
YTD426B
APPLICATION MANUAL
ITCM ISDN U Interface (TCM mode)
YTD426B APPLICATION MANUAL
CATALOG No. : LSI-6TD426B3
1998.9

IMPORTANT NOTICE
1. Yamaha reserves the right to makechanges to its Products and to this do cument with-
out notice. The information contained in this document has b een carefully checked and
is believed to be reliable. However, Yamaha assumes no responsibilities for inaccura-
cies and makes no commitment to update or to keep current the information contained
in this document.
2. These Yamaha Pro ducts are designed only for commercial and normal industrial ap-
plications, and are not suitable for other uses, such as medical life supp ort equipment,
nuclear facilities, critical care equipmentorany other application the failure of which
could lead to death, personal injury or environmental or property damage. Use of the
Products in any such application is at the customer's sole risk and expense.
3. Yamaha assumes no liability for incidental, consequential or special damages or injury
that may result from misapplication or improper use or op eration of the Pro ducts.
4. Yamaha makes no warranty or representation that the Pro ducts are sub ject to in-
tellectual property license from Yamaha or any third party, and Yamaha makes no
warranty or representation of non-infringement with resp ect to the Pro ducts. Yamaha
specically excludes any liability to the Customer or any third party arising from or
related to the Pro ducts' infringementofany third party's intellectual property rights,
including the patent, copyright, trademark or trade secret rights of any third party.
5. Examples of use described herein are merely to indicate the characteristics and per-
formance of Yamaha pro ducts. Yamaha assumes no resp onsibility for any intellectual
property claims or other problems that may result from applications based on the ex-
amples describ ed herein. Yamaha makes no warranty with respect to the products,
express or implied, including, but not limited to the warranties of merchantability,
tness for a particular use and title.

Contents
1 INTRODUCTION 3
1.1 General Description
: : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : :
3
1.2 Features
: : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : :
3
2 BLOCK DIAGRAM 5
2.1 YTD426B Internal Blo ck Diagram
: : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : :
5
2.2 DSU Block Diagram
: : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : :
6
3 PIN DESCRIPTIONS 7
3.1 Pin Assignments
: : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : :
7
3.2 Pin Functions
: : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : :
8
3.2.1 Common Section
: : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : :
8
3.2.2 AFE Interface
: : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : :
9
3.2.3 U Reference PointInterface
: : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : :
10
3.2.4 T Reference PointInterface
: : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : :
10
3.2.5 T Reference Point Option Setting
: : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : :
11
3.2.6 Mode Setting
: : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : :
12
3.2.7 B Channel Interface
: : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : :
12
3.2.8 Other
: : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : :
13
3.2.9 Testing
: : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : :
14
4 FUNCTIONS 15
4.1 Circuit Termination Block
: : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : :
15
4.2 Line Termination Block
: : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : :
15
4.3 B Channel Interface Block
: : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : :
15
4.4 Master/SlaveFunction
: : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : :
16
4.4.1 Master Mode
: : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : :
16
4.4.2 SlaveMode
: : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : :
17
5 HARDWARE INTERFACE 19
5.1 U Reference PointInterface
: : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : :
19
5.1.1 Receive Signal
: : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : :
19
5.1.2 Transmit Signal
: : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : :
20
5.2 T Reference PointInterface
: : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : :
21
5.3 B Channel Interface
: : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : :
22
5.3.1 Signal
: : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : :
22
5.3.2 B Channel Control
: : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : :
23
5.3.3 Loopback Control
: : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : :
24
5.4 Serial Control Interface
: : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : :
25
6 SOFTWARE INTERFACE 27
6.1 Serial Control Interface
: : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : :
27
6.1.1 MPH-DATA-INDICATION
: : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : :
27
6.1.2 B Channel Control, Loopback Control
: : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : :
27
1

2
CONTENTS
7 ELECTRICAL CHARACTERISTICS 29
7.1 Absolute Maximum Ratings
: : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : :
29
7.2 Recommended Operating Conditions
: : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : :
29
7.3 DC Characteristics
: : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : :
30
7.4 AC Characteristics
: : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : :
31
7.4.1 AFE interface
: : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : :
31
7.4.2 B Channel Interface
: : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : :
33
7.4.3 Serial Data Interface
: : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : :
35
7.4.4 T Reference PointInterface
: : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : :
37
7.4.5 Clock
: : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : :
38
8 PACKAGE OUTLINE 39
APPENDIX
A EXAMPLE OF APPLICATIONS 41
A.1 Example of Application Circuits
: : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : :
41
A.1.1 Example of A Slave Mode, Serial Control Circuit
: : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : :
43
B REVISION HISTORY 47

Chapter 1
INTRODUCTION
1.1 General Description
YTD426B is a communication LSI which provides the ISDN subscriber line interface (two-wire metaric time
compression multiplexing operation) and the NT side of the ISDN Basic Rate user-network interface function
(digital four-wire time-division full-duplex operation). It also provides the electric characteristics conforming
to TTC Standard JT-G961 and JT-I430.
A DSU (Digital Service Unit) can easily b e constructed by combining with YTD427 (Analog Front End).
It is equipp ed withaBchannel interface circuit and can easily realize the time-division multiplexing of the
Bchannel data on multiple ISDN lines.
In addition, with the Master/Slave function, leased lines and other lines which do not use the D channel can
be directly controlled (call origination, B channel control, lo opback control) without using the S/T reference
pointinterface LSI (YTD418, YTD423B, etc.).
1.2 Features
1. Circuit Termination(CT)
Conforms to TTC Standard JT-G961 and JT-I430
{
Two-wire metaric time compression multiplexing operation
{
Digital four{wire time{division full{duplex operation
{
Transmission rate at U reference p oint: 320 kbps, at T reference point: 192 kbps
{
Frame assembling and disassembling function
{
State transition control
{
Loopback function
{
U reference point driver control
{
T reference p oint timing control (switchbetween short passive bus and long passive bus, p oint{
to{point)
2. Line Termination(LT)
Conforms to TTC Standard JT-G961
{
p
f
equalizer
{
Bridged Tap (BT) equalizer
AFE (Analog Front End) Interface
{
AGC (Automatic Gain Control)
{
Data interface
3. Bchannel interface section
Bchannel multiplexing circuit (LSI external clock 128k to 2,048 kHz)
3

4
CHAPTER 1. INTRODUCTION
Bchannel connection/switching function
Loopback function
4. Other
Master/Slave function
{
Ability to control a circuit without the D channel (call origination, B channel control, lo opback
control)
CMOS technology
144-pin SQFP
Single +5V supply
Chapter 2
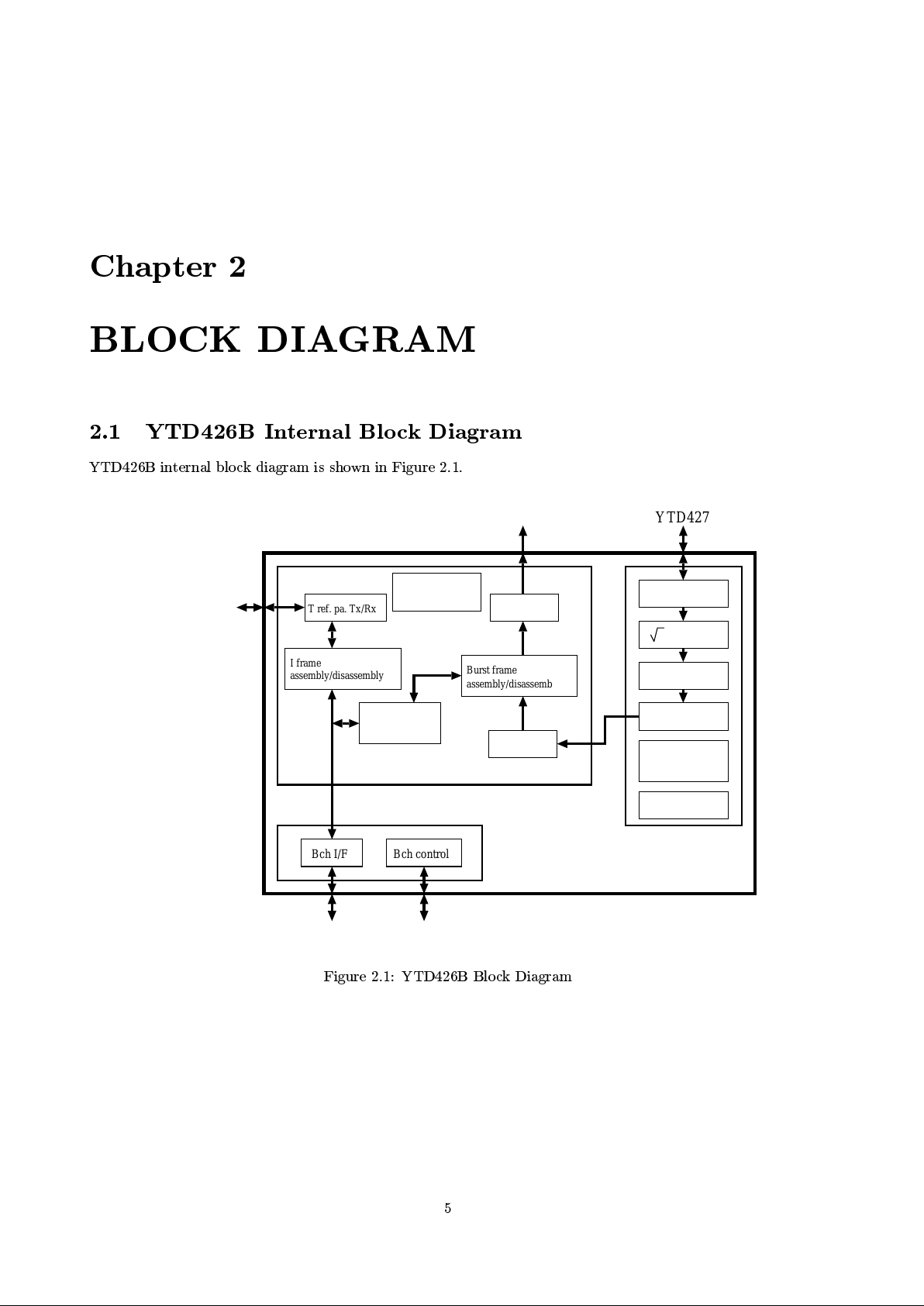
BLOCK DIAGRAM
2.1 YTD426B Internal Blo ck Diagram
YTD426B internal blo ck diagram is shown in Figure 2.1.
YTD427
Bch I/F Bch control
T ref. pa. Tx/Rx
I frame
assembly/disassembly
Burst frame
assembly/disassembly
Multiplexer
AFE I/F
f equalizer
BT equalizer
Decoder
U ref. pa. Tx
U ref. pa. Rx
Line Control (CT)
Line Termination (LT)
Bch Interface
LT state
transition control
PLL & clock
CT state
transition control
T ref. pa.
TTL interface
U ref. pa. driver
PCM highway
Controller
Figure 2.1: YTD426B Blo ck Diagram
5
6
CHAPTER 2. BLOCK DIAGRAM
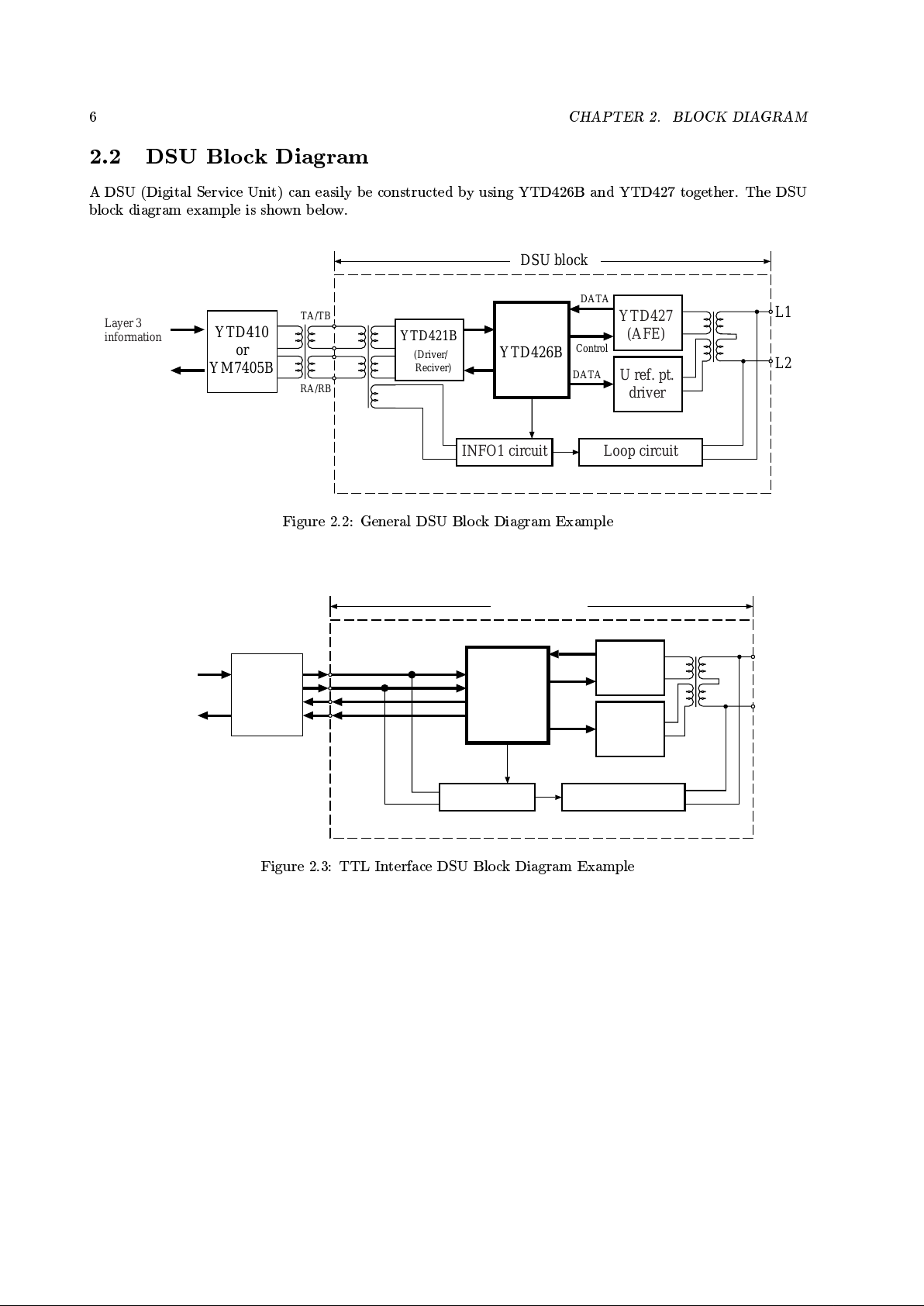
2.2 DSU Blo ck Diagram
A DSU (Digital Service Unit) can easily b e constructed by using YTD426B and YTD427 together. The DSU
block diagram example is shown b elow.
YTD426B
YTD421B
DATA
Control
YTD410
or
YM7405B
RA/RB
TA/TB
L1
L2
DSU block
DATA
(Driver/
Reciver)
INFO1 circuit Loop circuit
YTD427
(AFE)
U ref. pt.
driver
Layer 3
information
Bch data
Figure 2.2: General DSU Blo ck Diagram Example
L1
L2
YTD426B
DATA
TTL I/F
Control
DSU block
DATA
Layer 3
information
Bch data
INFO1 circuit Loop circuit
YTD427
(AFE)
U ref. pt.
driver
YTD423C
Figure 2.3: TTL Interface DSU Block Diagram Example

Chapter 3
PIN DESCRIPTIONS
3.1 Pin Assignments
The pin assignments of YTD426B are shown in Figure 3.1.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
646566
67
68
69
70
71
72
144
143
142
141
140
139
138
137
136
135
134
133
132
131
130
129
128
127
126
125
124
123
122
121
120
119
118
117
116
115
114
113
112
111
110
109
107
106
105
104
103
102
101
100
99
98
97
96
95
94
93
92
91
90
89
88
87
86
85
84
83
82
81
80
79
78
77
76
75
74
73
108
AFEDATA0
AFEDATA1
AFEDATA2
AFEDATA3
N.C.
AFEDATA4
AFEDATA5
AFEDATA6
AFEDATA7
AFEDATA8
AFEDATA9
AFEDATA10
AFEDATA11
N.C.
AFEDATA12
AFEDATA13
AFEDATA14
AFEDATA15
N.C.
STRBN
RWN
ADDRES0
ADDRES1
N.C.
TESTUDR
N.C.
UAMITMN
UAMITM
UAMITPN
UAMITP
LOOP2A
QINFO1C
EXID
TESTIN0
N.C.
TESTIN2
TESTIN3
TESTIN4
TESTIN5
TESTIN6
TESTIN7
TESTIN8
TESTIN1
N.C.
TESTIN9
TESTIN10
TESTIN11
TESTIN12
N.C.
TESTIN13
TESTOUT0
TESTOUT1
TESTOUT2
TESTOUT3
TESTOUT4
TESTOUT5
TESTOUT6
N.C.
TESTOUT7
TESTOUT8
TESTOUT9
TESTOUT10
TESTOUT11
TESTOUT12
TESTOUT13
TESTOUT14
N.C.
TESTOUT15
CLK1536
CLKOUT
TMODE0
TMODE1
TMODE2
N.C.
TMODE3
TMODE4
EXTCLK
RBHW
N.C.
TBHW
RSYNC
TSYNC
TESTIN14
LPA/SCLK
LP4B1/TRGO
N.C.
LP4B2/TRGI
BCHSET0/SDO
BCHSET1/SDI
BCHSET2
NTACT/TAMIRP
TAMIRM
TPSYC/TAMITP
TPACT/TAMITM
N.C.
TSMPSEL
MULTI
TESTIN15
POWMON
TESTIN16
TESTIN17
TESTIN18
N.C.
CLK400
CLK192K
RESET
N.C.
TRPSEL
TSMPAUT
IOSEL
BCHIF
MASLV
TESTIN19
TESTIN20
TESTIN21
TESTIN22
N.C.
TESTIN23
TESTIN24
CLK256K
CLK640K
V
SS
V
DD
V
SS
V
DD
V
SS
V
DD
V
DD
V
SS
V
DD
V
SS
V
DD
V
DD
V
SS
VDDV
SS
V
SS
V
DD
V
SS
V
SS
V
SS
V
SS
V
SS
V
SS
Figure 3.1: YTD426B-S (144-pin SQFP) Pin Assignments [Top View]
7
8
CHAPTER 3. PIN DESCRIPTIONS
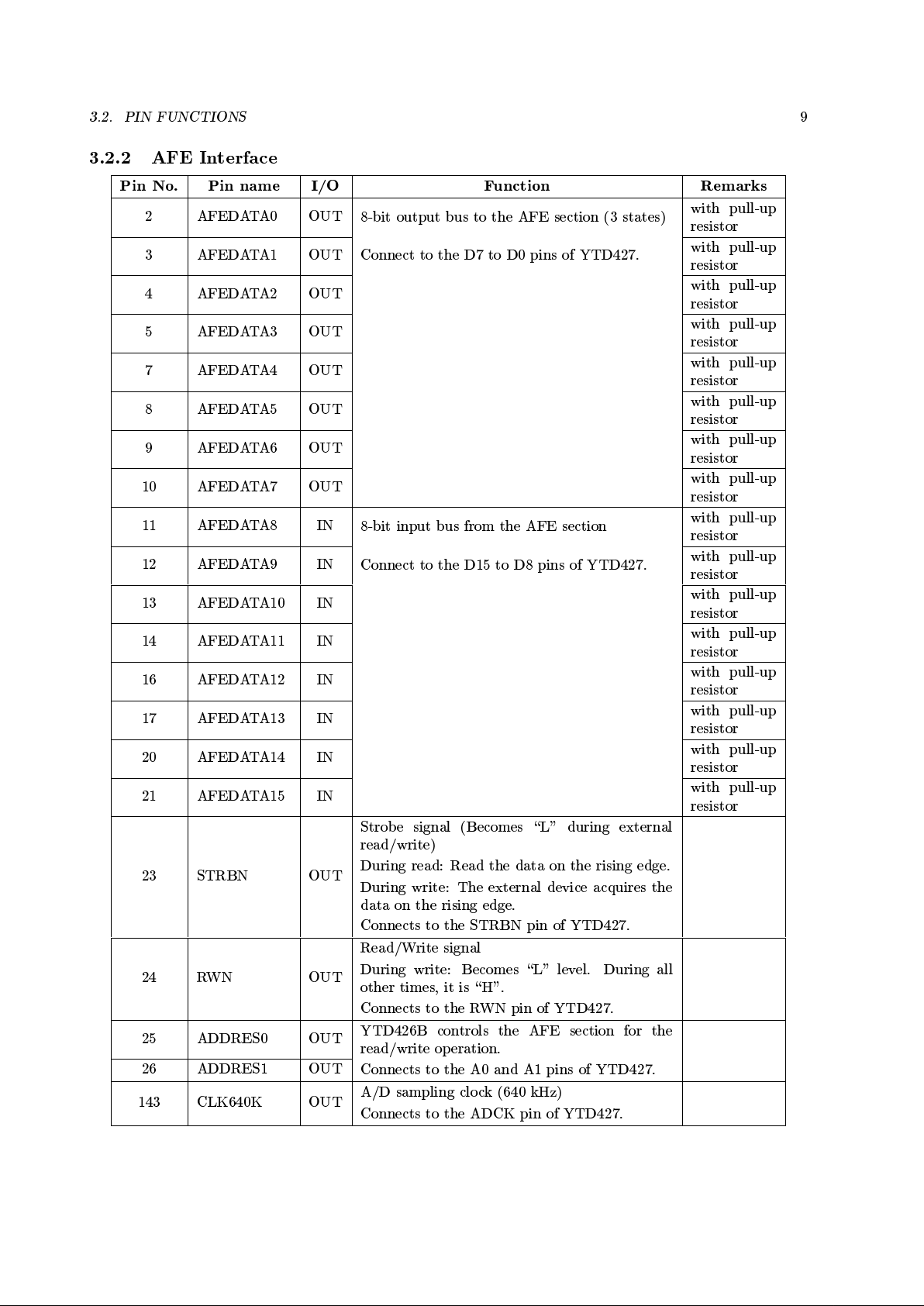
3.2 Pin Functions
3.2.1 Common Section
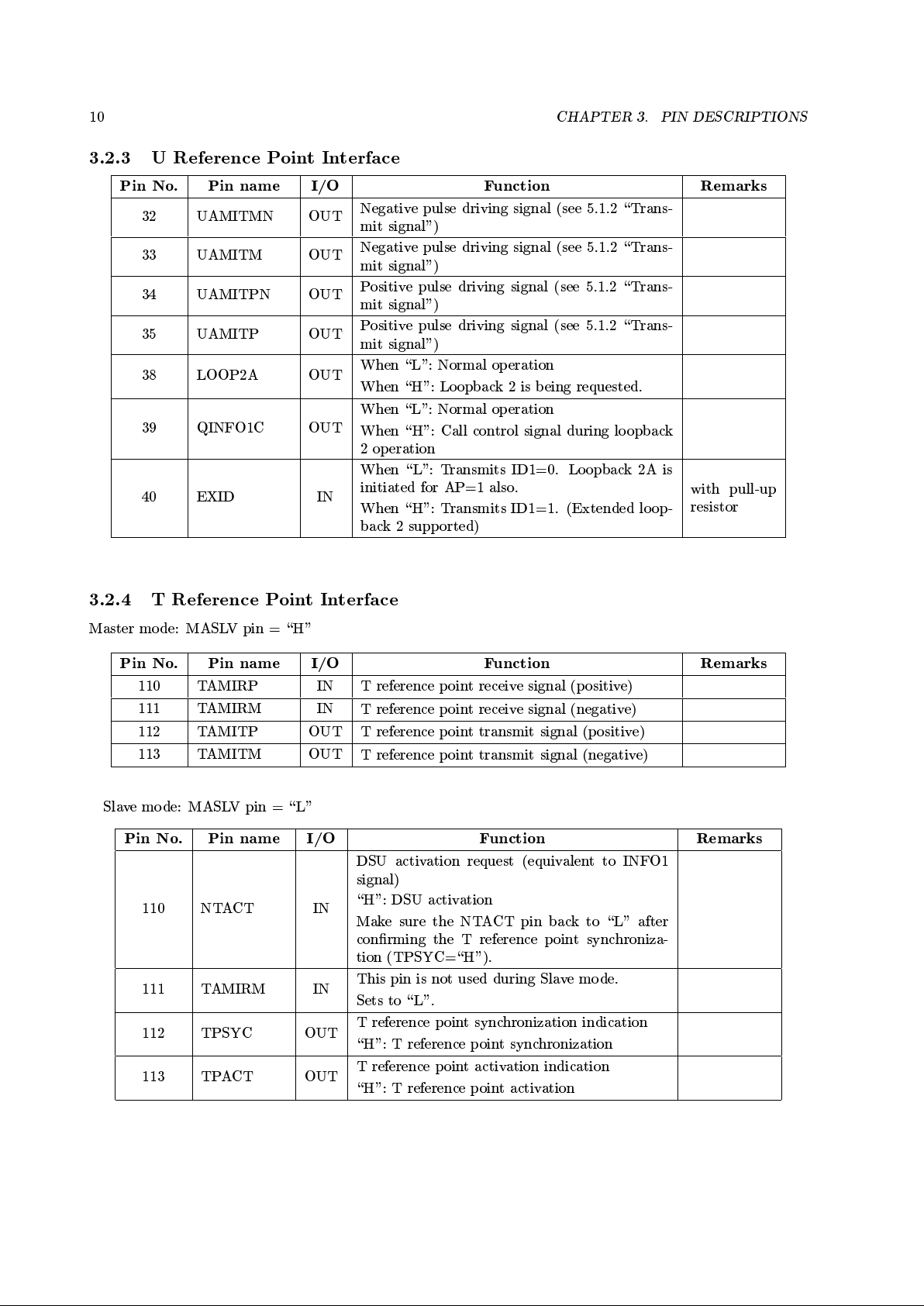
Pin No. Pin name I/O Function Remarks
19,36,55
73,90,99
109,127,144
V
DD
PWR
+5V power supply610%
All pins must
be joined
together.
1,18,27
29,37,54
72,80,83
91,95,108
115,126
V
SS
GND
ground
All pins must
be joined
together.
81 CLK1536 IN
Master clock or crystal oscillator input.
(15.36MHz650ppm or less)
82 CLKOUT OUT
Crystal oscillator output
119 POWMON IN
Power supply monitor pin of the equipmenton
the T reference point side
\H": Power supply OFF
\L": Power supply ON
128 RESET IN
Hardware reset
Apply the reset pulse for 1 ms or more after the
clock oscillation reset YTD426B.
If the pulse is less than 1 ms, the operation is
unpredictable.
During the voltage p olarity of U reference point
is positive, input \L" to this pin.
3.2. PIN FUNCTIONS
9
3.2.2 AFE Interface
Pin No. Pin name I/O Function Remarks
2 AFEDATA0 OUT
8-bit output bus to the AFE section (3 states)
with pull-up
resistor
3 AFEDATA1 OUT
Connect to the D7 to D0 pins of YTD427.
with pull-up
resistor
4 AFEDATA2 OUT
with pull-up
resistor
5 AFEDATA3 OUT
with pull-up
resistor
7 AFEDATA4 OUT
with pull-up
resistor
8 AFEDATA5 OUT
with pull-up
resistor
9 AFEDATA6 OUT
with pull-up
resistor
10 AFEDATA7 OUT
with pull-up
resistor
11 AFEDATA8 IN
8-bit input bus from the AFE section
with pull-up
resistor
12 AFEDATA9 IN
Connect to the D15 to D8 pins of YTD427.
with pull-up
resistor
13 AFEDATA10 IN
with pull-up
resistor
14 AFEDATA11 IN
with pull-up
resistor
16 AFEDATA12 IN
with pull-up
resistor
17 AFEDATA13 IN
with pull-up
resistor
20 AFEDATA14 IN
with pull-up
resistor
21 AFEDATA15 IN
with pull-up
resistor
23 STRBN OUT
Strobe signal (Becomes \L" during external
read/write)
During read: Read the data on the rising edge.
During write: The external device acquires the
data on the rising edge.
Connects to the STRBN pin of YTD427.
24 RWN OUT
Read/Write signal
During write: Becomes \L" level. During all
other times, it is \H".
Connects to the RWN pin of YTD427.
25 ADDRES0 OUT
YTD426B controls the AFE section for the
read/write operation.
26 ADDRES1 OUT
Connects to the A0 and A1 pins of YTD427.
143 CLK640K OUT
A/D sampling clock (640 kHz)
Connects to the ADCK pin of YTD427.
10
CHAPTER 3. PIN DESCRIPTIONS
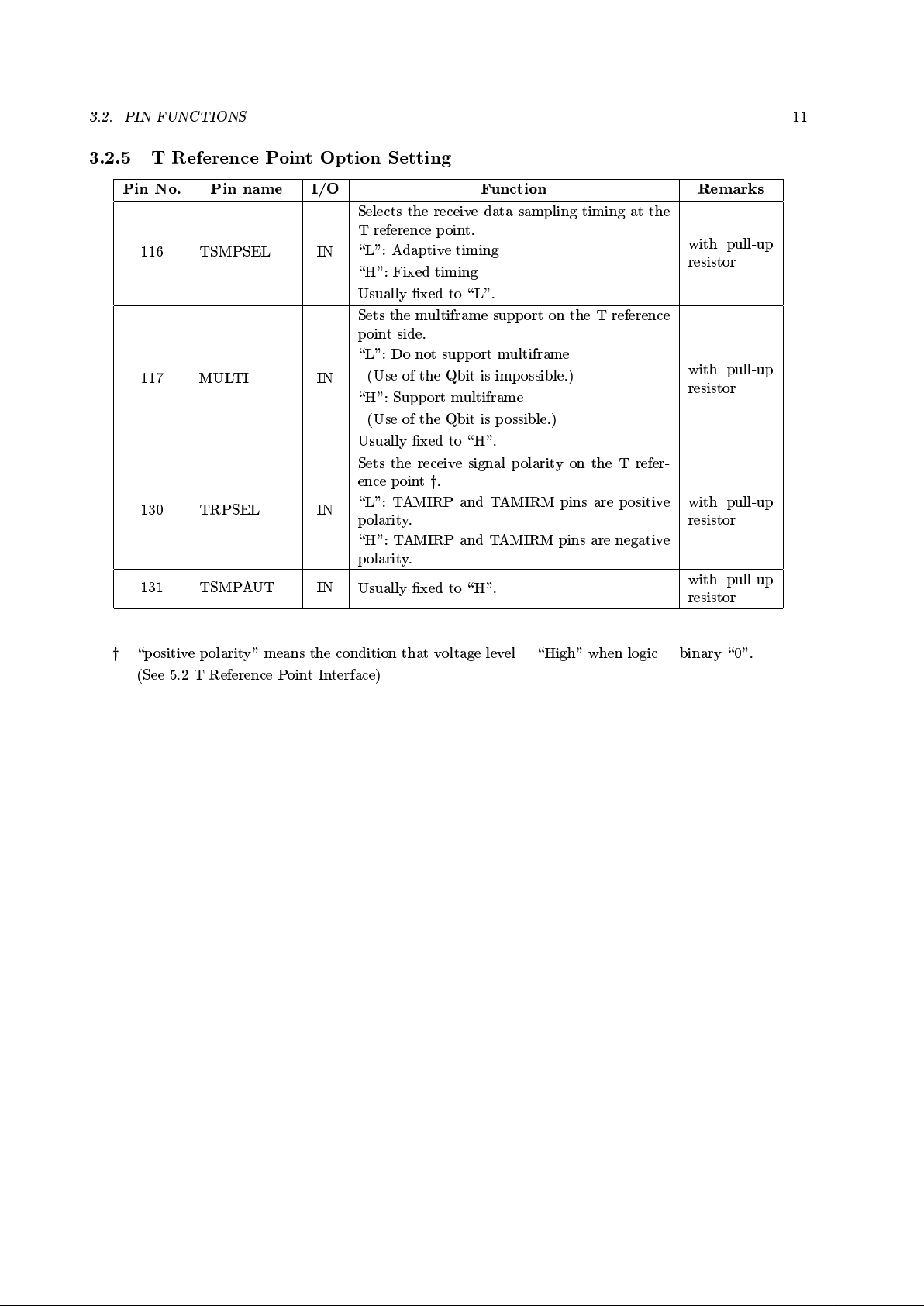
3.2.3 U Reference Point Interface
Pin No. Pin name I/O Function Remarks
32 UAMITMN OUT
Negative pulse driving signal (see 5.1.2 \Trans-
mit signal")
33 UAMITM OUT
Negative pulse driving signal (see 5.1.2 \Trans-
mit signal")
34 UAMITPN OUT
Positive pulse driving signal (see 5.1.2 \Trans-
mit signal")
35 UAMITP OUT
Positive pulse driving signal (see 5.1.2 \Trans-
mit signal")
38 LOOP2A OUT
When \L": Normal operation
When \H": Loopback 2 is b eing requested.
39 QINFO1C OUT
When \L": Normal operation
When \H": Call control signal during loopback
2 operation
40 EXID IN
When \L": Transmits ID1=0. Loopback2Ais
initiated for AP=1 also.
When \H": Transmits ID1=1. (Extended lo op-
back 2 supp orted)
with pull-up
resistor
3.2.4 T Reference Point Interface
Master mo de: MASLV pin = \H"
Pin No. Pin name I/O Function Remarks
110 TAMIRP IN
T reference point receive signal (positive)
111 TAMIRM IN
T reference point receive signal (negative)
112 TAMITP OUT
T reference point transmit signal (p ositive)
113 TAMITM OUT
T reference point transmit signal (negative)
Slave mode: MASLV pin = \L"
Pin No. Pin name I/O Function Remarks
110 NTACT IN
DSU activation request (equivalent to INFO1
signal)
\H": DSU activation
Make sure the NTACT pin back to \L" after
conrming the T reference point synchroniza-
tion (TPSYC=\H").
111 TAMIRM IN
This pin is not used during Slave mode.
Sets to \L".
112 TPSYC OUT
T reference point synchronization indication
\H": T reference point synchronization
113 TPACT OUT
T reference point activation indication
\H": T reference point activation
3.2. PIN FUNCTIONS
11
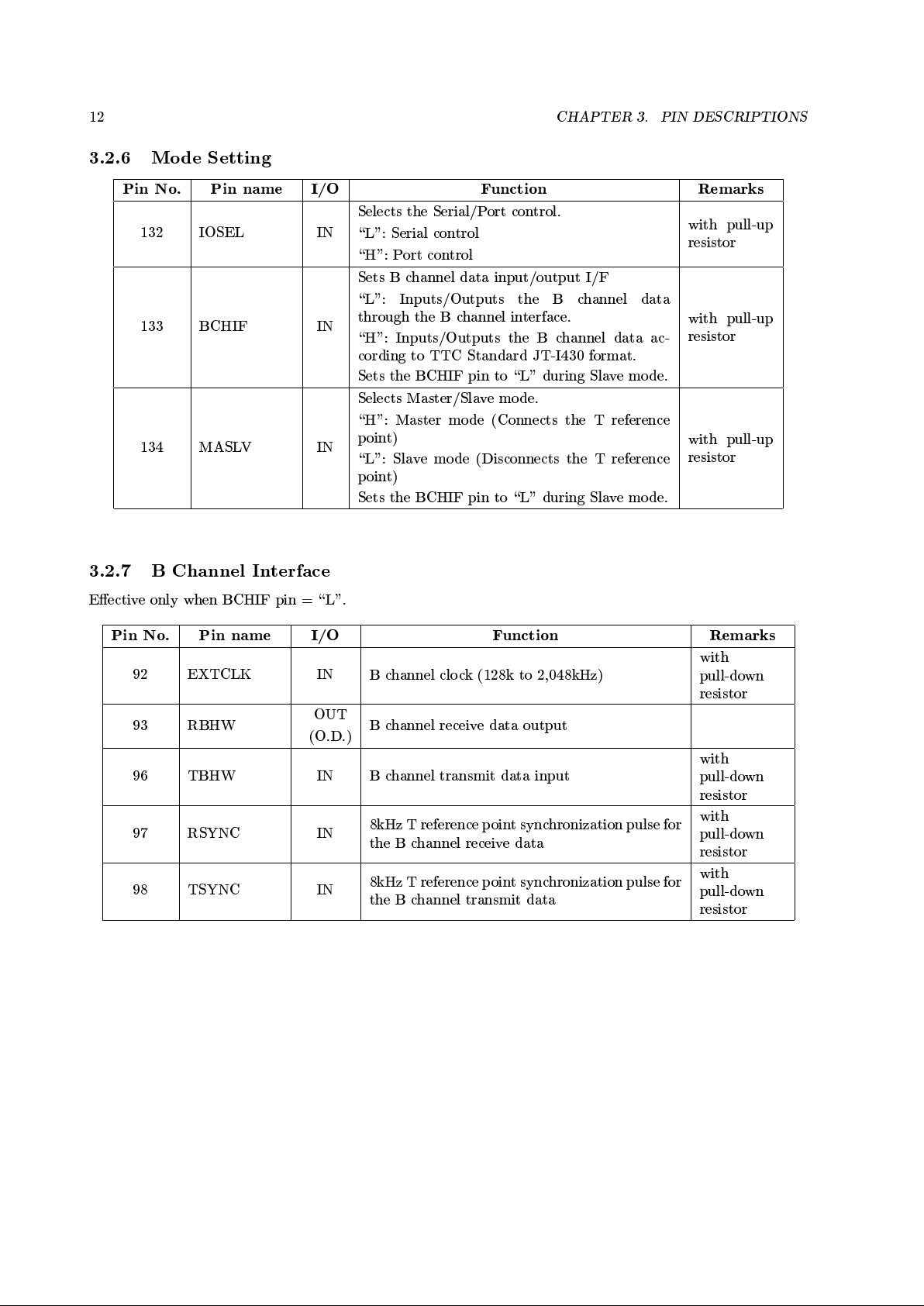
3.2.5 T Reference Point Option Setting
Pin No. Pin name I/O Function Remarks
116 TSMPSEL IN
Selects the receive data sampling timing at the
T reference point.
\L": Adaptive timing
\H": Fixed timing
Usually xed to \L".
with pull-up
resistor
117 MULTI IN
Sets the multiframe support on the T reference
point side.
\L": Do not support multiframe
(Use of the Qbit is imp ossible.)
\H": Support multiframe
(Use of the Qbit is p ossible.)
Usually xed to \H".
with pull-up
resistor
130 TRPSEL IN
Sets the receive signal polarity on the T refer-
ence pointy.
\L": TAMIRP and TAMIRM pins are p ositive
polarity.
\H": TAMIRP and TAMIRM pins are negative
polarity.
with pull-up
resistor
131 TSMPAUT IN
Usually xed to \H".
with pull-up
resistor
y
\positive polarity" means the condition that voltage level = \High" when logic = binary \0".
(See 5.2 T Reference PointInterface)
12
CHAPTER 3. PIN DESCRIPTIONS
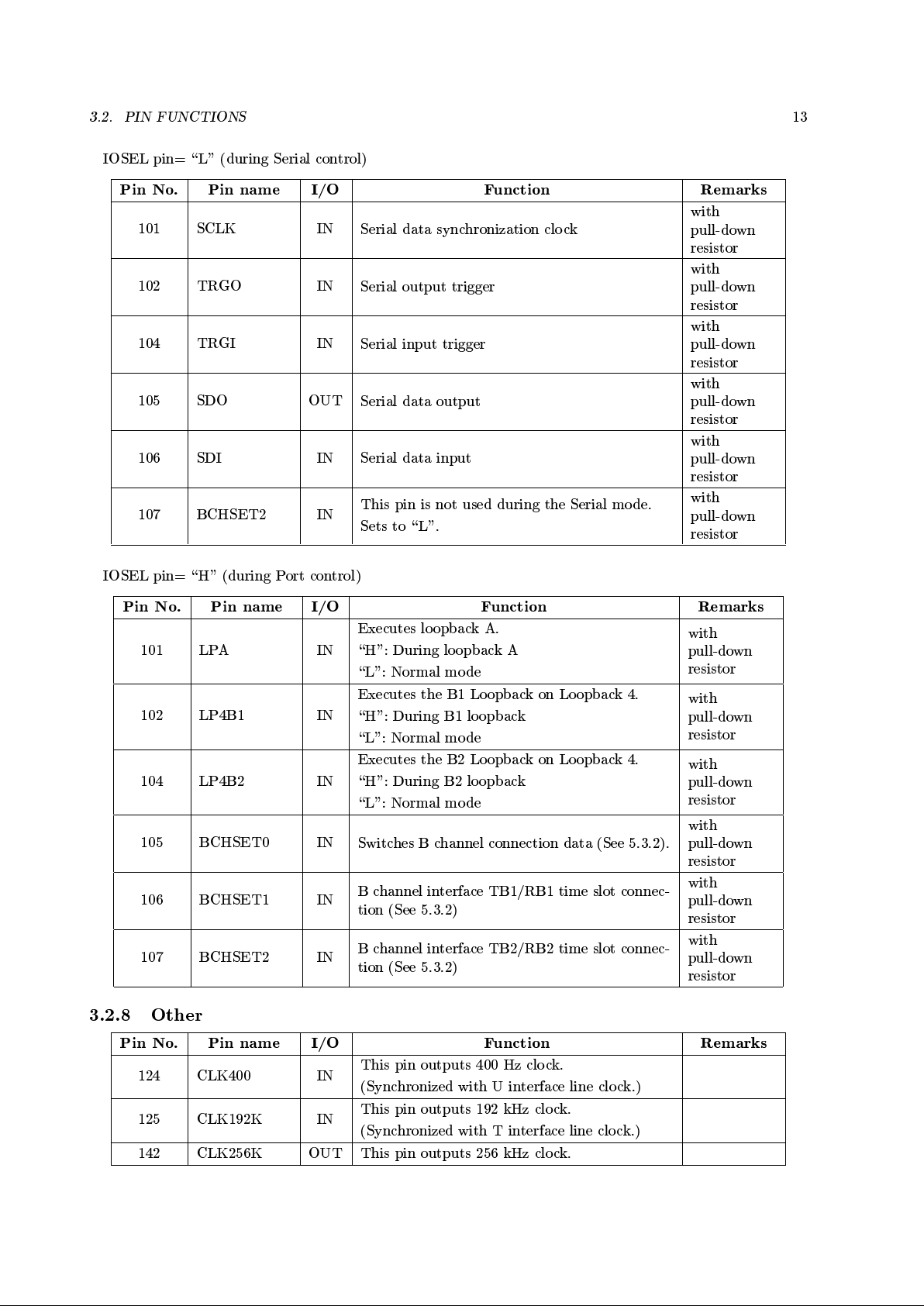
3.2.6 Mode Setting
Pin No. Pin name I/O Function Remarks
132 IOSEL IN
Selects the Serial/Port control.
\L": Serial control
\H": Port control
with pull-up
resistor
133 BCHIF IN
Sets B channel data input/output I/F
\L": Inputs/Outputs the B channel data
through the B channel interface.
\H": Inputs/Outputs the B channel data ac-
cording to TTC Standard JT-I430 format.
Sets the BCHIF pin to \L" during Slave mode.
with pull-up
resistor
134 MASLV IN
Selects Master/Slave mode.
\H": Master mo de (Connects the T reference
point)
\L": Slave mode (Disconnects the T reference
point)
Sets the BCHIF pin to \L" during Slave mode.
with pull-up
resistor
3.2.7 B Channel Interface
Eective only when BCHIF pin = \L".
Pin No. Pin name I/O Function Remarks
92 EXTCLK IN
Bchannel clo ck (128k to 2,048kHz)
with
pull-down
resistor
93 RBHW
OUT
(O.D.)
Bchannel receive data output
96 TBHW IN
Bchannel transmit data input
with
pull-down
resistor
97 RSYNC IN
8kHz T reference point synchronization pulse for
the B channel receive data
with
pull-down
resistor
98 TSYNC IN
8kHz T reference point synchronization pulse for
the B channel transmit data
with
pull-down
resistor
3.2. PIN FUNCTIONS
13
IOSEL pin= \L" (during Serial control)
Pin No. Pin name I/O Function Remarks
101 SCLK IN
Serial data synchronization clock
with
pull-down
resistor
102 TRGO IN
Serial output trigger
with
pull-down
resistor
104 TRGI IN
Serial input trigger
with
pull-down
resistor
105 SDO OUT
Serial data output
with
pull-down
resistor
106 SDI IN
Serial data input
with
pull-down
resistor
107 BCHSET2 IN
This pin is not used during the Serial mode.
Sets to \L".
with
pull-down
resistor
IOSEL pin= \H" (during Port control)
Pin No. Pin name I/O Function Remarks
101 LPA IN
Executes loopbackA.
\H": During loopbackA
\L": Normal mode
with
pull-down
resistor
102 LP4B1 IN
Executes the B1 Loopback on Loopback4.
\H": During B1 loopback
\L": Normal mode
with
pull-down
resistor
104 LP4B2 IN
Executes the B2 Loopback on Loopback4.
\H": During B2 loopback
\L": Normal mode
with
pull-down
resistor
105 BCHSET0 IN
SwitchesBchannel connection data (See 5.3.2).
with
pull-down
resistor
106 BCHSET1 IN
Bchannel interface TB1/RB1 time slot connec-
tion (See 5.3.2)
with
pull-down
resistor
107 BCHSET2 IN
Bchannel interface TB2/RB2 time slot connec-
tion (See 5.3.2)
with
pull-down
resistor
3.2.8 Other
Pin No. Pin name I/O Function Remarks
124 CLK400 IN
This pin outputs 400 Hz clo ck.
(Synchronized with U interface line clock.)
125 CLK192K IN
This pin outputs 192 kHz clo ck.
(Synchronized with T interface line clock.)
142 CLK256K OUT
This pin outputs 256 kHz clo ck.
14
CHAPTER 3. PIN DESCRIPTIONS
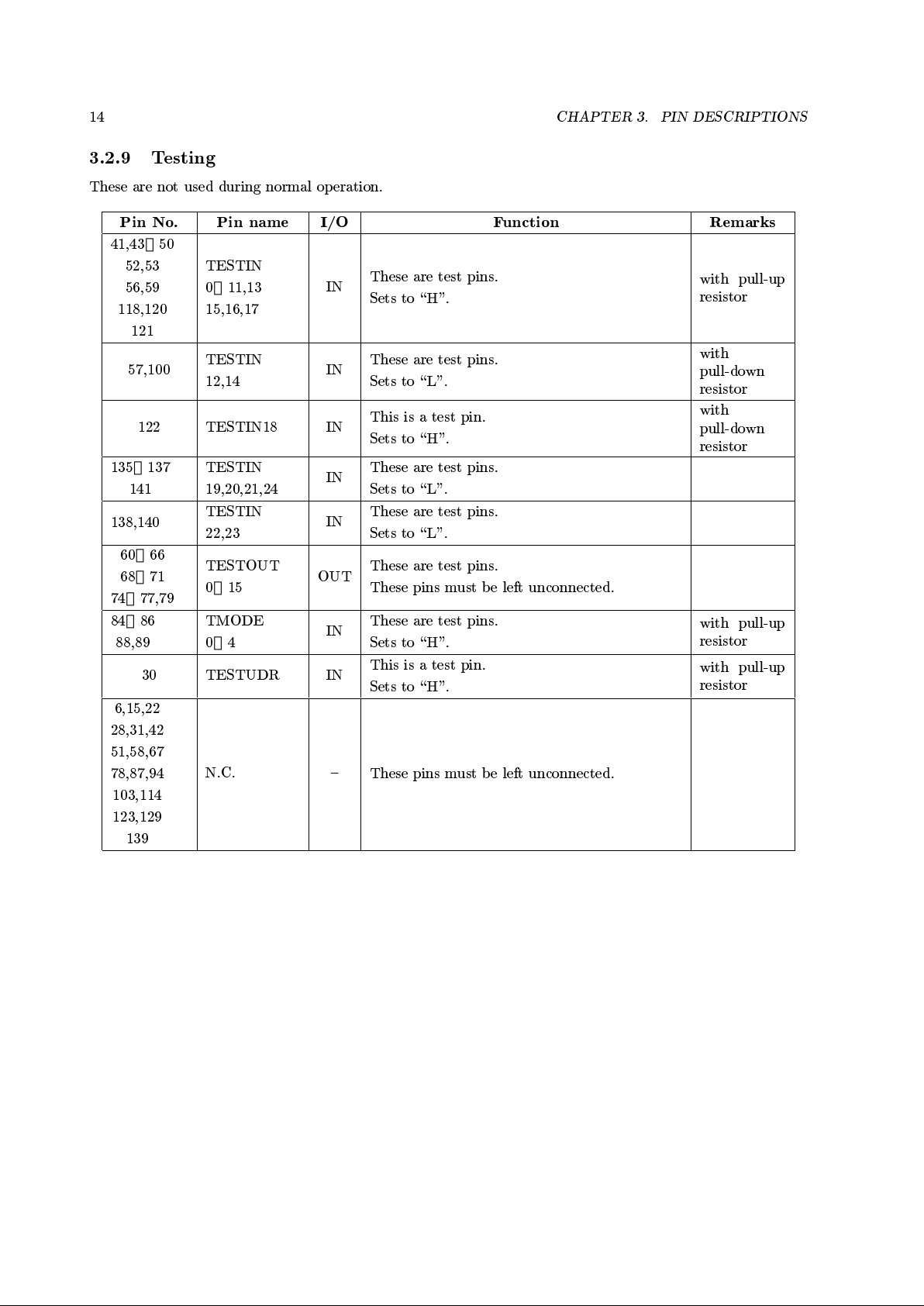
3.2.9 Testing
These are not used during normal op eration.
Pin No. Pin name I/O Function Remarks
41,43〜50
52,53
56,59
118,120
121
TESTIN
0〜11,13
15,16,17
IN
These are test pins.
Sets to \H".
with pull-up
resistor
57,100
TESTIN
12,14
IN
These are test pins.
Sets to \L".
with
pull-down
resistor
122 TESTIN18 IN
This is a test pin.
Sets to \H".
with
pull-down
resistor
135〜137
141
TESTIN
19,20,21,24
IN
These are test pins.
Sets to \L".
138,140
TESTIN
22,23
IN
These are test pins.
Sets to \L".
60〜66
68〜71
74〜77,79
TESTOUT
0〜15
OUT
These are test pins.
These pins must be left unconnected.
84〜86
88,89
TMODE
0〜4
IN
These are test pins.
Sets to \H".
with pull-up
resistor
30 TESTUDR IN
This is a test pin.
Sets to \H".
with pull-up
resistor
6,15,22
28,31,42
51,58,67
78,87,94
103,114
123,129
139
N.C. {
These pins must be left unconnected.
 Loading...
Loading...