Zebra ZXP Series 8 Secure Issuance Card Printer ZXP Series 7 and ZXP Series 8 Card Printer Wireless Reference Manual (en)
Page 1

Cover
COVER
P1035089-003
ZXP Series 7™ and ZXP Series 8™
Card Printer
Wireless
Reference Manual
Page 2

© 2013 ZIH Corp. The copyrights in this manual and the software and/or firmware in
the printer described therein are owned by ZIH Corp. and Zebra's licensors.
Unauthorized reproduction of this manual or the software and/or firmware in the
printer may result in imprisonment of up to one year and fines of up to $10,000
(17 U.S.C.506). Copyright violators may be subject to civil liability.
Proprietary Statement This manual contains proprietary information of Zebra
Technologies Corporation and its subsidiaries. It is intended solely for the information
and use of parties operating and maintaining the equipment described herein. Such
proprietary information may not be used, reproduced, or disclosed to any other parties
for any other purpose without the express, written permission of Zebra Technologies.
Product Improvements Continuous improvement of products is a policy of Zebra
Technologies. All specifications and designs are subject to change without notice.
Liability Disclaimer Zebra Technologies takes steps to ensure that it's published
Engineering specifications and manuals are correct; however, errors do occur. Zebra
Technologies reserves the right to correct any such errors and disclaims liability
resulting there from.
Limitation of Liability In no event shall Zebra Technologies or anyone else involved
in the creation, production, or delivery of the accompanying product (including
hardware and software) be liable for any damages whatsoever (including, without
limitation, consequential damages including loss of business profits, business
interruption, or loss of business information) arising out of the use of, the results of
use of, or inability to use such product, even if Zebra Technologies has been advised
of the possibility of such damages. Some jurisdictions do not allow the exclusion or
limitation of incidental or consequential damages, so the above limitation or exclusion
may not apply to you.
Important Use only the supplied antenna. Unauthorized
antennas, modifications or attachments could damage
the transmitter and may violate FCC regulations or local
regulatory requirements in your country.
P1035089-003 Rev. A
Page 3

Compliance and Regulatory Statements
FCC Compliance Statement (USA)
This device complies with Part 15 rules. Operation is subject to the following two conditions:
1. This device may not cause harmful interference, and
2. This device must accept any interference received, including interference that may cause
undesired operation.
This equipment has been tested and found to comply with the limits for Class A Digital
Devices, pursuant to Part 15 of the FCC Rules. These limits are designed to provide reasonable
protection against harmful interference when the equipment is operated in a residential
environment. This equipment generates, uses, and can radiate radio frequency energy and, if
not installed and used in accordance with the product manuals, may cause harmful interference
to radio communications. However, there is no guarantee that interference will not occur in a
particular installation. If this equipment does cause harmful interference to radio or television
reception, the user is encouraged to do one or more of the following measures:
:
• Reorient or relocate the receiving antenna.
• Increase the separation between the equipment and receiver.
• Connect the equipment into an outlet on a circuit different from that to which the receiver
is connected.
• Consult the dealer or an experienced RF service technician for help.
Important
1. The radio must be installed with a minimum 20 cm separation between the user and the
antenna.
2. The radio must not be co-located or used in simultaneous transmitting condition with
another radio.
3. The host system shall have a label to indicate that the system contains a certified module.
An example is “Contains FCC ID : I28-W2WLAN11G, IC ID: 3798B-W2WLAN11G.”
4. The radio is for indoor use only in the 2412-2472 MHz frequency range.
Modification Warning
The user is cautioned that any changes or modifications not expressly approved by Zebra
Technologies could void the user’s authority to operate the equipment. To ensure compliance,
this printer must be used with fully shielded communication cables.
RF Exposure Statement
This transmitter complies with FCC radiation exposure limits set forth for an uncontrolled
environment. The antenna(s) used for this transmitter must be installed to provide a separation
distance of at least 20 cm from all persons. This transmitter must not be co-located or
operating in conjunction with any other antenna or transmitter, except in accordance with FCC
multi-transmitter product procedures.
P1035089-003 Wireless Reference Manual 3
Page 4

:
Approved Antenna information
Only Zebra approved antennas are allowed and cannot be replaced by the user.
802.11 b/g
Antenna PN: Laird Technologies WCR2400SMRP
Gain: 1.3 dBi @ 2.4 GHz
Impedance: 50 Ω
Mexico — NOM-121-SCT1-2009
Este equipo ha sido diseñado para operar con las antenas que enseguida se enlistan y para una
ganancia máxima de antena de 3.1 dBi. El uso con este equipo de antenas no incluidas en esta
lista o que tengan una ganancia mayor que 3.1 dBi quedan prohibidas. La impedancia
requerida de la antena es de 50 ohms.
Canadian DOC Compliance Statement
Cet appareil numérique de la classe B est conforme à la norme NMB-003 du Canada.
This Class B digital apparatus complies with Canadian ICES-003.
Industry Canada (IC) Warning
Le présent appareil est conforme aux CNR d’Industrie Canada applicables aux appareils radio
exempts de licence. L’exploitation est autorisée aux deux conditions suivantes : (1) l’appareil
ne doit pas produire de brouillage, et (2) l’utilisateur de l’appareil doit accepter tout brouillage
radioélectrique subi, même si le brouillage est susceptible d’en compromettre le
fonctionnement.
This device complies with Industry Canada license-exempt RSS standard(s). Operation is
subject to the following two conditions: 1) This device may not cause interference., 2) This
device must accept any interference, including interference that may cause undesired operation
of the device.
Brasil — Aviso da Anatel
Este equipamento opera em caráter secundário, isto é, não tem direito a proteção contra
interferência prejudicial, mesmo de estações do mesmo tipo, e não pode causar interferência a
sistemas operando em caráter primário.
“Este produto está homologado pela ANATEL, de acordo com os procedimentos
regulamentados pela Resolução 242/2000, e atende aos requisitos técnicos aplicados”
Para maiores informações, consulte o site da ANATEL www.anatel.gov.br
This equipment's operation is of a secondary character; that is, it doesn't have the right to
protection against damaging interference, even from stations of the same type, nor can it cause
interference to systems with a primary operating character.
4 Wireless Reference Manual P1035089-003
Page 5

Japan Restricted Frequencies
ሶቑ⛷㽱㟿ゾቒ*+]ቑ㡴㦻ቊⒸ䞷ቊሰቮሸቯቡሾቶᇭ
For 5.725 - 5.825 GHz, this frequency band will not be available in Japan.
Taiwan Restricted Frequencies
5.15-5.25 GHz, 崁櫊㹄⺖⦷咉䋲ₜ♾䞷ᇭ
For 5.15 - 5.25 GHz, this frequency band will not be available in Taiwan.
Korean Compliance Statement
넩韥韥鱉閵뇊끞 % 鞾 놹녅볁놶뼞韥韥ꈑ늱ꈑ閵뇊꾅ꩡ끞뼍鱉阸냹ꑞ놶냱ꈑ
뼍ꐥ ꑝ麕덵꾢꾅ꩡ끞뼕ꯍ넽걪鱽鲙
The equipment is for home use (Class A) and has acquired electromagnetic conformity
registration, so it can be used not only in residential area but other areas as well.
This radio device is not allowed to be used for human safety since it has possibility of radio
interference during operation.
:
European Regulatory Information
Note • Member states in the EU with restrictive use for this device are crossed out. This
device is also authorized for use in all EFTA member states (CH, IS, LI, NO).
P1035089-003 Wireless Reference Manual 5
Page 6

:
NCC
倢⨚㆞崜巘⚗㫋⇝┮䘖⺓櫊榊㳮᧨槭倢峀♾᧨⏻⚇ᇬ⟕壮㒥∎䞷劔⧖ₜ㈦㝔呹帙
㦃櫊䘖ᇬ┯⮶┮䘖㒥帙㦃☮岼岗䔈㊶♙┮厌ᇭ⇝┮䘖⺓櫊榊㳮∎䞷ₜ㈦㈀檎歪
咹⸘⏷♙㞍⚗㽤抩≰᧷倢䤋䚍㦘㞍䚍廰㣑᧨㑘䵚☂⋫䞷᧨₵㟈⠓咂䎰㞍㣑㡈
㈦儋儛∎䞷ᇭⓜ檔⚗㽤抩≰᧨㖖∬榊≰㽤尞⸩⇫㯼䎰偩榊抩≰ᇭ⇝┮䘖⺓櫊榊㳮
檗㉜♦⚗㽤抩≰㒥ぴ㯼ᇬ䱠⸇♙携䣑䞷榊㽱懊⺓㊶榊㳮岼⌨㞍ᇭ
According to “Administrative Regulations on Low Power Radio Waves Radiated Devices”
Without permission granted by the NCC, any company, enterprise, or user is not allowed to
change frequency, enhance transmitting power or alter original characteristic as well as
performance to an approved low power radio-frequency devices. The low power radiofrequency devices shall not influence aircraft security and interfere legal communications; If
found, the user shall cease operating immediately until no interference is achieved. The said
legal communications means radio communications is operated in compliance with the
Telecommunications Act.
The low power radio-frequency devices must be susceptible with the interference from legal
communications or ISM radio wave radiated devices.
WLAN Radio Specification
802.11 b
• 2.4 GHz
• DSSS (DBPSK, DQPSK and CCK)
• RF power 17 mW (ZebraNet n Print Server)
802.11 g
• 2.4 GHz
• OFDM (16-QAM and 64-QAM with BPSK and QPSK)
• RF power 17 mW (ZebraNet n Print Server)
6 Wireless Reference Manual P1035089-003
Page 7

Icons
:
Throughout this manual, different icons highlight important information, as follows:
Note • Indicates information that emphasizes or supplements important points of the
main text.
Important • Advises you of information that is essential to complete a task, or points out the
importance of specific information in the text.
Provides an example or scenario to demonstrate or clarify a section of text.
Electrostatic Discharge • Warns you of the potential for electrostatic discharge damage
to parts and assemblies.
Electric Shock • Warns you of a potential electric shock situation.
Hot Surface • Warns you of a situation where excessive heat could cause a burn.
Caution • Advises you that failure to take or avoid a specific action could result in
physical harm to you, or could result in physical damage to the hardware.
Zebra Contacts
Support and Services: http://www.zebra.com/contact
Knowledge Base: https://km.zebra.com
P1035089-003 Wireless Reference Manual 7
Page 8

8 Wireless Reference Manual P1035089-003
Page 9

Contents
1 • Introduction . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1
2 • Networking Basics . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3
2.1 Overview . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3
2.2 Channels and communication modes . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4
2.3 Security . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5
2.4 Authentication . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5
2.5 Network name (SSID) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5
2.6 Encryption . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6
2.7 Media access control address authentication . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6
3 • Installing the Printer . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7
4 • Configuring the Printer. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 9
4.1 Overview . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 9
4.2 Configuration Options . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 10
4.3 Network Settings . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .11
4.4 Printer Web Page Option. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 12
4.5 ZXP Toolbox Option. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 16
4.6 Operator Control Panel Option . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 21
4.7 Using ZXP Toolbox Wireless Settings Load/Save . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 32
4.8 Using the RADIO CONTROL Menu . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 33
4.9 Using the SET DEFAULTS Menu . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 35
4.10 Simple Roaming Used During Connection . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 36
4.11 Setting Up an Ad-Hoc ( Peer ) Network. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 37
4.12 Multi-homing Considerations . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 41
P1035089-003 Wireless Reference Manual iii
Page 10

: Contents
5 • Monitor Wireless Performance . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 43
5.1 Overview . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 43
5.2 Wireless Info Pages. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 44
5.3 Signal Strength . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 46
5.4 Noise Floor . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 47
5.5 Data Rate . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 47
5.6 DHCP & MAC Address Info Page . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 48
5.7 Wireless Statistics Info Page . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 49
5.8 Wireless Statistics Success and Failure Rates . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 50
5.9 Main Status Display Wireless Errors . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 51
5.10 Viewing Wireless Information via Printer Web Page . . . . . . . . . . . . 53
5.11 Viewing Wireless Information via Driver Toolbox. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 54
6 • Troubleshooting . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 57
6.1 Introduction . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 57
6.2 Wireless Troubleshooting Checklist. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 58
6.3 Cannot Print Over Wireless Network. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 59
6.4 Improve Wireless Signal Strength . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 61
6.5 PSK 4-way Handshake Timeout . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 64
7 • Technical Specifications . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 65
8 • Glossary. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 69
iv Wireless Reference Manual P1035089-003
Page 11

1.1 Overview
This manual provides the following information about installing and connecting ZXP Series 7
and ZXP Series 8 Card Printers to a wireless network:
1
Introduction
1. The Networking basics chapter contains overview information about wireless networking
and the wireless features of the Printer.
2. The information for installing to a wireless network will be useful if you are installing the
printer to a wireless network for the first time, or if you wish to change printer or network
settings after you have installed the printer.
3. The Troubleshooting chapter contains a checklist on how to quickly diagnose set-up and
configuration issues.
References to “the Printer” in this document apply to either the ZXP Series 7 Card Printer or
the ZXP Series 8 Card Printer.
P1035089-003 Wireless Reference Manual 1
Page 12

2 Wireless Reference Manual P1035089-003
Page 13

2.1 Overview
ZXP Series 7 and ZXP Series 8 Card Printers have an internal print server that supports both
wired and wireless Ethernet connectivity. The wired Ethernet capability is standard with the
printer while the wireless capability is an option that can be ordered as a factory-installed
printer option. The wireless option is field upgradeable by a Zebra-authorized field technician,
but requires partial disassembly of the printer to remove the wired daughter card and replace it
with a wired/wireless daughter card (see separate document that describes daughter card
installation in the printer).
2
Networking Basics
The printer supports simultaneous wired and wireless connections, a capability referred to as
multi-homing, in this case having two separate interfaces with separate IP addresses. To
connect to a wireless network, the printer uses wireless protocol IEEE 802.11b/g that
communicates data through radio transmission. After installing the printer to a wireless
network, cables are not required to communicate with the computers or devices that are part of
the network.
A wireless local area network (WLAN) is a collection of two or more computers, printers, and
other devices linked by radio waves. A WLAN uses high-frequency airwaves (radio) to
communicate information from one point to another.
To connect a computer or device to a wireless network, the computer or device must have a
wireless network adapter. The Printer uses an internal networking component that contains a
wireless radio. No cabling is necessary between networked devices that use wireless
technology, although it is possible to use a USB or wired Ethernet cable to configure your
printer for a wireless network.
P1035089-003 Wireless Reference Manual 3
Page 14

2: Networking Basics
Channels and communication modes
2.2 Channels and communication modes
The band of radio signals used for IEEE 802.11b/g wireless networking is segmented into
specific frequencies, or channels. For IEEE 802.11b/g wireless networks, 13 channels are
available. Each country/region specifies the channels that are authorized for use. For example,
in North America, only channels 1 through 11 are allowed. In Japan, channels 1 through 14
can be used (channel 14 – 802.11b only). In most of Europe, channels 1 through 13 are
allowed. Because existing standards change frequently, you should check with your local
regulatory agencies for authorized channel use. In most countries/regions channels 10 and 11
may be used without restriction.
Channel selection depends on the communication mode of the network. The communication
mode defines how devices (i.e., computers and printers) communicate on a wireless network.
There are two primary types of wireless communication modes: infrastructure and ad-hoc.
• In infrastructure mode, the printer communicates with network computers through a
wireless access point (AP) or a base station. The access point acts as a central hub or
gateway connecting wireless and, optionally, wired devices (most access points have
integrated Ethernet controller to connect to an existing wired-Ethernet network).
an
• In the ad-hoc mode, which is sometimes called peer-to-peer mode, the printer
communicates with your computer directly, rather than through an access point or base
station. Each device on an ad-hoc network must have a wireless network adapter. The
adapter enables each device to communicate with the other devices on the network.
Ad-hoc mode is usually limited to simple, small wireless networks because performance
degrades significantly after connecting too many network devices. This option is most
often used if you are connecting only two network devices that are not sharing an
Internet connection. Only WEP security is available in ad-hoc mode.
4 Wireless Reference Manual P1035089-003
Page 15

2.3 Security
As with other networks, security for wireless networks focuses on access control and privacy.
Traditional wireless network security includes the use of Service Set Identifiers (SSIDs), open
or shared-key authentication and static Wired Equivalent Privacy (WEP) keys or WiFi
protected access (WPA or WPA2).
It is highly recommended that you implement a wireless security scheme (preferably WPA2)
prior to setup. While the printer can connect to an open AP, running an open wireless AP may
allow anyone within range of the AP full access to all devices connected to the AP with
potentially damaging results. While WEP security is still in use today, WEP security has been
broken for many years. There are tools available on the Internet that will allow anyone with
even basic networking knowledge to break the WEP security and derive the WEP key within 3
minutes, giving them full access to devices on your network. The best security is obtained by
using WPA2 security with CCMP/AES encryption.
Authentication and encryption are two different mechanisms to network security.
Authentication verifies the identity of a user or device before granting access to the network,
making it more difficult for unauthorized users to access network resources. Encryption
encodes the data being sent across the network, making the data unintelligible to unauthorized
users. Both of these mechanisms are on wireless networks.
2: Networking Basics
Security
2.4 Authentication
The Printer supports Open System authentication. A network with Open System
authentication does not screen network users based on their identities and usually involves
supplying the correct SSID. Such a network might use Wired Equivalent Privacy (WEP)
encryption to provide a first level of security, or WiFi protected access (WPA/WPA2) to
provide security by encrypting data sent over radio waves from one wireless device to another
wireless device. The printer allows for WEP, WPA or WPA2.
2.5 Network name (SSID)
Wireless devices are configured with the name of the network to which they will connect. The
network name is also called the SSID and identifies the ESS (Extended Service Set) that is
normally associated with larger infrastructure networks. The SSID should not be considered a
security feature because it can be easily identified. However, as a network administration or
management feature, it does provide basic network access control.
It is common practice to setup access points such that the SSID is not broadcast (i.e., hidden
invisible). The printer can connect to invisible access points, although the user must know
or
SSID name and correctly enter it into the printer. There is a belief that hiding the SSID
the
adds extra security to the network. This is, in fact, false as a device connecting to a network
must send the SSID in the clear and the SSID can be easily obtained from the association
management frame. Hiding the SSID makes it more error prone to connect to a network.
P1035089-003 Wireless Reference Manual 5
Page 16

2: Networking Basics
Encryption
2.6 Encryption
To reduce your network exposure to eavesdropping, establish a wireless security key for your
network. The printer supports the WEP RC4 encryption, WPA TKIP encryption and WPA2
CCMP encryption (a form of AES encryption), which hinders unauthorized users from
accessing data transmitted over the radio waves. For WEP, a single static WEP key (40 or
bits) is installed in the printer. Each computer or device is configured with the same key
104
communicate on that network. The most secure encryption is achieved using WPA2
to
CCMP.
with
WPA and WPA2 security provides the means to deploy dynamic encryption keys to devices on
the network. There are two approaches that are used for key deployment which are usually
referred to as Personal and Enterprise. In the Personal mode, a Pre-Shared Key (PSK) is
deployed on each network access point and device. The PSK is then used to derive Transient
Keys which are used between an access point and the devices which are connected to it. In the
Enterprise mode, an authentication server is used to deploy keys using one of several available
Extensible Authentication Protocols (EAP).
For WPA or WPA2 Personal, a single, 8 – 63 character passphrase is entered into the access
point. The same passphrase must be entered into the printer. The access point and printer each
derive the same 32 byte PSK from the passphrase using the password-based key derivation
function 2 (PBKDF2) from RFC 2898. The importance of picking a secure passphrase cannot
be overstressed. The most prevalent security attack against WPA-PSK is a brute force
dictionary attack, using a list of common words to “guess” your passphrase. So a passphrase
like “darthvader” could result in your security being quickly compromised.
When constructing your passphrase, keep the following suggestions in mind:
• Use more than 8 characters. The more characters, the more secure.
• Use a combination of uppercase, lower case, numeric and punctuation characters.
• Use random characters, avoid using recognizable words from any language.
2.7 Media access control address authentication
Some WLAN vendors support authentication based on the physical address, or MAC address,
of the client Network Interface Card (NIC). In this scenario, an access point allows association
by a client only if that client’s MAC address matches an address in an authentication table
used by the access point. This is not configurable through the printer.
6 Wireless Reference Manual P1035089-003
Page 17

3
Installing the Printer
Important • Only use the antenna that is shipped with the printer to ensure regulatory
compliance for the transmit power.
The printer with the wireless option ships with the wireless radio installed in the printer. An
antenna is shipped in the box with the printer. The antenna must be connected to the rear of the
printer before using the wireless interface. Lightly push the antenna onto the printer antenna
connector and rotate the knurled antenna connector until finger tight.
The antenna used for this transmitter must be installed to provide a separation distance of at
least 20 cm (8 inches) from all persons and must not be co-located or operating in conjunction
with any other antenna or transmitter
during use the antenna is no closer than 20 cm to the body of any persons in the area of the
printer and that the during normal use of the printer the distance is maintained. The antennas
for any other transmitters should be separated from the printer antenna by at least 20 cm. This
is required for RF exposure compliance.
The antenna orientation is important to maximize the wireless signal strength. Inspect the
access point antenna(s) and try to put the printer antenna in a similar orientation.
connecting the printer to the wireless network, the antenna orientation can be adjusted to
maximize signal strength.
802.11b/g has an indoor open range of 100 ft at maximum data rate and 300 ft at minimum
data rate.
decreases. If there are intervening walls, unpredictable signal strength attenuation will occur.
Decreasing signal strength results in automatic data rate reduction. At the longest distance,
network traffic can become very slow.
As the distance between the printer and the access point increases, the signal strength
. This means that the printer must be positioned such that
After
P1035089-003 Wireless Reference Manual 7
Page 18

3: Installing the Printer
Printer location is important to ensure that adequate signal strength is achieved. Follow these
suggestions:
• Position the printer as close to the access point that it will connect to as possible.
• If possible, orient the printer such that there is a clear line of sight between the printer
antenna and the access point antenna.
• Locate the printer such that there are no intervening walls in the line of sight
antennas.
between
• Do not put the printer in a cabinet, especially not a metal one.
• Do not locate large metal objects close to the printer antenna.
• Do not locate the printer close to devices that emit RF radiation in the 2.4 GHz range.
Such devices might include: microwave ovens, cordless phones, wireless surveillance
cameras, baby monitors, wireless video transmitter and Bluetooth
Once you have your printer connected to a wireless network, the printer can provide
information on the quality of the connection to the network. If the quality is poor, there are
several approaches that can be taken to improve the quality.
® devices.
8 Wireless Reference Manual P1035089-003
Page 19

Configuring the Printer
4.1 Overview
To set up the printer for wireless printing, you need to know:
4
• The name of your wireless network, also known as the Service Set Identifier (SSID).
• If encryption was used to secure your network.
• The security key (WEP key, WPA passphrase, or hex key) that allows other devices to
communicate on the network if encryption was used to secure your network.
• If the access point you will connect to doesn’t broadcast the SSID, you will need to
know the BSSID (MAC Address of the wireless interface) for the AP. Make sure that
you have the correct MAC address, your AP may have several.
If your wireless access point is using Wired Equivalent Privacy (WEP) security, the WEP key
should be exactly 10 or 26 hexadecimal characters. Hexadecimal characters are A–F, a–f,
0–9.
and
If your wireless access point is using WiFi Protected Access (WPA or WPA2) security, the
WPA passphrase should be from 8 to 63 ASCII characters. ASCII characters in a WPA
passphrase are case-sensitive.
If your wireless network is not using security, then you will not need a security key. Using a
wireless network with no security is not recommended because it can allow intruders to use
your network resources without your consent. Intruders could then read and decode your
transmissions with readily available tools found on the Internet.
P1035089-003 Wireless Reference Manual 9
Page 20

4: Configuring the Printer
Configuration Options
4.2 Configuration Options
Note • Make sure you copy down the security key and SSID exactly, including any capital
letters, and store it in a safe place for future reference. If you do not know the SSID of the
network that your computer is connected to, launch the wireless utility of the computer
network adapter and look for the network name. If you cannot find the SSID or the security
information for your network, see the documentation that came with the wireless access
point, or contact your network support person.
There are three ways to configure the printer to connect to a wireless network:
• Configure the printer through the printers Web Page using wired Ethernet; refer to
Section 4.4 on page 12 for details.
• Configure the printer through the Windows Printer Driver Toolbox using USB or
wired Ethernet; refer to Section 4.5 on page 16 for details.
• Configure the printer through the Operator Control Panel.; refer to Section 4.6 on
page 21 for details.
10 Wireless Reference Manual P1035089-003
Page 21

4.3 Network Settings
Every device connected to an Ethernet network must be assigned an IP Address, Subnet Mask
and Default Gateway Address. An IPv4 Address consists of a 32-bit binary number, which is
typically presented as four decimal numbers (one for each 8-bit byte) separated by decimal
points (for example: 192.168.0.100). The subnet mask determines what subnet an IP address
belongs to. A typical subnet would be 255.255.255.0. As applied to the previous example,
devices with IP Addresses in the range of 192.168.0.1 through 192.168.0.255 would all be in
the same subnet. The default gateway is the node connecting the internal networks and the
outside network (Internet).
In order to configure the printer, these settings must be known or DHCP must be used to
automatically configure the printer. If the network has a DHCP server, the printer can request
the network settings from the DHCP server after establishing a connection to the access point.
Otherwise, these settings must be known and manually entered into the printer. Check with
your network administrator if you are not sure about whether to use DHCP or manual settings.
When using DHCP, be aware that the DHCP server may periodically change the IP Address
assigned to the printer. If this happens, the Windows Printer Driver may no longer be able to
communicate with the printer. To prevent this, DHCP servers can be configured to lock an IP
Address to a specific MAC address. Obtain the wireless MAC address from the Operator
Control Panel (make sure you get the correct MAC Address, there are two, one for wired and
one for wireless) and use this to configure the DHCP server. Some DHCP servers are
configured to reject DHCP requests from unknown devices. Again, the MAC address can be
used to configure the DHCP server or access point to recognize the printer.
4: Configuring the Printer
Network Settings
If you plan to use both wired and wireless Ethernet interfaces at the same time, see the “Multihoming Considerations” section. The configuration of the IP Address and Subnet Mask on
each interface must be set correctly depending upon whether the two interfaces are connected
to the same network or totally separate networks. Improperly configured network settings may
result in a communications failure.
P1035089-003 Wireless Reference Manual 11
Page 22

4: Configuring the Printer
Printer Web Page Option
4.4 Printer Web Page Option
Note • The screens shown in this section are for the ZXP Series 7 Card Printer; the screens
for the ZXP Series 8 are virtually identical.
Configuring Wireless through the Printer Web Page requires that the printer be connected to
a computer through wired Ethernet. Set the DHCP mode, IP
Default Gateway as needed for the wired interface.
If DHCP is enabled, use the OCP INFO soft-key to determine the IP Address for the wired
Ethernet. Open a browser window on a computer connected to the same network as the printer
and enter the printer IP address; e.g., http://10.1.23.26
The printer web page should then display:
Address, Subnet Mask, and
Click on the “Wireless Parameters” entry from the list of the left of the web page, and enter
User name (admin) and Password (1234).
12 Wireless Reference Manual P1035089-003
Page 23

The web page should look like:
4: Configuring the Printer
Printer Web Page Option
If the access point you want to connect to is not shown, Click Scan for Wireless Networks
until it is shown. Pick the desired access point using the Select radio button on the left of
the list.
Note that Scan for
Points. Update Scan for Wireless Networks appends additional Access Points found without
first clearing the Access Point list.
Note the Alternate Connect check box.
• If Alternate Connect is left unchecked, the printer automatically selects the highest
Security & Encryption available.
• If the Alternate Connect check box is checked, the user will be allowed to select the
Security & Encryption that will be used if more than one is available.
Click Connect
Wireless Networks clears the Access Point list and scans for Access
To Selected Wireless Network to proceed.
P1035089-003 Wireless Reference Manual 13
Page 24

4: Configuring the Printer
Printer Web Page Option
The web page changes to:
Enter any information required, like: SSID, Security, Encryption, and Passphrase (in the above
example, only the Passphrase needs to be entered as indicated by the edit box).
Click Connect.
Wait for connection to complete or for an error message.
14 Wireless Reference Manual P1035089-003
Page 25

4: Configuring the Printer
Printer Web Page Option
When successfully connected to the wireless network, the web page changes to:
The wireless parameters were automatically saved so that the printer will automatically
connect the next time the printer is powered on. The wired Ethernet connection can now be
disconnected if desired.
P1035089-003 Wireless Reference Manual 15
Page 26
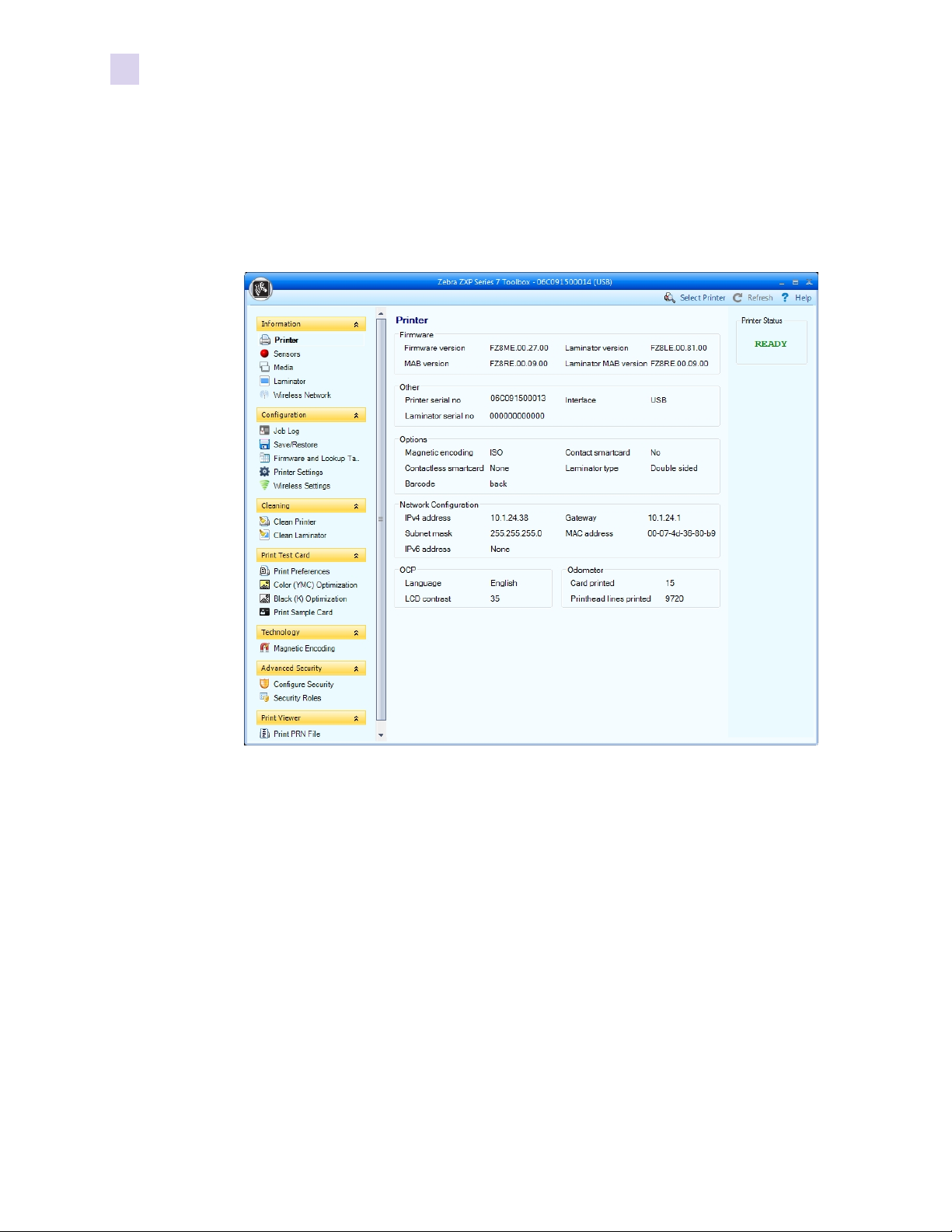
4: Configuring the Printer
ZXP Toolbox Option
4.5 ZXP Toolbox Option
This requires that the printer be connected to a computer through USB or wired Ethernet with
the Windows printer driver installed and functional. Refer to the appropriate Printer User’s
Manual for instructions on driver installation. Once the Windows printer driver is installed and
functioning, open the ZXP Toolbox. The following screen will be displayed:
Under the Configuration section, click on Wireless Settings.
16 Wireless Reference Manual P1035089-003
Page 27

The following screen will be displayed:
4: Configuring the Printer
ZXP Toolbox Option
There are two approaches that can be used to configure the printer’s wireless settings:
• If all the necessary information is known (SSID, BSSID, Channel, Security,
Encryption, and Passphrase) these parameters can be directly entered into the
W
ireless Configuration.
• The alternate approach is to request that the printer scan for wireless access points and
select one.
This automatically fills in most of the Wireless Configuration parameters.
Step 1:
Make any changes needed to DHCP Enable, IP Addr
ess, Subnet Mask, and Gateway.
If directly entering the wireless settings, skip to Step 4.
P1035089-003 Wireless Reference Manual 17
Page 28

4: Configuring the Printer
ZXP Toolbox Option
Step 2:
Press the Scan button to initiate a scan. Once the scan is complete, scroll through the wireless
access points and select the one you want to connect to using the associated checkbox.
display should look like:
The
Step 3:
If the SSID is not displayed (access point configured to not broadcast SSID), enter the SSID.
Select the desired Security and Encryption.
The choices will be limited to what the access
point can accept. If the access point is configured for WEP, you must choose correctly
between WEP40 and WEP104 (there is no way do determine the WEP key size via the ZXP
Toolbox). Skip to Step 5.
18 Wireless Reference Manual P1035089-003
Page 29

4: Configuring the Printer
ZXP Toolbox Option
Step 4:
Enter the SSID, BSSID (format xx:xx:xx:xx:xx:xx), Channel, Security, and Encryption.
Channel setting is a hint to the printer about which channel the access point will located
The
on. Providing the correct channel will result in a faster connection to the access point when
powering up the printer. If you enter the wrong channel it will not cause the connection to fail.
The printer will first scan for the access point on the indicated channel and if not found will
widen the search to all channels. Some wireless access points can be configured to auto
their channel when powered on (channel used may be different each time). In this case
select
set the channel to zero, which tells the printer to scan all channels to find the access point
before connecting. If you don’t know the correct channel, setting the channel to zero is the
choice.
best
Set the Security entry before Encryption. The Encryption choices will be limited by the
Security setting.
IMPORTANT! When using manual entry of wireless settings, you must be careful to enter all
the data correctly or the printer may fail to connect to an access point. If you are not sure about
the settings, check with your IT department. Most access points provide a web page for
configuration. If you can access this web page you can determine the proper settings for SSID,
BSSID, Channel, Security, and Encryption. Be careful with the Security and Encryption
settings. An access point may be configured to allow only certain Security/Encryption
capabilities, like only WPA2/CCMP. In this case, trying to connect with WPA/TKIP
fail.
would
Step 5:
Enter the Key (if using WEP40 or WEP104) or the Passphrase (if using WPA or WPA2). If
the security is WEP, you must enter exactly 10 (WEP40) or 26 (WEP104) hex characters
(0 – 9, A – F). If the security is WPA or WPA2, you must enter at least 8 printable ASCII
characters for the passphrase. The key or passphrase must be identical to the one that has
entered into the wireless access point. Check with your IT department to get the correct
been
passphrase.
key or
IMPORTANT! Entering an incorrect WEP key will not result in a failure to connect, but
communications with the printer will not work through the wireless interface. Entering an
incorrect WPA/WPA2 passphrase will result in a connection failure. It is very important to use
the correct key or passphrase and enter it correctly.
P1035089-003 Wireless Reference Manual 19
Page 30

4: Configuring the Printer
ZXP Toolbox Option
Step 6:
Press the Connect button.
A dialog box displays to indicate that the connection process has
been initiated. Press Ok to remove the dialog. Under the Information section on the left side
of the Toolbox click Wireless Network. The following dialog appears:
Check the Status section. If the connection succeeded, the State parameter should be
“connected”. If the State is “inactive”, then the connection failed, probably due to the WPA/
WPA2 passphrase being incorrect. If the State is “scanning”, then the access point wasn’t
found and periodic scans are underway to find the access point. This may mean that the SSID
or BSSID was entered incorrectly. If you are connecting with WEP security, the only way to
know that the WEP key is correct is to try to communicate with the printer through the
wireless interface. If the communication fails then it is likely the WEP key was entered wrong.
20 Wireless Reference Manual P1035089-003
Page 31

4.6 Operator Control Panel Option
When powered up, the OCP will display the following:
READY
MENU INFO
Press the MENU soft-key and the display changes to:
RETURN
> PRINT TEST CARDS
> NETWORK SETTINGS
> LAMINATOR SETTINGS
> ADVANCED SETTINGS
> WIRELESS SETTINGS
UP DOWN SELECT
4: Configuring the Printer
Operator Control Panel Option
Press the DOWN soft-key until “WIRELESS SETTINGS” is highlighted in reverse video then
press SELECT and the display changes to:
RETURN WITHOUT SAVE
SAVE SETTINGS
> RADIO CONTROL
> SETUP WIZARD
> DHCP MODE
> SET IP ADDRESS
UP DOWN SELECT
P1035089-003 Wireless Reference Manual 21
Page 32

4: Configuring the Printer
Operator Control Panel Option
There are several selections hidden. These can be seen by pressing the DOWN soft-key. The
selections are as follows:
Menu Selection Description
RETURN WITHOUT SAVE Exit the current menu, returning to the previous menu.
SAVE SETTINGS Save any setting that have been changed then return to the
RADIO CONTROL Turn the radio on or off.
SETUP WIZARD Enter the setup wizard, which takes you through the steps to
DHCP MODE Enable/disable DHCP mode.
SET IP ADDRESS Set the IP Address. Only needed if DHCP is disabled.
SET SUBNET MASK Set the Subnet Mask. Only needed if DHCP is disabled.
SET DEFAULT GATEWAY Set the Default Gateway. Only needed if DHCP is disabled.
previous menu.
after a power cycle.
connect to an access point one step at a time.
The printer will then remember these settings
SET DEFAULTS Erase all the wireless settings. If the radio is on, the radio is
turned of
need to also select “SAVE SETTINGS”.
f. If you want the defaults to be permanent, you will
22 Wireless Reference Manual P1035089-003
Page 33

4: Configuring the Printer
Operator Control Panel Option
Step 1:
Determine whether you plan to enable DHCP to automatically obtain the IP Address, Subnet
Mask, and Gateway
Address. Enter the DHCP Mode menu by pressing the DOWN soft-key
until “DHCP MODE” is highlighted then press SELECT and the display changes to:
RETURN
DHCP ENABLE
DHCP DISABLE
UP DOWN SELECT
Use the UP and DOWN soft-keys to highlight “DHCP ENABLE” or “DHCP DISABLE” then
press the SELECT soft-key.
If you enabled DHCP, you do not need to enter an IP Address, Subnet Mask, and Default
Gateway
. Skip to Step 5.
If you disable DHCP, it is very important that you enter the correct IP Address, Subnet Mask
and Default Gateway for the network. If any of them are entered wrong, the communications
may fail.
The IP Address that you use must not be assigned to any other device on your
network. If you are not sure what settings to use, check with your IT department.
You can also inspect the settings for a computer on your network. On Windows XP, click Start
then Run. In the Open box type “cmd” then click Ok to open a Command Prompt window and
type “ipconfig /all” at the prompt.
You can then see the IP Address, Subnet Mask, and Default
Gateway the computer is configured to use. It is likely that you can use the same Subnet Mask
and Gateway settings in your printer. You will need to use a different and unused IP Address.
To verify that the one you plan to use is available, type “ping xx.xx.xx.xx” at the command
prompt where xx.xx.xx.xx is the IP Address you plan to use. If the ping times out, that means
that no device on the network with that IP Address responded. This is not a guarantee that the
IP Address is available as a device with that IP Address could be powered down or temporarily
disconnected from the network.
P1035089-003 Wireless Reference Manual 23
Page 34

4: Configuring the Printer
Operator Control Panel Option
Step 2:
Enter the Set IP Address menu by pressing the DOWN soft-key until “SET IP
ADDRESS” is
highlighted then press SELECT and the display changes to:
IP: 000.000.000.000
CHANGE NEXT EXIT
Use the CHANGE soft-key to change the selected digit. Each press of CHANGE increases
the digit value by 1 with a roll-over to zero when necessary. The selected digit will flash. Use
the NEXT soft-key to advance to the next digit in the sequence. Pressing NEXT when the last
digit is selected will result in the first digit being selected.
Press EXIT to save the current IP
Address and exit the menu. Before pressing EXIT, all of the
digits on the display must match the desired IP Address.
Step 3:
Enter the Set Subnet Mask menu by pressing the DOWN soft-key until “SET SUBNET
MASK” is highlighted then press SELECT and the display changes to:
MASK: 000.000.000.000
CHANGE NEXT EXIT
Use the CHANGE soft-key to change the selected digit. Each press of CHANGE increases
the digit value by 1 with a roll-over to zero when necessary. The selected digit will flash. Use
the NEXT soft-key to select the next digit in the sequence. Pressing NEXT when the last digit
is selected will result in the first digit being selected.
Press EXIT to save the current Subnet Mask and exit the menu. Before pressing EXIT, all of
the digits on the display must match the desired Subnet Mask.
24 Wireless Reference Manual P1035089-003
Page 35

Step 4:
4: Configuring the Printer
Operator Control Panel Option
Enter the Set Default Gateway menu by pressing the DOWN soft-key until SET DEF
AULT
GATEWAY is highlighted then press SELECT and the display changes to:
GW: 000.000.000.000
CHANGE NEXT EXIT
Use the CHANGE soft-key to change the selected digit. Each press of CHANGE increases
the digit value by 1 with a roll-over to zero when necessary. The selected digit will flash. Use
the NEXT soft-key to select the next digit in the sequence. Pressing NEXT when the last digit
is selected will result in the first digit being selected.
Press EXIT to save the current Default Gateway
Address and exit the menu. Before pressing
EXIT, all of the digits on the display must match the desired Default Gateway Address.
Step 5:
Save the current configuration to permanent storage. This will insure that the DHCP Mode, IP
Address, Subnet Mask, and Default Gateway are remembered by the printer after a power
cycle. Use the UP and DOWN soft-keys to highlight SA
VE SETTINGS, then press the
SELECT soft-key. This will return you to the Wireless Settings menu.
P1035089-003 Wireless Reference Manual 25
Page 36

4: Configuring the Printer
Operator Control Panel Option
Step 6:
From the Wireless Settings menu, enter the Setup Wizard menu by pressing the DOWN softkey until SETUP
WIZARD is highlighted; then press SELECT and the display changes to:
Press the SCAN soft-key to begin scanning for access points that are within range of your
printer, or press EXIT to exit this menu and return to the Wireless Settings menu.
After pressing the SCAN soft-key, the display changes to:
BEGIN CONNECTING YOUR
PRINTER TO A WIRELESS
ACCESS POINT. PRESS
SCAN TO START.
SCAN EXIT
WAIT WHILE SCAN
COMPLETES. USE NEXT
TO SCROLL THROUGH
AP'S AND SELECT ONE.
CANCEL
The printer will conduct active scans on all the channels allowed for your regulatory domain.
The scanning process is repeated multiple times over all the channels to insure that all AP’s are
identified. This can take over a minute to complete. Once the scanning process completes the
display changes to:
SSID: Test
MAC:00:a0:f8:be:fe:72
Chan = 1 SIG = 52%
SEC MODE: WPA
CRYPTO: TKIP
MAX SPEED: 54 Mbps
NEXT SELECT CANCEL
26 Wireless Reference Manual P1035089-003
Page 37

4: Configuring the Printer
Operator Control Panel Option
The OCP will display the information for a single access point.
st
• The 1
• The 2
line indicates the SSID.
nd
line indicates the BSSID or MAC Address for the access point. If the SSID
name is too long to fit on the top line of the display, it will wrap to the 2
nd
BSSID will not be displayed. If the SSID of the access point is not broadcast (hidden or
invisible), the SSID will display as: SSID: <HIDDEN>
line and the
• The 3
rd
line indicates the channel the access point operates on (can be 1 – 13) and the
signal strength in percent (more information on signal strength is provided later in
this document).
• The 4
th
line indicates the security mode the access point is configured to use. This could
be: NONE, WEP, WPA, WPA2 or WPA & WPA2 (both available simultaneously).
• The 5
th
line indicates the type of encryption being used by the access point. This could
be: NONE, RC4 (used for WEP), TKIP, CCMP (a variant of AES) or TKIP & CCMP
(both available simultaneously). The 5
th
line indicates the maximum data rate supported
by the access point. This will usually be 11 Mbps if the access point is only capable of
802.11b and 54 Mbps if the access point is capable of 802.11g.
Pressing the NEXT soft-key advances the display to the next access point found during the
scan.
When the last access point found is displayed, pressing NEXT will cause the first access
point to display again. The CANCEL soft-key can be pressed at any time to abort the Setup
Wizard and return to the main Wireless menu.
By knowing the SSID and/or BSSID, the access point you wish to connect to can be found in
the scan list.
There may be occasions where the access point of interest is not displayed. This
can happen due to noise or interference during the scanning. If you can’t find the access point,
press the CANCEL soft-key and retry the Setup Wizard until the access point is found. Once
the access point you wish to use is displayed on the OCP, press the SELECT soft-key.
If the signal strength for the selected access point is less than 25%, the display changes to:
THE SIGNAL STRENGTH
IS < 25%. TRY
CHANGING ANTENNA
ORIENTATION OR MOVE
PRINTER CLOSER.
NEXT CANCEL
When the signal strength is less than 25%, it is likely that you will have problems connecting
to the access point or have problems after the connection is established. This is only a alert to
offer you the opportunity to resolve potential problems by improving the signal strength before
continuing. Press the CANCEL button to exit the Setup Wizard or NEXT to continue
connecting to this access point.
P1035089-003 Wireless Reference Manual 27
Page 38

4: Configuring the Printer
Operator Control Panel Option
If the SSID is hidden, it is necessary to enter the SSID manually, otherwise this step is
bypassed. The display for manually entering the SSID looks like:
The SSID must be entered one character at a time. Each character can be any visible ASCII
character. The character that is currently being set will slowly blink. Use the CHANGE soft
key to cycle through the ASCII character set until the desired character is shown (Remember
that the SSID is case sensitive). If there are more characters that need to be set, then press the
NEXT soft-key to add another character and use the CHANGE soft-key to select the correct
ASCII character.
ENTER SSID, 1 - 32
CHARACTERS:
0
CHANGE NEXT CANCEL
When the last character has been set (and while it is still blinking) press the EXIT soft-key to
complete the SSID entry
. (IMPORTANT - Do not press the NEXT soft-key after the last
character has been set, otherwise you will need to repeat this entire step.) Note that entering
the SSID text incorrectly will prevent successful connection to the access point.
If the access point security is set to WEP, the display changes to:
SELECT WEP KEY SIZE.
WEP40 WEP104 CANCEL
If the access point security supports both WPA and WPA2, the display changes to:
SELECT SECURITY MODE.
IF YOU ARE UNSURE,
PICK WPA2.
WPA WPA2 CANCEL
28 Wireless Reference Manual P1035089-003
Page 39

4: Configuring the Printer
Operator Control Panel Option
When selecting the WEP key size, you must know the key size that the access point is
configured with. Once you press either the WEP40 or WEP104 soft-key, you will need to
enter the WEP key and the display changes to:
ENTER WEP KEY, 10 HEX
CHARACTERS:
0000000000
CHANGE NEXT EXIT
-OR-
ENTER WEP KEY, 26 HEX
CHARACTERS:
000000000000000000000
00000
CHANGE NEXT EXIT
Use the CHANGE soft-key to scroll through the hex character choices (0 -9, A – F). Use the
NEXT soft-key to select the next character position to change. The blinking character
indicates the character position that is selected. When the display exactly matches the WEP
key of the access point, press the EXIT soft-key.
For WPA and WPA2, you may need to select the encryption mode if more than one is
available. If this is the case, the display changes to:
SELECT ENCRYPTION
MODE. IF YOU ARE
UNSURE, PICK CCMP.
CCMP TKIP CANCEL
P1035089-003 Wireless Reference Manual 29
Page 40

4: Configuring the Printer
Operator Control Panel Option
Press either the CCMP or TKIP soft-key to select the encryption mode. Remember that
CCMP is the stronger encryption. For WPA and WPA2, after the security mode and encryption
modes have been selected or automatically determined (if only one mode is available, the
selection display is bypassed), the WPA Passphrase must be entered. The display changes to:
The passphrase must be entered one character at a time. Each character can be any visible
ASCII character. The character that is currently being set will slowly blink. Use the CHANGE
soft key to cycle through the ASCII character set until the desired character is shown
(Remember that the passphrase is case sensitive). If there are more characters that need to be
set, then press the NEXT soft-key to add another character and use the CHANGE soft-key to
select the correct ASCII character.
ENTER WPA PASSPHRASE
8 – 63 CHARACTERS:
0
CHANGE NEXT EXIT
When the last character has been set (and while it is still blinking) press the EXIT soft-key to
complete the passphrase entry
. The EXIT key will not work until at least 8 characters have
been entered. (IMPORTANT - Do not press the NEXT soft-key after the last character has
been set otherwise you will need to repeat this entire step.) Note that entering the passphrase
text incorrectly will prevent successful connection to the access point.
At this point, all the information has been collected that is necessary to connect to the access
point. Please be aware that not all of the Setup
Wizard screens shown above will be seen. The
printer will bypass screens that are unnecessary to display. For instance, if an access point is
setup with only WPA security, only TKIP security and the SSID is broadcast, only the “Enter
WPA Passphrase” setup screen will be seen. The display should now be:
THE PRINTER IS READY
TO CONNECT TO THE AP.
PRESS CONNECT TO
PROCEED.
CONNECT CANCEL
30 Wireless Reference Manual P1035089-003
Page 41

4: Configuring the Printer
Operator Control Panel Option
The CANCEL soft-key can be used to exit the Setup Wizard without connecting. Press the
CONNECT soft-key to connect to the access point. The printer will conduct a wireless
authentication and association, and then proceed with security key handshaking with the
access point if necessary. The display changes to:
WAIT FOR THE AP
CONNECTION TO
COMPLETE.
CANCEL
If the connection completes successfully, the current wireless settings are automatically saved
so that the printer will automatically re-connect after a power cycle. The display changes back
to the main wireless menu. The “RETURN WITHOUT SAVE” selection can be used to exit
from the wireless menu.
The antenna icon on the OCP will be active, providing an indication of the signal strength with
up to 4 bars. If connection to the access point fails, the display will change to:
AP CONNECTION FAILED.
CHECK KEY, SSID AND
SIGNAL STRENGTH.
CANCEL
If this occurs, there is likely a problem with the data entered or the signal strength is too low to
reliably connect to the access point. Try improving the signal strength if below 50%. Make
sure that the SSID and security key/passphrase is correct then retry the Setup Wizard. If
connection still fails, refer to the troubleshooting section for additional help.
P1035089-003 Wireless Reference Manual 31
Page 42

4: Configuring the Printer
Using ZXP Toolbox Wireless Settings Load/Save
4.7 Using ZXP Toolbox Wireless Settings Load/Save
When configuring wireless through the toolbox, after you establish a successful connection,
you can click the Save button to save all the wireless settings as a profile to an XML file. The
Load button can then be used to load the settings from a previously saved profile XML file.
This provides a means to quickly restore connection to a particular access point or select
connection to one of several access points available using different profiles. It might also be
useful to setup a group of printers to all connect to the same access point.
IMPORTANT!
• When using the Save button (not recommended) the WEP key or WPA passphrase
be saved in the XML file.
can
• If you are concerned about the security risk of exposing the key or passphrase in a plain
text file, then check the Don’t save Key/Pass Phrase check box (recommended). In this
case, the key or passphrase will not be saved to the file.
When the Load button is used, the key or passphrase will need to be manually entered if not
saved in the file.
32 Wireless Reference Manual P1035089-003
Page 43

4.8 Using the RADIO CONTROL Menu
The Radio Control menu allows you to turn the radio on and off. After selecting the menu, the
display changes to:
RETURN
RADIO ENABLE
RADIO DISABLE
UP DOWN SELECT
Use the UP and DOWN soft-key to select enable or disable then press SELECT. If the radio is
connected and you select disable, the radio is disconnected from the access point. If the radio
is not connected and you select enable and the stored wireless parameters are valid, a
connection to the access point is attempted. The display changes to:
4: Configuring the Printer
Using the RADIO CONTROL Menu
WAIT FOR THE AP
CONNECTION TO
COMPLETE.
CANCEL
If the connection succeeds, the display changed back to the main wireless menu. Before
attempting a connection, the wireless parameters are checked to see if they are valid (this
doesn’t guarantee that a connection will occur as the parameters may be valid but not correct
for the access point). If the parameters are found to be invalid, the display changes to:
THE WIRELESS SETUP IS
INCOMPLETE AND THE
RADIO CAN'T BE TURNED
ON. SET DHCP, IP ADDR
AND NETMASK. RUN THE
SETUP WIZARD.
CANCEL
In this case, the Setup Wizard should be run again to establish valid wireless parameters.
P1035089-003 Wireless Reference Manual 33
Page 44

4: Configuring the Printer
Using the RADIO CONTROL Menu
If the wireless parameters are valid, but the connection still fails, the display changes to:
This could happen if the access point itself has been modified and the wireless parameters
stored in the printer are incorrect. Run the Setup Wizard to establish new parameters
that work.
If you change the state of the radio, the resulting change is not saved. If you wish the state to
be permanent, make sure you execute SA
AP CONNECTION FAILED.
TRY RUNNING SETUP
WIZARD INSTEAD.
CANCEL
VE SETTINGS in the main wireless menu.
34 Wireless Reference Manual P1035089-003
Page 45

4.9 Using the SET DEFAULTS Menu
Executing this menu results in all the wireless parameters being set to default and
saved.
permanently
This might be useful if you wish to flush the wireless settings from the printer for security
purposes or to enter all the settings from scratch for troubleshooting.
Once this is executed, you will need to conduct the entire setup procedure in order to connect
to an access point.
4: Configuring the Printer
Using the SET DEFAULTS Menu
P1035089-003 Wireless Reference Manual 35
Page 46

4: Configuring the Printer
Simple Roaming Used During Connection
4.10 Simple Roaming Used During Connection
While the printer does not support full roaming such as might be available in a mobile wireless
device such as an iPhone, the printer does support a limited roaming capability during
connection. When the printer tries to establish a connection to an access point, it takes the
following steps until connection is established:
1. Scan for the configured access point (using both SSID and BSSID) on the configured
channel. If no access point found, proceed to step 2. If found, connection is attempted. If
connection successful, proceed to step 6 (done). If connection fails, proceed to step 3.
2. Scan for the configured access point (using both SSID and BSSID) on all channels. If no
access point found, proceed to step 3. If found, connection is attempted. If connection
successful, proceed to step 6 (done). If connection fails, proceed to step 3.
3. Scan for all access points with the correct SSID (BSSID ignored) that have the identical
security settings as the configured access point on all channels. If no access point found,
proceed to step 5. If multiple access points found, connection is attempted on access point
with best signal strength. If connection successful, proceed to step 6 (done). If connection
fails, proceed to step 4. If single access point found, connection is attempted. If connection
successful, proceed to step 6 (done). If connection fails, proceed to step 5.
4. Delete access point to which connection failed in step 3. If another access point with
correct SSID and correct security settings is available, go to step 3. Otherwise, go
the
step 5.
to
5. Exhausted all connection attempt, delay for 5 seconds, then go to step 1.
6. Connection succeeded, done.
This approach will handle the following conditions:
• Configured access point can’t be reached (power is off).
• Configured access point can’t accept another station (load balancing is forcing the
printer to connect to a different access point).
36 Wireless Reference Manual P1035089-003
Page 47

Setting Up an Ad-Hoc ( Peer ) Network
4.11 Setting Up an Ad-Hoc ( Peer ) Network
On wireless computer networks, ad-hoc mode is a method for wireless devices to directly
communicate with each other. Operating in ad-hoc mode allows all wireless devices within
range of each other to discover and communicate in peer-to-peer fashion without using access
points. To set up an ad-hoc wireless network, each wireless adapter must be configured for adhoc mode versus the alternative infrastructure mode. In addition, all wireless adapters on the
ad-hoc network must use the same SSID and the same channel number. An ad-hoc network
tends to feature a small group of devices all in very close proximity to each other. Performance
suffers as the number of devices grows, and a large ad-hoc network quickly becomes difficult
to manage.
WiFi devices in ad-hoc mode offer minimal security against unwanted incoming connections.
Only WEP security is available in the ad-hoc mode. Ad-hoc WiFi devices cannot disable SSID
broadcast like infrastructure mode devices can. Attackers generally will have little difficulty
connecting to an ad-hoc device if they get within signal range.
The security hole provided by ad-hoc networking is not the ad-hoc network itself but the
bridge it provides into other networks, usually in the corporate environment. If a computer
using an ad-hoc connection is also using a wired or wireless infrastructure network at the same
time, it is providing a bridge to the secured organizational network through the unsecured Adhoc connection. Bridging is in two forms. A direct bridge requires the configuration of a
bridge between the two connections and is thus unlikely to be initiated unless explicitly
desired. An indirect bridge is the shared resources on the computer. The indirect bridge
provides two security hazards. The first is that critical organizational data obtained via the
secured network may be on the computer drive and thus exposed to discovery via the
unsecured Ad-hoc network. The second is that a computer virus or otherwise undesirable code
may be placed on the computer via the unsecured ad-hoc connection and thus has a route to the
organizational secured network. In this case, the person placing the malicious code need not
“crack” the passwords to the organizational network, the legitimate user has provided access
via a normal and routine log-in. The malefactor simply needs to place the malicious code on
the unsuspecting user's end node system via the open (unsecured) ad-hoc connection.
4: Configuring the Printer
P1035089-003 Wireless Reference Manual 37
Page 48

4: Configuring the Printer
Setting Up an Ad-Hoc ( Peer ) Network
The WiFi networking standards (including 802.11g) require only that ad-hoc mode
communication supports a maximum of 11 Mbps bandwidth. You should expect that WiFi
devices supporting 54 Mbps or higher in infrastructure mode, will drop back to a maximum of
11 Mbps when changed to ad-hoc mode. Ad-hoc mode should generally be viewed as “slower”
than infrastructure mode for this reason. Some wireless cards can be configured to provide 54
Mbps operation in ad-hoc mode. If this is desirable, all peers that will join the ad-hoc network
must be configured for 802.11g 54 Mbps. To configure this using Windows XP:
1. Open the Network Connections windows.
2. Right click the wireless network connection and select Properties.
3. At the top of the dialog, click Configure.
4. Click the Advanced tab.
5. Under Property, look for the appropriate setting, like IBSS Mode.
6. Select the desired Value and click OK.
In order to establish the ad-hoc network with the Printer for the first time, you must setup the
ad-hoc network on a computer first with a wireless adapter then connect the printer to the adhoc network. Once the printer has successfully connected to the ad-hoc network, it will save
the necessary parameters to re-connect to the same network the next time the printer is
powered on. If the ad-hoc network is not found when powered on, the printer will establish the
ad-hoc network with the same settings used when first connected to the ad-hoc network. A
computer can then connect to the ad-hoc network at a later time and access the printer. Once
the printer has been connected to the ad-hoc network, the order that the printer and computers
are powered on doesn’t matter. The printer will only look for the ad-hoc network or establish
an ad-hoc network on the same channel as the ad-hoc network that the printer was first
connected to.
Before establishing an ad-hoc network, you will need to establish IP Addresses and Subnet
Mask for the computers and printer. It is likely that a DHCP server will be unavailable. The
computers may power up and assign themselves Automatic Private IP Addresses in the range
of 169.254.0.0 to 169.254.255.255 if a DHCP server is unreachable. If this is the case, then
you will need to disable DHCP in the printer and assign an unused static IP Address to the
printer that is within this range and set the printer Subnet mask to 255.255.0.0. A better
approach would be to assign static IP addresses to the printer and all the computers that will be
part of the ad-hoc network. IP addresses in the range 192.168.0.0 to 192.168.0.255 with a
Subnet Mask of 255.255.255.0 are often used for this purpose. Remember that each device
must have a unique IP address and common Subnet Mask.
Be careful about the computer IP Address and Subnet Mask that the wired Ethernet
connection is using. If the computer wired IP address is on the same Subnet as the wireless
interface (i.e., both are using a 192.168.0.X IP Address with Subnet Mask of 255.255.255.0)
then communications over the wireless interface may fail because the Ethernet packets
intended for the wireless interface may be routed through the wired interface. This issue can be
addressed by disabling the computer wired interface or assigning a static IP Address to the
wireless interface that puts it on a different Subnet than the wired interface.
38 Wireless Reference Manual P1035089-003
Page 49

4: Configuring the Printer
Setting Up an Ad-Hoc ( Peer ) Network
If you plan to use both wired and wireless Ethernet printer interfaces at the same time, see the
“Multi-homing Considerations” section. The configuration of the IP Address and Subnet Mask
on each printer interface must be set correctly depending upon whether the two interfaces are
connected to the same network or totally separate networks. Improperly configured network
settings may result in a communications failure.
Instructions for establishing an ad-hoc network on a computer or laptop may vary between OS
versions and wireless adaptors. The following steps are generic but should be helpful for
getting started:
1. There is usually a wireless icon in the task bar which can be used to access a wireless
Setup Utility. Right click on the icon and open the Utility.
2. Add an ad-hoc network. There may be an Add button you can click, followed by clicking
on “Create an ad hoc network”.
3. You should be presented with a dialog to enter the SSID or network name. The name can
be 1 – 32 text characters. Pick a name that is meaningful and easy to remember. Write it
down! Click Next.
4. You should now enter a dialog for Security and Channel selection. The security choices
are: None or WEP. It is highly recommended that you choose WEP. While WEP security
is poor, it is better than none. Try to pick a channel that is quiet or not heavily used. Your
Setup Utility may offer Site Management and Congestion analysis that will help you pick
the best channel. Once the selections have been made click Next.
5. If you selected WEP security, you will now need to enter the WEP key. You can enter
either a 40 bit key (10 Hex characters) or a 104 bit key (26 Hex characters). Save the key,
you will need to use it when you connect the printer to the wireless network. Click Next.
6. Now click Connect to establish the ad-hoc network. Nothing exciting happens as the
network has no peers as yet. No signal strength will be shown.
Once you have created the ad-hoc network, power on your printer and follow the same
instructions as detailed above in the “Configure the Printer through the Operator Control
Panel” section.
P1035089-003 Wireless Reference Manual 39
Page 50

4: Configuring the Printer
Setting Up an Ad-Hoc ( Peer ) Network
After scanning is complete and you are scrolling through the access points, you will notice that
ad-hoc networks are announced by replacing “MAC:xx.xx.xx.xx.xx.xx” with
“ADH:xx.xx.xx.xx.xx.xx” as shown below:
Once you have selected the ad-hoc network, selected the WEP key size, entered the WEP key
and pressed connect, the printer should connect to the ad-hoc network. The computer wireless
antenna icon should show signal bars. The printer OCP should also show a solid antenna icon.
When there are more peers connected to the ad-hoc network than just the printer, the printer
will also turn on an additional OCP icon that looks like a folder:
SSID: Test
ADH:00:a0:f8:be:fe:72
Chan = 1 SIG = 52%
SEC MODE: WEP
CRYPTO: RC4
MAX SPEED: 54 Mbps
NEXT SELECT CANCEL
The folder icon is useful to determine whether another peer is connected to the same ad-hoc
network as the printer. When using the OCP Info display to see the Wireless Info, an ad-hoc
connection will display as follows:
WIRELESS INFO
SSID: Ed2
CHAN = 5 SIG = 100%
NOISE FLOOR =-90 dBm
AD-HOC WEP RC4
54 Mbps
PREV NEXT EXIT
40 Wireless Reference Manual P1035089-003
Page 51

4.12 Multi-homing Considerations
The printer has both wired and wireless Ethernet interfaces that can be used at the same time.
This capability is referred to as multi-homing, where a device has multiple interfaces with a
different IP address assigned to each interface. If you intend to use this capability, care must be
taken with regard to the IP addresses assigned and whether both interfaces connect to the same
network or different networks. If instead you intend to use only one interface then the
remainder of this section doesn’t apply. It is recommended, however, that if you plan to use
only the wireless interface that you disable DHCP on the wired interface and set the wired
interface network settings (IP Address, Subnet Mask and Gateway Address) to a different
subnet than the one the wireless interface is using. This can be as simple as setting the wired
interface IP Address to: 0.0.0.0. This will prevent a wireless interface communications error if
the wired interface is plugged into a network.
The primary multi-homing issue depends upon whether both wired and wireless interfaces are
configured for the same subnet. For example, if both interfaces are configured with a Subnet
Mask of 255.255.255.0, the wired interface IP Address is set to 192.168.0.11 and the wireless
interface IP Address is set to 192.168.0.47, both interfaces are on the same subnet. The Subnet
Mask determines the span of the subnet. In this case, any IP Address in the range of
192.168.0.0 to 192.168.0.255 falls within the same subnet. If the wired interface IP Address
was changed to 192.168.1.11, the interfaces would be on different subnets. If the Subnet Mask
was changed to 255.255.0.0 for both interfaces, then both interfaces would be on the same
subnet again and the IP Address range for that subnet would be 192.168.0.0 to
192.168.255.255.
4: Configuring the Printer
Multi-homing Considerations
When both wired and wireless interfaces are configured for the same subnet and connected to
a network, the printer can no longer distinguish between the two interfaces when routing
Ethernet packets to the network. While packets are received on both interfaces, packets that
are being routed to the network are likely to be returned on the wired interface. This is
the routing algorithm will look for the first interface available that satisfies the
because
requirements based upon the destination IP Address. Given this, both interfaces must
routing
connect to the same network so that any host that sends packets to the printer is reachable on
both interfaces.
There may be occasions where it is desirable to connect the printer to two entirely separate
networks. In this scenario, the hosts on one network are not reachable through the other
network. To make this work correctly, the two networks must be on different subnets. The IP
Address and Subnet Mask settings must be properly set to achieve this. For example, if both
interfaces are configured with a Subnet Mask of 255.255.255.0, the wired interface IP Address
is set to 192.168.0.11 and the wireless interface IP Address is set to 192.168.1.47, both
interfaces are on different subnets.
If the configuration of the printer network settings is not done correctly, communications may
fail due to packets being sent on the wrong interface. When configured for different subnets,
the printer does not provide a bridge between the two networks.
P1035089-003 Wireless Reference Manual 41
Page 52

42 Wireless Reference Manual P1035089-003
Page 53

5.1 Overview
Once you have connected your printer to a wireless access point there are several ways that
you can monitor the performance. Performance monitor is important to insure that the wireless
connection is working reliably.
5
Monitor Wireless
Performance
P1035089-003 Wireless Reference Manual 43
Page 54

5: Monitor Wireless Performance
Wireless Info Pages
5.2 Wireless Info Pages
Wireless information is available through the OCP using the INFO button. Press the INFO
soft-key and the display changes to:
The revision numbers and serial numbers displayed for your printer may be different. At any
time you can press the EXIT soft-key to return to the normal status display. Press the NEXT
soft-key several times until the display changes to:
PRINTER INFO
MCB FZ8ME.02.05.00
HCB FZ8ME.01.05.00
MAB FZ8RE.01.00.00
MSN: 06C092500013
PH S/N: 91-00254
PREV NEXT EXIT
WIRELESS INFO
SSID: Ed2
CHAN = 6SIG = 100%
NOISE FLOOR =-90 dBm
WPA2 CCMP
54 Mbps
PREV NEXT EXIT
This screen provides information about the status of the wireless information and if connected
to an access point additional information. If the radio is turned off or not connected to a
wireless access point, a display such as the following will be shown:
WIRELESS INFO
RADIO OFF
PREV NEXT EXIT
44 Wireless Reference Manual P1035089-003
Page 55

5: Monitor Wireless Performance
Wireless Info Pages
The “RADIO OFF” status location may be populated with one of several strings as shown in
the following table:
Radio Status Description
RADIO OFF The radio is turned off.
RADIO DISCONNECTED The radio has not yet started the process of connecting to an
access point or the link with the access point has been lost.
The radio will shortly attempt to reconnect.
RADIO INACTIVE The radio is inactive because the association with an access
point failed.
RADIO CONNECTING The radio is in the process of connecting to an access point
(scanning, associating or key handshaking).
When connected to an access point, the display shows the SSID of the access point, the
wireless channel, the current signal strength in percent, the noise floor, the security mode, the
type of encryption being used (if applicable) and the current data rate that recent packets have
been received.
P1035089-003 Wireless Reference Manual 45
Page 56

5: Monitor Wireless Performance
Signal Strength
5.3 Signal Strength
In addition to the signal strength value available on the Wireless Info screen, the printer also
uses an antenna icon on the OCP to indicate signal strength. The antenna icon has a body and
four bars associated with it. Thus five separate icon states are available from no bars (just icon
body) to four bars. The signal strength is based upon the SNR (Signal to Noise Ratio) with
which data packets are being received by the radio. The SNR is translated into a percentage in
order to make the number more intelligible to the user. For those that are interested, the SNR
can be derived from the signal strength in percent by using this equation:
SNR (dB) = 40 * Signal Strength (%) / 100
The following table outlines the SNR bands that are used to determine how many bars to
display for the antenna icon:
SNR (dB) Bars Signal
Strength %
40 and above 4 100 Robust connection, always fast.
25 to 39.99 3 62 - 99 Robust connection, mostly fast.
15 to 24.99 2 37 - 61 Robust connection, usually fast.
5 to 14.99 1 12 -36 Connection slow with packet retries and
0 to 4.99 0 0 - 11 Insufficient signal to connect.
0 - blinking Connection in progress.
Quality
intermittent loss of link.
It is very important to recognize that good signal strength is absolutely necessary for reliable
operation. Signal strength below 25% is likely to cause problems. Signal strength above 50%
will provide robust operation. Signal strength is not merely a factor of the distance between the
printer antenna and the access point antenna. Other factors such as ambient noise, intervening
walls and other nearby wireless equipment can result in poor signal strength. See the
Troubleshooting chapter for suggestions for improving signal strength.
46 Wireless Reference Manual P1035089-003
Page 57

5.4 Noise Floor
The noise floor is an instantaneous measure of the ambient noise that the wireless radio sees
when it is not transmitting or receiving a packet. There is always ambient thermal noise near a
level of -100 dBm that cannot be avoided. Added to this is man-made noise coming from:
microwave ovens, cordless telephones, baby monitors, wireless cameras, remote car starters,
DECT and residential wireless phones and Bluetooth products to name just a few. When you
add the noise sources together, the typical noise floor the wireless radio should see is
approximately -90 ±5 dBm. A more negative number is better (-95 is less noise than -90). The
noise floor value can be useful to evaluate whether the ambient noise is too high for robust
wireless operation. If the noise floor is higher than -85 dBm, then you may want to take steps
to reduce the noise level the wireless radio sees (see the Troubleshooting chapter). By using
the Signal Strength and Noise Floor values, the actual signal level can be calculated as
follows:
Signal Level (dBm) = Noise Floor (dBm) + (40 * Signal Strength (%) / 100)
5.5 Data Rate
5: Monitor Wireless Performance
Noise Floor
The data rate shown in the Wireless Info display can provide some insight into how well the
wireless interface is working. When there is a good SNR, the radio should typically show the
maximum data rate the access point can support (11 Mbps for 802.11b and 54 Mbps for
802.11g). You may notice at times that lower speeds are displayed. This is expected as long as
the maximum speed appears most of the time, particularly when a print job is being received.
When the SNR is poor, data will be sent at a slower speed to improve the signal quality
(receiver sensitivity is better at slower data rates). If you consistently see a low data rate, then
you may want to take steps to improve the signal quality; see
Troubleshooting on page 57
P1035089-003 Wireless Reference Manual 47
Page 58

5: Monitor Wireless Performance
DHCP & MAC Address Info Page
5.6 DHCP & MAC Address Info Page
Using first the INFO button then the NEXT button, go to the next page after the Wireless Info
page shown above. The display should look like:
WIRELESS INFO
DHCP Enabled
IP: 192.168.0.100
Mask: 255.255.255.0
GW: 192.168.0.1
MAC:00:19:88:06:4f:87
PREV NEXT EXIT
This screen shows the DHCP state, which can be Enabled or Disabled. If enabled, the screen
can show one of the states shown in the following table:
State Description
RADIO DISCONNECTED Radio is not currently connected to an AP.
DHCP WAIT Waiting for DHCP to be ready.
DHCP INITIALIZING DHCP initializing.
DHCP: Request Sent Request sent to DHCP server.
DHCP Timeout Timeout due to no response to request.
If DHCP is disabled or the printer has received a response from a DHCP server, the Info Page
displays the current IP Address, Subnet Mask and Default Gateway Address. The last line of
the display shows the MAC Address of the wireless interface (different from the wired
interface). If a DHCP Timeout occurs, the printer will fall-back to using the last good network
settings that have been used. In this case, the display will indicate the timeout and also display
the network settings that are currently being used, which are not settings received from a
current transaction with a DHCP server:
WIRELESS INFO
DHCP Timeout
IP: 192.168.0.100
Mask: 255.255.255.0
GW: 192.168.0.1
MAC:00:19:88:06:4f:87
PREV NEXT EXIT
48 Wireless Reference Manual P1035089-003
Page 59

5.7 Wireless Statistics Info Page
Pressing the NEXT soft-key again will display the Wireless Statistics screen, as follows:
WIRELESS STATISTICS
RX BYTES: 18862
DISCARDS: 0
TX BYTES: 361
DISCARDS: 0
ERRORS: 0
PREV NEXT EXIT
The RX Bytes value is the total number of bytes that have been received by the printer via its
radio. The number of discards represents the number of RX packets that were discarded
because there was no buffer available to receive the packet. This should almost always be zero.
A discard is not a hard failure as the packet will be resent by the sender at a later time. The TX
Bytes value is the total number of bytes that have been sent by the printer to the radio. The
number of discards represents the number of TX packets that were discarded because the
packet was malformed or dropped due to a communication error with the radio. This should
almost always be zero. A discard is not a hard failure as the packet will be resent by the printer
at a later time. The final value is a catchall error counter for errors. This should be zero as it
indicates a hard error. A non-zero error counter may mean that there is a hardware failure. The
wireless statistics counts are reset to zero on power-up.
5: Monitor Wireless Performance
Wireless Statistics Info Page
P1035089-003 Wireless Reference Manual 49
Page 60

5: Monitor Wireless Performance
Wireless Statistics Success and Failure Rates
5.8 Wireless Statistics Success and Failure Rates
Pressing the NEXT soft-key again will display the Wireless Statistics Success and Failure
Rates screen, as follows:
WIRELESS STATISTICS
TX SUCCESS = 100%
TX RETRY = 6%
RX SUCCESS = 96%
RX DUPLICATE = 0%
RTS SUCCESS = 67%
PREV NEXT EXIT
The meaning of these values is described in the following table:
Statistic Name Description
TX SUCCESS The percentage of packets successfully transmitted by the printer’s
A higher number is better.
radio.
TX RETRY The percentage of packets that need to be retransmitted. A lower
number is better. A retry happens because the access point failed
to receive the packet correctly.
RX SUCCESS The percentage of packet successfully received by the radio. A
higher number is better
Check Sequence error, meaning the packet was corrupted during
transmission.
RX DUPLICATE The percentage of frames that are received more than one. A lower
number is better
receive an ACK from the printer for the original frame.
RTS SUCCESS The percentage of times in which CTS is received in response to
an R
TS. Higher is better.
. A packet receive fails due to a Frame
. This can happen if the access point does not
The above numbers do not represent hard failures. Under normal circumstances, Success rates
will be lower than 100% and the Retry & Duplicate rates will be higher than 0%. These rates
do provide some information about the quality of the link. If you see low TX/RX Success
Rates or high Retry/Duplicate Rates, you may be experiencing an unacceptably high error rate
and need to take steps to improve the link quality (see Troubleshooting chapter). The statistics
are cleared only when the printer is powered up.
50 Wireless Reference Manual P1035089-003
Page 61

5: Monitor Wireless Performance
Main Status Display Wireless Errors
5.9 Main Status Display Wireless Errors
During normal operation the OCP displays the printer status, such as the following:
READY
MENU INFO
If the wireless interface is experiencing hard errors, an indication of this will be added to the
normal status display, such as the following:
READY
WIFI LINK LOST
ERROR CODE = 19003
MENU INFO
A wireless error is not considered an alarm condition, such as “Out of Cards”, so the display
does not change to ALARM. The wireless error display is simply informative. In most cases
communications with the printer will have been lost, so the wireless error condition will
usually not be seen by a host.
P1035089-003 Wireless Reference Manual 51
Page 62

5: Monitor Wireless Performance
Main Status Display Wireless Errors
The wireless errors are detailed in the following table:
Wireless Error Text Code Description
WIFI ACCESS POINT
MISSING
WIFI LINK LOST 19003 The connection to the access point was lost. This may
WIFI INCOMPATIBLE
NETWORK
WIFI ASSOCIATION
FAILED
WIFI CONNECTION
FAILED
19002 After power up, the printer tried to connect to the
access point specified by the wireless settings, but the
access point was not found during the scan.
printer will periodically retry to connect to the access
point.
be due to poor signal strength, interference or the
access point power has been lost.
periodically retry to connect to the access point.
19004 After power up, the printer tried to connect to the
access point specified by the wireless settings, but
found the access point settings incompatible.
could occur if the access point configuration is
modified. To correct, re-run the Setup Wizard to
establish new wireless settings.
19005 During association with an access point, the
association failed.
quality. If the signal strength is low, take steps to
improve it, then re-run the Setup Wizard to establish
new wireless settings.
19006 The key handshake following the association failed.
This may be because the WEP key or WP
passphrase is wrong. To correct, make sure that you
have the correct key passphrase then re-run the
Setup Wizard to establish new wireless settings.
This could be a result of poor signal
The printer will
The
This
A
52 Wireless Reference Manual P1035089-003
Page 63

5: Monitor Wireless Performance
Viewing Wireless Information via Printer Web Page
5.10 Viewing Wireless Information via Printer Web Page
From the Home page, click Wireless Parameters tab; and view Choose WiFi Connection
page. Click on Cancel button at the bottom of the page. View Set/Edit WiFi Address page,
and click the WiFi Diagnostics tab. The following page is displayed:
Note that the same information available from OCP Wireless Info pages is available in this
web page.
P1035089-003 Wireless Reference Manual 53
Page 64

5: Monitor Wireless Performance
Viewing Wireless Information via Driver Toolbox
5.11 Viewing Wireless Information via Driver Toolbox
Open the ZXP Toolbox and under the Information section, click on Wireless Network. The
following screen will be displayed:
See next page for details.
54 Wireless Reference Manual P1035089-003
Page 65

5: Monitor Wireless Performance
Viewing Wireless Information via Driver Toolbox
This Wireless Network screen provides some additional information not available through the
OCP or the printer web page:
RSSI – received signal strength indicator.
SNR – the signal to noise ratio in dB for the received signal.
Link lost – the number of times the connection to the access point has been lost.
Unicast packets – the number of unicast packets that have been sent or received.
Non unicast packets – the number of non unicast packets that have been sent or received.
Multicast transmission frame - Increments when the multi-cast bit is set in the
destination MAC address of a successfully transmitted MSDU.
Failed - Increments when an MSDU is not transmitted successfully.
Retry - Increments when an MSDU is successfully transmitted after one or more
retransmissions.
Multi retry - Increments when an MSDU is successfully transmitted after more than one
retransmission.
Framed up - Increments when a frame is received that the Sequence Control field is
indicating a duplicate count. Happens if the AP failed to receive an ACK from the STA
for the original frame.
RTS success - Increments when a CTS is received in response to an RTS.
RTS failure - Increments when a CTS is not received in response to an RTS.
ACK failure - Increments when an ACK is not received when Expected. The number of
MMPDUs and MPDUs unacknowledged by the peer.
Rx frag - Increments for each successfully received MPDU of type Data or Management.
Multicast receive frame - Increments when a MSDU is received with the multi-cast bit is
set in the destination MAC address of a successfully.
FCS error - Increments when a Frame Check Sequence error (FCS) is detected in a
received MPDU. Due to wireless link interference.
At the bottom of the ZXP Toolbox Wireless Network page there is a Save button. Pressing
this button will save all of the data displayed on this page to two XML files. This may be
useful as a diagnostic tool if you are having problems with the wireless connection. These
XML files can be emailed for analysis.
P1035089-003 Wireless Reference Manual 55
Page 66

56 Wireless Reference Manual P1035089-003
Page 67

6.1 Introduction
This section is an aid to troubleshoot wireless connections. The first steps to take is to
familiar with what kind of wireless link you use, and with what type of equipment.
become
From there, you can proceed and find identify problem and take the necessary steps to take to
resolve the issue.
6
Troubleshooting
P1035089-003 Wireless Reference Manual 57
Page 68

6: Troubleshooting
Wireless Troubleshooting Checklist
6.2 Wireless Troubleshooting Checklist
Before beginning to troubleshoot the wireless printer, verify the following:
• The power cord is connected to the printer, and the printer is on.
• The antenna is attached to the printer, and the polarity of the antenna matches that of
the access point.
• Your SSID is correct. If you are not sure if your SSID is correct, run the wireless
setup wizard again.
• Your WEP key or WPA passphrase is correct. Log into the wireless access point and
check the security settings. A security key is like a password. All devices on the same
wireless network using WEP, WPA, or WPA2 share the same security key. If you are
not sure if your security information is correct, run the wireless setup wizard again.
• The wireless network is working properly. Try accessing other computers on your
wireless network. If your network has Internet access, try connecting to the Internet
over a wireless connection.
• The printer is within the range of the wireless network. For most networks, the printer
should be within 100 feet (30 meters) of the wireless access point.
• The printer is located away from obstacles that could block the wireless signal.
Remove any large metal objects between the access point and the printer. Make sure
the printer and wireless access point are not separated by poles, walls, or support
columns containing metal or concrete.
• The printer is located away from other electronic devices that may interfere with the
wireless signal. Many devices can interfere with the wireless signal, including
microwave ovens, baby monitors, motors, cordless phones, security system cameras,
other wireless networks, and some Bluetooth devices.
• The printer driver is installed on the computer from which you are performing a task.
• The correct printer port is selected.
• The computer and printer are both connected to the same wireless network.
58 Wireless Reference Manual P1035089-003
Page 69

Cannot Print Over Wireless Network
6.3 Cannot Print Over Wireless Network
If you encountered problems while installing, or if your printer does not appear in the printers
folder or as a printer option when sending a print job, you can try uninstalling and reinstalling
the software.
These are possible solutions. Try one or more of the following:
1. Make Sure Your Computer Is Connected To Your Wireless Access Point
• See if you have access to the Internet by opening your Web browser and accessing
site.
any
• If there are other computers or resources on your wireless network, check to see if you
can access them from your computer.
2. Move the Computer and/or Printer Closer To the Wireless Access Point
Although the possible distance between devices in 802.11b or 802.11g networks is 300
feet, the maximum range for optimal performance is generally 100–150 feet.
3. Move Your Access Point to Minimize Interference
6: Troubleshooting
There may be temporary interference from other devices such as microwave ovens or
other appliances, cordless phones, baby monitors, and security system cameras. Make sure
your access point is not positioned too closely to these devices.
4. Check Whether the Printer Is On the Same Wireless Network as The Computer
The SSID of the printer must match the SSID of the wireless network. Type the IP address
of the wireless access point in the Web address field of your browser. If you do not know
the IP address of the wireless access point start with item a. If you know your access point
IP address, start with f:
a. Click Start.
b. Click All Programs or Programs->Accessories->Command Prompt.
c. Type ipconfig.
d. Press Enter.
e. The “Default Gateway” entry is typically the wireless access point. The IP address
appears as four sets of numbers separated by periods, such as 192.168.0.100. Your IP
address might also start with the numbers 10 or 169. This is determined by your
operating system or wireless network software.
f. Type the wireless access point IP address into your browser. Type your user name and
OK.
password for the wireless access point when prompted and Click
g. On the main page, click Wireless or another selection where settings are stored. The
SSID appears.
P1035089-003 Wireless Reference Manual 59
Page 70

6: Troubleshooting
Cannot Print Over Wireless Network
5. Check Your Security Keys
A security key is like a password. All devices on the same wireless network must share the
same security key.
• WEP key: Exactly 10 or 26 hexadecimal characters. Hexadecimal characters are A-F,
a-f, and 0-9.
• WPA or WPA2 passphrase: From 8 to 63 ASCII characters. ASCII characters in a
WPA passphrase are case-sensitive. The currently recommended minimum length for
a passphrase is twenty characters.
Note: If you do not know this information, see the documentation that came with the
wireless network, or contact the person who set up your wireless network.
6. Check Your Advanced Security Settings
• If you are using MAC address filtering to limit access to your wireless network, you
must add the printer MAC address to the list of addresses allowed to connect to the
wireless access point.
• If you set the wireless access point to issue a limited number of IP addresses, you
must change this so that the printer can be added.
Note: If you do not know how to make these changes, see the documentation that came
with the wireless network, or contact the person who set up your wireless network.
7. Ping the Access Point to Make Sure the Network Is Working
If you do not already know it, find the IP address of the access point.
a. Click Start.
b. Click All Programs or Programs ->Accessories->Command Prompt.
c. Type ping followed by a space and the IP address of the wireless access point. For
example: ping 192.168.0.100
d. Press Enter.
e. Check to see whether the access point responds:
• If the access point responds, you will see several lines appear that start with
“Reply from.” It is possible that the printer did not connect to the wireless
network. Turn off and then restart the printer to try to connect again.
• If the access point does not respond, it will take several seconds and then you will
see “Request timed out.” You will need to take steps to repair the connection
between the PC and the wireless network.
8. Ping the Printer to See if it is Accessible
Use the INFO and NEXT soft-keys on the OCP to display the wireless IP Address. As
shown above, print the printer with this address. If a timeout results, then the printer is not
connected to the wireless network.
60 Wireless Reference Manual P1035089-003
Page 71

6.4 Improve Wireless Signal Strength
A common reason wireless printers fail to communicate over a network is poor wireless signal
quality. If the signal is too weak, too distorted, or blocked by an object, it cannot carry
information between the access point and the printer. To determine if the printer is receiving a
strong signal from the access point, Use the INFO and NEXT soft-keys on the OCP to display
to display the Wireless Info pages and Statistics. The Signal Strength and Noise Floor values
may indicate poor signal strength or noisy environment. Drops in signal strength can be
intermittent, however, and although the signal quality appears high, it may drop during certain
conditions.
If you think signal strength is a problem between your access point and the printer, try one or
more of the following:
1. Move the Printer Closer to the Wireless Access Point
If the printer is too far away from the access point, it will not be able to communicate with
other devices on the network. For most indoor wireless networks, the maximum distance
between the access point and the printer is approximately 100 feet (30 meters). This
distance could be longer or shorter, depending upon the layout of the network and the
limitations of the access point.
6: Troubleshooting
Improve Wireless Signal Strength
2. Remove Obstacles between the Access Point and the Printer
The wireless signal from your access point will pass through most objects. Most walls,
floors, furniture and other objects will not block the wireless signal. However, there are
materials that are too dense for the signal to pass through. Objects containing metal and
concrete can block the signal, including:
• Cubicle walls
• Ducts
• Window frames
• Poles and interior support columns
• Metal office furniture and cabinets
• Elevators
• Steel doors
• Walls and other structural elements reinforced by rebar
Arrange your printer and access point so that the signal is not blocked by any of
objects.
these
P1035089-003 Wireless Reference Manual 61
Page 72

6: Troubleshooting
Improve Wireless Signal Strength
3. Remove Sources of Interference
Other types of radio frequencies can cause problems with the wireless signal on your
network. These sources of interference can cause printing issues that seem to come and
go. Some common sources of interference are:
• Microwave ovens
• Cordless phones
• Refrigerators and other appliances
• Bluetooth devices
• Other wireless networks
• Motors
Turn off these potential sources of interference where possible. Avoid using microwaves
and cordless phones when printing over your wireless network.
If another wireless network is operating in the vicinity, change the wireless channel on
access point.
the
Do not place your access point on a printer. Printers can also interfere with the
signal.
wireless
4. Arrange the Network to Reduce Signal Absorption
Even when the wireless signal is able to pass through an object, it is slightly weakened.
it passes through too many objects, it can be significantly weakened. All objects absorb
If
part of the wireless signal when it passes through them, but certain types of objects absorb
enough to cause communications problems. To avoid signal absorption, avoid placing the
following items between your access point and your printer:
• Multiple walls or floors
• Stacks of paper or books
• Crowds of people
• Objects containing water, such as fish tanks
• Plants
Place your access point as high in the room as possible to avoid signal absorption.
5. Add an Additional Access Point
If the access point is too far away from the printer or the current access point has too
wireless clients attached to it, try adding a second wireless access point to your
many
network that is closer to the printer. Make sure that you use different channels for the
access points. Note that 1, 6, and 11 are the preferred channel choices (in the
two
States).
United
62 Wireless Reference Manual P1035089-003
Page 73

6: Troubleshooting
Improve Wireless Signal Strength
6. Conduct Site Survey
The location of your wireless network may have too many access points within range of
the printer. Access points on the same or adjacent channels can interfere with each other,
causing reduced signal strength, retries and corrupted packets.
To find out about the access points in the area, use a tool such a NetStumbler or InSSIDer.
NetStumbler (also known as Network Stumbler) is a tool that facilitates detection of
Wireless LANs using the 802.11b and 802.11g WLAN standards. It will provide
information on access points found, the channels they are using and the signal strength.
Armed with this information, you may be able to reconfigure your wireless network to
reduce interference and improve signal strength.
P1035089-003 Wireless Reference Manual 63
Page 74

6: Troubleshooting
PSK 4-way Handshake Timeout
6.5 PSK 4-way Handshake Timeout
During WPA or WPA2 security negotiation 4 or 6 EAPOL frames are exchanged during the
process which is often referred to as the 4-way handshake and group handshake.
The security negotiation algorithms require the use of cryptographic algorithms and thus
require some time to complete. For each EAPOL frame sent to the printer, it may take as long
as 850 ms for the printer to respond with an EAPOL frame. Some Access Points (CISCO for
instance) are configured with timeouts shorter than this and thus timeout before the 4-way
handshake completes. The printer indicates this situation as a failure to connect. The only
solution is to re-configure the 4-way handshake timeout in the AP to be greater than 850 ms
(suggested timeout value is 1,000 ms or 1 second).
64 Wireless Reference Manual P1035089-003
Page 75

7
Technical Specifications
The wireless interface complies with IEEE 802.11-2007 with exceptions noted below:
IEEE 802.11 Standards
Standard Supported Description
802.11a N 54 Mbps, 5 GHz standard
802.11b Y Enhancements to 802.11 to support 5.5 and 11 Mbps
802.11d N International (country-to-country) roaming extensions
802.11e N Enhancements: QoS, including packet bursting
802.11g Y 54 Mbps maximum rate, 2.4 GHz standard
802.11h N Spectrum Managed 802.11a (5 GHz) for European compatibility
802.11i Partial Enhanced security (see Securities table below)
802.11j N Extensions for Japan
Securities
Security Supported
None Y
WEP (40 & 104 bit) – Only Open Authentication Y
WPA-PSK (Personal) Y
WPA2-PSK (Personal) Y
P1035089-003 Wireless Reference Manual 65
Page 76

7: Technical Specifications
Network Stack Protocols
Protocol Description Supported
IPv4 Internet Protocol Y
IPv6 Internet Protocol Y
Raw TCP Port 9100 Transmission Control Protocol Y
Raw UDP Port 9100 User Datagram Protocol Y
FTP Client File Transfer Protocol N
ICMP Internet Control Message Protocol Y
FTP Server File Transfer Protocol N
DHCP Client Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol Y
DHCP Options N
DHCP Address Retention When the printer reboots, if it had previously acquired a
N
DHCP IP address it will provide that address in a DHCP
request packet to the server.It is expected that if the
address is still available then the server will provide it
back to the printer.
BOOTP Client Bootstrap Protocol N
ARP Client Address Resolution Protocol Y
RARP Client Reverse Address Resolution Protocol N
Gleaning (PING) Method of specifying IP address by pinging N
Static IP Manual assignment of IP address Y
DNS Domain Name System Y
WINS Windows Internet Naming Service N
ESI Discovery N
ESI Multicast address N
Auto IP Server-less dynamic IPv4 address assignment N
LPR/LPD Line Printer Remote protocol /Line Printer Daemon
protocol
IPP v1 Internet Printing Protocol N
IPP v2 Internet Printing Protocol N
SSH Secure Shell N
SSL Secure Sockets Layer N
IP Access Control N
IP Filtering N
IPSec Internet Protocol Security N
Fast IPSec N
IKE Internet Key Exchange N
Open Crypto N
SNMP v1 Simple Network Management Protocol Y
N
66 Wireless Reference Manual P1035089-003
Page 77

7: Technical Specifications
Network Stack Protocols
Protocol Description Supported
SNMP v2 Simple Network Management Protocol Y
SNMP – Traps N
HTTP Server Y
HTTP static pages Y
HTTP HTML Y
NTP Client Network Time Protocol N
Telnet Configuration N
POP3 Client Post Office Protocol N
POP3 attachments N
SMTP Client Simple Mail Transfer Protocol N
SMTP Alerts N
TFTP Sever Trivial File Transfer Protocol N
Other Features
Feature Specification
Roaming Supported
Fast Re-association Not Supported
CCX v3 Not Supported
CCX v4 Not Supported
CCX v5 Not Supported
Ad-Hoc Network (IBBS) Supported (Security NONE or WEP only)
Data Rates 1, 2, 5.5, 11, 6, 9, 12, 18, 24, 36, 48 and 54 Mbps
Frequency Range 2.401 to 2.483 GHz
Receive Sensitivity -89 dBm (1 Mbps)
-85 dBm (11 Mbps)
-69 dBm (54 Mbps)
Transmit Output Power 10 dBm
External Antenna Type Reverse SMA plug connector, 1 dBi gain
P1035089-003 Wireless Reference Manual 67
Page 78

7: Technical Specifications
The wireless radio ships from the factory configured for one of three possible regions. The
region cannot be changed by the user. The region determines the channel utilization. For all
three regions, the maximum power output for any channel is 10 dBm as specified above. The
following table defines the regions, channel utilization and countries which are included in
the region:
Region Channels Countries
USA 1 – 11 Canada, Colombia, Dominican Republic, Grenada, Guatemala,
Guam, Mexico, Panama, Puerto Rico, Taiwan, United States,
Uzbekistan
EUROPE 1 – 13 United Arab Emirates, Armenia, Netherlands Antilles, Austria,
Australia, Aruba, Azerbaijan, Bosnia & Herzegovina, Barbados,
Belgium, Bulgaria, Bahrain, Saint Barthelme, Brunei, Darussalam,
Belarus, Switzerland, Chile, China, Costa Rica, Cyprus, Czech
Republic, Germany, Denmark, Ecuador, Estonia, Egypt, Spain,
Finland, France, Georgia, Great Britain, Greece, Greenland,
Honduras, Hong Kong, Croatia, Haiti, Hungary, Indonesia, Ireland,
Israel, India, Iceland, Iran, Italy, Jamaica, Jordan, Cambodia, North
Korea, Kuwait, Kazakhstan, Lebanon, Liechtenstein, Sri Lanka,
Lithuania, Luxembourg, Latvia, Monaco, Morocco, Macao,
Macedonia, Malta, Netherlands, Norway, Nepal, Oman, Peru,
Papua New Guinea, Philippines, Pakistan, Poland, Portugal,
Qatar, Romania, Russian Federation, Saudi Arabia, Sweden,
Singapore, Slovenia, Slovakia, El Salvador, Syrian Arab Republic,
Thailand, Trinidad & Tobago, Tunisia, Turkey, Ukraine, Uruguay,
Vietnam, Yemen, South Africa, Zimbabwe, Albania, Argentina,
Brazil, Algeria, South Korea, Malaysia, Bolivia, Belize, New
Zealand, Venezuela
JAPAN 1- 13 Japan (channel 14 not available)
68 Wireless Reference Manual P1035089-003
Page 79

8
Glossary
10/100 Base-T
A technical term for Ethernet. 10/100 refers to the speed at which the Ethernet network
functions. 10 indicates 10 megabits per second (Mb/s) for normal Ethernet, and 100 indicates
100 Mb/s for Fast Ethernet.
802.11a
A type of wireless networking that provides up to 54 Mbps transmission in the 5 GHz band.
802.11b
A type of wireless networking that provides up to 11 Mbps transmission (with a fall-back to
5.5, 2, and 1 Mb/s) in the 2.4 GHz band.
802.11g
A type of wireless networking that provides up to 54 Mbps transmission in the 2.4 GHz band.
Access Point
A device that shares a single Internet connection with multiple computers or other devices.
The basic access point controls network traffic.
Ad-hoc network
A type of wireless network in which devices directly communicate with each other rather than
through a Wireless Access Point (WAP). Also referred to as peer-to-peer. Ad-hoc networks are
typically small and simple, for example, a wireless PC and a wireless printer. Ad-hoc networks
are independent basic service stations (IBSS), or direct-connect wireless networks.
Authentication
Authentication is a wireless network security strategy. On a network with authentication,
devices use a shared key as a password and communicate only with devices that know the key.
Unlike WEP, authentication does not encrypt the data sent between wireless devices. However,
authentication can be used in conjunction with WEP. Authentication keys and WEP keys can
be identical.
P1035089-003 Wireless Reference Manual 69
Page 80

8: Glossary
AutoIP
A process by which a device on a network automatically assigns an IP address to itself.
BOOTP
Bootstrap Protocol (BOOTP) is an Internet protocol that enables a device to discover its own
IP address, the IP address of a BOOTP server on the network, and a file to be loaded into
memory to boot the machine. This enables the device to boot without requiring a hard or
floppy disk drive.
Broadcast packet
A packet sent from one device on a network to all devices on the network.
BSS (Basic Service Set)
Basic Service Set describes the type of wireless network that you are using. The BSS type can
be one of the following: Infrastructure network or Ad-Hoc network.
Channel
A specific radio frequency used by two or more wireless devices to communicate with each
other. All devices on the network must use the same channel. The number of channels
available varies by country/region.
dBm
The power ratio in decibels (dB) of the power referenced to one milliwatt (mW). Examples: 0
dBm = 1 milliwatt, 10 dBm = 10 milliwatt and 20 dBm = 100 milliwatt.
DHCP (Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol)
A protocol used to automatically assign an IP address to each device on a network.
DHCP IP address
An IP address automatically assigned by a DHCP server.
DHCP server
A computer or access point that gives a unique IP address to each device on the network from
a dynamically manages a pool of IP addresses. Unique addresses prevent conflicts. When a
user logs in, the server “loans” the user an IP address for the duration of the network
connection. When a user logs off, the IP address is returned to the pool for use by
device.
another
Digital Certificate
An electronic means of proving the identity of a network user or device. Certificates contain
detailed information about the user's device in a standard format. Digital certificates are
typically issued by a trusted third-party Certificate Authority (CA). Locally administered, or
self-signed, certificates are valid in some instances.
EAP
Extensible Authentication Protocol (EAP) is a general protocol for authentication that also
supports multiple authentication methods, such as token cards, one-time passwords,
certificates, and public key authentication.
Encryption keys
A sequence of characters or digits that a wireless device uses to encode data. Encryption keys
can be static (as they are in WEP) or dynamic (as they are in WPA).
70 Wireless Reference Manual P1035089-003
Page 81

8: Glossary
Encryption
A network security that encodes the data sent across a wireless network making the data
unintelligible to unauthorized users. The printer supports WEP and WPA.
Ethernet
A popular form of wired computer networking for Local Area Networks.
EWS (embedded Web server)
A server that is completely contained within a device. An EWS provides management
information about the device. This is helpful for managing single devices on a small network.
By using a Web browser to access an EWS, network users can perform such operations as
obtaining network printer status updates, simple troubleshooting and changing device
configuration settings.
Firewall
A combination of hardware and software tools that protects a network from unwanted entry.
Gateway
A dedicated device (access point or computer) that connects two different networks. For
example, a computer on an Ethernet network may act as a gateway between the network and
the Internet.
Infrastructure network
A type of wireless network in which devices communicate with each other through a Wireless
Access Point (WAP), such as a wireless network hub, access point, or gateway.
IP address (Internet Protocol address)
Each computer that connects to a network or the Internet, must have a unique address. IP
address numbers are in the form x.x.x.x—for example, 169.254.100.2. Most networks use
DHCP or AutoIP to dynamically assign IP addresses. However, a device can be manually
assigned a static IP address.
LAN (Local Area Network)
A high-speed type of computer network that connects devices that are a relatively short
distance from one another. An Ethernet network is one type of LAN.
MAC (Media Access Control) address
A hardware address that uniquely identifies each device on a network. You can usually find
the MAC address printed on the device.
MAC filtering
A method of limiting access to your wireless network by specifying which MAC addresses
may communicate on the network. This setting may be specified on wireless access points.
Mbps (megabits per second)
The measure for the rate at which a network functions. For example, 1 Mbps equals 1,000,000
bits per second (or 125,000 bytes per second).
P1035089-003 Wireless Reference Manual 71
Page 82

8: Glossary
Network adapter/card
A device that lets computers or printers talk to each other over a network.
Network name
A network name is an alphanumeric, case-sensitive character string that provides basic
control to a wireless network. A network name is also known as a Service Set
access
(SSID).
Identifier
Node
A network connection point, typically a computer.
Packet
A message sent from one device on a network to other devices on the network.
Peer-to-peer
See Ad-hoc network.
Ping
A test to see if your computer can communicate with another device.
Protocol
A language that devices on a network use to communicate with each other. A popular network
protocol is TCP/IP.
Security key
A password, such as a WEP key or a WPA pass phrase, used to make a network secure.
Server
A computer on a network that manages network resources. A network might have a number of
different server types. For example, a print server manages one or more printers, a file server
stores and manages files, and a network server manages network traffic.
Signal strength
Measure of how strongly a transmitted signal is being received.
SSID (Service Set Identifier)
A unique identifier (up to 32 characters) attached to the header of packets sent over a wireless
LAN. An SSID provides basic access control to a wireless network. It can also be used to
logically segment a wireless subgroup of users and devices. An SSID prevents access by any
client device that does not have the SSID. By default, an access point broadcasts it’s SSID in
its beacon. An SSID is also referred to as a Network Name because it is a name that identifies
a wireless network.
Static IP address
An IP address that is manually assigned to a device on a network. A static IP address
fixed until changed manually. Alternative methods for assigning IP addresses are
remains
DHCP and AutoIP.
72 Wireless Reference Manual P1035089-003
Page 83

8: Glossary
Subnet mask
A number that identifies the IP addresses that belong to a subnet.
Switch
A device similar to a network hub that can connect different networks together
Switch
A network device that manages network traffic in order to minimize collisions and
speed.
maximize
TCP/IP
Transmission Control Protocol/Internet Protocol (TCP/IP) is the network communication
protocol used on the Internet. The printer's built-in networking feature supports LANs that
TCP/IP.
use
TKIP
See WPA. Temporal Key Integrity Protocol (TKIP).
Unicast packet
A packet sent from one device on a network to another device on the network.
WEP key
A WEP key, or encryption key, is a sequence of alphanumeric characters or hexadecimal
digits. After creating a WEP key, you must remember it or store it in a secure location. You
may not be able to retrieve the WEP key if you lose it. A WEP key is either 64 or 128 bits
long. The first 24 bits of the key are provided automatically. When creating the WEP key, the
person creating the key provides the remaining bits (40 bits in the case of a 64-bit key, or 104
bits in the case of a 128-bit key).
WEP
Wired Equivalent Privacy (WEP) provides security by encrypting data sent over radio waves
from one wireless device to another wireless device. WEP encodes the data sent across the
network making the data unintelligible to unauthorized users. Only devices that share the same
WEP settings as the printer will be able to communicate with the printer. WEP depends on
encryption keys that are static and provides less security than WPA (TKIP).
WiFi (Wireless Fidelity)
A term used generically when referring to any type of 802.11 network, whether 802.11b/g,
802.11a, dual-band, or other. Any products tested and approved as “WiFi Certified” are
certified as inter-operable with each other, even if they are from different manufacturers.
Typically, however, any WiFi product using the same radio frequency (2.4 GHz for 802.11b or
11g; 5 GHz for 802.11a) will work with any other WiFi product, even if not WiFi Certified.
Wireless Access Point (WAP)
A Wireless Access Point (WAP) is a device through which devices (for example, computers
and printers) on an infrastructure wireless network communicate with one another. A WAP is
also called a base station.
P1035089-003 Wireless Reference Manual 73
Page 84

8: Glossary
Wireless network adapter
Each node (computer or device) on the WLAN uses a wireless network adapter into which a
wireless transceiver, with a small, integrated antenna, is built. Wireless network adapters
might be internal (inserted in a computer or device), external (housed in a separate case), or
built-in.
WPA (WiFi Protected Access)
WPA provides security by encrypting data sent over radio waves from one wireless device to
another wireless device and by controlling access to network resources through authentication
protocols. Only devices that share the same WPA settings as the printer will be able to
communicate with the printer. WPA uses encryption keys that change frequently. WPA
provides better security than WEP. WPA typically uses TKIP encryption. WPA is not
supported on ad hoc wireless networks.
WPA2
A newer version of WPA which typically uses CCMP (AES) encryption. Older access points
are less likely to support this. Other possible security settings are WPA and WEP.
74 Wireless Reference Manual P1035089-003
 Loading...
Loading...