Page 1

2015
SERVICE MANUAL
GPD150-A
2DP-F8197-E0
Page 2

EAS20002
GPD150-A
SERVICE MANUAL
©2015 by PT Yamaha Indonesia Motor
Manufacturing
First edition, Ju
ly 2015
All rights reserved.
Any reproduction or unauthorized use
without the written permission of
PT Yamaha Indonesia Motor Manufacturing
is expressly prohibited.
Page 3

EAS20003
T
IMPORTANT
This manual was produced by the PT Yamaha Indonesia Motor Manufacturing primarily for use by
Yamaha dealers and their qualified mechanics. It is not possible to include all the knowledge of a mechanic in one manual. Therefore, anyone who uses this book to perform maintenance and repairs on
Yamaha vehicles should have a basic understanding of mechanics and the techniques to repair these
types of vehicles. Repair and maintenance work attempted by anyone without this knowledge is likely
to render the vehicle unsafe and unfit for use.
PT Yamaha Indonesia Motor Manufacturing is continually striving to improve all of its models. Modifications and significant changes in specifications or procedures will be forwarded to all authorized
Yamaha dealers and will appear in future editions of this manual where applicable.
IP
Designs and specifications are subject to change without notice.
EAS30001
IMPORTANT MANUAL INFORMATION
Particularly important information is distinguished in this manual by the following notations.
This is the safety alert symbol. It is used to alert you to potential personal injury hazards. Obey all safety messages that follow this symbol to avoid possible
injury or death.
WARNING
NOTICE
TIP
A WARNING indicates a hazardous situation which, if not avoided, could result
in death or serious injury.
A NOTICE indicates special precautions that must be taken to avoid damage to
the vehicle or other property.
A TIP provides key information to make procedures easier or clearer.
Page 4

EAS20004
HOW TO USE THIS MANUAL
This manual is intended as a handy, easy-to-read reference book for the mechanic. Comprehensive
explanations of all installation, removal, disassembly, assembly, repair and check procedures are laid
out with the individual steps in sequential order.
• The manual is divided into chapters and each chapter is divided into sections. The current section title
“1” is shown at the top of each page.
• Sub-section titles “2” appear in smaller print than the section title.
• To help identify parts and clarify procedure steps, there are exploded diagrams “3” at the start of each
removal and disassembly section.
• Numbers “4” are given in the order of the jobs in the exploded diagram. A number indicates a disassembly step.
• Symbols “5” indicate parts to be lubricated or replaced.
Refer to “SYMBOLS”.
• A job instruction chart “6” accompanies the exploded diagram, providing the order of jobs, names of
parts, notes in jobs, etc. This step explains removal and disassembly procedure only. For installation
and assembly procedure, reverse the steps.
• Jobs “7” requiring more information (such as special tools and technical data) are described sequentially.
1
3
2
4
5
7
6
Page 5
EAS20005
T
SYMBOLS
The following symbols are used in this manual for easier understanding.
IP
The following symbols are not relevant to every vehicle.
SYMBOL DEFINITION SYMBOL DEFINITION
Serviceable with engine mounted Gear oil
G
Filling fluid Molybdenum disulfide oil
M
Lubricant Brake fluid
BF
Special tool Wheel bearing grease
Tightening torque Lithium-soap-based grease
T
.
R
.
Wear limit, clearance Molybdenum disulfide grease
Engine speed Silicone grease
B
LS
M
S
Electrical data Apply locking agent (LOCTITE®).
LT
Engine oil Replace the part with a new one.
New
E
Silicone fluid
S
Page 6

Page 7

EAS10003
TABLE OF CONTENTS
GENERAL INFORMATION
SPECIFICATIONS
PERIODIC CHECKS AND
ADJUSTMENTS
CHASSIS
ENGINE
1
2
3
4
5
COOLING SYSTEM
FUEL SYSTEM
ELECTRICAL SYSTEM
TROUBLESHOOTING
6
7
8
9
Page 8

Page 9

GENERAL INFORMATION
IDENTIFICATION ............................................................................................ 1-1
VEHICLE IDENTIFICATION NUMBER .....................................................1-1
ENGINE SERIAL NUMBER ......................................................................1-1
FEATURES......................................................................................................1-2
OUTLINE OF THE FI SYSTEM.................................................................1-2
FI SYSTEM................................................................................................ 1-3
OUTLINE OF THE ABS............................................................................. 1-4
ABS COMPONENT FUNCTIONS .............................................................1-8
ABS OPERATION ...................................................................................1-13
ABS WARNING LIGHT AND OPERATION.............................................1-16
INSTRUMENT FUNCTIONS ...................................................................1-18
IMPORTANT INFORMATION ....................................................................... 1-22
PREPARATION FOR REMOVAL AND DISASSEMBLY.........................1-22
REPLACEMENT PARTS.........................................................................1-22
GASKETS, OIL SEALS AND O-RINGS ..................................................1-22
LOCK WASHERS/PLATES AND COTTER PINS ...................................1-22
BEARINGS AND OIL SEALS ..................................................................1-23
CIRCLIPS ................................................................................................ 1-23
RUBBER PARTS.....................................................................................1-23
1
BASIC SERVICE INFORMATION................................................................. 1-24
QUICK FASTENERS...............................................................................1-24
ELECTRICAL SYSTEM...........................................................................1-25
SPECIAL TOOLS ..........................................................................................1-30
Page 10

EAS20007
IDENTIFICATION
EAS30002
VEHICLE IDENTIFICATION NUMBER
The vehicle identification number “1” is stamped
into the frame.
1
EAS30004
ENGINE SERIAL NUMBER
The engine serial number “1” is stamped into the
crankcase.
IDENTIFICATION
1
1-1
Page 11

FEATURES
EAS20008
FEATURES
EAS30005
OUTLINE OF THE FI SYSTEM
The main function of a fuel supply system is to provide fuel to the combustion chamber at the optimum
air-fuel ratio in accordance with the engine operating conditions and the atmospheric temperature. In
the conventional carburetor system, the air-fuel ratio of the mixture that is supplied to the combustion
chamber is created by the volume of the intake air and the fuel that is metered by the jet used in the
respective carburetor.
Despite the same volume of intake air, the fuel volume requirement varies by the engine operating conditions, such as acceleration, deceleration, or operating under a heavy load. Carburetors that meter the
fuel through the use of jets have been provided with various auxiliary devices, so that an optimum airfuel ratio can be achieved to accommodate the constant changes in the operating conditions of the engine.
As the requirements for the engine to deliver more performance and cleaner exhaust gases increase,
it becomes necessary to control the air-fuel ratio in a more precise and finely tuned manner. To accommodate this need, this model has adopted an electronically controlled fuel injection (FI) system, in place
of the conventional carburetor system. This system can achieve an optimum air-fuel ratio required by
the engine at all times by using a microprocessor that regulates the fuel injection volume according to
the engine operating conditions detected by various sensors.
The adoption of the FI system has resulted in a highly precise fuel supply, improved engine response,
better fuel economy, and reduced exhaust emissions.
9,10,11 12 13 14
1. Engine trouble warning light
2. ABS ECU
3. Front wheel sensor
4. VVA (variable valve actuator) solenoid
5. O
sensor
2
6. Spark plug
7. Coolant temperature sensor
8. Crankshaft position sensor
9. Intake air temperature sensor
10.Intake air pressure sensor
11. Throttle position sensor
12. ISC (Idle Speed Control) unit
13. Battery
1
2
1615
3
45678
14.ECU (Engine Control Unit)
15. Fuel injector
16. Ignition coil
1-2
Page 12
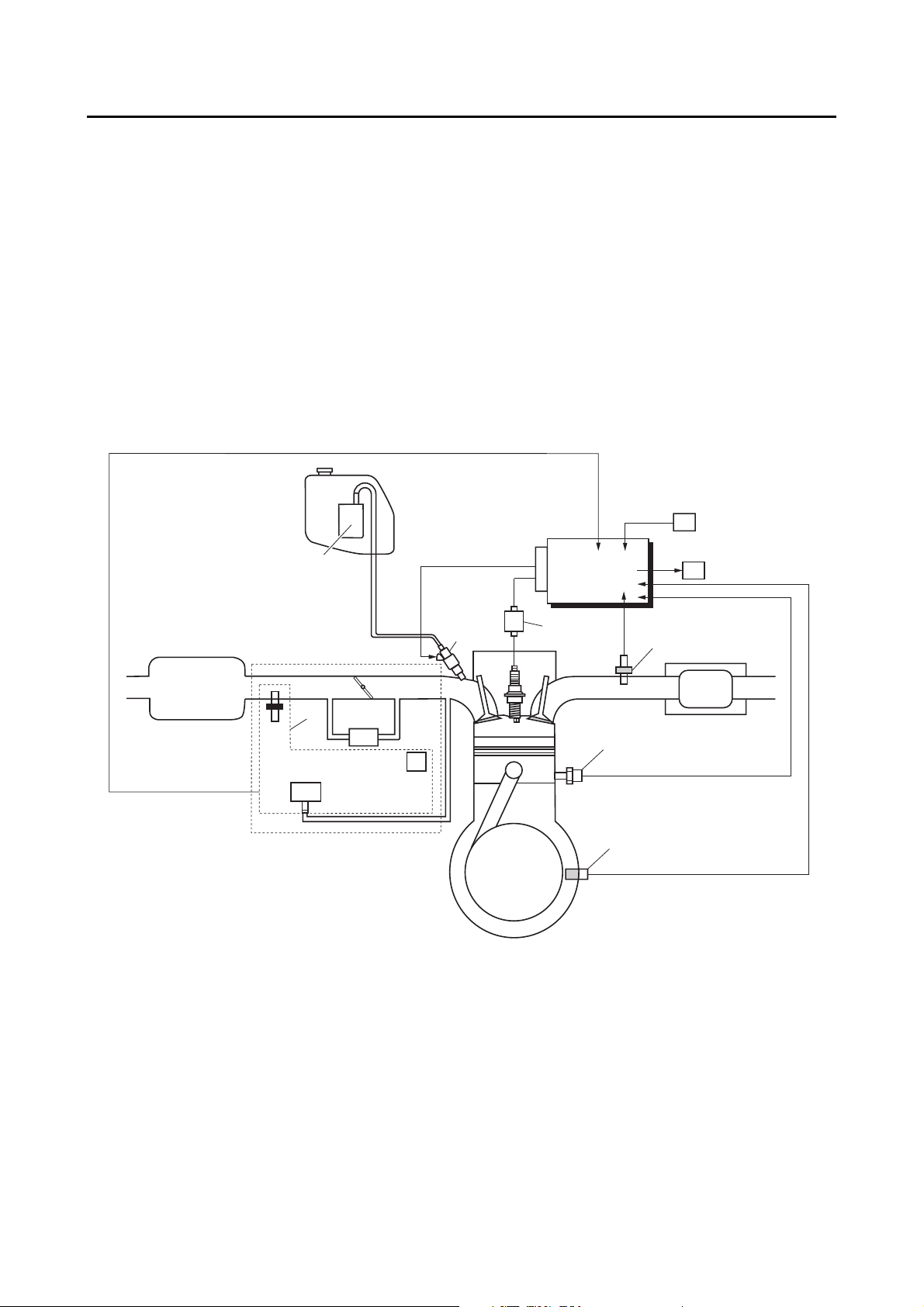
FEATURES
EAS30617
FI SYSTEM
The fuel pump delivers fuel to the fuel injector via the fuel filter. The pressure regulator maintains the
fuel pressure that is applied to the fuel injector at a certain level. Accordingly, when the energizing signal
from the ECU energizes the fuel injector, the fuel passage opens, causing the fuel to be injected into
the intake manifold only during the time the passage remains open. Therefore, the longer the length of
time the fuel injector is energized (injection duration), the greater the volume of fuel that is supplied.
Conversely, the shorter the length of time the fuel injector is energized (injection duration), the lesser
the volume of fuel that is supplied.
The injection duration and the injection timing are controlled by the ECU. Signals that are input from the
throttle position sensor, coolant temperature sensor, crankshaft position sensor, intake air pressure
sensor, intake air temperature sensor, front wheel sensor and O
the injection duration. The injection timing is determined through the signals from the crankshaft position sensor. As a result, the volume of fuel that is required by the engine can be supplied at all times in
accordance with the driving conditions.
sensor enable the ECU to determine
2
1
B
16
12
13
15
11
1. Fuel pump
2. Fuel injector
3. Ignition coil
4. ECU (Engine Control Unit)
5. Front wheel sensor
6. ISC (Idle Speed Control) unit
7. O
sensor
2
8. Catalytic converter
9. Coolant temperature sensor
10. Crankshaft position sensor
11. Throttle body
12. Throttle body sensor assembly
C
5
A
2
3
4
6
7
8
6
9
14
10
13. Intake air temperature sensor
14. Throttle position sensor
15.Intake air pressure sensor
16. Air filter case
A. Fuel system
B. Air system
C. Control system
1-3
Page 13
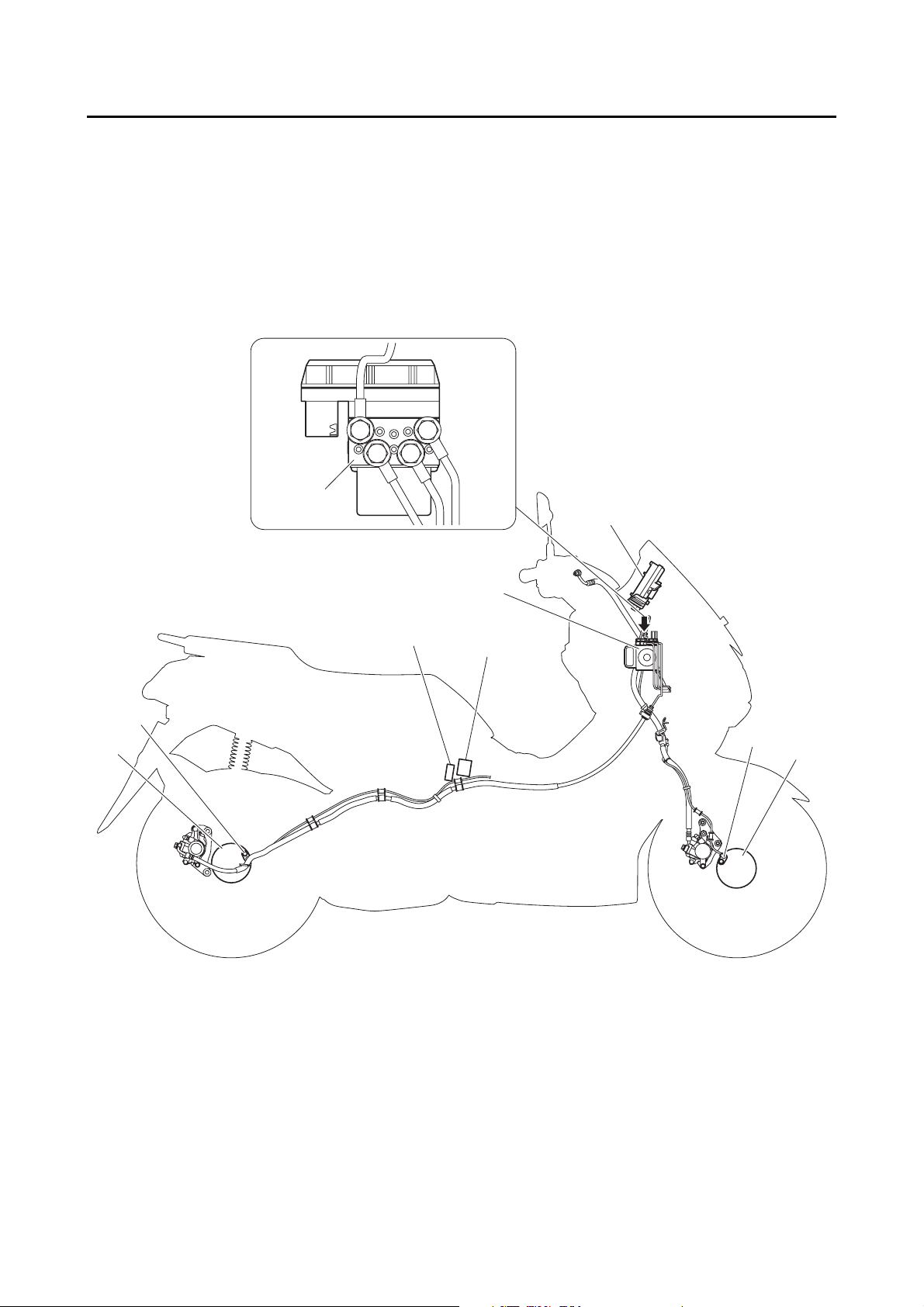
FEATURES
EAS30683
OUTLINE OF THE ABS
1. The Yamaha ABS (anti-lock brake system) features an electronic control system, which acts on the
front and rear brakes independently.
2. The ABS features a compact and lightweight design to help maintain the basic maneuverability of
the vehicle.
3. The hydraulic unit assembly, which is the main component of the ABS, is centrally located on the
vehicle to increase mass centralization.
ABS layout
1
2
6
5
1. Hydraulic unit assembly
2. ABS warning light
3. Front wheel sensor rotor
4. Front wheel sensor
5. Rear wheel sensor rotor
6. Rear wheel sensor
7. ABS test coupler
8. ABS control unit fuse
9. ABS solenoid fuse
10. ABS motor fuse
1
7
8,9,10
4
3
1-4
Page 14
FEATURES
ABS
The operation of the Yamaha ABS brakes is the same as conventional brakes on other vehicles, with
a front brake lever for operating the front brake and a rear brake lever for operating the rear brake.
When wheel lock is detected during braking, hydraulic control is performed by the hydraulic system on
the front and rear brakes independently.
Useful terms
• Wheel speed:
The rotation speed of the front and rear wheels.
• Chassis speed:
The speed of the chassis.
When the brakes are applied, wheel speed and chassis speed are reduced. However, the chassis
travels forward by its inertia even though the wheel speed is reduced.
• Brake force:
The force applied by braking to reduce the wheel speed.
• Wheel lock:
A condition that occurs when the rotation of one or both of the wheels has stopped, but the vehicle
continues to travel.
• Side force:
The force on the tires which supports the vehicle when cornering.
• Slip ratio:
When the brakes are applied, slipping occurs between the tires and the road surface. This causes a
difference between the wheel speed and the chassis speed.
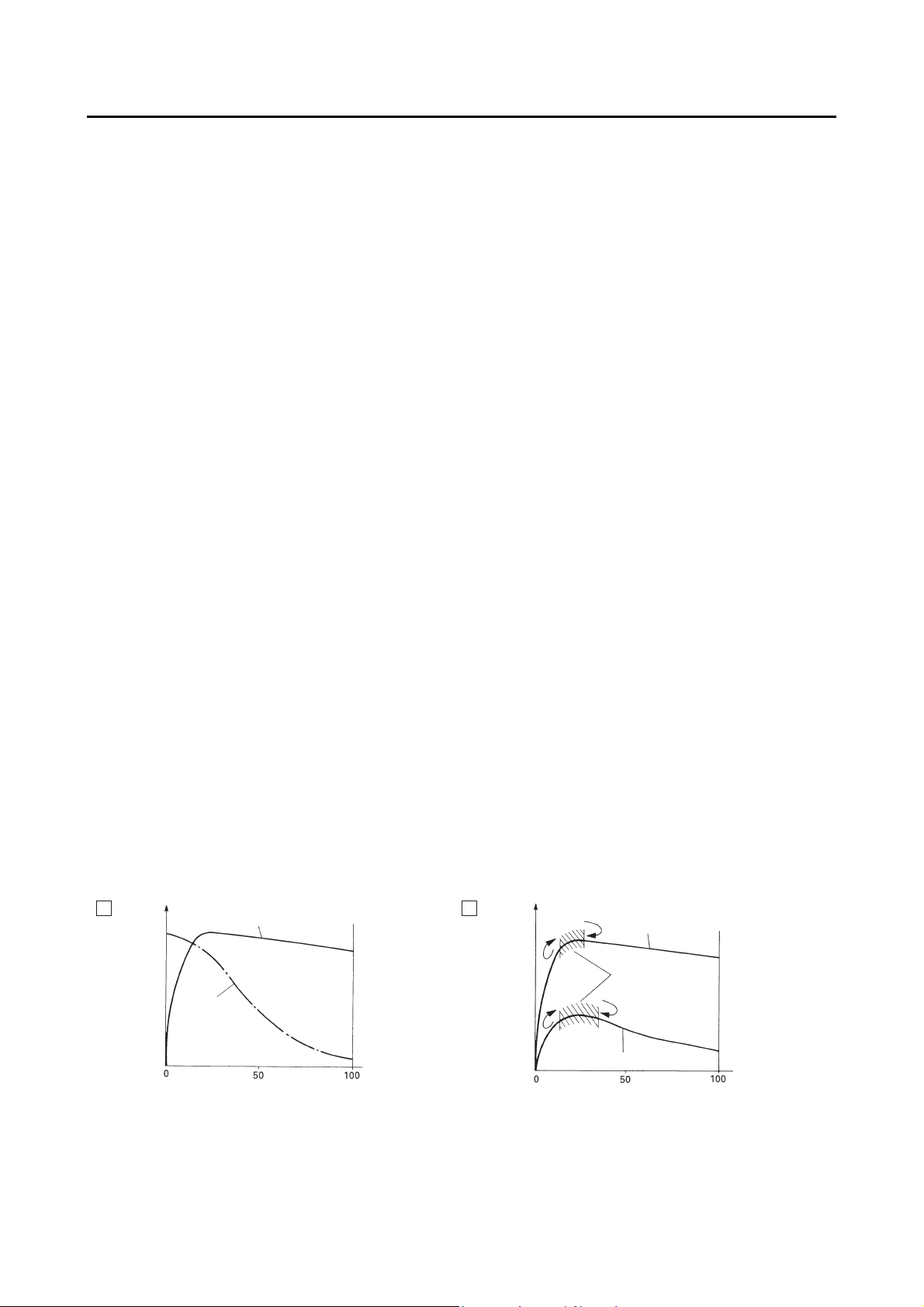
Slip ratio is the value that shows the rate of wheel slippage and is defined by the following formula.
Slip ratio = (Chassis speed – Wheel speed)/Chassis speed × 100 (%)
0%: There is no slipping between the wheel and the road surface. The chassis speed is equal to the
wheel speed.
100%: The wheel speed is “0”, but the chassis is moving (i.e., wheel lock).
Brake force and vehicle stability
When the brake pressure is increased, wheel speed is reduced. Slipping occurs between the tire and
the road surface and brake force is generated. The limit of this brake force is determined by the friction
force between the tire and the road surface and is closely related to wheel slippage. Wheel slippage is
represented by the slip ratio.
Side force is also closely related to wheel slippage. See figure “A”. If the brakes are applied while keeping the proper slip ratio, it is possible to obtain the maximum brake force without losing much side force.
ABS allows full use of the tires’ capabilities even on slippery road surfaces or less slippery road surfaces. See figure “B”.
A
b
B
e
f
a
c
a
g
(%)
d
a. Friction force between the tire and road
surface
b. Brake force
c. Side force
d. Slip ratio
e. Less slippery road surface
f. Controlling zone
g. Slippery road surface
(%)
d
1-5
Page 15
FEATURES
T
Wheel slip and hydraulic control
The ABS ECU calculates the wheel speed of each wheel according to the rotation signal received from
the front and rear wheel sensors. In addition, the ABS ECU calculates the vehicle chassis speed and
the rate of speed reduction based on the wheel speed values.
The difference between the chassis speed and the wheel speed calculated in the slip ratio formula is
equal to the wheel slip. When the wheel speed is suddenly reduced, the wheel has a tendency to lock.
When the wheel slip and the wheel speed reduction rate exceed the preset values, the ABS ECU determines that the wheel has a tendency to lock.
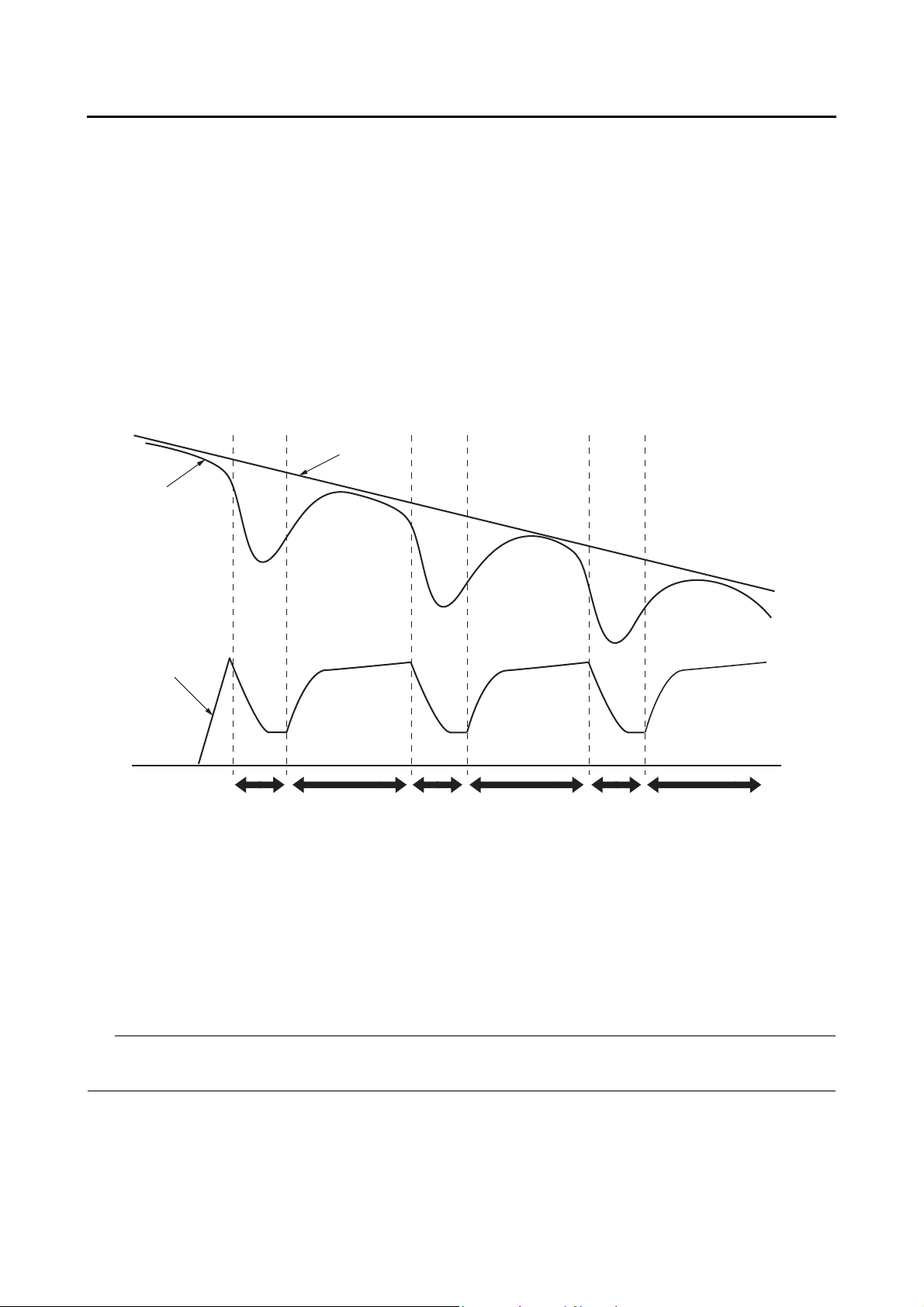
If the slip is large and the wheel has a tendency to lock (point “A” in the following figure), the ABS ECU
reduces the hydraulic pressure in the brake caliper. Once the ABS ECU determines that the tendency
of the wheel to lock has diminished after the hydraulic pressure is reduced, it increases the hydraulic
pressure (point “B” in the following figure). The hydraulic pressure is initially increased quickly, and then
it is increased gradually.
a
b
A
A
c
a. Chassis speed
b. Wheel speed
c. Brake force
B
A
B
A
B
A
B
ddede
e
B
d. Depressurizing phase
e. Pressurizing phase
A
B
ABS operation and vehicle control
If the ABS starts operating, there is a tendency of the wheel to lock, and the vehicle is approaching the
limit of control. To make the rider aware of this condition, the ABS has been designed to generate a
reaction-force pulsating action in the front brake lever and rear brake lever independently.
IP
When the ABS is activated, a pulsating action may be felt at the front brake lever or rear brake lever,
but this does not indicate a malfunction.
The higher the side force on a tire, the less traction there is available for braking. This is true whether
the vehicle is equipped with ABS or not. Therefore, sudden braking while cornering is not recommended. Excessive side force, which ABS cannot prevent, could cause the tire to slip sideways.
1-6
Page 16

FEATURES
EWA16510
WARNING
The braking of the vehicle, even in the worst case, is principally executed when the vehicle is
advancing straight ahead. During a turn, sudden braking is liable to cause a loss of traction of
the tires. Even in vehicles equipped with ABS, overturning of the vehicle cannot be prevented
if it is braked suddenly.
The ABS functions to prevent the tendency of the wheel to lock by controlling the hydraulic pressure.
However, if there is a tendency of the wheel to lock on a slippery road surface, due to engine braking,
the ABS may not be able to prevent the wheel from locking.
EWA13870
WARNING
The ABS controls only the tendency of the wheel to lock caused by applying the brakes. The
ABS cannot prevent wheel lock on slippery surfaces, such as ice, when it is caused by engine
braking, even if the ABS is operating.
(%)
a. Friction force between the tire and road
surface
b. Brake force
c. Side force
d. Slip ratio
Electronic ABS features
The Yamaha ABS (anti-lock brake system) has been developed with the most advanced electronic
technology.
The ABS control is processed with good response under various vehicle travel conditions.
The ABS also includes a highly developed self-diagnosis function. The ABS detects any problem condition and allows normal braking even if the ABS is not operating properly.
When this occurs, the ABS warning light on the meter assembly comes on.
The ABS stores the fault codes in the memory of the ABS ECU for easy problem identification and troubleshooting.
1-7
Page 17

ABS block diagram
FEATURES
1
10
11
1. Rear brake master cylinder
2. Hydraulic unit assembly
3. Front brake master cylinder
4. Inlet solenoid valve
5. ABS motor
6. Hydraulic pump
7. Outlet solenoid valve
8. ABS ECU
2
3
44
6
56
77
8
99
13
14
12
9. Buffer chamber
10. Rear brake caliper
11.Rear wheel sensor
12. ABS warning light
13.Front brake caliper
14. Front wheel sensor
EAS30684
ABS COMPONENT FUNCTIONS
Wheel sensors and wheel sensor rotors
Wheel sensors “1” detect the wheel speed and transmit the rotation signal to the ABS ECU.
Each wheel sensor is composed of a permanent magnet and a hall IC. The sensor rotors “2” rotate with
the wheels. The sensor rotors “2” have 40 slots and are installed close to the wheel sensors. As the
sensor rotor rotates, the hall element in the hall IC installed in the wheel sensor generates pulses. The
pulse frequency, which is proportional to the wheel speed, is converted into a wave in the hall IC so that
it can be output.
The ABS ECU calculates the wheel rotation speed by detecting the pulse frequency.
1-8
Page 18

FEATURES
T
2
1
3. At low speed
4. At high speed
5. Wheel sensor
6. Wheel sensor rotor
1
7
3
7
4
2
88
5
6
7. Voltage
8. Time
ABS warning light
The ABS warning light “1” comes on to warn the rider if a malfunction in the ABS occurs.
When the main switch is turned to “ON”, the ABS warning light comes on to check the electrical circuit
and the system function (ABS self-diagnosis), and goes off when the vehicle is operated (the function
check is properly completed at a speed of 10 km/h [6 mi/h]).
IP
After all checks and servicing are completed, the ABS warning light will go off when the vehicle is ridden
or pushed at a speed of 7 km/h (4 mi/h) or faster.
ECA22940
NOTICE
If the rear wheel is raced with the vehicle on a centerstand, the ABS warning light may flash or
come on. If this occurs, turn the main switch to “OFF”, then back to “ON”. The ABS operation
is normal if the ABS warning light goes off after the vehicle starts off. If the fault codes are not
deleted, the ABS warning light goes off after the vehicle is ridden at a speed of about 30 km/h
(19 mi/h).
1-9
Page 19

FEATURES
1
Hydraulic unit assembly
The hydraulic unit assembly “1” is composed of hydraulic control valves (each with a outlet solenoid
valve and inlet solenoid valve), buffer chambers, hydraulic pumps, an ABS motor, and ABS ECU. The
hydraulic unit adjusts the front and rear wheel brake fluid pressure to control the wheel speed according
to signals transmitted from the ABS ECU.
1
Hydraulic control valve
The hydraulic control valve is composed of a inlet solenoid valve and outlet solenoid valve.
The electromagnetic force generated in the inlet solenoid valve varies proportionally with the duty cycle
control voltage that is supplied to it. Since this voltage is continuously variable, the solenoid valve
moves smoothly and the hydraulic pressure is adjusted linearly.
1. When the brakes are operated normally, the inlet solenoid valve “1” is open and the outlet solenoid
valve “2” is closed. The brake line between the brake master cylinder and brake caliper is open.
3
4
3. Brake master cylinder
4. Brake caliper
2. When the ABS is activated, the inlet solenoid valve “1” closes and the outlet solenoid valve “2” opens
using the power supplied from the ABS ECU signals. This reduces the hydraulic pressure.
1-10
Page 20

FEATURES
4
3
3. Brake caliper
4. ABS motor
3. When the ABS ECU sends a signal to stop reducing the hydraulic pressure, the outlet solenoid valve
“2” closes and the brake fluid is pressurized again. The inlet solenoid valve “1” controls the hydraulic
pressure difference between the brake fluid in the upper brake lines (brake master cylinder side) and
the brake fluid in the lower brake lines (brake caliper side).
Buffer chamber
The buffer chamber accumulates the brake fluid that is depressurized while the ABS is operating.
1. Buffer chamber (pressurizing phase)
2. Buffer chamber (depressurizing phase)
ABS ECU
The ABS ECU is integrated with the hydraulic unit to achieve a compact and lightweight design.
As shown in the following block diagram, the ABS ECU receives wheel sensor signals from the front
and rear wheels and also receives signals from other monitor circuits.
3. Raised piston
1-11
Page 21

FEATURES
T
74
3
1
2
56
13
14
16
17
18
22
19
20
21
8
10 11
9
12
23
24
25
15
26
27
1. Battery
2. AC magneto
3. Rectifier/regulator
4. Main fuse
5. ABS motor fuse
6. ABS solenoid fuse
7. Main switch
8. ABS control unit fuse
9. Signaling system fuse
10. Rear brake light switch
11. Front brake light switch
12. Tail/brake light
13. ABS test coupler
14. Hydraulic unit assembly
15. ABS ECU
16. ABS motor relay
17. Solenoid relay
18. Front brake outlet solenoid
19. Front brake inlet solenoid
20. Rear brake outlet solenoid
21. Rear brake inlet solenoid
22. ABS motor
23. Meter assembly
24. ABS warning light
25.ECU (Engine Control Unit)
26. Front wheel sensor
27.Rear wheel sensor
The necessary actions are confirmed using the monitor circuit and control signals are transmitted to the
hydraulic unit assembly.
ABS control operation
The ABS control operation performed in the ABS ECU is divided into the following two parts.
• Hydraulic control
• Self-diagnosis
When a malfunction is detected in the ABS, a fault code is stored in the memory of the ABS ECU for
easy problem identification and troubleshooting.
IP
• Some types of malfunctions are not recorded in the memory of the ABS ECU (e.g., a blown ABS con-
trol unit fuse).
1-12
Page 22

FEATURES
• The ABS performs a self-diagnosis test for a few seconds each time the vehicle first starts off after the
main switch was turned on. During this test, a “clicking” noise can be heard from front side, and if the
front brake lever or rear brake lever is even slightly operated, a vibration can be felt at the levers, but
these do not indicate a malfunction.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
1. Software operation flow
2. Main switch “ON”
3. Initialize
4. Self-diagnosis (when static)
5. Self-diagnosis (when riding)
EAS30710
6. Receive signals
7. Control operation
8. Depressurize/pressurize
ABS OPERATION
The ABS hydraulic circuit consists of two systems: the front wheel, and rear wheel. The following describes the system for the front wheel only.
Normal braking (ABS not activated)
When the ABS is not activated, the inlet solenoid valve is open and the outlet solenoid valve is closed
because a control signal has not been transmitted from the ABS ECU. Therefore, when the brake lever
is squeezed, the hydraulic pressure in the brake master cylinder increases and the brake fluid is sent
to the brake caliper.
At this time, the inlet and outlet check valves of the hydraulic pump are closed. As a result of eliminating
the orifice, the brake master cylinder directly pressurizes the brake caliper during normal braking. When
the brake lever is released, the brake fluid in the brake caliper returns to the brake master cylinder.
1-13
Page 23

FEATURES
3
4
8
12
1. Brake master cylinder
2. Brake light switch
3. ABS motor
4. Hydraulic pump
5. Buffer chamber
6. Outlet solenoid valve
7. Inlet solenoid valve
13
7
6
5
9
10
11
8. Brake caliper
9. Wheel sensor
10. ABS ECU
11. ABS warning light
12. Brake fluid pressure
13. Time
Emergency braking (ABS activated)
1. Depressurizing phase
When the front wheel is about to lock, the outlet solenoid valve is opened by the “depressurization”
signal transmitted from the ABS ECU. When this occurs, the inlet solenoid valve compresses the
spring and closes the brake line from the brake master cylinder. Because the outlet solenoid valve
is open, the brake fluid is sent to the buffer chamber. As a result, the hydraulic pressure in the brake
caliper is reduced.
The brake fluid stored in the buffer chamber is pumped back to the brake master cylinder by the hydraulic pump linked to the ABS motor.
1-14
Page 24

FEATURES
1. Brake master cylinder
2. Brake light switch
3. ABS motor
4. Hydraulic pump
5. Buffer chamber
6. Outlet solenoid valve
7. Inlet solenoid valve
8. Brake caliper
9. Wheel sensor
10. ABS ECU
11. ABS warning light
12. Brake fluid pressure
13. Time
2. Pressurizing phase
The outlet solenoid valve is closed by the “pressurization” signal transmitted from the ABS ECU. At
this time, the ABS ECU controls the opening of the inlet solenoid valve. As the inlet solenoid valve
opens, the brake line from the brake master cylinder opens, allowing the brake fluid to be sent to the
brake caliper.
1-15
Page 25

FEATURES
1. Brake master cylinder
2. Brake light switch
3. ABS motor
4. Hydraulic pump
5. Buffer chamber
6. Outlet solenoid valve
7. Inlet solenoid valve
EAS30712
8. Brake caliper
9. Wheel sensor
10. ABS ECU
11. ABS warning light
12. Brake fluid pressure
13. Time
ABS WARNING LIGHT AND OPERATION
ABS warning light
• If the ABS warning light comes on while riding, stop the vehicle, and then turn the main switch to
“OFF”, then back to “ON”. The ABS operation is normal if the ABS warning light goes off after the vehicle starts off.
• If the rear wheel is raced with the vehicle on a centerstand, the ABS warning light may flash or come
on. If this occurs, turn the main switch to “OFF”, then back to “ON”. The ABS operation is normal if the
ABS warning light goes off after the vehicle starts off.
• The ABS operation is normal if the ABS warning light flashes.
• Even if the ABS warning light remains on and does not go off, or if it comes on after riding, conven-
tional braking performance of the vehicle is maintained.
1-16
Page 26

FEATURES
ABS function
EWA18300
WARNING
• When hydraulic control is performed by the ABS, the brake system alerts the rider that the
wheels have a tendency to lock by generating a reaction-force pulsating action in the front
brake lever or rear brake lever. When the ABS is activated, the grip between the road surface
and tires is close to the limit. The ABS cannot prevent wheel lock* on slippery surfaces, such
as ice, when it is caused by engine braking, even if the ABS is activated.
Use extreme care when operating the vehicle under these conditions.
• The ABS is not designed to shorten the braking distance or improve the cornering perfor-
mance.
• Depending on the road conditions, the braking distance may be longer compared to that of
vehicles not equipped with ABS. Therefore, ride at a safe speed and keep a safe distance between yourself and other vehicles.
• The braking of the vehicle, even in the worst case, is principally executed when the vehicle is
advancing straight ahead. During a turn, sudden braking is liable to cause a loss of traction of
the tires. Even vehicles equipped with ABS cannot be prevented from falling over if braked
suddenly.
• The ABS does not work when the main switch is turned to “OFF”. The conventional braking
function can be used.
* Wheel lock: A condition that occurs when the rotation of one or both of the wheels has
stopped, but the vehicle continues to travel.
1-17
Page 27

FEATURES
T
T
EAS30682
INSTRUMENT FUNCTIONS
Multi-function meter unit
2 31 4
67 5
1. Fuel meter
2. Clock
3. Speedometer
4. Instantaneous fuel consumption meter
5. “RESET” button
6. Multi-function display
7. “SELECT” button
EWA12423
WARNING
Be sure to stop the vehicle before making
any setting changes to the multi-function
meter unit. Changing settings while riding
can distract the operator and increase the
risk of an accident.
The multi-function meter unit is equipped with
the following:
• a speedometer
•a clock
• a fuel meter
• an instantaneous fuel consumption meter
• a multi-function display
IP
Be sure to turn the key to “ON” before using the
“SELECT” and “RESET” buttons.
Clock
1
1. Clock
The clock uses a 12-hour time system.
[To set the clock]
1. Turn the key to “ON”.
2. Push the “SELECT” button and “RESET” button together for at least two seconds.
3. When the hour digits start flashing, push the
“RESET” button to set the hours.
4. Push the “SELECT” button, and the minute
digits will start flashing.
5. Push the “RESET” button to set the minutes.
6. Push the “SELECT” button and then release
it to start the clock.
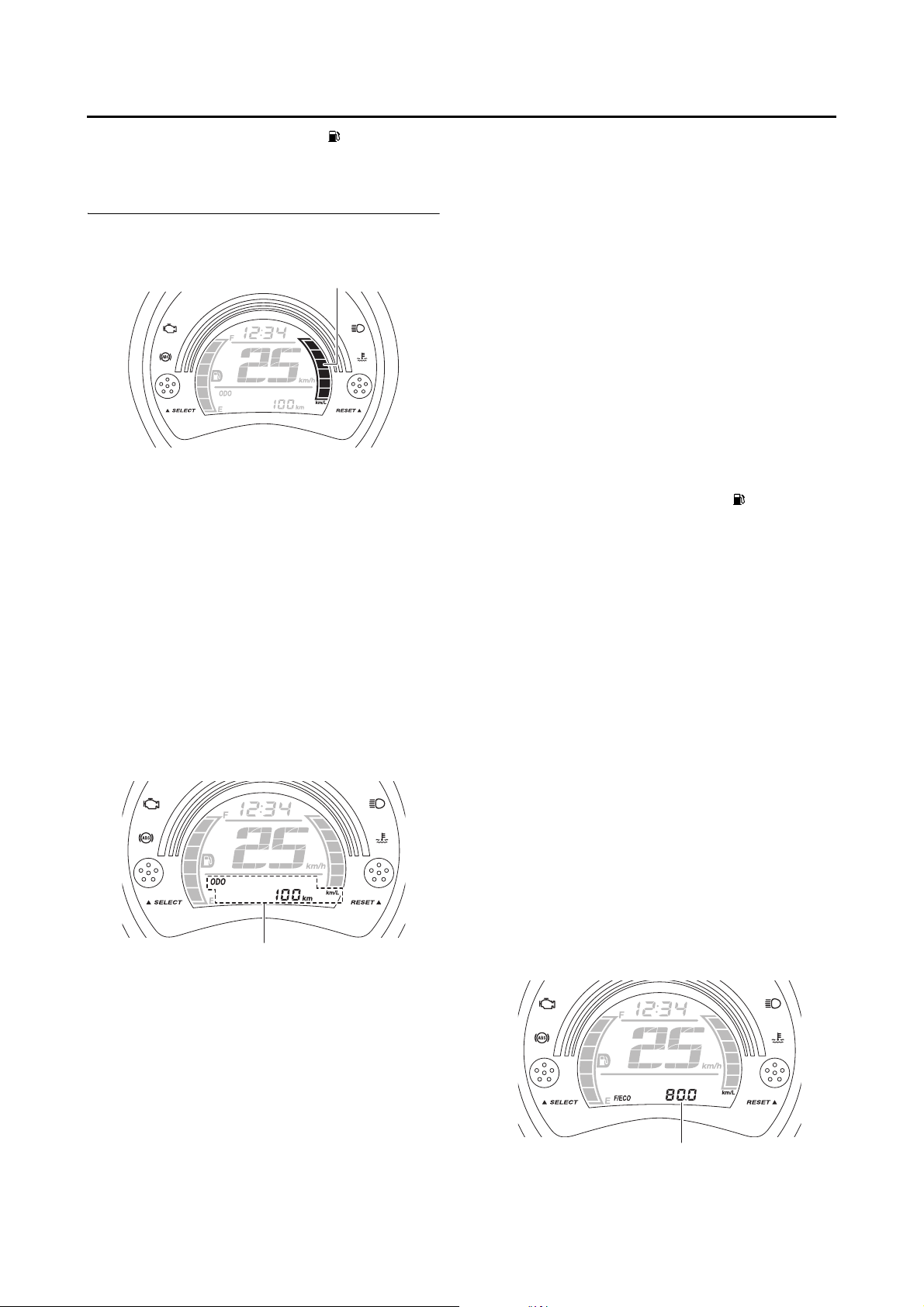
Fuel meter
1 2
1. Fuel meter
2. Fuel level warning indicator “ ”
Speedometer
The speedometer shows the vehicle’s traveling
speed.
The fuel meter indicates the amount of fuel in the
fuel tank. The display segments of the fuel meter
disappear towards “E” (Empty) as the fuel level
decreases. When the last segment and fuel level
warning indicator “ ” start flashing, refuel as
soon as possible.
IP
This fuel meter is equipped with a self-diagnosis
system. If a problem is detected in the electrical
circuit, the following cycle is repeated until the
malfunction is corrected: fuel level segments
1-18
Page 28
FEATURES
and fuel level warning indicator “ ” flash eight
times, then go off for approximately 3 seconds.
If this occurs, check the electrical circuit.
Refer to “SIGNALING SYSTEM” on page 8-19.
Instantaneous fuel consumption meter
1
1. Instantaneous fuel consumption meter
This meter shows the instantaneous fuel consumption.
Depending on the display setting selected for
the instantaneous fuel consumption mode
“F/ECO”, the displayed segments increase or
decrease.
• km/L: The number of segments displayed increases the more efficiently the vehicle is being
operated.
• L/100 km: The number of segments displayed
decreases the more efficiently the vehicle is
being operated.
Multi-function display
• an oil change tripmeter
• a V-belt replacement tripmeter
• an oil change indicator
• a V-belt replacement indicator
• a fault code display
Push the “SELECT” button to switch the display
between the odometer mode “ODO”, tripmeter
modes “TRIP 1” and “TRIP 2”, oil change tripmeter mode “OIL TRIP”, V-belt replacement tripmeter mode “V-BELT TRIP”, instantaneous fuel
consumption mode “F/ECO” (km/L or L/100 km)
and average fuel consumption mode “AVE
F/ECO” (km/L or L/100 km) in the following order:
ODO → TRIP 1 → TRIP 2 → OIL TRIP → VBELT TRIP → F/ECO → AVE F/ECO → ODO
If the fuel level warning indicator “ ” and last
segment of the fuel meter start flashing, the display automatically changes to the fuel reserve
tripmeter mode “TRIP F” and starts counting the
distance traveled from that point. In that case,
push the “SELECT” button to switch the display
between the various tripmeter, odometer, oil
change tripmeter, V-belt replacement tripmeter,
instantaneous fuel consumption and average
fuel consumption modes in the following order:
TRIP F → TRIP 1 → TRIP 2 → OIL TRIP → VBELT TRIP → F/ECO → AVE F/ECO → ODO
→ TRIP F
1
1. Multi-function display
The multi-function display is equipped with the
following:
• an odometer
• two tripmeters (which show the distance traveled since they were last set to zero)
• a fuel reserve tripmeter (which shows the distance traveled since the last segment of the
fuel meter started flashing)
• an instantaneous fuel consumption display
• an average fuel consumption display
To reset a tripmeter, select it by pushing the “SELECT” button, and then push the “RESET” button for at least one second.
If you do not reset the fuel reserve tripmeter
manually, it resets itself automatically and the
display returns to the prior mode after refueling
and traveling 5 km (3 mi).
Instantaneous fuel consumption mode
1
1. Instantaneous fuel consumption display
1-19
Page 29

FEATURES
The instantaneous fuel consumption display can
be set to either “km/L” or “L/100 km”.
• “km/L”: The distance that can be traveled on
1.0 L of fuel under the current riding conditions
is shown.
• “L/100 km”: The amount of fuel necessary to
travel 100 km under the current riding conditions is shown.
To switch between the instantaneous fuel consumption display settings, push the “SELECT”
button for one second.
TIP
If traveling at speeds under 10 km/h (6 mi/h), “_
_._” is displayed.
Average fuel consumption mode
1
1. Average fuel consumption display
This display shows the average fuel consumption since it was last reset.
The average fuel consumption display can be
set to either “km/L” or “L/100 km”.
• “km/L”: The average distance that can be traveled on 1.0 L of fuel is shown.
• “L/100 km”: The average amount of fuel necessary to travel 100 km is shown.
To switch between the average fuel consumption display settings, push the “SELECT” button
for one second.
To reset the average fuel consumption, push the
“RESET” button for at least one second.
TIP
After resetting the average fuel consumption, “_
_._” will be shown until the vehicle has traveled
0.1 km (0.06 mi).
Oil change tripmeter mode
21
1. Oil change indicator “OIL”
2. Oil change tripmeter
The oil change tripmeter shows the distance
traveled since it was last reset (i.e., since the last
oil change).
The oil change indicator “OIL” will flash at the ini-
tial 1000 km (600 mi), then at 4000 km (2500 mi)
and every 4000 km thereafter to indicate that the
engine oil should be changed.
After changing the engine oil, reset the oil
change tripmeter and the oil change indicator.
To reset them both, select the oil change tripmeter, and then push the “RESET” button for one
second. Then, while “OIL” and the oil change
tripmeter are flashing, push the “RESET” button
for three seconds. The oil change indicator will
be reset.
If the engine oil is changed before the oil change
indicator comes on (i.e., before the periodic oil
change interval has been reached), the oil
change tripmeter must be reset for the next periodic oil change to be indicated at the correct
time.
V-belt replacement tripmeter mode
21
1. V-belt replacement indicator “V-BELT”
2. V-belt replacement tripmeter
The V-belt replacement tripmeter shows the distance traveled since it was last reset (i.e., since
the last V-belt replacement).
1-20
Page 30

The V-belt replacement indicator “V-BELT” will
flash at every 25000 km (15500 mi) thereafter to
indicate that the V-belt should be replaced.
After replacing the V-belt, reset the V-belt replacement tripmeter and the V-belt replacement
indicator. To reset them both, select the V-belt
replacement tripmeter, and then push the “RESET” button for one second. Then, while “VBELT” and the V-belt replacement tripmeter are
flashing, push the “RESET” button for three seconds. The V-belt replacement indicator will be
reset.
If the V-belt is replaced before the V-belt replacement indicator comes on (i.e., before the
periodic V-belt replacement interval has been
reached), the V-belt replacement tripmeter must
be reset for the next periodic V-belt replacement
to be indicated at the correct time.
Self-diagnosis device
FEATURES
1
2
1. Engine trouble warning light “ ”
2. Fault code display
This model is equipped with a self-diagnosis device for various electrical circuits.
If a problem is detected in any of those circuits,
the engine trouble warning light will come on and
the display will indicate a fault code.
If the display indicates any fault codes, note the
code number, and then check the fuel injection
system. Refer to “FUEL INJECTION SYSTEM”
on page 8-25.
ECA20360
NOTICE
If the display indicates a fault code, the vehicle should be checked as soon as possible
in order to avoid engine damage.
1-21
Page 31

EAS20009
IMPORTANT INFORMATION
EAS30006
PREPARATION FOR REMOVAL AND
DISASSEMBLY
1. Before removal and disassembly, remove all
dirt, mud, dust and foreign material.
2. Use only the proper tools and cleaning equip-
ment.
Refer to “SPECIAL TOOLS” on page 1-30.
3. When disassembling, always keep mated
parts together. This includes gears, cylinders,
pistons and other parts that have been “mated” through normal wear. Mated parts must
always be reused or replaced as an assembly.
IMPORTANT INFORMATION
EAS30008
GASKETS, OIL SEALS AND O-RINGS
1. When overhauling the engine, replace all
gaskets, seals and O-rings. All gasket surfaces, oil seal lips and O-rings must be cleaned.
2. During reassembly, properly oil all mating
parts and bearings and lubricate the oil seal
lips with grease.
4. During disassembly, clean all of the parts and
place them in trays in the order of disassembly. This will speed up assembly and allow for
the correct installation of all parts.
5. Keep all parts away from any source of fire.
EAS30007
REPLACEMENT PARTS
Use only genuine Yamaha parts for all replacements. Use oil and grease recommended by
Yamaha for all lubrication jobs. Other brands
may be similar in function and appearance, but
inferior in quality.
1. Oil
2. Lip
3. Spring
4. Grease
EAS30009
LOCK WASHERS/PLATES AND COTTER
PINS
After removal, replace all lock washers/plates
“1” and cotter pins. After the bolt or nut has been
tightened to specification, bend the lock tabs
along a flat of the bolt or nut.
1-22
Page 32

IMPORTANT INFORMATION
EAS30010
BEARINGS AND OIL SEALS
Install bearings “1” and oil seals “2” so that the
manufacturer’s marks or numbers are visible.
When installing oil seals, lubricate the oil seal
lips with a light coat of lithium-soap-based
grease. Oil bearings liberally when installing, if
appropriate.
ECA13300
NOTICE
Do not spin the bearing with compressed air
because this will damage the bearing surfaces.
EAS30012
RUBBER PARTS
Check rubber parts for deterioration during inspection. Some of the rubber parts are sensitive
to gasoline, flammable oil, grease, etc. Do not allow any items other than the specified one to
contact the parts.
EAS30011
CIRCLIPS
Before reassembly, check all circlips carefully
and replace damaged or distorted circlips. Always replace piston pin clips after one use.
When installing a circlip “1”, make sure the
sharp-edged corner “2” is positioned opposite
the thrust “3” that the circlip receives.
1-23
Page 33

EAS20010
T
T
T
T
BASIC SERVICE INFORMATION
EAS30013
QUICK FASTENERS
Rivet type
1. Remove:
• Quick fastener
IP
To remove the quick fastener, push its pin with a
screwdriver, then pull the fastener out.
BASIC SERVICE INFORMATION
Screw type
1. Remove:
• Quick fastener
IP
To remove the quick fastener, loosen the screw
with a screwdriver, then pull the fastener out.
2. Install:
• Quick fastener
IP
To install the quick fastener, push its pin so that
it protrudes from the fastener head, then insert
the fastener into the part to be secured and push
the pin in with a screwdriver. Make sure that the
pin is flush with the fastener’s head.
2. Install:
• Quick fastener
IP
To install the quick fastener, insert the fastener
into the part to be secured and tighten the screw.
1-24
Page 34

BASIC SERVICE INFORMATION
T
EAS30014
ELECTRICAL SYSTEM
Electrical parts handling
ECA16600
NOTICE
Never disconnect a battery lead while the engine is running; otherwise, the electrical
components could be damaged.
ECA16751
NOTICE
When disconnecting the battery leads from
the battery, be sure to disconnect the negative battery lead first, then the positive battery lead. If the positive battery lead is
disconnected first and a tool or similar item
contacts the vehicle, a spark could be generated, which is extremely dangerous.
ECA16760
NOTICE
Be sure to connect the battery leads to the
correct battery terminals. Reversing the battery lead connections could damage the
electrical components.
ECA16771
NOTICE
When connecting the battery leads to the
battery, be sure to connect the positive battery lead first, then the negative battery lead.
If the negative battery lead is connected first
and a tool or similar item contacts the vehicle while the positive battery lead is being
connected, a spark could be generated,
which is extremely dangerous.
ECA16610
NOTICE
IP
If a battery lead is difficult to disconnect due to
rust on the battery terminal, remove the rust us-
Turn the main switch to “OFF” before disconnecting or connecting an electrical component.
ing hot water.
1-25
Page 35

BASIC SERVICE INFORMATION
T
T
ECA16620
NOTICE
Handle electrical components with special
care, and do not subject them to strong
shocks.
ECA16630
NOTICE
Electrical components are very sensitive to
and can be damaged by static electricity.
Therefore, never touch the terminals and be
sure to keep the contacts clean.
Checking the electrical system
IP
Before checking the electrical system, make
sure that the battery voltage is at least 12 V.
ECA14371
NOTICE
Never insert the tester probes into the coupler terminal slots. Always insert the probes
from the opposite end “a” of the coupler, taking care not to loosen or damage the leads.
IP
When resetting the ECU by turning the main
switch to “OFF”, be sure to wait approximately 5
seconds before turning the main switch back to
“ON”.
a
ECA16640
NOTICE
For waterproof couplers, never insert the
tester probes directly into the coupler. When
performing any checks using a waterproof
coupler, use the specified test harness or a
suitable commercially available test harness.
1-26
Page 36

BASIC SERVICE INFORMATION
T
Checking the connections
Check the leads, couplers, and connectors for
stains, rust, moisture, etc.
1. Disconnect:
• Lead
• Coupler
• Connector
ECA16780
NOTICE
• When disconnecting a coupler, release the
coupler lock, hold both sections of the coupler securely, and then disconnect the coupler.
• There are many types of coupler locks;
therefore, be sure to check the type of coupler lock before disconnecting the coupler.
2. Check:
• Lead
• Coupler
• Connector
Moisture → Dry with an air blower.
Rust/stains → Connect and disconnect several times.
3. Check:
• All connections
Loose connection → Connect properly.
IP
• If the pin “1” on the terminal is flattened, bend
it up.
• After disassembling and assembling a coupler,
pull on the leads to make sure that they are installed securely.
ECA16790
NOTICE
When disconnecting a connector, do not pull
the leads. Hold both sections of the connector securely, and then disconnect the connector.
1
1-27
Page 37

4. Connect:
T
T
T
• Lead
• Coupler
• Connector
IP
• When connecting a coupler or connector, push
both sections of the coupler or connector together until they are connected securely.
• Make sure all connections are tight.
BASIC SERVICE INFORMATION
• As a quick remedy, use a contact revitalizer
available at most part stores.
5. Check:
• Continuity
(with the pocket tester)
Pocket tester
90890-03112
Analog pocket tester
YU-03112-C
6. Check:
• Resistance
Pocket tester
90890-03112
Analog pocket tester
YU-03112-C
IP
The resistance values shown were obtained at
the standard measuring temperature of 20 °C
(68 °F). If the measuring temperature is not 20
°C (68 °F), the specified measuring conditions
will be shown.
Coolant temperature sensor resistance
2510–2770 Ω at 20 °C (2510–
2770 Ω at 68 °F)
Coolant temperature sensor resistance
210–221 Ω at 100 °C (210–221 Ω
at 212 °F)
IP
• If there is no continuity, clean the terminals.
• When checking the wire harness, perform
steps (1) to (3).
1-28
Page 38

BASIC SERVICE INFORMATION
1-29
Page 39

SPECIAL TOOLS
T
EAS20012
SPECIAL TOOLS
The following special tools are necessary for complete and accurate tune-up and assembly. Use only
the appropriate special tools as this will help prevent damage caused by the use of inappropriate tools
or improvised techniques. Special tools, part numbers or both may differ depending on the country.
When placing an order, refer to the list provided below to avoid any mistakes.
IP
• For U.S.A. and Canada, use part numbers starting with “YM-”, “YU-”, or “ACC-”.
• For others, use part numbers starting with “90890-”.
Tool name/Tool No. Illustration
Pocket tester
90890-03112
Analog pocket tester
YU-03112-C
Tappet adjusting tool
90890-01311
Six piece tappet set
YM-A5970
Yamaha diagnostic tool
90890-03231
Reference
pages
1-28, 1-28, 8-97,
8-98, 8-98, 8-99,
8-102, 8-103,
8-103, 8-103,
8-104, 8-104,
8-105, 8-105,
8-106, 8-107,
8-108, 8-108
3-7
YM-A5970
ø9ø8 ø10
ø3 ø4
3-7, 3-8, 4-65,
4-67, 7-14, 7-14,
8-28, 8-69, 8-90
Steering nut wrench
90890-01403
Exhaust flange nut wrench
YU-A9472
Thickness gauge
90890-03180
Feeler gauge set
YU-26900-9
T-handle
90890-01326
T-handle 3/8" drive 60 cm long
YM-01326
3-15, 3-16, 4-85
4-31
4-79, 4-80
1-30
Page 40

SPECIAL TOOLS
Tool name/Tool No. Illustration
Fork seal driver weight
90890-01367
Replacement hammer
YM-A9409-7
Fork seal driver attachment (ø30)
90890-01400
Compression gauge
90890-03081
Engine compression tester
YU-33223
YM-A9409-7/YM-A5142-4
90890-03081
Reference
pages
4-80, 4-81
4-80, 4-81
5-1
Extension
90890-04136
Camshaft wrench
90890-04162
Camshaft wrench
YM-04162
Yamaha bond No. 1215
90890-85505
(Three bond No.1215®)
Slide hammer bolt
90890-01085
Slide hammer bolt 8 mm
YU-01083-2
YU-33223
5-1
5-13, 5-17
5-16, 5-64
5-19
1-31
Page 41

SPECIAL TOOLS
Tool name/Tool No. Illustration
Weight
90890-01084
Weight
YU-01083-3
Valve spring compressor
90890-04019
Valve spring compressor
YM-04019
Valve spring compressor attachment
90890-04108
Valve spring compressor adapter 22 mm
YM-04108
Reference
pages
5-19
YU-01083-3
5-23, 5-28
5-23, 5-28
Valve guide remover (ø5)
90890-04097
Valve guide remover (5.0 mm)
YM-04097
Valve guide installer (ø5)
90890-04098
Valve guide installer (5.0 mm)
YM-04098
Valve guide reamer (ø5)
90890-04099
Valve guide reamer (5.0 mm)
YM-04099
Piston pin puller set
90890-01304
Piston pin puller
YU-01304
5-24
5-24
5-24
5-30
YU-01304
1-32
Page 42

SPECIAL TOOLS
Tool name/Tool No. Illustration
Rotor holding tool
90890-01235
Universal magneto and rotor holder
YU-01235
Rotor holding tool
90890-04166
YM-04166
Socket wrench (39 mm)
90890-01493
Sheave spring compressor
90890-04134
Sheave spring compressor
YM-04134
Reference
pages
5-38, 5-43, 5-49,
5-49
5-38, 5-38, 5-42,
5-42
5-38, 5-42
5-38, 5-41
Sheave fixed block
90890-04135
Sheave fixed bracket
YM-04135
Oil seal guide (37 mm)
90890-04177
Flywheel puller
90890-01189
Flywheel puller
YM-01189
5-38, 5-41
5-41
ø37
5-49
1-33
Page 43

SPECIAL TOOLS
Tool name/Tool No. Illustration
Digital circuit tester
90890-03174
Model 88 Multimeter with tachometer
YU-A1927
Crankcase separating tool
90890-01135
Crankcase separator
YU-01135-B
Crankshaft installer pot
90890-01274
Installing pot
YU-90058
Reference
pages
5-52, 8-106,
8-109
5-62
5-63
Crankshaft installer bolt
90890-01275
Bolt
YU-90060
Adapter (M12)
90890-01278
Adapter #3
YU-90063
YU-90058/YU-90059
5-63
5-63
1-34
Page 44

SPECIAL TOOLS
Tool name/Tool No. Illustration
Spacer (crankshaft installer)
90890-04081
Pot spacer
YM-91044
Radiator cap tester
90890-01325
Mityvac cooling system tester kit
YU-24460-A
Reference
pages
5-63
YM-91044
6-3, 6-3
YU-24460-A
Radiator cap tester adapter
90890-01352
Pressure tester adapter
YU-33984
Mechanical seal installer
90890-04145
Middle driven shaft bearing driver
90890-04058
Middle drive bearing installer 40 & 50 mm
YM-04058
6-3
YU-33984
6-9
ø30
ø10
6-9
1-35
Page 45

SPECIAL TOOLS
Tool name/Tool No. Illustration
Pressure gauge
90890-03153
Pressure gauge
YU-03153
Fuel pressure adapter 6.3mm
90890-03227
Ignition checker
90890-06754
Oppama pet–4000 spark checker
YM-34487
Reference
pages
7-4
7-4
8-105
1-36
Page 46

SPECIAL TOOLS
1-37
Page 47

SPECIFICATIONS
GENERAL SPECIFICATIONS ........................................................................ 2-1
ENGINE SPECIFICATIONS ............................................................................ 2-2
CHASSIS SPECIFICATIONS.......................................................................... 2-7
ELECTRICAL SPECIFICATIONS ................................................................... 2-9
TIGHTENING TORQUES ..............................................................................2-11
GENERAL TIGHTENING TORQUE SPECIFICATIONS.........................2-11
ENGINE TIGHTENING TORQUES .........................................................2-12
CHASSIS TIGHTENING TORQUES.......................................................2-15
LUBRICATION POINTS AND LUBRICANT TYPES .................................... 2-19
ENGINE ...................................................................................................2-19
LUBRICATION SYSTEM CHART AND DIAGRAMS.................................... 2-21
ENGINE OIL LUBRICATION CHART .....................................................2-21
LUBRICATION DIAGRAMS .................................................................... 2-23
2
COOLING SYSTEM DIAGRAMS ..................................................................2-27
CABLE ROUTING ......................................................................................... 2-29
Page 48

GENERAL SPECIFICATIONS
EAS20013
GENERAL SPECIFICATIONS
Model
Model 2DP5
Dimensions
Overall length 1955 mm (77.0 in)
Overall width 740 mm (29.1 in)
Overall height 1115 mm (43.9 in)
Seat height 765 mm (30.1 in)
Wheelbase 1350 mm (53.1 in)
Ground clearance 135 mm (5.31 in)
Minimum turning radius 2000 mm (78.7 in)
Weight
Curb weight 127 kg (280 lb)
Maximum load 168 kg (370 lb)
2-1
Page 49

ENGINE SPECIFICATIONS
EAS20014
ENGINE SPECIFICATIONS
Engine
Engine type Liquid cooled 4-stroke, SOHC
Displacement 155 cm³
Cylinder arrangement Single cylinder
Bore × stroke 58.0 × 58.7 mm (2.28 × 2.31 in)
Compression ratio 10.5 : 1
Standard compression pressure (at sea level) 1800 kPa/860 r/min (18.0 kgf/cm²/860 r/min,
256.0 psi/860 r/min)
Minimum–Maximum 1566–2016 kPa/860 r/min (15.6–20.1
kgf/cm²/860 r/min, 221.8–285.8 psi/860 r/min)
Starting system Electric starter
Fuel
Recommended fuel Regular unleaded gasoline (Gasohol [E10]
acceptable)
Fuel tank capacity 6.6 L (1.7
US gal, 1.5 Imp.gal)
Engine oil
Lubrication system Wet sump
Recommended brand YAMALUBE
Type SAE 10W-40
Recommended engine oil grade API service SG type or higher, JASO standard
MA or MB
Engine oil quantity
Quantity (disassembled) 1.00 L (1.06 US qt, 0.88 Imp.qt)
Periodic oil change 0.90 L (0.95 US qt, 0.79 Imp.qt)
Final transmission oil
Type Motor oil SAE 10W-30 Type SE or higher or
Gear oil SEA 85W SL-3
Quantity (disassembled) 0.16 L (0.17 US qt, 0.14 Imp.qt)
Quantity 0.15 L (0.16 US qt, 0.13 Imp.qt)
Oil filter
Oil filter type Centrifugal
Oil pump
Oil pump type Trochoid
Inner-rotor-to-outer-rotor-tip clearance 0.150 mm (0.0059 in)
Limit 0.23 mm (0.0091 in)
Outer-rotor-to-oil-pump-housing clearance 0.13–0.18 mm (0.0051–0.0071 in)
Limit 0.25 mm (0.0098 in)
Oil-pump-housing-to-inner-and-outer-rotor
clearance 0.06–0.11 mm (0.0024–0.0043 in)
Limit 0.18 mm (0.0071 in)
Rotor thickness 7.95–7.98 mm (0.3130–0.3142 in)
Coolant quantity
Radiator (including all routes) 0.46 L (0.49 US qt, 0.40 Imp.qt)
Coolant reservoir (up to the maximum level mark) 0.25 L (0.26 US qt, 0.22 Imp.qt)
2-2
Page 50

ENGINE SPECIFICATIONS
Radiator cap valve opening pressure 108.0–137.4 kPa (1.08–1.37 kgf/cm², 15.7–19.9
psi)
Thermostat
Valve opening temperature 74.0–78.0 °C (165.20–172.40 °F)
Valve full open temperature 90.0 °C (194.00 °F)
Valve lift (full open) 7.0 mm (0.28 in)
Radiator core
Width 158.6 mm (6.24 in)
Height 142.0 mm (5.59 in)
Depth 16.0 mm (0.63 in)
Water pump
Water pump type Single suction centrifugal pump
Spark plug(s)
Manufacturer/model NGK/CPR8EA-9
Spark plug gap 0.8–0.9 mm (0.031–0.035 in)
Cylinder head
Warpage limit 0.05 mm (0.0020 in)
Camshaft
Drive system Chain drive (left)
Camshaft lobe dimensions
Lobe height (Intake) 32.211–32.311 mm (1.2681–1.2721 in)
Limit 32.111 mm (1.2642 in)
Lobe height (Intake high speed) 32.587–32.686 mm (1.2830–1.2869 in)
Limit (High speed) 32.487 mm (1.2790 in)
Lobe height (Exhaust)
Limit 29.320 mm (1.1543 in)
Camshaft runout limit 0.030 mm (0.0012 in)
Rocker arm/rocker arm shaft
Rocker arm inside diameter 9.985–10.000 mm (0.3931–0.3937 in)
Limit 10.015 mm (0.3943 in)
Rocker arm shaft outside diameter 9.966–9.976 mm (0.3924–0.3928 in)
Limit 9.936 mm (0.3912 in)
Rocker-arm-to-rocker-arm-shaft clearance 0.009–0.034 mm (0.0004–0.0013 in)
Limit 0.080 mm (0.0032 in)
Valve, valve seat, valve guide
Valve clearance (cold)
Intake 0.10–0.14 mm (0.0039–0.0055 in)
Exhaust 0.21–0.25 mm (0.0083–0.0098 in)
Valve dimensions
Valve head diameter (intake) 19.40–19.60 mm (0.7638–0.7717 in)
Valve head diameter (exhaust) 16.90–17.10 mm (0.6654–0.6732 in)
Valve seat contact width (intake) 0.90–1.20 mm (0.0354–0.0472 in)
Limit 1.6 mm (0.06 in)
Valve seat contact width (exhaust) 0.90–1.20 mm (0.0354–0.0472 in)
Limit 1.6 mm (0.06 in)
29.420–29.520 mm (1.1583–1.1622 in)
2-3
Page 51

ENGINE SPECIFICATIONS
Valve stem diameter (intake) 4.975–4.990 mm (0.1959–0.1965 in)
Limit 4.920 mm (0.1937 in)
Valve stem diameter (exhaust) 4.960–4.975 mm (0.1953–0.1959 in)
Limit 4.925 mm (0.1939 in)
Valve guide inside diameter (intake) 5.000–5.012 mm (0.1969–0.1973 in)
Limit 5.050 mm (0.1988 in)
Valve guide inside diameter (exhaust) 5.000–5.012 mm (0.1969–0.1973 in)
Limit 5.050 mm (0.1988 in)
Valve-stem-to-valve-guide clearance (intake) 0.010–0.037 mm (0.0004–0.0015 in)
Limit 0.080 mm (0.0032 in)
Valve-stem-to-valve-guide clearance (exhaust) 0.025–0.052 mm (0.0010–0.0020 in)
Limit 0.110 mm (0.0043 in)
Valve stem runout 0.010 mm (0.0004 in)
Valve spring
Free length (intake) 33.79 mm (1.33 in)
Limit 32.10 mm (1.26 in)
Free length (exhaust) 33.80 mm (1.33 in)
Limit 32.06 mm (1.26 in)
Installed length (intake) 28.90 mm (1.14 in)
Installed length (exhaust) 28.90 mm (1.14 in)
Installed compression spring force (intake) 139.50–160.50 N (14.22–16.37 kgf, 31.36–
36.08 lbf)
Installed compression spring force (exhaust) 139.50–160.50 N (14.22–16.37 kgf, 31.36–
36.08 lbf)
Spring rate K1 (intake) 30.67 N/mm (3.13 kgf/mm, 175.13 lbf/in)
Spring rate K2 (intake) 49.28 N/mm (5.03 kgf/mm, 281.39 lbf/in)
Spring rate K1 (exhaust) 30.62 N/mm (3.12 kgf/mm, 174.84 lbf/in)
Spring rate K2 (exhaust) 39.71 N/mm (4.05 kgf/mm, 226.74 lbf/in)
Spring tilt (intake) 1.5 mm (0.06 in)
Spring tilt (exhaust) 1.5 mm (0.06 in)
Winding direction (intake) Clockwise
Winding direction (exhaust) Clockwise
Cylinder
Bore 58.000–58.010 mm (2.2835–2.2839 in)
Taper limit 0.050 mm (0.0020 in)
Out of round limit 0.050 mm (0.0020 in)
Measuring point H 20.0–40.0 mm (0.79–1.57 in)
Warp limit 0.03 mm (0.0012 in)
Piston
Piston-to-cylinder clearance 0.015–0.048 mm (0.0006–0.0019 in)
Diameter 57.962–57.985 mm (2.2820–2.2829 in)
Measuring point (from piston skirt bottom) 6.0 mm (0.24 in)
Piston pin bore inside diameter 14.002–14.013 mm (0.5513–0.5517 in)
Limit 14.043 mm (0.5529 in)
Piston pin outside diameter 13.995–14.000 mm (0.5510–0.5512 in)
Limit 13.975 mm (0.5502 in)
Piston-pin-to-piston-pin-bore clearance 0.002–0.018 mm (0.0001–0.0007 in)
2-4
Page 52

ENGINE SPECIFICATIONS
Piston ring
Top ring
Ring type Barrel
End gap (installed) 0.10–0.25 mm (0.0039–0.0098 in)
Limit 0.50 mm (0.0197 in)
Ring side clearance 0.030–0.065 mm (0.0012–0.0026 in)
Limit 0.115 mm (0.0045 in)
2nd ring
Ring type Taper
End gap (installed) 0.35–0.50 mm (0.0138–0.0197 in)
Limit 0.85 mm (0.0335 in)
Ring side clearance 0.020–0.055 mm (0.0008–0.0022 in)
Limit 0.115 mm (0.0045 in)
Oil ring
End gap (installed) 0.20–0.70 mm (0.0079–0.0276 in)
Crankshaft
Crank assembly width 51.45–51.50 mm (2.026–2.028 in)
Runout limit 0.030 mm (0.0012 in)
Big end side clearance 0.150–0.450 mm (0.0059–0.0177 in)
Big end radial clearance 0.004–0.014 mm (0.0002–0.0006 in)
Clutch
Clutch type Dry, centrifugal automatic
Automatic centrifugal clutch
Clutch shoe thickness 4.0 mm (0.16 in)
Limit 2.5 mm (0.10 in)
Clutch shoe spring free length 34.8 mm (1.37 in)
Clutch housing inside diameter 125.0 mm (4.92 in)
Limit 126.0 mm (4.96 in)
Compression spring free length 95.0 mm (3.74 in)
Limit 85.5 mm (3.37 in)
Weight outside diameter 20.0 mm (0.79 in)
Limit 19.5 mm (0.77 in)
Clutch-in revolution 2200–2600 r/min
Clutch-stall revolution 4700–5300 r/min
V-belt
V-belt width 25.5 mm (1.00 in)
Limit 23.0 mm (0.91 in)
Transmission
Transmission type V-belt automatic
Primary reduction ratio 1.000
Secondary reduction ratio 10.208 (56/16 × 35/12)
Final drive Gear
Gear ratio 2.248–0.708 : 1
Air filter
Air filter element Oil-coated paper element
2-5
Page 53

ENGINE SPECIFICATIONS
Fuel injector
Model/quantity 5D78 00/1
Throttle body
Type/quantity AC28/1
ID mark 2DP1 00
Fuel injection sensor
Crankshaft position sensor resistance 228–342 Ω
Intake air pressure sensor output voltage 3.88–4.12 V at 101.3 kPa (3.88–4.12 V at 1.01
kgf/cm², 3.88–4.12 V at 14.7 psi)
Intake air temperature sensor resistance 5700.0–6300.0 Ω at 0 °C (5700.0–6300.0 Ω at
32 °F)
Coolant temperature sensor resistance 2510–2770 Ω at 20 °C (2510–2770 Ω at 68 °F)
Coolant temperature sensor resistance 210–221 Ω at 100 °C (210–221 Ω at 212 °F)
Idling condition
Fuel line pressure at idling 220–300 kPa (2.2–3.0 kgf/cm², 31.9–43.5 psi)
Engine idling speed 1500–1700 r/min
CO% (Muffler tail pipe) 0.0–1.3 %
Water temperature 82.0–92.0 °C (179.60–197.60 °F)
Throttle grip free play 3.0–5.0 mm (0.12–0.20 in)
2-6
Page 54

CHASSIS SPECIFICATIONS
EAS20015
CHASSIS SPECIFICATIONS
Chassis
Frame type Underbone
Caster angle 26.00°
Trail 92 mm (3.6 in)
Front wheel
Wheel type Cast wheel
Rim size 13M/C × MT3.00
Rim material Aluminum
Wheel travel 100 mm (3.9 in)
Radial wheel runout limit 1.0 mm (0.04 in)
Lateral wheel runout limit 1.0 mm (0.04 in)
Rear wheel
Wheel type Cast wheel
Rim size 13M/C × MT3.50
Rim material Aluminum
Wheel travel 90 mm (3.5 in)
Radial wheel runout limit 1.0 mm (0.04 in)
Lateral wheel runout limit 1.0 mm (0.04 in)
Front tire
Type Tubeless
Size 110/70–13M/C 48P
Manufacturer/model IRC/SS-570F
Wear limit (front) 1.0 mm (0.04 in)
Rear tire
Type Tubeless
Size 130/70–13M/C 63P
Manufacturer/model IRC/SS-560R
Wear limit (rear) 1.0 mm (0.04 in)
Tire air pressure (measured on cold tires)
Front (1 person) 150 kPa (1.50 kgf/cm², 22 psi)
Rear (1 person) 250 kPa (2.50 kgf/cm², 36 psi)
Front (2 persons) 150 kPa (1.50 kgf/cm², 22 psi)
Rear (2 persons) 250 kPa (2.50 kgf/cm², 36 psi)
Front brake
Type Single disc brake
Operation Right hand operation
Front disc brake
Disc outside diameter × thickness 230.0 × 4.0 mm (9.06 × 0.16 in)
Brake disc thickness limit 3.5 mm (0.14 in)
Brake disc runout limit (as measured on wheel) 0.15 mm (0.0059 in)
Brake pad lining thickness (inner) 4.4 mm (0.17 in)
Limit 0.8 mm (0.03 in)
Brake pad lining thickness (outer) 4.4 mm (0.17 in)
Limit 0.8 mm (0.03 in)
2-7
Page 55

CHASSIS SPECIFICATIONS
Master cylinder inside diameter 11.00 mm (0.43 in)
Caliper cylinder inside diameter 33.34 mm (1.31 in)
Specified brake fluid YAMAHA GENUINE BRAKE FLUID (DOT 4)
Rear brake
Type Single disc brake
Operation Left hand operation
Rear disc brake
Disc outside diameter × thickness 230.0 × 4.5 mm (9.06 × 0.18 in)
Brake disc thickness limit 4.0 mm (0.16 in)
Brake disc runout limit (as measured on wheel) 0.15 mm (0.0059 in)
Brake pad lining thickness (inner) 5.3 mm (0.21 in)
Limit 0.8 mm (0.03 in)
Brake pad lining thickness (outer) 5.3 mm (0.21 in)
Limit 0.8 mm (0.03 in)
Master cylinder inside diameter 12.7 mm (0.50 in)
Caliper cylinder inside diameter 33.34 mm (1.31 in)
Specified brake fluid YAMAHA GENUINE BRAKE FLUID (DOT 4)
Steering
Steering bearing type Angular bearing
Center to lock angle (left) 47.5°
Center to lock angle (right) 47.5°
Front suspension
Type Telescopic fork
Spring/shock absorber type Coil spring/oil damper
Front fork travel 100.0 mm (3.94 in)
Fork spring free length 245.3 mm (9.66 in)
Limit 240.0 mm (9.45 in)
Spring rate K1 5.00 N/mm (0.51 kgf/mm, 28.55 lbf/in)
Spring rate K2 7.50 N/mm (0.76 kgf/mm, 42.83 lbf/in)
Spring stroke K1 0.0–68.5 mm (0.00–2.70 in)
Spring stroke K2 68.5–100.0 mm (2.70–3.94 in)
Inner tube outer diameter 30.0 mm (1.18 in)
Recommended oil Fork oil 10W or equivalent
Quantity 86.0 cm³ (2.91 US oz, 3.03 Imp.oz)
Level 78.0 mm (3.07 in)
Rear suspension
Type Unit swing
Spring/shock absorber type Coil spring/oil damper
Rear shock absorber assembly travel 86.0 mm (3.39 in)
Spring installed length 221.6 mm (8.72 in)
Spring rate K1 16.40 N/mm (1.67 kgf/mm, 93.64 lbf/in)
Spring rate K2 33.50 N/mm (3.42 kgf/mm, 191.29 lbf/in)
Spring stroke K1 0.0–54.0 mm (0.00–2.13 in)
Spring stroke K2 54.0–86.0 mm (2.13–3.39 in)
2-8
Page 56

ELECTRICAL SPECIFICATIONS
EAS20016
ELECTRICAL SPECIFICATIONS
Voltage
System voltage 12 V
Ignition system
Ignition system TCI
Advancer type Digital
Ignition timing (B.T.D.C.) 5.0°/1600 r/min
Ignition coil
Minimum ignition spark gap 6.0 mm (0.24 in)
Primary coil resistance 2.16–2.64 Ω
Secondary coil resistance 8.64–12.96 kΩ
Spark plug cap
Material Resin
Resistance 3.75–6.25 kΩ
AC magneto
Standard output 14.0 V, 150 W at 5000 r/min
Stator coil resistance 0.500–0.740 Ω
Rectifier/regulator
Regulated voltage (DC) 13.7–14.7 V
Rectifier capacity (DC) 15.0 A
Battery
Model YTZ7V
Voltage, capacity 12 V, 6.0 Ah
Manufacturer PT.YUASA
Ten hour rate charging current 0.60 A
Bulb voltage, wattage × quantity
Headlight LED
Auxiliary light 12 V, 5.0 W × 2
Tail/brake light 12 V, 10.0 W × 1/LED
Front turn signal light 12 V, 10.0 W × 2
Rear turn signal light 12 V, 10.0 W × 2
Meter lighting LED
Indicator light
Turn signal indicator light LED
High beam indicator light LED
Coolant temperature warning light LED
Engine trouble warning light LED
ABS warning light LED
Starter motor
Power output 0.36 kW
Armature coil resistance 0.0279–0.0341 Ω
Brush overall length 7.0 mm (0.28 in)
2-9
Page 57

ELECTRICAL SPECIFICATIONS
Limit 3.50 mm (0.14 in)
Brush spring force 3.92–5.88 N (400–600 gf, 14.11–21.17 oz)
Commutator diameter 17.6 mm (0.69 in)
Limit 16.6 mm (0.65 in)
Mica undercut (depth) 1.35 mm (0.05 in)
Starter relay
Amperage 50.0 A
Coil resistance 54.00–66.00 Ω
Horn
Horn type Plane
Quantity 1
Maximum amperage 3.0 A
Coil resistance 1.06–1.11 Ω
Turn signal relay
Relay type Condenser
Built-in, self-canceling device No
Fuel sender unit
Sender unit resistance (full) 10.0–14.0 Ω
Sender unit resistance (empty) 267.0–273.0 Ω
Fuses
Main fuse 1 15.0 A
Main fuse 2 7.5 A
Taillight fuse 7.5 A
Signaling system fuse 7.5 A
ABS motor fuse 30.0 A
ABS control unit fuse 7.5 A
ABS solenoid fuse 15.0 A
Spare fuse 30.0 A
Spare fuse 15.0 A
Spare fuse 7.5 A
2-10
Page 58

EAS20017
TIGHTENING TORQUES
EAS30015
GENERAL TIGHTENING TORQUE
SPECIFICATIONS
This chart specifies tightening torques for standard fasteners with a standard ISO thread pitch.
Tightening torque specifications for special components or assemblies are provided for each
chapter of this manual. To avoid warpage, tighten multi-fastener assemblies in a crisscross pattern and progressive stages until the specified
tightening torque is reached. Unless otherwise
specified, tightening torque specifications require clean, dry threads. Components should be
at room temperature.
TIGHTENING TORQUES
A. Distance between flats
B. Outside thread diameter
A (nut) B (bolt)
10 mm 6 mm 6 0.6 4.3
12 mm 8 mm 15 1.5 11
14 mm 10 mm 30 3.0 22
17 mm 12 mm 55 5.5 40
19 mm 14 mm 85 8.5 61
22 mm 16 mm 130 13.0 94
General tightening torques
Nm m·kgf ft·lbf
2-11
Page 59
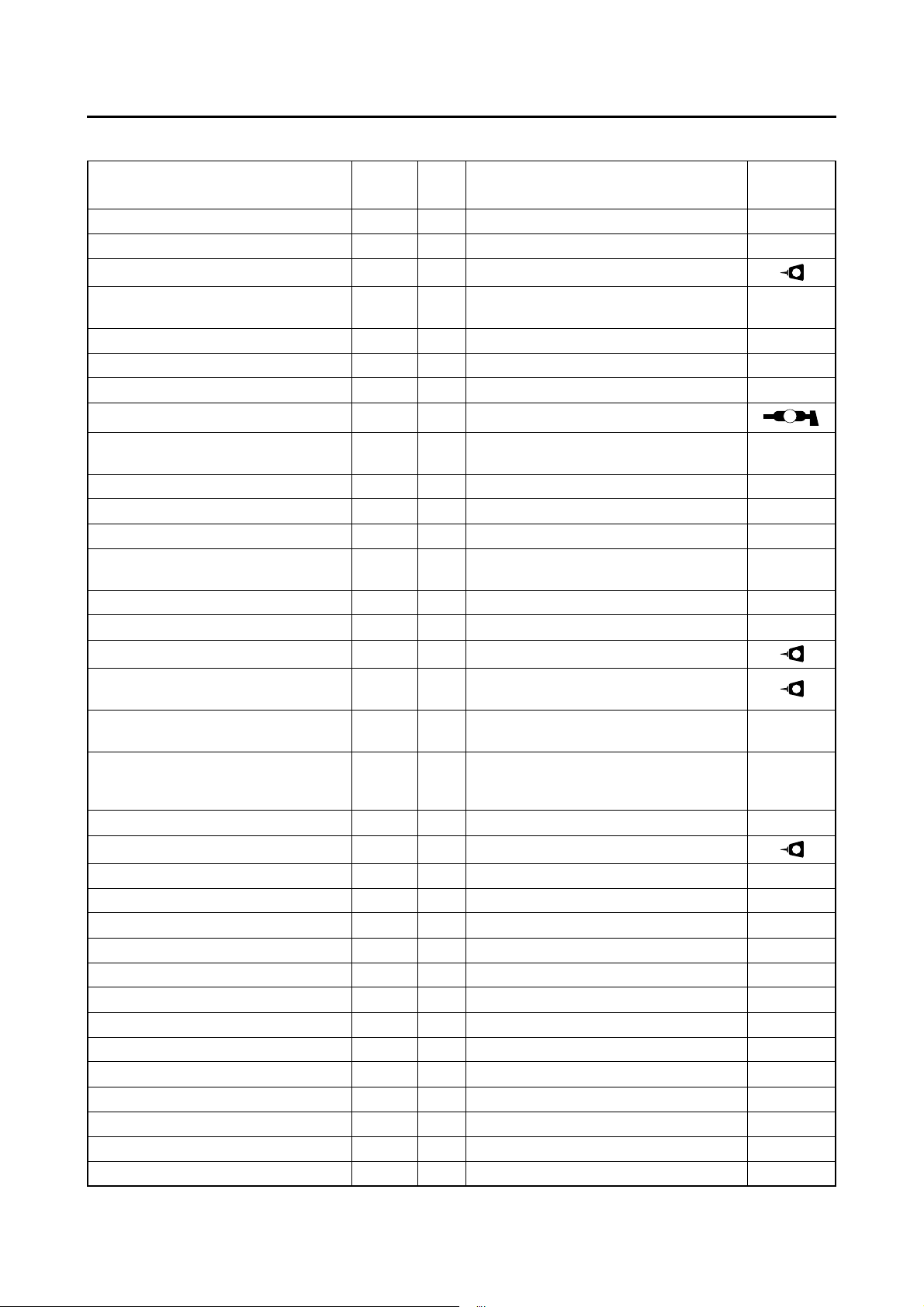
EAS30016
ENGINE TIGHTENING TORQUES
TIGHTENING TORQUES
Item
Thread
size
Q’ty Tightening torque Remarks
Muffler nut M8 2 15 Nm (1.5 m·kgf, 11 ft·lbf)
Muffler bolt M10 3 53 Nm (5.3 m·kgf, 38 ft·lbf)
Muffler protector bolt M6 2 8 Nm (0.8 m·kgf, 5.8 ft·lbf)
sensor
O
2
M12 1 25 Nm (2.5 m·kgf, 18 ft·lbf)
Camshaft stopper plate bolt (M5×16) M5 2 8 Nm (0.8 m·kgf, 5.8 ft·lbf)
Camshaft stopper plate bolt (M6×14) M6 1 8 Nm (0.8 m·kgf, 5.8 ft·lbf)
Cylinder head bolt M6 2 10 Nm (1.0 m·kgf, 7.2 ft·lbf)
Cylinder head nut M8 4 24 Nm (2.4 m·kgf, 17 ft·lbf)
VVA (variable valve actuator) solenoid bolt
M6 2 10 Nm (1.0 m·kgf, 7.2 ft·lbf)
Fuel hose holder M6 1 7 Nm (0.7 m·kgf, 5.1 ft·lbf)
Cylinder head cover bolt M6 4 10 Nm (1.0 m·kgf, 7.2 ft·lbf)
Engine oil check bolt M6 1 7 Nm (0.7 m·kgf, 5.1 ft·lbf)
Cylinder head stud bolt (exhaust
pipe)
M8 2 15 Nm (1.5 m·kgf, 11 ft·lbf)
Camshaft sprocket bolt M8 1 30 Nm (3.0 m·kgf, 22 ft·lbf)
Spark plug M10 1 13 Nm (1.3 m·kgf, 9.4 ft·lbf)
LT
M
Cylinder head blind plug M12 1 28 Nm (2.8 m·kgf, 20 ft·lbf)
Cylinder head cover breather plate
bolt
Valve clearance adjusting screw
locknut
M5 4 4.0 Nm (0.40 m·kgf, 2.9 ft·lbf)
M5 4 7 Nm (0.7 m·kgf, 5.1 ft·lbf)
Timing chain tensioner bolt M6 2 10 Nm (1.0 m·kgf, 7.2 ft·lbf)
Timing chain guide bolt (intake side) M6 1 10 Nm (1.0 m·kgf, 7.2 ft·lbf)
Timing chain guide stopper bolt M6 2 10 Nm (1.0 m·kgf, 7.2 ft·lbf)
Coolant temperature sensor M10 1 15 Nm (1.5 m·kgf, 11 ft·lbf)
Coolant drain bolt (cylinder side) M6 1 10 Nm (1.0 m·kgf, 7.2 ft·lbf)
Water pump assembly bolt M6 3 10 Nm (1.0 m·kgf, 7.2 ft·lbf)
Water pump housing bolt M6 4 10 Nm (1.0 m·kgf, 7.2 ft·lbf)
Radiator fan case bolt M6 5 10 Nm (1.0 m·kgf, 7.2 ft·lbf)
Thermostat assembly bolt M6 2 9 Nm (0.9 m·kgf, 6.5 ft·lbf)
Radiator fan bolt M6 3 10 Nm (1.0 m·kgf, 7.2 ft·lbf)
Radiator bolt M6 4 10 Nm (1.0 m·kgf, 7.2 ft·lbf)
Coolant drain bolt (radiator side) M12 1 1.0 Nm (0.10 m·kgf, 0.72 ft·lbf)
Radiator cover bolt M6 3 10 Nm (1.0 m·kgf, 7.2 ft·lbf)
Oil pump assembly screw M5 2 4.0 Nm (0.40 m·kgf, 2.9 ft·lbf)
Oil pump housing cover screw M3 1 1.0 Nm (0.10 m·kgf, 0.72 ft·lbf)
Oil strainer cover M35 1 32 Nm (3.2 m·kgf, 23 ft·lbf)
LT
LT
Yamaha
bond No.
1215
LT
2-12
Page 60
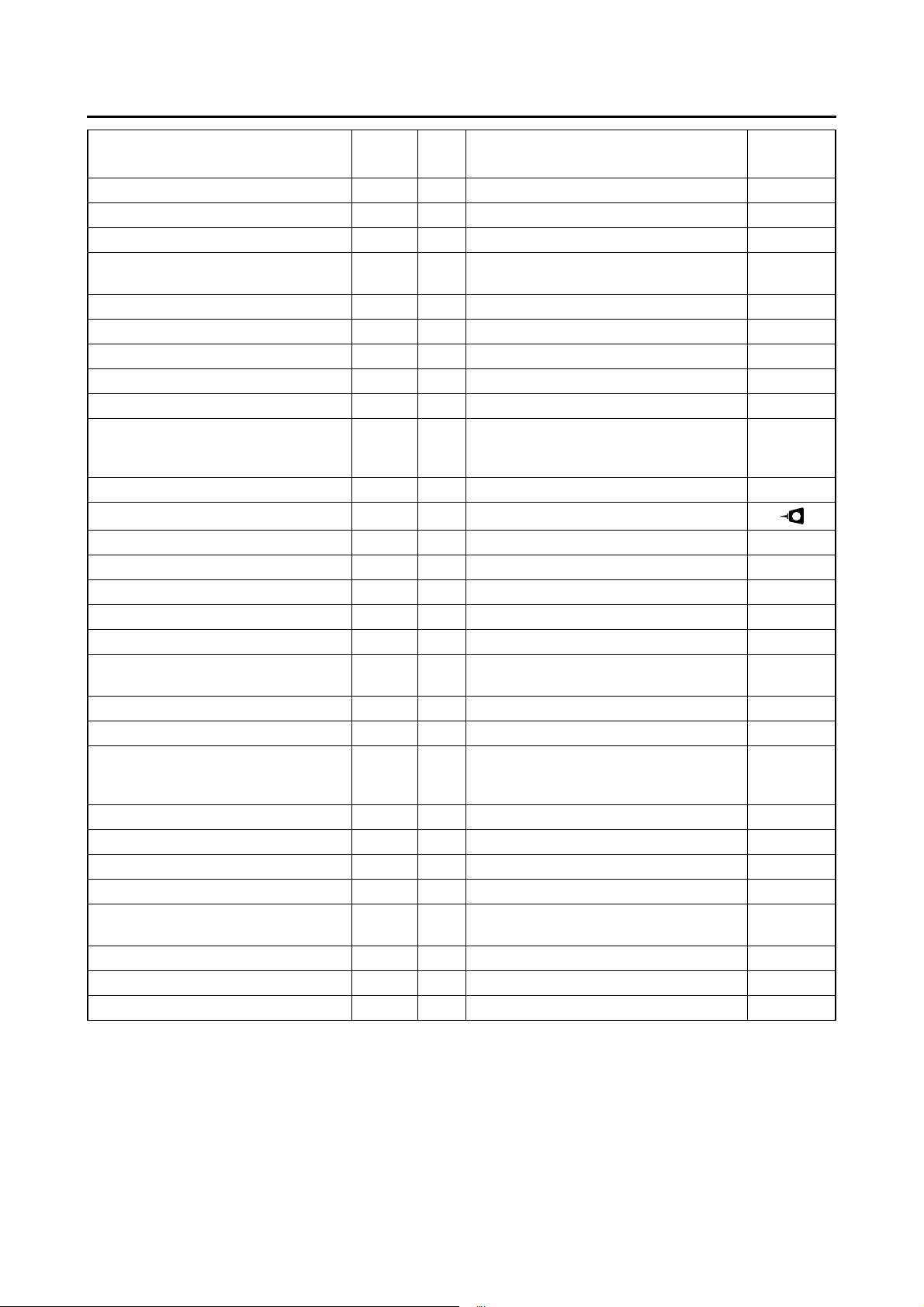
TIGHTENING TORQUES
Item
Fuel injector bolt M6 1 10 Nm (1.0 m·kgf, 7.2 ft·lbf)
Intake manifold bolt M6 2 10 Nm (1.0 m·kgf, 7.2 ft·lbf)
Intake manifold clamp screw M5 1 3.0 Nm (0.30 m·kgf, 2.2 ft·lbf)
ISC (Idle Speed Control) unit holder
screw
Air filter case joint clamp screw M5 1 3.0 Nm (0.30 m·kgf, 2.2 ft·lbf)
Air filter case bolt M6 2 10 Nm (1.0 m·kgf, 7.2 ft·lbf)
Air filter case cover screw M5 6 1.2 Nm (0.12 m·kgf, 0.87 ft·lbf)
Air filter case duct cover screw M5 2 1.2 Nm (0.12 m·kgf, 0.87 ft·lbf)
AC magneto rotor nut M12 1 80 Nm (8.0 m·kgf, 58 ft·lbf)
Crankcase cover bolt 1 M6 3 10 Nm (1.0 m·kgf, 7.2 ft·lbf)
Crankcase cover bolt 2 M6 4 10 Nm (1.0 m·kgf, 7.2 ft·lbf)
Stator coil assembly bolt M6 3 10 Nm (1.0 m·kgf, 7.2 ft·lbf)
Starter motor bolt M6 2 10 Nm (1.0 m·kgf, 7.2 ft·lbf)
Starter motor sub-wire harness bolt M5 1 3.5 Nm (0.35 m·kgf, 2.5 ft·lbf)
Starter motor cover bolt M4 2 2.5 Nm (0.25 m·kgf, 1.8 ft·lbf)
Brush holder screw M4 2 1.5 Nm (0.15 m·kgf, 1.1 ft·lbf)
Crankcase bolt M6 11 10 Nm (1.0 m·kgf, 7.2 ft·lbf)
Crankshaft position sensor holder
bolt
Transmission case cover bolt M8 6 19 Nm (1.9 m·kgf, 14 ft·lbf)
Final transmission oil drain bolt M8 1 20 Nm (2.0 m·kgf, 14 ft·lbf)
Starter clutch cover bolt 1 M6 2 10 Nm (1.0 m·kgf, 7.2 ft·lbf)
Starter clutch cover bolt 2 M6 5 10 Nm (1.0 m·kgf, 7.2 ft·lbf)
V-belt case bolt M6 11 10 Nm (1.0 m·kgf, 7.2 ft·lbf)
Engine oil drain bolt M12 1 20 Nm (2.0 m·kgf, 14 ft·lbf)
Crankcase stud bolt M8 4 13 Nm (1.3 m·kgf, 9.4 ft·lbf)
V-belt case air filter element cover
bolt
Primary fixed sheave nut M12 1 49 Nm (4.9 m·kgf, 35 ft·lbf)
Clutch housing nut M12 1 45 Nm (4.5 m·kgf, 33 ft·lbf)
Secondary sheave nut M28 1 55 Nm (5.5 m·kgf, 40 ft·lbf)
Thread
size
M6 1 5 Nm (0.5 m·kgf, 3.6 ft·lbf)
M6 2 10 Nm (1.0 m·kgf, 7.2 ft·lbf)
M6 6 7 Nm (0.7 m·kgf, 5.1 ft·lbf)
Q’ty Tightening torque Remarks
Yamaha
bond No.
1215
LT
Yamaha
bond No.
1215
2-13
Page 61
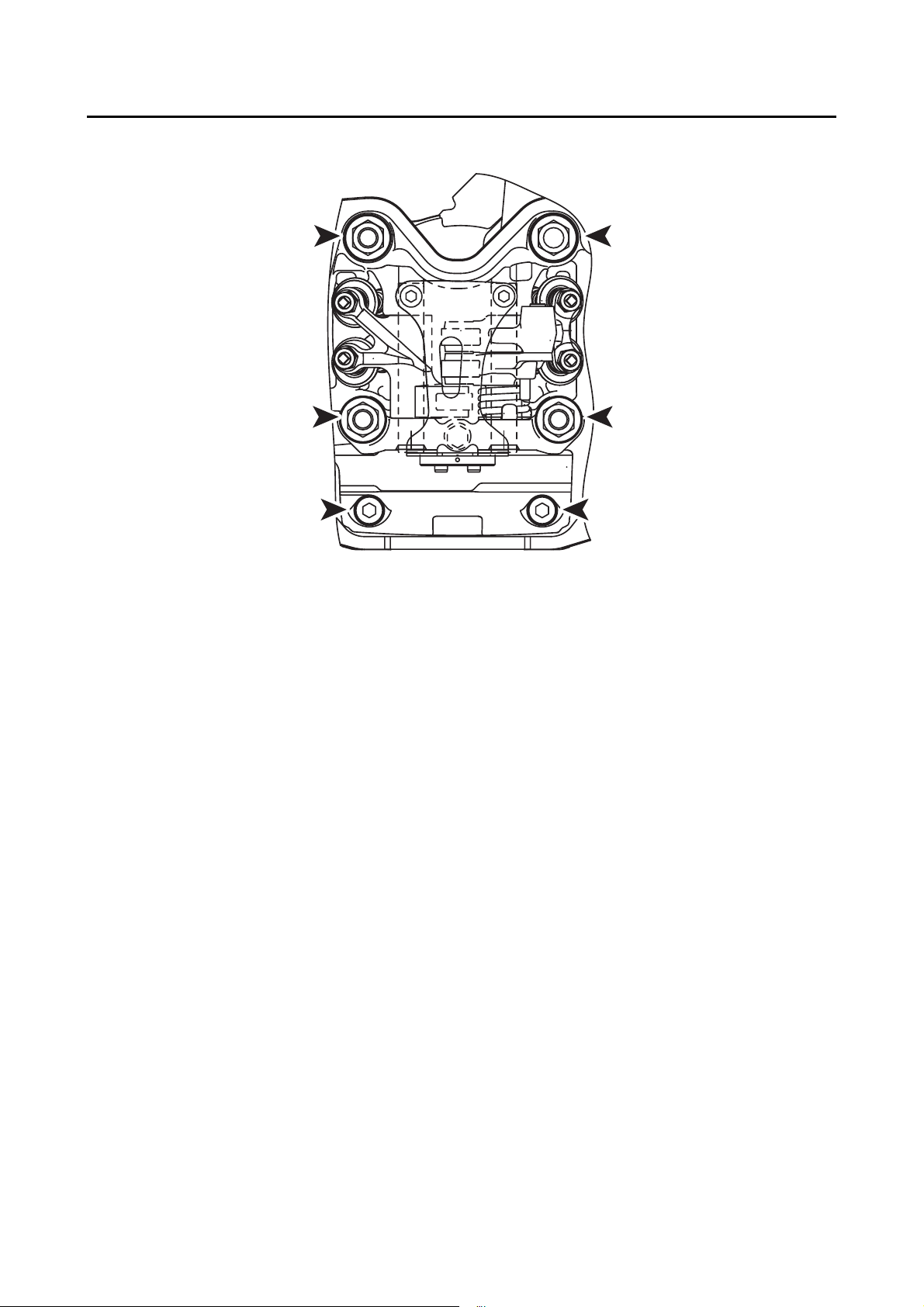
Cylinder head tightening sequence:
TIGHTENING TORQUES
3
1
6
4
2
5
2-14
Page 62

EAS30017
CHASSIS TIGHTENING TORQUES
TIGHTENING TORQUES
Item
Engine bracket nut M10 1 52 Nm (5.2 m·kgf, 38 ft·lbf)
Engine mounting nut (front right
side)
Engine mounting bolt (front left side) M10 1 68 Nm (6.8 m·kgf, 49 ft·lbf)
Engine mounting nut (rear side) M10 1 68 Nm (6.8 m·kgf, 49 ft·lbf)
Engine ground lead bolt M6 1 7 Nm (0.7 m·kgf, 5.1 ft·lbf)
Headlight unit screw M6 2 7 Nm (0.7 m·kgf, 5.1 ft·lbf)
Lower handlebar cover screw M5 1 1.8 Nm (0.18 m·kgf, 1.3 ft·lbf)
Front lower cowling screw M5 2 1.8 Nm (0.18 m·kgf, 1.3 ft·lbf)
Meter assembly screw M5 4 1.8 Nm (0.18 m·kgf, 1.3 ft·lbf)
Front upper cowling assembly screw M5 3 1.8 Nm (0.18 m·kgf, 1.3 ft·lbf)
Meter assembly panel screw M5 2 1.8 Nm (0.18 m·kgf, 1.3 ft·lbf)
Leg shield bolt M6 1 7 Nm (0.7 m·kgf, 5.1 ft·lbf)
Key shutter screw M5 1 3.5 Nm (0.35 m·kgf, 2.5 ft·lbf)
Front upper panel screw M5 6 1.8 Nm (0.18 m·kgf, 1.3 ft·lbf)
Front side cowling screw M5 8 1.8 Nm (0.18 m·kgf, 1.3 ft·lbf)
Front side cover screw M5 6 1.8 Nm (0.18 m·kgf, 1.3 ft·lbf)
Front cowling assembly screw (M5 ×
15)
Front cowling assembly screw (M5 ×
11)
Meter assembly panel bolt M6 2 3.8 Nm (0.38 m·kgf, 2.8 ft·lbf)
Footrest board and rear side cover
bolt
Footrest board assembly bolt M6 4 3.8 Nm (0.38 m·kgf, 2.8 ft·lbf)
Footrest board screw M5 6 1.8 Nm (0.18 m·kgf, 1.3 ft·lbf)
Grab bar bolt M8 4 17 Nm (1.7 m·kgf, 12 ft·lbf)
Upper handlebar cover assembly
screw
Turn signal light screw M5 6 1.8 Nm (0.18 m·kgf, 1.3 ft·lbf)
Handlebar switch screw (right) M5 2 2.3 Nm (0.23 m·kgf, 1.7 ft·lbf)
Fuel tank cover screw M5 4 1.8 Nm (0.18 m·kgf, 1.3 ft·lbf)
Center side cover screw M5 2 1.8 Nm (0.18 m·kgf, 1.3 ft·lbf)
Tail/brake light outer cover screw M5 2 1.8 Nm (0.18 m·kgf, 1.3 ft·lbf)
Rear side cover assembly screw M5 2 1.8 Nm (0.18 m·kgf, 1.3 ft·lbf)
Seat lock bolt M6 2 7 Nm (0.7 m·kgf, 5.1 ft·lbf)
Seat nut M6 3 7 Nm (0.7 m·kgf, 5.1 ft·lbf)
Seat hinge nut M6 1 7 Nm (0.7 m·kgf, 5.1 ft·lbf)
Seat lock cable guide bolt M5 1 1.5 Nm (0.15 m·kgf, 1.1 ft·lbf)
Center cover bolt M5 1 1.8 Nm (0.18 m·kgf, 1.3 ft·lbf)
Thread
size
M10 1 68 Nm (6.8 m·kgf, 49 ft·lbf)
M5 4 1.8 Nm (0.18 m·kgf, 1.3 ft·lbf)
M5 2 1.8 Nm (0.18 m·kgf, 1.3 ft·lbf)
M6 2 7 Nm (0.7 m·kgf, 5.1 ft·lbf)
M5 2 1.8 Nm (0.18 m·kgf, 1.3 ft·lbf)
Q’ty Tightening torque Remarks
2-15
Page 63

TIGHTENING TORQUES
Item
Thread
size
Q’ty Tightening torque Remarks
Battery cover screw M5 2 1.8 Nm (0.18 m·kgf, 1.3 ft·lbf)
Storage box bolt M6 4 7 Nm (0.7 m·kgf, 5.1 ft·lbf)
Seat hinge bolt M6 4 7 Nm (0.7 m·kgf, 5.1 ft·lbf)
Rear fender bolt M6 4 7 Nm (0.7 m·kgf, 5.1 ft·lbf)
Front brake master cylinder holder
bolt
Brake master cylinder reservoir cap
screw
Front brake hose union bolt (master
cylinder side)
Rear brake hose union bolt (master
cylinder side)
Throttle cable holder bolt (handlebar
switch side)
M6 2 11 Nm (1.1 m·kgf, 8.0 ft·lbf)
M4 4 1.5 Nm (0.15 m·kgf, 1.1 ft·lbf)
M10 1 29 Nm (2.9 m·kgf, 21 ft·lbf)
M10 1 29 Nm (2.9 m·kgf, 21 ft·lbf)
M5 1 2.5 Nm (0.25 m·kgf, 1.8 ft·lbf)
Throttle cable adjusting locknut M7 1 3.8 Nm (0.38 m·kgf, 2.8 ft·lbf)
Rearview mirror locknut M10 2 22 Nm (2.2 m·kgf, 16 ft·lbf)
Rearview mirror adaptor M10 2 22 Nm (2.2 m·kgf, 16 ft·lbf)
Handlebar switch screw (left) M5 2 2.3 Nm (0.23 m·kgf, 1.7 ft·lbf)
Rear brake master cylinder holder
bolt
M6 2 11 Nm (1.1 m·kgf, 8.0 ft·lbf)
Rear brake lever pivot bolt M6 1 6 Nm (0.6 m·kgf, 4.3 ft·lbf)
Rear brake lever pivot nut M6 1 6 Nm (0.6 m·kgf, 4.3 ft·lbf)
Front brake lever pivot bolt M6 1 6 Nm (0.6 m·kgf, 4.3 ft·lbf)
Front brake lever pivot nut M6 1 6 Nm (0.6 m·kgf, 4.3 ft·lbf)
Grip end bolt (left) M6 1 7 Nm (0.7 m·kgf, 5.1 ft·lbf)
Grip end bolt (right) M6 1 7 Nm (0.7 m·kgf, 5.1 ft·lbf)
Brake light switch screw M4 2 1.2 Nm (0.12 m·kgf, 0.87 ft·lbf)
Handlebar bracket nut M10 1 63 Nm (6.3 m·kgf, 46 ft·lbf)
Upper handlebar holder bolt M8 4 21 Nm (2.1 m·kgf, 15 ft·lbf)
Main switch bolt M8 2 19 Nm (1.9 m·kgf, 14 ft·lbf)
Lower ring nut M25 1 See TIP.
Upper ring nut M25 1 See TIP.
Horn bracket bolt M6 1 7 Nm (0.7 m·kgf, 5.1 ft·lbf)
Horn bolt M6 1 7 Nm (0.7 m·kgf, 5.1 ft·lbf)
Lower bracket pinch bolt M10 4 53 Nm (5.3 m·kgf, 38 ft·lbf)
Front fork damper rod bolt M10 2 23 Nm (2.3 m·kgf, 17 ft·lbf)
Ignition coil bolt M6 2 7 Nm (0.7 m·kgf, 5.1 ft·lbf)
Ignition coil bracket bolt M6 2 7 Nm (0.7 m·kgf, 5.1 ft·lbf)
Throttle cable guide bolt M6 1 7 Nm (0.7 m·kgf, 5.1 ft·lbf)
Front fender bolt M6 4 8 Nm (0.8 m·kgf, 5.8 ft·lbf)
Front wheel sensor bolt M6 1 7 Nm (0.7 m·kgf, 5.1 ft·lbf)
Front brake caliper bolt M10 2 35 Nm (3.5 m·kgf, 25 ft·lbf)
S
S
LT
2-16
Page 64

TIGHTENING TORQUES
Item
Front brake hose union bolt (brake
caliper side)
Thread
size
Q’ty Tightening torque Remarks
M10 1 29 Nm (2.9 m·kgf, 21 ft·lbf)
Brake caliper bleed screw M8 2 6 Nm (0.6 m·kgf, 4.3 ft·lbf)
Front brake hose guide bolt M6 1 7 Nm (0.7 m·kgf, 5.1 ft·lbf)
Front wheel axle nut M10 1 40 Nm (4.0 m·kgf, 29 ft·lbf)
Front brake hose holder bolt M6 1 7 Nm (0.7 m·kgf, 5.1 ft·lbf)
Front brake disc bolt M8 3 23 Nm (2.3 m·kgf, 17 ft·lbf)
Front wheel sensor rotor bolt M5 3 8 Nm (0.8 m·kgf, 5.8 ft·lbf)
Rear wheel sensor rotor bolt M5 3 8 Nm (0.8 m·kgf, 5.8 ft·lbf)
Rear brake hose bracket bolt M6 1 7 Nm (0.7 m·kgf, 5.1 ft·lbf)
Rear brake hose holder bolt (front
side)
Rear brake hose holder bolt (rear
side)
M6 1 7 Nm (0.7 m·kgf, 5.1 ft·lbf)
M6 1 7 Nm (0.7 m·kgf, 5.1 ft·lbf)
Rear brake disc bolt M8 3 23 Nm (2.3 m·kgf, 17 ft·lbf)
Rear brake caliper bolt M10 2 35 Nm (3.5 m·kgf, 25 ft·lbf)
Rear wheel sensor bolt M6 1 7 Nm (0.7 m·kgf, 5.1 ft·lbf)
Rear wheel axle nut M16 1 125 Nm (12.5 m·kgf, 90 ft·lbf)
Rear brake hose union bolt (brake
caliper side)
M10 1 29 Nm (2.9 m·kgf, 21 ft·lbf)
Front brake hose guide bolt M6 1 7 Nm (0.7 m·kgf, 5.1 ft·lbf)
Hydraulic unit assembly bolt M6 3 7 Nm (0.7 m·kgf, 5.1 ft·lbf)
Front brake hose union bolt (hydraulic unit assembly side)
Rear brake hose union bolt (hydraulic unit assembly side)
M10 2 29 Nm (2.9 m·kgf, 21 ft·lbf)
M10 2 29 Nm (2.9 m·kgf, 21 ft·lbf)
Rectifier/regulator nut M6 2 7 Nm (0.7 m·kgf, 5.1 ft·lbf)
Front cowling assembly bracket M8 2 23 Nm (2.3 m·kgf, 17 ft·lbf)
Rear shock absorber assembly nut M8 2 16 Nm (1.6 m·kgf, 12 ft·lbf)
Rear shock absorber assembly bolt M8 2 21 Nm (2.1 m·kgf, 15 ft·lbf)
Swingarm mounting bolt M10 2 57 Nm (5.7 m·kgf, 41 ft·lbf)
Bearing retaining plate bolt M6 3 7 Nm (0.7 m·kgf, 5.1 ft·lbf)
Fuel tank bolt M6 4 7 Nm (0.7 m·kgf, 5.1 ft·lbf)
Fuel pump bracket bolt M5 4 4.0 Nm (0.40 m·kgf, 2.9 ft·lbf)
Throttle cable holder bolt (throttle
body side)
M6 2 7 Nm (0.7 m·kgf, 5.1 ft·lbf)
Coolant reservoir bolt M6 1 7 Nm (0.7 m·kgf, 5.1 ft·lbf)
LT
LT
LT
LT
Sidestand switch bolt M5 2 4.0 Nm (0.40 m·kgf, 2.9 ft·lbf)
Centerstand spring hook bolt M6 1 7 Nm (0.7 m·kgf, 5.1 ft·lbf)
Sidestand nut M8 1 24 Nm (2.4 m·kgf, 17 ft·lbf)
Passenger footrest assembly bolt M8 4 28 Nm (2.8 m·kgf, 20 ft·lbf)
2-17
LT
Page 65

TIGHTENING TORQUES
T
IP
Steering column ring nut
1. Tighten the lower ring nut 38 Nm (3.8 m·kgf, 27 ft·lbf) with a torque wrench and the steering nut
wrench, and then loosen the nut 1/4 turn.
2. Tighten the lower ring nut 16 Nm (1.6 m·kgf, 12 ft·lbf) with a torque wrench and the steering nut
wrench.
3. Install the rubber washer and the center ring nut.
4. Finger tighten the center ring nut, align the slots of both ring nuts, and then install the lock washer.
5. Hold the lower and center ring nuts, and then tighten the upper ring nut 75 Nm (7.5 m·kgf, 54 ft·lbf)
with a torque wrench and the steering nut wrench.
2-18
Page 66

LUBRICATION POINTS AND LUBRICANT TYPES
EAS20018
LUBRICATION POINTS AND LUBRICANT TYPES
EAS30018
ENGINE
Lubrication point Lubricant
Bearings
O-rings
O-rings (cam shaft)
Oil seals
Rocker arm stopper pin
Cylinder head nut contact face and stud bolt thread
Camshaft lobes
Decompression cam
Rocker arm shafts
Valve stems and valve guide (intake and exhaust)
Valve stem seals
Valve stem ends (intake and exhaust)
Rocker arm valve inner surface
Camshaft sprocket
Connecting rod big end face
Piston pin outer surface
E
LS
M
LS
M
M
M
M
M
M
E
M
M
M
E
E
Piston, piston ring, and cylinder inner surface
Crank pin
Cam chain sprocket inner surface
Oil pump drive gear inner surface
Oil pump shaft
O-ring (fuel injector)
Starter wheel and bearing
Starter clutch idle gear inner surface
Drive axle and bearings
Crankshaft threads and conical spring washer outer mating surface
Timing chain tensioner bolts
Crankcase mating surfaces
Crankcase bolt
E
E
M
M
E
E
E
M
LS
LS
Yamaha bond
No.1215®
Yamaha bond
No.1215®
Yamaha bond
No.1215®
2-19
Page 67

LUBRICATION POINTS AND LUBRICANT TYPES
2-20
Page 68

LUBRICATION SYSTEM CHART AND DIAGRAMS
EAS20019
LUBRICATION SYSTEM CHART AND DIAGRAMS
EAS30020
ENGINE OIL LUBRICATION CHART
5
4
3
2
1
2-21
Page 69

1. Oil strainer
2. Oil pump assembly
3. Crankshaft
4. Oil nozzle
5. Camshaft
LUBRICATION SYSTEM CHART AND DIAGRAMS
2-22
Page 70
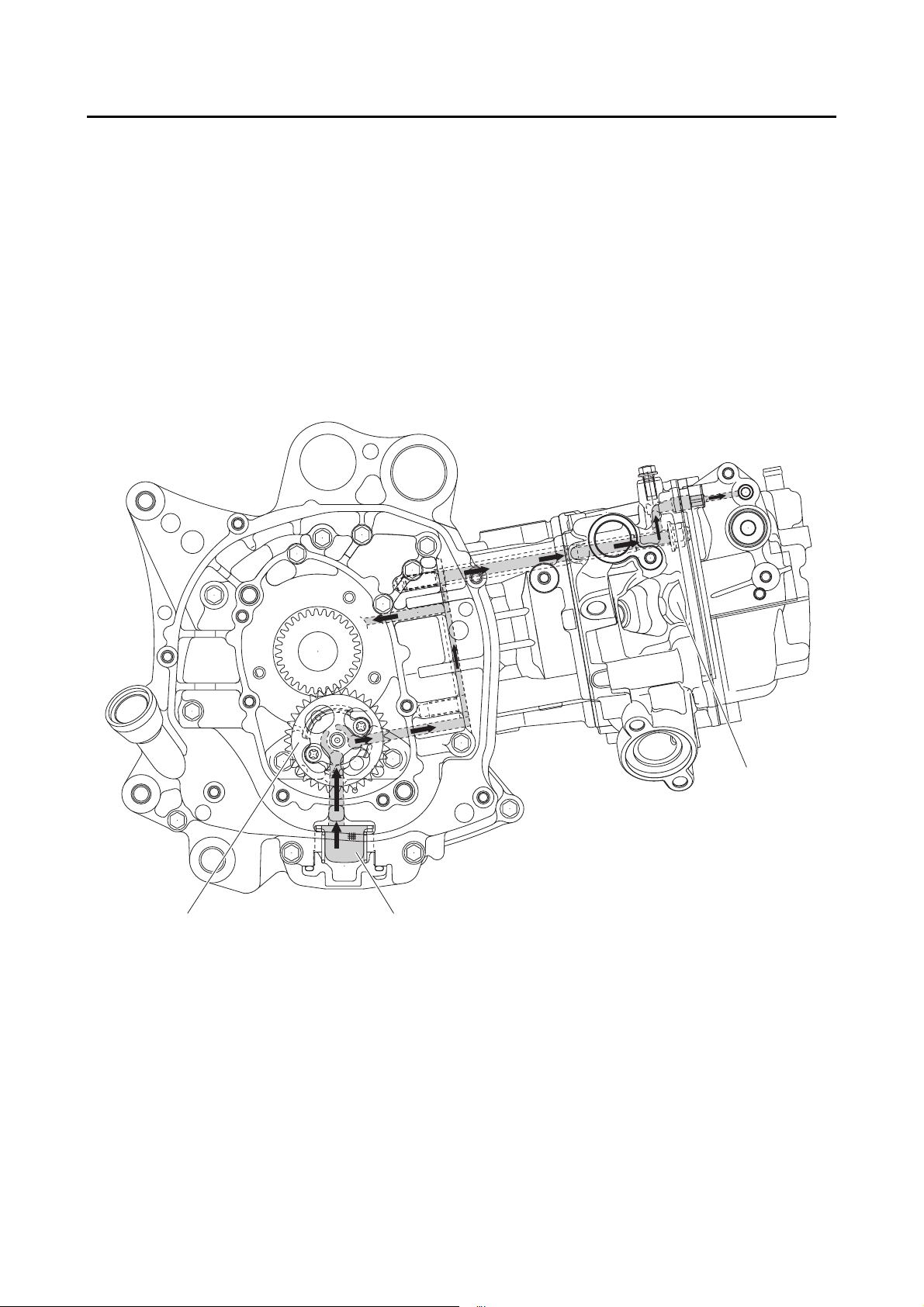
LUBRICATION SYSTEM CHART AND DIAGRAMS
EAS30021
LUBRICATION DIAGRAMS
3
2
1
2-23
Page 71

1. Oil strainer
2. Oil pump assembly
3. Camshaft
LUBRICATION SYSTEM CHART AND DIAGRAMS
2-24
Page 72

LUBRICATION SYSTEM CHART AND DIAGRAMS
4
3
2
1
2-25
Page 73

LUBRICATION SYSTEM CHART AND DIAGRAMS
1. Oil strainer
2. Oil pump assembly
3. Crankshaft
4. Rocker arm/Valve stem end
2-26
Page 74
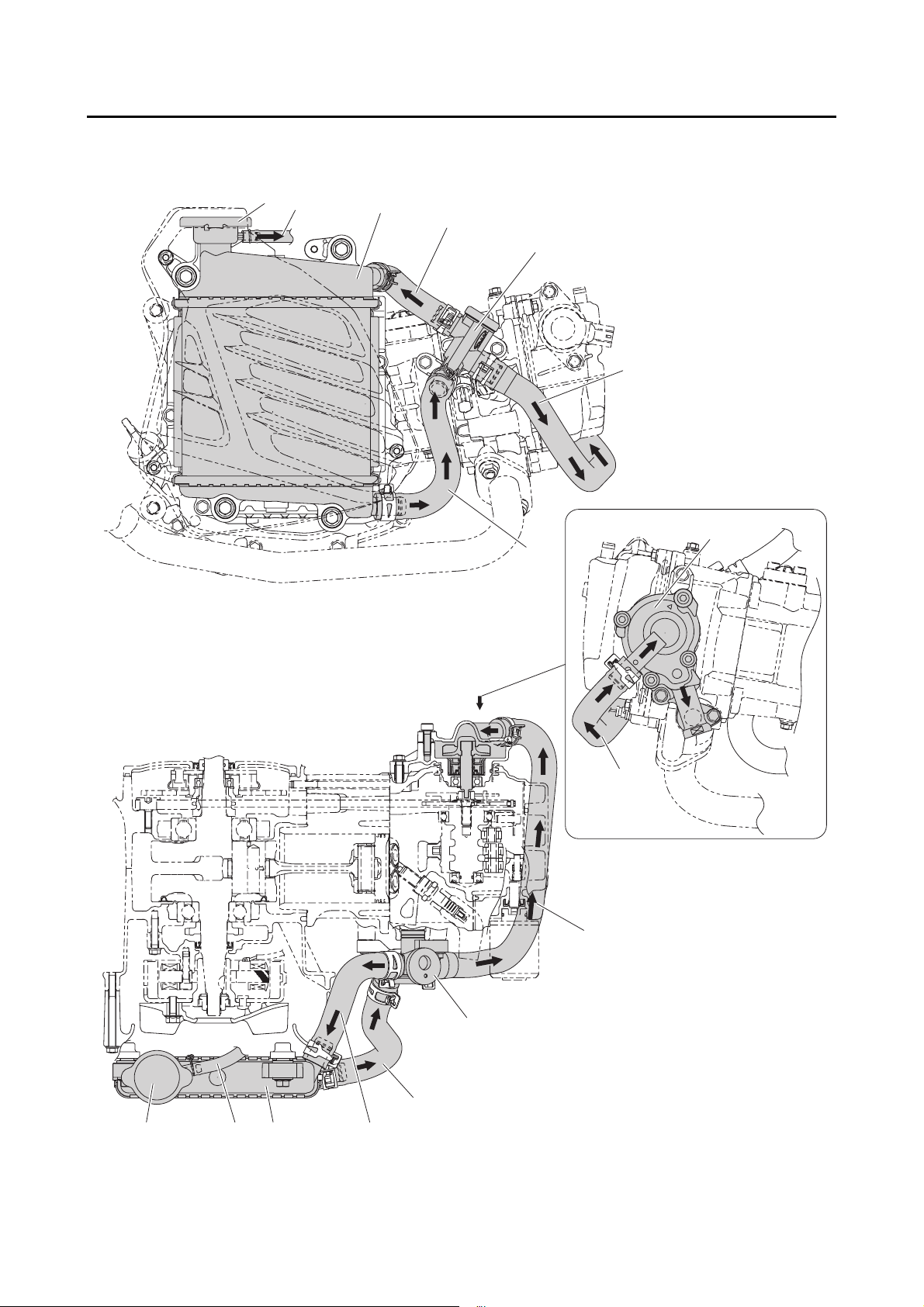
EAS20020
COOLING SYSTEM DIAGRAMS
1
2
3
COOLING SYSTEM DIAGRAMS
4
6
7
8
5
7
7
6
5
4321
2-27
Page 75

1. Radiator cap
2. Coolant reservoir hose
3. Radiator
4. Radiator inlet hose
5. Radiator outlet hose
6. Thermostat assembly
7. Water pump inlet hose
8. Water pump assembly
COOLING SYSTEM DIAGRAMS
2-28
Page 76

EAS20021
CABLE ROUTING
Handlebar (front view)
CABLE ROUTING
1
4
5
A
1
1
B
2
2
2
6
5
4
7
C
3
2-29
Page 77

1. Front brake hose (front brake master cylinder to
hydraulic unit)
2. Rear brake hose (rear brake master cylinder to
hydraulic unit)
3. Rear brake light switch lead
4. Throttle cable (decelerator cable)
5. Throttle cable (accelerator cable)
6. Front brake light switch lead
7. Lower handlebar cover
A. 40
–44 mm (1.57–1.73 in)
B. 5–9 mm (0.20–0.35 in)
C. Route the throttle cables through the hole in the
lower handlebar cover.
CABLE ROUTING
2-30
Page 78

Handlebar (left side view)
CABLE ROUTING
4
3
7
7
1
3
4
6
A
7
1
1
3
4
2
1
6
8
5
4
5
2
5
6
B
11
6
3
10
9
8
6
2-31
Page 79

1. Rear brake hose (rear brake master cylinder to
hydraulic unit)
2. Rear brake light switch lead
3. Throttle cable (decelerator cable)
4. Throttle cable (accelerator cable)
5. Handlebar switch coupler (left handlebar switch)
6. Wire harness
7. Front brake hose (front brake master cylinder to
hydraulic unit)
8. Handlebar switch coupler (right handlebar switch)
9. Front brake light switch lead
10. Handlebar switch connector (left handlebar switch)
11. Bracket
A. Route the throttle cable (accelerator cable) to the
front of the throttle cable (decelerator cable).
B. Insert the projection on the wire harness holder
into the hole in the bracket.
CABLE ROUTING
2-32
Page 80

Front frame (front and left side view)
CABLE ROUTING
4
19
14
15
18
10
19
22
20
21
B
18
2
1
13
12
11
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
3
5
23
A
9
10
11
9
16
4
17
14
19
18
12
19
18
11
9
10
15
C
24
2-33
Page 81

1. Main switch lead
2. Rectifier/regulator
3. Meter assembly lead
4. Turn signal relay
5. Turn signal relay lead
6. Headlight lead
7. Auxiliary light lead
8. Front turn signal light lead (front left turn signal
light)
9. Front wheel sensor lead
10. Front brake hose (hydraulic unit to front brake
caliper)
11. Wire harness
12. Rear brake hose (hydraulic unit to rear brake
caliper)
13. Hydraulic unit assembly lead
14. Hydraulic unit assembly
15. Front turn signal light lead (front right turn signal
light)
16. Meter assembly
17. Front wheel sensor coupler
18. Rear brake hose (rear brake master cylinder to
hydraulic unit)
19. Front brake hose (front brake master cylinder to
hydraulic unit)
20. Throttle cable (decelerator cable)
21. Throttle cable (accelerator cable)
22. Seat lock cable
23. Rectifier/regulator lead
24. Front turn signal light
A. After connecting the meter assembly coupler,
install the coupler cover completely until it contacts
the meter assembly.
B. Route the throttle cable (accelerator cable) to the
outside of the throttle cable (decelerator cable).
C. Route the front turn signal light lead as shown in
the illustration.
CABLE ROUTING
2-34
Page 82

Front fork (rear and right side view)
CABLE ROUTING
1
1
C
2
3
F
G
B
3
6
7
7
B
C
7
6
2
C
1
A
6
5
4
D
E
3
7
6
6
6
7
B
5
I
6 7
F
H
G
2-35
Page 83

1. Horn lead
2. Front brake hose holder
3. Horn
4. Front wheel sensor
5. Front brake caliper
6. Front brake hose (hydraulic unit to front brake
caliper)
7. Front wheel sensor lead
A. Route the front brake hose (hydraulic unit to front
brake caliper) through the guide.
B. Position the holder within the range shown in the
illustration.
C. Route the horn lead through the holder.
D. Connect the horn lead (pink) to the horn terminal.
E. Connect the horn lead (brown) to the horn
terminal.
F. I n w a r d
G. Outward
H. Forward
I. Rearward
CABLE ROUTING
2-36
Page 84

Frame (left side view)
10
11
16
C
9
16
14
10
CABLE ROUTING
18
21
20
19
17
16
10
14
E
C
11
12
13
15
E
9
A
1
9
8
7
6
2
15
2
1
B
3
D
3
4
11
4
5
6
8
6
F
G
7
H
2-37
Page 85

1. Throttle cable (decelerator cable)
2. Throttle cable (accelerator cable)
3. Seat lock cable
4. Tail/brake light assembly lead
5. Sidestand switch
6. Frame ground lead
7. Fuel pump lead
8. Sidestand switch lead
9. Wire harness
10. AC magneto lead
11. Starter motor lead
12. Starter motor sub-wire harness
13. Engine ground lead
14. Ignition coil lead
15. Positive battery lead
16. Negative battery lead
17.
Ya m a h a diagnostic tool lead
18. ABS test coupler lead
19. ECU lead
20. Fuse box 1
21. Fuse box 2
A. White tape
B. Route the throttle cable (accelerator cable) and
throttle cable (decelerator cable) through the guide.
Be sure to route the throttle cable (accelerator
cable) above the throttle cable (decelerator cable).
C. Fasten the wire harness and negative battery lead
with the plastic band.
D. Make sure that the engine ground lead terminal
contacts the stopper on the crankcase.
E. To starter relay
F. Install the frame ground terminal as shown in the
illustration.
G. 90
°
H. Install the frame ground lead terminal so that the
crimped section of the terminal that secures the
lead is facing upward.
CABLE ROUTING
2-38
Page 86

Frame (right side view)
4
CABLE ROUTING
21
7
22
23
1
2
1
20
2
6
5
4
3
6
8
7
9
8
10
15
13
1211
14
19
C
1
20
18
17
A
16
15
13
B
12
24
9
2-39
Page 87

1. Coolant temperature sensor lead
2. Throttle body sensor assembly lead
3. Starter motor lead
4. ISC (Idle Speed Control) unit lead
5. AC magneto lead
6. Fuel injector lead
7. O
sensor lead
2
8. VVA (variable valve actuator) solenoid lead
9. Ignition coil
10. Rear brake hose (hydraulic unit to rear brake
caliper)
11. Rear wheel sensor lead
12. Fuel tank overflow tray
13. Rear wheel sensor coupler
14. Wire harness
15. Fuel hose
16. VVA (variable valve actuator) solenoid
17. Spark plug lead
18. Water pump inlet hose
19. Thermostat assembly
20. Radiator inlet hose
21. Sidestand switch lead
22. Fuel pump lead
23. Fuel pump
24. Ignition coil lead
A. Route the spark plug lead between the VVA
(variable valve actuator) solenoid and the water
pump inlet hose. Make sure that the spark plug
lead does not contact the VVA (variable valve
actuator) solenoid or water pump inlet hose.
B. Insert the projection on the rear wheel sensor
coupler into the hole in the fuel tank overflow tray.
C. Fasten the coolant temperature sensor lead to the
radiator inlet hose with the plastic band. Point the
end of the plastic band outward.
CABLE ROUTING
2-40
Page 88

Frame (top view)
CABLE ROUTING
E
9
5
3
4
3
2
1
6
9
D
6
5
7
8
13
9
9
B
4
12
C
11
A
10
2-41
Page 89

1. ECU lead
2. Positive battery lead
3. Fuse box 1
4. Fuse box 2
5. Fuel tank overflow tray
6. Negative battery lead
7. ABS test coupler lead
8.
Ya m a h a diagnostic tool lead
9. Storage box
10. Tail/brake light assembly lead
11. Seat lock cable
12. ABS test coupler
13.
Ya m a h a diagnostic tool coupler
A. Route the seat lock cable through the hole in the
frame.
B. Install fuse box 2 completely onto the tab on the
storage box.
C. Install the protective cap onto the ABS test
coupler.
D. Route the negative battery lead through the hole in
the storage box.
E. Install fuse box 1 completely onto the tab on the
storage box.
CABLE ROUTING
2-42
Page 90
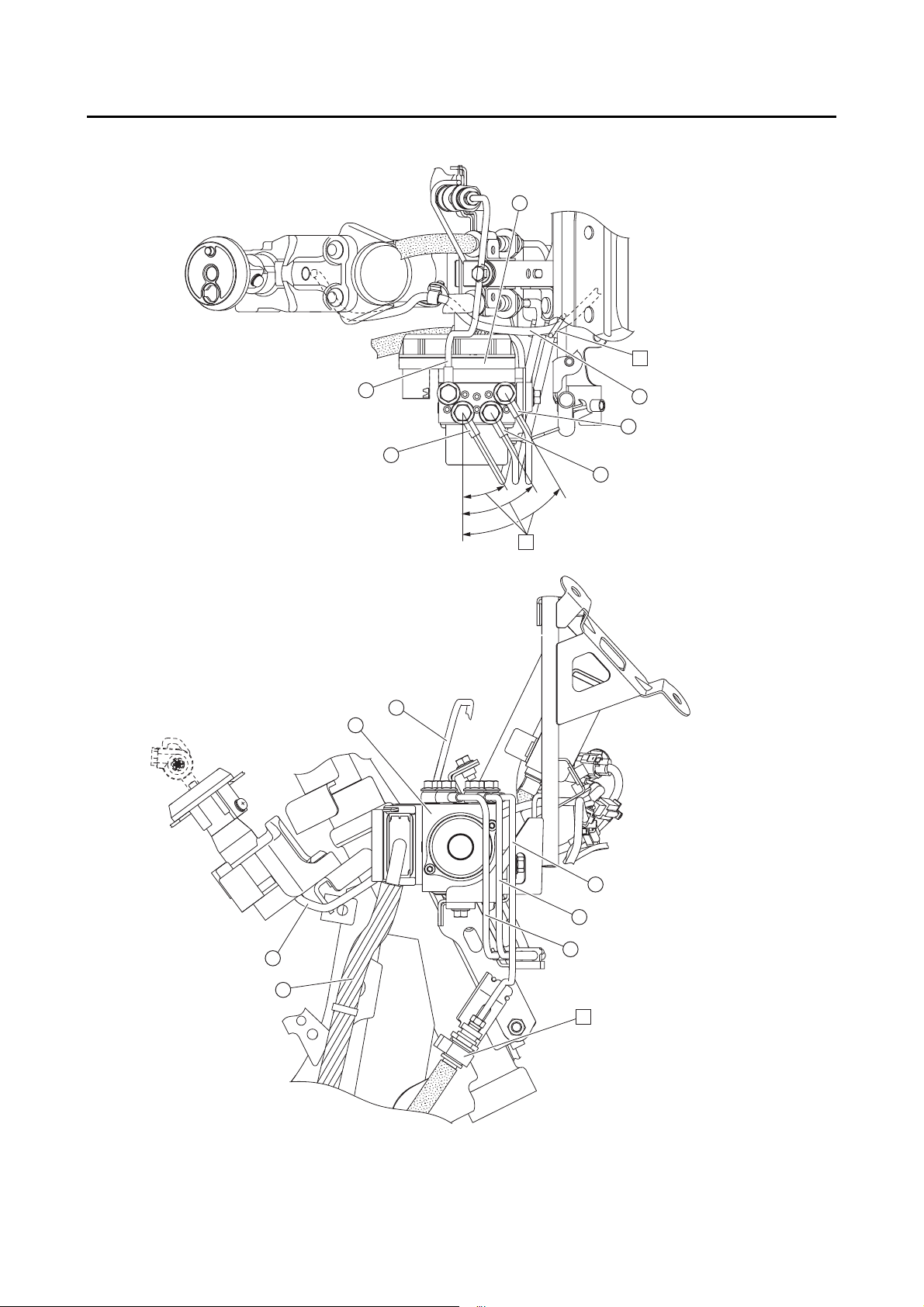
Hydraulic unit (top and right side view)
CABLE ROUTING
1
A
6
5
B
6
1
2
3
4
3
4
2
7
5
C
2-43
Page 91

1. Hydraulic unit assembly
2. Main switch lead
3. Rear brake hose (hydraulic unit to rear brake
caliper)
4. Rear brake hose (rear brake master cylinder to
hydraulic unit)
5. Front brake hose (front brake master cylinder to
hydraulic unit)
6. Front brake hose (hydraulic unit to front brake
caliper)
7. Hydraulic unit assembly lead
A. Route the main switch lead through the guide.
B. 30
°
C. The holder may be facing in any direction.
CABLE ROUTING
2-44
Page 92
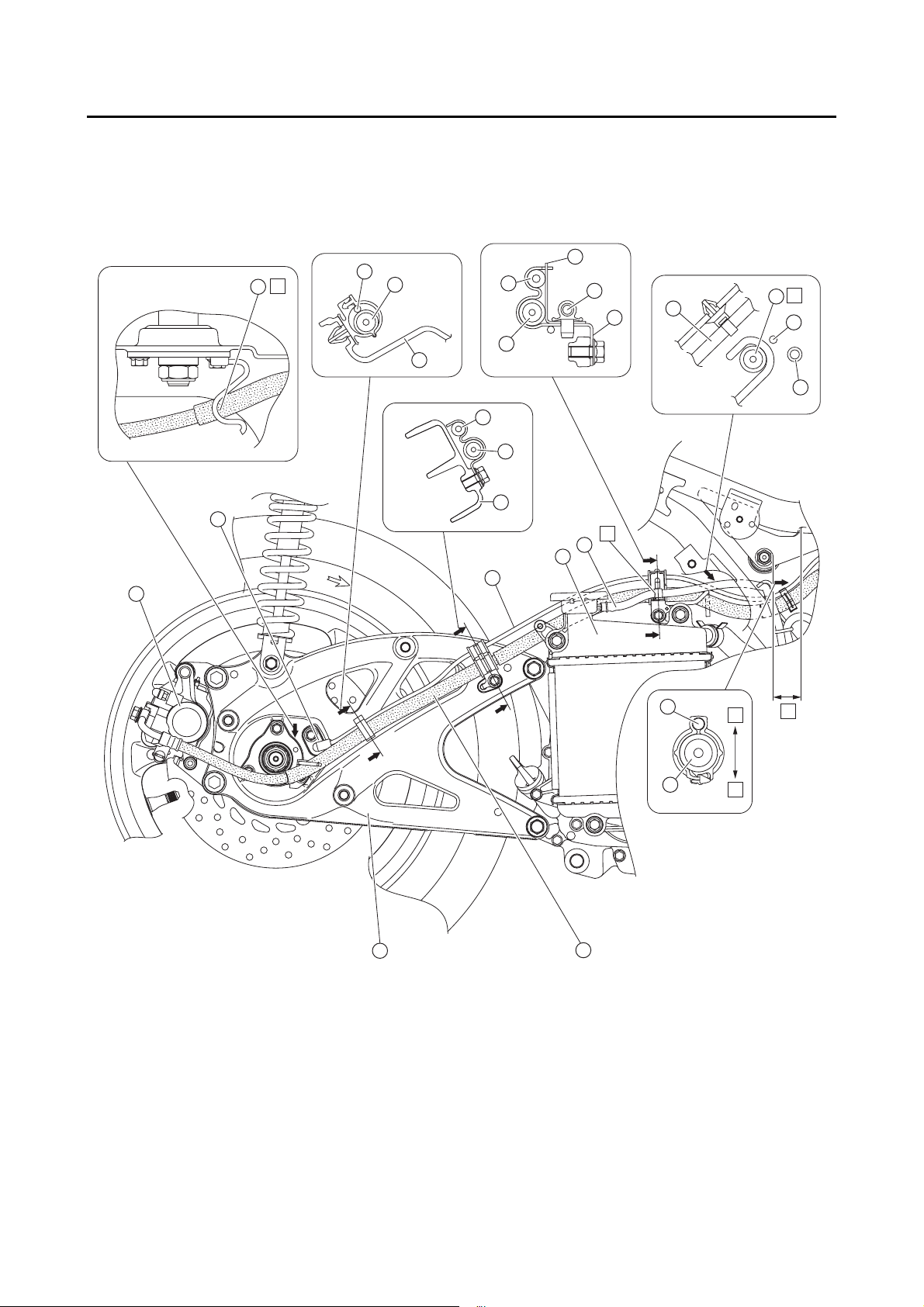
Rear brake (right side view)
CABLE ROUTING
3
C
6
2
1
6
7
3
6
3
6
7
3
8
5
9
A
5
4
10
C
6
3
5
3
6
7
6
D
E
B
2-45
Page 93

1. Rear brake caliper
2. Rear wheel sensor
3. Rear wheel sensor lead
4. Radiator
5. Coolant reservoir hose
6. Rear brake hose (hydraulic unit to rear brake
caliper)
7. Swingarm
8. Rear brake hose bracket
9. Rear brake hose holder
10. AC magneto lead
A. Connect the coolant reservoir hose to the radiator,
and then fasten the hose by inserting the projection
on the holder into the hole in the rear brake hose
bracket and rear brake hose holder.
B. Position the holder within the range shown in the
illustration.
C. Route the rear brake hose (hydraulic unit to rear
brake caliper) through the guide.
D. Upward
E. Downward
CABLE ROUTING
2-46
Page 94

Fuel tank (right side view)
CABLE ROUTING
8
2
C
1
9
3
1
2
7
A
3
9
4
B
5
A6
4
5
D
2-47
Page 95

1. Rear brake hose (hydraulic unit to rear brake
caliper)
2. Rear wheel sensor lead
3. Fuel hose
4. Fuel tank overflow hose
5. Center lower cover
6. Coolant reservoir hose
7. Coolant reservoir breather hose
8. Fuel hose holder
9. O
sensor lead
2
A. Install the hose completely onto the hose fitting.
B. Position the hose clamp 3
from the end of the hose. Point the ends of the
hose clamp upward.
C. Fasten the grommet on the fuel hose with the
holder.
D. Insert the end of the fuel tank overflow hose into
the center lower cover. Make sure that the end of
the hose protector on the fuel tank overflow hose
contacts the edge of the hole in the center lower
cover.
–7 mm (0.12–0.28 in)
CABLE ROUTING
2-48
Page 96

Fuel tank (top and bottom view)
B3
CABLE ROUTING
B2
A1
C
4
2-49
Page 97

1. Coolant reservoir cap
2. Coolant reservoir breather hose
3. Coolant reservoir hose
4. Fuel hose
A. Install the coolant reservoir cap as shown in the
illustration.
B. Align the white paint mark on the hose with the
projection on the coolant reservoir.
C. Fasten the grommet on the fuel hose with the
holder.
CABLE ROUTING
2-50
Page 98

Radiator (top and right side view)
CABLE ROUTING
2
B
G F
C
1
1
2
7
D
E
3
A
4
D
G F
D
E
E
D
N M
E
A
J
2
K
6
6
A H
O
D
E
5
A
D
I
5
7
B
N M
A
J
E
3
4
L
A
2-51
Page 99

1. Water pump
2. Water pump inlet hose
3. Thermostat assembly
4. Radiator outlet hose
5. Radiator
6. Coolant reservoir hose
7. Radiator inlet hose
A. Install the hose completely onto the hose fitting.
B. Face the white paint mark on the hose to the left.
C. 3
–5 mm (0.12–0.20 in)
D. Upward
E. Downward
F. F o r w a r d
G. Rearward
H. Point the ends of the hose clamp to the left. Make
sure not to install the hose clamp on the raised
portion of the hose fitting.
I. To coolant reservoir
J. Face the yellow paint mark on the hose to the right.
K. Align the yellow paint mark on the hose with the
center of the thermostat assembly.
L. Face the white paint mark on the hose upward.
M. Outward
N. Inward
O. Make sure that the hose clamp does not contact
the radiator fan cover.
CABLE ROUTING
2-52
Page 100
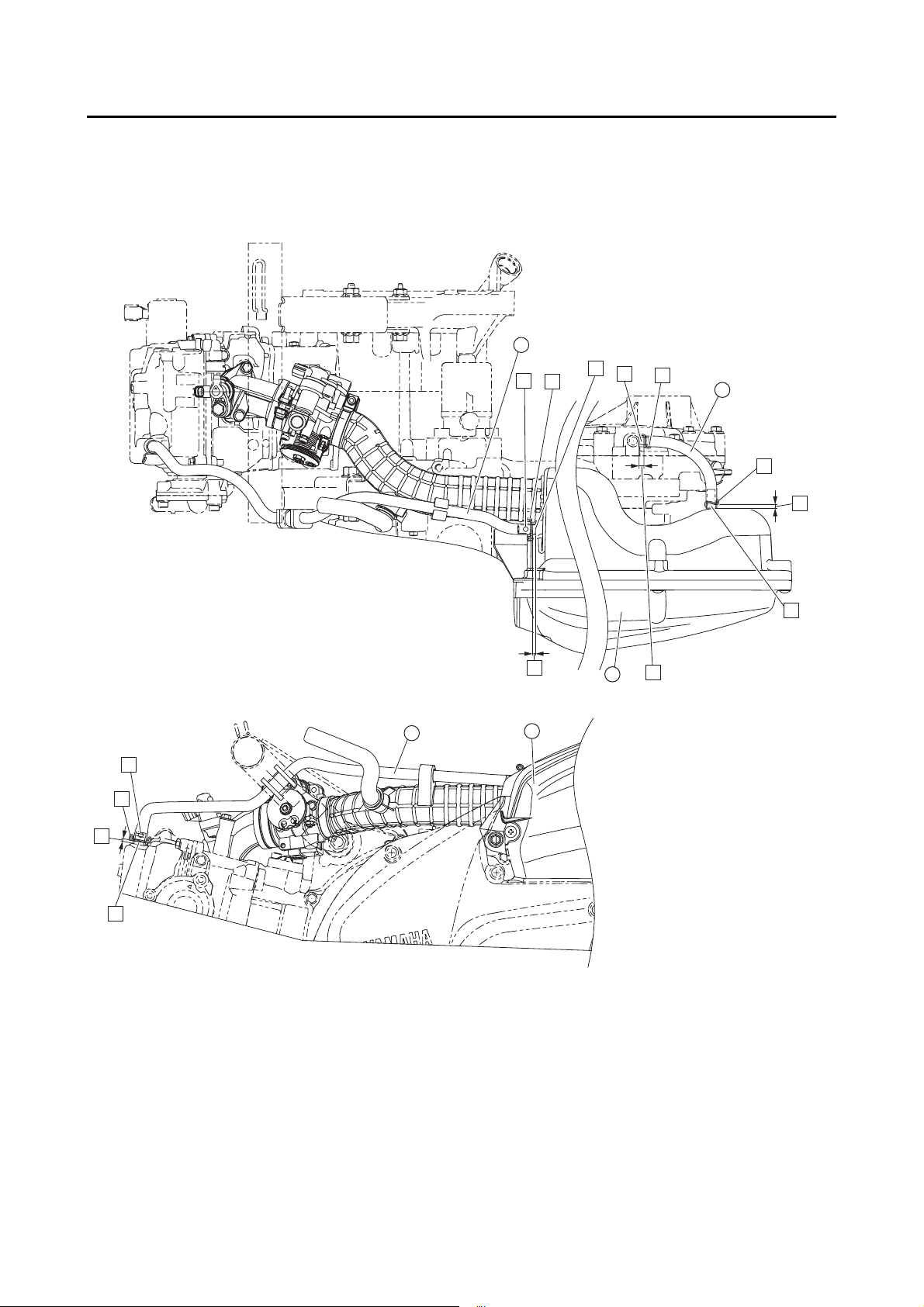
Air filter case (top and left side view)
CABLE ROUTING
1
C
C
A
B
B
2
B
D
C
D
1
F
G
D
C
3
E
3
2-53
 Loading...
Loading...