Page 1

ZyWALL (ZLD)
CLI Reference Guide
Version 2.20, 2.21
2/2011
Edition 3
DEFAULT LOGIN
User Name admin
Password 1234
www.zyxel.com
Page 2

Page 3
About This CLI Reference Guide
About This CLI Reference Guide
Intended Audience
This manual is intended for people who want to configure ZLD-based ZyWALLs via
Command Line Interface (CLI). You should have at least a basic knowledge of TCP/IP
networking concepts and topology. Generally, it is organized by feature as outlined in the web
configurator.
" This guide is intended as a command reference for a series of products.
Therefore many commands or command options in this guide may not be
available in your product. See your User’s Guide for a list of supported
features and details about feature implementation.
Please refer to www.zyxel.com or your product’s CD for product specific User Guides and
product certifications.
How To Use This Guide
1 Read Chapter 1 on page 11 for how to access and use the CLI (Command Line
Interface).
2 Read Chapter 2 on page 27 to learn about the CLI user and privilege modes.
3 Subsequent chapters are arranged by menu item as defined in the web configurator . Read
each chapter carefully for detailed information on that menu item.
" Some features cannot be configured in both the web configurator and CLI.
CLI Reference Guide Feedback
Help us help you. Send all Reference Guide-related comments, questions or suggestions for
improvement to the following address, or use e-mail instead. . Thank you!
The Technical Writing Team,
ZyXEL Communications Corp.,
6 Innovation Road II,
Science-Based Industrial Park,
Hsinchu, 300, Taiwan.
E-mail: techwriters@zyxel.com.tw
ZyWALL (ZLD) CLI Reference Guide
3
Page 4
Document Conventions
Document Conventions
Warnings and Notes
These are how warnings and notes are shown in this User’s Guide.
1 Warnings tell you about things that could harm you or your device.
" Notes tell you other important information (for example, other things you may
need to configure or helpful tips) or recommendations.
Syntax Conventions
• The ZLD-based ZyWALL may be referred to as the “ZyWALL”, the “device”, the
“system” or the “product” in this User’s Guide.
• Product labels, screen names, field labels and field choices are all in bold font.
• A key stroke is denoted by square brackets and uppercase text, for example, [ENTER]
means the “enter” or “return” key on your keyboard.
• “Enter” means for you to type one or more characters and then press the [ENTER] key.
“Select” or “choose” means for you to use one of the predefined choices.
• A right angle bracket ( > ) within a screen name denotes a mouse click. For example,
Maintenance > Log > Log Setting means you first click Maintenance in the navigation
panel, then the Log sub menu and finally the Log Setting tab to get to that screen.
• Units of measurement may denote the “metric” value or the “scientific” value. For
example, “k” for kilo may denote “1000” or “1024”, “M” for mega may denote “1000000”
or “1048576” and so on.
• “e.g.,” is a shorthand for “for instance”, and “i.e.,” means “that is” or “in other words”.
4
ZyWALL (ZLD) CLI Reference Guide
Page 5
Document Conventions
Icons Used in Figures
Figures in this User’s Guide may use the following generic icons. The ZyWALL icon is not an
exact representation of your device.
ZyWALL Computer Notebook computer
Server Firewall Telephone
Switch Router
ZyWALL (ZLD) CLI Reference Guide
5
Page 6

Document Conventions
6
ZyWALL (ZLD) CLI Reference Guide
Page 7

Contents Overview
Contents Overview
Introduction ..............................................................................................................................9
Command Line Interface ............................................................................................................11
User and Privilege Modes ......................................................................................................... 27
Object Reference ................ ... ... ... .... ... ... ... ... .......................................... .... ... ... ... ....................... 31
Status ............................................................... ...................... ....................... ............................. 33
Registration ............................................................................................................................... 37
Network ...................................................................................................................................45
Interfaces ..................................... ....................................................... ....................................... 47
Trunks .................................................... .......................................... .......................................... 85
Route ......................................................................................................................................... 91
Routing Protocol ........................................................................................................................ 99
Zones .................................. ................... ................... .................... ................... ........................ 103
DDNS ...................................................................................................................................... 107
Virtual Servers ..........................................................................................................................111
HTTP Redirect ..........................................................................................................................117
ALG ......................................................................................................................................... 121
Firewall ..................................................................................................................................125
Firewall .................................................................................................................................... 127
VPN ........................................................................................................................................135
IPSec VPN ................... ... ....................................... ... .... ... ... ... .... ... ... ........................................ 137
SSL VPN ................................................................................................................................. 147
L2TP VPN ................................................................................................................................ 153
Application Patrol ................................................................................................................161
Application Patrol ..................................................................................................................... 163
Anti-X ....................................................................................................................................175
Anti-Virus .................................................................................................................................177
IDP Commands ....................................................................................................................... 185
Content Filtering ............. .... ... .......................................... ... .......................................... ........... 203
Anti-Spam ................................................................................................................................ 215
Device HA .............................................................................................................................225
Device HA ................................................................................................................................ 227
ZyWALL (ZLD) CLI Reference Guide
7
Page 8

Contents Overview
Objects ..................................................................................................................................235
User/Group .............................................................................................................................. 237
Addresses .............................. ................... .................... ................... ................... ..................... 245
Services ................................. ....................................................... ........................................... 249
Schedules ................................. ................................................. .............................................. 253
AAA Server .............................................................................................................................. 255
Authentication Objects ................. .... ... ... ... ... .......................................... .... ... ... ... ..................... 263
Certificates ................................... ....................... ....................... ...................... ........................ 267
ISP Accounts ............................................... .... ... ... ... .... ... .......................................... ..............273
SSL Application ....................................................................................................................... 277
Endpoint Security .................................................................................................................... 281
System ..................................................................................................................................289
System ................................... ...................... ....................... ....................... .............................. 291
System Remote Management ................................................................................................. 299
Maintenance .........................................................................................................................313
File Manager ............................................................................................................................ 315
Logs ....................................... .................................................... .............................................. 333
Reports and Reboot ................................................................................................................ 339
Session Timeout .......................... .......................................... .... ..............................................345
Diagnostics .............................................................................................................................347
Packet Flow Explore ................................................................................................................ 349
Maintenance Tools ................................................................................................................... 353
Watchdog Timer .......................................................................................................................359
Command List ......................................................................................................................363
List of Commands (Alphabetical) ........................ ....................... ...................... ....................... . 365
8
ZyWALL (ZLD) CLI Reference Guide
Page 9

PART I
Introduction
Command Line Interface (11)
User and Privilege Modes (27)
Object Reference (31)
Status (33)
Registration (37)
9
Page 10

10
Page 11
CHAPTER 1
Command Line Interface
This chapter describes how to access and use the CLI (Command Line Interface).
1.1 Overview
If you have problems with your ZyWALL, customer support may request that you issue some
of these commands to assist them in troubleshooting.
1 Use of undocumented commands or misconfiguration can damage the
ZyWALL and possibly render it unusable.
1.1.1 The Configuration File
When you configure the ZyWALL using either the CLI (Command Line Interface) or t he web
configurator, the settings are saved as a series of commands in a configuration file on the
ZyWALL. Y ou can sto re more than one configuration file on the ZyWALL. However , only one
configuration file is used at a time.
You can perform the following with a configuration file:
• Back up ZyWALL configuration once the ZyWALL is set up to work in your network.
• Restore ZyWALL configuration.
• Save and edit a configuration file and upload it to multiple ZyWALLs (of the same model)
in your network to have the same settings.
" You may also edit a configuration file using a text editor.
1.2 Accessing the CLI
You can access the CLI using a terminal emulation program on a computer connected to the
console port, from the web configurator or access the ZyWALL using Telnet or SSH (Secure
SHell).
ZyWALL (ZLD) CLI Reference Guide
11
Page 12
Chapter 1 Command Line Interface
" The ZyWALL might force you to log out of your session if reauthentication
time, lease time, or idle timeout is reached. See Chapter 25 on page 237 for
more information about these settings.
1.2.1 Console Port
The default settings for the console port are as follows.
Table 1 Managing the ZyWALL: Console Port
SETTING VALUE
Speed 115200 bps
Data Bits 8
Parity None
Stop Bit 1
Flow Control Off
When you turn on your ZyWALL, it performs several internal tests as well as line
initialization. You can view the initialization information using the console port.
• Garbled text displays if your terminal emulation program’s speed is set lower than the
ZyWALL’s.
• No text displays if the speed is set higher than the ZyWALL’s.
• If changing your terminal emulation program’s speed does not get anything to display,
restart the ZyWALL.
• If restarting the ZyWALL does not get anything to display, contact your local customer
support.
Figure 1 Console Port Power-on Display
FLASH: AMD 16M
BootModule Version: V1.08 | 12/04/2007 15:36:17
DRAM: Size = 256 Mbytes
DRAM POST: Testing: 262144K
After the initialization, the login screen displays.
12
Figure 2 Login Screen
Welcome to ZyWALL 1050
Username:
ZyWALL (ZLD) CLI Reference Guide
Page 13

Chapter 1 Command Line Interface
Enter the user name and password at the prompts.
" The default login username is admin and password is 1234. The username
and password are case-sensitive.
1.2.2 Web Configurator Console
" Before you can access the CLI through the web configurator, make sure your
computer supports the Java Runtime Environment. You will be prompted to
download and install the Java plug-in if it is not already installed.
When you access the CLI using the web console, your computer establishes a SSH (Secure
SHell) connection to the ZyWALL. Follow the steps below to access the web console.
1 Log into the web configurator.
2 Click the Console icon in the top-right corner of the web configurator screen.
3 If the Java plug-in is already installed, skip to step 4.
Otherwise, you will be prompted to install the Java plug-in. If the prompt does not
display and the screen remains gray, you have to download the setup program.
4 The web console starts. This might take a few seconds. One or more security screens
may display. Click Yes or Always.
Figure 3 Web Console: Security Warnings
Finally , the User Name screen appears.
ZyWALL (ZLD) CLI Reference Guide
13
Page 14
Chapter 1 Command Line Interface
Figure 4 Web Console: User Name
5 Enter the user name you want to use to log in to the console. The console begins to
connect to the ZyWALL.
" The default login username is admin. It is case-sensitive.
Figure 5 Web Console: Connecting
14
Then, the Password screen appears.
Figure 6 Web Console: Password
6 Enter the password for the user name you specified earlier, and click OK. If you enter
the password incorrectly, you get an error message, and you may have to close the
console window and open it again. If you enter the password correctly, the console
screen appears.
ZyWALL (ZLD) CLI Reference Guide
Page 15

Figure 7 Web Console
7 T o use most commands in this User’s Guide, enter configure terminal. The prompt
1.2.3 Telnet
should change to
Chapter 1 Command Line Interface
Router(config)#.
Use the following steps to Telnet into your ZyWALL.
1 If your computer is connected to the ZyWALL over the Internet, skip to the next step.
Make sure your computer IP address and the ZyWALL IP address are on the same
subnet.
2 In Windows, click Start (usually in the bottom left corner) and Run. Then type
and the ZyWALL’s IP address. For example, enter telnet 192.168.1.1 (the default
management IP address).
3 Click OK. A login screen displays. Enter the user name and password at the prompts.
telnet
" The default login username is admin and password is 1234. The username
and password are case-sensitive.
1.2.4 SSH (Secure SHell)
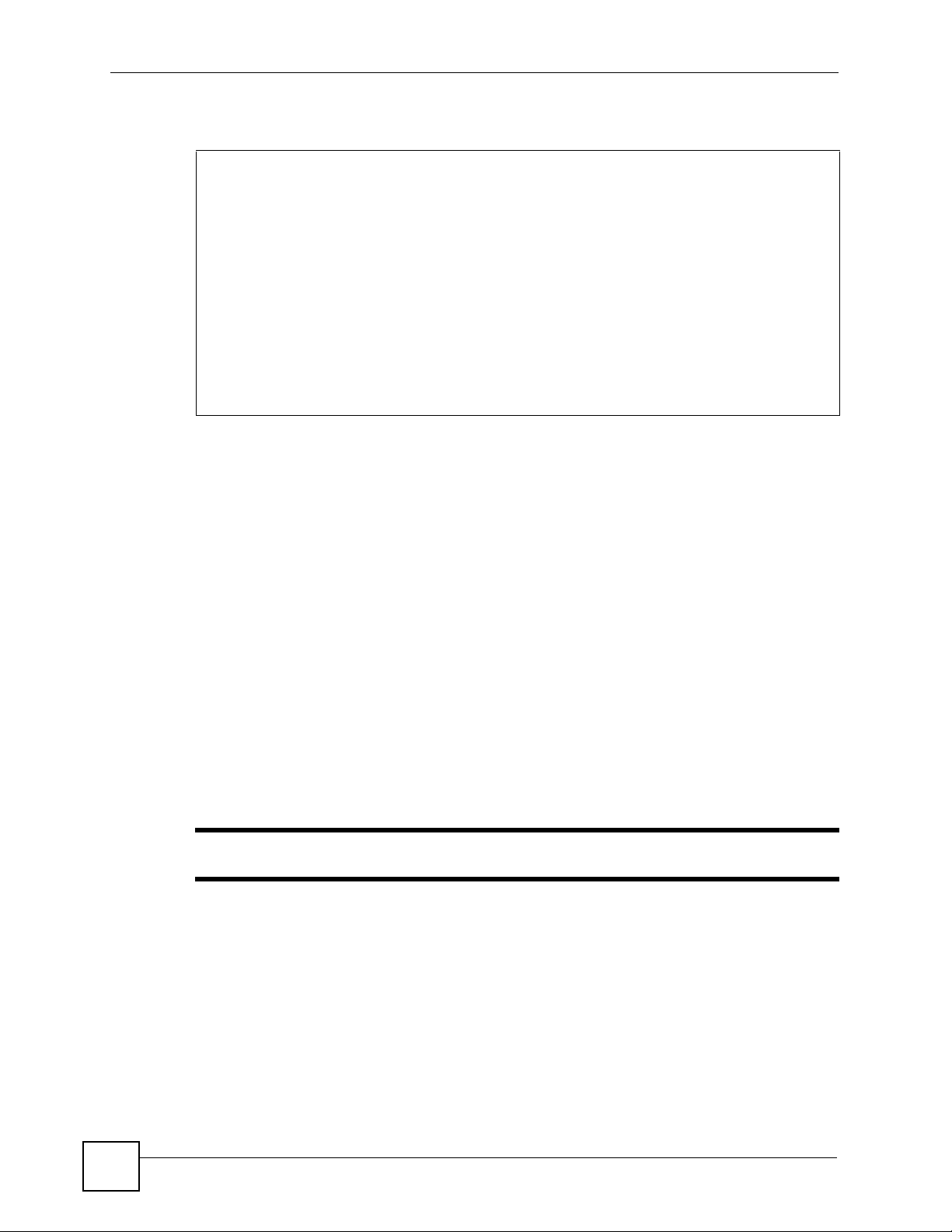
You can use an SSH client program to access the CLI. The following figure shows an example
using a text-based SSH client program. Refer to the documentation that comes with your SSH
program for information on using it.
" The default login username is admin and password is 1234. The username
and password are case-sensitive.
ZyWALL (ZLD) CLI Reference Guide
15
Page 16
Chapter 1 Command Line Interface
Figure 8 SSH Login Example
C:\>ssh2 admin@192.168.1.1
Host key not found from database.
Key fingerprint:
xolor-takel-fipef-zevit-visom-gydog-vetan-bisol-lysob-cuvun-muxex
You can get a public key's fingerprint by running
% ssh-keygen -F publickey.pub
on the keyfile.
Are you sure you want to continue connecting (yes/no)? yes
Host key saved to C:/Documents and Settings/user/Application Data/SSH/
hostkeys/
ey_22_192.168.1.1.pub
host key for 192.168.1.1, accepted by user Tue Aug 09 2005 07:38:28
admin's password:
Authentication successful.
1.3 How to Find Commands in this Guide
You can simply look for the feature chapter to find commands. In addition, you can use the
List of Commands (Alphabetical) at the end of the guide. This section lists the commands in
alphabetical order that they appear in this guide.
If you are looking at the CLI Reference Guide electronically, you might have additional
options (for example, bookmarks or Find...) as well.
1.4 How Commands Are Explained
Each chapter explains the commands for one keyword. The chapters ar e divided into the
following sections.
1.4.1 Background Information (Optional)
" See the User’s Guide for background information about most features.
This section provides background information about features that you cannot configure in the
web configurator. In addition, this section identifies related commands in other chapters.
1.4.2 Command Input Values (Optional)
This section lists common input values for the commands for the feature in one or more tables
16
ZyWALL (ZLD) CLI Reference Guide
Page 17

1.4.3 Command Summary
This section lists the commands for the feature in one or more tables.
1.4.4 Command Examples (Optional)
This section contains any examples for the commands in this feature.
1.4.5 Command Syntax
The following conventions are used in this User’s Guide.
• A command or keyword in courier new must be entered literally as shown. Do not
abbreviate.
• Values that you need to provide are in italics.
• Required fields that have multiple choices are enclosed in curly brackets
• A range of numbers is enclosed in angle brackets
• Optional fields are enclosed in square brackets
•The
| symbol means OR.
Chapter 1 Command Line Interface
{}.
<>.
[].
For example, look at the following command to create a TCP/UDP service object.
service-object object-name {tcp | udp} {eq <1..65535> | range <1..65535>
<1..65535>}
1 Enter service-object exactly as it appears.
2 Enter the name of the object where you see object-name.
3 Enter
tcp or udp, depending on the service object you want to create.
4 Finally , do one of the following.
•Enter
•Enter
eq exactly as it appears, followed by a number between 1 and 65535.
range exactly as it appears, followed by two numbers between 1 and 65535.
1.4.6 Changing the Password
It is highly recommended that you change the password for accessing the ZyWALL. See
Section 25.2 on page 238 for the appropriate commands.
1.5 CLI Modes
You run CLI commands in one of several modes.
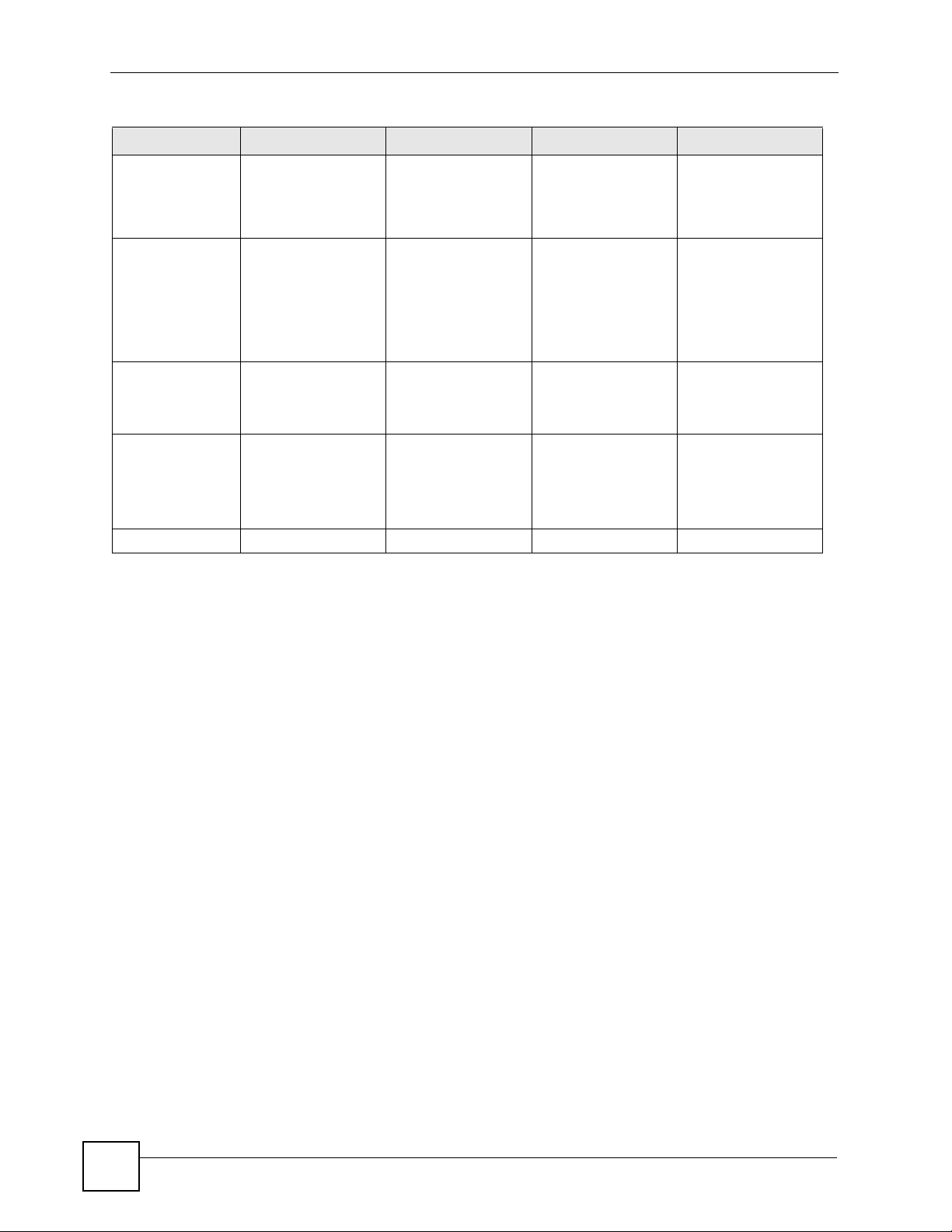
Table 2 CLI Modes
USER PRIVILEGE CONFIGURATION SUB-COMMAND
What Guest users
can do
What User users
can do
Unable to access Unable to access Unable to access Unable to access
• Look at (but not
run) available
commands
Unable to access Unable to access Unable to access
ZyWALL (ZLD) CLI Reference Guide
17
Page 18
Chapter 1 Command Line Interface
Table 2 CLI Modes (continued)
USER PRIVILEGE CONFIGURATION SUB-COMMAND
What LimitedAdmin users can
do
What Admin
users can do
How you enter it Log in to the ZyWALL Type enable in User
What the prompt
looks like
How you exit it Type exit Type disable Type exit Type exit
• Look at system
information (like
Status screen)
• Run basic
diagnostics
• Look at system
information (like
Status screen)
• Run basic
diagnostics
Router> Router# Router(config)# (varies by part)
• Look at system
information (like
Status screen)
• Run basic
diagnostics
• Look at system
information (like
Status screen)
• Run basic
diagnostics
mode
Unable to access Unable to access
• Configure simple
features (such as
an address
object)
• Create or remove
complex parts
(such as an
interface)
Type configure
terminal in User or
Privilege mode
• Configure
complex parts
(such as an
interface) in the
ZyWALL
Type the command
used to create the
specific part in
Configuration mode
Router(zone)#
Router(configif-ge)#
...
See Chapter 25 on page 237 for more information about the user types. User users can only
log in, look at (but not run) the available commands in User mode, and log out. Limited-
Admin users can look at the configuration in the web configurator and CLI, and they can run
basic diagnostics in the CLI. Admin users can configure the ZyWALL in the web configurator
or CLI.
At the time of writing, there is not much difference between User and Privilege mode for
admin users. This is reserved for future use.
1.6 Shortcuts and Help
1.6.1 List of Available Commands
A list of valid commands can be found by typing ? or [TAB] at the command prompt. To view a
list of available commands within a command group, enter
[TAB].
<command> ? or <command>
18
ZyWALL (ZLD) CLI Reference Guide
Page 19

Figure 9 Help: Available Commands Example 1
Router> ?
<cr>
apply
atse
clear
configure
------------------[Snip]-------------------shutdown
telnet
test
traceroute
write
Router>
Figure 10 Help: Available Command Example 2
Router> show ?
<wlan ap interface>
aaa
access-page
account
ad-server
address-object
------------------[Snip]-------------------wlan
workspace
zone
Router> show
Chapter 1 Command Line Interface
1.6.2 List of Sub-commands or Required User Input
To view detailed help information for a command, enter <command> <sub command> ?.
Figure 11 Help: Sub-command Information Example
Router(config)# ip telnet server ?
;
<cr>
port
rule
|
Router(config)# ip telnet server
Figure 12 Help: Required User Input Example
Router(config)# ip telnet server port ?
<1..65535>
Router(config)# ip telnet server port
ZyWALL (ZLD) CLI Reference Guide
19
Page 20

Chapter 1 Command Line Interface
1.6.3 Entering Partial Commands
The CLI does not accept partial or incomplete commands. You may enter a unique part of a
command and press
[TAB] to have the ZyWALL automatically display the full command.
For example, if you enter
config and press [TAB] , the full command of configure
automatically displays.
If you enter a partial command that is not unique and press
of commands that start with the partial command.
Figure 13 Non-Unique Partial Command Example
Router# c [TAB]
clear configure copy
Router# co [TAB]
configure copy
1.6.4 Entering a ? in a Command
Typing a ? (question mark) usua lly displays help information. However, some commands
allow you to input a ?, for example as part of a string. Press [CTRL+V] on your keyboard to
enter a ? without the ZyWALL treating it as a help query.
1.6.5 Command History
The ZyWALL keeps a list of commands you have entered for the current CLI session. You can
use any commands in the history again by pressing the up (y) or down (z) arrow key to scroll
through the previously used commands and press
[TAB], the ZyWALL displays a list
[ENTER].
1.6.6 Navigation
Press [CTRL]+A to move the cursor to the beginning of the line. Press [CTRL]+E to move the
cursor to the end of the line.
1.6.7 Erase Current Command
Press [CTRL]+U to erase whatever you have currently typed at the prompt (before pressing
[ENTER]).
1.6.8 The no Commands
When entering the no commands discribed in this document, you may not need to type the
whole command. For example, with the “[no] mss <536..1452>” command, you use
“mss 536” to specify the MSS value. But to disable the MSS setting, you only need to type
“no mss” instead of “no mss 536”.
20
ZyWALL (ZLD) CLI Reference Guide
Page 21
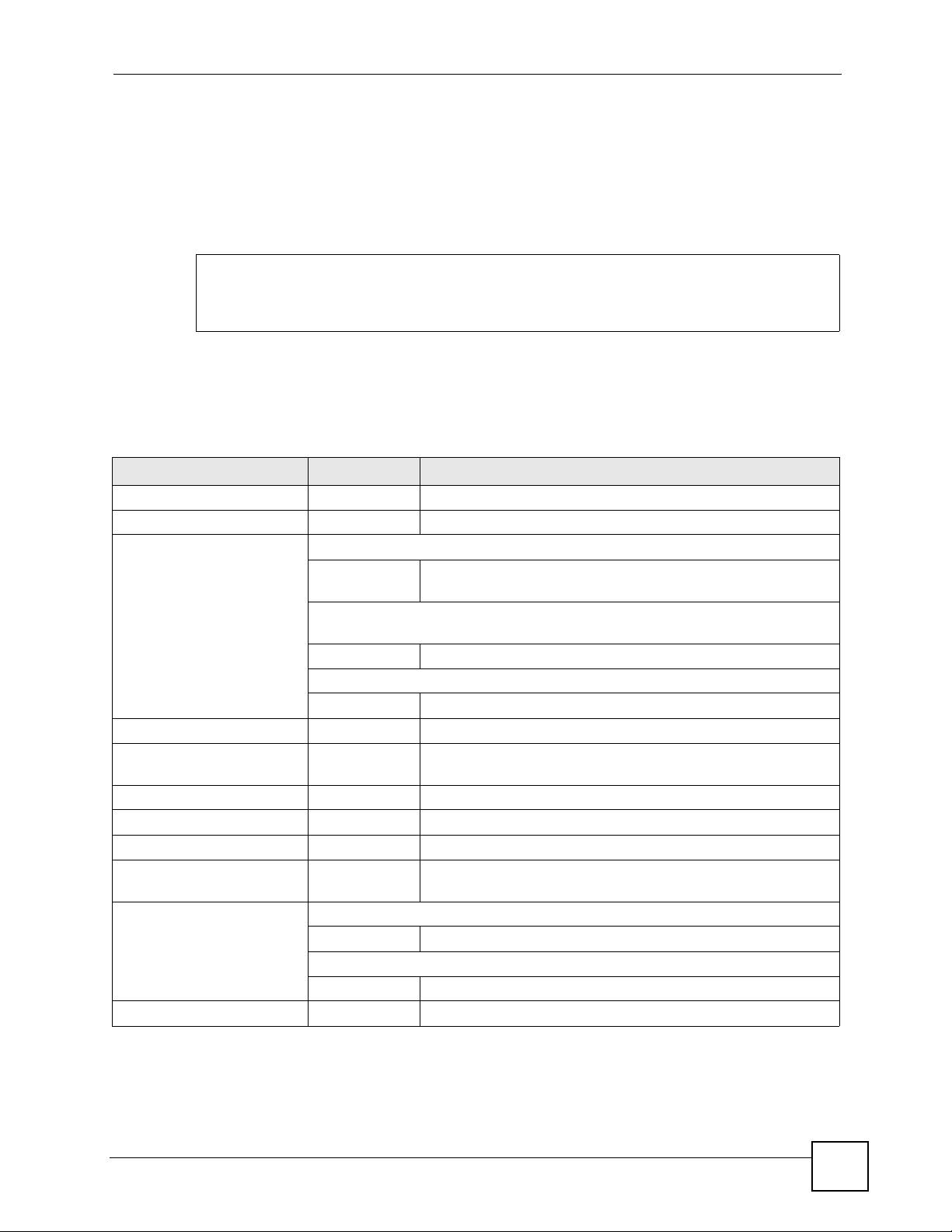
1.7 Input Values
You can use the ? or [TAB] to get more information about the next input value that is required
for a command. In some cases, the next input value is a string whose length and allowable
characters may not be displayed in the screen. For example, in the following example, the next
input value is a string called
Router# configure terminal
Router(config)# interface ge1
Router(config-if-ge)# description
<description>
When you use the example above, note that ZyWALL USG 100 and 200 models use a name
such as wan1, wan2, opt, lan1, ext-wlan, or dmz.
Chapter 1 Command Line Interface
<description>.
The following table provides more information about input values like
<description>.
Table 3 Input-Value Formats for Strings in CLI Commands
TAG # VALUES LEGAL VALUES
* 1*
all -- ALL
authentication key Used in IPSec SA
32-40
16-20
Used in MD5 authentication keys for RIP/OSPF and text
authentication key for RIP
0-16 alphanumeric or _Used in text authentication keys for OSPF
0-8 alphanumeric or _-
certificate name 1-31 alphanumeric or ;`~!@#$%^&()_+[\]{}',.=-
community string 0-63 alphanumeric or .-
connection_id 1+ alphanumeric or -_:
contact 1-61 alphanumeric, spaces, or '()+,/:=?;!*#@$_%-.
country code 0 or 2 alphanumeric
custom signature file
name
description Used in keyword criteria for log entries
distinguished name 1-511 alphanumeric, spaces, or .@=,_-
0-30 alphanumeric or _-.
1-64 alphanumeric, spaces, or '()+,/:=?;!*#@$_%-.
Used in other commands
1-61 alphanumeric, spaces, or '()+,/:=?;!*#@$_%-
“0x” or “0X” + 32-40 hexadecimal values
alphanumeric or ;|`~!@#$%^&*()_+\\{}':,./<>=-
first character: alphanumeric or -
first character: letter
ZyWALL (ZLD) CLI Reference Guide
21
Page 22
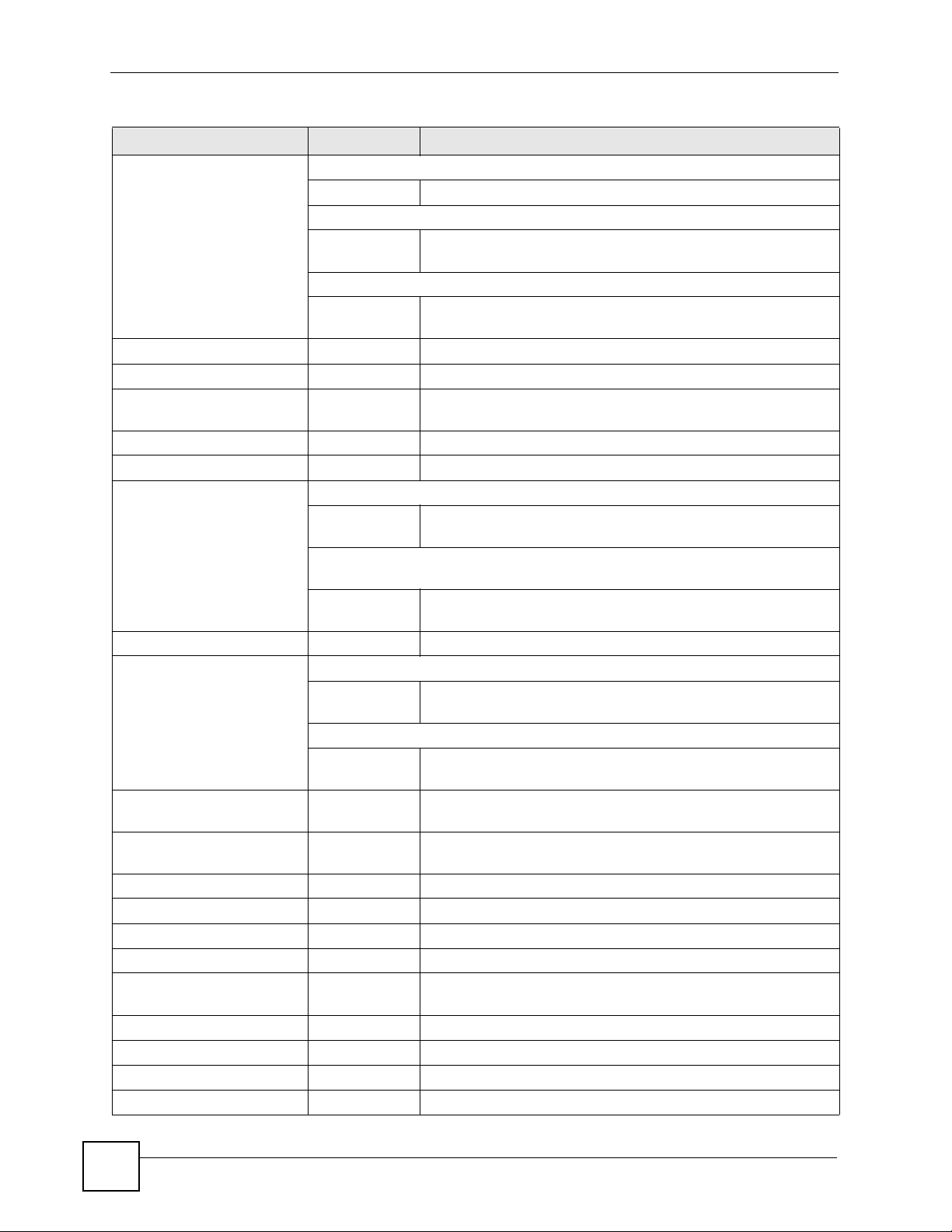
Chapter 1 Command Line Interface
Table 3 Input-Value Formats for Strings in CLI Commands (continued)
TAG # VALUES LEGAL VALUES
domain name Used in content filtering
0+ lower-case letters, numbers, or .Used in ip dns server
0-247 alphanumeric or .-
first character: alphanumeric or Used in domainname, ip dhcp pool, and ip domain
0-254 alphanumeric or ._-
first character: alphanumeric or -
email 1-63 alphanumeric or .@_-
e-mail 1-64 alphanumeric or .@_-
encryption key 16-64
8-32
file name 0-31 alphanumeric or _-
filter extension 1-256 alphanumeric, spaces, or '()+,/:=?;!*#@$_%.-
fqdn Used in ip dns server
0-252 alphanumeric or .-
Used in ip ddns, time server, device HA, VPN, certificates,
and interface ping check
0-254 alphanumeric or .-
full file name 0-256 alphanumeric or _/.-
hostname Used in hostname command
0-63 alphanumeric or .-_
Used in other commands
0-252 alphanumeric or .-
import configuration
file
import shell script 1-
initial string 1-64 alphanumeric, spaces, or '()+,/:=!*#@$_%-.&
isp account password 0-63 alphanumeric or `~!@#$%^&*()_\-+={}|\;:'<,>./
isp account username 0-30 alphanumeric or -_@$./
key length -- 512, 768, 1024, 1536, 2048
license key 25 “S-” + 6 upper-case letters or numbers + “-” + 16
mac address -- aa:bb:cc:dd:ee:ff (hexadecimal)
mail server fqdn lower-case letters, numbers, or -.
name 1-31 alphanumeric or _-
notification message 1-81 alphanumeric, spaces, or '()+,/:=?;!*#@$_%-
126+”.conf”
26+”.zysh”
“0x” or “0X” + 16-64 hexadecimal values
alphanumeric or ;\|`~!@#$%^&*()_+\\{}':,./<>=-
first character: alphanumeric or -
first character: alphanumeric or -
first character: alphanumeric or -
first character: alphanumeric or -
alphanumeric or ;`~!@#$%^&()_+[]{}',.=-
add “.conf” at the end
alphanumeric or ;`~!@#$%^&()_+[]{}',.=-
add “.zysh” at the end
upper-case letters or numbers
22
ZyWALL (ZLD) CLI Reference Guide
Page 23
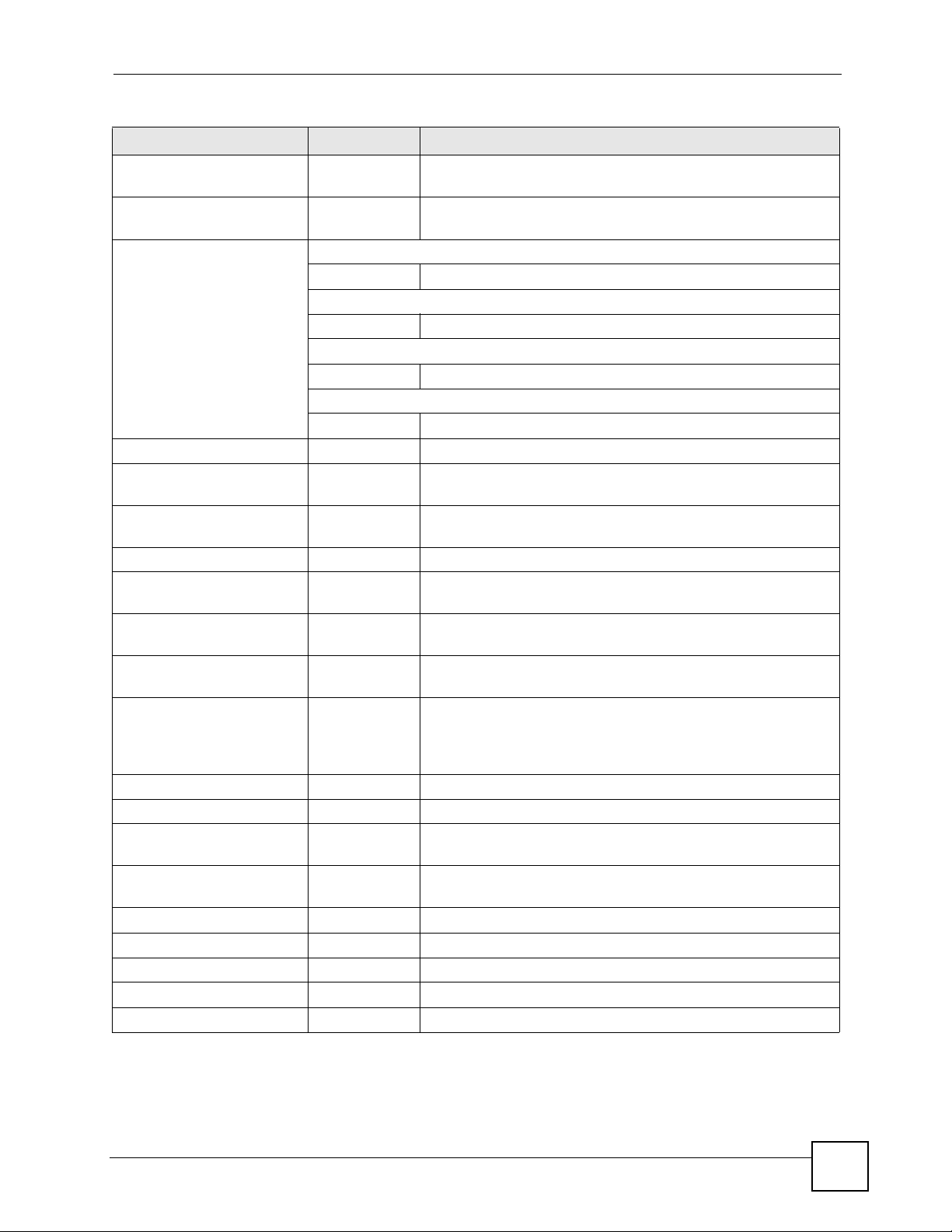
Chapter 1 Command Line Interface
Table 3 Input-Value Formats for Strings in CLI Commands (continued)
TAG # VALUES LEGAL VALUES
password: less than 15
chars
password: less than 8
chars
password Used in user and ip ddns
phone number 1-20 numbers or ,+
preshared key 16-64 “0x” or “0X” + 16-64 hexadecimal values
profile name 0-30 alphanumeric or _-
proto name 1-16 lower-case letters, numbers, or -
protocol name 0-30 alphanumeric or _-
quoted string less
than 127 chars
quoted string less
than 63 chars
quoted string 0+ alphanumeric, spaces, or punctuation marks
service name 0-63 alphanumeric or -_@$./
spi 2-8 hexadecimal
string less than 15
chars
string: less than 63
chars
string 1+ alphanumeric or -_@
subject 1-61 alphanumeric, spaces, or '()+,./:=?;!*#@$_%-
system type 0-2 hexadecimal
timezone [-+]hh -- -12 through +12 (with or without “+”)
url 1-511 alphanumeric or '()+,/:.=?;!*#@$_%-
1-15 alphanumeric or `~!@#$%^&*()_\-+={}|\;:'<,>./
1-8 alphanumeric or ;/?:@&=+$\.-_!~*'()%,#$
1-63 alphanumeric or `~!@#$%^&*()_-+={}|\;:'<,>./
Used in e-mail log profile SMTP authentication
1-63 alphanumeric or `~!@#$%^&*()_-+={}|\;:'<>./
Used in device HA synchronization
1-63 alphanumeric or ~#%^*_-={}:,.
Used in registration
6-20 alphanumeric or .@_-
alphanumeric or ;|`~!@#$%^&*()_+\{}':,./<>=-
first character: letters or _-
first character: letters or _1-255 alphanumeric, spaces, or ;/?:@&=+$\.-_!~*'()%,
1-63 alphanumeric, spaces, or ;/?:@&=+$\.-_!~*'()%
enclosed in double quotation marks (“)
must put a backslash (\) before double quotation
marks that are part of input value itself
1-15 alphanumeric or -_
1-63 alphanumeric or `~!@#$%^&*()_-+={}|\;:'<,>./
ZyWALL (ZLD) CLI Reference Guide
23
Page 24
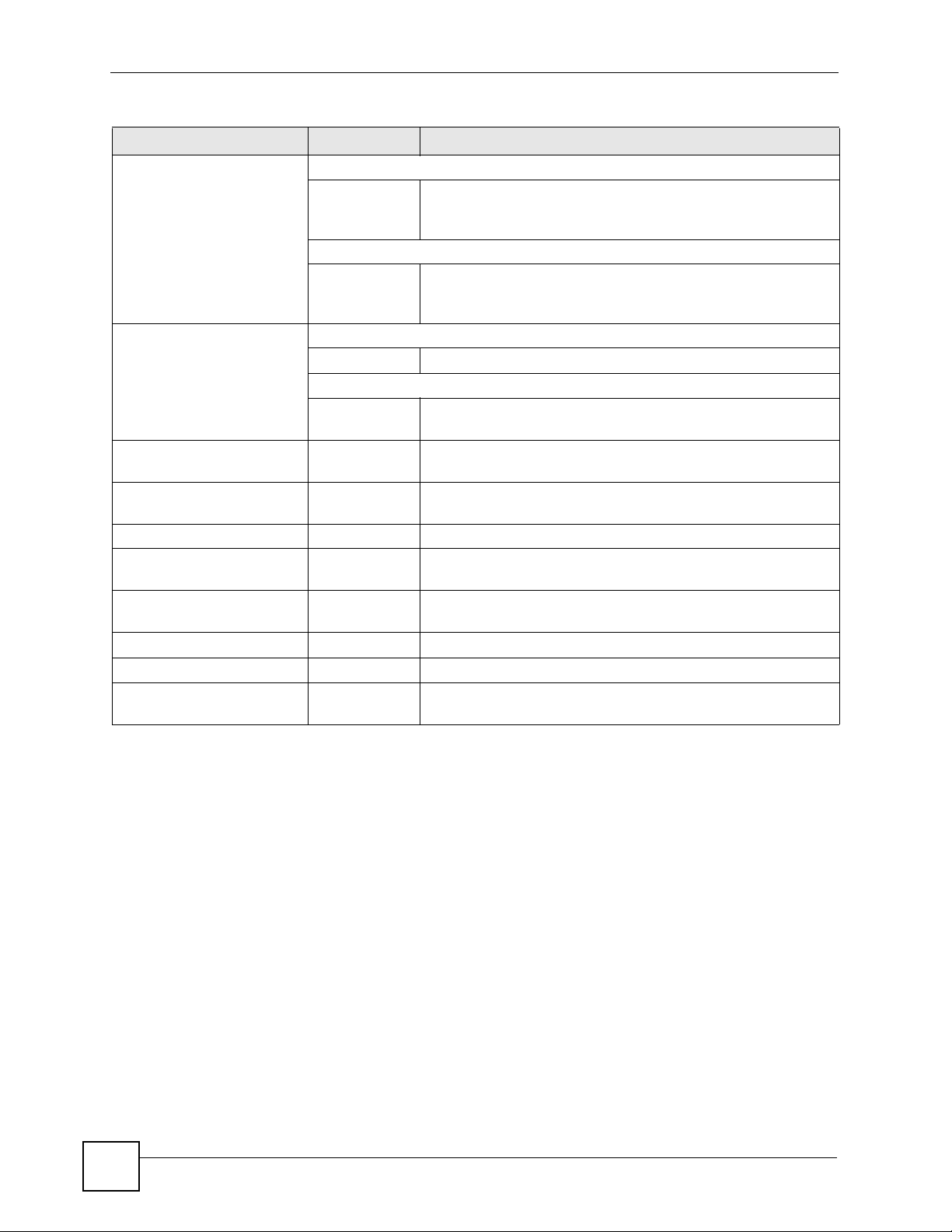
Chapter 1 Command Line Interface
Table 3 Input-Value Formats for Strings in CLI Commands (continued)
TAG # VALUES LEGAL VALUES
url Used in content filtering redirect
“http://”+
“https://”+
Used in other content filtering commands
“http://”+ alphanumeric or ;/?:@&=+$\.-_!~*'()%,
user name Used in VPN extended authentication
1-31 alphanumeric or _Used in other commands
0-30 alphanumeric or _-
username 6-20 alphanumeric or .@_-
user name 1+ alphanumeric or -_.
user@domainname 1-80 alphanumeric or .@_-
vrrp group name: less
than 15 chars
week-day sequence,
i.e. 1=first,2=second
xauth method 1-31 alphanumeric or _-
xauth password 1-31 alphanumeric or ;|`~!@#$%^&*()_+\{}':,./<>=-
mac address 0-12 (even
1-15 alphanumeric or _-
11-4
number)
alphanumeric or ;/?:@&=+$\.-_!~*'()%,
starts with “http://” or “https://”
may contain one pound sign (#)
starts with “http://”
may contain one pound sign (#)
first character: letters or _-
registration
logging commands
hexadecimal
for example: aa aabbcc aabbccddeeff
1.8 Ethernet Interfaces
How you specify an Ethernet interface depends on the ZyWALL mo del.
• For the ZyWALL USG 300 and above, use gex, x = 1~N, where N equals the highest
numbered Ethernet interface for your ZyWALL model.
• The ZyWALL USG 100 and 200 models use a name such as wan1, wan2, opt, lan1, extwlan, or dmz.
1.9 Saving Configuration Changes
Use the write command to save the current configuration to the ZyWALL.
24
ZyWALL (ZLD) CLI Reference Guide
Page 25

Chapter 1 Command Line Interface
" Always save the changes before you log out after each management session.
All unsaved changes will be lost after the system restarts.
1.10 Logging Out
Enter the exit or end command in configure mode to go to privilege mode.
Enter the
exit command in user mode or privilege mode to log out of the CLI.
ZyWALL (ZLD) CLI Reference Guide
25
Page 26

Chapter 1 Command Line Interface
26
ZyWALL (ZLD) CLI Reference Guide
Page 27

CHAPTER 2
User and Privilege Modes
This chapter describes how to use these two modes.
2.1 User And Privilege Modes
This is the mode you are in when you first log into the CLI. (Do not confuse ‘user mode’ with
types of user accounts the ZyWALL uses. See Chapter 25 on page 237 for more information
about the user types. ‘User’ type accounts can only run ‘exit’ in this mode. However, they may
need to log into the device in order to be authenticated for ‘user-aware’ policies, for example a
firewall rule that a particular user is exempt from or a VPN tunnel that only certain people may
use.)
Type ‘enable’ to go to ‘privilege mode’. No password is required. All commands can be run
from here except those marked with an asterisk. Many of these commands are for troubleshooting purposes, for example the htm (hardware test module) and debug commands.
Customer support may ask you to run some of these commands and send the results if you
need assistance troubleshooting your device.
For admin logins, all commands are visible in ‘user mode’ but not all can be run there. The
following table displays which commands can be run in ‘user mode’. All commands can be
run in ‘privilege mode’.
1 The htm and psm commands are for ZyXEL’s internal manufacturing process.
Table 4 User (U) and Privilege (P) Mode Commands
COMMAND MODE DESCRIPTION
apply P Applies a configuration file.
atse U/P Displays the seed code
clear U/P Clears system or debug logs or DHCP binding.
configure U/P Use ‘configure terminal’ to enter configuration mode.
copy P Copies configuration files.
debug (*) U/P For support personnel only! The device needs to have the debug flag enabled.
delete P Deletes configuration files.
details P Performs diagnostic commands.
ZyWALL (ZLD) CLI Reference Guide
27
Page 28
Chapter 2 User and Privilege Modes
Table 4 User (U) and Privilege (P) Mode Commands (continued)
COMMAND MODE DESCRIPTION
diag P Provided for support personnel to collect internal system information. It is not
recommended that you use these.
diag-info P Has the ZyWALL create a new diagnostic file.
dir P Lists files in a directory.
disable U/P Goes from privilege mode to user mode
enable U/P Goes from user mode to privilege mode
exit U/P Goes to a previous mode or logs out.
htm U/P Goes to htm (hardware test module) mode for testing hardware components. You
may need to use the htm commands if your customer support Engineer asks you
to during troubleshooting.
Note: These commands are for ZyXEL’s internal manufacturing
process.
interface U/P Dials or disconnects an interface.
no packet-trace U/P Turns of packet tracing.
nslookup U/P Resol ves an IP add ress to a host name and vice-versa.
packet-trace U/P Performs a packet trace.
ping U/P Pings an IP address or host name.
psm U/P Goes to psm (product support module) mode for setting product parameters. You
may need to use the htm commands if your customer support Engineer asks you
to during troubleshooting.
Note: These commands are for ZyXEL’s internal manufacturing
process.
reboot P Restarts the device.
release P Releases DHCP information from an interface.
rename P Renames a configuration file.
renew P Renews DHCP information for an interface.
run P Runs a script.
setenv U/P Turns stop-on-error on (terminates booting if an error is found in a configuration
file) or off (ignores configuration file errors and continues booting).
show U/P Displays command statistics. See the associated command chapter in this guide.
shutdown P Writes all d data to disk and stops the system processes. It does not turn off the
power.
telnet U/P Establishes a connection to the TCP port number 23 of the specified host name or
test aaa U/P Tests whether the specified user name can be successfully authenticated by an
traceroute P Traces the route to the specified host name or IP address.
write P Saves the current configuration to the ZyWALL. All unsaved changes are lost after
IP address.
external authentication server.
the ZyWALL restarts.
28
ZyWALL (ZLD) CLI Reference Guide
Page 29
Chapter 2 User and Privilege Modes
Subsequent chapters in this guide describe the configuration commands. User/privilege mode
commands that are also configuration commands (for example, ‘show’) are described in more
detail in the related configuration command chapter.
2.1.1 Debug Commands
Debug commands marked with an asterisk (*) are not available when the debug flag is on and
are for ZyXEL service personnel use only. The debug commands follow a syntax that is
Linux-based, so if there is a Linux equivalent, it is displayed in this chapter for your reference.
You must know a command listed here well before you use it. Otherwise, it may cause
undesired results.
Table 5 Debug Commands
COMMAND SYNTAX DESCRIPTION LINUX COMMAND EQUIVALENT
debug alg FTP/SIP ALG debug commands
debug anti-spam Anti-Spam debug commands
debug app Application patrol debug command
debug app show l7protocol
(*)
debug ca (*) Certificate debug commands
debug content-filter Content Filtering debug commands
debug device-ha (*) Device HA debug commands
debug eps Endpoint security debug commands
debug force-auth (*) Authentication policy debug commands
debug gui (*) GUI cgi related debug commands
debug gui (*) Web Configurator releated debug
debug hardware (*) Hardware debug commands
debug idp IDP debug commands
debug idp-av IDP and Anti-Virus debug commands
debug interface Interface debug commands
debug interface ifconfig
[interface]
debug interface-group Port grouping debug commands
debug ip dns DNS debug commands
debug ip virtual-server Virtual Server (NAT) debug commands.
debug ipsec IPSec VPN debug commands
debug logging System logging debug commands
debug manufacture Manufacturing related debug
debug myzyxel server (*) Myzyxel.com debug commands
debug network arpignore (*) Enable/Display the ignoring of ARP
Shows app patrol protocol list > cat /etc/l7_protocols/
protocol.list
commands
Shows system interfaces detail > ifconfig [interface]
commands
cat /proc/sys/net/ipv4/
responses for interfaces which don't
own the IP address
conf/*/arp_ignore
ZyWALL (ZLD) CLI Reference Guide
29
Page 30
Chapter 2 User and Privilege Modes
Table 5 Debug Commands (continued)
COMMAND SYNTAX DESCRIPTION LINUX COMMAND EQUIVALENT
debug no myzyxel server (*) Set the myZyXEL.com registration/
update server to the official site
debug policy-route (*) Policy route debug command
debug reset content-filter
profiling
debug service-register Service registration debug command
debug show content-filter
server
debug show myzyxel server
status
debug show ipset Lists the ZyWALL‘s received cards
debug show myzyxel server
status
debug sslvpn SSL VPN debug commands
debug [cmdexec|corefile|ip
|kernel|mac-idrewrite|observer|switch
|system|zyinetpkt|zysh-iptop] (*)
debug update server (*) Update server debug command
Content Filtering debug commands
Category-based content filtering debug
command
Myzyxel.com debug commands
Myzyxel.com debug commands
ZLD internal debug commands
30
ZyWALL (ZLD) CLI Reference Guide
Page 31

CHAPTER 3
Object Reference
This chapter describes how to use object reference commands.
3.1 Object Reference Commands
The object reference commands are used to see which configuration settings reference a
specfic object. You can use this table when you want to delete an object because you have to
remove references to the object first.
Table 6 show reference Commands
COMMAND DESCRIPTION
show reference object username
[username]
show reference object address
[profile]
show reference object eps
[profile]
show reference object service
[profile]
show reference object schedule
[profile]
show reference object interface
[interface_name |
virtual_interface_name]
show reference object aaa
authentication [default |
auth_method]
show reference object ca
category {local|remote}
[cert_name]
show reference object account
pppoe [profile]
show reference object account
pptp [profile]
show reference object sslvpn
application [profile]
show reference object crypto map
[crypto_name]
Displays which configuration settings reference the
specified user object.
Displays which configuration settings reference the
specified address object.
Displays which configuration settings reference the
specified endpoint security object.
Displays which configuration settings reference the
specified service object.
Displays which configuration settings reference the
specified schedule object.
Displays which configuration settings reference the
specified interface or virtual interface object.
Displays which configuration settings reference the
specified AAA authentication object.
Displays which configuration settings reference the
specified authentication method object.
Displays which configuration settings reference the
specified PPPoE account object.
Displays which configuration settings reference the
specified PPTP account object.
Displays which configuration settings reference the
specified SSL VPN application object.
Displays which configuration settings reference the
specified VPN connection object.
ZyWALL (ZLD) CLI Reference Guide
31
Page 32

Chapter 3 Object Reference
Table 6 show reference Commands (continued)
COMMAND DESCRIPTION
show reference object isakmp
policy [isakmp_name]
show reference object sslvpn
policy [profile]
show reference object zone
[profile]
show reference object-group
username [username]
show reference object-group
address [profile]
show reference object-group
service [profile]
show reference object-group
interface [profile]
show reference object-group aaa
ad [group_name]
show reference object-group aaa
ldap [group_name]
show reference object-group aaa
radius [group_name]
Displays which configuration settings reference the
specified VPN gateway object.
Displays which configuration settings reference the
specified SSL VPN object.
Displays which configuration settings reference the
specified zone object.
Displays which configuration settings reference the
specified user group object.
Displays which configuration settings reference the
specified address group object.
Displays which configuration settings reference the
specified service group object.
Displays which configuration settings reference the
specified trunk object.
Displays which configuration settings reference the
specified AAA AD group object.
Displays which configuration settings reference the
specified AAA LDAP group object.
Displays which configuration settings reference the
specified AAA RADIUS group object.
3.1.1 Object Reference Command Example
This example shows how to check which configuration is using an address object named
LAN1_SUBNET. For the command output, firewall rule 3 named LAN1-to-USG-2000 is
using the address object.
Router(config)# show reference object address LAN1_SUBNET
LAN1_SUBNET References:
Category
Rule Priority Rule Name
Description
===========================================================================
Firewall
3 N/A
LAN1-to-USG-2000
Router(config)#
32
ZyWALL (ZLD) CLI Reference Guide
Page 33

CHAPTER 4
Status
This chapter explains some commands you can use to display information about the
ZyWALL’s current operational state.
Table 7 Status Show Commands
COMMAND DESCRIPTION
show boot status Displays details about the ZyWALL’s startup state.
show comport status Displays whether the console and auxiliary ports are on or off.
show cpu status Displays the CPU utilization.
show disk Displays the disk utilization.
show extension-slot Displays the status of the extension card slot and the USB ports and the names of any
connected devices.
show fan-speed Displays the current fan speed.
show led status Displays the status of each LED on the ZyWALL.
show mac Displays the ZyWALL’s MAC address.
show mem status Displays what percentage of the ZyWALL’s memory is currently being used.
show ram-size Displays the size of the ZyWALL’s on-board RAM.
show redundant-
power status
show serial-number Displays the serial number of this ZyWALL.
show socket listen Displays the ZyWALL’s listening ports
show socket open Displays the ports that are open on the ZyWALL.
show system uptime Displays how long the ZyWALL has been running since it last restarted or was turned
show version Displays the ZyWALL’s model, firmware and build information.
Displays the status of the ZyWALL’s power modules. The ZyWALL has two power
modules. It can continue operating on a single power module if one fails.
on.
Here are examples of the commands that display the CPU and disk utilization.
Router(config)# show cpu status
CPU utilization: 0 %
CPU utilization for 1 min: 0 %
CPU utilization for 5 min: 0 %
Router(config)# show disk
; <cr> |
Router(config)# show disk
No. Disk Size(MB) Usage
===========================================================================
1 image 67 83%
2 onboard flash 163 15%
ZyWALL (ZLD) CLI Reference Guide
33
Page 34

Chapter 4 Status
Here are examples of the commands that display the fan speed, MAC address, memory usage,
RAM size, and serial number.
Router(config)# show fan-speed
FAN1(F00)(rpm): limit(hi)=6500, limit(lo)=1400, max=6650, min=6642, avg=6644
FAN2(F01)(rpm): limit(hi)=6500, limit(lo)=1400, max=6809, min=6783, avg=6795
FAN3(F02)(rpm): limit(hi)=6500, limit(lo)=1400, max=6683, min=6666, avg=6674
FAN4(F03)(rpm): limit(hi)=6500, limit(lo)=1400, max=6633, min=6617, avg=6627
Router(config)# show mac
MAC address: 28:61:32:89:37:61-28:61:32:89:37:67
Router(config)# show mem status
memory usage: 39%
Router(config)# show ram-size
ram size: 510MB
Router(config)# show serial-number
serial number: S060Z12020460
Here is an example of the command that displays the listening ports.
Router(config)# show socket listen
No. Proto Local_Address Foreign_Address State
===========================================================================
1 tcp 0.0.0.0:2601 0.0.0.0:0 LISTEN
2 tcp 0.0.0.0:2602 0.0.0.0:0 LISTEN
3 tcp 127.0.0.1:10443 0.0.0.0:0 LISTEN
4 tcp 0.0.0.0:2604 0.0.0.0:0 LISTEN
5 tcp 0.0.0.0:80 0.0.0.0:0 LISTEN
6 tcp 127.0.0.1:8085 0.0.0.0:0 LISTEN
7 tcp 1.1.1.1:53 0.0.0.0:0 LISTEN
8 tcp 172.23.37.205:53 0.0.0.0:0 LISTEN
9 tcp 10.0.0.8:53 0.0.0.0:0 LISTEN
10 tcp 172.23.37.240:53 0.0.0.0:0 LISTEN
11 tcp 192.168.1.1:53 0.0.0.0:0 LISTEN
12 tcp 127.0.0.1:53 0.0.0.0:0 LISTEN
13 tcp 0.0.0.0:21 0.0.0.0:0 LISTEN
14 tcp 0.0.0.0:22 0.0.0.0:0 LISTEN
15 tcp 127.0.0.1:953 0.0.0.0:0 LISTEN
16 tcp 0.0.0.0:443 0.0.0.0:0 LISTEN
17 tcp 127.0.0.1:1723 0.0.0.0:0 LISTEN
34
ZyWALL (ZLD) CLI Reference Guide
Page 35

Chapter 4 Status
Here is an example of the command that displays the open ports.
Router(config)# show socket open
No. Proto Local_Address Foreign_Address State
===========================================================================
1 tcp 172.23.37.240:22 172.23.37.10:1179 ESTABLISHED
2 udp 127.0.0.1:64002 0.0.0.0:0
3 udp 0.0.0.0:520 0.0.0.0:0
4 udp 0.0.0.0:138 0.0.0.0:0
5 udp 0.0.0.0:138 0.0.0.0:0
6 udp 0.0.0.0:138 0.0.0.0:0
7 udp 0.0.0.0:138 0.0.0.0:0
8 udp 0.0.0.0:138 0.0.0.0:0
9 udp 0.0.0.0:138 0.0.0.0:0
10 udp 0.0.0.0:138 0.0.0.0:0
11 udp 0.0.0.0:32779 0.0.0.0:0
12 udp 192.168.1.1:4500 0.0.0.0:0
13 udp 1.1.1.1:4500 0.0.0.0:0
14 udp 10.0.0.8:4500 0.0.0.0:0
15 udp 172.23.37.205:4500 0.0.0.0:0
16 udp 172.23.37.240:4500 0.0.0.0:0
17 udp 127.0.0.1:4500 0.0.0.0:0
18 udp 127.0.0.1:63000 0.0.0.0:0
19 udp 127.0.0.1:63001 0.0.0.0:0
20 udp 127.0.0.1:63002 0.0.0.0:0
21 udp 0.0.0.0:161 0.0.0.0:0
22 udp 127.0.0.1:63009 0.0.0.0:0
23 udp 192.168.1.1:1701 0.0.0.0:0
24 udp 1.1.1.1:1701 0.0.0.0:0
25 udp 10.0.0.8:1701 0.0.0.0:0
26 udp 172.23.37.205:1701 0.0.0.0:0
27 udp 172.23.37.240:1701 0.0.0.0:0
28 udp 127.0.0.1:1701 0.0.0.0:0
29 udp 127.0.0.1:63024 0.0.0.0:0
30 udp 127.0.0.1:30000 0.0.0.0:0
31 udp 1.1.1.1:53 0.0.0.0:0
32 udp 172.23.37.205:53 0.0.0.0:0
33 udp 10.0.0.8:53 0.0.0.0:0
34 udp 172.23.37.240:53 0.0.0.0:0
35 udp 192.168.1.1:53 0.0.0.0:0
36 udp 127.0.0.1:53 0.0.0.0:0
37 udp 0.0.0.0:67 0.0.0.0:0
38 udp 127.0.0.1:63046 0.0.0.0:0
39 udp 127.0.0.1:65097 0.0.0.0:0
40 udp 0.0.0.0:65098 0.0.0.0:0
41 udp 192.168.1.1:500 0.0.0.0:0
42 udp 1.1.1.1:500 0.0.0.0:0
43 udp 10.0.0.8:500 0.0.0.0:0
44 udp 172.23.37.205:500 0.0.0.0:0
45 udp 172.23.37.240:500 0.0.0.0:0
46 udp 127.0.0.1:500 0.0.0.0:0
ZyWALL (ZLD) CLI Reference Guide
35
Page 36

Chapter 4 Status
Here are examples of the commands that display the system uptime and model, firmware, and
build information.
Router> show system uptime
system uptime: 04:18:00
Router> show version
ZyXEL Communications Corp.
model : ZyWALL USG 100
firmware version: 2.20(AQQ.0)b3
BM version : 1.08
build date : 2009-11-21 01:18:06
This example shows the current LED states on the ZyWALL. The SYS LED lights on and
green. The AUX and HDD LEDs are both off.
Router> show led status
sys: green
aux: off
hdd: off
Router>
36
ZyWALL (ZLD) CLI Reference Guide
Page 37

CHAPTER 5
Registration
This chapter introduces myzyxel.com and shows you how to register the ZyWALL for IDP/
AppPatrol, anti-virus, content filtering, and SSL VPN services using commands.
5.1 myZyXEL.com overview
myZyXEL.com is ZyXEL’s online services center where you can register your ZyWALL and
manage subscription services available for the ZyWALL.
" You need to create an account before you can register your device and
activate the services at myZyXEL.com.
You can directly create a myZyXEL.com account, register your ZyWALL and activate a
service using the Licensing > Registration screens. Alternatively, go to http://
www .myZyXEL.com with the ZyWALL’s serial number and LAN MAC address to register it.
Refer to the web site’s on-line help for details.
" To activate a service on a ZyW ALL, you need to access myZyXEL.com via that
ZyWALL.
5.1.1 Subscription Services Available on the ZyWALL
The ZyWALL can use anti-virus, IDP/AppPatrol (Intrusion Detection and Prevention and
application patrol), SSL VPN, and content filtering subscription services.
• The ZyWALL’s anti-virus packet scanner uses the signature files on the ZyWALL to
detect virus files. Your ZyWALL scans files transmitting through the enabled interfaces
into the network. Subscribe to signature files for ZyXEL’s anti-virus engine or one
powered by Kaspersky. After the service is activated, the ZyWALL can download the upto-date signature files from the update server (http://myupdate.zywall.zyxel.com).
ZyWALL (ZLD) CLI Reference Guide
37
Page 38

Chapter 5 Registration
When using the trial, you can switch from one engine to the other in the Registration
screen. There is no limit on the number of times you can change the anti-virus engine
selection during the trial, but you only get a total of one anti-virus trial period (not a
separate trial period for each anti-virus engine). After the service is activated, the
ZyWALL can download the up-to-date signature files from the update server (http://
myupdate.zywall.zyxel.com).
After the trial expires, you need to purchase an iCard for the anti-virus engine you want to
use and enter the PIN number (license key) in the Registration > Service screen. You
must use the ZyXEL anti-virus iCard for the ZyXEL anti-virus engine and the Kaspersky
anti-virus iCard for the Kaspersky anti-virus engine. If you were already using an iCard
anti-virus subscription, any remaining time on your earlier subscription is automatically
added to the new subscription. Even if the earlier iCard anti-virus subscription was for a
different anti-virus engine. For example, suppose you purchase a one-year Kaspersky
engine anti-virus service subscription and use it for six months. Then you purchase a oneyear ZyXEL engine anti-virus service subscription and enter the iCard’s PIN number
(license key) in the Registration > Service screen. The one-year ZyXEL engine anti-virus
service subscription is automatically extended to 18 months.
• The IDP and application patrol features use the IDP/AppPatrol signature files on the
ZyWALL. IDP detects malicious or suspicious packets and responds immediately.
Application patrol conveniently manages the use of various applications on the network.
After the service is activated, the ZyWALL can download the up-to-date signature files
from the update server (http://myupdate.zywall.zyxel.com).
• SSL VPN tunnels provide secure network access to remote users. You can purchase and
enter a license key to have the ZyWALL use more SSL VPN tunnels.
• The content filter allows or blocks access to web sites. Subscribe to category-based
content filtering to block access to categories of web sites based on content. Your
ZyWALL accesses an external database that has millions of web sites categorized based
on content. You can have the ZyWALL block, block and/or log access to web sites based
on these categories.
• You will get automatic e-mail notification of new signature releases from mySecurityZone
after you activate the IDP/AppPatrol service. You can also check for new signatures at
http://mysecurity.zyxel.com.
See the respective chapters for more information about these features.
" To update the signature file or use a subscription service, you have to register
the ZyWALL and activate the corresponding service at myZyXEL.com (through
the ZyWALL).
38
ZyWALL (ZLD) CLI Reference Guide
Page 39

Chapter 5 Registration
5.2 Registration Commands
The following table identifies the values required for many of these commands. Other input
values are discussed with the corresponding commands.
Table 8 Input Values for General Registration Commands
LABEL DESCRIPTION
user_name The user name of your myZyXEL.com account. You must use six to 20
password The password for the myZyXEL.com account. You must use six to 20
The following table describes the commands available for registration. You must use the
configure terminal command to enter the configuration mode before you can use these
commands.
Table 9 Command Summary: Registration
COMMAND DESCRIPTION
device-register checkuser user_name Checks if the user name exists in the
device-register username user_name password
password [e-mail user@domainname] [country-code
country_code] [reseller-name name] [reseller-
mail email-address] [reseller-phone phonenumber] [vat vat-number]
service-register checkexpire Gets information of all service subscriptions from
service-register service-type standard licensekey key_value
service-register service-type trial service
{content-filter|idp}
service-register service-type trial service all
{kav|zav}
service-register service-type trial service av
{kav|zav}
service-register service-type trial av-engine
{kav|zav}
show device-register status Displays whether the device is registered and
show service-register reseller-info Displays your seller’s information that you have
show service-register server-type Displays the type of the register server to which
show service-register status {all|contentfilter|idp|sslvpn|av}
alphanumeric characters (and the underscore). Spaces are not allowed.
alphanumeric characters (and the underscore). Spaces are not allowed.
myZyXEL.com database.
Registers the device with an existing account or
creates a new account and registers the device at
one time.
country_code: see Table 10 on page 41
myZyXEL.com and updates the status table.
Activates a standard service subscription with the
license key.
Activates the content filter or IDP trial service
subscription.
Activates all of the trial service subscriptions,
including Kaspersky or ZyXEL anti-virus.
Activates a Kaspersky or ZyXEL anti-virus trial
service subscription.
Changes from one anti-virus engine to the other.
account information.
entered when registration.
your ZyWALL is connected.
Displays service license information.
ZyWALL (ZLD) CLI Reference Guide
39
Page 40

Chapter 5 Registration
5.2.1 Command Examples
The following commands allow you to register your device with an existing account or create
a new account and register the device at one time, and activate a trial service subscription.
Router# configure terminal
Router(config)# device-register username alexctsui password 123456
Router(config)# service-register service-type trial service content-filter
The following command displays the account information and whether the device is
registered.
Router# configure terminal
Router(config)# show device-register status
username : example
password : 123456
device register status : yes
expiration self check : no
The following command displays the service registration status and type and how many days
remain before the service expires.
Router# configure terminal
Router(config)# show service-register status all
Service Status Type Count Expiration
===========================================================================
IDP Signature Licensed Standard N/A 176
Anti-Virus Not Licensed None N/A 0
SSLVPN Not Licensed None 5 N/A
Content-Filter Not Licensed None N/A 0
The following command displays the seller details you have entered on the ZyWALL.
Router# configure terminal
Router(config)# show service-register reseller-info
seller’s name: ABC
seller’s e-mail: abc@example.com
seller’s contact number: 12345678
vat number:
40
ZyWALL (ZLD) CLI Reference Guide
Page 41

Chapter 5 Registration
5.3 Country Code
The following table displays the number for each country.
Table 10 Country Codes
COUNTRY CODE COUNTRY NAME COUNTRY CODE COUNTRY NAME
001 Afghanistan 002 Albania
003 Algeria 004 American Samoa
005 Andorra 006 Angola
007 Anguilla 008 Antarctica
009 Antigua & Barbuda 010 Argentina
011 Armenia 012 Aruba
013 Ascension Island 014 Australia
015 Austria 016 Azerbaijan
017 Bahamas 018 Bahrain
019 Bangladesh 020 Barbados
021 Belarus 022 Belgium
023 Belize 024 Benin
025 Bermuda 026 Bhutan
027 Bolivia 028 Bosnia and Herzegovina
029 Botswana 030 Bouvet Island
031 Brazil 032 British Indian Ocean Territory
033 Brunei Darussalam 034 Bulgaria
035 Burkina Faso 036 Burundi
037 Cambodia 038 Cameroon
039 Canada 040 Cape Verde
041 Cayman Islands 042 Central African Republic
043 Chad 044 Chile
045 China 046 Christmas Island
047 Cocos (Keeling) Islands 048 Colombia
049 Comoros 050 Congo, Democratic Republic of the
051 Congo, Republic of 052 Cook Islands
053 Costa Rica 054 Co te d'Ivoire
055 Croatia/H rvatska 056 Cyprus
057 Czech Republic 058 Denmark
059 Djibouti 060 Dominica
061 Dominican Republic 062 East Timor
063 Ecuador 064 Egypt
065 El Salvador 066 Equatorial Guinea
067 Eritrea 068 Estonia
069 Ethiopia 070 Falkland Islands (Malvina)
ZyWALL (ZLD) CLI Reference Guide
41
Page 42

Chapter 5 Registration
Table 10 Country Codes (continued)
COUNTRY CODE COUNTRY NAME COUNTRY CODE COUNTRY NAME
071 Faroe Islands 072 Fiji
073 Finland 074 France
075 France (Metropolitan) 076 French Guiana
077 French Polynesia 078 French Southern Territories
079 Gabon 080 Gambia
081 Georgia 082 Germany
083 Ghana 084 Gibraltar
085 Great Britain 086 Greece
087 Greenland 088 Grenada
089 Guadeloupe 090 Guam
091 Guatemala 092 Guernsey
093 Guinea 094 Guinea-Bissau
095 Guyana 096 Haiti
097 Heard and McDonald Islands 098 Ho ly See (City Vatican State)
099 Honduras 100 Hong Kong
101 Hungary 102 Iceland
103 India 104 Indonesia
105 Ireland 106 Isle of Man
107 Italy 108 Jamaica
109 Japan 110 Jersey
111 Jordan 112 Kazakhstan
113 Kenya 114 Kiribati
115 Korea, Republic of 116 Kuwait
117 Kyrgyzstan 118 Lao People’s Democratic Republic
119 Latvia 120 Lebanon
121 Lesotho 122 Liberia
123 Liechtenstein 124 Lithuania
125 Luxembourg 126 Macau
127 Macedonia, Former Yugoslav
Republic
129 Malawi 130 Malaysia
131 Maldives 132 Mali
133 Malta 134 Marshall Islands
135 Martinique 136 Mauritania
137 Mauritius 138 Mayotte
139 Mexico 140 Micronesia, Federal State of
141 Moldova, Republic of 142 Monaco
143 Mongolia 144 Montserrat
145 Morocco 146 Mozambique
128 Madagascar
42
ZyWALL (ZLD) CLI Reference Guide
Page 43

Chapter 5 Registration
Table 10 Country Codes (continued)
COUNTRY CODE COUNTRY NAME COUNTRY CODE COUNTRY NAME
147 Namibia 148 Nauru
149 Nepal 150 Netherlands
151 Netherlands Antilles 152 New Caledonia
153 New Zealand 154 Nicaragua
155 Niger 156 Nigeria
157 Niue 158 Norfolk Island
159 Northern Mariana Islands 160 Norway
161 Not Determined 162 Oman
163 Pakistan 164 Palau
165 Panama 166 Papua New Guinea
167 Paraguay 168 Peru
169 Philippines 170 Pitcairn Island
171 Poland 172 Portugal
173 Puerto Rico 174 Qatar
175 Reunion Island 176 Romania
177 Russian Federation 178 Rwanda
179 Saint Kitts and Nevis 180 Saint Lucia
181 Saint Vincent and the Grenadines 182 San Marino
183 Sao Tome and Principe 184 Saudi Arabia
185 Senegal 186 Seychelles
187 Sierra Leone 188 Singapore
189 Slovak Republic 190 Slovenia
191 Solomon Islands 192 Somalia
193 South Africa 194 South Georgia and the South
185 Spain 196 Sri Lanka
197 St Pierre and Miquelon 198 St. Helena
199 Suriname 200 Svalbard and Jan Mayen Islands
201 Swaziland 202 Sweden
203 Switzerland 204 Taiwan
205 Tajikistan 206 Tanzania
207 Thailand 208 Togo
209 Tokelau 210 Tonga
211 Trinidad and Tobago 212 Tunisia
213 Turkey 214 Turkmenistan
215 Turks and Caicos Islands 216 Tuvalu
217 US Minor Outlying Islands 218 Uganda
219 Ukraine 220 United Arab Emirates
221 United Kingdom 222 United States
Sandwich Islands
ZyWALL (ZLD) CLI Reference Guide
43
Page 44

Chapter 5 Registration
Table 10 Country Codes (continued)
COUNTRY CODE COUNTRY NAME COUNTRY CODE COUNTRY NAME
223 Uruguay 224 Uzbekistan
225 Vanuatu 226 Venezuela
227 Vietnam 228 Virgin Islands (British)
229 Virgin Islands (USA) 230 Wallis And Futuna Islands
231 Western Sahara 232 Western Samoa
233 Yemen 234 Yugoslavia
235 Zambia 236 Zimbabwe
44
ZyWALL (ZLD) CLI Reference Guide
Page 45

PART II
Network
Interfaces (47)
Trunks (85)
Route (91)
Routing Protocol (99)
Zones (103)
DDNS (107)
V irtual Servers (111)
HTTP Redirect (117)
ALG (121)
45
Page 46

46
Page 47

CHAPTER 6
Interfaces
This chapter shows you how to use interface-related commands.
6.1 Interface Overview
In general, an interface has the following characteristics.
• An interface is a logical entity through which (layer-3) packets pass.
• An interface is bound to a physical port or another interface.
• Many interfaces can share the same physical port.
• An interface is bound to at most one zone.
• Many interface can belong to the same zone.
• Layer-3 virtualization (IP alias, for example) is a kind of interface.
Some characteristics do not apply to some types of interfaces.
6.1.1 Types of Interfaces
You can create several types of interfaces in the ZyWALL. The types supported vary by
ZyWALL model.
• Port groups create a hardware connection between physical ports at the layer-2 (data link,
MAC address) level.
• Ethernet interfaces are the foundation for defining other interfaces and network policies.
RIP and OSPF are also configured in these interfaces.
• VLAN interfaces receive and send tagged frames. The ZyWALL automatically adds or
removes the tags as needed. Each VLAN can only be associated with one Ethernet
interface.
• Bridge interfaces create a software connection between Ethernet or VLAN interfaces at
the layer-2 (data link, MAC address) level. Unlike port groups, bridge interfaces can take
advantage of some security features in the ZyWALL. You can also assign an IP address
and subnet mask to the bridge.
• PPPoE/PPTP interfaces support Point-to-Point Protocols (PPP). ISP accounts are
required for PPPoE/PPTP interfaces.
• Cellular interfaces are for 3G WAN connections via a connected 3G device.
• WLAN interfaces are for wireless LAN (IEEE 802.11b/g) connections via an installed
wireless LAN card.
ZyWALL (ZLD) CLI Reference Guide
47
Page 48

Chapter 6 Interfaces
• Virtual interfaces (IP alias) provide additional routing information in the ZyWALL.
There are three types: virtual Ethernet interfaces, virtual VLAN interfaces, and virtual
bridge interfaces.
•The auxiliary interface, along with an external modem, provides an interface the
ZyWALL can use to dial out. This interface can be used as a backup WAN interface, for
example. The auxiliary interface controls the DIAL BACKUP port (labeled AUX on
some models).
• Trunks manage load balancing between interfaces.
Port groups, trunks, and the auxiliary interface have a lot of characteristics that are specific to
each type of interface. These characteristics are listed in the following tables and discussed in
more detail farther on.
Table 11 Characteristics of Ethernet, VLAN, Bridge, PPPoE/PPTP, and Virtual Interface (ZyWALL USG
300 and Above)
CHARACTERISTICS ETHERNET VLAN BRIDGE PPPOE/PPTP VIRTUAL
Name* gex vlanx brx pppx **
IP Address Assignment
static IP address
DHCP client Yes Yes Yes Yes No
routing metric Yes Yes Yes Yes Yes
Interface Parameters
bandwidth restrictions
packet size (MTU) Yes Yes Yes Yes No
data size (MSS)
traffic prioritization Yes Yes Yes Yes No
DHCP
DHCP server
DHCP relay Yes Yes Yes No No
Ping Check Yes Yes Yes Yes No
Yes Yes Yes Yes Yes
Yes Yes Yes Yes Yes
Yes Yes Yes Yes No
Yes Yes Yes No No
48
* - The format of interface names is strict. Each name consists of 2-4 letters (interface type), followed by a
number (x, limited by the maximum number of each type of interface). For example, Ethernet interface
names are ge1, ge2, ge3, ...; VLAN interfaces are vlan0, vlan1, vlan2, ...; and so on.
** - The names of virtual interfaces are derived from the interfaces on which they are created. For example,
virtual interfaces created on Ethernet interface ge1 are called ge1:1, ge1:2, and so on. Virtual interfaces
created on VLAN interface vlan2 are called vlan2:1, vlan2:2, and so on. You cannot specify the number
after the colon(:) in the web configurator; it is a sequential number. You can specify the number after the
colon if you use the CLI to set up a virtual Interface Parameters
Table 12 Ethernet, VLAN, Bridge, PPP, and Virtual Interface Characteristics (ZyWALL USG
100 and 200 Models)
CHARACTERISTICS ETHERNET ETHERNET ETHERNET VLAN BRIDGE PPP VIRTUAL
Name* opt wan1, wan2 lan1, ext-
Configurable Zone
IP Address
Assignment
Static IP address
Yes No No Yes Yes No No
Yes Yes Yes Yes Yes Yes Yes
wlan, dmz
vlanx brx pppx **
ZyWALL (ZLD) CLI Reference Guide
Page 49

Chapter 6 Interfaces
Table 12 Ethernet, VLAN, Bridge, PPP, and Virtual Interface Characteristics (ZyWALL USG
100 and 200 Models) (continued)
CHARACTERISTICS ETHERNET ETHERNET ETHERNET VLAN BRIDGE PPP VIRTUAL
DHCP client Yes Yes No Yes Yes Yes No
Routing metric Yes Yes Yes Yes Yes Yes Yes
Interface Parameters
Bandwidth
restrictions
Packet size
(MTU)
Data size (MSS) Yes Yes Yes Yes Yes Yes No
DHCP
DHCP server
DHCP relay Yes No Yes Yes Yes No No
Connectivity Check
* - Each name consists of 2-4 letters (interface type), followed by a number (x). For most interfaces, x is limited
by the maximum number of the type of interface. For VLAN interfaces, x is defined by the number you
enter in the VLAN name field. For example, Ethernet interface names are wan1, wan2, opt, lan1, extwlan, dmz; VLAN interfaces are vlan0, vlan1, vlan2, ...; and so on.
** - The names of virtual interfaces are derived from the interfaces on which they are created. For example,
virtual interfaces created on Ethernet interface wan1 are called wan1:1, wan1:2, and so on. Virtual
interfaces created on VLAN interface vlan2 are called vlan2:1, vlan2:2, and so on. You cannot specify the
number after the colon(:) in the web configurator; it is a sequential number. You can specify the number
after the colon if you use the CLI to set up a virtual interface.
Yes Yes Yes Yes Yes Yes Yes
Yes Yes Yes Yes Yes Yes No
Yes No Yes Yes Yes No No
Yes Yes No Yes Yes Yes No
Table 13 Cellular and WLAN Interface Characteristics
CHARACTERISTICS CELLULAR WLAN
Name* cellularx wlan-x-x
Configurable Zone
IP Address
Assignment
Static IP address
DHCP client Yes No
Routing metric
Interface Parameters
Bandwidth
restrictions
Packet size
(MTU)
Data size (MSS)
DHCP
DHCP server No
DHCP relay N o
Connectivity Check
Yes** Yes
Yes Yes
Yes No
Yes Yes
Yes Yes
Yes Yes
Yes
Yes
Yes No
* - Each name consists of letters (interface type), followed by a number (x). For most interfaces, x is limited by
the maximum number of the type of interface. For WLAN interfaces, the first number identifies the slot
and the second number identifies the individual interface.
ZyWALL (ZLD) CLI Reference Guide
49
Page 50

Chapter 6 Interfaces
** - Cellular interfaces can be added to the WAN zone or no zone.
6.1.2 Relationships Between Interfaces
In the ZyWALL, interfaces are usually created on top of other interfaces. Only Ethernet
interfaces are created directly on top of the physical ports (or port groups). The relationships
between interfaces are explained in the following table.
Table 14 Relationships Between Different Types of Interfaces
INTERFACE
auxiliary interface auxiliary port
port group physical port
Ethernet interface physical port
VLAN interface Ethernet interface
bridge interface Ethernet interface*
PPPoE/PPTP interface
(ZyWALL USG 300 and above)
PPPoE/PPTP interface
(ZyWALL USG 100 and 200
models)
virtual interface
(virtual Ethernet interface)
(virtual VLAN interface)
(virtual bridge interface)
trunk Ethernet interface
REQUIRED PORT /
INTERFACE
port group
WLAN interface*
VLAN interface*
Ethernet interface*
VLAN interface*
bridge interface
WAN1, WAN2, OPT*
Ethernet interface*
VLAN interface*
bridge interface
Cellular interface
VLAN interface
bridge interface
PPPoE/PPTP interface
auxiliary interface
50
* - You cannot set up a PPPoE/PPTP interface, virtual Ethernet interface, or virtual VLAN interface if the
underlying interface is a member of a bridge. You also cannot add an Ethernet interface or VLAN interface
to a bridge if the member interface has a virtual interface or PPPoE/PPTP interface on top of it.
ZyWALL (ZLD) CLI Reference Guide
Page 51

6.2 Interface General Commands Summary
The following table identifies the values required for many of these commands. Other input
values are discussed with the corresponding commands.
Table 15 Input Values for General Interface Commands
LABEL DESCRIPTION
interface_name The name of the interface.
Ethernet interface: For the ZyWALL USG 300 and above, use gex, x = 1 - N,
where N equals the highest numbered Ethernet interface for your ZyWALL model.
ZyWALL USG 100 and 200 models use a name such as wan1, wan2, opt,
lan1, ext-wlan, or dmz.
virtual interface on top of Ethernet interface: add a colon (:) and the number of the
virtual interface. For example: gex:y, x = 1 - N, y = 1 - 4
VLAN interface: vlanx, x = 0 - 4094
virtual interface on top of VLAN interface: vlanx:y, x = 0 - 4094, y = 1 - 4
bridge interface: brx, x = 0 - N, where N depends on the number of bridge
interfaces your ZyWALL model supports.
virtual interface on top of bridge interface: brx:y, x = the number of the bridge
interface, y = 1 - 4
PPPoE/PPTP interface: pppx, x = 0 - N, where N depends on the number of
PPPoE/PPTP interfaces your ZyWALL model supports.
profile_name The name of the DHCP pool . You may use 1-31 alphanumeric characters,
domain_name Fully-qualified domain name. You may up to 254 alphanumeric characters,
underscores(
value is case-sensitive.
dashes (-), or periods (.), but the first character cannot be a period.
_), or dashes (-), but the first character cannot be a number. This
Chapter 6 Interfaces
The following sections introduce commands that are supported by several types of interfaces.
See Section 6.6 on page 68 for the unique commands for each type of interface.
6.2.1 Basic Interface Properties and IP Address Commands
This table lists basic properties and IP address commands.
Table 16 interface General Commands: Basic Properties and IP Address Assignment
COMMAND DESCRIPTION
show interface {ethernet | vlan | bridge | ppp
| auxiliary} status
show interface {interface_name | ethernet |
vlan | bridge | ppp | virtual ethernet |
virtual vlan | virtual bridge | auxiliary |
all}
show interface send statistics interval Displays the interval for how often the ZyWALL
show interface summary all Displays basic information about the interfaces.
show interface summary all status Displays the connection status of the interfaces.
[no] interface interface_name Creates the specified interface if necessary and
Displays the connection status of the specified type
of interfaces.
Displays information about the specified interface,
specified type of interfaces, or all interfaces. See
Section 6.6.1 on page 71 for all possible cellular
status description.
refreshes the sent packet statistics for the
interfaces.
enters sub-command mode. The
deletes the specified interface.
no command
ZyWALL (ZLD) CLI Reference Guide
51
Page 52

Chapter 6 Interfaces
Table 16 interface General Commands: Basic Properties and IP Address Assignment (continued)
COMMAND DESCRIPTION
[no] description description Specifies the description for the specified interface.
The
no command clears the description.
description: You can use alphanumeric and
()+/:=?!*#@$_%- characters, and it can be up
to 60 characters long.
[no] downstream <0..1048576> This is reserved for future use.
Specifies the downstream bandwidth for the
specified interface. The
downstream bandwidth to 1048576.
exit Leaves the sub-command mode.
[no] ip address dhcp Makes the specified interface a DHCP client; the
[no] ip address ip subnet_mask Assigns the specified IP address and subnet mask
[no] ip gateway ip Adds the specified gateway using the specified
ip gateway ip metric <0..15> Sets the priority (relative to every gateway on every
[no] metric <0..15> Sets the PPPoE/PPTP or cellular interface’s priority
[no] mss <536..1460> Specifies the maximum segment size (MSS) the
[no] mtu <576..1500> S pecifies the Maximum Transmission Unit, which is
[no] shutdown Deactivates the specified interface. The
traffic-prioritize {tcp-ack|contentfilter|dns|ipsec-vpn|ssl-vpn} bandwidth
<0..1048576> priority <1..7> [maximizebandwidth-usage];
traffic-prioritize {tcp-ack|contentfilter|dns|ipsec-vpn|ssl-vpn} deactivate
[no] upstream <0..1048576> Specifies the upstream bandwidth for the specified
DHCP server gives the specified interface its IP
address, subnet mask, and gateway. The
command makes the IP address static IP address
for the specified interface. (See the next comma nd
to set this IP address.)
to the specified interface. The no command clears
the IP address and the subnet mask.
interface. The no command removes the gateway.
interface) for the specified gateway. The lower the
number, the higher the priority.
relative to other interfaces. The lower the number,
the higher the priority.
interface is to use. MSS is the largest amount of
data, specified in bytes, that the interface can
handle in a single, unfragmented piece. The
command has the interface use its default MSS.
the maximum number of bytes in each packet
moving through this interface. The ZyWALL divides
larger packets into smaller fragments. The
command resets the MTU to 1500.
command activates it.
Applies traffic priority when the interface sends
TCP-ACK traffic, traffic for querying the content
filter, traffic for resolving domain names, or
encrypted traffic for an IPSec or SSL VPN tunnel. It
also sets how much bandwidth the traffic can use
and can turn on maximize bandwidth usage.
Turns off traffic priority settings for when the
interface sends the specified type of traffic.
interface. The
bandwidth to 1048576.
no command sets the upstream
no command sets the
no
no
no
no
52
ZyWALL (ZLD) CLI Reference Guide
Page 53

Chapter 6 Interfaces
Table 16 interface General Commands: Basic Properties and IP Address Assignment (continued)
COMMAND DESCRIPTION
interface reset
{interface_name|virtual_interface_name|all}
interface send statistics interval <15..3600> Sets how often the ZyWALL sends interface
show interface-name Displays all PPP and Ethernet interface system
interface-name {ppp_interface |
ethernet_interface} user_defined_name
interface-rename old_user_defined_name
new_user_defined_name
Resets the interface statistics TxPkts (transmitted
packets) and RxPkts (received packets) counts to
0. You can use the show interface summary
all status command to see the interface
statistics.
statistics to external servers. For example, syslog
server and Vantage Report server.
name and user-defined name mappings.
Specifies a name for a PPP or an Ethernet
interface. It can use alphanumeric characters,
hyphens, and underscores, and it can be up to 11
characters long.
ppp_interface | ethernet_interface: This
must be the system name of a PPP or an Ethernet
interface. Use the show interface-name
command to see the system name of interfaces.
user_defined_name:
• This name cannot be one of the follows:
"ethernet", "ppp", "vlan", "bridge", "virtual",
"wlan", "cellular", "aux", "tunnel", "status",
"summary", "all"
• This name cannot begin with one of the follows
either:
"ge", "ppp", "vlan", "wlan-", "br", "cellular",
"aux", "tunnel".
Modifies the user-defined name of a PPP or an
Ethernet interface.
6.2.1.1 Basic Interface Properties Command Examples
The following commands make Ethernet interface ge1 a DHCP client.
Router# configure terminal
Router(config)# interface ge1
Router(config-if)# ip address dhcp
Router(config-if)# exit
ZyWALL (ZLD) CLI Reference Guide
53
Page 54

Chapter 6 Interfaces
This example shows how to modify the name of interface ge4 to “VIP”. First you have to
check the interface system name (ge4 in this example) on the ZyWALL. Then change the
name and display the result.
Router> show interface-name
No. System Name User Defined Name
===========================================================================
1 ge1 ge1
2 ge2 ge2
3 ge3 ge3
4 ge4 ge4
5 ge5 ge5
Router> configure terminal
Router(config)# interface-name ge4 VIP
Router(config)# show interface-name
No. System Name User Defined Name
===========================================================================
1 ge1 ge1
2 ge2 ge2
3 ge3 ge3
4 ge4 VIP
5 ge5 ge5
Router(config)#
This example shows how to change the user defined name from VIP to Partner. Note that you
have to use the “interface-rename” command if you do not know the system name of the
interface. To use the “interface-name” command, you have to find out the corresponding
system name first (ge4 in this example). This example also shows how to change the user
defined name from Partner to Customer using the “interface-nam e” command.
Router(config)# interface-rename VIP Partner
Router(config)# show interface-name
No. System Name User Defined Name
===========================================================================
1 ge1 ge1
2 ge2 ge2
3 ge3 ge3
4 ge4 Partner
5 ge5 ge5
Router(config)#
Router(config)# interface-name ge4 Customer
Router(config)# show interface-name
No. System Name User Defined Name
===========================================================================
1 ge1 ge1
2 ge2 ge2
3 ge3 ge3
4 ge4 Customer
5 ge5 ge5
54
ZyWALL (ZLD) CLI Reference Guide
Page 55

This example shows how to restart an interface. You can check all interface names on the
ZyWALL. Then use either the system name or user-defined name of an interface (ge4 or
Customer in this example) to restart it.
Router> show interface-name
No. System Name User Defined Name
===========================================================================
1 ge1 ge1
2 ge2 ge2
3 ge3 ge3
4 ge4 Customer
5 ge5 ge5
Router> configure terminal
Router(config)# interface reset ge4
Router(config)# interface reset Customer
Router(config)#
6.2.2 DHCP Setting Commands
This table lists DHCP setting commands. DHCP is based on DHCP pools. Create a DHCP
pool if you want to assign a static IP address to a MAC address or if you want to specify the
starting IP address and pool size of a range of IP addresses that can be assigned to DHCP
clients. There are different commands for each configuration. Afterwards, in either case, you
have to bind the DHCP pool to the interface.
Chapter 6 Interfaces
Table 17 interface Commands: DHCP Settings
COMMAND DESCRIPTION
show ip dhcp pool [profile_name] Shows information about the specified DHCP poo l
or about all DHCP pools.
ip dhcp pool rename profile_name profile_name Renames the specified DHCP pool from the first
[no] ip dhcp pool profile_name Creates a DHCP pool if necessary and enters sub-
profile_name to the second profile_name.
command mode. You can use the DHCP pool to
create a static entry or to set up a range of IP
addresses to assign dynamically.
About the sub-command settings:
• If you use the
treats this DHCP pool as a static DHCP entry.
• If you do not use the
the network command, the ZyWALL treats
this DHCP pool as a pool of IP addresses.
• If you do not use the
host command, the ZyWALL
host command and use
host command or the
network command, the DHCP pool is not
properly configured and cannot be bound to
any interface.
no command removes the specified DHCP
The
pool.
show Shows information about the specified DHCP pool.
Use the following commands if you want to create
a static DHCP entry. If you do not use the host
command, the commands that are not in this
section have no effect, but you can still set them.
ZyWALL (ZLD) CLI Reference Guide
55
Page 56

Chapter 6 Interfaces
Table 17 interface Commands: DHCP Settings (continued)
COMMAND DESCRIPTION
[no] host ip Specifies the static IP address the ZyWALL should
assign. Use this command, along with
hardware-address, to create a static DHCP
entry.
Note: The IP address must be in the
same subnet as the interface to
which you plan to bind the DHCP
pool.
When this command is used, the ZyWALL treats
this DHCP pool like a static entry, regardless of the
network setting. The no command clears this
field.
[no] hardware-address mac_address Reserves the DHCP pool for the specified MAC
[no] client-identifier mac_address Specifies the MAC address that appears in the
[no] client-name host_name Specifies the host name that appears in the DHCP
network IP/<1..32>
network ip mask
no network
address. Use this command, along with host, to
create a static DHCP entry. The
clears this field.
DHCP client list. The
client list. The
host_name: You may use 1-31 alphanumeric
characters, underscores(
first character cannot be a number. This value is
case-sensitive.
Use the following commands if you want to create
a pool of IP addresses. These commands have no
effect if you use the host command. You can still
set them, however.
Specifies the IP address and subnet mask of the
specified DHCP pool. The subnet mask can be
written in w.x.y.z format or in /<1..32> format.
no command clears this field.
no command clears this field.
no command
_), or dashes (-), but the
56
Note: The DHCP pool must have the
same subnet as the interface to
which you plan to bind it.
The no command clears these fields.
[no] default-router ip Specifies the default gateway DHCP clients should
use. The
[no] description description Specifies a description for the DHCP pool for
identification. The
description.
[no] domain-name domain_name Specifies the domain name assigned to DHCP
clients. The
no command clears this field.
no command removes the
no command clears this field.
ZyWALL (ZLD) CLI Reference Guide
Page 57

Chapter 6 Interfaces
Table 17 interface Commands: DHCP Settings (continued)
COMMAND DESCRIPTION
[no] starting-address ip pool-size
<1..65535>
Sets the IP start address and maximum pool size of
the specified DHCP pool. The final pool size is
limited by the subnet mask.
Note: You must specify the network
number
first, and the start address
must be in the same subnet.
The no command clears the IP start address and
maximum pool size.
[no] first-dns-server {ip | interface_name
{1st-dns | 2nd-dns | 3rd-dns} | ZyWALL}
[no] second-dns-server {ip |
interface_name {1st-dns | 2nd-dns | 3rddns} | ZyWALL}
[no] third-dns-server {ip | interface_name
{1st-dns | 2nd-dns | 3rd-dns} | ZyWALL}
[no] first-wins-server ip Specifies the first WINS server IP address to
[no] second-wins-server ip Specifies the second WINS server IP address to
[no] lease {<0..365> [<0..23> [<0..59>]] |
infinite}
interface interface_name Enters sub-command mode.
[no] ip dhcp-pool profile_name Binds the specified interface to the specified DHCP
[no] ip helper-address ip Creates the specified DHCP relay. You have to
release dhcp interface-name Releases the TCP/IP configuration of the specified
renew dhcp interface-name Renews the TCP/IP configuration of the specified
show ip dhcp binding [ip] Displays information about DHCP bindings for the
clear ip dhcp binding {ip | *} Removes the DHCP bindings for the specified IP
Sets the first DNS server to the specified IP
address, the specified interface’s first, second, or
third DNS server, or the ZyWALL itself. The
command resets the setting to its default value.
Sets the second DNS server to the specified IP
address, the specified interface’s first, second, or
third DNS server, or the ZyWALL itself. The
command resets the setting to its default value.
Sets the third DNS server to the specified IP
address, the specified interface’s first, second, or
third DNS server, or the ZyWALL itself. The
command resets the setting to its default value.
assign to the remote users. The no command
removes the setting.
assign to the remote users. The no command
removes the setting.
Sets the lease time to the specified number of
days, hours, and minutes or makes the lease time
infinite. The
server setting to its default value.
pool. You have to remove any DHCP relays first.
The
no command removes the binding.
remove the DHCP pool first, if the DHCP pool is
bound to the specified interface. The
removes the specified DHCP relay.
interface. The interface must be a DHCP client.
This command is available in privilege mode, not
configuration mode.
interface. The interface must be a DHCP client.
This command is available in privilege mode, not
configuration mode.
specified IP address or for all IP addresses.
address or for all IP addresses.
no command resets the first DNS
no
no
no
no command
ZyWALL (ZLD) CLI Reference Guide
57
Page 58

Chapter 6 Interfaces
6.2.2.1 DHCP Setting Command Examples
The following example uses these commands to configure DHCP pool DHCP_TEST.
Router# configure terminal
Router(config)# ip dhcp pool DHCP_TEST
Router(config-ip-dhcp-pool)# network 192.168.1.0 /24
Router(config-ip-dhcp-pool)# domain-name zyxel.com
Router(config-ip-dhcp-pool)# first-dns-server 10.1.5.1
Router(config-ip-dhcp-pool)# second-dns-server ge1 1st-dns
Router(config-ip-dhcp-pool)# third-dns-server 10.1.5.2
Router(config-ip-dhcp-pool)# default-router 192.168.1.1
Router(config-ip-dhcp-pool)# lease 0 1 30
Router(config-ip-dhcp-pool)# starting-address 192.168.1.10 pool-size 30
Router(config-ip-dhcp-pool)# hardware-address 00:0F:20:74:B8:18
Router(config-ip-dhcp-pool)# client-identifier 00:0F:20:74:B8:18
Router(config-ip-dhcp-pool)# client-name TWtester1
Router(config-ip-dhcp-pool)# exit
Router(config)# interface ge1
Router(config-if)# ip dhcp-pool DHCP_TEST
Router(config-if)# exit
Router(config)# show ip dhcp server status
binding interface : ge1
binding pool : DHCP_TEST
6.2.3 Interface Parameter Command Examples
This table shows an example of each interface type’s sub-commands. The sub-commands vary
for different interface types.
Table 18 Examples for Different Interface Parameters
ETHERNET VIRTUAL INTERFACE PPPOE/PPTP
Router(config)# interface wan1
Router(config-if-wan1)#
description
downstream
exit
ip
mac
mss
mtu
no
ping-check
property
shutdown
traffic-prioritize
type
upstream
use-defined-mac
CELLULAR WLAN VLAN
Router(config)# interface wan1:1
Router(config-if-vir)#
description
downstream
exit
ip
no
shutdown
upstream
Router(config)# interface wan1_ppp
Router(config-if-ppp)#
account
bind
connectivity
description
downstream
exit
local-address
metric
mss
mtu
no
ping-check
remote-address
shutdown
traffic-prioritize
upstream
58
ZyWALL (ZLD) CLI Reference Guide
Page 59

Table 18 Examples for Different Interface Parameters
ETHERNET VIRTUAL INTERFACE PPPOE/PPTP
Router(config)# interface cellular1
Router(config-if-cellular)#
account
band
budget
connectivity
description
device
downstream
exit
local-address
metric
mtu
no
pin
ping-check
remote-address
shutdown
traffic-prioritize
upstream
Router(config)# interface wlan-1-1
Router(config-if-wlan)#
block-intra
description
downstream
exit
group-key
hide
idle
ip
mtu
no
ping-check
reauth
security
shutdown
ssid
station-limit
traffic-prioritize
upstream
wep-key
BRIDGE AUXILIARY
Router(config)# interface br0
Router(config-if-brg)#
description
downstream
exit
ip
join
mss
mtu
no
ping-check
shutdown
traffic-prioritize
upstream
Router(config)# interface aux
Router(config-if-aux)#
authentication
description
dial-timeout
dialing-type
exit
idle
initial-string
no
password
phone-number
port-speed
shutdown
traffic-prioritize
username
Router(config)# interface vlan1
Router(config-if-vlan)#
description
downstream
exit
ip
mss
mtu
no
ping-check
port
shutdown
traffic-prioritize
upstream
vlan-id
Chapter 6 Interfaces
6.2.4 RIP Commands
This table lists the commands for RIP settings.
Table 19 interface Commands: RIP Settings
COMMAND DESCRIPTION
router rip Enters sub-command mode.
[no] network interface_name Enables RIP for the specified interface. The
command disables RIP for the specified interface.
[no] passive-interface interface_name Sets the RIP direction of the specified interface to
in-only. The
in the specified interface.
[no] outonly-interface interface_name Sets the RIP direction of the specified interface to
out-only. The
directional in the specified interface.
interface interface_name Enters sub-command mode.
ZyWALL (ZLD) CLI Reference Guide
no command makes RIP bi-directional
no command makes RIP bi-
no
59
Page 60

Chapter 6 Interfaces
Table 19 interface Commands: RIP Settings (continued)
COMMAND DESCRIPTION
[no] ip rip {send | receive} version
<1..2>
[no] ip rip v2-broadcast Enables RIP-2 packets using subnet broadcasting.
show rip {global | interface {all |
interface_name}}
Sets the send or receive version to the specified
version number. The
received version to the current global setting for
RIP. See Chapter 9 on page 99 for more
information about routing protocols.
The no command uses multi-casting.
Displays RIP settings.
no command sets the send or
6.2.5 OSPF Commands
This table lists the commands for OSPF settings.
Table 20 interface Commands: OSPF Settings
COMMAND DESCRIPTION
router ospf Enters sub-command mode.
[no] network interface_name area ip Makes the specified interface part of the specified
area. The
interface from the specified area, disabling OSPF
in this interface.
[no] passive-interface interface_name Sets the OSPF direction of the specified interface
to in-only. The
directional in the specified interface.
interface interface_name Enters sub-command mode.
[no] ip ospf priority <0..255> Sets the priority of the specified interface to the
specified value. The
to 1.
[no] ip ospf cost <1..65535> Sets the cost to route packets through the specified
interface. The no command sets the cost to 10.
no ip ospf authentication Disables authentication for OSPF in the specified
interface.
ip ospf authentication Enab les text authentication for OSPF in the
specified interface.
ip ospf authentication message-digest Enables MD5 authentication for OSPF in the
specified interface.
ip ospf authentication same-as-area To exchange OSPF routing information with peer
border routers, you must use the same
authentication method that they use. This
command makes OSPF authentication in the
specified interface follow the settings in the
corresponding area.
[no] ip ospf authentication-key password Sets the simple text password for OSPF text
authentication in the specified interface. The
command clears the text password.
password: 1-8 alphanumeric charact ers or
underscores
no command removes the specified
no command makes OSPF bi-
no command sets the priority
no
60
ZyWALL (ZLD) CLI Reference Guide
Page 61

Chapter 6 Interfaces
Table 20 interface Commands: OSPF Settings (continued)
COMMAND DESCRIPTION
ip ospf message-digest-key <1..255> md5
password
no ip ospf message-digest-key Clears the ID and password for OSPF MD5
[no] ip ospf hello-interval <1..65535> Sets the number of seconds between “hello”
Sets the ID and password for OSPF MD5
authentication in the specified interface.
password: 1-16 alphanumeric characters or
underscores
authentication in the specified interface.
messages to peer routers. These messages let
peer routers know the ZyW ALL is available. The
no command sets the number of seconds to 10.
ip ospf dead-interval for more
See
information.
[no] ip ospf dead-interval <1..65535> Sets the number of seconds the ZyWALL waits for
“hello” messages from peer routers before it
assumes the peer router is not available and
deletes associated routing information. The
command sets the number of seconds to 40. See
ip ospf hello-interval for more
information.
[no] ip ospf retransmit-interval
<1..65535>
Sets the number of seconds the ZyWALL waits for
an acknowledgment in response to a link state
advertisement before it re-sends the
advertisement.
Link state advertisements (LSA) are used to share
the link state and routing information between
routers.
no
ZyWALL (ZLD) CLI Reference Guide
61
Page 62

Chapter 6 Interfaces
6.2.6 Connectivity Check (Ping-check) Commands
Use these commands to have an interface regularly check the connection to the gateway you
specified to make sure it is still available. You specify how often the interface checks the
connection, how long to wait for a response before the attempt is a failure, and how many
consecutive failures are required before the ZyWALL stops routing to the gateway. The
ZyWALL resumes routing to the gateway the first time the gateway passes the connectivity
check.
This table lists the ping-check commands
Table 21 interface Commands: Ping Check
COMMAND DESCRIPTION
show ping-check [interface_name | status] Displays information about ping check settings for
show ping-check [interface_name] Displays information about ping check settings for
[no] connectivity-check continuous-log
activate
show connectivity-check continuous-log status Displays the continuous log setting about
interface interface_name Enters sub-command mode.
[no] ping-check activate Enables ping check for the specified interface. The
ping-check {domain_name | ip | defaultgateway}
ping-check {domain_name | ip | defaultgateway} period <5..30>
ping-check {domain_name | ip | defaultgateway} timeout <1..10>
ping-check {domain_name | ip | defaultgateway} fail-tolerance <1..10>
ping-check {domain_name | ip | defaultgateway} method {icmp | tcp}
ping-check {domain_name | ip | defaultgateway} port <1..65535>
the specified interface or for all interfaces.
status: displays the current connectivity check
status for any interfaces upon which it is activated.
the specified interface or for all interfaces.
Use this command to have the ZyWALL logs
connectivity check result continously. The no
command disables the setting.
connectivity check.
no command disables ping check for the specified
interface.
Specifies what the ZyWALL pings for the ping
check; you can specify a fully-qualified domain
name, IP address, or the default gateway for the
interface.
Specifies what the ZyWALL pings for the ping
check and sets the number of seconds between
each ping check.
Specifies what the ZyWALL pings for the ping
check and sets the number of seconds the
ZyWALL waits for a response.
Specifies what the ZyWALL pings for the ping
check and sets the number of times the ZyWALL
times out before it stops routing through the
specified interface.
Sets how the ZyWALL checks the connection to the
gateway.
icmp: ping the gateway you specify to make sure it
is still available.
tcp: perform a TCP handshake with the gateway
you specify to make sure it is still available.
Specifies the port number to use for a TCP
connectivity check.
62
ZyWALL (ZLD) CLI Reference Guide
Page 63

6.2.6.1 Connectivity Check Command Example
The following commands show you how to set the WAN1 interface to use a TCP handshake
on port 8080 to check the connection to IP address 1.1.1.2
Router# configure terminal
Router(config)# interface wan1
Router(config-if-wan1)# ping-check 1.1.1.2 method tcp port 8080
Router(config-if-wan1)# exit
Router(config)# show ping-check
Interface: wan1
Check Method: tcp
IP Address: 1.1.1.2
Period: 30
Timeout: 5
Fail Tolerance: 5
Activate: yes
Port: 8080
Router(config)#
6.3 Ethernet Interface Specific Commands
Chapter 6 Interfaces
This section covers commands that are specific to Ethernet interfaces.
The following table identifies the values required for many of these commands. Other input
values are discussed with the corresponding commands.
Table 22 Input Values for Ethernet Interface Commands
LABEL DESCRIPTION
interface_name The name of the Ethernet interface. This depends on the ZyWALL model.
For the ZyWALL USG 300 and above, use gex, x = 1~N, where N equals
the highest numbered Ethernet interface for your ZyWALL model.
The ZyWALL USG 100 and 200 models use a name such as wan1, wan2,
opt, lan1, ext-wlan, or dmz.
6.3.1 MAC Address Setting Commands
This table lists the commands you can use to set the MAC address of an interface. On the
ZyWALL USG 100 and 200 models, these commands only apply to a WAN or OPT interface.
Table 23 interface Commands: MAC Setting
COMMAND DESCRIPTION
interface interface_name Enters sub-command mode.
no mac Has the interface use its default MAC address.
mac mac Specifies the MAC address the interface is to use.
ZyWALL (ZLD) CLI Reference Guide
63
Page 64

Chapter 6 Interfaces
Table 23 interface Commands: MAC Setting (continued)
COMMAND DESCRIPTION
type {internal|external|general} Sets which type of network you will connect this
interface. The ZyWALL automatically adds default
route and SNAT settings for traffic it routes from
internal interfaces to external interfaces; for
example LAN to WAN traffic.
internal: Set this to connect to a local network.
Other corresponding configuration options: DHCP
server and DHCP relay. The ZyW ALL automatically
adds default SNAT settings for traffic flowing from
this interface to an external interface.
external: Set this to connect to an external
network (like the Internet). The ZyWALL
automatically adds this interface to the default
WAN trunk.
general: Set this if you want to manually
configure a policy route to add routing and SNAT
settings for the interface.
no use-defined-mac Has the interface use its default MAC address.
use-defined-mac Has the interface use a MAC address that you
specify.
6.3.2 Port Grouping Commands
This section covers commands that are specific to port grouping.
" In CLI, representative interfaces are also called representative ports.
Table 24 Basic Interface Setting Commands
COMMAND DESCRIPTION
show port-grouping Displays which physical ports are assigned to each
representative interface.
port-grouping representative_interface port
<1..x>
no port <1..x> Removes the specified physical port from its
port status Port<1..x> Enters a sub-command mode to configure the
[no] duplex <full | half> Sets the port’s duplex mode. The no command
exit Leaves the sub-command mode.
Adds the specified physical port to the specified
representative interface.
representative_interface: gex in a ZyWALL
USG 300 or above.
A dmz, ext-wlan, or lan1 interface in a ZyWALL
USG 100 or 200.
<1..x> where x equals the highest numbered port
for your ZyWALL model.
current representative interface and adds it to its
default representative interface (for example, port x
--> gex).
specified port’s settings.
returns the default setting.
64
ZyWALL (ZLD) CLI Reference Guide
Page 65

Chapter 6 Interfaces
Table 24 Basic Interface Setting Commands (continued)
COMMAND DESCRIPTION
[no] negotiation auto Sets the port to use auto-negotiation to determine
the port speed and duplex. The no command turns
off auto-negotiation.
[no] speed <100,10> Sets the Ethernet port’s connection speed in Mbps.
The no command returns the default setting.
show port setting Displays the Ethernet port negotiation, duplex, and
show port status Displays statistics for the Ethernet ports.
speed settings.
6.3.2.1 Port Grouping Command Examples
The following commands add physical port 5 to representative interface ge1.
Router# configure terminal
Router(config)# show port-grouping
No. Representative Name Port1 Port2 Port3 Port4 Port5
=========================================================
1 ge1 yes no no no no
2 ge2 no yes no no no
3 ge3 no no yes no no
4 ge4 no no no yes no
5 ge5 no no no no yes
Router(config)# port-grouping ge1
Router(config-port-grouping)# port 5
Router(config-port-grouping)# exit
Router(config)# show port-grouping
No. Representative Name Port1 Port2 Port3 Port4 Port5
=========================================================
1 ge1 yes no no no yes
2 ge2 no yes no no no
3 ge3 no no yes no no
4 ge4 no no no yes no
5 ge5 no no no no no
The following commands set port 1 to use auto-negotiation auto and port 2 to use a 10 Mbps
connection speed and half duplex.
Router(config)# port status Port1
Router(config-port-status)# negotiation auto
Router(config-port-status)# exit
Router(config)# port status Port2
Router(config-port-status)# duplex half
Router(config-port-status)# speed 10
Router(config-port-status)# exit
Router(config)# exit
ZyWALL (ZLD) CLI Reference Guide
65
Page 66

Chapter 6 Interfaces
6.4 Virtual Interface Specific Commands
Virtual interfaces use many of the general interface commands discussed at the beginning of
Section 6.2 on page 51. There are no additional commands for virtual interfaces.
6.4.1 Virtual Interface Command Examples
The following commands set up a virtual interface on top of Ethernet interface ge1. The virtual
interface is named ge1:1 with the following parameters: IP 1.2.3.4, subnet 255.255.255.0,
gateway 4.6.7.8, upstream bandwidth 345, downstream bandwidth 123, and description “I am
vir interface”.
Router# configure terminal
Router(config)# interface ge1:1
Router(config-if-vir)# ip address 1.2.3.4 255.255.255.0
Router(config-if-vir)# ip gateway 4.6.7.8
Router(config-if-vir)# upstream 345
Router(config-if-vir)# downstream 123
Router(config-if-vir)# description I am vir interface
Router(config-if-vir)# exit
6.5 PPPoE/PPTP Specific Commands
This section covers commands that are specific to PPPoE/PPTP interfaces. PPPoE/PPTP
interfaces also use many of the general interface commands discuss ed at the beginning of
Section 6.2 on page 51.
The following table identifies the values required for many of these commands. Other input
values are discussed with the corresponding commands.
Table 25 Input Values for PPPoE/PPTP Interface Commands
LABEL DESCRIPTION
interface_name PPPoE/PPTP interface: pppx, x = 0 - N, where N depends on the number of
PPPoE/PPTP interfaces your ZyWALL model supports.
profile_name The name of the ISP account. You may use 1-31 alphan umeric characters,
underscores(
value is case-sensitive.
This table lists the PPPoE/PPTP interface commands.
Table 26 interface Commands: PPPoE/PPTP Interfaces
COMMAND DESCRIPTION
interface dial interface_name Connects the specified PPPoE/PPTP interface.
interface disconnect interface_name Disconnects the specified PPPoE/PPTP interface.
interface interface_name Creates the specified interface if necessary and
[no] account profile_name Specifies the ISP account for the specified PPPoE/
_), or dashes (-), but the first character cannot be a number. This
enters sub-command mode.
PPTP interface. The
account field.
no command clears the ISP
66
ZyWALL (ZLD) CLI Reference Guide
Page 67

Chapter 6 Interfaces
Table 26 interface Commands: PPPoE/PPTP Interfaces (continued)
COMMAND DESCRIPTION
[no] bind interface_name Specifies the base interface for the PPPoE/PPTP
[no] connectivity {nail-up | dial-ondemand}
interface. The
interface.
Specifies whether the specified PPPoE/PPTP
interface is always connected (nail-up) or
connected only when used (dial-on-demand). The
no command removes the base
no command sets it to dial-on-demand.
[no] local-address ip Specifies a static IP address for the specified
PPPoE/PPTP interface. The
the PPPoE/PPTP interface a DHCP client; the
other computer assigns the IP address.
[no] remote-address ip Specifies the IP address of the PPPoE/PPTP
server. If the PPPoE/PPTP server is not available
at this IP address, no connection is made. The no
command lets the ZyWALL get the IP address of
the PPPoE/PPTP server automatically when it
establishes the connection.
[no] mss <536..1452> Specifies the maximum segment size (MSS) th e
interface can use. MSS is the largest amount of
data, specified in bytes, that the interface can
handle in a single, unfragmented piece. The
command has the ZyWALL use its default MSS
setting.
mtu <576..1492> Sets the Maximum Transmission Unit in bytes.
show interface ppp system-default Displays system default PPP interfaces (non-
deletable) that come with the ZyWALL.
show interface ppp user-define Displays all PPP interfaces that were manually
configured on the ZyWALL.
no command makes
no
6.5.1 PPPoE/PPTP Interface Command Examples
The following commands show you how to configure PPPoE/PPTP interface ppp0 with the
following characteristics: base interface ge1, ISP account Hinet, local address 1.1.1.1, remote
address 2.2.2.2, MTU 1200, upstream bandwidth 345, downstream bandwidth 123, description
“I am ppp0”, and dialed only when used.
Router# configure terminal
Router(config)# interface ppp0
Router(config-if-ppp)# account Hinet
Router(config-if-ppp)# bind ge1
Router(config-if-ppp)# local-address 1.1.1.1
Router(config-if-ppp)# remote-address 2.2.2.2
Router(config-if-ppp)# mtu 1200
Router(config-if-ppp)# upstream 345
Router(config-if-ppp)# downstream 123
Router(config-if-ppp)# connectivity dial-on-demand
Router(config-if-ppp)# description I am ppp0
Router(config-if-ppp)# exit
ZyWALL (ZLD) CLI Reference Guide
67
Page 68

Chapter 6 Interfaces
The following commands show you how to connect and disconnect ppp0.
Router# interface dial ppp0
Router# interface disconnect ppp0
6.6 Cellular Interface Specific Commands
Use a 3G (Third Generation) cellular device with the ZyWALL for wireless broadband
Internet access.
Use these commands to add, edit , dial, disconnect, or delete cellular interfaces. When you add
a new cellular interface, make sure you enter the account. You must use the
terminal
Table 27 Cellular Interface Commands
COMMAND DESCRIPTION
[no] interface interface_name Creates the specified interface if necessary and enters sub-
[no] account profile_name Specifies the ISP account for the specified cellular interface.
[no] band {auto|wcdma|gsm} Sets (or clears) the cellular band that the cellular interface
[no] network-selection {auto|home} Home network is the network to which you are originally
[no] budget active Sets a monthly limit for the user account of the installed 3G
[no] budget time active <1..672> Sets the amount of time (in hours) that the 3G connection can
command to enter the configuration mode before you can use these commands.
command mode. The
interface.
The no command clears the ISP account field.
uses.
auto has the ZyWALL always use the fastest network that is
in range.
gsm has this interface only use a 2.5G or 2.75G network
(respectively). If you only have a GSM network available to
you, you may want to use this so the ZyWALL does not spend
time looking for a WCDMA network.
wcdma has this interface only use a 3G or 3.5G network
(respectively). You may want to use this if you want to make
sure the interface does not use the GSM network.
subscribed.
Home has the 3G device connect only to the home network. If
the home network is down, the ZyWALL's 3G Internet
connection is also unavailable.
Auto is the default setting and allows the 3G device to
connect to a network to which you are not subscribed when
necessary, for example when the home network is down or
another 3G base station's signal is stronger. This is
recommended if you need continuous Internet connectivity. If
you select this, you may be charged using the rate of a
different network.
card. You can set a limit on the total traffic and/or call time.
The ZyWALL takes the actions you specified when a limit is
exceeded during the month. Use the no command to disable
budget control.
be used within one month. If you change the value, the
ZyWALL resets the statistics. Use the no command to disable
time budget control.
no command deletes the specified
configure
68
ZyWALL (ZLD) CLI Reference Guide
Page 69

Chapter 6 Interfaces
Table 27 Cellular Interface Commands (continued)
COMMAND DESCRIPTION
[no] budget data active {downloadupload|download|upload}
<1..100000>
budget reset-day <0..31> Sets the date on which the ZyWALL resets the budget every
budget reset-counters Resets the time and data budgets immediately. The count
budget {log|log-alert}[recursive
<1..65535>]
no budget log [recursive] Sets the ZyWALL to not create a log when the time or data
budget new-connection
{allow|disallow}
budget current-connection
{keep|drop}
budget percentage {ptime|pdata}
<0..99>
budget {log-percentage|logpercentage-alert} [recursive
<1..65535>]
Sets how much downstream and/or upstream data (in Mega
bytes) can be transmitted via the 3G connection within one
month.
download: set a limit on the downstream traf fic (from the ISP
to the ZyWALL).
upload: set a limit on the upstream traffic (from the ZyWALL
to the ISP).
download-upload: set a limit on the total traffic in both
directions.
If you change the value, the ZyWALL resets the statistics.
Use the no command to disable data budget control.
month. If the date you selected is not available in a month,
such as 30th or 31th, the ZyWALL resets the budget on the
last day of the month.
starts over with the 3G connection’s full configured monthly
time and data budgets. This does not affect the normal
monthly budget restart.
Sets the ZyWALL to create a log (log) or an alert log (logalert) when the time or data limit is exceeded. You can also
specify how often (from 1 to 65535 minutes) to generate a log
or an alert.
limit is exceeded. Specify recursive to have the ZyWALL
only create a log one time when the time or data limit is
exceeded.
Sets to permit (allow) or drop/block (disallow) new 3G
connections when the time or data limit is exceeded.
Sets to maintain the existing 3G connection (keep) or
disconnect it (drop) when the time or data limit is exceeded.
You cannot set budget new-connection to allow and budget
current-connection to drop at the same time.
If you set budget new-connection to disallow and budget
current-connection to keep, the ZyWALL allows you to
transmit data using the current connection, but you cannot
build a new connection if the existing connection is
disconnected.
Sets a percentage (0~99) of time budget (ptime) or data
(pdata) limit. When the specified limit is exceeded, the
ZyWALL takes the action configured using the budget
{log-percentage|log-percentage-alert}
command.
Sets to have the ZyWALL create a log (log-percentage) or
an alart log (log-percentage-alert) when the set
percentage of time budget or data limit is exceeded. You can
configure the percentage using the budget percentage
command.
Y ou can also set how often (from 1 to 65535 minutes) to send
the log or alert.
ZyWALL (ZLD) CLI Reference Guide
69
Page 70

Chapter 6 Interfaces
Table 27 Cellular Interface Commands (continued)
COMMAND DESCRIPTION
no budget log-percentage
[recursive]
connectivity {nail-up | dial-ondemand}
[no] device <device_model_name> Sets (or clears) the model name of the cellular device that the
[no] local-address <ip> Sets (or clears) the cellular interface’s local (own) IP address.
mtu <576..1492> Sets the Maximum Transmission Unit in bytes.
[no] pin <pin code> Sets (or clears) the PIN code for the cellular device’s 3G card.
[no] remote-address <ip> Sets (or clears) the IP address of the cellular interface’s peer
interface cellular budget-auto-save
<5..1440>
show interface cellular
[corresponding-slot|devicestatus|support-device]
show interface cellular correspondingslot
show interface cellular device-status Displays the installed SIM card and 3G card status.
show interface cellular support-device Displays all 3G card models the ZyWALL can support.
show interface cellular budget-auto-
save
show interface cellular status Displays the traffic statistics and connection status for your
show interface interface_name [budget] Displays the budget control settings for the specified cellular
show interface interface_name device
status
show interface interface_name device
profile
Sets the ZyWALL to not create a log when the set percentage
of time budget or data limit is exceeded. You can configure
the percentage using the budget percentage command.
You can also specify recursive to have the ZyWALL only
create a log one time when the set percentage of time budget
or data limit is exceeded.
Sets the connection to be always on or only when there is
traffic.
cellular interface uses. Use 0-30 alphanumeric characters,
underscores(
Use 1-4 alphanumeric characters, underscores(
(-).
(like a gateway or PPPoE server).
Sets how often (in minutes) the ZyWALL saves time and dat a
usage records for a connection using the 3G card.
Shows the status of the specified cellular interface.
Shows which cellular interface is on which slot and whether
which cellular interface has been configured.
Displays how often (in minutes) the ZyWALL records time and
data usage of your 3G budgets.
cellular interfaces. See Section 6.6.1 on page 71 for all
possible cellular status descriptions.
interface.
Displays the 3G card and SIM card information for the
specified cellular interface.
Displays the 3G connection profile settings of the specified
cellular interface.
_), or dashes (-).
_), or dashes
70
ZyWALL (ZLD) CLI Reference Guide
Page 71

6.6.1 Cellular Status
The following table describes the different kinds of cellular connection status on the
ZyWALL.
Table 28 Cellular Status
STATUS DESCRIPTION
No device no 3G device is connected to the ZyWALL.
No service no 3G network is available in the area; you cannot connect to the Internet.
Limited service returned by the service provider in cases where the SIM card is expired, the
Device detected displays when you connect a 3G device.
Device error a 3G device is connected but there is an error.
Probe device fail the ZyWALL’s test of the 3G device failed.
Probe device ok the ZyWALL’s test of the 3G device failed.
Init device fail the ZyWALL was not able to initialize the 3G device.
Init device ok the ZyWALL initialized the 3G card.
Check lock fail the ZyWALL’s check of whether or not the 3G device is locked failed.
Device locked the 3G device is locked.
SIM error there is a SIM card error on the 3G device.
SIM locked-PUK the PUK is locked on the 3G device’s SIM card.
SIM locked-PIN the PIN is locked on the 3G device’s SIM card.
Unlock PUK fail Your attempt to unlock a WCDMA 3G device’s PUK failed because you entered
Unlock PIN fail Your attempt to unlock a WCDMA 3G device’s PIN failed because you entered
Unlock device fail Y our attempt to unlock a CDMA2000 3G device failed because you entered an
Device unlocked You entered the correct device code and unlocked a CDMA2000 3G device.
Get dev-info fail The ZyWALL cannot get cellular device information.
Get dev-info ok The ZyWALL succeeded in retrieving 3G device information.
Searching network The 3G device is searching for a network.
Get signal fail The 3G device cannot get a signal from a network.
Network found The 3G device found a network.
Apply config The ZyWALL is applying your configuration to the 3G device.
Inactive The 3G interface is disabled.
Active The 3G interface is enabled.
Incorrect device The connected 3G device is not compatible with the ZyWALL.
Correct device The ZyWALL detected a compatible 3G device.
Set band fail Ap plying your band selection was not successful.
Set band ok The ZyWALL successfully applied your band selection.
Set profile fail Applying your ISP settings was not successful.
Set profile ok The ZyWALL successfully applied your ISP settings.
Chapter 6 Interfaces
user failed to pay for the service and so on; you cannot connect to the Internet.
an incorrect PUK.
an incorrect PIN.
incorrect device code.
ZyWALL (ZLD) CLI Reference Guide
71
Page 72

Chapter 6 Interfaces
Table 28 Cellular Status
STATUS DESCRIPTION
PPP fail The ZyWALL failed to create a PPP connection for the cellular interface.
Need auth-password You need to enter the password for the 3G card in the cellular edit screen.
Device ready The ZyWALL successfully applied all of your configuration and you can use the
3G connection.
6.6.2 Cellular Interface Command Examples
This example shows the configuration of a cellular interface named cellular2 for use with a
Sierra Wireless AC850 3G card. It uses only a 3G (or 3.5G) connection, PIN code 1234, an
MTU of 1200 bytes, a description of "This is cellular2” and sets the connection to be nailedup.
Router(config)# interface cellular2
Router(config-if-cellular)# device AC850
Router(config-if-cellular)# band wcdma
Router(config-if-cellular)# pin 1234
Router(config-if-cellular)# connectivity nail-up
Router(config-if-cellular)# description This is cellular2
Router(config-if-cellular)# mtu 1200
Router(config-if-cellular)# exit
This second example shows specifying a new PIN code of 4567.
Router(config)# interface cellular2
Router(config-if-cellular)# pin 4567
Router(config-if-cellular)# exit
This example shows the 3G and SIM card information for interface cellular2 on the ZyWALL.
Router(config)# show interface cellular2 device status
interface name: cellular2
extension slot: USB 1
service provider: Chunghwa Telecom
cellular system: WCDMA
signal strength: -95 dBm
signal quality: Poor
device type: WCDMA
device manufacturer: Huawei
device model: E220/E270/E800A
device firmware: 076.11.07.106
device IMEI/ESN: 351827019784694
SIM card IMSI: 466923100565274
72
ZyWALL (ZLD) CLI Reference Guide
Page 73

This example shows the 3G connection profile settings for interface cellular2 on the ZyWALL.
You have to dial *99***1# to use profile 1, but authentication is not required. Dail *99***2#
to use profile 2 and authentication is required.
Router(config)# show interface cellular2 device profile
profile: 1
apn: internet
dial-string: *99***1#
authentication: none
user: n/a
password: n/a
profile: 2
apn: internet
dial-string: *99***2#
authentication: chap
user:
password: ***
----------------------SNIP!------------------------------------------------
6.7 USB Storage Specific Commands
Chapter 6 Interfaces
Use these commands to configure settings that apply to the USB storage device connected to
the ZyWALL.
" For the ZyWALL which supports more than one USB ports, these commands
only apply to the USB storage device that is first attached to the ZyWALL.
Table 29 USB Storage General Commands
COMMAND DESCRIPTION
show usb-storage Displays the status of the connected USB storage device.
[no] usb-storage activate Enables or disables the connected USB storage service.
usb-storage warn number
<percentage|megabyte>
usb-storage mount Mounts the connected USB storage device.
usb-storage umount Unmounts the connected USB storage device.
[no] logging usb-storage Sets to have the ZyWA LL log or not log any information about
show logging status usb-storage Displays the logging settings for the connected USB storage
logging usb-storage category category
level <all|normal>
logging usb-storage category category
disable
Sets a number and the unit (percentage or megabyte) to
have the ZyWALL send a warning message when the
remaining USB storage space is less than the set value.
the connected USB storage device(s) for the system log.
device.
Configures the logging settings for the specified category for
the connected USB storage device.
Stops logging for the specified category to the connected
USB storage device.
ZyWALL (ZLD) CLI Reference Guide
73
Page 74

Chapter 6 Interfaces
Table 29 USB Storage General Commands (continued)
COMMAND DESCRIPTION
logging usb-storage flushThreshold
<1..100>
[no] diag-info copy usb-storage Sets to have the ZyWALL save or stop saving the current
show diag-info copy usb-storage Displays whether (enable or disable) the ZyWALL saves the
[no] corefile copy usb-storage Sets to have the ZyWALL save or not save a process’s core
show corefile copy usb-storage Displays whether (enable or disable) the ZyWALL saves core
Configures the maximum storage space (in percentage) for
storing syetem logs on the connected USB storage device.
system diagnostics information to the connected USB storage
device. Y ou may need to send this file to customer support for
troubleshooting.
current system diagnostics information to the connected USB
storage device.
dump to the connected USB storage device if the process
terminates abnormally (crashes). You may need to send this
file to customer support for troubleshooting.
dump files to the connected USB storage device.
6.7.1 USB Storage General Commands Example
This example shows how to display the status of the connected USB storage device.
Router> show usb-storage
USBStorage Configuration:
Activation: enable
Criterion Number: 100
Criterion Unit: megabyte
USB Storage Status:
Device description: N/A
Usage: N/A
Filesystem: N/A
Speed: N/A
Status: none
Detail: none
6.8 WLAN Specific Commands
You can install a compatible WLAN card to use the ZyWALL as an access point (AP) for a
wireless network.
The following table identifies the values required for several WLAN commands. Other input
values are discussed with the corresponding commands.
Table 30 Input Values for WLAN Interface Commands
LABEL DESCRIPTION
psk-key Use 8 to 63 case-sensitive alphanumeric characters or 64 hexadecimal
characters. This is used for WLAN interface commands. See Table 32 on page 76
74
ZyWALL (ZLD) CLI Reference Guide
Page 75

Chapter 6 Interfaces
6.8.1 WLAN General Commands
Use these commands to configure global settings that apply to all of the wireless LAN
interfaces you create on the WLAN card.
Table 31 WLAN General Commands
COMMAND DESCRIPTION
wlan slot_name Specifies the slot the WLAN card is installed in and enters
sub-command mode.
slot_name: The name of the slot where the WLAN card is
installed in the ZyWALL. Use slotx where x equals the
number of the card slot.
[no] activate Turns the wireless device on. The
band <b | g | bg> Sets whether wireless clients can connect to the ZyWALL
using IEEE 802.1 1 b, IE EE 802.11g, or both.
channel <wireless_channel | auto> Sets the wireless operating channel.
wireless_channel: Specify the channel number. The
numbers available vary by region.
[no] ctsrts <256..2346> Sets the Clear To Send/Request To Send threshold. CTS/
RTS reduces data collisions caused by wireless clients that
are associated with the same AP but out of range of one
another. The no command turns off CTS/RTS.
[no] frag <256..2346> Sets the threshold (number of bytes) for the fragmentation
[no] super
role ap Sets the ZyWALL to act as an AP (only the AP role is
output-power [100% | 50% | 25% |
12.5%]
qos [none | wmm} Applies Wi-Fi Multimedia Quality of Service (QoS) or no
guard-interval [short | long] Sets Guard Interval to Short (increases data throughput) or
[no] amsdu Enables Aggregated Mac Service Data Unit (AMSDU) for
[no] ampdu Enables Aggregated Mac Protocol Data Unit (AMPDU) for
[no] block-ack Adds the block ACK (BA) mechanism to increase data output.
exit Leaves the sub-command mode.
boundary for directed messages. It is the maximum data
fragment size that can be sent.
Enables super mode (fast frame and packet bursting).
supported at the time of writing.
Sets the wireless output power. Reducing output power can
help reduce interference with other nearby APs.
wireless QoS.
Long (prioritize data integrity).
faster data transfer rates.
faster data transfer rates.
no command turns it off.
ZyWALL (ZLD) CLI Reference Guide
75
Page 76

Chapter 6 Interfaces
6.8.1.1 WLAN General Commands Example
This example sets wireless slot 1 to use the IEEE 802.11b and IEEE 802.11 g bands, channel 5,
super mode, 50 % output power, and enables it.
Router(config)# wlan slot1
Router(config-wlan-slot)# band bg
Router(config-wlan-slot)# channel 5
Router(config-wlan-slot)# super
Router(config-wlan-slot)# output-power 50%
Router(config-wlan-slot)# activate
Router(config-wlan-slot)# exit
Router(config)#
6.8.2 WLAN Interface Commands
Use these commands to configure global settings that apply to all of the wireless LAN
interfaces you create on the WLAN card.
Table 32 WLAN Interface Commands
COMMAND DESCRIPTION
[no] interface ap_interface Creates the specified interface if necessary and enters sub-
command mode. The
interface.
ap_interface: The name of the WLAN Access Point
interface. Use wlan-x-y where x equals the number of the
card slot and y equals the number of the individual WLAN
interface. For example, wlan-1-1.
[no] block-intra Enables intra-BSS blocking (prevents) wireless clients in this
profile’s BSS from communicating with one another.
group-key <30..30000> Sets the WPA2 group key update timer. This is the interval in
seconds for how often the AP sends a new group key out to
all clients.
[no] hide Obscures the SSID in the outgoing beacon frame so a station
cannot obtain the SSID through scanning.
idle <30..30000> Sets the WPA2 idle timeout. The ZyWALL automatically
disconnects a wireless station that has been inactive for this
number of seconds. The wireless station needs to enter the
username and password again before access to the wired
network is allowed.
[no] ip address ip subnet_mask Assigns the specified IP address and subnet mask to the
specified interface. The
and the subnet mask.
[no]ip gateway ip [metric <0..15>] Adds the specified gateway for the interface. Sets the priority
(relative to every gateway on every interface) for the specified
gateway. The lower the number, the higher the priority. The
no command removes the gateway .
[no] mtu <576..2304> Specifies the Maximum Transmission Unit, which is the
maximum number of bytes in each packet moving through
this interface. The ZyWALL divides larger packets into smaller
fragments. The
no command deletes the specified
no command clears the IP address
no command resets the MTU to 1500.
76
ZyWALL (ZLD) CLI Reference Guide
Page 77

Chapter 6 Interfaces
Table 32 WLAN Interface Commands (continued)
COMMAND DESCRIPTION
reauth <30..30000> Sets the WP A2 reauthentication timer . This is at what interval
wireless stations have to resend usernames and passwords
in order to stay connected. If a RADIUS server authenticates
wireless stations, the reauthentication timer on the RADIUS
server has priority.
security mode {none | wep | wpa |
wpa-wpa2 | wpa2}
security wep <64 | 128> default-key
<1..4>
security wep mode <open | share> Sets the WEP encryption to use open or shared key
security wpa <tkip | aes> eap
internal profile-name tls-cert
certificate name
security wpa <tkip | aes> eap
external
security wpa <tkip | aes> psk key
psk-key
security wpa-wpa2 <tkip | aes> eap
internal profile-name tls-cert
certificate name
security wpa-wpa2 <tkip | aes> eap
external
security wpa-wpa2 <tkip | aes> psk
key psk-key
security wpa2 <tkip | aes> eap
internal profile-name tls-cert
certificate name
security wpa2 <tkip | aes> eap
external
security wpa2 <tkip | aes> psk key
psk-key
Sets what type of security the wireless interface uses.
none: applies no security.
wep: WEP security (extremely weak).
wpa: WPA security.
wpa-wpa2: WPA/WPA2-Enterprise or WPA/WPA2-PSK
security.
wpa2: WP A2 security (strongest option).
Sets WEP encryption to use a 64 or 128 bit key and selects
the default key.
authentication.
Configures WPA enterprise security using TKIP or AES and
an existing AAA authentication method object (profile-
name). Set the certificate the ZyWALL uses to authenticate
itself to the wireless clients. The wireless clients must use
TTLS authentication protocol and PAP inside the TTLS
secure tunnel.
Configures WPA enterprise security using TKIP or AES and
an external server. Use the security external command
to specify the server’s address.
Configures WPA security using TKIP or AES and a PreShared Key (PSK).
This allows users to either use WPA or WPA2 enterprise
security to connect to the wireless interface. You have to also
configure to use either TKIP or AES and an existing AAA
authentication method object (profile-name). Set the
certificate the ZyWALL uses to authenticate itself to the
wireless clients. The wireless clients must use TTLS
authentication protocol and PAP inside the TTLS secure
tunnel.
Configures WPA or WPA2 enterprise security using TKIP or
AES and an external server. Use the security external
command to specify the server’s address.
Configures WPA or WPA2 security using TKIP or AES and a
Pre-Shared Key (PSK).
Configures WPA2 enterprise security using TKIP or AES and
an existing AAA authentication method object (profile-
name). Select the certificate the ZyWALL uses to authenticate
itself to the wireless clients. The wireless clients must use
TTLS authentication protocol and PAP inside the TTLS
secure tunnel.
Configures WPA2 enterprise security using TKIP or AES and
an external server. Use the security external command
to specify the server’s address.
Configures WPA2 security using TKIP or AES and a PreShared Key (PSK).
ZyWALL (ZLD) CLI Reference Guide
77
Page 78

Chapter 6 Interfaces
Table 32 WLAN Interface Commands (continued)
COMMAND DESCRIPTION
[no] security dot1x acct ip port
<1..65535>
[no] security dot1x auth ip port
<1..65535>
[no] security dot1x activate Enables IEEE 802.1x accounting and authentication.
[no] security external acct ip port
<1..65535>
[no] security external auth ip port
<1..65535>
no security {none | wep | wpa |
wpa-wpa2 | wpa2}
ssid ssid Sets the (Service Set IDentity). This identifies the Service Set
station-limit <1..255> Sets the highest number of wireless clients that are allowed to
wep-key <1..4> key There are four data encryption keys to secure your data from
Sets the IP address and port number of an external
accounting server.
Sets the IP address and port number of an external
authentication (RADIUS) server.
Sets the IP address and port number of an external
accounting server.
Sets the IP address and port number of an external
authentication (RADIUS) server.
Disables the specified security mode for the wireless
interface.
with which a wireless station is associated. Wireless stations
associating to the ZyWALL must have the same SSID.
ssid: Use up to 32 printable 7-bit ASCII characters as a
name for the wireless LAN.
connect to the wireless interface at the same time.
eavesdropping by unauthorized wireless users. The values
for the keys must be set up exactly the same on the access
points as they are on the wireless stations.
If you set WEP encryption to use a 64 bit key using the
security mode and security wep 64 commands, type
any 5 characters (ASCII string) or 5 pairs of hexadecimal
characters ("0-9", "A-F") preceded by 0x for each key.
If you set WEP encryption to use a 128 bit key using the
security mode and security wep 128 commands, type
13 characters (ASCII string) or 13 pairs of hexadecimal
characters ("0-9", "A-F") preceded by 0x for each key.
6.8.2.1 WLAN Interface Commands Example
This example configures WLAN AP interface 2 for slot 1 to use SSID WLAN_test, WPA
security modes with a pre-shared key of 1234 5678, IP address 1.1.1.1, netmask 255.255.255.0,
and a gateway IP address of 1.2.3.4 with a priority of 10.
Router(config)# interface wlan-1-2
Router(config-if-wlan)# ssid WLAN_test
Router(config-if-wlan)# security wpa tkip psk key 12345678
Router(config-if-wlan)# security mode wpa
Router(config-if-wlan)# ip address 1.1.1.1 255.255.255.0
Router(config-if-wlan)# ip gateway 1.2.3.4 metric 10
Router(config-if-wlan)# exit
78
ZyWALL (ZLD) CLI Reference Guide
Page 79

Chapter 6 Interfaces
6.8.3 WLAN MAC Filter Commands
Use these commands to give specific wireless clients exclusive access to the ZyW ALL (allow
association) or block specific devices from accessing the ZyWALL (deny association) based
on the devices’ MAC addresses.
Table 33 WLAN General Commands
COMMAND DESCRIPTION
[no] wlan mac-filter mac_address
[description description]
[no] wlan mac-filter activate Turns the MAC address filter on or off.
wlan mac-filter associate <allow |
deny>
show wlan mac-filter status Displays the MAC filter’s activation and association settings.
show wlan mac-filter Displays the WLAN MAC filter entries.
Specifies the MAC address (in XX:XX:XX:XX:XX:XX format)
of the wireless station that is to be allowed or denied access
to the ZyWALL. The no command removes the entry.
description: You can use alphanumeric and
:=?!*#@$_%-
characters long.
Defines the filter action for the list of MAC addresses in the
MAC address filter table. Allow permits them to access to the
ZyWALL, MAC addresses not listed will be blocked.
Deny blocks the listed addresses from accessing the router,
MAC addresses not listed will be allowed to access the router.
characters, and it can be up to 60
()+/
6.8.3.1 WLAN MAC Filter Commands Example
This example creates a MAC filter entry for MAC address 01:02:03:04:05:06 and sets the
ZyWALL to allow wireless access from that entry’s MAC address only.
Router(config)# wlan mac-filter 01:02:03:04:05:06 description example
Router(config)# wlan mac-filter associate allow
Router(config)# wlan mac-filter activate
Router(config)# show wlan mac-filter status
Enable: yes
Association: allow
Router(config)# show wlan mac-filter
No. MAC Description
===========================================================================
1 01:02:03:04:05:06 example
6.9 VLAN Interface Specific Commands
This section covers commands that are specific to VLAN interfaces. VLAN interfaces also use
many of the general interface commands discussed at the beginning of Section 6.2 on page 51.
ZyWALL (ZLD) CLI Reference Guide
79
Page 80

Chapter 6 Interfaces
The following table identifies the values required for many of these commands. Other input
values are discussed with the corresponding commands.
Table 34 Input Values for VLAN Interface Commands
LABEL DESCRIPTION
interface_name VLAN interface: vlanx, x = 0 - 4094
Ethernet interface: For the ZyWALL USG 300 and above, use gex, x = 1 N, where N equals the highest numbered Ethernet interface for your
ZyWALL model.
The ZyWALL USG 100 and 200 models use a name such as wan1,
wan2, opt, lan1, ext-wlan, or dmz.
This table lists the VLAN interface commands.
Table 35 interface Commands: VLAN Interfaces
COMMAND DESCRIPTION
interface interface_name Creates the specified interface if necessary and
enters sub-command mode.
[no] port interface_name Specifies the Ethernet interface on which the VLAN
[no] vlan-id <1..4094> Specifies the VLAN ID used to identify the VLAN.
show port vlanid Displays the Ethernet interface VLAN se tti n gs .
interface runs. The
The
no command clears the VLAN ID.
no command clears the port.
6.9.1 VLAN Interface Command Examples
The following commands show you how to set up VLAN vlan100 with the following
parameters: VLAN ID 100, interface ge1, IP 1.2.3.4, subnet 255.255.255.0, MTU 598,
gateway 2.2.2.2, description "I am vlan100”, upstream bandwidth 345, and downstream
bandwidth 123.
Router# configure terminal
Router(config)# interface vlan100
Router(config-if-vlan)# vlan-id 100
Router(config-if-vlan)# port ge1
Router(config-if-vlan)# ip address 1.2.3.4 255.255.255.0
Router(config-if-vlan)# ip gateway 2.2.2.2
Router(config-if-vlan)# mtu 598
Router(config-if-vlan)# upstream 345
Router(config-if-vlan)# downstream 123
Router(config-if-vlan)# description I am vlan100
Router(config-if-vlan)# exit
6.10 Bridge Specific Commands
This section covers commands that are specific to bridge interfaces. Bridge interfaces also use
many of the general interface commands discussed at the beginning of Section 6.2 on page 51.
80
ZyWALL (ZLD) CLI Reference Guide
Page 81

Chapter 6 Interfaces
The following table identifies the values required for many of these commands. Other input
values are discussed with the corresponding commands.
Table 36 Input Values for Bridge Interface Commands
LABEL DESCRIPTION
interface_name The name of the interface.
Ethernet interface: For the ZyWALL USG 300 and above, use gex, x = 1 - N,
where N equals the highest numbered Ethernet interface for your ZyWALL
model.
The ZyWALL USG 100 and 200 models use a name such as wan1, wan2,
opt, lan1, ext-wlan, or dmz.
VLAN interface: vlanx, x = 0 - 4094
bridge interface: brx, x = 0 - N, where N depends on the number of bridge
interfaces your ZyWALL model supports.
This table lists the bridge interface commands.
Table 37 interface Commands: Bridge Interfaces
COMMAND DESCRIPTION
interface interface_name Creates the specified interface if necessary and
enters sub-command mode.
[no] join interface_name Adds the specified Ethernet interface or VLAN
show bridge available member Displays the available interfaces that could be
interface to the specified bridge. The
removes the specified interface from the specified
bridge.
added to a bridge.
no command
6.10.1 Bridge Interface Command Examples
The following commands show you how to set up a bridge interface named br0 with the
following parameters: member ge1, IP 1.2.3.4, subnet 255.255.255.0, MTU 598, gateway
2.2.2.2, upstream bandwidth 345, downstream bandwidth 123, and description “I am br0”.
Router# configure terminal
Router(config)# interface br0
Router(config-if-brg)# join ge1
Router(config-if-brg)# ip address 1.2.3.4 255.255.255.0
Router(config-if-brg)# ip gateway 2.2.2.2
Router(config-if-brg)# mtu 598
Router(config-if-brg)# upstream 345
Router(config-if-brg)# downstream 123
Router(config-if-brg)# description I am br0
Router(config-if-brg)# exit
ZyWALL (ZLD) CLI Reference Guide
81
Page 82

Chapter 6 Interfaces
6.11 Auxiliary Interface Specific Commands
The first table below lists the auxiliary interface commands, and the second table explains
the values you can input with these commands.
Table 38 interface Commands: Auxiliary Interface
COMMAND DESCRIPTION
interface dial aux
interface disconnect aux
interface aux Enters sub-command mode.
[no] authentication {chap-pap | chap | pap
| mschap | mschap-v2}
[no] dial-timeout <30..120> Specifies the number of seconds the auxiliary
[no] dialing-type {tone | pulse} Specifies the dial type of the auxiliary interface. The
[no] idle <0..360> Specifies the number of seconds the auxiliary
[no] initial-string initial_string Specifies the initial string of the auxiliary interface.
[no] password password Specifies the password of the auxiliary interface.
[no] phone-number phone Specifies the phone number of the auxiliary
[no] port-speed {9600 | 19200 | 38400 |
57600 | 115200}
[no] username username Specifies the username of the auxiliary interface.
Dials or disconnects the auxiliary interface.
Specifies the authentication type of the auxiliary
interface. The
to chap-pap.
interface waits for an answer each time it tries to
connect. The
no command sets the authentication
no command disables the timeout.
no command sets the dial type to tone.
interface waits for activity before it automatically
disconnects. The no command disables the idle
timeout.
The no command sets the initial string to “ATZ”.
initial_string: You can use up to 64
characters. Semicolons (;) and backslashes (\) are
not allowed.
The
no command clears the password.
password: You can use up to 63 printable ASCII
characters. Spaces are not allowed.
interface. You can use 1-20 numbers, commas (,),
or plus signs (+). Use a comma to pause during
dialing. Use a plus sign to tell the external modem
to make an international call. The
clears the phone number.
Specifies the baud rate of the auxiliary interface.
The
no command sets the baud rate to 115200.
The no command clears the username.
username: You can use alphanumeric,
underscores (_), dashes (-), and
and it can be up to 30 characters long.
no command
/@$ characters,
82
ZyWALL (ZLD) CLI Reference Guide
Page 83

6.11.1 Auxiliary Interface Command Examples
The following commands show you how to set up the auxiliary interface aux with the
following parameters: phone-number 0340508888, tone dialing, port speed 115200, initialstring ATZ, timeout 10 seconds, retry count 2, retry interval 100 seconds, username kk,
password kk@u2online, chap-pap authentication, and description “I am aux interface”.
Router# configure terminal
Router(config)# interface aux
Router(config-if-aux)# phone-number 0340508888
Router(config-if-aux)# dialing-type tone
Router(config-if-aux)# port-speed 115200
Router(config-if-aux)# initial-string ATZ
Router(config-if-aux)# timeout 10
Router(config-if-aux)# retry-count 2
Router(config-if-aux)# retry-interval 100
Router(config-if-aux)# username kk
Router(config-if-aux)# password kk@u2online
Router(config-if-aux)# authentication chap-pap
Router(config-if-aux)# description I am aux interface
Router(config-if-aux)# exit
Chapter 6 Interfaces
The following commands show how to dial, disconnect, and stop the auxiliary interface.
Router# interface dial aux
Router# interface disconnect aux
ZyWALL (ZLD) CLI Reference Guide
83
Page 84

Chapter 6 Interfaces
84
ZyWALL (ZLD) CLI Reference Guide
Page 85

CHAPTER 7
Trunks
This chapter shows you how to configure trunks on your ZyWALL.
7.1 Trunks Overview
You can group multiple interfaces together into trunks to have multiple connections share the
traffic load to increase overall network throughput and enhance network reliability. If one
interface’s connection goes down, the ZyWALL sends traffic through another member of the
trunk. For example, you can use two interfaces for WAN connections. You can connect one
interface to one ISP (or network) and connect the another to a second ISP (or network). The
ZyWALL can balance the load between multiple connections. If one interface's connection
goes down, the ZyWALL can automatically send its traffic through another interface.
You can use policy routing to specify through which interface to send specific traffic types.
You can use trunks in combination with policy routing. Y ou can also define multiple trunks for
the same physical interfaces. This allows you to send specific traffic types through the
interface that works best for that type of traffic, and if that interface’s connection goes down,
the ZyWALL can still send its traffic through another interface.
7.2 Trunk Scenario Examples
Suppose one of the ZyWALL's interfaces is connected to an ISP that is also your V oice over IP
(VoIP) service provider. You may want to set that interface as active and set another interface
(connected to another ISP) to passive. This way VoIP traffic goes through the interface
connected to the VoIP service provider whenever the interface’s connection is up.
Another example would be if you use multiple ISPs that provide different levels of service to
different places. Suppose ISP A has better connections to Europe while ISP B has better
connections to Australia. You could use po licy routing and trunks to send traffic for your
European branch offices primarily through ISP A and traffic for your Australian branch offices
primarily through ISP B.
ZyWALL (ZLD) CLI Reference Guide
85
Page 86

Chapter 7 Trunks
7.3 Trunk Commands Input Values
The following table explains the values you can input with the interface-group
commands.
Table 39 interface-group Command Input Values
LABEL DESCRIPTION
group-name A descriptive name for the trunk.
For the ZyWALL USG 300 and above, use up to 31 characters (a-zA-Z0-9_-). The
name cannot start with a number. This value is case-sensitive.
The ZyWALL USG 100 and 200 models use WAN_TRUNK or WAN_TRUNK2-5.
interfacename
num The interface’s position in the trunk’s list of members <1..8>.
<CR> Carriage Return (the “enter” key).
The name of an interface, it could be an Ethernet, PPP , VLAN or brid ge interf ace. The
possible number of each interface type and the abbreviation to use are as follows.
Ethernet interface: For the ZyWALL USG 300 and above, use gex, x = 1 - N, where N
equals the highest numbered Ethernet interface for your ZyWALL model.
The ZyWALL USG 100 and 200 models use a name such as wan1, wan2, opt,
lan1, ext-wlan, or dmz.
PPPoE/PPTP interface: pppx, x = 0 - N, where N depends on the number of PPPoE/
PPTP interfaces your ZyWALL model supports.
VLAN interface: vlanx, x = 0 - 4094
bridge interface: brx, x = 0 - N, where N depends on the number of bridge interfaces
your ZyWALL model supports.
7.4 Trunk Commands Summary
The following table lists the interface-group commands. You must use the configure
terminal
See Table 39 on page 86 for details about the values you can input with these commands.
Table 40 interface-group Commands Summary
COMMAND DESCRIPTION
show interface-group {systemdefault|user-define|group-name}
[no] interface-group group-name Creates a trunk name and enters the trunk sub-
command to enter the configuration mode before you can use these commands.
algorithm {wrr|llf|spillover}
exit Leaves the trunk sub-command mode.
flush Deletes a trunk’s in t erface settings.
interface {num|append|insert
num} interface-name [weight
<1..10>|limit
<1..2097152>|passive]
Displays pre-configured system default trunks, your
own user configuration trunks or a specified trunk’s
settings.
command mode where you can configure the trunk.
no command removes the trunk.
The
Sets the trunk’s load balancing algorithm.
This subcommand adds an interface to a trunk. Sets
the interface’s number. It also sets the interface’s
weight and spillover limit or sets it to be passive.
86
ZyWALL (ZLD) CLI Reference Guide
Page 87

Chapter 7 Trunks
Table 40 interface-group Commands Summary (continued)
COMMAND DESCRIPTION
loadbalancing-index
<outbound|inbound|total>
mode {normal|trunk} Sets the mode for a trunk. Do this first in the trunk’s
move <1..8> to <1..8> Changes a the interface order in a trunk.
[no] interface
{num|interface-name}
system default-interface-group
group-name
[no] system default-snat Enables or disables Source NAT (SNAT). When SNAT
show system default-snat Displays whether the ZyWALL enable SNAT or not.
show system default-interfacegroup
Use this command only if you use least load first or
spill-over as the trunk’s load balancing algorithm.
Set either outbound, inbound or outbound and
inbound traffic (total) to which the ZyWALL will apply
the specified algorithm. Outbound traffic means the
traffic travelling from an internal interface (ex. LAN) to
an external interface (ex. WAN). Inbound traffic means
the opposite.
sub-command mode.
Removes an interface from the trunk.
Sets the ZyWALL to first attempt to use the the
specified WAN trunk.
is enabled, the ZyWALL uses the IP address of the
outgoing interface as the source IP address of the
packets it sends out through the WAN interfaces.
The ZyWALL performs SNA T by default for traffic going
to or from the WAN interfaces.
Dispalys the W A N trun k th e ZyWALL first attempts to
use.
7.5 Trunk Command Examples
The following example creates a weighted round robin trunk for Ethernet interfaces ge1 and
ge2. The ZyWALL sends twice as much traffic through ge1.
Router# configure terminal
Router(config)# interface-group wrr-example
Router(if-group)# mode trunk
Router(if-group)# algorithm wrr
Router(if-group)# interface 1 ge1 weight 2
Router(if-group)# interface 2 ge2 weight 1
Router(if-group)# exit
Router(config)#
ZyWALL (ZLD) CLI Reference Guide
87
Page 88

Chapter 7 Trunks
The following example creates a least load first trunk for Ethernet interface ge3 and VLAN 5,
which will only apply to outgoing traffic through the trunk. The
traffic through the least utilized of these interfaces.
Router# configure terminal
Router(config)# interface-group llf-example
Router(if-group)# mode trunk
Router(if-group)# algorithm llf
Router(if-group)# interface 1 ge3
Router(if-group)# interface 2 vlan5
Router(if-group)# loadbalancing-index outbound
Router(if-group)# exit
Router(config)#
The following example creates a spill-over trunk for Ethernet interfaces ge1 and ge3, which
will apply to both incoming and outgoing traffic through the trunk.. The
traffic through ge1 until it hits the limit of 1000 kbps. The
1000 kbps through ge3.
Router# configure terminal
Router(config)# interface-group spill-example
Router(if-group)# mode trunk
Router(if-group)# algorithm spill-over
Router(if-group)# interface 1 ge1 limit 1000
Router(if-group)# interface 2 ge3 limit 1000
Router(if-group)# loadbalancing-index total
Router(if-group)# exit
Router(config)#
ZyWALL sends new session
ZyWALL sends
ZyWALL sends anything over
88
ZyWALL (ZLD) CLI Reference Guide
Page 89

7.6 Link Sticking
You can have the ZyW ALL send each local computer’ s traf fic through a single WAN interface
for a specified period of time. This is useful when a redirect server forwards a user request for
a file and informs the file server that a particular WAN IP address is requesting the file. If the
user’s subsequent sessions came from a different WAN IP address, the file server would deny
the request. Here is an example.
Figure 14 Link Sticking
1
Chapter 7 Trunks
B
WAN1
3
WAN2
2
4
LAN
A
1 LAN user A tries to download a file from server B on the Internet. The ZyWALL uses
WAN1 to send the request to server B.
2 However remote server B is actually a redirect server. So server B sends a file list to
LAN user A. The file list lets LAN user A’s computer know that the desired file is
actually on file server (C). At the same time, register server B informs file server C that
a computer located at the WAN1’s IP address will download a file.
3 The ZyWALL is using active/active load balancing. So when LAN user A tries to
retrieve the file from file server C, the request goes out through WAN2.
4 File server C finds that the request comes from WAN2’s IP address instead of WAN1’s
IP address and rejects the request.
5 If link sticking had been configured, the ZyWALL would have still used WAN1 to send
LAN user A’s request to file server C and the file server would have given the file to A.
C
ZyWALL (ZLD) CLI Reference Guide
89
Page 90

Chapter 7 Trunks
7.7 Link Sticking Commands Summary
The following table lists the ip load-balancing link-sticking commands for
link sticking. (The link sticking commands have the prefix ip load-balancing because
they affect the ZyWALL’s load balancing behavior.) You must use the
terminal
command to enter the configuration mode before you can use these commands.
See Table 39 on page 86 for details about the values you can input with these commands.
Table 41 ip load-balancing link-sticking Commands Summary
COMMAND DESCRIPTION
[no] ip load-balancing linksticking activate
[no] ip load-balancing linksticking timeout timeout
show ip load-balancing linksticking status
Turns link sticking on or off.
Sets for how many seconds (30-3600) the ZyWALL
sends all of each local computer’s traffic through one
WAN interface.
Displays the current link sticking settings.
7.8 Link Sticking Command Example
configure
This example shows how to activate link sticking and set the timeout to 600 seconds (ten
minutes).
Router(config)# ip load-balancing link-sticking activate
Router(config)# ip load-balancing link-sticking timeout 600
Router(config)# show ip load-balancing link-sticking status
active : yes
timeout : 300
90
ZyWALL (ZLD) CLI Reference Guide
Page 91

CHAPTER 8
Route
This chapter shows you how to configure policies for IP routing and static routes on your
ZyWALL.
8.1 Policy Route
Traditionally, routing is based on the destination address only and the ZyWALL takes the
shortest path to forward a packet. IP Policy Routing (IPPR) provides a mechanism to override
the default routing behavior and alter the packet forwarding based on the policy defined by the
network administrator. Policy-based routing is applied to incoming packets on a per interface
basis, prior to the normal routing.
8.2 Policy Route Commands
The following table identifies the values required for many of these commands. Other input
values are discussed with the corresponding commands.
Table 42 Input Values for General Policy Route Commands
LABEL DESCRIPTION
address_object The name of the IP address (group) object. You may use 1-31 alphanumeric
characters, underscores(
number. This value is case-sensitive.
interface_name The name of the interface.
Ethernet interface: For the ZyWALL USG 300 and above, use gex, x = 1 - N,
where N equals the highest numbered Ethernet interface for your ZyWALL
model.
The ZyWALL USG 100 and 200 models use a name such as wan1, wan2,
opt, lan1, ext-wlan, or dmz.
virtual interface on top of Ethernet interface: add a colon (:) and the number of
the virtual interface. For example: gex:y, x = 1 - N, y = 1 - 4
VLAN interface: vlanx, x = 0 - 4094
virtual interface on top of VLAN interface: vlanx:y, x = 0 - 4094, y = 1 - 12
bridge interface: brx, x = 0 - N, where N depends on the number of bridge
interfaces your ZyWALL model supports.
virtual interface on top of bridge interface: brx:y, x = the number of the brid g e
interface, y = 1 - 4
PPPoE/PPTP interface: pppx, x = 0 - N, where N depends on the number of
PPPoE/PPTP interfaces your ZyWALL model support s.
policy_number The number of a policy route. 1 - X where X is the highest number of policy
routes the ZyWALL model supports. See the ZyWALL’ s User’s Guide for details.
_), or dashes (-), but the first character cannot be a
ZyWALL (ZLD) CLI Reference Guide
91
Page 92

Chapter 8 Route
Table 42 Input Values for General Policy Route Commands (continued)
LABEL DESCRIPTION
schedule_object The name of the schedule. You may use 1-31 alphanumeric characters,
underscores(
value is case-sensitive.
service_name The name of the service (group). You may use 1-31 alphanumeric characters,
underscores(_), or dashes (-), but the first character cannot be a number. This
value is case-sensitive.
user_name The name of a user (group). You may use 1-31 alphanumeric characte rs,
underscores(
value is case-sensitive.
_), or dashes (-), but the first character cannot be a number. This
_), or dashes (-), but the first character cannot be a number. This
The following table describes the commands available for policy route. You must use the
configure terminal command to enter the configuration mode before you can use these
commands.
Table 43 Command Summary: Policy Route
COMMAND DESCRIPTION
[no] bwm activate Globally enables bandwidth management. You
must globally activate bandwidth management to
have individual policy routes or application patrol
policies apply bandwidth management. The
command globally disables bandwidth
management.
policy {policy_number | append | insert
policy_number}
[no] auto-destination When you set tunnel as the next-hop type
[no] auto-disable When you set interface or trunk as the next-
[no] bandwidth <1..1048576> priority
<1..1024> [maximize-bandwidth-usage]
[no] deactivate Disables the specified policy. The no command
[no] description description Sets a descriptive name for the policy. The
[no] destination {address_object|any} Sets the destination IP address the matched
Enters the policy-route sub-command mode to
configure, add or insert a policy.
(using the next-hop tunnel command) for
this route, you can use this command to have the
ZyWALL use the local network of the peer router
that initiated an incoming dynamic IPSec tunnel
as the destination address of the policy instead of
what you configure by using the destination
command. The no command disables the setting.
hop type (using the next-hop interface or
next-hop trunk command) for this route, you
can use this command to have the ZyWALL
automatically disable this policy route when the
next-hop’s connection is down. The no command
disables the setting.
Sets the maximum bandwidth and priority for the
policy. The
settings from the rule. You can also turn
maximize bandwidth usage on or off.
enables the specified policy.
command removes the name for the policy.
packets must have. The no command resets the
destination IP address to the default (any). any
means all IP addresses.
no command removes bandwidth
no
no
92
ZyWALL (ZLD) CLI Reference Guide
Page 93

Chapter 8 Route
Table 43 Command Summary: Policy Route (continued)
COMMAND DESCRIPTION
[no] dscp {any | <0..63>} Sets a custom DSCP code point (0~63). This is
the DSCP value of incoming packets to which
this policy route applies. any means all DSCP
value or no DSCP marker.
[no] dscp class {default | dscp_class} Sets a DSCP class. Use default to apply this
policy route to incoming packets that are marked
with DSCP value 0. Use one of the pre-defined
AF classes (including af11~af13, af21~af23,
af31~af33, and af41~af43) to apply this policy
route to incoming packets that are marked with
the DSCP AF class.
The “af” entries stand for Assured Forwarding.
The number following the “af” identifies one of
four classes and one of three drop preferences.
See Assured Forwarding (AF) PHB for DiffServ
on page 95 for more details.
dscp-marking <0..63> Sets a DSCP value to have the ZyWALL apply
that DSCP value to the route’s outgoing packets.
dscp-marking class {default | dscp_class} Sets how the ZyWALL handles the DSCP value
no dscp-marking Use this command to have the ZyWALL not
[no] interface interface_name Sets the interface on which the incoming packets
[no] next-hop {auto|gateway address object
|interface interface_name |trunk
trunk_name|tunnel tunnel_name}
[no] schedule schedule_object Sets the schedule. The no command removes
[no] service {service_name|any} Sets the IP protocol. The
[no] snat {outgoing-interface|pool
{address_object}}
[no] source {address_object|any} Sets the source IP address that the matched
of the outgoing packets that match this route. Set
this to default to have the ZyWALL set the
DSCP value of the packets to 0. Set this to an “af”
class (including af11~af13, af21~af23,
af31~af33, and af41~af43) which stands for
Assured Forwarding. The number following the
“af” identifies one of four classes and one of three
drop preferences. See Assured Forwarding (AF)
PHB for DiffServ on page 95 for more details.
modify the DSCP value of the route’s outgoing
packets.
are received. The
incoming interface to the default (
means all interfaces.
Sets the next-hop to which the matched packets
are routed. The no command resets next-hop
settings to the default (
the schedule setting to the default (
means any time.
no command resets the
any). any
auto).
no command resets
service settings to the default (
all services.
Sets the source IP address of the matched
packets that use SNAT. The
removes source NAT settings from the rule.
packets must have. The
source IP address to the default (
means all IP addresses.
any). any means
no command
no command resets the
any). any
none). none
ZyWALL (ZLD) CLI Reference Guide
93
Page 94

Chapter 8 Route
Table 43 Command Summary: Policy Route (continued)
COMMAND DESCRIPTION
[no] sslvpn tunnel_name Sets the incoming interface to an SSL VPN
tunnel. The
tunnel through which the incoming packets are
received.
[no] trigger <1..8> incoming service_name
trigger service_name
trigger append incoming service_name trigger
service_name
trigger delete <1..8> Removes a port triggering rule.
trigger insert <1..8> incoming service_name
trigger service_name
trigger move <1..8> to <1..8> Moves a port triggering rule to the number that
[no] tunnel tunnel_name Sets the incoming interface to an IPSec VPN
[no] user user_name Sets the user name. The no command resets the
[no] policy controll-ipsec-dynamic-rules
activate
policy default-route Enters the policy-route sub-command mode to
policy delete policy_number Removes a routing policy.
policy flush Clears the policy routing table.
policy list table Displays all policy route settings.
policy move policy_number to policy_number Moves a routing policy to the number that you
[no] policy override-direct-route activate Use this command to have the ZyWALL forward
show bwm activation Displays whether or not the global setting for
show bwm-usage < [policy-route policy_number] |
[interface interface_name]
show policy-route [policy_number] Displays all or specified policy route settings.
Sets a port triggering rule. The no command
removes port trigger settings from the rule.
Adds a new port triggering rule to the end of the
list.
Adds a new port triggering rule before the
specified number.
you specified.
tunnel. The no command removes the IPSec
VPN tunnel through which the incoming packets
are received.
user name to the default (
users.
Enables the ZyWALL to use policy routes to
manually specify the destination addresses of
dynamic IPSec rules. You must manually create
these policy routes. The ZyWALL automatically
obtains source and destination addresses for
dynamic IPSec rules that do not match any of the
policy routes.
The no command has the ZyWALL automatically
obtain source and destination addresses for all
dynamic IPSec rules.
set a route with the name “default-route”.
specified.
packets that match a policy route according to
the policy route instead of sending the packets to
a directly connected network. Use the no
command to disable it.
bandwidth management on the ZyWALL is
enabled.
Displays the specified policy route or interface’s
bandwidth allotment, current bandwidth usage,
and bandwidth usage statistics.
no command removes the SSL VPN
any). any means all
94
ZyWALL (ZLD) CLI Reference Guide
Page 95

Chapter 8 Route
Table 43 Command Summary: Policy Route (continued)
COMMAND DESCRIPTION
show policy-route begin <1..200> end <1..200> Displays the specified range of policy route
settings.
show policy-route controll-ipsec-dynamic-rules Displays whether the ZyWALL checks policy
routes first before IPSec dynamic rules.
show policy-route override-direct-route Displays whether or not the ZyWALL forwards
packets that match a policy route according to
the policy route instead of sending the packets to
a directly connected network.
show policy-route rule_count Displays the number of policy routes that have
show policy-route underlayer-rules Displays all policy route rule details for advanced
been configured on the ZyWALL.
debugging.
8.2.1 Assured Forwarding (AF) PHB for DiffServ
Assured Forwarding (AF) behavior is defined in RFC 2597. The AF behavior group defines
four AF classes. Inside each class, packets are given a high, medium or low drop precedence.
The drop precedence determines the probability that routers in the network will drop packets
when congestion occurs. If congestion occurs between classes, the traffic in the higher class
(smaller numbered class) is generally given priority. Combining the classes and drop
precedence produces the following twelve DSCP encodings from AF11 through AF43. The
decimal equivalent is listed in brackets.
Table 44 Assured Forwarding (AF) Behavior Group
CLASS 1 CLASS 2 CLASS 3 CLASS 4
Low Drop Precedence AF11 (10) AF21 (18) AF31 (26) AF41 (34)
Medium Drop Precedence AF12 (12) AF22 (20) AF 32 (28) AF42 (36)
High Drop Precedence AF13 (14) AF23 (22) AF33 (30) AF43 (38)
ZyWALL (ZLD) CLI Reference Guide
95
Page 96

Chapter 8 Route
8.2.2 Policy Route Command Example
The following commands create two address objects (TW_SUBNET and GW_1) and insert a
policy that routes the packets (with the source IP address TW_SUBNET and any destination
IP address) through the interface ge1 to the next-hop router GW_1. This route uses the IP
address of the outgoing interface as the matched packets’ source IP address.
Router(config)# address-object TW_SUBNET 192.168.2.0 255.255.255.0
Router(config)# address-object GW_1 192.168.2.250
Router(config)# policy insert 1
Router(policy-route)# description example
Router(policy-route)# destination any
Router(policy-route)# interface ge1
Router(policy-route)# next-hop gateway GW_1
Router(policy-route)# snat outgoing-interface
Router(policy-route)# source TW_SUBNET
Router(policy-route)# exit
Router(config)# show policy-route 1
index: 1
active: yes
description: example
user: any
schedule: none
interface: ge1
tunnel: none
sslvpn: none
source: TW_SUBNET
destination: any
DSCP code: any
service: any
nexthop type: Gateway
nexthop: GW_1
nexthop state: Not support
auto destination: no
bandwidth: 0
bandwidth priority: 0
maximize bandwidth usage: no
SNAT: outgoing-interface
DSCP marking: preserve
amount of port trigger: 0
Router(config)#
8.3 IP Static Route
The ZyWALL has no knowledge of the networks beyond the network that is directly
connected to the ZyWALL. For instance, the ZyWALL knows about network N2 in the
following figure through gateway R1. However, the ZyWALL is unable to route a packet to
network N3 because it doesn't know that there is a route through the same gateway R1 (via
gateway R2). The static routes are for you to tell the ZyWALL about the networks beyond the
network connected to the ZyWALL directly.
96
ZyWALL (ZLD) CLI Reference Guide
Page 97

Figure 15 Example of Static Routing Topology
8.4 Static Route Commands
The following table describes the commands available for static route. You must use the
configure terminal command to enter the configuration mode before you can use these
commands.
Chapter 8 Route
Table 45 Command Summary: Static Route
COMMAND DESCRIPTION
[no] ip route {w.x.y.z} {w.x.y.z}
{interface|w.x.y.z} <0..127>
ip route replace {w.x.y.z} {w.x.y.z}
{interface|w.x.y.z} <0..127> with {w.x.y.z}
{w.x.y.z} {interface|w.x.y.z} <0..127>
show ip route-settings Displays static route information. Use show ip
Sets a static route. The no command disables a
static route.
Changes an existing route’s settings.
route to see learned route information. See
Section 9.2.5 on page 102.
8.4.1 Static Route Commands Example
The following command sets a static route with IP address 10.10.10.0 and subnet mask
255.255.255.0 and with the next-hop interface ge1. Then use th e show command to display
the setting.
Router(config)# ip route 10.10.10.0 255.255.255.0 ge1
Router(config)#
Router(config)# show ip route-settings
Route Netmask Nexthop Metric
===========================================================================
10.10.10.0 255.255.255.0 ge1 0
ZyWALL (ZLD) CLI Reference Guide
97
Page 98

Chapter 8 Route
98
ZyWALL (ZLD) CLI Reference Guide
Page 99

CHAPTER 9
Routing Protocol
This chapter describes how to set up RIP and OSPF routing protocols for the ZyWALL.
9.1 Routing Protocol Overview
Routing protocols give the ZyWALL routing information about the network from other
routers. The ZyWALL then stores this routing information in the routing table, which it uses
when it makes routing decisions. In turn, the ZyWALL can also provide routing information
via routing protocols to other routers.
The ZyWALL supports two standards, RIP and OSPF, for routing protocols. RIP and OSPF
are compared in Table 46 on page 99, and they are discussed further in the next two sections.
Table 46 OSPF vs. RIP
OSPF RIP
Network Size Large Small (with up to 15 routers)
Metric Bandwidth, hop count, throughput, round
trip time and reliability.
Convergence Fast Slow
Hop count
9.2 Routing Protocol Commands Summary
The following table describes the values required for many routing protocol commands. Other
values are discussed with the corresponding commands.
Table 47 Input Values for Routing Protocol Commands
LABEL DESCRIPTION
ip The 32-bit name of the area or virtual link in IP add ress format.
authkey The password for text or MD5 authentication. You may use alphanumeric
characters or underscores(
text password: 1-8 characters long
MD5 password: 1-16 characters long
The following sections list the routing protocol commands.
ZyWALL (ZLD) CLI Reference Guide
_).
99
Page 100

Chapter 9 Routing Protocol
9.2.1 RIP Commands
This table lists the commands for RIP.
Table 48 router Commands: RIP
COMMAND DESCRIPTION
router rip Enters sub-command mode.
[no] network interface_name Enables RIP on the specified Ethernet interface.
The
no command disables RIP on the specified
interface.
[no] redistribute {static | ospf} Enables redistribution of routing information
learned from the specified source. The no
command disables redistribution from the specified
source.
redistribute {static | ospf} metric
<0..16>
[no] version <1..2> Sets the default RIP version for all interfaces with
[no] passive-interface interface_name Sets the direction to “In-Only” for the specified
[no] authentication mode {md5 | text} Sets the authentication mode for RIP. The
[no] authentication string authkey Sets the password for text authentication. The
authentication key <1..255> key-string
authkey
no authentication key Clears the MD5 ID and password.
[no] outonly-interface interface_name Sets the direction to “Out-Only” for the specified
Sets the metric when redistributing routing
information learned from the specified source.
RIP enabled. If the interface RIP version is blank,
the interface uses the default version. This is not
available in the GUI. The
default RIP version to 2.
interface. The no command sets the direction to bidirectional.
command sets the authentication mode to “none”.
command clears the password.
Sets the MD5 ID and password for MD5
authentication.
interface. The
“BiDir”.
no command sets the direction to
no command sets the
no
no
9.2.2 General OSPF Commands
This table lists the commands for general OSPF configuration.
Table 49 router Commands: General OSPF Configuration
COMMAND DESCRIPTION
router ospf Enters sub-command mode.
[no] redistribute {static | rip} Enables redistribution of routing information
learned from the specified non-OSPF source. The
no command disables redistribution from the
specified non-OSPF source.
[no] redistribute {static | rip} metrictype <1..2> metric <0..16777214>
100
Sets the metric for routing information learned from
the specified non-OSPF source. The
clears the metric.
ZyWALL (ZLD) CLI Reference Guide
no command
 Loading...
Loading...