
CC600/CC6000
Customer Concierge
Product Reference
Guide
For Android ™ 10
MN-003909-03EN Rev A

ZEBRA and the stylized Zebra head are trademarks of Zebra Technologies Corporation, registered in many
jurisdictions worldwide. Google, Android, Google Play and other marks are trademarks of Google LLC. All
other trademarks are the property of their respective owners.
© 2020 Zebra Technologies Corporation and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved.
For further information regarding legal and proprietary statements, please go to:
COPYRIGHTS:zebra.com/copyright
WARRANTY:zebra.com/warranty
END USER LICENSE AGREEMENT: zebra.com/eula
Terms of Use
Proprietary Statement
This manual contains proprietary information of Zebra Technologies Corporation and its subsidiaries (“Zebra
Technologies”). It is intended solely for the information and use of parties operating and maintaining the
equipment described herein. Such proprietary information may not be used, reproduced, or disclosed to any
other parties for any other purpose without the express, written permission of Zebra Technologies.
Product Improvements
Continuous improvement of products is a policy of Zebra Technologies. All specifications and designs are
subject to change without notice.
Liability Disclaimer
Zebra Technologies takes steps to ensure that its published Engineering specifications and manuals are
correct; however, errors do occur. Zebra Technologies reserves the right to correct any such errors and
disclaims liability resulting therefrom.
Limitation of Liability
In no event shall Zebra Technologies or anyone else involved in the creation, production, or delivery of the
accompanying product (including hardware and software) be liable for any damages whatsoever (including,
without limitation, consequential damages including loss of business profits, business interruption, or loss of
business information) arising out of the use of, the results of use of, or inability to use such product, even if
Zebra Technologies has been advised of the possibility of such damages. Some jurisdictions do not allow the
exclusion or limitation of incidental or consequential damages, so the above limitation or exclusion may not
apply to you.
2

Revision History
Changes to the original guide are listed below:
Change Date Description
-01EN Rev A 7/2020 Initial Release
-02EN Rev A 10/2020 Updated Settings, Application, Application Deployment, and
-03EN Rev A 08/2021 Updated the GMS Restricted section.
Wireless sections.
3

Contents
Terms of Use ..................................................................................................................2
Proprietary Statement ............................................................................................. 2
Product Improvements ............................................................................................ 2
Liability Disclaimer ................................................................................................... 2
Limitation of Liability ................................................................................................ 2
Revision History ..............................................................................................................3
About This Guide.......................................................................................................... 8
Introduction ..................................................................................................................... 8
Configurations ................................................................................................................. 8
Chapter Descriptions ...................................................................................................... 9
Related Documents ........................................................................................................ 9
Notational Conventions ................................................................................................ 10
Icon Conventions .......................................................................................................... 10
Service Information ....................................................................................................... 10
Determining Software Versions .................................................................................... 11
Determining the Serial Number ..................................................................................... 11
Getting Started............................................................................................................ 12
Introduction ................................................................................................................... 12
Unpacking .....................................................................................................................12
Features ....................................................................................................................... 13
Setting Up the Device ................................................................................................... 17
Inserting the microSD Card (Optional) .......................................................................... 18
Mounting the Device ..................................................................................................... 18
Resetting the Device ..................................................................................................... 25
Using the Device ......................................................................................................... 26
Introduction ................................................................................................................... 26
1

Contents
Home Screen ................................................................................................................ 26
Status Bar .............................................................................................................. 28
Notification Icons ............................................................................................. 28
Status Icons .................................................................................................... 29
Managing Notifications .......................................................................................... 30
Opening the Quick Access Panel .......................................................................... 30
Quick Access Panel Icons .............................................................................. 31
Editing Icons on Quick Settings ............................................................................. 31
Un-Locking the Screen ................................................................................................. 32
USB Communication ..................................................................................................... 32
Transferring Files .................................................................................................. 32
Transferring Photos ............................................................................................... 32
Disconnect from the Host Computer ..................................................................... 33
Settings........................................................................................................................ 34
Introduction ................................................................................................................... 34
Accessing Settings ........................................................................................................ 34
Display Settings ............................................................................................................ 34
Setting the Screen Brightness ............................................................................... 34
Setting Night Light ................................................................................................. 34
Setting Screen Timeout ......................................................................................... 35
Lock Screen Display .............................................................................................. 35
Setting Font Size ................................................................................................... 35
Setting the Date and Time ............................................................................................ 36
General Sound Setting .................................................................................................. 37
Sound Options ....................................................................................................... 37
Remapping a Button ..................................................................................................... 37
Remappable Keys ......................................................................................................... 38
Setting Screen Lock ...................................................................................................... 39
Setting Screen Lock Using PIN ............................................................................. 39
Setting Screen Unlock Using Password ................................................................ 40
Setting Screen Unlock Using Pattern .................................................................... 40
Keyboards .....................................................................................................................40
Keyboard Configuration ......................................................................................... 41
Enabling Keyboards ........................................................................................ 41
Switching Between Keyboards ....................................................................... 41
Using the Android and Gboard Keyboards ............................................................ 41
Edit Text .......................................................................................................... 41
Entering Numbers, Symbols, and Special Characters .................................... 41
Using the Enterprise Keyboard ............................................................................. 41
Numeric Tab ................................................................................................... 42
Alpha Tab ........................................................................................................ 42
2

Contents
Additional Character Tab ................................................................................ 42
Scan Tab ......................................................................................................... 42
Language Usage ........................................................................................................... 42
Changing the Language Setting ............................................................................ 42
Adding Words to the Dictionary ............................................................................. 42
Notifications .................................................................................................................. 43
Setting App Notifications ....................................................................................... 43
Viewing Notification Settings for All Apps ....................................................... 43
Controlling Lock Screen Notifications ............................................................. 43
Applications ................................................................................................................ 45
Introduction ................................................................................................................... 45
Apps .............................................................................................................................. 45
Accessing Apps ............................................................................................................ 48
Switching Between Recent Apps .......................................................................... 48
Camera ........................................................................................................................ 49
Taking Photos ....................................................................................................... 49
Recording Videos .................................................................................................. 50
Photo Settings ....................................................................................................... 51
Video Settings ....................................................................................................... 51
DataWedge Demonstration .......................................................................................... 53
Scanner Selection ................................................................................................. 53
PTT Express Voice Client ............................................................................................ 54
PTT Express User Interface .................................................................................. 54
PTT Audible Indicators .......................................................................................... 55
PTT Notification Icons ........................................................................................... 55
Enabling PTT Communication ............................................................................... 56
Selecting a Talk Group .......................................................................................... 56
PTT Communication .............................................................................................. 56
Creating a Group Call ..................................................................................... 56
Responding with a Private Response ............................................................. 56
Disabling PTT Communication .............................................................................. 57
RxLogger ..................................................................................................................... 58
RxLogger Configuration ........................................................................................ 58
Configuration File .................................................................................................. 58
Enabling Logging ................................................................................................... 58
Disabling Logging .................................................................................................. 58
Extracting Log Files ............................................................................................... 58
Backing Up ............................................................................................................ 59
RxLogger Utility ..................................................................................................... 59
Initiating the Main Chat Head .......................................................................... 59
Removing the Main Chat Head ....................................................................... 59
3

Contents
Viewing Logs ................................................................................................... 59
Removing a Sub Chat Head Icon ................................................................... 59
Backing Up In Overlay View ........................................................................... 59
Sound Recorder ............................................................................................................ 60
Data Capture................................................................................................................ 61
Introduction ................................................................................................................... 61
Imaging ......................................................................................................................... 61
Linear Imager ................................................................................................................ 61
Operational Modes ................................................................................................ 62
RS507/RS507x Hands-Free Imager ............................................................................ 63
RS6000 Bluetooth Ring Scanner .................................................................................. 63
RS5100 Ring Scanner .................................................................................................. 64
DS3678 Digital Scanner ................................................................................................ 64
DS2278 Digital Scanner ................................................................................................ 65
Scanning Considerations .............................................................................................. 65
Scanning with Internal Imager ..................................................................................... 66
Settings ................................................................................................................. 67
Scanning Mode ............................................................................................... 68
Proximity Range .............................................................................................. 68
Barcode Capture with an Imager .................................................................................. 68
Scanning with RS507/RS507X Hands-Free Imager ............................................. 69
Scanning with RS6000 Bluetooth Ring Scanner ................................................... 70
Scanning with RS5100 Ring Scanner ................................................................... 72
Scanning with the DS3678 Bluetooth Scanner ..................................................... 73
Scanning with LI3678 Linear Imager ..................................................................... 74
Scanning with DS2278 Digital Scanner ................................................................. 75
Pairing the Bluetooth Ring Scanner .............................................................................. 76
Pairing Using Near Field Communication ............................................................. 77
Pairing in HID Mode Using Near Field Communication ........................................ 77
Pairing Using Simple Serial Interface .................................................................... 79
Pairing Using Bluetooth Human Interface Device ................................................. 79
Pairing a Bluetooth Scanner ........................................................................................ 81
Pairing Using Simple Serial Interface (SSI) ........................................................... 81
Pairing Using Bluetooth Human Interface Device ................................................. 82
DataWedge .................................................................................................................. 83
Enabling DataWedge ............................................................................................ 83
Disabling DataWedge ............................................................................................ 83
Supported Decoders ............................................................................................. 84
Wireless ....................................................................................................................... 86
4

Contents
Introduction ................................................................................................................... 86
Wireless Local Area Networks ...................................................................................... 86
Connecting to a Wi-Fi Network .............................................................................. 86
Removing a Wi-Fi Network .................................................................................... 87
WLAN Configuration ..................................................................................................... 87
Configuring a Secure Wi-Fi Network ..................................................................... 87
Manually Adding a Wi-Fi Network ......................................................................... 88
Configuring for a Proxy Server .............................................................................. 89
Configuring the Device to Use a Static IP Address ............................................... 90
Wi-Fi Preferences .................................................................................................. 91
Additional Wi-Fi Settings ....................................................................................... 91
Wi-Fi Direct ............................................................................................................ 92
Bluetooth ....................................................................................................................... 92
Adaptive Frequency Hopping ................................................................................ 92
Security ................................................................................................................. 93
Bluetooth Profiles .................................................................................................. 93
Bluetooth Power States ......................................................................................... 95
Bluetooth Radio Power .......................................................................................... 95
Enabling Bluetooth .......................................................................................... 95
Disabling Bluetooth ......................................................................................... 95
Discovering Bluetooth Device(s) ........................................................................... 95
Changing the Bluetooth Name .............................................................................. 96
Connecting to a Bluetooth Device ......................................................................... 96
Selecting Profiles on the Bluetooth Device ........................................................... 96
Unpairing a Bluetooth Device ................................................................................ 96
Cast ............................................................................................................................... 97
Near Field Communications (CC6000 Only) ................................................................. 97
Reading NFC Cards .............................................................................................. 98
Sharing Information Using NFC ............................................................................ 98
Enterprise NFC Settings ........................................................................................ 99
Accessories............................................................................................................... 100
Introduction ................................................................................................................. 100
Accessories ................................................................................................................. 100
Headset (CC6000 Only) .............................................................................................. 101
USB cable .................................................................................................................. 102
USB Communication ........................................................................................... 102
Application Deployment........................................................................................... 103
Security ....................................................................................................................... 103
5

Contents
Secure Certificates ...................................................................................................... 103
Installing a Secure Certificate ..................................................................................... 103
Configuring Credential Storage Settings ............................................................. 104
Development Tools ..................................................................................................... 104
Android Application Development ....................................................................... 104
Development Workstation ............................................................................. 104
Enabling Developer Options ......................................................................... 104
EMDK for Android ............................................................................................... 105
StageNow ............................................................................................................ 105
GMS Restricted ........................................................................................................... 105
ADB USB Setup .......................................................................................................... 105
Enabling USB Debugging .................................................................................... 106
Application Installation ................................................................................................ 106
Installing Applications Using the USB Connection .............................................. 107
Installing Applications Using the Android Debug Bridge ..................................... 107
Installing Applications Using a microSD Card ..................................................... 108
Uninstalling an Application .................................................................................. 108
Performing a System Update ..................................................................................... 109
Downloading the System Update Package ......................................................... 109
Performing a System Update Using microSD Card ............................................ 109
Performing a System Update Using ADB ............................................................ 109
Verifying System Update Installation ................................................................... 110
Performing an Enterprise Reset ................................................................................. 111
Performing an Enterprise Reset from Device Settings ........................................ 111
Downloading the Enterprise Reset Package ....................................................... 111
Performing an Enterprise Reset Using microSD Card ........................................ 111
Performing an Enterprise Reset Using ADB ....................................................... 112
Performing a Factory Reset ........................................................................................ 112
Downloading the Factory Reset Package ........................................................... 113
Performing a Factory Reset Using microSD Card ............................................... 113
Performing a Factory Reset Using ADB .............................................................. 113
Storage .......................................................................................................................114
Random Access Memory .................................................................................... 114
Viewing Memory ........................................................................................... 115
Internal Storage ................................................................................................... 115
Viewing Internal Storage ............................................................................... 115
External Storage .................................................................................................. 115
Viewing External Storage .............................................................................. 115
Formatting a microSD Card or USB Drive as Portable Storage ................... 115
Formatting a microSD Card as Internal Memory .......................................... 116
Enterprise Folder ................................................................................................. 116
Managing Apps ........................................................................................................... 116
6

Contents
App Details .......................................................................................................... 116
Managing Downloads ................................................................................................. 117
Maintenance and Troubleshooting ......................................................................... 118
Maintaining the Device ................................................................................................ 118
Cleaning Instructions .................................................................................................. 118
Approved Cleanser Active Ingredients ................................................................ 119
Harmful Ingredients ............................................................................................. 119
Device Cleaning Instructions ...................................................................................... 119
Special Cleaning Notes ....................................................................................... 119
Cleaning Materials Required ............................................................................... 120
Cleaning Frequency ............................................................................................ 120
Cleaning the Device .................................................................................................... 120
Housing ............................................................................................................... 120
Display ................................................................................................................. 120
Camera and Exit Window .................................................................................... 120
Troubleshooting ......................................................................................................... 121
Technical Specifications.......................................................................................... 123
Introduction ................................................................................................................. 123
Technical Specifications ............................................................................................. 123
CC6000 ............................................................................................................... 123
CC600 ................................................................................................................. 125
Decode Distances ...................................................................................................... 127
CC6000 - SE4710 Scan Engine .......................................................................... 127
CC600 - SE2100 Scan Engine ............................................................................ 128
Index
7

About This Guide
Introduction
This guide provides information about using the CC600 and CC6000 Customer Concierge interactive kiosk
and accessories.
NOTE: Screens and windows pictured in this guide are samples and can differ from actual screens.
Configurations
This guide covers the configurations listed in Table 1 and Table 2.
Table 1 CC600 Device Configurations
Configuration Description
CC600-5-3200LNWW 5 inch, OS: Android ™ 10, 32GB,
Ethernet/Wi-Fi, Imager, Worldwide
Configuration
CC600-5-3200LNNA 5 inch, OS: Android ™ 10, 32GB,
Ethernet/Wi-Fi, Imager, North America
Configuration
CC600-5-3200LNEU 5 inch, OS: Android ™ 10, 32GB,
Ethernet/Wi-Fi, Imager, Europe Configuration
CC600-5-3200LNIN 5 inch, OS: Android ™ 10, 32GB,
Ethernet/Wi-Fi, Imager, India Configuration
Front
Camera
No SE2100
No SE2100
No SE2100
No SE2100
Scan
Engine
8

About This Guide
Table 2 CC6000 Device Configurations
Configuration Description
CC6000-10-3200LCWW 10 inch, OS: Android ™ 10, 32GB,
CC6000-10-3200PCWW 10 inch, OS: Android ™ 10, 32GB, Portrait,
CC6000-10-3200LCNA 10 inch, OS: Android ™ 10, 32GB,
CC6000-10-3200PCNA 10 inch, OS: Android ™ 10, 32GB, Portrait,
CC6000-10-3200LNNA 10 inch, OS: Android ™ 10, 32GB,
Chapter Descriptions
Topics covered in this guide are as follows:
• Getting Started provides information on getting the device up and running for the first time.
• Using the Device provides information for operating the device.
• Settings provides information provides information for operating the device.
• Applications provides information on using applications installed on the device.
• Data Capture describes how to capture data using the device.
• Wireless provides information on the various wireless options.
• Accessories provides information for using the accessories for the device.
• Application Deployment provides information for developing and managing applications.
• Maintenance and Troubleshooting includes instructions on cleaning and provides troubleshooting
solutions for potential problems during device operation.
• Technical Specifications provides the technical specifications for the device.
Landscape, Imager, Worldwide Configuration
Imager, Worldwide Configuration
Landscape, Imager, North America
Configuration
Imager, North America Configuration
Landscape, Imager, North America
Configuration
Front
Camera
No SE4710
Yes SE4710
Yes SE4710
Yes SE4710
No SE4710
Scan
Engine
Related Documents
• CC600/CC6000 Customer Concierge Quick Start Guide, p/n MN-003314-xx.
• CC600/CC6000 Customer Concierge Regulatory Guide, p/n MN-003435-xx.
For the latest version of this guide and all guides, go to: zebra.com/support
.
9

Notational Conventions
Notational conventions are used to highlight important information.
• “Device” refers to all configurations of the CC600 Customer Concierge and CC6000 Customer
Concierge.
• Bold text is used to highlight the following:
• Dialog box, window and screen names
• Drop-down list and list box names
• Check box and radio button names
• Icons on a screen
• Key names on a keypad
• Button names on a screen.
• Bullets (•) indicate:
• Action items
• Lists of alternatives
• Lists of required steps that are not necessarily sequential.
• Sequential lists (e.g., those that describe step-by-step procedures) appear as numbered lists.
About This Guide
Icon Conventions
The documentation set is designed to give the reader more visual clues. The following graphic icons are
used throughout the documentation set. These icons and their associated meanings are described below.
NOTE: The text here indicates information that is supplemental for the user to know and that is not required
to complete a task.
IMPORTANT: The text here indicates information that is important for the user to know.
CAUTION: The text here indicates information that is important for the user to know.
WARNING: If danger is not avoided, the user CAN be seriously injured or killed.
Service Information
If you have a problem with your equipment, contact Customer Support for your region. Contact information
is available at: zebra.com/support
When contacting support, please have the following information available:
• Serial number of the unit (found on manufacturing label)
• Model number or product name (found on manufacturing label)
• Software type and version number
• IMEI number
.
Customer Support responds to calls by email or telephone within the time limits set forth in support
agreements.
10

About This Guide
If the problem cannot be solved by Customer Support, the user may need to return the equipment for
servicing and will be given specific directions. We are not responsible for any damages incurred during
shipment if the approved shipping container is not used. Shipping the units improperly can possibly void
the warranty. Remove the SIM card and/or microSD card from the device before shipping for service.
If the device was purchased from a business partner, contact that business partner for support.
Determining Software Versions
To determine the current software versions:
1. Swipe down from the Status bar with two fingers to open the Quick Access panel and then touch .
2. Touch About phone.
3. Scroll to view the following information:
• Device name
• Emergency information
• SWComponents
• Legal Informaiton
• Model & hardware
• Android version
• IP address
• Wi-Fi MAC adress
• Ethernet MAC address
• Bluetooth address
• Up time
• Build Fingerprint
• Build number.
Determining the Serial Number
Before contacting Customer Support, determine the serial number of your device.
Touch About phone > Model & hardware.
11

Getting Started
Introduction
This chapter provides information for getting the device up and running for the first time.
Unpacking
1. Carefully remove all protective material from the device and save the shipping container for later
storage and shipping.
2. Verify that the following are included:
• CC600 or CC6000 interactive kiosk.
• Regulatory Guide.
• CC600 only: Ferrite bead for EMI. Attaches to the DC power module.
3. Inspect the equipment for damage. If any equipment is missing or damaged, contact the Global
Customer Support center immediately.
4. Prior to using the device for the first time, remove the protective shipping film that covers the display.
12

Features
Front
Facing
Camera
Touch
Screen and
Display
Speaker
NFC
Antenna
Speaker
Exit Window
(Scanner)
Microphone
Proximity Sensor
Mounting
Bracket Screw
Holders
Micro SD
Card Slot
Audio
Adjustment/
Programmable
Buttons
Reset Button
Getting Started
NOTE: Although the orientations differ, the features on the CC6000 landscape and portrait devices are the
same.
Figure 1 CC6000 Front View
Figure 2 CC6000 Back View
13

Getting Started
USB C Port
(Used for
External
display or
OTG)
Power
Port
Audio
Port
USB A
Port
USB A
Port
Ethernet with POE
Figure 3 CC6000 Power and Cable Ports
14

Getting Started
Mounting
Bracket
Mounting
Bracket Screw
Holders
Mounting
Bracket
Locking
Screw
Wall Mount
Screw Holes
Speaker
Exit Window
(Scanner)
Proximity Sensor
Microphone
Touch Screen
and Display
Figure 4 CC6000 Back With Bracket View
Figure 5 CC600 Front Views
15

Figure 6 CC600 Back View
Reset Button
Mounting
Bracket
Screw
Holders (4)
Micro SD
Card Slot
Audio
Adjustment/Programmable
Buttons
x
USB C Port
(Used for
External
display or
OTG and other
USB-2
peripherals)
Power
Port
Micro SD
Card Slot
Ethernet with POE
Getting Started
21
Figure 7 CC600 Power and Cable Ports
16

Getting Started
21
Mounting
Bracket
Mounting
Bracket Screw
Holders
Mounting
Bracket
Locking
Screw
Wall Mount
Screw
Holes
Figure 8 CC600 Back With Bracket View
Table 3 Feature Descriptions
Item Function
Touch Screen and
Displays all information needed to operate the device.
Display
Exit Window
(Scanner)
Provides data capture using the imager and reads a barcode.
Note: To read a barcode, a scan-enabled app is required on the device.
Speaker Provides audio output for video and music playback. Provides audio in
speaker-phone mode.
NFC Antenna Reads NFC tags. (CC6000 Only)
Proximity Sensor Identifies the proximity of a user for turning up the display.
Microphone Use for communications in Speakerphone mode.
Front Facing Camera Captures still photos and videos.
Note: Select CC6000 devices only.
Interface Connectors See Figure 3 and Figure 7.
Volume Up/Down
Increase and decrease audio volume (programmable).
Button
External Display Designated for USB-C port utilization.
Reset button Press and hold to reset the device. See Resetting the Device on page 25 for
more information.
Setting Up the Device
Perform this procedure to start using the device for the first time.
• Install a micro secure digital (SD) card (optional).
17

Getting Started
• Connect the power supply to power on the device.
• Configure the device.
• Mount the device with the mounting bracket.
• Setup a Google account.
Inserting the microSD Card (Optional)
The microSD card slot provides secondary non-volatile storage. The slot is located on the back of the
device to the right of the audio jack. Refer to the documentation provided with the card for more
information, and follow the manufacturer’s recommendations for use.
CAUTION: Follow proper electrostatic discharge (ESD) precautions to avoid damaging the microSD card.
Proper ESD precautions include, but are not limited to, working on an ESD mat and ensuring that the operator is properly grounded.
To install the microSD card:
1. Remove the device from the mounting bracket, if installed.
2. Slide the microSD card, connectors down, into the device as shown in Figure 9.
Figure 9 Inserting microSD Card
Mounting the Device
Each configuration of the device requires the appropriate mounting bracket to mount the device to a wall or
other flat surface. The diameter of the holes for the wall screws is 5.8mm (0.228 in).
NOTE: Device measurements in Figure 10, Figure 11 and Figure 12 are in millimeters.
18

Figure 10 CC600 Measurements
Getting Started
Figure 11 CC6000 Portrait Measurements
19

Getting Started
Shoulder Screw Hole (4)
Wall Screw Hole (3)
Securing Screw
21
Securing Screw Hole
Figure 12 CC6000 Landscape Measurements
Figure 13 CC600 Mounting Bracket
20

Getting Started
Shoulder Screw Hole (4)
Power Supply
Wall Screw Hole (4)
Shoulder Screw Hole (4)
Wall Screw Hole (4)
Securing Screw
Securing
Screw Hole
Power Supply
Figure 14 CC6000 Mounting Bracket - Portrait Orientation
Figure 15 CC6000 Mounting Bracket (KT-152098-03) - Landscape Orientation
21

Getting Started
To Wall
To Wall
To mount the device:
1. Determine the CC600 or CC6000 mounting location.
2. Secure the mounting plate to the wall using the screws provided (three screws for the CC600 plate and
four screws for the CC6000).
Figure 16 Attaching the CC600 Bracket To Wall
Figure 17 Attaching the CC6000 Bracket To Wall
3. Insert the four shoulder screws, also provided, into the mounting holes in the back of the device.
22

Getting Started
Figure 18 Inserting Shoulder Screws
4. Connect the power supply to the power port. Connect any additional cables into the appropriate ports
shown in Figure 3 and Figure 7.
5. Mount the device by placing the shoulder screws through the four keyholes on the mounting plate, and
slide the device down to secure in place.
23

Getting Started
Locking
Screw
Locking
Screw
Locking
Screw
Figure 19 Attaching the Device to the Bracket
6. Insert the locking screw through the hole in the tab at the top of the mounting plate. Hand tighten the
screw to secure the device.
24

Resetting the Device
The device has a recessed reset button (see CC6000 Back View on page 13 and CC600 Back View on
page 16 for the location of the button).
To activate the reset button, use the tip of a small paper clip (1mm in diameter), insert into the recess, push
and hold for 3 seconds.
Device has a recovery console accessible via pressing the Button #1 on the back of the device upon power
up or via ADB connection and command.
The following reset functions are supported:
• Soft reset is performed with an ADB command.
• Enterprise reset (see Performing an Enterprise Reset on page 111 for more information).
• Factory reset (see Performing a Factory Reset on page 112 for more information).
The device recovery mode supports the following functions:
• Flash image from zip file on an SD card or from internal flash.
• Apply a system update from an SD card or from internal flash.
Getting Started
25

Using the Device
Introduction
This chapter explains the buttons, status icons, and controls on the device, and provides basic instructions
for using the device including resetting the device and entering data.
Home Screen
Turn on the device to display the Home screen. Depending on the configuration, the Home screen may
appear different. Contact your system administrator for more information.
Touch the screen and slide up to unlock. For screen locking information see Un-Locking the Screen on
page 32.
NOTE: By default, non-GMS devices do not have the same icons on the Home screen as GMS. Icons are
shown below for example only. Home screen icons can be configured by the user and may look different
than shown.
26

Figure 20 Home Screen
Using the Device
Table 4 Home Screen Features
1 Status Bar Displays the time, status icons (right side), and notification icons (left side).
For more information see Table 6 on page 29 and Table 5 on page 28.
2 Widgets Launches stand-alone apps that run on the Home screen.
3 Folder Contains apps.
4 Shortcut Icons Opens apps installed on the device.
5 Back Displays the previous screen.
6 Home Displays the Home screen.
7 Recent Displays recently used applications.
27

Status Bar
1
2
The Status bar displays the time, notification icons (left side), and status icons (right side).
If there are more notifications than can fit in the Status bar, a dot displays indicating that more notifications
exist. Swipe down from the Status bar to open the Notification panel and view all notifications and status.
NOTE: Some Status icons may not appear in the Status bar if there are too many icons to display.
Figure 21 Notification and Status Icons
1 Notification Icons. See Notification Icons on page 28.
2 Status Icons. See Status Icons on page 29.
Using the Device
Notification Icons
Notification icons indicate app events and messages.
Table 5 Notification Icons
Icon Description
More notifications are available for viewing.
Data is syncing.
Indicates an upcoming event. Non-GMS devices only.
Indicates an upcoming event. GMS devices only.
Open Wi-Fi network is available.
Song is playing.
Problem with sign-in or sync has occurred.
Device is uploading data.
Device is downloading data when animated and download is complete when static.
Device is connected to or disconnected from virtual private network (VPN).
Preparing internal storage by checking it for errors.
USB debugging is enabled on the device.
Headset is connected to the device.
28

Table 5 Notification Icons (Continued)
Icon Description
Status Icons
Status icons display system information for the device.
Table 6 Status Icons
Icon Description
Using the Device
PTT Express Voice client status. See the PTT Express PTT Notification Icons on page 55 for a
complete list.
Indicates that RxLogger app is running.
Indicates the Bluetooth scanner is connected to the device.
Indicates the ring scanner is connected to the device in HID mode.
Alarm is active.
Indicates that all sounds except media and alarms are silenced.
Do Not Disturb mode active.
Airplane Mode is active. All radios are turned off.
Bluetooth is on.
The device is connected to a Bluetooth device.
Connected to a Wi-Fi network. Indicates the Wi-Fi version number.
Not connected to a Wi-Fi network or no Wi-Fi signal.
Connected to an Ethernet network.
Indicates that a headset is connected to the device.
29

Managing Notifications
Quick Settings Bar
Notification icons report the arrival of new messages, calendar events, alarms, and ongoing events. When
a notification occurs, an icon appears in the Status bar with a brief description. See Table 5 on page 28 for
a list of possible notification icons and their description. Open the Notification panel to view a list of all the
notifications.
• To view a list of all notifications, open the Notification panel by dragging the Status bar down from the
top of the screen.
Figure 22 Notification Panel
Using the Device
Opening the Quick Access Panel
• To respond to a notification, open the Notification panel and then touch a notification. The Notification
panel closes and the corresponding app opens.
• To manage recent or frequently used notifications, open the Notification panel and then touch Manage.
Touch the toggle switch next to an app to turn off all notifications, or touch an app for more notification
options.
• To clear all notifications, open the Notification panel and then touch CLEAR ALL. All event-based
notifications are removed. Ongoing notifications remain in the list.
• To close the Notification panel, swipe the Notification panel up.
Use the Quick Access panel to access frequently used settings (for example, Airplane mode).
• If the device is locked, swipe down once.
• If the device is unlocked, swipe down once with two fingers, or twice with one finger.
30

Using the Device
• If the Notification panel is open, swipe down from the Quick Settings bar.
Figure 23 Quick Access Panel
NOTE: Not all icons are pictured. Icons may vary.
Quick Access Panel Icons
• Display brightness - Use the slider to decrease or increase the brightness of the screen.
• Wi-Fi network - Turn Wi-Fi on or off. To open Wi-Fi settings, touch the Wi-Fi network name.
• Bluetooth settings - Turn Bluetooth on or off. To open Bluetooth settings, touch Bluetooth.
• Invert colors - Invert the display colors.
• Do not disturb - Control how and when to receive notifications.
• Airplane mode - Turn Airplane mode on or off. When Airplane mode is on the device does not connect
to Wi-Fi or Bluetooth.
• Night Light - Tint the screen amber to make it easier to look at the screen in dim light. Set Night Light to
turn on automatically from sunset to sunrise, or at other times.
• Screen Cast - Share phone content on Chromecast or a television with Google Cast built-in. Touch cast
screen to display a list of devices, then touch a device to begin casting.
• Dark Theme - Toggles dark theme on and off. Dark themes reduce the luminance emitted by the
screen, while meeting minimum color contrast ratios. It helps improve visual ergonomics by reducing
eye strain, adjusting brightness to current lighting conditions, and facilitating screen use in dark
environments.
• Bedtime mode - Turn on to block all data usage during set time periods. To open Bedtime mode
settings, touch and hold.
• Focus mode - Turn on to pause distracting apps. To open Focus mode settings, touch and hold.
• Nearby Share - Helps find and interact with services and devices close to the device.
Editing Icons on Quick Settings
The first several setting tiles from the Quick Access panel become the Quick Settings bar.
31

• Open the Quick Access panel and touch to edit, add, or remove settings tiles.
Un-Locking the Screen
Users can set the Lock screen upon initial boot. Use the Lock screen to protect access to data on the
device. Got to Setting Screen Lock on page 39 for information on setting up the locking feature.
When set to lock screen during an initial boot, a pattern, PIN, or password is required to unlock the device.
When the Lock screen displays, swipe the screen up to unlock. If the Pattern screen unlock feature is
enabled, the Pattern screen appears instead of the Lock screen. If the PIN or Password screen unlock
feature is enabled, enter the PIN or password after unlocking the screen.
USB Communication
Connect the device to a host computer to transfer files between the device and the host computer.
When connecting the device to a host computer, follow the host computer’s instructions for connecting and
disconnecting USB devices, to avoid damaging or corrupting files. For information on USB communication
accessories available for this device, see Accessories on page 100.
Using the Device
Transferring Files
Use Transfer files to copy files between the device and the host computer.
1. Connect the device to a host computer using a USB accessory.
2. On the device, pull down the Notification panel and touch Connect this device via USB.
By default, No data transfer is selected.
3. Touch File Transfer.
NOTE: After you change the setting to File Transfer, and then disconnect the USB cable, the setting reverts
back to No data transfer. If the USB cable is reconnected, select File Transfer again.
4. On the host computer, open a file explorer application.
5. Locate the device as a portable device.
6. Open the Internal storage folder.
7. Copy files to and from the device or delete files as required.
Transferring Photos
Use PTP to copy photos from the device to the host computer.
1. Connect the device to a host computer using a USB accessory.
2. On the device, pull down the Notification panel and touch Connect this device via USB.
3. Touch PTP.
4. On the host computer, open a file explorer application.
32

Using the Device
5.
Open the Internal storage folder.
6. Copy or delete photos as required.
Disconnect from the Host Computer
CAUTION: Carefully follow the host computer’s instructions to disconnect USB devices correctly to avoid los-
ing information.
To disconnect the device from the host computer:
1. On the host computer, unmount the device.
2. Remove the device from the USB accessory.
33

Settings
Introduction
This chapter describes settings available for configuring the device.
Accessing Settings
There are multiple ways to access settings on a device.
• Swipe down with two fingers from the top of the Home screen to open the Quick Access panel and
touch .
• Double-swipe down from the top of the Home screen to open the Quick Access panel and touch .
• Swipe up from the bottom of the Home screen to open APPS and touch .
Display Settings
Use Display settings to change the screen brightness, enable night light, change the background image,
enable dark theme, set sleep time, and change font size.
Setting the Screen Brightness
Manually set the screen brightness using the touchscreen.
1. Swipe down with two fingers from the Status bar to open the Quick Access panel.
2. Slide the icon to adjust the screen brightness level.
Setting Night Light
The Night Light setting tints the screen amber, making the screen easier to look at in low light.
1. Go to Settings.
2. Touch Display.
3. Touch Night Light.
4. Touch Schedule.
34

5.
Select one of the schedule values:
• None (default)
• Turns on at custom time
• Turns on from sunset to sunrise.
6. By default, Night Light is disabled. Touch TURN ON NOW to enable.
7. Adjust the tint using the Intensity slider.
8. Touch the Home button.
Setting Screen Timeout
Set the screen sleep time.
1. Go to Settings.
2. Touch Display > Screen timeout.
3. Select one of the sleep values.
• 15 seconds
• 30 seconds
• 1 minute
• 2 minutes
• 5 minutes
•10 minutes
•30 minutes
• Never (default).
Settings
4. Touch the Home button.
Lock Screen Display
The lock screen display setting wakes the screen when notifications are received.
1. Go to Settings.
2. Touch Display > Advanced.
3. Touch Lock screen display.
4. In the When to show section, enable or disable an option using the switch.
5. Touch the Home button.
Setting Font Size
Set the size of the font in system apps.
1. Go to Settings.
2. Touch Display > Advanced.
35

3.
Touch Font size.
4. Select one of the font size values.
•Small
• Default
•Large
• Largest.
5. Touch the Home button.
Setting Display Size
By default, display size is set to default.
To change the display size:
1. Swipe down from the Status bar to open the Quick Settings bar and then touch .
2. Touch Display > Advanced.
3. Touch Display size.
4. Touch - and + to change the display size.
Settings
•Small
• Default
•Large
•Larger
• Largest.
5. Touch the Home button.
Setting the Date and Time
You are only required to set the time zone or set the date and time if the wireless LAN does not support
Network Time Protocol (NTP).
1. Go to Settings.
2. Touch System > Date & time.
3. Touch Use network-provided time zone to disable automatic time zone synchronization.
4. Touch Update Interval.
5. Select the interval time to synchronize your device time from the network.
6. Touch Date.
7. In the calendar, set today’s date.
8. Touch OK.
9. Touch Time.
10. Touch the green circle, drag to the current hour and then release.
11. Touch the green circle, drag to the current minute and then release.
36

12.
Touch AM or PM.
13. Touch OK.
14. Touch Time zone.
15. Select the current time zone from the list.
16. Touch Use 24-hour format.
17. Touch the Home button.
General Sound Setting
Use the Sound settings to configure media and alarm volumes.
1. Go to Settings.
2. Touch Sound.
3. Touch an option to set sounds.
Sound Options
Settings
• Zebra volume controls
• Ring volume - Controls the ringtone volume.
• Media volume - Controls the music, games, and media volume.
• Alarm volume - Controls the alarm clock volume.
• Notifications volume - Controls the notification volume.
• In call volume - Controls the volume during a call.
• Scanner volume - Controls the scanner volume.
• Volume presets
• - Mutes the ring, notifications, and scanner so that the device does not make sounds or
vibrate.
• - Enables all sounds at the user defined levels.
• Do Not Disturb - Mutes some or all sounds and notifications.
• Shortcut to prevent ringing - Select how the shortcut method prevents ringing.
• Default notification sound - Select a sound to play for all system notifications.
• Default alarm sound - Select a sound to play for alarms.
• Other sounds and vibrations
• Screen locking sounds - Play a sound when locking and unlocking the screen (default – enabled).
• Touch sounds - Play a sound when making screen selections (default – enabled).
Remapping a Button
Buttons on the device can be programmed to perform different functions or as shortcuts to installed apps.
For a list of key names and descriptions, refer to techdocs.zebra.com
1. Go to Settings.
2. Touch Key Programmer. Two programmable buttons display.
.
37

3.
2
1
x
2
1
Select the button to remap.
4. Touch the BUTTON REMAPPING tab or the SHORTCUT tab that lists the available functions and
applications.
5. Touch a function or application shortcut to map to the button.
NOTE: If you select an application shortcut, the application icon appears next to the button on the Key
Programmer screen.
6. Touch the Home button.
7. If remapping the Back, Home, Search, or Menu button, perform a Soft Reset.
Remappable Keys
Figure 24 CC6000 Key Positions
Settings
Figure 25 CC600 Key Positions
21
1 VOLUME_UP Volume up button.
2 VOLUME_DOWN Volume down button.
38

Setting Screen Lock
Use the Device security settings to set preferences for locking the screen on an initial boot.
1. Swipe down from the Status bar to open the Quick Access panel and then touch .
2. Touch Security.
NOTE: Options vary depending upon the policy of some apps, such as email.
• Screen lock - Touch to configure the device to require a slide, pattern, PIN, or password to unlock the
screen.
• None - Disable screen unlock security.
• Swipe - Slide the lock icon to unlock the screen.
• Pattern - Draw a pattern to unlock screen. See Setting Screen Unlock Using Pattern on page 40 for
more information.
• PIN - Enter a numeric PIN to unlock screen. See Setting Screen Lock Using PIN on page 39 for
more information.
• Password - Enter a password to unlock screen. See Setting Screen Unlock Using Password on
page 40 for more information.
Settings
Lock the screen to protect access to data on the device. Some email accounts require locking the screen.
The Locking feature functions differently in Single-user versus Multiple-user mode.
Slide the screen up to unlock. If the Pattern screen unlock feature is enabled, the Pattern screen appears
instead of the Lock screen.
If the PIN or Password screen unlock feature is enabled, enter the PIN or password after unlocking the
screen.
Setting Screen Lock Using PIN
1. Swipe down from the Status bar to open the Quick Access panel and then touch .
2. Touch Security.
3. Touch Screen lock.
4. Touch PIN.
5. To require a PIN upon device start up select Yes, or select No not to require a PIN.
6. Touch in the text field.
7. Enter a PIN (4 numbers) then touch Next.
8. Re-enter PIN and then touch Next.
9. Select the type of notifications that appear when the screen is locked and then touch Done.
10. Touch the Home button. The next time the device is powered on, a PIN is required.
39

Settings
Setting Screen Unlock Using Password
1. Swipe down from the Status bar to open the Quick Access panel and then touch .
2. Touch Security.
3. Touch Screen lock.
4. Touch Password.
5. To require a password upon device start up select Yes, or select No not to require a password.
6. Touch in the text field.
7. Enter a password (between 4 and 16 characters) then touch Next.
8. Re-enter the password and then touch Next.
9. Select the type of notifications that appear when the screen is locked and then touch Done.
10. Touch the Home button. The next time the device is powered on, a password is required.
Setting Screen Unlock Using Pattern
1. Swipe down from the Status bar to open the Quick Access panel and then touch .
2. Touch Security.
3. Touch Screen lock.
4. Touch Pattern.
5. To require a pattern upon device start up select Yes, or select No not to require a pattern.
6. Draw a pattern connecting at least four dots.
7. Touch Continue.
8. Re-draw the pattern.
9. Touch Confirm.
10. Select the type of notifications that appear when the screen is locked and then touch Done.
11. Touch the Home button. The next time the device is powered on, a pattern is required.
Keyboards
The device provides multiple keyboard options.
• Android Keyboard - Non-GMS devices only
• Gboard - GMS devices only
• Enterprise Keyboard - Not pre-installed on the device. Contact Zebra Support for more information.
NOTE: By default the Enterprise and Virtual Keyboards are disabled.
40

Settings
Keyboard Configuration
Enabling Keyboards
1. Go to Settings.
2. Touch System > Languages & input > Virtual keyboard > Manage keyboards.
3. Touch a keyboard to enable.
Switching Between Keyboards
To switch between keyboards, touch in a text box to display the current keyboard.
• On the Gboard keyboard, touch and hold (GMS devices only).
• On the Android keyboard, touch and hold (Non-GMS devices only).
• On the Enterprise keyboard, touch .
Using the Android and Gboard Keyboards
Use the Android or Gboard keyboards to enter text in a text field.
To configure the keyboard settings, touch and hold
settings.
, (comma) and then select Android keyboard
Edit Text
Edit entered text and use menu commands to cut, copy, and paste text within or across apps. Some apps
do not support editing some or all of the text they display; others may offer their own way to select text.
Entering Numbers, Symbols, and Special Characters
1. Enter numbers and symbols.
• Touch and hold one of the top-row keys until a menu appears then select a number or special
character.
• Touch the Shift key once for a single capital letter. Touch the Shift key twice to lock in uppercase.
Touch the Shift key a third time to unlock Capslock.
• Touch
• Touch the
2. Enter special characters.
• Touch and hold a number or symbol key to open a menu of additional symbols. A larger version of
the key displays briefly over the keyboard.
?123 to switch to the numbers and symbols keyboard.
=\< key on the numbers and symbols keyboard to view additional symbols.
Using the Enterprise Keyboard
The Enterprise Keyboard contains multiple keyboard types.
• Numeric
•Alpha
• Special characters
41

• Data capture.
Numeric Tab
The numeric keyboard is labeled 123. The keys displayed vary on the app being used. For example, an
arrow displays in Contacts, however Done displays in Email account setup.
Alpha Tab
The alpha keyboard is labeled using the language code. For English, the alpha keyboard is labeled EN.
Additional Character Tab
The additional characters keyboard is labeled #*/.
Touch to enter emoji icons in a text message.
Touch ABC to return to the Symbols keyboard.
Scan Tab
The Scan tab provides an easy data capture feature for scanning barcodes.
Settings
Language Usage
Use the Language & input settings to change the device’s language, including words added to the
dictionary.
Changing the Language Setting
1. Go to Settings.
2. Touch System > Languages & input.
3. Touch Languages. A list of available languages displays.
4. If the desired language is not listed, touch Add a language and select a language from the list.
5. Touch and hold to the right of the desired language, then drag it to the top of the list.
6. The operating system text changes to the selected language.
Adding Words to the Dictionary
1. Go to Settings.
2. Touch System > Languages & input > Advanced > Personal dictionary.
3. If prompted, select the language where this word or phase is stored.
4. Touch + to add a new word or phrase to the dictionary.
5. Enter the word or phrase.
6. In the Shortcut text box, enter a shortcut for the word or phrase.
42

7.
Touch the Home button.
Notifications
Control when and how notifications are received for specific apps or all apps.
Setting App Notifications
To set notification settings for a specific app:
1. Go to Settings.
2. Touch Apps & notifications > SEE ALL XX APPS. The App info screen displays.
3. Select an app.
4. Touch Notifications.
Options vary depending on the app selected.
5. Select an available option:
• Show notifications - Select to turn all notifications from this app on (default) or off.
• Touch a notification category to display additional options.
• Alerting - Allow notifications from this app to make sound to the device.
• Pop on screen - Allow notifications from this app to pop notifications on the screen.
• Silent - Do not allow notifications from this app to make sound or vibrate.
• Minimize - In the Notification panel, collapse notifications to one line.
• Advanced - Touch for additional options.
• Sound - Select sound notifications for this app.
• Show notification dot - Allow notifications from this app to add a notification dot to the app icon.
• Override Do Not Disturb - Allow these notifications to interrupt when Do Not Disturb is enabled.
• Allow notification dot - Do not allow this app to add a notification dot to the app icon.
• Additional settings in the app - Open the app settings.
Settings
Viewing Notification Settings for All Apps
To view the notification settings for all apps:
1. Go to Settings.
2. Touch Apps & Notifications.
3. Scroll down to Notifications to view how many apps have notifications turned off.
4. To set or view notifications settings for a specific app, see Setting App Notifications on page 43.
Controlling Lock Screen Notifications
To control whether notifications can be seen when the device is locked:
1. Go to Settings.
2. Touch Apps & notifications > Notifications.
43

Settings
3.
Touch Notifications on lockscreen and select one of the following:
• Show alerting and silent notifications (default)
• Show alerting notifications only
• Don’t show notifications.
44

Applications
Introduction
This section describes the applications installed on the device.
Apps
The APPS screen displays icons for all installed apps. See Application Deployment for information on
installing and uninstalling apps. For information on standard Android apps, go to support.google.com
The following table describes the apps installed on the device.
Table 7 Apps
Icon Description
Bluetooth Pairing Utility – Use to pair a Zebra Bluetooth scanner with the device by
scanning a barcode.
.
Calculator - Provides the basic and scientific arithmetic functions.
Calendar - Use to manage events and appointments. GMS devices only.
Calendar - Use to manage events and appointments. Non-GMS devices only.
Camera - Take photos or record videos. For more information see
Chrome - Use to access the Internet or intranet. GMS devices only.
Chromium - Use to access the Internet or intranet. Non-GMS devices only.
45
Camera on page 49.

Applications
Table 7 Apps (Continued)
Icon Description
Clock - Use to schedule alarms for appointments or as a wake-up.
Contacts - Use to manage contact information.
DataWedge - Enables data capture using the imager.
DisplayLink Presenter - Use to present the device screen onto a connected monitor.
Drive - Upload photos, videos, documents, and other files to personal storage site. GMS
devices only.
DWDemo - Provides a way to demonstrate the data capture features using the imager.
DataWedge Demonstration on page 53 for more information.
See
Email - Use to send and receive email. Non-GMS devices only.
Files - Organize and manage files on the device.
Gallery - Use to view photos stored on the microSD cardinternal storage. For more
information, see Gallery for more information. Non-GMS devices only.
Gmail - Use to send and receive email using a Google email account. GMS devices
only.
Google - Launches Google ™ search app. GMS devices only.
Keep Notes - Use to create, edit, and share notes. GMS devices only.
License Manager - Use to manage software licenses on the device.
Maps - Use to see your location on a map (with public transit, traffic, or satellite
overlays). Search for any business or place of interest. Provides turn-by-turn navigation
with voice guidance, traffic-avoidance, and alternate routes, for drivers, cyclists, walkers,
and users of public transportation. GMS devices only.
46

Applications
Table 7 Apps (Continued)
Icon Description
Music - Play music stored on the microSD card or internal storage. Non-GMS devices
only.
Notes - Use to take and save notes. Non-GMS devices only.
Photos - Use to sync photos with Google account. GMS devices only.
Play Movies & TV - View movies and video on your device. GMS devices only.
Play Store - Download music, movies, books, and Android apps and games from the
Google Play Store. GMS devices only.
PTT Express - Use to launch PTT Express client for VoIP communication.
RxLogger - Use to diagnose device and app issues.
Search - Use to search the Web. Requires an Internet connection. Non-GMS devices
only.
Settings - Use to configure the device.
Sound Recorder - Use to record audio.
StageNow - Allows the device to stage a device for initial use by initiating the
deployment of settings, firmware, and software.
VoD - The Video on Device basic app provides a how-to video for proper device
cleaning. For Video on Device licensing information, go to learning.zebra.com
.
Worry Free Wifi - A diagnostic intelligent app. Use to diagnose surrounding area and
display network stats, such as coverage hole detection, or AP in vicinity. Refer to the
Worry Free Wi-Fi Analyzer Administrator Guide for Android.
YouTube - Use to view videos on the YouTube
47
™ web site. GMS devices only.

Table 7 Apps (Continued)
Icon Description
Accessing Apps
All apps installed on the device are accessed using the APPS window.
1. On the Home screen, swipe up from the bottom of the screen.
Applications
YT Music - Use to listen to music. GMS devices only.
Zebra Bluetooth Settings - Use to configure Bluetooth logging.
Zebra Data Services - Use to enable or disable Zebra Data Services. Some options are
set by your system administrator.
2. Slide the APPS window up or down to view more app icons.
3. Touch an icon to open the app.
Switching Between Recent Apps
1. Touch Recent button.
A window appears on the screen with icons of recently used apps.
2. Slide the apps displayed up and down to view all recently used apps.
3. Swipe left or right to remove app from the list and force close the app.
4. Touch an icon to open an app or touch Back button to return to the current screen.
48

Camera
Camera Mode
Settings
Scene Mode
Shutter Button
Gallery
Color Effect
High Dynamic Range
Taking Photos
Applications
This section provides information for taking photos and recording videos using the integrated digital
cameras.
NOTE: The device saves photos and videos on the microSD card, if installed and the storage path is
changed manually. By default, or if a microSD card is not installed, the device saves photos and videos on
the internal storage.
NOTE: See Photo Settings on page 51 for camera setting descriptions.
1. Swipe up from the bottom of the Home screen and touch Camera.
Figure 26 Camera Mode
2. If necessary, touch the Camera Mode icon and touch .
3. Frame the subject on the screen.
4. To zoom in or out, press two fingers on the display and pinch or expand fingers. The zoom controls
appear on the screen.
5. Touch an area on the screen to focus. The focus circle appears. The two bars turn green when in focus.
49

6. Touch .
Camera Mode
Settings
Audio
Shutter Button
Gallery
Color Effect
The camera takes a photo and a shutter sound plays.
The photo momentarily displays as a thumbnail in the lower left corner.
Recording Videos
1. Swipe up from the bottom of the Home screen and touch Camera.
2. Touch the camera mode menu and touch .
Figure 27 Video Mode
Applications
3. Point the camera and frame the scene.
4. To zoom in or out, press two fingers on the display and pinch or expand fingers. The zoom controls
appear on the screen.
5. Touch to start recording.
The video time remaining appears in the top left of the screen.
6. Touch to the end recording.
The video momentarily displays as a thumbnail in the lower left corner.
50

Photo Settings
• Selfie Flash - Turns screen white to help produce a little extra light in dimmer settings. Options: Off
(default), or On.
• Picture size - Set the size (in pixels) of the photo to: 5M pixels (default), 3M pixels, HD1080, 2M
pixels, HD720, 1M pixels, WVGA, VGA, or QVGA.
• Picture quality - Set the picture quality setting to: Low, Standard (default) or High (default).
• Countdown timer - Set to: Off (default), 2 seconds, 5 seconds or 10 seconds.
• Storage – Set location to store the photo to: Phone or SD Card.
• Continuous Shot - Select to take a series of photos quickly while holding the capture button. Off
(default) or On.
• Face Detection - Select to turn face detection Off (default) or On.
• ISO - Set how sensitive the camera is to light. Options: Auto (default), ISO Auto (HJR), ISO100,
ISO200, ISO400, ISO800 or ISO1600.
• Exposure - Touch to adjust the exposure settings. Options: +2, +1,
• White balance - Select how the camera adjusts colors in different kinds of light, to achieve the most
natural-looking colors:
• Incandescent - Adjust the white balance for incandescent lighting.
Applications
0 (default), -1 or -2.
• Fluorescent - Adjust the white balance for florescent lighting.
• Auto - Adjust the white balance automatically (default).
• Daylight - Adjust the white balance for daylight.
• Cloudy - Adjust the white balance for a cloudy environment.
• Redeye reduction - Helps eliminate redeye effect. Options: Disabled (default), or Enable.
• ZSL - Set the camera to immediately take a picture when the button is pressed (default – enabled)
• Selfie Mirror - Select to save a mirror image of the photo. Options: Disable (default), or Enable.
• Shutter Sound - Select to play a shutter sound when taking a photo. Options: Disable (default) or
Enable.
• Anti Banding - Allows the camera to avoid problems caused by artificial light sources that are not
constant. These sources cycle (flicker) fast enough to go unnoticed to the human eye, appearing
continuous. The camera’s eye (its sensor) can still see this flicker. Options: Auto (default), 60 Hz, 50
Hz, or Off.
Video Settings
In Video mode, video settings appear on screen. Touch to display the video settings options.
• Video quality - Set video quality to: HD1080 (default), HD 720p (default), SD 480p, VGA, CIF, or
QVGA.
• Video duration - Set to: 30 seconds (MMS) or 30 minutes (default).
• Storage – Set the location to store the photo to: Phone (default) or SD Card.
51

Applications
• White balance - Select how the camera adjusts colors in different kinds of light, to achieve the most
natural-looking colors.
• Incandescent - Adjust the white balance for incandescent lighting.
• Fluorescent - Adjust the white balance for florescent lighting.
• Auto - Adjust the white balance automatically (default).
• Daylight - Adjust the white balance for daylight.
• Cloudy - Adjust the white balance for a cloudy environment.
• Image Stabilization - Set to reduce blurry videos due to device movement. Options: On or Off
(default).
52

DataWedge Demonstration
NOTE: DataWedge is enabled on the Home screen. To disable this feature, go to the DataWedge settings
and disable the Launcher profile.
Use DataWedge Demonstration to demonstrate data capture functionality.
Table 8 DataWedge Demonstration Icons
Icon Description
Illumination Imager illumination is on. Touch to turn illumination off.
Data Capture The data capture function is through the internal imager.
Applications
Imager illumination is off. Touch to turn illumination on.
Indicates a USB scanner is connected to the device.
Scan Mode Imager is in picklist mode. Touch to change to normal scan mode.
Menu Opens a menu to view the application information or to set the
NOTE: To configure DataWedge, refer to techdocs.zebra.com/datawedge/.
Scanner Selection
To select a scanner, touch > Settings > Scanner selection.
Indicates a USB scanner is not connected to the device.
A Bluetooth scanner is connected.
A Bluetooth scanner is not connected.
Imager is in normal scan mode. Touch to change to picklist mode.
application DataWedge profile.
See
Data Capture for more information.
Touch the Data Capture icon to select the data capture mode. The data appears in the text field below the
yellow button.
53

PTT Express Voice Client
3
2
1
4
5
NOTE: Requires a PTT Express License.
PTT Express Voice Client enables Push-To-Talk (PTT) communication between disparate enterprise
devices. Leveraging existing Wireless Local Area Network (WLAN) infrastructure, PTT Express delivers
simple PTT communication without requiring a voice communication server.
• Group Call: Press and hold the GROUP CALL button to start communicating with other voice client
users.
• Private Response: Press and hold the PRIVATE CALL button to respond to the originator of the last
broadcast or to make a Private Response.
NOTE: Refer to the PTT Express V1.2 User Guide (p/n MN000935Axx) for more information on the PTT
Express Voice client configuration.
PTT Express User Interface
Applications
Figure 28 PTT Express Default User Interface
Table 9 PTT Express Default User Interface Descriptions
Number Item Description
1 Notification Icon Indicates the current state of the PTT Express client.
2 Service Indication Indicates the status of the PTT Express client. Options: Service Enabled, Service
Disabled or Service Unavailable.
3 Talk Groups Lists all 32 Talk Groups available for PTT communication.
54

Applications
Table 9 PTT Express Default User Interface Descriptions (Continued)
Number Item Description
4 Settings Opens the PTT Express Settings screen.
5 Enable/Disable
Switch
Turns the PTT service on and off.
PTT Audible Indicators
The following tones provide helpful cues when using the voice client.
• Talk Tone: Double chirp. Plays when the Talk button is depressed. This is a prompt for you to start
talking.
• Access Tone: Single beep. Plays when another user just finished a broadcast or response. You can
now initiate a Group Broadcast or Private Response.
• Busy Tone: Continuous tone. Plays when the Talk button is depressed and another user is already
communicating on the same talkgroup. Plays after the maximum allowed talk time is reached (60
seconds).
• Network Tone:
• Three increasing pitch beeps. Plays when PTT Express acquires the WLAN connection and the
service is enabled.
• Three decreasing pitch beeps. Plays when PTT Express loses the WLAN connection or the service
is disabled.
PTT Notification Icons
Notification icons indicate the current state of the PTT Express Voice client.
Table 10 PTT Express Icon Descriptions
Status Icon Description
The PTT Express Voice client is disabled.
The PTT Express Voice client is enabled but not connected to a WLAN.
The PTT Express Voice client is enabled, connected to a WLAN, and listening on the
Talk Group indicated by the number next to the icon.
The PTT Express Voice client is enabled, connected to a WLAN, and communicating on
the Talk Group indicated by the number next to the icon.
The PTT Express Voice client is enabled, connected to a WLAN, and in a private
response.
55
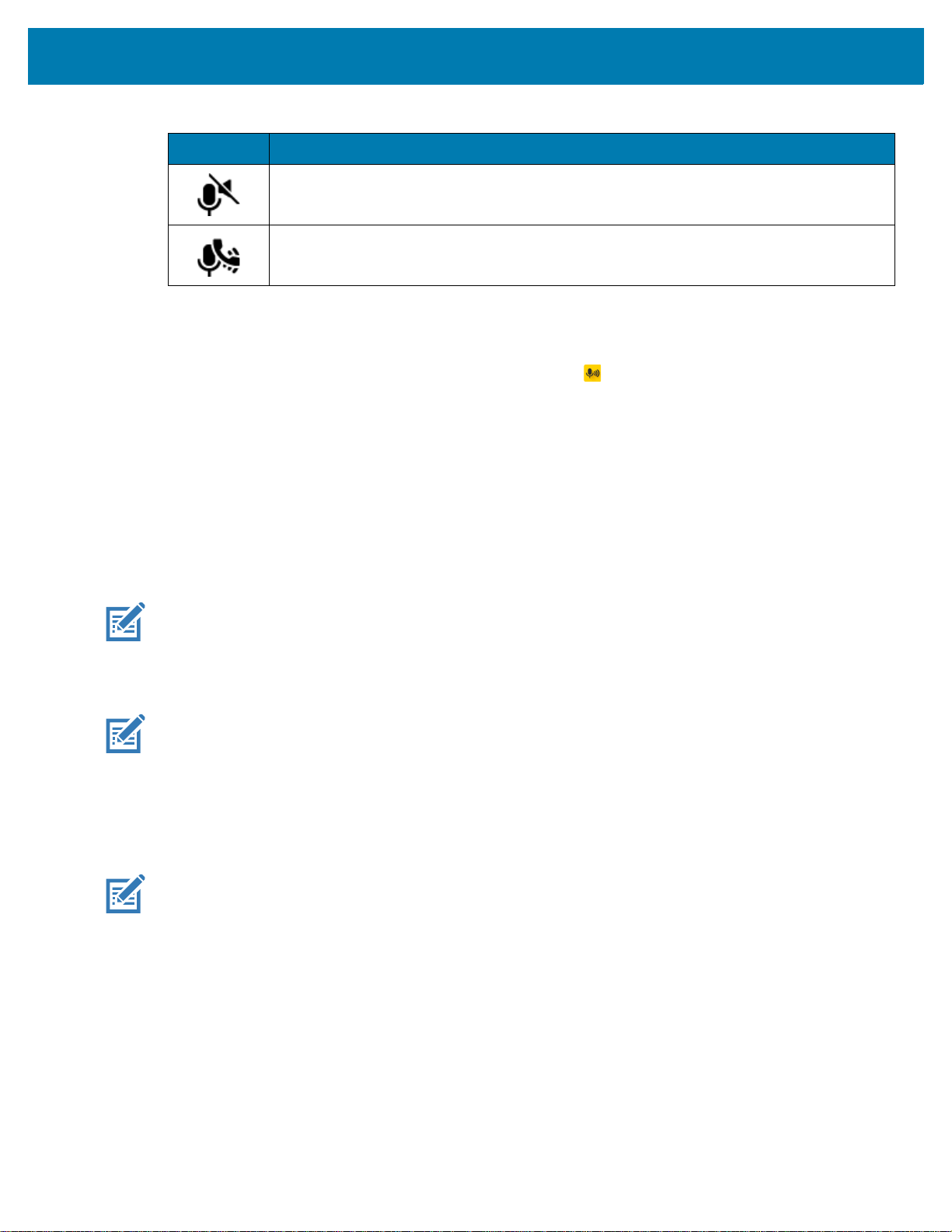
Table 10 PTT Express Icon Descriptions (Continued)
Status Icon Description
The PTT Express Voice client is enabled and muted.
The PTT Express Voice client is enabled but it is not able to communicate due to a VoIP
telephony call in progress.
Enabling PTT Communication
1. Swipe up from the bottom of the Home screen and touch .
2. Slide the Enable/Disable Switch to the ON position. The button changes to ON.
Selecting a Talk Group
One of 32 Talk Groups can be selected by PTT Express users. However, only one talk group may be
enabled at a time on the device. Touch one of the 32 Talk Groups. The selected Talk Group is highlighted.
Applications
PTT Communication
NOTE: This section describes the default PTT Express client configuration. Refer to the PTT Express V1.2
User Guide for detailed information on using the client.
Creating a Group Call
NOTE: When using a wired headset, use only Zebra approved wired headsets with a PTT button.
1. Press and hold the Group Call button (or the Talk button on the headset) and listen for the talk tone.
If you hear a busy tone, release the button and wait a moment before making another attempt. Ensure
that PTT Express and the WLAN are enabled.
2. Start talking after hearing the talk tone.
NOTE: Holding the button for more than 60 seconds (default) drops the call, allowing others to make Group
calls. Release the button when finished talking to allow others to make calls.
Responding with a Private Response
The Private Response can only be initiated once a Group Call has been established. The initial Private
Response is made to the originator of the Group Call.
1. After the Group Call is completed, wait until you receive an access tone.
2. Press and hold the configured PRIVATE CALL button.
3. If you hear a busy tone, release the PRIVATE CALL button and wait a moment before making another
attempt. Ensure that PTT Express and the WLAN are enabled.
56

4.
Start talking after the talk tone plays.
5. Release the button when finished talking.
Disabling PTT Communication
1. Swipe up from the bottom of the Home screen and touch .
2. Slide the Enable/Disable Switch to the OFF position. The button changes to OFF.
3. Touch the Home button.
Applications
57
RxLogger
RxLogger is a comprehensive diagnostic tool that provides application and system metrics, and diagnoses
device and application issues. RxLogger logs the following information: CPU load, memory load, memory
snapshots, battery consumption, power states, wireless logging, cellular logging, TCP dumps, Bluetooth
logging, GPS logging, logcat, FTP push/pull, ANR dumps, etc. All generated logs and files are saved onto
flash storage on the device (internal or external).
RxLogger Configuration
RxLogger is built with an extensible plug-in architecture and comes packaged with a number of plug-ins
already built-in. For information on configuring RxLogger, refer to techdocs.zebra.com/rxlogger/
To open the configuration screen, from the RxLogger home screen touch Settings.
Configuration File
RxLogger configuration can be set using an XML file. The config.xml configuration file is located on the
microSD card in the
connection. Edit the configuration file and then replace the XML file on the device. There is no need to stop
and restart the RxLogger service since the file change is automatically detected.
Applications
.
RxLogger\config folder. Copy the file from the device to a host computer using a USB
Enabling Logging
To enable logging:
1. Swipe the screen up and select .
2. Touch Start.
3. Touch the Home button.
Disabling Logging
To disable logging:
1. Swipe the screen up and select .
2. Touch Stop.
3. Touch the Home button.
Extracting Log Files
1. Connect the device to a host computer using an USB connection.
2. Using a file explorer, navigate to the RxLogger folder.
3. Copy the file from the device to the host computer.
4. Disconnect the device from the host computer.
58

Backing Up
RxLogger Utility allows the user to make a zip file of the RxLogger folder in the device, which by default
contains all the RxLogger logs stored in the device.
To save the backup data, touch > BackupNow.
RxLogger Utility
RxLogger Utility is a data monitoring application for viewing logs in the device while RxLogger is running.
Logs and RxLogger Utility features are accessed using Main Chat Head.
Initiating the Main Chat Head
To initiate the Main Chat Head:
1. Open RxLogger.
2. Touch > Toggle Chat Head. The Main Chat Head icon appears on the screen.
Applications
3. Touch and drag the Main Chat head icon to move it around the screen.
Removing the Main Chat Head
To remove the Main Chat Head icon:
1. Touch and drag the icon. A circle with an X appears.
2. Move the icon over the circle and then release.
Viewing Logs
To view logs:
1. Touch the Main Chat Head icon. The RxLogger Utility screen appears.
2. Touch a log to open it. The user can open many logs with each displaying a new sub Chat Head.
3. If necessary, scroll left or right to view additional Sub Chat Head icons.
4. Touch a Sub Chat Head to display the log contents.
Removing a Sub Chat Head Icon
To remove a sub chat Head icon, press and hold the icon until it disappears.
Backing Up In Overlay View
RxLogger Utility allows the user to make a zip file of the RxLogger folder in the device, which by default
contains all the RxLogger logs stored in the device.
The Backup icon is always available in Overlay View.
1. Touch . The Backup dialog box appears.
2. Touch Yes to create the back up.
59

Sound Recorder
Use Sound Recorder to record audio messages.
Recordings are saved on the microSD card (if installed) or the internal storage and are available in the
Music application (non-GMS devices) or the Play Music application (GMS devices).
Touch to open options menu.
• File type - Select the file type for the recording file.
•AMR
•3GPP
• AAC
•WAV
• AMR-WB
• AMR-WB-3GPP.
• Storage location - Select the location for the recording file.
• Phone storage
•SD card.
Applications
60

Data Capture
Introduction
The device supports data capture using:
• Internal linear imager
• RS507/RS507x Hands-free imager
• RS6000 Bluetooth Ring Scanner
• RS5100 Bluetooth Ring Scanner
• DS3678 Digital Scanner
• LI3678 Linear Imager
• DS2278 Digital Scanner
• DS8178 Digital Scanner.
Imaging
The imager uses imaging technology to take a picture of a barcode, stores the resulting image in its
memory, and executes state-of-the-art software decoding algorithms to extract the bar code data from the
image. With a 2D imager, the device has the following features:
• Omnidirectional reading of a variety of bar code symbologies, including the most popular linear, postal,
PDF417, and 2D matrix code types.
• Advanced intuitive laser aiming cross-hair and dot aiming for easy point-and-shoot operation.
Linear Imager
The device with an integrated linear imager has the following features:
• Reading a variety of bar code symbologies, including the most popular 1-D code types.
• Intuitive aiming for easy point-and-shoot operation.
The imager uses imaging technology to take a picture of a bar code, stores the resulting image in its
memory, and executes state-of-the-art software decoding algorithms to extract the bar code data from the
image.
61

Operational Modes
The device with an integrated imager supports two modes of operation, listed below. Activate each mode
by pressing the Scan button.
• Decode Mode: In this mode, the device attempts to locate and decode enabled barcodes within its field
of view. The imager remains in this mode as long as the user holds the scan button, or until it decodes
a barcode.
NOTE: To enable Pick List Mode, configure in DataWedge or set in an application using a API command.
• Pick List Mode: This mode allows the user to selectively decode a barcode when more than one
barcode is in the device’s field of view. To accomplish this, move the aiming crosshair or dot over the
required barcode to decode only this barcode. This feature is ideal for pick lists containing multiple
barcodes and manufacturing or transport labels containing more than one barcode type (either 1D or
2D).
NOTE: To enable Basic MultiBarcode Mode, configure in DataWedge or set in an application using a API
command.
Data Capture
• Basic MultiBarcode Mode: In this mode, the device attempts to locate and decode a specific number
of unique barcodes within its field of view. The device remains in this mode as long as the user holds
the scan button, or until it decodes all the barcodes.
• The device attempts to scan the programmed number of unique barcodes (from 2 through 100).
• If there are duplicate barcodes (same symbology type and data), only one of the duplicate barcodes
is decoded and the remainder are ignored. If the label has two duplicate barcodes plus another two
different barcodes, a maximum of three barcodes will be decoded from that label; one will be
ignored as a duplicate.
• Barcodes can be of multiple symbology types and still be acquired together. For example, if the
specified quantity for a Basic MultiBarcode scan is four, two barcodes can be symbology type Code
128 and the other two can be symbology type Code 39.
• If the specified number of unique barcodes is not initially in view of the device, the device will not
decode any data until the device is moved to capture the additional barcode(s) or time out occurs. If
the device field of view contains a number of barcodes greater than the specified quantity, the
device randomly decodes barcode(s) until the specified number of unique barcodes is reached. For
example, if the count is set to two and eight barcodes are in the field of view, the device decodes the
first two unique barcodes it sees, returning the data in random order.
• Basic MultiBarcode Mode does not support concatenated barcodes.
62

Data Capture
RS507/RS507x Hands-Free Imager
The RS507 and RS507x Hands-free Imagers are wearable barcode scan solution for both 1D and 2D bar
code symbologies. The scanner supports Bluetooth Human Interface Device (HID) connection to the
device.
Figure 29 RS507/RS507x Hands-Free Imager
Refer to the RS507/RS507x Hands-free Imager Product Reference Guide for more information.
RS6000 Bluetooth Ring Scanner
The RS6000 Bluetooth Ring Scanner is a wearable bar code scan solution for both 1D and 2D bar code
symbologies.
Figure 30 RS6000 Bluetooth Ring Scanner
Refer to the RS6000 Bluetooth Ring Scanner Product Reference Guide for more information.
63

RS5100 Ring Scanner
The RS5100 Ring Scanner is a wearable barcode scan solution for both 1D and 2D bar code symbologies.
The scanner supports Bluetooth Human Interface Device (HID) connection to the device.
Figure 31 RS5100 Bluetooth Ring Scanner
Refer to the RS5100 Ring Scanner Product Reference Guide for more information.
DS3678 Digital Scanner
Data Capture
The cordless DS3678 combines superior 1D and 2D omnidirectional bar code scanning performance and
advanced ergonomics in a lightweight design.
Figure 32 DS3678 Digital Scanner
Refer to the DS36X8 Digital Scanner Product Reference Guide for more information.
64

DS2278 Digital Scanner
The DS2278 digital imager scanner scans both 1D and 2D bar codes and does not compromise
performance or features.
Figure 33 DS2278 Digital Scanner
Data Capture
Refer to the DS22788 Digital Scanner Product Reference Guide for more information.
Scanning Considerations
Typically, scanning is a simple matter of aim, scan, and decode, with a few quick trial efforts to master it.
However, consider the following to optimize scanning performance:
•Range
Scanners decode best over a particular working range — minimum and maximum distances from the
barcode. This range varies according to barcode density and scanning device optics. Scan within range
for quick and constant decodes; scanning too close or too far away prevents decodes. Move the
scanner closer and further away to find the right working range for the barcodes being scanned.
• Angle
Scanning angle is important for quick decodes. When the illumination/flash reflects directly back into
the imager, the specular reflection can blind/saturate the imager. To avoid this, scan the barcode so
that the beam does not bounce directly back. Do not scan at too sharp an angle; the scanner needs to
collect scattered reflections from the scan to make a successful decode. Practice quickly shows what
tolerances to work within.
• Hold the device farther away for larger symbols.
• Move the device closer for symbols with bars that are close together.
NOTE: Scanning procedures depend on the app and device configuration. An app may use different
scanning procedures from the one listed above.
65

Scanning with Internal Imager
To read a barcode, a scan-enabled app is required. The device contains the DataWedge app that allows
the user to enable the imager, decode the barcode data, and display the barcode content.
To scan with the internal imager:
NOTE: Configure the imager illumination setting in the DataWedge application.
1. Ensure that an application is open on the device and a text field is in focus (text cursor in text field).
2. Place the barcode in the field of view of the device’s scan window. Ensure the barcode is within the
scanner’s aiming pattern.
Figure 34 Imager capturing
Data Capture
3. By default, a beep sounds indicates that the barcode was decoded successfully. Note that when the
device is in Pick List Mode, the device does not decode the barcode until the center of the illuminated
line or dot touches the barcode.
66

Data Capture
4.
The barcode content data displays in the text field.
Figure 35 Aiming Pattern
Figure 36 Pick List Mode with Multiple Barcodes
Settings
Use the Hands Free Scanning setting to configure scanning mode and the proximity trigger sensitivity.
Swipe up from the bottom of the Home screen and touch Settings > Hands Free Scanning.
Figure 37 Hands Free Scanning Settings
67

Scanning Mode
Use the Scanning Mode settings to configure how the device functions while in hands-free scanning
mode.
Figure 38 Scanning Mode Dialog Box
• Hands Free in Cart/Mount - Select to enable scanning when the device is in the Cart/Mount.
• Hands Free Always On - Select to place the device in hands free scanning mode.
• Hands Free Off - Select to disable hands free scanning mode (default).
Proximity Range
Data Capture
To configure the proximity sensor range sensitivity, touch Proximity Trigger Range.
Figure 39 Proximity Trigger Range Dialog Box
• Near - Proximity sensor detects and generates a trigger when the barcode is within 0 to 15 cm
(nominal) (default).
• Far - Proximity sensor detects and generates a trigger when the barcode is within 0 to 26 cm (nominal).
Barcode Capture with an Imager
To capture barcode data with the DS22X8 or DS81X8 imager:
1. Ensure that an application is open on the device and a text field is in focus (text cursor in text field).
2. Press and hold the trigger until either:
a. The imaging scanner reads the bar code. The imaging scanner beeps, the LED flashes, and the
scan line turns off.
or
b. The imaging scanner does not read the bar code and the scan line turns off.
Note that when the device is in Pick List Mode, the device does not decode the barcode until the center
of the illuminated line or dot touches the barcode.
68

Data Capture
Figure 40 Aiming Pattern on Bar Code - DS22X8 and DS81X8
.
3. Release the trigger.
4. The barcode content data appears in the text field.
Scanning with RS507/RS507X Hands-Free Imager
To read a barcode, a scan-enabled app is required. The device contains the DataWedge app that allows
you to enable the scanner to decode barcode data and display the barcode content.
To scan with the RS507/RS507X:
1. Pair the RS507/RS507X with the device. See Pairing Using Pairing Using Simple Serial Interface on
page 79 or
2. Ensure that an app is open on the device and a text field is in focus (text cursor in text field).
3. Point the RS507/RS507X at a barcode.
Pairing Using Bluetooth Human Interface Device on page 79 for more information.
Figure 41 Barcode Scanning with RS507/RS507X
69

Data Capture
4.
Press and hold the trigger.
The red laser aiming pattern turns on to assist in aiming. Ensure the barcode is within the area formed
by the cross-hairs in the aiming pattern. The aiming dot increases visibility in bright lighting conditions.
The RS507/RS507X LEDs light green and a beep sounds to indicate the barcode was decoded
successfully. When the RS507/RS507X is in Pick List mode, the RS507/RS507X does not decode the
barcode until the center of the crosshair touches the barcode.
Figure 42 RS507/RS507X Aiming Pattern
Figure 43 RS507/RS507X Pick List Mode with Multiple Barcodes in Aiming Pattern
5. The captured data appears in the text field.
Scanning with RS6000 Bluetooth Ring Scanner
To read a barcode, a scan-enabled app is required. Devices that contain the Zebra DataWedge app allows
you to enable the scanner to decode barcode data and display the barcode content.
To scan with the RS6000:
1. Pair the RS6000 with the device. See Pairing the Bluetooth Ring Scanner on page 76 for more
information.
70

Data Capture
2.
Ensure that an app is open on the device and a text field is in focus (text cursor in text field).
Figure 44 Barcode Scanning with RS6000
3. Point the RS6000 at a barcode.
4. Press and hold the trigger.
The red laser aiming pattern turns on to assist in aiming. Ensure the barcode is within the area formed
by the cross-hairs in the aiming pattern. The aiming dot increases visibility in bright lighting conditions.
The RS6000 LEDs light green and a beep sounds to indicate the barcode was decoded successfully.
When the RS6000 is in Pick List mode, the RS6000 does not decode the barcode until the center of the
crosshair touches the barcode.
Figure 45 RS6000 Aiming Pattern
Figure 46 RS6000 Pick List Mode with Multiple Barcodes in Aiming Pattern
5. The captured data appears in the text field.
71

Data Capture
Scanning with RS5100 Ring Scanner
To read a barcode, a scan-enabled app is required. The device contains the DataWedge app that allows
you to enable the scanner to decode barcode data and display the barcode content.
To scan with the RS5100:
1. Pair the RS5100 with the device. See Pairing the Bluetooth Ring Scanner on page 76 for more
information.
2. Ensure that an app is open on the device and a text field is in focus (text cursor in text field).
3. Point the RS5100 at a barcode.
Figure 47 Barcode Scanning with RS5100
4. Press and hold the trigger.
The red laser aiming pattern turns on to assist in aiming. Ensure the barcode is within the area formed
by the cross-hairs in the aiming pattern. The aiming dot increases visibility in bright lighting conditions.
The RS5100 LEDs light green and a beep sounds to indicate the barcode was decoded successfully.
When the RS5100 is in Pick List mode, the RS5100 does not decode the barcode until the center of the
crosshair touches the barcode.
Figure 48 RS5100 Aiming Pattern
72

Data Capture
Figure 49 RS5100 Pick List Mode with Multiple Barcodes in Aiming Pattern
5. The captured data appears in the text field.
Scanning with the DS3678 Bluetooth Scanner
To scan with the DS3678 Bluetooth Scanner:
1. Pair the scanner with the device. For more information, see Pairing a Bluetooth Scanner on page 81.
2. Ensure that an app is open on the device and a text field is in focus (text cursor in text field).
3. Point the scanner at a barcode.
Figure 50 Barcode Scanning (DS3678 shown)
73

Data Capture
4.
Press and hold the trigger.
Ensure the barcode is within the area formed by the aiming pattern. The aiming dot increases visibility
in bright lighting conditions.
Figure 51 DS3678 Aiming Pattern
Figure 52 DS3678 Pick List Mode with Multiple Barcodes in Aiming Pattern
5. The captured data appears in the text field.
Scanning with LI3678 Linear Imager
To scan with the LI3678:
1. Pair the LI3678 with the device. See Pairing a Bluetooth Scanner on page 81 for more information.
2. Ensure that an app is open on the device and a text field is in focus (text cursor in text field).
74

Data Capture
3.
Point the LI3678 at a barcode.
Figure 53 Barcode Scanning with LI3678
4. Press and hold the trigger.
5. Ensure the aiming pattern covers the barcode.
Figure 54 LI3678-SR Aiming Pattern
6. Upon successful decode, the scanner beeps and the LED displays a single green flash.
7. The captured data appears in the text field.
Scanning with DS2278 Digital Scanner
To scan with the DS2278:
1. Pair the DS278 with the device. See Pairing a Bluetooth Scanner on page 81 for more information.
2. Ensure that an app is open on the device and a text field is in focus (text cursor in text field).
75

Data Capture
3.
Point the scanner at a barcode.
Figure 55 Barcode Scanning with DS2278
4. Press and hold the trigger.
5. Ensure the aiming pattern covers the barcode.
Figure 56 DS2278 Aiming Pattern
6. Upon successful decode, the scanner beeps and the LED flashes, and the scan line turns off.
7. The captured data appears in the text field.
Pairing the Bluetooth Ring Scanner
To connect the RS507/RS507X, RS6000, or RS5100 Bluetooth Ring Scanner to the device, use one of the
following methods:
• Near Field Communication (NFC) (CC6000 with RS5100 and RS6000 imagers only)
• Simple Serial Interface (SSI)
• Bluetooth Human Interface Device (HID) Mode.
76

Data Capture
NFC Logo
NFC
Antenna
Pairing Using Near Field Communication
The device provides the ability to pair the RS5100 or RS6000 using NFC.
NOTE: Applicable to CC6000 with RS5100 and RS6000 imagers only.
To pair using NFC:
1. Ensure that the RS5100 or RS6000 is in SSI mode. Refer to the RS5100 or RS6000 User Guide for
more information.
2. Ensure that NFC is enabled on the device.
3. Align the NFC icon on the RS5100 or RS6000 with the NFC antenna on the device.
The RS6000 Status LED blinks blue indicating that the RS5100 or RS6000 is attempting to establish
connection with the device. When connection is established, the Status LED turns off and the RS5100
or RS6000 emits a single string of low/high beeps.
A notification appears on the device screen and the icon appears in the Status bar.
Figure 57 Align NFC Antennas
Pairing in HID Mode Using Near Field Communication
The device provides the ability to pair the RS5100 or RS6000 in HID mode using NFC.
NOTE: Applicable to CC6000 with RS5100 and RS6000 imagers only.
To pair in HID mode using NFC:
1. Ensure that NFC is enabled on the device.
2. Ensure that Bluetooth is enabled on the device.
3. Place the RS5100 or RS6000 in Human Interface Device (HID) mode. If the RS5100 or RS6000 is
already in HID mode, skip to step 4.
a. Remove the battery from the RS5100 or RS6000.
b. Press and hold the Restore key.
c. Install the battery onto the RS5100 or RS6000.
77

Data Capture
NFC Logo
NFC
Antenna
d.
Keep holding the Restore key for about five seconds until a chirp is heard and the Scan LEDs flash
green.
e. Scan the barcode below to place the RS5100 or RS6000 in HID mode.
Figure 58 RS6000 Bluetooth HID Barcode
4. Remove the battery from the RS5100 or RS6000.
5. Re-install the battery into the RS5100 or RS6000.
6. Align the NFC icon on the RS5100 or RS6000 with the NFC antenna on the device.
The RS5100 or RS6000 Status LED blinks blue indicating that the RS5100 or RS6000 is attempting to
establish connection with the device. When connection is established, the Status LED turns off and the
RS5100 or RS6000 emits a single string of low/high beeps.
A notification appears on the device screen and the icon appears in the Status bar.
Figure 59 Align NFC Antennas
78

Data Capture
Pairing Using Simple Serial Interface
To pair the Bluetooth Ring Scanner with the device using SSI.
1. Swipe up from the bottom of the Home screen and touch .
Figure 60 Bluetooth Pairing Utility
2. Using the Bluetooth Ring Scanner, scan the barcode on the screen.
The Bluetooth Ring Scanner emits a string of high/low/high/low beeps. The Scan LED flashes green
indicating that the Bluetooth Ring Scanner is attempting to establish connection with the device. When
connection is established, the Scan LED turns off and the Bluetooth Ring Scanner emits one string of
low/high beeps.
A notification appears on the Notification panel and the icon appears in the Status bar.
Pairing Using Bluetooth Human Interface Device
To pair the Bluetooth Ring Scanner with the device using Human Interface Device (HID):
1. Ensure that the two devices are within 10 meters (32.8 feet) of one another.
2. Place the Bluetooth Ring Scanner in HID mode. If the Bluetooth Ring Scanner is already in HID mode,
skip to step 5.
a. Remove the battery from the Bluetooth Ring Scanner.
b. Press and hold the Restore key.
c. Install the battery onto the Bluetooth Ring Scanner.
d. Keep holding the Restore key for about five seconds until a chirp is heard and the Scan LEDs flash
green.
79

Data Capture
e.
Scan the barcode below to place the Bluetooth Ring Scanner in HID mode.
Figure 61 RS507 Bluetooth HID Barcode
Figure 62 RS6000 Bluetooth HID Barcode
3. Remove the battery from the Bluetooth Ring Scanner.
4. Re-install the battery into the Bluetooth Ring Scanner.
5. Swipe down from the Status bar to open the Quick Access panel and then touch .
6. Touch Bluetooth.
7. Touch Pair new device. The device begins searching for discoverable Bluetooth devices in the area
and displays them under Available devices.
8. Scroll through the list and select RS507/RS507X or RS6000.
The device connects to the RS507/RS507X or RS6000 and Connected appears below the device
name. The Bluetooth device is added to the Paired devices list and a trusted (“paired”) connection is
established.
A notification appears on Notification panel and the icon appears in the Status bar.
80

Data Capture
Pairing a Bluetooth Scanner
Connect the scanner to the device using one of the following methods:
• Simple Serial Interface (SSI) mode
• Bluetooth Human Interface Device (HID) mode.
Pairing Using Simple Serial Interface (SSI)
To pair the scanner with the device using SSI:
1. Ensure that the two devices are within 10 meters (32.8 feet) of one another.
2. Install the battery into the scanner.
3. On the device swipe up from the bottom of the Home screen and touch .
Figure 63 Bluetooth Pairing Utility
4. Using the scanner, scan the barcode on the screen.
The scanner emits a high/low/high/low beeps. The Scan LED flashes green indicating that the scanner
is attempting to establish connection with the device. When connection is established, the Scan LED
turns off and the scanner emits one string of low/high beeps.
5. On the device touch Home button.
81

Data Capture
Pairing Using Bluetooth Human Interface Device
To pair the Bluetooth scanner with the device using HID:
1. Ensure that the two devices are within 10 meters (32.8 feet) of one another.
2. Remove the battery from the scanner.
3. Replace the battery.
4. After the scanner reboots, scan the barcode below to place the scanner in HID mode.
Figure 64 Bluetooth HID Classic Barcode
5. On the device, swipe down from the Status bar to open the Quick Access panel and then touch .
6. Touch Bluetooth.
7. Touch Pair new device. The device begins searching for discoverable Bluetooth devices in the area
and displays them under Available devices.
8. Scroll through the list and select XXXXX xxxxxx, where XXXXX is the scanner and xxxxxx is the serial
number.
The device connects to the scanner, the scanner beeps once and Connected appears below the
device name. The Bluetooth device is added to the Paired devices list and a trusted (“paired”)
connection is established.
82

DataWedge
DataWedge is a utility that adds advanced barcode scanning capability to any application without writing
code. It runs in the background and handles the interface to built-in barcode scanners. The captured
barcode data is converted to keystrokes and sent to the target application as if it was copied and pasted, or
typed on the keypad.
DataWedge allows any app on the device to get data from input sources such as a barcode scanner, MSR,
RFID, voice, or serial port and manipulate the data based on options or rules.
Configure DataWedge to
• Provide data capture services from any app.
• Use a particular scanner, reader or other peripheral device.
• Properly format and transmit data to a specific app.
Data Capture
To configure DataWedge refer to techdocs.zebra.com/datawedge/
Enabling DataWedge
Datawedge is enabled by default on this device. Re-enable DataWedge on the device from the
DataWedge app.
1. Swipe up from the bottom of the Home screen and touch .
2. Touch > Settings.
3. Touch the DataWedge enabled checkbox. A blue checkmark appears in the checkbox indicating that
DataWedge is enabled.
4. Touch the Home button.
Disabling DataWedge
1. Touch .
2. Touch Settings.
3. Touch DataWedge enabled.
The blue check disappears from the checkbox indicating that DataWedge is disabled.
.
83

Supported Decoders
NOTE: DataWedge supports the decoders listed below but not all are validated on this device.
Table 11 Supported Decoders
Decoders
Australian
Postal
Aztec XXXXXXX--X
Canadian
Postal
Chinese 2 of 5OOOOOOOOO
Codabar XXXXXXXXX
Data Capture
SE2100
Internal Imager
OOOOOOO--O
O O -- O O -- -- -- --
SE4710
Internal Imager
RS507/RS507X
RS6000
RS5100
DS2278
DS3678
LI3678
DS8178
Code 11 OOOOOOOOO
Code 128 XXXXXXXXX
Code 39 XXXXXXXXX
Code 93 OOOOOOOOO
Composite ABOOOOOOO--O
Composite COOOOOOO--O
Discrete 2 of 5OOOOOOOOO
Datamatrix XXXXXXX--X
Dutch PostalOOOOOOO--O
DotCode OOOOOOOOO
EAN13 XXXXXXXXX
EAN8 XXXXXXXXX
Grid Matrix OOOOOOOOO
GS1 DataBarXXXXXXXXX
GS1 DataBar
Expanded
GS1 DataBar
Limited
GS1
Datamatrix
XXXXXXXXX
OOOOOOOOO
OO--OOOO--O
GS1 QRCodeOO--OOOO--O
HAN XIN -- -- -- O O -- O O --
Interleaved 2
of 5
OOOOOOOOO
84

Data Capture
Table 11 Supported Decoders (Continued)
Decoders
SE2100
Internal Imager
Japanese
Postal
Korean 3 of 5OOOOOOOOO
MAIL MARK XX--XXXX--X
Matrix 2 of 5 OOOOOOOOO
Maxicode XXXXXXX--X
MicroPDF OOOOOOO--O
MicroQR OOOOOOO--O
MSI OOOOOOOOO
PDF417 XXXXXXX--X
OOOOOOO--O
SE4710
Internal Imager
RS507/RS507X
RS6000
RS5100
DS2278
DS3678
LI3678
DS8178
QR Code XXXXXXX--X
Decoder
Signature
TLC 39 OOOOOOOOO
Trioptic 39 OOOOOOOOO
UK Postal OOOOOOO--O
UPCA XXXXXXXXX
UPCE0 XXXXXXXXX
UPCE1 OOOOOOOOO
US4state OOOOOOO-- O
US4state FICSOOOOOOO--O
US Planet OOOOOOO--O
US Postnet OOOOOOO--O
Key
X = Enabled
O = Disabled
-- = Not Supported
OOOOOO---- --
Touch the Back button to return to the previous screen.
85

Wireless
Introduction
This section provides information on the wireless features:
• Wireless Local Area Network (WLAN)
• Bluetooth
•Cast
• Near Field Communications (NFC).
Wireless Local Area Networks
Wireless local area networks (WLANs) allow the device to communicate wirelessly inside a building.
Before using the device on a WLAN, the facility must be set up with the required hardware to run the
WLAN (sometimes known as infrastructure). The infrastructure and the device must both be properly
configured to enable this communication.
Refer to the documentation provided with the infrastructure (access points (APs), access ports, switches,
Radius servers, etc.) for instructions on how to set up the infrastructure.
Once the infrastructure is set up to enforce the chosen WLAN security scheme, use the Wireless &
networks settings configure the device to match the security scheme.
The device supports the following WLAN security options:
•None
• Enhanced Open
• Wireless Equivalent Privacy (WEP)
• Wi-Fi Protected Access (WPA)/WPA2 Personal (PSK)
• WPA3-Personal
• WPA/WPA2/WPA3 Enterprise (EAP)
• WPA3-Enterprise 192-bit
The Status bar displays icons that indicate Wi-Fi network availability and Wi-Fi status.
Connecting to a Wi-Fi Network
To connect to a Wi-Fi network:
1. Go to Settings.
86

2.
Touch Network & internet.
3. Touch Wi-Fi to open the Wi-Fi screen. The device searches for WLANs in the area and lists them.
4. Scroll through the list and select the desired WLAN network.
5. For open networks, touch profile once or press and hold and then select Connect or for secure
networks enter the required password or other credentials then touch Connect. See the system
administrator for more information.
The device obtains a network address and other required information from the network using the
dynamic host configuration protocol (DHCP) protocol. To configure the device with a fixed internet
protocol (IP) address, see Configuring the Device to Use a Static IP Address on page 90.
6. In the Wi-Fi setting field, Connected appears indicating that the device is connected to the WLAN.
Removing a Wi-Fi Network
To remove a remembered or connected network:
1. Go to Settings.
2. Touch Network & internet > W-Fi.
Wireless
3. Scroll down to the bottom of the list and touch Saved networks.
4. Touch the name of the network.
5. Touch FORGET.
6. Touch the Home button.
WLAN Configuration
This section provides information on configuring Wi-Fi settings.
Configuring a Secure Wi-Fi Network
1. Go to Settings.
2. Touch Network & internet > Wi-Fi.
3. Slide the switch to the ON position.
4. The device searches for WLANs in the area and lists them on the screen.
5. Scroll through the list and select the desired WLAN network.
6. Touch the desired network. If the network security is Enhanced Open, the device automatically
connects to the network. For all other network security a dialog box appears.
7. If the network security is WPA/WPA2-Personal, WPA3-Personal, or WEP, enter the required
password and then touch Connect.
8. If the network security is WPA/WPA2/WPA3 Enterprise:
• Touch the EAP method drop-down list and select one of the following:
• PEAP
•TLS
87

Wireless
•TTLS
•PWD
• LEAP.
• Touch the Phase 2 authentication drop-down list and select an authentication method.
• If required, touch CA certificate and select a Certification Authority (CA) certificate. Note:
Certificates are installed using the Security settings.
• If required, touch User certificate and select a user certificate. Note: User certificates are installed
using the Location & security settings.
• If required, in the Identity text box, enter the username credentials.
• If desired, in the Anonymous identity text box, enter an anonymous identity username.
• If required, in the Password text box, enter the password for then given identity.
9. If the network security is WPA3-Enterprise 192-bit:
• Touch CA certificate and select a Certification Authority (CA) certificate. Note: Certificates are
installed using the Security settings.
•Touch User certificate and select a user certificate. Note: User certificates are installed using the
Security settings.
• In the Identity text box, enter the username credentials.
NOTE: By default, the network Proxy is set to None and the IP settings is set to DHCP. See Configuring for
a Proxy Server on page 89 for setting connection to a proxy server and see Configuring the Device to Use
a Static IP Address on page 90 for setting the device to use a static IP address.
10. Touch Connect.
11. Touch the Home button.
Manually Adding a Wi-Fi Network
Manually add a Wi-Fi network if the network does not broadcast its name (SSID) or to add a Wi-Fi network
when out of range.
1. Go to Settings.
2. Touch Network & internet > Wi-Fi.
3. Slide the Wi-Fi switch to the On position.
4. Scroll to the bottom of the list and select Add network.
5. In the Network name text box, enter the name of the Wi-Fi network.
6. In the Security drop-down list, set the type of security to:
• None
• Enhanced Open
• WEP
• WPA/WPA2-Personal
• WPA3-Personal
• WPA/WPA2/WPA3-Enterprise
• WPA3-Enterprise 192-bit
88

Wireless
7.
If the network security is None or Enhanced Open, touch Save.
8. If the network security is WEP, WPA3-Personal, or WPA/WPA2-Personal, enter the required
password and then touch Save.
9. If the network security is WPA/WPA2/WPA3-Enterprise:
• Touch the EAP method drop-down list and select one of the following:
• PEAP
•TLS
•TTLS
•PWD
• LEAP.
• Touch the Phase 2 authentication drop-down list and select an authentication method.
• If required, touch CA certificate and select a Certification Authority (CA) certificate. Note:
Certificates are installed using the Security settings.
• If required, touch User certificate and select a user certificate. Note: User certificates are installed
using the Security settings.
• If required, in the Identity text box, enter the username credentials.
• If desired, in the Anonymous identity text box, enter an anonymous identity username.
• If required, in the Password text box, enter the password for the given identity.
10. If the network security is WPA3-Enterprise 192-bit:
• Touch CA certificate and select a Certification Authority (CA) certificate. Note: Certificates are
installed using the Security settings.
•Touch User certificate and select a user certificate. Note: User certificates are installed using the
Security settings.
• In the Identity text box, enter the username credentials.
NOTE: By default, the network Proxy is set to None and the IP settings is set to DHCP. See Configuring for
a Proxy Server on page 89 for setting connection to a proxy server and see Configuring the Device to Use
a Static IP Address on page 90 for setting the device to use a static IP address.
11. Touch Save. To connect to the saved network, touch and hold on the saved network and select
Connect to network.
12. Touch the Home button.
Configuring for a Proxy Server
A proxy server is a server that acts as an intermediary for requests from clients seeking resources from
other servers. A client connects to the proxy server and requests some service, such as a file, connection,
web page, or other resource, available from a different server. The proxy server evaluates the request
according to its filtering rules. For example, it may filter traffic by IP address or protocol. If the request is
validated by the filter, the proxy provides the resource by connecting to the relevant server and requesting
the service on behalf of the client.
It is important for enterprise customers to be able to set up secure computing environments within their
companies, making proxy configuration essential. Proxy configuration acts as a security barrier ensuring
that the proxy server monitors all traffic between the Internet and the intranet. This is normally an integral
part of security enforcement in corporate firewalls within intranets.
89

Wireless
1.
Go to Settings.
2. Touch Network & internet > Wi-Fi.
3. Slide the Wi-Fi switch to the On position.
4. In the network dialog box, select and touch a network.
5. Touch to edit the network details.
6. Touch the down arrow to hide the keyboard.
7. Touch Advanced options.
8. Touch Proxy and select Manual.
9. In the Proxy hostname text box, enter the address of the proxy server.
10. In the Proxy port text box, enter the port number for the proxy server.
11. In the Bypass proxy for text box, enter addresses for web sites that are not required to go through the
proxy server. Use a comma “,” between addresses. Do not use spaces or carriage returns between
addresses.
12. Touch Save.
13. Touch Connect.
14. Touch the Home button.
Configuring the Device to Use a Static IP Address
By default, the device is configured to use Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP) to assign an
Internet protocol (IP) address when connecting to a wireless network.
1. Go to Settings.
2. Touch Network & internet > Wi-Fi.
3. Slide the Wi-Fi switch to the On position.
4. In the network dialog box, select and touch a network.
5. Touch to edit the network details.
6. Touch the down arrow to hide the keyboard.
7. Touch Advanced options.
8. Touch IP settings and select Static.
9. In the IP address text box, enter an IP address for the device.
10. If required, in the Gateway text box, enter a gateway address for the device.
11. If required, in the Network prefix length text box, enter the prefix length.
12. If required, in the DNS 1 text box, enter a Domain Name System (DNS) address.
13. If required, in the DNS 2 text box, enter a DNS address.
14. Touch Save.
90

15.
Touch Connect.
16. Touch the Home button.
Wi-Fi Preferences
Use the Wi-Fi preferences to configure advanced Wi-Fi settings. From the Wi-Fi screen scroll down to the
bottom of the screen and touch Wi-Fi preferences.
• Turn on W-Fi automatically - When enabled, Wi-Fi automatically turns back on when near high quality
saved networks.
• Open network notification - When enabled, notifies the user when an open network is available.
•Advanced - Touch to expand options.
• Additional settings - See Additional Wi-Fi Settings.
• Install Certificates – Touch to install certificates.
• Network rating provider - To help determine what constitutes a good Wi-Fi network, Android
supports external Network rating providers that provide information about the quality of open Wi-Fi
networks. Select one of the providers listed or None. If none are available or selected, the Connect
to open networks feature is disabled.
• Wi-Fi Direct - Displays a list of devices available for a direct Wi-Fi connection.
• MAC address - Displays the Media Access Control (MAC) address of the device when connecting
to Wi-Fi networks.
• IP address - Displays the IP address of the device when connecting to Wi-Fi networks.
Wireless
Additional Wi-Fi Settings
NOTE: Additional Wi-Fi settings are for the device, not for a specific wireless network.
Use the Additional Settings to configure additional Wi-Fi settings. To view the additional Wi-Fi settings,
scroll to the bottom of the Wi-Fi screen and touch Wi-Fi Preferences > Advanced > Additional settings.
• Regulatory
• Country Selection - Displays the acquired country code if 802.11d is enabled, else it displays the
currently selected country code.
• Region code - Displays the current region code.
• Band and Channel Selection
• Wi-Fi frequency band - Set the frequency band to: Auto (default), 5 GHz only or 2.4 GHz only.
• Available channels (2.4 GHz) - Touch to display the Available channels menu. Select specific
channels and touch OK.
• Available channels (5 GHz) - Touch to display the Available channels menu. Select specific
channels and touch OK.
• Logging
• Advanced Logging – Touch to enable advanced logging or change the log directory.
• Wireless logs - Use to capture Wi-Fi log files.
• Fusion Logger - Touch to open the Fusion Logger application. This application maintains a
history of high level WLAN events which helps to understand the status of connectivity.
91

• About
• Version - Displays the current Fusion information.
Wi-Fi Direct
Wi-Fi Direct devices can connect to each other without having to go through an access point. Wi-Fi Direct
devices establish their own ad-hoc network when required, letting you see which devices are available and
choose which one you want to connect to.
1. Go to Settings.
2. Touch Wi-Fi > Wi-Fi preferences > Advanced > Wi-Fi Direct. The device begins searching for
another Wi-Fi Direct device.
3. Under Peer devices, touch the other device name.
4. On the other device, select Accept.
Connected appears on the device. On both devices, in their respective Wi-Fi Direct screens, the other
device name appears in the list.
Wireless
• Fusion Status - Touch to display live status of WLAN state. Also provides information about the
device and connected profile.
Bluetooth
Bluetooth devices can communicate without wires, using frequency-hopping spread spectrum (FHSS)
radio frequency (RF) to transmit and receive data in the 2.4 GHz Industry Scientific and Medical (ISM)
band (802.15.1). Bluetooth wireless technology is specifically designed for short-range (10 m (32.8 ft))
communication and low power consumption.
Devices with Bluetooth capabilities can exchange information (for example, files, appointments, and tasks)
with other Bluetooth enabled devices such as printers, access points, and other mobile devices.
The device supports Bluetooth Low Energy. Bluetooth Low Energy is targeted at applications in the
healthcare, fitness, security, and home entertainment industries. It provides reduced power consumption
and cost while maintaining standard Bluetooth range.
Adaptive Frequency Hopping
Adaptive Frequency Hopping (AFH) is a method of avoiding fixed frequency interferers, and can be used
with Bluetooth voice. All devices in the piconet (Bluetooth network) must be AFH-capable in order for AFH
to work. There is no AFH when connecting and discovering devices. Avoid making Bluetooth connections
and discoveries during critical 802.11b communications. AFH for Bluetooth consists of four main sections:
• Channel Classification - A method of detecting an interference on a channel-by-channel basis, or
pre-defined channel mask.
• Link Management - Coordinates and distributes the AFH information to the rest of the Bluetooth
network.
• Hop Sequence Modification - Avoids interference by selectively reducing the number of hopping
channels.
• Channel Maintenance - A method for periodically re-evaluating the channels.
92

Security
Wireless
When AFH is enabled, the Bluetooth radio “hops around” (instead of through) the 802.11b high-rate
channels. AFH coexistence allows enterprise devices to operate in any infrastructure.
The Bluetooth radio in this device operates as a Class 2 device power class. The maximum output power
is 2.5 mW and the expected range is 10 m (32.8 ft). A definition of ranges based on power class is difficult
to obtain due to power and device differences, and whether in open space or closed office space.
NOTE: It is not recommended to perform Bluetooth wireless technology inquiry when high rate 802.11b op-
eration is required.
The current Bluetooth specification defines security at the link level. Application-level security is not
specified. This allows application developers to define security mechanisms tailored to their specific need.
Link-level security occurs between devices, not users, while application-level security can be implemented
on a per-user basis. The Bluetooth specification defines security algorithms and procedures required to
authenticate devices, and if needed, encrypt the data flowing on the link between the devices. Device
authentication is a mandatory feature of Bluetooth while link encryption is optional.
Pairing of Bluetooth devices is accomplished by creating an initialization key used to authenticate the
devices and create a link key for them. Entering a common personal identification number (PIN) in the
devices being paired generates the initialization key. The PIN is never sent over the air. By default, the
Bluetooth stack responds with no key when a key is requested (it is up to user to respond to the key
request event). Authentication of Bluetooth devices is based-upon a challenge-response transaction.
Bluetooth allows for a PIN or passkey used to create other 128-bit keys used for security and encryption.
The encryption key is derived from the link key used to authenticate the pairing devices. Also worthy of
note is the limited range and fast frequency hopping of the Bluetooth radios that makes long-distance
eavesdropping difficult.
Recommendations are:
• Perform pairing in a secure environment
• Keep PIN codes private and do not store the PIN codes in the device
• Implement application-level security.
Bluetooth Profiles
The device supports the Bluetooth services listed.
Table 12 Bluetooth Profiles
Service Discovery Protocol
(SDP)
Serial Port Profile (SPP) Allows use of RFCOMM protocol to emulate serial cable connection
Object Push Profile (OPP) Allows the device to push and pull objects to and from a push
Advanced Audio Distribution
Profile (A2DP)
Profile Description
Handles the search for known and specific services as well as
general services.
between two Bluetooth peer devices. For example, connecting the
device to a printer.
server.
Allows the device to stream stereo-quality audio to a wireless
headset or wireless stereo speakers.
93

Wireless
Table 12 Bluetooth Profiles (Continued)
Profile Description
Audio/Video Remote Control
Profile (AVRCP)
Personal Area Network (PAN) Allows the use of Bluetooth Network Encapsulation Protocol to
Human Interface Device Profile
(HID)
Headset Profile (HSP) Allows a hands-free device, such as a Bluetooth headset, to place
Hands-Free Profile (HFP) Allows car hands-free kits to communicate with the device in the car.
Allows the device to control A/V equipment to which a user has
access. It may be used in concert with A2DP.
provide L3 networking capabilities over a Bluetooth link. Only PANU
role is supported.
Allows Bluetooth keyboards, pointing devices, gaming devices and
remote monitoring devices to connect to the device.
and receive calls on the device.
Phone Book Access Profile
(PBAP)
Out of Band (OOB) Allows exchange of information used in the pairing process. Pairing
Symbol Serial Interface (SSI) Allows for communication with Bluetooth Imager.
File Transfer Profile (FTP) Provides the capability to browse, manipulate and transfer files in
Generic Attribute Profile (GATT) Provides profile discovery and description services for Bluetooth
HID Over GATT Profile (HOGP) Defines the procedures and features used by Bluetooth low energy
Scan Parameters Profile (ScPP) Provides devices with information to assist them in managing their
Message Access Profile (MAP) Defines the features and procedures used by devices that exchange
Allows exchange of Phone Book Objects between a car kit and a
mobile device to allow the car kit to display the name of the incoming
caller; allow the car kit to download the phone book so the user can
initiate a call from the car display.
is completed using the Bluetooth radio, but requires information from
the OOB mechanism. Using OOB with NFC enables pairing when
devices simply get close, rather than requiring a lengthy discovery
process.
file system of another system. Uses GOEP as a basis.
Low Energy protocol. It defines how attributes are grouped together
into sets to form services.
HID Devices using GATT and Bluetooth HID Hosts using GATT.
connection idle timeout and advertising parameters to optimize for
power consumption and/or reconnection latency.
message objects.
Dial Up Networking (DUN) Provides a standard to access the Internet and other dial-up
services over Bluetooth.
Generic Access Profile (GAP) Use for device discovery and authentication.
OBject EXchange (OBEX) Facilitates the exchange of binary objects between devices.
Generic Object Exchange Profile
(GOEP)
Generic Audio/Video Distribution
Profile (GAVDP)
Provides a basis for other data profiles. Based on OBEX.
Provides the basis for A2DP and VDP, the basis of the systems
designed for distributing video and audio streams using Bluetooth
technology.
94

Bluetooth Power States
The Bluetooth radio is off by default.
• Suspend - When the device goes into suspend mode, the Bluetooth radio stays on.
• Airplane Mode - When the device is placed in Airplane Mode, the Bluetooth radio turns off. When
Airplane mode is disabled, the Bluetooth radio returns to the prior state. When in Airplane Mode, the
Bluetooth radio can be turned back on if desired.
Bluetooth Radio Power
Turn off the Bluetooth radio to save power or if entering an area with radio restrictions (for example, an
airplane). When the radio is off, other Bluetooth devices cannot see or connect to the device. Turn on the
Bluetooth radio to exchange information with other Bluetooth devices (within range). Communicate only
with Bluetooth radios in close proximity.
Enabling Bluetooth
1. Swipe down from the Status bar to open the Notification panel.
Wireless
2. Touch to turn Bluetooth on.
3. Touch the Home button.
Disabling Bluetooth
1. Swipe down from the Status bar to open the Notification panel.
2. Touch to turn Bluetooth off.
3. Touch the Home button.
Discovering Bluetooth Device(s)
The device can receive information from discovered devices without pairing. However, once paired, the
device and a paired device exchange information automatically when the Bluetooth radio is on.
1. Ensure that Bluetooth is enabled on both devices.
2. Ensure that the Bluetooth device to discover is in discoverable mode.
3. Ensure that the two devices are within 10 meters (32.8 feet) of one another.
4. Swipe down from the Status bar to open the Quick Access panel.
5. Touch and hold Bluetooth.
6. Touch Pair new device. The device begins searching for discoverable Bluetooth devices in the area
and displays them under Available devices.
7. Scroll through the list and select a device. The Bluetooth pairing request dialog box appears.
8. Touch Pair on both devices.
9. The Bluetooth device is added to the Paired devices list and a trusted (“paired”) connection is
established.
95

Changing the Bluetooth Name
By default, the device has a generic Bluetooth name that is visible to other devices when connected.
1. Go to Settings.
2. Touch Connected devices > Connection preferences > Bluetooth.
3. If Bluetooth is not on, move the switch to turn Bluetooth on.
4. Touch Device name.
5. Enter a name and touch RENAME.
6. Touch the Home button.
Connecting to a Bluetooth Device
Once paired, connect to a Bluetooth device.
1. Go to Settings.
Wireless
2. Touch Connected devices > Connection preferences > Bluetooth.
3. In the list, touch the unconnected Bluetooth device.
When connected, Connected appears below the device name.
Selecting Profiles on the Bluetooth Device
Some Bluetooth devices have multiple profiles.
1. Go to Settings.
2. Touch Connected devices > Connection preferences > Bluetooth.
3. In the Paired Devices list, touch next to the device name.
4. Turn on or off a profile to allow the device to use that profile.
5. Touch the Home button.
Unpairing a Bluetooth Device
Unpairing a Bluetooth device erases all pairing information.
1. Go to Settings.
2. Touch Connected devices > Connection preferences > Bluetooth.
3. In the Paired Devices list, touch next to the device name.
4. Touch FORGET.
5. Touch the Home button.
96

Wireless
Cast
Use Cast to mirror the device screen on a Miracast enabled wireless display.
1. Go to Settings.
2. Touch Connected devices > Connection preferences > Cast.
3. Touch > Enable wireless display. The device searches for nearby Miracast devices and lists them.
4. Touch a device to begin casting.
5. Touch the Home button.
Near Field Communications (CC6000 Only)
NFC/HF RFID is a short-range wireless connectivity technology standard that enables secure transaction
between a reader and a contactless smartcard. The technology is based on ISO/IEC 14443 type A and B
(proximity), ISO/IEC 15693 (vicinity), and FeliCa standards, using the HF 13.56 MHz unlicensed band.
The device supports the following operating modes:
• Reader mode
• Peer-to-Peer communication
• Card Emulation mode.
Using NFC, the device can:
• Read contactless cards such as contactless tickets, ID cards and ePassport.
• Read and write information to contactless cards such as SmartPosters and tickets, as well as devices
with NFC interface such as vending machines.
• Read information from supported medical sensors.
• Pair with supported Bluetooth devices such as printers, ring scanners (ex. RS6000), and headsets (ex.
HS3100).
• Exchange data with another NFC device.
• Emulate contactless card such as payment, ticket, or SmartPoster.
The device NFC antenna is positioned to read NFC cards from the top of the device while the device is
being held.
97
 Loading...
Loading...