Page 1

User’s
Manual
EJX110B, EJX310B and EJX430B
Differential Pressure and
Pressure Transmitters
IM 01C27B01-01EN
Yokogawa Electric Corporation
IM 01C27B01-01EN
9th Edition
Page 2

EJX110B, EJX310B and EJX430B
Differential Pressure and Pressure Transmitters
IM 01C27B01-01EN 9th Edition
Contents
1. Introduction ............................................................................................... 1-1
1.1 Safe Use of This Product .................................................................................1-2
1.2 Radio Wave ........................................................................................................1-3
1.3 Warranty .............................................................................................................1-3
1.4 Trademarks ........................................................................................................1-3
1.5 ATEX Documentation .......................................................................................1-4
2. Handling Cautions .................................................................................... 2-1
2.1 Model and Specications Check .....................................................................2-1
2.2 Unpacking ..........................................................................................................2-1
2.3 Storage ...............................................................................................................2-1
2.4 Selecting the Installation Location ................................................................ 2-2
2.5 Pressure Connection ........................................................................................ 2-2
2.6 Restrictions on Use of Radio Transceivers ...................................................2-3
2.7 Insulation Resistance and Dielectric Strength Test ......................................2-3
2.8 Installation of an Explosion-Protected Instrument .......................................2-4
2.8.1 FM Approval .......................................................................................2-4
2.8.2 CSA Certication ................................................................................2-5
2.8.3 ATEX Certication ..............................................................................2-6
2.8.4 IECEx Certication .............................................................................2-7
2.9 EMC Conformity Standards .............................................................................2-8
2.10 Pressure Equipment Directive (PED)
2.11 Low Voltage Directive .......................................................................................2-9
2.12 Regulatory Compliance for Radio and Telecommunication ........................2-9
2.12.1 Radio and Telecommunications .........................................................2-9
2.12.2 FCC compliance ................................................................................2-9
2.12.3 Industry Canada (IC) compliance ....................................................2-10
.................................................. 2-8
i
3. Component Names .................................................................................. 3-1
4. Installation ................................................................................................. 4-1
4.1 Precautions .......................................................................................................4-1
4.2 Mounting ........................................................................................................... 4-1
4.3 Changing the Process Connection .................................................................4-3
4.4 Swapping the High/Low-pressure Side Connection ..................................... 4-3
4.4.1 Rotating Pressure-detector Section 180° .........................................4-3
9th Edition: Jan. 2014 (YK)
All Rights Reserved, Copyright © 2009, Yokogawa Electric Corporation
IM 01C27B01-01EN
Page 3

4.4.2 Using the Conguration Tool ..............................................................4-4
4.5 Rotating Transmitter Section ...........................................................................4-4
4.6 Changing the Direction of Integral Indicator ................................................. 4-5
4.7 Changing the direction of the antenna ...........................................................4-5
5. Installing Impulse Piping ......................................................................... 5-1
5.1 Impulse Piping Installation Precautions ........................................................5-1
5.1.1 Connecting Impulse Piping to a Transmitter ......................................5-1
5.1.2 Routing the Impulse Piping ................................................................5-3
5.2 Impulse Piping Connection Examples ...........................................................5-4
6. Wiring ......................................................................................................... 6-1
6.1 Mounting Antenna and Wiring .........................................................................6-1
6.1.1 Mounting the antenna ........................................................................6-1
6.1.2 Mounting External Antenna and Wiring Antenna Extension Cable ...6-2
6.1.2.1 Mounting of External Antenna ............................................................6-2
6.1.2.2 Wiring of Antenna Extension Cable ...................................................6-2
6.1.2.3 Mounting of Arrester and Wiring ........................................................6-4
6.2 Grounding ..........................................................................................................6-4
ii
7. Operation ................................................................................................... 7-1
7.1 Preparation for Starting Operation ................................................................. 7-1
7.2 Zero Point Adjustment ..................................................................................... 7-2
7.3 Starting Operation ............................................................................................ 7-3
7.4 Connecting to the Field Wireless Network ..................................................... 7-3
7.5 Shutting Down the Transmitter .......................................................................7-5
7.6 Venting or Draining Transmitter Pressure-detector Section .......................7-6
7.6.1 Draining Condensate .........................................................................7-6
7.6.2 Venting Gas........................................................................................7-6
8. Setting Parameters ................................................................................... 8-1
8.1 Environment for parameter setting .................................................................8-1
8.2 Preparing Software ...........................................................................................8-1
8.2.1 Softwares for the Field Wireless Conguration Tool and the Device
Conguration Tool ..............................................................................8-1
8.2.2 Software Download ............................................................................8-1
8.3 Setting Parameters ...........................................................................................8-1
8.3.1 Parameter Usage and Selection ........................................................8-1
8.3.2 Function Block and Menu Tree ..........................................................8-2
8.3.3 Parameters for Wireless Communication ........................................8-17
8.3.4 Tag and Device Information .............................................................8-18
8.3.5 Unit ...................................................................................................8-18
8.3.6 Range Change .................................................................................8-18
8.3.7 Output Mode ....................................................................................8-18
8.3.8 Output Signal Low Cut Mode Setup ................................................8-19
8.3.9 Impulse Line Connection Orientation Setup ....................................8-19
IM 01C27B01-01EN
Page 4

8.3.10 Integral Indicator Display Mode .......................................................8-19
8.3.11 Integral Indicator Scale Setup ..........................................................8-20
8.3.12 Unit for Displayed Temperature .......................................................8-20
8.3.13 Unit for Displayed Static Pressure ...................................................8-20
8.3.14 Zero Point Adjustment and Span Adjustment ..................................8-21
8.3.15 Software Write Protect .....................................................................8-23
8.3.16 Switching to Deep Sleep Mode ........................................................8-23
8.3.17 Switching to Silence Mode ...............................................................8-23
8.4 Self-Diagnostics ..............................................................................................8-24
8.4.1 Identify Problems by Using the Device Conguration Tool ..............8-24
8.4.2 Alert Report ......................................................................................8-25
8.4.3 Checking with Integral Indicator .......................................................8-27
9. Maintenance .............................................................................................. 9-1
9.1 Overview ............................................................................................................ 9-1
9.2 Calibration Instruments Selection .................................................................. 9-1
9.3 Calibration .........................................................................................................9-1
9.4 Disassembly and Reassembly ........................................................................9-3
9.4.1 Replacing the Integral Indicator .........................................................9-3
9.4.2 Replacing the RF Assembly ...............................................................9-4
9.4.3 Replacing the CPU Assembly ............................................................9-4
9.4.4 Cleaning and Replacing the Capsule Assembly ...............................9-5
9.4.5 Replacing the Process Connector Gaskets .......................................9-6
9.4.6 Replacing the Battery Pack ...............................................................9-6
9.4.7 Replacing the Batteries ......................................................................9-7
9.4.8 Handling Batteries ..............................................................................9-7
9.5 Troubleshooting ................................................................................................9-8
9.5.1 Basic Troubleshooting .......................................................................9-8
9.5.2 Troubleshooting Flowcharts ...............................................................9-9
9.5.3 Errors and Countermeasures ..........................................................9-11
iii
10. Parameter Summary ..............................................................................10-1
11. General Specications .......................................................................... 11-1
11.1 Standard Specications .................................................................................11-1
11.2 Model and Sufx Codes ................................................................................. 11-4
11.3 Optional Specications ................................................................................. 11-8
11.4 Dimensions .................................................................................................... 11-11
Revision Information ...............................................................................................i
IM 01C27B01-01EN
Page 5
<1. Introduction>
1. Introduction
1-1
Thank you for purchasing the DPharp EJX
Differential Pressure and pressure transmitter.
Your EJX Pressure Transmitter was precisely
calibrated at the factory before shipment. To ensure
both safety and efciency, please read this manual
carefully before you operate the instrument.
NOTE
This manual covers the EJX110B differential
pressure transmitter, EJX430B gauge pressure
transmitter and EJX310B absolute pressure
transmitter and describes how to use for not only
the integral antenna type transmitters but also
the detachable antenna ones.
Unless otherwise stated, the illustrations in this
manual are of the EJX110B differential pressure
transmitter with an integral antenna type.
Users of the other models and specications
should bear in mind that certain features of their
instrument will differ from those shown in the
illustrations of the EJX110B.
• The specications covered by this manual are
limited to those for the standard type under the
specied model number break-down and do not
cover custom-made instruments.
• Please note that changes in the specications,
construction, or component parts of the
instrument may not immediately be reected
in this manual at the time of change, provided
that postponement of revisions will not cause
difculty to the user from a functional or
performance standpoint.
• Yokogawa assumes no responsibilities for this
product except as stated in the warranty.
• If the customer or any third party is harmed by
the use of this product, Yokogawa assumes
no responsibility for any such harm owing to
any defects in the product which were not
predictable, or for any indirect damages.
• The following safety symbols are used in this
manual and on the product:
Model
EJX110B
EJX310B
EJX430B
Regarding This Manual
• This manual should be provided to the end
user.
• The contents of this manual are subject to
change without prior notice.
• All rights reserved. No part of this manual may
be reproduced in any form without Yokogawa’s
written permission.
• Yokogawa makes no warranty of any kind with
regard to this manual, including, but not limited
to, implied warranty of merchantability and
tness for a particular purpose.
• If any question arises or errors are found, or if
any information is missing from this manual,
please inform the nearest Yokogawa sales
ofce.
WARNING
Indicates a potentially hazardous situation which,
if not avoided, could result in death or serious
injury.
CAUTION
Indicates a potentially hazardous situation which,
if not avoided, may result in minor or moderate
injury or physical damage. It may also be used to
alert against unsafe practices.
IMPORTANT
Indicates that operating the hardware or software
in this manner may damage it or lead to system
failure.
IM 01C27B01-01EN
Page 6

<1. Introduction>
(b) Wiring
NOTE
Draws attention to information essential for
understanding the operation and features.
Functional grounding terminal
• The instrument must be installed by an
engineer or technician who has an expert
knowledge of this instrument. Operators are not
permitted to carry out wiring unless they meet
this condition.
(c) Maintenance
1-2
Caution
This symbol indicates that the operator
must refer to an explanation in the user’s
manual in order to avoid the risk of injury
or death of personnel or damage to the
instrument.
1.1 Safe Use of This Product
For the safety of the operator and to protect the
instrument and the system, please be sure to follow
this manual’s safety instructions when handling this
instrument. If these instructions are not heeded,
the protection provided by this instrument may be
impaired. In this case, Yokogawa cannot guarantee
that the instrument can be safely operated. Please
pay special attention to the following points:
(a) Installation
• This instrument may only be installed by an
engineer or technician who has an expert
knowledge of this device. Operators are not
allowed to carry out installation unless they
meet this condition.
• With high process temperatures, care must
be taken not to burn yourself by touching the
instrument or its casing.
• Never loosen the process connector nuts when
the instrument is installed in a process. This can
lead to a sudden, explosive release of process
uids.
• Please carry out only the maintenance
procedures described in this manual. If you
require further assistance, please contact the
nearest Yokogawa ofce.
• Care should be taken to prevent the build up of
dust or other materials on the display glass and
the name plate. To clean these surfaces, use a
soft, dry cloth.
(d) Explosion Protected Type Instrument
• Users of explosion proof instruments should
refer rst to section 2.8 (Installation of an
Explosion Protected Instrument) of this manual.
• The use of this instrument is restricted to those
who have received appropriate training in the
device.
• Take care not to create sparks when accessing
the instrument or peripheral devices in a
hazardous location.
• Repair or modication to this instrument by
customer will cause malfunction of explosion
protect function and hazardous situation. If you
need to repair or modication, please contact
the nearest Yokogawa ofce.
(e) Modication
• Yokogawa will not be liable for malfunctions or
damage resulting from any modication made
to this instrument by the customer.
• When draining condensate from the pressure
detector section, take appropriate precautions
to prevent the inhalation of harmful vapors and
the contact of toxic process uids with the skin
or eyes.
• When removing the instrument from a
hazardous process, avoid contact with the uid
and the interior of the meter.
• All installation shall comply with local installation
requirements and the local electrical code.
IM 01C27B01-01EN
Page 7

<1. Introduction>
1-3
1.2 Radio Wave
IMPORTANT
- This instrument is equipped with a wireless
module which is designated as a certication
of construction type as a wireless
facility for 2.4 GHz band low-power data
communication system of the Radio Act.
Refer to 2.12 “Regulatory Compliance for
Radio and Telecommunication” for detail.
- Due to the designated certication of
construction type, users may be subject to
legal punishment in case of:
- Disassembling or modifying the wireless
module or antenna in this instrument
- Peeling off the certication label attached
to the wireless module in this instrument
- Preventing interference with other wireless
stations
The operating frequency bandwidth of this
instrument may overlap the same range
as industrial devices, scientic devices,
medical devices, microwave ovens, licensed
premises radio stations and non-licensed
specied low-power radio stations for mobile
object identication systems used in factory
production lines.
Before using this instrument, ensure that
neither a premises radio station nor specied
low power radio station for mobile object
identication systems is in use nearby.
If this instrument causes radio wave
interference to a wireless station for mobile
object identication systems, promptly
change the frequency being used or turn
off the source of radio wave emissions.
Then, contact a Yokogawa ofce regarding
countermeasures to prevent interference,
such as setting up partitions.
• If any problems are experienced with this
instrument, the customer should contact the
Yokogawa representative from which this
instrument was purchased or the nearest
Yokogawa ofce.
• If a problem arises with this instrument,
please inform us of the nature of the problem
and the circumstances under which it
developed, including the model specication
and serial number. Any diagrams, data and
other information you can include in your
communication will also be helpful.
• The party responsible for the cost of xing the
problem shall be determined by Yokogawa
following an investigation conducted by
Yokogawa.
• The purchaser shall bear the responsibility for
repair costs, even during the warranty period, if
the malfunction is due to:
- Improper and/or inadequate maintenance by
the purchaser.
- Malfunction or damage due to a failure
to handle, use, or store the instrument in
accordance with the design specications.
- Use of the product in question in a location
not conforming to the standards specied by
Yokogawa, or due to improper maintenance
of the installation location.
- Failure or damage due to modication or
repair by any party except Yokogawa or an
approved representative of Yokogawa.
- Malfunction or damage from improper
relocation of the product in question after
delivery.
- Reason of force majeure such as res,
earthquakes, storms/oods, thunder/
lightening, or other natural disasters, or
disturbances, riots, warfare, or radioactive
contamination.
1.3 Warranty
• The warranty shall cover the period noted on
the quotation presented to the purchaser at the
time of purchase. Problems occurring during
the warranty period shall basically be repaired
free of charge.
1.4 Trademarks
In this document, trademarks or registered
trademarks are not marked with “™” or “®”.
Product names and company names in this
document are trademarks or registered trademarks
of the respective companies
IM 01C27B01-01EN
Page 8

<1. Introduction>
1.5 ATEX Documentation
This is only applicable to the countries in European Union.
1-4
GB
DK
E
NL
SK
CZ
I
LT
LV
EST
PL
SF
P
F
D
S
SLO
H
BG
RO
M
GR
IM 01C27B01-01EN
Page 9
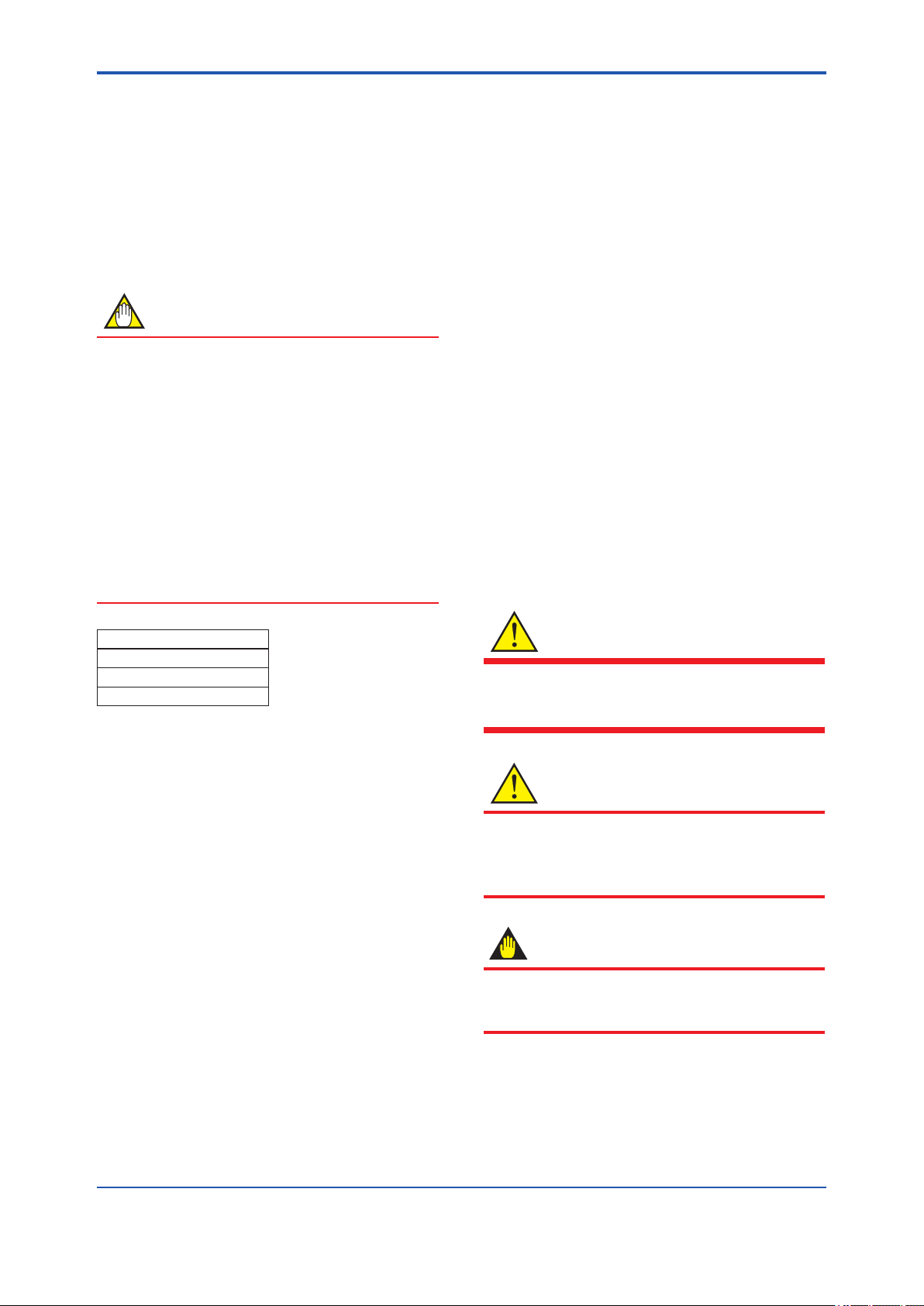
<2. Handling Cautions>
2. Handling Cautions
2-1
This chapter provides important information on how
to handle the transmitter. Read this carefully before
using the transmitter.
EJX Series transmitters are thoroughly tested at the
factory before shipment. When taking delivery of an
instrument, visually check them to make sure that
no damage occurred during shipment.
Also check that all transmitter mounting hardware
shown in gure 2.1 is included. If the transmitter
is ordered without the mounting bracket and the
process connector, the transmitter mounting
hardware will not be included. After checking the
transmitter, carefully repack it in its box and keep it
there until you are ready to install it.
Antenna
The antenna is a detachable type when
Amplifier housing code 8 is selected,
and no antenna is provided for Amplifier
housing code 9.
Bolt
Process connector
Process connector gasket
U-bolt
2.1 Model and Specications
Check
The model name and specications are written on
the name plate attached to the case.
CAL
MODEL
SUFFIX
SUPPLY
OUTPUT
MWP
STYLE
mA DC
Figure 2.2 Name Plate
RNG
V DC
NO.
Made in Japan
TOKYO 180-8750 JAPAN
: Refer to USER'S MANUAL.
F0202.ai
2.2 Unpacking
Keep the transmitter in its original packaging to
prevent it from being damaged during shipment.
Do not unpack the transmitter until it reaches the
installation site.
2.3 Storage
The following precautions must be observed when
storing the instrument, especially for a long period.
Mounting bracket
U-bolt nut
Spacer
U-bolt nut
(L type)
Transmitter
mounting bolt
Transmitter
mounting bolt
Mounting bracket
(Flat type)
Figure 2.1 Transmitter Mounting Hardware
U-bolt
F0201.ai
(a) Select a storage area which meets the following
conditions:
• It is not exposed to rain or subject to water
seepage/leaks.
• Vibration and shock are kept to a minimum.
• It has an ambient temperature and relative
humidity within the following ranges.
Ambient temperature:
–40 to 85°C
–30 to 80°C LCD visible range
Relative humidity:
0% to 100% R.H.
Preferred temperature and humidity:
approx. 25°C and 65% R.H.
(b) When storing the transmitter, repack it carefully in
the packaging that it was originally shipped with.
(c) If the transmitter has been used, thoroughly
clean the chambers inside the cover anges, so
that there is no process uid remaining inside.
Before placing it in storage, also make sure that
the pressure-detector is securely connected to
the transmitter section.
(d) Preferably remove the batteries for storage. For
maximum battery life, the storage temperature
should not exceed 30°C.
IM 01C27B01-01EN
Page 10
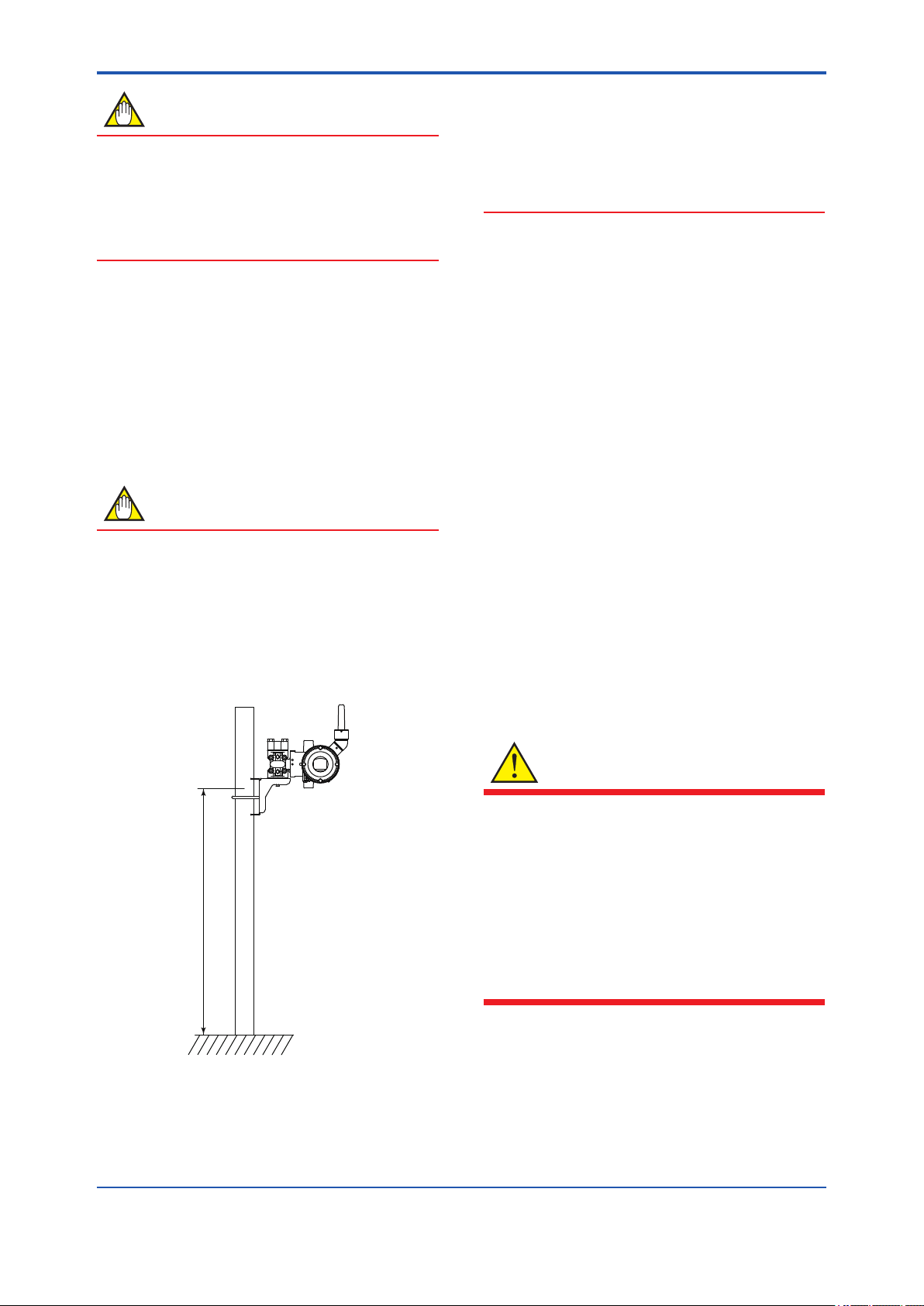
<2. Handling Cautions>
1.5m or more
2-2
NOTE
When storing the instrument with a battery
pack, it is recommended to put the instrument in
Deep Sleep mode to conserve the batteries. For
details on how to switch to Deep Sleep mode,
refer to subsection 8.3.16 “Switching to Deep
Sleep Mode”.
2.4 Selecting the Installation Location
The transmitter is designed to withstand severe
environmental conditions. However, to ensure
that it will provide years of stable and accurate
performance, take the following precautions when
selecting the installation location.
(a) Wireless Communication
NOTE
The installation location of this transmitter must
meet the following conditions:
- Adjust the direction of the antenna to be
in the upright position regardless of the
orientation of this transmitter. See section 4
for adjusting the antenna.
- Install the transmitter at least 1.5m above
the ground or oor.
- Conrm that each eld wireless equipment
compliant with ISA100.11a can see the
antenna of other devices which locate within
its own communication range. In the star
topology network, the visibility to the antenna
of gateway is a mandatory clause.
(b) Ambient Temperature
Avoid locations subject to wide temperature
variations or a signicant temperature gradient.
If the location is exposed to radiant heat from
plant equipment, provide adequate thermal
insulation and/or ventilation.
(c) Ambient Atmosphere
Do not install the transmitter in a corrosive
atmosphere. If this cannot be avoided, there
must be adequate ventilation.
(d) Shock and Vibration
Although the transmitter is designed to be
relatively resistant to shock and vibration, an
installation site should be selected where this is
kept to a minimum.
(e) Installation of Explosion-protected Transmitters
An explosion-protected transmitters is
certied for installation in a hazardous area
containing specic gas types. See subsection
2.8 “Installation of an Explosion-Protected
Transmitters.”
F0203.ai
- Ensure that there are no obstacles such as
walls or pipes within a 30-cm radius of each
antenna.
2.5 Pressure Connection
WARNING
• Never loosen the process connector bolts
when an instrument is installed in a process.
The device is under pressure, and a loss of
seal can result in a sudden and uncontrolled
release of process uid.
• When draining toxic process uids that have
condensed inside the pressure detector,
take appropriate steps to prevent the contact
of such uids with the skin or eyes and the
inhalation of vapors from these uids.
IM 01C27B01-01EN
Page 11
<2. Handling Cautions>
2-3
The following precautions must be observed
in order to safely operate the transmitter under
pressure.
(a) Make sure that all the process connector bolts
are tightened rmly.
(b) Make sure that there are no leaks in the impulse
piping.
(c) Never apply a pressure higher than the
specied maximum working pressure.
2.6 Restrictions on Use of Radio Transceivers
IMPORTANT
Although the transmitter has been designed to
resist high frequency electrical noise, if a radio
transceiver is used near the transmitter or its
external wiring, the transmitter may be affected
by high frequency noise pickup. To test this, start
out from a distance of several meters and slowly
approach the transmitter with the transceiver
while observing the measurement loop for noise
effects. Thereafter use the transceiver outside
the range where the noise effects were rst
observed.
2.7 Insulation Resistance and
• Insulation Resistance Test
1) Remove the battery pack. See subsection 9.4.6
for details on how to remove it.
2) Short-circuit the battery connection terminals in
the terminal box.
3) Turn OFF the insulation tester. Then connect
the insulation tester plus (+) lead wire to the
shorted battery connection terminals and the
minus (–) leadwire to the grounding terminal.
4) Turn ON the insulation tester power and
measure the insulation resistance. The voltage
should be applied as briey as possible to verify
that the insulation resistance is at least 20 MΩ.
5) After completing the test and being very careful
not to touch exposed conductors disconnect the
insulation tester and connect a 100 kΩ resistor
between the grounding terminal and the shortcircuiting battery connection terminals. Leave
this resistor connected at least one second to
discharge any static potential. Do not touch the
terminals while it is discharging.
NOTE
When storing the instrument with a battery
pack, it is recommended to put the instrument in
Deep Sleep mode to conserve the batteries. For
details on how to switch to Deep Sleep mode,
refer to subsection 8.3.16 “Switching to Deep
Sleep Mode”.
Dielectric Strength Test
Since the transmitter has undergone insulation
resistance and dielectric strength tests at the factory
before shipment, normally these tests are not
required. If the need arises to conduct these tests,
heed the following:
(a) Do not perform such tests more frequently than
is absolutely necessary. Even test voltages that
do not cause visible damage to the insulation
may degrade the insulation and reduce safety
margins.
(b) Never apply a voltage exceeding 500 V DC
(100 V DC with an internal lightning protector)
for the insulation resistance test, nor a voltage
exceeding 500 V AC (100 V AC with an internal
lightning protector) for the dielectric strength
test.
(c) The procedure for conducting these tests is as
follows:
• Dielectric Strength Test
1) Remove the battery pack. See subsection 9.4.6
for details on how to remove it.
2) Short-circuit the battery connection terminals in
the terminal box.
3) Turn OFF the dielectric strength tester. Then
connect the tester between the shorted battery
connection terminals and the grounding
terminal. Be sure to connect the grounding lead
of the dielectric strength tester to the ground
terminal.
4) Set the current limit on the dielectric strength
tester to 0.1 mA, then turn ON the power and
gradually increase the test voltage from ‘0’ to
the specied voltage.
5) When the specied voltage is reached, hold it
for one minute.
6) After completing this test, slowly decrease the
voltage to avoid any voltage surges.
IM 01C27B01-01EN
Page 12

<2. Handling Cautions>
• Applicable Standard: Class 3600, Class
NOTE
When storing the instrument with a battery
pack, it is recommended to put the instrument in
Deep Sleep mode to conserve the batteries. For
details on how to switch to Deep Sleep mode,
refer to subsection 8.3.16 “Switching to Deep
Sleep Mode”.
2.8 Installation of an ExplosionProtected Instrument
If a customer makes a repair or modication to an
intrinsically safe instrument and the instrument is
not restored to its original condition, its intrinsically
safe construction may be compromised and the
instrument may be hazardous to operate. Please
contact Yokogawa before making any repair or
modication to an instrument.
CAUTION
This instrument has been tested and certied
as being intrinsically safe. Please note that
severe restrictions apply to this instrument’s
construction, installation, external wiring,
maintenance and repair. A failure to abide by
these restrictions could make the instrument a
hazard to operate.
3610, Class 3611, Class 3810, NEMA 250,
ANSI/ISA-60079-0, ANSI/ISA-60079-11
• Intrinsically Safe for Class I, Division 1,
Groups A, B, C & D, Class II, Division 1,
Groups E, F & G and Class III, Division 1,
Class I, Zone 0, in Hazardous Locations, AEx
ia IIC
• Nonincendive for Class I, Division 2, Groups
A, B, C & D, Class II, Division 2, Groups F &
G and Class III, Division 1, Class I, Zone 2,
Groups IIC, in Hazardous Locations.
• Enclosure: NEMA 4X (Indoors and outdoors).
• Temperature Class: T4
• Ambient temperature: -50 to 70°C
Note 2. Installation
• Installation should be in accordance with
ANSI/ISA-RP12.06.01 and the National
Electric Code (NFPA 70).
• Dust-tight conduit seal must be used when
installed in a Class II, III, Group E, F and G
environments.
• Note a warning label worded
“SUBSTITUTION OF COMPONENTS MAY
IMPAIR INTRINSIC SAFETY,” and “INSTALL
IN ACCORDANCE WITH DOC. NO.
IFM037-A20”.
2-4
WARNING
The battery pack may be replaced in a
hazardous area. The battery pack has
surface resistivity greater than 1G ohm and
must be properly installed in the enclosure
of the transmitter. Care must be taken during
transportation to and from the point of installation
to prevent electrostatic charge build-up.
2.8.1 FM Approval
Caution for FM intrinsically safe type. (Following
contents refer “DOC. No. IFM037-A20”)
Note 1. Model EJX Series Differential, gauge
and absolute pressure transmitters with
optional code /FS17 are applicable for use
in hazardous locations.
IM 01C27B01-01EN
Page 13

<2. Handling Cautions>
[Installation Diagram]
Amplifier housing code 7
[Intrinsically Safe]
Class I, II, III, Division 1,
Groups A,B,C,D,E,F,G
Class I, Zone 0
in Hazardous (Classified)
Locations
AEx ia IIC
Amplifier housing codes other than 7
[Intrinsically Safe]
Class I, II, III, Division 1,
Groups A,B,C,D,E,F,G
Class I, Zone 0
in Hazardous (Classified)
Locations
AEx ia IIC
Note 3. Maintenance and Repair
Note 4. Battery Pack
USE ONLY BATTERY PACK YOKOGAWA
Hazardous Location
Transmitter
Battery Pack
[Nonincendive]
Class I, II, Division 2,
Groups A,B,C,D,F,G
Class III, Division 1.
Class I, Zone 2, Group IIC,
in Hazardous (Classified)
Locations
Hazardous Location
Arrester
(*1, *2)
Antenna Connector
Transmitter
Battery Pack
*1: These apparatus are simple apparatus.
*2: Arrester may not be connected.
Antenna
(*1)
[Nonincendive]
Class I, II, Division 2,
Groups A,B,C,D,F,G
Class III, Division 1.
Class I, Zone 2, Group IIC,
in Hazardous (Classified)
Locations
• The instrument modication or parts
replacement by other than authorized
representative of Yokogawa Electric
Corporation is prohibited and will void FM
Approvals approval.
F9915MA OR F9915NS.
F0210.ai
2-5
Note 1. Model EJX Series differential, gauge,
and absolute pressure transmitters with
optional code /CS17 are applicable for use
in hazardous locations
Certicate: 2325443
• Applicable standard: CAN/CSA-C22.2 No.0,
CAN/CSA-C22.2 No.0.4, C22.2 No.25,
CAN/CSA-C22.2 No.94,
CAN/CSA-C22.2 No.157, C22.2 No.213,
CAN/CSA-C22.2 No.61010-1,
CAN/CSA- C22.2 No.60079-0,
CAN/CSA-E60079-11, IEC60529
• Ex ia IIC T4
• Intrinsically Safe for Class I, Division 1,
Groups A, B, C & D, Class II, Division 1,
Groups E, F & G, Class III, Division 1
• Nonincendive for Class I, Division2,
Groups A, B, C & D, Class II, Division2,
Groups F & G, Class III, Division1
• Enclosure: IP66/IP67 and Type 4X
• Temperature Code: T4
• Ambient Temperature: -50 to 70°C
• Max. Process Temp.: 120°C
Note 2. Installation
• Installation should be in accordance with
Canadian Electrical Code Part I and Local
Electrical Code.
• Do not alter drawing without authorization
from CSA.
• The instrument modication or parts
replacement by other than authorized
representative of Yokogawa Electric
Corporation is prohibited and will void
Canadian Standards Intrinsically safe and
nonincendive Certication.
Note 5. Special Conditions for safe use
POTENTIAL ELECTROSTATIC CHARGING
HAZARD-SECURE DISTANCE OF 100MM
FROM ANTENNA.
DO NOT OPEN WHEN CL II, III, DIV 1,2
ATMOSPHERE IS PRESENT.
2.8.2 CSA Certication
Caution for CSA Intrinsically safe type. (Following
contents refer to “DOC No. ICS030”)
IM 01C27B01-01EN
Page 14
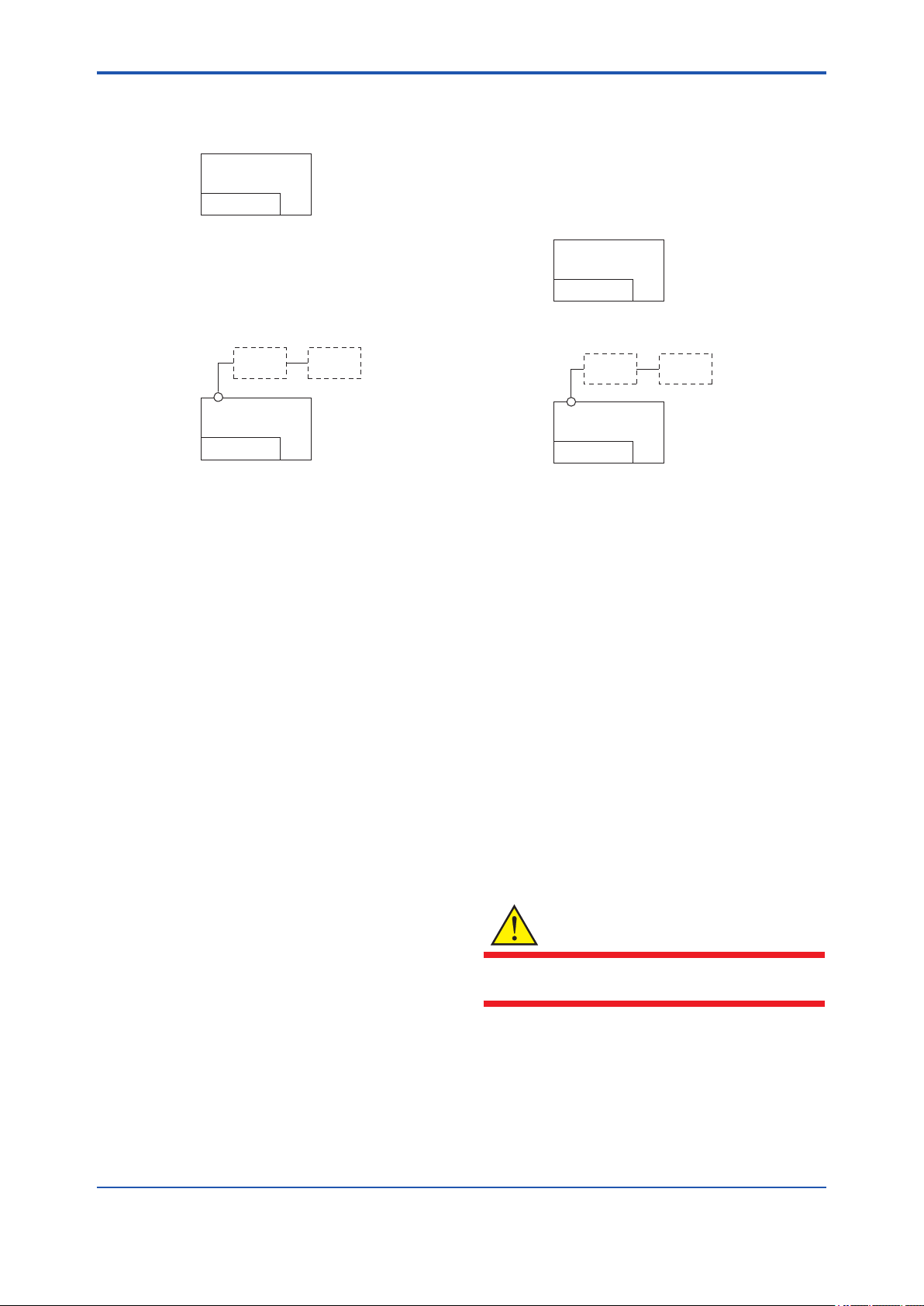
<2. Handling Cautions>
2-6
[Installation Diagram]
Amplifier housing code 7
Hazardous Area
Transmitter
Battery Pack
[Intrinsically Safe]
Group IIC, Zone 0
Class I, II, III, Division 1,
Groups A,B,C,D,E,F,G
Amplifier housing code 8 and 9
Hazardous Area
Arrester
(*1, *2)
Antenna Connector
Transmitter
Battery Pack
*1: These apparatus are simple apparatus.
*2: Arrester may not be connected.
[Intrinsically Safe]
Group IIC, Zone 0
Class I, II, III, Division 1,
Groups A,B,C,D,E,F,G
[Nonincendive]
Class I, II, Division 2,
Groups A,B,C,D,F,G
Class III, Division 1
Antenna
(*1)
[Nonincendive]
Class I, II, Division 2,
Groups A,B,C,D,F,G
Class III, Division 1
Note 3. Battery Pack
• Use only YOKOGAWA battery pack
F9915MA or F9915NS.
Note 4. Special Conditions for safe use
• Potential electrostatic charging hazard secure distance of 100mm from antenna.
2.8.3 ATEX Certication
F0205.ai
Note 2. Installation
• Installation should be in accordance with
local installation requirements. (Refer to the
Control Drawing)
[Control Drawing]
Amplifier housing code 7
Hazardous Area
Transmitter
Battery Pack
Amplifier housing code 8 and 9
Hazardous Area
Arrester
(*1, *2)
Antenna connector
Transmitter
Battery Pack
*1: These apparatus are simple apparatus.
*2: Arrester may not be connected.
Antenna
(*1)
Note 3. Battery Pack
• Use only YOKOGAWA battery pack
F9915MA or F9915NS.
Note 4. Special conditions for Safe Use
• In case the enclosure of the Pressure
Transmitter is made of aluminum, if it
is mounted in an area where the use of
category 1 G apparatus is required, it must
be installed such, that, even in the event of
rare incidents, ignition sources due to impact
and friction sparks are excluded.
F0206.ai
(1) Technical Data
Caution for ATEX Intrinsically safe type.
Note 1. Model EJX Series pressure transmitters
with optional code /KS27 for potentially
explosive atmospheres:
• No. KEMA 10ATEX0164 X
• Applicable Standard:
EN 60079-0:2009, EN 60079-11:2012,
EN 60079-26:2007
• Type of Protection and Marking code:
Ex ia IIC T4 Ga
• Group: II
• Category: 1 G
• Ambient Temperature: –50°C to 70°C
• Process Temperature (Tp.): 120°C max.
• Enclosure: IP66/IP67
• For applications in explosive atmospheres
caused by gases, vapors or mists and
where category 1 G apparatus is required,
electrostatic charges on the non-metallic
parts of the Pressure Transmitter shall be
avoided.
WARNING
Potential electrostatic charging hazard - secure
distance of 100mm from antenna.
IM 01C27B01-01EN
Page 15
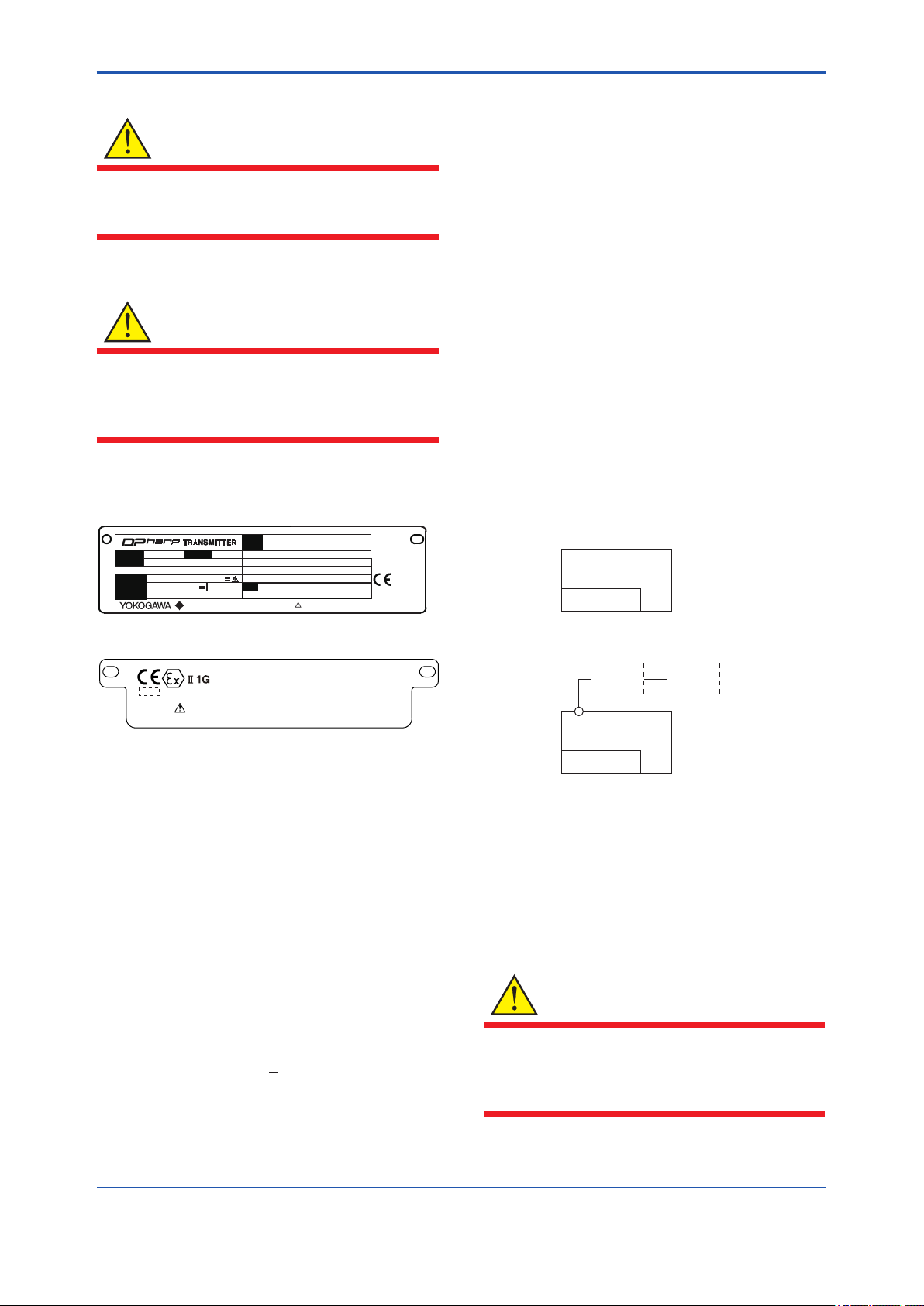
<2. Handling Cautions>
2-7
(2) Operation
WARNING
Take care not to generate mechanical sparking
when access to the instrument and peripheral
devices in a hazardous location.
(3) Maintenance and repair
WARNING
The instrument modication or parts replacement
by other than an authorized Representative of
Yokogawa Electric Corporation is prohibited and
will void the certication.
(4) Name Plate
• Name Plate
CAL
MODEL
SUFFIX
SUPPLY
OUTPUT
MWP
STYLE
mA DC
RNG
V DC
NO.
Made in Japan
TOKYO 180-8750 JAPAN
: Refer to USER'S MANUAL.
F0207.ai
• Tag plate for intrinsically safe type
No. KEMA 10ATEX016 4 X
Ex ia IIC T4 Ga
KS27
*3
WARNIN G
ENCLOSUR E: IP66/IP67
Tamb.: -50 TO 70°C
MAX PROC ESS TEMP.: 120°C
POTENTIAL ELEC TROSTATIC CHARGING HA ZARD - SECURE D ISTANCE
OF 100MM FROM A NTENNA.
USE ONLY BATTERY PACK YOKOGAWA F9915 MA OR F9915NS.
POTENTIAL ELEC TROSTATIC CHARGING HA ZARD - SEE USER 'S MANUAL.
F0208.ai
MODEL: Specied model code.
STYLE: Style code.
SUFFIX: Specied sufx code.
SUPPLY: Supply voltage.
OUTPUT: Output signal.
MWP: Maximum working pressure.
CAL RNG: Specied calibration range.
NO.: Serial number and year of production
TOKYO 180-8750 JAPAN:
The manufacturer name and the address
*1: The rst digit in the nal three numbers of the serial
number appearing after “NO.” on the nameplate indicates
the year of production. The following is an example of a
serial number for a product that was produced in 2010:
91K819857 032
↑
The year 2010
*2: “180-8750” is a zip code which represents the following
address.
2-9-32 Nakacho, Musashino-shi, Tokyo Japan
*3: The identication number of Notied Body.
*1
*2
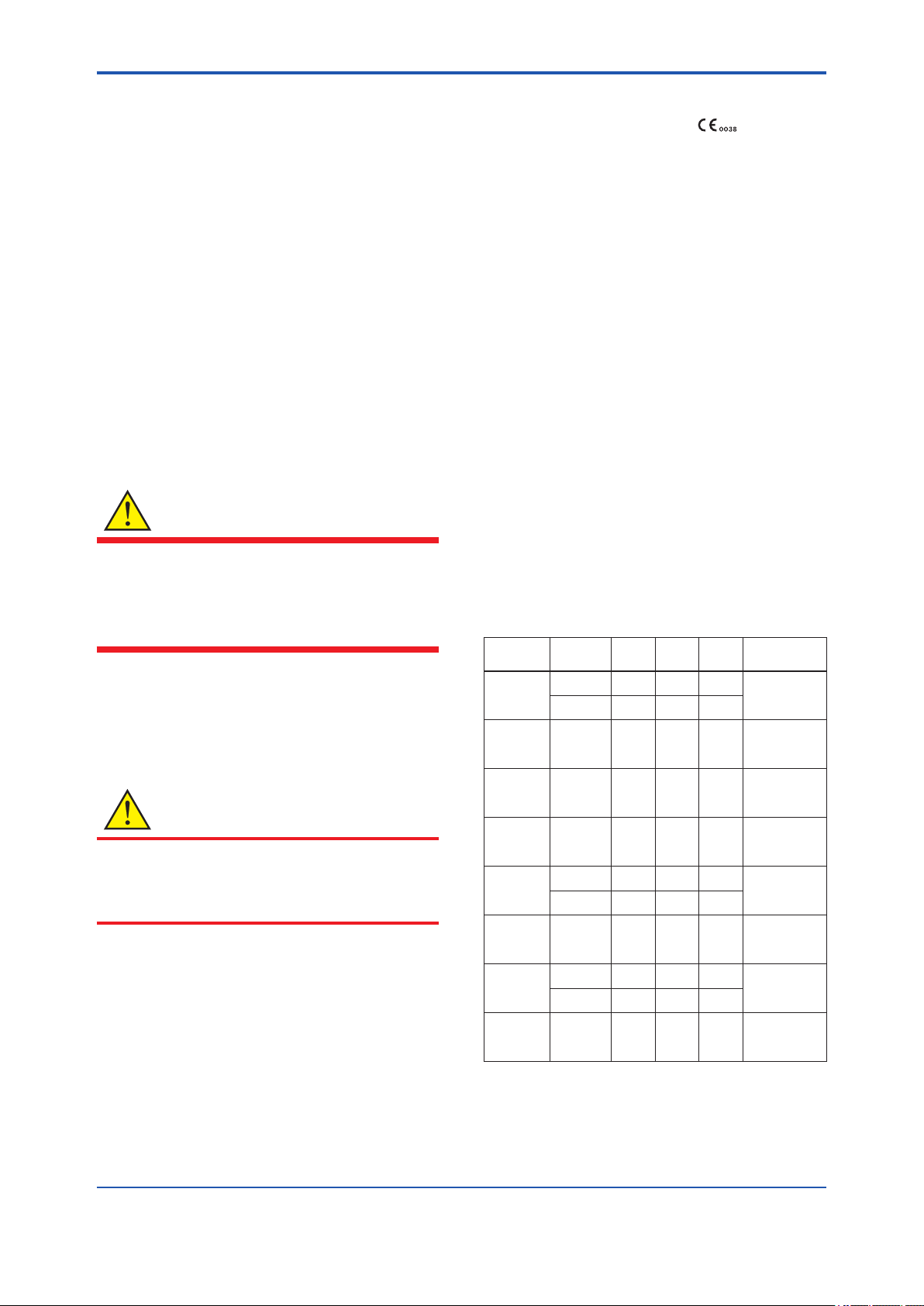
2.8.4 IECEx Certication
Caution for IECEx Intrinsically safe type.
Note 1. Model EJX Series pressure transmitters
with optional code /SS27 for potentially
explosive atmospheres:
• No. IECEx KEM 10.0074X
• Applicable Standard:
IEC 60079-0:2011, IEC 60079-11:2011,
IEC 60079-26:2006
• Type of Protection and Marking code:
Ex ia IIC T4 Ga
• Ambient Temperature: –50°C to 70°C
• Process Temperature (Tp.): 120°C max.
• Enclosure: IP66/IP67
Note 2. Installation
• Installation should be in accordance with
local installation requirements.
(Refer to the Control Drawing)
[Control Drawing]
Amplifier housing code 7
Hazardous Area
Transmitter
Battery Pack
Amplifier housing code 8 and 9
Hazardous Area
Arrester
(*1, *2)
Antenna connector
Transmitter
Battery Pack
*1: These apparatus are simple apparatus.
*2: Arrester may not be connected.
Note 3. Maintenance and Repair
• The instrument modication or parts
.
.
replacement by other than authorized
representative of Yokogawa Electric
Corporation is prohibited and will void IECEx
Intrinsically safe Certication.
WARNING
The instrument modication or parts replacement
by other than an authorized Representative of
Yokogawa Electric Corporation is prohibited and
will void the certication.
Antenna
(*1)
F0209.ai
IM 01C27B01-01EN
Page 16
<2. Handling Cautions>
2-8
Note 4. Battery Pack
• Use only YOKOGAWA battery pack
F9915MA or F9915NS.
Note 5. Special conditions for Safe Use
• In case the enclosure of the Pressure
Transmitter is made of aluminum, if it
is mounted in an area where the use of
apparatus of equipment protection level Ga
is required, it must be installed such, that,
even in the event of rare incidents, ignition
sources due to impact and friction sparks are
excluded.
• For applications in explosive atmospheres
caused by gases, vapors or mists and
mounted in an area where the use of
apparatus of equipment protection level Ga
is required, electrostatic charges on the nonmetallic parts of the Pressure Transmitter
shall be avoided.
WARNING
• Potential electrostatic charging hazard secure distance of 100mm from antenna.
• Take care not to generate mechanical
sparking when access to the instrument and
peripheral devices in a hazardous location.
2.9 EMC Conformity Standards
EN61326-1 Class A, Table 2 (For use in
industrial locations), EN61326-2-3
CAUTION
This instrument is a Class A product, and it is
designed for use in the industrial environment.
Please use this instrument in the industrial
environment only.
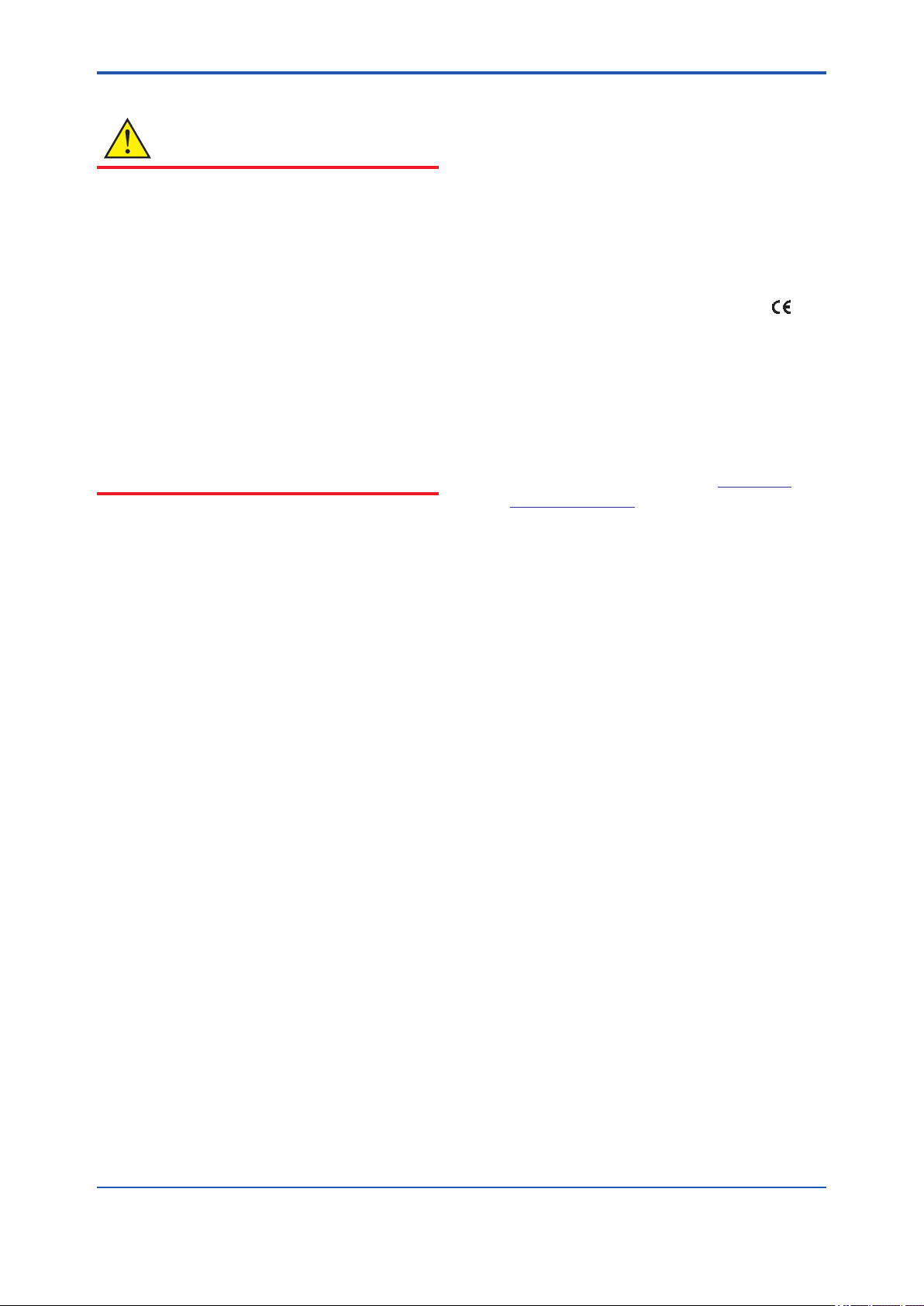
2.10 Pressure Equipment Directive (PED)
(1) General
• EJX Series pressure transmitters are
categorized as pressure accessories under
the vessel section of directive 97/23/EC, which
corresponds to Article 3, Paragraph 3 of PED,
denoted as Sound Engineering Practice (SEP).
• EJX110B-MS, EJX110B-HS,
EJX110B-VS, EJX510B-D, and
EJX530B-D can be used above 200 bar and
therefore considered as a part of a pressure
retaining vessel where category III, Module H
applies. These models with option code /PE3
conform to that category.
(2) Technical Data
• Models without /PE3
Article 3, Paragraph 3 of PED, denoted as
Sound Engineering Practice (SEP).
• Models with /PE3
Module: H
Type of Equipment: Pressure Accessory-Vessel
Type of uid: Liquid and Gas
Group of uid: 1 and 2
Model
EJX110B
EJX110B
with code
/PE3
EJX310B L, M, A, B 160 0.01 1.6
EJX430B H, A, B 160 0.01 1.6
EJX510B
EJX510B
with code
/PE3
EJX530B
EJX530B
with code
/PE3
*1: PS is maximum allowable pressure for vessel itself.
*2: Referred to Table 1 covered by ANNEX II of EC Directive
Capsule
codePS(bar)*
F, L 160 0.01 1.6
M, H, V 250 0.01 2.5
M, H, V 250 0.01 2.5 III
A, B, C 100 0.1 10
D 700 0.1 70
D 700 0.1 70 III
A, B, C 100 0.1 10
D 700 0.1 70
D 700 0.1 70 III
on Pressure Equipment Directive 97/23/EC
1
V(L)
PS·V
(bar·L)
Category*
Article 3,
Paragraph 3
(SEP)
Article 3,
Paragraph 3
(SEP)
Article 3,
Paragraph 3
(SEP)
Article 3,
Paragraph 3
(SEP)
Article 3,
Paragraph 3
(SEP)
2
IM 01C27B01-01EN
Page 17
<2. Handling Cautions>
2-9
(3) Operation
CAUTION
• The temperature and pressure of uid should
be maintained at levels that are consistent
with normal operating conditions.
• The ambient temperature should be
maintained at a level that is consistent with
normal operating conditions.
• Please take care to prevent water hammer
and the like from inducing excessive
pressures in pipes and valves. If phenomena
are likely, install a safety valve or take
some other appropriate measure to prevent
pressure from exceeding PS.
• Take appropriate measures at the device or
system level to protect transmitters if they
are to be operated near an external heat
source.
2.11 Low Voltage Directive
Applicable standard:
EN61010-1, EN61010-2-030
(1) Pollution Degree 2
"Pollution degree" describes the degree to
which a solid, liquid, or gas which deteriorates
dielectric strength or surface resistivity is
adhering. " 2 " applies to normal indoor
atmosphere. Normally, only non-conductive
pollution occurs. Occasionally, however,
temporary conductivity caused by condensation
must be expected.
(2) Installation Category I
(Anticipated transient overvoltage 330 V)
2.12 Regulatory Compliance for Radio and Telecommunication
Please conrm that a installation region fulls
a standards, require additional regulatory
information and approvals, contact to
Yokogawa Electric Corporation.
2.12.1 Radio and Telecommunications
Terminal Equipment Directive (R&TTE)
We, Yokogawa Electric Corporation hereby
declare that this equipment, model EJX-L series
is in compliance with the essential requirements
and other relevant provisions of Directive
1999/5/EC.
The CE declaration of conformity for R&TTE
for this product can be found at http://www.
yokogawa.com/d/
2.12.2 FCC compliance
This equipment contains transmitter module
FCC ID: SGJ-WFC001.
This device complies with Part 15 of FCC
Rules. Operation is subject to the following
two conditions: (1) this device may not cause
interference, and (2) this device must accept
any interference, including interference that
may cause undesired operation of this device.
Co-located:
This transmitter must not be co-located or
operated in conjunction with any other antenna
or transmitter.
FCC WARNING:
"Overvoltage category (Installation category)"
describes a number which denes a transient
overvoltage condition. It implies the regulation
for impulse withstand voltage. " I " applies to
electrical equipment which is supplied from the
circuit when appropriate transient overvoltage
control means (interfaces) are provided.
Changes or modications not expressly
approved by the party responsible for
compliance could void the user’s authority to
operate the equipment.
IM 01C27B01-01EN
Page 18

<2. Handling Cautions>
This radio transmitter IC Number
NOTE
This equipment has been tested and found
to comply with the limits for a Class A digital
device, pursuant to part 15 of the FCC Rules.
These limits are designed to provide reasonable
protection against harmful interference when
the equipment is operated in a commercial
environment.
This equipment generates, uses, and can radiate
radio frequency energy and, if not installed
and used in accordance with the instruction
manual,may cause harmful interference to radio
communications. Operation of this equipment
in a residential area is likely to cause harmful
interference in which case the user will be
required to correct the interference at his own
expense.
2.12.3 Industry Canada (IC) compliance
This equipment contains transmitter module IC:
8999A-WIC001.
This Class A digital apparatus complies with
Canadian ICES-003.
This device complies with Industry Canada
license-exempt RSS standard(s). Operation is
subject to the following two conditions: (1) this
device may not cause interference, and (2) this
device must accept any interference, including
interference that may cause undesired,
operation of the device.
Under Industry Canada regulations, this
radio transmitter may only operate using an
antenna of a type and maximum (or lesser)
gain approved for the transmitter by Industry
Canada. To reduce potential radio interference
to other users, the antenna type and its gain
should be so chosen that the equivalent
isotropically radiated power (e.i.r.p.) is not
more than that necessary for successful
communication.
8999A-WIC001 has been approved by Industry
Canada to operate with the antenna types
listed below with the maximum permissible
gain and required antenna impedance for each
antenna type indicated. Antenna types not
included in this list, having a gain greater than
the maximum gain indicated for that type, are
strictly prohibited for use with this device.
Antenna type: Gain:
COLLINEAR 9 dBi, 50 Ω
Sleeve 2.14 dBi, 50 Ω
French:
Cet appareil numérique de la classe A est
conforme à la norme NMB-003 du Canada.
Le présent appareil est conforme aux CNR
d’Industrie Canada applicables aux appareils
radio exempts de licence. L’exploitation est
autorisée aux deux conditions suivantes : (1)
l’appareil ne doit pas produire de brouillage,
et (2) l’utilisateur de l’appareil doit accepter
tout brouillage radioélectrique subi, même si le
brouillage est susceptible d’en compromettre le
fonctionnement.
Conformément à la réglementation d’Industrie
Canada, le présent émetteur radio peut
fonctionner avec une antenne d’un type et
d’un gain maximal (ou inférieur) approuvé pour
l’émetteur par Industrie Canada. Dans le but de
réduire les risques de brouillage radioélectrique
à l’intention des autres utilisateurs, il faut choisir
le type d’antenne et son gain de sorte que
la puissance isotrope rayonnée équivalente
(p.i.r.e.) ne dépasse pas l’intensité nécessaire
à l’établissement d’une communication
satisfaisante.
Le présent émetteur radio IC Number
8999A-WIC001 a été approuvé par Industrie
Canada pour fonctionner avec les types
d’antenne énumérés ci-dessous et ayant
un gain admissible maximal et l’impédance
requise pour chaque type d’antenne. Les types
d’antenne non inclus dans cette liste, ou dont
le gain est supérieur au gain maximal indiqué,
sont strictement interdits pour l’exploitation de
l’émetteur.
Antenne type: Gain:
COLLINEAR 9 dBi, 50 Ω
Sleeve 2.14 dBi, 50 Ω
2-10
IM 01C27B01-01EN
Page 19
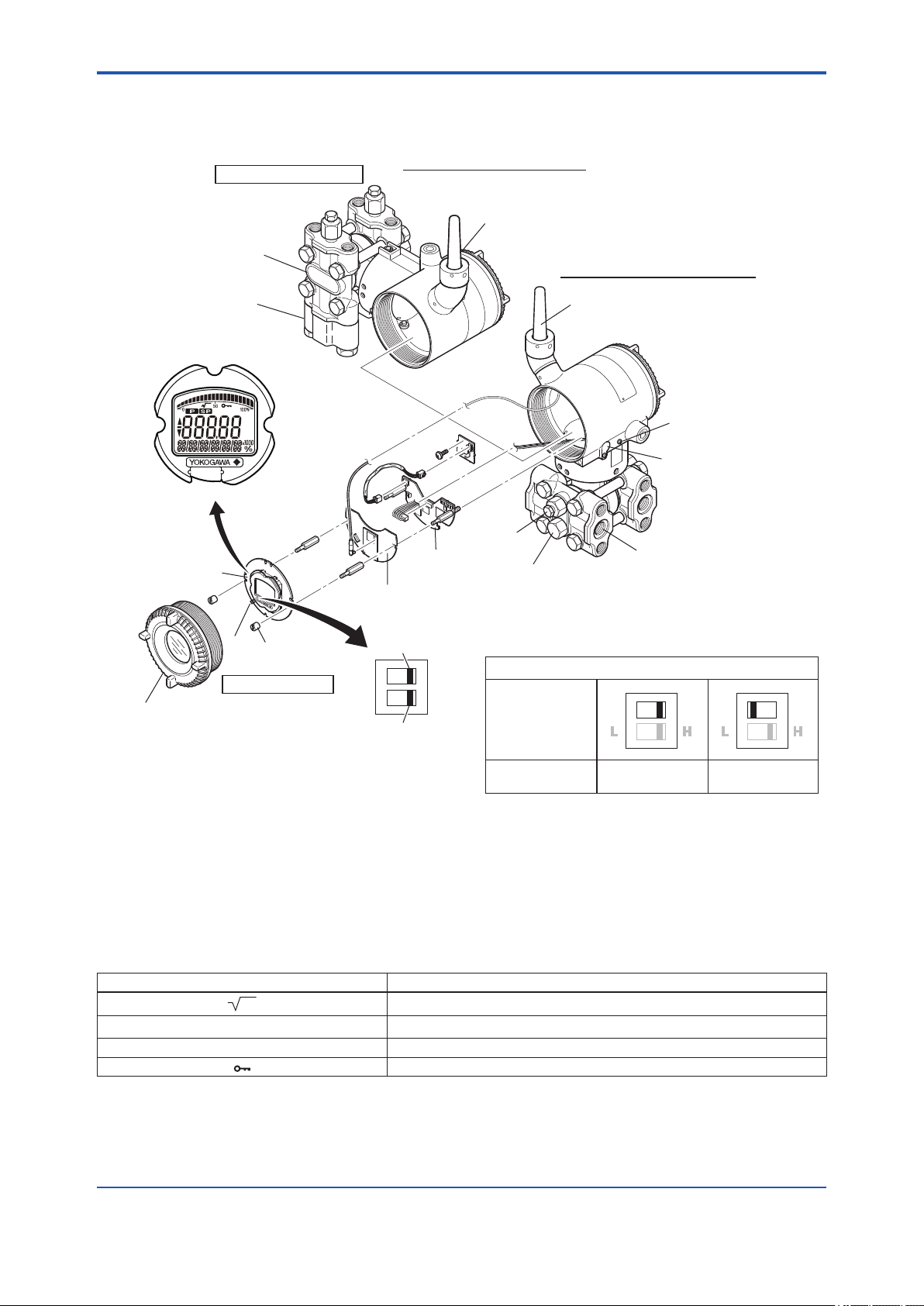
<3. Component Names>
3. Component Names
3-1
Cover flange
Process connector
Integral indicator
Preccure-detector section
(Note1)
Vertical impulse pipimg type
Vent plug
CPU assembly
RF assembly
Terminal box cover
Horizontal impulse piping type
Drain plug
Antenna (Note 4)
Ground terminal
Zero-adjustment
screw
Process
connction
Slide
Mounting
switch
screw
Transmitter section
Amplifier Cover
Note 1: A process connector will not be applied for lower side of EJX430B and EJX310B.
Note 2: Set the switch as shown in the gure above to set the write protection. The hardware write protection switch is set to E side. Set
Note 3: When the switch is D side (write protection setting), provisioning is acceptable. For details of provisioning, refer to section 7.4
Note 4: The detachable antenna is applied when the amplier housing code 7 or 8 is specied.
to H side for the switch of not-in-use.
“ Connecting to the Field Wireless Network ”.
Write protection switch
E WRD
Not in use
Hardware write protection switch (WR)
Write protection
Switch Position
(Note 2)
Write protection
L
NO
(Write enabled)
ED
H
(Write disabled)
L
YES
ED
H
(Note 3)
F0301.ai
Figure 3.1 Component Names
Table 3.1 Display Symbol
Display Symbol Meaning of Display Symbol
Display mode is ‘square root’. (Display is not lit when ‘linear’ mode.)
▲ The output signal being zero-adjusted is increasing.
▼ The output signal being zero-adjusted is decreasing.
Write protect function is enabled.
IM 01C27B01-01EN
Page 20
<4. Installation>
4. Installation
4-1
4.1 Precautions
Before installing the transmitter, read the cautionary
notes in section 2.4, “Selecting the Installation
Location.” For additional information on the
ambient conditions allowed at the installation
location, refer to subsection 11.1 “Standard
Specications.”
NOTE
To connect this transmitter to the Field Wireless
Network, information for connecting to the eld
wireless devices needs to be set beforehand.
Refer to 7.4 “Connecting to the Field Wireless
Network.”
IMPORTANT
• When welding piping during construction,
take care not to allow welding currents to
ow through the transmitter.
• Do not step on this instrument after
installation.
• For the EJX430B, the atmospheric opening
is located on the low pressure side cover
ange. Take care do not enter rain into the
opening. The opening must not face upward.
See section 11.4, “Dimensions,” for the
location of the opening.
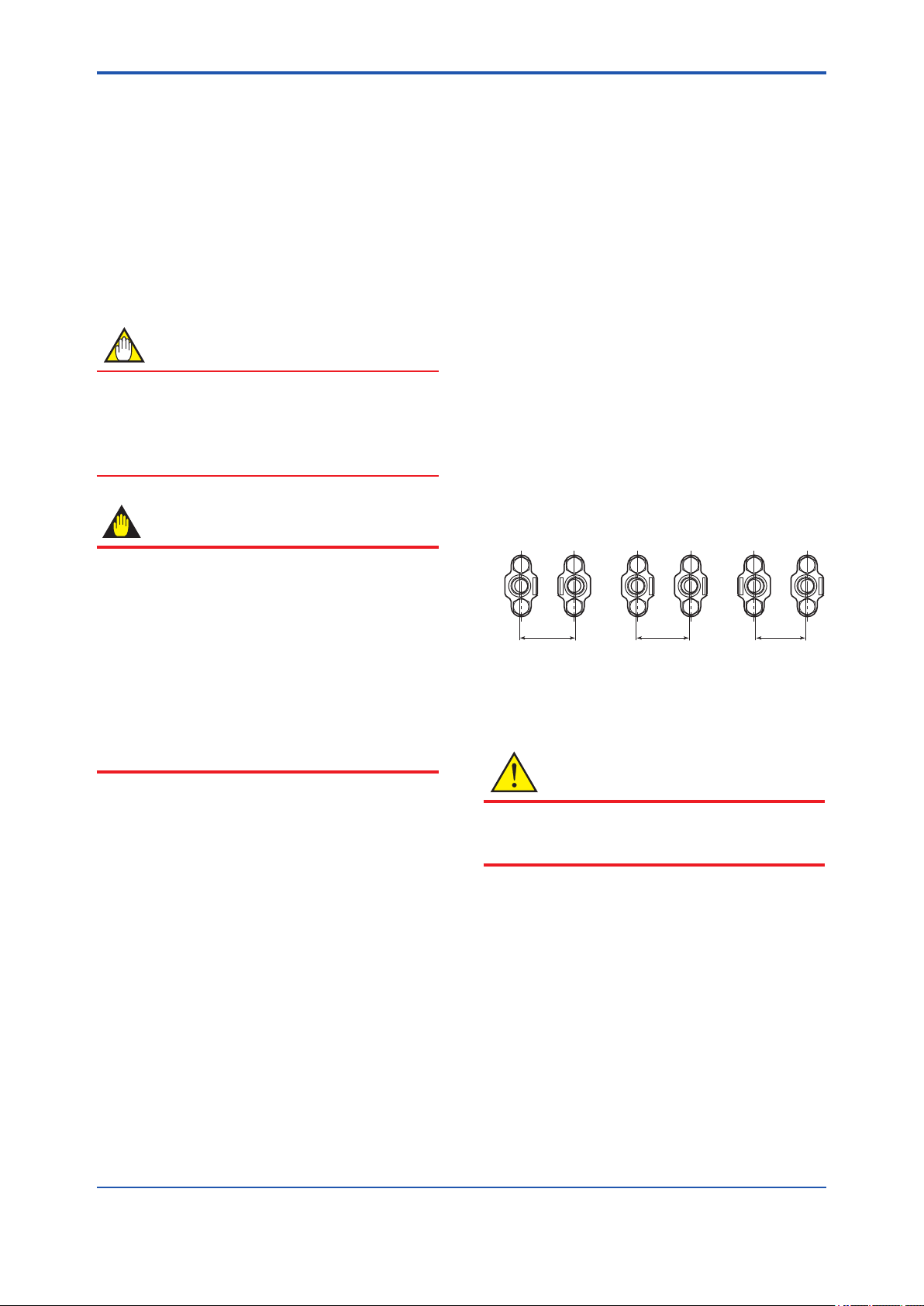
4.2 Mounting
■ The transmitter is shipped with the process
connection, according to the ordering
specications. To change the orientation of the
process connections, refer to section 4.3.
■ With differential pressure transmitters,
the distance between the impulse piping
connection ports is usually 54 mm (gure 4.1).
By changing the orientation of the process
connector, the dimension can be changed to
51 mm or 57 mm.
■ The transmitter can be mounted on a nominal
50 mm (2-inch) pipe using the mounting bracket
supplied, as shown in gure 4.2 and 4.3.
The transmitter can be mounted on either a
horizontal or a vertical pipe.
■ When mounting the bracket on the transmitter,
tighten the (four) bolts that hold the transmitter
with a torque of approximately 39 N·m {4kgf·m}.
57 mm 54 mm 51 mm
F0401.ai
Figure 4.1 Process Connector Impulse Piping
Connection Distances for Differential
Pressure Transmitters
CAUTION
When the sufx code of the mounting bracket
is “B,” make sure to put the spacer between the
bracket and transmitter as shown in Figure 4.2.
IM 01C27B01-01EN
Page 21
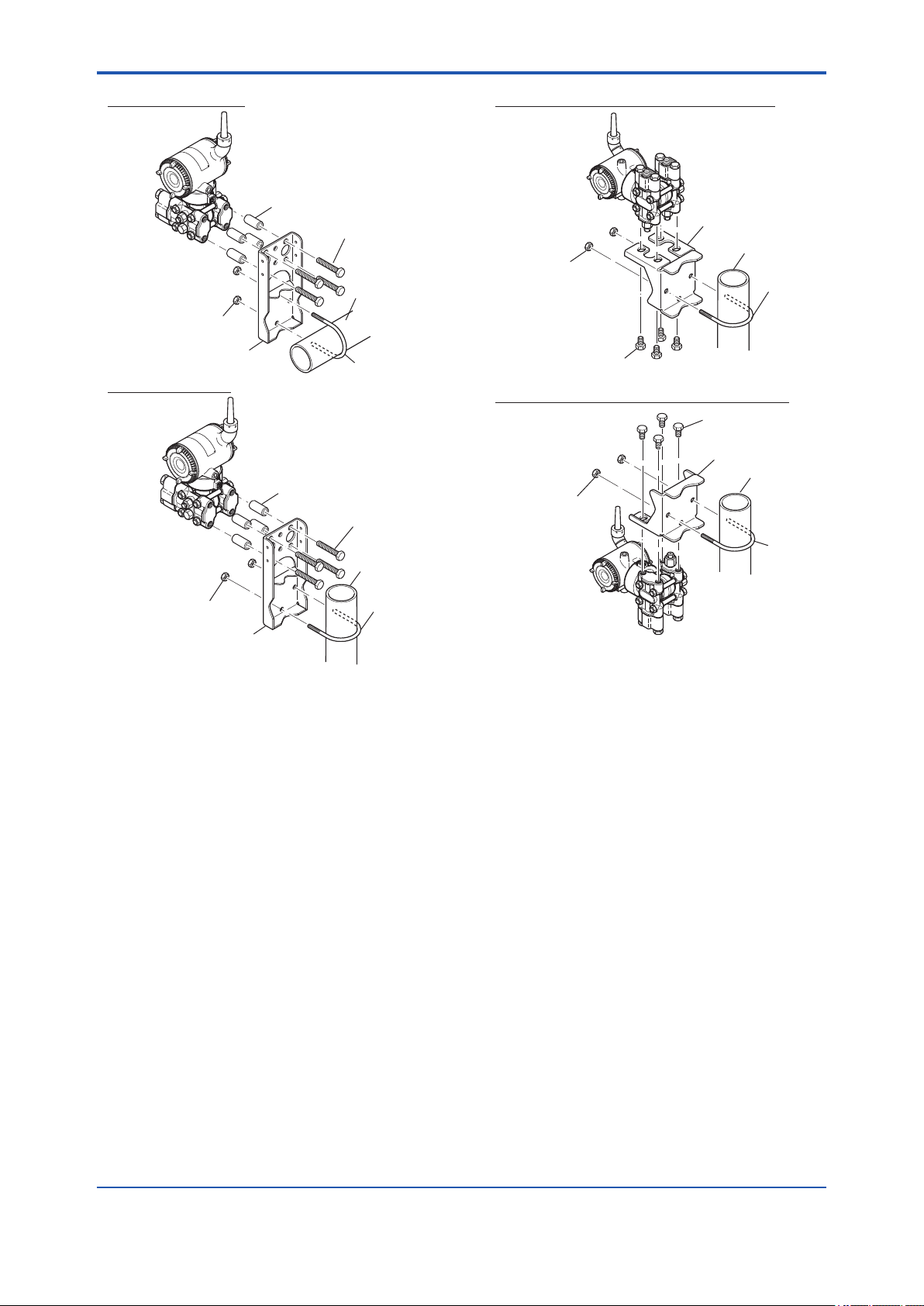
<4. Installation>
4-2
Horizontal pipe mounting
U-bolt nut
Mounting bracket
Vertical pipe mounting
Spacer
Spacer
Transmitter
mounting bolt
50 mm (2-inch)
pipe
U-bolt
Transmitter
mounting bolt
50 mm (2-inch)
pipe
Vertical pipe mounting (Process connector upside)
Mounting bracket
50 mm (2-inch) pipe
U-bolt nut
U-bolt
Transmitter mounting bolt
Vertical pipe mounting (Process connector downside)
Transmitter
mounting bolt
Mounting bracket
50 mm (2-inch) pipe
U-bolt nut
U-bolt
U-bolt nut
Mounting bracket
U-bolt
Figure 4.2 Transmitter Mounting (Horizontal
Impulse Piping Type)
F0402.ai
F0403.ai
Figure 4.3 Transmitter Mounting (Vertical Impulse
Piping Type)
IM 01C27B01-01EN
Page 22
<4. Installation>
4-3
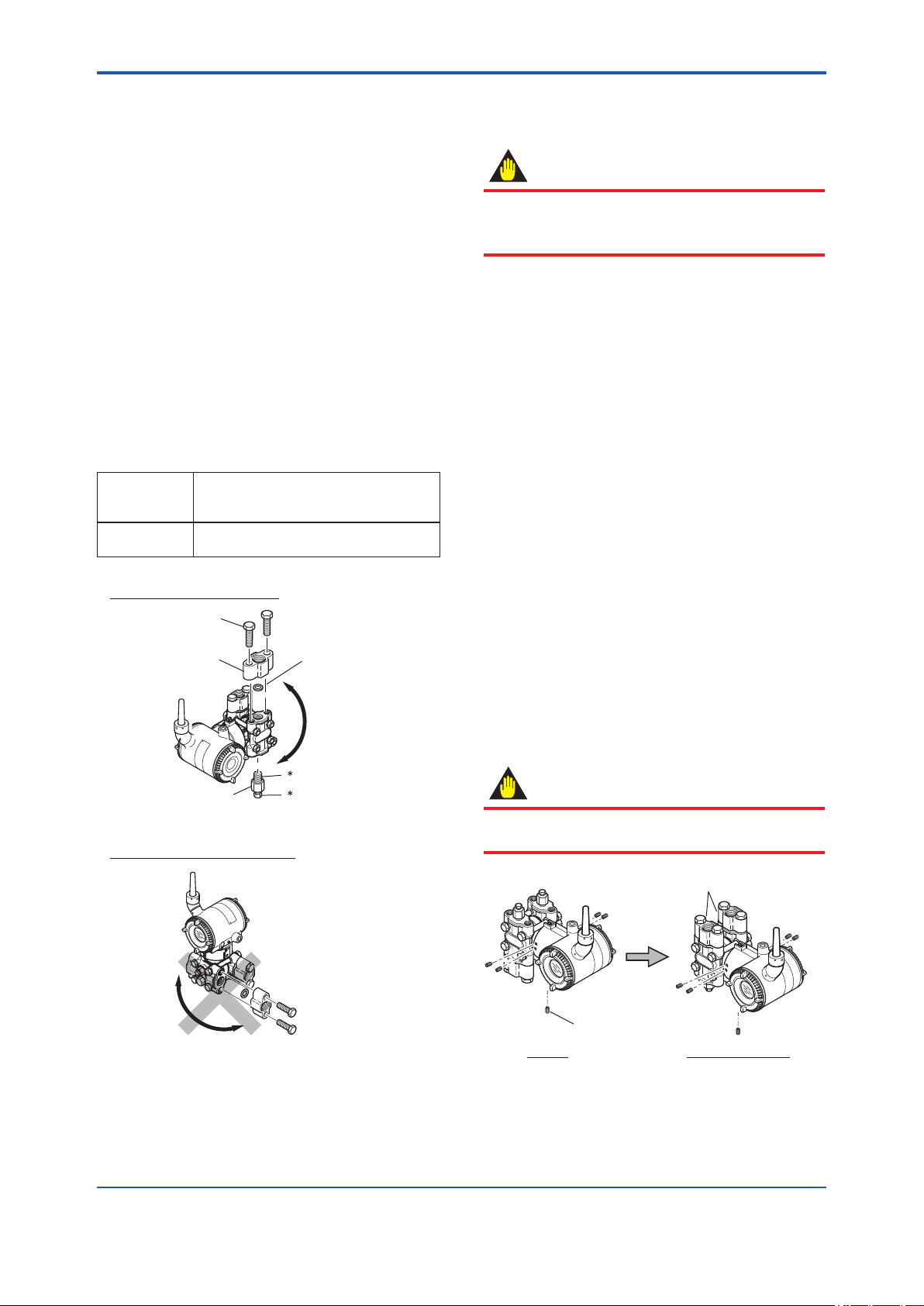
4.3 Changing the Process Connection
The transmitter is shipped with the process
connection specied at the time of ordering. To
change the process connection, the drain (vent)
plug must be repositioned.
To reposition a drain (vent) plug, refer to Figure 4.4
and use a wrench slowly and gently to unscrew
it. Then, remove and remount it on the opposite
side. Wrap sealing tape around the drain (vent)
plug threads (*1 in the gure below), and apply a
lubricant to the threads of the drain (vent) screw(s)
(*2 below). To tighten the drain (vent) plugs, apply
a torque of 34 to 39 N·m (3.5 to 4 kgf·m). Process
connector bolts are to be tightened uniformly to a
torque shown in table 4.1.
Table 4.1 Torque
Model
Torque(N·m)
{kgf·m}
Vertical impulse piping type
Bolt
Process connector
EJX110B
EJX310B
EJX430B
39 to 49 {4 to 5}
gasket
4.4 Swapping the High/Lowpressure Side Connection
IMPORTANT
This section is applicable only for EJX110B
differential transmitters, and not applicable for
gauge or absolute pressure transmitters.
4.4.1 Rotating Pressure-detector Section 180°
This procedure can be applied only to a transmitter
with a vertical impulse piping type.
The procedure below can be used to turn the
pressure detector assembly 180°. Perform
this operation in a maintenance shop with the
necessary tools laid out and ready for use, and then
install the transmitter in the eld after making the
change.
1) Use an Allen wrench (JIS B4648, nominal 2.5
mm) to remove the ve setscrews at the joint
between the pressure-detector section and
transmitter section.
2) Leaving the transmitter section in position,
rotate the pressure-detector section 180°.
3) Tighten the ve setscrews to x the pressuredetector section and transmitter section
together (at a torque of 1.5 N·m).
Reposition the process connector and drain
(vent) plugs to the opposite side as described in
subsection 4.3.
1
Drain/vent plug
Horizontal impulse piping type
Figure 4.4 Changing Process Connection
2
Note: For a horizontal impulse
piping type, moving the
process connectors from
the front side to the back
cannot be made.
F0404.ai
IMPORTANT
Do not rotate the transmitter section more than
above limit.
Process connector
Setscrew
Before
Figure 4.5 Before and After Modication
After rotating 180°
IM 01C27B01-01EN
F0405.ai
Page 23

<4. Installation>
4-4
4.4.2 Using the Conguration Tool
This method is applicable only to the Model
EJX110B.
With a conguration tool, you can change which
process connection is used as the high-pressure
side without mechanically rotating the pressuredetector section 180 as described in subsection
4.4.1. To change, call up the ‘H/L_SWAP’ parameter
and select REVERSE (right side: low pressure; left
side: high pressure) or select NORMAL to change
back to normal (right side: high pressure; left side:
low pressure).
NORMAL
Output
Input
REVERSE
Figure 4.6 Input/Output Relationship
F0406.ai
IMPORTANT
4.5 Rotating Transmitter Section
WARNING
Intrinsic safe type transmitters must be, as a rule,
do not rotate transmitter section if it is powered.
In case you need to rotate when the transmitter
is powered, using gas detector and conrm no
existence of explosive gas before rotating.
The transmitter section can be rotated
approximately 360° (180° to either direction or
360° to one direction from the original position at
shipment, depending on the conguration of the
instrument.) It can be xed at any angle within
above range.
1) Remove the ve setscrews that fasten the
transmitter section and capsule assembly,
using the Allen wrench.
2) Rotate the transmitter section slowly and stop it
at designated position.
3) Tighten the ve setscrews to a torque of 1.5
N·m.
IMPORTANT
Do not rotate the transmitter section more than
the above limit.
Since the H/L label plate on the capsule
assembly will remain unchanged, use this
function only when you cannot switch the
impulse piping. If the ‘H/L_SWAP’ parameter
setting is changed, the input/output relationship
is reversed as shown in Figure 4.6; be sure this
is understood by all. After reversing the setting,
modify the H/L label plate to clearly indicate this
change.
IM 01C27B01-01EN
Page 24
<4. Installation>
4-5
Vertical impulse piping type
Pressure-detector section
Horizontal impulse piping type
Transmitter section
Rotate 0 to ±180°
segments
Transmitter section
Rotate 0 to ±180°
segments
Zero-adjustment screw
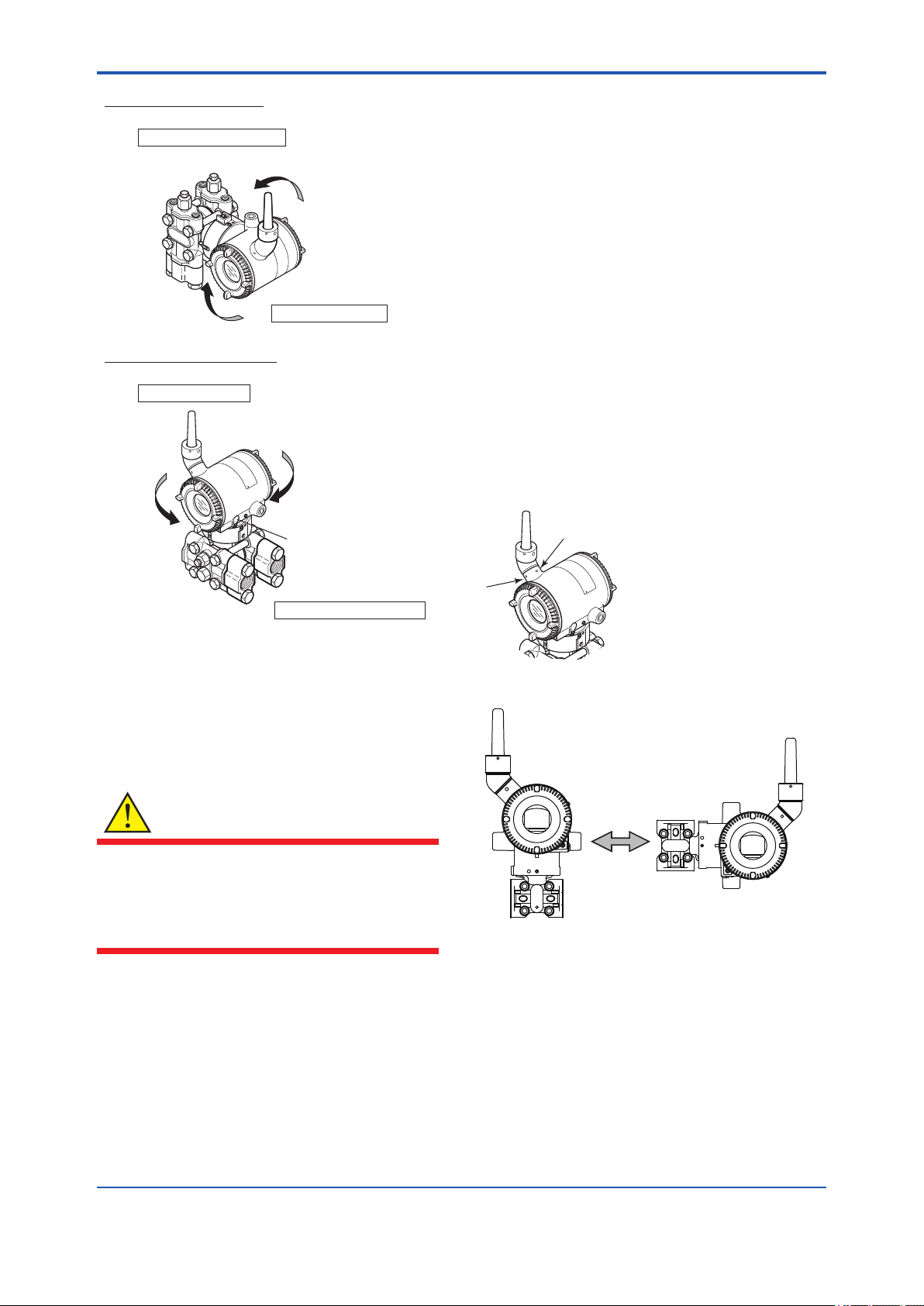
4.7 Changing the direction of the antenna
Adjust the direction of the antenna to be in the
upright position. Figure4.8 shows factory setup
antenna position. If the transmitter is installed to
vertical impulse piping, follow the procedure below
and change the antenna position.
1) Loosen the two mounting screws at the bottom
of the antenna by using a 2.5 mm Allen wrench
(see Figure 4.8).
The screws might come off and be lost if
loosened too much; loosen the screws by about
three rotations.
2) Press forward and down 90 degrees by rotating
the axis at the bottom of the antenna.
3) Tighten the two screws to a torque of 1.5 N·m
by using a torque wrench. When doing this, be
careful not leave a gap between the antenna
and housing.
Pressure-detector section
F0407.ai
Figure 4.7 Rotating Transmitter Section (Left Side
High Pressure Type)
4.6 Changing the Direction of Integral Indicator
WARNING
Intrinsic safe type transmitters must be, as a
rule, remove a battery pack in non-hazardous
area before open/close the Amplier Cover or
disassembling and reassembling the Integral
Indicator.
An integral indicator can be rotated in four positions
at 90°. Follow the instructions in section 9.4.1 for
removing and attaching the integral indicator.
F0408.ai
Figure 4.8 Mounting Screw Position
F0409.ai
Figure 4.9 Adjusting Antenna Position
IM 01C27B01-01EN
Page 25
<5. Installing Impulse Piping>
Differential Pressure Transmitter
5. Installing Impulse Piping
5-1
5.1 Impulse Piping Installation Precautions
The impulse piping that connects the process
outputs to the transmitter must convey the process
pressure accurately. If, for example, gas collects
in a liquid-lled impulse line, or the drain for a
gas-lled impulse line becomes plugged, it will
not convey the pressure accurately. Since this will
cause errors in the measurement output, select
the proper piping method for the process uid
(gas, liquid, or steam). Pay careful attention to the
following points when routing the impulse piping
and connecting the impulse piping to a transmitter.
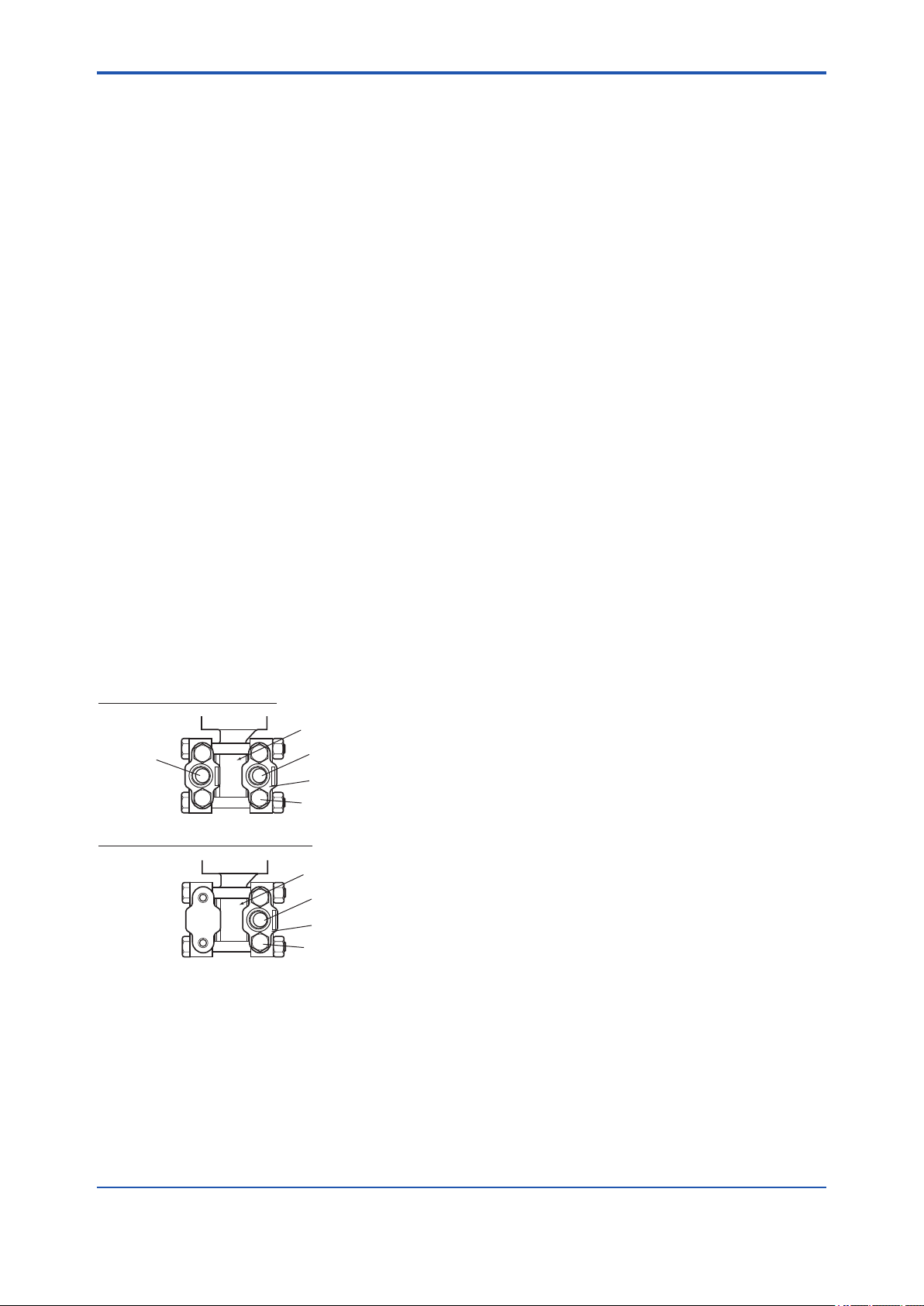
5.1.1 Connecting Impulse Piping to a Transmitter
(1) Check the High and Low Pressure
Connections on the Transmitter (Figure 5.1)
Symbols “H” and “L” have been placed on the
capsule assembly to indicate high and low pressure
side. With differential pressure transmitters, connect
the high pressure side impulse line to the “H” side,
and the low pressure side impulse line to the “L”
side.
“H” and “L” are shown
Process
connection
Gauge/Absolute Pressure Transmitters
Figure 5.1 “H” and “L” Symbols on a Capsule
Assembly
Process connection
Process connector
Bolt
“H” and “L” are shown
Process connection
Process connector
Bolt
F0501.ai
(2) Changing the Process Connector Piping
Connections (Figure 4.1) (for differential
pressure transmitters)
The impulse piping connection distances can be
changed between 51 mm, 54 mm and 57 mm by
changing the orientation of the process connectors.
This is convenient for aligning an impulse line with a
process connectors.
(3) Tightening the Process Connector
Mounting Bolts
After connecting an impulse line, tighten the
process connector mounting bolts uniformly.
(Apply a torque of 39~49N·m {4~5kgf·m})
(4) Removing the Impulse Piping Connecting
Port Dustproof Cap
The impulse piping and a 3-valve manifold
connecting port on the transmitter is covered with
a plastic cap to keep out dust. This cap must be
removed before connecting the line. (Be careful not
to damage the threads when removing this cap.
Never insert a screwdriver or other tool between the
cap and port threads to remove the cap.)
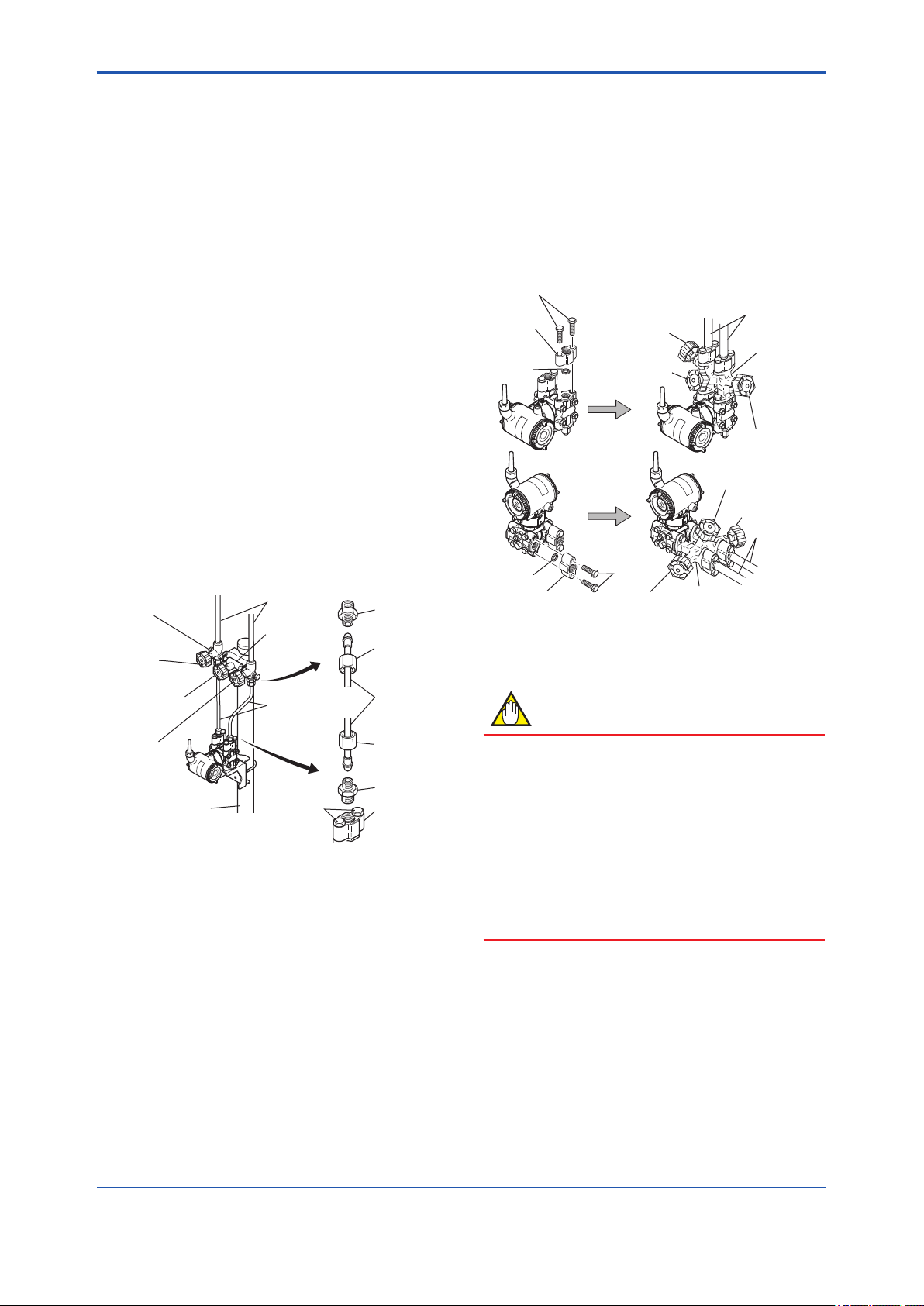
(5) Connecting the Transmitter and 3-
Valve Manifold (for differential pressure
transmitters)
A 3-valve manifold consists of two stop valves to
block process pressure and an equalizing valve
to equalize the pressures on the high and low
pressure sides of the transmitter. Such a manifold
makes it easier to disconnect the transmitter
from the impulse piping, and is convenient when
adjusting the transmitter zero point.
There are two 3-valve manifold types: the pipemounting type and the direct-mounting type; care
should be taken with respect to the following points
when connecting the manifold to the transmitter.
IM 01C27B01-01EN
Page 26
<5. Installing Impulse Piping>
Impulse
Bolts
5-2
Pipe-Mounting Type 3-Valve Manifold
(Figure 5.2)
1) Screw nipples into the connection ports on the
transmitter side of the 3-valve manifold, and
into the impulse piping connecting ports on
the process connectors. (To maintain proper
sealing, wind sealing tape around the nipple
threads.)
2) Mount the 3-valve manifold on the 50 mm (2-
inch) pipe by fastening a U-bolt to its mounting
bracket. Tighten the U-bolt nuts only lightly at
this time.
3) Install the pipe assemblies between the 3-valve
manifold and the process connectors and lightly
tighten the ball head lock nuts. (The ball-shaped
ends of the pipes must be handled carefully,
since they will not seal properly if the ball
surface is scratched or otherwise damaged.)
4) Now tighten the nuts and bolts securely in the
following sequence:
Process connector bolts → transmitter-end ball
head lock nuts → 3-valve manifold ball head
lock nuts → 3-valve manifold mounting bracket
U-bolt nuts
Vent plug
(optional)
Stop valve
(low pressure side)
Equalizing valve
(balancing)
piping
3-valve
manifold
Pipe assembly
Nipple
Ball head
lock nut
Pipe assembly
Direct-Mounting Type 3-Valve Manifold
(Figure 5.3)
1) Mount the 3-valve manifold on the transmitter.
(When mounting, use the two gaskets and the
four bolts provided with the 3-valve manifold.
Tighten the bolts evenly.)
2) Mount the process connectors and gaskets
on the top of the 3-valve manifold (the side on
which the impulse piping will be connected).
Stop valve
Process
connector
Gasket
Gasket
Process
connector
(low pressure side)
Equalizing
valve
(high
pressure side)
Bolts
Stop valve
(low pressure side)
3-valve
manifold
Figure 5.3 3-Valve Manifold (Direct-Mounting
Type)
Impulse
piping
3-valve
manifold
Stop valve
(high pressure side)
Equalizing valve
Stop valve
(high pressure side)
Impulse
piping
F0503.ai
NOTE
Stop valve
(high pressure
side)
50 mm (2-inch) pipe
Process
connector
bolts
Ball head
lock nut
Nipple
Process
connector
F0502.ai
Figure 5.2 3-Valve Manifold (Pipe-Mounting Type)
After completing the connection of the transmitter
and 3-valve manifold, be sure to CLOSE the low
pressure and high pressure stop valves, OPEN
the equalizing valve, and leave the manifold with
the equalizing valve OPEN.
You must do this in order to avoid overloading
the transmitter from either the high or the low
pressure side when beginning operation.
This instruction must also be followed as part of
the startup procedure (chapter 7.)
IM 01C27B01-01EN
Page 27
<5. Installing Impulse Piping>
5-3
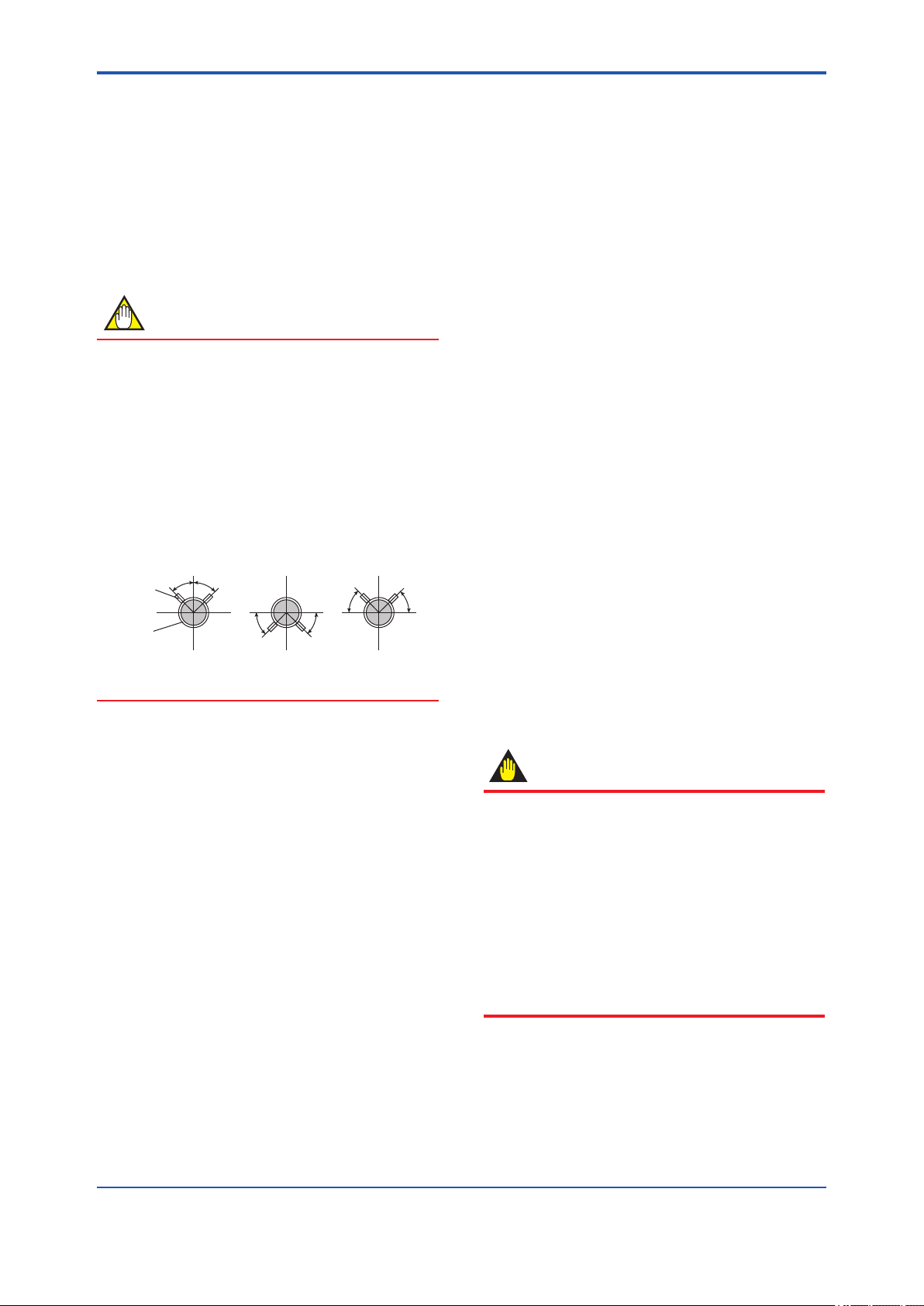
5.1.2 Routing the Impulse Piping
(1) Process Pressure Tap Angles
If condensate, gas, sediment or other extraneous
material in the process piping gets into the impulse
piping, pressure measurement errors may result. To
prevent such problems, the process pressure taps
must be angled as shown in gure 5.4 according to
the kind of uid being measured.
NOTE
• If the process uid is a gas, the taps must be
vertical or within 45° either side of vertical.
• If the process uid is a liquid, the taps must
be horizontal or below horizontal, but not
more than 45° below horizontal.
• If the process uid is steam or other
condensing vapor, the taps must be
horizontal or above horizontal, but not more
than 45° above horizontal.
[Gas]
45°
Pressure
taps
Process
piping
Figure 5.4 Process Pressure Tap Angle
45°
45° 45°
(For Horizontal Piping)
(2) Position of Process Pressure Taps and
Transmitter
If condensate (or gas) accumulates in the impulse
piping, it should be removed periodically by
opening the drain (or vent) plugs. However, this will
generate a transient disturbance in the pressure
measurement, and therefore it is necessary to
position the taps and route the impulse piping so
that any extraneous liquid or gas generated in the
leadlines returns naturally to the process piping.
• If the process uid is a gas, then as a rule the
transmitter must be located higher than the
process pressure taps.
• If the process uid is a liquid or steam, then as a
rule the transmitter must be located lower than
the process pressure taps.
45°
[Steam][Liquid]
45°
F0504.ai
(3) Impulse Piping Slope
The impulse piping must be routed with only an
upward or downward slope. Even for horizontal
routing, the impulse piping should have a slope of
at least 1/10 to prevent condensate (or gases) from
accumulating in the pipes.
(4) Temperature Difference Between Impulse
Lines (for differential pressure transmitters)
If there is a temperature difference between the
high and low impulse lines, the density difference
of the uids in the two lines will cause an error in
the measurement pressure. When measuring ow,
impulse lines must be routed together so that there
is no temperature difference between them.
(5) Condensate Pots for Steam Flow
Measurement (for differential pressure
transmitters)
If the liquid in the impulse piping repeatedly
condenses or vaporizes as a result of changes
in the ambient or process temperature, this will
cause a difference in the uid head between the
high pressure and low pressure sides. To prevent
measurement errors due to these head differences,
condensate pots are used when measuring steam
ow.
(6) Preventing Wind Speed Effects in Very Low
Differential Pressure Measurement
(for differential pressure transmitters)
IMPORTANT
When using a differential pressure transmitter
to measure very low pressures (draft pressure),
the low pressure connection port is left open
to atmospheric pressure (the reference
pressure). Any wind around the differential
pressure transmitter will therefore cause errors
in the measurement. To prevent this, it will be
necessary either to enclose the transmitter in
a box, or to connect an impulse line to the low
pressure side and insert its end into a windexcluding pot (cylindrical with a base plate).
(7) Preventing Freezing
If there is any risk that the process uid in the
impulse piping or transmitter could freeze, use a
steam jacket or heater to maintain the temperature
of the uid.
IM 01C27B01-01EN
Page 28

<5. Installing Impulse Piping>
5-4
NOTE
After completing the connections, close the
valves on the process pressure taps (main
valves), the valves at the transmitter (stop
valves), and the impulse piping drain valves,
so that condensate, sediment, dust and other
extraneous material cannot enter the impulse
piping.
5.2 Impulse Piping Connection Examples
Figure 5.5 and 5.6 show examples of typical
impulse piping connections. Before connecting the
transmitter to the process, study the transmitter
installation location, the process piping layout,
and the characteristics of the process uid
(corrosiveness, toxicity, ammability, etc.), in order
to make appropriate changes and additions to the
connection congurations.
Note the following points when referring to these
piping examples.
• The high pressure connecting port on the
transmitter is shown on the right (as viewed
from the front).
• The transmitter impulse piping connection is
shown for a vertical impulse piping connection
conguration in which the direction of
connection is either upwards or downwards.
• If the impulse line is long, bracing or supports
should be provided to prevent vibration.
• The impulse piping material used must
be compatible with the process pressure,
temperature, and other conditions.
• A variety of process pressure tap valves (main
valves) are available according to the type
of connection (anged, screwed, welded),
construction (globe, gate, or ball valve),
temperature and pressure. Select the type of
valve most appropriate for the application.
Liguid Gas
Tap
valve
Union
or flange
Tee
3-valve
manifold
Drain
valve
Figure 5.5 Impulse Piping Connection Examples
Liquid Gas Steam
Tap
valve
Union or flange
Union
or
flange
Union or flange
Figure 5.6 Impulse Piping Connection Examples
Orifice
Drain
plug
for Differential Pressure Transmitters
Tee
Tap valve
Drain valve
Drain plug
for Gauge/absolute Pressure
Transmitters
Condensate pot
Union or flange
Drain plug
Drain valve
Tee
Steam
F0505.ai
Tap valve
Tee
Drain valve
Drain plug
F0506.ai
IM 01C27B01-01EN
Page 29
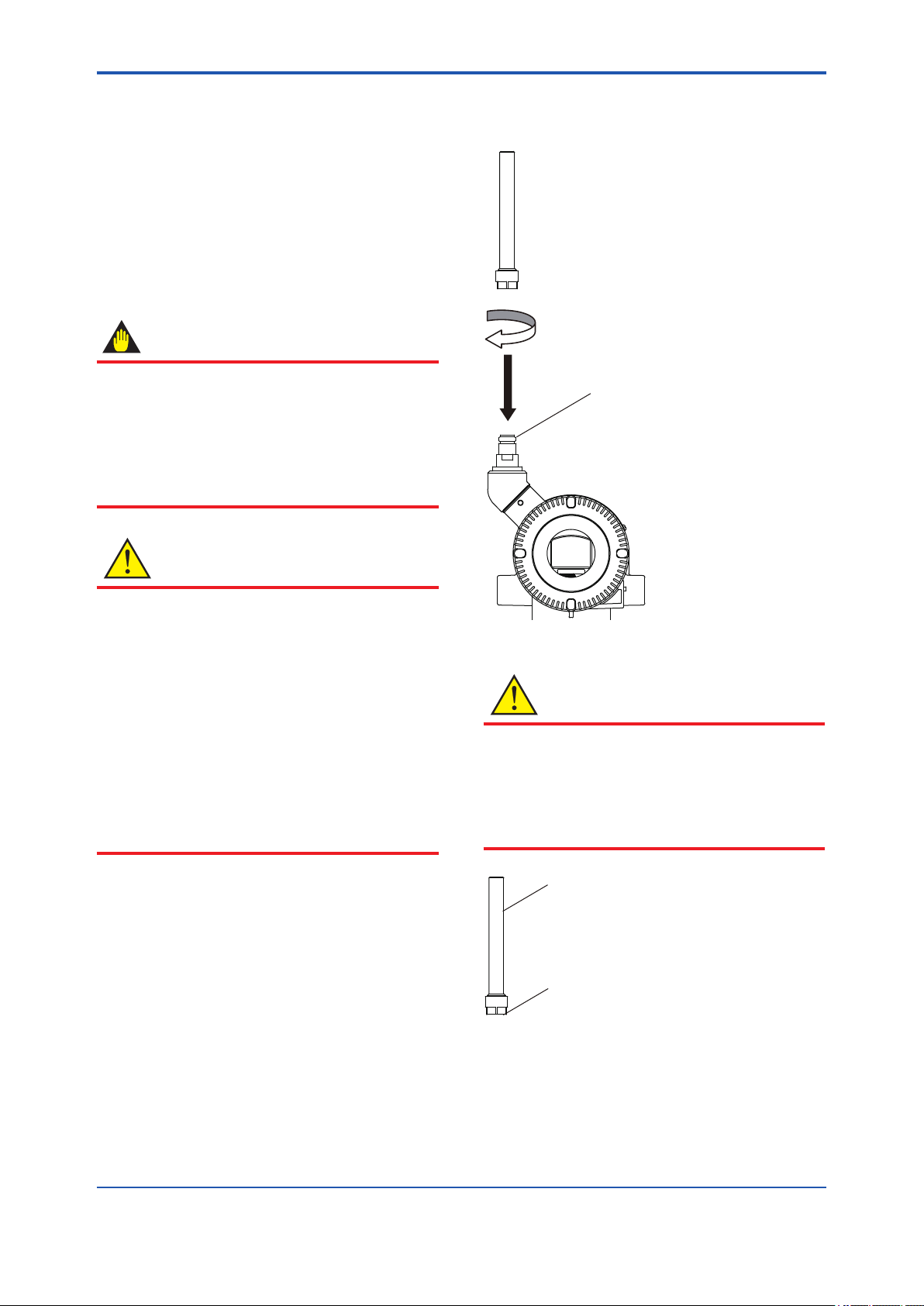
<6. Wiring>
6. Wiring
6.1 Mounting Antenna and Wiring
For Amplier housing code 8 and 9, an antenna
is not attached to the transmitter. The following
provides the instructions for mounting the antenna
and installing the remote antenna and wiring using
antenna extension cable.
IMPORTANT
6-1
The antenna connector is covered with a cap
at the time of delivery. Keep the cap attached
until the installation of the antenna or antenna
cables to protect the inside connection part.
The unscrewed cap should be stored in order
to replace it immediately after the antenna or
antenna cables are removed.
CAUTION
To maintain the ultimate conditions of radiofrequency signal, protect the connectors of
antenna, extension antenna cable, and arrester
from the corrosive atmosphere by the following
treatment.
1. Clean the connection to be protected.
2. Wind the butyl rubber self-bonding tape
around the connection. See the manual of
the tape about the winding.
3. To protect the butyl rubber self-bonding tape
from the environment such as ultraviolet rays
and so on, wind vinyl tape (or a vinyl type
self-bonding tape) on it.
Antenna connector
F0601.ai
Figure 6.1 Mounting the antenna
CAUTION
When installing the antenna, screw the antenna
by tightening the lower nut part. Screwing the
antenna by holding the antenna body may cause
failure such as cable disconnection. The same
manner should be taken when unscrewing the
antenna.
6.1.1 Mounting the antenna
Screw the provided antenna into the antenna
connector of the transmitter. The antenna may
be sold as available accessories and supplied
separately.
1. Unscrew the antenna connector cap on the
antenna connector.
2. Screw the provided antenna into the antenna
connector. Tighten the antenna connector with
a torque of 2 to 3 N∙m.
Antenna body
Nut part
F0602.ai
Figure 6.2 Antenna
IM 01C27B01-01EN
Page 30
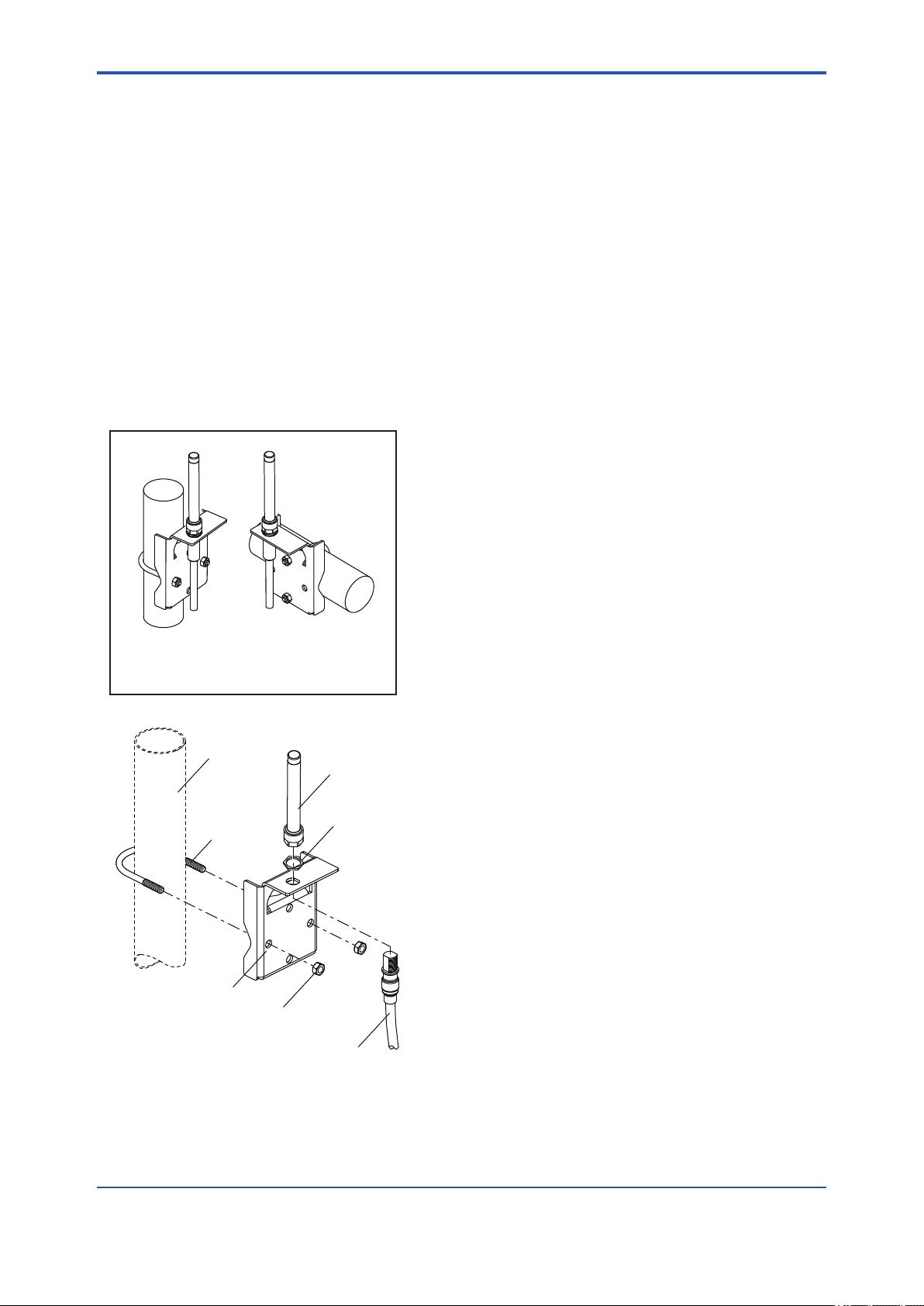
<6. Wiring>
6-2
6.1.2 Mounting External Antenna and Wiring Antenna Extension Cable
6.1.2.1 Mounting of External Antenna
Mount the external antenna at the proper location
according to the wireless environment described
in 2.4 Selecting the Installation Location. The
mounting to the pipe such as 50 mm (2-inch) pipe
needs to secure the enough strength to endure a
strong wind, vibration and so on. The antenna must
be mounted vertically.
Fixing of External Antenna
Fix an external antenna appropriately using the
bracket provided as the external antenna option to
50 mm (2-inch) pipe.
Vertical pipe
mounting
2-inch pipe
U Bolt
Horizontal pipe
mounting
Antenna
Nut
Mounting Procedure of External
Antenna
1. Fix the bracket by U-bolt and nut to 50 mm (2inch) pipe.
2. Fix the antenna extension cable to the bracket
1 using the provided nut with a torque of 6 to 7
N∙m as shown in the Figure 6.3 above. Use the
nut which is attached to the antenna extension
cable.
3. Screw the antenna into the antenna connector
of the antenna extension cable on the bracket
1.
Tighten the antenna connector with a torque of
2 to 3 N∙m.
4. Protect the connection as necessary. For
details of the protection, see “6.1 Mounting
Antenna and Wiring.”
6.1.2.2 Wiring of Antenna Extension Cable
1. Use the provided antenna extension cable
to connect the antenna connector with the
external antenna. Tighten the connector of the
antenna extension cable with a torque of 2
to 3 N∙m. The minimum bending radius while
checking the wiring position should be more
than 200 mm.
2. When using two extension cables, the provided
arrester should be inserted between these
cables.
3. Before the wiring work, conrm the polarities
(male/female) of the connectors of antenna,
extension antenna cable, and arrester. Tighten
the connector of the antenna extension cable
with a torque of 2 to 3 N∙m.
4. Protect the connectors of antenna, extension
antenna cable, and arrester as necessary. See
“6.1 Mounting Antenna and Wiring.”
5. Fix the extension antenna cable to the
appropriate structure to protect the cable from
the vibration, wind, and so on. The minimum
bending radius for xing in the state maintained
for a long period should be more than 80 mm.
Bracket
Nut
Antenna
Extension Cable
Figure 6.3 Fixing the remote antenna
F0603.ai
IM 01C27B01-01EN
Page 31

<6. Wiring>
Antenna
Antenna extension cable 2: 10 m
Antenna
6-3
Protect by self-bonding tape
Protect by self-bonding tape
Transmitter body
Antenna extension cable 1: 3 m
Figure 6.4 Wiring the antenna extension cable
CAUTION
Use the dedicated antenna extension cable
provided by Yokogawa as accessories for the
transmitters.
Arrester
Grounding cable
Antenna extension cable 1: 3 m
Transmitter body
F0604.ai
IM 01C27B01-01EN
Page 32

<6. Wiring>
6-4
6.1.2.3 Mounting of Arrester and Wiring
Mount an arrester between the extension cables
and connect the grounding cable to the grounding
terminal of the arrester as required.
Connect the grounding cable to the grounding
terminal on the transmitter body. Class C grounding
with the grounding resistance of 10 Ω or less is
necessary. Do not share the ground with other
devices.
Antenna side
Antenna extension cable 2
Grounding cable
Arrester
6.2 Grounding
When using the antenna extension cable with an
arrestor, Class C grounding with the grounding
resistance of 10 Ω is required. Always ground the
transmitter case in accordance with national and
local electrical codes. The most effective transmitter
case grounding method is a direct connection to
earth ground with minimal impedance.
CAUTION
Grounding is recommended for safe operation.
Ground terminal
F0607.ai
Figure 6.7 Ground Terminal
Antenna extension cable 1
Transmitter side
Figure 6.5 Connection of the arrester and antenna
extension cable
Antenna side
Protect by self-bonding tape
Grounding cable
F0605.ai
Transmitter side
Figure 6.6 Arrester protection by self-bonding
tape
F0606.ai
IM 01C27B01-01EN
Page 33

<7. Operation>
7. Operation
7-1
7.1 Preparation for Starting Operation
This section describes the operation procedure
for the EJX110B as shown in gure 7.1 (vertical
impulse piping type, high-pressure connection:
right side) when measuring the liquid ow rate, and
EJX430B as shown in gure 7.2 when measuring
pressure.
NOTE
It is required to set security and network
information to enable the transmitter to be
connected to the Field Wireless Network. For
more details, refer to section 7.4 “Connecting to
the Field Wireless Network”.
NOTE
Check that the process pressure tap valves,
drain valves, and 3-valve manifold stop valves
on both the low pressure and high pressure
sides are closed, and that the 3-valve manifold
equalizing valve is opened.
■ Gauge/Absolute Pressure Transmitters
1) Open the tap valve (main valve) to ll the
impulse piping with process uid.
2) Gradually open the stop valve to introduce
process uid into the transmitter pressuredetector section.
3) Conrm that there is no pressure leak in
the impulse piping, transmitter, or other
components.
(b) Venting Gas from the Transmitter Pressure-
detector Section
Since the piping in the example of gure 7.1
is constructed to be self-venting, no venting
operation is required. If it is not possible to
make the piping self-venting, refer to subsection
7.5 for instructions. Leave the equalizing valve
open even after venting gas.
(c) Insert batteries into the battery case, and install
to the transmitter. To insert batteries into the
battery case, be careful to polarity of batteries
and battery case. For details of Installation of
battery, refer to section 9.4.6 and 9.4.7.
Battery case is installed in the transmitter when
shipped from the factory, however, batteries are
sold separately and not included.
(a) Follow the procedures below to introduce
process pressure into the impulse piping and
transmitter.
■ Differential Pressure Transmitters
1) Open the low pressure and high pressure tap
valves to ll the impulse piping with process
liquid.
2) Slowly open the high pressure stop valve to ll
the transmitter pressure-detector section with
process liquid.
3) Close the high pressure stop valve.
4) Gradually open the low pressure stop valve and
completely ll the transmitter pressure-detector
section with process liquid.
5) Close the low pressure stop valve.
6) Gradually open the high pressure stop valve. At
this time, equal pressure is applied to the low
and high pressure sides of the transmitter.
7) Check that there are no liquid leaks in the
impulse piping, 3-valve manifold, transmitter, or
other components.
(d) Using the device conguration tool, conrm
that the transmitter is operating properly. Check
parameter values or change the setpoints as
necessary.
Integral Indicator’s indication can be used
to conrm that the transmitter is operating
properly. For details on how to conrm, refer to
subsection 8.4 “Self-Diagnostics.”
ISA100 devices display self-diagnostic
information in an easy-to-understand manner
using four categories (Check function,
Maintenance required, Failure, and Offspecication) according to NAMUR NE107*.
* NAMUR NE107 “Self-Monitoring and Diagnosis of Field
Devices”
IM 01C27B01-01EN
Page 34

<7. Operation>
7-2
Orifice
Tap valve
(low pressure)
Stop valve
(low pressure)
Equalizing valve
Stop valve
(high pressure)
Figure 7.1 Liquid Flow Measurement
Vent plug (Fill plug)
3-valve manifold
Drain valve
(high pressure)
Tap valve
(high pressure)
F0701.ai
■ Conrm that transmitter is operating
properly by integral indicator.
If the transmitter is faulty, an error code is displayed.
Self-diagnostic error on integral indicator
(Faulity transmitter)
F0703.ai
Figure 7.3 Integral Indicator with Error Code
NOTE
If any of the above errors are indicated on the
display of the integral indicator or the device
conguration tool, refer to subsection 9.5.3 for
the corrective action.
Tap valve
Stop valve
Drain valve
F0702.ai
Figure 7.2 Liquid Pressure Measurement
■ Verify and Change Transmitter Parameter
Setting and Values
The parameters related to the following items are
minimum required to be set for operation, and set at
factory as specied in order. Conrm or change the
parameters if needed.
• Measurement range(measurement lower/upper
limit, unit)
• Output (Non linearization mode / Sq root mode)
7.2 Zero Point Adjustment
After completing preparations for operating the
transmitter, adjust the zero point. There are two
zero point adjusting ways.
IMPORTANT
Do not turn off the power to the transmitter
immediately after performing a zero point
adjustment. Powering off within 30 seconds of
performing this procedure will return the zero
point to its previous setting.
IM 01C27B01-01EN
Page 35

<7. Operation>
7-3
(1) When you can obtain the Low Range Value
from the actual measured value of 0%
(0 kPa, atmospheric pressure);
■ Using the transmitter’s zero-adjustment
screw
Before adjusting zero point, make sure followings.
• The External zero trim parameter (External
Zero Trim) is “Trim on”. For details, refer to
section 8 “Setting Parameters”.
• Use a slotted screwdriver to turn the zeroadjustment screw. Turn the screw clockwise
to increase the output or counterclockwise to
decrease the output.
The zero point adjustment can be made with
a resolution of 0.01% of the setting range. The
degree of zero adjustments varies with the screw
turning speed; turn the screw slowly to make a ne
adjustment, quickly to make a rough adjustment.
■ Using the Device Conguration Tool
Refer to subsection 8.3.14 “Zero Point Adjustment
and Span Adjustment”.
7.3 Starting Operation
After completing the zero point adjustment, follow
the procedures below to start operation. Steps
1) and 2) are specic to the differential pressure
transmitters.
1) Close the equalizing valve.
2) Gradually open the low pressure stop valve.
This places the transmitter in an operational
condition.
3) After conrming the operating status, perform
the following.
IMPORTANT
• Close the terminal box cover and the
amplier cover. Screw each cover in tightly
until it will not turn further.
• Tighten the zero-adjustment cover mounting
screw to secure the cover.
7.4 Connecting to the Field
(2) When you cannot obtain the Low Range
Value from the actual measured value of
0%;
Adjust the transmitter output value matches to
the actual measured value obtained by precise
pressure measurement equipment.
[Example]
The measuring range of 50 to 250 kPa; the actual
measured value of 130 kPa.
Actual measured value=
■ Using the transmitter’s zero-adjustment
screw
Turn the zero adjustment screw to match the output
signal to the actual measured value.
■ Using the Device Conguration Tool
Refer to subsection 8.3.14 ”Zero Point Adjustment
and Span Adjustment”.
130–50
250–50
x100=40.0%
Wireless Network
■ Preparation work prior to connecting to a
Field Wireless Network
This transmitter does not need to be connected
with a physical wire. Instead of physical wiring, it
is necessary to set the eld wireless devices to
communicate with before installing the transmitter.
This procedure is called a provisioning.
This transmitter supports provisioning via infrared
communication using a provisioning device and
can be securely connected to a network. If the
provisioning information is not set, the transmitter
cannot be connected to the eld wireless network.
Provisioning:
Provisioning is work to set the security and
network information to enable the transmitter
to be connected to the eld wireless network.
This transmitter supports a provisioning method
using infrared communication.
For details on provisioning using a provisioning
device, and procedure for connecting the
transmitter to the Field Wireless Network, refer
to the User’s Manual, FieldMate Versatile Device
Management Wizard (IM 01R01A01-01E),
YFGW710 Field Wireless Integrated Gateway (IM
01W01F01-01EN) and YFGW410 Field Wireless
Management Station (IM 01W02D01-01EN).
IM 01C27B01-01EN
Page 36

<7. Operation>
2) Creating a provisioning information le
The following provisioned information is stored
in the provisioning information le.
within 30cm
• Network ID
• Device tag
• EUI64
• Join key
• Provisioner (name of the user who performed
provisioning work by FieldMate)
• Date (Time and date when provisioning was
F0705.ai
Figure 7.5 Provisioning Example
performed by FieldMate)
This provisioning information le is required to
load from the Field Wireless Congurator to the
■ Provisioning work
Field Wireless Integrated Gateway. Store the
le carefully.
This subsection describes provisioning work using
FieldMate as the provisioning device.
Provisioning work performs provisioning for each
eld wireless device using FieldMate and an
infrared adapter. If Yokogawa - recommended
infrared device is used for provisioning, distance
between the transmitter glass window and the
infrared device should be within 30cm. For details of
Yokogawa - recommended infrared device, refer to
subsection 9.2 “Calibration Instruments Selection”.
Perform the following provisioning tasks.
• Setting provisioning information
• Creating a provisioning information le
■ Connecting to a eld wireless network
The action after installing the battery pack varies
depending on the silence setting.
Mounting the battery pack automatically starts a
search for the eld wireless network. When the
Field Wireless Integrated Gateway is found, the
instrument enters the join status.
When the eld wireless gateway is not found and
a specied time based on the silence mode has
elapsed, a cycle of a one-hour pause and sixminutes search is repeated until the instrument can
join the eld wireless network.
For details on the procedure to switch to silence
1) Setting provisioning information
Set the device tag and network ID using a
mode, refer to subsection 8.3.17 “Switching to
Silence Mode.”
FieldMate provisioning function. The device
tag, network ID, and join key are set in the Field
Mounting battery pack
Wireless Device. It is not necessary to input
a join key because FieldMate automatically
generates it.
Setting device tag
The device tag is used for the user to
recognize the Field Wireless Device.
Setting network ID
This is the network ID for the eld wireless
network to which the eld wireless device is
connected. Set a value from 2 to 65535.
The eld wireless device is connected to the
eld wireless network corresponding to the
network ID set by provisioning work.
Infrared communication
Deep sleep (a)
(Disconnect)
Deep sleep
setting
Operation (d)
Figure 7.6 Wireless Connection Process
Boot
Search failure for
the specified time
Infrared
communication
Ready 1:
Searching (b)
Infrared
communication
(Disconnect)
(Connect)
Confirm connecting
status: Join (c)
(Publish)
7-4
Pause (b)
1 hour
passed
Search failure
for 6 minutes
Ready 2:
Searching (b)
(Connect)
F0706.ai
IM 01C27B01-01EN
Page 37

<7. Operation>
(a) Deep sleep
NOTE
If the transmitter searches the Field Wireless
Network for long time at low ambient
temperature condition, sometimes error “AL.70
LOWBAT” is displayed on the Integral Indicator.
Even though using new batteries, it can occur. It
occurs because of battery characteristics. After
joining to the Field Wireless Network, this error
will be cleared within one hour if battery has no
F0707.ai
failure.
(b) Ready and pause
7.5 Shutting Down the Transmitter
Shut down the transmitter as follows.
1) Remove the battery pack or set the
transmitter to deep sleep mode by the Device
Conguration Tool.
2) Close the low pressure stop valve.
F0708.ai
(c) Conrm connecting status
3) Open the equalizing valve.
4) Close the high pressure stop valve.
5) Close the high pressure and low pressure tap
valves.
7-5
(d) Join
F0709.ai
F0710.ai
NOTE
• Whenever shutting down the transmitter for
a long period, remove any process uid that
is in the impulse piping and in the transmitter
pressure-detector section.
• The equalizing valve must be left OPEN.
• Refer to subsection 9.4.6 “Replacing the
Battery Pack” for the battery pack removing.
• When storing the instrument with a battery
pack inserted, it is recommended to put the
instrument into deep sleep mode to conserve
battery power. For details on how to switch to
deep sleep mode, refer to subsection 8.3.16
“Switching to the Deep Sleep Mode.”
IM 01C27B01-01EN
Page 38

<7. Operation>
7.6 Venting or Draining
Transmitter Pressuredetector Section
Since this transmitter is designed to be selfdraining and self-venting with vertical impulse
piping connections, neither draining nor venting
will be required if the impulse piping is congured
appropriately for self-draining or self-venting
operation.
If condensate (or gas) collects in the transmitter
pressure-detector section, the measured pressure
may be in error. If it is not possible to congure the
piping for self-draining (or self-venting) operation,
you will need to loosen the drain (vent) screw on the
transmitter to completely drain (vent) any stagnated
liquid (gas.) After venting or draining, fasten the
drain (vent) screw on the transmitter.
Drain screw
When you loosen the drain screw or drain
plug, the accumulated liquid will be expelled
in the direction of the arrow.
Figure 7.7 Draining the Transmitter
7.6.2 Venting Gas
Drain plug
7-6
F0711.ai
IMPORTANT
Draining condensate or bleeding off gas disturbs
the pressure measurement, this should not be
done when the loop is in operation.
7.6.1 Draining Condensate
1) Gradually open the drain screw or drain plug
and drain the transmitter pressure-detector
section. (See gure 7.7.)
2) When all accumulated liquid is completely
removed, close the drain screw or drain plug.
3) Tighten the drain screw to a torque of 10 N·m,
and the drain plug to a torque of 34 to 39 N·m.
WARNING
Since the accumulated liquid (or gas) may be
toxic or otherwise harmful, take appropriate care
to avoid contact with the body, or inhalation of
vapors.
1) Gradually open the vent screw to vent gas from
the transmitter pressure-detector section. (See
gure 7.8.)
2) When the transmitter is completely vented,
close the vent screw.
3) Tighten the vent screw to a torque of 10 N·m.
WARNING
Since the accumulated liquid (or gas) may be
toxic or otherwise harmful, take appropriate care
to avoid contact with the body, or inhalation of
vapors.
Vent screw
Vent screw
When you loosen the vent screw, the gas
escpes in the direction of the arrow.
Figure 7.8 Venting the Transmitter
F0712.ai
IM 01C27B01-01EN
Page 39

<8. Setting Parameters>
8. Setting Parameters
8-1
This transmitter can remotely handle range
changes, Tag No. setup, monitoring of selfdiagnostic results, and Zero Point Adjustment, etc.
according to communication with the eld wireless
conguration tool or the device conguration tool.
8.1 Environment for parameter setting
After installing the battery pack, perform
provisioning and have the transmitter join the eld
wireless network.
This transmitter supports the OOB (out-of-band)
method using the infrared communication as a
provisioning method.
Refer to Subsection 7.4 “Connecting to the Field
Wireless Network” for details of the provisioning.
CF (Capabilities File)/DD (Device Description)
A CF le contains information, such as the
vendor of the eld device, its model and
revision, available types of process data (ow
rate, temperature, pressure, etc.), and number
of data items. A DD le contains the information
on parameters, such as data structures and
attributes.
DeviceDTM
DeviceDTM (Device Type Manager) is driver
software for eld devices provided based on the
FDT (Field Device Tool) technology.
The eld wireless conguration tool or the device
conguration tool allows conrming the device
information.
Refer to Subsection 9.2 “Calibration Instruments
Selection” for the eld wireless conguration
tool or the device conguration tool of our
recommendation.
8.2.2 Software Download
Infrared port
F0801.ai
Figure 8.1 Infrared port of the transmitter
8.2 Preparing Software
8.2.1 Softwares for the Field Wireless
Conguration Tool and the Device
Conguration Tool
Before using the device conguration tool,
conrm that CF/DD and DeviceDTM for your
transmitter (wireless EJX) are installed in the device
conguration tool.
CF/DD and DeviceDTM are provided by DVD-ROM
attached to YFGW710 Field Wireless Integrated
Gateway.
Refer to YFGW710 Field Wireless Integrated
Gateway (IM 01W01F01-01EN) for details.
Software download function permits to update
wireless eld device software via ISA100.11a
wireless communication. For details, refer to
YFGW710 Field Wireless Integrated Gateway (IM
01W01F01-01EN) or YFGW410 Field Wireless
Management Station (IM 01W02D01-01EN).
8.3 Setting Parameters
8.3.1 Parameter Usage and Selection
Before setting a parameter, please see the following
table for a summary of how and when each
parameter is used.
IMPORTANT
After setting and sending data with the eld
wireless conguration tool or the device
conguration tool, wait 30 seconds before
turning off the transmitter. If it is turned off
too soon, the settings will not be stored in the
transmitter.
IM 01C27B01-01EN
Page 40

<8. Setting Parameters>
Table 8.1 Parameter Usage and Selection
Item Description
Tag No Sets the tag No. as Device Tag (Software Tag). Sixteen characters
Output The process variable and the diagnostic result can be output.
Range Adjust the range corresponding for 0% to 100%.
Damping time constant Damping time constant is used to reduce the large uctuation of pressure
Output signal and integral indicator mode Sets mode for output signal and integral indicator to “linear mode”
Output signal low cut mode Used mainly to stabilize output near 0 if output signal is the square root
Integral indicator range of scale and unit Sets one of differential pressure/pressure value, static pressure value, or
Unit for displayed temperature Sets a temperature unit to be displayed.
Unit for displayed static pressure Sets a pressure unit for the static pressure to be displayed
Direction of impulse piping connection
(which is high pressure, L side or R side)
Range with actual input applied Range corresponding for 0% to 100% signal is set with actual input
Zero Point Adjustment and Span Adjustment Handle Zero Point Adjustment and Span Adjustment.
Reset adjustment The amount of the adjustment set by user can be cleared.
Software write protect Prohibit writing the setting data.
Operational mode Set the operational mode of the sensor and integral indicator, etc.
Note: Some of the parameter settings are in the dialogue form called method, the on-line instructions you can congure the parameters
easily.
(alphanumeric characters, including - and •) can be set.
Either or all of differential pressure/pressure (AI1:Process Value), static
pressure (AI2:Process Value), temperature(AI3:Process Value) of capsule
or amplier and self-diagnostic information (UAPMO:Diagnostic Status)
can be set to the output
The unit of the range, input value at 0% (LRV) and input value at 100%
(URV) is set.
Note: LRV and URV can be set within the range of -32000 to 32000.
signal and given by each Process Value Filter Time parameter for
differential Pressure/pressure (AI1) and Static pressure (AI2).
(proportional to input differential pressure) or to “Square root mode”
(proportional to ow).
mode. Two modes are available: forcing output to 0% for input below a
specic value, or changing to proportional output for input below a specic
value.
temperature value for the integral indicator scale.
Note: LRV and URV can be set within the range of -32000 to 32000.
Used where installation conditions makes it imperative to connect high
pressure side impulse line to low pressure side of transmitter.
Normally, correspond by replacing impulse line, and use this function only
when unavoidable.
applied.
The output setting can be done just 100% to user’s reference pressure
output.
However, when shipping it, the calibration is done in high accuracy as for
DPharp. Please do the span setting by a usual range setting.
There are two methods of Zero Point Adjustment, using external zeroadjustment screw and using the device conguration tool.
8-2
8.3.2 Function Block and Menu Tree
(1) Function Block
The function of this transmitter is shown below.
A specic function might not be able to be used
according to the eld wireless conguration tool
used. When the eld wireless conguration tool
of our recommendation is used, the software
attached to the Field Wireless Integrated Gateway is
necessary for setting the dotted line part.
Refer to Subsection 9.2 “Calibration Instruments
Selection” for the eld wireless conguration tool of
our recommendation.
IM 01C27B01-01EN
Page 41

<8. Setting Parameters>
(a) Integral antenna type (Amplier housing code: 7)
8-3
Online Menu
• UAPMO
• UDO
• CO
• TRANSDUCER
• AI1 DP
• AI2 SP
• AI3 Temp
(UAPMO)
• Configuration
• Diagnostics/Alerts
• Power Status
• Identification
(UDO)
• APP Download
(CO)
• Configuration
• Others
(TRANSDUCER)
• Block Info
• Configuration/
Calibration
• Others
(Configuration)
• UAP Option
• Hardware Write Protect
• Static Revision
• Reset Energy Left
• Radio Silence
(Diagnostics/Alerts)
• Diagnostic Status
• Diagnostic Status Detail1,
Diagnostic Status Detail2
• Diagnostic Switch
• Diagnostic Configuration
(Power Status)
• Energy Left
• Power Supply Status
(Identification)
• Version Revision
• CTS Version
• ITS Version
• Identification Number
(APP Download)
• DESCRIPTION
• STATE
• MAX_BLOCK_SIZE
• LAST_BLOCK_DOWNLOADED
• ERROR_CODE
(Configuration)
• COMM_ENDPOINT
• COMM_CONTRACT
• PUB_ITEM_MAX
• PUB_ITEM_NUM
• PUB_ITEM
(Others)
• REVISION
(Block Info)
• Tag Description
(Configuration/Calibration)
• Auto Recovery
• Model
• Sensor Serial Number
• Measurement Rate
• Measurement Mode
• Wireless Status
• Display Selection
• LCD Mode
• Special Order ID
• Unit Sel1
• Display Unit1
• EJX Key
• Test Key 1
• Test Key 2
• Test Key 3
(Others)
• Special Cmd
(COMM_ENDPOINT)
• Network address of remote endpoint
• Transport layer port at remote endpoint
• Object ID at remote endpoint
• Stale data limit
• Data publication period
• Ideal publication phase
• PublishAutoRetransmit
• Configuration status
(COMM_CONTRACT)
• ContractID
• Contract_Status
• Actual_Phase
(PUB_ITEM)
• ObjectID
• AttributeID
• AttributeIndex
• Size
F0802-1.ai
IM 01C27B01-01EN
Page 42

<8. Setting Parameters>
Online Menu (continued)
8-4
(AI1 DP)
• Block Info
• Block Mode
• Dynamic Variables
• Configuration
• Calibration
• Others
(Block Info)
• Tag Description
(Block Mode )
• Mode.Target
• Mode.Actual
• Mode.Permitted
• Mode.Normal
(Dynamic Variables)
• Process Value
• Simulation
(Configuration)
• Block Mode
• Concentrator OID
• Scale *
• Process Value Filter Time
(Process Value)
• Process Value.Status
• Process Value.Value **
(Simulation)
• Simulate Switch
• Transducer Value
• Simulate Value
(Block Mode)
• Mode.Target
• Mode.Actual
• Mode.Permitted
• Mode.Normal
(Scale)
• Scale.EU at 100% *
• Scale.EU at 0% *
• Scale.Units Index *
• Scale.Decimal *
(Transducer Value)
• Transducer Value.
Status
• Transducer Value.
Value
(Simulate Value)
• Simulate Value.
Status
• Simulate Value.
Value
(Calibration)
• Block Mode
• Cal Cmd *
• Cal Status
• Calibration Highest Point *
• Calibration Lowest Point *
• Calibration Minimum Span
• External Zero Trim *
(Others)
• Upper Limit
• Lower Limit
• PV Range *
• Linerization Type *
• Flow Constant *
• Lower cutoff
• Low Cut Mode *
• H/L Swap *
• T Zero Cmp *
• Temp Zero *
• Temp Select *
(Block Mode)
• Mode.Target
• Mode.Actual
• Mode.Permitted
• Mode.Normal
(PV Range)
• PV Range.EU at 100% *
• PV Range.EU at 0% *
• PV Range.Units Index *
• PV Range.Decimal *
F0802-2.ai
*: When the data of these parameters is rewritten, it is necessary to set the operational mode of the block to O/S (Out of Service).
**: When the data of these parameters is rewritten, it is necessary to set the operational mode of the block to Manual.
IM 01C27B01-01EN
Page 43

<8. Setting Parameters>
Online Menu (continued)
8-5
(AI2 SP)
• Block Info
• Block Mode
• Dynamic Variables
• Configuration
• Others
(Block Info)
• Tag Description
(Block Mode )
• Mode.Target
• Mode.Actual
• Mode.Permitted
• Mode.Normal
(Dynamic Variables)
• Process Value
• Simulation
(Configuration)
• Block Mode
• Concentrator OID
• Scale *
• Process Value Filter
Time
(Process Value)
• Process Value.Status
• Process Value.Value **
(Simulation)
• Simulate Switch
• Transducer Value
• Simulate Value
(Block Mode)
• Mode.Target
• Mode.Actual
• Mode.Permitted
• Mode.Normal
(Scale)
• Scale.EU at 100% *
• Scale.EU at 0% *
• Scale.Units Index *
• Scale.Decimal *
(Transducer Value)
• Transducer Value.
Status
• Transducer Value.
Value
(Simulate Value)
• Simulate Value.
Status
• Simulate Value.
Value
(Others)
• Upper Limit
• Lower Limit
• PV Range *
• Linerization Type *
• Flow Constant *
• Lower cutoff
• Cal Cmd *
• Cal Status
• Calibration Highest
Point *
• Calibration Lowest
Point *
• Calibration Minimum
Span
• Static Pres Type *
• SP Select *
(PV Range)
• PV Range.EU at 100% *
• PV Range.EU at 0% *
• PV Range.Units Index *
• PV Range.Decimal *
F0802-3.ai
*: When the data of these parameters is rewritten, it is necessary to set the operational mode of the block to O/S (Out of Service).
**: When the data of these parameters is rewritten, it is necessary to set the operational mode of the block to Manual.
IM 01C27B01-01EN
Page 44

<8. Setting Parameters>
Online Menu (continued)
8-6
(AI3 Temp)
• Block Info
• Block Mode
• Dynamic Variables
• Configuration
• Others
(Block Info)
• Tag Description
(Block Mode )
• Mode.Target
• Mode.Actual
• Mode.Permitted
• Mode.Normal
(Dynamic Variables)
• Process Value
• Simulation
(Configuration)
• Block Mode
• Concentrator OID
• Scale *
• Process Value Filter Time
(Process Value)
• Process Value.Status
• Process Value.Value **
(Simulation)
• Simulate Switch
• Transducer Value
• Simulate Value
(Block Mode)
• Mode.Target
• Mode.Actual
• Mode.Permitted
• Mode.Normal
(Transducer Value)
• Transducer Value.
Status
• Transducer Value.
Value
(Simulate Value)
• Simulate Value.
Status
• Simulate Value.
Value
(Scale)
• Scale.EU at 100% *
• Scale.EU at 0% *
• Scale.Units Index *
• Scale.Decimal *
(Others)
• Sensor Range
• Tertiary Value Sel *
(Sensor Range)
• Sensor Range.EU at 100%
• Sensor Range.EU at 0%
• Sensor Range.Units Index **
• Sensor Range.Decimal **
F0802-4.ai
*: When the data of these parameters is rewritten, it is necessary to set the operational mode of the block to O/S (Out of Service).
**: When the data of these parameters is rewritten, it is necessary to set the operational mode of the block to Manual.
IM 01C27B01-01EN
Page 45

<8. Setting Parameters>
(b) Detachable antenna type (Amplier housing code: 8 or 9)
8-7
Online Menu
• UAPMO
• UDO
• CO
• TRANSDUCER
• AI1 DP
• AI2 SP
• AI3 Temp
(UAPMO)
• Configuration
• Diagnostics
• Alerts
• Power Status
• Identification
(UDO)
• APP Download
(CO)
• Configuration
• Others
(TRANSDUCER)
• Block Info
• Configuration/
Calibration
• Others
(Configuration)
• UAP Option
• Hardware Write Protect
• Static Revision
• Reset Energy Left
• Radio Silence
• Energy Harvest Type
(Diagnostics)
• Diagnostic Status
• Diagnostic Status Detail.1
• Diagnostic Status Detail.2
• Diagnostic Switch
• Diagnostic Configuration
(Power Status)
• Energy Left
• Power Supply Status
• Power Supply Voltage
(Identification)
• Version Revision
• CTS Version
• ITS Version
• Identification Number
(APP Download)
• DESCRIPTION
• STATE
• MAX_BLOCK_SIZE
• LAST_BLOCK_DOWNLOADED
• ERROR_CODE
(Configuration)
• COMM_ENDPOINT
• COMM_CONTRACT
• PUB_ITEM_MAX
• PUB_ITEM_NUM
• PUB_ITEM
(Others)
• REVISION
(Block Info)
• Tag Description
(Configuration/Calibration)
• Auto Recovery
• Model
• Sensor Serial Number
• Measurement Rate
• Measurement Mode
• Wireless Status
• Display Selection
• LCD Mode
• Special Order ID
• Unit Sel1
• Display Unit1
• LCD Intermittent Time
• XD Filter
• EJX Key
• Test Key 1
• Test Key 2
• Test Key 3
(Others)
• Special Cmd
(Alerts)
• Other Faults Alert
• Faults Non-compliance Alert
• Faults Process Influence Alert
• Simulation Active Alert
• Soft Update Incomplete Alert
• Power Low Alert
• Power Critical Low Alert
• Fault Prediction Alert
• Environmental Conditions Alert
• Outside Sensor Limits Alert
• Out of Service Alert
• Calibration Problem Alert
• Faults Sensor or Actuator Alert
• Faults Electronics Alert
(COMM_ENDPOINT)
• Network address of remote endpoint
• Transport layer port at remote endpoint
• Object ID at remote endpoint
• Stale data limit
• Data publication period
• Ideal publication phase
• PublishAutoRetransmit
• Configuration status
(COMM_CONTRACT)
• ContractID
• Contract_Status
• Actual_Phase
(PUB_ITEM)
• ObjectID
• AttributeID
• AttributeIndex
• Size
F0802-5.ai
IM 01C27B01-01EN
Page 46

<8. Setting Parameters>
Online Menu (continued)
8-8
(AI1 DP)
• Block Info
• Block Mode
• Dynamic Variables
• Configuration
• Calibration
• Others
(Block Info)
• Tag Description
(Block Mode )
• Mode.Target
• Mode.Actual
• Mode.Permitted
• Mode.Normal
(Dynamic Variables)
• Process Value
• Simulation
(Configuration)
• Block Mode
• Concentrator OID
• Scale *
• Process Value Filter Time
(Process Value)
• Process Value.Status
• Process Value.Value **
(Simulation)
• Simulate Switch
• Transducer Value
• Simulate Value
(Block Mode)
• Mode.Target
• Mode.Actual
• Mode.Permitted
• Mode.Normal
(Scale)
• Scale.EU at 100% *
• Scale.EU at 0% *
• Scale.Units Index *
• Scale.Decimal *
(Transducer Value)
• Transducer Value.
Status
• Transducer Value.
Value
(Simulate Value)
• Simulate Value.
Status
• Simulate Value.
Value
(Calibration)
• Block Mode
• Cal Cmd *
• Cal Status
• Calibration Highest Point *
• Calibration Lowest Point *
• Calibration Minimum Span
• External Zero Trim *
(Others)
• Upper Limit
• Lower Limit
• PV Range *
• Linerization Type *
• Flow Constant *
• Lower Cutoff
• Low Cut Mode *
• H/L Swap *
• T Zero Cmp *
• Temp Zero *
• Temp Select *
(Block Mode)
• Mode.Target
• Mode.Actual
• Mode.Permitted
• Mode.Normal
(PV Range)
• PV Range.EU at 100% *
• PV Range.EU at 0% *
• PV Range.Units Index *
• PV Range.Decimal *
F0802-6.ai
*: When the data of these parameters is rewritten, it is necessary to set the operational mode of the block to O/S (Out of Service).
**: When the data of these parameters is rewritten, it is necessary to set the operational mode of the block to Manual.
IM 01C27B01-01EN
Page 47

<8. Setting Parameters>
Online Menu (continued)
8-9
(AI2 SP)
• Block Info
• Block Mode
• Dynamic Variables
• Configuration
• Others
(Block Info)
• Tag Description
(Block Mode )
• Mode.Target
• Mode.Actual
• Mode.Permitted
• Mode.Normal
(Dynamic Variables)
• Process Value
• Simulation
(Configuration)
• Block Mode
• Concentrator OID
• Scale *
• Process Value Filter
Time
(Process Value)
• Process Value.Status
• Process Value.Value **
(Simulation)
• Simulate Switch
• Transducer Value
• Simulate Value
(Block Mode)
• Mode.Target
• Mode.Actual
• Mode.Permitted
• Mode.Normal
(Scale)
• Scale.EU at 100% *
• Scale.EU at 0% *
• Scale.Units Index *
• Scale.Decimal *
(Transducer Value)
• Transducer Value.
Status
• Transducer Value.
Value
(Simulate Value)
• Simulate Value.
Status
• Simulate Value.
Value
(Others)
• Upper Limit
• Lower Limit
• PV Range *
• Linerization Type *
• Flow Constant *
• Lower Cutoff
• Cal Cmd *
• Cal Status
• Calibration Highest
Point *
• Calibration Lowest
Point *
• Calibration Minimum
Span
• Static Pres Type *
• SP Select *
(PV Range)
• PV Range.EU at 100% *
• PV Range.EU at 0% *
• PV Range.Units Index *
• PV Range.Decimal *
F0802-7.ai
*: When the data of these parameters is rewritten, it is necessary to set the operational mode of the block to O/S (Out of Service).
**: When the data of these parameters is rewritten, it is necessary to set the operational mode of the block to Manual.
IM 01C27B01-01EN
Page 48

<8. Setting Parameters>
Online Menu (continued)
8-10
(AI3 Temp)
• Block Info
• Block Mode
• Dynamic Variables
• Configuration
• Others
(Block Info)
• Tag Description
(Block Mode )
• Mode.Target
• Mode.Actual
• Mode.Permitted
• Mode.Normal
(Dynamic Variables)
• Process Value
• Simulation
(Configuration)
• Block Mode
• Concentrator OID
• Scale *
• Process Value Filter Time
(Process Value)
• Process Value.Status
• Process Value.Value **
(Simulation)
• Simulate Switch
• Transducer Value
• Simulate Value
(Block Mode)
• Mode.Target
• Mode.Actual
• Mode.Permitted
• Mode.Normal
(Transducer Value)
• Transducer Value.
Status
• Transducer Value.
Value
(Simulate Value)
• Simulate Value.
Status
• Simulate Value.
Value
(Scale)
• Scale.EU at 100% *
• Scale.EU at 0% *
• Scale.Units Index *
• Scale.Decimal *
(Others)
• Sensor Range
• Tertiary Value Sel *
(Sensor Range)
• Sensor Range.EU at 100%
• Sensor Range.EU at 0%
• Sensor Range.Units Index **
• Sensor Range.Decimal **
F0802-8.ai
*: When the data of these parameters is rewritten, it is necessary to set the operational mode of the block to O/S (Out of Service).
**: When the data of these parameters is rewritten, it is necessary to set the operational mode of the block to Manual.
IM 01C27B01-01EN
Page 49

<8. Setting Parameters>
8-11
(2) Menu Tree
The menu tree of the device conguration tool of our recommendation is shown below. Refer to Subsection 9.2
“Calibration Instruments Selection” for the device conguration tool of our recommendation.
(a) Integral antenna type (Amplier housing code: 7)
Online Menu
• Device Configuration
• Diagnostic
• Process Variable
(Device Configuration)
• UAPMO
• TRANSDUCER
• AI1 DP
• AI2 SP
• AI3 Temp
(UAPMO)
• Configure/Setup
(TRANSDUCER)
• Configure/Setup
(AI1 DP)
• Configure/Setup
(Configuration)
• UAP Option
• Hardware Write Protect
• Static Revision
• Reset Energy Left
• Radio Silence
(Identification)
• Version Revision
• CTS Version
• ITS Version
• Identification Number
(Block Info)
• Tag Description
(Configuration/Calibration)
• Auto Recovery
• Model
• Sensor Serial Number
• Measurement Rate
• Measurement Mode
• Wireless Status
• Display Selection
• LCD Mode
• Special Order ID
• Unit Sel1
• Display Unit1
• EJX Key
• Test Key 1
• Test Key 2
• Test Key 3
(Others)
• Special Cmd
(Block Info)
• Tag Description
(Block Mode)
• Mode.Target
• Mode.Actual
• Mode.Permitted
• Mode.Normal
(Configuration)
• Block Mode
• Concentrator OID
• Scale *
• Process Value Filter Time
(Calibration)
• Block Mode
• Cal Cmd *
• Cal Status
• Calibration Highest Point *
• Calibration Lowest Point *
• Calibration Minimum Span
• External Zero Trim *
(Others)
• Upper Limit
• Lower Limit
• PV Range *
• Linerization Type *
• Flow Constant *
• Lower cutoff
• Low Cut Mode *
• H/L Swap *
• T Zero Cmp *
• Temp Zero *
• Temp Select *
(Block Mode)
• Mode.Target
• Mode.Actual
• Mode.Permitted
• Mode.Normal
(Scale)
• Scale.EU at 100% *
• Scale.EU at 0% *
• Scale.Units Index *
• Scale.Decimal *
(Block Mode)
• Mode.Target
• Mode.Actual
• Mode.Permitted
• Mode.Normal
(PV Range)
• PV Range.EU at 100% *
• PV Range.EU at 0% *
• PV Range.Units Index *
• PV Range.Decimal*
F0803-1.ai
*: When the data of these parameters is rewritten, it is necessary to set the operational mode of the block to O/S (Out of Service).
IM 01C27B01-01EN
Page 50

<8. Setting Parameters>
8-12
Online Menu (continued)
Device Configuration
(continued)
(AI2 SP)
• Configure/Setup
(Block Info)
• Tag Description
(Block Mode)
• Mode.Target
• Mode.Actual
• Mode.Permitted
• Mode.Normal
(Configuration)
• Block Mode
• Concentrator OID
• Scale *
• Process Value Filter Time
(Others)
• Upper Limit
• Lower Limit
• PV Range *
• Linerization Type *
• Flow Constant *
• Lower cutoff
• Cal Cmd *
• Cal Status
• Calibration Highest Point *
• Calibration Lowest Point *
• Calibration Minimum Span
• Static Pres Type *
• SP Select *
(Block Mode)
• Mode.Target
• Mode.Actual
• Mode.Permitted
• Mode.Normal
(Scale)
• Scale.EU at 100% *
• Scale.EU at 0% *
• Scale.Units Index *
• Scale.Decimal *
(PV Range)
• PV Range.EU at
100% *
• PV Range.EU at
0% *
• PV Range.Units
Index *
• PV Range.
Decimal *
(AI3 Temp)
• Configure/Setup
(Block Info)
• Tag Description
(Block Mode)
• Mode.Target
• Mode.Actual
• Mode.Permitted
• Mode.Normal
(Configuration)
• Block Mode
• Concentrator OID
• Scale *
• Process Value Filter Time
(Others)
• Sensor Range
• Tertiary Value Sel *
(Block Mode)
• Mode.Target
• Mode.Actual
• Mode.Permitted
• Mode.Normal
(Scale)
• Scale.EU at 100% *
• Scale.EU at 0% *
• Scale.Units Index *
• Scale.Decimal *
(Sensor Range)
• Sensor Range.EU
at 100%
• Sensor Range.EU
at 0%
• Sensor Range.Units
Index *
• Sensor Range.
Decimal *
F0803-2.ai
*: When the data of these parameters is rewritten, it is necessary to set the operational mode of the block to O/S (Out of Service).
IM 01C27B01-01EN
Page 51

<8. Setting Parameters>
Online Menu (continued)
8-13
(Diagnostic)
• UAPMO
(Process Variable)
• AI1 DP
• AI2 SP
• AI3 Temp
(UAPMO)
• Device Diagnostics
(AI1 DP)
• Process Variable
(Diagnostics/Alerts)
• Diagnostic Status
• Diagnostic Status Detail1,
• Diagnostic Status Detail2
• Diagnostic Switch
• Diagnostic Configuration
(Power Status)
• Energy Left
• Power Supply Status
(Dynamic
Variables)
• Process Value
• Simulation
(Process Value)
• Process Value.Status
• Process Value.Value **
(Simulation)
• Simulate Switch
• Transducer Value
• Simulate Value
(Transducer Value)
• Transducer Value.
Status
• Transducer Value.
Value
(Simulate Value)
• Simulate Value.
Status
• Simulate Value.
Value
(AI2 SP)
• Process Variable
(AI3 Temp)
• Process Variable
(Dynamic
Variables)
• Process Value
• Simulation
(Dynamic
Variables)
• Process Value
• Simulation
(Process Value)
• Process Value.Status
• Process Value.Value **
(Simulation)
• Simulate Switch
• Transducer Value
• Simulate Value
(Process Value)
• Process Value.Status
• Process Value.Value **
(Simulation)
• Simulate Switch
• Transducer Value
• Simulate Value
(Transducer Value)
• Transducer Value.
Status
• Transducer Value.
Value
(Simulate Value)
• Simulate Value.
Status
• Simulate Value.
Value
(Transducer Value)
• Transducer Value.
Status
• Transducer Value.
Value
(Simulate Value)
• Simulate Value.
Status
• Simulate Value.
Value
*: When the data of these parameters is rewritten, it is necessary to set the operational mode of the block to O/S (Out of Service).
F0803-3.ai
IM 01C27B01-01EN
Page 52

<8. Setting Parameters>
8-14
(b) Detachable antenna type (Amplier housing code: 8 or 9)
Menu (Online)
• Device Configuration
• Diagnostic
• Process Variable
(Device Configuration)
• UAPMO
• TRANSDUCER
• AI1 DP
• AI2 SP
• AI3 Temp
(UAPMO)
• Configure/Setup
(TRANSDUCER)
• Configure/Setup
(AI1 DP)
• Configure/Setup
*: When the data of these parameters is rewritten, it is necessary to set the operational mode of the block to O/S (Out of Service).
(Configuration)
• UAP Option
• Hardware Write Protect
• Static Revision
• Reset Energy Left
• Radio Silence
• Energy Harvest Type
(Identification)
• Version Revision
• CTS Version
• ITS Version
• Identification Number
(Block Info)
• Tag Description
(Configuration/Calibration)
• Auto Recovery
• Model
• Sensor Serial Number
• Measurement Rate
• Measurement Mode
• Wireless Status
• Display Selection
• LCD Mode
• Special Order ID
• Unit Sel1
• Display Unit1
• LCD Intermittent Time
• XD Filter
• EJX Key
• Test Key 1
• Test Key 2
• Test Key 3
(Others)
• Special Cmd
(Block Info)
• Tag Description
(Block Mode)
• Mode.Target
• Mode.Actual
• Mode.Permitted
• Mode.Normal
(Configuration)
• Block Mode
• Concentrator OID
• Scale *
• Process Value Filter Time
(Calibration)
• Block Mode
• Cal Cmd *
• Cal Status
• Calibration Highest Point
Set Calibration Highest Point *
•
• Calibration Lowest Point
•
Set Calibration Lowest Point *
• Calibration Minimum Span
• External Zero Trim *
(Others)
• Upper Limit
• Lower Limit
• PV Range *
• Linerization Type *
• Flow Constant *
• Lower Cutoff
• Low Cut Mode *
• H/L Swap *
• T Zero Cmp *
• Temp Zero *
• Temp Select *
(Alerts)
• Other Faults Alert
• Faults Non-compliance
Alert
• Faults Process Influence
Alert
• Simulation Active Alert
• Soft Update Incomplete
Alert
• Power Low Alert
• Power Critical Low Alert
• Fault Prediction Alert
• Environmental
Conditions Alert
• Outside Sensor Limits
Alert
• Out of Service Alert
• Calibration Problem
Alert
• Faults Sensor or
Actuator Alert
• Faults Electronics Alert
(Block Mode)
• Mode.Target
• Mode.Actual
• Mode.Permitted
• Mode.Normal
(Scale)
• Scale.EU at 100% *
• Scale.EU at 0% *
• Scale.Units Index *
• Scale.Decimal *
(Block Mode)
• Mode.Target
• Mode.Actual
• Mode.Permitted
• Mode.Normal
(PV Range)
• PV Range.EU at 100% *
• PV Range.EU at 0% *
• PV Range.Units Index *
• PV Range.Decimal*
F0803-4.ai
IM 01C27B01-01EN
Page 53

<8. Setting Parameters>
8-15
Menu (Online)
(continued)
Device Configuration
(continued)
(AI2 SP)
• Configure/Setup
(AI3 Temp)
• Configure/Setup
(Block Info)
• Tag Description
(Block Mode)
• Mode.Target
• Mode.Actual
• Mode.Permitted
• Mode.Normal
(Configuration)
• Block Mode
• Concentrator OID
• Scale *
• Process Value Filter Time
(Others)
• Upper Limit
• Lower Limit
• PV Range *
• Linerization Type *
• Flow Constant *
• Lower Cutoff
• Cal Cmd *
• Cal Status
• Calibration Highest Point
• Set Calibration Highest Point *
• Calibration Lowest Point
• Set Calibration Lowest Point *
• Calibration Minimum Span
• Static Pres Type *
• SP Select *
(Block Info)
• Tag Description
(Block Mode)
• Mode.Target
• Mode.Actual
• Mode.Permitted
• Mode.Normal
(Configuration)
• Block Mode
• Concentrator OID
• Scale *
• Process Value Filter Time
(Others)
• Sensor Range
• Tertiary Value Sel *
(Block Mode)
• Mode.Target
• Mode.Actual
• Mode.Permitted
• Mode.Normal
(Scale)
• Scale.EU at 100% *
• Scale.EU at 0% *
• Scale.Units Index *
• Scale.Decimal *
(PV Range)
• PV Range.EU at
100% *
• PV Range.EU at
0% *
• PV Range.Units
Index *
• PV Range.
Decimal *
(Block Mode)
• Mode.Target
• Mode.Actual
• Mode.Permitted
• Mode.Normal
(Scale)
• Scale.EU at 100% *
• Scale.EU at 0% *
• Scale.Units Index *
• Scale.Decimal *
(Sensor Range)
• Sensor Range.EU
at 100%
• Sensor Range.EU
at 0%
• Sensor Range.Units
Index *
• Sensor Range.
Decimal *
F0803-5.ai
*: When the data of these parameters is rewritten, it is necessary to set the operational mode of the block to O/S (Out of Service).
IM 01C27B01-01EN
Page 54

<8. Setting Parameters>
Menu (Online)
(continued)
8-16
(Diagnostic)
• UAPMO
(Process Variable)
• AI1 DP
• AI2 SP
• AI3 Temp
(UAPMO)
• Device Diagnostics
(AI1 DP)
• Process Variable
(Diagnostics)
• Diagnostic Status
• Diagnostic Status Detail.1
• Diagnostic Status Detail.2
• Diagnostic Switch
• Diagnostic Configuration
(Power Status)
• Energy Left
• Power Supply Status
• Power Supply Voltage
(Dynamic
Variables)
• Process Value
• Simulation
(Process Value)
• Process Value.Status
• Process Value.Value **
(Simulation)
• Simulate Switch
• Transducer Value
• Simulate Value
(Diagnostic Configuration)
• Diagnostic.Other Faults
• Diagnostic.Faults Non-Compliance
• Diagnostic.Faults Process Influence
• Diagnostic.Simulation Active
• Diagnostic.Soft Update Incomplete
• Diagnostic.Power Low
• Diagnostic.Power Critical Low
• Diagnostic.Fault Prediction
• Diagnostic.Environmental Conditions
• Diagnostic.Outside Sensor Limits
• Diagnostic.Out of Service
• Diagnostic.Calibration Problem
• Diagnostic.Faults Sensor or Actuator
• Diagnostic.Faults Electronics
(Transducer Value)
• Transducer Value.
Status
• Transducer Value.
Value
(Simulate Value)
• Simulate Value.
Status
• Simulate Value.
Value
(AI2 SP)
• Process Variable
(AI3 Temp)
• Process Variable
(Dynamic
Variables)
• Process Value
• Simulation
(Dynamic
Variables)
• Process Value
• Simulation
(Process Value)
• Process Value.Status
• Process Value.Value **
(Simulation)
• Simulate Switch
• Transducer Value
• Simulate Value
(Process Value)
• Process Value.Status
• Process Value.Value **
(Simulation)
• Simulate Switch
• Transducer Value
• Simulate Value
(Transducer Value)
• Transducer Value.
Status
• Transducer Value.
Value
(Simulate Value)
• Simulate Value.
Status
• Simulate Value.
Value
(Transducer Value)
• Transducer Value.
Status
• Transducer Value.
Value
(Simulate Value)
• Simulate Value.
Status
• Simulate Value.
Value
*: When the data of these parameters is rewritten, it is necessary to set the operational mode of the block to O/S (Out of Service).
F0803-6.ai
IM 01C27B01-01EN
Page 55

<8. Setting Parameters>
8-17
8.3.3 Parameters for Wireless Communication
(1) Network Information
Concentrator object block: Conguration
Allows conrming the network information.
(2) Update Time
CO block: Data publication period
Sets the update time value to 0.5 to 3,600 seconds.
When amplier housing code 7 is specied, note
that more than one second is available. The setting
affects the battery life.
When update time is set 0 seconds, the transmitter
is stopped to update process variables by way
of the eld wireless network. And the transmitter
continues to measure process variables with
special interval time internally.
(3) Measurement Mode
TRANSDUCER block: Measurement Mode
The setting affects the battery life; it becomes
shorter in the continuous mode.
When the update period is set to 1 second or less
in intermittent mode, the mode is continuous mode,
regardless of the measurement mode and the
display.
(4) Measurement Rate
(6) LCD display
The following steps describe how to set LCD
display.
● Integral antenna type (Amplier housing
code: 7)
1. On/Off of display
When “LCD Intermittent” in LCD Mode is
parameter is selected, the LCD rst displays a
set of screens to be shown and then turns off
for a minute, and the display keeps the cycle
repeatedly. Not selecting this parameter turns
the LCD off.
2. On/Off of continuous display mode
When “LCD Continue” in LCD Mode is
selected, the LCD displays for 5 minutes
continuously then transits to the setting in the
LCD Intermittent.
When measurement mode is set as continuous
mode, the LCD displays continuously
regardless of display mode.
When the update time is set to 1 second, the
LCD display stays on regardless of the status in
LCD Mode.
3. On/Off of bar graph
Select “LCD Bargraph ON” in LCD Mode when
the bar graph is required.
● Detachable antenna type (Amplier housing
code: 8 or 9)
TRANSDUCER block: Measurement Rate
Reads the measurement rate value from 0.5 to
3600 seconds. When amplier housing code 7
is specied, note that the period more than one
second is displayed.The shorter the measurement
period, the shorter the battery life.
(5) Remaining battery life
UAPMO block: Energy Left
The number of days of remaining battery life is
indicated assuming that a transmitter has been
working under ambient temperature condition as
23 degrees Celsius. It takes several days for the
indicated value to be stabiilzed after the power on
and initialization of the remaining battery life.
UAPMO block: Reset Energy Left
When changing batteries, the remaining battery life
is initialized by Reset Energy Left parameter.
1. On/Off of display
When “Enable” in LCD Mode is selected, the
LCD displays a set of screens to be shown and
turns off for the specied time based on LCD
Intermittent Time, and the display keeps the
cycle repeatedly. Not selecting this parameter
turns the LCD off.
2. On/Off of continuous display mode
When “Enable” is set to LCD Mode and zero is
set to LCD Intermittent Time, the LCD displays
continuously.
3. On/Off of bar graph
Select “LCD Bargraph ON” in LCD Mode when
the bar graph is required.
When the wireless connection process is in the
status of “ready,” “pause,” or “join,” the LCD display
stays on regardless of the status in LCD Mode.
IM 01C27B01-01EN
Page 56

<8. Setting Parameters>
8.3.6 Range Change
NOTE
When the device detects AL01 and AL02, the
LCD display stays on regardless of the status
in LCD mode. See Table 9.3 and 9.4 Error
Message Summary for details.
8.3.4 Tag and Device Information
If these are specied when ordering, the designated
Tag No. and device information are set and
shipped. Tag No. and device information can be
checked as follows.
• Procedure to call up the tag No. and device
information
- Device Tag ( Software Tag )
This is specied when writing characters (up
to 16 characters) of ampliers TAG that differ
from characters specied in Tag No.
Refer to section 7.4 “Connection to the Field
Wireless Network” for conrmation.
- Tag Description
This is a universal parameter to store the
comment that describes the content of the
tag located in the TRANSDUCER and AI
blocks.
The AI1, AI2, and AI3 blocks of the AI blocks
correspond to the differential pressure/
pressure, static pressure, and temperature,
respectively.
The range values are factory-set as specied by
the customer. To change the range, follow the steps
below.
The measurement span is determined by the upper
and lower range values. In this method, the upper
and lower range values can be set independently,
and the span changes according to the range limit
values sent to the transmitter.
• Procedure to call up the PV Range display.
AI1, Al2 block: PV Range
Select the AI1 block for the differential pressure/
pressure and the AI2 block for the static
pressure, then select “EU at 0%” and “EU at
100%” displayed in the PV Range parameters,
and input the lower range and upper range
values for the range, respectively.
8.3.7 Output Mode
The output mode of the output signal can be set as
No Linearization or Sq root.
• Procedure to call up the Linearization Type
display
AI1 block: Linearization Type
Select the AI1 block for the differential pressure
and then select No Linearization or Sq root for
the Linearization Type parameter.
8-18
• When changing the device information, input
the information based on the following limitation
on the number of characters.
- Message function (up to 32 characters)
TRANSDUCER block: Tag Description
AI1-AI3 block: Tag Description
8.3.5 Unit
The unit parameter is set at the factory before
shipment if specied at the time of order. Follow the
procedure below to change the unit parameter.
• Procedure to call up the Unit display (Units
Index)
Al1 - Al3 block: SCALE: Units Index
To change the Unit display, choose desired unit
among the list of displayed unit selecting AI1
block as for the differential pressure/pressure,
AI2 as for the static pressure and AI3 block as
for temperature in the AI blocks.
IM 01C27B01-01EN
Page 57

<8. Setting Parameters>
[ sq root output ]
Low
8-19
8.3.8 Output Signal Low Cut Mode Setup
Low cut mode can be used to stabilize the output
signal near the zero point.
( There is 10% of hysteresis at only point of
transition from low to high)
[Setup Low Cut Value]
• Procedure to call up the Lower cutoff* display
AI1 block: Lower cutoff*
Example: setup LOW_CUT of output to 15%
Lower cutoff*
= (“Eu at 100%” - “Eu at 0%”) × 0.15 + “Eu at 0%”
*: “Low Cutoff” is used instead of “Lower cutoff” for
[Setup Low Cut Mode]
Detachable antenna type (Amplier housing code: 8 or
9).
• Procedure to call up the Low Cut Mode display
AI1 block: Low Cut Mode
Example: Low cut at 20%
For low cut in Linear mode For low cut zero mode
(%)
50
Output
20
Example: Low cut 20%
0 50 (%)
Input
(%)
50
Output
20
Example: Low cut 20%
0 50 (%)
Input
The low cut point has hysterisis so that the output
around the point is behaved as below gure.
<Example>
Output mode: Linear
Low cut mode: Zero
Low cut: 20.00%
cut
point
2%
Hystrersis fixed at 10%
of the cut point
F0805.ai
(20%)
0%
Output
Input
Setting range:
0 to 20%
8.3.9 Impulse Line Connection Orientation Setup
This function reverses the impulse line orientation.
Follow the procedure below to assign the high
pressure impulse line connection to the L side of the
transmitter.
• Procedure to call up the H/L Swap display
TRANSDUCER block: H/L Swap
Select Reverse among two choices ( Normal /
Reverse) in a H/L Swap parameter.
Normal is chosen at the time of shipment.
[ Linear output ]
For low cut in Linear mode
(%)
50
Output
20
0 50 (%)
Example:
Low cut 20%
Input
Figure 8.3 Low Cut Mode
8.3.10 Integral Indicator Display Mode
It is easy to check on the LCD whether Non
Linearization or Sq root is set in the Linearization
Type parameter selected in the output mode for the
output signal.
When Linear is set in the Linearization Type
parameter, “√” is displayed on the integral indicator.
F0804.ai
IM 01C27B01-01EN
Page 58

<8. Setting Parameters>
8-20
8.3.11 Integral Indicator Scale Setup
The following three displays are available for the
integral indictor: differential pressure/pressure,
static pressure, and temperature. The following
three variables can be displayed on the integral
indicator: % of differential pressure range, % of
static pressure range, and % of temperature range.
Available displays
% of range
(PRES %)
% of static pressure
range (SP %)
*1: Available for differential pressure transmitter.
Indicates input pressure in –10 to
110% range depending on the set
range (LRV and URV).
PRES % 45.6 %
Indicates input static pressure in
*1
–10 to 110% range depending on
the set range (SP LRV and SP
URV).
SP % 52.6 %
Follow the procedure described in (1) to (2) below
to set the integral indicator.
(1) Display Selection
Display set to Display Selection is displayed on the
integral indicator.
• Procedure to call up the Display Selection
display
TRANSDUCER block: Display Selection
The Display Selection parameter enables
the differential pressure/pressure (AI1 block),
static pressure (AI2 block), and temperature
(AI3 block) to be displayed on the LCD. Select
whether or not to enable each block to be
displayed
(2) Cyclic Display
Description
and related parameters
8.3.12 Unit for Displayed Temperature
When the instrument is shipped, the temperature
units are set to C (Centigrade). Follow the
procedure below to change this setting.
• Procedure to call up the Sensor Range.Units
Index display
AI3 block : Sensor Range.Units Index
Conrm that °C(deg C) is selected in the
Sensor Range.Units Index parameter for the
temperature (AI3 block).
Note: When the unit is changed by Sensor Range.Units Index
parameter in temperature ( Al3 block) , units of capsule
temperature is also changed.
8.3.13 Unit for Displayed Static Pressure
Follow the procedure to change the static pressure
unit.
Changing this parameter also changes the unit for
the static pressure display.
• Procedure to call up the Sensor Range.Units
Index display
AI2 block : Sensor Range.Units Index
Conrm that KPa is selected in the Sensor
Range.Units Index parameter for the static
pressure (AI2 block).
Monitoring the high or low static pressure of the
capsule depends on the setting of parameter
‘SP Select.’
• Procedure to call up the SP Select display
AI2 block: SP Select
Select High or Low in the SP Select parameter
for the static pressure (AI2 block).
Type of static pressure is set Absolute
pressure(Abs) at shipment.
When changing monitoring type of static pressure,
Follow below procedure.
Information in the AI1 to AI3 blocks can be
displayed cyclically according to the display On/Off
setting for the differential pressure (AI1 block), static
pressure (AI2 block), and temperature (AI3 block)
selected in the Display Selection parameter.
• Procedure to call up the Static Press Type
display
AI2 block: Static Press Type
Select gauge pressure (Gauge) or absolute
pressure (Abs) in the Static Press Type
parameter for the static pressure (AI2 block).
IM 01C27B01-01EN
Page 59

<8. Setting Parameters>
8-21
8.3.14 Zero Point Adjustment and Span Adjustment
Each EJX-B Series Differential Pressure/Pressure
Transmitter is characterized by factory. But there
are some errors caused by environment and
installed posture.
There are Zero and Span Adjustments to ne-tune
those errors.
Zero Adjustment is adjustment for one point to
adjust the bottom value of the measurement range
as 0 % of output.
.
The Span Adjustment denes input and output
characteristic between two points that’s one side
assumed as standard.
This is used when there is doubt of span drift or
when it is impossible to make zero at absolute
pressure with adjustment for user’s pressure
standard.
(1) Zero Point Adjustment
a. To set 0% at current input, perform
following procedure.
This method is used only when the pressure at
bottom of measurement range is zero.
b. To match current input and output value,
follow procedure
Like tank level measurement that is impossible to
set actual level to zero, output value is adjustment
to actual level by other measurement using
glassgage.
Example:
Differential Pressure and Pressure
Transmitter’s span is 0 to 25.00kPa, current
level is 13.50kPa, current output is 13.83kPa.
• Procedure to call up the lower limit adjustment
parameter (Calibration Lowest Point).
AI1 block : Calibration Lowest Point
.
Set the actual level value of 13.50 kPa to the
Calibration Lowest Point parameter for the
differential pressure (AI1 block). Apply an
actual input and conrm the value specied in
Calibration Lowest Point as the output value.
• Procedure to call up the calibration adjustment
parameter (Cal Cmd).
AI1 block : Cal Cmd : CAL_LOW
The present output is changed from 13.83 kPa
to 13.50 kPa in CAL_LOW of the differential
pressure (AI1 block) Cal Cmd parameter.
• Procedure to call up the lower limit adjustment
parameter (Calibration Lowest Point).
AI1 block: Calibration Lowest Point
Set 0 to Calibration Lowest Point parameter for
differential pressure (Al1 block).
• Procedure to call up the calibration adjustment
parameter (Cal Cmd).
AI1 block: Cal Cmd : CAL_LOW
Lower limit is changed by using Cal Cmd
parameter for differential pressure/pressure
(Al1 block).
• Procedure to call up the calibration status
parameter (Cal Status).
AI1 block: Cal Status
Conrm the calibration status of CAL_
SUCCESS(1) using the Cal Status parameter.
• Procedure to call up the calibration status
parameter (Cal Status).
AI1 block : Cal Status
Conrm the calibration status of CAL_
SUCCESS(1) using the Cal Status parameter.
DPharp span: 0~25.00 kPa
Actual level: 13.50 kPa
Transmitter output: 13.83 kPa
25.00 kPa
Actual level
13.50 kPa
0.00 kPa
DPharp
F0806.ai
Figure 8.4 Tank level measurement
IM 01C27B01-01EN
Page 60

<8. Setting Parameters>
8-22
c. Using External Zero-adjustment Screw
External Zero-adjustment parameter (External
Zero Trim) can set permission or prohibition to
adjustment by External Zero-adjustment Screw.
Set “Trim on” to use the External Zero-adjustment
Screw. (“Trim on” at shipment)
Use a slotted screwdriver to turn the zeroadjustment screw. Equalize the transmitter, then
turn the screw clockwise to increase the output or
counterclockwise to decrease the output. The zero
point adjustment can be made with a resolution
of 0.01% of the setting range. The degree of zero
adjustments varies with the screw turning speed;
turn the screw slowly to make a ne adjustment,
quickly to make a rough adjustment.
• Procedure to call up the calibration adjustment
parameter (Cal Cmd).
AI1 block: Cal Cmd: CAL_LOW
Conrm the lower limit of the measurement
range in CAL_LOW of the differential pressure
(AI1 block) Cal Cmd parameter.
• Procedure to call up the calibration status
parameter (Cal Status).
AI1 block: Cal Status
Conrm the calibration status of CAL_
SUCCESS(1) using the Cal Status parameter.
• Procedure to call up the upper limit adjustment
parameter (Calibration Highest Point).
AI1 block: Calibration Highest Point
Set the upper limit adjustment value for the
differential pressure (AI1 block) Calibration
Highest Point parameter. Apply a reference
pressure corresponding to the upper limit of the
measurement range to the differential pressure/
pressure transmitter and conrm the reference
pressure when it has stabilized.
Zero-adjustment Screw
F0807.ai
Figure 8.5 Zero-adjustment Screw
(2) Span Adjustment
Span Adjustment is function to change the input and
output characteristic that assumed the bottom value
(zero point) of measurement range a standard.
Therefore, perform span adjustment (adjustment
of the upper limit value) after zero adjustment
(adjustment of bottom limit value).
After adding the pressure at point of adjustment and
setting pressure value as parameter, the transmitter
calculates quantity of adjustment and performs
adjustment automatically.
• Procedure to call up the lower limit value
parameter (Calibration Lowest Point).
AI1 block: Calibration Lowest Point
Set the lower limit adjustment value on the
differential pressure/pressure (AI1 block)
Calibration Lowest Point parameter screen.
Apply a reference pressure corresponding to
the lower limit of the measurement range to
the differential pressure/pressure transmitter
and conrm the reference pressure when it has
stabilized.
• Procedure to call up the calibration adjustment
parameter (Cal Cmd).
AI1 block: Cal Cmd: CAL_HIGH
Conrm the upper limit of the measurement
range in CAL_HIGH of the differential pressure/
pressure (AI1 block) Cal Cmd parameter.
• Procedure to call up the calibration status
parameter (Cal Status).
AI1 block: Cal Status
Conrm the calibration status of CAL_
SUCCESS(1) using the Cal Status parameter.
(3) Adjustments for Static Pressure
For the EJX differential transmitters, zero point and
span adjustments of static pressure is performed in
the same way as with the primary process variable
(PV).
Adjustment should be performed using the static
pressure (AI2 block) Cal Cmd parameter. After
calibration, conrm the status by using the static
pressure (AI2 block) Cal Status.
• Procedure to call up the calibration adjustment
parameter (Cal Cmd).
AI2 block: Cal Cmd
Perform differential pressure zero/span adjustment
before static pressure zero/span adjustment.
IM 01C27B01-01EN
Page 61

<8. Setting Parameters>
8-23
(4) Reset Adjustment
Reset Adjustment clear the amount of adjustment.
Reset Ajustment can be performed using CAL_
CLEAR of the differential pressure (AI1 block) Cal
Cmd parameter for the input pressure and using
CAL_CLEAR of the static pressure (AI2 block) Cal
Cmd parameter for the static pressure. After Reset
Adjustment, conrm the status by using Cal Status
of the cleared block. The amount of adjustment
made by the external zero-adjustment screw can be
reset to the initial setting as well.
• Procedure to call up the calibration adjustment
parameter (Cal Cmd).
AI1 block: Cal Cmd: CAL_CLEAR
AI2 block: Cal Cmd: CAL_CLEAR
8.3.15 Software Write Protect
Hardware write protection and software write
protection functions are available for this
transmitter.
• Procedure to call up the protection setting
parameter (UAP Option)
UAPMO block: UAP Option
The following settings can be congured in the
UAP Option parameter.
- Setting to enable or disable software write
protection.
- Setting to enable or disable the hardware
write protection switch.
- Setting to enable or disable changing
the setting to the Diagnostic Switch and
Diagnostic Conguration parameters.
• Procedure to call up the protection setting
display parameter (Hardware Write Protect)
UAPMO block: Hardware Write Protect
The Hardware Write Protect parameter enables
the switch status of hardware write protection to
be displayed.
For the relationship between hardware write
protection and software write protection, refer to
section 10. “Parameter Summary.”
8.3.16 Switching to Deep Sleep Mode
When the instrument will not be used for a long
time, switch the instrument to deep sleep mode to
conserve battery power. To switch to deep sleep
mode, follow the procedure below.
• Procedure to call up the switch-to-deep-sleep
parameter
TRANSDUCER block: Special Cmd
Set Deep Sleep mode(Standby) to the Special
Cmd parameter for the TRANSDUCER
block. To start from deep sleep mode, either
remove and insert the battery pack, or using
the provisioning device tool or the device
conguration tool via infrared communication.
CAUTION
After setting the deep sleep mode by infrared
device conguration tool, keep the infrared port
of device away from any other infrared signals.
NOTE
• Transmitter becomes the stop state after
setting deep sleep mode and cannot reply
any request from the device conguration
tool via wireless communication.
• For this reason, there is the case that an
error is display on the device conguration
tool via wireless communication.
• To wake up from deep sleep mode, please
pull battery pack and wait more than 30
seconds before attaching battery pack.
8.3.17 Switching to Silence Mode
This is a function to pause the instrument when
it cannot join the eld wireless network after a
specied time has elapsed. This function is effective
in conserving battery power when, for example, the
installation of the eld wireless integrated gateway
is delayed compared to that of eld wireless
devices. The default value is 28800 seconds (8
hours). Thereafter, a cycle of a one-hour pause and
six-minute search is repeated until the instrument
can join the eld wireless network.
• Procedure to call up the switch-to-silence
parameter (Radio Silence)
UAPMO block: Radio Silence
Set 0 to 231 seconds for the Radio Silence
parameter of the UAPMO block. If 0 is set, the
Radio Silence parameter is invalid. To start from
deep sleep mode, either remove and insert the
battery pack, or use the provisioning device
tool or device conguration tool via infrared
communication.
IM 01C27B01-01EN
Page 62

<8. Setting Parameters>
8-24
8.4 Self-Diagnostics
UAPMO block: Diagnostic Status
Any of the four categories (Check function,
8.4.1 Identify Problems by Using the
Device Conguration Tool
First, check Diagnostic Status of the self-diagnostic
result.
Table 8.3 Diagnostic Status
Bits
Bit31 (MSB) F: Failure status --Bit30 C: Function check status --Bit29 O: Out of specication status --Bit28 M: Maintenance required status --Bit27 Faults in electronics F
Bit26 Faults in sensor or actuator element F
Bit25 Installation, calibration problem C
Bit24 Out of service C
Bit23 Outside sensor limits O
Bit22 Environmental conditions out of device specication O
Bit21 Fault prediction: Maintenance required M
Bit20 Power is critical low: maintenance need short-term M
Bit19 Power is low: maintenance need mid-term M
Bit18 Software update incomplete C
Bit17 Simulation is active C
Bit16** Faults due to process inuence F
Bit15** Faults due to non-compliance with specied operating conditions F
Bit14** Other faults F
Bit13-Bit08 reserved by WCI --Bit07-Bit01 vendor specic area --Bit00 Detail information available
1: available
0: no available
Contents
Maintenance required, Failure, and Off
specication) according to NAMUR NE107* is
supplied to Diagnostic Status of each diagnostic
result.
Example
NAMUR NE107
Categorization
---
Checking the Diagnostic Status category allows
taking the proper action. The Diagnostic Status
contents are common for all ISA devices, and the
setting for the Diagnostic Status category can be
changed. For further details, refer to Diagnostic
Status Detail.
In Diagnostic Status Contents that can be
diagnosed by the EJX, the alert category set in Out
of Service can be changed to Check function. To do
so, follow one of the procedures below.
a) UAPMO block: UAP Option, select enable.
b) UAPMO block: Diagnostic Conguration,
change Out of Service from Failure to Check
function.
c) UAPMO block: UAP Option, select disable.
The contents of diagnostic status are dened either
valid or invalid at Diagnostic Switch parameter.
Follow the example below to change “Out of
Service” to invalid.
a) UAPMO block: UAP Option, select enable.
b) UAPMO block: Diagnostic Switch, turn ON
Turn off “Out of Service”. Out of Service.
c) UAPMO block: UAP Option, select disable.
Note: Be careful when changing the alert category and turning
detection on and off as described above. Be sure to set
UAP OPTION to disable again to prevent setting errors.
*: NAMUR NE107 “Self-Monitoring and Diagnosis of
Field Devices”
In Diagnostic Conguration setting, select one from the
followings; F: Failure status, C: Function check status,
O: Out of specication status, or M: Maintenance
required status.
**: Applicable for Detachable antenna type (Amplier
housing code: 8 or 9).
IM 01C27B01-01EN
Page 63

<8. Setting Parameters>
8.4.2 Alert Report
EJX generates alert information related to
Diagnostic Status and automatically sends to a eld
wireless gateway. To use this function, the following
alert setting is necessary. When “Out of Service” for
Diagnostic Status alert is required, choose “FALSE”
for [Out of Service.Alert Disable] in the UAPMO
block. Refer to the eld wireless gateway User’s
Manual for the setting procedure to obtain the alert
information from the gateway.
The alert report consists of the list of parameter
names as shown Table 8.4 below.
Table 8.4 Contents of Alert Report
Parameter name Description
DetectObjectTLPort Alert detection port UAP (0xF0B2)
xed
DetectObject Alert detection block UAPMO (1)
xed
DetectTime Time stamp
AlertDirection 1: generated, 0: clear
AlertPriority Alert priorities set by users
AlertType Alert types, see 8.4 Self-
Diagnostics
AlertValue NAMUR107 category
0:Failure, 1:checkFunction,
2:OffSpec, 3:MaintenaceRequired
8-25
CAUTION
For a wireless gateway which does not support
the alert report function, the alert setting in
UAPMO block for the transmitter must be set
to “Disable.” Note that YFGW710 eld wireless
integrated gateway does not have the alert
report function.
IM 01C27B01-01EN
Page 64

<8. Setting Parameters>
Table 8.5 Diagnostic Results Summary
8-26
Diagnostic Status
Contents
Alert
Type
Faults in electronics 78 F
Faults in sensor or actuator
element
Installation, calibration
problem
77 F
76 C
Out of service 75 O
Outside sensor limits 74 C
Environmental conditions
out of device specication.
73 O
NAMUR
NE107
Category
Diagnostic Status Detail Description
AMP_T_SENSOR_FAIL* Amplier temperature sensor failure
AMP_EEPROM_FAIL Amplier EEPROM failure
AMP_EEP_IRREGULAR AMP EEPROM version not correct
G_A_COMM_FAIL G/A failure
FC_DELTA_T_FAIL C-side delta T circuit failure
FR_DELTA_T_FAIL R-side delta T circuit failure
WL_AD_FAIL
Battery voltage not detected (AMP
failure)
FC_SENSOR_FAIL C sensor frequency failure
FR_SENSOR_FAIL R sensor frequency failure
CAP_T_SENSOR_FAIL Capsule temperature sensor failure
CAP_EEPROM_FAIL Capsule EEPROM failure
CAP_EEP_IRREGULAR CAP EEPROM version not correct
FC_UNOSC_FAIL C sensor oscillation stop failure
FR_UNOSC_FAIL R sensor oscillation stop failure
DP_TRIM_SPAN_OUTSIDE
DP_TRIM_ZERO_OUTSIDE
SP_TRIM_SPAN_OUTSIDE
SP_TRIM_ZERO_OUTSIDE
"Pressure span adjustment variable
outside of range"
"Pressure zero adjustment variable
outside of range"
"Static pressure span adjustment
variable outside of range"
"Static pressure zero adjustment
variable outside of range"
LCD_OUTSIDE_LIMIT LCD display outside of limits
AI1_OUT_OF_SERVICE AI1 O/S mode
AI2_OUT_OF_SERVICE AI2 O/S mode
AI3_OUT_OF_SERVICE AI3 O/S mode
DP_OUTSIDE_LIMIT Pressure outside of range
SP_OUTSIDE_LIMIT Static pressure outside of range
CAPT_OUTSIDE_LIMIT Capsule temperature outside of range
AMPT_OUTSIDE_LIMIT Amplier temperature outside of range
DP_OUTSIDE_RANGE Pressure setting outside of range
SP_OUTSIDE_RANGE
Static pressure setting outside of
range
Power is critical low:
maintenance need shortterm.
Power is low:
maintenance need mid-term
71 M
70 M WL_LOWBAT_ALM Low battery
WL_DEEPSLP_ALM * Deep sleep due to low battery
CRITICAL_LOWBAT ** Deep sleep due to low battery
AI1_SIMULATION_ACTIVE AI1 Simulation mode
Simulation is active 68 C
AI2_SIMULATION_ACTIVE AI2 Simulation mode
AI3_SIMULATION_ACTIVE AI3 Simulation mode
Not applicable for the diagnostic regarding AI2 object and static pressure measurement.
*: Applicable for Integral antenna type (Amplier housing code: 7).
**: Applicable for Detachable antenna type (Amplier housing code: 8 or 9).
IM 01C27B01-01EN
Page 65

<8. Setting Parameters>
8.4.3 Checking with Integral Indicator
NOTE
If an error is detected by running self-diagnostics,
an error number is displayed on the integral
indicator. If there is more than one error, the error
number changes at three-second intervals. See
Table 9.3 regarding the error codes.
F0808.ai
Figure 8.6 Integral Indicator
8-27
IM 01C27B01-01EN
Page 66

<9. Maintenance>
9. Maintenance
9-1
9.1 Overview
WARNING
Since the accumulated process uid may be
toxic or otherwise harmful, take appropriate care
to avoid contact with the body or inhalation of
vapors when draining condensate or venting gas
from the transmitter pressure-detector section
and even after dismounting the instrument from
the process line for maintenance.
Maintenance of the transmitter is easy due to its
modular construction. This chapter describes the
procedures for calibration, adjustment, and the
disassembly and reassembly procedures required
for component replacement.
Transmitters are precision instruments. Please
carefully and thoroughly read the following sections
for information on how to properly handle them
while performing maintenance.
IMPORTANT
• As a rule, maintenance of this transmitter
should be done in a maintenance room that
has all the necessary tools.
• The CPU assembly, RF assembly and
Integral indicator contain sensitive parts that
can be damaged by static electricity.
Take precautions such as using a grounded
wrist strap when handling electronic parts or
touching the board circuit patterns. Also be
sure to place the removed CPU assembly,
RF assembly and Integral indicator into a
bag with an antistatic coating.
9.2 Calibration Instruments Selection
Table 9.1 lists the instruments that can be used
to calibrate a transmitter. When selecting an
instrument, consider the required accuracy level.
Exercise care when handling these instruments to
ensure they maintain the specied accuracy.
9.3 Calibration
Use the procedure below to check instrument
operation and accuracy during periodic
maintenance or troubleshooting.
1) Insert the battery pack and then perform
provisioning to have the transmitter join the
Field Wireless Network or preparing the infrared
communication for calibration.
2) Set measurement mode to continuous using
the eld device conguration tool and the
update period to 1 second using the eld
wireless conguration tool.
3) Connect the devices as shown in Figure 9.1
and allow the transmitter to warm up for at least
5 minutes.
IMPORTANT
If the measurement range 0% point is 0 kPa
or shifted in the positive direction (suppressed
zero), the reference pressure should be applied
as shown in the gure.
If the measurement range 0% point is shifted
in the negative direction (elevated zero), the
reference pressure should be applied using a
vacuum pump.
4) Apply reference pressures of 0%, 50%,
and 100% of the measurement range to the
transmitter. Calculate the errors (differences
between the device conguration tool readings
and reference pressures) as the pressure is
increased from 0% to 100% and is decreased
from 100% to 0%, and conrm that the errors
are within the required accuracy.
(Note) When the output mode is set to “Sg root,” apply reference
pressures of 0, 6.25, 25, 56.25, and 100% instead.
5) When the test is nished, reset measurement
mode and update time to the initial value using
the eld device conguration tool and the eld
wireless conguration tool.
IM 01C27B01-01EN
Page 67

<9. Maintenance>
Table 9.1 Instruments Required for Calibration
Name Yokogawa-recommended Instrument Remarks
Provisioning
device tool
• FieldMate (R2.02.01 or later)
• Provisioning Device Tool
• Infrared Adapter certied by Yokogawa
Supplier: ACTiSYS
Product name: IrDA InfraRed USB Adaptor
Product number: IR224UN
Field wireless
conguration
tool
• Field Wireless Integrated Gateway attached Software
Field Wireless Congurator
Field Wireless Management Tool
• Field Wireless System related Product
Plant Resource Manager (PRM) (R3.05 or later)
• Device Conguration Tool via ISA100.11a Wireless Communication
FieldMate (R2.02.01 or later)
DeviceFile (R3.01.01 or later)
• Device Conguration Tool via Infrared Communication
FieldMate (R2.03.00 or later)
DeviceFile (R3.02.01 or later)
Digital
manometer
Model MT220 precision digital manometer
1) For 10 kPa class
Accuracy: ±(0.015% of rdg + 0.015% of F.S.). . . . for 0 to 10 kPa
Select a manometer having
a pressure range close to
that of the transmitter.
±(0.2% of rdg + 0.1% of F.S.). . . . . . . . for -10 to 0 kPa
2) For 130 kPa class
Accuracy: ±0.02% of rdg . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . for 25 to 130 kPa
±5digits. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . for 0 to 25 kPa
±(0.2% of rdg + 0.1% of F.S.). . . . . . . . for -80 to 0 kPa
3) For 700 kPa class
Accuracy: ±(0.02% of rdg + 3digits) . . . . . . . . . . . for 100 to 700 kPa
±5 digits . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . for 0 to 100 kPa
±(0.2% of rdg + 0.1% of F.S.). . . . . . . . for -80 to 0 kPa
4) For 3000 kPa class
Accuracy: ±(0.02% of rdg + 10 digits). . . . . . . . . . for 0 to 3000 kPa
±(0.2% of rdg + 0.1% of F.S.). . . . . . . . for -80 to 0 kPa
5) For 130 kPa abs class
Accuracy: ±(0.03% of rdg + 6 digits). . . . . . . . . . . for 0 to 130 kPa abs
Pressure
generator
Model MC100 pneumatic pressure standard for 200 kPa { 2 kgf/cm
kPa { 2500 mmH
2O }
2
}, 25
Requires air pressure
supply.
Accuracy: ±0.05% of F.S.
Dead weight gauge tester 25 kPa { 2500 mmH
Accuracy: ±0.03% of setting
2O }
Select the one having a
pressure range close to that
of the transmitter.
Pressure
source
Model 6919 pressure regulator ( pressure pump )
Pressure range: 0 to 133 kPa { 1000 mmHg }
Prepare the vacuum pump
for negative pressure
ranges.
9-2
Note: The above table contains the instruments capable of performing calibration to the 0.2% level. Since special maintenance and
management procedures involving traceability of each instrument to higher-level standards are required for calibration to the 0.1%
or higher level, there may be difculties in calibration to this level in the eld. For calibration to the 0.1% level, contact Yokogawa
representatives from which the instrument was purchased or the nearest Yokogawa ofce.
Using pressure generator
Supply pressure
Low pressure side
open to atmosphere
P
L H
Pressure generator
Reference pressure
High pressure side
Using pressure source with manometer
Pressure source
Precision digital manometer
Low pressure side
open to atmosphere
L H
P
Reference pressure
High pressure side
F0901.ai
Figure 9.1 Instrument Connections
IM 01C27B01-01EN
Page 68

<9. Maintenance>
9-3
9.4 Disassembly and Reassembly
CAUTION
Precautions for the intrinsic safety explosion
prevention type instrument
Intrinsic safe type transmitters must be, as
a rule, removed to a non-hazardous area
for maintenance and be disassembled and
reassembled to the original state. Check and
conrm the insulation when it is reassembled to
the original state.
Check and conrm the insulation when it is
reassembled to the original state.
Refer to section 2.7 “Insulation Resistance and
Dielectric Strength Test” for details of Resistance
Test.
IMPORTANT
• Perform the provisioning when replacing the
RF assembly. Refer to 7.4 Connecting to the
Field Wireless Network for details.
• Replace the batteries and perform the
parameter settings when replacing the CPU
assembly. Refer to 9.4.7 Replacing the
Batteries.
This section describes procedures for disassembly
and reassembly for maintenance and component
replacement.
Table 9.2 shows the tools required.
Table 9.2 Tools for Disassembly and Reassembly
Tool Quantity Remarks
Phillips
screwdriver
Slotted
screwdriver
Allen wrenches 3 JIS B4648
Wrench 1 Width across ats, 17 mm
Torque wrench 1
Adjustable
wrench
Socket wrench 1 Width across ats, 16 mm
Socket driver 1 Width across ats, 5.5 mm
Tweezers 1
1 JIS B4633, No. 2
1
One each, nominal 3,
4 and 2.5 mm Allen
wrenches
1
9.4.1 Replacing the Integral Indicator
This subsection describes the procedure for
replacing an integral indicator. (See gure 9.2)
■ Removing the Integral Indicator
1) Remove the cover.
2) While supporting the integral indicator with one
hand, loosen its two mounting screws.
3) Dismount the integral indicator from the RF
assembly.
When doing this, carefully pull the integral
indicator straight forward so as not to damage
the connector pins between it and the RF
assembly.
CAUTION
Always remove Battery pack and shut off
pressures before disassembly and assembly.
Use proper tools for all operations.
IM 01C27B01-01EN
Page 69

<9. Maintenance>
9-4
■ Attaching the Integral Indicator
1) Align both the integral indicator and RF
assembly connectors and engage them.
2) Insert and tighten the two mounting screws.
3) Replace the cover.
Power
cable
Press
Forward
Stud
Integral
indicator
CPU assembly
RF assembly
Mounting screw
Amplifier cover
Figure 9.2 Removing and Attaching Integral
indicator, RF assembly and CPU
Assembly
Boss
Zero
adjustment
screw
Zero-adjustment
screw pin
F0902.ai
9.4.2 Replacing the RF Assembly
This subsection describes how to replace the RF
assembly (see Figure 9.2).
■ Removing the RF assembly
1) Remove the cover.
2) Remove the integral indicator (refer to
subsection 9.4.1).
3) Remove the two stud bolts by using a socket
driver (width across ats: 5.5 mm).
4) Disconnect the RF assembly from the CPU
assembly. When doing this, carefully pull the RF
assembly straight forward so as not to damage
the connector pins between it and the CPU
assembly.
5) Disconnect the antenna cable that connects the
RF assembly and the antenna.
NOTE
Be careful not to apply excessive force to the
RF assembly and the connector of the antenna
cable when removing it.
■ Mounting the RF assembly
1) Connect the antenna cable between the RF
assembly and the antenna.
2) Align both the RF assembly and CPU assembly
connectors and engage them.
3) Tighten the two stud bolts.
4) Mount the integral indicator (refer to subsection
9.4.1).
5) Replace the cover.
9.4.3 Replacing the CPU Assembly
This subsection describes how to replace the CPU
assembly (see Figure 9.2).
■ Removing the CPU assembly
1) Remove the cover.
Remove the integral indicator and the RF
assembly (refer to subsections 9.4.1 and 9.4.2).
2) Turn the zero-adjustment screw to the position
as shown in Figure 9.2.
3) Disconnect the power cable (cable with brown
connector at the end).
When doing this, lightly press the side of the
CPU assembly connector and pull the cable
connector to disengage (see the upper left of
Figure 9.2).
4) Use a socket driver (width across ats, 5.5 mm)
to loosen the two bosses.
5) Carefully pull the CPU assembly straight
forward to remove it.
6) Disconnect the at cable (cable with white
connector at the end) that connects the CPU
assembly and the capsule.
NOTE
Be careful not to apply excessive force to the
CPU assembly when removing it.
■ Mounting the CPU assembly
1) Connect the at cable (with white connector)
between the CPU assembly and the capsule.
2) Connect the power cable (with brown
connector) to the CPU assembly.
NOTE
Make certain that the cables do not get pinched
between the case and the edge of the CPU
assembly.
IM 01C27B01-01EN
Page 70

<9. Maintenance>
9-5
3) Align and engage the zero-adjustment screw
pin with the groove on the bracket on the CPU
assembly. Then insert the CPU assembly
straight onto the post in the amplier case.
4) Tighten the two bosses. Mount the RF
assembly, and the integral indicator (refer to
subsections 9.4.1 and 9.4.2).
IMPORTANT
Conrm that the zero-adjustment screw pin is
placed properly in the groove on the bracket prior
to tightening the two bosses. If it is not, the zeroadjustment mechanism will be damaged.
5) Replace the cover.
9.4.4 Cleaning and Replacing the Capsule
Assembly
CAUTION
Precautions for the intrinsic safety explosion
prevention type instrument
Modication is not permitted by the user for
intrinsic safety explosion prevention type
transmitter. Consult our company when you want
to exchange capsule assembly.
Execute it only at time when the following points
were conrmed for exchange capsule assembly
in the same range of measurement.
• Exchanged capsule assembly uses the one
of the same specication.
• Tighten Setscrew to x the transmitter
section and the pressure detector section
surely after ending maintenance.
This subsection describes the procedures for
cleaning and replacing the capsule assembly. (See
gure 9.3.)
■ Removing the Capsule Assembly
IMPORTANT
Exercise care as follows when cleaning the
capsule assembly.
• Handle the capsule assembly with care, and
be especially careful not to damage or distort
the diaphragms that contact the process
uid.
• Do not use a chlorinated or acidic solution for
cleaning.
• Rinse with clean water after cleaning, please
dry until completely dry.
1) Remove the CPU assembly as shown in
subsection 9.4.3.
2) Remove the ve setscrews, the stopper bolt,
and the stopper that connect the transmitter
section and pressure-detector section.
3) Remove the hexagon-head screw and the
stopper.
4) Separate the transmitter section and pressuredetector section.
5) Remove the nuts from the four ange bolts.
6) While supporting the capsule assembly with
one hand, remove the cover ange.
7) Remove the capsule assembly.
8) Clean the capsule assembly or replace with a
new one.
■ Reassembling the Capsule Assembly
1) Insert the capsule assembly between the ange
bolts, paying close attention to the relative
positions of the H (high pressure side) and
L (low pressure side) marks on the capsule
assembly.
Replace the two capsule gaskets with new
gaskets.
2) Install the cover ange on the high pressure
side, and use a torque wrench to tighten the
four nuts uniformly to a torque shown below.
Model
Torque(N·m)
{kgf·m}
EJX110B, EJX310B, EJX430B
Wetted parts material code
S (except for
Measurement
span code F)
17
{1.7}
H,M,T,A,D,B or
S (Measurement
span code F)
40
{4.1}
IM 01C27B01-01EN
Page 71

<9. Maintenance>
Bolt
3) After the pressure-detector section has been
reassembled, a leak test must be performed to
verify that there are no pressure leaks.
Process connector
4) Reattach the transmitter section to the
pressure-detector section.
Process connector gasket
5) Reattach the stopper and stopper bolt. Tighten
the ve set screws. (Tighten the screws to a
torque of 1.5 N·m)
6) Install the CPU assembly according to
subsection 9.4.3.
7) After completing reassembly, adjust the zero
point and recheck the parameters.
Transmitter section
Stopper bolt
Stopper
Figure 9.4 Removing and Mounting the Process
Connector
9-6
F0904.ai
Setscrew
Nut
Capsule
gasket
Flange bolt
Pressure-detector
Cover flange
Figure 9.3 Removing and Mounting the Pressure-
detector Section
section
F0903.ai
9.4.5 Replacing the Process Connector
Gaskets
This subsection describes process connector
gasket replacement. (See gure 9.4.)
(a) Loosen the two bolts, and remove the process
connectors.
(b) Replace the process connector gaskets.
(c) Remount the process connectors. Tighten the
bolts securely and uniformly to a torque shown
below, and verify that there are no pressure
leaks.
9.4.6 Replacing the Battery Pack
Regarding the transmitter with intrinsically safe
approval, the battery pack can be replaced without
removing the device in hazardous area.
■ Preparation
Initialize the remaining battery life by using the
parameter of Reset Energy Left in UAPMO block.
When the battery power is burned and emptied,
initialize the remaining battery after prompt
replacement of the battery pack.
■ Removing
1) Remove the terminal box cover.
2) Loosen the two battery pack mounting screws
(see Figure 9.5).
3) Pull out the Battery pack.
The battery pack mounting
screws cannot be separated
from the battery pack so as
to prevent drop-off.
Model
Torque(N·m)
{kgf·m}
EJX110B, EJX310B, EJX430B
39 to 49 {4 to 5}
F0905.ai
Figure 9.5 Removing the Battery Pack
IM 01C27B01-01EN
Page 72

<9. Maintenance>
The battery pack mounting screws
9-7
■ Remounting
1) Insert the new battery pack lightly.
2) Push the center of the battery pack and insert it
securely.
3) Tighten the two battery pack mounting screws
to a torque of approximately 0.7 N·m.
4) Replace the terminal box cover.
9.4.7 Replacing the Batteries
The batteries in the battery pack can be replaced.
Batteries are not installed when shipped from the
factory. Assemble the battery pack as follows.
WARNING
Be sure to replace the batteries or disassemble
and assemble the battery pack in a safe location.
Doing so in an explosive area could cause an
explosion.
CAUTION
When replacing the batteries, be sure to replace
the two batteries at the same time and do not
use an old and a new battery together.
■ Disassembling
9.4.8 Handling Batteries
This battery pack uses two primary lithium/
thionyl chloride batteries. Each battery contains
approximately 5 grams of lithium, for a total of 10
grams in each pack. Under normal conditions,
the battery materials are self-contained and are
not reactive as long as the batteries and the pack
integrity are maintained. Care should be taken to
prevent thermal, electrical or mechanical damage.
Protect the electrode of the battery pack to avoid
rapid electrical discharge. Discharged a battery may
lead to uid leakage and excessive heat. Batteries
should be stored in a clean and dry area. For
maximum battery life, storage temperature should
not exceed 30°C.
WARNING
Handling the battery pack
The following precautions must be observed
in order to safely and effectively use a battery
pack. Improper use may lead to uid leakage,
excessive heat, ignition, or explosion.
• Never charge it.
• Do not short-circuit it.
• Do not disassemble, transform, or modify it.
• Do not heat it or throw it into a re.
• Do not soak it in fresh water or seawater.
1) Loosen the two battery case mounting screws
(Figure 9.6).
2) Separate the battery case into two parts.
3) Remove the old batteries.
■ Assembling
1) Insert new batteries into the battery case. Be
careful of the orientation of the batteries.
2) Attach the two parts of the battery case to each
other.
3) Tighten the two battery case mounting screws
to a torque of approximately 0.7 N·m.
cannot be separated from battery
pack so as to prevent drop-off.
Figure 9.6 Removing the Battery Pack
CAUTION
Observe the following precautions for the safe
disposal of batteries.
• Do not incinerate the battery, and do not
expose it to a high temperature of 100°C
or more. This may lead to uid leakage or
explosion.
• Dispose of the battery according to laws and
regulations.
Use the following dedicated parts for the battery
pack and batteries.
■ Battery Pack
Part number: F9915NQ (with batteries)
Part number: F9915NK (without batteries)
■ Batteries
Part number: F9915NR
Alternatively, Tadiran TL-5930/S batteries may
be purchased and used.
F0906.ai
IM 01C27B01-01EN
Page 73

<9. Maintenance>
9-8
■ Transportation of products containing
lithium batteries:
Batteries used for this transmitter contain
lithium. Primary lithium batteries are regulated
in transportation by the U.S. Department of
Transportation, and are also covered by the
International Air Transport Association (IATA), the
International Civil Aviation Organization (ICAO), and
the European Ground Transportation of Dangerous
Goods (ARD). It is the responsibility of the shipper
to ensure compliance with these or any other local
requirements. Consult current regulations and
requirements before shipping. When transporting
this transmitter with the battery pack inserted, keep
it in deep sleep mode in order to conserve battery
power. For details on how to switch to deep sleep
mode, refer to subsection 8.3.16 “Switching to Deep
Sleep Mode.”
■ How to replace and dispose of the
batteries:
This is an explanation about the new EU Battery
Directive(DIRECTIVE 2006/66/EC). This directive is
only valid in the EU.
Batteries are used for this product.
When you remove batteries from this product and
dispose them, discard them in accordance with
domestic law concerning disposal.
Take a right action on waste batteries, because the
collection system in the EU on waste batteries are
regulated.
9.5 Troubleshooting
If any abnormality appears in the measured values,
use the troubleshooting ow chart below to isolate
and remedy the problem. Since some problems
have complex causes, these ow charts may
not identify all. If you have difculty isolating or
correcting a problem, contact Yokogawa service
personnel.
9.5.1 Basic Troubleshooting
First determine whether the process variable
is actually abnormal or a problem exists in the
measurement system.
If the problem is in the measurement system,
isolate the problem and decide what corrective
action to take.
This transmitter is equipped with a self-diagnostic
function which will be useful in troubleshooting,
and the transmitter equipped with an integral
indicator will show an alarm code as a result of selfdiagnosis.
See subsection 9.5.3 for the list of alarms.
Battery type: Primary lithium-thionyl chloride battery
CAUTION
The symbol (see above), which is marked on the
batteries, means they shall be sorted out and
collected as ordained in ANNEX II in DIRECTIVE
2006/66/EC.
■ Procedure to remove the batteries safely:
Refer to subsection 9.4.6 “Replacing the Battery
Pack” and subsection 9.4.7 “Replacing the
Batteries.”
IM 01C27B01-01EN
Page 74

<9. Maintenance>
9-9
YES
Inspect the
process system.
YES
Inspect receiver.
: Areas where self-diagnostic offers support
Abnormalities appear in measurement.
Is process variable
itself abnormal?
NO
Measurement system problem
Isolate problem in
measurement system.
Does problem exist in
receiving instrument?
NO
9.5.2 Troubleshooting Flowcharts
The following sorts of symptoms indicate that transmitter
may not be operating properly.
Example : • There is no output signal.
• Output signal does not change even though
process variable is known to be varying.
• Output value is inconsistent with value
inferred for process variable.
Check display of the error code.
Check self-diagnostics by the device configuration tools.
Does the self-diagnostic
indicate problem location?
NO
Are valves opened or
closed correctly?
Refer to Alarm Message Summary in
Subsection 9.5.3.
YES
NO
Environmental conditions
Check/correct
environmental conditions.
Operating conditions
Check/correct operating
conditions.
Transmitter itself
Check transmitter.
Figure 9.7 Basic Flow and Self-Diagnostics
F0907.ai
YES
Is there any pressure leak?
NO
Is the Field Wireless Network
setting correct?
YES
Contact Yokogawa service personnel.
Fully close equalizing valve, and fully
open high pressure and low pressure
valves.
Fix pressure leaks, paying particular
attention to connections for impulse
piping,pressure-detector section, etc.
Reconnect to the Field Wireless
Network.
YES
NO
F0908.ai
IM 01C27B01-01EN
Page 75

<9. Maintenance>
9-10
Output travels beyond 0% or 100%.
Connect the device configuration tool and check self-diagnostics.
Does the self-
diagnostic indicate problem
location?
NO
Are valves opened or
closed correctly?
YES
Is there any pressure leak?
NO
Refer to Alarm Message Summary in
Subsection 9.5.3.
Fully close equalizing valve, and fully
open high pressure and low pressure
valves.
Fix pressure leaks, paying particular
attention to connections for impulse
piping, pressure-detector section, etc.
YES
NO
YES
Large output error.
Connect the device configuration tool and check self-diagnostics.
Does the self-
diagnostic indicate problem
location?
NO
Are valves opened or
closed correctly?
YES
Is impulse piping
connected correctly?
YES
Refer to Alarm Message Summary in
Subsection 9.5.3.
Fully close equalizing valve, and fully
open high pressure and low pressure
valves.
Refer to individual model user manuals
and connect piping as appropriate for
the measurement purpose.
YES
NO
NO
Is impulse piping
to high pressure and low
pressure side correct?
YES
Is zero point
adjusted correctly?
YES
Contact Yokogawa service personnel.
Refer to individual model user manuals
and connect piping as appropriate for
the measurement purpose.
Adjust the zero point.
NO
NO
F0909.ai
Is transmitter
installed where there is
marked variation in
temperature?
NO
Were appropriate
instruments used for
calibration?
YES
Is output adjusted correctly?
YES
Contact Yokogawa service personnel.
Provide lagging and/or cooling, or allow
adequate ventilation.
Refer to Section 9.2 "Calibration
Instruments Selection".
Adjust the output.
YES
NO
NO
F0910.ai
IM 01C27B01-01EN
Page 76

<9. Maintenance>
9.5.3 Errors and Countermeasures
Table 9.3 Error Message Summary (Causes and Actions)
Release/
recovery
conditions
(except
restart)
Recovers only
when AUTO
RECOVER is
ON and within
the range
when AUTO
RECOVER
is ON and
oscillation does
not stop
None
Recovers
when returns to
normal.
None
Recovers
when returns to
normal.
Recovers when
input pressure
returns within
the range.
Recovers when
static pressure
returns within
the range.
Recovers when
temperature
returns within
the range.
Recovers when
temperature
returns within
the range.
Integral
indicator
AL. 01
CAP. ERR
*2
AL. 02
AMP. ERR
*2
AL. 10
PRESS
AL. 11
ST. PRSS
AL. 12
CAP. TMP
AL. 13
AMP. TMP
Factory
NAMUR
category
F Bit 26
F Bit 27
O Bit 23
Bit
Diagnostic
Status
Faults
in sensor or
actuator
element
Faults in
electronics
Outside sensor
limits
Diagnostic Status Detail Cause
FC_SENSOR_FAIL
FR_SENSOR_FAIL
FC_UNOSC_FAIL Recovers only
FR_UNOSC_FAIL
CAP_T_SENSOR_FAIL Capsule
CAP_EEPROM_FAIL Capsule
CAP_EEP_IRREGULAR None
AMP_T_SENSOR_FAIL
AMP_EEPROM_FAIL
AMP_EEP_IRREGULAR None
FC_DELTA_T_FAIL
FR_DELTA_T_FAIL
G_A_COMM_FAIL
WL_AD_FAIL
DP_OUTSIDE_LIMIT Pressure
SP_OUTSIDE_LIMIT Static pressure
CAPT_OUTSIDE_LMIT Capsule
AMPT_OUTSIDE_LIMIT Amplier
Pressure sensor
failure
temperature
sensor failure
EEPROM
memory failure
*3
Amplier
temperature
sensor failure
Amplier
EEPROM failure
Amplier failure None
outside of
specied range
outside of
specied range
temperature
outside of range
(-50 to 130°C)
temperature
outside of range
(-50 to 95°C)
9-11
Action
Replace the
capsule.
Replace the
amplier.
Check
the input
pressure.
Check
the input
pressure.
Retain heat
or insulate
so that
temperature
returns within
the specied
range.
Retain heat
or insulate
so that
temperature
returns within
the specied
range.
IM 01C27B01-01EN
Page 77

<9. Maintenance>
9-12
Integral
indicator
AL.53
P. ADJ
AL.53
P. ADJ
AL. 55
SP. ADJ
AL. 55
SP. ADJ
AL. 79
OV. DISP
AL. 30
RANGE
AL. 31
SP. RNG
AL. 70
LOWBAT
AL. 70
LOWBAT
AL. 60
AI OOS
AL. 61
AI OOS
AL. 62
AI OOS
Factory
NAMUR
category
C Bit 25
C Bit 25
O Bit 22
M
C Bit 24 O/S
Bit
Bit 20
Bit 19
Installation,
calibration
problem
Installation,
calibration
problem
Environmental
conditions out
of device
specication
Power is critical
low:
maintenance
need short term
Power is
low:
maintenance
need mid - term
Diagnostic
Status
Diagnostic Status Detail Cause
DP_TRIM_SPAN_OUTSIDE Pressure span
adjustment
variable outside
of range
DP_TRIM_ZERO_OUTSIDE Pressure zero
adjustment
variable outside
of range
SP_TRIM_SPAN_OUTSIDE Static pressure
span adjustment
variable outside
of range
SP_TRIM_ZERO_OUTSIDE Static pressure
zero adjustment
variable outside
of range
LCD_OUTSIDE_LIMIT LCD display
outside of
specied range
DP_OUTSIDE_RANGE Input pressure
setting outside
of range
SP_OUTSIDE_RANGE Static pressure
setting outside
of range
WL_DEEPSLP_ALM
CRITICAL_LOWBAT
WL_LOWBAT_ALM Low remaining
AI1_OUT_OF_SERVICE AI1 block is O/S
AI2_OUT_OF_SERVICE AI2 block is O/S
AI3_OUT_OF_SERVICE AI3 block is O/S
*3
*4
Low remaining
battery voltage
results in
switching to
deep sleep.
Battery voltage
is the lowest.
battery voltage
mode.
mode.
mode.
Release/
recovery
conditions
(except
restart)
Recovers
when span
adjustment
variable/point
returns within
the range.
Recovers
when zero
adjustment
variable/point
returns within
the range.
Recovers
when span
adjustment
variable /point
returns within
the range.
Recovers
when zero
adjustment
variable/point
returns within
the range.
Recovers when
display value
returns within
the range.
Recovers when
setting returns
within the
range.
Recovers when
setting returns
within the
range.
None
None
Returns when
the mode target
of AI1 block is
other than O/S.
Returns when
the mode target
of AI2 block is
other than O/S.
Returns when
the mode target
of AI3 block is
other than O/S.
Action
Check
the span
adjustment
variable for
the Pressure.
Check
the zero
adjustment
variable for
the Pressure.
Check
the static
pressure
span
adjustment
variable.
Check
the static
pressure zero
adjustment
variable.
Check the
display
setting.
Check the
input pressure
setting.
Check
the static
pressure
setting.
Replace the
batteries.
Replace the
batteries.
Set the mode
target to
AUTO.
Set the mode
target to
AUTO.
Set the mode
target to
AUTO.
IM 01C27B01-01EN
Page 78

<9. Maintenance>
9-13
Factory
Integral
indicator
AL. 63
AI SIM
AL. 64
AI SIM
AL. 65
AI SIM
*1: "Factory NAMUR category” refers to the four categories (C: Check function, M: Maintenance required, F: Failure, and O: Off
* NAMUR NE107 “Self-Monitoring and Diagnosis of Field Devices”
*2: When the device detects “AL01 CAP.ERR” and “AL02 AMP.ERR”, the LCD display stays on regardless of the status in LCD mode.
*3: Applicable for Integral antenna type (Amplier housing code: 7).
*4: Applicable for Detachable antenna type (Amplier housing code: 8 or 9).
NAMUR
category
C Bit 17
C Bit 17
specication) according to NAMUR NE107*.
Bit
Diagnostic
Status
Simulation is
active
Simulation is
active
Diagnostic Status Detail Cause
SimulationActive
(AI1)
SimulationActive
(AI2)
SimulationActive
(AI3)
AI1 block is
simulate mode.
AI2 block is
simulate mode.
AI3 block is
simulate mode.
Release/
recovery
conditions
(except
restart)
Returns when
the simulate
mode of AI1
block is set
to disable. 1
(Disable)
Returns when
the simulate
mode of AI2
block is set
to disable. 1
(Disable)
Returns when
the simulate
mode of AI3
block is set
to disable. 1
(Disable)
Action
Check the
simulate
mode of AI1
block.
Check the
simulate
mode of AI2
block.
Check the
simulate
mode of AI3
block.
IM 01C27B01-01EN
Page 79

<9. Maintenance>
Table 9.4 Error Message Summary (Output Actions)
Output actions
Static
Pressure
Output value
(hold value)
Output status
(BAD: Sensor
Failure)
Output value
(hold value)
Output status
(BAD: Device
Failure)
Output value
(hold value)
Output status
(BAD: Device
Failure)
Output value
(hold value)
Output status
(BAD: Device
Failure)
Capsule
Temp
Value
Normal action
(calculated in
a normal way)
Output status
(BAD: Sensor
Failure)
Output value
(calculated in
a normal way)
Output status
(BAD: Device
Failure)
Output value
(calculated in
a normal way)
Output status
(BAD: Device
Failure)
Normal action
(calculated in
a normal way)
Output status
(BAD: Device
Failure)
Integral
Indicator
AL. 01
CAP. ERR
*2
AL. 02
AMP.ERR
*2
Factory
NAMUR
Bit
category
F Bit 26
F Bit 27
Diagnostic
Status
Faults
in sensor or
actuator
element
Faults in
electronics
Diagnostic Status Detail
Pressure
FC_SENSOR_FAIL Output value
FR_SENSOR_FAIL
FC_UNOSC_FAIL
FR_UNOSC_FAIL
(hold value)
Output status
(BAD: Sensor
Failure)
CAP_T_SENSOR_FAIL Normal action Normal action Output value
CAP_EEPROM_FAIL Output value
(hold value)
Output status
CAP_EEP_IRREGULAR
(BAD: Device
Failure)
AMP_T_SENSOR_FAIL
*3
Normal action Normal action Normal action
AMP_EEPROM_FAIL Output value
(hold value)
Output status
AMP_EEP_IRREGULAR
(BAD: Device
Failure)
FC_DELTA_T_FAIL Output value
(hold value)
output status
FR_DELTA_T_FAIL
(BAD: Device
Failure)
Output value
G_A_COMM_FAIL Output value
(calculated in
a normal way)
Output status
WL_AD_FAIL
(BAD: Device
Failure)
9-14
Amp
Temp
Value
Normal action
Output value
(calculated in
a normal way)
Output status
(BAD: Device
Failure)
Output value
(calculated in
a normal way)
Output status
(BAD: Sensor
Failure)
Output value
*4
(hold value)
Output status
(BAD: Device
Failure)
Output value
*4
(hold value)
output status
(BAD: Device
Failure)
Output value
(calculated in
a normal way)
Output status
(BAD: Device
Failure)
IM 01C27B01-01EN
Page 80

<9. Maintenance>
9-15
Integral
Indicator
AL. 10
PRESS
AL. 11
ST. PRSS
AL. 12
CAP. TMP
AL. 13
AMP. TMP
AL. 53
P. ADJ
AL. 53
P. ADJ
AL. 55
SP. ADJ
AL. 55
SP.ADJ
AL. 79
OV. DISP
Factory
NAMUR
category
O Bit 23
C Bit 25
Bit
Diagnostic
Status
Outside sensor
limits
Installation,
calibration
problem
Diagnostic Status Detail
DP_OUTSIDE_LIMIT Output value
SP_OUTSIDE_LIMIT Output value
CAPT_OUTSIDE_LIMIT Output value
AMPT_OUTSIDE_LIMIT
DP_TRIM_SPAN_
OUTSIDE
DP_TRIM_ZERO_
OUTSIDE
SP_TRIM_SPAN_
OUTSIDE
SP_TRIM_ZERO_
OUTSIDE
LCD_OUTSIDE_LIMIT
Pressure
(calculated in
a normal way)
Output status
(UNCERTAIN:
Sensor
Conversion
not Accurate)
(calculated in
a normal way)
Output status
(UNCERTAIN:
Non Specic)
(calculated in
a normal way)
Output status
(UNCERTAIN:
Non Specic)
Normal action Normal action Normal action
Output value
(calculated in
a normal way)
Output status
(UNCERTAIN:
Range Limits
Exceeded)
Output value
(calculated in
a normal way)
Output status
(UNCERTAIN:
Range Limits
Exceeded)
Normal action
Normal action
Normal action Normal action Normal action Normal action
Output actions
Static
Pressure
Output value
(calculated in
a normal way)
Output status
(UNCERTAIN:
Non Specic)
Output value
(calculated in
a normal way)
Output status
(UNCERTAIN:
Sensor
Conversion
not Accurate)
Output value
(calculated in
a normal way)
Output status
(UNCERTAIN:
Non Specic)
Normal action Normal action Normal action
Normal action Normal action Normal action
Output value
(calculated in
a normal way)
Output status
(UNCERTAIN:
Range Limits
Exceeded)
Output value
(calculated in
a normal way)
Output status
(UNCERTAIN:
Range Limits
Exceeded)
Capsule
Temp
Value
Normal action Normal action
Normal action Normal action
Output value
(calculated in
a normal way)
Output status
(UNCERTAIN:
Sensor
Conversion
not Accurate)
Normal action Normal action
Normal action Normal action
Amp
Temp
Value
Normal action
Output value
(calculated in
a normal way)
Output status
(UNCERTAIN:
Sensor
Conversion
not Accurate)
IM 01C27B01-01EN
Page 81

<9. Maintenance>
9-16
Output actions
Static
Pressure
Capsule
Temp
Value
Amp
Temp
Value
Integral
Indicator
AL. 30
RANGE
AL. 31
SP. RNG
Factory
NAMUR
Bit
category
O Bit 22
Diagnostic
Status
Environmental
conditions out
of device
specication
Power is
Diagnostic Status Detail
DP_OUTSIDE_RANGE
SP_OUTSIDE_RANGE
WL_DEEPSLP_ALM
*3
Pressure
Normal action Normal action Normal action Normal action
Normal action Normal action Normal action Normal action
critical
*6
AL. 70
LOWBAT
Bit 20
low:
maintenance
CRITICAL_LOWBAT
Normal action Normal action Normal action Normal action
*4
need
*6
AL. 70
LOWBAT
M
Bit 19
short - term
Power is
low:
maintenance
need
WL_LOWBAT_ALM
Normal action Normal action Normal action Normal action
mid - term
AI1_OUT_OF_SERVICE Output value
AL. 60
AI OOS
(hold value)
Output status
(BAD: Out of
Normal action Normal action Normal action
Service)
AL. 61
AI OOS
C Bit 24 O/S
AI2_OUT_OF_SERVICE
Normal action
Output value
(hold value)
Output status
(BAD: Out of
Normal action Normal action
Service)
AL. 62
AI OOS
AL. 63
AI SIM
AL. 64
AI SIM
AL. 65
AI SIM
C Bit 17
Simulation is
active
AI3_OUT_OF_SERVICE
SimulationActive
(AI1)
SimulationActive
(AI2)
SimulationActive
(AI3)
Normal action Normal action
Normal action Normal action Normal action Normal action
Normal action Normal action Normal action Normal action
Normal action Normal action Normal action Normal action
Output value
(hold value)
Output status
(BAD: Out of
Service)
Output value
(hold value)
Output status
(BAD: Out of
Service)
*1: “Factory NAMUR category” refers to the four categories (C: Check function, M: Maintenance required, F: Failure, and O: Off
specication) according to NAMUR NE107*.
* NAMUR NE107 “Self-Monitoring and Diagnosis of Field Devices”
*2: When the device detects “AL01 CAP.ERR” and “AL02 AMP.ERR”, the LCD display stays on regardless of the status in LCD mode.
*3: Applicable for Integral antenna type (Amplier housing code: 7).
*4: Amplier temperature value is calculated in a normal way for Detachable antenna type (Amplier housing code: 8 or 9).
*5: Applicable for Detachable antenna type (Amplier housing code: 8 or 9).
*6: When the ambient temperature is higher than 60°C, AL.70 may be generated despite the indication of Energy Left shows sufciently
remained. However, it does not affect the device operation. This is caused by the change of battery inner status with extremely
low power consumption under high temperature environment. It is recommended to set the data updating period to 15 seconds or
shorter.
IM 01C27B01-01EN
Page 82

<10. Parameter Summary>
10. Parameter Summary
Table 10.1 Parameter
Object
ID
1.
UAPMO
block
Attribute
ID
1 Version Revision Indicates the application revision of EJX This revision
10 Static Revision Indicates the revision level of the xed parameters of
64 Identication
65 CTS Version Indicates the version of the communication stack test
66 ITS Version Indicates the version of the inter operability test system
67 Diagnostic Status Indicates the diagnostic results of the device based on
68 UAP Option Allows setting the Diagnostic Status and write protection
69 Diagnostic
70 Diagnostic
102 Diagnostic Status
103 Energy Left Indicates the number of days of remaining battery life
104 Reset Energy Left Initialize the remaining battery life (Energy Left) and
Label Description
when the application software is downloaded.
UAP Used, for example, to check whether parameters
have been change.
Indicates the vender ID, model ID, and revision of the
Number
Switch
Conguration
Detail[2]
device.
system (CTS).
(ITS).
the NAMUR NE107
Setting Enable diagnostic status conguration in UAP
Option to Enable allows turning OFF and ON the
display of the diagnostic results for each summary,
and changing Categorize For Categorize at the time of
shipment, refer to tables 8.3 and 10.2.
of UAP.
Software write protect
1: On, 0: Off
Enable hardware write protect
1: Enable, 0: Disable (default)
Enable diagnostic status conguration
1: Enable, 0: Disable (default)
The following table shows the relationship between the
hardware write protection and software write protection.
Enable
hardware
write
protect
Disable Off or On Off No
Disable Off or On On Yes
Enable Off Off or On No
Enable On Off or On Yes
Allows setting On/Off for each summary of Diagnostic
Status when Enable diagnostic status conguration in
UAP Option is set to Enable.
Allows Categorize for each summary of Diagnostic
Status when Enable diagnostic status conguration in
UAP Option is set to Enable.
Detailed information on Diagnostic Status. For
Categorize at the time of shipment, refer to Table 10.2.
assuming ambient temperature condition as 23 degrees
Celsius.
The unit is day.
reset it as new batteries.
Perform the battery replacement.
0 = Continue (Cancel)
1 = Reset (Initialization)
Hardware
protect
*1
model.
write
Software
write
protect
Write
protect
(Writable)
(Unwritable)
(Writable)
(Unwritable)
--- R
0 R
--- R
0 R
0 R
--- R
0 W
On W
Refer to Table
10.2.
Refer to Table
10.2.
--- R
0 (reading value
is always 0)
Default
value
10-1
Handling
W
R
W
IM 01C27B01-01EN
Page 83

<10. Parameter Summary>
10-2
Object
ID
1.
UAPMO
block
(continued)
Attribute
ID
105 Power Supply
Label Description
Indicates the predicted battery level and the power
Status
supply method.
0 = external power supply
1 = battery level 75% or more
2 = battery level 25% ~ 75%
3 = battery level 25% or less
106 EHType
*2
107 Power Supply
*2
Voltage
110 Hardware Write
Protect
Available to write note into this parameter. --- W
Indicates the measured power supply voltage (V). --- R
Allows recognizing the status of the hardware write
protection switch.
(Switch Off, Switch On)
111 Radio Silence Repeats a cycle of a 1-hour pause and 6-minute
search if the instrument cannot join the network after a
time specied in Radio Silence has elapsed.
When 0 is set, the Radio Silence is invalid.
112 Simulation Active
*2
Alert
The On/Off or priority for Simulation Active Alert can
be set.
1. On/Off setting
0 = FALSE, 255 =TRUE
2. Alert report priority: 0 to 15
113 Soft Update
incomplete Alert
The On/Off or priority for Soft Update incomplete Alert
*2
can be set.
1. On/Off setting
0 = FALSE, 255 =TRUE
2. Alert report priority: 0 to 15
Not available for EJX.
114 Power low Alert
*2
The On/Off or priority for Power low Alert can be set.
1. On/Off setting
0 = FALSE, 255 =TRUE
2. Alert report priority: 0 to 15
115 Power Critical low
*2
Alert
The On/Off or priority for Power Critical low Alert can
be set.
1. On/Off setting
0 = FALSE, 255 =TRUE
2. Alert report priority: 0 to 15
116 Fault prediction
*2
Alert
The On/Off or priority for Fault prediction Alert can be
set.
1. On/Off setting
0 = FALSE, 255 =TRUE
2. Alert report priority: 0 to 15
Not available for EJX.
117 Environmental
conditions Alert
The On/Off or priority for Environmental conditions
*2
Alert can be set.
1. On/Off setting
0 = FALSE, 255 =TRUE
2. Alert report priority: 0 to 15
118 Outside sensor
limits Alert
*2
The On/Off or priority for Outside sensor limits Alert
can be set.
1. On/Off setting
0 = FALSE, 255 =TRUE
2. Alert report priority: 0 to 15
119 Out of service
*2
Alert
The On/Off or priority for Out of service Alert can be
set.
1. On/Off setting
0 = FALSE, 255 =TRUE
2. Alert report priority: 0 to 15
120 Callibration
problem Alert
The On/Off or priority for callibration problem Alert can
*2
be set.
1. On/Off setting
0 = FALSE, 255 =TRUE
2. Alert report priority: 0 to 15
Default
value
Handling
28800 W
1. TRUE
2. 15
1. TRUE
2. 15
1. TRUE
2. 15
1. TRUE
2. 15
1. TRUE
2. 15
1. TRUE
2. 15
1. TRUE
2. 15
1. TRUE
2. 15
1. TRUE
2. 15
R
R
W
W
W
W
W
W
W
W
W
IM 01C27B01-01EN
Page 84

<10. Parameter Summary>
10-3
Object
ID
1.
UAPMO
block
(continued)
2.
UDO
block
3.
CO
block
Attribute
ID
121 Faults Sensor or
122 Faults Electronics
123 Faults process
124 Faults non-
125 Other faults Alert
2 DESCRIPTION Indicates the version and model information of the
3 STATE Indicates the status of UAP block.
5 MAX_BLOCK_
14 LAST_BLOCK_
16 ERROR_CODE Indicates the error codes for DLError.
1 REVISION Indicates the revision number such as COMM_
2 COMM_
3 COMM_
Label Description
The On/Off or priority for Faults Sensor or actuator
*2
actuator Alert
*2
Alert
inuence Alert
compliance Alert
SIZE
DOWNLOADED
ENDPOINT
CONTRACT
Alert can be set.
1. On/Off setting
0 = FALSE, 255 =TRUE
2. Alert report priority: 0 to 15
The On/Off or priority for Faults Electronics Alert can
be set.
1. On/Off setting
0 = FALSE, 255 =TRUE
2. Alert report priority: 0 to 1
The On/Off or priority for Faults process inuence Alert
*2
can be set.
1. On/Off setting
0 = FALSE, 255 =TRUE
2. Alert report priority: 0 to 15
Not available for EJX.
The On/Off or priority for Faults non-compliance Alert
*2
can be set.
1. On/Off setting
0 = FALSE, 255 =TRUE
2. Alert report priority: 0 to 15
Not available for EJX.
*2
The On/Off or priority for Other faults Alert can be set.
1. On/Off setting
0 = FALSE, 255 =TRUE
2. Alert report priority: 0 to 15
Not available for EJX.
downloaded data.
0 Idle
1 Downloading
3 Applying
4 DLComplete
6 DLError
Maximum block size. This value is smaller than the
maximum data size of APDU.
Indicates the last downloaded block number.
0 means that no block has been downloaded.
0 = noError
1 = Timeout
2 = ClientAbort
64 = Apply failure
ENDPOINT, etc.
Indicates the Endpoint information. The following
shows the components.
1. Network address of remote endpoint
2. Transport layer port at remote endpoint
3. Object ID at remote endpoint
4. Stale data limit
5. Data publication period
6. Ideal publication phase
7. PublishAutoRetransmit
8. Conguration status
Indicates the Contract information. The following
shows the components.
1. ContractID
2. Contract_Status
3. Actual_Phase
Default
value
1. TRUE
2. 15
1. TRUE
2. 15
1. TRUE
2. 15
1. TRUE
2. 15
1. TRUE
2. 15
--- R
--- R
--- R
--- R
--- R
--- R
--- W
--- R
Handling
W
W
W
W
W
IM 01C27B01-01EN
Page 85

<10. Parameter Summary>
10-4
Object
ID
3.
CO
block
(continued)
4.
TRANSDUCER
block
Attribute
ID
4 PUB_ITEM_MAX Maximum PUB_ITEM value --- R
5 PUB_ITEM_NUM PUB_ITEM number --- R
6 PUB_ITEM Indicates the PUB_ITEM information. The following
1 Tag Description Memo eld available to write anything. Transducer W
2 Auto Recovery Allows specifying the action when the cause of a
3 Model Indicates the model name of the transmitter. --- R
4 Sensor Serial
5 Measurement
6 Measurement
7 Wireless Status Indicate the communication status.
8 Display Selection Select PV Value displaying on the LCD indicator.
9 LCD Mode Select the display mode on the LCD indicator.
10 Special Cmd Special function parameter.
Label Description
shows the components
1. ObjectID
2. AttributeID
3. AttributeIndex
4. Size
sensor failure is removed.
OFF (=0): AL continues to be indicated
even after the cause of the sensor
error is removed, and the BURN
OUT state is not released.
ON (=1): The AL indication for sensor
failure disappears and normal
action is resumed when the cause
of the sensor failure is removed.
Indicates the device number of the transmitter. --- R
Number
Indicates the measurement period of process values. --- R
Measurement mode selects continuous mode or
intermittent mode.
When the update time is set to 0.5 second
intermittent mode, the mode is automatically switched
to continuous mode.
When the update time is set to 0.5 second*4,
the computation process is in continuous mode,
regardless of the measurement mode.
When 0 is set, measurement period is set to 30
seconds regardless of measurement setting.
1. Indicates the initial idle status or join status.
(idle status, join status)
2. Indicates whether Contract(Pub) is established.
(not establishment, establishment)
3. Indicates whether Contract(R/W) is
established.
(not establishment, establishment)
1. Indicates display status of PV Value of AI1
(displayed, not displayed)
2. Indicates display status of PV Value of AI2
(displayed, not displayed)
3. Indicates display status of PV Value of AI3
(displayed, not displayed)
1. Indicates the ON mode. (off, intermittent)
2. Indicates whether continuous or not.
(continuous off, continuous on)
3. Indicates the bar graph display.
(bar graph not displayed, bar graph displayed)
0 = initialize value at READ (None)
1 = Squawk status
2 = deep sleep status
To start from deep sleep mode, either remove and
insert the battery pack, or use the provisioning device
tool or the device conguration tool via infrared
communication.
Rate
Mode
*3
*4
in
*3
Default
value
--- W
ON W
intermittent
mode
1. idle status
2. not
estabilishment
3. not
esabilishment
1. displayed
2. not
displayed
3. not
displayed
1. OFF
2. continuous
*3
OFF
3. bar graph
not displayed
0 W
Handling
W
R
W
W
IM 01C27B01-01EN
Page 86

<10. Parameter Summary>
10-5
Object
ID
4.
TRANSDUCER
block
(continued)
5.
AI1 block
Attribute
ID
11 Special Order ID Displays the special order number, if applicable. --- R
12 Unit Sel1 Selects whether to automatically apply the unit to the
13 Display Unit11 When Custom is selected in Unit Sel1, set the display
14 LCD Intermittetnt
15 XD Filter
16 Measurement
1 Process Value AL1 is a pressure output object.
2 Block Mode A universal parameter to indicate the block’s operation
3 Concentrator OID Indicates the Concentrator object value that
4 Scale Allows specifying the upper or lower limit for the PV
26 Tag Description A universal parameter to store the comment that
27 Process Value
28 Simulate Switch A simulation function switch for the AI object test
29 Transducer Value When Simulate Switch is set to Disable, this value
30 Simulate Value When Simulate Switch is set to Enable, this value is
51 Upper Limit Indicates the upper limit (URL) for the pressure. --- R
Label Description
word for the parameter for which the unit display is
selected, or apply the characters that are written to
Display Unit1. (Auto, Custom)
unit using 6 characters or less.
*2
Time
*2
Rate
Filter Time
*2
Set the time to turn off display on the LCD indicator.
When 0 is set, it is diplayed in continuous mode.
Unit: second
Set the damping time to Tranceducer value in the AI1
ans AI2 blocks.
Unit: second
When Measurement mode is set to continuous mode,
it is valid.
Indicates the cycle to publish the measurement value
and status
Indicates the primary analog value (or corresponding
process value) and status used to execute this
function.
Allows updating data by specifying this for the
Concentrator object.
1. Value: output value of Al object
2. Status: Specify output status of Al object.
status. Each O/S, Auto, and Man can select from.
1. Target : Specify Al object mode.
2. Actual : Indicates current mode of Al object.
3. Permitted : Indicates the mode selected by
Target of Al object.
4. Normal : Indicate normal status mode of Al
object.
corresponds to the data update of the PV value.
scaling, unit code, etc.
1. EU at 100% : Indicate the upper limit of the PV
value.
2. EU at 0% : Indicate the lower limit of the PV value.
3. Units Index : Indicate the setting unit used for the
PV value.
4. Decimal : Indicate the digit number below the
decimal point displayed in the LCD indicator.
describes the tag
Allows adjusting the time constant for ltering the PV
value. Setting unit: Second. This is enabled for the
Continuous mode.
(Disable, Enable)
is used as the input value for the AI object. Refer to
Figure 10.1.
used as the input value for the AI object.
The input value can be changed.
*5
Default
value
Auto W
NULL W
60 seconds W
2 seconds W
0 R
1. Value = ---
2. Status = ---
1.
Target=Auto
2.
Actual=Auto
3.
Permitted=
Auto
4.
Normal=Auto
3 R
1. EU at 100%
= 100
2. EU at 0%
= 0
3. Units Index
= %
4. Decimal = 2
Al1:
Differential
Pressure
0 second W
1 (Disable) W
Disable R
--- W
Handling
W
W
W
W
IM 01C27B01-01EN
Page 87

<10. Parameter Summary>
10-6
Object
ID
5.
AI1
block
(continued)
Attribute
ID
52 Lower Limit Indicates the lower limit (LRL) for the pressure. --- R
53 PV Range Sets the measurement range.
54 Linearization Type Select either No Linearization or Square root as a
55 Flow Constant Indicates the ow coefcient, which shows the
56 Lower Cutoff Species the low cut value. The unit is subject to
57 Cal Cmd Species the calibration method.
58 Cal Status Indicates the calibration status.
59 Calibration Highest
60 Calibration Lowest
61 Calibration
104 External Zero Trim Allows performing external zero adjustment.
105 Low Cut Mode Species the low cut mode.
106 H/L Swap Allows performing reverse connection of the impulse
Label Description
1. EU at 100% : Indicates input value of the upper
limit.
2. EU at 0% : Indicates input value of the lower limit.
3. Units Index : Indicates the units of the
measurement range.
4. Decimal : Indicates the digit number below the
decimal point.
setting of the output range.
0 = No Linearization :
Provides an output value scaled according to the
PV Range and Scale range settings.
(To use Direct with FF, set the same value for PV
Range and Scale.)
10 = Square root :
Provides a square root output computed for the
value scaled according to the PV Range and Scale
range settings.
correlation between the ow rate value and square root
value of the differential pressure.
Scale.Units Index.
0 = CAL_NONE : Initial state in which calibration is
not performed
1 = CAL_LOW : Applies an actual input and adjusts
the lower limit using the value specied in
Calibration Lowest Point.
2 = CAL_HIGH : Applies an actual input and adjusts
the higher limit using the value specied in
Calibration Highest Point.
5 = CAL_CLEAR : Clears the adjustment variable.
0 = CAL_NONE : Start-up and default value
1 = CAL_SUCCESS : Indicates that calibration was
successful.
7 = CAL_BAD_TRIM_POINT : Indicates this status
when the adjustment variable is outside of range.
Species the higher limit adjustment variable for
Point
Point
Minimum Span
adjustment between two points.
Species the lower limit adjustment variable for the
adjustment between two points.
Indicates the minimum span of the adjustment
variable.
(Trim on, Trim off)
(Linear, Zero)
line.
(NORMAL, REVERSE : reverse connection)
Used when the lower pressure side and higher
pressure side of the impulse line were connected
wrongly when installing the pressure transmitter.
Default
value
EU at 100%
= 100
EU at 0%
= 0
Units Index
= kPa (1133)
Decimal
= 2
0 W
1.0 W
10 W
0 (reading
value is
always 0)
--- R
--- W
--- W
--- R
Trim on W
Linear W
Normal W
Handling
W
W
IM 01C27B01-01EN
Page 88

<10. Parameter Summary>
10-7
Object
ID
5.
AI1
block
(continued)
6.
AI2
block
Attribute
ID
107 T Zero Cmp Parameter to select the temperature zero shift
108 Temp Zero Parameter to set the temperature gradient value for the
109 Temp Select Parameter to select the temperature (amplier-side
1 Process Value AI2 is a static pressure output object.
2 Block Mode A universal parameter to indicate the block’s operation
3 Concentrator OID Indicates the Concentrator object value that
4 Scale Allows specifying the upper or lower limit for the PV
26 Tag Description A universal parameter to store the comment that
27 Process Value
28 Simulate Switch A simulation function switch for the AI object test
29 Transducer Value When Simulate Switch is set to Disable, this value is
30 Simulate Value When Simulate Switch is set to Enable, this value is
51 Upper Limit Indicates the upper limit (URL) for the pressure. --- R
52 Lower Limit Indicates the lower limit (LRL) for the pressure. --- R
Label Description
compensation mode
0 = OFF : Does not perform temperature zero shift
compensation.
1 = ON : Performs temperature zero shift
compensation.
temperature zero shift compensation
/ capsule-side) used for the temperature zero shift
compensation.
0 = AMP TEMP : the value of the amplier-side
temperature sensor is used.
1 = CAP TEMP : the value of the capsule-side
temperature sensor is used.
Indicates the primary analog value (or corresponding
process value) and status used to execute this
function.
Allows updating data by specifying this for the
Concentrator object.
1. Value: output value of Al object
2. Status: Specify output status of Al object.
status. O/S, Auto, and Man can be selected.
1. Target : Specify Al object mode.
2. Actual : Indicates current mode of Al object.
3. Permitted : Indicates the mode selected by Target
of Al object.
4. Normal : Indicate normal status mode of Al object.
corresponds to the data update of the PV value.
scaling, unit code, etc.
1. EU at 100% : Indicate the upper limit of the PV
value.
2. EU at 0% : Indicate the lower limit of the PV value.
3. Units Index : Indicate the setting unit used for the
PV value.
4. Decimal : Indicate the digit number below the
decimal point displayed in the LCD indicator.
describes the tag.
Allows adjusting the time constant for ltering the PV
Filter Time
value. Setting unit: Second. This is enabled for the
Continuous mode.
(Disable, Enable)
used as the input value for the AI object.
used as the input value for the AI object.
The input value can be changed.
Default
value
Off w
0 w
1 w
--- W
1.Target
= O/S
2.Actual
= O/S
3.Permitted
= O/S
4.Normal
= O/S
3 R
1. EU at 100%
= 100
2. EU at 0%
= 0
3. Units Index
= %
4. Decimal
= 2
AI2: Static
Pressure
0 second W
Disable W
--- R
--- W
Handling
W
W
W
IM 01C27B01-01EN
Page 89

<10. Parameter Summary>
10-8
Object
ID
6.
AI2
block
(continued)
7.
AI3
block
Attribute
ID
53 PV Range Sets the measurement range.
54 Linearization Type Select either No Linearization or Square root as a
55 Flow Constant Indicates the ow coefcient, which shows the
56 Lower Cutoff Species the low cut value. The unit is subject to
57 Cal Cmd Species the calibration method.
58 Cal Status Indicates the calibration status.
59 Calibration Highest
60 Calibration Lowest
61 Calibration
102 Static Process
103 SP Select Parameter to select the High-side pressure or the Low-
1 Process Value Al3 is a temperature pressure output object.
Label Description
1. EU at 100% : Indicates input value of the upper
limit.
2. EU at 0% : Indicates input value of the lower limit.
3. Units Index : Indicates the units of the
measurement range.
4. Decimal : Indicates the digit number below the
decimal point.
setting of the output range.
0 = No Linearization :
Provides an output value scaled according to the
PV Range and Scale range settings.
(To use Direct with FF, set the same value for PV
Range and Scale.)
correlation between the ow rate value and square root
value of the pressure.
Scale.Units Index.
0 = CAL_NONE : Initial state in which calibration is
not performed
1 = CAL_LOW : Applies an actual input and adjusts
the lower limit using the value specied in
Calibration Lowest Point.
2 = CAL_HIGH : Applies an actual input and adjusts
the higher limit using the value specied in
Calibration Highest Point.
5 = CAL_CLEAR : Clears the adjustment variable.
0 = CAL_NONE : Start-up and default value
1 = CAL_SUCCESS : Indicates that calibration was
successful.
7 = CAL_BAD_TRIM_POINT : Indicates this status
when the adjustment variable is outside of range.
Species the higher limit adjustment variable for
Point
Point
Minimum Span
Type
adjustment between two points.
Species the lower limit adjustment variable for the
adjustment between two points.
Indicates the minimum span of the adjustment
variable.
108 = Gauge pressure
109 = Absolute pressure
Selects the gauge pressure or the absolute pressure. Abs W
side pressure as the static pressure output.
0 = High : Displays the H-side pressure as the static
pressure
1 = Low : Displays the L-side pressure as the static
pressure
Indicates the primary analog value (or corresponding
process value) and status used to execute this
function.
Allows updating data by specifying this for the
Concentrator object.
1. Value: output value of Al object
2. Status: Specify output status of Al object.
Default
value
1. EU at
100% =
25000.000000
EU at 0%
= 0
Units Index
= kPa
Decimal
= 2
0 W
1.0 W
10 W
0 (reading
value is
always 0)
--- W
--- W
--- R
High W
1. Value = ---
2. Status = ---
Handling
W
W
R
W
IM 01C27B01-01EN
Page 90

<10. Parameter Summary>
10-9
Object
ID
7.
AI3
block
(continued)
(Note) Handling: R=Read only, W=Read & Write
(Note) “Factory NAMUR category” refers to the four categories (C: Check function, M: Maintenance required, F: Failure, and O: Off
specication) according to NAMUR NE107*.
Attribute
ID
2 Block Mode A universal parameter to indicate the block’s operation
3 Concentrator OID Indicates the Concentrator object value that
4 Scale Allows specifying the upper or lower limit for the PV
26 Tag Description A universal parameter to store the comment that
27 Process Value
28 Simulate Switch A simulation function switch for the AI object test
29 Transducer Value When Simulate Switch is set to Disable, this value is
30 Simulate Value When Simulate Switch is set to Enable, this value is
53 Sensor Range Parameter to nondimensionalize the sensor output
102 Tertiary Value
Label Description
status. O/S, Auto, and Man can be selected.
1. Target : Specify Al object mode.
2. Actual : Indicates current mode of Al object.
3. Permitted : Indicates the mode selected by Target
of Al object.
4. Normal : Indicate normal status mode of Al object.
corresponds to the data update of the PV value.
scaling, unit code, etc.
1. EU at 100% : Indicate the upper limit of the PV
value.
2. EU at 0% : Indicate the lower limit of the PV value.
3. Units Index : Indicate the setting unit used for the
PV value.
4. Decimal : Indicate the digit number below the
decimal point displayed in the LCD indicator.
describes the tag
Allows adjusting the time constant for ltering the PV
Filter Time
Select
value.
Setting unit: Second. This is enabled for the
Continuous mode.
(Disable, Enable)
used as the input value for the AI object.
used as the input value for the AI object.
The input value can be changed.
value.
K and deg C are selectable for the temperature unit.
1. EU at 100% : Indicates input value of the upper
limit.
2. EU at 0% : Indicates input value of the lower limit.
3. Units Index : Indicates the units of the
measurement range.
4. Decimal : Indicates the digit number below the
decimal point.
Species either the capsule temperature or amplier
temperature as the output value.
(CAP, AMP)
Default
value
1. Target =
Auto
2. Actual =
Auto
3. Permitted =
O/S+Auto
+Man
4. Normal =
Auto
3 R
1. EU at 100%
= 100
2. EU at 0%
= 0
3. Units Index
= %
4. Decimal = 2
AI3: Capsule
temperature
0 second W
Disable W
--- R
--- W
1. EU at 100%
= 130
2. EU at 0%
= -50
3. Units Index
= deg C
4. Decimal = 0
CAP W
Handling
W
W
W
W
*1: NAMUR NE107 “Self-Monitoring and Diagnosis of Field Devices”
*2: Applicable for Detachable antenna type (Amplier housing code: 8 or 9).
*3: Applicable for amplier housing code 7.
*4: Applicable for amplier housing code 8 or 9.
*5: Minimum value is 1 second, when amplier housing code 7 is specied.
*6: It is valid for not only continuous mode but also intermittent mode, when amplier housing code 8 or 9 is specied.
IM 01C27B01-01EN
Page 91

<10. Parameter Summary>
Table 10.2 Diagnostic Status Detail[0]
Bit Diagnostic Status Detail Description
DiagnosticDetail_1
31 FC_SENSOR_FAIL C sensor frequency error Bit26 F
30 FR_SENSOR_FAIL R sensor frequency error Bit26 F
29 CAP_T_SENSOR_FAIL Capsule temperature sensor failure Bit26 F
28 CAP_EEPROM_FAIL Capsule EEPROM failure Bit26 F
27 CAP_EEP_IRREGULAR CAP EEPROM version not correct Bit26 F
26 AMP_T_SENSOR_FAIL Amplier temperature sensor failure Bit27 F
25 AMP_EEPROM_FAIL Amplier EEPROM failure Bit27 F
24 AMP_EEP_IRREGULAR AMP EEPROM version not correct Bit27 F
22 G_A_COMM_FAIL G/A failure Bit27 F
21 FC_UNOSC_FAIL C sensor oscillation stop failure Bit26 F
20 FC_DELTA_T_FAIL C-side deltaT circuit failure Bit27 F
19 FR_DELTA_T_FAIL R-side deltaT circuit failure Bit27 F
18 WL_AD_FAIL Battery voltage not detected (AMP failure) Bit27 F
17 FR_UNOSC_FAIL R sensor oscillation stop failure Bit26 F
15 DP_OUTSIDE_LIMIT Pressure outside of specied range Bit23 O
14 SP_OUTSIDE_LIMIT Static pressure outside of specied range Bit23 O
13 CAPT_OUTSIDE_LIMIT Capsule temperature outside of specied range Bit23 O
12 AMPT_OUTSIDE_LIMIT Amplier temperature outside of specied range Bit23 O
7 DP_OUTSIDE_RANGE Input pressure setting outside of range Bit22 O
6 SP_OUTSIDE_RANGE Static pressure setting outside of range Bit22 O
DiagnosticDetail_2
31 AI1_OUT_OF_SERVICE AI1 O/S mode Bit24 C
30 AI2_OUT_OF_SERVICE AI2 O/S mode Bit24 C
29 AI3_OUT_OF_SERVICE AI3 O/S mode Bit24 C
28 AI1_SIMULATION_ACTIVE AI1 simulation mode Bit17 C
27 AI2_SIMULATION_ACTIVE AI2 simulation mode Bit17 C
26 AI3_SIMULATION_ACTIVE AI3 simulation mode Bit17 C
20 DP_TRIM_SPAN_OUTSIDE Pressure span adjustment variable outside of range Bit25 C
19 DP_TRIM_ZERO_OUTSIDE Pressure zero adjustment variable outside of range Bit25 C
15 SP_TRIM_SPAN_OUTSIDE Static pressure span adjustment variable outside of
range
14 SP_TRIM_ZERO_OUTSIDE Static pressure zero adjustment variable outside of
range
13 WL_LOWBAT_ALM Low battery Bit19 M
12 CRITICAL_LOWBAT
*1
Detect a decrease in the lowest drive voltage. Bit20 M
10 WL_DEEPSLP_ALM Deep sleep due to low battery Bit20 M
8 LCD_OUTSIDE_LIMIT LCD display outside of specied range Bit25 C
*1: Applicable for amplier housing code 8 or 9.
*2: Applicable for amplier housing code 7.
Diagnostic Status
assignment bit
Bit25 C
Bit25 C
10-10
NAMUR
AI algoritm
from operator
from operator
Value
& Status
from transducer
Value
& Status
from operator
Value
& Status
MODE Target
SIMULATE
SWITCH
SIMULATE
_VALUE
On
Off
PV.Status handling
AI
algorithm
Linearization
scaling,
filter
Figure 10.1 Example schema of analog input object
Mode and
Alert
report
HiHi etc
PV
PV
Auto
O/S
Man
PV
Publish
Value
& Status
F1001.ai
IM 01C27B01-01EN
Page 92

<11. General Specications>
11. General Specications
11-1
11.1 Standard Specications
Communication protocol:
ISA100.11a protocol
Data rate:
250 kbps
Frequency:
2400 - 2483.5 MHz license free ISM band
Radio security:
AES 128 bit codied
RF Transmitter power:
Max. 11.6 dBm (xed)
Antenna:
+2 dBi Omni directional monopole type
Span and range limits:
EJX110B
Measurement
Span/Range
Span 0.1 to 5 0.4 to 20 1 to 50 10 to 500
F
Range -5 to 5 -20 to 20 -50 to 50 -500 to 500
Span 0.1 to 10 0.4 to 40 1 to 100 10 to 1000
L
Range -10 to 10 -40 to 40 -100 to 100 -1000 to 1000
Span 0.5 to 100 2 to 400 5 to 1000 50 to 10000
M
Range -100 to 100 -400 to 400 -1000 to 1000
Span 2.5 to 500 10 to 2000 25 to 5000
H
Range -500 to 500 -2000 to 2000 -5000 to 5000
Span
V
Range
kPa inH2O(/D1) mbar(/D3) mmH2O(/D4)
0.07 to 14
-0.5 to 14
10 to 2000 psi 0.7 to 140 bar
MPa
-71 to 2000
MPa
psi
-5 to 140 bar
-10000 to
10000
0.025 to 5
kgf/cm
-5 to 5
kgf/cm
0.7 to 140
kgf/cm
-5 to 140
kgf/cm
EJX430B
Measurement
Span/Range
Span
H
Range
Span
A
Range -0.1 to 3.5 -14.5 to 500 -1 to 35 -1 to 35
Span 0.08 to 16 12 to 2300 0.8 to 160 0.8 to 160
B
Range -0.1 to 16 -14.5 to 2300 -1 to 160 -1 to 160
MPa psi(/D1) bar(/D3) kgf/cm2(/D4)
2.5 to 500
kPa
-100 to 500
kPa
0.0175 to
3.5
10 to 2000
inH
-400 to 2000
inH
2.5 to 500 0.175 to 35 0.175 to 35
0.025 to 5 0.025 to 5
2O
2O
-1 to 5 -1 to 5
Performance specications:
Refer to GS01C27B01-01EN.
Update Time
Measurement
mode
Continuous 100 ms 100 ms
Intermittent
Differential
pressure
0.5 to 3600 s
selectable
Pressure
0.5 to 3600 s
selectable
For amplier housing code 7:
The transmitter shifts to the countinuous mode
when the update time is set to 1 second.
Minimum update time is 1 second.
For amplier housing code 8 and 9:
The transmitter shifts to the countinuous mode
when the update time is set to 0.5 second.
Power Supply Specications
Battery:
Use the dedicated battery pack.
2
2
2
2
Rated voltage: 7.2 V
Rated capacity: 19 Ah
Output:
ISA100.11a protocol
Output mode (EJX110B):
linear or square root
EJX310B
Measurement
Span/Range
Span 0.5 to 10
L
Range 0 to 10 0 to 2.95 inHg 0 to 100 0 to 75
Span 1.3 to 130
M
Range 0 to 130 0 to 38 inHg 0 to 1300 0 to 970
Span
A
Range
Span
B
Range 0 to 16 MPa 0 to 2300 0 to 160 bar
kPa abs psi abs(/D1)
0.15 to 2.95
inHg
0.39 to 38
inHg
0.0175 to
3.5 MPa
0 to 3.5
MPa
0.08 to 16
MPa
2.5 to 500
0 to 500 0 to 35 bar
12 to 2300 0.8 to 160 bar
mbar abs
(/D3)
5 to 100 3.8 to 75
13 to 1300 9.8 to 970
0.175 to 35
bar
mmHg abs
(/D4)
0.175 to 35
2
kgf/cm
0 to 35
2
kgf/cm
0.8 to 160
2
kgf/cm
0 to 160
2
kgf/cm
Ambient Temperature Limits:
-40 to 85°C (-40 to 185°F)
-30 to 80°C (-22 to 176°F) LCD visible range
Process Temperature Limits:
-40 to 120°C (-40 to 248°F)
– Except EJX310B L capsule
-40 to 100°C (-40 to 212°F)
– EJX310B L capsule
Ambient Humidity Limits:
0 to 100% RH
IM 01C27B01-01EN
Page 93

<11. General Specications>
11-2
Working Pressure Limits (Silicone oil)
Maximum Pressure Limits:
EJX110B
Capsule Pressure
F, L 16 MPa (2300 psi)
M, H, V 25 MPa (3600 psi)*
* 16 MPa for wetted parts material code H, M, T, A, D, and
B.
EJX310B
Capsule Pressure
L 10 kPa abs (2.95 inHg abs)
M 130 kPa abs (38 inHg abs)
A 3.5 MPa abs (500 psia)
B 16 MPa abs (2300 psia)
EJX430B
Capsule Pressure
H 500 kPa (2000 inH
A 3.5 MPa (500 psi)
B 16 MPa (2300 psi)
2O)
Zero Adjustment Limits:
Zero can be fully elevated or suppressed, within
the lower and upper range limits of the capsule.
External Zero Adjustment:
External zero is continuously adjustable with
0.01% incremental resolution of span. Re-range
can be done locally using the digital indicator
with rangesetting switch.
Integral Indicator (LCD display):
5-digit numerical display, 6-digit unit display and
bar graph.
The indicator is congurable to display one
or up to three of the following variables
periodically.;
Differential pressure, static pressure,
temperature.
EMC Conformity Standards
EN61326-1 Class A, Table 2 (For use in
industrial locations), EN61326-2-3
R&TTE Conformity Standards
ETSI EN 300 328, ETSI EN 301 489-1,
ETSI EN 301 489-17, EN61010-1,
EN61010-2-030, EN62311
• Indoor/Outdoor use
Safety Requirement Standards
EN61010-1, EN61010-2-030
• Altitude of installation site:
Max. 2,000 m above sea level
• Installation category: I
(Anticipated transient overvoltage 330 V)
• Pollution degree: 2
• Indoor/Outdoor use
Degrees of Protection
IP66/IP67, NEMA4X
Connections:
Refer to “MODEL AND SUFFIX CODES.”
Wetted Parts Materials:
Diaphragm, Cover Flange, Process
Connector, Capsule Gasket, and Vent/Drain
Plug
Refer to “MODEL AND SUFFIX CODES.”
Process Connector Gasket
PTFE Teon
Fluorinated rubber for option code N2 and N3
Non-wetted Parts Materials:
Bolting
ASTM-B7 carbon steel, 316L SST stainless
steel, or ASTM grade 660 stainless steel
Housing
Low copper cast aluminum alloy with
polyurethane, mint-green paint (Munsell
5.6BG 3.3/2.9 or its equivalent)
Name plate and tag
316 SST tag plate wired onto transmitter
Weight:
4.9 kg (10.8 lb) for wetted parts material code S
except for Measurement span code F without
battery pack, mounting bracket, and process
connector
5.8 kg (12.8 lb) for wetted parts material code
H, M, T, A, D and B or Measurement span code
F without battery pack, mounting bracket, and
process connector
Regulation Conformity of the Wireless Module
• FCC Approval
• IC Approval
IM 01C27B01-01EN
Page 94

<11. General Specications>
Minimum Pressure Limit:
See graph below
EJX110B and EJX430B
11-3
100(14.5)
Working
pressure
kPa abs
(psi abs)
10(1.4)
2.7(0.38)
1(0.14)
EJX310B
100(750)
Working
pressure
kPa abs
(mmHg abs)
0.1(0.75)
Applicable range
-40
(-40)
10(75)
2.7(20)
1(7.5)
0.13(1)
0
(32)
Process temperature °C (°F)
M,A and B capsule
Applicable range
40
(104)
80
(176)
L capsule
Atmospheric
pressure
120
(248)
F01.ai
0.46
(3.45)
0.013(0.1)
0.01(0.075)
-40
(-40)0(32)40(104)80(176)
Process temperature °C (°F)
120 (248)
85
(185)
F02.ai
Figure 1. Working pressure and Process Temperature
IM 01C27B01-01EN
Page 95

<11. General Specications>
11-4
11.2 Model and Sufx Codes
Model EJX110B
Model Sufx Codes Description
EJX110B . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Differential pressure transmitter
Output signal -L . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Wireless communication (ISA100.11a protocol)
Measurement
span (capsule)
F . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
L . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
0.1 to 5 kPa (0.4 to 20 inH
0.1 to 10 kPa (0.4 to 40 inH
D and B)
M . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
H. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
V . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Wetted parts
material
*1
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Process connections►0 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
1 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
2 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
3 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
4 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
5 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Bolts and nuts material J . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
G. . . . . . . . . . . . . .
C. . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Installation
-7 . . . . . . . . . . .
-8 . . . . . . . . . . .
►
-9 . . . . . . . . . . .
-B . . . . . . . . . . .
-U . . . . . . . . . . .
Amplier housing 7 . . . . . . . . . .
8 . . . . . . . . . .
9 . . . . . . . . . .
0.5 to 100 kPa (2 to 400 inH
2.5 to 500 kPa (10 to 2000 inH
0.07 to 14 MPa (10 to 2000 psi)
Refer to “Wetted Parts Materials” Table 1.
without process connector (Rc1/4 female on the cover anges)
with Rc1/4 female process connector
with Rc1/2 female process connector
with 1/4 NPT female process connector
with 1/2 NPT female process connector
without process connector (1/4 NPT female on the cover anges)
ASTM-B7 carbon steel
316L SST stainless steel
ASTM grade 660 stainless steel
Vertical piping, left side high pressure, and process connection downside
Horizontal piping and right side high pressure
Horizontal piping and left side high pressure
Bottom Process Connection, left side high pressure
Universal ange
*2
Cast aluminum alloy with integral antenna
Cast aluminum alloy with detachable antenna (2 dBi)
Cast aluminum alloy without antenna (N connector)
Electrical connection J . . . . . . . . . No electrical connection, battery-powered type (battery case only; battery
cells not included)
Integral indicator ► D. . . . . . . Digital indicator
Mounting bracket ► B . . . . .
D. . . . .
G. . . . .
K. . . . .
M . . . .
N. . . . .
Optional codes
The “►” marks indicate the most typical selection for each specication.
*1:! Users must consider the characteristics of selected wetted parts material and the inuence of process uids. The use of
inappropriate materials can result in the leakage of corrosive process uids and cause injury to personnel and/or damage to plant
facilities. It is also possible that the diaphragm itself can be damaged and that material from the broken diaphragm and the ll uid
can contaminate the user’s process uids.
Be very careful with highly corrosive process uids such as hydrochloric acid, sulfuric acid, hydrogen sulde, sodium hypochlorite,
and high-temperature steam (150°C [302°F] or above). Contact Yokogawa for detailed information of the wetted parts material.
*2: Applicable for wetted parts material code S.
*3: Order the antenna separately from accessary option.
*4: Remote antenna cables can be attached. Order separately from accessary option.
304 SST 2-inch pipe mounting, at type (for horizontal piping)
304 SST 2-inch pipe mounting, L type (for vertical piping)
304 SST 2-inch pipe mounting (for bottom process connection type)
316 SST 2-inch pipe mounting, L type (for vertical piping)
316 SST 2-inch pipe mounting (for bottom process connection type)
None
/ Optional specication
O) (For wetted parts material code S)
2
O) (For wetted parts material code M, H, T, A,
2
O)
2
O)
2
*2
*4
*3*4
IM 01C27B01-01EN
Page 96

<11. General Specications>
Table 1. Wetted Parts Materials
Wetted parts
material code
#
S
H ASTM CF-8M *
M ASTM CF-8M *
T ASTM CF-8M *
A
D
B Monel equivalent *
*1: Cast version of 316 SST. Equivalent to SCS14A.
*2: Hastelloy C-276 or ASTM N10276.
*3: Indicated material is equivalent to ASTM CW-12MW.
*4: Indicated material is equivalent to ASTM M35-2.
The ‘#’marks indicate the construction materials conform to NACE material recommendations per MR01-75. For the use of 316 SST
material, there may be certain limitations for pressure and temperature. Please refer to NACE standards for details.
Cover ange and
process connector
ASTM CF-8M *
1
1
1
1
Hastelloy C-276
equivalent *
3
Hastelloy C-276
equivalent *
3
Capsule Capsule gasket Drain/Vent plug
Hastelloy C-276 *2 (Diaphragm)
F316L SST, 316L SST (Others)
Hastelloy C-276 *
Monel PTFE Teon 316 SST
Tantalum PTFE Teon 316 SST
Hastelloy C-276 *
Tantalum PTFE Teon Hastelloy C-276 *
4
Monel PTFE Teon Monel
Teon-coated 316L SST 316 SST
2
2
PTFE Teon 316 SST
PTFE Teon Hastelloy C-276 *
11-5
2
2
IM 01C27B01-01EN
Page 97

<11. General Specications>
11-6
Model EJX310B
Model Sufx Codes Description
EJX310B . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Absolute pressure transmitter
Output
signal
Measurement
span (capsule)
Wetted parts
material *
Process
connections
Bolts and nuts
material
Installation
Amplier housing 7 . . . . . . . . . .
Electrical connection J . . . . . . . . . No electrical connection, battery-powered type (battery case only; battery
Integral indicator D. . . . . . . Digital indicator
Mounting bracket ► B. . . . .
Optional codes
The “►” marks indicate the most typical selection for each specication.
*1:! Users must consider the characteristics of selected wetted parts material and inuence of process uids. Specifying inappropriate
materials has the potential to cause serious damage to human body and plant facilities resulted from an unexpected leak of the
corrosive process uids.
*2: Order the antenna separately from accessary option.
*3: Remote antenna cables can be attached. Order separately from accessary option.
-L . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Wireless communication (ISA100.11a protocol)
L . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
M . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
A. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
B. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
0.5 to 10 kPa abs (0.15 to 2.95 inHg abs)
1.3 to 130 kPa abs (0.39 to 38 inHg abs)
0.0175 to 3.5 MPa abs (2.5 to 500 psia)
0.08 to 16 MPa abs (12 to 2300 psia)
S . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Refer to “Wetted Parts Materials” Table 2.
1
0 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
1 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
2 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
3 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
4 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
5 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
►
J . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
G. . . . . . . . . . . . . .
C. . . . . . . . . . . . . .
-3 . . . . . . . . . . .
-7 . . . . . . . . . . .
-8 . . . . . . . . . . .
►
-9 . . . . . . . . . . .
-B . . . . . . . . . . .
-U . . . . . . . . . . .
without process connector (Rc1/4 female on the cover anges)
with Rc1/4 female process connector
with Rc1/2 female process connector
with 1/4 NPT female process connector
with 1/2 NPT female process connector
without process connector (1/4 NPT female on the cover anges)
ASTM-B7 carbon steel
316L SST stainless steel
ASTM grade 660 stainless steel
Vertical piping, right side high pressure, and process connection down side
Vertical piping, left side high pressure, and process connection down side
Horizontal piping and right side high pressure
Horizontal piping and left side high pressure
Bottom Process Connection, left side high pressure
Universal ange
Cast aluminum alloy with integral antenna
8 . . . . . . . . . .
9 . . . . . . . . . .
Cast aluminum alloy with detachable antenna (2 dBi)
Cast aluminum alloy without antenna (N connector)
cells not included)
304 SST 2-inch pipe mounting, at type (for horizontal piping)
D. . . . .
G. . . . .
K. . . . .
M . . . .
N. . . . .
304 SST 2-inch pipe mounting, L type (for vertical piping)
304 SST 2-inch pipe mounting (for bottom process connection type)
316 SST 2-inch pipe mounting, L type (for vertical piping)
316 SST 2-inch pipe mounting (for bottom process connection type)
None
/ Optional specication
*3
*2*3
Table 2. Wetted Parts Materials
Wetted parts
material code
#
S
*1: Cast version of 316 SST. Equivalent to SCS14A.
*2: Hastelloy C-276 or ASTM N10276.
The ‘#’marks indicate the construction materials conform to NACE material recommendations per MR01-75. For the use of 316 SST
material, there may be certain limitations for pressure and temperature. Please refer to NACE standards for details.
Cover ange and
process connector
ASTM CF-8M *
1
Capsule Capsule gasket Drain/Vent plug
Hastelloy C-276 *2 (Diaphragm)
316L SST (Others)
Teon-coated 316L SST 316 SST
IM 01C27B01-01EN
Page 98

<11. General Specications>
11-7
Model EJX430B
Model Sufx Codes Description
EJX430B . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Gauge pressure transmitter
Output
signal
Measurement
span (capsule)
Wetted parts
material *
Process
connections
Bolts and nuts
materia
Installation
Amplier housing 7 . . . . . . . . . .
Electrical connection J . . . . . . . . . No electrical connection, battery-powered type (battery case only; battery
Integral indicator D. . . . . . . Digital indicator
Mounting bracket ► B. . . . .
Optional Codes
The “►” marks indicate the most typical selection for each specication.
*1:! Users must consider the characteristics of selected wetted parts material and the inuence of process uids. The use of
inappropriate materials can result in the leakage of corrosive process uids and cause injury to personnel and/or damage to plant
facilities. It is also possible that the diaphragm itself can be damaged and that material from the broken diaphragm and the ll uid
can contaminate the user’s process uids.
Be very careful with highly corrosive process uids such as hydrochloric acid, sulfuric acid, hydrogen sulde, sodium hypochlorite,
and high-temperature steam (150°C [302°F] or above). Contact Yokogawa for detailed information of the wetted parts material.
*2: Applicable for Wetted parts material code S.
*3: Order the antenna separately from accessary option.
*4: Remote antenna cables can be attached. Order separately from accessary option.
Table 3. Wetted Parts Materials
Wetted parts
material code
S
H ASTM CF-8M *
M ASTM CF-8M *
T ASTM CF-8M *
A
D
B Monel equivalent *
*1: Cast version of 316 SST. Equivalent to SCS14A.
*2: Hastelloy C-276 or ASTM N10276.
*3: Indicated material is equivalent to ASTM CW-12MW.
*4: Indicated material is equivalent to ASTM M35-2.
The ‘#’marks indicate the construction materials conform to NACE material recommendations per MR01-75. For the use of 316 SST
material, there may be certain limitations for pressure and temperature. Please refer to NACE standards for details.
-L . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Wireless communication (ISA100.11a protocol)
H. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
A. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
B. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
1
0 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
1 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
2 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
3 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
4 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
5 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
►
J . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
G. . . . . . . . . . . . . .
C. . . . . . . . . . . . . .
►
-3 . . . . . . . . . . .
-7 . . . . . . . . . . .
-8 . . . . . . . . . . .
-9 . . . . . . . . . . .
-B . . . . . . . . . . .
-U . . . . . . . . . . .
2.5 to 500 kPa (10 to 2000 inH
2
0.0175 to 3.5 MPa (2.5 to 500 psi)
0.08 to 16 MPa (12 to 2300 psi)
Refer to “Wetted Parts Materials” Table 3.
without process connector (Rc1/4 female on the cover anges)
with Rc1/4 female process connector
with Rc1/2 female process connector
with 1/4 NPT female process connector
with 1/2 NPT female process connector
without process connector (1/4 NPT female on the cover anges)
ASTM-B7 carbon steel
316L SST stainless steel
ASTM grade 660 stainless steel
Vertical piping, right side high pressure, and process connection down side
Vertical piping, left side high pressure, and process connection down side
Horizontal piping and right side high pressure
Horizontal piping and left side high pressure
Bottom Process Connection, left side high pressure*
Universal ange*
2
Cast aluminum alloy with integral antenna
8 . . . . . . . . . .
9 . . . . . . . . . .
Cast aluminum alloy with detachable antenna (2 dBi)
Cast aluminum alloy without antenna (N connector)
cells not included)
304 SST 2-inch pipe mounting, at type (for horizontal piping)
D. . . . .
G. . . . .
K. . . . .
M . . . .
N. . . . .
304 SST 2-inch pipe mounting, L type (for vertical piping)
304 SST 2-inch pipe mounting (for bottom process connection type)
316 SST 2-inch pipe mounting, L type (for vertical piping)
316 SST 2-inch pipe mounting (for bottom process connection type)
None
/ Optional specication
Cover ange and
process connector
#
ASTM CF-8M *
Hastelloy C-276 *2 (Diaphragm)
1
1
1
1
Hastelloy C-276
equivalent *
3
Hastelloy C-276
equivalent *
3
4
Capsule Capsule gasket Drain/Vent plug
316L SST (Others)
Hastelloy C-276 *
2
Teon-coated 316L SST 316 SST
Monel PTFE Teon 316 SST
Tantalum PTFE Teon 316 SST
Hastelloy C-276 *
2
Tantalum PTFE Teon Hastelloy C-276 *
Monel PTFE Teon Monel
O)
2
*4
*3*4
PTFE Teon 316 SST
PTFE Teon Hastelloy C-276 *
2
2
IM 01C27B01-01EN
Page 99

<11. General Specications>
11.3 Optional Specications
OPTIONAL SPECIFICATIONS (For Explosion Protected type)
Item Description Code
Factory Mutual (FM) FM Intrinsically safe Approval FS17
ATEX ATEX Intrinsically safe Approval KS27
Canadian Standards Association (CSA) CSA Intrinsically safe Approval CS17
IECEx IECEx Intrinsically safe Approval SS27
11-8
IM 01C27B01-01EN
Page 100

<11. General Specications>
11-9
OPTIONAL SPECIFICATIONS
Item Description Code
Color change Amplier cover only
Painting
Coating
change
Anti-corrosion coating
*1
Degrease cleansing treatment K1
Oil-prohibited use
*2
Degrease cleansing treatment and with uorinated oillled capsule.
Operating temperature -20 to 80°C ( -4 to 176°F)
Degrease cleansing treatment and dehydrating treatment K5
Oil-prohibited use
with dehydrating treatment
Degrease cleansing treatment and dehydrating treatment with uorinated oillled
*2
capsule.
Operating temperature -20 to 80°C ( -4 to 176°F)
Capsule ll uid
Fluorinated oil lled in capsule
Operating temperature -20 to 80°C ( -4 to 176°F)
P calibration (psi unit)
Calibration units
Long vent
Gold-plated capsule gasket
Gold-plated diaphragm*
130 Pa abs calibration*
*3
*4
7
bar calibration (bar unit) D3
2
M calibration (kgf/cm
unit) D4
Total length: 119 mm (standard: 34 mm); Total length when combining with option
code K1, K2, K5, and K6: 130 mm. Material: 316 SST
*5
Gold-plated 316L SST capsule gasket. Without drain and vent plugs. GS
Inside of isolating diaphragms (ll uid side) are gold plated, effective for hydrogen
6
permeation.
Minimum input puressure at calibration testing: 130 Pa abs (1 mmHg abs) S1
(See Table for Span and Range Limits.)
Without drain and vent plugs. N1
Body option
*8
N1 and Process connection, based on IEC61518 with female thread on both sides
of cover ange, with blind kidney anges on back.
N2 and Material certicate for cover ange, diaphragm, capsule body, and blind
kidney ange.
European Pressure
Directive
Material certicate
*9
*10
Pressure test/
Leak test certicate
*1: Not applicable with color change option.
*2: Applicable for Wetted parts material code S, H, M, and T.
*3: The unit of MWP (Max. working pressure) on the name plate of the housing is the same unit as specied by Option code D1, D3,
and D4.
*4: Applicable for vertical impulse piping type (Installation code 7) and Wetted parts material code S, H, M, and T.
*5: Applicable for wetted parts material code S; process connection code 0 and 5; and installation code 8 and 9. Not applicable for
option code U1, N2, N3 and M11. No PTFE is used for wetted parts.
*6: Applicable for wetted parts material code S.
Overpressure effects for EJX110B M, H, and V capsules: ±0.06% of URL.
*7: Applicable only for EJX310B M and A capsules whose upper range value is set as smaller than 53.3 kPa abs.
*8: Applicable for Wetted parts material code S, H, M, and T; Process connection code 3, 4, and 5; Installation code 9; and Mounting
bracket code N. Process connection faces on the other side of zero adjustment screw.
*9: Applicable for M, H and V capsules of EJX110B with wetted parts material code S.
*10: Material traceability certication, per EN 10204 3.1B.
*11: Applicable for Process connections code 0 and 5.
*12: Applicable for Process connections code 1, 2, 3, and 4.
*13: Applicable for Capsule code L of EJX110B, Capsule code B of EJX430B and EJX310B, and all the capsules of EJX110B with
wetted parts maerial code H, M, T, A, D, and B.
*14: Applicable for Capsule code M, H, and V of EJX110B with wetted parts material code S.
*15: Applicable for Capsule code A of EJX430B and EJX310B.
*16: Applicable for Capsule code H of EJX430B.
*17: Applicable for Capsule code L and M of EJX310B.
*18: Pure nitrogen gas is used for oil-prohibited use (Option code K1, K2, K5, and K6).
PED 97/23/EC
Category III, Module H, Type of Equipment: Pressure Accessory-Vessel,
Type of Fluid: Liquid and Gas, Group of Fluid: 1 and 2.
Cover ange
Cover ange, Process connector
Test Pressure: 16 MPa (2300 psi)*
Test Pressure: 25 MPa (3600 psi)*
Test Pressure: 3.5 MPa (500 psi)*
Test Pressure: 500 kPa (2000 inH
Test Pressure: 50 kPa (200 inH
*11
O)*
2
*12
15
2
13
14
Nitrogen(N2) Gas
Retention time: one minute
16
O)*
17
*18
P
PE3
M01
M11
T12
T13
T01
T11
T04
X2
K2
K6
K3
D1
U1
A1
N2
N3
IM 01C27B01-01EN
 Loading...
Loading...