacting your Customer Support Representative, please have the following information ready:
! Product model and serial number.
! Warranty Information.
! Date you received your product.
! Brief description of the problem and the steps you took to solve it.
LOCATION
CORPORATE
HEADQUARTERS
(WORLDWIDE)
NORTH
AMERICA
CZECH
REPUBLIC
DENMARK
FINLAND
FRANCE
GERMANY
SUPPORT E-MAIL TELEPHONE1 WEB SITE METHOD
SALES E-MAIL FAX FTP SITE
support@zyxel.com.tw +886-3-578-3942 www.zyxel.com
www.europe.zyxel.com
sales@zyxel.com.tw
support@zyxel.com
info@cz.zyxel.com +420 241 091 350 www.zyxel.cz
info@cz.zyxel.com
support@zyxel.dk +45 39 55 07 00 www.zyxel.dk
sales@zyxel.dk +45 39 55 07 07
support@zyxel.fi +358-9-4780-8411
sales@zyxel.fi
info@zyxel.fr +33 (0)4 72 52 97 97 www.zyxel.fr
+33 (0)4 72 52 19 20
support@zyxel.de +49-2405-6909-0 www.zyxel.de
sales@zyxel.de +49-2405-6909-99
sales@zyxel.com
+886-3-578-2439 ftp.zyxel.com
ftp.europe.zyxel.com
+1-800-978-7222
+1-714-632-0882
+420 241 091 359
+358-9-4780 8448
+1-714-632-0858 ftp.us.zyxel.com
www.us.zyxel.com ZyXEL Communications Inc.
www.zyxel.fi
ZyXEL Communications Corp.
6 Innovation Road II
Science Park
Hsinchu 300
Taiwan
1130 N. Miller St.
Anaheim
CA 92806-2001
U.S.A.
ZyXEL Communications Czech s.r.o.
Modranská 621
143 01 Praha 4 – Modrany
Ceská Republika
ZyXEL Communications A/S
Columbusvej 5
2860 Soeborg
Denmark
ZyXEL Communications Oy
Malminkaari 10
00700 Helsinki
Finland
ZyXEL France
1 rue des Vergers
Bat. 1 / C
69760 Limonest
France
ZyXEL Deutschland GmbH.
Adenauerstr. 20/A2 D-52146
Wuerselen
Germany
REGULAR MAIL
1
“+” is the (prefix) number you enter to make an international telephone call.
Customer Support v
Page 6
ZyXEL AG-225H User’s Guide
LOCATION
NORWAY
SPAIN
SWEDEN
UNITED
KINGDOM
SUPPORT E-MAIL TELEPHONE1 WEB SITE METHOD
SALES E-MAIL FAX FTP SITE
support@zyxel.no +47 22 80 61 80 www.zyxel.no
sales@zyxel.no
support@zyxel.es +34 902 195 420 www.zyxel.es
sales@zyxel.es +34 913 005 345
support@zyxel.se +46 31 744 7700 www.zyxel.se
sales@zyxel.se
support@zyxel.co.uk +44 (0) 1344 303044
sales@zyxel.co.uk
+47 22 80 61 81
+46 31 744 7701
www.zyxel.co.uk
08707 555779 (UK
only)
+44 (0) 1344 303034 ftp.zyxel.co.uk
REGULAR MAIL
ZyXEL Communications A/S
Nils Hansens vei 13
0667 Oslo
Norway
ZyXEL Communications
Alejandro Villegas 33
1º, 28043 Madrid
Spain
ZyXEL Communications A/S
Sjöporten 4, 41764 Göteborg
Sweden
ZyXEL Communications UK Ltd.,
11, The Courtyard, Eastern Road,
Bracknell, Berkshire, RG12 2XB,
United Kingdom (UK)
vi FCC Statement
Page 7

ZyXEL AG-225H User’s Guide
Table of Contents
Copyright.......................................................................................................................................................ii
ZyXEL Limited Warranty..........................................................................................................................iii
Federal Communications Commission (FCC) Interference Statement...................................................iv
Customer Support.........................................................................................................................................v
Preface............................................................................................................................................................x
Chapter 1 Getting Started.........................................................................................................................1-1
1.1 About Your ZyXEL AG-225H.......................................................................................................1-1
1.2 ZyXEL AG-225H Wi-Fi Finder User Interface............................................................................1-1
1.3 LCM Description..........................................................................................................................1-2
1.4 Basic Operation...........................................................................................................................1-2
1.5 ZyXEL AG-225H Adapter Hardware and Utility Installation......................................................1-2
1.6 Using the ZyXEL Utility to Configure Your Network...................................................................1-2
1.6.1 Network................................................................................................................................1-4
1.6.2 Profile...................................................................................................................................1-5
1.6.3 Site Survey.........................................................................................................................1-13
1.6.4 Options...............................................................................................................................1-16
1.6.5 Version...............................................................................................................................1-17
1.7 ZyAIR Modes..............................................................................................................................1-17
1.7.1 Change ZyAIR Modes .......................................................................................................1-18
Chapter 2 Wireless LAN Networking......................................................................................................2-1
2.1 Overview......................................................................................................................................2-1
2.1.1 SSID.....................................................................................................................................2-1
2.1.2 Channel................................................................................................................................2-1
2.1.3 Transmission Rate (Transfer Rate) ......................................................................................2-1
2.1.4 Wireless Network Application.............................................................................................2-1
2.1.5 Roaming............................................................................................................................... 2-3
2.2 Wireless LAN Security .................................................................................................................2-4
vii Table of Contents
Page 8

ZyXEL AG-225H User’s Guide
2.2.1
Data Encryption with WEP..................................................................................................2-5
2.2.2 IEEE 802.1x.........................................................................................................................2-5
2.2.3 WPA/WPA2.........................................................................................................................2-6
2.2.4 WPA-PSK/WPA2-PSK Application Example....................................................................2-7
2.2.5 WPA/WPA2 with RADIUS Application Example..............................................................2-7
2.3 Fragmentation Threshold............................................................................................................2-8
2.4 RTS/CTS Threshold......................................................................................................................2-8
2.5 Authentication Type.....................................................................................................................2-9
Chapter 3 Access Point Mode Configuration..........................................................................................3-1
3.1 Introduction................................................................................................................................. 3-1
3.1.1 Additional Setup Requirements...........................................................................................3-1
3.2 The Profile Screen .......................................................................................................................3-1
3.3 How to configure in Access Point Mode......................................................................................3-3
3.3.1 Profile ..................................................................................................................................3-3
3.3.2 The MAC Filter ...................................................................................................................3-8
3.3.3 Version...............................................................................................................................3-10
Chapter 4 Maintenance.......................................................................................................... ...................4-1
4.1 The Version Screen......................................................................................................................4-1
4.2 Uninstalling the ZyXEL Utility.................................................................................................... 4-2
4.3 Upgrading the ZyXEL Utility.......................................................................................................4-3
Chapter 5 Configuring Wireless Security................................................................................................5-1
5.1 Configuring Security ...................................................................................................................5-1
5.2 Configuring WEP.........................................................................................................................5-1
5.3 Configuring WPA-PSK................................................................................................................5-3
5.4 Configuring WPA2-PSK..............................................................................................................5-4
Chapter 6 Troubleshooting.......................................................................................................................6-1
6.1 Problems Starting the ZyXEL Utility Program............................................................................6-1
6.2 Problem with the Link Status.......................................................................................................6-1
6.3 Problems Communicating With Other Computers ......................................................................6-2
viii Table Of Contents
Page 9

6.4
Problem Connecting to an Access Point......................................................................................6-2
Table Of Contents ix
Page 10

ZyXEL AG-225H User’s Guide
Preface
Congratulations on the purchase of your new ZyXEL AG-225H!
About This User's Guide
This manual provides information about the ZyXEL Wireless LAN Utility.
Syntax Conventions
• “Type” or “Enter” means for you to type one or more characters. "Select" or "Choose" means for
you to use one of the predefined choices.
• Mouse action sequences are denoted using a comma. For example, “click the Apple icon, Control
Panels and then Modem” means first click the Apple icon, then point your mouse pointer to
Control Panels and then click Modem.
• Window and command choices are in Bold Times New Roman font. Predefined field choices are
in Bold Arial font.
• The ZyXEL AG-225H 802.11a/g Wireless USB 2.0 Adapter is referre d to as the ZyXEL AG 225H in this guide.
• The ZyXEL Wireless LAN Utility may be referred to as the ZyXEL WLAN Utility or, simply, as
the ZyXEL Utility in this guide.
•
Related Documentation
! Support Disk
Refer to the included CD for support documents and device drivers.
! Quick Start Guide
Our Quick Start Guide is designed to help you get your ZyXEL AG-225H up and running right
away. It contains a detailed easy-to-follow connection diagram and information on installing your
ZyXEL AG-225H.
! ZyXEL Glossary and Web Site
Please refer to www.zyxel.com
documentation.
User Guide Feedback
Help us help you. E-mail all User’s Guide-related comments, questions or suggestions for improvement to
techwriters@zyxel.com.tw or send regular mail to The Technical Writing Team, ZyXEL Communications
Corp., 6 Innovation Road II, Science Part, Hsin-Chu, Taiwan. Thank you.
for an online glossary of networking terms and additional support
x Preface
Page 11
Graphics Icons Key
Wireless Access Point
Server
Telephone
Computer
Modem
Switch
Notebook computer
Wireless Signal
Router
Preface xi
Page 12

Page 13
Chapter 1
Getting Started
This chapter introduces the ZyXEL AG-225H and prepares you to use the ZyXEL Utility.
1.1 About Your ZyXEL AG-225H
The ZyXEL AG-225H is an IEEE 802.11a, 802.11b, and 802.11g compliant wireless LAN adapter. With
the ZyXEL AG-225H, you can enjoy wireless mobility within almost any wireless networking environment.
The following lists the main features of your ZyXEL AG-225H.
•
ZyXEL AG-225H Wireless USB 2.0 Client Adapter with Integrated Hotspot Finder
•
ZyXEL AG-225H can communicate with other IEEE 802.11a/b/g compliant wireless devices.
•
Automatic rate selection.
•
Standard data transmission rates up to 54 Mbps.
•
Offers 64-bit, 128-bit and 256-bit WEP (Wired Equivalent Privacy) data encryption for network
security.
•
Supports IEEE802.1x, WPA (Wi-Fi Protected Access) and WPA2.
•
Support Soft-AP.
•
Low CPU utilization allowing more computer system resources for other programs.
•
A built-in antenna.
•
Driver support for Windows XP/2000.
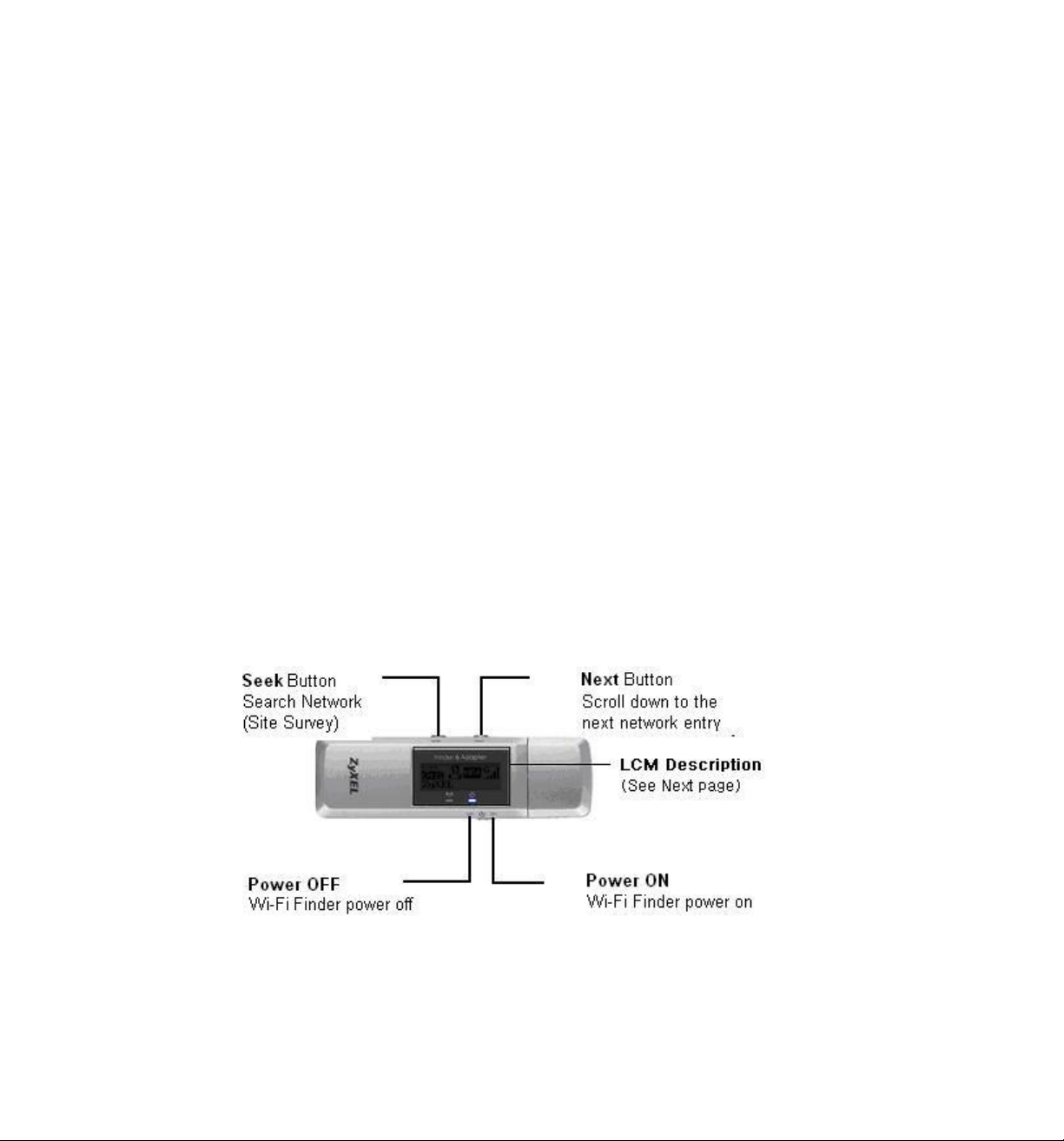
1.2 ZyXEL AG-225H Wi-Fi Finder User Interface
Getting Started 1-1
Page 14
ZyXEL AG-225H User’s Guide
A
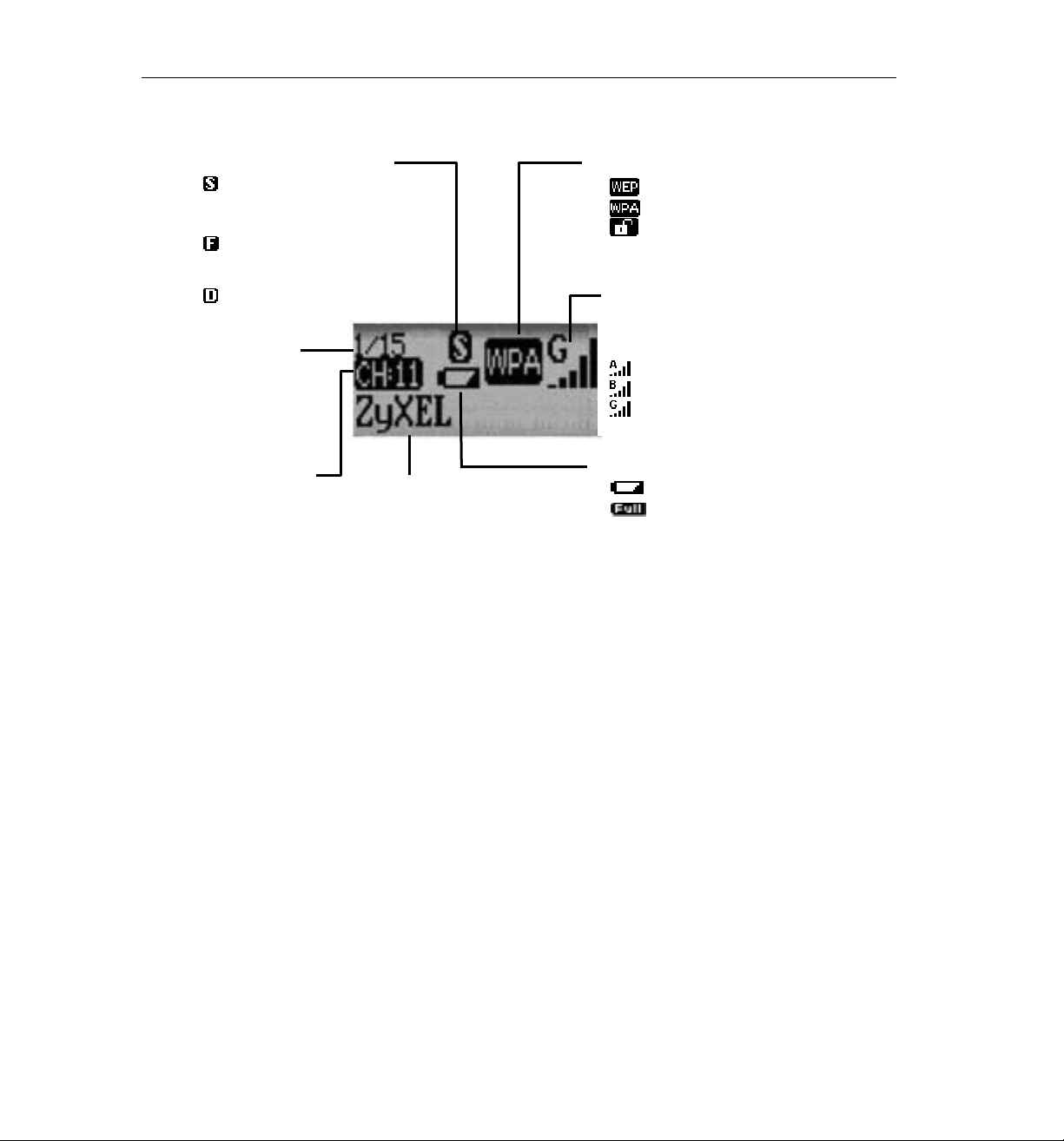
1.3 LCM Description
Detect Mode
Display up to 15 detected
networks in the order of the
signal strength
Display the detected networks
without any security setting
(free hot spot).
Display the dedicated network
you choose to use
Entry
Display the current
entry of the detected
ccess Points. Users
can detect up to 15
networks at one time.
Channel
Display the radio
channel of the
detected network.
SSID
The SSID identifies the Service Set
to the network users detect. When
the length of SSID is longer than 12
characters, it will be scrolled
horizontally.
Security Information
WEP security is enabled.
WPA security is enabled.
Wireless security is disabled
(no security)
Signal
Indicate A/B/G World Wide Radio
Band.
5 levels of signal strength.
802.11a mode at 5 GHz band
802.11b mode at 2.4 GHz band
802.11g mode at 2.4 GHz band
Power
Display Low Battery
Display Full Battery
1.4 Basic Operation
Follow the instructions in the Quick Start Guide to know how to operate AG-225H Wi-Fi Finder Mode.
1.5 ZyXEL AG-225H Adapter Hardware and Utility Installation
Follow the instructions in the Quick Start Guide to install the ZyXEL Utility and make hardware
connections.
1.6 Using the ZyXEL Utility to Configure Your Network
The following are explanations on how to configure and use the ZyXEL Utility program. For initial
setup, please see the included Quick Start Guide.
1-2 Getting Started
Page 15
After completing the installation procedure, a Z icon as shown below will automatically appear in the
lower right tray bar.
Double-clicking on the icon will display the following ZyXEL utility window.
Each of the pages (Network, Profile, Site Survey, Options, Version) presented in the ZyXEL Utility are
explained in the following sections.
Getting Started 1-3
Page 16
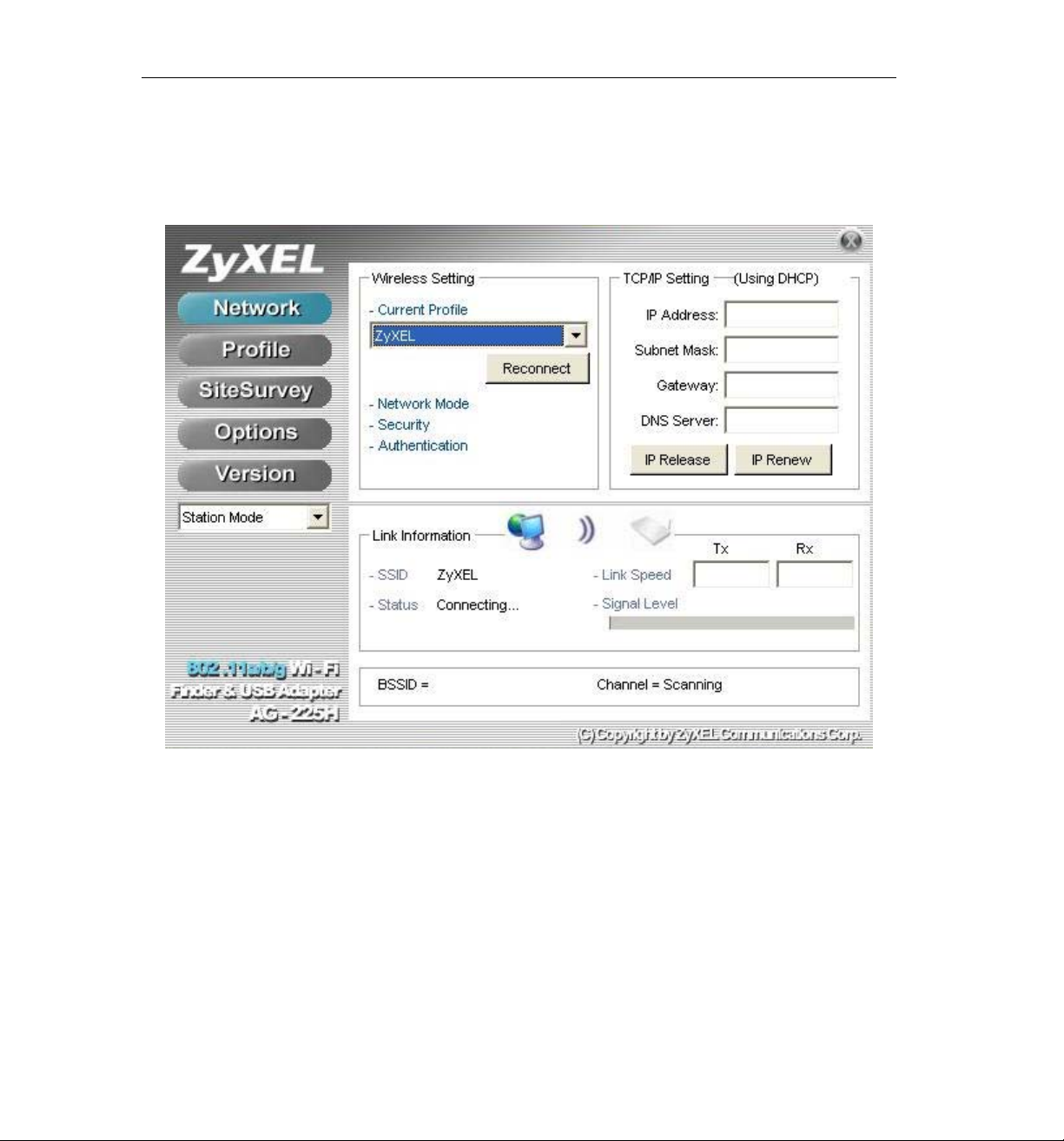
ZyXEL AG-225H User’s Guide
1.6.1 Network
This page shows how the network is presently configured: network mode, information on the connected
AP, TCP/IP, etc. This information cannot be modified in the Network screen.
The “Link Information” (lower) window shows the signal quality, signal strength, channel, etc. between
the client and AP. It is always in view regardless of which page (Network, Profile, Search, Option,
Version) is selected within the ZyXEL Utility.
1-4 Getting Started
Page 17
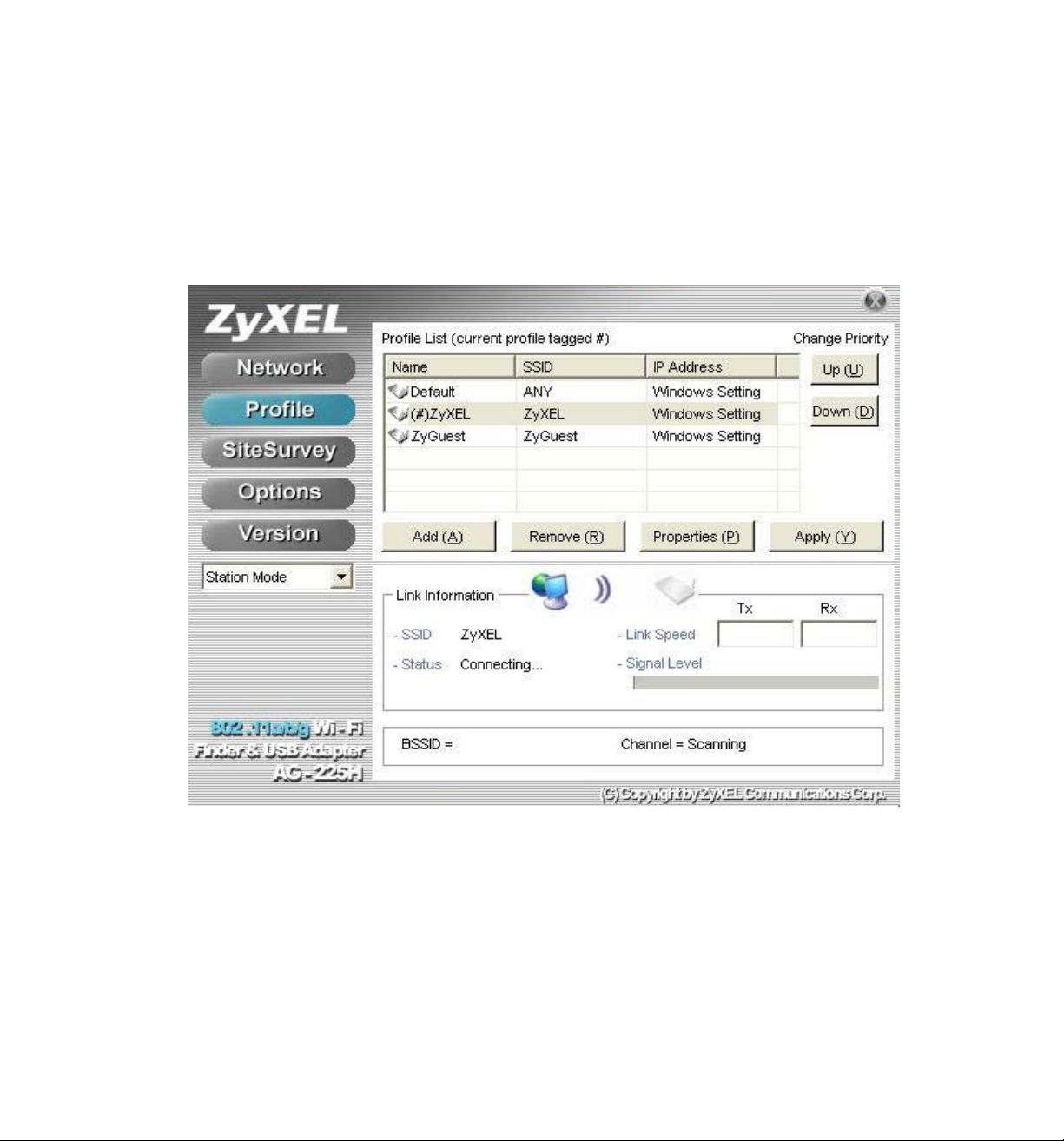
1.6.2 Profile
This page is used to manage connections with Access Points. You can create different configuration
profiles for connections with different APs and SSIDs.
The advantage of saving different profiles is the easiness of quickly changing connections without having
to configure the PC with every single variable each time a connection change is made. Also, when
configuring TCP/IP via the ZyXEL Utility you do not need to reboot the PC as when TCP/IP configuration
is done via Windows' Control Panel.
Explanation of each button in this page is shown below.
Add
Clicking on this button enables you to create a new profile. The following steps show how this can be done.
Getting Started 1-5
Page 18
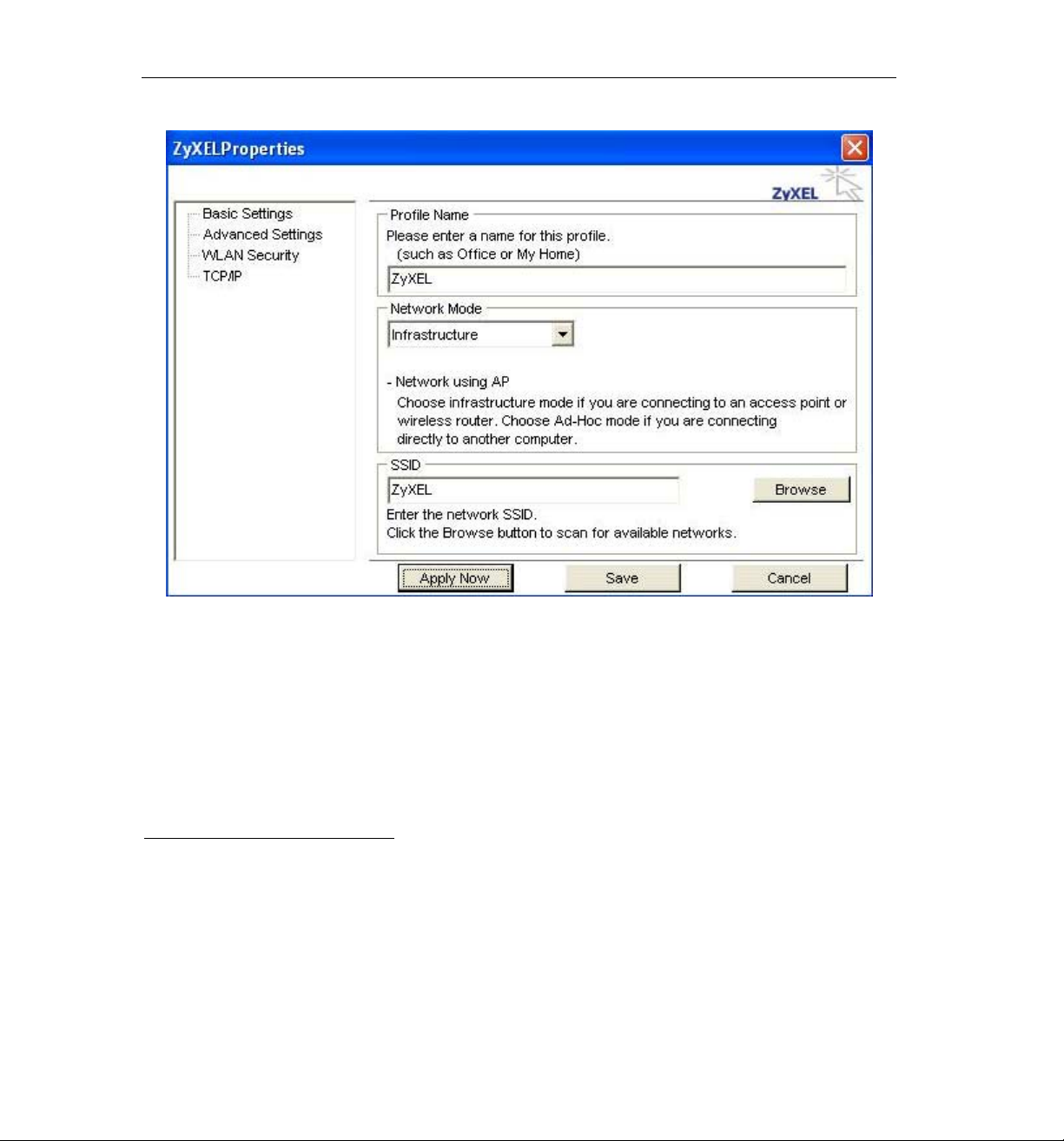
ZyXEL AG-225H User’s Guide
1) Click on [Add] and the following screen will appear.
2) On this screen you will insert some basic settings for your wireless network.
a. [Profile Name] Enter in a descriptive name for this profile.
b. [Network Mode] If connecting to an access point or wireless router, choose
“Infrastructure”
2
. If you are going to network one computer directly to another
computer without an access point, then choose “Ad-Hoc”3.
c. [SSID] Select [Browse] The utility will perform a brief site survey and display the
results to you. Click on the SSID
2
Infrastructure: You will need an access point to use the ZyXEL wireless adapter in Infrastructure mode. Because all
communication will be done via the Access Point, the Access Point’s SSID must be used.
3
Ad-Hoc: In Ad-Hoc mode communication is made peer-to-peer between the client PCs and without the use of an
Access Point. All PCs communicating in an Ad-Hoc should use the same SSID (whatever your choice is).
4
of the access point you would like to connect to and
1-6 Getting Started
Page 19
then click on [Add to Profile]. If the access point you choose has encryption enabled, a
window will pop up reminding you to enter the encryption information on the next page.
If your access point is not listed, close the [Site Survey] window, and type the name of
the SSID into the [SSID] field.
d. Click [Next]. The following screen will appear.
This screen will vary in appearance depending on whether any encryption was detected with your access
point.
3) Enter in the appropriate security information.
4
SSID: The SSID is a group name used by users of a common wireless network. Only those
devices using the same SSID are able to access each other. Also, you must use the same SSID as
the Access Point you want to connect with. SSIDs are case sensitive so take care to make sure
your capitalization matches.
Getting Started 1-7
Page 20

ZyXEL AG-225H User’s Guide
Remove
To remove a profile from the “Profile List” select it and then click on [Remove].
Apply
If you want to change the current profile with another profile from the “Profile List”, select the desired
profile and click on [Apply]. The new profile will immediately become the current profile and you will be
connected with its SSID.
Properties
Selecting a profile from the “Profile List” and clicking on [Properties] will allow you to check and/or
modify the properties of the selected profile. Clicking on [Properties] will take you to the following screen.
Each page in [Properties] is explained below.
1-8 Getting Started
Page 21

Basic Settings: In this page, you can verify the name of the current profile.
[Profile Name] Allows you to change the name of the current profile.
[Network Mode] Allows you to change between Infrastructure and Ad-Hoc networking modes.
[SSID] Allows you to change the SSID that this profile will associate with. Use the [Browse] button to
perform a site survey and select the SSID from a list of available SSIDs. Keep in mind when manually
entering an SSID that SSIDs are case sensitive.
Getting Started 1-9
Page 22

ZyXEL AG-225H User’s Guide
Advanced Settings: This screen allows you to make changes to the default ways the adapter operates
including advanced 802.11 settings. Unless you are an advanced user and have deep knowledge about each
property on this page, it is recommended that you leave them at the default settings.
1-10 Getting Started
Page 23

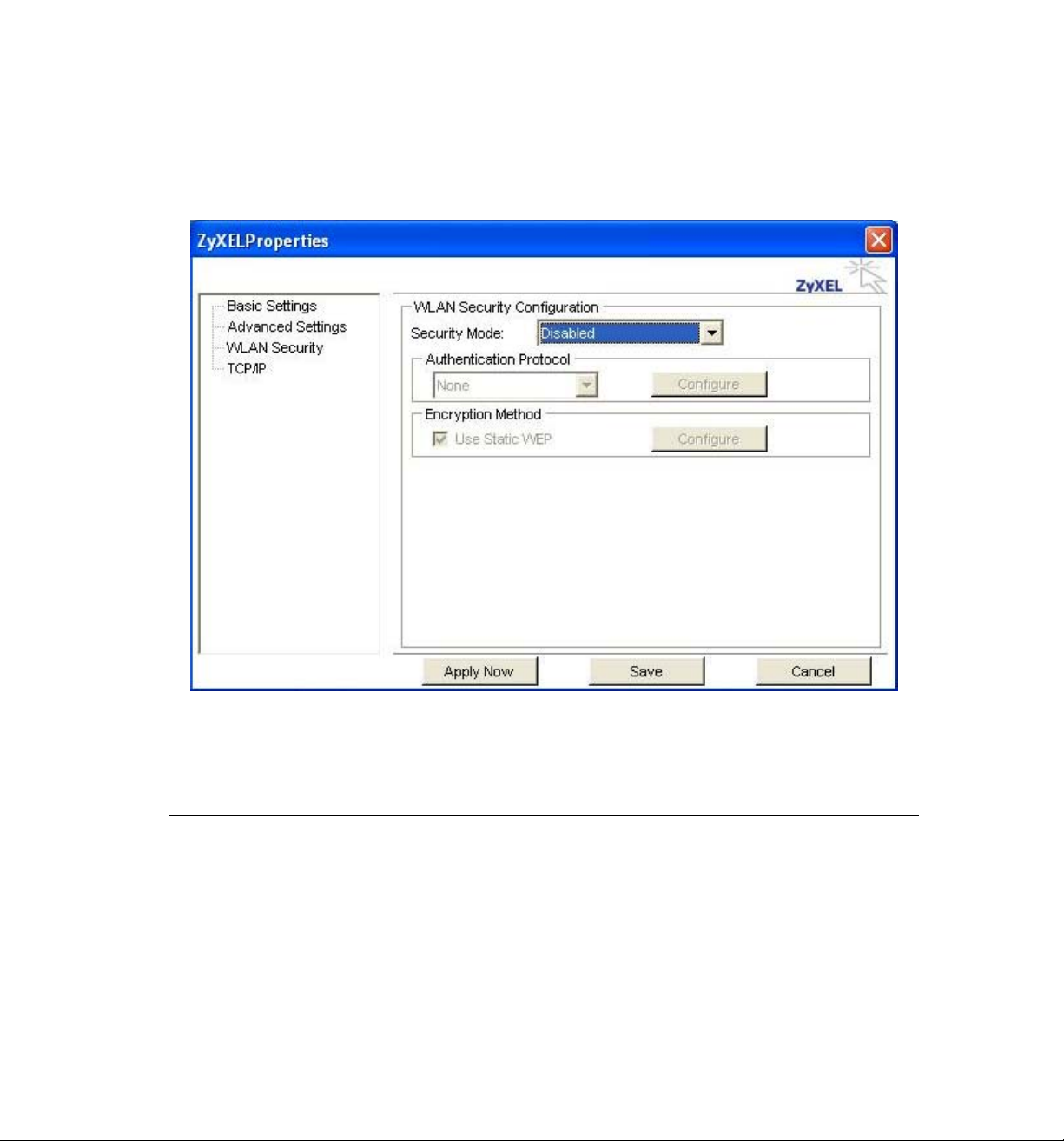
WLAN Security: This screen allows you to configure the security settings of your wireless LAN.
Security Mode
1) Disabled
All data sent between the AP and the client is left unencrypted and may be viewed by other
wireless devices.
2) WEP
Wired Equivalent Privacy – Encrypts all traffic sent between the AP and the client using a
shared key. When using WEP encryption (avail abl e in 64, 12 8, or 2 56 -bit), only those APs
and PCs using the same WEP Key are allowed to communicate with each other.
3) WPA-PSK or WPA2-PSK
WPA-PSK or WPA2-PSK is a compromise between WPA and WEP. Like WEP, it uses a
pre-shared key that every user of the network must have in order to be able to send and
receive data. Like WPA, it uses either TKIP or AES, which improve greatly over the
encryption found in WEP. In the utility, WPA-PSK or WPA2-PSK is enabled and it will
automatically depend on the AP/Router’s setting to switch either WPA-PSK or WPA2-PSK.
Getting Started 1-11
Page 24

ZyXEL AG-225H User’s Guide
We recommend you use WPA-PSK or WPA2-PSK whenever possible.
TCP/IP: This allows you to change your TCP/IP settings.
[Use IP Changer] By putting a checkmark in the box, you will overwrite your existing WLAN TCP/IP
configuration and use the IP Changer software built-into the ZyXEL Utility. This allows you to configure
TCP/IP settings for each profile.
1-12 Getting Started
Page 25

1.6.3 Site Survey
This page shows a list of SSIDs in your vicinity. Information regarding each SSID is also shown: SSID,
mode, signal strength, channel, BSSID (MAC address), data rate, and WEP, WPA, WPA-PSK, etc status.
Refresh
[Refresh] will scan the vicinity for a certain amount of time and display the scan results.
Getting Started 1-13
Page 26

ZyXEL AG-225H User’s Guide
Selecting a network from the [Available Networks] list will enable the [Detail Info], [Connect] and [Add to
profile] buttons.
Detail Info
[Detail info] will display the following screen showing the selected device's configuration information. An
alternative to clicking on [Detail info] is double-clicking on the SSID of choice.
1-14 Getting Started
Page 27

Connect
[Connect] will immediately connect you with the selected network.
Add to profile
[Add to profile] will have the same effect as clicking on [Add] in the [Profile] page
Getting Started 1-15
Page 28

ZyXEL AG-225H User’s Guide
1.6.4 Options
In this page you can configure the behavior of the ZyXEL utility.
Let Windows manage this wireless adapter – Windows Zero configuration
Allows you to use Windows to configure your wireless network settings. Check this box to configure.
Auto DHCP renewal
Automatically renews the DHCP information after changing profiles.
1-16 Getting Started
Page 29

1.6.5 Version
Software and Hardware information of the current client device.
1.7 ZyAIR Modes
You can set your ZyAIR to operate in either wireless station or access point (AP) modes.
In wireless station mode, your ZyAIR must connect to a peer wireless station or an AP to take part in your
wireless network.
In access point mode, your ZyAIR functions as an access point. This allows you to set up your wireless
network without using a dedicated AP device. Up to 15 wireless stations can associate to the ZyAIR to
form a wireless network.
Getting Started 1-17
Page 30

ZyXEL AG-225H User’s Guide
1.7.1 Change ZyAIR Modes
You may change between the modes; select either the Station Mode or AP Mode option in the ZyXEL
Utility screen.
1-18 Getting Started
Page 31

Chapter 2
Wireless LAN Networking
This chapter provides background information on general wireless LAN networking technology
and terminology.
2.1 Overview
This section describes the wireless LAN network terms and applications.
2.1.1 SSID
The SSID (Service Set Identity) is a unique name shared among all wireless devices in a wireless network.
Wireless devices must have the same SSID to communicate with each other.
2.1.2 Channel
A radio frequency used by a wireless device is called a channel.
2.1.3 Transmission Rate (Transfer Rate)
The ZyXEL AG-225H provides various transmission (data) rate options for you to select. Options include
Fully Auto, 1 Mbps, 2 Mbps, 5.5 Mbps, 11 Mbps, 6 Mbps, 9 Mbps, 12 Mbps, 18 Mb ps, 24 Mbps, 36
Mbps, 48 Mbps and 54 Mbps. In most networking scenarios, the factory default Fully Auto setting proves
the most efficient. This setting allows your ZyXEL AG-225H to operate at the maximum transmission
(data) rate. When the communication quality drops below a certain level, the ZyXEL AG-225H
automatically switches to a lower transmission (data) rate. Transmission at lower data speeds is usually
more reliable. However, when the communication quality improves again, the ZyXEL AG-225H gradually
increases the transmission (data) rate again until it reaches the highest available transmission rate.
2.1.4 Wireless Network Application
Wireless LAN works in either of the two modes: ad-hoc and infrastructure.
To connect to a wired network within a coverage area using Access Points (APs), set the ZyXEL AG-225H
operation mode to Infrastructure (BSS). An AP acts as a bridge between the wireless stations and the
wired network. In case you do not wish to connect to a wired network, but prefer to set up a small
independent wireless workgroup without an AP , use the Ad-hoc (IBSS) (Independent Basic Service Set)
mode.
WLAN Networking 2-1
Page 32

ZyXEL AG-225H User’s Guide
Ad-Hoc (IBSS)
Ad-hoc mode does not require an AP or a wired networ k. Tw o or more wireless stations communicate
directly to each other. An ad-hoc network may sometimes be referred to as an Independent Basic Service
Set (IBSS).
Figure 2-1 IBSS Example
To set up an ad-hoc network, configure all wireless stations in ad-hoc network
type and use the same SSID and channel.
Infrastructure (BSS)
When a number of wireless stations are connected using a single AP, you have a Basic Service Set (BSS).
Figure 2-2 BSS Example
A series of overlapping BSS and a network medium, such as an Ethernet forms an Extended Service Set
(ESS) or infrastructure network. All communication is done through the AP, which relays data packets to
other wireless stations or devices connected to the wired network. Wireless stations can then access
resource, such as the printer, on the wired network.
2-2 WLAN Networking
Page 33

Figure 2-3 Infrastructure Network Example
Access Point Mode
The following figure depicts a network example in which you set the ZyAIR in access point mode.
Figure 2-4 ZyAIR as an Access Point Example
In the example, the ZyAIR is installed on computer A and set to operate in access point mode. Computer A
shares Internet connection to the wireless LAN, so wireless stations B and C can access the Internet.
2.1.5 Roaming
In an infrastructure network, wireless stations are able to switch from one BSS to another as they move
between the coverage areas. During this period, the wireless stations maintain uninterrupted connection to
the network. This is roaming. As the wireless station moves from place to place, it is responsible for
choosing the most appropriate AP depending on the signal strength, network utilization or other factors.
WLAN Networking 2-3
Page 34

ZyXEL AG-225H User’s Guide
The following figure depicts a roaming example. When wireless station B moves to position X, the ZyXEL
AG-225H in wireless station B automatically switches the channel to the one used by access point 2 in
order to stay connected to the network.
Figure 2-5 Roaming Example
2.2 Wireless LAN Security
Wireless LAN security is vital to your network to protect wireless communication between wir e less
stations and the wired network.
The figure below shows the possible wireless security levels on your ZyXEL AG-225H. EAP (Extensible
Authentication Protocol) is used for authentication and utilizes dynamic WEP key exchange. It requires
interaction with a RADIUS (Remote Authentication Dial-In User Service) server either on the WAN or
your LAN to provide authentication service for wireless stations.
2-4 WLAN Networking
Page 35

Figure 2-6 Wireless LAN Security Levels
Configure the wireless LAN security using the Profile Security Settings screen. If you do not enable any
wireless security on your ZyXEL AG-225H, the ZyXEL AG-225H’s wireless communications are
accessible to any wireless networking device that is in the coverage area.
2.2.1 Data Encryption with WEP
WEP (Wired Equivalent Privacy) encryption scrambles all data packets transmitted between the ZyXEL
AG-225H and the AP or other wireless stations to keep network communications private. Both the wireless
stations and the access points must use the same WEP key for data encryption and decryption.
There are two ways to create WEP keys in your ZyXEL AG-225H.
Automatic WEP key generation based on a “password phrase” called a passphrase. The passphrase
•
is case sensitive. You must use the same passphrase for all WLAN adapters with this feature in the
same WLAN.
For WLAN adapters without the passphrase feature, you can still take advantage of this feature by
writing down the four automatically generated WEP keys from the Security Settings screen of the
ZyXEL Utility and entering them manually as the WEP keys in the other WLAN adapter(s).
• Enter the WEP keys manually.
Your ZyXEL AG-225H allows you to configure up to four 64-bit, 128-bit or 152-bit WEP keys and only
one key is used as the default key at any one time.
2.2.2 IEEE 802.1x
The IEEE 802.1x standard outlines enhanced security methods for both the authentication of wireless
stations and encryption key management. Authentication can be done using an external RADIUS server.
EAP Authentication
EAP (Extensible Authentication Protocol) is an authentication protocol that runs on top of the IEEE802.1x
transport mechanism in order to support multiple types of user authentication. By using EAP to interact
WLAN Networking 2-5
Page 36

ZyXEL AG-225H User’s Guide
with an EAP-compatible RADIUS server, an access point helps a wireless station and a RADIUS server
perform authentication.
The type of authentication you use depends on the RADIUS server and an intermediary AP(s) that supports
IEEE802.1x. The ZyXEL AG-225H supports EAP-TLS, EAP-TTLS and EAP-PEAP.
For EAP-TLS authentication type, you must first have a wired connection to the network and obtain the
certificate(s) from a certificate authority (CA). A certificate (also called digital IDs) can be used to
authenticate users and a CA issues certificates and guarantees the identity of each certificate owner.
2.2.3 WPA/WPA2
Wi-Fi Protected Access (WPA) and WPA2 is a subset of the IEEE 802.11i security specification draft. Key
differences between WPA and WEP are user authentication and improved data encryption. WPA2 is a
wireless security standard that defines stronger encryption, authentication and key management than WPA.
User Authentication
WPA applies IEEE 802.1x and Extensible Authentication Protocol (EAP) to authenticate wireless clients
using an external RADIUS database.
Therefore, if you don’t have an external RADIUS server, you should use WPA-PSK (WPA -Pre-Shared
Key) that only requires a single (identical) password entered into each access point, wireless gateway and
wireless client. As long as the passwords match, a client will be granted access to a WLAN.
Encryption
WPA improves data encryption by using either Temporal Key Integrity Protocol (TKIP) or Advanced
Encryption Standard (AES), Message Integrity Check (MIC) and IEEE 802.1x.
Temporal Key Integrity Protocol (TKIP) uses 128-bit keys that are dynamically generated and distributed
by the authentication server. It includes a per-packet key mixing function, a Message Integrity Check (MIC)
named Michael, an extended initialization vector (IV) with sequencing rules, and a re-keying mechanism.
TKIP regularly changes and rotates the encryption keys so that the same encryption key is never us ed twice.
The RADIUS server distributes a Pairwise Master Key (PMK) key to the AP that then sets up a key
hierarchy and management system, using the pair-wise key to dynamically generate unique data encryption
keys to encrypt every data packet that is wirelessly communicated between the AP and the wireless clients.
This all happens in the background automatically.
The Message Integrity Check (MIC) is designed to prevent an attacker from capturing data packets, altering
them and resending them. The MIC provides a strong mathematical function in which the receiver and the
transmitter each compute and then compare the MIC. If they do not match, it is assumed that the data has
been tampered with and the packet is dropped.
By generating unique data encryption keys for every data packet and by creating an integrity checking
mechanism (MIC), TKIP makes it much more difficult to decode data on a Wi-Fi network than WEP,
making it difficult for an intruder to break into the network.
The encryption mechanisms used for WPA and WPA-PSK are the same. The only difference between the
two is that WPA-PSK uses a simple common password, instead of user-specific credentials. The common-
2-6 WLAN Networking
Page 37

password approach makes WPA-PSK susceptible to brute-force password-guessing attacks but it’s still an
improvement over WEP as it employs an easier-to-use, consistent, single, alphanumeric password.
2.2.4 WPA-PSK/WPA2-PSK Application Example
A WPA-PSK application looks as follows.
Step 1. First enter identical passwords into the AP and all wireless clients. The Pre-Shared Key (PSK)
must consist of between 8 and 63 ASCII characters (including spaces and symbols).
Step 2. The AP checks each client’s password and (only) allows it to join the network if it matches its
password.
Step 3. The AP derives and distributes keys to the wireless clients.
Step 4. The AP and wireless clients use the TKIP encryption process to encrypt data exchanged
between them.
Figure 2-7
WPA-PSK/WPA2-PSK Authentication
2.2.5 WPA/WPA2 with RADIUS Application Example
You need the IP address of the RADIUS server, its port number (defau lt is 18 12), and the RADIUS shared
secret. A WPA/WPA2 application example with an external RADIUS server looks as follows. “A” is the
RADIUS server. “DS” is the distribution system.
Step 1. The AP passes the wireless client’s authentication request to the RADIUS server.
Step 2. The RADIUS server then checks the user's identification against its database and grants or
denies network access accordingly.
Step 3. The RADIUS server distributes a Pairwise Master Key (PMK) key to the AP that then sets up a
key hierarchy and management system, using the pair-wise key to dynamically generate unique
WLAN Networking 2-7
Page 38

ZyXEL AG-225H User’s Guide
data encryption keys to encrypt every data packet that is wirelessly communicated between the
AP and the wireless clients.
Figure 2-8 WPA/WPA2 with RADIUS Application Example
2.3 Fragmentation Threshold
The Fragmentation Threshold is the maximum data fragment size (between 256 and 2432 bytes) that can be sent in the wireless network before the ZyXEL AG-225H will fragment the packet into smaller data frames.
A large Fragmentation Threshold is recommended for networks not prone to interference while you
should set a smaller threshold for busy networks or networks that are prone to interference.
If the Fragmentation Threshold value is smaller than the RTS/CTS Threshold value (see previously) you set then the RTS (Request To Send)/CTS (Clear to Send) handshake will never occur as data frames will be fragmented before they reach RTS/CTS Threshold size.
2.4 RTS/CTS Threshold
A hidden node occurs when two stations are within range of the same access point, but are not within range
of each other. The following figure illustrates a hidden node. Both stations are within range of the access
point (AP) or wireless gateway, but out-of-range of each other, so they cannot “hear” each other, that is
2-8 WLAN Networking
Page 39

they do not know if the channel is currently being used. Therefore, they are considered hidden from each
other.
Figure 2-9 RTS Threshold
When station A sends data to the AP, it might not know that the station B is already using the channel. If
these two stations send data at the same time, collisions may occur when both sets of data arrive at the AP
at the same time, resulting in a loss of messages for both stations.
RTS/CTS Threshold is designed to prevent collisions due to hidden nodes. An RTS/CTS Threshold
defines the biggest size data frame you can send before an RTS (Request To Send)/CTS (Clear to Send)
handshake is invoked.
When a data frame exceeds the RTS/CTS Threshold value you set (between 0 to 2432 bytes), the station
that wants to transmit this frame must first send an RTS (Request To Send) message to the AP for
permission to send it. The AP then responds with a CTS (Clear to Send) message to all other stations within
its range to notify them to defer their transmission. It also reserves and confirms with the requesting station
the time frame for the requested transmission.
Stations can send frames smaller than the specified RTS/CTS Threshold directly to the AP without the
RTS (Request To Send)/CTS (Clear to Send) handshake.
You should only configure RTS/CTS Threshold if the possibility of hidden nodes exists on your network
and the “cost” of resending large frames is more than the extra network overhead involved in the RTS
(Request To Send)/CTS (Clear to Send) handshake.
If the RTS/CTS Threshold value is greater than the Fragmentation Threshold value (see next), then the
RTS (Request To Send)/CTS (Clear to Send) handshake will never occur as data frames will be fragmented
before they reach RTS/CTS Threshold size.
Enabling the RTS Threshold causes redundant network overhead that could
negatively affect the throughput performance.
2.5 Authentication Type
The IEEE 802.11b standard describes a simple authentication method between the wireless stations and AP.
Two authentication modes are defined: Open and Share.
WLAN Networking 2-9
Page 40

ZyXEL AG-225H User’s Guide
Open authentication mode is implemented for ease-of-use and when security is no t an issue. The wireless
station and the AP do not share a secret key. Thus the wireless stations can associate with any AP and listen
to any data transmitted plaintext.
Shared authentication mode involves a shared secret key to authenticate th e wireless station to th e AP.
This requires you to enable the wireless LAN security and use same settings on both the wireless station
and the AP.
2-10 WLAN Networking
Page 41

Chapter 3
Access Point Mode Configuration
This chapter shows you how to configure your ZyAIR in access point mode.
3.1 Introduction
In access point mode, your ZyAIR functions as an access point. This allows you to set up your wireless
networks without using a dedicated AP device. Up to 15 wireless stations can associate to the ZyAIR.
3.1.1 Additional Setup Requirements
To bridge your wired and wireless network using the ZyAIR, the following requirements must be met:
1. The ZyAIR must be installed on a computer connected to the wired network.
2. Either configure network sharing (refer to the appendix for an example) or bridge the two interfaces
(wireless and wired) on the computer.
3. Set the wireless station’s IP address to be in the same subnet as the computer in which the ZyAIR is
installed. Refer to the Setting Up Your Computer’s IP Address appendix.
3.2 The Profile Screen
Select the Access Point Mode and wait for about five seconds to display the screen as shown.
WLAN Networking 3-1
Page 42

ZyXEL AG-225H User’s Guide
Profile
LABEL DESCRIPTION
Status
SSID This field displays the name that identifies your ZyAIR in the wireless LAN network.
Channel This field displays the radio channel the ZyAIR is currently using.
Security This field displays the authentication type of the ZyAIR.
Authentication
TX Frame This field shows the number of frame when transmitting
Select an authentication method. Choices are Shared and Open
Refer to section 2.5 for detail information
3-2 WLAN Networking
Page 43

Profile
LABEL DESCRIPTION
RX Frame This field shows the number of frame when receiving
MAC Address This field displays the MAC addresses of up to 15 wireless stations that are currently
connected to the ZyAIR.
3.3 How to configure in Access Point Mode
3.3.1 Profile
This page is used to manage connections in the Access Point Mode.
WLAN Networking 3-3
Page 44

ZyXEL AG-225H User’s Guide
Explanation of each button in this page is shown below.
Add
Clicking on this button enables you to create a new profile. The following steps show how this can be done.
1) Click on [Add] and the following screen will appear.
2) On this screen you will insert some basic settings for your wireless network.
a. [Profile Name] You may enter in a descriptive name for this profile.
b. [SSID] The SSID identifies the Service Set to which a wireless station is associated.
Wireless stations associating to the access point (the ZyAIR) must have the same SSID.
Enter a descriptive name (up to 32 printable 7-bit ASCII characters) for the wireless
LAN.
c. [Hide SSID] Select this check box to hide the SSID in the outgoing beacon frame so a
station cannot obtain the SSID through passive scanning using a site survey tool.
3-4 WLAN Networking
Page 45

d. [Wireless Mode]: Set the operating frequency depending on your geographical region.
e. [Channel]: Set the operating channel depending on your geographical region.
f. Click [Next]. The following screen will appear.
This screen will vary in appearance depending on whether any encryption was detected with your access
point.
3) Enter in the appropriate security information.
a. Click [Next]. The following screen will appear.
WLAN Networking 3-5
Page 46

ZyXEL AG-225H User’s Guide
b. See 3.3.2 MAC Filter Screen
c. Click [Next]. The following screen will appear.
3-6 WLAN Networking
Page 47

4) Final Step
a. Uncheck the box [Apply this profile now] if you do not want to activate this pro file at
this time.
b. Click [Save] to complete the wizard and save the profile you have just created.
Remove
To remove a profile from the “Profile List” select it and then click on [Remove].
Apply
If you want to change the current profile with another profile from the “Profile List”, select the desired
profile and click on [Apply]. The new profile will immediately become the current profile and you will be
connected with its SSID.
Properties
Selecting a profile from the “Profile List” and clicking on [Properties] will allow you to check and/or
modify the properties of the selected profile. Clicking on [Properties] will take you to the following screen.
WLAN Networking 3-7
Page 48

ZyXEL AG-225H User’s Guide
3.3.2 The MAC Filter
The MAC Filter screen allows you to configure the ZyAIR to give exclusive access to (Accept) devices or
exclude devices from (Reject) connecting to the ZyAIR. Every Ethernet device has a unique MAC (Media
Access Control) address. The MAC address is assigned at the factory and consists of six pairs of
hexadecimal characters, for example, 00:A0:C5:00:00:02. You need to know the MAC address of the
device(s) to configure this screen.
MAC Filter
LABEL DESCRIPTION
Filter Type Define the filter action for the list of MAC addresses in the MAC address filter table.
Select Disable to deactivate the MAC filter feature.
Select Accept to permit access to the ZyAIR, MAC addresses not listed will be denied
access to the ZyAIR.
Select Reject to block access to the ZyAIR, MAC addresses not listed will be allowed
to access the ZyAIR.
3-8 WLAN Networking
Page 49

Filter MAC Address
1-15 Specify the MAC address(es) of the wireless station(s) that is allowed or denied
Save
Cancel
association to the ZyAIR.
Enter six pairs of hexadecimal digits (separated by colons) in the range of “A-F”, “a-f”
and “0-9” (for example, 00:A0:C5:00:00:02).
If you enter an invalid MAC address, once you click Save to save the values, a
warning screen will be displayed.
Click Save to save the changes back to the ZyAIR.
Click Cancel to discard changes.
WLAN Networking 3-9
Page 50

ZyXEL AG-225H User’s Guide
3.3.3 Version
Software, Hardware and Status information of the current Access Point Mode.
3-10 WLAN Networking
Page 51

Maintenance
This chapter describes how to uninstall or upgrade the ZyXEL Utility.
4.1 The Version Screen
The Version screen displays related version numbers of the ZyXEL AG-225H.
Chapter 4
The following table describes the read-only fields in this screen.
Maintenance 4-1
Page 52

ZyXEL AG-225H User’s Guide
About
LABEL DESCRIPTION
Package Version This field displays the version number of the combination driver/utility package.
Driver Version This field displays the version number of the ZyXEL driver.
Utility Version This field displays the version number of the Z yXEL utility.
4.2 Uninstalling the ZyXEL Utility
Follow the steps below to remove (or uninstall) the ZyXEL Utility from your computer.
Step 1. Click Start, Programs, ZyXEL ZyAIR SW, Uninstall.
Step 2. When prompted, click [OK] to remove the driver and the utility software.
Step 3. Click [Ok] to finish the uninstall process. Reboot your computer if prompted to do so.
4-2 Maintenance
Page 53

4.3 Upgrading the ZyXEL Utility
Before you uninstall the ZyXEL Utility , take note of the current network
configuration.
To perform the upgrade, follow the steps below.
Step 1. Download the latest version of the utility from the ZyXEL web site and save the file on your
computer.
Step 2. Follow the steps in Section 4.2 to remove the current ZyXEL Utility from your computer.
Step 3. Restart your computer if prompted.
Step 4. After restarting, refer to the procedure in the Quick Start Guide to install the new utility.
Step 5. Check the version numbers in the Version screen to make sure the new utility is installed
properly.
Maintenance 4-3
Page 54

Page 55

Chapter 5
Configuring Wireless Security
This chapter covers the configuration of security options in the ZyXEL Utility.
5.1 Configuring Security
You can configure your security settings at any time. Simply select the profile you wish to edit under the
[Profile] tab, select [Properties] and then choose [WLAN Security]. You are also presented with the option
to configure security during the profile creation process. Whether changing the security settings of an
existing profile or creating a new profile, the steps to configure your security settings remain the same.
5.2 Configuring WEP
1. Select [WEP] under [Security Mode]
Wireless Security 5-1
Page 56

ZyXEL AG-225H User’s Guide
2. Put a check mark next to [Using Static WEP]
3. Click [Config]. You will then see the screen below.
4. [WEP Method] Select the correct encryption level to match your access point. Either 64,
128, or 256-bit. The encryption level set her must match the encryption level used by
your access point.
a. [Authentication] You can choose between Auto Switch, Open, and Shared. Please see
section 2.5 for more information on the different types of authentication. For most
installations choosing “Auto Switch” is the best choice.
b. Enter the WEP key exactly as you did in your access point.
There are three ways of generating a WEP Key:
Make key using PassPhrase: a WEP Key is automatically generated as you type in any
PassPhrase of your choice. Use this feature when you have used a PassPhrase to generate
your WEP key on your access point.
Manual Input (ASCII): You generate your own WEP Key using ASCII characters (5
characters for 64-bit, 13 characters for 128-bit, 29 characters for 256-bit)
5-2 Wireless Security
Page 57

Manual Input (Hexadecimal): You generate your own WEP Key using hexadecimal
characters (10 characters for 64-bit, 26 characters for 128-bit, 58 characters for 256-bit).
5. Click [OK] to save your settings and return to the previous screen.
5.3 Configuring WPA-PSK
1. Select [WPA-PSK] under [Security Mode].
2. Select [Encryption method]. You can choose between TKIP or AES. Most access points use
TKIP for WPA-PSK.
3. Under [PSK Pass Phrase] enter the same pass phrase used to configure WPA-PSK on your access
point.
Wireless Security 5-3
Page 58

ZyXEL AG-225H User’s Guide
5.4 Configuring WPA2-PSK
1. Select [WPA2-PSK] under [Security Mode].
2. Select [Encryption method]. You can choose between TKIP or AES. Most access points use AES
for WPA2-PSK.
3. Under [PSK Pass Phrase] enter the same pass phrase used to configure WPA2-PSK on your access
point.
5-4 Wireless Security
Page 59

Chapter 6
Troubleshooting
This chapter covers potential problems and possible remedies. After each p roblem description,
some instructions are provided to help you diagnose and solve the problem.
6.1 Problems Starting the ZyXEL Utility Program
Table 6-1 Troubleshooting Starting ZyXEL Utility Program
PROBLEM CORRECTIVE ACTION
Cannot start the ZyXEL
Wireless LAN Utility
6.2 Problem with the Link Status
Make sure the ZyXEL AG-225H is properly plugged in your USB port and the
LED(s) is on. Refer to the Quick Start Guide for LED descriptions.
Use the Device Manager to check for possible hardware conflicts.
Click Start, Settings, Control Panel, System, Hardware and Device
Manager. Verify the status of the ZyXEL AG-225H under Network Adapter.
(Steps may vary depending on the version of Windows).
Install the ZyXEL AG-225H in another computer.
If the error persists, you may have a hardware problem. In this case, you
should contact your local vendor.
Table 6-2 Troubleshooting Link Quality
PROBLEM CORRECTIVE ACTION
The link quality and/or signal
strength is poor all the time.
Troubleshooting 6-1
Search and connect to another AP with a better link quality using the Site
Survey screen.
Change the channel used by your AP.
Move your computer closer to the AP or the peer computer(s) within the
transmission range.
There may be too much radio interference (for example microwave or
another AP using the same channel) around your wireless network.
Relocate or reduce the radio interference.
Page 60

ZyXEL AG-225H User’s Guide
6.3 Problems Communicating With Other Computers
Table 6-3 Troubleshooting Communication Problems
PROBLEM CORRECTIVE ACTION
The ZyXEL AG-225H
computer cannot
communicate with the other
computer.
A. Infrastructure
B. Ad-Hoc (IBSS)
Make sure you are connected to the network.
Make sure that the AP and the associated computers are turned on and
working properly.
Make sure the ZyXEL AG-225H computer and the associated AP use the
same SSID.
Change the AP and the associated wireless clients to use another radio
channel if interference is high.
Make sure that the computer and the AP share the same security option
and key. Verify the settings in the Profile Security Settings screen.
Verify that the peer computer(s) is turned on.
Make sure the ZyXEL AG-225H computer and the peer computer(s) are
using the same SS ID and channel.
Make sure that the computer and the peer computer(s) share the same
security option and key.
Change the wireless clients to use another radio channel if interference is
high.
6.4 Problem Connecting to an Access Point
Table 6-4 Troubleshooting Access Point Connection Problem
PROBLEM CORRECTIVE ACTION
When using the Windows
XP configuration tool, cannot
scan for or connect to any
access points.
6-2 Troubleshooting
The ZyAIR might still be operating in access point mode. This results
when you set the ZyAIR to operate in access point mode using the ZyXEL
Utility, close the ZyXEL Utility and then use the Windows XP configuration
tool.
Before you use the Windows XP configuration tool, make sure you set the
ZyAIR to operate in station mode before you close and exit the ZyXEL
Utility.
Page 61

 Loading...
Loading...