Page 1

ZXR10 2920/2928/2952
Access Switch
User Manual(V olume I)
ZTE CORPORATION
ZTE Plaza, Keji Road South,
Hi-Tech Industrial Park,
Nanshan District, Shenzhen,
P. R. China
518057
Tel: (86) 755 26771900 800-9830-9830
Fax: (86) 755 26772236
URL:
http://support. zte. com. cn
E-mail:
doc@zte. com. cn
V ersion 1.0
Page 2
LEGAL INFORMATION
Copyright © 2006 ZTE CORPORATION.
The contents of this document are protected by copyright laws and international treaties. Any reproduction or
distribution of this document or any portion of this document, in any form by any means, without the prior written
consent of ZTE CORPORATION is prohibited. Additionally, the contents of this document are protected by
contractual confidentiality obligations.
All company, brand and product names are trade or service marks, or registered trade or servi ce marks, of ZTE
CORPORATION or of their respective owners.
This document is provided “as is”, and all express, implied, or statutory warranties, representations or conditions
are disclaimed, including without limitation any implied warranty of merchantability, fitness for a particular
purpose, title or non-infringement. ZTE CORPOR AT I O N and its licensors shall not be liable for damages resulting
from the use of or reliance on the information contained herein.
ZTE CORPORATION or its licensors may have current or pending intellectual property rights or applications
covering the subject matter of this docum e nt. Except as expressly provided in any written license between ZTE
CORPORATION and its licensee, the user of this document shall not acquire any license to the subject matter
herein.
ZTE CORPORATION reserves the right to upgrade or make technical change to this product without further notice.
Users may visit ZTE technical support w ebsite http://ensupport. zte. com. cn to inquire related information.
The ultimate right to interpret this product resides in ZTE CORPORATION.
Revision History
Date Revision No. Serial No. Reason for Issue
7/11/2007 R1.0 sjzl20071746 First edition
Page 3

ZTE CORPORATION
Values Your Comments & Suggestions!
Your opinion is of great value and will help us improve the quality of our product
documentation and offer better services to our customers.
Please fax to (86) 755-26772236 or mail to Documentation R&D Department, ZTE
CORPORATION, ZTE Plaza, A Wing, Keji Road South, Hi-Tech Industrial Park,
Shenzhen, P. R. China 518057.
Thank you for your cooperation!
Document
Name
Product Version V1.0
Serial No.
Your evaluation
of this
documentation
Your
suggestions for
improvement of
this
documentation
ZXR10 2920/2928/2952(V1.00) Access Switch User Manual (Volume I)
sjzl20071746
Presentation:
(Introductions, Procedures, Illustrations, Completeness, Level of Detail, Organization,
Appearance)
Good Fair Average Poor Bad N/A
Accessibility:
(Contents, Index, Headings, Numbering, Glossary)
Good Fair Average Poor Bad N/A
Intelligibility:
(Language, Vocabulary, Readability & Clarity, Technical Accuracy, Content)
Good Fair Average Poor Bad N/A
Please check the suggestions which you feel can improve this documentation:
Improve the overview/introduction Make it more concise/brief
Improve the Contents Add more step-by-step procedures/tutorials
Improve the organization Add more troubleshooting information
Include more figures Make it less technical
Add more examples Add more/better quick reference aids
Add more detail Improve the index
Other suggestions
__________________________________________________________________________
__________________________________________________________________________
__________________________________________________________________________
__________________________________________________________________________
__________________________________________________________________________
# Please feel free to write any comments on an attached sheet.
Document Revision
Number
Equipment
Installation Date
R1.0
If you wish to be contacted regarding your comments, please complete the following:
Name Company
Postcode Address
Telephone E-mail
Page 4

This page is intentionally blank.
Page 5

Contents
About This Manual ............................................................ i
Purpose................................................................................ i
Intended Audience .................................................................i
Prerequisite Skill and Knowledge ..............................................i
What Is in This Manual ...........................................................i
Conventions ......................................................................... ii
How to Get in Touch............................................................. iii
Chapter 1.......................................................................... 1
Safety Instruction............................................................ 1
Overview .............................................................................1
Safety Instructions................................................................ 1
Chapter 2.......................................................................... 3
System Overview............................................................. 3
Overview .............................................................................3
Product Overview.................................................................. 3
Switching Capability ..............................................................4
Reliability and characteristics .................................................. 4
Particular function ................................................................ 4
Security Controls ..................................................................5
QoS Guarantee..................................................................... 5
Management ........................................................................6
Functions............................................................................. 6
Technical Features and Parameters..........................................7
Chapter 3.......................................................................... 9
Structure and Principle.................................................... 9
Overview .............................................................................9
Working Principle .................................................................. 9
Hardware Structure............................................................. 10
Page 6

ZXR10 2920 .......................................................................11
ZXR10 2928 ....................................................................... 12
ZXR10 2952 ....................................................................... 13
ZXR10 2928-FI ...................................................................14
Power Supply Module........................................................... 17
Chapter 4........................................................................19
Installation and Debugging ...........................................19
Overview ...........................................................................19
Equipment Installation ......................................................... 19
Switch Installation on Desktop ..............................................20
Switch Installation onto a Cabinet.......................................... 20
Cable Types........................................................................23
Power Cables Installation......................................................24
Console Cable Installation.....................................................25
Network Cable Installation....................................................26
Optical Fiber.......................................................................28
Labels ...............................................................................29
Cable Lightning Protection Requirements ................................ 32
Chapter 5........................................................................35
Usage and Operation .....................................................35
Overview ...........................................................................35
Configuration Modes ............................................................36
Configuration through Console Port Connection........................36
Configuring through Telnet ................................................... 37
Simple Network Management Protocol (SNMP).........................38
Configuring through WEB Connection .....................................39
Command Modes.................................................................40
Configuring User Mode ......................................................... 40
Configuring Global Mode.......................................................41
Configuring SNMP Mode .......................................................42
Configuring Layer 3 Mode.....................................................42
Configuring File System Mode ............................................... 42
Configuring NAS Mode .........................................................43
Configuring Cluster Management ...........................................43
Configuring Basic ACL ..........................................................44
Configuring Extended ACL ....................................................44
Configuring L2 ACL Mode......................................................45
Page 7

Configuring Hybrid ACL Mode................................................ 45
Using Command Line........................................................... 45
Command Abbreviations ...................................................... 47
History Commands.............................................................. 47
Function Key ...................................................................... 48
Chapter 6........................................................................49
System Management .....................................................49
Overview ........................................................................... 49
File System........................................................................ 49
Operating File System ......................................................... 50
Configuring ZXR10 2920/2928/2952 as an TFTP Client ............. 52
Configuring Imports and Exports........................................... 54
Setting File Backup and Recovery.......................................... 55
Software Version Upgrade.................................................... 56
Viewing System Information................................................. 57
Upgrading Version at Normality............................................. 57
Upgrading Version at Abnormality ......................................... 59
Chapter 7........................................................................65
Service Configuration ....................................................65
Overview ........................................................................... 65
Configuring Basic Port Parameters......................................... 68
Displaying Port Information .................................................. 74
Port Mirroring..................................................................... 75
Configuring Port Mirroring .................................................... 75
VLAN ................................................................................ 77
Configuring VLAN................................................................ 78
Introduction to FDB............................................................. 83
MAC Table Operations ......................................................... 83
Configuring FDB.................................................................. 84
LACP Overview ................................................................... 86
Configuring LACP ................................................................ 87
IGMP Snooping................................................................... 91
Configuring IGMP Snooping .................................................. 91
Internet Protocol Television ................................................ 101
Configuring IPTV Global Parameters..................................... 102
Configuring IPTV Channels ................................................. 103
Configuring Channel Access Control (CAC)............................ 104
Page 8

Configuring Administrative Command of IPTV Users ............... 106
Maintenance and Diagnosis of IPTV...................................... 108
MSTP Mode ...................................................................... 110
Configuring STP ................................................................ 112
ACL................................................................................. 124
Configuring Basic ACL ........................................................ 126
Configuring Extended ACL .................................................. 127
Configuring L2 ACL............................................................ 128
Configuring Hybrid ACL ...................................................... 128
Configuring Global ACL....................................................... 129
Configuring Time-Range..................................................... 131
Configuring ACL to a Physical Port ....................................... 131
Quality of Service (QoS)..................................................... 132
Configuring QoS................................................................ 133
Private Virtual LAN Overview............................................... 145
Configuring PVLAN ............................................................ 146
802. 1x Transparent Transmission ..................................... 149
Configuring 802. 1x Transparent Transmission..................... 150
Layer 3 Configuration......................................................... 150
Configuring IP Port ............................................................ 151
Static Route Configuration .................................................. 153
Configuring ARP Table Entry ............................................... 154
Chapter 8......................................................................159
Access Service..............................................................159
Configuring 802. 1x ......................................................... 163
Configuring Protocol Parameters of 802. 1x......................... 166
Configuring RADIUS........................................................... 169
QinQ Overview.................................................................. 177
Configuring QinQ............................................................... 178
SQinQ Overview................................................................ 180
Configuring SQinQ............................................................. 181
Syslog Overview ............................................................... 185
Configuring Syslog ............................................................ 186
Configuring NTP ................................................................ 187
GARP/GVRP Overview ........................................................ 189
Configuring GARP .............................................................. 190
Configuring GVRP .............................................................. 191
DHCP Snooping/Option82 ................................................... 194
Page 9

Configuring Global DHCP.................................................... 195
Configuring DHCP Snooping................................................ 197
Configuring IP Source Guard............................................... 198
Configuring DHCP Option82................................................ 199
VBAS Overview................................................................. 204
Configuring VBAS.............................................................. 205
sFlow Monitoring Overview................................................. 207
Configuring sFlow ............................................................. 207
ZESR Overview................................................................. 210
Configuring ZESR.............................................................. 211
Chapter 9......................................................................217
Network Management .................................................217
Overview ......................................................................... 217
Remote Access Overview ................................................... 219
Configuring Remote-Access ................................................ 219
Remote-Access Configuration Examples ............................... 220
SSH Overview .................................................................. 221
Configuring SSH ............................................................... 222
Configuring SSH v2. 0 ..................................................... 223
SNMP Overview ................................................................ 226
Configuring SNMP ............................................................. 227
RMON Overview................................................................ 233
Configuring RMON............................................................. 234
Cluster Management Overview............................................ 241
Configuring a ZDP............................................................. 243
Configuring ZTP................................................................ 245
Configuring Cluster ........................................................... 249
Configuring a Cluster Member............................................. 250
Configuring Cluster Parameters........................................... 251
Configuring Access and Control Cluster Members................... 253
Displaying Cluster Configuration.......................................... 255
Web Management Overview ............................................... 262
Logging On Using Web Management .................................... 262
Configuring a System ........................................................ 264
Configuring Port and Parameters......................................... 265
Configuring Vlan Management ............................................ 270
Configuring PVLAN ............................................................ 273
Configuring Mirroring Management ...................................... 275
Page 10

Configuring LACP Management............................................ 278
Configuring Terminal Record ............................................... 281
Configuring Port Statistics .................................................. 282
Configuring Information ..................................................... 283
Saving Configuration ......................................................... 284
Rebooting an Equipment .................................................... 285
Uploading a File ................................................................ 286
Configuring User Management............................................. 288
Chapter 10....................................................................291
Maintenance.................................................................291
Overview .........................................................................291
Routine Maintenance ......................................................... 292
Daily Routine Maintenance.................................................. 292
Monthly Maintenance ......................................................... 292
Maintenance Period ........................................................... 293
Single Loop Test Method .................................................... 294
Configuring Single-Port Loop Test ........................................ 294
Virtual Circuit Test............................................................. 297
Common Troubleshooting ................................................... 298
Troubleshooting through Console Port .................................. 298
Troubleshooting through Telnet ........................................... 299
Troubleshooting a Telnet connection with switch .................... 299
Troubleshooting the browser............................................... 300
Troubleshooting the Switch through Web .............................. 300
Troubleshooting the User Name/Password............................. 301
Troubleshooting Password .................................................. 303
Troubleshooting a Device Connection .................................. 303
Abbreviations ...............................................................305
Acronyms and Abbreviations ............................................... 305
Tables...........................................................................313
Index............................................................................327
Page 11

About This Manual
Purpose
This manual provides procedures and guidelines that support the
ZXR10 2920/2928/2952.
Intended Audience
This manual is intended for engineers and technicians who
perform operation on Layer 2 switches.
Prerequisite Skill and Knowledge
To use this document effectively, users should have a general
understanding of Layer 2 Switches and protocols. This is
Volume 1 and the Volume 2 is based on Commands. Familiarity
with the following is helpful:
Virtual Local Area Network
Link Aggregation Control Protocol
Spanning Tree Protocol
Access Control List
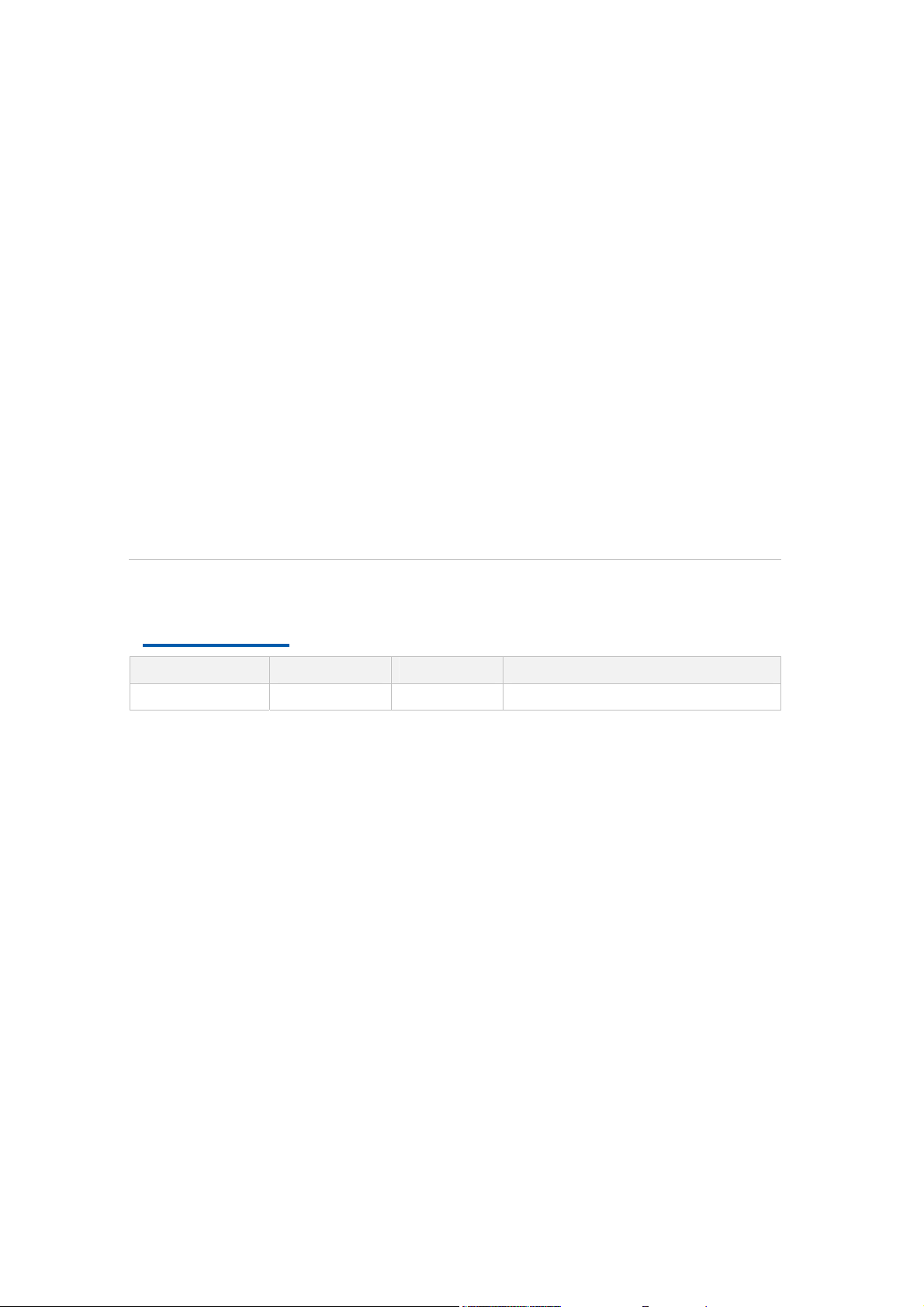
What Is in This Manual
This manual contains the following chapters:
TABLE 1 CHAPTER SUMMARY
Chapter Summary
Chapter 1, Safety
Instruction
Chapter 2, System
Overview
Chapter 3, Structure This chapter introduces the working
Confidential and Proprietary Information of ZTE CORPORATION i
This chapter introduces the safety
instructions and sign descriptions.
This chapter introduces the produce
overview, functions and technical
features.
Page 12

ZXR10 2920/2928/2952
(V1.00) Access Switch User Manual (Volume I)
Chapter Summary
and Principle principle, technical and hardware
structural information on each of the
ZXR10 2920/2928/2952
Chapter 4, Installation
and Debugging
Chapter 5, Usage
and Operation
Chapter 6, System
Management
Chapter 7, Service
Configuration
Chapter 8, Network
Management
Chapter 9,
Maintenance
This chapter provides an overview of
installation and debugging processes of
ZXR10 2920/2928/2952.
This chapter provides an overview of
configuration mode, command mode and
command line use.
This chapter introduces file system
management FTP/TFTP configuration, file
backup and restoration, software version
upgrade.
This chapter provides and overview of
configuration methods for various services
of ZXR10 2920/2928/2952.
This chapter provides and overview of
network management functions of the
ZXR10 2920/2928/2952, such as RemoteAccess, SSH, SNMP, RMON and cluster
management.
This chapter provides routine
maintenance, common test methods and
troubleshooting of ZXR10
2920/2928/2952.
Typographical
Conventions
Conventions
ZTE documents employ the following typographical conventions.
TABLE 2 TYPOGRAPHICAL CONVENTIONS
Typeface Meaning
Italics References to other Manuals and documents.
“Quotes” Links on screens.
Bold Menus, menu options, function names, input
fields, radio button names, check boxes, dropdown lists, dialog box names, window names.
CAPS Keys on the keyboard and buttons on screens
and company name.
Constant width
Text that you type, program code, files and
directory names, and function names.
ii Confidential and Proprietary Information of ZTE CORPORATION
Page 13

About This Manual
Mouse
Operation
Conventions
Customer
Support
TABLE 3 MOUSE OPERATION CONVENTIONS
Typeface Meaning
Click Refers to clicking the primary mouse button (usually
the left mouse button) once.
Double-click Refers to quickly clicking the primary mouse button
(usually the left mouse button) twice.
Right-click Refers to clicking the secondary mouse button
(usually the right mouse button) once.
Drag Refers to pressing and holding a mouse button and
moving the mouse.
How to Get in Touch
The following sections provide information on how to obtain
support for the documentation and the software.
If you have problems, questions, comments, or suggestions
regarding your product, contact us by e-mail at support@zte.
com. cn. You can also call our customer support center at (86)
755 26771900 and (86) 800-9830-9830.
Documentation
Support
ZTE welcomes your comments and suggestions on the quality
and usefulness of this document. For further questions,
comments, or suggestions on the documentation, you can
contact us by e-mail at doc@zte. com. cn; or you can fax your
comments and suggestions to (86) 755 26772236. You can
also browse our website at http://support. zte. com. cn,
which contains various interesting subjects like documentation,
knowledge base, forum and service request.
Confidential and Proprietary Information of ZTE CORPORATION iii
Page 14

This Page is intentionally blank.
iv Confidential and Proprietary Information of ZTE CORPORATION
Page 15

Chapter 1
Safety Instruction
Overview
Introduction
Contents
Equipment
Installation
Local Safety
This chapter introduces the safety instructions and sign
descriptions.
This chapter includes the following topics.
TABLE 4 TOPICS IF CHAPTER 1
Topics Page No.
Safety Instructions 1
Safety Instructions
This equipment can only be installed, operated and maintained
by professional user.
Please observe local safety specifications and relevant operating
procedures in equipment installation, operation and
maintenance. Otherwise, personal injury or equipment
damage may occur. Safety precautions introduced in this
manual are only supplementary to local safety codes.
ZTE shall not bear any liabilities incurred by violation of the
universal safety operation requirements or violation of the safety
standards for designing, manufacturing and using the equipment.
Confidential and Proprietary Information of ZTE CORPORATION 1
Page 16

This page is intentionally blank.
2 Confidential and Proprietary Information of ZTE CORPORATION
Page 17

Chapter 2
System Overview
Overview
Introduction
Contents
This chapter introduces the product overview, functions and
technical features.
This chapter includes the following topics.
TABLE 5 TOPICS IN CHAPTER 2
Topics Page No.
Product Overview 3
Switching Capability 4
Reliability and characteristics 4
Security Controls 5
QoS Guarantee 5
Management 6
Functions 6
Technical Features and Parameters 7
Product Overview
background
3 Confidential and Proprietary Information of ZTE CORPORATION
ZXR10 2920/2928/2952 series products are megabit L2+
Ethernet switch, providing gigabit upward Ethernet ports. They
can provide different quantity of & interface-types of Ethernet
port, mainly located at megabit access & converge to provide
fast, efficient, and cost-effective access and convergence
solutions.
Port & insert-card expanding instance that ZXR10
2920/2928/2952 switch series support are as follows:
Page 18

ZXR10 2920/2928/2952
(V1.0) Access Switch User Manual (Volume I)
ZXR10 2920:support sixteen 100M & four 1000M ports
ZXR10 2928: support twenty-four 100M & four 1000M ports
ZXR10 2952: support forty-four 100M & four 1000M ports
Note:2920 & 2928 support insert-card expand.ZXR10
2920/2928/2952 switch series have the following characters.
Switching Capability
All the ports of ZXR10 2920/2928/2952 megabit switch series
support the layer-2 switching at wire-speed. The filtration and
stream sort transact based on port do not weaken the switching
capability. Ports provide high throughput, packet discarding rate,
time delay and dithering can satisfy the demand of the key
application.
Features
Reliability and characteristics
ZXR10 2920/2928/2952 megabit switch series ensures the link
redundancy backup through STP/RSTP/MSTP. RSTP switching
that is based on IEEE-802.1w ensures the usability of the
network. These switches support the LACP function of 802. 3ad
function, and it supplies the load equalization backup and the
link. Switches support Ethernet ring network mode through
ZESR. High switching capability ensures that the operation do
not be interrupted.
Particular function
The following are the kinds of operation characteristics and
control:
Use of different modes of VLAN sort. It can be classified by
types of port, protocol, and strategy.
Provide VPN on layer-2 through QinQ, in addition to
SelectiveQinQ, and supply flexible control ability for optional
outer layer label, which makes it convenient to operate and
scheme.
Supports the client-end VBAS function, and supplies efficient
orientation technology support for client end.
Milticast support technology, includes igmp-snooping and
proxy function, fast-leaving characteristic and Multicast-Vlan
Switching (MVS) function & IPTV support.
4 Confidential and Proprietary Information of ZTE CORPORATION
Page 19

Chapter 2 System Overview
Security Controls
User Security
Control
Equipment
Level Security
The following are user level security control:
IEEE 802.1x implements dynamic and port-based security
provides the user ID authentication function and
MAC/IP/VLAN/PORT combines at random, and prevent illegal
user to accessing the network.
Segregating the ports is helpful to make sure that users can
not monitor or access to other users on the same switch.
DHCP monitoring prevents spiteful users deceiving the server
and sending spurious address, so it can start protecting IP
source and create a binding table for the IP address of the
user, MAC address, ports and VLAN to prevent user deceiving
or use IP address of other users.
The following are the equipment level security control:
CPU security control technology can resist DoS attack from
CPU.
SSH/SNMPv3 protocol supplies network management
security.
Multilevel security of console can prevent unauthenticated
users changing the switch configuration.
RADIUS authentication may carry on the common control to
the switchboard.
Network
Security
The following are the network security control:
ACL based on port or Trunk makes it possible for users to
apply security strategy to the ports of switches or Trunk.
Binding MAC address and the filtration based on source or
destination supply effective control over the flux based on
address.
Port MIRROR function is an effective tool for network
management analyses.
QoS Guarantee
Applications of QoS are shown below:
Standard 802.1p QoS and DSCP field sort label and sort
again based on single group with source and destination IP
address, source and destination MAC address, and TCP/UDP
port number.
Queue schedule arithmetic, Strict Priority(SP) & combination
schedule.
Support CAR(Committed Access Rate)function. Manage the
asynchronous upward and downward data stream from end
Confidential and Proprietary Information of ZTE CORPORATION 5
Page 20

ZXR10 2920/2928/2952
(V1.0) Access Switch User Manual (Volume I)
stage or up link. Input strategy control supplies the
bandwidth control with minimal increment by 64kbps. It can
satisfy the demand of discarding packets, time delay and
time dithering when network congestion occurs, and supply
the congestion avoiding function for the alignment.
Management
Switch management is described with the following statement:
Supports SNMPv1/v2c/v3 and RMON.
Supports ZXNM01 uniform network management platform.
Supports CLI command lines, including Console, Telnet and
SSH to access the switch.
GUI method supports Web network management.
Manage through ZGMP group.
Store and
Forward Mode
Functions
ZXR10 2920/2928/2952 adopts Store and Forward mode and
supports layer-2 switching at wire-speed. Full wire-speed
switching is implemented at all ports.
ZXR10 2920/2928/2952 has the following functions:
Megabit ports support port 10/100/1000M self-adapting and
MDI/MDIX self-adapting.
Kilomega ports support port 10/100/1000M self-adapting and
MDI/MDIX self-adapting.
Support 802.3x-compliant flow control (full duplex) and
back-pressure flow control (half duplex).
(VCT) function and faulty circuit test.
Support 802.1q-compliant VLAN and private border VLAN.
Maximum number of VLANs can be up to 4094.
Support VLAN stacks function, and outer label is optional.
Support GVRP dynamic VLAN.
MAC addresses self-learning capability. The size of the MAC
address table is 8K.
Port MAC address bundling and address filtering.
Support port security and segregating.
Support the STP defined in the 802.1d, RSTP defined in the
802.1w, and MSTP defined in the 802.1s. The maximum
number of the example can be up to 16.
Support ZESR technology.
6 Confidential and Proprietary Information of ZTE CORPORATION
Page 21

Support LACP port bundling defined in 802.3ad and port
Chapter 2 System Overview
static bundling. At most 15 port groups can be bundled and
each group contains at most eight ports.
Support multi-VLAN IGMP snooping & MVS controllable group
broadcast technology.
Support single port loop test.
Support 802.1x transparent transmission and authentication.
Port orientation support VBAS and DHCP-OPTION82.
Support DHCP-snooping.
Support Broadcast storm suppression.
Port ingress and egress mirror, and flow-based mirror and
statistics.
Support ACL function of port and Trunk, and can be set
according to time segment.
Support IETF-DiffServ and IEEE-802.1p standard, the ports
support 4 PRI queue. Ingress supports CAR. The queue
attempering supports SP&combination(SP+WRR)attempering
method. Egress is based on the queue, and discarding the
toned tail.
Port-based speed control includes input speed limit and
output speed limit. Input speed limit strategy includes
unicast, unknown unicast, broadcast and groupcast. Input
speed limit is based on stream, and output speed limit is
based on queue. The minimal is 64Kbps.
Provide detailed port flow statistics.
Support syslog.
Support NTP client end.
Configuration of NM static route.
Support ZGMP group manage.
SNMPv1/v2c/v3 and RMON.
Support Console configuration, Telnet remote login.
Support SSHv2. 0.
Support WEB function.
Support unified network management of ZXNM01.
Uploading and downloading of TFTP version.
Technical Features and Parameters
ZXR10 2920/2928/2952 technical features and parameters are
given in
Table 6.
Confidential and Proprietary Information of ZTE CORPORATION 7
Page 22

ZXR10 2920/2928/2952
(V1.0) Access Switch User Manual (Volume I)
TABLE 6 TECHNICAL FEATURES AND PARAMET ERS
model
item
Dimensions
(HxWxD,
mm)
Weigh
(Fully
equipped,
kg)
Maximum
power
consumption
(W)
ZXR10 2920
43. 6×436× 200
ZXR10
2928
43.
6×436×
200
ZXR10
2952
43.
6×442×
280
≈2 ≈2 ≈2. 5
16 20 27
Power
supply
AC power supply: 100V~240V, 48Hz~62Hz.
Wave shape distortion <5%
DC power supply: –57V to –40V
8 Confidential and Proprietary Information of ZTE CORPORATION
Page 23

Chapter 3
Structure and Principle
Overview
Introduction
Contents
This chapter introduces the working principle, technical and
hardware structural information on each of the ZXR10
2920/2928/2952.
This chapter includes the following topics.
TABLE 7 TOPICS IN CHAPTER 3
Topics Page No.
Working Principle 9
Hardware Structure 10
ZXR10 2920 11
ZXR10 2928 12
ZXR10 2952 13
ZXR10 2928-FI 14
Power Supply Module 17
Working Principle
ZXR10 2920/2928/2952 series are important parts of ZXR10
Ethernet switches that are launched by ZTE. They define a pure
megabit L2+ user Ethernet switch. They are intended for gigabit
upward access and used widely in large-scale enterprise network
and top grade industry. This series of products features powerful
functions and outstanding performance. Switch consists of:
Control module
Switching module
Interface module
9 Confidential and Proprietary Information of ZTE CORPORATION
Page 24

ZXR10 2920/2928/2952
(V1.0) Access Switch User Manual (Volume I)
Power supply module
Control Module
Switch module
Interface
module
Power Module
Control module consists of main processor and external
functional chips to implement applications such as switching
module control & manage for the system. It provides
operational interfaces, such as serial ports and Ethernet
interfaces for data operation and maintenance.
Switching module has Ethernet switching processing chips. Its
primary function is simply switching traffic from multiple devices.
This chip is interlinked with data packet transceiver and can
directly provide hundred megabit or gigabit service interface to
the users.
Interface module is composed of interface boards to accomplish
the external user connection and transceivers packets. The
interface module & switching module are interlinked by standard
interface.
Power module adopts the 220 VAC or -48 VDC for power supply
to offer required power supply for other parts of the system.
FIGURE 1 ZXR10 2920/2928/2952FI WORKING PRINCIPLE
ZXR10 2920/2928/2952 uses the “19(inch)” su-brack that is in
compliance with the international standard. Sub-rack can be
used as standalone equipment or installed in a standard cabinet.
Hardware Structure
ZXR10 2920/2928/2952 adopts the box structure, which is 1U
high. It employs independent power supply and natural
dissipation method. It has vents on the left and right sides of the
box. The box is composed of a bottom case and a shell. It
features light weight and simple structure. It allows an easy
installation and un-installation.
10 Confidential and Proprietary Information of ZTE CORPORATION
Page 25

Chapter 3 Structure and Principle
On the front panel of ZXR10 2920/2928/2952, there are power
indicators, RUN indicators, fixed Ethernet electrical interfaces,
Ethernet optical interfaces, and one serial configuration port.
The AC or DC power socket and power switch are located on the
rear panel.
Major hardware of the ZXR10 2920/2928/2952 is the Ethernet
switching main board, which is indispensable in any type of
configuration.
ZXR10 2920
Front Panel
Interfaces
Front panel of the ZXR10 2920 is shown in Figure 2.
FIGURE 2 FRONT PANEL O F ZXR10 2920
Ethernet switching main board of ZXR10 2920 is KEBT.
ZXR10 2920 provides the following types of access ports:
Sixteen fixed 10/100BASE-T Ethernet ports, support
fullduplex or semiduplex, 10/100M & MDI/MDIX self-adaption
function, VCT auto test.
Two fixed 10/100/1000BASE-T interface.
One expand slot, expansile dual-channel 1000M optical
interface, double 1000M electrical interface, 1000M one
optical & one electrical upward subboard.
One Console port is to realize the management and
configuration of various services.
Indicators
There are 32 indicators on the front panel of the ZXR10 2920,
indicating the status of the 16 10/100Base-T ports. Every
interface has two indicators, indicating semiduplex/fullduplex &
LNK/ACT;four indicators show two 10/100/1000 BASE-T port &
two indicators for each port showing LNK & LNK/ACT status;two
system indicators show the system running work status.
System indicators include power indicator (PWR) and running
indicator (RUN).
f After the system is powered up, the PWR indicator is on
and the RUN indicator is off.
f BootROM starts to load the version. If the version is
unavailable, the states of indicators do not change. If
the version is loaded normally, the RUN indicator flashes
at 1Hz.
Confidential and Proprietary Information of ZTE CORPORATION 11
Page 26

ZXR10 2920/2928/2952
(V1.0) Access Switch User Manual (Volume I)
f If the power indicator (PWR) is flashing , it indicates that
the switch is the main or standby role of the stack
system. Flashing in the same frequency with RUN shows
it is the main equipment. Flashing in the half frequency
with RUN shows it is the standby equipment.
32 indicators corresponds to 10/100 Base-T port , each port
with two:one is semiduplex/fullduplex, & the other is link
activation indicator.
f Semiduplex/fullduplex indicator is on in the condition of
fullduplex, is off in the condition of semiduplex. , & is
flashing in the condition of collision.
f Link activation indicator is flashing when the link is
activated.
4 interface indicators correspond to the 2 10/100/1000 Base-
T interfaces. Every interface has two indicators. When one
of the indicators is on, it indicates that the LINK is normal.
When the other indicator is on, it indicates that the LINK is
normal. If the indicator is flashing, it indicates that data
sending or receiving is under way.
Front Panel
Interface
ZXR10 2928
Front panel of the ZXR10 2928 is shown in Figure 3.
FIGURE 3 FRONT PANEL O F ZXR10 2928
Ethernet switching main board of ZXR10 2928 is KEBT.
ZXR10 2928 provides the following types of access ports:
Twenty-four 10/100BASE-T Ethernet ports. These ports
support duplex/semiduplex, 10/100M & MDI/MDIX self
adapter & VCT automatically check.
Two fixed 10/100/1000BASE-T ports.
One expand slot. It can expand double 1000M optical
interface, double 1000M electrical interfaces, one optical &
one electrical interfaces.
One console port is to realize the management and
configuration of various services.
Indicators
There are 48 indicators on the front panel of the ZXR10 2928,
indicating the status of the 24 10/100 Base-T ports. Every
interface has two indicators, indicating half-duplex/full-duplex
and LNK/ACT;Four indicators indicate two 10/100/1000 Base-T
port. Two system indicators indicate PWR & RUN.
12 Confidential and Proprietary Information of ZTE CORPORATION
Page 27

System indicators include power indicator (PWR) and running
Chapter 3 Structure and Principle
indicator (RUN).
f After the system is powered on, PWR indicator is on and
the RUN indicator is off.
f BootROM starts to load the version. If the version is
unavailable, the states of indicators do not change. If
the version is loaded normally, the RUN indicator flashes
at 1Hz.
f If the power indicator (PWR) is flashing , it indicates that
the switch is the main or standby role of the stack
system. Flashing in the same frequency with RUN shows
it is the main equipment. Flashing in the half frequency
with RUN shows it is the standby equipment.
48 interface indicators correspond to the 24 10/100 Base-T
interfaces. Every interface has two indicators:one is
semiduplex/fullduplex indicator, the other is link activation
indicator
Front panel
f Semiduplex/fullduplex indicator is on in the condition of
fullduplex, is off in the condition of semiduplex & is
flashing in the condition of collision.
f Link activation indicator is flashing when the link is
activated.
4 interface indicators correspond to the 2 10/100/1000 Base-
T interfaces. Every interface has two indicators. When one
of the indicators is on, it indicates that the LINK is normal.
When the other indicator is on, it indicates that the LINK is
normal. If the indicator is flashing, it indicates that data
sending or receiving is underway
ZXR10 2952
Front panel of the ZXR10 2952 is shown in Figure 4.
FIGURE 4 FRONT PANEL O F ZXR102952
Interfaces
Ethernet switching main board of ZXR10 2952 is KEBF.
ZXR10 2952 provides the following types of access ports:
Forty-eight fixed 10/100BASE-T Ethernet ports. These ports
support full-duplex/half-duplex, 10/100M & MDI/MDIX selfadaption & VCT self-check.
Two fixed 10/100/1000BASE-T interface.
Confidential and Proprietary Information of ZTE CORPORATION 13
Page 28

ZXR10 2920/2928/2952
(V1.0) Access Switch User Manual (Volume I)
Two fixed 1000BASE-X interface.
One console port is to realize the management and
configuration of various services.
Indicators
There are 48 indicators on the front panel of the ZXR10 2952,
indicating the status of the 48 10/100 Base-T ports. Every
interface has one indicators, indicating LNK and ACT. Four
indicators show two 10/100/1000 BASE-T port & two indicators
for each port showing LNK & LNK/ACT status;two indicators
indicate 2 1000Base-X port, each port with one indicator,
showing LNK/ACT status of the port;two system indicators show
power indicator(PWR) & running indicator(RUN) .
System indicators include power indicator (PWR) and running
indicator (RUN).
f After the system is powered on, PWR indicator is on and
the RUN indicator is off.
f BootROM starts to load the version. If the version is
unavailable, the states of indicators do not change. If the
version is loaded normally, the RUN indicator flashes at
1Hz.
f If the power indicator (PWR) is flashing , it indicates that
the switch is the main or standby role of the stack
system. Flashing in the same frequency with RUN shows
it is the main equipment. Flashing in the half frequency
with RUN shows it is the standby equipment.
48 indicators respond to 48 10/100 Base-T port. Every port
has 1 indicator indicating LNK/ACT. If the link indicator is on,
it indicates that the LINK is normal. If the indicator is
flashing, it indicates that data sending or receiving is
underway.
There are 2 indicators, indicating the status of the two 1000
Base-X ports. Every port has 1 indicator: If the link indicator
is on, it indicates that the LINK is normal. If the indicator is
flashing, it indicates that data sending or receiving is
underway.
4 interface indicators correspond to the two
10/100/1000Base-T interfaces. Every interface has two
indicators. When one of the indicators is on, it indicates
that the LINK is normal. When the other indicator is on, it
indicates that the LINK is normal. If the indicator is flashing,
it indicates that data sending or receiving is underway.
ZXR10 2928-FI
Sub-board
14 Confidential and Proprietary Information of ZTE CORPORATION
FGEI 、 FGFI 、 FGFE can be chosen for ZXR10 2920/2928
according to the practical networking. Corresponding types &
functions are shown in
table5 ZXR10 .
Page 29

TABLE5 ZXR10 2920/2928 SUBBOARD LIST
Subboard Type Function
FGEI SF-2GE-2RJ45
FGFI SF-2GE-2SFP
FGFE
SF-2GE-SFPRJ45
Chapter 3 Structure and Principle
2 gigabit
Ethernet
electrical
port
2 gigabit
Ethernet
light port
1 gigabit
Ethernet
light port+1
gigabit
Ethernet
electrical
port
FGEI offer 2 gigabit ethernet upward electrical port, the type is
SF-2GE-2RJ45,as shown in
Figure 5.
Indicators
FGFI
FIGURE 5 FGEI SUBBOARD
There are 4 indicators on the FGEI panel. Each gigabit ethernet
electrical port has 2 indicators, & one is link activation indicator,
& the other one is link status indicator.
If the link activation indicator is flashing, it indicates that
data sending or receiving is underway.
When link status indicator is on, it indicates that the LINK is
normal.
FGFI subboard offer two gigabit Ethernet up-go light port, & the
type is SF-2GE-2SFP,as shown in
Figure 6.
Confidential and Proprietary Information of ZTE CORPORATION 15
Page 30

ZXR10 2920/2928/2952
(V1.0) Access Switch User Manual (Volume I)
Figure 6 SF-2GE-2SFP subboard(FGFI)
Indicators
FGFE
Indicators
There are 2 indicators on the FGFIpanel: ACT1&ACT2 ,
corresponding to the two gigabit light port. When the indicator
is on, it indicates that LINKis normal;if the indicator is flashing,
it indicates that data sending or receiving is underway.
FGFI subboard offers 1 gigabit Ethernet up-go light port + 1 gigabit
Ethernet up-go electrical port,& the type is SF-2GE-SFPRJ45, as
shown in.
FIGURE 7 SF-2GE-SFPRJ45SUBBOARD( FGFE)
There are 3 indicators on the FGFIpanel. The gigabit Ethernet
up-go light port has an indicator ACT. When the indicator is on,
it indicates that LINKis normal;if the indicator is flashing, it
indicates that data sending or receiving is underway. The
gigabit Ethernet up-go electrical port has two indicators:one
is link activation indicator, & the other one is link status
indicator.
figure 7
If the link activation indicator is flashing, it indicates that
data sending or receiving is underway.
When link status indicator is on, it indicates that the LINK is
normal.
16 Confidential and Proprietary Information of ZTE CORPORATION
Page 31

Chapter 3 Structure and Principle
Power Supply Module
Mode
ZXR10 2920/2928/2952 supports two power supply modes:
-48V DC power supply
110V/220V AC power supply
When the -48V DC power supply is adopted, use 48V DC power cables. When the AC
power supply is adopted, use AC power cables. Both of the two modes
support a backup power supply of 12v DC power supply.
FIGURE 9 respectively show rear panel of the switch when the -48V DC
FIGURE 8 and
power supply and 110V/220V AC power supply are adopted.
FIGURE 8 ZXR10 2920/2928/2952 BACK PANEL( DC POWER)
OFF ON
FIGURE 9 ZXR10 2920/2928/2952 BACK PANEL( AC POWER)
N
T
D
R
N
V
V
8
8
G
4
P
-
-4
Confidential and Proprietary Information of ZTE CORPORATION 17
Page 32

ZXR10 2920/2928/2952
(V1.0) Access Switch User Manual (Volume I)
This page is intentionally blank.
18 Confidential and Proprietary Information of ZTE CORPORATION
Page 33

Chapter 4
Inst allation and Debugging
Overview
Introduction
Contents
This chapter provides an overview of installation and debugging
processes of ZXR10 2920/2928/2952.
This chapter includes the following topics.
TABLE 8 TOPICS IN CHAPTER 4
Topics Page No.
Equipment 19
Switch Installation on Desktop 20
Switch Installation onto a Cabinet 20
Cable 23
Power Cables 24
Console Cable 25
Network Cable 26
Optical Fiber 28
Labels 29
Cable Lightning Protection Requirements 32
Equipment Installation
ZXR10 2920/2928/2952 can be placed on desktop and can be
installed on a 19-inch standard cabinet.
19-inch standard cabinet can be provided by customer. If ZTE
provides the cabinet, install cabinet as per 19-inch Standard
Cabinet.
Confidential and Proprietary Information of ZTE CORPORATION 19
Page 34

ZXR10 2920/2928/2952
(V1.0) Access Switch User Manual (Volume I)
Switch Installation on Desktop
When switch is placed on desktop, install four plastic pads (the
plastic pads and screws are part of the accessories) on bottom
plate of switch. Four pads support switch and form a lower
ventilation channel for power to cool down. It is shown in
8.
FIGURE 8 INSTALLING PLASTIC PADS
Figure
1
2
1
Installation
Procedures
1 Case 2 Pad
Switch Installation onto a Cabinet
To install the switch into the 19-inch cabinet, install a flange to
each of the two sides of the switch shell (the flange and screws
are part of the accessories), as shown in
Figure 9.
2
1
2
20 Confidential and Proprietary Information of ZTE CORPORATION
Page 35

FIGURE 9 INSTALLING FLANGES
Chapter 4 Installation and Debugging
1
3
1
1 Case 2 Flange 3 Screw
Install two symmetrical brackets at both sides of the 19-inch
cabinet to support the switch, as shown in
Figure 10.
2
3
2
Confidential and Proprietary Information of ZTE CORPORATION 21
Page 36

ZXR10 2920/2928/2952
(V1.0) Access Switch User Manual (Volume I)
FIGURE 10 INSTALLING BRACKETS
2
1
3
1 Holder 2 Cabinet 3 Screw
After installation, push switch along with bracket, and fix
flanges with screws onto cabinet, as shown in
Figure 11.
22 Confidential and Proprietary Information of ZTE CORPORATION
Page 37

FIGURE 11 FIXING THE SWITCH
Chapter 4 Installation and Debugging
1
2
3
1
2
3
1
3
1 Cabinet 2 Box 3 Screw
Cable Types
2
ZXR10 2920/2928/2952 consists of:
Power cables
Console cables
Network cables
Fiber optics.
Confidential and Proprietary Information of ZTE CORPORATION 23
Page 38

ZXR10 2920/2928/2952
(V1.0) Access Switch User Manual (Volume I)
Power Cables Installation
Power cables are classified as per power supply module:
AC power cables
DC power cables
AC power
cable
DC power
socket
An AC power cable looks the same as standard printer power
cable, as shown in
FIGURE 12 AC POWER CABLE
Figure 12.
One end of the AC power cable connects the AC power socket of
the ZXR10 2920/2928/2952 power module and the other end
connects the 220 VAC power socket.
Appearance and description of -48V power socket on DC power
supply module of ZXR10 2920/2928/2952 is shown in
FIGURE 13 -48 POWER SOCKET
Figure 13.
-48VGND
DC power
Cable
24 Confidential and Proprietary Information of ZTE CORPORATION
DC power cable is a 3-core power cable, as shown in
GNDP
-48V
Figure 14.
Page 39

FIGURE 14 DC POWER CABLE
Label
End A
Chapter 4 Installation and Debugging
End B
Grounding
Power Cable
Detail description of two ends of power cable is given in
TABLE 9 DESCRIPTIONS OF POWER CAB LES
End A End B Power Signal
1 Brown -48VGND
2 Blue -48V
3 Yellow GNDP
Table 9.
One end of the DC power cable is connected to the power socket
on the DC power supply module of the ZXR10 2920/2928/2952,
and the other end to the corresponding terminal of –48V DC
power supply.
There is a grounding screw on the back of ZXR10
2920/2928/2952, figuring by
.When connecting with kelly
protect cable, one end of the cable is connected to the grouding
screw, and the other end to the grouding protect of the cabinet
of the ZXR10 2920/2928/2952. Grounding protect cable shape
is shown in
FIGURE 17 GROUNDING PROTECT CABLE
Figure 17 .
Serial port
cable
connections
Console Cable Installation
Serial port configuration cable is for configuration and routine
maintenance of ZXR10 2920/2928/2952 switches.
ZXR10 2920/2928/2952 is delivered with serial port
configuration cable. One end of the cable is a DB9 serial port,
Confidential and Proprietary Information of ZTE CORPORATION 25
Page 40

ZXR10 2920/2928/2952
(V1.0) Access Switch User Manual (Volume I)
which connects to serial port on computer. Other end is an
RJ45 port, which connects to Console port of ZXR10
2920/2928/2952.
Console cable is shown in FIGURE 18 .
Linear ordering of serial port console cable is shown in
TABLE 10 .
FIGURE 18 CONSOLE CABL E INST ALLATION
TABLE 10 LINEAR ORDERING OF SERIAL PORT CONSOLE CAB LE
Side A Color Side B
2 White 3
3 Blue 6
White 4
5
Orange 5
4 White 7
6 Green 2
7 White 8
8 Brown 1
Network Cable Installation
Both ends of network cable are crimped with RJ45 connectors,
as shown in
FIGURE 19 .
Name of the cable connector: 8P8C straight crimping cable
connector
Specification: E5088-001023
Technical parameters
f Rated current 1.5A
f Rated voltage 125V
f Crimped with AWG24-28# round wire
26 Confidential and Proprietary Information of ZTE CORPORATION
Page 41

through RJ45
Straight-
Chapter 4 Installation and Debugging
FIGURE 19 NETWORK CABLE
Direction A
Connectors, cables can be classified into two categories:
Straight-through RJ45 network cable, with pins at both ends in
one-to-one correspondence. Specific pin outs are shown in
Table 10.
Crossover
RJ45J cable
TABLE 10 STRAIGHT-THROUGH NETWORK CABLE RJ4 5 LINEAR ORDERING
End A Cable Color End B
1 White-orange 1
2 Orange 2
3 White-green 3
6 Green 6
4 Blue 4
5 White-blue 5
7 White-brown 7
8 Brown 8
Crossover RJ45J cable, with two twisted pairs at both ends
corresponding to each other in crossover mode. The specific
connection relationship is shown in
Table 11.
Confidential and Proprietary Information of ZTE CORPORATION 27
Page 42

ZXR10 2920/2928/2952
(V1.0) Access Switch User Manual (Volume I)
TABLE 11 CROSSOVER CAB LE RJ45J’S LINEAR ORDERING
End A Cable Color End B
1 White-orange 3
2 Orange 6
3 White-green 1
6 Green 2
4 Blue 4
5 White-blue 5
7 White-brown 7
8 Brown 8
Optical Fiber
Classification
Fiber
protection
Each optical interface of ZXR10 2920/2928/2952 has two fibers
to send and receive data respectively.
Note: Ensure proper connection to TX and RX marks on panel.
There are two kinds of optical fibers, single-mode and multimode optical fibers. Six types of optical fibers are available for
configuration, as shown in
TABLE 12 FIBER TYPES
Mode
Single-mode fiber
Multi-mode fiber
Type of Connector to
Switch
SC-PC connector
(square flat connector)
SC-PC connector
(square flat connector)
Table 12.
Type of Connector
on the Peer End
FC/PC connector
SC/PC connector
ST/PC connector
LC/PC connector
FC/PC connector
SC/PC connector
ST/PC connector
LC/PC connector
For fiber cabinet layout of cabinet, make sure to protect fibers
against any damages with plastic corrugated protection tubes.
Fibers inside protection tube should not entangle with one
another. They should be bent into a round shape at the
bending position, if any.
Labels at two ends of fiber should be clear and legible.
Meanings of labels should clearly reflect corresponding
28 Confidential and Proprietary Information of ZTE CORPORATION
Page 43

Chapter 4 Installation and Debugging
numbers and relationship between cabinets and between
rows.
Labels
Pattern and meanings of the labels attached to the connector:
Label attached to the connector is called transverse English
label on panels and connectors. Structure and dimensions
of the label is shown in
FIGURE 20 TRANSVERSE ENGLISH LABE L ON PANELS AND CONNECTORS
FIGURE 20 .
These contents are described in the following section:
Confidential and Proprietary Information of ZTE CORPORATION 29
Page 44

ZXR10 2920/2928/2952
(V1.0) Access Switch User Manual (Volume I)
RJ45——Cable code
Port A——End A of the cable connector, corresponding to
End B or another end.
5m——Length of the finished cable. It refers to the straight
line length of the cable from the connector at one end to the
connector at the other end.
TIC 10/100Base-T 1——Connection position, the first
10/100Base-T network port of the TIC board.
Pattern and meanings of the label attached to the cable:
Label attached to the cable is called roll-type self-cover laser
print label model II. Structure and dimensions of the label is
shown in
FIGURE 21 ROLL-TYPE SELF-COVER LASER PRINT LABE L MODEL II
FIGURE 21 .
Label Features
Transparent area
Printable area
Transparent area
HD182 Port B 1.30m
#1-L5-DTI1 D25~32
Contents of the label in the above figure have same meanings as
those in
FIGURE 20 . These two types of labels are used in
different places.
Transverse English label on panels and connectors is only
applicable to the connectors where the attachment area is
larger than the label area or to panels.
Roll-up self-mulching laser printing label is rolled around the
cable with its own scotch adhesive tapes. It is used when
horizontal English label cannot be used because cable
connector is small.
Before the cabinet equipment is delivered, all the internal
interconnected cables shall be attached with flag-type direction
labels.
This label attached to the cable is called Transverse English Type
I Label. Structure and dimensions of label is shown in
Figure 15.
30 Confidential and Proprietary Information of ZTE CORPORATION
Page 45

FIGURE 15 TRANSVERSE ENGLISH TYPE I LAB EL
Chapter 4 Installation and Debugging
Meaning of the content and the structure of a fiber engineering
label is shown in
FIGURE 16 P ATTERN AND MEANINGS OF ENGINEERING LABE L ON OPTICAL
FIBER
Figure 16.
Engineering
Labels
Optical fible(R) Optical fible(L)
The side marked with
"L" must be filled in
Fill in the
ODF.
Row No.
Rack No.
Serial No.Row No.
Layer No.
Two sides of the engineering label on the optical fiber are
marked “L” and “R” with the specific meanings given as follows:
When label is pasted on fiber at ZXR10 2920/2928/2952 side,
row and column number of cabinet at side of connected
remote optical interface device as well as the layer No. of
the fiber in the cabinet and the fiber No. must be filled in
the R area of the label.
The side marked with
"R" must be filled in
Serial No.
Column No
In this case, row and column Nos.of ZXR10 2920/2928/2952
where the fiber is located as well as the layer No. of the fiber
and fiber number shall be filled in the L area of the label.
Confidential and Proprietary Information of ZTE CORPORATION 31
Page 46

ZXR10 2920/2928/2952
(V1.0) Access Switch User Manual (Volume I)
If the label is attached on the optical interface equipment of
the customer, contents filled on the label are just contrary
to those at the ZXR10 2920/2928/2952 side.
Cable Lightning Protection Requirements
Lightning
Protection
Switch cabling
Lightning can be direct lightning strike and induction. Damage of
direct lightning strike is hard to avoid. Following lightning
protection requirements are proposed to reduce equipment
failure rate in the areas where lightning is frequent.
Place the ethernet switch in the corridor, preferably on the first
floor to avoid the direct sunshine, rains, and lightning. Ensure
that all subscriber lines are distributed inside building to avoid
lightning induction. Uplink, downlink, and cascading lines are
distributed outside.
Cabling of Ethernet switch in a four-floor building with three
units is shown in
FIGURE 17 C ABLING OF THE ETHERNET SWITCH IN A BUILDING
Figure 17.
Switch
...
Explanation
Switch placement in fourth floor is explained below.
Switch A is in Unit 1 and is convergence switch of the whole
building. Switches B and C are access switches.
Switches A, B, and C are cascaded. Cascading cables refers
to connecting two switches. Cascading cable of switch A is
the uplink cable of switch B, and cascading cable of switch B
is uplink cable of switch C. Rest of subscriber lines are
32 Confidential and Proprietary Information of ZTE CORPORATION
Switch
...
Switch
...
Page 47

Chapter 4 Installation and Debugging
distributed inside the building and connected to subscriber
terminals from bottom to top in the corridor.
Lightning protection bars must be added for the uplink,
downlink, and cascading Ethernet ports that are outdoors.
Lightning protection bar must reach 6 KV or above and the
current discharge capability must reach 5 KA. Grounding
cable of lightning protection bar must have a diameter of 16
mm2 and a length less than 30 cm. It is recommended to
use the optical port as uplink port for convergence switch in
the building. If the electrical port is used, lightning protection
bars must be added.
Convergence
switch cabling
Cabling of a convergence switch is shown in
Figure 18.
Uplink port is optical port and lightning protection bars are
added for downlink or cascaded cables. Lightning bars are
connected to ground through shell. Rest of subscriber lines
are distributed inside building.
FIGURE 18 C ABLING OF A CONVERGENCE SWITCH
Ethernet switch
。。。
Lightning
protection bar
Uplink cable
(optical interface)
Subscriber line
Shell ground
Less than 30 cm
Uplink cable or
cascading cable
Explanation
Explanations are as follows:
Grounding system with good ground grid is preferred for
switch. Many residential buildings with proper grounding
have a grounding resistance of 1 ohm. If the test shows
that grounding system is not up to standard. It is
recommended to equip an independent grounding post and
the grounding cable must be of 16 mm2 in diameter and as
short as possible. What ever grounding method is used,
the grounding resistance must be less than 5 ohm and
cannot exceed 10 ohm.
It is prohibited that switch directly gets power from outdoor
overhead power cable. If switch gets direct power from
outdoor overhead power cables, special lightning protection
measures must be taken into account. Lightning protection
Confidential and Proprietary Information of ZTE CORPORATION 33
Page 48

ZXR10 2920/2928/2952
(V1.0) Access Switch User Manual (Volume I)
socket and lightning protection bar, must be added to power
supply. Lightning protection bar for power supply must have
better lightning protection index than that for port cable.
Note: Ethernet switch suffers lightning strike due to
grounding, power supply, and wiring. Lightning strike leadin mechanism also varies a lot. Taking one measure does not
prevent lightning strike. Therefore, several measures must
be implemented at same time. Proper grounding,
appropriate power supply, reasonable wiring, and suitable
lightning protection measures will definitely reduce chances
of switch damage resulted from lighting strike.
34 Confidential and Proprietary Information of ZTE CORPORATION
Page 49

Chapter 5
Usage and Operation
Overview
Introduction
Contents
This chapter provides an overview of configuration mode,
command mode and command line use.
This chapter includes the following topics.
TABLE 13 TOPICS IN CHAPTER 5
Topics Page No.
Configuration Modes 36
Configuration through Console Port Connection 36
Configuring through Telnet 37
Simple Network Management Protocol (SNMP) 38
Configuring through WEB Connection 39
Command Modes 40
Configuring User Mode 40
Configuring Global Mode 41
Configuring SNMP Mode 42
Configuring Layer 3 Mode 42
Configuring File System Mode 42
Configuring NAS Mode 43
Configuring Cluster Management 43
Configuring Basic ACL 44
Configuring Extended ACL 44
Configuring L2 ACL Mode 45
Configuring Hybrid ACL Mode 45
Using Command Line 45
Command Abbreviations 47
Confidential and Proprietary Information of ZTE CORPORATION 35
Page 50

ZXR10 2920/2928/2952
(V1.0) Access Switch User Manual (Volume I)
Topics Page No.
History Commands 47
Function Key 48
Configuration Modes
ZXR10 2920/2928/2952 offers multiple configuration modes. A
user can select configuration mode based on the connected
network, as shown in
Configuration through serial port connection
Configuration through TELNET session
Configuration through SNMP connection
Figure 19.
Configuration through WEB connection
FIGURE 19 ZXR1 0 2920/2928/2952 CONFIGURATION MODES
Configuration through Console Port Connection
Console Port
Connection
36 Confidential and Proprietary Information of ZTE CORPORATION
Configuration through console port connection is the main
configuration mode of the ZXR10 2920/2928/2952. The
connection can be configured when the equipment is running.
Page 51

Chapter 5 Usage and Operation
Configuring through Telnet
Purpose
Prerequisite
Steps
This topic describes the configuration of ZXR10 2920/2928/2952
through Telnet.
Telnet mode is usually used when configuring the switch by
telnet. Configure the switch through the host connecting to the
local Ethernet interface logs in the telnet switch. Set username
& password on the switch & make sure that local computer can
ping the IP address of the layer-3 port in the switch. (Layer-3
port address configuration refers to section 7. 13)
Create a new user using command create user <name>
admin|guest. Set login password using command set user
local <name> login-password [<string>].
Note: by default, the username & password is admin/zhongxing.
To configure through telnet, perform the following steps.
1. Run the telnet command on the host and input the IP
address of the switch management Ethernet port, as shown
Figure 20.
in
FIGURE 20 RUN TELNET
2. Click OK to enter the interface as shown in
Confidential and Proprietary Information of ZTE CORPORATION 37
Figure 21.
Page 52

ZXR10 2920/2928/2952
(V1.0) Access Switch User Manual (Volume I)
FIGURE 21 TELNET L OGIN
Result
Overview
Features of
SNMP
3. Type the correct user name and password at the prompt
to enter into switch user mode.
E
ND OF STEPS
Configuring of ZXR10 2920/2928/2952 through Telnet is
completed successfully.
Simple Network Management Protocol (SNMP)
Network Management Protocol (SNMP) is one of the most
popular network protocols. An NM server can manage all devices
on the network through this protocol.
SNMP adopts the management based on the server and client.
Background NM server serves as SNMP server and the
foreground network device ZXR10 2920/2928/2952 serves as
the SNMP client. Foreground and background share one MIB
management database and the SNMP is used for
communications.
NMS software supporting the SNMP shall be installed in the
background NM server to manage and configure the ZXR10
2920/2928/2952.
38 Confidential and Proprietary Information of ZTE CORPORATION
Page 53

Chapter 5 Usage and Operation
Configuring through WEB Connection
Introduction
Purpose
Steps
Web is a long-distance management switchboard and is similar
to Telnet. Users can access some Web services through a peerto-peer arrangement rather than by going to a central server.
The user should have the access along with password and
management password for the switch, enable Web function.
This topic describes the configuration of Web connection.
For the configuration of Web connection, perform the following
steps.
1. To create user, use command create user <name>
admin|guest in global configuration mode. This is shown
Table 14.
in
TABLE 14 CREATE USER COMMAND
Format Mode Function
create user <name>
admin|guest
config This creates user
Result: This creates user.
2. To configure user password, use command set user local
<name> login-password <string> in global configuration
mode. This is shown in
Table 15.
TABLE 15 USER P ASSWORD COMMAND
Format Mode Function
set user local
<name> loginpassword <string>
config
This configures user
password
Result: This configures user password.
3. To configure admin password, use command set user
local|radius <name> admin-password <string> in global
configuration mode. This is shown in
TABLE 16 ADMIN PASSWORD
Format Mode Function
set user local|radius
<name> adminpassword <string>
config
Table 16.
This configures admin
password
Result: This configures admin password.
4. To enable web function and to establish the monitor port,
use command set web enable and set web listen-port
Confidential and Proprietary Information of ZTE CORPORATION 39
Page 54

ZXR10 2920/2928/2952
(V1.0) Access Switch User Manual (Volume I)
<80, 025-49151> in global configuration mode. This is
shown in
TABLE 17 WEB C OMMANDS
Format Mode Function
set web enable This enables web function
set web listen-port
<80, 025-49151>
Table 17.
config
This establishes the monitor
port
Result: This enables web function and establishes the
monitor port.
Note: By default username is admin, password is
zhongxing and http monitor port is 80.
ND OF STEPS
E
Result
Overview
Configuration of Web management is completed successfully.
Command Modes
ZXR10 2920/2928/2952 allocates the commands to various
modes based on the function. In order to authorize the
facilitation to user’s configuration and management for the
switch only one command can be executed in the special mode
only.
ZXR10 2920/2928/2952 command modes include:
User mode
Global configuration mode
SNMP configuration mode
Layer 3 configuration mode
File system configuration mode
NAS configuration mode
Cluster management configuration mode
Basic ACL configuration mode
Global ACL configuration mode
Extended ACL configuration mode
L2 ACL configuration mode
Hybrid ACL configuration mode
Configuring User Mode
Purpose
40 Confidential and Proprietary Information of ZTE CORPORATION
This topic describes the configuration of user mode.
Page 55

Chapter 5 Usage and Operation
Steps
Result
For the configuration of user mode, perform the following steps.
1. When using HyperTerminal mode to log on to system,
system enters into user mode automatically.
Result: The prompt character in the user mode is the host
name followed by “>”, as shown below:
zte>
Note: By default host name is zte. Modify the host name
by using the command hostname.
2. In the user mode, execute the command exit to exit the
switch configuration.
3. In the user mode, execute the command show to display
the system configuration and operation information.
Note: The command show can be executed in any mode.
E
ND OF STEPS
User mode has been configured.
Configuring Global Mode
Purpose
Steps
Result
This topic describes the global configuration mode.
For the configuration of global mode, perform the following
steps.
1. In user mode, enter the enable command and the
corresponding password to enter the global configuration
mode, as follows:
zte>enable
Password:***
zte(cfg)#
2. In the global configuration mode, various functions of the
switch can be configured. Use command set user
local|radius <name> admin-password [<string>] to set
the password for entering the global configuration mode to
prevent the login of unauthorized users.
Result: This sets the password for entering the global
configuration mode.
3. To return to the user mode from the global configuration
mode, use the exit command.
ND OF STEPS
E
Global mode has been configured.
Confidential and Proprietary Information of ZTE CORPORATION 41
Page 56

ZXR10 2920/2928/2952
(V1.0) Access Switch User Manual (Volume I)
Configuring SNMP Mode
Purpose
Steps
Result
Purpose
This topic describes the configuration of SNMP mode.
For the configuration of SNMP mode, perform the following
steps.
1. In the global configuration mode, use the command config
snmp to enter the SNMP configuration mode, as shown
below:
zte(cfg)#config snmp
zte(cfg-snmp)#
Note: In SNMP configuration mode, SNMP and RMON
parameters can be set.
2. To return to the global configuration mode from the SNMP
configuration mode, use command exit or press Ctrl+Z.
ND OF STEPS
E
SNMP mode has been configured.
Configuring Layer 3 Mode
This topic describes the Layer 3 configuration mode.
Steps
Result
Purpose
Steps
For the configuration of Layer 3 mode, perform the following
steps.
1. In the global configuration mode, execute the command
config router to enter the Layer 3 configuration mode, as
shown in the following example:
zte(cfg)#config router
zte(cfg-router)#
Note: In the Layer 3 configuration mode, you can configure
the Layer 3 port, static router, and ARP entities.
2. To return to the global configuration mode from the Layer 3
configuration mode, use command exit or press Ctrl+Z.
ND OF STEPS
E
Layer 3 mode has been configured.
Configuring File System Mode
This topic describes the file system configuration mode.
For the configuration of file system, perform the following steps.
42 Confidential and Proprietary Information of ZTE CORPORATION
Page 57

1. In the global configuration mode, execute the command
config tffs to enter the file system configuration mode, as
shown below:
zte(cfg)#config tffs
zte(cfg-tffs)#
Note: In the file system configuration mode, switch file
system can be operated, including adding file directory,
deleting file or directory, modifying file name, displaying file
or directory, changing file directory, uploading/downloading
files through TFTP, copying files, formatting Flash, and so
on.
2. To return to the global configuration mode from the file
system configuration mode, use command exit or press
Ctrl+Z.
ND OF STEPS
E
Chapter 5 Usage and Operation
Result
Purpose
Steps
Result
File system mode has been configured.
Configuring NAS Mode
This topic describes the NAS configuration mode.
For the configuration of NAS mode, perform the following steps.
1. In the global configuration mode, execute the command
config nas to enter into NAS configuration mode, as shown
below:
zte(cfg)#config nas
zte(cfg-nas)#
Note: In the NAS configuration mode, configuration of
switch access service including user access authentication
and management.
2. To return to the global configuration mode from the NAS
configuration mode, use command exit or press Ctrl+Z.
ND OF STEPS
E
NAS mode has been configured.
Purpose
Steps
Configuring Cluster Management
This topic describes the cluster management configuration mode.
For the configuration of cluster management, perform the
following steps.
1. In the global configuration mode, execute command config
group to enter the cluster management configuration mode,
as shown below:
Confidential and Proprietary Information of ZTE CORPORATION 43
Page 58

ZXR10 2920/2928/2952
(V1.0) Access Switch User Manual (Volume I)
zte(cfg)#config group
zte(cfg-group)#
Note: In the cluster management configuration mode,
configuration of switch cluster management service.
2. To return to the global configuration mode from the cluster
management configuration mode, use command exit or
press Ctrl+Z.
ND OF STEPS
E
Result
Purpose
Steps
Result
Cluster management is configured.
Configuring Basic ACL
This topic describes the basic ACL configuration mode.
For the configuration of basic ACL, perform the following steps.
1. In the global configuration mode, execute command config
acl basic number <1-99> to enter into basic ACL
configuration mode, as shown below:
zte(cfg)#config acl basic number 10
zte(basic-acl-group)#
Note: In the basic ACL configuration mode, it is possible to
add, delete, move the ACL rule for the specified ACL id.
2. To return to the global configuration mode from basic ACL
configuration mode, use command exit or press Ctrl + Z.
E
ND OF STEPS
Basic ACL is configured.
Configuring Extended ACL
Purpose
Steps
44 Confidential and Proprietary Information of ZTE CORPORATION
This topic describes the extended ACL configuration mode.
For the configuration of extended ACL, perform the following
steps.
1. In the global configuration mode, execute command config
acl extend number <100-199> to enter into extended ACL
configuration mode, as shown in:
zte(cfg)#config acl extend number 100
zte(extend-acl-group)#
Note: Extended ACL configuration mode includes configuring
ACL parameters and moving ACL rule sequence id.
2. To return to global configuration mode from the extended
ACL configuration mode, use command exit or press Ctrl+Z.
Page 59

END OF STEPS
Chapter 5 Usage and Operation
Result
Purpose
Steps
Result
Extended ACL is configured.
Configuring L2 ACL Mode
This topic describes the L2 ACL configuration mode.
For the configuration of L2 ACL, perform the following steps.
1. In the global configuration mode, execute command config
acl link number <200-299> to enter into L2 ACL
configuration mode, as shown in:
zte(cfg)#config acl link number 200
zte(link-acl-group)#
Note: L2 ACL configuration mode includes configuring ACL
parameters and moves ACL rule sequence id.
2. To return to global configuration mode from the L2 ACL
configuration mode, use command exit or press Ctrl+Z.
ND OF STEPS
E
L2 ACL is configured.
Purpose
Steps
Online Help
Configuring Hybrid ACL Mode
This topic describes the Hybrid ACL configuration mode.
For the configuration of Hybrid ACL, perform the following steps.
1. In the global configuration mode, execute command config
acl hybrid number <300-349> to enter into Hybrid ACL
configuration mode, as shown in:
zte(cfg)# config acl hybrid number 333
zte(hybrid-acl-group)#
Note: Hybrid ACL configuration mode includes configuring
ACL parameters and moves ACL rule sequence id.
2. To return to global configuration mode from the Hybrid ACL
configuration mode, use command exit or press Ctrl+Z.
Using Command Line
In any command mode, enter a question mark (?) after DOS
prompt of system, a list of available commands in command
mode is displayed. With context-sensitive help function,
keywords and parameter lists of any commands can be obtained.
Purpose
This topic describes the configuration of online command help.
Confidential and Proprietary Information of ZTE CORPORATION 45
Page 60

ZXR10 2920/2928/2952
(V1.0) Access Switch User Manual (Volume I)
Steps
For the configuration of online command help, perform the
following steps.
1. Input ? behind the prompt of any command mode to view all
commands and brief descriptions of this mode.
Result: Command mode is viewed.
Example: An example given below shows ? behind the
prompt of the command mode.
zte>?
enable enable configure mode
exit exit from user mode
help description of the interactive
help system
show show config information
list print command list
zte>
2. Input the question mark behind a character or character
string.
Result: This will view the list of commands or keywords
beginning with that character or character string.
Example: An example given below shows the character
string.
zte(cfg)#c?
config clear create
zte(cfg)#c
3. Input ? behind the command, keyword and parameter.
Result: It shows the keyword or parameter to be input next
and its brief explanation.
Example: An example is given below.
zte(cfg)#config ?
snmp enter SNMP config mode
router enter router config mode
tffs enter file system config mode
nas enter nas config mode
group enter group management config mode
acl enter acl config mode
zte(cfg)#config
4. If a wrong command, keyword or parameter is entered then
press Enter.
Result: It will show message “Command not found” will be
displayed on the interface.
Example: An example is given below:
46 Confidential and Proprietary Information of ZTE CORPORATION
Page 61

zte(cfg)#conf ter
% Command not found (0x40000066)
zte(cfg)#
Chapter 5 Usage and Operation
5. Online help is used to create user.
Result: Online help creates user.
Example: An example is given below:
zte(cfg)#cre?
create
zte(cfg)#create ?
port create descriptive name for port
vlan create descriptive name for vlan
user create user
zte(cfg)#create user
% Parameter not enough (0x40000071)
zte(cfg)#create user ?
<string> user name
zte(cfg)#create user wangkc
zte(cfg)#
Result
Input
Command
END OF STEPS
Online command help has been configured.
Command Abbreviations
In ZXR10 2920/2928/2952, a command or keyword can be
shortened into a character or string that can uniquely identify
this command or keyword. For example, the command exit
can be shortened as ex, and the command show port
shortened as sh po.
History Commands
Input command can be recorded in the user interface, up to 10
history commands can be recorded and this function is useful for
invoking a long or complicated command again.
Execute one of the following operations to re-invoke a command
from the record buffer, as shown in
Table 18.
TABLE 18 INVOKING A COMMAND
Command Function
CTRL+P or ↑
Confidential and Proprietary Information of ZTE CORPORATION 47
Invoke a history command in the buffer forward
Page 62

ZXR10 2920/2928/2952
(V1.0) Access Switch User Manual (Volume I)
Command Function
User Interface
CTRL+N or ↓
Invoke a history command in the buffer backward
In the privileged mode, execute the show history command to
list the commands input the latest in this mode.
Function Key
ZXR10 2920/2928/2952 provides a lot of functional keys for the
user interface to facilitate user operations. Functional keys are
shown in
TABLE 19 FUNCTIONAL KEYS
Functional
Key
Ctrl-P or Ç
Ctrl-N or È
Ctrl-B or Å
Table 19.
Usage
Recover the last command (Roll back in the
historical records of commands).
Recover the next command (Roll forward in the
historical records of commands).
Move left in the command line currently indicated
by the prompt.
Ctrl-F or Æ
Tab
Ctrl-A Skip to the beginning of the command line.
Ctrl-E Skip to the end of the command line.
Ctrl-K Delete the characters from the cursor to the end.
Ctrl-H or
Backspace
Ctrl-C
Ctrl-L Clear screen.
Ctrl-Y Recover the last command executed.
Ctrl-Z Return to the global configuration mode.
Move right in the command line where the prompt
is currently located.
Display commands starting with the character or
string. If there is only one command, make this
command a complete one.
Delete the character on the left of the cursor.
Cancel the command and display the prompt
character.
When the command output exceeds one page, output is split
into several pages automatically and the prompt “----- more ----
- Press Q or Ctrl+C to break -----” appears at the bottom of
current page. Press any key to turn pages or press Q or Ctrl+C
to stop the output.
48 Confidential and Proprietary Information of ZTE CORPORATION
Page 63

Chapter 6
System Management
Overview
Introduction
Contents
This chapter introduces file system management FTP/TFTP
configuration, file backup and restoration, software version
upgrade.
This chapter includes the following contents:
TABLE 20 TOPICS IN CHAPTER 6
Topics Page No.
File System Management
File System 49
Operating File System 50
Configuring Imports and Exports 54
Setting File Backup and Recovery 55
Software Version Upgrade 56
Viewing System Information 57
Upgrading Version at Normality 57
Upgrading Version at Abnormality 59
File System
Flash memory
In ZXR10 2920/2928/2952 Flash is the major storage device on
the main control board. Software version file and configuration
file of the ZXR10 2920/2928/2952 are saved in the Flash
memory. Operations, such as version upgrading and
configuration saving, should be conducted in the Flash memory.
There are three directories in Flash by default:
Confidential and Proprietary Information of ZTE CORPORATION 49
Page 64

ZXR10 2920/2928/2952
(V1.0) Access Switch User Manual (Volume I)
The name of the version file is kernel.z.
The name of the configuration file is running.cfg.
The name of the directory file is config.txt.
Operating File System
Introduction
Purpose
Prerequisite
Steps
ZXR10 2920/2928/2952 provides many commands for file
operations. Command format is similar to DOS commands as
present in Microsoft Windows Operating System.
This topic describes file system operation of ZXR10
2920/2928/2952.
To do file management, there must have an access to Command
Line Interface (CLI). CLI is a text-based interface that can be
accessed through a direct serial connection to device and
through telnet connections.
For file system operation, perform the following steps.
1. To enter the file system configuration mode, use command
config tffs in global configuration mode. This is shown in
Table 21.
TABLE 21 CONFIG TFFS COMMAND
Format Mode Function
config tffs config
This enters into the file
system configuration mode
Result: This enters into the file system configuration mode.
2. To create new directory, use command md <directory
name> in file system configuration mode. This is shown in
Table 22.
TABLE 22 MD COMMAND
Format Mode Function
File
md <directory name>
system
config
Result: This creates new directory.
3. To delete a file or directory, use command remove <file-
name> in file system configuration mode. This is shown in
Table 23.
TABLE 23 REMOVE COMMAND
Format Mode Function
remove <file-name>
50 Confidential and Proprietary Information of ZTE CORPORATION
File
system
This creates new directory
This creates new directory
Page 65

Format Mode Function
config
Chapter 6 System Management
Result: This deletes a file or directory.
4. To rename a file, use command rename <file-name><file-
name> in file system configuration mode. This is shown in
Table 24.
TABLE 24 RENAME COMMAND
Format Mode Function
rename <file-
name><file-name>
File
system
config
This renames the file
Result: This renames the file.
5. To modify the current directory, use command cd <directory
name> in file system configuration mode. This is shown in
Table 25.
TABLE 25 CD COMMAND
Format Mode Function
cd <directory name>
File
system
config
This modifies the current
directory
Result: This modifies the current directory.
6. To displays the current directory list, use command ls in file
system configuration mode. This is shown in
TABLE 26 LS COMMAND
Format Mode Function
ls
File
system
config
This displays the current
directory
Table 26.
Result: This displays the current directory.
7. To upload or download a version through TFTP, use
command tftp <A. B. C. D> {download|upload}
<name> in file system configuration mode. This is shown
Table 27.
in
TABLE 27 TFTP COMMAND
Format Mode Function
tftp <A. B. C. D>
{download|upload}
<name>
File
system
config
This uploads or downloads a
version through TFTP
Result: This uploads or downloads a version through TFTP.
Confidential and Proprietary Information of ZTE CORPORATION 51
Page 66

ZXR10 2920/2928/2952
(V1.0) Access Switch User Manual (Volume I)
8. To copy a file, use command copy <source-
pathname><dest-pathname> in file system configuration
mode. This is shown in
TABLE 28 COPY COMMAND
Format Mode Function
Table 28.
Result
copy <source-
pathname><destpathname>
File
system
config
This copies a file
Result: This copies a file.
9. To format the FLASH memory, use command format in file
system configuration mode. This is shown in
TABLE 29 FORMAT COMMAND
Format Mode Function
format
File
system
config
This formats the FLASH
memory
Table 29.
Result: This formats the FLASH memory.
E
ND OF STEPS
File system operation of ZXR10 2920/2928/2952 is configured.
Configuring ZXR10 2920/2928/2952 as an TFTP Client
Purpose
Prerequisite
This topic describes the background TFTP server configuration.
To configure background TFTP server, meet the following
requirements.
Start TFTP server on the background host, and access
ZXR10 2920/2928/2952 as a TFTP client from the TFTP
server.
Steps
The following describes the background TFTP server
configuration taking tftpd as an example.
1. Run tftpd on the background host, and an interface as
shown in
52 Confidential and Proprietary Information of ZTE CORPORATION
Figure 22.
Page 67

FIGURE 22 TFTPD I NTERFACE
Chapter 6 System Management
2. Select Tftpd > Configure, click Browse on the popup
dialog box, and select a directory to store the
version/configuration file, such as D:\IMG. The following
dialog box will appear as shown in
FIGURE 23 CONFIGURE D IALOG BOX
Figure 23.
Result
3. Click OK in
E
ND OF STEPS
Confidential and Proprietary Information of ZTE CORPORATION 53
Figure 23 to finish the settings.
Page 68

ZXR10 2920/2928/2952
(V1.0) Access Switch User Manual (Volume I)
Background of TFTP server is implemented. Start the TFTP
server, and run copy on the switch to backup/restore files or
import/export configurations.
Configuring Imports and Exports
Purpose
Steps
This topic describes the import and export functions of
configuration information of ZXR10 2920/2928/2952.
For the configuration of import and export functions, perform
the following steps.
1. The command show running-config toFile is used to
export the execution result of show running-config to a
config. txt and to save it in the FLASH memory.
Result: This command exports and saves it in the FLASH
memory.
Example: This file can also be uploaded to the TFTP server
to view a file.
Zte(cfg-tffs)#tftp 192. 168. 1. 102 upload
config. txt
In normal condition, when rebooting the switch, use
command running. cfg file to recover configurations.
When switch can not find running. cfg file, it will check
whether the config. txt file exists and when file exists,
switch will use it to recover configurations.
Config. txt file is used for version update. When the span
between new version and old one is big, using running. cfg
file of the primary version may cause mistakes after version
update. Consider the following recommendations:
f Create config. txt file before version update.
f Use the newly downloaded version to reboot switch after
deleting running. cfg file of old version.
Important! Switch will use config. txt file to recover
configurations. When command format is not modified or
deleted in new version, configurations will be recovered
successfully. If configurations is not recovered, recover
them manually.
f Use command saveconfig to create a running. cfg file
for new version after update is finished.
2. The command readconfig is to read the configuration
commands in the config. txt in the FLASH and sends them
to the switch for resolution and execution.
Result: Contents of the config. txt can be edited manually
as needed and then downloaded to the switch by using the
command tftp.
54 Confidential and Proprietary Information of ZTE CORPORATION
Page 69

Chapter 6 System Management
Example: This command downloads the file to the switch as
shown below in the example.
zte(cfg-tffs)#tftp 192. 168. 1. 102 download
config. txt
END OF STEPS
Result
Purpose
Prerequisites
Steps
Import and export function has been configured.
Setting File Backup and Recovery
This topic describes the procedure of file backups and recovery.
To backup files and recover, meet the following requirements:
To do Data backup and Recovery, there must have an
access to Command Line Interface (CLI). CLI is a textbased interface that can be accessed through a direct serial
connection to device and through telnet connections.
Make sure the TFTP server is up and running as described
above.
For file backup and recovery, perform the following steps.
1. Use command saveconfig in global configuration mode.
This is shown in
Note: When a command is used to modify the switch
configuration, data is running in the memory of the switch.
When the switch is restarted, all the contents newly
configured will be lost.In order to save the current
configuration into the FLASH memory,
Table 30.
TABLE 30 SAVECONFIG COMMAND
Format Mode Function
This saves the current
saveconfig config
configuration into the FLASH
memory
Result: This saves the current configuration into the FLASH
memory.
Example: The following shows the saveconfig command
zte(cfg)#saveconfig
To prevent damage to the configuration data, use command
tftp in file system configuration mode. This is shown in
below table:
Format Mode Function
tftp <A. B. C. D>
{download|upload}
<name>
Confidential and Proprietary Information of ZTE CORPORATION 55
File
system
config
This uploads or downloads a
version through TFTP
Page 70

ZXR10 2920/2928/2952
(V1.0) Access Switch User Manual (Volume I)
Result: This command is used to back up a configuration file
in the FLASH memory to the background TFTP Server.
Example: The following shows the back up of a configuration
file in the FLASH MEMORY to the background of TFTP Server.
zte(cfg-tffs)#tftp 192. 168. 1. 102 upload
running. cfg
This command can also be used show running-config
toFile to write the configuration information into the config.
txt and then back up the file to the TFTP server. For
detailed method, refer to
Configuring Imports and Exports .
2. Execute the following command to download the
configuration file in background TFTP server to the FLASH
memory.
zte(cfg-tffs)#tftp 192. 168. 1. 102 download
running. cfg
3. Similar to the configuration file, use command tftp to
upload the foreground version file to the background TFTP
server.
Result
Introduction
Example: This example shows the upload of the foreground
version file to the background TFTP server.
Zte(cfg-tffs)#tftp 192. 168. 1. 102 upload
kernel. z
4. Version file recovery is used to retransmit the background
backup version file to the foreground through TFTP.
Recovery is very important in the case of upgrading failure.
The version recovery operation is basically the same with the
version upgrade procedure.
ND OF STEPS
E
File backup and recovery has been configured.
Software Version Upgrade
Software version upgrade is only made when the original version
fails to support certain functions. Improper operation may lead
to upgrade failure and hence system booting failure. Therefore,
version upgrading must be done with the understanding of
principle, operation and upgrade procedure of the ZXR10
2920/2928/2952 before start to upgrade the version.
Version Upgrading occurs in the following two cases:
Version Upgrade in case of System Abnormality
Version Upgrade in case of Normal System.
56 Confidential and Proprietary Information of ZTE CORPORATION
Page 71

Chapter 6 System Management
Viewing System Information
Purpose
Steps
This topic describes the procedure for viewing system
information.
For system view, perform the following steps.
1. To view hardware and software versions of the System, use
show version command in global configuration mode as
shown in
TABLE 31 SHOW VERSION COMMAND WINDOW
Format Mode Function
Show
version
Table 31.
config
This display the version
information about the software
and hardware of system
Result: This shows the running software and hardware
information of system.
Example: The following information is displayed after
carrying out show version command.
zte(cfg)#version
The System's Hardware Info:
Switch's Mac Address: 00. d0. d0. f0. 11.
22
Module 0: ZXR10 5124; fasteth: 0; gbit: 24;
The System's Software Info:
Version number : V1. 1. 11. b
Version make date: Jun 16 2006
Version make time: 16:27:13
System has run 0 years 2 days 3 hours 8 minutes 43
seconds
Zte(cfg)#
Result
Purpose
END OF STEPS
System information has been viewed.
Upgrading Version at Normality
This topic describes the procedure of software version upgrade
for ZXR10 2920/2928/2952 in normal case.
Confidential and Proprietary Information of ZTE CORPORATION 57
Page 72

ZXR10 2920/2928/2952
(V1.0) Access Switch User Manual (Volume I)
Prerequisites
Steps
To upgrade software version, meet the following requirements.
Connect ZXR10 2920/2928/2952 console port (on the main
control board) to the serial port of the background host with
a console cable attached to the switch. Connect the
management Ethernet port to the background host’s network
port with a straight through network cable. Make sure that
both connections are correct.
Set the IP address of the Ethernet port on the switch. Set
the IP address of the background host used for upgrade.
The two IP addresses must be in the same network segment
so that the host can ping the switch.
On the background host, start the TFTP server software and
Configuring ZXR10 2920/2928/2952 as an TFTP Client.
set
For software version upgrade, perform the following steps.
1. View the information about the currently running image by
using show version command in privileged mode as shown
Table 32.
in
TABLE 32 SHOW VERSION COMMAND WINDOW
Format Mode Function
Show
version
Privileged
mode
This indicated software version flash
and image file present in directory
Result: This indicates new image file present in directory.
2. To delete the old version file in FLASH memory, use
command remove <file-name> in file system configuration
mode. This is shown in
Table 33. If the FLASH memory has
sufficient space, change the name of the old version file and
keep it in FLASH memory.
TABLE 33 REMOVE COMMAND
Format Mode Function
remove <file-
name>
File
system
config
This deletes the old version file in
FLASH memory
Result: This deletes the old version file in the FLASH
memory.
Example: The example of remove command is given below:
zte(cfg)#config tffs
zte(cfg-tffs)#remove kernel. z
3. Use command tftp to upgrade the version. The following
shows how to download the version file from the TFTP server
to the FLASH memory:
58 Confidential and Proprietary Information of ZTE CORPORATION
Page 73

zte(cfg-tffs)#tftp 192. 168. 1. 102 download
kernel. z
. . . . . . . . . . . . . .
. . . . . . . . . . . . . .
. . . . . . . . . . . . . .
. . . . . . . . . . . . .
. . . . . . . . . . . . . .
. . . . . . . . . . . . . .
. . . . . . . . . . . . . .
. . . . . . . . .
1, 979, 157 bytes downloaded
zte(cfg-tffs)#
Chapter 6 System Management
4. Restart the switch. After successful startup, check the
version under running and confirm whether the upgrading is
successful.
ND OF STEPS
E
Result
Note
Purpose
Prerequisite
Version upgrade has been installed.
When updating the version, there is configuration compatibility
problem of old and new versions. running. cfg file is of binary
and has poor compatibility. It is advised to test configuration
recovery first, then check whether the configuration recovery
needs to use config. txt file. When the old version has big
span with the new one, use config. txt file to recover
configuration. After upadate, check the recovered
configurations are of same primary configurations or not. If
they are not the same, configure according to facts and avoid
the mistakes caused by update.
Upgrading Version at Abnormality
This topic describes the procedure of software version upgrade
for ZXR10 2920/2928/2952 if it fails to start.
Connect Console port of the switch to the serial port of the
background host using the self-contained configuration cable.
Connect an Ethernet port of the switch to the network port of
the background host using a network cable. Check whether
the connections are correct.
Steps
For software version upgrade, perform the following steps.
1. Restart the switch. At the HyperTerminal, press any key
as prompted to enter the [VxWorks Boot] state.
Confidential and Proprietary Information of ZTE CORPORATION 59
Page 74

ZXR10 2920/2928/2952
(V1.0) Access Switch User Manual (Volume I)
Welcome to use ZTE eCarrier!!
Copyright(c) 2004-2006, ZTE Co. , Ltd.
System Booting. . . . . .
CPU: DB-88E6218
Version: VxWorks5. 5. 1
BSP version: 1. 2/6-b
Creation date: Aug 1 2006, 09:40:27
Press any key to stop auto-boot. . .
7
[ZxR10 Boot]:
2. Enter c in the [ZxR10 Boot] state and press Enter to enter
the parameter modification status. Set the IP addresses of
the Ethernet port and the TFTP server. Generally, these
two addresses are set to the same network segment.
60 Confidential and Proprietary Information of ZTE CORPORATION
Page 75

[ZxR10 Boot]: c
'. ' = clear field; '-' = go to previous
field; ^D = quit
boot device : wbdEnd1 */Use
the default value. /*
processor number : 0 */ Use
the default value. /*
host name : tiger */Use
the default value. /*
file name : vxWorks */Use
the default value. /*
inet on ethernet (e) : 10. 40. 89. 106
*/ IP address of the Ethernet port /*
inet on backplane (b): */Use
the default value. /*
host inet (h) : 10. 40. 89. 78
*/IP address of the TFTP server/*
gateway inet (g) : 10. 40. 89. 78
*/Use the default value. /*
user (u) : (Use
the default value)
ftp password (pw) (blank = use rsh): (Use
the default value)
flags (f) : 0x80 */Use
the default value. /*
target name (tn) : */Use
the default value. /*
startup script (s) : */Use
the default value. /*
other (o) : */Use
the default value. /*
[ZxR10 Boot]:
Chapter 6 System Management
3. Set the IP address of the background host as the same with
the IP address of the above TFTP server.
4. Start the TFTP server software on the background server and
configure the TFTP server as per description in
Configuring
ZXR10 2920/2928/2952 as an TFTP Client.
5. In the [ZxR10 Boot] state, input zte to enter the
[BootManager] state of the switch. Input ? to display the
command list for this state.
Confidential and Proprietary Information of ZTE CORPORATION 61
Page 76

ZXR10 2920/2928/2952
(V1.0) Access Switch User Manual (Volume I)
[ZxR10 Boot]: zte
Load wbdEnd Begin
W90N740 MAC0: 10MB - Full Duplex
Board 2818s !
Marvell has been initialized !
boot device : wbdEnd
unit number : 0
processor number : 0
host name : tiger
file name : vxWorks
inet on ethernet (e) : 10. 40. 89. 106
host inet (h) : 10. 40. 89. 78
gateway inet (g) : 10. 40. 89. 78
flags (f) : 0x80
Attached TCP/IP interface to wbdEnd0.
Warning! no netmask specified.
Attaching network interface lo0. . .
done.
Attaching to TFFS. . .
test flash passed perfectly!
Welcome to boot manager!
Type for help
[BootManager]:?
ls */Display the current
directory list. /*
pwd */Display the current
absolution path. /*
devs */Display the FLASH
information. /*
show */Display the switch
type and mac address. /*
reboot */Restart the switch.
/*
format */Format the FLASH. /*
del file_name */Delete the specified
file. /*
md dir_name */Create a directory.
/*
mf file_name */Create a file. /*
cd absolue-pathname */Change the
current directory. /*
tftp ip_address file_name */Download/upload
62 Confidential and Proprietary Information of ZTE CORPORATION
a version file through TFTP /*
update file_name */Upgrade boot/*
rename file_name newname */Rename the file.
/*
Page 77

Chapter 6 System Management
6. In the [BootManager] state, use the command tftp to
upgrade the version. The following shows how to download
the version file from the TFTP server to the FLASH memory:
[BootManager]:tftp 10. 40. 89. 78 kernel. z
Loading. . . done!
[BootManager]:ls
snmpboots. v3 35
startcfg. txt 1378
running. cfg 231916
kernel. z 1311339
[BootManager]:
7. In the [BootManager] state, execute the command reboot
to restart the switch by using the new version. If the
switch is started normally, use the command version to
check whether the new version is running in the memory.
When the switch is not started normally, it indicates the
version upgrade fails. In this case, repeat the above
upgrade procedure.
Result
ND OF STEPS
E
Software version upgrade has been completed.
Confidential and Proprietary Information of ZTE CORPORATION 63
Page 78

ZXR10 2920/2928/2952
(V1.0) Access Switch User Manual (Volume I)
This page is intentionally blank.
64 Confidential and Proprietary Information of ZTE CORPORATION
Page 79

Chapter 7
Service Configuration
Overview
Introduction
Contents
This chapter provides an overview of configuration methods for
various services of ZXR10 2920/2928/2952.
This chapter includes the following contents:
Topics Page No.
Port Configuration
Configuring Basic Port Parameters 68
Displaying Port Information 74
Port Mirroring 75
Configuring Port Mirroring 75
VLAN 77
Configuring VLAN 78
Introduction to FDB 83
MAC Table Operations 83
Configuring FDB 84
LACP Overview 86
Configuring LACP 87
IGMP Snooping 91
Configuring IGMP Snooping 91
Internet Protocol Television 101
Configuring IPTV Global Parameters 102
Configuring IPTV Channels 103
Configuring Channel Access Control (CAC) 104
Configuring Administrative Command of IPTV
Users
Maintenance and Diagnosis of IPTV 108
Confidential and Proprietary Information of ZTE CORPORATION 65
106
Page 80

ZXR10 2920/2928/2952
(V1.0) Access Switch User Manual (Volume I)
Topics Page No.
MSTP Mode 110
Configuring STP 112
The following ports are active!
PortId : 2 MSTI : 00
Priority : 128 Cost : 200000
Status : Forward Role : Designated
EdgePort : Disabled GuardType : None
LinkType : P2P PacketType : IEEE
PortId : 2 MSTI : 01
Priority : 112 Cost : 200000
Status : Forward Role : Designated
EdgePort : Disabled GuardType : None
LinkType : P2P PacketType : IEEE
ACL
124
Configuring Basic ACL 126
Configuring Extended ACL 127
Configuring L2 ACL 128
Configuring Hybrid ACL 128
Configuring Hybrid ACL 128
Configuring Global ACL 129
Configuring Time-Range 131
Configuring ACL to a Physical Port 131
Quality of Service (QoS) 132
Configuring QoS 133
Private Virtual LAN Overview 145
Configuring PVLAN 146
802. 1x Transparent Transmission 149
Configuring 802. 1x Transparent Transmission 150
Layer 3 Configuration 150
Configuring IP Port 151
Static Route Configuration 153
Configuring ARP Table Entry 154
Access Service 159
Configuring 802. 1x 163
Configuring Protocol Parameters of 802. 1x 166
Configuring RADIUS 169
QinQ Overview 177
66 Confidential and Proprietary Information of ZTE CORPORATION
Page 81

Chapter 7 Service Configuration
Topics Page No.
Configuring QinQ 178
SQinQ Overview 180
Configuring SQinQ 181
Syslog Overview 185
Configuring Syslog 186
Configuring NTP 187
GARP/GVRP Overview 189
Configuring GARP 190
Configuring GVRP 191
DHCP Snooping/Option82 194
Configuring Global DHCP 195
Configuring DHCP Snooping 197
Configuring IP Source Guard 198
Configuring DHCP Option82 199
VBAS Overview 204
Configuring VBAS 205
sFlow Monitoring Overview 207
Configuring sFlow 207
ZESR Overview 210
Configuring ZESR 211
Confidential and Proprietary Information of ZTE CORPORATION 67
Page 82

ZXR10 2920/2928/2952
(V1.0) Access Switch User Manual (Volume I)
Configuring Basic Port Parameters
Introduction
Purpose
Steps
On the ZXR10 2920/2928/2952, configuration of the following
port parameters: auto negotiation, duplex mode, rate, flow
control, port priority, MAC address number restriction, and so
on.
This topic describes the configuration of basic port parameters.
For basic port parameters, perform the following steps.
1. To clear port name/statistics data, use clear port <portlist>
{name|statistics|description}
TABLE 34 SET PORT COMMAND
Format Mode Function
clear port <portlist>
{name|statistics|descripti
on}
Global
config
This clear port
name/statistics
data.
Result: This clear port name/statistics data.
2. To create port description name, use command create port
<portname> name <name> in global configuration mode.
This is shown in
Table 35.
TABLE 35 AUTO-SENSING COMM AND
Format Mode Function
clear port <portlist>
{name|statistics|descripti
on}
Global
config
This creates port
description
name.
Result: This creates port description name.
3. To enable or disable the port, use command set port
<portlist> {enable|disable} in global configuration mode.
This is shown in
TABLE 36 WORK MODE COMMAND
Format Mode Function
set port
<portlist>
{enable|disable}
Table 36.
Global
config
This enables or disables the port.
Result: This enables or disables the port.
4. To set the port auto, use command set port <portlist> auto
{enable|disable} in global configuration mode. This is
shown in
Table 37.
68 Confidential and Proprietary Information of ZTE CORPORATION
Page 83

TABLE 37 DUPLEX COMMAND
Format Mode Function
Chapter 7 Service Configuration
set port
<portlist> auto
{enable|disable}
Global
config
This sets the port auto.
Result: This sets the port auto.
5. To set the port speedadvertise, use command set port
<portlist>speedadvertise{maxspeed|speed10|speed10
0|speed1000} in global configuration mode. This is
shown in
TABLE 38 SPEED COMMAND
Format Mode Function
set <portlist> speedadvertise
{maxspeed|speed10|speed100|speed1000}
Table 38.
Global
config
This sets
speed of
the port.
Result: This sets speed of the port.
6. To set the working manner of the port, use command set
port <portlist> duplex {full|half}.
Format Mode Function
set port
<portlist>
duplex
Global
config
This sets the working manner of
the port.
{full|half}
7. To set the speed of the port, use command set port
<portlist> speed {10|100|1000}.
Table 39 Set Port speed Commands
Format Mode Function
set port
<portlist> speed
{10|100|1000}}
Global
config
This sets port's speed.
Result: This sets port’s speed.
8. To set port <portlist> queue-schedule, use command set
port <portlist> queue-schedule { WRR0 |SP |WRR1SP|WRR2-SP}.
Table 40 Set port queue-schedule command
Confidential and Proprietary Information of ZTE CORPORATION 69
Page 84

ZXR10 2920/2928/2952
(V1.0) Access Switch User Manual (Volume I)
TABLE 40 PORT Q UEUE-SCHEDULE COMMANDS
Format Mode Function
set port <portlist>
queue-scedule
{WRR0|SP|WRR1-
SP|WRR2-SP}
Global
config
This sets packet type of
ingress direction
7. To set the priority of the source MAC address, use command
set port <portlist> sa-priority {enable|disable}
TABLE 41 THE PRIORITY OF THE SOURCE MAC ADDRESS ON COMMAND
Format Mode Function
set port
<portlist> sapriority
{enable|disable}
Global
config
This sets the priority of the source
MAC address.
Result: This sets the priority of the source MAC address.
8. To set the priority of the source VLAN, use command set
port <portlist> vlan-priority {enable|disable}.
TABLE 42 QUEUE-SCHEDULE COMMAND
Format Mode Function
set port
<portlist> vlanpriority
{enable|disable}
Global
config
This sets port’s priority of the
source VLAN.
Result: This sets port’s queue-schedule profile.
9. To set the priority of a port, use command set port
<portlist> default-priority <0-7> in global configuration
mode. This is shown in
TABLE 43 DEFAULT-PRIORITY COMMAND
Format Mode Function
set port
<portlist>
defaultpriority <0-7>
Global
config
Table 43.
This sets the priority of a port
Result: This sets the priority of a port.
12. To set remapping-tag priority of a port, use command set
port <portlist> remapping-tag <0-7>priority in global
configuration mode. This is shown in
TABLE 44 SET PORT SECURITY COMM AND
Format Mode Function
70 Confidential and Proprietary Information of ZTE CORPORATION
Table 44.
Page 85

Format Mode Function
set
port<portlist>
remapping-tag
<0-7> priority
<0-7>
Global
config
This sets remapping-tag priority
of a port.
Chapter 7 Service Configuration
Result: This sets remapping-tag priority of a port.
13. To set the port security, use command set port <portlist>
security {enable|disable} in global configuration mode.
This is shown in
TABLE 45 MULTICAST-FILTER COMMAND
Format Mode Function
Table 45.
set port <portlist>
security
{enable|disable }
Global
config
This sets the multicast filter of a
port
Result: This sets the port security.
14. To enable or disable the port unit-statistics, use command
set port <portlist> unit-statistics {enable |disable} in
global configuration mode. This is shown in
TABLE 46 RATE ADVERTISEMENT COMMAND
Format Mode Function
Table 46.
set port <portlist>
unit-statistics
{enable |disable}
Global
config
This sets the port unitstatistics
Result: This sets the port unit-statistics.
15. To set the multicast-filter, use command set port
<portlist> macaddress {on <1-16>|off} in global
configuration mode. This is shown in
TABLE 47 MAC ADDRESS COMMAND
Table 47.
Format Mode Function
set port
<portlist>
macaddress {on
<1-16>|off}
Global
config
This sets multicast-filter
Result: This sets the number of MAC addresses.
16. To set port on Vlan, use command set port <portname>
description <string> in global configuration mode. This is
shown in
Table 48.
Confidential and Proprietary Information of ZTE CORPORATION 71
Page 86

ZXR10 2920/2928/2952
(V1.0) Access Switch User Manual (Volume I)
TABLE 48 PROTO COL-VLAN COMMAND
Format Mode Function
set port
<portname>
description
<string>
Global
config
This sets port description
Result: This sets port description.
17. To set port’s macaddress, use command set port
<portlist> macaddress {on <1-16> | off } in global
configuration mode. This is shown in
TABLE 49 PORT J UMBO COMMAND
Format Mode Function
set port
<portlist>
macaddress
{on <1-16> |
off }
Global
config
This sets port’s macaddress
Table 49.
Result: This sets port’s macaddress.
18. To set the ACL info, use command set port <portlist> acl
<acl-number> {enable | disable} in global configuration
mode. This is shown in
TABLE 50 CREATE PORT COMMAND
Format Mode Function
set port
<portlist> acl
<acl-number>
{enable |
disable}
Global
config
Table 50.
This sets the ACL info
Result: This sets the ACL info.
19. To set port vlanjump, use command set port
<portlist>vlanjump {enable [defaultauthvlan<1-4094>]
| disable }in global configuration mode. This is shown in
Table 51.
TABLE 51 PORT DESCRIPTION COMMAND
Format Mode Function
set port
<portlist>vlanjump
{enable
[defaultauthvlan<1-
4094>] | disable
Global
config
This sets port vlanjump
Result: This sets port vlanjump.
72 Confidential and Proprietary Information of ZTE CORPORATION
Page 87

Chapter 7 Service Configuration
20. To set port trust-up, use command set port <portlist>
trust-up {enable | disable}in global configuration mode.
This is shown in
TABLE 52 PORT DESCRIPTION COMMAND
Format Mode Function
set port
<portlist>
trust-up {enable
| disable}
Table 51.
Global
config
This sets port trust-up
Result: This sets port trust-up.
21. To set port trust-dscp, use command set port <portlist>
trust-dscp {enable | disable }in global configuration mode.
This is shown in
TABLE 53 PORT DESCRIPTION COMMAND
Table 51.
Format Mode Function
set port
<portlist>
trust-dscp
{enable |
disable}
Global
config
This sets port trust-dscp
Result: This sets port trust-dscp.
Note:When setting megabit port trust-dscp, the switch also
converts it to the corresponding UP. The flow is as follows:
When the IP message enterS from port A that trusts in DSCP,
firstly, we get the default priority def[2:0](0-7, aggregately
3 bits). Then mapping the global DSCP-TC table according
to DSCP value of the message, we can get the initial TC
value TC[1:0](0-3, aggregately 2 bits) of the message. We
adopt TC[1:0] as the [2:1]digit of UP, the last digit of port
default priority def[0]as the new UP digit of the message(0-7,
aggregately 3 bits). Finally, switch mapping the global UPTC table according to the new UP, & get the queue that the
message will enter.
Example:the DSCP of a item of message is 60, the entry
default priority is 7, trust DSCP, DSCP-TC mapping table is
60-2. Then in the switch, the UP message converts to 5, &
obtain the queue to enter according to global UP-TC table.
Result
If port trust UP & DSCP at the same time, the gigabit port
will trust DSCP firstly, & the megabit port will trust UP firstly.
ND OF STEPS
E
Basic port parameters are configured.
Confidential and Proprietary Information of ZTE CORPORATION 73
Page 88

ZXR10 2920/2928/2952
(V1.0) Access Switch User Manual (Volume I)
Displaying Port Information
Purpose
Steps
This topic describes the displaying of port information.
To view of port information, perform the following steps.
1. To display the configuration and work state of the port, use
command show port [<portlist>] in global configuration
mode. This is shown in
TABLE 54 SHOW PORT COMMAND
Format Mode Function
show port
[<portlist>]
Global
config
Table 54.
This displays the configuration and
work state of the port
Result: This displays the configuration and work state of the
port.
2. To displays Vlan information of the port, use command
show port <portlist> vlan in global configuration mode.
This is shown in
TABLE 55 SHOW PORT VLAN COMMAND
Format Mode Function
show port
<portlist> vlan
Table 55.
Global
config
This displays Vlan information of
the port
Result: This displays Vlan information of the port.
3. To display statistics information of the port in unit time, use
command show port <portlist> statistics
1min_unit|5min_unit in global configuration mode. This
is shown in
TABLE 56 SHOW PORT STATISTICS TIME C OMMAND
Format Mode Function
show port <portlist>
statistics
1min_unit|5min_unit
Table 56.
Global
config
This displays statistics
information of the port in unit
time
Result: This displays statistics information of the port in unit
time.
4. To display the QoS configuration data of the port, use
command show port <portlist> qos in global configuration
mode. This is shown in
TABLE 57 SHOW PORT QOS COMMAND
Format Mode Function
Table 57.
74 Confidential and Proprietary Information of ZTE CORPORATION
Page 89

Format Mode Function
Chapter 7 Service Configuration
Result
show port
<portlist> qos
Global
config
This displays the QoS configuration
data of the port
Result: This displays the QoS configuration data of the port.
5. To display the bandwidth information of the port, use
command show port <portlist> bandwidth session <0-3>
in global configuration mode. This is shown in
TABLE 58 SHOW PORT BAND WIDTH COMMAND
Format Mode Function
show port
<portlist>
bandwidth
session <0-3>
Global
config
This displays the bandwidth
information of the port
Table 58.
Result: This displays the bandwidth information of the port.
E
ND OF STEPS
Port information is displayed.
Port Mirroring
Introduction
Port mirroring is used to mirror data packets of the switch port
(ingress mirroring port) to an ingress destination port (ingress
monitoring port), or mirror the data packets of the switch port
(egress mirroring port) to an egress destination port (egress
monitoring port).
Through mirroring, data packets flowing in or out of a certain
port can be monitored. Port mirroring provides an effective
tool for the maintenance and monitoring of the switch.
Switch can be configured with only one ingress monitoring port
and one egress monitoring port. Ingress monitoring port and
egress monitoring port can be configured on same port.
Whereas multiple source ingress monitoring ports and source
egress monitoring ports can be configured at the same time.
Note: In default case, switch does not have mirroring port.
The GOOD data packets received by ingress mirroring port are
mirrored onto the monitoring ports, but data packets directly
discarded on the ingress port (for example, because of CRC
errors) are not mirrored. The source mirror port & the
destination port must be in the same vlan.
Configuring Port Mirroring
Purpose
Confidential and Proprietary Information of ZTE CORPORATION 75
Page 90

ZXR10 2920/2928/2952
(V1.0) Access Switch User Manual (Volume I)
This topic describes the procedure of port mirroring configuration
of ZXR10 2920/2928/2952.
Steps
To mirror the ports, perform the following steps.
1. To add a mirroring port, use command set mirror add
source-port <portlist> {ingress|egress} in global
configuration mode. This is shown in
TABLE 59 SET MIRROR COMMAND
Format Mode Function
set mirror add
source-port
<portlist>
{ingress|egress}
Global
config
This adds a mirroring port
Table 59.
Result: This adds a mirroring port.
2. To delete mirroring port, use command set mirror delete
source-port <portlist> {ingress|egress} in global
configuration mode. This is shown in
TABLE 60 DELETE MIRRORING PORT COMMAND
Format Mode Function
set mirror delete
source-port
<portlist>
{ingress|egress}
Global
config
This deletes mirroring port
Table 60.
Result: This deletes mirroring port.
3. To set a monitoring port, use command set mirror add
dest-port <portname> {ingress|egress} in global
configuration mode. This is shown in
TABLE 61 SET MIRROR DEST-PORT COMMAND
Format Mode Function
set mirror add
dest-port
<portname>
{ingress|egress}
Global
config
This sets a monitoring port
Table 61.
Result: This sets a monitoring port.
4. To delete destination monitoring port, use command set
mirror delete dest-port <portname> {ingress|egress}
in global configuration mode. This is shown in
TABLE 62 SET MIRROR DELETE DEST-PORT COMMAND
Format Mode Function
set mirror delete
dest-port
<portname>
Global
config
This deletes destination
monitoring port
Table 62.
76 Confidential and Proprietary Information of ZTE CORPORATION
Page 91

Format Mode Function
{ingress|egress}
Chapter 7 Service Configuration
Result: This deletes destination port.
2. To display the port mirroring configuration, use command
show mirror in global configuration mode. This is shown
Table 63.
in
TABLE 63 SHOW MIRROR COMMAND
Format Mode Function
Result
Example
show mirror
Global
config
This displays port mirroring
configuration
Result: This displays port mirroring configuration.
E
ND OF STEPS]
Port mirroring is configured on ZXR10 2920/2928/2952.
To mirror data packets received by port 1 and port 16 onto the
monitoring port 10, configuration is as follows:
zte(cfg)# set mirror add dest-port 10 ingress
zte(cfg)# set mirror add source-port 1, 16 ingress
Use the command show mirror to view the port mirroring
configuration.
zte(cfg)#show mirror
ingress mirror infomation
-------------------------- source port: 1 16
dest port : 10
egress mirror infomation
-------------------------- source port: none
dest port : none
zte(cfg)#
To mirror the data packets received by port 2 and port 3 onto
the monitoring port 4, configuration is as follows:
zte(cfg)# set mirror add dest-port 4 egress
zte(cfg)# set mirror add source-port 2, 3 egress
VLAN
Confidential and Proprietary Information of ZTE CORPORATION 77
Page 92

ZXR10 2920/2928/2952
(V1.0) Access Switch User Manual (Volume I)
Definition
Description
Virtual Local Area Network (VLAN) is a technology that divides a
physical network into several logical (virtual) Local Area
Networks (LANs). Each VLAN is identified by a VLAN ID (VID).
Several VLANs share the switch & link of the physical local
network.
Each VLAN is like an independent local area network logically.
In the same VLAN, all the frame flow is limited in this VLAN.
Cross-VLAN visit can only be implemented through forwarding
on layer 3. This improve the network capability greatly.
Reduce the whole flow of the physical local network.
ZXR102920/2928/2952 support tagged-based VLAN which is
VLAN based on lable. This is the mode IEEE 802. 1Q defined,
& the universal work mode. In this mode, VLAN partition is
based on port’s VLAN info(PVID:port VLAN ID)or the information
in VLAN lable.
VLAN provides the following advantages:
Lower broadcast traffic on the network
Enhanced network security
Streamlined network management
Purpose
Steps
Configuring VLAN
This topic describes the configuration of VLAN on ZXR10
2920/2928/2952.
For configuration of VLAN, perform the following steps.
1. To remove a VLAN name, use command clear vlan
<vlanlist> name in global configuration mode. This is
shown in
TABLE 64 CLEAR VLAN COMMAND
Format Mode Function
clear vlan
<vlanlist>
name
Result: This removes a VLAN name.
2. To create a VLAN name, use command create vlan <14094> name <sting> in global configuration mode. This is
shown in
TABLE 65 CREATE VLAN COMMAND
Table 64.
Global
config
Table 65.
This removes a VLAN name
Format Mode Function
create vlan <1-
4094> name
<string>
78 Confidential and Proprietary Information of ZTE CORPORATION
Global
config
This creates a VLAN name
Page 93

Chapter 7 Service Configuration
Result: This creates a VLAN name.
3. To set port PVID, use command set port <portlist> pvid
<1-4094> in global configuration mode. This is shown in
Table 66.
TABLE 66 SET PORT PVID COMMAND
Format Mode Function
set port
<portlist> pvid
<1-4094>
Global
config
This sets port PVID
Result: This sets port PVID.
4. To set trunk PVID, use command set trunk < trunklist >
pvid <1-4094> in global configuration mode. This is
shown in
TABLE 67 SET TRUNK PVID COMMAND
Format Mode Function
set trunk <
trunklist > pvid
<1-4094>
Table 67.
Global
config
This sets trunk PVID
Result: This sets trunk PVID.
5. To Enable/Disable the VLAN, use command set vlan
<vlanlist> {enable|disable} in global configuration mode.
This is shown in
TABLE 68 SET VLAN COMM AND
Format Mode Function
Table 68.
set vlan
<vlanlist>
{enable|disable}
Global
config
This Enable/Disable the VLAN
Result: This Enable/Disable the VLAN.
6. To add a specified port to the VLAN, use command set vlan
<vlanlist> add port <portlist> [tag|untag] in global
configuration mode. This is shown in
TABLE 69 SET VLAN ADD PORT COMMAND
Format Mode Function
set vlan
<vlanlist> add
port <portlist>
[tag|untag]
Global
config
This adds a specified port to the
VLAN
Table 69.
Result: This adds a specified port to the VLAN.
Confidential and Proprietary Information of ZTE CORPORATION 79
Page 94

ZXR10 2920/2928/2952
(V1.0) Access Switch User Manual (Volume I)
7. To add a specified trunk to the VLAN, use command set
vlan <vlanlist> add trunk <trunklist> [tag|untag] in
global configuration mode. This is shown in
TABLE 70 SET VLAN ADD TRUNK COMMAND
Format Mode Function
set vlan
<vlanlist> add
trunk
<trunklist>
[tag|untag]
Global
config
This adds a specified trunk to the
VLAN
Table 70.
Result: This adds a specified trunk to the VLAN.
8. To delete a specified port to the VLAN, use command set
vlan <vlanlist> delete port <portlist> in global
configuration mode. This is shown in
TABLE 71 SET VLAN DELETE P ORT COMMAND
Table 71.
Format Mode Function
set vlan
<vlanlist>
delete port
<portlist>
Global
config
This deletes a specified port to the
VLAN
Result: This deletes a specified port to the VLAN.
9. To delete a specified trunk to the VLAN, use command set
vlan <vlanlist> delete trunk <trunklist> in global
configuration mode. This is shown in
TABLE 72 SET VLAN DELETE T RUNK COMMAND
Format Mode Function
set vlan
<vlanlist>
delete trunk
<trunklist>
Global
config
This deletes a specified trunk to the
VLAN
Table 72.
Result: This deletes a specified trunk to the VLAN.
10. To forbid port from VLAN, use command set vlan
<vlanlist> forbid port <portlist> in global configuration
mode. This is shown in
Table 73.
TABLE 73 SET VLAN FORBID P ORT COMMAND
Format Mode Function
set vlan
<vlanlist>
forbid port
<portlist>
Global
config
This forbids port from VLAN
Result: This forbids port from VLAN.
80 Confidential and Proprietary Information of ZTE CORPORATION
Page 95

Chapter 7 Service Configuration
11. To permit port on VLAN, use command set vlan <vlanlist>
permit port <portlist> in global configuration mode. This
is shown in
TABLE 74 SET VLAN PERMIT PORT COMM AND
Format Mode Function
set vlan
<vlanlist>
permit port
<portlist>
Table 74.
Global
config
This permits port on VLAN
Result: This permits port on VLAN.
12. To forbid trunk on VLAN, use command set vlan <vlanlist>
forbid trunk <trunklist> in global configuration mode.
This is shown in
TABLE 75 SET VLAN FORBID T RUNK COMMAND
Table 75.
Format Mode Function
set vlan
<vlanlist>
forbid trunk
<trunklist>
Global
config
This forbids trunk on VLAN
Result: This forbids trunk on VLAN.
13. To permit trunk on VLAN, use command set vlan
<vlanlist> permit trunk <trunklist> in global configuration
mode. This is shown in
TABLE 76 SET VLAN PERMIT TRUNK COMMAND
Format Mode Function
set vlan
<vlanlist>
permit trunk
<trunklist>
Global
config
Table 76.
This permits trunk on VLAN
Result: This permits trunk on VLAN.
14. To displays VLAN information, use command show vlan
[<vlanlist>] in global configuration mode. This is shown in
Table 77.
TABLE 77 SHOW VLAN COMMAND
Format Mode Function
show vlan
[<vlanlist>]
Global
config
This displays VLAN information
Result: This displays VLAN information.
E
ND OF STEPS
Confidential and Proprietary Information of ZTE CORPORATION 81
Page 96

ZXR10 2920/2928/2952
(V1.0) Access Switch User Manual (Volume I)
Result
Example
VLAN is configured on ZXR10 2920/2928/2952.
This example shows the configuration of VLAN 100. Add
untagged ports 1 and 2 and tagged ports 7 and 8. The detailed
configuration is as follows:
Note: It is recommended to delete default VLAN before the
configuration.
zte(cfg)#set vlan 100 add port 1, 2 untag
zte(cfg)#set vlan 100 add port 7, 8 tag
zte(cfg)#set port 1, 2 pvid 100
zte(cfg)#set vlan 100 enable
zte(cfg)#show vlan 100
VlanId : 100 Fid : 100 Priority: off
VlanStatus: enabled
VlanName:
Tagged ports : 7-8
Untagged ports: 1-2
zte(cfg)#
Configuration of VLAN transparent transmission
This example describes how Switch A is connected to switch B
through port 16. Port 1 of switch A and port 2 of switch B
belong to VLAN2, and port 3 of switch A and port 4 of switch B
belong to VLAN3. Members of the same VLAN can
communicate with each other. This is shown in
FIGURE 24 VLAN TRANSPARENT TRANSMISSION
Switch A
p1
p3
p16p16
p2
Figure 24.
Switch B
p4
Switch A configuration
82 Confidential and Proprietary Information of ZTE CORPORATION
Page 97

zte(cfg)#set vlan 2 add port 16 tag
zte(cfg)#set vlan 2 add port 1 untag
zte(cfg)#set vlan 3 add port 16 tag
zte(cfg)#set vlan 3 add port 3 untag
zte(cfg)#set port 1 pvid 2
zte(cfg)#set port 3 pvid 3
zte(cfg)#set vlan 2-3 enable
Chapter 7 Service Configuration
Switch B configuration
zte(cfg)#set vlan 2 add port 16 tag
zte(cfg)#set vlan 2 add port 2 untag
zte(cfg)#set vlan 3 add port 16 tag
zte(cfg)#set vlan 3 add port 4 untag
zte(cfg)#set port 2 pvid 2
zte(cfg)#set port 4 pvid 3
zte(cfg)#set vlan 2-3 enable
MAC Address
Table
MAC filter
function
Introduction to FDB
Media Access Control (MAC) address is the hardware
identification of a network device, based on which the switch
forwards packets. MAC address is unique, ensuring accurate
packet forwarding.
Each switch maintains a MAC address table called forwarding
database (FDB). FDB records one-to-one mapping relationship
between MAC addresses and switch ports. Upon receiving a
data frame, the switch decides whether to drop it or forward it
to the proper port based on this table. The FDB is the basis
and prerequisite for fast forwarding.
MAC Table Operations
MAC table operations include the configuration of MAC filter
function, static address binding function, and MAC table aging
time.
MAC filter function is to enable the switch to discard the received
data packets whose source or destination MAC address is the
specified MAC address. There are 3 filter mode:according to
source mac address filter, destination mac addressfilter & both
of them.
Static address
binding
function
Static address binding function is to bind the specified MAC
address with the switch port. After the binding, this MAC is
kept away from the dynamic study.
Confidential and Proprietary Information of ZTE CORPORATION 83
Page 98

ZXR10 2920/2928/2952
(V1.0) Access Switch User Manual (Volume I)
MAC table
aging time
Purpose
Steps
MAC table aging time refers to the period from the latest update
of dynamic MAC address in the FDB table to the deletion of this
address.
Configuration of the MAC filter function and static address
binding function prevents illegal access to the network and
fraudulent use of key MAC addresses, and play an important
role in ensuring the network security.
Configuring FDB
This topic describes the configuration of FDB.
For the configuration of FDB, perform the following steps.
1. To add the static binding address to the address table,
use command set fdb add <xx. xx. xx. xx. xx. xx>
vlan <1-4094> {port <portid>|trunk <trunkid>} in global
configuration mode. This is shown in
TABLE 78 SET FDB ADD VLAN COMM AND
Format Mode Function
Table 78.
set fdb add <xx.
xx. xx. xx. xx.
xx> vlan <14094> {port
<portid>|trunk
<trunkid>}
Global
config
This adds the static binding
address to the address table
Result: This adds the static binding address to the address
table.
2. To set the aging time of MAC address, use command set
fdb agingtime <40-1260> in global configuration mode.
This is shown in
TABLE 79 SET FDB AGINGTIME COMM AND
Format Mode Function
set fdb
agingtime
<40-1260>
Table 79.
Global
config
This sets the aging time of MAC
address
Result: This sets the aging time of MAC address.
3. To delete a record in the table, use command set fdb
delete <xx. xx. xx. xx. xx. xx> vlan <1-4094> in
global configuration mode. This is shown in
Table 80.
TABLE 80 SET FDB DELETE COMMAND
Format Mode Function
84 Confidential and Proprietary Information of ZTE CORPORATION
Page 99

Format Mode Function
set fdb delete
<xx. xx. xx.
xx. xx. xx>
vlan <1-4094>
Global
config
Chapter 7 Service Configuration
This deletes a record in the table
Result: This deletes a record in the table.
4. To set the filter address of fdb, use command set fdb
filter<xx. xx. xx. xx. xx. xx>vlan<1-4094>
{dest_mac|src_mac|both}in global configuration mode.
This is shown in
TABLE 81 SET FDB FILTER COMMAND
Format Mode Function
Table 81.
set fdb filter <xx. xx. xx.
xx. xx. xx>vlan<1-4094>
{dest_mac|src_mac|both}
Global
config
This sets the filter
address of fdb
Result: This sets the filter address of fdb.
5. To display fdb information, use command show fdb
[static|dynamic|filter] [detail] in global configuration
mode. This is shown in
TABLE 82 SHOW FDB COMMAND
Format Mode Function
show fdb
[static|dynamic|filter]
{detail}
Table 82.
Global
config
This displays fdb information
Result: This displays fdb information.
6. To display the aging time of fdb address, use command
show fdb agingtime in global configuration mode. This is
shown in
TABLE 83 SHOW FDB AGINGTIME COMM AND
Format Mode Function
Table 83.
show fdb
agingtime
Global
config
This displays the aging time of fdb
address
Result: This displays the aging time of fdb address.
7. To display the MAC-based fdb information, use command
show fdb mac <xx. xx. xx. xx. xx. xx> in global
configuration mode. This is shown in
Table 84.
Confidential and Proprietary Information of ZTE CORPORATION 85
Page 100

ZXR10 2920/2928/2952
(V1.0) Access Switch User Manual (Volume I)
TABLE 84 SHOW FDB MAC COMMAND
Format Mode Function
show fdb mac
<xx. xx. xx.
xx. xx. xx>
Global
config
This displays the MAC-based fdb
information
Result: This displays the MAC-based fdb information.
8. To display the port-based fdb information, use command
show fdb port <portname> {detail} in global
configuration mode. This is shown in
TABLE 85 SHOW FDB PORT COMMAND
Format Mode Function
show fdb port
<portname>
{detail}
Global
config
This displays the port-based fdb
information
Table 85.
Result: This displays the port-based fdb information.
9. To display Trunk fdb information, use command show
fdb trunk <trunkname> [detail]in global configuration
mode. This is shown in
TABLE 86 SHOW FDB TRUNK COMM AND
Format Mode Function
Table 86.
Result
show fdb trunk
<trunkname>
{detail}
Global
config
This displays Trunk fdb information
Result: This displays Trunk fdb information.
10. To display the VLAN-based fdb information, use
command show fdb vlan <vlanname> [detail]in global
configuration mode. This is shown in
TABLE 87 SHOW FDB VLAN COMMAND
Format Mode Function
show fdb vlan
<vlanname>[detail]
Global
config
This displays VLAN-based fdb
information
Table 87.
Result: This displays VLAN-based fdb information.
E
ND OF STEPS
FDB is configured on the switch.
LACP Overview
LACP
Link Aggregation Control Protocol (LACP) follows IEEE 802. 3ad
standards.
86 Confidential and Proprietary Information of ZTE CORPORATION
 Loading...
Loading...