Page 1
YASKAWA AC Drive V1000 Option
Modbus TCP/IP
Technical Manual
Type: SI-EM3D/V
To properly use the product, read this manual thoroughly and retain
for easy reference, inspection, and maintenance. Ensure the end user
receives this manual.
TM
MANUAL NO. SIEP YAICOM 17A
Page 2

Copyright © 2014 YASKAWA AMERICA, INC. All rights reserved.
No part of this publication may be reproduced, stored in a retrieval system, or transmitted, in any form or by any means,
mechanical, electronic, photocopying, recording, or otherwise, without the prior written permission of Yaskawa. No patent
liability is assumed with respect to the use of the information contained herein. Moreover, because Yaskawa is constantly
striving to improve its high-quality products, the information contained in this manual is subject to change without notice.
Every precaution has been taken in the preparation of this manual. Yaskawa assumes no responsibility for errors or omissions.
Neither is any liability assumed for damages resulting from the use of the information contained in this publication.
Page 3

Table of Contents
1 PREFACE AND SAFETY.........................................................................................4
2 PRODUCT OVERVIEW............................................................................................7
3 RECEIVING..............................................................................................................8
4 OPTION COMPONENTS..........................................................................................9
5 INSTALLATION PROCEDURE..............................................................................12
6 RELATED DRIVE PARAMETERS.........................................................................20
7 MODBUS TCP/IP MESSAGING.............................................................................23
8 WEB INTERFACE..................................................................................................33
9 RAPID SPANNING TREE PROTOCOL.................................................................41
10 TROUBLESHOOTING............................................................................................45
11 SPECIFICATIONS..................................................................................................48
YASKAWA SIEP YAICOM 17A V1000 Option Dual-Port Modbus TCP/IP SI-EM3D/V Technical Manual
3
Page 4

1 Preface and Safety
1 Preface and Safety
Yaskawa manufactures products used as components in a wide variety of industrial systems and equipment. The selection and
application of Yaskawa products remain the responsibility of the equipment manufacturer or end user. Yaskawa accepts no
responsibility for the way its products are incorporated into the final system design. Under no circumstances should any
Yaskawa product be incorporated into any product or design as the exclusive or sole safety control. Without exception, all
controls should be designed to detect faults dynamically and fail safely under all circumstances. All systems or equipment
designed to incorporate a product manufactured by Yaskawa must be supplied to the end user with appropriate warnings and
instructions as to the safe use and operation of that part. Any warnings provided by Yaskawa must be promptly provided to
the end user. Yaskawa offers an express warranty only as to the quality of its products in conforming to standards and
specifications published in the Yaskawa manual. NO OTHER WARRANTY, EXPRESS OR IMPLIED, IS OFFERED.
Yaskawa assumes no liability for any personal injury, property damage, losses, or claims arising from misapplication of its
products.
u
Applicable Documentation
The following manuals are available for the SI-EM3D/V option:
Yaskawa AC Drive V1000 Option SI-EM3D/V Dual-Port Modbus TCP/IP Installation Manual (TOEPYAICOM17)
The Installation Manual contains information required to install the option and set up related drive parameters.
Yaskawa AC Drive V1000 Option SI-EM3D/V Dual-Port Modbus TCP/IP Technical Manual (SIEPYAICOM17)
The Technical Manual contains detailed information about the option. In the U.S., access http://www.yaskawa.com
to obtain the Technical Manual. Customers in other areas should contact a Yaskawa representative.
V1000 Series AC Drive Quick Start Guide
This guide contains basic information required to install and wire the drive. It also gives an overview of fault
diagnostics, maintenance, and parameter settings. The purpose of this guide is to prepare the drive for a trial run
with an application and for basic operation. This manual is available for download on our documentation website,
www.yaskawa.com.
V1000 Series AC Drive Technical Manual
This manual provides detailed information on parameter settings, drive functions, and MEMOBUS/Modbus
specifications. Use this manual to expand drive functionality and to take advantage of higher performance features.
This manual is available for download on our documentation website, www.yaskawa.com.
u
Terms
Note: Indicates supplemental information that is not related to safety messages.
Drive: Yaskawa V1000 Series AC Drive
Option: Yaskawa AC Drive V1000 SI-EM3D/V Dual-Port Modbus TCP/IP Option
u
Registered Trademarks
• Modbus TCP/IP is a trademark of Modbus-IDA.
• All trademarks are the property of their respective owners.
u
Supplemental Safety Information
Read and understand this manual before installing, operating, or servicing this option. The option must be installed according
to this manual and local codes.
The following conventions are used to indicate safety messages in this manual. Failure to heed these messages could result in
serious or possibly even fatal injury or damage to the products or to related equipment and systems.
DANGER
Indicates a hazardous situation, which, if not avoided, will result in death or serious injury.
4
YASKAWA SIEP YAICOM 17A V1000 Option Dual-Port Modbus TCP/IP SI-EM3D/V Technical Manual
Page 5
1 Preface and Safety
WARNING
Indicates a hazardous situation, which, if not avoided, could result in death or serious injury.
WARNING! may also be indicated by a bold key word embedded in the text followed by an italicized safety message.
CAUTION
Indicates a hazardous situation, which, if not avoided, could result in minor or moderate injury.
CAUTION! may also be indicated by a bold key word embedded in the text followed by an italicized safety message.
NOTICE
Indicates a property damage message.
NOTICE: may also be indicated by a bold key word embedded in the text followed by an italicized safety message.
General Safety
n
General Precautions
• The diagrams in this manual may be indicated without covers or safety shields to show details. Replace the covers or shields before
operating the drive and run the drive according to the instructions described in this manual.
• Any illustrations, photographs, or examples used in this manual are provided as examples only and may not apply to all products to
which this manual is applicable.
• The products and specifications described in this manual or the content and presentation of the manual may be changed without notice
to improve the product and/or the manual.
• When ordering a new copy of the manual due to damage or loss, contact your Yaskawa representative or the nearest Yaskawa sales
office and provide the manual number shown on the front cover.
• If nameplate becomes worn or damaged, order a replacement from your Yaskawa representative or the nearest Yaskawa sales office.
DANGER
Heed the safety messages in this manual.
Failure to comply will result in death or serious injury.
The operating company is responsible for any injuries or equipment damage resulting from failure to heed the warnings in
this manual.
Electrical Shock Hazard
Do not connect or disconnect wiring while the power is on.
Failure to comply will result in death or serious injury.
Failure to comply will result in death or serious injury. Before servicing, disconnect all power to the equipment. The internal
capacitor remains charged even after the power supply is turned off. The charge indicator LED will extinguish when the DC
bus voltage is below 50 Vdc. To prevent electric shock, wait for at least the time specified on the warning label once all
indicators are OFF, and then measure the DC bus voltage level to confirm it has reached a safe level.
NOTICE
Observe proper electrostatic discharge procedures (ESD) when handling the drive and circuit boards.
Failure to comply may result in ESD damage to the drive circuitry.
Do not perform a withstand voltage test on any part of the drive.
Failure to comply could result in damage to the sensitive devices within the drive.
Do not operate damaged equipment.
Failure to comply could result in further damage to the equipment.
Do not connect or operate any equipment with visible damage or missing parts.
YASKAWA SIEP YAICOM 17A V1000 Option Dual-Port Modbus TCP/IP SI-EM3D/V Technical Manual
5
Page 6
V1000
Warning
information
AVERTISSEMENT
Lire le manuel avant l'installation.
Attendre 5 minutes apres la coupure de l'alimentation,
pour permettre la decharge des condensateurs.
Pour repondre aux exigences , s assurer que le
neutre soit relie a la terre, pour la serie 400V.
WARNING
Read manual before installing.
Wait 5 minutes for capacitor discharge after
disconnecting power supply.
To conform to requirements, make sure
to ground the supply neutral for 400V class.
Risk of electric shock.
Risque de decharge
electrique.
AVERTISSEMENT
Lire le manuel avant l'installation.
Attendre 5 minutes apres la coupure de l'alimentation,
pour permettre la decharge des condensateurs.
Pour repondre aux exigences , s assurer que le
neutre soit relie a la terre, pour la serie 400V.
WARNING
Read manual before installing.
Wait 5 minutes for capacitor discharge after
disconnecting power supply.
To conform to requirements, make sure
to ground the supply neutral for 400V class.
Risk of electric shock.
Risque de decharge
electrique.
1 Preface and Safety
NOTICE
Do not expose the drive to halogen group disinfectants.
Failure to comply may cause damage to the electrical components in the drive.
Do not pack the drive in wooden materials that have been fumigated or sterilized.
Do not sterilize the entire package after the product is packed.
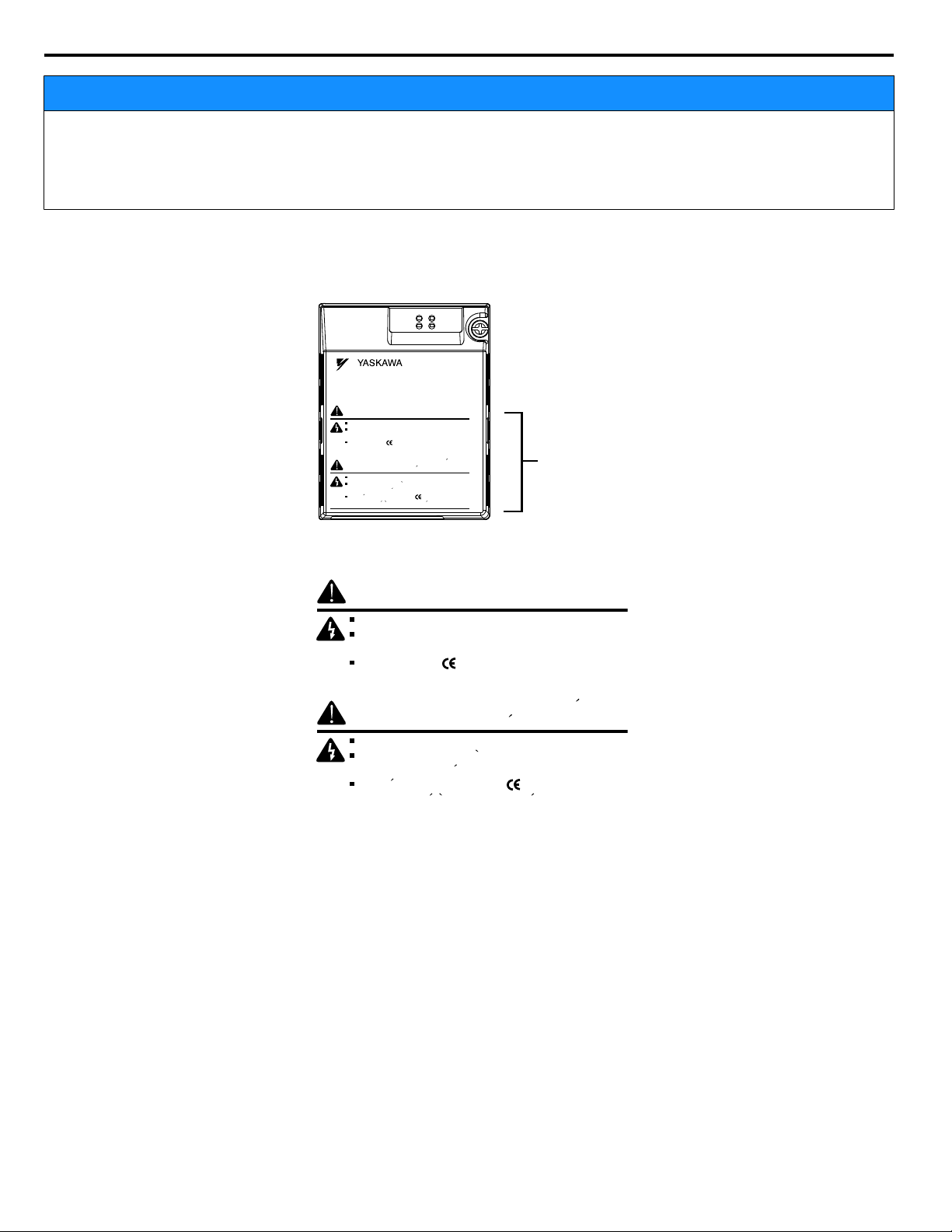
Option Unit Warning Labels
n
Warning information is displayed on the option unit as shown in the figure below. Follow all warnings and safety instructions
when using the product.
Warning Contents
n
6
YASKAWA SIEP YAICOM 17A V1000 Option Dual-Port Modbus TCP/IP SI-EM3D/V Technical Manual
Page 7

2 Product Overview
2 Product Overview
u
About this Product
This option provides a communications connection between the drive and a Modbus TCP/IP network. The option connects
the drive to a Modbus TCP/IP network and facilitates the exchange of data.
This manual explains the handling, installation and specifications of this product.
The option is a communications link to connect industrial devices (such as smart motor controllers, operator interfaces, and
variable frequency drives) as well as control devices (such as programmable controllers and computers) to a network. The
option is a simple, networking solution that reduces the cost and time to wire and install factory automation devices, while
providing interchangeability of like components from multiple vendors.
By installing the option to a drive, it is possible to do the following from a Modbus TCP/IP master device:
• Operate the drive
• Monitor drive status
• Change drive parameter settings.
u
Applicable Models
The option can be used with the drive models in Table 1.
Table 1 Applicable Models
Drive Series Drive Model Number
V1000
<1> See “PRG” on the drive nameplate for the software version number.
CIMR-VooAoooo
Software Version
1012 and later
<1>
YASKAWA SIEP YAICOM 17A V1000 Option Dual-Port Modbus TCP/IP SI-EM3D/V Technical Manual
7
Page 8
MANUAL
3 Receiving
3 Receiving
Please perform the following tasks upon receipt of the option:
• Inspect the option for damage. Contact the shipper immediately if the option appears damaged upon receipt.
• Verify receipt of the correct model by checking the model number printed on the name plate of the option package.
• Contact your supplier if you have received the wrong model or the option does not function properly.
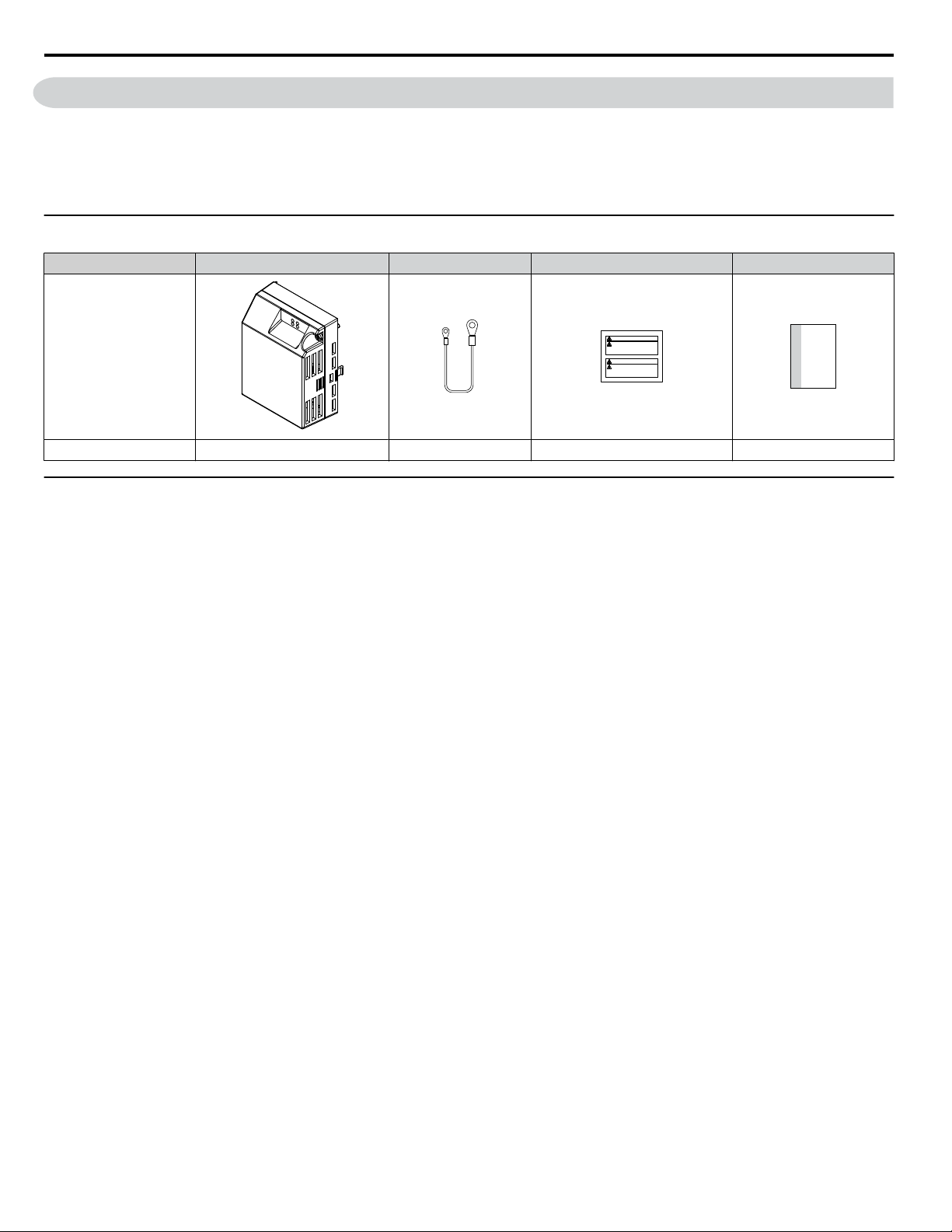
u
Option Package Contents
Description Option Unit Ground Wire Warning Labels Installation Manual
–
Quantity 1 4 1 1
u
Tools Required for Installation
A Phillips screwdriver (M3, M3.5 to M6 metric or #1, #2 U.S. standard) is required to install the option. Screw sizes vary by
drive capacity. Select a screwdriver appropriate for the drive capacity.
Note: Tools required to prepare the option cables for wiring are not listed in this manual.
8
YASKAWA SIEP YAICOM 17A V1000 Option Dual-Port Modbus TCP/IP SI-EM3D/V Technical Manual
Page 9
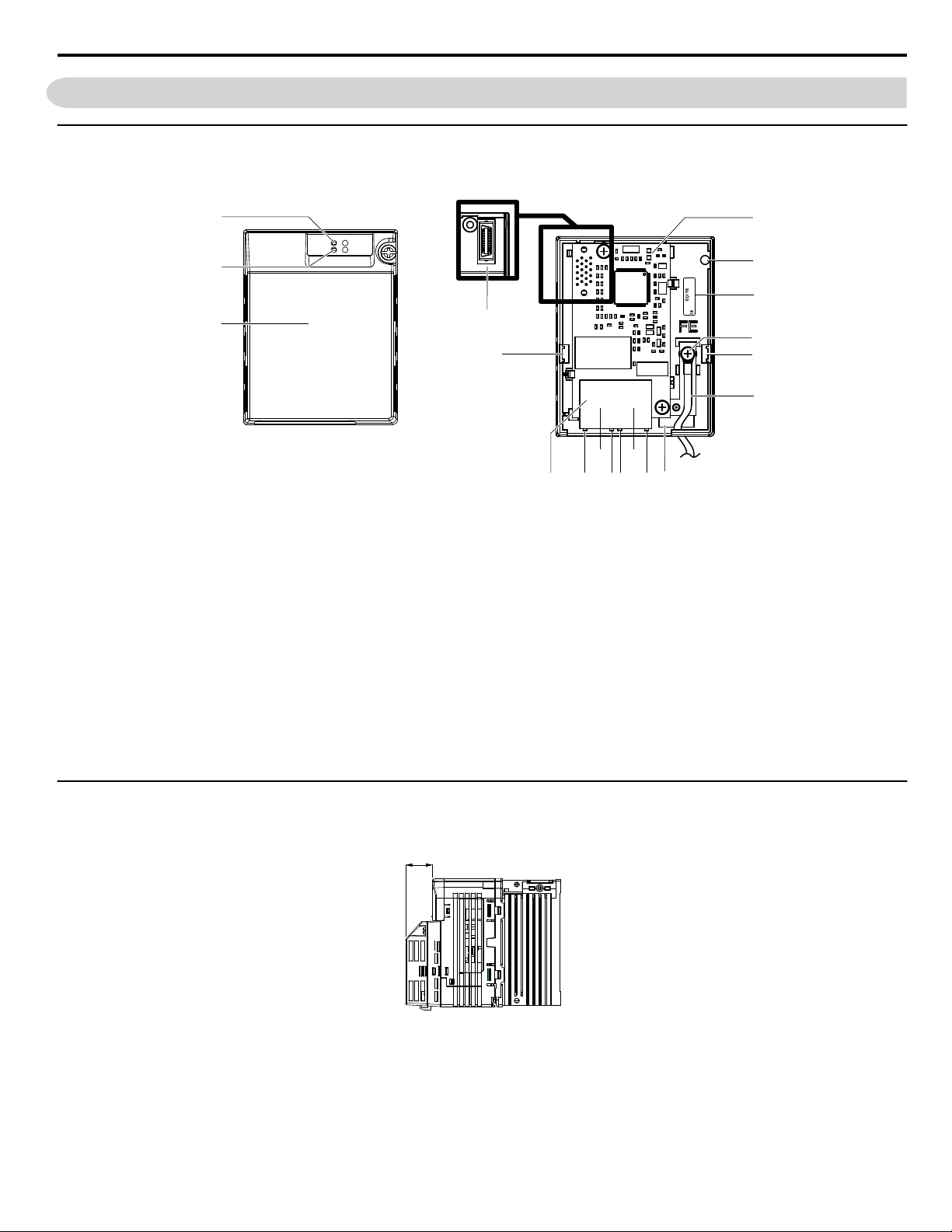
4 Option Components
A
B
C
H
E
D
H
G
I
J
R
F
Q
00000000000000
SI-EN3D/V
1XXX
P
N
K
M
O L
Option with cover removed
Underside
Option with cover attached
27 mm (1.06 in.)
u
SI-EM3D/V Dual-Port Modbus TCP/IP Option Unit
4 Option Components
A –
LED (NS)
B –
LED (MS)
<2>
<2>
C – Option cover
D – Modbus TCP/IP PCB
E – Attachment screw hole for option
cover
F – Nameplate
G – Functional earth cable connection
(FE)
H – Mounting tab
I –
Ground wire
<1>
Figure 1 Option Unit Components
<1> A selection of ground wires are packaged loose in the option shipping package. Connect the appropriate ground wire based on
drive model during installation.
<2> Refer to Option LED Display on page 11 for details on the LEDs.
u
Dimensions
The installed option adds 27 mm (1.06 in.) to the total depth of the drive.
J – Pass-through hole for ground wire
K –
Port 2 LED (10/100)
<2>
L – Port 2
M –
Port 2 LED (LINK/ACT)
N –
Port 1 LED (10/100)
<2>
<2>
O – Port 1
P –
Port 1 LED (LINK/ACT)
<2>
Q – Modbus TCP/IP cable connector
R – Option connector
YASKAWA SIEP YAICOM 17A V1000 Option Dual-Port Modbus TCP/IP SI-EM3D/V Technical Manual
Figure 2 Dimensions
9
Page 10
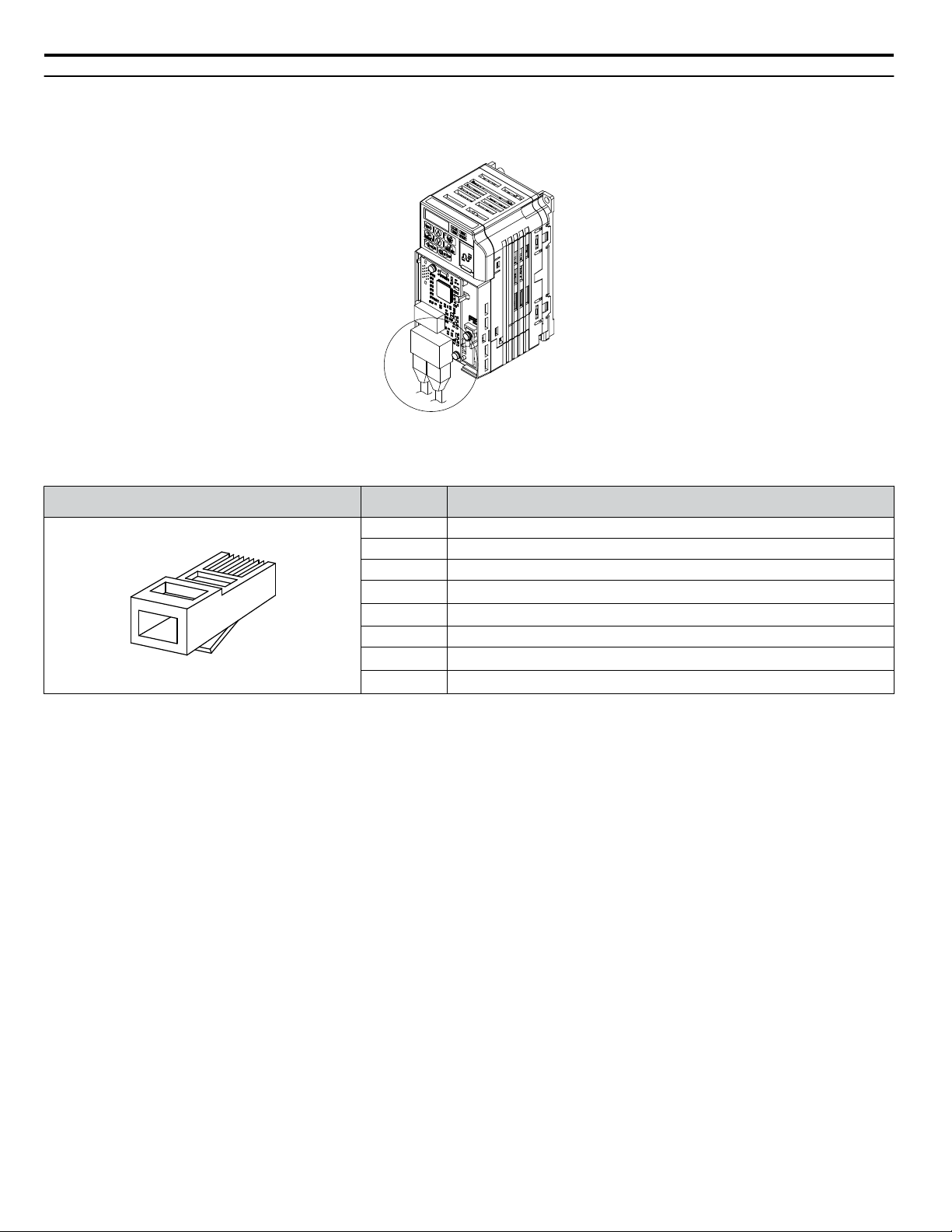
Latch release
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8
4 Option Components
u
Communication Connector CN1
Communication Connector CN1 is a modular RJ45 female connector and the connection point for a customer-supplied male
Modbus network communication cable.
Figure 3 Communication Connector CN1 (RJ45)
Table 2 Male, 8-Way Modular Connector (Customer-Supplied)
Male 8-Way Modular Connector Pin Description
<1> Not used for 10 Mbps and 100 Mbps networks.
1 (Pair 2) Transmit data (TXD) +
2 (Pair 2) Transmit data (TXD) -
3 (Pair 3) Receive data (RXD) +
4 (Pair 1)
5 (Pair 1)
Not used
Not used
<1>
<1>
6 (Pair 3) Receive data (RXD) -
7 (Pair 4)
8 (Pair 4)
Not used
Not used
<1>
<1>
10
YASKAWA SIEP YAICOM 17A V1000 Option Dual-Port Modbus TCP/IP SI-EM3D/V Technical Manual
Page 11
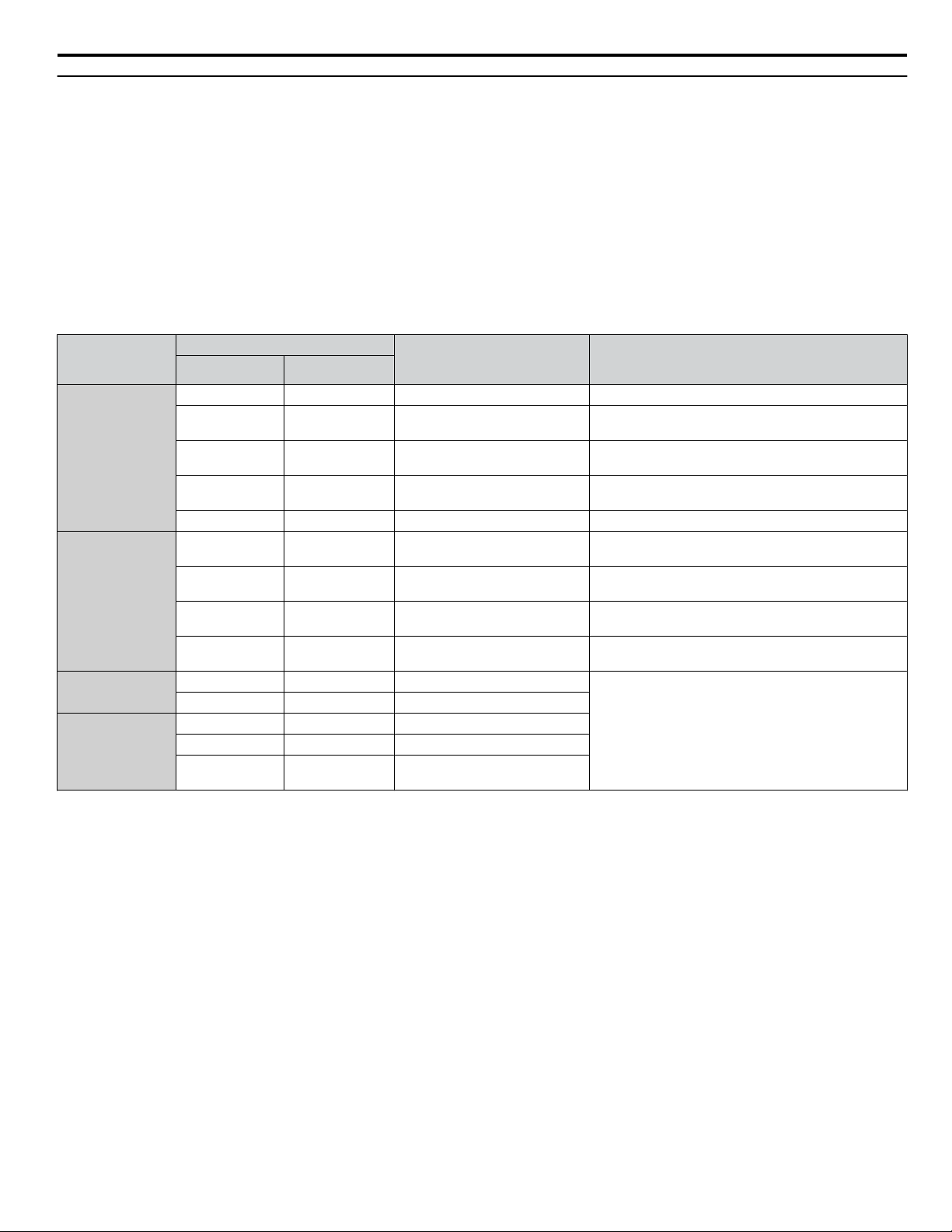
4 Option Components
u
Option LED Display
The option has four LEDs.
Bi-color Status LEDs:
• Module status (MS) red/green
• Network status (NS) red/green
Ethernet LEDs:
• Network speed - 10/100 (MS) green
• Link status and network activity - LINK/ACT (NS) red/green
The operational states of the option LEDs after completion of the power-up diagnostic LED sequence are described in Table
3. Wait at least 2 seconds for the power-up diagnostic process to complete before verifying LED states.
Table 3 Option LED States
Name
MS
NS
<1>
10/100
LINK/ACT
<1> Remove the cover to check the status of the LED. Be careful not to touch the main circuit terminals or the control board in the drive.
<1>
Color Status
Green ON Normal operation
Green Flashing Standby/Initializing
Red Flashing Non-fatal error occurred
Red ON Fatal error occurred The option has detected an unrecoverable major fault.
Green ON
Green Flashing
Red ON Major fault
Green OFF 10 Mbps is established
Green ON 100 Mbps is established
Green OFF LINK is not established
Green ON LINK is established
Green Flashing
Display
– OFF Power supply OFF Power is not being supplied to the drive.
– OFF
Operating Status Remarks
The option is operating normally and initialization is
complete.
The option is in process of configuring or waiting for
configuration information.
The option has detected a recoverable minor fault such
as incomplete configuration.
Power supply OFF or no network
connection established.
Online communications
established
Control communications
established
LINK is established and there is
network activity.
The option is online and has established connections.
The option is online with a control connection.
The option detected a duplicate IP address or the control
connection timed out.
–
–
YASKAWA SIEP YAICOM 17A V1000 Option Dual-Port Modbus TCP/IP SI-EM3D/V Technical Manual
11
Page 12

5 Installation Procedure
5 Installation Procedure
u
Section Safety
DANGER
Electrical Shock Hazard
Do not connect or disconnect wiring while the power is on.
Failure to comply will result in death or serious injury.
Disconnect all power to the drive and wait at least the amount of time specified on the drive front cover safety label. After
all indicators are off, measure the DC bus voltage to confirm safe level, and check for unsafe voltages before servicing. The
internal capacitor remains charged after the power supply is turned off.
WARNING
Electrical Shock Hazard
Do not remove the option unit cover while the power is on.
Failure to comply could result in death or serious injury.
The diagrams in this section may include options and drives without covers or safety shields to show details. Be sure to
reinstall covers or shields before operating any devices. The option should be used according to the instructions described
in this manual.
Do not allow unqualified personnel to use equipment.
Failure to comply could result in death or serious injury.
Maintenance, inspection, and replacement of parts must be performed only by authorized personnel familiar with installation,
adjustment, and maintenance of this product.
Do not use damaged wires, stress the wiring, or damage the wire insulation.
Failure to comply could result in death or serious injury.
Do not use damaged wires, place excessive stress on wiring, or damage the wire insulation.
Failure to comply could result in death or serious injury.
Fire Hazard
Tighten all terminal screws to the specified tightening torque.
Loose electrical connections could result in death or serious injury by fire due to overheating of electrical connections.
NOTICE
Observe proper electrostatic discharge procedures (ESD) when handling the drive and circuit boards.
Failure to comply may result in ESD damage to the drive circuitry.
Never shut the power off while the drive is outputting voltage.
Failure to comply may cause the application to operate incorrectly or damage the drive.
Do not operate damaged equipment.
Failure to comply may cause further damage to the equipment.
Do not connect or operate any equipment with visible damage or missing parts.
Do not use unshielded cable for control wiring.
Failure to comply may cause electrical interference resulting in poor system performance.
Use shielded twisted-pair wires and ground the shield to the ground terminal of the drive.
12
YASKAWA SIEP YAICOM 17A V1000 Option Dual-Port Modbus TCP/IP SI-EM3D/V Technical Manual
Page 13
5 Installation Procedure
NOTICE
Properly connect all pins and connectors.
Failure to comply may prevent proper operation and possibly damage equipment.
Check wiring to ensure that all connections are correct after installing the option and connecting any other devices.
Failure to comply could result in damage to the option.
u
Prior to Installing the Option
Prior to installing the option, wire the drive, make necessary connections to the drive terminals, and verify that the drive
functions normally without the option installed. Refer to the drive Quick Start Guide for information on wiring and connecting
the drive.
u
Installing the Option
DANGER! DANGER! Electrical Shock Hazard. Do not connect or disconnect wiring while the power is on. Failure to comply could result in
death or serious injury. Before installing the option, disconnect all power to the drive and wait at least the amount of time specified on the
drive front cover safety label. After all indicators are off, measure the DC bus voltage to confirm safe level, and check for unsafe voltages
before servicing. The internal capacitor remains charged after the power supply is turned off.
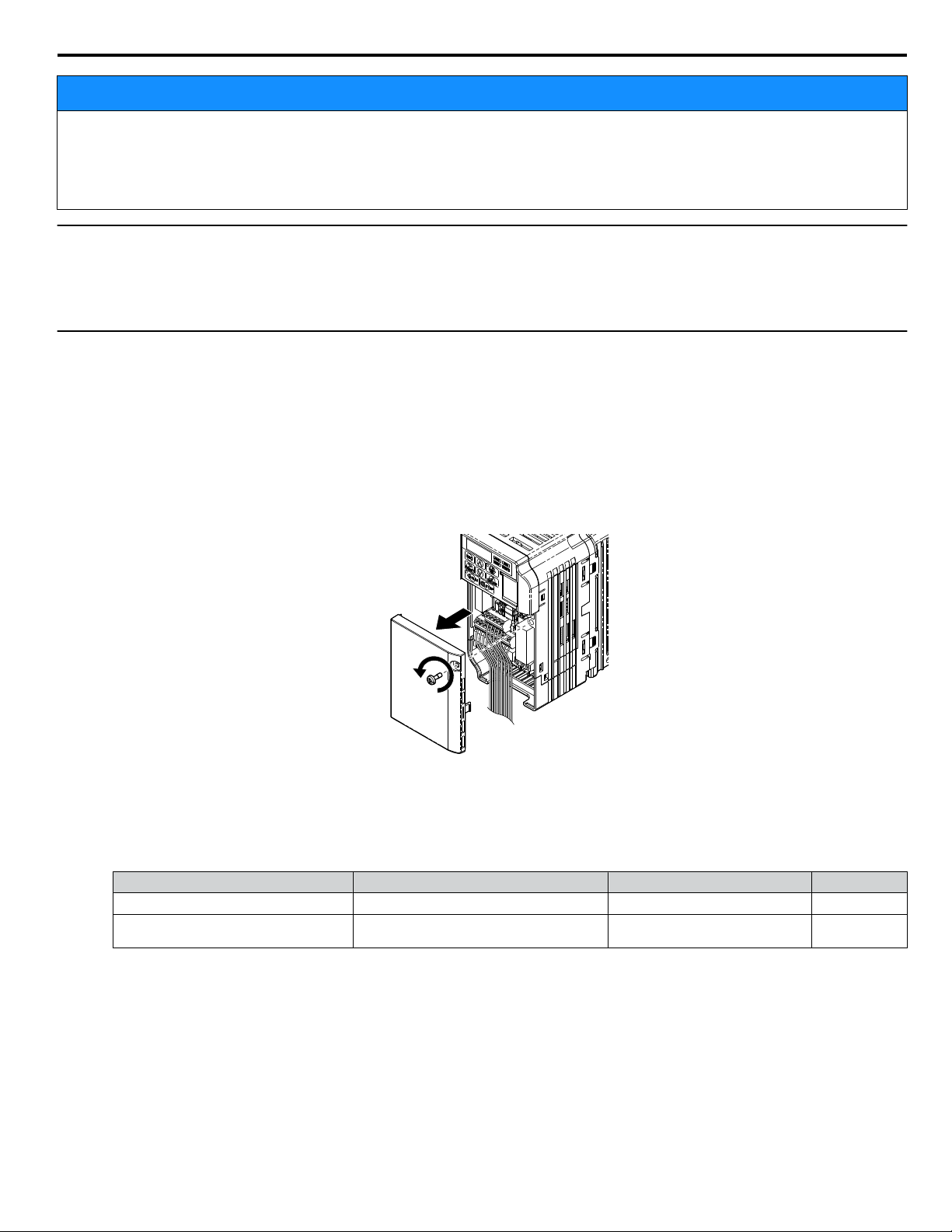
Shut off power to the drive, wait at least five minutes after confirming the DC bus voltage is safe, then loosen the
1.
screw that fastens the front cover in place and remove the front cover. This drive front cover will be replaced by the
option cover. Cover removal varies depending on drive size.
NOTICE: Damage to Equipment. Observe proper electrostatic discharge procedures (ESD) when handling the option, drive, and
circuit boards. Failure to comply may result in ESD damage to circuitry.
Figure 4 Remove the Front Cover
The remaining installation steps differ based on drive model. Find the drive model number on the drive nameplate
2.
and refer to the step indicated in Table 4 based on your model number
Table 4 Installation Steps Based on Drive Model
Enclosure Type Drive Model Proceed to Step Page
IP20/Open-Chassis
IP20/NEMA Type 1
<1>
CIMR-VooAooooB
CIMR-VooAooooF
3 13
6 15
<1>Installing the option on an IP20/NEMA Type 1 enclosure drive voids NEMA Type 1 protection while maintaining IP20 conformity.
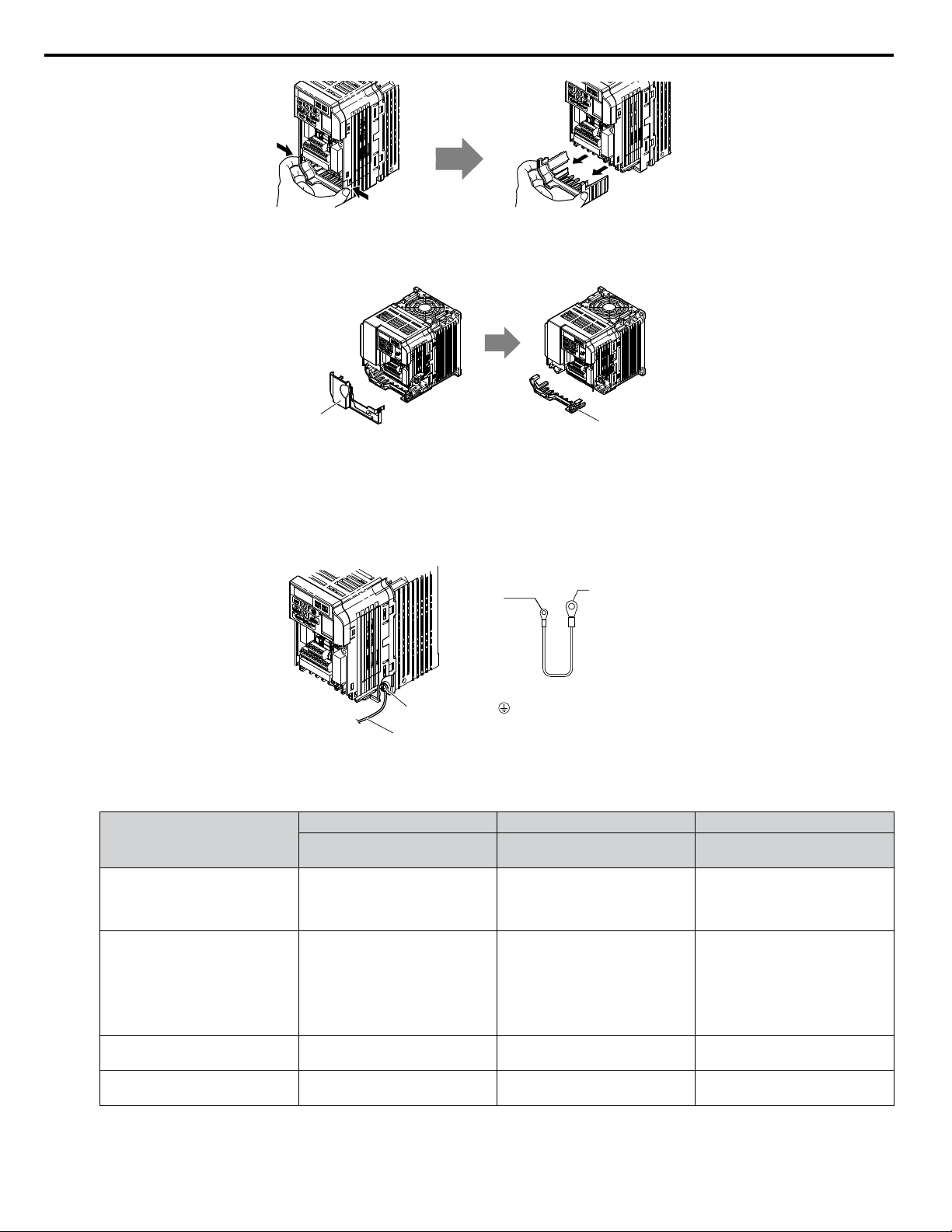
For IP20/Open-Chassis models CIMR-VooAooooB, remove the bottom cover of the drive by applying pressure
3.
to the tabs on each side of the bottom cover. Pull the bottom cover away from the drive while pushing in on the tabs
to release the cover from the drive. Refer to Figure 5 for details.
Refer to Figure 6 for drive models BA0006B to BA0018B, 2A0008B to 2A0069B, and 4A0001B to 4A0038B, which
require removing the terminal cover prior to removing the bottom cover.
YASKAWA SIEP YAICOM 17A V1000 Option Dual-Port Modbus TCP/IP SI-EM3D/V Technical Manual
13
Page 14
Bottom Cover
Terminal Cover
Ground terminal
Ground wire
Drive-side
connector
Screw size:
M3.5 to M6
Option unit
connector
Screw size: M3
5 Installation Procedure
Figure 6 Remove the Terminal Cover and Bottom Cover on an IP20/Open-Chassis Drive
(Models BA0006B to BA0018B; 2A0008B to 2A0069B; 4A0001B to 4A0038B)
Figure 5 Remove the Bottom Cover on an IP20/Open-Chassis Drive
(Models BA0001B to BA0003B and 2A0001B to 2A0006B)
On IP20/Open-Chassis models, connect the drive side of the ground wire to the drive ground terminal.
4.
Note: The different ground wires packaged with the option connect the option to different drive models. Select the proper ground wire
depending on drive size. Refer to Table 5 for ground wire selection by drive model.
Figure 7 Connect the Ground Wire on an IP20/Open-Chassis Drive
Table 5 Ground Wire Selection
Ground Wire Length
(mm/in)
150/5.9
Single-Phase
200 V Class
BA0001
BA0002
BA0003
Drive Model
Three-Phase
200 V Class
2A0001
2A0002
2A0004
2A0006
Three-Phase
400 V Class
–
4A0001
4A0002
4A0004
4A0005
4A0007
4A0009
200/7.9
BA0006
BA0010
BA0012
BA0018
2A0010
2A0012
2A0020
4A0011
250/9.8 –
400/15.7 –
For IP20/Open-Chassis models, go to Step 9. on page 36.
5.
2A0030
2A0040
2A0056
2A0069
4A0018
4A0023
4A0031
4A0038
14
YASKAWA SIEP YAICOM 17A V1000 Option Dual-Port Modbus TCP/IP SI-EM3D/V Technical Manual
Page 15
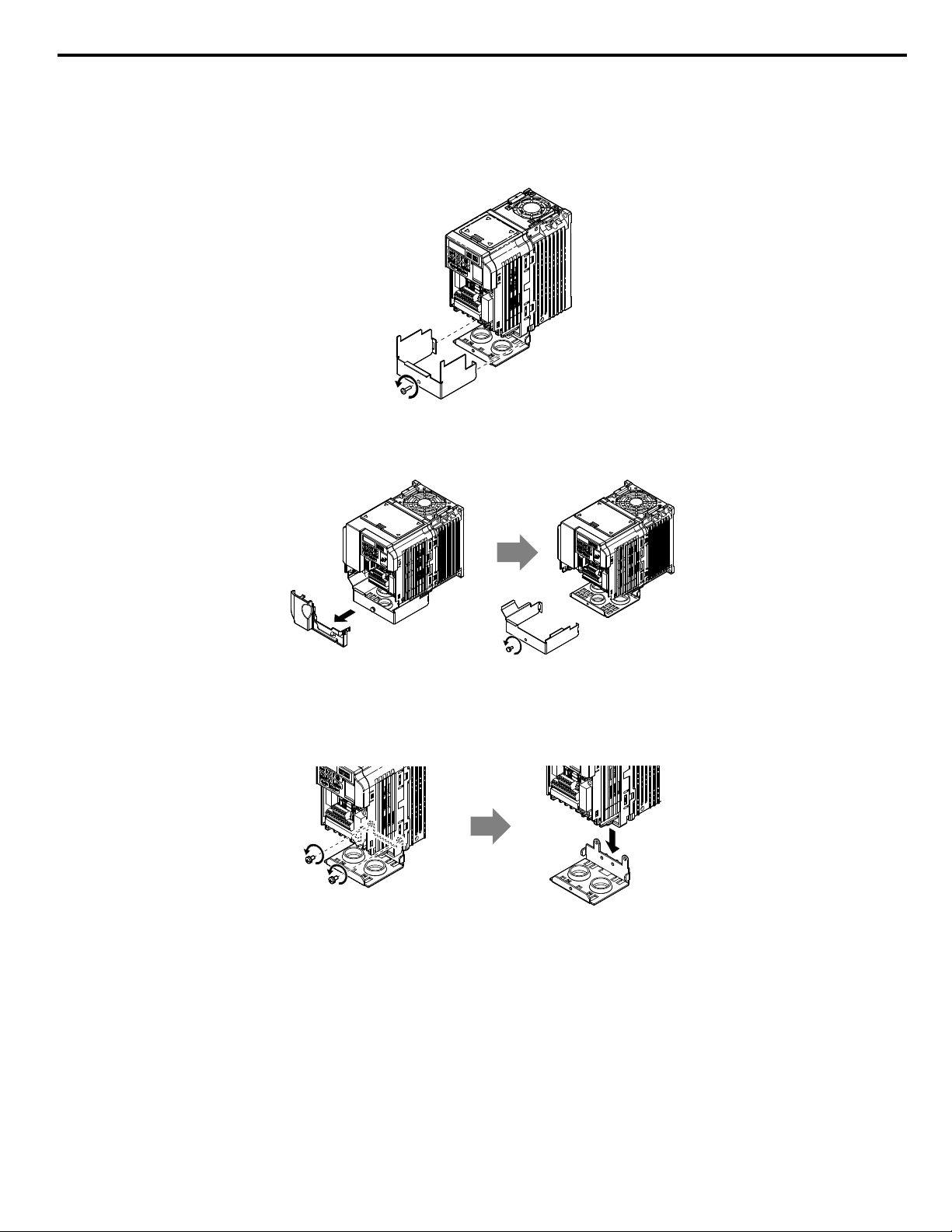
5 Installation Procedure
For IP20/NEMA Type 1 enclosure models CIMR-VooAooooF, loosen the screw on the front of the NEMA Type
6.
1 terminal cover and remove it from the drive. Refer to Figure 8 for details.
Refer to Figure 9 for drive models BA0006F to BA0018F, 2A0010F to 2A0069F, and 4A0001F to 4A0038F, which
require removing the plastic terminal cover prior to removing the NEMA Type 1 terminal cover.
Note: Installing the option on an IP20/NEMA Type 1 enclosure drive voids NEMA Type 1 protection while maintaining IP20 conformity.
Figure 8 Remove the NEMA Type 1 Terminal Cover
(Models BA0001F to BA0003F and 2A0001F to 2A0006F)
Figure 9 Remove the Terminal Cover on an IP20/NEMA Type 1 Drive
(Models BA0006F to BA0018F; 2A0008F to 2A0069F; 4A0001F to 4A0038F)
For models BA0001F to BA0003F and 2A0001F to 2A0006F, loosen the screws attaching the NEMA Type 1 conduit
7.
bracket to the drive to remove the NEMA Type 1 conduit bracket.
Figure 10 Remove the NEMA Type 1 Conduit Bracket
(Models BA0001F to BA0003F and 2A0001F to 2A0006F)
On models (BA0001F to BA0003F and 2A0001F to 2A0006F), the screw for the drive ground terminal also acts as
8.
one of the screws that attaches the NEMA Type 1 conduit bracket to the drive. Reattach the NEMA Type 1 conduit
bracket according to Figure 27 and connect the drive-side of the ground wire to the drive ground terminal.
Note: The different ground wires packaged with the option connect the option to different drive models. Select the proper ground wire
depending on drive size. Refer to Table 5 on page 14 for ground wire selection by drive model.
YASKAWA SIEP YAICOM 17A V1000 Option Dual-Port Modbus TCP/IP SI-EM3D/V Technical Manual
15
Page 16
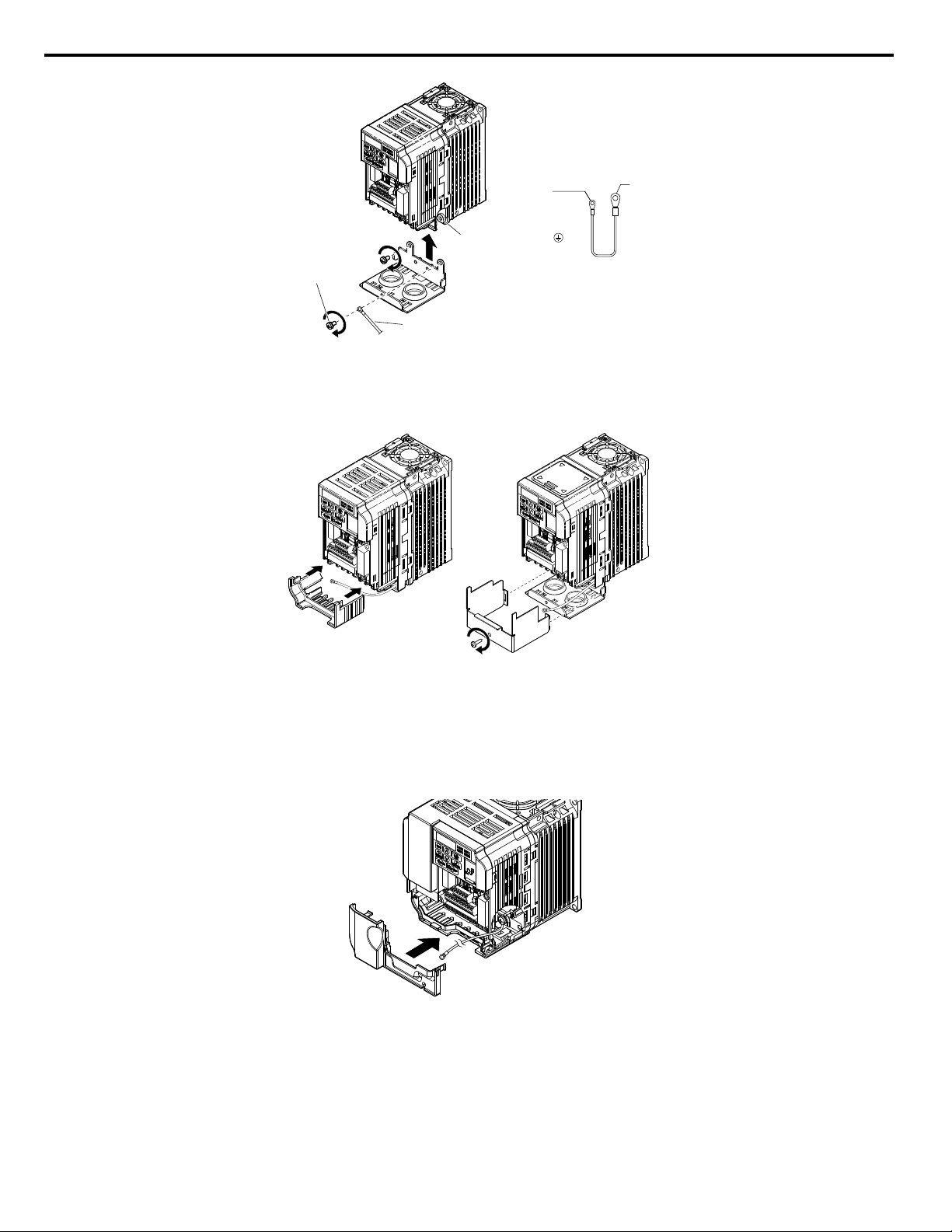
Ground terminal
Ground wire
Drive ground terminal/
NEMA Type 1 conduit
bracket screw
Ground wire
Drive-side
connector
Screw size:
M3.5 to M6
Option unit
connector
Screw size: M3
IP20/Open-Chassis IP20/NEMA Type 1 Enclosure
5 Installation Procedure
Figure 11 Reattach the NEMA Type 1 Conduit Bracket and Connect the Ground Wire
Reattach the bottom cover. Keep the ground wire inside of the bottom cover when reattaching.
9.
(Models BA0001F to BA0003F and 2A0001F to 2A0006F)
On models BA0006 to BA0018, 2A0008 to 2A0069, and 4A0001 to 4A0038, reattach the terminal cover.
10.
Refer to Figure 13 and Figure 14 for drive models BA0006 to BA0018, 2A0008 to 2A0020, and 4A0001 to 4A0011,
which require routing the ground wire through the provided notch when reinstalling the terminal cover.
Figure 12 Reattach the Bottom Cover
Figure 13 Reattach the Terminal Cover
(Models BA0006 to BA0018; 2A0008 to 2A0069; 4A0001 to 4A0038)
16
YASKAWA SIEP YAICOM 17A V1000 Option Dual-Port Modbus TCP/IP SI-EM3D/V Technical Manual
Page 17

Ground wire
routing notch
Line up tabs
Line up tabs
5 Installation Procedure
Figure 14 Terminal Cover Ground Wire Notch
(Models BA0006 to BA0018; 2A0008 to 2A0020; 4A0001 to 4A0011)
Remove the option cover and pass the ground wire through the inside of the drive bottom cover and into the through-
11.
hole for the ground wire at the front of the option.
Figure 15 Ground Wire Routing
Attach the option to the drive. Properly seat the tabs on the left and right sides of the option to the drive case.
12.
Figure 16 Connect the Option
Connect the ground wire at the option ground terminal. Tighten the screw to 0.5 to 0.6 N•m or (4.4 to 5.3 in lbs) using
13.
an M3 Phillips screwdriver.
YASKAWA SIEP YAICOM 17A V1000 Option Dual-Port Modbus TCP/IP SI-EM3D/V Technical Manual
17
Page 18

Option ground terminal
STOP
(Hz)
(Hz)
(A)
(V)
V1000
STOP
(Hz)
(Hz)
(A)
(V)
V1000
STOP
(Hz)
(Hz)
(A)
(V)
V1000
STOP
(Hz)
(Hz)
(A)
(V)
V1000
STOP
(Hz)
(Hz)
(A)
(V)
V1000
STOP
(Hz)
(Hz)
(A)
(V)
V1000
STOP
(Hz)
(Hz)
(A)
(V)
V1000
STOP
(Hz)
(Hz)
(A)
(V)
V1000
STOP
(Hz)
(Hz)
(A)
(V)
V1000
Star Topology
Daisy-Chained Topology
Ring Topology
5 Installation Procedure
Connect the communication cable to the option modular connector (CN1) port 1.
14.
To connect the option to a network, firmly connect RJ45 8-pin shielded twisted pair Cat5e cable(s) into the modular
connector ports (see Figure 18).
Communication Cable Specifications
Only use cable recommended for Modbus TCP/IP. Using a cable not specifically recommended may cause the option
or drive to malfunction.
The dual RJ45 network ports on the option board act as a switch to allow for flexibility in cabling topology. For example,
a traditional star network topology may be employed by using a single port on the option board. Alternatively, a daisychained approach may be employed by using both RJ45 ports. The daisy-chained approach reduces the requirements
of central switch ports. A ring topology is also possible. When implementing a ring topology, Rapid Spanning Tree
Protocol (RSTP) must be enabled to function correctly.
Figure 17 Connect the Ground Wire to the Option
18
Figure 18 Communication Cable Ports
Figure 19 Topology Options
YASKAWA SIEP YAICOM 17A V1000 Option Dual-Port Modbus TCP/IP SI-EM3D/V Technical Manual
Page 19

V1000
M
U/T1
V/T2
W/T3
R/L1
S/L2
T/L3
SI-EM3D/V
Modbus TCP/IP
Option
FE
<1>
Modbus
TCP/IP Cable
MotorPower
Modbus
TCP/IP Cable
Line up tabs
5 Installation Procedure
Figure 20 Option Connection Diagram
Use the second communication cable port to daisy chain a series of drives where applicable.
15.
Attach the option cover by aligning the tabs with the mounting holes, seat the front cover into place, and tighten the
16.
screw on the front.
Figure 21 Attach the Option Cover
Note: Take proper precautions when wiring the option so that the front covers will easily fit back onto the drive. Make sure no cables
are pinched between the front covers and the drive when replacing the covers.
Set drive parameters in Table 6 for proper option performance.
17.
YASKAWA SIEP YAICOM 17A V1000 Option Dual-Port Modbus TCP/IP SI-EM3D/V Technical Manual
19
Page 20

6 Related Drive Parameters
6 Related Drive Parameters
The following parameters are used to set up the drive for operation with the option. Parameter setting instructions can be found
in the drive manual.
Confirm proper setting of the parameters in Table 6 before starting network communications. After changing parameter
settings, cycle power to the drive for the new settings to take effect.
Table 6 Related Parameters
No.
(Addr.
Hex)
b1-01
(0180)
<1>
b1-02
(0181)
<1>
F6-01
(03A2)
F6-02
(03A3)
F6-03
(03A4)
F6-07
(03A8)
F6-08
(036A)
<4>
F6-14
(03BB)
F7-01
(03E5)
<5>
F7-02
(03E6)
<5>
F7-03
(03E7)
<5>
F7-04
(03E8)
<5>
F7-05
(03E9)
F7-06
(03EA)
F7-07
(03EB)
F7-08
(03EC)
F7-09
(03ED)
Frequency Reference Selection
1
Run Command
Selection 1
Communications Error
Operation Selection
External Fault from Comm.
Option Detection Selection
External Fault from Comm.
Option Operation Selection
Multi-Step Speed Enable/
Disable Selection when
NefRef/ComRef is Selected
Reset Communication
Parameters
bUS Error Auto Reset
IP Address 1 Sets the most significant octet of network static IP address.
IP Address 2 Sets the second most significant octet of network static IP address.
IP Address 3 Sets the third most significant octet of network static IP address.
IP Address 4 Sets the fourth most significant octet of network static IP address.
Subnet Mask 1 Sets the most significant octet of network static Subnet Mask.
Subnet Mask 2 Sets the second most significant octet of network static Subnet Mask.
Subnet Mask 3 Sets the third most significant octet of network static Subnet Mask.
Subnet Mask 4 Sets the fourth most significant octet of network static Subnet Mask.
Gateway Address 1 Sets the most significant octet of network Gateway address.
Name Description Values
0: Digital operator
1: Analog input terminals
2: MEMOBUS/Modbus communications
3: Option PCB
Default: 1
Range: 0 to 4
4: Pulse input (terminal RP)
0: Digital operator
1: Digital input terminals
2: MEMOBUS/Modbus communications
Default: 1
Range: 0 to 3
3: Option PCB
0: Ramp to stop. Decelerate to stop using the deceleration time in C1-02.
1: Coast to stop
2: Fast Stop. Decelerate to stop using the deceleration time in C1-09.
3: Alarm only
4: Alarm (d1-04)
5: Alarm Ramp to Stop
<2>
<3>
<3>
1: Detection during run only
Default: 1
Range: 0 to 5
Default: 0
Range: 0, 1
0: Ramp to stop. Decelerate to stop using the deceleration time in C1-02.
1: Coast to stop
2: Fast Stop. Decelerate to stop using the deceleration time in C1-09.
3: Alarm only
<2>
0: Multi-step reference disabled (same as F7)
1: Multi-step reference enabled (same as V7)
Default: 1
Range: 0 to 3
Default: 1
Range: 0, 1
0: Communication-related parameters (F6-oo/F7-oo) are not reset when
the drive is initialized using A1-03.
1: Reset all communication-related parameters
Default: 0
Range: 0, 1
(F6-oo/F7-oo) when the drive is initialized using A1-03.
0: Disabled
1: Enabled
Default: 0
Range: 0, 1
Default: 192
Range: 0 to 255
Default: 168
Range: 0 to 255
Default: 1
Range: 0 to 255
Default: 20
Range: 0 to 255
Default: 255
Range: 0 to 255
Default: 255
Range: 0 to 255
Default: 255
Range: 0 to 255
Default: 0
Range: 0 to 255
Default: 192
Range: 0 to 255
20
YASKAWA SIEP YAICOM 17A V1000 Option Dual-Port Modbus TCP/IP SI-EM3D/V Technical Manual
Page 21

6 Related Drive Parameters
No.
(Addr.
Hex)
F7-10
(03EE)
F7-11
(03EF)
F7-12
(03E0)
F7-13
(03F1)
F7-14
(03F2)
F7-15
(03F3)
F7-16
(03F4)
H5-11
(043C)
Gateway Address 2 Sets the second most significant octet of network Gateway address.
Gateway Address 3 Sets the third most significant octet of network Gateway address.
Gateway Address 4 Sets the fourth most significant octet of network Gateway address.
Address Mode at Startup
Duplex Mode Selection
Communication Speed
Selection
Communication Loss Timeout
Communications ENTER
Function Selection
<1> To start and stop the drive with the master device using serial communications, set b1-02 to 3. To control the drive frequency reference of the drive
via the master device, set b1-01 to 3.
<2> When set to 3, 4, or 5, the drive will continue to operate when a fault is detected. Take safety measures, such as installing an emergency stop switch.
<3> Available in drive software versions PRG: 1024 and later.
<4> Parameter setting value is not reset to the default value when the drive is initialized.
<5> Cycle power for setting changes to take effect.
<6> When F7-13 is set to 0, parameters F7-01 to F7-12 must be set, and all IP Addresses (as defined with parameters F7-01 to F7-04) must be unique.
<7> When F7-14 is set to 0 or 2, parameter F7-15 must be set.
<8> Default setting differs depending on drive software version. PRG: 1012 to 1015: 0
PRG: 1016 and later: 1
<9> Setting range differs depending on drive software version. PRG: 1012 to 1023, Range: 0 to 2
PRG: 1024 and later, Range: 0 to 8
<10> Setting values differ depending on drive software version. PRG: 1012 to 1015, Default: 0; Range: 0, 10, 100
PRG: 1016 to 1023, Default: 10; Range: 10, 100
PRG: 1024 and later, Default: 10; Range: 10; 100 to 102
Name Description Values
Default: 168
Range: 0 to 255
Default: 1
Range: 0 to 255
Default: 1
Range: 0 to 255
Select the option address setting method
<6>
0: Static
1: BOOTP
Default: 2
Range: 0 to 2
2: DHCP
Selects duplex mode setting.
0: Half duplex forced (both ports)
1: Auto-negotiate duplex mode and communication speed (both ports)
2: Full duplex forced (both ports)
3: Half (port 1)/Auto (port 2)
4: Half (Port 1)/Full (port 2)
<7>
<7>
Default:
<8>
Range: 0 to 8
<9>
5: Auto (port 1)/Half (port 2)
6: Auto (port 1)/Full (port 2)
7: Full (port 1)/Half (port 2)
8: Full (port 1)/Auto (port 2)
Sets the communication speed
0: 10 Mbps
10: 10 Mbps
100: 100 Mbps
101: 10 (Port 1)/100 Mbps (port 2)
Default: 10
Range: 10; 100 to 102
<10>
102: 100 (Port 1)/10 Mbps (port 2)
Sets the timeout value for communication loss detection in tenths of a second.
A value of 0 disables the connection timeout.
Example: An entered value of 100 represents 10.0 seconds.
Default: 0.0
Min.: 0.0
Max.: 30.0
Selects the function for the ENTER command that saves parameter data to
the drive.
0: Parameter changes are activated when ENTER command is written
1: Parameter changes are activated immediately without use of ENTER
Default: 1
Range: 0, 1
command
<10>
Table 7 Option Monitors
No. Name Description Value Range
U6-80 to
U6-83
U6-84 to
U6-87
U6-88 to
U6-91
U6-92 Online Speed Link Speed
Online IP Address IP Address currently available; U6-80 is the most significant octet 0 to 255
Online Subnet Subnet currently available; U6-84 is the most significant octet 0 to 255
Online Gateway Gateway currently available; U6-88 is the most significant octet 0 to 255
10: 10 Mbps
100: 100 Mbps
YASKAWA SIEP YAICOM 17A V1000 Option Dual-Port Modbus TCP/IP SI-EM3D/V Technical Manual
21
Page 22

6 Related Drive Parameters
No. Name Description Value Range
U6-93 Online Duplex Duplex Setting 0: Half, 1: Full
U6-94 Port 2 Speed Port 2 Link Speed 0: Half, 1: Full
U6-95 Port 2 Duplex Port 2 Duplex Setting
U6-96 RSTP RSTP Role and State 0000 to 9292
U6-98 First Fault First Option Fault –
U6-99 Current Fault Current Option Fault –
10: 10 Mbps
100: 100 Mbps
22
YASKAWA SIEP YAICOM 17A V1000 Option Dual-Port Modbus TCP/IP SI-EM3D/V Technical Manual
Page 23

7 Modbus TCP/IP Messaging
7 Modbus TCP/IP Messaging
u
Modbus TCP/IP Overview
The Modbus TCP/IP protocol is essentially the Modbus protocol over an Modbus TCP/IP network. A master controller
(typically a PLC) sends commands to slave devices, which then perform the specified functions and send a response to the
master. The drive using the option has slave functionality.
Supported Modbus TCP/IP Commands
n
Table 8 Supported Modbus TCP/IP Commands
Function Code Function Name
03H Read Multiple Registers
06H Write Single Register
10H Write Multiple Registers
17H Read/Write Multiple Registers
Drive Modbus TCP/IP Option Registers
n
All of the command registers, monitor registers, and parameters documented in the drive Technical Manual are accessible via
the option.
High Speed Access Drive Modbus TCP/IP Option Registers
n
Many of the registers required for control have been specially mapped to provide higher speed access to increase network
performance. Use these registers for the best response times.
All of the drive command registers have been mapped to this high speed access area (Modbus TCP/IP registers 01H to 01FH).
In addition, the monitors shown in Table 9 are mapped for high speed access.
Table 9 Drive Registers
Address
(hex)
2000 4B
2001 44 Motor Speed Monitor (U1-05)
2002 48 Torque Reference Monitor (U1-09)
2003 F0 PG Count Channel 1
2004 40 Frequency Reference Monitor (U1-01)
2005 41 Output Frequency Monitor (U1-02)
2006 26
2007 4F Terminal A2 Input Level Monitor (U1-14)
Drive
Register
(hex)
Description Bit Description
0 During Run
1 During Zero Speed
2 During Reverse Direction
3 During Fault Reset Signal Input
4 During Speed Agree
5 Drive Ready
6 Alarm
Status Word
(U1-12)
7 Fault
8 During Operation Error (oPEoo)
9 During Momentary Power Loss
A Motor 2 Selected
B Reserved
C Reserved
D Reserved
E ComRef Status, NetRef Status
F ComCtrl Status, NetCtrl Status
Output Current (U1-03)
0.1 A
YASKAWA SIEP YAICOM 17A V1000 Option Dual-Port Modbus TCP/IP SI-EM3D/V Technical Manual
23
Page 24

7 Modbus TCP/IP Messaging
Address
(hex)
2008 46 DC Bus Voltage Monitor (U1-07)
2009 C0 Error Signal 1
200A C1 Error Signal 2
Drive
Register
(hex)
Description Bit Description
0 Reserved
1 Undervoltage (Uv1)
2 Control Power Supply Undervoltage (Uv2)
3 Soft Charge Circuit Fault (Uv3)
4 Reserved
5 Ground Fault (GF)
6 Overcurrent (oC)
7 Overvoltage (ov)
8 Heatsink Overheat (oH)
9 Heatsink Overheat (oH1)
A Motor Overload (oL1)
B Drive Overload (oL2)
C Overtorque Detection 1 (oL3)
D Overtorque Detection 2 (oL4)
E Dynamic Braking Transistor Fault (rr)
F Braking Resister Overheat (rH)
0 External Fault at input terminal S3 (EF3)
1 External Fault at input terminal S4 (EF4)
2 External Fault at input terminal S5 (EF5)
3 External Fault at input terminal S6 (EF6)
4 External Fault at input terminal S7 (EF7)
5 External Fault at input terminal S8 (EF8)
6 Cooling fan Error (FAn)
5 Reserved
6 Reserved
7 Overspeed (os)
8 Excessive Speed Deviation (dEv)
9 PG Disconnected (PGo)
A Input Phase Loss (PF)
B Output Phase Loss (LF)
C Motor Overheat (PTC input) (oH3)
D Digital Operator Connection Fault (oPr)
E EEPROM Write Error (Err)
F Motor Overheat Fault (PTC input) (oH4)
24
YASKAWA SIEP YAICOM 17A V1000 Option Dual-Port Modbus TCP/IP SI-EM3D/V Technical Manual
Page 25

7 Modbus TCP/IP Messaging
Address
(hex)
200B C2 Error Signal 3
200C 4E Terminal A1 Input Level Monitor (U1-13)
200D 49 Digital Input Terminal Status (U1-10)
200E 50 Terminal A3 Input Level Monitor (U1-15)
200F F1 PG Count Channel 2
2010 4D Drive Software Number (Flash) (U1-25)
Drive
Register
(hex)
Description Bit Description
0 MEMOBUS/Modbus Communication Error (CE)
1 Option Communication Error (bUS)
2 Reserved
3 Reserved
4 Control Fault (CF)
5 Zero Servo Fault (SvE)
5 Reserved
6 Option External Fault (EF0)
7 PID Feedback Loss (FbL)
8 Undertorque Detection 1 (UL3)
9 UL4 Undertorque Detection 2 (UL4)
A High Slip Braking Overload (oL7)
B Reserved
C Reserved
D Reserved
E Reserved
F Hardware Fault (includes oFo)
u
Enter Command Types
The drive supports two types of Enter commands as shown in Table 10. An Enter command is enabled by writing 0 to register
number 0900H or 0910H. These registers can be written to only. An error will occur if the user attempts to read from these
registers.
Table 10 Enter Command Types
Register No. Description
0900H
0910H Writes data in the RAM only. Parameter changes are lost when the drive is shut off.
Note: 1. Because the EEPROM can be written to a maximum of 100,000 times, refrain from writing to the EEPROM too often. The Enter
2. Parameter data cannot be written to EEPROM during undervoltage, even using 0900H.
3. If undervoltage occurs when a making several parameter changes issued with a single ENTER command, the writing process may be
u
Enter Command Settings when Upgrading the Drive
Writes data into the EEPROM (non-volatile memory) of the drive and enables the data in RAM at the same time. Parameter
changes remain even if the power supply is cycled.
command registers are write-only. Consequently, if these registers are read, then the register address will be invalid (Error code: 02H).
An Enter command is not required if reference or broadcast data are sent to the drive.
aborted before all of the new changes have been written. Because all of the data has not yet been written, the EEPROM data error
“CPF06” will be displayed the next time power to the drive is cycled. To prevent this problem, wait approximately 5 seconds after
issuing the ENTER command before shutting off drive power.
When replacing earlier Yaskawa drive models with a V1000 and keeping the MEMOBUS/Modbus communications settings,
parameter H5-11 needs to be set in accordance with how the Enter command functions in the older drive. H5-11 determines
if an Enter command is needed to activate parameter changes in the drive.
• Set parameter H5-11 to 0 when upgrading from a G7 or F7 series drive to V1000-Series drive.
• Set parameter H5-11 to 1 when upgrading from a V7 series drive to V1000-Series drive.
YASKAWA SIEP YAICOM 17A V1000 Option Dual-Port Modbus TCP/IP SI-EM3D/V Technical Manual
25
Page 26

7 Modbus TCP/IP Messaging
H5-11 and the Enter Command
n
H5-11 Settings H5-11 = 0 H5-11 = 1
Drive being replaced G7, F7 V7
How parameter settings are enabled When the Enter command is received from the master. As soon as the value is changed.
Upper/lower limit check
Default value of related parameters
Error handling when setting
multiple parameters
u
Message Content
Upper/lower limit check is performed taking the settings
of related parameters into account.
Not affected. The settings of related parameters remain
unchanged. They must be changed manually if needed.
Data is accepted even if one setting is invalid. The invalid
setting will be discarded. No error message occurs.
The upper/lower limit of the changed parameter is
checked only.
The default settings of related parameters are changed
automatically.
Error occurs if only one setting is invalid. All data sent
are discarded.
The data section of the Modbus packet contains the Modbus message. In this data section, the master sends commands to the
slave, and the slave responds. The message format is configured for both sending and receiving as shown below, and the length
of data packets depends on the command (function) content.
SLAVE ADDRESS
FUNCTION CODE
DATA
ERROR CHECK
Unit Identifier
n
This field is used for intra-system routing purposes. It is typically used to communicate to a Modbus+ or a Modbus serial line
slave through a gateway between an Modbus TCP/IP network and a Modbus serial line. This field is set by the Modbus master
in the command and must be returned with the same value in the response by the slave. This is sometimes referred to as the
Unit ID. A drive using the option has no gateway functionality.
Function Code
n
When sent by the master, this field identifies the command to be undertaken by the slave. It also identifies the format for the
DATA section of the message. The slave normally echoes this command back to the master in its response message. When
the most significant bit of this field is set in the response message, it signals an error condition has occurred.
Data
n
This field contains multiple bytes of varying length based upon the Function Code for commands and based upon the results
of the command in the response. When sent by the master, this field contains details of the command that the slave will require
to carry out the function. When sent by the slave, this field contains details of the response and sometimes error information.
u
Modbus TCP/IP Option Function Details
Read Multiple Registers 03 (03 H)
n
This function code is used to read the contents of a contiguous block of registers. The command specifies the starting register
and the number of registers. The normal response packs two bytes per register. For each register in the response, the first byte
contains the most significant bits and the second byte contains the least significant bits.
Table 11 Read Multiple Registers Command
Description Byte Data (Hex)
Slave Address 1 00 to FF
Function Code 1 03
Starting Register 2 0000 to FFFF
Quantity of Registers 2
<1> N = Quantity of Registers (range is 1 - 16)
<1>
N
26
Table 12 Read Multiple Registers Response
Description Byte Data (Hex)
Slave Address 1 00 to FF
Function Code 1 03
YASKAWA SIEP YAICOM 17A V1000 Option Dual-Port Modbus TCP/IP SI-EM3D/V Technical Manual
Page 27

7 Modbus TCP/IP Messaging
Description Byte Data (Hex)
Number of Data Bytes 1
Register Values
<1> N = Quantity of Registers
Description Byte Data (Hex)
Slave Address 1 00 to FF
Error Code 1 83
Exception Code 1
<1>
N
x 2
Table 13 Read Multiple Registers Error Response
Values contained in slave registers.
Refer to Modbus TCP/IP Exception Codes
on page 31 for details.
2 x N
<1>
Examples of Fault Response, Read Response, and Read Multiple Registers Command
Note: In option software version VST800380, any invalid register in the range will return an error response.
In option versions VST800381 and later, invalid registers in the range will not return an error response provided at least 1 register is valid.
Invalid registers will be set to 0 in the response.
Table 14 lists command examples to read register contents (register addresses 0020H to 0023H) from a drive with the slave
address (unit identifier) 02H.
Table 15 shows examples of responses indicating that multiple registers have been read successfully. The contents read from
0020H are 1770H, 1770H, 0109H, and 0000H.
Table 16 shows examples of an error response when reading multiple registers. The exception code is 02H (indicating a register
number error).
Starting Register
Quantity of Registers
Starting Register
Next Register
Next Register
Last Register
Table 14 Example Read Multiple Registers Command
Description Data (Hex)
Slave Address 02
Function Code 03
Upper 00
Lower 20
Upper 00
Lower 04
Table 15 Example Read Multiple Registers Response
Description Data (Hex)
Slave Address 02
Function Code 03
Number of Data Bytes 08
Upper 17
Lower 70
Upper 17
Lower 70
Upper 01
Lower 09
Upper 00
Lower 00
Table 16 Example Read Multiple Registers Error Response
Description Data (Hex)
Slave Address 02
Error Code 83
Exception Code 02
Write Single Register 06 (06 H)
n
This function code is used to write to a single register in the drive. The command specifies the address of the register to be
written and the value to write. The normal response is an echo of the request, returned after the register contents have been
written.
YASKAWA SIEP YAICOM 17A V1000 Option Dual-Port Modbus TCP/IP SI-EM3D/V Technical Manual
27
Page 28

7 Modbus TCP/IP Messaging
Table 17 Table 19 Write Single Register Command
Description Byte Data (Hex)
Slave Address 1 00 to FF
Function Code 1 06
Register Address 2 0000 to FFFF
Register Value 2 0000 to FFFF
Table 18 Write Single Register Response
Description Byte Data (Hex)
Slave Address 1 00 to FF
Function Code 1 06
Register Address 2 0000 to FFFF
Register Value 2 0000 to FFFF
Table 19 Write Single Register Error Response
Description Byte Data (Hex)
Slave Address 1 00 to FF
Error Code 1 86
Exception Code 1
Refer to Modbus TCP/IP Exception Codes
on page 31 for details.
Examples of Register Write Command
Table 20 lists command examples when writing register value 0003H to register address 0001H in a drive with the slave
address (unit identifier) 01H.
Table 21 shows examples of responses indicating that the write command has been executed successfully. The command
specifies the value and the register address to write to.
Table 22 shows examples of an error response when writing to a register. The exception code is 21H (indicating an invalid
value).
Register Address
Register Value
Register Address
Register Value
Description Data (Hex)
Slave Address 01
Exception Code 21
Table 20 Example Write Single Registers Command
Description Data (Hex)
Slave Address 01
Function Code 03
Upper 00
Lower 01
Upper 00
Lower 03
Table 21 Example Write Single Register Response
Description Data (Hex)
Slave Address 01
Function Code 06
Upper 00
Lower 01
Upper 00
Lower 03
Table 22 Example Write Single Register Error Response
Error Code 86
28
YASKAWA SIEP YAICOM 17A V1000 Option Dual-Port Modbus TCP/IP SI-EM3D/V Technical Manual
Page 29

7 Modbus TCP/IP Messaging
Write Multiple Registers 16 (10 H)
n
This function code is used to write to a contiguous block of registers in the drive. The command specifies the starting register
address, the number of registers and the values to be written. The command packs two bytes per register. For each register in
the command the first byte contains the most significant bits and the second byte contains the least significant bits. The normal
response returns the function code, starting address and quantity of registers written.
Table 23 Write Multiple Registers Command
Description Byte Data (Hex)
Slave Address 1 00 to FF
Function Code 1 10
Starting Register 2 0000 to FFFF
Quantity of Registers 2
Number of Data Bytes 1
Register Values
<1> N = Quantity of Registers (range is 1 - 16)
Description Byte Data (Hex)
Slave Address 1 00 to FF
Function Code 1 10
Starting Register 2 0000 to FFFF
Quantity of Registers 2
<1> N = Quantity of Registers
<1>
N
x 2
Table 24 Write Multiple Registers Response
<1>
N
<1>
N
x 2
0000 to FFFF
<1>
N
Table 25 Write Multiple Registers Error Response
Description Byte Data (Hex)
Slave Address 1 01
Error Code 1 90
Exception Code 1
Refer to Modbus TCP/IP Exception Codes
on page 31 for details.
Examples of Multiple Registers Write Command
Table 26 lists command examples when writing register values 0001H and 0258H to register addresses 0001H and 0002H in
a drive with the slave address (unit identifier) 01H.
Table 27 shows examples of responses indicating that the write command has been executed successfully. The command
specifies the beginning of the register address and the number of registers.
Table 28 shows examples of an error response when writing to a register. The exception code is 02H (indicating a register
number error).
Table 26 Example Write Multiple Registers Command
Description Data (Hex)
Slave Address 01
Function Code 10
Starting Register
Quantity of Registers
Number of Data Bytes 04
First Register Data
Next Register Data
Upper 00
Lower 01
Upper 00
Lower 02
Upper 00
Lower 01
Upper 02
Lower 58
YASKAWA SIEP YAICOM 17A V1000 Option Dual-Port Modbus TCP/IP SI-EM3D/V Technical Manual
29
Page 30

7 Modbus TCP/IP Messaging
Table 27 Example Write Multiple Registers Response
Description Data (Hex)
Slave Address 01
Function Code 10
Starting Register
Quantity of Registers
Table 28 Example Write Multiple Registers Error Response
Description Data (Hex)
Slave Address 01
Error Code 90
Exception Code 02
Read/Write Multiple Registers 23 (17 H)
n
Upper 00
Lower 01
Upper 00
Lower 02
This function code performs a combination of one read operation and one write operation in a single Modbus TCP/IP
transaction. The write operation is performed before the read. The command specifies the starting read address, quantity of
contiguous registers to read, starting write address, quantity of contiguous registers to write and the values to be written. The
normal response contains the values of the registers that were read.
For both the address and the values, the first byte contains the most significant bits and the second byte contains the least
significant bits.
Note: In option software version VST800380, any invalid register in the range will return an error response.
<1> M = Quantity of Registers to Read (range is 1 - 16)
<2> N = Quantity of Registers to Write (range is 1 - 16)
In option versions VST800381 and later, invalid registers in the range will not return an error response provided at least 1 register is valid.
Invalid registers will be set to 0 in the response.
Table 29 Read/Write Multiple Registers Command
Description Byte Data (Hex)
Slave Address 1 00 to FF
Function Code 1 17
Read Starting Register 2 0000 to FFFF
Quantity of Registers to Read 2
Write Starting Register 2 0000 to FFFF
Quantity of Registers to Write 2
Write Byte Count 1
Write Register Values
N
<2>
X 2
<1>
M
<2>
N
<2>
N
X 2
0000 to FFFF
Description Byte Data (Hex)
Slave Address 1 00 to FF
Function Code 1 17
Number of Data Bytes 1
Read Register Values 2 Values contained in slave registers
<1> M = Quantity of Registers
Description Byte Data (Hex)
Slave Address 1 00 to FF
Error Code 1 97
Exception Code 1
30
Table 30 Read/Write Multiple Registers Response
Table 31 Read/Write Multiple Registers Error Response
YASKAWA SIEP YAICOM 17A V1000 Option Dual-Port Modbus TCP/IP SI-EM3D/V Technical Manual
<1>
M
x 2
Refer to Modbus TCP/IP Exception Codes
on page 31 for details.
Page 31

7 Modbus TCP/IP Messaging
Read/Write Multiple Registers
Table 32 lists command examples when reading registers 0001H and 0002H and then writing register values 0103H and 0258H
to register addresses 0102H and 0103H in a drive with the slave address (unit identifier) 01H.
Table 33 shows examples of responses indicating that the read/write multiple registers command has been executed
successfully. Read data 1 contains the value of register address 0001H (0001H). Read data 2 contains the value of the register
address 0002H (0002H).
Table 34 shows examples of an error response when the command to read and write to multiple registers has failed. The
exception code is 02H (indicating a register number error).
Table 32 Example Read/Write Multiple Registers Command
Description Data (Hex)
Slave Address 01
Function Code 17
Read Starting Register
Quantity of Registers to Read
Write Starting Register
Quantity of Registers to Write
Number of Data Bytes 04
First Write Register Data
Next Write Register Data
Upper 00
Lower 01
Upper 00
Lower 02
Upper 01
Lower 02
Upper 00
Lower 02
Upper 01
Lower 03
Upper 02
Lower 58
Table 33 Example Read/Write Multiple Registers Response
Description Data (Hex)
Slave Address 01
Function Code 17
Number of Data Bytes 04
Read Data 1
Read Data 2
Table 34 Example Read/Write Multiple Registers Error Response
Description Data (Hex)
Slave Address 01
Error Code 97
Exception Code 02
u
Modbus TCP/IP Exception Codes
When an error occurs, remove the cause and restart communications.
Error Code
01H
02H
Function Code Error
• Attempted to set a function code from a PLC other than 03H, 06H, 10H, and 17H.
Register Number Error
• A register number specified in the command message does not exist.
• Attempted to send a broadcast message using other register numbers than 0001H or 0002H.
Upper 00
Lower 01
Upper 00
Lower 02
Error Name
Cause
YASKAWA SIEP YAICOM 17A V1000 Option Dual-Port Modbus TCP/IP SI-EM3D/V Technical Manual
31
Page 32

7 Modbus TCP/IP Messaging
Error Code
Byte Count Error
03H
21H
22H
23H
24H
u
Control Connection Timeout
• Read data or write data is greater than 16 bytes. Invalid command message quantity.
• In a write message, the “Number of Data Items” contained within the message does not equal twice the amount of data words
(i.e., the total of Data 1+ Data 2, etc.).
Data Setting Error
• Control data or parameter write data is outside the allowable setting range.
• Attempted to write a contradictory parameter setting.
Write Mode Error
• Attempted to write while the drive was operating to a parameter that cannot be written to during run.
• During an EEPROM data error (CPF06), the master attempted to write to a parameter other than A1-00 to -05, E1-03, or o2-04.
• Attempted to write to read-only data.
DC Bus Undervoltage Write Error
• Attempted to write from the master during an undervoltage fault (Uv1).
• Attempted to execute and Enter command during Uv1.
Write Error During Parameter Process
• Master attempted writing to the drive while the drive was processing parameter data.
Error Name
Cause
The option has a safety feature that declares a fault if communications between the master and drive is lost after the master
commanded the drive to run.
A controlled connection is defined as one in which a master commands the drive by writing to register 01H. After this write,
the option will begin a timer. The timer will be reset upon subsequent writes to register 01H. If the timer exceeds the value
programmed in drive parameter F7-16, the option will declare a BUS ERROR if the option card has an active run command
to the drive. A value of 0 in F7-16 means that the timeout is disabled.
The drive reaction to a BUS ERROR is programmable through drive parameter F6-01.
32
YASKAWA SIEP YAICOM 17A V1000 Option Dual-Port Modbus TCP/IP SI-EM3D/V Technical Manual
Page 33

8 Web Interface
8 Web Interface
The option contains a series of web pages that allow for viewing of status and diagnostic information through a standard web
browser.
The web page is accessed through a self-contained web server at port 80. Access the home page by typing the IP address of
the option in a web browser. Example: "http://192.168.1.20"
The IP address of the option can be read using monitors U6-80 to U6-83 on the digital operator if it is unknown. Refer to
Option Monitors on page 21 for details.
The home page is an HTML-based page providing basic drive and option data and a link to an enhanced web page requiring
a Java© enabled web browser.
Enhanced Web Page Notes:
• The Enhanced Web Pages use a series of Java© applets.
• PCs must have Java SE 6 Update 14 or later installed to view the enhanced web pages.
• The Java© applets require an internet connection to check the revocation status.
• When no internet connection is available, disable the revocation check by changing a Java setting in the PC: All Programs /
Java / Configure Java / Advanced Tab. Set "Perform certificate checks on" to "Do not check".
Enhanced Web Page Tab Page
Main Tab 35
Drive Status Tab 35
Network Tab 36
Email Alerts Tab 37
Parameter Access Tab
Configuration Tab
Custom Tab 40
<1> Accessible after entering a valid password.
<1>
<1>
38
39
YASKAWA SIEP YAICOM 17A V1000 Option Dual-Port Modbus TCP/IP SI-EM3D/V Technical Manual
33
Page 34

8 Web Interface
u
HTML Home Page
The main HTML home page provides basic drive and option data and a link to an enhanced web page. The RSTP enabled
home page provides Rapid Spanning Tree Protocol data. Refer to Rapid Spanning Tree Protocol on page 41 for details on
RSTP.
Main HTML Home Page
n
RSTP Enabled HTML Home Page
n
Figure 22 Main HTML Home Page
Figure 23 RSTP Enabled HTML Home Page
34
YASKAWA SIEP YAICOM 17A V1000 Option Dual-Port Modbus TCP/IP SI-EM3D/V Technical Manual
Page 35

u
Main Tab
The Main tab shows basic option information such as IP address, MAC address, and firmware version.
8 Web Interface
Figure 24 Main Tab View
u
Drive Status Tab
The Drive Status tab shows basic I/O information and drive state information.
Figure 25 Drive Status Tab View
YASKAWA SIEP YAICOM 17A V1000 Option Dual-Port Modbus TCP/IP SI-EM3D/V Technical Manual
35
Page 36

8 Web Interface
u
Network Tab
The Network tab shows the status of the option network traffic and the status of open I/O connections.
Figure 26 Network Tab View
Table 35 Network Monitor Descriptions
Network Monitor Explanation
Msg Tx OK Cumulative number of messages transmitted successfully from the option.
Msg Rx OK Cumulative number of messages received successfully to the option.
Current Connections Current number of open connections.
Control Connection Delta
Time
Msg Tx Dropped Cumulative number of messages dropped due to output network buffer being full and unable to hold the new message.
Msg Rx Dropped Cumulative number of messages dropped due to input network buffer being full and unable to hold the new message.
Collisions
Msg Tx Errors Cumulative number of transmit underruns and transmit stops reported by the MAC/PHY.
Msg Rx Errors Cumulative number of receive overruns, receive stops, and receive error frames reported by the MAC/PHY.
Tx Retry Cumulative number of transmits in which the 1st attempt was delayed due to busy medium reported by the MAC/PHY.
The time between the last two writes to the Control register, MEMOBUS/Modbus address 0001H.
Cumulative number of collisions (half duplex only) reported by the MAC/PHY (Media Access Control/Physical
Connection).
36
YASKAWA SIEP YAICOM 17A V1000 Option Dual-Port Modbus TCP/IP SI-EM3D/V Technical Manual
Page 37

8 Web Interface
u
Email Alerts Tab
The Email Alerts tab allows the user to configure four Email Fault/Alarm conditions. When the condition is true, one email
will be sent to the provided email address. Another email will not be sent until the condition becomes false and then true again.
A 30-second timer prevents emails from being sent when conditions reoccur immediately after being removed. The timer helps
limit the amount of emails sent regarding the same intermittent condition and helps to reduce network traffic by reducing
emails about reoccurring errors.
Figure 27 Email Alerts Tab View
Conditional Email Set-up
n
Define the condition that will trigger the email by selecting a monitor parameter, a comparator, and a value. Set up
1.
comparator values for the range of values to check in the chosen condition. If choosing only one condition and no OR
or AND are needed, set the “OR/AND” drop-down selection to “NotUsed”.
Enter the email address where the alert will be sent.
2.
Enter the message that will appear in the email contents.
3.
Enter the email subject.
4.
Click the “Email Active” check box to enable the alert.
5.
Clicking “Save to device” will save the entered information into the option memory.
Clicking “Cancel and reload” will cancel any pending edits and display the most recently saved settings from the option board.
YASKAWA SIEP YAICOM 17A V1000 Option Dual-Port Modbus TCP/IP SI-EM3D/V Technical Manual
37
Page 38

8 Web Interface
u
Parameter Access Tab
The Parameter Access tab allows the user to read and write parameters from the drive. Write access is restricted until a valid
password is entered.
Figure 28 Parameter Access Tab View
The MEMOBUS/Modbus address for the drive parameter being accessed must be entered in hexadecimal. The number must
begin with “0x” to signify hexadecimal. Clicking “Read” will load and display the current value of the given MEMOBUS/
Modbus Address.
Clicking “Set” will save the given value to the given MEMOBUS/Modbus address.
After a “Read” or “Set” command is given, Status will display “Waiting” while the action is being carried out, then “Complete”
is displayed when finished.
38
YASKAWA SIEP YAICOM 17A V1000 Option Dual-Port Modbus TCP/IP SI-EM3D/V Technical Manual
Page 39

8 Web Interface
u
Configuration Tab
The Configuration tab sets web page behavior parameters. Access is restricted unless a valid password is entered.
Figure 29 Configuration Tab View
Security Login
n
Enter a valid password and click “Log in”. The button text changes to “Log out” and the status changes to “Logged in”.
Note: The default security password is “yaskawa”.
This password can be changed in the “Change Password” section of the tab. Entering a valid password allows access to the
settings in the Configuration tab, Email Alerts tab, and the Parameter Access tab.
Change Password
n
To change the password, enter the new password in the “New Password:” and “Confirm Password:” text boxes then click
“Change password”. The Status display will change to “Idle” then “Changing Password” then “Password Changed”. If the
passwords in the two text boxes do not match, the Status will display “Passwords don’t match”.
Option Card
n
The values displayed in the various tabs are refreshed at the rate defined in the “Applet Refresh Rate (ms)” text box. Enter
values in the range of 1000 ms to 65.535 seconds.
Parameter Security can be enabled or disabled by clicking one of the radio buttons. When “Disabled” is selected, no password
is necessary and all functions in the web pages will be available. When “Enabled” is selected, a valid password must be entered
to edit email settings and to write parameters.
Email Settings
n
The “Email Server IP” text box must contain the IP address of the email server. The subnet address is configured in drive
parameters F7-05 through F7-08. The configured email alerts will use the server at this address when sending emails.
Enter the email server port in the “Email Port” text box.
The value in the “From Email Address” text box identifies the origin of the email alerts to the recipient.
Click “Submit Email Parameters” to save the email settings to the option.
Click “Save Configuration Parameters to Flash” to save the entered values from this tab into non-volatile memory. These
values will then be remembered after cycling power.
General Settings
n
Click “Save Options Card Parameters” to save the Applet Refresh Rate and the Parameter Security settings to the option.
YASKAWA SIEP YAICOM 17A V1000 Option Dual-Port Modbus TCP/IP SI-EM3D/V Technical Manual
39
Page 40

8 Web Interface
u
Custom Tab
The Custom tab displays a selection of quick setting parameters.
Figure 30 Custom Tab View
40
YASKAWA SIEP YAICOM 17A V1000 Option Dual-Port Modbus TCP/IP SI-EM3D/V Technical Manual
Page 41

9 Rapid Spanning Tree Protocol
9 Rapid Spanning Tree Protocol
Rapid Spanning Tree Protocol (RSTP) is a mechanism that allows an Ethernet network to be configured as a ring or other
topology that may have more than one pathway to each node. The RSTP protocol automatically determines the most efficient
pathway to each node and disables any redundant pathways.
If one path fails, RSTP activates another pathway to keep the network traffic flowing. After restoring the failed path, RSTP
disables any redundant paths without disrupting network traffic.
u
Convergence Time
Convergence is the process that RSTP performs to identify the root node and which pathways to disable. Convergence occurs
on power up and when the network changes (e.g., path failures and restorations).
Take special care when using parameter F7-16, Communication Timeout Loss, and be sure to give RSTP enough time for
convergence. When F7-16 is set too short, convergence will not be able to complete before it expires. The complexity of the
network and the number of drives on the network will both factor into the value of the timeout.
RSTP is unnecessary and should be disabled when using star or line topology network configurations (RSTP is disabled by
default).
u
Topology
The option is ideal for use in ring topologies. With RSTP enabled, a ring topology provides redundancy to the network. RSTP
determines the fastest paths to each node on the network and virtually splits the ring by disabling one port on one node to
prevent data from being transmitted endlessly around the ring. If a path on the ring fails, RSTP re-enables the disabled port
and reconnects the split. All nodes on the network remain accessible without any interruptions.
RSTP is unnecessary and should be disabled when using star or line topology network configurations (RSTP is disabled by
default).
u
Enabling RSTP
RSTP is enabled from the webpage on the option.
The IP address of the option card is necessary to access the webpage. Use the operator to read the IP address values from
monitors U6-80, U6-81, U6-82, and U6-83.
These monitors display the IP address whether the card is configured to receive its IP address from a master controller (BOOTP
or DHCP) or if it is configured statically.
Refer to Table 36 for example values of the monitors for an option IP address of 192.168.1.20.
Table 36 Example IP Address Monitor Values
Monitor Value
U6-80 192
U6-81 168
U6-82 1
U6-83 20
Enter the IP address to address bar of your web browser (Ex. http://192.168.1.20) and hit enter to load the main page for the
option. Refer to Figure 22 for an example of the main page.
At the top of the page, click the RSTP button. The RSTP webpage will be displayed with “N/A” values.
YASKAWA SIEP YAICOM 17A V1000 Option Dual-Port Modbus TCP/IP SI-EM3D/V Technical Manual
41
Page 42

9 Rapid Spanning Tree Protocol
Figure 31 RSTP Page Initial View
Change the select box labeled “STP / RSTP” from “DISABLED” to “ENABLED” then click “Save Changes”. The webpage
will automatically refresh and enable RSTP. Refer to Figure 23 for an example of an RSTP enabled home page.
u
Rapid Spanning Tree Protocol Webpage
There are two groups of data displayed on the RSTP webpage: General and Port Information.
General
n
STP / RSTP Enable
To enable RSTP, Change this setting to “ENABLED” and click “Save Changes” to enable RSTP.
Priority
The RSTP Priority controls which bridge in the network becomes the root bridge. For most installations, the PLC or controller
should be configured as the root bridge. A lower value in the “Priority” field indicates a higher priority. The priority ranges
from 0 to 61440 in increments of 4096. The option defaults to the lowest priority, 61440. Table 37 lists the possible priorities.
Table 37 Priority Values
0 16384 32678 49152
4096 20480 36864 53248
8192 24576 40960 57344
12288 28672 45056 61440
To change the priority, select the desired priority from the list and click “Save Changes”.
Root Bridge
This field displays the MAC address of the root bridge on the network.
Hello Time (secs)
The Hello Time is displayed in seconds. This value is set by the root bridge and indicates how often bridge packets will be
sent out.
Forward Delay (secs)
The Forward Delay is displayed in seconds. This value is set by the root bridge. When the port is using STP and not RSTP,
the Forward Delay is the length of time the bridge will wait before transitioning between states.
42
YASKAWA SIEP YAICOM 17A V1000 Option Dual-Port Modbus TCP/IP SI-EM3D/V Technical Manual
Page 43

9 Rapid Spanning Tree Protocol
Max Age (secs)
The Max Age is displayed in seconds. This value is set by the root bridge and indicates how long a message can be passed
along before being discarded.
Port Information
n
Port Role
The Port Role identifies how the port is being used. The seven possible values for Port Role are described in Table 38.
Table 38 Port Role Values
Port Role Description
Unknown An unknown error has occurred within RSTP.
Root This port leads to the root bridge.
Designated This port leads away from the root bridge.
Alternate This port is an alternate path to the root bridge.
Backup This port is an alternate path away from the root bridge.
Disabled This port does not have an active link.
N/A RSTP is disabled.
Port State
The Port State indicates if the port is accepting and sending messages. The four possible values for Port State and the features
of each state are shown in Table 39.
Table 39 Port State Values
Port State Accept Packets Forward Packets Learn MAC Addresses
Discarding NO NO NO
Learning NO NO YES
Forwarding YES YES YES
N/A RSTP is disabled.
Port Version
RSTP can operate in normal RSTP mode or support STP mode. When an STP-only node is detected on the network, this port
operates in STP mode and displays “STP”. “RSTP” will be displayed in all other cases.
Port BPDU Rx Count
The Port BPDU Rx Count shows the number of BPDU packets received on that port. In general, root ports receive far more
BPDU packets than designated ports.
YASKAWA SIEP YAICOM 17A V1000 Option Dual-Port Modbus TCP/IP SI-EM3D/V Technical Manual
43
Page 44

3 2 2 2
Port 1 Role
Port 1 State
Port 2 Role
Port 2 State
0 Unknown
2 Root
3 Designated
4 Alternate
5 Backup
6 Disabled
9 RSTP Disabled
0 Discarding
1 Learning
2 Forwarding
0 Unknown
2 Root
3 Designated
4 Alternate
5 Backup
6 Disabled
9 RSTP Disabled
0 Discarding
1 Learning
2 Forwarding
9 Rapid Spanning Tree Protocol
u
RSTP Monitor U6-96
Monitor U6-96 is dedicated to RSTP. U6-96 shows the role and state for each port.
The displayed value has four digits. The first two digits belong to port 1 and the last two digits belong to port 2. The first and
third digits represent port role while the second and fourth digits represent port state.
The possible port role and state values are shown in Figure 32.
Figure 32 U6-96 Monitor Values
Refer to Table 38 for descriptions of the port role values.
Refer to Table 39 for descriptions of the port state values.
Below are a few examples:
• 9292 = RSTP is disabled and both ports are forwarding.
• 3222 = Port 1 is forwarding and is the designated port. Port 2 is forwarding and is the root port.
• 2232 = Port 1 is forwarding and is the root port. Port 2 is forwarding and is the designated port.
• 3232 = Both ports are forwarding and are designated ports. This only occurs when the option is the root bridge.
• 4022 = Port 1 is discarding and is the alternate port. Port 2 is forwarding and is the root port.
• 2260 = Port 1 is forwarding and is the root port. Port 2 is discarding and is the disabled port.
44
YASKAWA SIEP YAICOM 17A V1000 Option Dual-Port Modbus TCP/IP SI-EM3D/V Technical Manual
Page 45

10 Troubleshooting
10 Troubleshooting
u
Drive-Side Error Codes
Drive-side error codes appear on the drive digital operator. Causes of the errors and corrective actions are listed below. Refer
to the drive manual for additional error codes that may appear on the drive digital operator.
Faults
n
Both bUS (Option Communication Error) and EF0 (Option Card External Fault) can appear as an alarm or as a fault. When a
fault occurs, the digital operator ALM LED remains lit. When an alarm occurs, the ALM LED flashes.
If communication stops while the drive is running, use the following questions as a guide to help remedy the fault:
• Is the option properly installed?
• Are the communication lines properly connected to the option? Are the wires loose?
• Is the controller program working? Has the controller/PLC CPU stopped?
• Did a momentary power loss interrupt communications?
Digital Operator Display Fault Name
Option Communication Error
bUS
Cause Possible Solution
Master controller (PLC) has stopped
communicating
Communication cable is not connected
properly
A data error occurred due to noise
Option is damaged If there are no problems with the wiring and the error continues to occur, replace the option.
• The connection was lost after establishing initial communication.
• Only detected when the Run command or frequency reference is assigned to the option (b1-01 = 3 or
b1-02 = 3).
• Check that power is supplied to the PLC
• Check that PLC is not in program mode
• Check for faulty wiring
• Correct any wiring problems
• Check the various options available to minimize the effects of noise
• Counteract noise in the control circuit, main circuit, and ground wiring
• If a magnetic contactor is identified as a source of noise, install a surge absorber to the contactor coil
• Make sure the cable used meets requirements
• Make sure the option ground wire is connected between option FE terminal and the drive ground
terminal connected to earth ground
Digital Operator Display Fault Name
EF0
Cause Possible Solutions
An external fault was received from the PLC
and F6-03 is set to a value other than 3.
Problem with the PLC program Check the PLC program and correct problems.
Digital Operator Display Fault Name
oFA00
Cause Possible Solution
Digital Operator Display Fault Name
oFA01
Cause Possible Solution
The option card connection is faulty
Option Card External Fault
The alarm function for an external device has been triggered.
• Remove the cause of the external fault.
• Remove the external fault input from the PLC.
Option Card Connection Error at Option Port CN5-A
The option card is incompatible with the drive.
Option Card Fault
Option not properly connected
• Turn off the power and reconnect the option card.
• Check if the option card is properly plugged into the option port. Make sure the card is fixed properly.
YASKAWA SIEP YAICOM 17A V1000 Option Dual-Port Modbus TCP/IP SI-EM3D/V Technical Manual
45
Page 46

10 Troubleshooting
Digital Operator Display Fault Name
oFA03
oFA04
to
Option card or hardware is damaged. Replace the option card. Contact Yaskawa for consultation.
Minor Faults and Alarms
n
Digital Operator Display Minor Fault Name
Communications wiring is faulty, there is a
short circuit, the wiring is incorrect, or the
connections are poor.
Programming error on the master side. Check communications at start-up and correct programming errors.
Communications circuitry is damaged.
oFA30 to oFA43
Cause Possible Solution
CALL
Cause Possible Solutions
Option Card Fault (port A)
Option card self-diagnostic error
Option Card Fault (port A)
An error occurred attempting to write to the option card memory.
Option Card Fault (port A)
Communication ID error
Serial Communication Transmission Error
Communication has not yet been established.
• Check for wiring errors.
• Correct the wiring.
• Check for disconnected cables and short circuits. Repair as needed.
• Perform a self-diagnostics check.
• If the problem continues, replace the control board or the entire drive. Contact
Yaskawa for instructions on replacing the control board.
Minor Fault
(H2-oo = 10)
YES
bUS Fault Tolerance
n
bUS Fault Auto-Restart
Parameter F6-14, bUS Fault Auto Reset Select, will appear when the option is installed.
Setting F6-14 = 0 (Disabled) or F6-01 = 3 or greater (Alarm only) will not affect standard default drive behavior.
Setting F6-14 = 1 (Enabled) AND F6-01 < 3 (Fault) will cause the following operation: The bUS fault occurs after the F7-16
delay and the Run command is removed from the drive. Then the option throws a bUS fault to the drive. When the condition
is removed, the option commands a fault reset and returns control of the drive to the Modbus TCP/IP network.
Note: The option will only read parameter F6-01 and F6-14 from the drive during power-up.
bUS Fault Delay
Parameter F7-16, Communications Loss Detection Time Delay, will appear when the option is installed.
The setting value of F7-16 is the length of time that the option will delay sending the bUS fault to the drive.
The status LEDs on the option are not affected by the delay time set in F7-16; the LEDs will indicate the bUS condition
immediately.
Note: The option will only read parameter F7-16 from the drive during power-up.
u
Option Error Codes
Option Fault Monitors U6-98 and U6-99
n
The option can declare error/warning conditions via drive monitor parameters on the drive digital operator as shown in Table
40.
Table 40 Option Fault Monitor Descriptions
Fault Condition Fault Declared
No Fault n/a 0 No faults
Force Fault EF0 3
Connection Timeout BUS ERROR 1101 The control connection timed out.
Status Value
(U6-98/U6-99)
Description
Network sent a message to force this node to the fault
state.
46
YASKAWA SIEP YAICOM 17A V1000 Option Dual-Port Modbus TCP/IP SI-EM3D/V Technical Manual
Page 47

10 Troubleshooting
Fault Condition Fault Declared
Duplicate IP Address BUS ERROR 1102
Default MAC Address None 1103
Network Link Down BUS ERROR 1104 No network link to option.
Hardware Error BUS ERROR 1105
Status Value
(U6-98/U6-99)
Description
This node and at least one other node have the same IP
Address.
Factory default MAC Address programmed into the
option. Return for reprogramming.
Option card hardware has stopped functioning. Cycle
power to the drive.
Two drive monitor parameters, U6-98 and U6-99 assist the user in network troubleshooting.
• U6-98 displays the first declared fault since the last power cycle. U6-98 is only cleared upon drive power-up.
• U6-99 displays the present option status. U6-99 is cleared upon a network-issued fault reset and upon power-up.
If another fault occurs while the original fault is still active, parameter U6-98 retains the original fault value and U6-99 stores
the new fault status value.
YASKAWA SIEP YAICOM 17A V1000 Option Dual-Port Modbus TCP/IP SI-EM3D/V Technical Manual
47
Page 48

11 Specifications
11 Specifications
Table 41 Option Specifications
Item Specification
Model SI-EM3D/V
• Read Multiple Registers (03H)
• Write Single Register (06H)
Supported Messages
Option Conformance Modbus-IDA Passed
Connector Type RJ45 8-pin Shielded Twisted Pair Cat5e cable
Physical Layer Type Isolated Physical Layer
IP Address Setting Programmable from drive keypad or network
Communication Speed
Number of Connections
Duplex Mode Half-forced, Auto-negotiate, Full-forced
Address Startup Mode Static, BOOTP, DHCP
Ambient Temperature -10 °C to +50 °C (14 °F to 122 °F)
Humidity 95% RH or lower with no condensation
Storage Temperature -20 °C to +60 °C (-4 °F to +140 °F) allowed for short-term transport of the product
Area of Use Indoor (free of corrosive gas, airborne particles, etc.)
Altitude 1000 m (3280 ft.) or lower
• Write Multiple Registers (10H)
• Read and Write Registers (17H)
Commands that support multiple registers have a maximum Read and Write size of 16 registers.
Programmable from drive keypad or network:
10/100 Mbps, auto-negotiate
Modbus TCP/IP: 10
Web Page Access: 2
48
YASKAWA SIEP YAICOM 17A V1000 Option Dual-Port Modbus TCP/IP SI-EM3D/V Technical Manual
Page 49

This Page Intentionally Blank
YASKAWA SIEP YAICOM 17A V1000 Option Dual-Port Modbus TCP/IP SI-EM3D/V Technical Manual
49
Page 50

Revision History
MANUAL NO.
Example:
SIEP YAICOM 17A
Published in USA July 2014 14-7
Date of publication
Date of original publication
The revision dates and the numbers of the revised manuals appear on the bottom of the back cover.
Date of Publication
Revision
Number
Section Revised Content
July 2014 - - First Edition
50
YASKAWA SIEP YAICOM 17A V1000 Option Dual-Port Modbus TCP/IP SI-EM3D/V Technical Manual
Page 51

Page 52

YASKAWA AC Drive V1000 Option
Modbus TCP/IP
Technical Manual
YASKAWA AMERICA, INC.
2121 Norman Drive South, Waukegan, IL 60085, U.S.A.
Phone: 1-800-YASKAWA (927-5292) or 1-847-887-7000 Fax: 1-847-887-7310
http://www.yaskawa.com
DRIVE CENTER (INVERTER PLANT)
2-13-1, Nishimiyaichi, Yukuhashi, Fukuoka, 824-8511, Japan
Phone: 81-930-25-3844 Fax: 81-930-25-4369
http://www.yaskawa.co.jp
YASKAWA ELECTRIC CORPORATION
New Pier Takeshiba South Tower, 1-16-1, Kaigan, Minatoku, Tokyo, 105-6891, Japan
Phone: 81-3-5402-4502 Fax: 81-3-5402-4580
http://www.yaskawa.co.jp
YASKAWA ELÉTRICO DO BRASIL LTDA.
Avenida Piraporinha 777, Diadema, São Paulo, 09950-000, Brasil
Phone: 55-11-3585-1100
http://www.yaskawa.com.br
YASKAWA EUROPE GmbH
Hauptstrasse 185, 65760 Eschborn, Germany
Phone: 49-6196-569-300 Fax: 49-6196-569-398
http://www.yaskawa.eu.com
YASKAWA ELECTRIC KOREA CORPORATION
9F, Kyobo Securities Bldg., 26-4, Yeouido-dong, Yeongdeungpo-gu, Seoul, 150-737, Korea
Phone: 82-2-784-7844
http://www.yaskawa.co.kr
YASKAWA ELECTRIC (SINGAPORE) PTE. LTD.
151 Lorong Chuan, #04-02A, New Tech Park, 556741, Singapore
Phone: 65-6282-3003
http://www.yaskawa.com.sg
YASKAWA ELECTRIC (CHINA) CO., LTD.
12F, Carlton Bld., No.21 HuangHe Road, HuangPu District, Shanghai 200003, China
Phone: 86-21-5385-2200
http://www.yaskawa.com.cn
YASKAWA ELECTRIC (CHINA) CO., LTD. BEIJING OFFICE
Room 1011, Tower W3 Oriental Plaza, No. 1 East Chang An Ave.,
Dong Cheng District, Beijing, 100738, China
Phone: 86-10-8518-4086
YASKAWA ELECTRIC TAIWAN CORPORATION
9F, 16, Nanking E. Rd., Sec. 3, Taipei, 104, Taiwan
Phone: 886-2-2502-5003
YASKAWA INDIA PRIVATE LIMITED
#17/A Electronics City, Hosur Road Bangalore 560 100 (Karnataka), India
Phone: 91-80-4244-1900
http://www.yaskawaindia.in
Fax: 55-11-3585-1187
Fax: 82-2-784-8495
Fax: 65-6289-3003
Fax: 86-21-5385-3299
Fax: 86-10-8518-4082
Fax: 886-2-2505-1280
Fax: 91-80-4244-1901
YASKAWA AMERICA, INC.
In the event that the end user of this p roduct is to be the militar y and said product is to be employed in any weapons syste ms or the manufacture
thereof, the export will fall under the relevant regulations as stipulated in the Foreign Exchange and Foreign Trade Regulations. Therefore, be sure
to follow all procedures and submit all relevant documentation accordin g to any and all r ules, regulations and law s that may ap
Specifications are subject to change without notice for ongoing product modifications and improvements.
© 2014 YASKAWA AMERICA, INC. All rights reserved.
MANUAL NO. SIEP YAICOM 17A
Published in USA July 2014 14-7
ply.
 Loading...
Loading...