Page 1

Instruction
Manual
Model EJA438W and EJA438N
Diaphragm Sealed Gauge
Pressure Transmitters
[Style: S2]
IM 1C22J1-01E
Yokogawa Electric Corporation
IM 1C22J1-01E
10th Edition
Page 2

Blank Page
Page 3

CONTENTS
CONTENTS
1. INTRODUCTION ............................................................................................ 1-1
WARRANTY.................................................................................................. 1-2
2. HANDLING CAUTIONS ................................................................................ 2-1
2.1 Model and Specifications Check......................................................... 2-1
2.2 Unpacking ........................................................................................... 2-1
2.3 Storage................................................................................................ 2-1
2.4 Selecting the Installation Location ...................................................... 2-1
2.5 Pressure Connection........................................................................... 2-2
2.6 Waterproofing of Cable Conduit Connections .................................... 2-2
2.7 Restrictions on Use of Radio Transceiver .......................................... 2-2
2.8 Insulation Resistance and Dielectric Strength Test............................ 2-2
2.9 Installation of Explosion Protected Type ............................................ 2-3
2.9.1 FM Approval ................................................................................. 2-3
2.9.2 CSA Certification .......................................................................... 2-4
2.9.3 SAA Certification .......................................................................... 2-6
2.9.4 CENELEC (KEMA)/IEC (KEMA) Certification.............................. 2-7
2.9.5 JIS Certification ............................................................................ 2-8
2.10 EMC Conformity Standards ................................................................ 2-9
3. COMPONENT NAMES .................................................................................. 3-1
4. INSTALLATION.............................................................................................4-1
4.1 Precautions ......................................................................................... 4-1
4.2 Mounting the Diaphragm Seals .......................................................... 4-1
4.3 Transmitter Mounting .......................................................................... 4-1
4.4 Affixing the Teflon Film ....................................................................... 4-3
4.5 Rotating Transmitter Section .............................................................. 4-3
5. WIRING..........................................................................................................5-1
5.1 Wiring Precautions .............................................................................. 5-1
5.2 Selecting the Wiring Materials ............................................................ 5-1
5.3 Connections of External Wiring to Terminal Box................................ 5-1
5.3.1 Power Supply Wiring Connection ................................................ 5-1
5.3.2 External Indicator Connection ...................................................... 5-1
5.3.3 BRAIN TERMINAL BT200 Connection ........................................ 5-2
5.3.4 Check Meter Connection.............................................................. 5-2
5.4 Wiring .................................................................................................. 5-2
5.4.1 Loop Configuration ....................................................................... 5-2
(1) General-use Type and Flameproof Type ...................................... 5-2
(2) Intrinsically Safe Type................................................................... 5-2
5.4.2 Wiring Installation ......................................................................... 5-3
(1) General-use Type and Intrinsically Safe Type.............................. 5-3
(2) Flameproof Type (JIS).................................................................. 5-3
5.5 Grounding............................................................................................ 5-4
5.6 Power Supply Voltage and Load Resistance ..................................... 5-4
FD No. IM 1C22J1-01E
10th Edition: Feb. 2000(YK)
All Rights Reserved, Copyright © 1995, Yokogawa Electric Corporation
i
IM 1C22J1-01E
Page 4

CONTENTS
6. OPERATION..................................................................................................6-1
6.1 Preparation for Starting Operation...................................................... 6-1
6.2 Zero Point Adjustment ........................................................................ 6-2
6.2.1 When you can obtain Low Range Value from actual
measured value of 0% (0 kPa, atmospheric pressure); .............. 6-2
6.2.2 When you cannot obtain Low Range Value from actual
measured value of 0%; ................................................................ 6-3
6.3 Starting Operation ............................................................................... 6-3
6.4 Shutting Down Operation.................................................................... 6-3
6.5 Setting the Range Using the Range-setting Switch ........................... 6-4
7. BRAIN TERMINAL BT200 OPERATION ..................................................... 7-1
7.1 BT200 Operation Precautions............................................................. 7-1
7.1.1 Connecting the BT200 ................................................................. 7-1
7.1.2 Conditions of Communication Line .............................................. 7-1
7.2 BT200 Operating Procedures ............................................................. 7-1
7.2.1 Key Layout and Screen Display................................................... 7-1
7.2.2 Operating Key Functions.............................................................. 7-2
(1) Alphanumeric Keys and Shift Keys .............................................. 7-2
(2) Function Keys............................................................................... 7-2
7.2.3 Calling Up Menu Addresses Using the Operating Keys.............. 7-3
7.3 Setting Parameters Using the BT200 ................................................. 7-4
7.3.1 Parameter Summary .................................................................... 7-4
7.3.2 Parameter Usage and Selection .................................................. 7-6
7.3.3 Setting Parameters ....................................................................... 7-7
(1) Tag No. Setup ............................................................................... 7-7
(2) Calibration Range Setup .............................................................. 7-7
(3) Damping Time Constant Setup..................................................... 7-8
(4) Output Signal Low Cut Mode Setup ............................................. 7-9
(5) Integral Indicator Scale Setup ...................................................... 7-9
(6) Unit Setup for Displayed Temperature........................................ 7-11
(7) Operation Mode Setup ............................................................... 7-11
(8) Output Status Display/Setup when a CPU Failure ..................... 7-11
(9) Output Status Setup when a Hardware Error Occurs................. 7-11
(10)Range Change while Applying Actual Inputs.............................. 7-12
(11)Zero Point Adjustment ................................................................ 7-12
(12)Test Output Setup....................................................................... 7-14
(13)User Memo Fields ...................................................................... 7-14
7.4 Displaying Data Using the BT200..................................................... 7-14
7.4.1 Displaying Measured Data ......................................................... 7-14
7.4.2 Display Transmitter Model and Specifications........................... 7-14
7.5 Self-Diagnostics ................................................................................ 7-15
7.5.1 Checking for Problems............................................................... 7-15
(1) Identifying Problems with BT200................................................ 7-15
(2) Checking with Integral Indicator ................................................. 7-16
7.5.2 Errors and Countermeasures..................................................... 7-17
8. MAINTENANCE ............................................................................................. 8-1
8.1 Overview ............................................................................................. 8-1
8.2 Calibration Instruments Selection ....................................................... 8-1
8.3 Calibration ........................................................................................... 8-1
ii
IM 1C22J1-01E
Page 5

CONTENTS
8.4 Disassembly and Reassembly............................................................ 8-3
8.4.1 Replacing the Integral Indicator ................................................... 8-3
8.4.2 Replacing the CPU Assembly...................................................... 8-4
8.5 Troubleshooting................................................................................... 8-5
8.5.1 Basic Troubleshooting.................................................................. 8-5
8.5.2 Troubleshooting Flow Charts ....................................................... 8-5
9. GENERAL SPECIFICATIONS ...................................................................... 9-1
9.1 Standard Specifications ...................................................................... 9-1
9.2 Model and Suffix Codes...................................................................... 9-3
9.3 Optional Specifications........................................................................ 9-5
9.4 Dimensions.......................................................................................... 9-7
INSTALLATION AND OPERATING PRECAUTIONS FOR
JIS INTRINSICALLY SAFE EQUIPMENT.......................................... EX-A03E
INSTALLATION AND OPERATING PRECAUTIONS FOR
JIS FLAMEPROOF EQUIPMENT....................................................... EX-B03E
Customer Maintenance Parts List
DPharp EJA Series Transmitter Section ............................ CMPL 1C22A1-02E
Models EJA438W and EJA438N Diaphragm Sealed
REVISION RECORD
Gauge Pressure Transmitter..................................... CMPL 1C22J3-01E
iii
IM 1C22J1-01E
Page 6

Blank Page
Page 7

1. INTRODUCTION
NOTE
1. INTRODUCTION
Thank you for purchasing the DPharp electronic
pressure transmitter.
The DPharp Pressure Transmitters are precisely
calibrated at the factory before shipment. To ensure
correct and efficient use of the instrument, please read
this manual thoroughly and fully understand how to
operate the instrument before operating it.
j Regarding This Manual
• This manual should be passed on to the end user.
• The contents of this manual are subject to change
without prior notice.
• All rights reserved. No part of this manual may be
reproduced in any form without Yokogawa’s written
permission.
• Yokogawa makes no warranty of any kind with
regard to this manual, including, but not limited to,
implied warranty of merchantability and fitness for a
particular purpose.
• If any question arises or errors are found, or if any
information is missing from this manual, please
inform the nearest Yokogawa sales office.
• The specifications covered by this manual are
limited to those for the standard type under the
specified model number break-down and do not
cover custom-made instruments.
• Please note that changes in the specifications,
construction, or component parts of the instrument
may not immediately be reflected in this manual at
the time of change, provided that postponement of
revisions will not cause difficulty to the user from a
functional or performance standpoint.
j Safety Precautions
• For the protection and safety of the operator and the
instrument or the system including the instrument,
please be sure to follow the instructions on safety
described in this manual when handling this instrument. In case the instrument is handled in contradiction to these instructions, Yokogawa does not
guarantee safety.
• For the intrinsically safe equipment and
explosionproof equipment, in case the instrument is
not restored to its original condition after any repair
or modification undertaken by the customer,
intrinsically safe construction or explosionproof
construction is damaged and may cause dangerous
condition. Please contact Yokogawa for any repair
or modification required to the instrument.
• The following safety symbol marks are used in this
Manual:
WARNING
Indicates a potentially hazardous situation which,
if not avoided,
injury.
CAUTION
Indicates a potentially hazardous situation which,
if not avoided, may result in minor or moderate
injury. It may also be used to alert against
unsafe practices
could
result in death or serious
.
NOTE
For FOUNDATION Fieldbus and HART protocol
versions, please refer to IM 1C22T2-01E and IM
1C22T1-01E respectively, in addition to this IM.
IMPORTANT
Indicates that operating the hardware or software
in this manner may damage it or lead to system
failure.
Draws attention to information essential for
understanding the operation and features.
1-1
IM 1C22J1-01E
Page 8

1. INTRODUCTION
WARRANTY
• The warranty shall cover the period noted on the
quotation presented to the purchaser at the time of
purchase. Problems occurred during the warranty
period shall basically be repaired free of charge.
• In case of problems, the customer should contact the
Yokogawa representative from which the instrument
was purchased, or the nearest Yokogawa office.
• If a problem arises with this instrument, please
inform us of the nature of the problem and the
circumstances under which it developed, including
the model specification and serial number. Any
diagrams, data and other information you can
include in your communication will also be helpful.
• Responsible party for repair cost for the problems
shall be determined by Yokogawa based on our
investigation.
• The Purchaser shall bear the responsibility for repair
costs, even during the warranty period, if the
malfunction is due to:
- Improper and/or inadequate maintenance by the
purchaser.
- Failure or damage due to improper handling, use or
storage which is out of design conditions.
- Use of the product in question in a location not
conforming to the standards specified by
Yokogawa, or due to improper maintenance of the
installation location.
- Failure or damage due to modification or repair by
any party except Yokogawa or an approved
representative of Yokogawa.
- Malfunction or damage from improper relocation
of the product in question after delivery.
- Reason of force majeure such as fires, earthquakes,
storms/floods, thunder/lightening, or other natural
disasters, or disturbances, riots, warfare, or
radioactive contamination.
WARNING
• Instrument installed in the process is under
pressure. Never loosen or tighten the flange
bolts as it may cause dangerous spouting of
process fluid.
• Since the accumulated process fluid may be
toxic or otherwise harmful, take appropriate
care to avoid contact with the body, or inhalation of vapors even after dismounting the
instrument from the process line for maintenance.
CAUTION
This instrument is tested and certified as intrinsically safe type or explosionproof type. Please
note that the construction of the instrument,
installation, external wiring, maintenance or
repair is strictly restricted, and non-observance
or negligence of this restriction would result in
dangerous condition.
1-2
IM 1C22J1-01E
Page 9
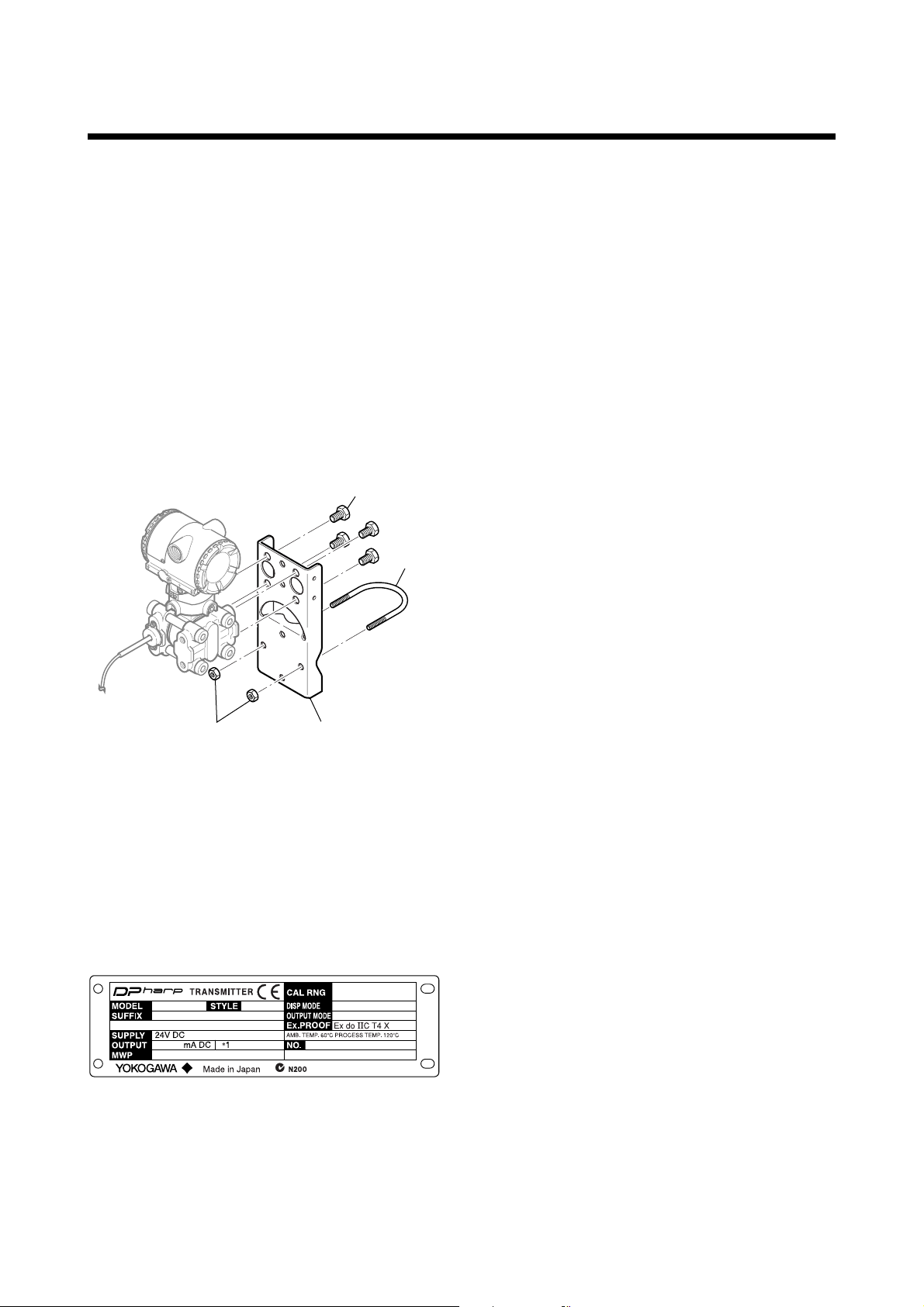
2. HANDLING CAUTIONS
2. HANDLING CAUTIONS
This chapter describes important cautions regarding
how to handle the transmitter. Read carefully before
using the transmitter.
The EJA Series pressure transmitters are thoroughly
tested at the factory before shipment. When the
transmitter is delivered, visually check them to make
sure that no damage occurred during shipment.
Also check that all transmitter mounting hardware
shown in Figure 2.1 is included. If the transmitter was
ordered without the mounting bracket, the transmitter
mounting hardware is not included. After checking the
transmitter, repack it in the way it was delivered until
installation.
Transmitter
mounting bolt
U-bolt
2.2 Unpacking
When moving the transmitter to the installation site,
keep it in its original packaging. Then, unpack the
transmitter there to avoid damage on the way.
2.3 Storage
The following precautions must be observed when
storing the instrument, especially for a long period.
(a) Select a storage area which meets the following
conditions:
• It is not exposed to rain or water.
• It suffers minimum vibration and shock.
• It has an ambient temperature and relative
humidity within the following ranges.
Ambient temperature:
–40 to 85°C without integral indicator
–30 to 80°C with integral indicator
Relative humidity:
5% to 100% R.H. (at 40°C)
Preferred temperature and humidity:
approx. 25°C and 65% R.H.
U-bolt nut
Figure 2.1 Transmitter Mounting Hardware
Mounting bracket
F0201.EPS
2.1 Model and Specifications Check
The model name and specifications are indicated on the
name plate attached to the case. If the reverse operating mode was ordered (reverse signal), ‘REVERSE’
will be inscribed in field *1.
Figure 2.2 Name Plate Example of JIS Flameproof Type
(b) When storing the transmitter, repack it as nearly
as possible to the way it was packed when
delivered from the factory.
(c) If storing a transmitter that has been used,
thoroughly clean the diaphragm surface of the
diaphragm seal (pressure-detector section), so that
no measured fluid remains on them. Also make
sure before storing that the pressure-detector and
transmitter assemblies are securely mounted.
2.4 Selecting the Installation Location
The transmitter is designed to withstand severe
environmental conditions. However, to ensure stable
and accurate operation for years, observe the following precautions when selecting an installation location.
(a) Ambient Temperature
Avoid locations subject to wide temperature
variations or a significant temperature gradient. If
the location is exposed to radiant heat from plant
equipments, provide adequate thermal insulation
and/or ventilation.
2-1
IM 1C22J1-01E
Page 10
2. HANDLING CAUTIONS
(b) Ambient Atmosphere
Avoid installing the transmitter in a corrosive
atmosphere. If the transmitter must be installed in a
corrosive atmosphere, there must be adequate
ventilation as well as measures to prevent intrusion
or stagnation of rain water in conduits.
(c) Shock and Vibration
Select an installation site suffering minimum shock
and vibration (although the transmitter is designed
to be relatively resistant to shock and vibration).
(d) Installation of Explosion-protected Transmitters
Explosion-protected transmitters can be installed in
hazardous areas according to the types of gases for
which they are certified. See Subsection 2.9
“Installation of Explosion Protected Type Transmitters.”
2.5 Pressure Connection
WARNING
• Instrument installed in the process is under
pressure. Never loosen or tighten the flange
bolts to avoid the dangerous spouting of
process fluid.
• Since the accumulated process fluid may be
toxic or otherwise harmful, take appropriate
care to avoid contact with the skin, eyes or
body, or inhalation of vapors even after dismounting the instrument from process line for
maintenance.
The following precautions must be observed in order to
safely operate the transmitter under pressure.
(a) Never apply a pressure higher than the specified
maximum working pressure.
(b) Never loosen or tighten the bolts securing the
diaphragm seal flanges when the assembly is under
pressure. Do it after releasing the process pressure
if required.
2.6 Waterproofing of Cable Conduit Connections
Apply a non-hardening sealant to the threads to
waterproof the transmitter cable conduit connections.
(See Figure 5.4.2a, 5.4.2b and 5.4.2d.)
2.7 Restrictions on Use of Radio Transceiver
IMPORTANT
Although the transmitter has been designed to
resist high frequency electrical noise, if a radio
transceiver is used near the transmitter or its
external wiring, the transmitter may be affected
by high frequency noise pickup. To test for such
effects, bring the transceiver in use slowly from a
distance of several meters from the transmitter,
and observe the measurement loop for noise
effects. Thereafter, always use the transceiver
outside the area affected by noise.
2.8 Insulation Resistance and Dielectric Strength Test
Since the transmitter has undergone insulation resistance and dielectric strength tests at the factory before
shipment, normally these tests are not required.
However, if required, observe the following precautions in the test procedures.
(a) Do not perform such tests more frequently than is
absolutely necessary. Even test voltages that do not
cause visible damage to the insulation may degrade
the insulation and reduce safety margins.
(b) Never apply a voltage exceeding 500 V DC (100 V
DC with an internal lightning protector) for the
insulation resistance test, nor a voltage exceeding
500 V AC (100 V AC with an internal lightning
protector) for the dielectric strength test.
(c) Before conducting these tests, disconnect all signal
lines from the transmitter terminals. Perform the
tests in the following procedure:
• Insulation Resistance Test
1) Short-circuit the + and – SUPPLY terminals in the
terminal box.
2) Turn OFF the insulation tester. Then connect the
insulation tester plus (+) lead wire to the shorted
SUPPLY terminals and the minus (–) leadwire to
the grounding terminal.
3) Turn ON the insulation tester power and measure
the insulation resistance. The voltage should be
applied short as possible to verify that the insulation resistance is at least 20 MΩ.
2-2
IM 1C22J1-01E
Page 11

2. HANDLING CAUTIONS
4) After completing the test and being very careful not
to touch exposed conductors disconnect the
insulation tester and connect a 100 kΩ resistor
between the grounding terminal and the shortcircuiting SUPPLY terminals. Leave this resistor
connected at least one second to discharge any
static potential. Do not touch the terminals while it
is discharging.
• Dielectric Strength Test
1) Short-circuit the + and – SUPPLY terminals in the
terminal box.
2) Turn OFF the dielectric strength tester. Then
connect the tester between the shorted SUPPLY
terminals and the grounding terminal. Be sure to
connect the grounding lead of the dielectric strength
tester to the ground terminal.
3) Set the current limit on the dielectric strength tester
to 10 mA, then turn ON the power and gradually
increase the test voltage from ‘0’ to the specified
voltage.
4) When the specified voltage is reached, hold it for
one minute.
5) After completing this test, slowly decrease the
voltage to avoid any voltage surges.
2.9 Installation of Explosion
Protected Type
NOTE
For FOUNDATION Fieldbus explosion protected
type, please refer to IM 1C22T2-01E.
WARNING
To pressure the safety of explosionproof equipment requires great care during mounting,
wiring, and piping. Safety requirements also
place restrictions on maintenance and repair
activities. Please read the following sections very
carefully.
2.9.1 FM Approval
a. FM Intrinsically Safe Type
Caution for FM intrinsically safe type. (Following
contents refer “DOC. No. IFM012-A12 P.1 and 2.”)
Note 1. Model EJA Series pressure transmitters
with optional code /FS1 are applicable for
use in hazardous locations.
• Intrinsically Safe for Class I, Division 1, Groups A,
B, C & D. Class II, Division 1, Groups E, F & G
and Class III, Division 1 Hazardous Locations.
• Nonincendive for Class I, Division 2, Groups A, B,
C & D. Class II, Division 2, Groups E, F & G and
Class III, Division 1 Hazardous Locations.
• Outdoor hazardous locations, NEMA 4X.
• Temperature Class: T4
• Ambient temperature: –40 to 60°C
Note 2. Entity Parameters
• Intrinsically Safe Apparatus Parameters
[Groups A, B, C, D, E, F and G]
Vmax = 30 V Ci = 22.5 nF
Imax = 165 mA Li = 730 µH
Pmax = 0.9 W
* Associated Apparatus Parameters
(FM approved barriers)
Voc ≤ 30 V Ca > 22.5 nF
Isc ≤ 165 mA La > 730 µH
Pmax ≤ 0.9W
• Intrinsically Safe Apparatus Parameters
[Groups C, D, E, F and G]
Vmax = 30 V Ci = 22.5 nF
Imax = 225 mA Li = 730 µH
Pmax = 0.9 W
* Associated Apparatus Parameters
(FM approved barriers)
Voc ≤ 30 V Ca > 22.5 nF
Isc ≤ 225 mA La > 730 µH
Pmax ≤ 0.9 W
• Entity Installation Requirements
Vmax ≥ Voc or Vt, Imax ≥ Isc or It,
Pmax (IS Apparatus) ≥ Pmax (Barrier)
Ca ≥ Ci + Ccable, La ≥ Li + Lcable
Note 3. Installation
• Barrier must be installed in an enclosure that meets
the requirements of ANSI/ISA S82.01.
• Control equipment connected to barrier must not
use or generate more than 250 V rms or V dc.
• Installation should be in accordance with ANSI/
ISA RP12.6 “Installation of Intrinsically Safe
Systems for Hazardous (Classified) Locations” and
the National Electric Code (ANSI/NFPA 70).
• The configuration of associated apparatus must be
FMRC Approved.
2-3
IM 1C22J1-01E
Page 12
2. HANDLING CAUTIONS
• Dust-tight conduit seal must be used when installed
in a Class II, III, Group E, F and G environments.
• Associated apparatus manufacturer’s installation
drawing must be followed when installing this
apparatus.
• The maximum power delivered from the barrier
must not exceed 0.9 W.
• Note a warning label worded “SUBSTITUTION OF
COMPONENTS MAY IMPAIR INTRINSIC
SAFETY,” and “INSTALL IN ACCORDANCE
WITH DOC. No. IFM012-A12 P.1 and 2.”
Note 4. Maintenance and Repair
• The instrument modification or parts replacement by
other than authorized representative of Yokogawa
Electric Corporation is prohibited and will void
Factory Mutual Intrinsically safe and Nonincendive
Approval.
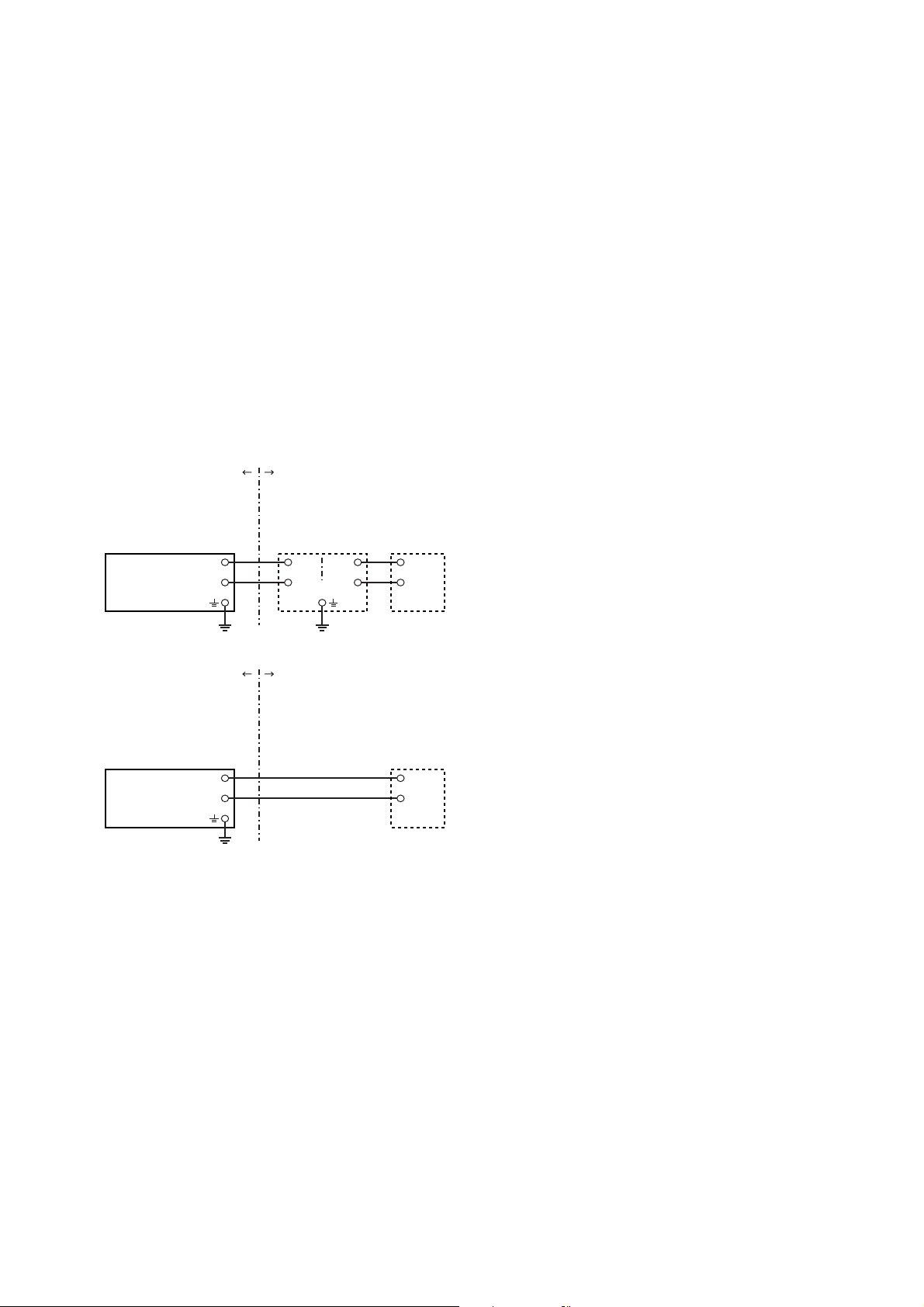
[Intrinsically Safe]
Hazardous Location Nonhazardous Location
Class I, II, III, Division 1,
Groups A, B, C, D, E, F, G
EJA Series Pressure
Transmitters
+
Supply
Hazardous Location Nonhazardous Location
Class I, II, Division 2,
Groups A, B, C, D, E, F, G
Class III, Division 1.
EJA Series Pressure
Transmitters
Supply
–
[Nonincendive]
+
–
Safety Barrier
+
–
Not Use
Safety Barrier
+
–
General
Purpose
Equipment
+
–
General
Purpose
Equipment
+
–
F0203.EPS
b. FM Explosionproof Type
Caution for FM explosionproof type.
Note 1. Model EJA Series differential, gauge, and
absolute pressure transmitters with
optional code /FF1 are applicable for use
in hazardous locations.
• Explosionproof for Class I, Division 1, Groups B, C
and D.
• Dust-ignitionproof for Class II/III, Division 1,
Groups E, F and G.
• Outdoor hazardous locations, NEMA 4X.
• Temperature Class: T6
• Ambient Temperature: –40 to 60°C
• Supply Voltage: 42 V dc max.
• Output signal: 4 to 20 mA
Note 2. Wiring
• All wiring shall comply with National Electrical
Code ANSI/NEPA70 and Local Electrical Codes.
• When installed in Division 1, “FACTORY
SEALED, CONDUIT SEAL NOT REQUIRED.”
Note 3. Operation
• Keep the “CAUTION” nameplate attached to the
transmitter.
CAUTION: OPEN CIRCUIT BEFORE REMOVING COVER. SEAL ALL CONDUITS WITHIN
18 INCHES. WHEN INSTALLED IN DIV.1,
“FACTORY SEALED, CONDUIT SEAL NOT
REQUIRED.” INSTALL IN ACCORDANCE
WITH THE INSTRUCTION MANUAL IM 1C22.
• Take care not to generate mechanical sparking
when accessing to the instrument and peripheral
devices in a hazardous location.
Note 4. Maintenance and Repair
• The instrument modification or parts replacement
by other than authorized representative of
Yokogawa Electric Corporation is prohibited and
will void Factory Mutual Explosionproof Approval.
c. FM Intrinsically Safe Type/FM
Explosionproof Type
Model EJA Series pressure transmitters with
optional code /FU1 can be selected the type
of protection (FM Intrinsically Safe or FM
Explosionproof) for use in hazardous locations.
Note 1. For the installation of this transmitter,
once a particular type of protection is
selected, any other type of protection
cannot be used. The installation must
be in accordance with the description
about the type of protection in this
instruction manual.
Note 2. In order to avoid confusion, unnecessary
marking is crossed out on the label
other than the selected type of protection when the transmitter is installed.
2.9.2 CSA Certification
a. CSA Intrinsically Safe Type
Caution for CSA Intrinsically safe type. (Following contents refer to “DOC No. ICS003-A12 P.1-1
and P.1-2.”)
Note 1. Model EJA Series differential, gauge,
and absolute pressure transmitters with
optional code /CS1 are applicable for
use in hazardous locations
2-4
IM 1C22J1-01E
Page 13
2. HANDLING CAUTIONS
• Intrinsically Safe for Class I, Division 1, Groups A,
B, C & D. Class II, Division 1, Groups E, F & G
and Class III, Division 1 Hazardous Locations.
• Nonincendive for Class I, Division 2, Groups A, B,
C & D, Class II, Division 2, Groups F & G, and
Class III, Hazardous Locations. (not use Safety
Barrier)
• Encl. “Type 4X”
• Temperature Class: T4
• Ambient temperature: –40 to 60°C
• Process Temperature: 120°C max.
Note 2. Entity Parameters
• Intrinsically safe ratings are as follows:
Maximum Input Voltage (Vmax) = 30 V
Maximum Input Current (Imax) = 165 mA
Maximum Input Power (Pmax) = 0.9 W
Maximum Internal Capacitance (Ci) = 22.5 nF
Maximum Internal Inductance (Li) = 730 µH
* Associated apparatus (CSA certified barriers)
Maximum output voltage (Voc) ≤ 30 V
Maximum output current (Isc) ≤ 165 mA
Maximum output power (Pmax) ≤ 0.9 W
Note 3. Installation
• All wiring shall comply with Canadian Electrical
Code Part I and Local Electrical Codes.
• The instrument modification or parts replacement
by other than authorized representative of
Yokogawa Electric Corporation and Yokogawa
Corporation of America is prohibited and will void
Canadian Standards Intrinsically safe and
nonincendive Certification.
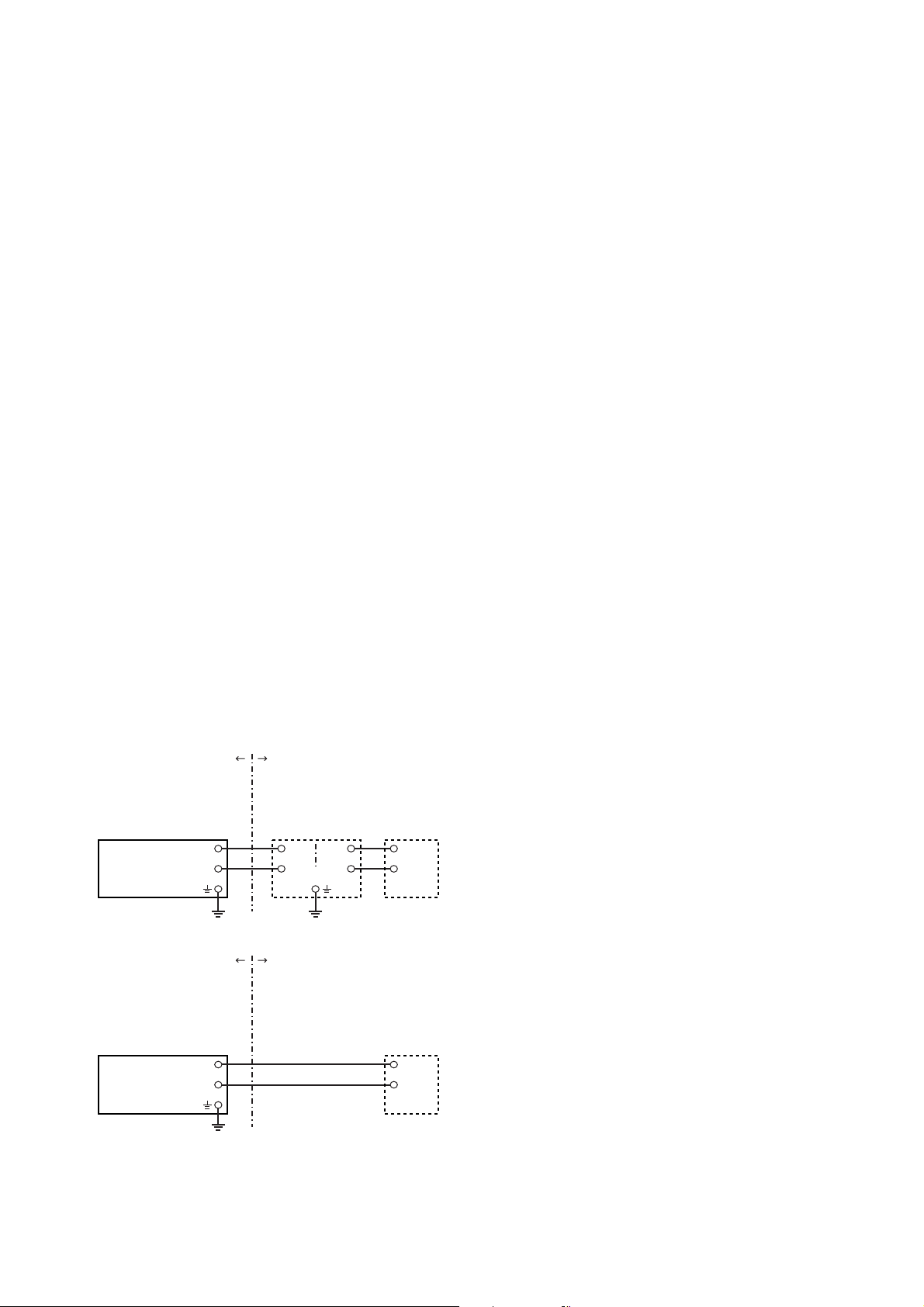
[Intrinsically Safe]
Hazardous Location Nonhazardous Location
Class I, II, III, Division 1,
Groups A, B, C, D, E, F, G
EJA Series Pressure
Transmitters
+
Supply
Hazardous Location Nonhazardous Location
Class I, II, Division 2,
Groups A, B, C, D, E, F, G
Class III
EJA Series Pressure
Transmitters
Supply
–
[Nonincendive]
+
–
Safety Barrier
+
+
–
–
Not Use
Safety Barrier
General
Purpose
Equipment
General
Purpose
Equipment
+
–
+
–
F0204.EPS
b. CSA Explosionproof Type
Caution for CSA explosionproof type.
Note 1. Model EJA Series differential, gauge, and
absolute pressure transmitters with
optional code /CF1 are applicable for use
in hazardous locations:
• Explosionproof for Class I, Division 1, Groups B,
C and D.
• Dust-ignitionproof for Class II/III, Division 1,
Groups E, F and G.
• Encl “Type 4X”
• Temperature Class: T6, T5, and T4
• Process Temperature: 85°C (T6), 100°C (T5), and
120°C (T4)
• Ambient Temperature: –40 to 80°C
• Supply Voltage: 42 V dc max.
• Output Signal: 4 to 20 mA
Note 2. Wiring
• All wiring shall comply with Canadian Electrical
Code Part I and Local Electrical Codes.
• In hazardous location, wiring shall be in conduit as
shown in the figure.
CAUTION: SEAL ALL CONDUITS
WITHIN 50 cm OF THE ENCLOSURE.
UN SCELLEMENT DOIT ÊTRE
INSTALLÉ À MOINS DE 50 cm DU
BÎTIER.
• When installed in Division 2, “SEALS NOT
REQUIRED.”
Note 3. Operation
• Keep the “CAUTION” label attached to the
transmitter.
CAUTION: OPEN CIRCUIT BEFORE
REMOVING COVER.
OUVRIR LE CIRCUIT AVANT
D´NLEVER LE COUVERCLE.
• Take care not to generate mechanical sparking
when accessing to the instrument and peripheral
devices in a hazardous location.
Note 4. Maintenance and Repair
• The instrument modification or parts replacement
by other than authorized representative of
Yokogawa Electric Corporation and Yokogawa
Corporation of America is prohibited and will void
Canadian Standards Explosionproof Certification.
2-5
IM 1C22J1-01E
Page 14

2. HANDLING CAUTIONS
Non-Hazardous
Locations
Non-hazardous
Location
Equipment
42 V DC Max.
4 to 20 mA DC
Signal
Non-Hazardous
Locations
Non-hazardous
Location
Equipment
42 V DC Max.
4 to 20 mA DC
Signal
Hazardous Locations Division 1
50 cm Max.
Sealing Fitting
Hazardous Locations Division 2
Sealing Fitting
Conduit
EJA Series
EJA Series
F0205.EPS
c. CSA Intrinsically Safe Type/CSA
Explosionproof Type
Model EJA Series pressure transmitters with
optional code /CU1 can be selected the type of
protection (CSA Intrinsically Safe or CSA
Explosionproof) for use in hazardous locations.
Note 1. For the installation of this transmitter,
once a particular type of protection is
selected, any other type of protection
cannot be used. The installation must be
in accordance with the description about
the type of protection in this instruction
manual.
Note 2. In order to avoid confusion, unnecessary
marking is crossed out on the label other
than the selected type of protection when
the transmitter is installed.
Note 2. Entity Parameters
• Intrinsically safe rating of the transmitters are as
follows.
Maximum Input Voltage (Ui) = 30 V
Maximum Input Current (Ii) = 165 mA
Maximum Input Power (Pi) = 0.9 W
Maximum Internal Capacitance (Ci) = 0.02 µF
Maximum Internal Inductance (Li) = 0.73 mH
Note 3. Wiring
• All Wiring shall comply with the Australian
Standard.
Note 4. Maintenance and Repair
• The instrument modification or parts replacement
by other than authorized representative of
Yokogawa Electric Corporation is prohibited and
will void Standards Association of Australia
Intrinsically safe and Type n Certification.
[Intrinsic Safety]
Hazardous Location Nonhazardous Location
(Zone 0)
EJA Series
Pressure
Transmitter
*1: Any safety barriers used for the output current must be
limited by a resistor “R” such that Imaxout-Uz/R.
Hazardous Location
EJA Series
Pressure
Transmitter
+
–
[Type n]
(Zone 2)
+
–
+
Safety Barrier
–
+
Power Supply
–
*1
F0206.EPS
*2
2.9.3 SAA Certification
a. SAA Intrinsically Safe Type
Caution for SAA Intrinsically safe type and Type n.
Note 1. Model EJA Series differential, gauge, and
absolute pressure transmitters with
optional code /SU1 are applicable for use
in hazardous locations.
• Type of Protection and Marking Code:
Ex ia IIC T4 (Tamb = 60°C) IP67 Class I Zone 0
• Type of Protection and Marking Code:
Ex n IIC T4 (Tamb = 60°C) IP67 Class I Zone 2
• Ambient Temperature: –40 to 60°C
*2: The voltage of the power supply is not exceed 30V dc.
b. SAA Flameproof Type
Caution for SAA flameproof type.
Note 1. Model EJA Series differential, gauge, and
absolute pressure transmitters with
optional code /SU1 are applicable for use
in hazardous locations:
• Type of Protection and marking Code:
Ex d II C T* IP67 Class I Zone 1 (T* see schedule)
• Temperature Class: T6, T5, and T4
• Process Temperature:
85°C (T6), 100°C (T5), and 120°C (T4)
2-6
IM 1C22J1-01E
F0207.EPS
Page 15

2. HANDLING CAUTIONS
• Supply voltage: 42 V dc max.
• Output Signal: 4 to 20 mA
• Ambient Temperature: –40 to 80°C
Note 2. Wiring
• All wiring shall comply with the Australian
Standard.
Note 3. Operation
• Keep the “CAUTION” label attached to the
transmitter.
CAUTION: AMBIENT TEMPERATURE
ABOVE 75 DEG C SELECT SUITABLE
CABLE. DISCONNECT POWER AND
WAIT 1 MINUTE BEFORE REMAKING
COVER.
• Take care not to generate mechanical sparking
when accessing to the instrument and peripheral
devices in a hazardous location.
Note 4. Maintenance and Repair
• The instrument modification or parts replacement
by other than authorized representative of
Yokogawa Electric Corporation is prohibited and
will void Standards Association of Australia
Flameproof Certification.
2.9.4 CENELEC (KEMA)/IEC (KEMA) Certification
a. CENELEC (KEMA) Intrinsically Safe Type
Caution for CENELEC (KEMA) intrinsically safe
type.
Note 1. Model EJA Series differential, gauge, and
absolute pressure transmitters with
optional code /KS1 for potentially explosive atmospheres:
• Type of Protection and Marking code:
EEx ia IIC T4
• Temperature Class: T4
• Process Temperature: 120°C max.
• Ambient Temperature: –40 to 60°C
Note 2. Electrical Data
• In type of explosion protection intrinsic safety EEx
ia IIC only for connection to a certified intrinsically
safe circuit with following maximum values:
Ui = 30 V
Ii = 165 mA
Pi = 0.9 W
Effective internal capacitance; Ci = 22.5 nF
Effective internal inductance; Li = 730 µH
Note 3. Installation
• All wiring shall comply with local installation
requirements. (Refer to the installation diagram)
Note 4. Maintenance and Repair
• The instrument modification or parts replacement
by other than authorized representative of
Yokogawa Electric Corporation is prohibited and
will void KEMA Intrinsically safe Certification.
[Installation Diagram]
Hazardous Location
Transmitter
+
Supply
–
*1: In any safety barriers used the output current must be limited
by a resistor “R” such that Imaxout-Uz/R.
Nonhazardous Location
+
Safety Barrier
–
F0208.EPS
*1
b. CENELEC (KEMA) Flameproof Type
Caution for CENELEC (KEMA) flameproof type.
Note 1. Model EJA Series differential, gauge, and
absolute pressure transmitters with
optional code /KF1 for potentially explosive atmospheres:
• Type of Protection and Marking Code: EEx d IIC
T6···T4
• Temperature Class: T6, T5, and T4
• Maximum Process Temperature:
85°C (T6), 100°C (T5), and 120°C
• Ambient Temperature: –40 to 80°C
Note 2. Electrical Data
• Supply voltage: 42 V dc max.
• Output signal: 4 to 20 mA
Note 3. Installation
• All wiring shall comply with local installation
requirement.
• The cable entry devices shall be of a certified
flameproof type, suitable for the conditions of use.
Note 4. Operation
• Keep the “CAUTION” label to the transmitter.
CAUTION: WAIT 1 MIN. AFTER
POWER-DISCONNECTION, BEFORE
OPENING THE ENCLOSURE.
• Take care not to generate mechanical sparking
when accessing to the instrument and peripheral
devices in a hazardous location.
Note 5. Maintenance and Repair
• The instrument modification or parts replacement
by other than authorized representative of
Yokogawa Electric Corporation is prohibited and
will void KEMA Flameproof Certification.
2-7
IM 1C22J1-01E
Page 16
2. HANDLING CAUTIONS
c. IEC (KEMA) Type of Protection “n”
Caution for IEC (KEMA) Type of Protection “n.”
Note 1. Model EJA Series pressure transmitters
with optional code /KU1 for potentially
explosive atmospheres.
• Type of Protection and Marking Code:
Ex nA IIC T4
• Temperature Class: T4
• Process Temperature: 120°C max.
• Ambient Temperature: –40 to 60°C
Note 2. Electrical Data
• Supply and output circuit ≤ 30 V dc, 165 mA
(terminals + and –)
Note 3. Installation
• All wiring shall comply with local installation
requirements. (refer to the installation diagram)
Note 4. Maintenance and Repair
• The instrument modification or parts replacement
by other than authorized representative of
Yokogawa Electric Corporation is prohibited and
will void KEMA Type of Protection “n” Certification.
[Installation Diagram]
Hazardous Location
(Zone 2 only)
Transmitter
+
Supply
–
Nonhazardous Location
+
Power Supply
–
Note 2. In order to avoid confusion, unnecessary
marking is crossed out on the label other
than the selected type of protection when
the transmitter is installed.
2.9.5 JIS Certification
JIS Flameproof and Intrinsically Safe Type
The model EJA Series pressure transmitters with
optional code /JF1 and /JS1, which have obtained
certification according to technical criteria for explosion-protected construction of electric machinery and
equipment(Standards Notification No. 556 from the
Japanese Ministry of Labor) conforming to IEC
standards, are designed for hazardous areas where
explosive gases and/or inflammable vapors may be
present. [JIS Flameproof Type(optional code /JF1)
allows installation in Division 1 and 2 areas, and JIS
Intrinsically Safe Type(optional code /JS1) allows
installation in Division 0, 1, and 2 areas.]
To observe the safety of flameproof equipment requires
great care during mounting, wiring, and piping. Safety
requirements also place restrictions on maintenance
and repair activities. Users absolutely must read
“Installation and Operating Precautions for JIS Intrinsically Safe Equipment and Flameproof Equipment” at
the end of this manual.
CAUTION
(For JIS flameproof type without integral indicator)
F0209.EPS
Ratings of the Power Supply as follows;
Maximum Voltage: 30 V
Maximum Current: 165 mA
d. CENELEC (KEMA) Intrinsically Safe Type/
CENELEC (KEMA) Flameproof Type/IEC
(KEMA) Type of Protection “n”
Model EJA Series pressure transmitters with
optional code /KU1 can be selected the type of
protection (CENELEC (KEMA) Intrinsically
Safe or CENELEC (KEMA) Flameproof or IEC
(KEMA) Type of Protection “n”) for use in
hazardous locations.
Note 1. For the installation of this transmitter,
once a particular type of protection is
selected, any other type of protection
cannot be used. The installation must be
in accordance with the description about
the type of protection in this instruction
manual.
When the fill fluid near the sensor part moves
from within, the instrument outputs a failure
signal either high or low of the specific signal. In
that case, generate the alarm to identify that the
failure signal is output since the event may
invalidate the flameproof approval.
If the optional integral indicator is equipped, the
indicator identifies the alarm on its display.
Therefore, no other alarm generation is necessary.
Hazardous Location Nonhazardous Location
4 to 20 mA DC 1 to 5 V DC
Transmitter
Figure 2.3 Example of using DCS (Distributed Control
System)
Power
Supply
DCS
Display
F0210.EPS
2-8
IM 1C22J1-01E
Page 17

2.10 EMC Conformity Standards
For EMI (Emission): EN55011, AS/NZS 2064 1/2
For EMS (Immunity): EN50082–2
NOTE
YOKOGAWA recommends customer to apply
the Metal Conduit Wiring or to use the twisted
pair Shield Cable for signal wiring to conform the
requirement of EMC Regulation, when customer
installs the EJA Series Transmitters to the plant.
2. HANDLING CAUTIONS
2-9
IM 1C22J1-01E
Page 18
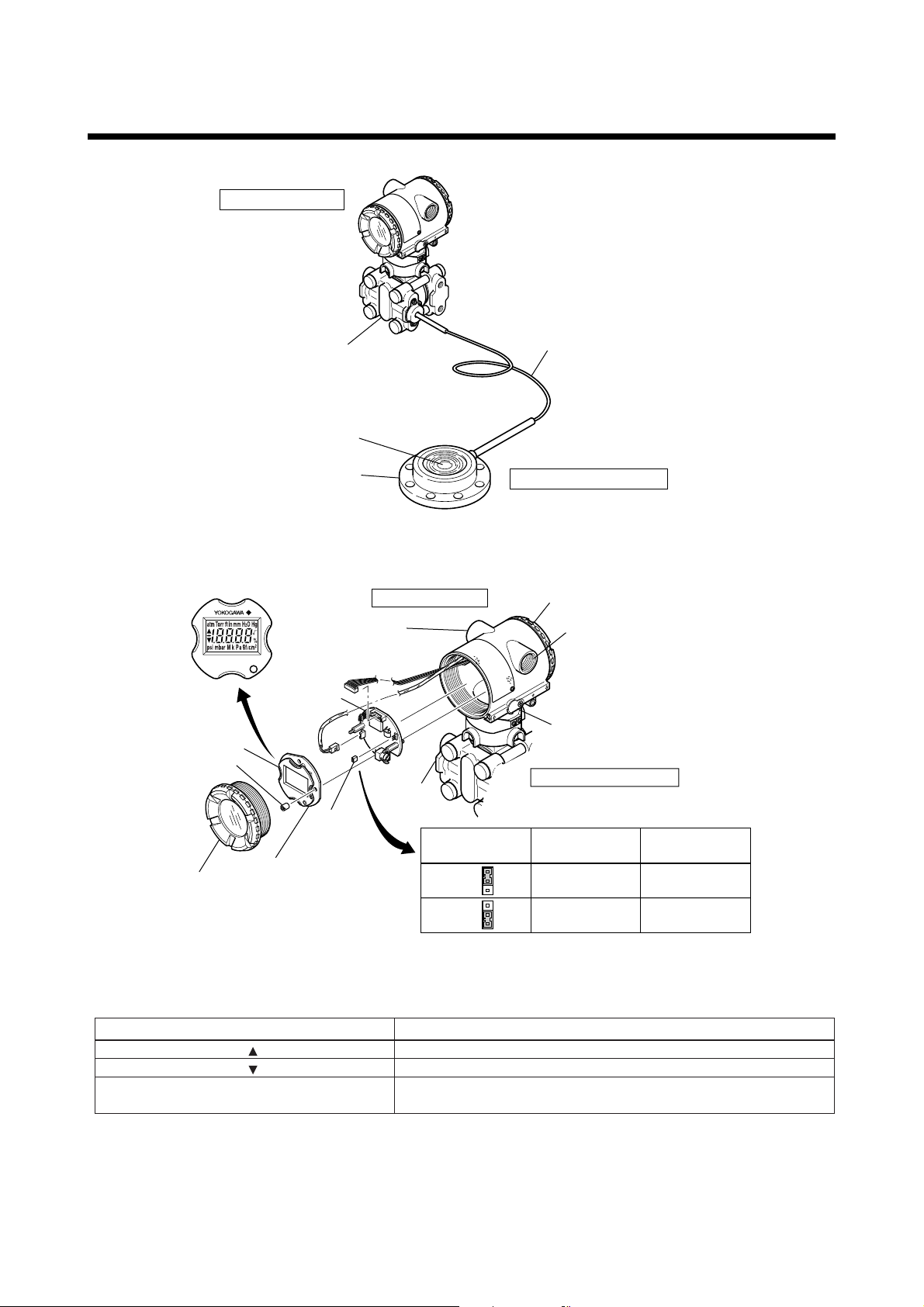
3. COMPONENT NAMES
Transmitter section*
*See below for details.
3. COMPONENT NAMES
Cover flange
Capillary tube
Diaphragm seal
Diaphragm
Flange
Pressure-detector section
F0301.EPS
Figure 3.1.1 Component Names (Model EJA438W External View)
Transmitter section
External indicator
conduit connection
(Note 1)
Terminal box cover
Conduit connection
CPU assembly
Integral
indicator
(Note 1)
Zero-adjustment screw
Mounting screw
Cover
Pressure-detector section
flange
Setting pin
Amplifier cover
(CN4)
Range-setting switch
(See Subsection 6.5)
(Note 1)
Setting pin (CN4)
(Note 2)
position
H
L
H
L
Burn-out
direction
HIGH
LOW
Output at
burn-out
110% or
higher
-
5% or
lower
F0302.EPS
Note 1: Options depend on your order specifications. For details, see Subsection 9.2, “Model and Suffix Codes.”
Note 2: • Insert the pin (CN4) as shown in the above figure into the H or L side. The pin is set to the H side for delivery (unless
option code /C1 is otherwise specified in the order).
• The setting can be confirmed by calling up parameter D52 using the BRAIN TERMINAL. Refer to Subsection. 7.3.2 (8).
Display Symbol
Meaning of Display Symbol
The output signal being zero-adjusted is increasing.
The output signal being zero-adjusted is decreasing.
2
%, Pa, hPa, kPa, MPa, kgf/cm
atm, mmHg, mmH
O, inH2O, inHg, ftH2O, psi, Torr
2
, gf/cm2, mbar, bar,
Select one of these seventeen available engineering units for the display.
Figure 3.1.2 Component Names (Transmitter Section Details)
T0301.EPS
3-1
IM 1C22J1-01E
Page 19
4. INSTALLATION
4. INSTALLATION
4.1 Precautions
j Before installing the transmitter, read the cautionary
notes in Section 2.4, “Selecting the Installation
Location.” For additional information on the
ambient conditions allowed at the installation
location, refer to Subsection 9.1 “Standard Specifications.”
IMPORTANT
• When welding piping during construction, take
care not to allow welding currents to flow
through the transmitter.
• Do not step on this instrument after installation.
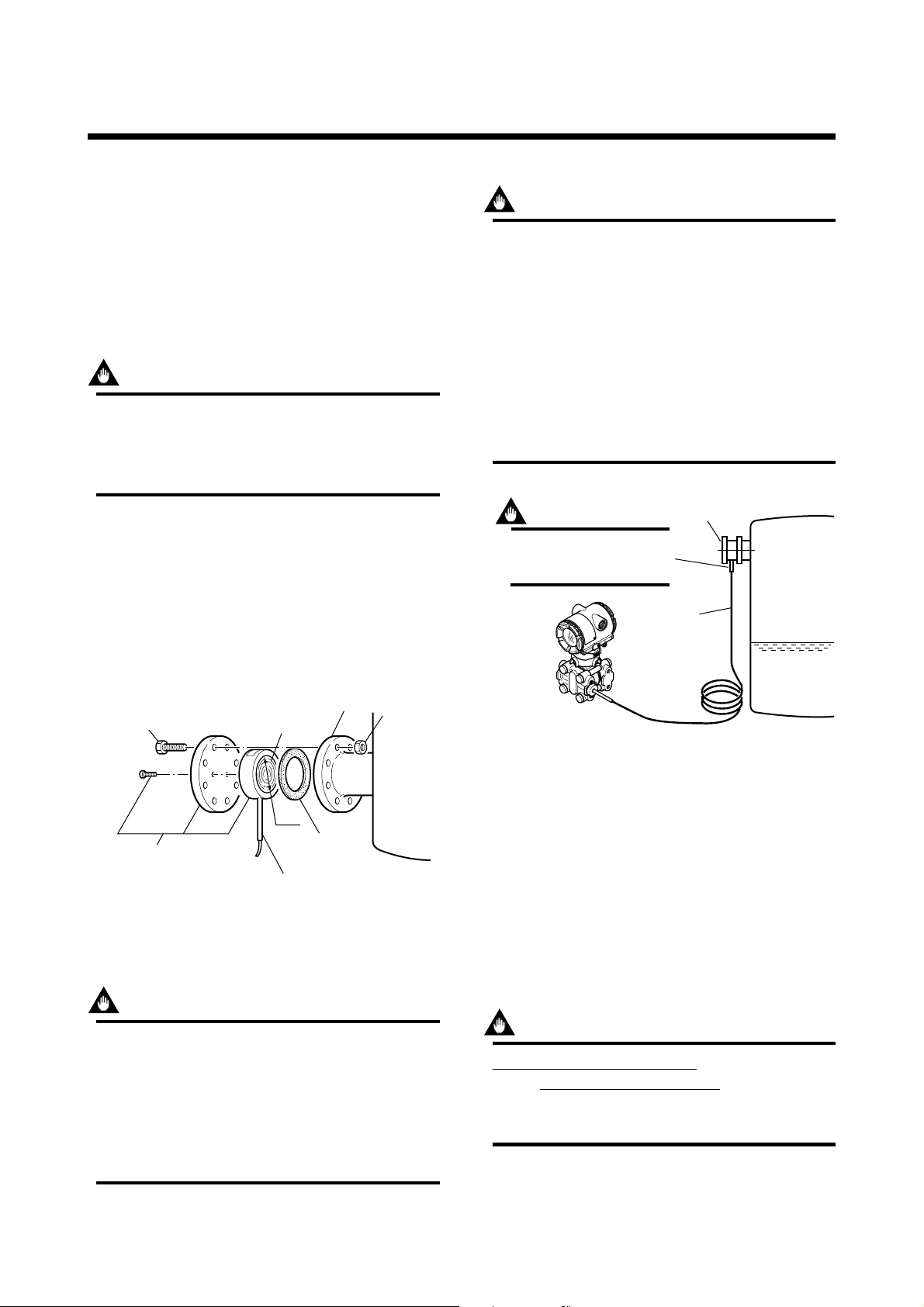
4.2 Mounting the Diaphragm Seals
Mount the diaphragm seals using the flanges as shown
in Figure 4.2.1. Figure 4.2.2 shows how to mount the
diaphragm seals on a tank. The customer should
prepare the mating flange, gasket, bolts and nuts.
IMPORTANT
• During the diaphragm seal installation, ensure
as far as possible that no seal liquid head is
applied to the diaphragm seal.
• Exercise care so as not to damage diaphragm
surface. Since the diaphragm protrudes approx.
1mm from the flange surface, placing the
diaphragm seals with its diaphragm surface
facing downward may damage the diaphragm
surface.
• Do not sharply bend or twist capillary tube or
apply excessive stress to it.
IMPORTANT
Install the sealed diaphragm
so that the shank positions
downward.
Capillary tube
Diaphragm seal
Flange
Bolt
The product is shipped with
these parts assembled.
Correctly install the diaphragm seals on
the high and low pressure sides of the
process, checking the label on each seal.
Figure 4.2.1 Mounting the Diaphragm Seals
Diaphragm
ød
Gasket
Nut
IMPORTANT
Please use a gasket which has a bigger inside
diameter than that of gasket facing (ød) on
diaphragm seal. In case a gasket which has a
smaller inside diameter than that of gasket
facing is used, it may cause an error as the
gasket prevents diaphragm from working correctly. (Refer to Subsection 9.4 ‘Dimensions’)
F0401.EPS
F0402.EPS
Figure 4.2.2 Installing the Diaphragm Seals to a Tank
4.3 Transmitter Mounting
j The transmitter can be mounted on a nominal 50
mm (2-inch) pipe using the mounting bracket
supplied, as shown in Figure 4.3.1 The transmitter
can be mounted on either a horizontal or a vertical
pipe.
j When mounting the bracket on the transmitter,
tighten the (four) bolts that hold the transmitter to a
torque of approximately 39 N·m {4 kgf·m}.
IMPORTANT
Never loosen the four screws securing the cover
flange or the screws at the joints between the
capillary tube and cover flanges (if the seal liquid
leaks, the transmitter cannot be used).
4-1
IM 1C22J1-01E
Page 20
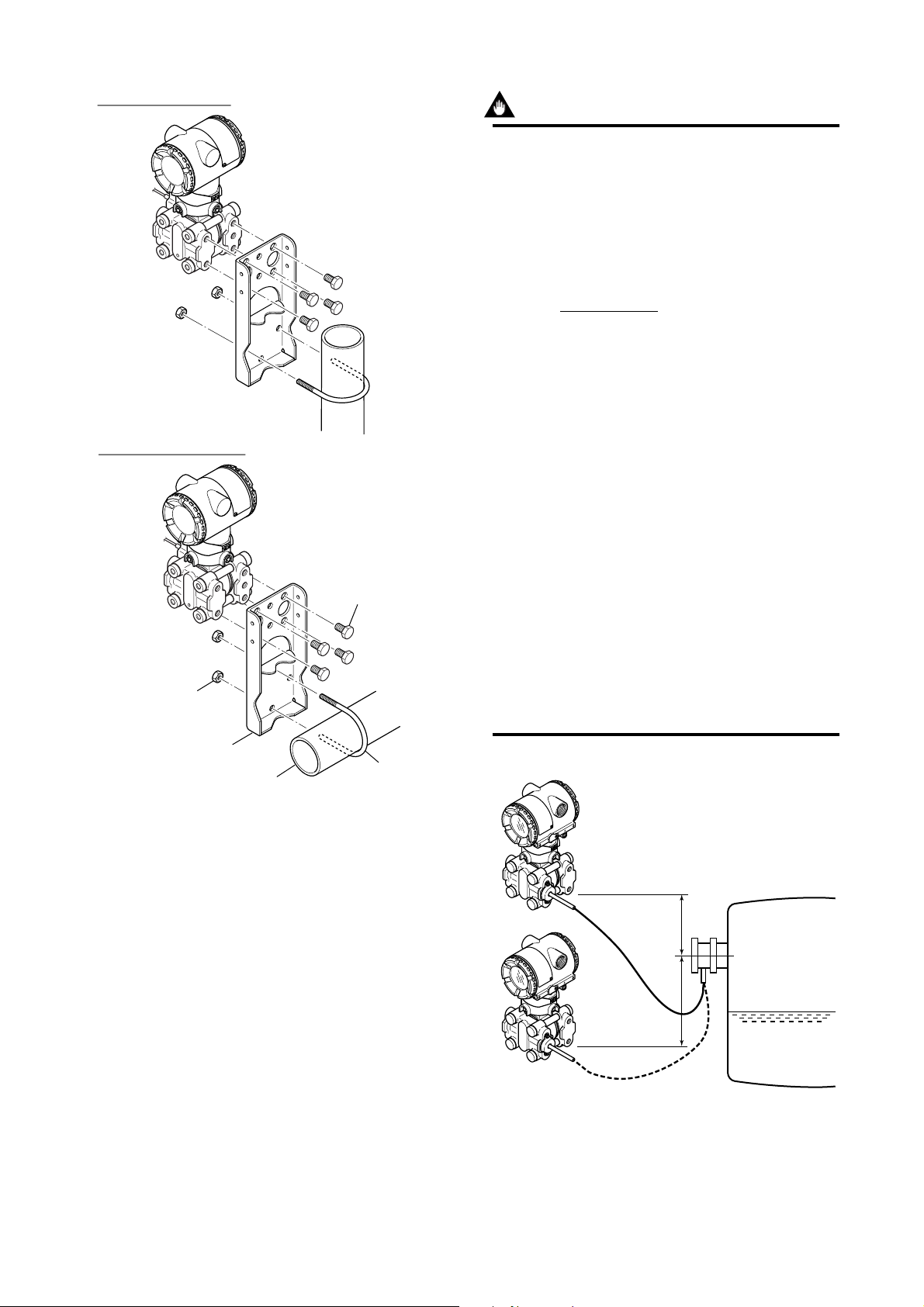
Vertical pipe mounting
Horizontal pipe mounting
U-bolt nut
Transmitter
mounting bolt
4. INSTALLATION
IMPORTANT
The transmitter should be installed at least 700
mm (when the model code of the material of the
wetted part is H, at least 1300 mm) below the
process connection to ensure a positive head
pressure of fill fluid. If it can not be installed at
least 700 mm below the process connection,
please use the equation below:
(P–P0)3dHg
h= 37.5310–3 [mm]
ds
h: Vertical height between the process
connection and the transmitter (mm)
h≤0: Install the transmitter at least h (mm)
below the process connection
h>0: Install the transmitter at most h (mm)
above the process connection
P: Pressure in the tank (Pa abs)
P0: Minimum working pressure limit of the
transmitter (Pa abs)
If the ambient temperature range is
–10 to 50°C.
5254 (Wetted parts material code S)
6980 (Wetted parts material code T)
13019 (Wetted parts material code H)
6980 (Wetted parts material code U)
ds: Specific gravity of fill fluid (at 25°C), refer
to GS 1C22J3-E.
dHg:Specific gravity of the Mercury 13.6 (at
25°C)
Mounting bracket
50mm (2-inch) pipe
Figure 4.3.1 Transmitter Mounting
U-bolt
F0403.EPS
h
(+)
0
P
(–)
F0404.EPS
Figure 4.3.2 Example of Installation to Tank (Caution on
Installation)
4-2
IM 1C22J1-01E
Page 21
4. INSTALLATION
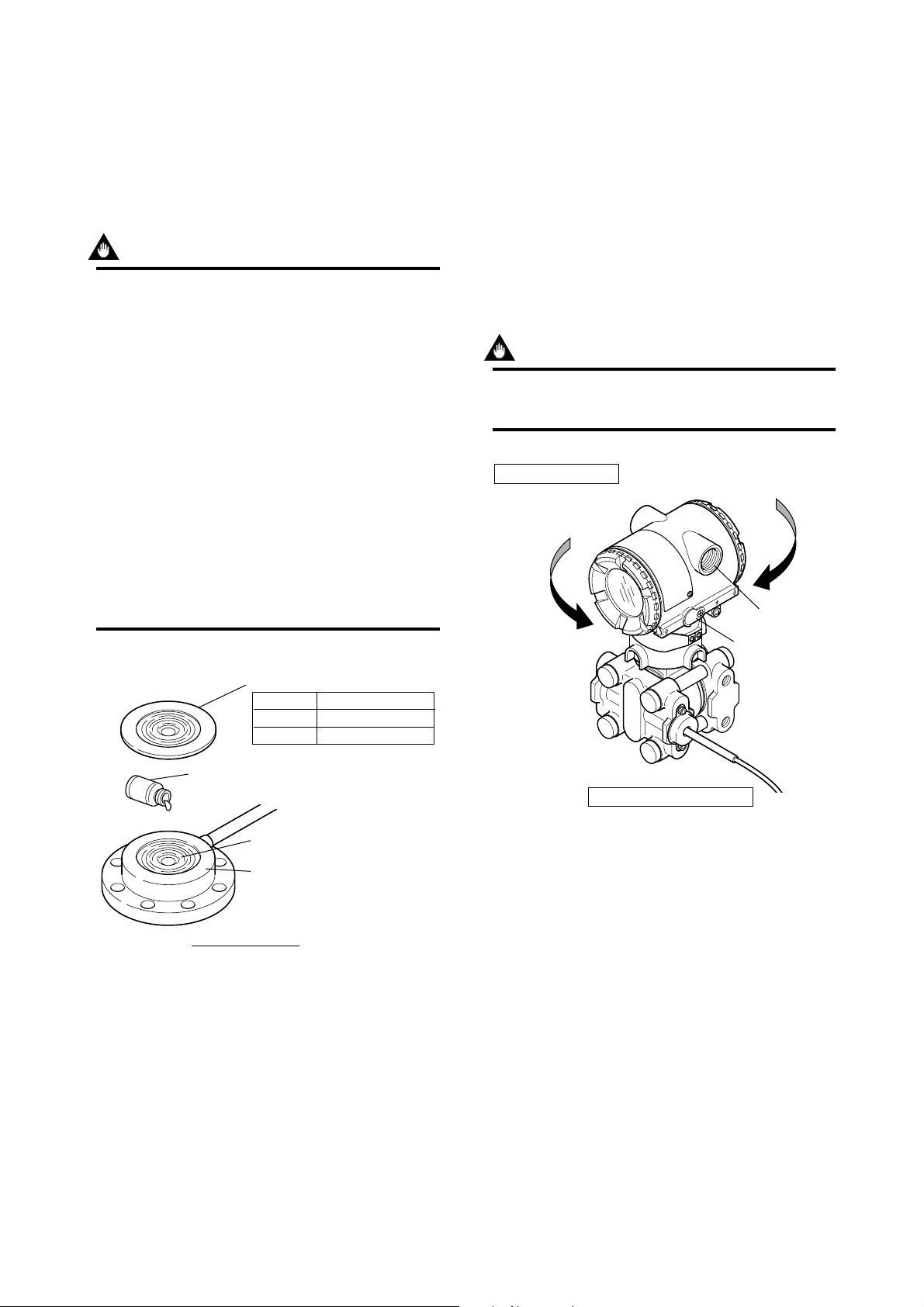
4.4 Affixing the Teflon Film
The FEP Teflon option includes a teflon film and
fluorinated oil.
Before mounting the diaphragm seal to the process
flange, affix the teflon film as follows :
IMPORTANT
(1) Position the diaphragm seal so that the
diaphragm is in a upward position.
(2) Pour the fluorinated oil on the diaphragm and
gasket area covering it completely and
evenly. Be careful not to scratch the diaphragm or change the its shape.
(3) Affix the teflon film over the diaphragm and
gasket area.
(4) Next, carefully inspect the cover and try to
identify any entrapped air between the
diaphragm and the teflon film. The air must
be removed to ensure accuracy. If air
pockets are present, use your fingers to
remove the air by starting at the center of the
diaphragm and work your way out.
(5) Place the gasket with the teflon film and affix
to the process flange.
Teflon film
PART No.
F9347XA
F9347YA
Process flange size
For 3inch (80 mm)
For 2inch (50 mm)
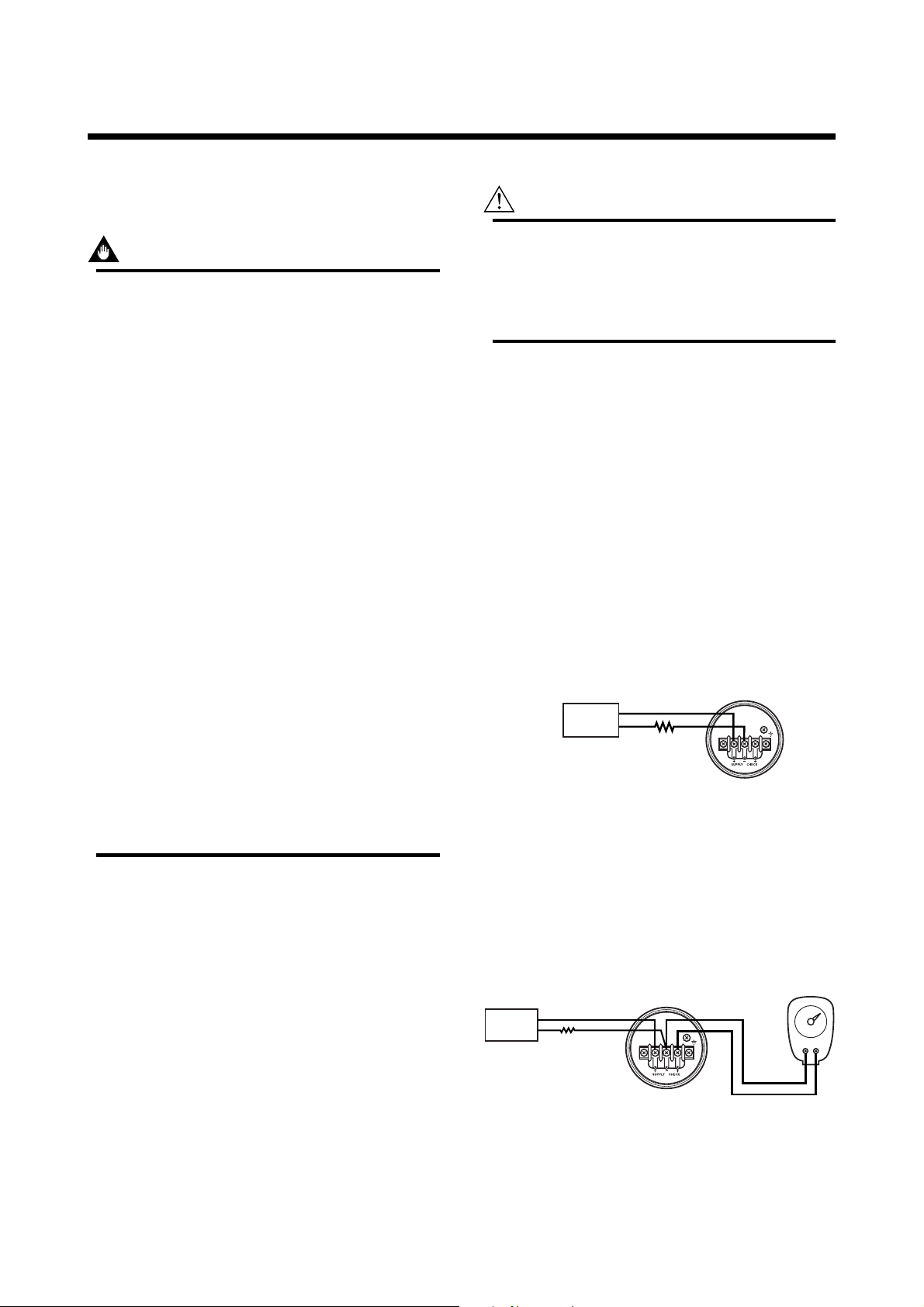
4.5 Rotating Transmitter Section
The DPharp transmitter section can be rotated in 90°
segments.
(1) Remove the two Allen screws that fasten the
transmitter section and pressure-detector section,
using the Allen wrench supplied with the transmitter.
(2) Rotate the transmitter section slowly in 90°
segments.
(3) Tighten the two Allen screws.
IMPORTANT
Do not rotate the transmitter section more than
180°.
Transmitter section
Rotate 90° or 180°
segments
Rotate 90° or 180°
segments
Conduit
connection
Zero-adjustment
screw
Fluorinated oil
[PART No.: F9145YN]
Diaphragm
Gasket area
Diaphragm seal
Figure 4.4.1 Affixing the Teflon Film
F0405.EPS
Pressure-detector section
Figure 4.5.1 Rotating Transmitter Section
4-3
F0406.EPS
IM 1C22J1-01E
Page 22
5. WIRING
5. WIRING
5.1 Wiring Precautions
IMPORTANT
• Lay wiring as far as possible from electrical
noise sources such as large capacity transformers, motors, and power supplies.
• Remove electrical connection dust cap before
wiring.
• All threaded parts must be treated with waterproofing sealant. (A non-hardening silicone
group sealant is recommended.)
• To prevent noise pickup, do not pass signal
and power cables through the same ducts.
• Explosion-protected instruments must be wired
in accordance with specific requirements (and,
in certain countries, legal regulations) in order
to preserve the effectiveness of their explosionprotected features.
• The terminal box cover is locked by an Allen
head bolt (a shrouding bolt) on CENELEC,
SAA, and JIS flameproof type transmitters.
When the shrouding bolt is driven clockwise by
an Allen wrench, it is going in and cover lock is
released, and then the cover can be opened.
See Subsection 8.4 “Disassembly and Reassembly” for details.
Refer to The “Installation and Operating
Precautions for JIS Flameproof Equipment”
and “Installation and Operating Precautions
for JIS Intrinsically Safe Equipment” at the
end of this manual for correct wiring.
CAUTION
If the transmitter is flameproof and the ambient
temperature is 50°C or more, use cables having
a maximum allowable heat resistance of at least
75°C in consideration of the instrument's generation of heat or the cables' self-heating.
(d) In environment where oils, solvents, corrosive gases
or liquids may be present, use wires or cables that
are resistant to such substances.
(e) It is recommended that crimp-on solderless terminal
lugs (for 4 mm screws) with insulating sleeves be
used for leadwire ends.
5.3 Connections of External Wiring to Terminal Box
5.3.1 Power Supply Wiring Connection
Connect the power supply wiring to the SUPPLY +
and – terminals.
Transmitter terminal box
+
Power supply
–
F0501.EPS
Figure 5.3.1 Power Supply Wiring Connection
5.2 Selecting the Wiring Materials
(a) Use stranded leadwires or cables which are the
same as or better than 600 V grade PVC insulated
wire (JIS C3307) or equivalent.
(b) Use shielded wires in areas that are susceptible to
electrical noise.
(c) In areas with higher or lower ambient temperatures,
use appropriate wires or cables.
5.3.2 External Indicator Connection
Connect wiring for external indicators to the CHECK +
and – terminals.
(Note) Use a external indicator whose internal resistance is 10 Ω or
less.
Power supply
+
–
Transmitter terminal box
Figure 5.3.2 External Indicator Connection
5-1
External indicator
IM 1C22J1-01E
F0502.EPS
Page 23

5. WIRING
5.3.3 BRAIN TERMINAL BT200 Connec-
tion
Connect the BT200 to the SUPPLY + and – terminals
(Use hooks).
Transmitter terminal box
BT200
Figure 5.3.3 BT200 Connection
+
Power supply
–
Ignore the polarity
since the BT200 is
AC-coupled to the
terminal box.
F0503.EPS
5.3.4 Check Meter Connection
Connect the check meter to the CHECK + and –
terminals (use hooks).
• A 4 to 20 mA DC output signal from the CHECK +
and – terminals.
(Note) Use a check meter whose internal resistance is 10 Ω or less.
Power supply
+
5.4.1 Loop Configuration
Since the DPharp uses a two-wire transmission system,
signal wiring is also used as power wiring.
DC power is required for the transmitter loop. The
transmitter and distributor are connected as shown
below.
For details of the power supply voltage and load
resistance, see Section 5.6; for communications line
requirements, see Subsection 7.1.2.
(1) General-use Type and Flameproof Type
Hazardous Location Nonhazardous Location
Transmitter terminal box
Figure 5.4.1a Connection between Transmitter and
Distributor
Distributor
(Power supply unit)
Receiver
instrument
F0505.EPS
–
Check meter
Figure 5.3.4 Check Meter Connection
Transmitter terminal box
F0504.EPS
5.4 Wiring
CAUTION
For the intrinsically safe equipment and flameproof equipment, wiring materials and wiring
work for these equipment including peripherals
are strictly restricted. Users absolutely must read
“Installation and Operating Precautions for JIS
Intrinsically Safe Equipment” and “Installation
and Operating Precautions for JIS Flameproof
Equipment” at the end of this manual prior to the
work.
(2) Intrinsically Safe Type
For intrinsically safe type, a safety barrier must be
included in the loop.
Hazardous Location Nonhazardous Location
Transmitter terminal box
Distributor
(Power supply unit)
Receiver
instrument
Safety barrier
Figure 5.4.1b Connection between Transmitter and
Distributor
F0506.EPS
5-2
IM 1C22J1-01E
Page 24

5. WIRING
5.4.2 Wiring Installation
(1) General-use Type and Intrinsically Safe
Type
Make cable wiring using metallic conduit or waterproof glands.
• Apply a non-hardening sealant to the terminal box
connection port and to the threads on the flexible
metal conduit for waterproofing.
Flexible metal conduit
Apply a non-hardening
Wiring metal
conduit
Tee
Drain plug
Figure 5.4.2a Typical Wiring Using Flexible Metal Conduit
(2) Flameproof Type (JIS)
Wire cables through a flameproof packing adapter, or
using a flameproof metal conduit.
j Wiring cable through flameproof packing adapter
for only JIS flameproof type (see Figure 5.4.2b).
• Use only flameproof packing adapters approved by
Yokogawa.
• Apply a nonhardening sealant to the terminal box
connection port and to the threads on the flameproof
packing adapter for waterproofing.
sealant to the threads for
waterproofing.
F0507.EPS
• Measure the cable outer diameter in two directions to
within 1 mm.
• Calculate the average of the two diameters, and use
packing with an internal diameter nearest to this value
(see Table 5.4.2).
Table 5.4.2 Flameproof Packings and Applicable Cable
Optional
Code
G11
G12
Outer Diameters
Wiring Port
Thread
Diameter
G 1/2
Applicable
Cable OD
(mm)
8 to 10
10.1 to 12
Identifying
Mark
16 8-10
16 10-12
Part
Number
G9601AM
T0501.EPS
• Mounting flameproof packing adapter body to conduit
connection (see Figure 5.4.2c)
1) Screw the flameproof packing adapter into the
terminal box until the O-ring touches the wiring
port (at least 6 full turns), and firmly tighten the
lock nut.
2) Insert the cable through the union cover, the union
coupling, the clamp nut, the clamp ring, the gland,
the washer, the rubber packing, and the packing
box, in that order.
3) Insert the end of the cable into the terminal box.
4) Tighten the union cover to grip the cable. When
tightening the union cover, tighten approximately
one turn past the point where the cable will no
longer move up and down.
Proper tightening is important. If it is too tight, a
circuit break in the cable may occur; if not tight
enough, the flameproof effectiveness will be
compromised.
5) Fasten the cable by tightening the clamp nut.
6) Tighten the lock nut on the union cover.
7) Connect the cable wires to each terminal.
Flameproof packing adapter
Flexible metal conduit
Wiring metal
conduit
Tee
Drain plug
Figure 5.4.2b Typical Cable Wiring Using Flameproof
Packing Adapter
Apply a non-hardening
sealant to the threads for
waterproofing.
F0508.EPS
Apply a non-hardnening
sealant to the threads for
waterproofing.
O-ring
Adapter body
Lock nut
Wrench
Packing box
Rubber packing
Washer
Gland
Clamp ring
Figure 5.4.2c Installing Flameproof Packing Adapter
Clamp nut
Union coupling
Lock nut
Wrench
Union cover
Cable
5-3
F0509.EPS
IM 1C22J1-01E
Page 25

5. WIRING
600
250
0 10.5 16.4 24.7 42
External
load
resistance
R (Ω)
Power supply voltage E (V DC)
F0512.EPS
Communication
applicable range
BRAIN and HART
R=
E–10.5
0.0236
j Flameproof metal conduit wiring
• A seal fitting must be installed near the terminal box
connection port for a sealed construction.
• Apply a non-hardening sealant to the threads of the
terminal box connection port, flexible metal conduit
and seal fitting for waterproofing.
Non-hazardous area
Hazardous area
Flameproof
heavy-gauge
steel conduit
Tee
Drain plug
Figure 5.4.2d Typical Wiring Using Flameproof Metal
Conduit
Gas sealing device
Flameproof flexible
metal conduit
Apply a non-hardening
sealant to the threads of
these fittings for
waterproofing
Seal fitting
After wiring, impregnate the fitting
with a compound to seal tubing.
F0510.EPS
5.5 Grounding
5.6 Power Supply Voltage and Load Resistance
When configuring the loop, make sure that the external
load resistance is within the range in the figure below.
(Note) In case of an intrinsically safe transmitter, external load
resistance includes safety barrier resistance.
Figure 5.6 Relationship between Power Supply Voltage
and External Load Resistance
(a) Grounding should satisfy JIS Class 3 requirements
(grounding resistance, 100 Ω or less). Grounding is
required for JIS flameproof type and intrinsically
safe type.
(Note) If equipped with built-in Lightning Protector, grounding
should satisfy Special JIS class 3 requirements (grounding
resistance, 10 Ω or less).
(b) There are ground terminals on the inside and
outside of the terminal box. Either of these terminals may be used.
(c) Use 600 V grade PVC insulated wires for ground-
ing.
Transmitter terminal box
Ground terminal
Ground terminal
F0511.EPS
Figure 5.5 Ground Terminals
5-4
IM 1C22J1-01E
Page 26

6. OPERATION
NOTE
6. OPERATION
6.1 Preparation for Starting Operation
The Model EJA438W and EJA438N diaphragm sealed
gauge pressure transmitter measures the pressure of
liquids, gases, and steam. This section describes the
operation procedure for the EJA438W as shown in
Figure 6.1.1 when measuring pressure in a tank.
(a) Confirm that there is no leak in the connecting part
of each diaphragm seal mounting flange.
(b) Turn ON power and connect the BT200.
Open the terminal box cover and connect the
BT200 to the SUPPLY + and –terminals.
(c) Using the BT200, confirm that the transmitter is
operating properly. Check parameter values or
change the setpoints as necessary.
For BT200 operating procedures, see Chapter 7. If
the transmitter is equipped with an integral
indicator, its indication can be used to confirm that
the transmitter is operating properly.
j Confirming that Transmitter is Operating
Properly
Confirmation using the BT200
• If the wiring system is faulty, ‘communication error’
appears on the display.
• If the transmitter is faulty, ‘SELF CHECK ERROR’
appears on the display.
PARAM
C60:SELF CHECK
ERROR
communication error
DATA DIAG PRNT ESC
Communication error
(Faulty wiring)
Self-diagnostic error
(Faulty transmitter)
F0602.EPS
Confirmation using the integral indicator
• If the wiring system is faulty, the display is blank.
• If the transmitter is faulty, an error number will
appear on the display according to the nature of the
error.
Diaphragm seal
Capillary tube
Pressure transmitter
Transmitter mounting pipe
50mm (2 inches)
Figure 6.1.1 Pressure Measurement
F0601.EPS
Self-diagnostic error
(Faulty transmitter)
F0603.EPS
If any of the error indications above appears on
the display of the integral indicator or BT200,
refer to Subsection 7.5.2 for corrective action.
j Verify and Change Transmitter Parameter
Setting and Values
The following parameters are the minimum settings
required for operation. The transmitter has been
shipped with these parameters. To confirm or change
the values, see Subsection 7.3.3.
• Measuring range........See Subsection 7.3.3 (2)
• Operation mode.........See Subsection 7.3.3 (7)
6-1
IM 1C22J1-01E
Page 27

6. OPERATION
6.2 Zero Point Adjustment
Adjust the zero point after operating preparation is
completed.
IMPORTANT
Do not turn off the power to the transmitter
immediately after a zero adjustment. Powering
off within 30 seconds after a zero adjustment will
return the adjustment back to the previous
settings.
The zero point adjustment can be made in either way:
using the zero-adjustment screw of the transmitter or
the BT200 operation.
For output signal checking, display the parameter A10:
OUTPUT (%) in the BT200.
dBT200
PARAM
A10:OUTPUT(%)
0.0 %
A11:ENGR OUTPUT
A20:AMP TEMP
DATA DIAG PRNT ESC
Output signal (%)
display
6.2.1 When you can obtain Low Range
Value from actual measured value
of 0% (0 kPa, atmospheric pressure);
For pressure measurement using gauge pressure
transmitters, follow the step below before zero point
adjustment.
1) Close the tap valve (main valve).
2) Loosen the fill plug so that the pressure applied to
the transmitter is only the head of the seal liquid.
3) Adjust the zero point at this status.
4) After the adjustment, close the fill plug and then
gradually open the tap valve.
j Using the Transmitter Zero-adjustment
Screw
Before adjusting a screw, check that the parameter
J20: EXT ZERO ADJ displays ENABLE. See
Subsection 7.3.3 (11) for the setting procedure.
Use a slotted screwdriver to turn the zero-adjustment
screw. Turn the screw clockwise to increase the output
or counterclockwise to decrease the output. The zero
point adjustment can be made with a resolution of
0.01% of the setting range. Since the degree of zero
adjustments varies with the screw turning speed, turn
the screw slowly for fine adjustment and quickly for
coarse adjustment.
dZero-adjustment Screw
Zero-adjustment
screw
F0604.EPS
After reviewing this parameter you are prepared to
adjust the zero point. When making the zero adjustment on a pressure transmitter, the process pressure
value does not have to be set to the low limit of the
measurement range (0%). In such case, adjust the
transmitter output signal to the actual measured value
obtained from a high-accuracy pressure measuring
instrument.
j Using the BT200
Zero point can be adjusted by simple key operation of
the BT200.
Select parameter J10: ZERO ADJ, and press the
ENTER key twice. The zero point will be adjusted
automatically to the output signal 0% (4 mA DC).
Confirm that the setting value displayed for the
parameter is ‘0.0%’ before pressing the ENTER key.
See Subsection 7.3.3 (11) for BT200 operating procedures.
SET
J10:ZERO ADJ
–0.0 %
+ 000.0
CLR ESC
A display when parameter
J10 is selected.
Press key
twice for 0% output 4 mA DC.
F0605.EPS
6-2
IM 1C22J1-01E
Page 28

6. OPERATION
NOTE
6.2.2 When you cannot obtain Low Range
Value from actual measured value
of 0%;
Convert the actual measured value obtained by a digital
manometer or a glass gauge into %.
[Example]
The measuring range of 50 to 250 kPa; the actual
measured value of 130 kPa.
Actual measured value= 3100=40.0%
j Using the Transmitter Zero-Adjustment
Screw
Turn the screw to match the output signal to the actual
measured value in %.
j Using the BT200
Select the parameter J10: ZERO ADJ. Change the
set point (%) displayed for the parameter to the actual
measured value (%), and press the ENTER key twice.
See Subsection 7.3.3 (11) for operation details.
SET
J10:ZERO ADJ
–0.0 %
+ 000.0
CLR ESC
SET
J10:ZERO ADJ
–0.0 %
+ 040.0
130–50
250–50
A display at J10
Change setting to the actually
measured value (40.0%).
Press key twice
for 40% output 10.4 mA DC.
6.3 Starting Operation
After completing the zero point adjustment, use the
procedure below to start operation.
1) Confirm the operating status.
There will be cases in which the output signal
exhibits wide fluctuations (hunting) due to periodic
variation in the process pressure. In such cases,
BT200 operation can dampen the transmitter
output signal. Confirm the hunting using a receiving instrument or the integral indicator, and set the
optimum damping time constant. See Subsection
7.3.2 (3), “Damping Time Constant Setup.”
2) After confirming the operating status, perform the
following.
IMPORTANT
• Remove the BT200 from the terminal box, and
confirm that none of the terminal screws are
loosened.
• Close the terminal box cover and the amplifier
cover. Screw each cover in tightly until it will
not turn further.
• Two covers are required to be locked on the
CENELEC, SAA, and JIS Flameproof type
transmitters. An Allen head bolts (shrouding
bolts) are provided under edge of the each
cover for locking. When a shrouding bolts are
driven counterclockwise by an Allen wrench, it
is coming out and locks up a cover. (See page
8-4)
After locking, the covers shoud be confirmed
not to be opened.
• Tighten the zero-adjustment cover mounting
screw to fix the cover in position.
CLR ESC
F0606.EPS
6.4 Shutting Down Operation
Turn off the power.
Whenever shutting down the transmitter for a
long period, detach the transmitter (diaphragm
seals) from the tank.
6-3
IM 1C22J1-01E
Page 29

6. OPERATION
6.5 Setting the Range Using the Range-setting Switch
With actual pressure being applied to the transmitter,
the range-setting switch (push-button) located on the
optional integral indicator plate and the external zeroadjustment screw allow users to change (re-range) the
low- and high-limit values for the measurement range
(LRV and HRV) without using BT200. However, other
changes in the display settings (scale range and
engineering unit) for the integral indicator requires
BT200.
Follow the procedure below to change the LRV and
HRV settings.
[Example]
Rerange LRV to 0 and HRV to 3 MPa.
1) Connect the transmitter and apparatus as shown in
Figure 8.3.1 and warm up for at least five minutes.
2) Press the range-setting push-button.
The integral indicator then displays “LSET.”
3) Apply a pressure of 0 kPa (atmospheric pressure) to
the transmitter.
4) Turn the external zero-adjustment screw in the
desired direction. The integral indicator displays the
output signal in %.
5) Adjust the output signal to 0% (1 V DC) by rotating
the external zero-adjustment screw. Doing so
completes the LRV setting.
6) Press the range-setting push-button. The integral
indicator then displays “HSET.”
7) Apply a pressure of 3 MPa to the transmitter.
8) Turn the external zero-adjustment screw in the
desired direction. The integral indicator displays the
output signal in %.
9) Adjust the output signal to 100% (5 V DC) by
rotating the external zero-adjustment screw. Doing
so completes the HRV setting.
10) Press the range-setting push-button. The transmitter
then switches back to the normal operation mode
with the measurement range of 0 to 3 MPa.
Note 1: Wait until the pressure inside the pressure-detector section
has stabilized before proceeding to the next step.
Note 2: If the pressure applied to the transmitter exceeds the previous
LRV (or HRV), the integral indicator may display error
number “Er.07” (In this case, the output signal percent and
“Er.07” are displayed alternately every two seconds).
Although “Er.07” is displayed, you may proceed to the next
step. However, should any other error number be displayed,
take the appropriate measure in reference to Subsection 7.5.2,
“Errors and Countermeasures.”
(Note 1)
(Note 2)
(Note 1)
(Note 2)
IMPORTANT
• Do not turn off the power to the transmitter
immediately after completion of the change in
the LRV and/or HRV setting(s). Note that
powering off within thirty seconds after setting
will cause a return to the previous settings.
• Changing LRV automatically changes HRV to
the following value.
HRV = previous HRV + (new LRV – previous LRV)
• If the range-setting push-button and external
zero-adjustment screw are not touched during a
range-change operation, the transmitter automatically switches back to the normal operation
mode.
Integral indicator
Note : Use a thin bar which
has a blunt tip, e.g.,
a hexagonal wrench,
to press the rangesetting push-button
Range-setting switch
(Push-button)
Figure 6.5.1 Range-setting Switch
F0607.EPS
6-4
IM 1C22J1-01E
Page 30

7. BRAIN TERMINAL BT200 OPERATION
7. BRAIN TERMINAL BT200
OPERATION
The DPharp is equipped with BRAIN communications capabilities, so that range changes, Tag No.
setup, monitoring of self-diagnostic results, and zero
point adjustment can be handled by remote control
via BT200 BRAIN TERMINAL or CENTUM CS
console. This section describes procedures for setting
parameters using the BT200. For details concerning
the BT200, see IM 1C0A10-E, “BT200 User’s
Manual.”
7.1 BT200 Operation Precau-
tions
7.1.1 Connecting the BT200
The transmitter and the BT200 can be connected
either to the BT200 connection hooks in the transmitter terminal box or to a relaying terminal board.
Relaying
terminals
Control room
Terminal board
7.2
BT200 Operating Procedures
7.2.1 Key Layout and Screen Display
Figure 7.2.1a shows the arrangement of the operating
keys on the BT200 keypad, and Figure 7.2.1b shows
the BT200 screen component.
LCD
(21 character × 8 lines)
Function keys
Movement keys
ENTER key
Power ON/OFF key
Alphanumeric keys
Distributor
F0701.EPS
Figure 7.1.1 Connecting the BT200
7.1.2 Conditions of Communication Line
Cable resistance Rc
Power
supply
Load
resistance R
d Loop resistance = R + 2Rc
= 250 to 600 Ω
d Loop capacitance = 0.22 µF max.
Figure 7.1.2 Conditions of Communication Line
resistance Rc
Cable
cc
DPharp
BT200
F0702.EPS
Figure 7.2.1a BT200 Key Layout
MENU SCREEN
MENU
A:DISPLAY
B:SENSOR TYPE
Screen title
HOME SET ADJ ESC
PARAMETER SCREEN
PARAM
A10:OUTPUT
100.0 %
Parameters
Figure 7.2.1b BT200 Screen Component
A11:ENGR. OUTPUT
1000 mmH20
A20:AMP TEMP
23 deg C
DATA DI AG PRNT
7-1
BATTERY
Shift keys
Menu choices
IM 1C22J1-01E
F0703.EPS
Messages
Function
commands
F0704.EPS
Page 31

7. BRAIN TERMINAL BT200 OPERATION
7.2.2 Operating Key Functions
(1) Alphanumeric Keys and Shift Keys
You can use the alphanumeric keys in conjunction
with the shift keys to enter symbols, as well as
alphanumeric keys.
Alphanumeric keys
Shift keys
a. Entering Digits, Symbols, and Spaces
Simply press the alphanumeric keys.
Entry Key-in Sequence
–4
0.3
1 –9
b. Entering Letters (A through Z)
Press an alphanumeric key following a shift key to
enter the letter shown on that side which the shift key
represents. You must press the shift key before
entering each letter.
Left-side letter on the
alphanumeric key
Entry Key-in Sequence
W
IC
J. B
Use the function key [F2]
Right-side letter on
the alphanumeric key
CAPS
to select between
uppercase and lowercase (for letters only). The case
toggles between uppercase and lowercase each time
you press [F2] CAPS.
Entering uppercase
CODE CAPS CLR ESC
Entry
Boy
( B ) ( y )( o )
Entering lowercase
CODE caps CLR ESC
Key-in Sequence
to lower case
F0705.EPS
T0701.EPS
F0706 .EPS
T0702.EPS
F0707.EPS
Use the function key [F1]
CODE
to enter symbols.
The following symbols will appear in sequence, one
at a time, at the cursor each time you press [F1]
CODE:
/ . – , + * ) ( ’ & % $ # ” !
To enter characters next to these symbols, press [ > ]
to move the cursor.
Entry
symbol command
l/m
Key-in Sequence
( / )
( m )( I )
T0703.EPS
(2) Function Keys
The functions of the function keys depend on the
function commands on display.
MENU
A:DISPLAY
B:SENSOR TYPE
HOME SET ADJ ESC
Function commands
Function keys
F0708.EPS
Function Command List
Command Function
ADJ Displays the ADJ menu
CAPS/caps
CODE
CLR
DATA
DEL
DIAG
ESC
HOME
NO
OK
PARM
SET
SLOT
UTIL
*COPY
*FEED
*LIST
*PON/POFF
*PRNT
*GO
*STOP
* Available on BT200-P00 (with printer).
Selects uppercase or lowercase
Selects symbols
Erases input data or deletes all data
Updates parameter data
Deletes one character
Calls the self-check panel
Returns to the most recent display
Displays the menu panel
Quits setup and returns to the previous display
Proceeds to the next panel
Enters the parameter number setup mode
Displays the SET menu
Returns to the slot selection panel
Calls the utility panel
Prints out parameters on display
Paper feed
Lists all parameters in the menu
Automatic printout mode on or off
Changes to the print mode
Starts printing
Cancels printing
T0704.EPS
7-2
IM 1C22J1-01E
Page 32

7. BRAIN TERMINAL BT200 OPERATION
7.2.3 Calling Up Menu Addresses Using the Operating Keys
STARTUP
SCREEN
INITIAL
DATA
SCREEN
MENU
SCREEN
––WELCOME––
BRAIN TERMINAL
ID: BT200
check connection
push ENTER key
UTIL FEED
UTILITY
1.ID
2.SECURITY CODE
3.LANGUAGE SELECT
4.LCD CONTRAST
5.PRINTER ADJUST
The utility screen contains the
following items.
1. BT200 ID settings
2. Security code settings
3. Switching language of messages
(Japanese or English)
esc
4. LCD contrast setting
(UTIL)
PARAM
01:MODEL
EJA438W-DA
02:TAG NO.
YOKOGAWA
03:SELF CHECK
GOOD
OK
(ESC)
(SET)
(HOME MENU SCREEN) (SET MENU SCREEN) (ADJ MENU SCREEN)
MENU
A.DISPLAY
B.SENSOR TYPE
HOME SET ADJ ESC
MENU
C.SETTING
D.AUX SET 1
E.AUX SET 2
H:AUTO SET
HOME SET ADJ ESC
5. Adjusting printout tone
(BT200-P00 only)
FUNC
1.MENU
2.UPLOAD TO BT200
3.DOWNLOAD TO INST
4.PRINT ALL DATA
HOME SET ADJ ESC
(ADJ)
MENU
J.ADJUST
K.TEST
M.MEMO
P:RECORD
HOME SET ADJ ESC
PARAMETER
SCREEN
SETUP
SCREEN
PARAM
A60:SELF CHECK
GOOD
PARAM
A21:CAPSULE TEMP
26.5 deg C
DATA DIAG PRNT ESC
PARAM
A10:OUTPUT(%)
50.0 %
A11:ENGR, OUTPUT
20.0 M
A20:AMP TEMP
24.5 deg C
DATA DIAG PRNT ESC
SET
C10:TAG NO.
YOKOGAWA
YOKOGAWA
CODE CAPS CLR ESC
PARAM
C60:SELF CHECK
GOOD
PARAM
C22:HIGH RANGE
100 kPa
DATA DIAG PRNT ESC
PARAM
C10:TAG NO.
YOKOGAWA
C20:PRESS UNIT
kPa
C21:LOW RANGE
0 kPa
DATA DIAG PRNT ESC
See “BT200 Instruction Manual” for details
concerning uploading and downloading parameters
and printouts (BT200-P00).
PARAM
J60:SELF CHECK
GOOD
PARAM
J10:ZERO ADJ
0.0 %
DATA DIAG PRNT ESCDATA DIAG PRNT ESC DATA DIAG PRNT ESC
J11:ZERO DEV
22.2 %
J20:EXT. ZERO ADJ
ENABLE
DATA DIAG PRNT ESC
F0709.EPS
7-3
IM 1C22J1-01E
Page 33

7. BRAIN TERMINAL BT200 OPERATION
7.3 Setting Parameters Using the BT200
7.3.1 Parameter Summary
Instruments to which applicable:
F: Differential pressure transmitters EJA110, EJA120, EJA118W, EJA118N, EJA118Y, and EJA115
P: Pressure transmitters EJA310, EJA430, EJA438W, and EJA438N
L: Liquid level transmitters EJA210 and EJA220
No. Description
01
02
03 SELF CHECK
Item
MODEL
TAG NO.
Model+capsule type
Tag number
Self-diagnostic result
Measured data displayA
Output (in %)A10 OUTPUT (%)
A11 ENGR.
OUTPUT
units)
TEMP
PRESS
A40 INPUT
A60 SELF CHECK
engineering DP unit)
Self-diagnostic
messages
Rewrita-
bility
—
—
—
—
—
—
—
—
—
—
—
Remarks
16 alphanumerics
GOOD/ERROR
Menu nameDISPLAY
–5 to 110%
–19999 to 19999Output (in engineering
Unit specified in D30Amplifier temperatureA20 AMP TEMP
Unit specified in D30Capsule temperatureA21 CAPSULE
Unit specified in D31*Static pressureA30 STATIC
–32000 to 32000Input (indicated in
GOOD/ERROR, CAP MODULE
FAULT, AMP MODULE FAULT,
OUT OF RANGE, OUT OF SP
RANGE*, OVER TEMP (CAP),
OVER TEMP (AMP),
OVER OUTPUT, OVER DISPLAY,
ILLEGAL LRV, ILLEGAL HRV,
ILLEGAL SPAN, and
ZERO ADJ OVER
TYPE
B40
MAX STAT.P.
B60 SELF CHECK
C20 PRESS UNIT
C21 LOW RANGE
C22 HIGH
RANGE
DAMPING
C40 OUTPUT
MODE
C60 Same as A60SELF CHECK
Sensor typeB
Model+spanB10 MODEL
Style numberB11 STYLE NO.
Upper range-limitB21 URL
Maximum atatic
pressure
Self-diagnostic
messages
Setting dataC
Tag numberC10 TAG. NO.
Measurement range
units
Measurement range,
lower range value
Measurement range,
higher range value
Damping time constantC30 AMP
Output mode and
integral indicator mode
Self-diagnostic
messages
Auxiliary setting data 1D Menu nameAUX SET 1
Low cutD10 LOW CUT
Low cut modeD11 LOW CUT
Menu nameSENSOR
—
16 uppercase alphanumerics
—
—
–32000 to 32000Lower range-limitB20 LRL
—
—
–32000 to 32000
–32000 to 32000Minimum spanB30 MIN SPAN
—
—
Same as A60
—
Menu nameSETTING
—
16 alphanumerics
Selected from mmH
mmWG, mmHg, Torr, Pa, hPa, kPa,
2
MPa, mbar, bar, gf/cm
inH
O, inHg, ftH2O, psi, or atm
2
–32000 to 32000(but within
measurement range)
–32000 to 32000(but within
measurement range)
Selected from 0.2, 0.5, 1.0, 2.0,
4.0, 8.0, 16.0, 32.0, or 64.0 sec.
Selected from OUT:LIN; DSP:LIN,
OUT:LIN; DSP:SQR,
OUT:SQR; DSP:SQR
—
—
0.0 to 20.0%
LINEAR/ZERO
O, mmAq,
2
, kgf/cm2,
As specified when ordered.
As specified when ordered.
As specified when ordered.
As specified when ordered.
2 s
As specified when ordered.
If not specified,
OUT: LIN; DSP: LIN.
MODE
Display selectionD20 DISP SELECT
NORMAL %/USER SET,
USER & %/INP PRES, PRES & %
* In case of Model EJA120, static pressure cannot be measured. The display is always 0 MPa, but
this is not a measured value.
7-4
Default Value
Applica-
bility
T0705.EPS
IM 1C22J1-01E
PLF
—
—
—
—
Page 34

7. BRAIN TERMINAL BT200 OPERATION
T0706.EPS
Auxiliary setting data 1D Menu nameAUX SET 1
—
NORMAL/REVERSE
NORMAL/REVERSE**
Output reversalD40 REV OUTPUT
Impulse piping
accessing direction
D45 H/L SWAP
—
HIGH/LOWCPU errorD52 BURN OUT
–19999 to 19999Engineering range,
lower range value
D22 DISP LRV
–19999 to 19999Engineering range,
higher range value
D23 DISP HRV
deg C/deg FTemperature setting
units
D30 TEMP UNIT
Selected from mmH2O, mmAq,
mmWG, mmHg, Torr, Pa, hPa, kPa,
MPa, mbar, bar, gf/cm
2
, kgf/cm2,
inH2O, inHg, ftH2O, psi, or atm
Static pressure setting
units
D31 STAT. P. UNIT
Hardware errorD53
Same as A60
HOLD/HIGH/LOWERROR OUT
Self-diagnostic
messages
—
D60 SELF CHECK
Auxiliary setting data 2E
OFF/ON
Menu nameAUX SET 2
Bidirectional modeE30 BI DIRE
MODE
Same as A60Self-diagnostic
messages
E60 SELF CHECK
—
—
No. Description RemarksItem
Menu nameAutomatic setupH AUTO SET
—
Adjustment dataJ
–5 to 110.0%
Menu nameADJUST
Automatic zero
adjustment
J10 ZERO ADJ
—
—
—
—
—
—
—
—
—
Manual zero
adjustment
J11 ZERO DEV.
ENABLE/INHIBITExternal zeroadjustment screw
permission
J20 EXT. ZERO
ADJ
Same as A60Self-diagnostic
messages
J60 SELF CHECK
Display the error
History of the errorsRECORD
Last errorP10
P11
ERROR REC 1
Display the errorOne time beforeERROR REC 2
P12 Display the errorTwo time beforeERROR REC 3
Menu nameTestsK TEST
–5 to 110.0% Displays ‘ACTIVE’
while executing
Test output % settingK10 OUTPUT in %
Same as A60Self-diagnostic
messages
K60 SELF CHECK
Menu nameMemoM
P
MEMO
8 uppercase alphanumericsMemoM10 MEMO 1
8 uppercase alphanumericsMemoM20 MEMO 2
8 uppercase alphanumerics
P13 Display the errorThree time beforeERROR REC 4
P60 Same as A60Self-diagnostic
messages
SELF CHECK
MemoM30 MEMO 3
8 uppercase alphanumericsMemoM40 MEMO 4
8 uppercase alphanumericsMemoM50 MEMO 5
Same as A60Self-diagnostic
messages
M60 SELF CHECK
–32000 to 32000Automatic measurement range lower
range value setup
H10 AUTO LRV
–32000 to 32000Automatic
measurement range
higher range value
setup
H11 AUTO HRV
———
—
—
Same as A60Self-diagnostic
messages
H60 SELF CHECK
Applica-
bility
PLF
8 uppercase
alphanumerics
Engineering unit for
display
D21 DISP UNIT
As specified when ordered.
As specified when ordered.
deg C
As specified when ordered.
If not specified, MPa.
If not specified, NORMAL.
NORMAL
HIGH
HIGH
OFF
Displays the same data as
C21.
Displays the same data as
C22.
Rewrita-
bility
Default Value
** Not applicable for Model EJA115.
7-5
IM 1C22J1-01E
Page 35

7. BRAIN TERMINAL BT200 OPERATION
7.3.2 Parameter Usage and Selection
Before describing the procedure for setting parameters, we present the following table showing how
the parameters are used and in what case.
Table 7.3.1 Parameter Usage and Selection
Setup Item Description
Tag No. setup
c P.7-7
Calibration range setup
c P.7-7
Damping time constant setup
c P.7-8
Output signal low cut mode setup
c P.7-9
Integral indicator scale range and
unit setup
c P.7-9
Unit setup for displayed temperature
c P.7-11
Operation mode (normal/reverse
signal) setup
c P.7-11
Output status display/setup when
a CPU failure c P.7-11
Output status setup when a hardware
error occurs
c P.7-11
Range change (while applying
actual inputs)
c P.7-12
Zero point adjustment
c P.7-12
Test output (fixed current output)
setup c P.7-14
User memo fields
c P.7-14
Sets the Tag No. (using 16 alphanumeric characters).
Note: Up to 8 alphanumerics (upper case letters) can be used in the BT100.
Sets the calibration range for 4 to 20 mA DC. Sets three data items: range unit, input value
at 4 mA DC (LRV), and input value at 20 mA DC (HRV).
Note: LRV and HRV can be specified with range value specifications up to 5 digits
(excluding any decimal point) within the range of –32000 to 32000.
Adjusts the output response speed for 4 to 20 mA DC.
Can be set in 9 increments from 0.2 to 64 s.
Used to stabilize output near 0%: forcing output to 0% for input below a specific value.
Sets the following 5 types of integral indicator scale ranges and units:
% scale indicator, user set scale indicator, alternate indication of user set scale
and % scale, input pressure display, alternate indication of input pressure and % scale
When using the user set scale, 4 types of data can be set:
user set scale setting, unit (BT200 only), display value at 4 mA DC (LRV), and display
value at 20 mA DC (HRV).
Note: LRV and HRV can be specified with range value specifications up to 5
digits (excluding any decimal point) within the range of –19999 to 19999.
Sets a unit for temperatures displayed on the BT200.
Reverses the direction for 4 to 20 mA DC output relative to input.
Reverse mode is used for applications in which safety requires that output be
driven toward 20 mA if input is lost.
Displays the status of 4 to 20 mA DC output when a CPU failure. The parameter
of the standard unit is fixed to the high limit value.
Sets the status of the 4 to 20 mA DC output when an abnormal status is detected
with the capsule or the amplifier as the result of self-diagnosis. One of the
following statuses; last held, high limit, and low limit values, can be selected.
Range for 4 to 20 mA DC signal is set with actual input applied. Sets 20 mA DC output
precisely with respect to user’s reference instrument output. Note that DPharp is calibrated
with high accuracy before shipment, so span should be set using the normal range setup.
Adjusts zero point. This can be done either using the external zero-adjustment screw on
the transmitteror using the BT200.
Used for loop checks.
Output can be set freely from –5% to 110% in 1% steps.
Allows user to enter up to 5 items of any desired text in up to 8 uppercase
alphanumeric characters per item.
IMPORTANT
If the transmitter is turned off within 30 seconds
after parameters have been set, the set data
will not be stored and the terminal returns to
previous settings.
T0707.EPS
7-6
IM 1C22J1-01E
Page 36

7.3.3 Setting Parameters
SET
C10:TAG NO.
FIC-1a
FEED NO OK
DATA DIAG PRNT ESC
This is the panel for confirming
set data. The set data items flash.
When all items have been confirmed, press the
again. (To go back to the setting
panel, press the (NO) key.
SET
C10:TAG NO.
YOKOGAWA
FIC-1a
PRINTER OFF
F2:PRINTER ON
PARAM
C10:TAG NO.
FIC-1a
C20:PRESS UNIT
kPa
C21:LOW RANGE
0 kPa
FEED POFF NO
The DPharp TAG NO. was
overwritten.
Press the (OK) key to
return to the parameter panel.
Press the (NO) key to
return to the setting panel.
F0711.EPS
mmH2O
mmAq
mmWG
mmHg
Torr
kPa
MPa
mbar
bar
gf/cm
2
kgf/cm
2
inH2O
inHg
ftH
2
O
psi
atm
Pa
hPa
• Example: Change the unit from mmH2O to kPa.
ESC
SET
C20:PRESS UNIT
kPa
FEED NO OK
SET
C20:PRESS UNIT
mmH20
< mmWG >
< mmHG >
< Torr >
< kPa >
Use the or
key to select “kPa.”
Press the key twice
to enter the setting.
Press the (OK) key.
F0712.EPS
Set or change the parameters as necessary. After
completing these, do not fail to use the “DIAG” key
to confirm that “GOOD” is displayed for the selfdiagnostic result at _60: SELF CHECK.
(1) Tag No. Setup (C10: TAG NO)
Use the procedure below to change the Tag No. Up
to 16 alphanumeric characters can be entered.
• Example: Set a Tag No. to FIC-1a
Press the key to turn on
the BT200.
<When power is off>
7. BRAIN TERMINAL BT200 OPERATION
––WELCOME––
BRAIN TERMINAL
ID: BT200
check connection
push ENTER key
UTIL FEED
PARAM
01:MODEL
EJA438W-DA
02:TAG NO.
YOKOGAWA
03:SELF CHECK
GOOD
MENU
A:DISPLAY
B:SENSOR TYPE
HOME SET ADJ ESC
MENU
C:SETTING
D:AUX SET 1
E:AUX SET 2
H:AUTO SET
HOME SET ADJ ESC
MENU
C10:TAG NO.
YOKOGAWA
C20:PRESS UNIT
kPa
C21:LOW RANGE
0 kPa
DATA DIAG PRNT ESC
SET
C10:TAG NO.
YOKOGAWA
YOKOGAWA
CODE CAPS CLR ESC
SET
C10:TAG NO.
YOKOGAWA
FIC-1a _
CODE caps CLE ESC
When you have made an entry mistake, return
the cursor using the key, then reenter.
Connect DPharp and BT200 using
a communication cable and press
the key.
Displays the name of connected
DPharp model, TAG NO. and
diagnostics information. Press the
(OK) key after confirmation.
OK
Press the (SET) key to
display the SET menu panel.
Select C: SETTING and press the
key.
Select C10: TAG NO. and press
the key.
Set the new TAG NO. (FIC-1a).
Set TAG NO. and press the
key.
FOKOGAWA
FIKOGAWA
FICOGAWA
FIC-GAWA
FIC-1AWA
FIC-1aWA
FIC-1a
F0710.EPS
(2) Calibration Range Setup
a. Setting Calibration Range Unit
(C20: PRESS UNIT)
The unit is set at the factory before shipment if
specified at the time of order. Follow the procedure
below to change the unit.
7-7
IM 1C22J1-01E
Page 37

b. Setting Calibration Range Lower
• Example 2: With present settings of 0 to 30 kPa,
set the Higher range value to10 kPa.
FEED NO OK
SET
C22:HIGH RANGE
10 kPa
DATA DIAG PRNT ESC
PARAM
C20:PRESS UNIT
kPa
C21:LOW RANGE
0 kPa
C22:HIGH RANGE
10 kPa
DEL CLR ESC
SET
C22:HIGH RANGE
30 kPa
+ 10
The low range value is not
changed, so the span changes.
Set 10.
Press the key twice
to enter the setting.
F0714.EPS
Press the (OK) key.
Range Value and Higher Range Value
(C21: LOW RANGE, C22: HIGH
RANGE)
These range values are set as specified in the order
before the instrument is shipped. Follow the procedure below to change the range.
• The measurement span is determined by the high
and low range limit values. In this instrument,
changing the low range value also automatically
changes the high range value, keeping the span
constant.
• Example 1: With present settings of 0 to 30 kPa,
set the lower range value to 0.5 kPa.
7. BRAIN TERMINAL BT200 OPERATION
SET
C21:LOW RANGE
0 kPa
+ 0.5
Set 0.5.
Press the key twice to
enter the setting.
DEL CLR ESC
SET
C21:LOW RANGE
0.5 kPa
FEED NO OK
SET
C20:PRESS UNIT
kPa
C21:LOW RANGE
0.5 kPa
C22:HIGH RANGE
30.5 kPa
DATA DIAG PRNT ESC
Press the (OK) key.
The higher range value is changed
while the span remains constant.
Span = Higher range value – Lower range value
• Note, however, that changing the higher range value
does not cause the lower range value to change.
Thus, changing the higher range value also changes
the span.
• Calibration range can be specified with range value
specifications up to 5 digits (excluding any decimal
point) for low or high range limits within the range
of –32000 to 32000.
F0713.EPS
(3) Damping Time Constant Setup
(C30: AMP DAMPING)
When the instrument is shipped, the damping time
constant is set at 2.0 seconds. Follow the procedure
below to change the time constant.
• Example: Change from 2.0 sec to 4.0 sec.
SET
C30:AMP DAMPING
2.0 sec
< 2.0 sec >
< 4.0 sec >
< 8.0 sec >
< 16.0 sec >
SET
C30:AMP DAMPING
4.0 sec
FEED NO OK
0.2sec
0.5sec
1.0sec
2.0sec
4.0sec
8.0sec
16.0sec
32.0sec
64.0sec
Note: The damping time constant set here is the damping time
constant for the amplifier assembly. The damping time
constant for the entire transmitter is the sum of the values for
the amplifier assembly and for the capsule assembly. For the
capsule assembly damping time constant (fixed), see the
“General Specifications” found at the end of this manual.
(See Chapter 9.)
Use the or key to
select 4.0 sec.
Press the key twice to
enter the setting.
ESC
Press the (OK) key.
F0715.EPS
7-8
IM 1C22J1-01E
Page 38

7. BRAIN TERMINAL BT200 OPERATION
(4) Output Signal Low Cut Mode Setup
(D10: LOW CUT, D11: LOW CUT MODE)
Low cut mode can be used to stabilize the output
signal near the zero point. The low cut point can be
set in a range from 0 to 20% of output. (Hysteresis of
cut point: ±1%)
Select “ZERO” as the low cut mode.
d LOW CUT mode ZERO at 10%
50
(%)
Output
10
0
10
Input(%)
50
F0716.EPS
• Example: Change the low cut setting range
from 5% to 10%, and the low
cut mode from LINEAR to ZERO.
SET
D10:LOW CUT
5.0 %
+ 10.0
CLR ESC
SET
D10:LOW CUT
10.0 %
FEED NO OK
SET
C11:LOW CUT MODE
LINEAR
< LINEAR >
< ZERO >
SET
D11:LOW CUT MODE
ZERO
Set “10.”
Press the key twice to
enter the setting.
Press the (OK) key.
Next, the [D11: LOW CUT MODE]
setting panel is displayed.
Use the or key
to select ZERO.
Press the key twice to
ESC
enter the setting.
Press the (OK) key.
(5) Integral Indicator Scale Setup
The following 5 displays are available for integral
indicators.
D20: DISP SELECT
and Display
NORMAL %
Indicates –5 to 110% range
depending on the Measurement
range (C21, C22).
USER SET
Indicates values depending on the
Engineering range (D22, D23).
Units set using Engineering unit
(D21) are not indicated.
USER & %
Indicates user set and % alternately
in 3 second intervals.
INP PRES
Indicates input pressure. Indication
limits –19999 to 19999.
PRES & %
Indicates input pressure and %
alternately in 3 second intervals.
(Note 1) Scale range can be specified with range limit specifications up
to 5 digits (excluding any decimal point) for low or high range
limits within the range of –19999 to 19999.
Description
and Related parameters
A10:OUTPUT (%)
45.6 %
(Note 1)
A11:ENGR.OUTPUT
20.0 M
A10:OUTPUT (%)
45.6 %
A11:ENGR. OUTPUT
20.0 M
A40:INPUT
456 kPa
A10:OUTPUT (%)
45.6 %
A40:INPUT
456 kPa
T0708.EPS
See (a.) through (c.) for each setting procedure.
FEED NO OK
PARAM
D10:LOW CUT
10.0 %
D11:LOW CUT MODE
ZERO
D20:DISP SELECT
NORMAL %
DATA DIAG PRNT ESC
F0717.EPS
7-9
IM 1C22J1-01E
Page 39

7. BRAIN TERMINAL BT200 OPERATION
% indication and
input pressure
User-set engineering
unit display
indication
D20: DISP SELECT
NORMAL %
INP PRES
PRES & %
Transmitter is set
for “% display” when
shipped.
D20: DISP SELECT
USER SET
USER & %
Set for user-set
engineering unit display.
D21: DISP UNIT
Set a unit to be
displayed on the BT200.
D22: DISP LRV
Set a numeric value for
engineering unit for 4 mA
output (LRV).
D23: DISP HRV
Set a numeric value for
engineering unit for 20 mA
output (HRV).
F0718.EPS
a. Display Selection (D20: DISP SELECT)
Follow the instructions given to the below to change
the range of integral indication scales.
When USER SET is selected, the user set values of
integral indication and A11: ENGR. OUTPUT
parameter are indicated.
b. Setting User-set Engineering Unit
(D21: DISP UNIT)
This parameter allows entry of the engineering units
to be displayed on the BT200. When the instrument
is shipped, this is set as specified in the order.
Follow the procedure below to change this setting.
Since these units are not displayed on the integral
indicator, use the adhesive labels provided. This
parameter need not be set for % display.
• Example: Set an engineering unit M.
SET
D21:DISP UNIT
M_
CODE CAPS CLR ESC
SET
D21:DISP UNIT
M
FEED NO OK
Set “M.”
Press the key twice to
enter the setting.
Press the (OK) key.
F0720.EPS
c. Lower and Higher Range Value Setup
in Engineering Unit (D22: DISP LRV,
D23: DISP HRV)
These parameter items are used to set the lower and
higher range values for the engineering unit display.
When the instrument is shipped, these are set as
specified in the order. Follow the procedure below to
change these settings. Note that these parameters
need not be set for % display.
• Example: Set lower range value (LRV) to –50
and higher range value (HRV) to 50.
• Example: Set the integral indicator scale to
engineering units display.
SET
D20:DISP SELECT
NORMAL %
<NORMAL %>
<USER SET>
<USER & %>
<INP PRES>
SET
D20:DISP SELECT
USER SET
FEED NO OK
Use the or key
to select “USER SET.”
Press the key twice to
ESC
enter the setting.
Press the (OK) key.
The “%” disappears from the
integral indicator display.
F0719.EPS
7-10
Setting LRV
SET
D22:DISP LRV
0M
- 50
DEL CLR ESC
Setting HRV
SET
D23:DISP HRV
100M
+ 50
DEL CLR ESC
SET
D23:DISP HRV
50M
FEED NO OK
PARAM
D21:DISP UNT
M
D22:DISP LRV
– 50M
D23:DISP HRV
50M
DATA DIAG PRNT ESC
Set “–50.”
Press the key twice to
enter the setting.
Set “50.”
Press the key twice to
enter the setting.
Press the (OK) key.
F0721.EPS
IM 1C22J1-01E
Page 40

7. BRAIN TERMINAL BT200 OPERATION
• Example: Standard specifications
pin (CN4) position: H
D52: BURN OUT
HIGH
F0724.EPS
• Example: Optional code/C1
pin (CN4) position: L
D52: BURN OUT
LOW
(6) Unit Setup for Displayed Temperature
(D30: TEMP UNIT)
When the instrument is shipped, the temperature units
are set to degC. Follow the procedure below to
change this setting. Note that changing the unit here
changes the unit for A20: AMP TEMP (amplifier
temperature) and A21: CAPSULE TEMP (capsule
temperature).
• Example: Change the unit for the temperature
display.
SET
D30:TEMP UNIT
deg C
< deg C >
< deg F >
Use the or key to
select “deg F.”
Press the key twice to
ESC
enter the setting.
F0722.EPS
(7) Operation Mode Setup
(D40: REV OUTPUT)
This parameter allows the direction of the 4 to 20
mA output to be reversed with respect to input.
Follow the procedure below to make this change.
(8) Output Status Display/Setup when a CPU
Failure (D52: BURN OUT)
This parameter displays the status of 4 to 20 mA DC
output if a CPU failure occurs. In case of a failure,
communication is disabled.
Setting of HIGH or LOW is enabled. This is done
with the pin (CN4) on the CPU assembly. See
Chapter 3 for details.
Standard specifications
The parameter is set to HIGH. If a failure, the
transmitter outputs the signal of 110% or higher. The
parameter D53: ERROR OUT is set to HIGH from
the factory.
Optional code/C1
The parameter is set to LOW. If a failure, output
which is –5% or lower is generated. The parameter
D53: ERROR OUT is set to LOW from the factory.
• Example: Change 4 to 20 mA output to 20 to
4 mA output.
SET
D40:REV OUTPUT
NORMAL
< NORMAL >
< REVERSE>
Use the or key
to select REVERSE.
Press the key twice to
ESC
enter the setting.
F0723.EPS
(9) Output Status Setup when a Hardware
Error Occurs (D53: ERROR OUT)
This parameter allows the setting of the output status
when a hardware error occurs. The following three
selections are available.
(a) HOLD; Outputs the last value held before the
error occurred.
(b) HIGH; Outputs an output of 110% when an error
has occurred.
(c) LOW; Outputs an output of –5% when an error
has occurred.
Note: A hardware error means CAP MODULE FAULT of Er.01 or
AMP MODULE FAULT of Er. 02 which are shown in 7.5.2
“Errors and Countermeasures.”)
• Example: Set the output status to LOW when
a hardware error occurs.
SET
D53:ERROR OUT
HIGH
< HIGH>
< LOW>
< HOLD>
Use the or key
to select “LOW.”
Press the key twice to
ESC
enter the setting.
F0725.EPS
7-11
IM 1C22J1-01E
Page 41

7. BRAIN TERMINAL BT200 OPERATION
(10) Range Change while Applying Actual
Inputs (H10: AUTO LRV, H11: AUTO
HRV)
This feature allows the lower and higher range values
to be set up automatically with the actual input
applied. If the lower and higher range values are set,
C21: LOW RANGE and C22: HIGH RANGE are
changed at this same time.
Follow the procedure in the figure below.
The measurement span is determined by the higher
and lower range values. Changing the lower range
value results in the higher range value changing automatically, keeping the span constant.
• Example 1: When changing the lower range
value to 0.5 kPa for the present
setting of 0 to 30 kPa, take the
following action with input pressure
of 0.5 kPa applied.
SET
H10:AUTO LRV
0 kPa
+ 0
SET
H10:AUTO LRV
0.5000 kPa
FEED NO OK
PARAM
H10:AUTO LRV
0.5000 kPa
H11:AUTO HRV
30.500 kPa
H60:SELF CHEC
GOOD
DATA DIAG PRNT ESC
Press the key twice.
The lower range value is changed
to 0.5 kPa.
ESC
Press the (OK) key.
The higher range value is changed
keeping the span constant.
Parameters C21 and C22 are
changed at the same time.
F0726.EPS
Note that changing the higher range value does not
cause the lower range value to change but does
change the span.
• Example 2: When the higher range value is to
be changed to 10 kPa with the
present setting of 0 to 30 kPa, take
the following action with an input
pressure of 10 kPa applied.
SET
H10:AUTO HRV
30 kPa
+ 30
SET
H11:AUTO HRV
10.000 kPa
FEED NO OK
PARAM
H10:AUTO LRV
0 kPa
H11:AUTO HRV
10.000 kPa
H60:SELF CHECK
GOOD
DATA DIAG PRNT ESC
Press the key twice.
The higher range value is changed
to 10 kPa.
ESC
Press the (OK) key.
The lower range value is not
changed, so the span changes.
Parameter C22 is changed at the
same time.
F0727.EPS
(11) Zero Point Adjustment
(J10: ZERO ADJ, J11: ZERO DEV,
J20: EXT ZERO ADJ)
The DPharp supports several adjustment methods.
Select the method best suited for the conditions of
your application.
Note that output signal can be checked by displaying
parameter A10:OUTPUT (%) on the BT200.
Adjustment Method Description
Using the BT200 Set the present input to 0%.
Adjust for 0% output at input level of
0%.
Adjust output to the reference value
obtained using other means.
If the input level cannot easily be
made 0% (because of tank level,
etc.), adjust output to the reference
value obtained using other means,
such as a sight glass.
Using the external
zero-adjustment
screw
Adjust zero point using the zeroadjustment screw on the transmitter.
This permits zero adjustment without
using the BT200. Accurately adjust
the output current to 4 mA DC or
other target output value using an
ammeter that accuratly reads output
currents.
T0709.EPS
7-12
IM 1C22J1-01E
Page 42

7. BRAIN TERMINAL BT200 OPERATION
ECS
ESC
SET
J11:ZERO DEV.
2.50 %
0
Since “J11: ZERO DEV.” contains
the previous correction, obtain the
correction value by adding –1.0% to
it. 2.50% + (–1.0%) = 1.50%
Set the correction value, 1.50.
Press the key twice.
F0730.EPS
Present output is 41.0%.
Output error = 40.0 – 41.0 = –1.0%.
A10:OUTPUT (%)
41.0 %
The output is changed to 40%.
A10:OUTPUT (%)
40.0 %
SET
J11:ZERO DEV.
2.50 %
1.50
(a) Follow the procedure below when setting the
present output to 0% (4 mA).
A10:OUTPUT (%)
0.5 %
SET
J10:ZERO ADJ
0.0 %
+ 000.0
CLR ESC
SET
J10:ZERO ADJ
0.0 %
FEED NO OK
A10:OUTPUT (%)
0.0 %
Output is 0.5%.
Press the key twice.
Zero adjustment is completed.
Press the (OK) key.
Output is 0%.
(b) In tank level measurement, if the actual level
cannot be brought to zero for zero adjustment,
then the output can be adjusted to correspond to
the actual level obtained using another measuring
instrument such as a glass gauge.
(b)-2 Follow the procedure below to use J11: ZERO
DEV.
F0728.EPS
(c) Zero Point Adjustment Using the External Zero
Adjustment Screw
• Enabling/inhibiting of zero point adjustment using
the external zero-adjustment screw on the transmitter
(J20: EXT ZERO ADJ)
[Example]
Measurement range: 50 to 250 kPa, Actual value:
130 kPa.
Actual value
x 100
Actual
value(%)
–Measurement range lower range value
=
Measurement range higher range value
–Measurement range lower range value
130–50
= x 100=40.0%
250–50
(b)-1 Follow the procedure below to use J10: ZERO
ADJ.
A10:OUTPUT (%)
41.0 %
SET
J10:ZERO ADJ
0.0 %
+ 040.0
CLR ESC
A10:OUTPUT (%)
40.0 %
Present output is 41.0%.
Enter the present actual level, 40%.
Press the key twice.
The output is changed to 40%.
F0729.EPS
Follow the procedure below to enable or inhibit zero
point adjustment from the zero-adjustment screw on
the transmitter.
This is set to “ENABLE” when the instrument is
shipped.
• Example: Inhibiting zero adjustment by the
external zero-adjustment screw
SET
J20:EXIT ZERO ADJ
ENABLE
< ENABLE >
< INHIBIT>
Use the or key to
select “INHIBIT.”
Press the key twice to
ESC
enter the setting.
F0731.EPS
• Zero point adjustment using external zero-adjustment screw on the transmitter
Turn the zero-adjustment screw on the outside of the
transmitter case using a slotted screwdriver. Turn the
screw to the right to increase the zero point or to the
left to decrease the zero output; the zero adjusts in
increments of 0.01% of the range setting.
Note that the amount of adjustment to the zero point
changes according to the speed at which the screw is
turned. To make fine adjustments, turn the screw
slowly; to make coarse adjustments, turn the screw
quickly.
Note: When a zero point adjustment has been made, do not turn
off the transmitter less than 30 seconds after adjustment.
7-13
IM 1C22J1-01E
Page 43

7. BRAIN TERMINAL BT200 OPERATION
(12) Test Output Setup (K10: OUTPUT X%)
This feature can be used to output a fixed current
from 3.2 mA (–5%) to 21.6 mA (110%) for loop
checks.
• Example: Output 12 mA (50%) fixed current.
SET
K10:OUTPUT X %
0.0 %
+ 050.0
SET
K10:OUTPUT X %
50.0 % ACTIVE
FEED NO OK
Set “50.0%.”
Press the key twice to
output a fixed current at 50%.
ESC
“Active” is displayed while this is
being executed.
Press the (OK) key to cancel
the fixed current output.
F0732.EPS
IMPORTANT
1. Test output is held for approximately 10
minutes, and then released automatically after
the time has elapsed. Even if the BT200
power supply is turned off or the communication cable is disconnected during test output,
it is held for approximately 10 minutes.
2. Press the (OK) key to release test output
immediately.
7.4 Displaying Data Using the BT200
7.4.1 Displaying Measured Data
The BT200 can be used to display measured data.
The measured data is updated automatically every 7
seconds. In addition, the display can be updated to
the present data value at any time by pressing the
(DATA) key. For parameters associated with the
display of measured data, see Subsection 7.3.1,
“Parameter Summary.”
• Example: Display output.
MENU
A:DISPLAY
B:SENSOR TYPE
HOME SET ADJ ESC
PARAM
A10:OUTPUT (%)
XX.X %
A11:ENGR.OUTPUT
YY.Y %
A20:AMP TEMP
ZZ deg C
DATA DIAG PRNT ESC
PARAM
A10:OUTPUT (%)
A11:ENGR.OUTPUT
A20:AMP TEMP
Display “A10: OUTPUT (%).”
Data is updated automatically
communi
at 7-second intervals.
F0734.EPS
(13) User Memo Fields (M: MEMO)
This feature provides 5 user memo fields, each
holding up to 8 alphanumeric characters. Up to 5
items such as inspection date, inspector, and other
information can be saved in these fields.
• Example: Save an inspection date of January
30, 1995.
PARAM
M10:MEMO 1
M20:MEMO 2
M30:MEMO 3
DATA DIAG PRNT ESC
SET
M10:MEMO 1
95.1.30_
Set “95.1.30” in the order of year,
month, and day.
Press the key twice to
enter the setting.
ESC
F0733.EPS
7.4.2 Display Transmitter Model and Specifications
The BT200 can be used to display the model and
specifications of the transmitter.
• Example: View transmitter model name.
MENU
A:DISPLAY
B:SENSOR TYPE
HOME SET ADJ ESC
PARAM
B10:MODEL
EJA438W-DA
B11:STYLE NO.
S1.01
B20:LRL
– 98.07 kPa
DATA DIAG PRNT ESC
Press .
For the associated
parameters, see Subsection
7.3.1, Parameter Summary.
F0735.EPS
7-14
IM 1C22J1-01E
Page 44

7.5 Self-Diagnostics
• Example 3: Checking the history of the errors
Connect the BT200 to the
transmitter, and call item “P.”
The history of up to four errors can be stored. When the 5th
error has occurred, it is stored in “P10”. The error stored in
“P13” will be deleted, and then, the error in “P12” will be
copied to “P13”. In this sequence, the history of the most
previously occurred error will be removed from memory.
“GOOD” will be displayed if there was no previous error.
F0737.EPS
HOME SET ADJ ESC
MENU
J:ADJUST
K:TEST
M:MEMO
P:RECORD
DATA DIAG PRNT ESC
PARAM
P10:ERROR REC 1
ERROR
P11:ERROR REC 2
ERROR
P12:ERROR REC 3
GOOD
For the details of the messages listed below, see Table
8.5.1 Error Message Summary.
ESC
SET
P10:ERROR REC 1
ERROR
< ERROR >
< ILLEGAL LRV >
< ILLEGAL HRV >
<(a) SETUP PANEL>
Note 1: Press the key twice in the setting panel
(panel 1) to clear all error message (P10 to P13)
information.
Note 2: After two hours from when an error occurs, the error
message of that error will be recorded. Therefore,
if you switch off the transmitter within two hours from
when the error occurs, there is no history of that
error stored in the transmitter, and this function is
meaningless.
CAP MODULE FAULT
AMP MODULE FAULT
OUT OF RANGE
OUT OF SP RANGE
OVER TEMP (CAP)
OVER TEMP (AMP)
OVER OUTPUT
OVER DISPLAY
ILLEGAL LRV
ILLEGAL HRV
ILLEGAL SPAN
ZERO ADJ OVER
P10: “ERROR REC 1” displays the last error.
P11: “ERROR REC 2” displays the error one time before
the last error occurred.
P12: “ERROR REC 3” displays the error two times before
the last error occurred.
P13: “ERROR REC 4” displays the error three times before
the last error occurred.
Select P10: ERROR REC1 and
press the key to display
the error message.
7.5.1 Checking for Problems
(1) Identifying Problems with BT200
The following four areas can be checked.
(a) Whether connections are good.
(b) Whether BT200 was properly operated.
(c) Whether settings were properly entered.
(d) History of the errors.
See examples below.
• Example 1: Connection errors
––WELCOME––
BRAIN TERMINAL
ID: BT200
check connection
push ENTER key
UTIL FEED
communication error
Press the key.
When the panel shown on the left
appears, press the key.
Since communications will be
unsuccessful if there is a problem
in the connection to the BT200, the
ESC
display at the left will appear.
Recheck the connection.
Press the (OK) key.
7. BRAIN TERMINAL BT200 OPERATION
• Example 2: Setting entry errors
PARAM
01:MODEL
EJA438W-DA
02:DAG NO.
YOKOGAWA
03:SELF CHECK
ERROR
PARAM
C20:PRESS UNIT
kPa
C21:LOW RANGE
600 kPa
C22:HIGH RANGE
600 kPa
DATA DIAG PRNT ESC
DIAG
C60:SELF CHECK
ERROR
< ERROR >
< ILLEGAL LRV >
FEED PRNT ESC
The initial data panel shows the
result of current transmitter
diagnostics.
OK
Press the (DIAG) key in the
parameter panel to go to the
diagnostics panel
(C60: SELF CHECK).
An error message is displayed
when an error occurs in the
diagnostics panel.
F0736.EPS
7-15
IM 1C22J1-01E
Page 45

(2) Checking with Integral Indicator
NOTE
If an error is detected in the self-diagnostic, an
error number is displayed on the integral
indicator. If there is more than one error, the
error number changes at two-second intervals.
See Table 7.5.1 regarding the error numbers.
7. BRAIN TERMINAL BT200 OPERATION
F0738.EPS
Figure 7.5.1 Identifying Problems Using the Integral
Indicator
7-16
IM 1C22J1-01E
Page 46

7.5.2 Errors and Countermeasures
The table below shows a summary of error messages.
Table 7.5.1 Error Message Summary
7. BRAIN TERMINAL BT200 OPERATION
Integral
Indicator
Display
None
---Er. 01
Er. 02
Er. 03
Er. 04
Er. 05
Er. 06
Er. 07
Er. 08
Er. 09
Er. 10
Er. 11
Er. 12
*1: For Model EJA120, static pressure cannot be measured. The display is always 0 MPa, but this is
not a measured value.
BT200 Display Cause Countermeasure
GOOD
ERROR
CAP MODULE
FAULT
AMP MODULE
FAULT
OUT OF RANGE
OUT OF SP
RANGE
OVER TEMP
(CAP)
OVER TEMP
(AMP)
OVER OUTPUT
OVER DISPLAY
ILLEGAL LRV
ILLEGAL HRV
ILLEGAL SPAN
ZERO ADJ OVER
Capsule problem.
Amplifier problem.
Input is outside
measurement range
limit of capsule.
Static pressure
exceeds specified
*1
range.
Capsule temperature
is outside range
(–50 to 130°C).
Amplifier temperature
is outside range
(–50 to 95°C).
Output is outside high
or low range limit
value.
Displayed value is
outside high or low
range limit value.
LRV is outside setting
range.
HRV is outside setting
range.
SPAN is outside
setting range.
Zero adjustment is too
large.
Output Operation
during Error
Outputs the signal
(Hold, High, or Low)
set with parameter
D53.
Outputs the signal
(Hold, High, or Low)
set with parameter
D53.
Outputs high range
limit value or low
range limit value.
Displays present
output.
Displays present
output.
Displays present
output.
Outputs high or low
range limit value.
Displays high or low
range limit value.
Holds output
immediately before
error occurrence.
Holds output
immediately before
error occurrence.
Holds output
immediately before
error occurrence.
Displays present
output.
Replace capsule.
Replace amplifier.
Check input.
Check line pressure
(static pressure).
Use heat insulation or
make lagging to keep
temperature within
range.
Use heat insulation or
make lagging to keep
temperature within
range.
Check input and range
setting, and change
them as needed.
Check input and
display conditions and
modify them as
needed.
Check LRV and
modify as needed.
Check HRV and
modify as needed.
Check SPAN and
change as needed.
Readjust zero point.
T0710 .EPS
7-17
IM 1C22J1-01E
Page 47

8. MAINTENANCE
8. MAINTENANCE
8.1 Overview
WARNING
Since the accumulated process fluid may be
toxic or otherwise harmful, take appropriate care
to avoid contact with the body, or inhalation of
vapors during draining condensate or venting
gas in transmitter pressure-detector section even
after dismounting the instrument from process
line for maintenance.
Maintenance of the transmitter is easy due to its
modular construction. This chapter describes the
procedures for calibration, adjustment, and the disassembly and reassembly procedures required for
component replacement.
Since the transmitters are precision instruments,
carefully and thoroughly read the following sections
for proper handling during maintenance.
IMPORTANT
• As a rule, maintenance of this transmitter
should be implemented in a maintenance
service shop where the necessary tools are
provided.
• The CPU assembly contains sensitive parts
that may be damaged by static electricity.
Exercise care so as not to directly touch the
electronic parts or circuit patterns on the board,
for example, by preventing static electrification
by using grounded wrist straps when handling
the assembly.
Also take precautions such as placing a removed CPU assembly into a bag with an
antistatic coating.
8.2 Calibration Instruments Selection
Table 8.2.1 shows the instruments required for calibration. Select instruments that will enable the transmitter
to be calibrated or adjusted to the required accuracy.
The calibration instruments should be handled carefully
so as to maintain the specified accuracy.
8.3 Calibration
Use the procedure below to check instrument operation
and accuracy during periodic maintenance or troubleshooting.
1) Connect the instruments as shown in Figure 8.3.1
and warm up the instruments for at least five
minutes.
IMPORTANT
• To adjust the transmitter for highest accuracy,
make adjustments with the power supply
voltage and load resistance including leadwire
resistances set close to the conditions under
which the transmitter is installed.
• If the measurement range 0% point is 0 kPa or
shifted in the positive direction (suppressed
zero), the reference pressure should be applied
on the high pressure side, as shown in the
figure. If the measurement range 0% point is
shifted in the negative direction (elevated zero),
the reference pressure should be applied using
the vacuum pump.
2) Apply reference pressures of 0%, 50%, and 100%
of the measurement range to the transmitter.
Calculate the errors (differences between digital
voltmeter readings and reference pressures) as the
pressure is increased from 0% to 100% and is
decreased from 100% to 0%, and confirm that the
errors are within the required accuracy.
8-1
IM 1C22J1-01E
Page 48

8. MAINTENANCE
Table 8.2.1 Tools for Disassembly and Reassembly
Name RemarksYokogawa-recommended Instrument
Power
supply
Load
resistor
Voltmeter
Model SDBT or SDBS distributor
Model 2792 standard resistor [250 Ω ±0.005%, 3 W]
Load adjustment resistor [100 Ω ±1%, 1 W]
Model 2501 A digital multimeter
Accuracy (10V DC range): ±(0.002% of rdg + 1 dgt)
4 to 20 mA DC signal
Model MT110, MT120 precision digital manometer
1) For 10 kPa class
Accuracy: ±(0.015% of rdg + 0.015% of F.S.)
±(0.2% of rdg + 0.1% of F.S.)
. . . . . . . . .
for 0 to 10 kPa
. . . . .
for -10 to 0 kPa
2) For 130 kPa class
Digital
manometer
Accuracy: ±0.02% of rdg
±5digits
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
±(0.2% of rdg + 0.1% of F.S.)
3) For 700 kPa class
Accuracy: ±(0.02% of rdg + 3digits)
±5 digits
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
±(0.2% of rdg + 0.1% of F.S.)
. . . . . . . . .
. . . . . . . . . . . . .
. . . . . . . . .
for 25 to 130 kPa
for 0 to 25 kPa
for -80 to 0 kPa
for 100 to 700 kPa
for 0 to 100 kPa
for -80 to 0 kPa
Select a manometer having
a pressure range close to
that of the transmitter.
4) For 3000 kPa class
Accuracy: ±(0.02% of rdg + 10 digits)
±(0.2% of rdg + 0.1% of F.S.)
. . . . . . . . . . .
. . . . . . . . .
for 0 to 3000 kPa
for -80 to 0 kPa
5) For 130 kPa abs class
Pressure
generator
Accuracy: ±(0.03% of rdg + 6 digits)
. . . . . . . . . . . .
Model 2657 pneumatic pressure standard for 200 kPa {2 kgf/cm
Accuracy: ±0.05% of F.S. or ±0.1% setting (whichever is greater)
Dead weight gauge tester 25 kPa {2500mmH2O}
Accuracy: ±0.03% of setting
for 0 to 130 kPa abs
2
}, 25 kPa {2500 mmH2O}
Requires air pressure
supply.
Select a pressure generator
having a pressure range
close to that of the transmitter.
Pressure
source
Model 6919 pressure regulator (pressure pump)
Pressure range: 0 to 133 kPa {1000 mmHg}
Prepare the vacuum pump
for negative pressure
ranges.
T0801.EPS
Note : The above table contains the instruments capable of performing calibration to the 0.2% level. Since special maintenance and management
procedures involving traceability of each instrument to higher-level standards are required for calibration to the 0.1% level, there are
difficulties in calibration to this level in the field.
For calibration to the 0.1% level, contact Yokogawa representatives from which the instrument was purchased or the nearest Yokogawa
office.
Mating calibration flange
Diaphragm seal
Figure 8.3.1 Instrument Connections
Reference
pressure
Load resistance, 250Ω
Rc
Load adjustment
resistance, 100Ω
Model MT110, MT120
precision digital manometer
P
P
Model 2657 pneumatic
pressure standards
Power
supply
R
E
V
Digital voltmeter
8-2
If a pressure source
and a manometer
are combined:
Pressure source
Supply pressure
If a pressure
generator is used:
F0801.EPS
IM 1C22J1-01E
Page 49

8. MAINTENANCE
t
S
8.4 Disassembly and Reassembly
This section describes procedures for disassembly and
reassembly for maintenance and component replacement.
Always turn OFF power and shut off and release
pressures before disassembly. Use proper tools for all
operations. Table 8.4.1 shows the tools required.
Table 8.4.1 Instruments Required for Calibration
Tool RemarksQuantity
Phillips screwdriver
Slotted screwdriver
Allen wrenches
Wrench
Torque wrench
Adjustable wrench
Socket wrench
Socket driver
Tweezers
CAUTION
Precautions for CENELEC, SAA, and JIS
Flameproof Type Transmitters
• Flameproof type transmitters must be, as a
rule, removed to a non-hazardous area for
maintenance and be disassembled and reassembled to the original state. For details, see
“Installation and Operating Precautions for JIS
Flameproof Equipment” later in this manual.
• Two covers are locked by each of an Allen
head bolt (shrouding bolt) on the flameproof
type transmitters. When a shrouding bolt is
driven clockwise by an Allen wrench, it is going
in and cover lock is released, and then a cover
can be opened.
When a cover is closed it should be locked by
a shrouding bolt without fail. Tighten the
shrouding bolt to a torque of 0.7 N·m.
1
JIS B4633, No. 2
1
2
JIS B4648
One each, nominal 3 and
5 mm Allen wrenches
1
Width across flats, 17 mm
1
1
1
Width across flats, 16 mm
1
Width across flats, 5.5 mm
1
T0902.EPS
8.4.1 Replacing the Integral Indicator
This subsection describes the procedure for replacing
an integral indicator. (See Figure 8.4.2)
CAUTION
Precautions for JIS Flameproof Type Trans-
mitters
Users are prohibited by law from modifying the
construction of a flameproof type transmitter.
Thus the user is prohibited from using a flameproof type transmitter with its integral indicator
removed, or from adding an integral indicator to
a transmitter. If such modification is absolutely
required, contact Yokogawa.
j Removing the Integral Indicator
1) Remove the cover.
2) Supporting the integral indicator by hand, loosen
its two mounting screws.
3) Dismount the LCD board assembly from the CPU
assembly.
When doing this, carefully pull the LCD board
assembly straight forward so as not to damage the
connector between it and the CPU assembly.
j Attaching the Integral Indicator
1) Align both the LCD board assembly and CPU
assembly connectors and engage them.
2) Insert and tighten the two mounting screws.
3) Replace the cover.
Output terminal cable
Press
forward
LCD board
assembly
Integral
indicator
Shrouding bolt
Figure 8.4.1 Shrouding Bolts
Shrouding bol
F0802.EP
Boss
Bracket
(for zero-adjustment
screw pin)
Cover
Figure 8.4.2 Removing and Attaching LCD Board
Mounting
screw
Assembly and CPU Assembly
CPU assembly
Flat cable
8-3
Zero-adjustment
screw pin
F0803.EPS
IM 1C22J1-01E
Page 50

8.4.2 Replacing the CPU Assembly
NOTE
This subsection describes the procedure for replacing
the CPU assembly. (See Figure 8.4.2)
j Removing the CPU Assembly
1) Remove the cover. If an integral indicator is
mounted, refer to Subsection 8.4.1 and remove the
indicator.
2) Turn the zero-adjustment screw to the position
(where the screw head slot is horizontal) shown in
Figure 8.4.2.
3) Disconnect the output terminal cable (cable with
brown connector at the end). When doing this,
lightly press the side of the CPU assembly connector and pull the cable connector to disengage.
4) Use a socket driver (width across flats, 5.5mm) to
loosen the two bosses.
5) Carefully pull the CPU assembly straight forward
to remove it.
6) Disconnect the flat cable (cable with black connector at the end) that connects the CPU assembly and
the capsule.
8. MAINTENANCE
Confirm that the zero-adjustment screw pin is
placed properly in the groove on the bracket
prior to tightening the two bosses. If it is not, the
zero-adjustment mechanism will be damaged.
5) Replace the cover.
NOTE
Be careful not to apply excessive force to the
CPU assembly when removing it.
j Mounting the CPU Assembly
1) Connect the flat cable (with black connector)
between the CPU assembly and the capsule.
2) Connect the output terminal cable (with brown
connector).
NOTE
Make certain that the cables are free of pinching
between the case and the CPU assembly edge.
3) Align and engage the zero-adjustment screw pin
with the groove on the bracket on the CPU
assembly. Then insert the CPU board assembly
straight onto the post in the amplifier case.
4) Tighten the two bosses. If the transmitter is
equipped with an integral indicator, refer to
Subsection 8.4.1 to mount the indicator.
8-4
IM 1C22J1-01E
Page 51

8. MAINTENANCE
8.5 Troubleshooting
If any abnormality appears in the measured values, use
the troubleshooting flow chart below to isolate and
remedy the problem. Since some problems have
complex causes, these flow charts may not identify all.
If you have difficulty isolating or correcting a problem,
contact Yokogawa service personnel.
8.5.1 Basic Troubleshooting
First determine whether the process variable is actually
abnormal or a problem exists in the measurement
system.
If the problem is in the measurement system, isolate
the problem and decide what corrective action to take.
This transmitter is equipped with a self-diagnostic
function which will be useful in troubleshooting; see
Section 7.5 for information on using this function.
: Areas where self-diagnostic offers support
Abnormalities appear in measurement.
8.5.2 Troubleshooting Flow Charts
The following sorts of symptoms indicate that transmitter
may not be operating properly.
Example : • There is no output signal.
• Output signal does not change even though
process variable is known to be varying.
• Output value is inconsistent with value
inferred for process variable.
Connect BRAIN TERMINAL and check self-diagnostics.
Does the self-diagnostic
indicate problem location?
NO
Is power supply
polarity correct?
YES
Refer to error message summary in
Subsection 7.5.2 to take actions.
Refer to Section 5.3 to check/correct
polarity at each terminal from power
supply to the terminal box.
YES
NO
YES
Inspect the
process system.
YES
Inspect receiver.
Environmental conditions
Check/correct
environmental conditions.
Is process variable
itself abnormal?
NO
Measurement system problem
Isolate problem in
measurement system.
Does problem exist in
receiving instrument?
NO
Operating conditions
Transmitter itself
Check transmitter.
Are power
supply voltage and load
resistance correct?
YES
Is there
continuity through the
transmitter loop wiring?
Do the loop numbers
match?
YES
Contact Yokogawa service personnel.
Refer to Section 5.6 to obtain rated
voltage and load resistance.
Find/correct broken conductor or
wiring error.
NO
NO
F0805.EPS
Check/correct operating
conditions.
Figure 8.5.1 Basic Flow and Self-Diagnostics
F0804.EPS
8-5
IM 1C22J1-01E
Page 52

8. MAINTENANCE
Output travels beyond 0% or 100%.
Connect BRAIN TERMINAL and check self-diagnostics.
Does the self-
diagnostic indicate problem
YES
location?
NO
Refer to error message summary in
Subsection 7.5.2 to take actions.
Is the
diaphragm seal correctly
NO
connected to the
process?
YES
Is power supply
Correct the connections.
NO
polarity correct?
Large output error.
Connect BRAIN TERMINAL and check self-diagnostics.
Does the self-
diagnostic indicate the problem
YES
location?
NO
Are power
supply voltage and load
Refer to error message summary in
Subsection 7.5.2 to take actions.
NO
resistance correct?
YES
Refer to Section 5.6 to obtain the rated
voltage and load resistance.
Is external noise
YES
contained in the outout?
NO
Avoid noise by providing complete
grounding, or using shielded wires.
YES
Check/correct polarity at each terminal
from power supply to the terminal box.
Is the pressure as specified?
YES
Use the transmitter within the
measurement range shown on the
data plate.
Is zero point
adjusted correctly?
YES
Adjust the zero point.
Contact Yokogawa service personnel.
NO
NO
F0806.EPS
Is excess capillary secured?
YES
Is transmitter
installed where there is
marked variation in
temperature?
NO
Were appropriate
instruments used for
calibration?
YES
Is output adjusted correctly?
YES
NO
Secure it so that it is not moved by
wind or vibration.
YES
Provide lagging and/or heat insulation,
or allow adequate ventilation.
NO
Refer to Section 8.2 when selecting
instruments for calibration.
NO
Adjust the output.
8-6
Contact Yokogawa service personnel.
F0807.EPS
IM 1C22J1-01E
Page 53

9. GENERAL SPECIFICATIONS
L= -
65 x 10
6
(R x C)
(Cf + 10,000)
C
9. GENERAL SPECIFICATIONS
9.1 Standard Specifications
Refer to GS 1C22T2-E for Fieldbus communication type marked with “e”.
d Performance Specifications
See General Specifications sheet, GS 1C22J3-E.
d Functional Specifications
Span & Range Limits
Measurement
Span
and Range
Span
A
Range
Span
Range
EJA438WEJA438N
B
Span
Range
MPa
0.06 to 3
–0.1 to 3
0.46 to 14
–0.1 to 14
0.46 to 7
–0.1 to 7
Measurement range is within the flange rating.
Zero Adjustment Limits:
Zero can be fully elevated or suppressed, within
the Lower and Upper Range Limits of the capsule.
External Zero Adjustment “e”:
External zero is continuously adjustable with
0.01% incremental resolution of span. Span may
be adjusted locally using the digital indicator with
range switch.
Output “e”:
Two wire 4 to 20 mA DC output with digital
communications, linear or square root programmable. BRAIN or HART FSK protocol are superimposed on the 4 to 20 mA signal.
Failure Alarm:
Output status at CPU failure and hardware error;
Up-scale: 110%, 21.6 mA DC or more (standard)
Down-scale: –5%, 3.2 mA DC
Note: Applicable for Output signal code D and E
Damping Time Constant (1st order):
The sum of the amplifier and capsule damping
time constant must be used for the overall time
constant. Amp damping time constant is adjustable
from 0.2 to 64 seconds.
Capsule (Silicone Oil)
Time Constant (approx. sec) 0.4
When the capillary length 3 m and the fill fluid code
A.
psi
(/D1)
8.6 to 430
–15 to 430
66 to 2000
–15 to 2000
66 to 1000
–15 to 1000
bar
(/D3)
0.6 to 30
–1 to 30
4.6 to 140
–1 to 140
4.6 to 70
–1 to 70
A and B
kgf/cm
(/D4)
0.6 to 30
–1 to 30
4.6 to 140
–1 to 140
4.6 to 70
–1 to 70
T0901.EPS
T0902.EPS
Ambient Temperature Limits:
* Safety approval codes may affect limits.
–40 to 60°C (–40 to 140°F),
–30 to 60°C (–22 to 140°F) with LCD Display
Note: The ambient temperature limits must be within the
fill fluid operating temperature range, see Table 1.
Process Temperature Limits:
* Safety approval codes may affect limits.
See Table 1.
2
Working Pressure Limits:
2.7 kPa abs {20 mmHg abs} to flange rating
pressure.
For atmospheric pressure or below, see Figure 1.
d Installation
Supply & Load Requirements “e”:
* Safety approvals can affect electrical requirements.
See Section 5.6, ‘Power Supply Voltage and Load
Resistance.’
EMC Conformity Standards: ,
For EMI (Emission): EN55011, AS/NZS 2064 1/2
For EMS (Immunity): EN50082-2
Communication Requirements “e”:
BRAIN
Communication Distance;
Up to 2 km (1.25 miles) when using CEV polyethylene-insulated PVC-sheathed cables.
Communication distance varies depending on type
of cable used.
Load Capacitance;
0.22 µF or less (see note)
Load Inductance;
3.3 mH or less (see note)
Input Impedance of communicating device;
10 kΩ or more at 2.4 kHz.
Note: For general-use and Flameproof type.
For Intrinsically safe type, please refer to
‘Optional Specifications.’
HART
Communication Distance;
Up to 1.5 km (1 mile) when using multiple twisted
pair cables. Communication distance varies
depending on type of cable used.
Use the following formula to determine cable
length for specific applications:
Where:
L = length in meters or feet
R = resistance in Ω (including barrier resistance)
C = cable capacitance in pF/m or pF/ft
Cf = maximum shunt capacitance of receiving
devices in pF/m or pF/ft
9-1
IM 1C22J1-01E
Page 54

9. GENERAL SPECIFICATIONS
d Physical Specifications
Wetted Parts Materials:
Diaphragm and other wetted parts;
See ‘Model and Suffix Codes’
Non-wetted Parts Materials:
Capillary tube;
SUS316
Protection tube;
SUS304, PVC-sheathed [Max. operating temperature: 100°C (212°F)]
Fill Fluid;
See Table 1.
Housing;
Low copper cast-aluminum alloy with polyurethane
paint (Munsell 0.6GY3.1/2.0)
Enclosure Classification;
JIS C0920 immersion proof (equivalent to NEMA
4X and IEC IP67)
Cover O-rings;
Buna-N
Data plate and tag;
SUS304
Weight:
9.3 kg (20.5 lb): Model EJA438W, 2-inch ANSI
Class 150 flange, without mounting bracket. Add
1.4 kg (3.1 lb) for JIS SCS14A stainless steel
amplifier housing.
Connections:
Refer to the ‘Model and Suffix Codes’ to specify
the process and electrical connection type.
Process temperature
for fill fluid code B
Transmitter ambient
temperature range
(For fill fluid code A,B)
100{750}
Working
pressure
kPa abs
{mmHg abs}
10{75}
2.7{20}
1{7.5}
0.1{0.75}
Figure 1. Working Pressure and Process Temperature
Process temperature
for fill fluid code A
-50 0 50 100 150 200 250 300
Process Temperature (8C)
Process temperature
for fill fluid code C
F0901.EPS
Flange max.
working
pressure
Atmospheric
pressure
Table 1. Process Temperature and Ambient Temperature
Silicone Oil Fluorinated Oil Ethylene Glycol
Process
Ambient
Specific
(Note 3)
(Note 1)
(Note 2)
Temperature
temperature
Working pressure
gravity
Fill Fluid
Code ‘A’
–10 to 2508C
(14 to 4828F)
–10 to 608C
(14 to 1408F)
Note 1: See Figure 1. ‘Working Pressure and Process Temperature.’
Note 2: This ambient temperature is the transmitter ambient temperature.
Note 3: Approximate values at a temperature of 25°C(77°F)
Note 4: The pressure transmitter should be installed at least 600 mm below the process connection.
However, this value(600 mm) may be affected by ambient temperature, operating pressure, fill
fluid or material of the wetted diaphragm. Contact YOKOGAWA when the transmitter can not be
installed at least 600 mm below the process connection.
Fill Fluid
Code ‘B’
–30 to 1808C
(–22 to 3568F)
–15 to 608C
(5 to 1408F)
See Figure 1.
0.941.07 1.09
<Settings When Shipped “e”>
Tag Number
Output Mode
Display Mode
Operation Mode
Damping Time
Constant
As specified in order
‘Linear’
‘Linear’
‘Normal’ unless otherwise specified in order
‘2 sec.’
*1
Fill Fluid
Code ‘C’
10 to 3008C
(50 to 5728F)
10 to 608C
(50 to 1408F)
Calibration Range
Lower Range Value
Calibration Range
Higher Range Value
Calibration Range
Units
Fill Fluid
Code ‘D’
–20 to 1208C
(–4 to 2488F )
–10 to 608C
(–14 to 1408F )
51 kPa abs or more
{380 mmHg abs}
1.90 to 1.92 1.09
As specified in order
As specified in order
Selected from mmH2O, mmAq, mmWG,
mmHg, Torr, Pa, hPa, kPa, MPa, mbar,
bar, gf/cm2, kgf/cm2, inH2O, inHg, ftH2O,
psi, or atm.(Only one unit can be specified)
Fill Fluid
Code ‘E’
–50 to 1008C
(–58 to 2128F)
–40 to 608C
(–40 to 1408F)
Vacuum pressure
not allowed
T0903.EPS
T0908.EPS
Note 1: If Tag No. is no more than 16 alphanumeric characters (including - and ·), it will be written into
the tag plate and amplifier memory settings.
9-2
IM 1C22J1-01E
Page 55

9. GENERAL SPECIFICATIONS
9.2 Model and Suffix Codes
d Model EJA438W [Style: S2]
Model Suffix Codes Description
EJA438W
Output Signal
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
-D
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
-E
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
-F
Measurement span
(capsule)
Wetted parts material
Process flange rating
Process flange
size / material
Cover flange bolts material
Fill fluid
Capillary length (m)
Installation
Electrical connection
Integral indicator
Mounting bracket
Optional codes
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
A
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
B
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
S
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
H
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
T
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
U
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
J1
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
J2
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
J4
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
J6
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
A1
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
A2
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
A4
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
D2
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
D4
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
D5
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
A
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
B
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
C
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
D
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
E
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
F
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
A
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
B
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
-A
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
-B
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
-C
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
-D
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
-E
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
A
. . . . . . . . . . . . .
h h
. . . . . . . . . . . . . .
-9
. . . . . . . . . . . . .
0
. . . . . . . . . . . . .
2
. . . . . . . . . . . . .
3
. . . . . . . . . . . . .
4
. . . . . . . . . . . . .
5
. . . . . . . . . . . . .
7
. . . . . . . . . . . . .
8
. . . . . . . . . . . . .
9
. . . . . . . . . .
D
. . . . . . . . . .
E
. . . . . . . . . .
N
. . . . . . . . .
A
. . . . . . . . .
B
. . . . . . . . .
N
/h Optional specification
Example: EJA438W-DASA1AA-AA02-92NA/h
Note 1: Refer to GS 1C22T1-E for HART Protocol version.
Note 2: In case of wetted parts material code T(Tantalum), maximum process temperature limits is 200°C.
Note 3: Refer to GS 1C22T2-E for Fieldbus communication.
Diaphragm sealed differential pressure transmitter
(Flush diaphragm type)
4 to 20 mA DC with digital communication (BRAIN protocol)
4 to 20 mA DC with digital communication (HART protocol)
Digital communication (FOUNDATION Fieldbus protocol)
(Note 1)
(Note 3)
0.06 to 3 MPa {0.6 to 30 kgf/cm2}
2
0.46 to 14 MPa {4.6 to 140 kgf/cm
}
[Diaphragm] [Others]
JIS SUS316L JIS SUS316L
Hastelloy C-276 Hastelloy C-276
Tantalum Tantalum
(Note 2)
Titanium Titanium
JIS 10K
JIS 20K
JIS 40K
JIS 63K
ANSI class 150 P1
ANSI class 300 P2
ANSI class 600 P4
. . . . . . . . . .
. . . . . . . . . .
. . . . . . . . . .
JPI class 150
JPI class 300
JPI class 600
DIN PN10/16
DIN PN25/40
DIN PN64
2-inch (50 mm) / JIS S25C
2-inch (50 mm) / JIS SUS304
2-inch (50 mm) / JIS SUS316
3-inch (80 mm) / JIS S25C
3-inch (80 mm) / JIS SUS304
3-inch (80 mm) / JIS SUS316
JIS SCM435
JIS SUS630
[Process temp.] [Ambient temp.]
For general use (silicone oil) –10 to 250 8C –10 to 60 8C
For general use (silicone oil) –30 to 180 8C –15 to 60 8C
For high temperature use (silicone oil) 10 to 300 8C 10 to 60 8C
For oil-prohibited use (fluorinated oil) –20 to 120 8C –10 to 60 8C
For low temperature use (ethylene glycol) –50 to 100 8C –40 to 60 8C
Always A
Specify capillary length from 1 to 10 m in h h. (Example for 2 m: 02)
Horizontal impulse piping type, left side high pressure
G1/2 female, one electrical connection
1/2 NPT female, two electrical connections without blind plug
PG 13.5 female, two electrical connections without blind plug
M20 female, two electrical connections without blind plug
G1/2 female, two electrical connections and a blind plug
1/2 NPT female, two electrical connections and a blind plug
PG 13.5 female, two electrical connections and a blind plug
M20 female, two electrical connections and a blind plug
Digital indicator
Digital indicator with the range setting switch
(None)
JIS SECC 2-inch pipe mounting (flat type)
JIS SUS304 2-inch pipe mounting (flat type)
(None)
T0904.EPS
9-3
IM 1C22J1-01E
Page 56

9. GENERAL SPECIFICATIONS
d Model EJA438N [Style: S2]
Model Suffix Codes Description
EJA438N
Output Signal
Measurement span
(capsule)
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
-D
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
-E
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
-F
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
A
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
B
Wetted parts material
S
Process flange rating
Diaphragm extension
length (X
2
)
Process flange size / material
Cover flange bolts material
Fill fluid
Capillary length (m)
Installation
Electrical connection
Integral indicator
Mounting bracket
Optional codes
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
J1
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
J2
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
J4
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
A1
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
A2
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
P1
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
P2
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
D2
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
D4
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
2
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
4
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
6
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
G
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
H
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
J
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
D
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
E
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
F
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
A
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
B
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
-A
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
-B
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
-C
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
-D
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
-E
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
B
. . . . . . . . . .
h h
. . . . . . . . . . . .
-9
. . . . . . . . . . .
0
. . . . . . . . . . .
2
. . . . . . . . . . .
3
. . . . . . . . . . .
4
. . . . . . . . . . .
5
. . . . . . . . . . .
7
. . . . . . . . . . .
8
. . . . . . . . . . .
9
. . . . . . . . .
D
. . . . . . . . .
E
. . . . . . . . .
N
. . . . . . . .
A
. . . . . . . .
B
. . . . . . . .
N
/h Optional specification
Example: EJA438N-DASA12GA-AB02-92NA/h
Note 1: Refer to GS 1C22T1-E for HART Protocol version.
Note 2: Refer to GS 1C22T2-E for Fieldbus communication.
Diaphragm sealed differential pressure transmitter
(Extended diaphragm type)
4 to 20 mA DC with digital communication (BRAIN protocol)
4 to 20 mA DC with digital communication (HART protocol)
Digital communication (FOUNDATION Fieldbus protocol)
(note 1)
(note 2)
0.06 to 3 MPa {0.6 to 30 kgf/cm2}
0.46 to 7 MPa {46 to 70 kgf/cm
2
}
[Diaphragm] [Pipe] [Others]
JIS SUS316L JIS SUS316 JIS SUS316
JIS 10K
JIS 20K
JIS 40K
ANSI class 150
ANSI class 300
JIP class 150
JIP class 300
DIN PN10/16
DIN PN25/40
X
2
= 50 mm
X
2
= 100 mm
2
= 150 mm
X
4-inch (100 mm) / JIS S25C
4-inch (100 mm) / JIS SUS304
4-inch (100 mm) / JIS SUS316
3-inch (80 mm) / JIS S25C
3-inch (80 mm) / JIS SUS304
3-inch (80 mm) / JIS SUS316
JIS SCM435
JIS SUS630
[Process [Ambient
temperature] temperature]
For general use (silicone oil) –10 to 250 8C –10 to 60 8C
For general use (silicone oil) –30 to 180 8C –15 to 60 8C
For high temperature use (silicone oil) 10 to 300 8C 10 to 60 8C
For oil-prohibited use (fluorinated oil) –20 to 120 8C –10 to 60 8C
For low temperature use (ethylene glycol) –50 to 100 8C –40 to 60 8C
Always B
Specify capillary length from 1 to 10 m in h h. (Example for 2 m: 02)
Horizontal impulse piping type, left side high pressure
G1/2 female, one electrical connection
1/2 NPT female, two electrical connections without blind plug
PG 13.5 female, two electrical connections without blind plug
M20 female, two electrical connections without blind plug
G1/2 female, two electrical connections and a blind plug
1/2 NPT female, two electrical connections and a blind plug
PG 13.5 female, two electrical connections and a blind plug
M20 female, two electrical connections and a blind plug
Digital indicator
Digital indicator with the range setting switch
(None)
JIS SECC 2-inch pipe mounting (flat type)
JIS SUS304 2-inch pipe mounting (flat type)
(None)
T0905.EPS
9-4
IM 1C22J1-01E
Page 57

9.3 Optional Specifications
Item Description Code
FM Explosionproof Approval
Explosionproof for Class I, Division 1, Groups B, C and D
Dust-ignitionproof for Class II/III, Division 1, Groups E, F and G
Hazardous (classified) locations, indoors and outdoors ( NEMA 4X )
Temperature class: T6
Amb. Temp.:–40 to 60 8C (–40 to 140 8F)
Electrical connection: 1/2 NPT female
FM Intrinsically safe Approval
Intrinsically Safe for Class I, Division 1, Groups A, B, C & D, Class II, Division 1,
Factory Mutual (FM)
CENELEC (KEMA)
Canadian Standards
Association (CSA)
Standards Association of
Australia (SAA)
Japanese Industrial
Standards (JIS)
Attached flameproof
Packing adapter
Groups E, F & G and Class III, Division 1 Hazardous Locations.
Nonincendive for Class I, Division 2, Groups A, B, C & D, Class II, Division. 2,
Groups E, F & G, and Class III, Division 1 Hazardous Locations.
Enclosure: “NEMA 4X”, Temp. Class: T4, Amb. Temp.: –40 to 60 8C (–40 to 140 8F)
Intrinsically Safe Apparatus Parameters
[Groups A, B, C, D, E, F and G]
Vmax=30 V, Imax=165 mA, Pmax=0.9 W, Ci=22.5 nF, Li=730 mH
[Groups C, D, E, F and G]
Vmax=30 V, Imax=225 mA, Pmax=0.9 W, Ci=22.5 nF, Li=730 mH
Electrical connection: 1/2 NPT female
Combined FF1and FS1
Electrical connection: 1/2 NPT female
CENELEC (KEMA) Flameproof Approval
EExd IIC T4, T5, T6, Amb. Temp.: –40 to 80 8C (–40 to 176 8F)
Max. process Temp.: T4; 120 8C (248 8F), T5; 100 8C (212 8F), T6; 85 8C (185 8F)
Electrical connection: 1/2 NPT female, Pg 13.5 female and M20 female
CENELEC (KEMA) Intrinsically safe Approval
EEx ia IIC T4, Amb. Temp.: –40 to 60 8C(–40 to 140 8F)
Ui=30 V, Ii=165 mA, Pi=0.9 W, Ci=22.5 nF, Li=730 mH
Electrical connection: 1/2 NPT female, Pg 13.5 female and M20 female
Combined KF1, KS1 and Type N Approval
KEMA Type N Approval
Ex nA IIC T4, Amb. Temp.: –40 to 60 8C(–40 to 140 8F)
U=30 V, I=165 mA
Electrical connection: 1/2 NPT female, Pg 13.5 female and M20 female
CSA Explosionproof Approval
Explosionproof for Class I, Division 1, Groups B, C and D
Dustignitionproof for Class II/III, Division 1, Groups E, F and G
Division2 ‘SEALS NOT REQUIRED’ , Temp. Class : T4, T5, T6 Encl Type 4x
Max. Process Temp.: T4; 120 8C (248 8F), T5; 100 8C (212 8F), T6; 85 8C (185 8F)
Amb. Temp.:–40 to 80 8C (–40 to 176 8F)
Electrical connection: 1/2 NPT female
CSA Intrinsically safe Approval
Class I, Groups A, B, C and D Class II and III, Groups E, F and G
Encl Type 4x, Temp. Class: T4, Amb. Temp.: –40 to 60 8C (–40 to 140 8F)
Vmax=30 V, Imax=165 mA, Pmax=0.9 W, Ci=22.5 nF, Li=730 mH
Electrical connection: 1/2 NPT female
Combined CF1 and CS1
Electrical connection: 1/2 NPT female
SAA Flameproof, Intrinsically safe and Non-sparking Approval
Ex d IIC T4/T5/T6, IP67 class I, Zone 1, Amb. Temp. : –40 to 80 8C (–40 to 176 8F)
Max. Process Temp.: T4; 120 8C (248 8F), T5; 100 8C (212 8F), T6; 85 8C (185 8F)
Ex ia IIC T4, IP67 class I, Zone 0
Ex n IIC T4, IP67 class I, Zone 2
Ui=30 V DC, Ii=165 mA DC, Wi=0.9 W, Amb. Temp.: –40 to 60 8C (–40 to 140 8F)
Electrical connection: 1/2 NPT female, Pg 13.5 female and M20 female
JIS Flameproof Approval, Ex do IIC T4X
Amb. Temp. –20 to 60 8C, Process Temp. –20 to 120 8C
JIS Intrinsically safe Approval, Ex ia IIC T4
Amb. Temp. –20 to 60
Electrical connection: G1/2 female
Applicable cable O.D.: 8 to 12 mm
8C, Process Temp. –20 to 120 8C
9. GENERAL SPECIFICATIONS
FF1
FS1
FU1
KF1
KS1
KU1
CF1
CS1
CU1
SU1
JF3
JS1
1 pc.
2 pcs.
G11
G12
T0906.EPS
9-5
IM 1C22J1-01E
Page 58

Item Description Code
Color change
Painting
Coating change
Lightning protector
Oil-prohibited use
Oil-prohibited use with
dehydrating treatment
Calibration units
Sealing treatment to JIS
SUS630 nuts
No serration
Teflon film
Operating temperature
correction
(Note 1)
(Note 2)
(Note 3)
Capillary without PVC
sheaths
Fast response
Failure alarm down-scale
(Note 4)
Stainless steel amplifier
housing
(Note 5)
Gold-plate
Mill Certificate
Pressure test/Leak test
Certificate
9. GENERAL SPECIFICATIONS
Amplifier cover only
Epoxy resin-baked coating
Ph
X1
Transmitter power supply voltage: 10.5 to 32 V DC (9 to 32 V DC for Fieldbus
communication type) Allowable current: Max. 6000 A (1x40 µs),
A
Repeating 1000 A (1x40 µs) 100 times
Degrease cleansing treatment
Degrease cleansing and dehydrating treatment
P calibration (psi unit)
bar calibration (bar unit)
(See Table for Span and
Range Limits)
M calibration (kgf/cm2 unit)
Sealant (liquided silicone rubber) is coated on surfaces of JIS SUS630 nuts used for cover
flange mounting.
No serration work on the flange gasket surface (for ANSI flange only)
With FEP film and fluorinated oil
Working range: 20 to 150°C, 0 to 2 MPa {0 to 20 kgf/cm2} (Not usable under vacuum)
Adjusting range: 80 to 300°C
When ambient temperature exceeds 100°C, or use of PVC is prohibited
Update time: 0.125 sec or less, see GS for the response time
Output status at CPU failure and hardware error: –5%, 3.2 mA DC or less.
When combining with Optional code F1, output signal is –2.5%, 3.6 mA DC or less.
Amplifier housing material: JIS SCS14A stainless steel (equivalent to JIS SUS316 cast
stainless steel or ASTM CF-8M)
Gold-plated diaphragm
Process flange, Block
For model EJA438W
For model EJA438N
Process flange, Block, Pipe, Base
( Flange rating )
JIS 10K
JIS 20K
JIS 40K
JIS 63K
ANSI/JPI Class 150
For A-capsuleFor B-capsule
ANSI/JPI Class 300
ANSI/JPI Class 600
JIS 10K
JIS 20K
JIS 40K
JIS 40K
JIS 63K
ANSI/JPI Class 150
ANSI/JPI Class 300
ANSI/JPI Class 300
ANSI/JPI Class 600
( Test Pressure )
2 MPa {20 kgf/cm
3 MPa {30 kgf/cm
3 MPa {30 kgf/cm
3 MPa {30 kgf/cm
3 MPa {29.8 kgf/cm
3 MPa {30 kgf/cm
3 MPa {30 kgf/cm
2 MPa {20 kgf/cm
5 MPa {50 kgf/cm
10 MPa {100 kgf/cm
7 MPa {70 kgf/cm
14 MPa {140 kgf/cm
3 MPa {29.8 kgf/cm
7.7 MPa {77 kgf/cm
7 MPa {70 kgf/cm
14 MPa {140 kgf/cm
(Applicable model)
2
}
2
EJA438W/EJA438N
}
2
}
2
EJA438W
}
2
}
EJA438W/EJA438N
2
}
2
EJA438W
}
2
}
EJA438W/EJA438N
2
}
2
EJA438W
}
2
EJA438N
}
2
EJA438W
}
2
}
EJA438W/EJA438N
2
EJA438W
}
2
EJA438N
}
2
EJA438W
}
Nitrogen(N2) Gas
Retention time:
10 minutes
K1
K5
D1
D3
D4
Y
Q
T
R
V
F1
C1
E1
A1
M05
M06
T41
T42
T43
T45
T46
T47
T49
T31
T32
T33
T34
T35
T36
T37
T38
T39
T0907.EPS
Note 1: This item cannot be applied to Model EJA438W wetted parts material code H (Hastelloy C), T
(Tantalum), or U (Titanium). (In case for code H, T or U, serration work on the flange gasket
surface is not possible)
Note 2: Teflon film can only be specified for model EJA438W.
Note 3: Specify the process operating temperature for zero correction.
Example: Zero correction by process temperature 90°C.
Note 4: The hardware error indicates faulty amplifier or capsule. Standard output status (without /C1) is
up-scale of 110%, 21.6 mA DC or more.
Note 5: Applicable only for electrical connection code ‘2’, ‘3’ or ‘4’. Not applicable for optional code Ph
and X1. Not applicable for optional code JF1 and JS1.
9-6
IM 1C22J1-01E
Page 59

9.4 Dimensions
d Model EJA438W [Style: S2]
1
ød*
25 (0.98)
9. GENERAL SPECIFICATIONS
Unit: mm(approx. inch)
t
f
34
(1.34)
n-øh
140(5.51)
External indicator
conduit connection
(Optional)
333(13.11)
124
(4.88)
47
(1.85)
*1: Indicates inside diameter of gasket contact surface.
94(3.70)
92
(3.62)
2-inch pipe
(O.D. 60.5mm)
Process flange size: 3-inch(80mm)
Flange Rating
JIS 10K
JIS 20K
JIS 40K
JIS 63K
ANSI Class 150
ANSI Class 300
ANSI Class 600
JPI Class 150
JPI Class 300
JPI Class 600
DIN PN 10/16
DIN PN 25/40
DIN PN 64
Process flange size: 2-inch(50 mm)
Flange Rating
JIS 10K
JIS 20K
JIS 40K
JIS 63K
ANSI Class 150
ANSI Class 300
ANSI Class 600
JPI Class 150
JPI Class 300
JPI Class 600
DIN PN 10/16
DIN PN 25/40
DIN PN 64
* In case where process flange material is JIS S25C, value of f is 0.
øD
185(7.28)
200(7.87)
210(8.27)
230(9.06)
190.5(7.50)
209.6(8.25)
209.6(8.25)
190(7.48)
210(8.27)
210(8.27)
200(7.78)
200(7.78)
215(8.46)
øD
155(6.10)
155(6.10)
165(6.50)
185(7.28)
152.4(6.00)
165.1(6.50)
165.1(6.50)
152(6.10)
165(6.50)
165(6.50)
165(6.50)
165(6.50)
180(7.09)
Conduit
connection
Internal
indicator
(Optional)
Clamps (Only for JIS
Flameproof type)
øC
150(5.91)
160(6.30)
170(6.69)
185(7.28)
152.4(6)
168.1(6.62)
168.1(6.62)
152.4(6)
168.1(6.62)
168.1(6.62)
160(6.30)
160(6.30)
170(6.69)
øC
120(4.72)
120(4.72)
130(5.12)
145(5.12)
120.7(4.75)
127.0(5.00)
127.0(5.00)
120.6(4.75)
127.0(5.00)
127.0(5.00)
125(4.92)
125(4.92)
135(5.31)
øg
197(7.76)
Zero
adjustment
Mounting bracket
(Flat-type, Optional)
øg
130(5.12)
130(5.12)
130(5.12)
130(5.12)
130(5.12)
130(5.12)
130(5.12)
130(5.12)
130(5.12)
130(5.12)
130(5.12)
130(5.12)
130(5.12)
øg
100(3.94)
100(3.94)
100(3.94)
100(3.94)
100(3.94)
100(3.94)
100(3.94)
100(3.94)
100(3.94)
100(3.94)
100(3.94)
100(3.94)
100(3.94)
ød
90(3.54)
90(3.54)
90(3.54)
90(3.54)
90(3.54)
90(3.54)
90(3.54)
90(3.54)
90(3.54)
90(3.54)
90(3.54)
90(3.54)
90(3.54)
ød
61(2.40)
61(2.40)
61(2.40)
61(2.40)
61(2.40)
61(2.40)
61(2.40)
61(2.40)
61(2.40)
61(2.40)
61(2.40)
61(2.40)
61(2.40)
ø78
øC
12
(0.47)
(3.07)
18(0.71)
22(0.87)
32(1.26)
40(1.57)
23.9(0.94)
28.5(1.12)
31.8(1.25)
24(0.94)
28.5(1.12)
38.4(1.51)
20(0.79)
24(0.94)
28(1.10)
16(0.63)
18(0.71)
26(1.02)
34(1.34)
19.1(0.75)
22.4(0.88)
31.8(1.25)
19.5(0.77)
22.5(0.89)
31.9(1.26)
18(0.71)
20(0.78)
26(1.02)
øD
110 (4.33)
t
1.6(0.06)
1.6(0.06)
6.4(0.25)
1.6(0.06)
1.6(0.06)
6.4(0.25)
t
1.6(0.06)
1.6(0.06)
6.4(0.25)
1.6(0.06)
1.6(0.06)
6.4(0.25)
Terminal
side
Ground
terminal
Open to
atmosphere
(ø5mm)
f *
n
0
8
0
8
0
8
0
8
4
8
8
4
8
8
0
8
0
8
0
8
f *
n
0
4
0
8
0
8
0
8
4
8
8
4
8
8
0
4
0
4
0
4
Wetted parts material
code U (Titanium)
146(5.75)
øh
19(0.75)
23(0.91)
23(0.91)
25(0.98)
19.1(0.75)
22.4(0.88)
22.4(0.88)
19(0.75)
22(0.87)
22(0.87)
18(0.71)
18(0.71)
22(0.87)
øh
19(0.75)
19(0.75)
19(0.75)
23(0.91)
19.1(0.75)
19.1(0.75)
19.1(0.75)
19(0.75)
19(0.75)
19(0.75)
18(0.71)
18(0.71)
22(0.87)
F0902.EPS
9-7
IM 1C22J1-01E
Page 60

d Model EJA438N [Style: S2]
9. GENERAL SPECIFICATIONS
External indicator
conduit connection
(Optional)
333(13.11)
124
(4.88)
47
(1.85)
140(5.51)
94(3.70)
92
(3.62)
2-inch pipe
(O.D. 60.5mm)
120
(4.72)
Conduit
connection
Internal
indicator
(Optional)
197(7.76)
Zero
adjustment
Clamps (Only for JIS
Flameproof type)
Mounting bracket
(Flat-type, Optional)
øD
øC
øg
øA
ø30
(1.18)
ø78
(3.07)
n-øh
110 (4.33)
12
(0.47)
Unit : mm (approx. inch)
tX2f
14 (0.55)
Terminal
side
Ground
terminal
Open to
atmosphere
(ø5mm)
146(5.75)
Process flange size : 4 inch (100 mm)
Flange Rating
JIS 10K
JIS 20K
JIS 40K
ANSI Class 150
ANSI Class 300
JPI Class 150
JPI Class 300
DIN PN 10/16
DIN PN 25/40
Process flange size : 3 inch (80 mm)
Flange Rating
JIS 10K
JIS 20K
JIS 40K
ANSI Class 150
ANSI Class 300
JPI Class 150
JPI Class 300
DIN PN 10/16
DIN PN 25/40
* In case where process flange material is JIS S25C, value of f is 0.
øD
210(8.72)
225(8.86)
250(9.84)
228.6(9.00)
254(10.00)
229(9.02)
254(10.00)
220(8.66)
235(9.25)
øD
185(7.28)
200(7.87)
210(8.27)
190.5(7.50)
209.6(8.25)
190(7.48)
210(8.27)
200(7.78)
200(7.78)
øC
175(6.89)
185(7.28)
205(8.07)
190.5(7.50)
200.2(7.88)
190.5(7.50)
200.2(7.88)
180(7.09)
190(7.48)
øC
150(5.91)
160(6.30)
170(6.69)
152.4(6)
168.1(6.62)
152.4(6)
168.1(6.62)
160(6.30)
160(6.30)
øg
155(6.10)
155(6.10)
155(6.10)
155(6.10)
155(6.10)
155(6.10)
155(6.10)
155(6.10)
155(6.10)
øg
130(5.12)
130(5.12)
130(5.12)
130(5.12)
130(5.12)
130(5.12)
130(5.12)
130(5.12)
130(5.12)
øA
96(3.78)
96(3.78)
96(3.78)
96(3.78)
96(3.78)
96(3.78)
96(3.78)
96(3.78)
96(3.78)
øA
71(2.80)
71(2.80)
71(2.80)
71(2.80)
71(2.80)
71(2.80)
71(2.80)
71(2.80)
71(2.80)
Diaphramg extension length code
= 50 mm (2 inch)
2 : X
2
4 : X2 = 100 mm (4 inch)
= 150 mm (6 inch)
6 : X
2
f *
t
18(0.71)
24(0.94)
36(1.42)
23.9(0.94)
31.8(1.25)
24(0.94)
32(1.26)
20(0.79)
24(0.94)
t
18(0.71)
22(0.87)
32(1.26)
23.9(0.94)
28.5(1.12)
24(0.94)
28.5(1.12)
20(0.79)
24(0.94)
0
0
0
1.6(0.06)
1.6(0.06)
1.6(0.06)
1.6(0.06)
0
0
f *
0
0
0
1.6(0.06)
1.6(0.06)
1.6(0.06)
1.6(0.06)
0
0
n
8
8
8
8
8
8
8
8
8
n
8
8
8
4
8
4
8
8
8
øh
19(0.75)
23(0.91)
25(0.98)
19.1(0.75)
22.4(0.88)
19(0.75)
22(0.87)
18(0.71)
22(0.87)
øh
19(0.75)
23(0.91)
23(0.91)
19.1(0.75)
22.4(0.88)
19(0.75)
22(0.87)
18(0.71)
18(0.71)
F0903.EPS
9-8
IM 1C22J1-01E
Page 61

Customer
Maintenance
Parts List
DPharp EJA Series
Transmitter Section
2
11
A
12
13
2
1
14
Item Part No. Description
1
Bellow
F9341RA
F9341RJ
2
F9341JP
3
Below
F9341AA
F9341AC
F9341AE
F9341AH
F9341AJ
F9341AR
4
F9341KA
5
Bellow
F9300AG
F9303JU
6
F9341KL
7-1
Below
F9342BB
F9342BH
F9342BJ
F9342AF
F9342AM
7-2
F9342BF
8
Y9406ZU
9
Y9612YU
10
11
12
13
14
Below
F9340NW
F9340NX
G9330DP
G9612EB
Bellow
F9341FM
F9341FJ
Below
F9342BL
F9342BM
F9342MK
F9300PB
Qty
Cover
2
Cast-aluminum alloy
SCS14A stainless steel
O-ring
2
Case Assembly
1
Name Plate
1
Screw
4
Tag Plate
1
CPU Assembly
1
Cap Screw
2
Screw
2
Plug
1
Cover Assembly
1
LCD Board Assembly
1
Mounting Screw
2
Label
2
Cast-aluminum alloy for G1/2
Cast-aluminum alloy for G1/2 (two electrical connections)
Cast-aluminum alloy for 1/2 NPT (two electrical connections)
Cast-aluminum alloy for M20 (two electrical connections)
Cast-aluminum alloy for Pg13.5 (two electrical connections)
SCS14A stainless steel for 1/2 NPT (two electrical connections)
For cast-aluminum alloy case assembly
For SCS14A stainless steel case assembly
For BRAIN protocol version (Except JIS Intrinsically safe type)
For HART protocol version (Except JIS Intrinsically safe type)
For BRAIN protocol version JIS Intrinsically safe type (Optional code /JS1)
For BRAIN protocol version (Optional code /F1)
For HART protocol version with write protection switch (Optional code /F1)
For FOUNDATION Fieldbus protocol
For Pg13.5
For M20
For G1/2
For 1/2 NPT
Cast-aluminum alloy
SCS14A stainless steel
Without range-setting switch
With range-setting switch
4
5
10
3
1
2
A
6
7-1
8
9
For integral indicator
5
7-2
Yokogawa Electric Corporation
All Rights Reserved, Copyright © 1995, Yokogawa Electric Corporation.
CMPL 1C22A1-02E
6th Edition: Feb. 2000(YK)
Page 62

Blank Page
2
Subject to change without notice. Printed in Japan.
CMPL 1C22A1-01E
Page 63

Customer
Maintenance
Parts List
Models EJA438W and EJA438N
Diaphragm Sealed
Gauge Pressure Transmitter
(Pressure-detector Section)
Item Part No.
1
F9300AJ
2
3
4
Below
Y9625YU
Y9630YU
Y9640YU
Y9635YU
5
Y9612HU
6
Below
F9270AW
F9300TA
7
D0117XL-A
8
Below
F9270AX
F9300TE
9
Below
F9270AY
F9273CZ
Yokogawa Electric Corporation
Qty
Model
EJA438W
EJA438N
Description
1
O-Ring
1
—
—
Flange
2
Bolt
2
Bolt
4
Screw, M6 x 12
1
1
Bracket Assembly
1
1
U-Bolt / Nut Assembly, SUS304 Stainless Steel
1
1
Bracket
1
1
4
4
Bolt
All Rights Reserved, Copyright © 1995, Yokogawa Electric Corporation.
See Table 1
For JIS 10K
For JIS 20K, ANSI Class 150 and JPI Class 150
For JIS 40K, ANSI Class 300 and JPI Class 300
(for Flange Size 100 mm, 4 inch)
For JIS 40K, ANSI Class 300 and JPI Class 300
(for Flange Size 80 mm, 3 inch)
SECC Carbon Steel
SUS304 Stainless Steel
SECC Carbon Steel
SUS304 Stainless Steel
S15C Carbon Steel
SUS XM7 Stainless Steel
CMPL 1C22J3-01E
3rd Edition: Oct. 1999(YK)
Page 64

Table 1. Flange and Bolt Parts Number
Flange Rating
50 mm JIS 10K
50 mm JIS 20K
50 mm JIS 40K
50 mm JIS 63K
2 inch ANSI Class 150
2 inch ANSI Class 300
2 inch ANSI Class 600
2 inch JPI Class 150
2 inch JPI Class 300
2 inch JPI Class 600
80 mm JIS 10K
80 mm JIS 20K
80 mm JIS 40K
80 mm JIS 63K
3 inch ANSI Class 150
3 inch ANSI Class 300
3 inch ANSI Class 600
3 inch JPI Class 150
3 inch JPI Class 300
3 inch JPI Class 600
S25C
Carbon Steel
F9351KP
F9351KQ
F9351KR
F9351KS
F9351KT
F9351KU
F9351KV
F9351KW
F9351KX
F9351KY
F9351KA
F9351KB
F9351KC
F9351KD
F9351KE
F9351KF
F9351KG
F9351KH
F9351KJ
F9351KK
Flange Material (Item 2)
SUS304
Stainless Steel
F9351GP
F9351GQ
F9351GR
F9351GS
F9351GT
F9351GU
F9351GV
F9351GW
F9351GX
F9351GY
F9351GA
F9351GB
F9351GC
F9351GD
F9351GE
F9351GF
F9351GG
F9351GH
F9351GJ
F9351GK
SUS316
Stainless Steel
F9351WA
F9351WB
F9351WC
F9351YE
F9351WG
F9351WH
F9351WJ
F9351WN
F9351WP
F9351WQ
F9351WD
F9351WE
F9351WF
F9351YF
F9351WK
F9351WL
F9351WM
F9351WR
F9351WS
F9351WT
Bolt (Item 3)
Y9520ZU
Y9525ZU
Y9530ZU
Y9540ZU
Y9525ZU
Y9530ZU
F9347VX
Y9525ZU
Y9530ZU
F9347VX
Y9525ZU
Y9530ZU
Y9540ZU
Y9545ZU
Y9530ZU
F9347VX
Y9540ZU
Y9530ZU
F9347VX
Y9540ZU
2
Oct. 1999
Subject to change without notice. Printed in Japan.
CMPL 1C22J3-01E
Page 65

INSTALLATION AND OPERATING PRECAUTIONS FOR JIS INTRINSICALLY SAFE EQUIPMENT
INSTALLATION AND OPERATING PRECAUTIONS FOR
JIS INTRINSICALLY SAFE EQUIPMENT
Apparatus Certified Under Technical Criteria (IEC-compatible Standards)
and from “RECOMMENDED PRACTICES for Explosion-Protected Electrical Installations in General Industries,” published in 1979
1.General
The following describes precautions on electrical apparatus
of intrinsically safe construction (hereinafter referred to as
intrinsically safe apparatus).
Following the Labor Safety and Health Laws of Japan, an
intrinsically safe apparatus must undergo type tests in order
to be certified by the Technical Institute of Industrial Safety,
Inc. These tests are required to satisfy either the technical
criteria for electrical machinery and equipment in compliance
with explosionproof standards involving inflammable gases
or vapors and for machinery and equipment having
explosionproof performance (standards notification no. 556
from the Japanese Ministry of Labor) (hereinafter referred to
as technical criteria), in conformity with IEC Standards, or
the “Recommended Practice for Explosion-Protected
Electrical Installations in General Industries,” published in
1979. Such a certified apparatus can be used in hazardous
locations where inflammable gases or vapors may be present.
Certified apparatus includes a certification label and an
equipment nameplate with the specifications necessary for
explosion requirements as well as precautions on explosion
protection. Please confirm these precautionary items and use
them to meet specification requirements.
For electrical wiring and maintenance servicing, please refer
to “Internal Wiring Rules” in the Electrical Installation
Technical Standards as well as “USER’S GUIDELINES for
Electrical Installations for Explosive Gas Atmospheres in
General Industry,” published in 1994.
To meet intrinsically safe requirements, equipment that can
be termed an “intrinsically safe apparatus” must:
(1) be certified by the Technical Institute of Industrial
Safety, Inc. in accordance with the Labor Safety and
Health Laws of Japan and have the appropriate mark of
certification labeled on its case, and
(2) be used in compliance with the specifications marked on
its certification label, equipment nameplate and
precautionary information furnished.
Note: Intrinsically safe apparatus satisfy their performance under
specific conditions. They are not always absolutely safe under
every operational and environmental condition. In other
words, they are not safe products involved with factors such
as chemical reactions, geographical changes or the like other
than affected by electric energy from the equipment itself.
2.Electrical Apparatus of Intrinsic
Safety Type of ExplosionProtected Construction
The intrinsic safety type of explosion-protected construction
is a method of protection applicable to a circuit or part of a
circuit in which, under prescribed test conditions, no spark or
thermal effect, whether produced normally or accidentally, is
capable of causing a prescribed explosive gas to ignite. In
other words, electrical apparatus of this construction is
intended to suppress electrical energy thereby preventing
ignition of a given explosive gas atmosphere even though
spark or high thermal effect occurs in the electric circuitry.
Intrinsically safe electrical apparatus generally comprise
intrinsically safe apparatus installed in a hazardous location
and a safety barrier (associated apparatus), installed in a nonhazardous location, aimed at preventing electrical energy
from flowing into the electric circuitry of intrinsically safe
apparatus.
However, battery-operated, portable intrinsically safe
apparatus or the like may be used alone.
3.Terminology
(1) Intrinsically safe apparatus: Electrical apparatus in which
all the circuits are intrinsically safe circuits.
(2) Associated apparatus: Electrical apparatus in which there
are both intrinsically safe circuits and non-intrinsically
safe circuits that can affect the safety of intrinsically safe
circuits.
(3) Safety barrier: A specific type of associated apparatus,
which consists mainly of safety barrier elements, and
serves to limit the flow of excessive electrical energy,
which is capable of causing ignition of a given explosive
gas or vapour of a non-intrinsically safe circuit into
concerned intrinsically safe circuits.
(4) Apparatus of category “ia”: Intrinsically safe electrical
apparatus and associated apparatus which are incapable
of causing ignition of a given explosive gas or vapour
with the appropriate safety factors such as:
1
EX-A03E
Page 66

INSTALLATION AND OPERATING PRECAUTIONS FOR JIS INTRINSICALLY SAFE EQUIPMENT
— when up to two countable faults are applied and, in
addition,
— when non-countable faults produce an onerous
condition.
(5) Apparatus of category “ib”: Intrinsically safe electrical
apparatus and associated apparatus which are incapable
of causing ignition of a given explosive gas or vapour,
with the appropriate safety factors such as:
— when up to one countable fault is applied and, in
addition,
— when non-countable faults produce an onerous
condition.
(6) Safety rating: A rating to be designated to intrinsically
safe apparatus as well as associated apparatus and is the
maximum rating allowable for maintaining intrinsic
safety of concerned intrinsically safe circuits.
4.Caution on Combining Intrinsically Safe Apparatus and
Safety Barriers
(1) A combination of certified intrinsically safe apparatus
and safety barriers needs to satisfy combination
requirements. If intrinsically safe apparatus specify
safety barriers for combination, safety barriers other than
specified cannot be used (see Note 1 for more details).
(2) Certified intrinsically safe systems specify specific safety
barriers in combination with intrinsically safe apparatus.
So safety barriers other than specified cannot be used
(see Note 2 for more details).
(3) Other than limitations of combining intrinsically safe
apparatus and safety barriers as given in (1) and (2)
above, two or more pieces of apparatus certified under
different standards cannot be combined with each other
(see Note 3 for more details). In addition, bear in mind
that classifications of explosion protection such as “IIA,”
“IIB” and “IIC” and category “ia” and “ib” limit a
combination of intrinsically safe apparatus and safety
barriers.
For more details, see the “Type Certificate Guide for
Explosion-Protected Constructionfor Electrical
Machinery and Equipment,” issued by the Japanese
Ministry of Labour, the Research Institute of Industrial
Safety.
Note 1: Testing Apparatus
Intrinsically safe apparatus and safety barriers are assessed
individually to ensure that their safety requirements are
satisfied. Tested and certified intrinsically safe apparatus and
safety barriers incorporate individual certification numbers.
A combination of intrinsically safe apparatus and safety
barriers involves the following two limitations:
(1) A safety barrier which meets the combination require-
ments by referring to its safety rating and combination
parameters shall be selected.
(2) For pressure transmitters, pH transmitters, temperature
detectors and the like, safety barriers that can be
combined are already specified. Other safety barriers
cannot be used.
Note 2: Testing Intrinsically Safe System
An assembly (as a system) in which intrinsically safe
apparatus and safety barriers are combined is assessed to
ensure that its safety requirements are satisfied. A tested and
certified system incorporates a certification number
(intrinsically safe apparatus and safety barriers have the same
certification number).
Note 3: Impossible Combinations of Apparatus Certified Under
Different Standards
Intrinsically safe apparatus certified under technical criteria
and safety barriers certified under the “Recommended
Practice for Explosion-Protected Electrical Installations in
General Industries” (1979) and vice versa cannot be
combined even if their combination requirements are
satisfied.
5.Installation of Intrinsically Safe
Apparatus and Safety Barriers
(1) Classification of installation location
Intrinsically safe apparatus may be installed, depending upon
applicable gases, in a hazardous area in Zone 0, 1 or 2 (Note
4 below), where the specified gases are present. However,
note that apparatus certified under Technical Criteria, in
category “ib” shall be installed only in Zone 1 or 2. Safety
barriers (associated apparatus) that are combined with these
intrinsically safe apparatus shall be installed only in a nonhazardous area. In cases where safety barriers are installed in
a hazardous area, they shall be enclosed, for example, in a
flameproof enclosure.
Note 4: Hazardous areas are classified in zones based upon the
frequency of the appearance and the duration of an explosive
gas atmosphere as follows:
Zone 0: An area in which an explosive gas atmosphere is
present continuously or is present for long periods.
Zone 1: An area in which an explosive gas atmosphere is
likely to occur in normal operation.
Zone 2: An area in which an explosive gas atmosphere is not
likely to occur in normal operation and if it does
occur it will exist for a short period only.
(2) Ambient temperature limits for intrinsically
safe apparatus
Intrinsically safe apparatus shall be installed in a location
where the ambient temperature ranges from –20° to +40°C
(for those certified under Technical Criteria) or –10° to
+40°C (for those certified under the “Recommended Practice
for Explosion-Protected Electrical Installations in General
Industries” (1979). However, some field-mounted
2
EX-A03E
Page 67

INSTALLATION AND OPERATING PRECAUTIONS FOR JIS INTRINSICALLY SAFE EQUIPMENT
intrinsically safe apparatus may be used at an ambient
temperature up to 60°C. So, specifications should be checked
before installing intrinsically safe apparatus.
If the intrinsically safe apparatus are exposed to direct
sunshine or radiant heat from plant facilities, appropriate
thermal protection measures shall be taken.
6.Wiring for Intrinsically Safe
Circuits
In intrinsically safe construction, safety shall be maintained
as an intrinsically safe system involving intrinsically safe
apparatus and safety barriers connected thereto, and electrical
wiring (through intrinsically safe circuits) interconnected
between them. In other words, even when safety
requirements are maintained individually by intrinsically safe
apparatus and safety barriers, they shall not be affected by
electrical or magnetic energy caused by electrical wiring.
To make electrical wiring for intrinsically safe circuits, you
must:
(a) refer to the equipment configuration diagram and make
electrical wiring properly;
(b) prevent intrinsically safe wiring from being contacted
with non-intrinsically safe wiring, and separate the
intrinsically safe circuit from other electrical circuits;
(c) prevent intrinsically safe wiring from being
electrostatically and magnetically affected by nonintrinsically safe wiring;
(d) reduce wiring inductance and capacitance produced
between the intrinsically safe apparatus and safety
barrier where possible, and use a shorter cable between
the intrinsically safe apparatus and safety barrier than
specified if the maximum permissible inductance of the
cable is specified as operating conditions;
(e) conform to conditions of installation such as wiring
method, earthing or the like, if any; and
(f) protect the outer sheath of cables from damage with
appropriate measures.
7.Maintenance and Inspection of
Intrinsically Safe Apparatus
and Safety Barriers
Installations for Explosive Gas Atmospheres in General
Industry” issued in 1994 by the Japanese Ministry of Labour,
the Research Institute of Industrial Safety.
(1) Requirements for maintenance personnel
Maintenance and inspection of intrinsically safe apparatus
and safety barriers shall be conducted by maintenance
personnel skilled in intrinsically safe construction and
installation of electrical devices as well as capable of
applying associated rules.
(2) Maintenance and Inspection
(a) Visual inspection
Visually inspect the external connections of intrinsically
safe apparatus and safety barriers, and cables for damage
or corrosion as well as other mechanical and structural
defects.
(b) Adjustments
Zero, span and sensitivity adjustments shall be made
with applicable adjusting potentiometers and mechanical
adjustment screws.
These maintenance adjustments shall be made in a nonhazardous location.
CAUTION
If intrinsically safe apparatus and safety barriers
require maintenance service and checking, a
gas detector shall be used to ensure that there
is no explosive gas in the location (maintenance servicing shall be conducted in a nonhazardous location).
(3) Repair
Intrinsically safe apparatus and safety barriers shall be
repaired by manufacturers.
(4) Prohibition of modifications and specifica-
tion changes
Do not attempt to make modifications or change specifications which may affect safety.
Maintenance and inspection of intrinsically safe apparatus
and safety barriers shall be limited to within the instructions
described in applicable instruction manuals. If other than this
is required, contact the manufacturers. For more information,
refer to the “USER’S GUIDELINES for Electrical
3
EX-A03E
Page 68

INSTALLATION AND OPERATING PRECAUTIONS FOR JIS FLAMEPROOF EQUIPMENT
INSTALLATION AND OPERATING PRECAUTIONS FOR
JIS FLAMEPROOF EQUIPMENT
Apparatus Certified Under Technical Criteria
(IEC-compatible Standards)
1.General
The following describes precautions on electrical apparatus
of flameproof construction (hereinafter referred to as
flameproof apparatus) in explosion-protected apparatus.
Following the Labour Safety and Health Laws of Japan,
flameproof apparatus is subjected to type tests to meet either
the technical criteria for explosionproof electrical machinery
and equipment (standards notification no. 556 from the
Japanese Ministry of Labour) (hereinafter referred to as
technical criteria), in conformity with the IEC Standards, or
the “Recommended Practice for Explosion-Protected
Electrical Installations in General Industries,” published in
1979. These certified apparatus can be used in hazardous
locations where explosive or inflammable gases or vapours
may be present.
Certified apparatus includes a certification label and an
equipment nameplate with the specifications necessary for
explosion requirements as well as precautions on explosion
protection. Please confirm these precautionary items and use
them to meet specification requirements.
For electrical wiring and maintenance servicing, please refer
to “Internal Wiring Rules” in the Electrical Installation
Technical Standards as well as “USER’S GUIDELINES for
Electrical Installations for Explosive Gas Atmospheres in
General Industry,” published in 1994.
construction is of completely enclosed type and its enclosure
shall endure explosive pressures in cases where explosive
gases or vapours entering the enclosure cause explosion. In
addition, the enclosure construction shall be such that flame
caused by explosion does not ignite gases or vapours outside
the enclosure.
In this manual, the word "flameproof" is applied to the
flameproof equipment combined with the types of protection
"e", "o", "i", and "d" as well as flameproof equipment.
3.Terminology
(1) Enclosure
An outer shell of an electrical apparatus, which encloses live
parts and thus is needed to configure explosion-protected
construction.
(2) Shroud
A component part which is so designed that the fastening of
joint surfaces cannot be loosened unless a special tool is
used.
(3) Enclosure internal volume
This is indicated by:— the total internal volume of the
flameproof enclosure minus the volume of the internal
components essential to equipment functions.
To meet flameproof requirements, equipment that can be
termed “flameproof” must:
(1) Be certified by a Japanese public authority in accordance
with the Labour Safety and Health Laws of Japan and
have a certification label in an appropriate location on its
case, and
(2) Be used in compliance with the specifications marked on
its certification label, equipment nameplate and
precautionary information furnished.
2.Electrical Apparatus of Flameproof Type of ExplosionProtected Construction
Electrical apparatus which is of flameproof construction is
subjected to a type test and certified by the Japanese Ministry
of Labour aiming at preventing explosion caused by electrical
apparatus in a factory or any location where inflammable
gases or vapours may be present. The flameproof
(4) Path length of joint surface
On a joint surface, the length of the shortest path through
which flame flows from the inside to outside of the
flameproof enclosure. This definition cannot be applied to
threaded joints.
(5) Gaps between joint surfaces
The physical distance between two mating surfaces, or
differences in diameters if the mating surfaces are cylindrical.
Note: The permissible sizes of gaps between joint surfaces, the path
length of a joint surface and the number of joint threads are
determined by such factors as the enclosure’s internal
volume, joint and mating surface construction, and the
explosion classification of the specified gases and vapours.
1
EX-B03E
Page 69

INSTALLATION AND OPERATING PRECAUTIONS FOR JIS FLAMEPROOF EQUIPMENT
4.Installation of Flameproof
Apparatus
(1) Installation Area
Flameproof apparatus may be installed, in accordance with
applicable gases, in a hazardous area in Zone 1 or 2, where
the specified gases are present. Those apparatus shall not be
installed in a hazardous area in Zone 0.
Note: Hazardous areas are classified in zones based upon the
frequency of the appearance and the duration of an explosive
gas atmosphere as follows:
Zone 0: An area in which an explosive gas atmosphere is
present continuously or is present for long periods.
Zone 1: An area in which an explosive gas atmosphere is
likely to occur in normal operation.
Zone 2: An area in which an explosive gas atmosphere is not
likely to occur in normal operation and if it does
occur it will exist for a short period only.
(2) Environmental Conditions
The standard environmental condition for the installation of
flameproof apparatus is limited to an ambient temperature
range from –20°C to +40°C (for products certified under
Technical Criteria). However, some field-mounted
instruments may be certified at an ambient temperature up to
+60°C as indicated on the instrument nameplates. If the
flameproof apparatus are exposed to direct sunshine or
radiant heat from plant facilities, appropriate thermal
protection measures shall be taken.
5.External Wiring for Flameproof
Apparatus
Flameproof apparatus require cable wiring or flameproof
metal conduits for their electrical connections. For cable
wiring, cable glands (cable entry devices for flameproof type)
to wiring connections shall be attached. For metal conduits,
attach sealing fittings as close to wiring connections as
possible and completely seal the apparatus. All non-live
metal parts such as the enclosure shall be securely grounded.
For details, see the “USER’S GUIDELINES for Electrical
Installations for Explosive Gas Atmospheres in General
Industry,” published in 1994.
(1) Cable Wiring
• For cable wiring, cable glands (cable entry devices for
flameproof type) specified or supplied with the apparatus
shall be directly attached to the wiring connections to
complete sealing of the apparatus.
• Screws that connect cable glands to the apparatus are
those for G-type parallel pipe threads (JIS B 0202) with
no sealing property. To protect the apparatus from
corrosive gases or moisture, apply nonhardening sealant
such as liquid gaskets to those threads for waterproofing.
• Specific cables shall be used as recommended by the
“USER’S GUIDELINES for Electrical Installations for
Explosive Gas Atmospheres in General Industry,”
published in 1994.
• In necessary, appropriate protective pipes (conduit or
flexible pipes), ducts or trays shall be used for
preventing the cable run (outside the cable glands) from
damage.
• To prevent explosive atmosphere from being propagated
form Zone 1 or 2 hazardous location to any different
location or non-hazardous location through the protective
pipe or duct, apply sealing of the protective pipes in the
vicinity of individual boundaries, or fill the ducts with
sand appropriately.
• When branch connections of cables, or cable connections
with insulated cables inside the conduit pipes are made,
a flameproof or increased-safety connection box shall be
used. In this case, flameproof or increased-safety cable
glands meeting the type of connection box must be used
for cable connections to the box.
(2) Flameproof Metal Conduit Wiring
• For the flameproof metal conduit wiring or insulated
wires shall be used as recommended by the USER’S
GUIDELINES for Electrical Installations for Explosive
Gas Atmospheres in General Industry, published in
1994.
• For conduit pipes, heavy-gauge steel conduits
conforming to JIS C 8305 Standard shall be used.
• Flameproof sealing fittings shall be used in the vicinity
of the wiring connections, and those fittings shall be
filled with sealing compounds to complete sealing of the
apparatus. In addition, to prevent explosive gases,
moisture, or flame caused by explosion form being
propagated through the conduit, always provide sealing
fittings to complete sealing of the conduit in the
following locations:
(a) In the boundaries between the hazardous and non-
hazardous locations.
(b) In the boundaries where there is a different
classification of hazardous location.
• For the connections of the apparatus with a conduit pipe
or its associated accessories, G-type parallel pipe threads
(JIS B 0202) shall be used to provide a minimum of
five-thread engagement to complete tightness. In
addition, since these parallel threads do not have sealing
property, nonhardening sealant such as liquid gaskets
shall thus be applied to those threads for ensuring
waterproofness.
• If metal conduits need flexibility, use flameproof flexible
fittings.
2
EX-B03E
Page 70

INSTALLATION AND OPERATING PRECAUTIONS FOR JIS FLAMEPROOF EQUIPMENT
6.Maintenance of Flameproof
Apparatus
To maintain the flameproof apparatus, do the following. (For
details, see Chapter 10 “MAINTENANCE OF EXPLOSIONPROTECTED ELECTRICAL INSTALLATION” in the
USER’S GUIDELINES for Electrical Installations for
Explosive Gas Atmospheres in General Industry.)
(1) Maintenance servicing with the power on.
Flameproof apparatus shall not be maintenance-serviced with
its power turned on. However, in cases where maintenance
servicing is to be conducted with the power turned on, with
the equipment cover removed, always use a gas detector to
check that there is no explosive gas in that location. If it
cannot be checked whether an explosive gas is present or not,
maintenance servicing shall be limited to the following two
items:
(a) Visual inspection
Visually inspect the flameproof apparatus, metal
conduits, and cables for damage or corrosion, and other
mechanical and structural defects.
(b) Zero and span adjustments
These adjustments should be made only to the extent
that they can be conducted from the outside without
opening the equipment cover. In doing this, great care
must be taken not to cause mechanical sparks with tools.
(2) Repair
If the flameproof apparatus requires repair, turn off the power
and transport it to a safety (non-hazardous) location. Observe
the following points before attempting to repair the
apparatus.
(a) Make only such electrical and mechanical repairs as will
restore the apparatus to its original condition. For the
flameproof apparatus, the gaps and path lengths of joints
and mating surfaces, and mechanical strength of
enclosures are critical factors in explosion protection.
Exercise great care not to damage the joints or shock the
enclosure.
(b) If any damage occurs in threads, joints or mating
surfaces, inspection windows, connections between the
transmitter and terminal box, shrouds or clamps, or
external wiring connections which are essential in
flameproofness, contact Yokogawa Electric Corporation.
requirements for flameproof apparatus (however, bear in
mind that the apparatus must always be restored to its
original condition). If you attempt to repair the
flameproof apparatus, company-specified components
shall be used.
(d) Before starting to service the apparatus, be sure to check
all parts necessary for retaining the requirements for
flameproof apparatus. For this, check that all screws,
bolts, nuts, and threaded connections have properly been
tightened.
(3) Prohibition of specification changes and
modifications
Do not attempt to change specifications or make
modifications involving addition of or changes in external
wiring connections.
7.Selection of Cable Entry
Devices for Flameproof Type
IMPORTANT
The cable glands (cable entry devices for flameproof
type) conforming to IEC Standards are certified in
combination with the flameproof apparatus. So,
Yokogawa-specified cable entry devices for flameproof
type shall be used to meet this demand.
References:
(1) Type Certificate Guide for Explosion-Protected
Construction Electrical Machinery and Equipment
(relating to Technical Standards Conforming to International Standards), issued by the Technical Institution of
Industrial Safety, Japan
(2) USER’S GUIDELINES for Electrical Installations for
Explosive Gas Atmospheres in General Industry (1994),
issued by the Japanese Ministry of Labour, the Research
Institute of Industrial Safet
CAUTION
Do not attempt to re-process threaded connections or
refinish joints or mating surfaces.
(c) Unless otherwise specified, the electrical circuitry and
internal mechanisms may be repaired by component
replacement, as this will not directly affect the
3
EX-B03E
Page 71

REVISION RECORD
Title: Model EJA438W and EJA438N Diaphragm Sealed Gauge Pressure
Transmitter
Manual No.: IM 1C22J1-01E
Edition Date Page Revised Item
8th
9th
10th
Mar. 1998 1-1
5-1
10-1
10-3
10-6
2-9+
CMPL
Sep. 1998
Feb. 2000
2-14
2-15
7-19
10-3
10-4
CMPL
2
1
5.1
10.1.1
10.1.2
10.1.3
CMPL 1C22A1-02E 3rd 4th
Page 2
2.10
2.10
7.3.2(8)
10.1.2
CMPL 1C22A1-02E 4th 5th
Page 2
CMPL 1C22J3-01E 1st 2nd
Page 4
Changed to Electronic File Format.
Revised a book in a new format.
Major Revised Items:
• Add FOUNDATION Fieldbus protcol version to ‘NOTE’ notice.
• Add Item 6 to the Wiring Precautions.
• Add FOUNDATION Fieldbus protocol.
• Add Output signal code F .
• Add Optional code A1.
• Change the figure of terminal configuration.
• Add Item 7-2.
• Delete EMC Conformity Standards Tables and move the
section to page 2-14.
• Remove Page 2-15.
• Correction made in BURN OUT figure.
• Add Process flange size/material code F and C.
• Add Electrical connection code 7, 8, and 9.
• Add Process flange size/material code F and J.
• Add Elactrical connection code 7, 8, and 9.
• Add Part No. to Item 3 (For PG13.5 and M20).
• Add Part No. to Item 10 (For 1/2 NPT, Pg13.5, and M20).
• Add 80 mm / 3-inch to Flange Rating and SUS316 Stainless
Steel Part No. to Flange material in Table 1.
(The location of contents and the associated page numbers may
not coincide with the one in old editions.)
1. Explosion class and option code of JIS flameproof approval.
Explosion class: Ex ds IIC T4(old) to Ex do IIC T4X(new).
Option code: /JF1(old) to /JF3(new)
2. Option code for flameproof packing adapter for JIS flameproof
approval.
Option code: /G1 and /G2(old) to /G11 and /G12(new)
3. Add “Pa” and “hPa” as the unit for calibration range.
4. Part number change for CPU Board Assembly.
2-8
2-9
5-1
5-3
7-4
–
9-6
CMPL
2.9
2.10
5.2
5.4.2
7.3.1
–
9.3
CMPL 1C22A1-02E 5th 6th
CMPL 1C22J3-01E 3rd
• Add Figure 2.3 Example of using DCS.
• Add AS/NZS 2064 1/2 to EMI, EMC Conformity Standards.
• Add selection in the case of JIS flameproof type.
• Change option code for flame packing adapter.
Option code: G1 and G2 G11 and G12
Change Applicable cable O.D. and Identifying mark.
Part number: G9601AH G9601AM
Change the figure of flame proof packing adapter in Figure 5.4.2c.
• Add Pa and hPa to C20 and D31.
• Installation and Operating Precautions for JIS Intrinsically Safe
and Explosionproof Equipment:
EX-A01E EX-A03E, EX-B01E EX-B03E
• Add Optional code F1.
• Change a format.
• Change and add Part No. of Item 7-1, CPU assembly:
Change; F9342BC F9342BB, F9342BK F9342BJ
Add; F9342AF, F9342AM
• Change Part No. of Item 10, Plug:
G9330DK G9330DP
• Change a format.
REVISION RECORD.EPS
IM 1C22J1-01E
Page 72

Blank Page
 Loading...
Loading...