Page 1
PC
Windows 95 or later
MIDI THRU
TC IN
Changed
USB
SERIAL
MIDI OUT
MIDI IN
GPI OUT
GPI IN
COMMUNICATION1
COMMUNICATION2
REMOTE
W.CLK I/O
Fixed
Fixed
DSP1D
INPUT 1-10
OUTPUT 1-6
CASCADE IN
CASCADE OUT
TO CONSOLE 1-2
68-pin port connections · Solid lines
· Dotted lines
·····
···
Fixed
Changed
Cascade
ID
change jig
Output
ID
change jig
TO CONSOLE
(output)
ID
change jig
Input
ID
change jig
D24
Jitter meter
oscilloscope
Func.
Generator
1. For the PM1D inspection PC software, start 16. DSP1D-JK6, LED2 Test.
2. When the pop-up box for connecting the USB cable is displayed, connect the USB cable.
3. After a short while, the system asks you to specify the driver. Specify the directory containing the PM1D inspection PC software.
4. The installation proceeds as indicated by the OS.
5. After installation is complete, press the OK button on the pop-up box that came up in 2.
6. If inspection is OK, the installation has completed normally.
* The only operating system supported is Windows98. The USB driver can not be used with Windows 98 Second Edition.
* The USB port is only activated in the state in 2. Beware. If you insert the USB cable in any other state, it is not
correctly recognized by the PCS1De and the wrong driver is installed.
* Once the driver has been installed, the above procedure is not necessary for USB tests.
* This driver is only for inspection. It does not add the DSP1D USB function.
* The CS1D inspection USB driver must be installed separately.
(There are two types of USB drivers for detection for DSP1D and CS1D.)
B. Inspection Method
The inspection items are given below. Except for 17., these items are inspected using the PM1D inspection PC software. For details
on each item, see from Page 49 on.
C. Inspection Using PM1D Inspection PC Software
Except for the all-group sound test, the inspections use the PM1D inspection PC software to control the DSP1D and the inspection is
carried out autonomously. The inspection configuration diagram is as follows.
DSP1D
45
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
No.
CIB Test 1-1. TCU
1-2. HIF
1-3. CIF
EMB Test 2-1. EMU
2-2. UIF
IFC Test
PDB Test 4-1. CPU
4-2. DSP6
4-3. DSP5
GDB Test 5-1. CPU
5-2. DSP6
5-3. DSP5
IDB1 Test 6-1. CPU
6-2. DSP6
6-3. DSP5
IDB2 Test 7-1. CPU
7-2. DSP6
7-3. DSP5
EDB Test 8-1. CPU
8-2. DSP6
Items
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
No.
Connection test 9-1. PDB
9-2. GDB
9-3. IDB1
9-4. IDB2
9-5. EDB
JK1 (INPUT x) Test 10-1. INPUT 1
:
10-10. INPUT 10
JK4 (TO CONSOLE x)
11-1. TO CONSOLE 1
INPUT Test 11-2. TO CONSOLE 2
JK2 (OUTPUT x) Test
12-1. OUTPUT 1
:
12-6. OUTPUT 6
JK4(TO CONSOLE x)
13-1. TO CONSOLE 1
OUTPUT Test 13-2. TO CONSOLE 2
JK3 (CASCADE) Test
JK5 Test
JK6 , LED2 Test
All-group sound inspection
(Inspects using DSP1D sound inspection data. See Page 49.)
Items
Page 2
ON
SW 101
12345678
Input ID change jig
[INPUT 1-10]
[TO CONSOLE (INPUT)]
SW 102
ON
12345678
ON
12345678
SW 200
12
3
4
MSB/LSB Line = Has been fixed at the low level.
MSB/LSB Line = Has been set as by pull amp as is.
2CH/4CH Line = Has been fixed at the low level.
2CH/4CH Line = Has been set as by pull amp as is.
1
2
3
4
In each inspection item, if there are instructions to
drop to the low level, set the relevant switches to ON.
For details on inspecting with this software, see from Page 49 on.
Locations with instructions for changes have instructions for that inspection item in the PC software, so change the connections
according to the instructions.
(* Even if the system is the DSP1D not the DSP1D-EX, inspect with IDB2 inserted for the bus check.)
For time code output, insert an MO disc (song data or the like) that can idle as long as possible. Also, switch On MMC Receive on
the Utility menu and set TC Select to Serial IN on the Setup menu.
In the 16 JK6 inspection, it is necessary to change the BNC cable. The connection method is as follows.
* Since the input and output functions are inspected separately for TO CONSOLE, there are two connection methods.
* There are three special 68-pin port ID change jigs (for INPUT, OUTPUT, and CASCADE) but these are the same jig
with just the DIP switch settings changed. In other words, you can work with just one ID change inspection jig by
changing the DIP switch settings appropriately. For information on the ID change jig, refer to the LMY-SLOT inspection
jig specifications.
D24 setting method
W. CLK connection method
68-pin port connection method table
ID change jig DIP switch settings
10. INPUT 1-10
11. TO CONSOLE
(INPUT) 1-2
12. OUTPUT 1-6
13. TO CONSOLE
(OUTPUT) 1-2
14. CASCADE IN/OUT
Input ID change jig
Output ID change jig
Altered ID change jig just for
TO CONSOLE (OUTPUT)
Cascade ID change jig
Necessary jigInspection item
To INPUT 1-10
To OUTPUT x
To Console 1-2
To INPUT x To OUTPUT 1-6
Connected TO CONSOLE 1-2 and INPUT; no polarity.
To CASCADE IN To CASCADE OUT
ID change jig connection method
From left side (CN103) From right side (CN102)
DSP1D
46
IN 48 kHz + 6 %
IN 44.1kHz - 10 %
Jitter 48 kHz
Jitter 44.1 kHz
DIR2
IN/OUT
JK6-W.CLK inspection sub-item
W.CLK In ········ Connect the function generator and output the clocks.
W.CLK Out ····· No need to connect
W.CLK In ······· Connect the function generator and output the clocks.
W.CLK Out ····· Connect the jitter meter and measure.
The same a jitter 44.1 khz connection.
Loopback connection between W.CLK Out and W.CLK In
Connection method
Page 3
ON
SW 101
12345678
SW 102
ON
12345678
ON
12345678
SW 200
Output ID change jig
[OUTPUT 1-6]
MSB/LSB Line = Has been fixed at the low level.
MSB/LSB Line = Has been set as by pull amp as is.
1
2
In each inspection item, if there are instructions to
drop to the low level, set the relevant switches to ON.
ON
12345678
ON
12345678
ON
12345678
SW 101
Cascade ID change jig
[for CASCADE IN check]
SW 102
SW 200
TO CONSOLE (OUTPUT)
ID change jig
[TO CONSOLE (OUTPUT)]
The ID is not inspected at TO CONSOLE (OUTPUT), so the DIP switch settings do
not matter. Connect the altered ID change jig just for TO CONSOLE (OUTPUT).
(Refer to drawing control number 8B87E (AI8) LMY-SLT detection jig specification
(ID conversion jig circuit drawing) for the method of revision.
ON
12345678
ON
12345678
ON
12345678
SW 101 SW 102
SW 200
Cascade ID change jig
[for CASCADE OUT check]
1
2
DSP1D
46-a
Page 4
OUTPUT1
INPUT1
OUTPUT2
OUTPUT3
OUTPUT4
OUTPUT5
OUTPUT6
INPUT2
INPUT3
INPUT4
INPUT5
INPUT6
INPUT7
INPUT8
INPUT9
INPUT10
CONSOLE I/O
CASCADE IN
CASCADE OUT
DIRECT
OUT
DSP1D
PC
Windows 95
or later
RS232C
RS232C
Altered ID change jig A (1 in 2 out)
Altered ID change jig A (1 in 2 out)
Altered ID change jig A (1 in 2 out)
Altered ID change jig A (1 in 2 out)
Altered ID change jig B (1 in 1 out)
Altered ID change jig B (1 in 1 out)
* ID change jigs A/B are altered versions that set the IDs for input and
output separately.
(Refer to (AI8) LMY-SLT detection jig specification.)
The AI8 IDs are output to the input connection terminals.
The AO8 IDs are output to the output connection terminals.
* ID change jig A gathers two ID change jig Bs in 1 input; the outputs
are distributed simply in parallel, so the 2-output side connections
can be either even or the odd input terminals.
* Connect 01V using an MIO card altered to output the console ID.
(Refer to the DSP1D Overall Inspection Specifications.)
Function
Generator
BNC
Repeat
OSC
Final output
01V
Altered MIO
Inspected auditorily.
DSP1D F/W Latest Version
TCU
xxxxxx
HIF
xxxxxx
EMU
xxxxxx
UIF
xxxxxx
PDB
xxxxxx
GDB
xxxxxx
IDB
xxxxxx
EDB
xxxxxx
Pressing this button automatically starts the check
of the item to be checked.
Input the latest firmware version.
When the version is checked,
this character string and the
version actually written in the
firmware are compared. The
value entered here is retained
in memory.
The check items and check results are displayed. Pressing
a check item button enables
inspection of only that item.
Only items whose checkboxes are checked are automatically checked.
ALL checks all the items.
CLEAR removes all the
checks.
Auto Test Start
ALL CLR CLOSE
1-1.
1-2.
1-3.
2-1.
2-2.
3.
CIB (TCU)
CIB (HIF)
CIB (CIF)
EMB (EMU)
EMB (UIF)
IFC Test
OK
OK
OK
OK
OK
:
OK
4-3.
5-1.
5-2.
5-3.
PDB (DSP5)
GDB (CPU)
GDB (DSP6)
GDB (DSP5)
OK
OK
OK
OK
6-1.
IDB1 (CPU)
:
:
OK
Version character string input column
DSP1D
47
Except for Item 17., the PM1D is inspected using PC inspection software. This inspection software is common for
AI8/AO8/DSP1D/CS1D.
For details on the basic operation methods, menu screen specifications, etc., refer to the CS1D Test Program Specifications.
The DSP test menus are shown below.
Before the inspection, the latest version of each piece of DSP1D software must be input. (This is necessary for the version check.)
For the version character string to be input, refer to version.txt in the same directory as the DSP1D firmware.
The following pages give details on each check item and how the PC software handles it.
PM1D inspection PC software summary
D. All-Group Sound Inspection
After all the inspections were carried out with the PM1D inspection PC software, the sound inspection is carried out.
After making the connections as in the diagram below, inspect with the procedure given from the next page on. Note that the altered
ID change jigs A/B are separate from the dedicated TO CONSOLE (OUTPUT) altered ID change jig. (If multiple ID change jigs can
be not be made available, substitute with the method given later in this document.)
Page 5

DSP1D
•Method using six altered ID change jigs (This is the method normally used.)
1. Refer to the following preparation methods and prepare the software version to be used.
2. Follow the connection drawing on page 47 and supply the clock from the function generator.
Refer to the DSP1D overall inspection specifications for the frequency settings.
3. Execute PM1D.EXE in the prepared folder.
(The basic usage of PM1D.EXE is the same as the CS1D screen software.Accordingly, refer to the software
version of the CS1D operation manual.)
4. Set ENGINE A to W.CLOCK IN with SYS/W.CLOCK - WORD CLOCK.
5. Set OSC OUT to 1AO8:1-1 with MON/CUE - OSCILLATOR, set ON. OSC to IN, then adjust the level.
6. Recall SCENE 00.1: SOUND THRU1 with SCENE - MEMORY.
7. Set the switch for the altered MIO connected to 01V to ST.
8. Check the audio through 01V.
9. Set the switch for the altered MIO connected to 01V to ST.
10. Check the audio through 01V.
•Method using only one altered ID change jig
1. As shown on page 47, connect all components other than the ID conversion jig and supply the clock from the
function generator. Refer to the DSP1D overall inspection specifications for the frequency settings.
2. Connect an altered ID change jig to INPUT 1 and 2 and OUTPUT 1.
3. In the same manner as the previous page, prepare the software for inspecting DSP1D sound for the version to
be used and from it, execute PM1D.EXE. (The basic usage of PM1D.EXE is the same as the CS1D screen software.
Accordingly, refer to the software version of the CS1D operation manual.)
4. Set ENGINE A to W.CLOCK IN with SYS/W.CLOCK - WORD CLOCK.
5. Set OSC OUT to 1AO8:1-1 with MON/CUE - OSCILLATOR, set ON. OSC to IN, then adjust the level.
6. Recall SCENE 00.1: SOUND THRU1 with SCENE - MEMORY.
7. Set the switch for the altered MIO to ST and check the audio through 01V.
8. Set the switch for the altered MIO to MON and check the audio through 01V.
9. Recall SCENE 00.2: SOUND THRU2 with SCENE - MEMORY. Check that the audio goes off.
10. Change the input side connections only to INPUT 3 and 4.
11. Repeat *1.
12. Recall SCENE 00.3: SOUND THRU3 with SCENE - MEMORY. Check that the audio goes off.
13. Change the input side connections only to INPUT 5 and 6.
14. Repeat *1.
15. Recall SCENE 00.4: SOUND THRU4 with SCENE - MEMORY. Check that the audio goes off.
16. Change the input side connections only to INPUT 7 and 8.
17. Repeat *1.
18. Recall SCENE 00.5: SOUND THRU5 with SCENE - MEMORY. Check that the audio goes off.
19. Change the input side connections only to INPUT 9 and 10.
20. Repeat *1.
21. Set OSC OUT to 2AO8:1-1.
22. Change the output side connection only to OUTPUT 2. (The INPUT remains 9 and 10 and the scene 00.5.)
23. Repeat *1.
24. Set OSC OUT to 3AO8:1-1.
25. Change the output side connection only to OUTPUT 3.
26. Repeat *1.
27. Set OSC OUT to 4AO8:1-1.
28. Change the output side connection only to OUTPUT 4.
29. Repeat *1.
30. Set OSC OUT to 5AO8:1-1.
31. Change the output side connection only to OUTPUT 5.
*1
{
Data used: DSP1D sound inspection software within PM1D system software
Version used: Files composed using a PM1D SYSTEM SOFTWARE with a version later than the version shown
on the cover. (Managed with the already drawn CD-R assembly drawing (3JL-XY714A0.)
Method of preparation:
Follow the instructions in the CS1D test program specifications (Drawing No: KES-92654) titled
"Procedure for extracting software groups for production and customer service applications". Once
the files have been extracted, refer to the Readme.txt in the SoundDiag directory.
48
Page 6
1-1. DSP1D-CIB
(TCU-IC129) Test
This test checks around the CIB TCU.
Check item
ID TCU [11h]
RAM
• Data Bus 16bit(15-0)
• Address Bus 20bit(19-0)
Flash (Check Sum)
Version
DPM
• EM BUS<->TC BUS R
1-2. DSP1D-CIB
(TCU-IC129) Test
This test checks around the CIB HIF.
1-3. DSP1D-CIB (ETC)Test
This test makes other checks of the CIB.
Check item
FPGA HIF [02h]
DPM
• EMU<->CONS L
FIFO
TC IC
Check item
ID TCU [12h]
RAM
• Data Bus 16bit(15-0)
• Address Bus 20bit(19-0)
Flash (Check Sum)
Version
DPM
• HI BUS<->EM BUS L
DSP1D
49
32. Repeat *1.
33. Set OSC OUT to 6AO8:1-1.
34. Change the output side connection only to OUTPUT 3.
35. Repeat *1.
1. DSP1D-CIB Test
This test checks the DSP1D-CIB. It checks the following items. Those items for which there are figures display the results in
binary. Detailed screen output specifications are given on the following pages.
The details for 1-2. are omitted because they are the same as for 1-1.
* For the DPM (dual port RAM) item, EM BUS <-> TC BUS R etc. is written. This indicates which of the DPM buses is
inspected. For example, for EM BUS <-> TC BUS R, this indicates the check of the TC BUS side seen from the DPM
(right side for the DPS BUS <-> CM BUS notation).
* RAM OK
DataBus
AddressBus
* DPM
EM BUS <-> TC BUS R
* Flash
* Version
OK
OK
OK
1-1. DSP1D-CIB (TCU-IC129) Test
OK
1-1. DSP1D-CIB (TCU-IC129) Test
OK
RAM(IC133): OK
Flash(IC132):
Version:
OK
OK
DPM: OK
OK
Now Checking …
DPM
NG example
* ID TCU [11h]
ID: TCU[11h]
* RAM NG
DataBus
AddressBus
* DPM
EM BUS <-> TC BUS R
* Flash
* Version
NG
NG
NG
1-1. DSP1D-CIB (TCU-IC129) Test
1-1. DSP1D-CIB (TCU-IC129) Test
NG
RAM(IC133): NG
Flash(IC132):
Version:
NG
NG
DPM: NG
NG
* ID xxx [xxh]
ID: xxx [xxh]
DBus[38-35,32-29,16-13,10-7 pin]
CheckSum = xxxx[xxxx]
Current = x.xx , Latest = x.xx
EM BUS <-> TC BUS R:
NG
11111111 11111111
ABus[18-21,24-27,42-44,1-5 pin] NG
NG
1 11111111 1111111-
1-1. DSP1D-CIB (TCU) Test
This test checks around the CIB TCU.
OK/NG display for the page as a whole
Displayed when all the checks have been completed.
If OK, sub-items are
not displayed.
Sub-item
Received ID displayed as
board name and hexadecimal
OK/NG display for
individual items
The NG is displayed the
moment the item is
found to be NG, even if
the test is still underway.
If there is no response
from the firmware,
"NO" is displayed.
Displays all the detailed results so
far. This display can be scrolled.
Current status display
Corresponding IC number
Corresponding pin number
Stopped the moment an
actual ID NG appears;
stopped at the end of the
page for any other NG.
Main item
Checked in order from top to bottom.
Completed main items have marks
next to them.
SRAM OK: LED lit up
NG: LED flashes on (0.2 s) - Off (0.2 s) - On (0.2 s) - Off (0.1 s)
Flash OK: LED lit up
NG: LED flashes on (0.1 s) - Off (0.1 s) - On (0.1 s) - Off (0.1 s)
()
Terminal status display
Delimited in units of 8
digits right justified in the
order upper then lower.
0: Normal 1: Abnormal
-: Ignored
Gives the current version
and the latest version
Abnormal port name
Previously read value.
[ ] gives the correct value.
4-digit hexadecimal notation
Page 7
DSP1D
50
* DPM
* FPGA
OK
EMU <-> CONS L
* FIFO
* TC IC
OK
OK
1-3. DSP1D-CIB (ETC) Test OK
1-3. DSP1D-CIB (ETC) Test
OK
DPM: OK
FIFO(IC118,119,122,123):
TC IC(IC136):
OK
OK
OK
Now Checking …
TC IC
NG example
FPGA(IC126):
NG
* DPM
* FPGA
NG
EMU <-> CONS L
* FIFO
* TC IC
NG
NG
1-3. DSP1D-CIB (ETC) Test
1-3. DSP1D-CIB (ETC) Test
NG
NG
FIFO(IC118,119,122,123):
TC IC(IC136):
NG
NG
FPGA(IC126):
NG
DPM:
EMU<->CONS L(IC116):
SRAM OK: LED lit up
NG: LED flashes on (0.2 s) - Off (0.2 s) - On (0.2 s) - Off (0.1 s)
Flash OK: LED lit up
NG: LED flashes on (0.1 s) - Off (0.1 s) - On (0.1 s) - Off (0.1 s)
()
1-3. DSP1D-CIB (ETC) Test
This test checks around the CIB ETC.
* FPGA
* DIR2
OK
3. DSP1D-IFC Test OK
3. DSP1D-IFC Test
OK
FPGA(IC503): OK
OK
Now Checking …
FPGA
NG example
DIR2(IC604,605,606):
* FPGA
* DIR2
NG
3. DSP1D-IFC Test
3. DSP1D-IFC Test
NG
FPGA(IC503): NG
NG
DIR2(IC604,605,606):
3. DSP1D-IFC (TCU) Test
This test checks the IFC board.
2-1. DSP1D-EMB
(EMU-IC114) Test
This test checks around the EMB EMU.
Check item
ID EMU [10h]
RAM
• Data Bus 16bit(15-0)
• Address Bus 20bit(19-0)
Flash (Check Sum)
Version
DPM
• EM BUS<->DPM BUS L
• UI BUS<->EM BUS R
• HI BUS<->EM BUS R
• EM BUS<->TC BUS L
Battery
2-2. DSP1D-EMB
(UIF-IC127) Test
This test checks around the EMB HIF.
Check item
ID UIF [13h]
RAM
• Data Bus 16bit(15-0)
• Address Bus 20bit(19-0)
DPM
• UI BUS<->EM BUS L
Flash (Check Sum)
Version
2. DSP1D-EMB Test
This test checks the EMB. It checks the following
items. Those items for which there are figures
display the results in binary. Detailed screen output
specifications are given on the following pages.
The battery check item is only for 2-1. Here the
voltage is checked and if it is within the correct
range, OK is displayed. If it is NG, how far it
deviates from the correct value is displayed.
4. DSP1D-PDB Test
This test checks the DSP1D-PDB. It checks the following items. Those items for which there are figures display the results in
binary. Detailed screen output specifications are given on the following pages.
DSP6 total count ···· 9
DSP5 total count ···· 11
Page 8
DSP1D
51
4-1. DSP1D-PDB
(CPU-IC101) Test
This test checks around the PDB CPU.
Check item
ID PDB [14h]
RAM
• Data Bus 16bit(15-0)
• Address Bus 16bit(16-1)
• Data Bus 16bit(15-0)
• Address Bus 15bit(15-1)
Flash (Check Sum)
Version
DPM
4-2. DSP1D-PDB
(DSP6) Test
This test checks around PDB DSP6.
4-3. DSP1D-PDB (DSP5) Test
This test checks around PDB DSP5.
Check item
Chip Select
DSP5 <-> CPU
DSP6 -> DSP5
• Serial I/O
• Serial I/O
• Serial I/O
DSP5 -> DSP6
DPM
Check item
Chip Select
DSP6 <-> CPU
• Data Bus 16bit(15-0)
• Address Bus 7bit( 7-1)
DSP6 <-> DRAM
• Data Bus 32bit(31-0)
• Address Bus 10bit( 9-0)
DSP6 -> DSP6
• Serial I/O
• Data Bus 16bit(15-0)
• Address Bus
• ParallelI/O 32bit(31-0)
* RAM
* ID PDB [14h]
OK
AddressBus
* Flash
DataBus
* Version
* DPM
AddressBus
DataBus
00000000 0000000-
00000000 00000000
OK
4-1.
DSP1D-PDB (CPU-IC101) Test
OK
4-1. DSP1D-PDB (CPU-IC101) Test
OK
RAM(IC107): OK
Flash(IC114): OK
Version: OK
DPM: OK
OK
OK
NG example
ID: PDB [14h]
* RAM
* ID xxx [xxh]
NG
AddressBus
* Flash
DataBus
* Version
* DPM
AddressBus
DataBus
11111111 1111111-
11111111 11111111
NG
4-1.
DSP1D-PDB (CPU-IC101) Test
4-1. DSP1D-PDB (CPU-IC101) Test
NG
RAM(IC107): NG
Flash(IC114): NG
Version: NG
DPM: NG
NG
NG
ID: xxx [xxh]
Now Checking …
Version
DBus[xx-xx,xx-xx pin]
CheckSum = xxxx [xxxx]
Current = x.xx , Latest = x.xx
NG
NG
11111111 11111111
ABus[xx-xx,xx-xx pin]
1111 11111111 11111111
SRAM OK: LED lit up
NG: LED flashes on (0.2 s) - Off (0.2 s) - On (0.2 s) - Off (0.1 s)
Flash OK: LED lit up
NG: LED flashes on (0.1 s) - Off (0.1 s) - On (0.1 s) - Off (0.1 s)
()
4-1. DSP1D-PDB (CPU-IC101) Test
This test checks around the PDB CPU.
* DSP6 <-> CPU
* ChipSelect 0 00000000
0 00000000
0 00000000
OK
AddressBus
DataBus
* DSP6 <-> DRAM
0 00000000
0 00000000
OK
AddressBus
DataBus
* DSP6 <-> DSP6
xxx/xxx
OK
Serial I/O
4-2. DSP1D-PDB (DSP6) Test OK
4-2. DSP1D-PDB (DSP6) Test
OK
DSP6<->CPU: OK
DSP6<->DRAM: OK
DSP6 -> DSP6: OK
OK
NG example
ChipSelect:
NG
Now Checking …
DSP6 -> DSP6 No. xxx
ICxxx
NG
NG
* DSP6 <-> CPU
* ChipSelect 0 00100000
0 00101000
0 00001000
NG
AddressBus
DataBus
* DSP6 <-> DRAM
0 00000100
0 00000100
NG
AddressBus
DataBus
* DSP6 <-> DSP6
xxx/xxx
NG
Serial I/O
4-2. DSP1D-PDB (DSP6) Test
4-2. DSP1D-PDB (DSP6) Test
NG
DSP6<->CPU:
ABus[25-31 pin]
NG
NG
NG
DSP6<->DRAM: NG
DSP6 -> DSP6: NG
NG
ChipSelect:
DBus[34-43,47-52 pin]
DBus
[
151-144,142-135,130-123,121-114pin
]
11111111 11111111ICxxx
ICxxx
1111111-ICxxx
ABus[163-154 pin]
11 11111111
11111111 11111111
11111111 11111111ICxxx
SI/SO
11111111 11111111
- ICxxx
ICxxx - ICxxx, ICxxx
ICxxx[SOx] - ICxxx[SIx]
- ICxxx
4-2. DSP1D-PDB (DSP6) Test
This test checks around PDB DSP6.
Stopped the moment an actual
Chip Select or TxB NG appears;
stopped at the end of the page for
any other NG.
The DSP check results are displayed for each DSP. The DSPs are displayed
in order from the right of the ChipSelect signals on the circuit diagram.
(Blank: Not yet checked; 0: Normal; 1: Abnormal; N: No response)
Gives the abnormal
DSP IC number.
Display when a number of
checks are complete and there
have been a number of NGs
Displayed in binary in the order
Upper: 16 bits, Lower: 16 bits
The corresponding DRAM IC
number is also displayed.
IC number display for
both upper and lower
Displays from which
SO to which SI is NG.
Page 9
5-1. DSP1D-GDB
(CPU-IC100) Test
This test checks around the GDB CPU.
Check item
ID GDB [15h]
RAM
• Data Bus 16bit(15-0)
• Address Bus 16bit(16-1)
• Data Bus 16bit(15-0)
• Address Bus 15bit(15-1)
Flash (Check Sum)
Version
DPM
5-2. DSP1D-GDB
(DSP6) Test
This test checks around GDB DSP6.
Check item
Chip Select
DSP6 <-> CPU
• Data Bus 16bit(15-0)
• Address Bus 7bit( 7-1)
• Data Bus 32bit(31-0)
• Address Bus 10bit( 9-0)
DSP6 <-> DRAM
• Serial I/O
DSP6 -> DSP6
5-3. DSP1D-GDB
(DSP5) Test
This test checks around GDB DSP5.
Check item
Chip Select
DSP5 <-> CPU
• Data Bus 16bit(15-0)
32bit(31-0)
• Address Bus
DSP6 -> DSP5
• Serial I/O
• Serial I/O
DSP5 -> DSP6
• Serial I/O
• Parallel I/O
DSP5 -> DSP5
DSP1D
52
* DSP5 <-> CPU
* ChipSelect 000 000000
000 000000
000 000000
OK
AddressBus
DataBus
* DSP6 -> DSP5 OK
OK
* DSP5 -> DSP6
xxx/xxx
Serial I/O
xxx/xxx
Serial I/O
xxx/xxx
OK
Parallel I/O
* DSP5 -> DSP5
xxx/xxx
Serial I/O
4-3.
DSP1D-PDB (DSP5) Test
OK
4-3. DSP1D-PDB (DSP5) Test
OK
DSP5<->CPU: OK
DSP6 -> DSP5: OK
DSP5 -> DSP5: OK
OK
NG example
ChipSelect:
Now Checking …
DSP5 -> DSP6 No. xxx
NGDBus[xx-xx,xx-xx pin]
11111111 11111111ICxxx
* DSP5 <-> CPU
* ChipSelect 000 00000000
000 00010000
000 00000100
NG
AddressBus
DataBus
* DSP6 -> DSP5 NG
NG
* DSP5 -> DSP6
xxx/xxx
Serial I/O
xxx/xxx
Serial I/O
xxx/xxx
NG
Parallel I/O
* DSP5 -> DSP5
xxx/xxx
Serial I/O
4-3.
DSP1D-PDB (DSP5) Test
4-3. DSP1D-PDB (DSP5) Test
OK
DSP5<->CPU:
NGSI/SO
SI/SO
SI/SO
ICxxx[SOxx] – ICxxx[SIOxx]
NG
DSP6 -> DSP5:
NG
ICxxx[SIOxx] – ICxxx[SIxx]
NG
DSP5 -> DSP6:
NGABus[xx pin]
1-------ICxxx
NG
NG
ICxxx[SIOxx] – ICxxx[SIOxx]
PI/PO NG
ICxxx – ICxxx
[xx-xx,xx-xx pin] 11111111 11111111
[xx-xx,xx-xx pin] 11111111 11111111
DSP5 -> DSP5: NG
OK
ChipSelect:
4-3. DSP1D-PDB (DSP5) Test
This test checks around PDB DSP6.
For the DSP5 address bus, only
the upper bits can be checked.
The pins are written as SIxx
and SOxx, but for DSP5, they
are written as SIOxx.
Displays which pin numbers are NG between which DSPs. 16 are
displayed at a time.
The display is three digits, including the IC number display.
Basically, the same
as up till here
5. DSP1D-GDB Test
This test checks the GDB. It checks the following items. The specifications are basically the same as for 4-1. through 4-3.
DSP6 total count ···· 13
DSP5 total count ···· 7
6-1. DSP1D-IDB1
(CPU-IC100) Test
This test checks around the IDB1 CPU.
Check item
ID IDB1 [16h]
RAM
• Data Bus 16bit(15-0)
• Address Bus 16bit(16-1)
• Data Bus 16bit(15-0)
• Address Bus 15bit(15-1)
Flash (Check Sum)
Version
DPM
6-2. DSP1D-IDB1
(DSP6) Test
This test checks around IDB1 DSP6.
Check item
Chip Select
DSP6 <-> CPU
• Data Bus 16bit(15-0)
• Address Bus 7bit( 7-1)
• Data Bus 32bit(31-0)
• Address Bus 10bit( 9-0)
DSP6 <-> DRAM
• Serial I/O
DSP6 -> DSP6
6-3. DSP1D-IDB1
(DSP5) Test
This test checks around IDB1 DSP5.
Check item
Chip Select
DSP5 <-> CPU
• Data Bus 16bit(15-0)
• Address Bus
DSP6 -> DSP5
• Serial I/O
• Serial I/O
DSP5 -> DSP5
6. DSP1D-IDB1 Test
This test checks the IDB1. It checks the following items. The specifications are basically the same as for 4-1. through 4-3.
DSP6 total count ···· 16
DSP5 total count ···· 8
Page 10
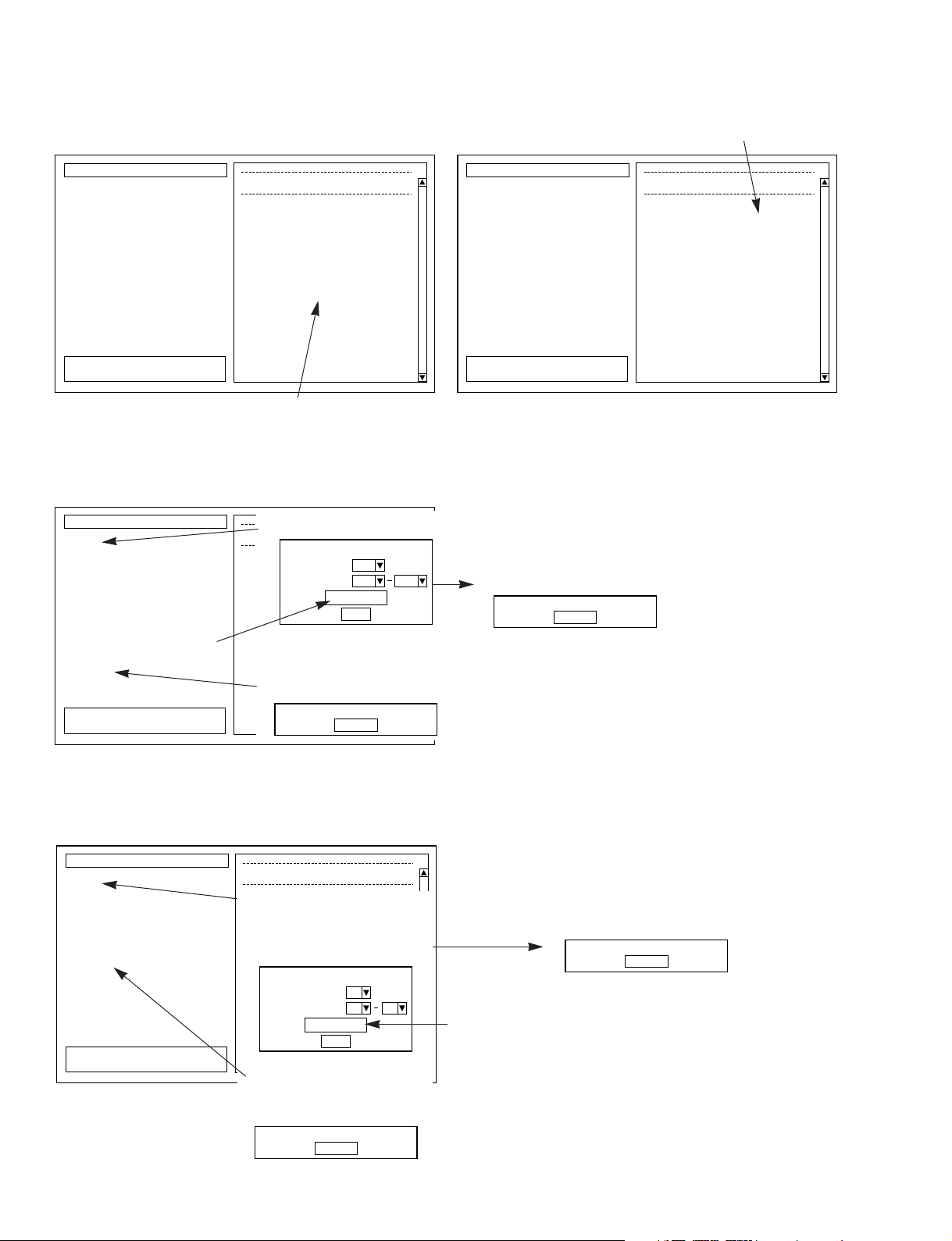
9-1. DSP1D-Connection
(PDB) Test
Checks the connections between the PDB
and the other boards.
Check item
PDB -> IDB1
PDB -> IDB2
PDB -> GDB
PDB -> EDB
IDB1 -> PDB
IDB2 -> PDB
GDB -> PDB
EDB -> PDB
9-2. DSP1D-Connection
(GDB) Test
Checks the connections between the GDB
and the other boards.
Check item
GDB -> PDB
IDB1 -> GDB
IDB2 -> GDB
PDB -> GDB
EDB -> GDB
9-4. DSP1D-Connection
(IDB2) Test
Checks the connections between the IDB2
and the other boards.
Check item
IDB2 -> GDB
IDB2 -> PDB
IDB1 -> IDB2
PDB->IDB2
9-5. DSP1D-Connection
(EDB) Test
Checks the connections between the EDB
and the other boards.
Check item
EDB -> GDB
EDB -> PDB
PDB -> EDB
9-3. DSP1D-Connection
(IDB1) Test
Checks the connections between the IDB1
and the other boards.
Check item
IDB1 -> GDB
IDB1 -> PDB
IDB1 -> IDB2
PDB->IDB1
DSP1D
53
7-1. DSP1D-IDB2
(CPU-IC100) Test
This test checks around the IDB2 CPU.
Check item
ID IDB2 [16h]
RAM
• Data Bus 16bit(15-0)
• Address Bus 16bit(16-1)
• Data Bus 16bit(15-0)
• Address Bus 15bit(15-1)
Flash (Check Sum)
Version
DPM
7-2. DSP1D-IDB2
(DSP6) Test
This test checks around IDB2 DSP6.
Check item
Chip Select
DSP6 <-> CPU
• Data Bus 16bit(15-0)
• Address Bus 7bit( 7-1)
• Data Bus 32bit(31-0)
• Address Bus 10bit( 9-0)
DSP6 <-> DRAM
• Serial I/O
DSP6 -> DSP6
7-3. DSP1D-IDB2
(DSP5) Test
This test checks around IDB2 DSP5.
Check item
Chip Select
DSP5 <-> CPU
• Data Bus 16bit(15-0)
• Address Bus
DSP6 -> DSP5
• Serial I/O
• Serial I/O
DSP5 -> DSP5
7. DSP1D-IDB2 Test
This test checks the IDB2. It checks the following items. The specifications are basically the same as for 4-1. through 4-3.
DSP6 total count ···· 16
DSP5 total count ···· 8
9. DSP1D Connection Test
This test checks the connections among the PDB,
GDB, IDB1, IDB2, and EDB. It checks the following
items. Detailed screen output specifications are given
on the following pages.
* There are duplicate checks, but for checking
just specific boards, these checks are not
omitted.
2-1. DSP1D-EMB
(EMU-IC114) Test
This test checks around the EMB EMU.
Check item
ID EMU [10h]
RAM
• Data Bus 16bit(15-0)
• Address Bus 20bit(19-0)
Flash (Check Sum)
Version
DPM
• EM BUS<->DPM BUS L
• UI BUS<->EM BUS R
• HI BUS<->EM BUS R
• EM BUS<->TC BUS L
Battery
2-2. DSP1D-EMB
(UIF-IC127) Test
This test checks around the EMB HIF.
Check item
ID UIF [13h]
RAM
• Data Bus 16bit(15-0)
• Address Bus 20bit(19-0)
DPM
• UI BUS<->EM BUS L
Flash (Check Sum)
Version
8. DSP1D-EDB Test
This test checks the EDB. It checks the following
items. The specifications are basically the same as
for 4-1. through 4-2.
DSP6 total count ···· 12
Page 11
DSP1D
54
10-1.
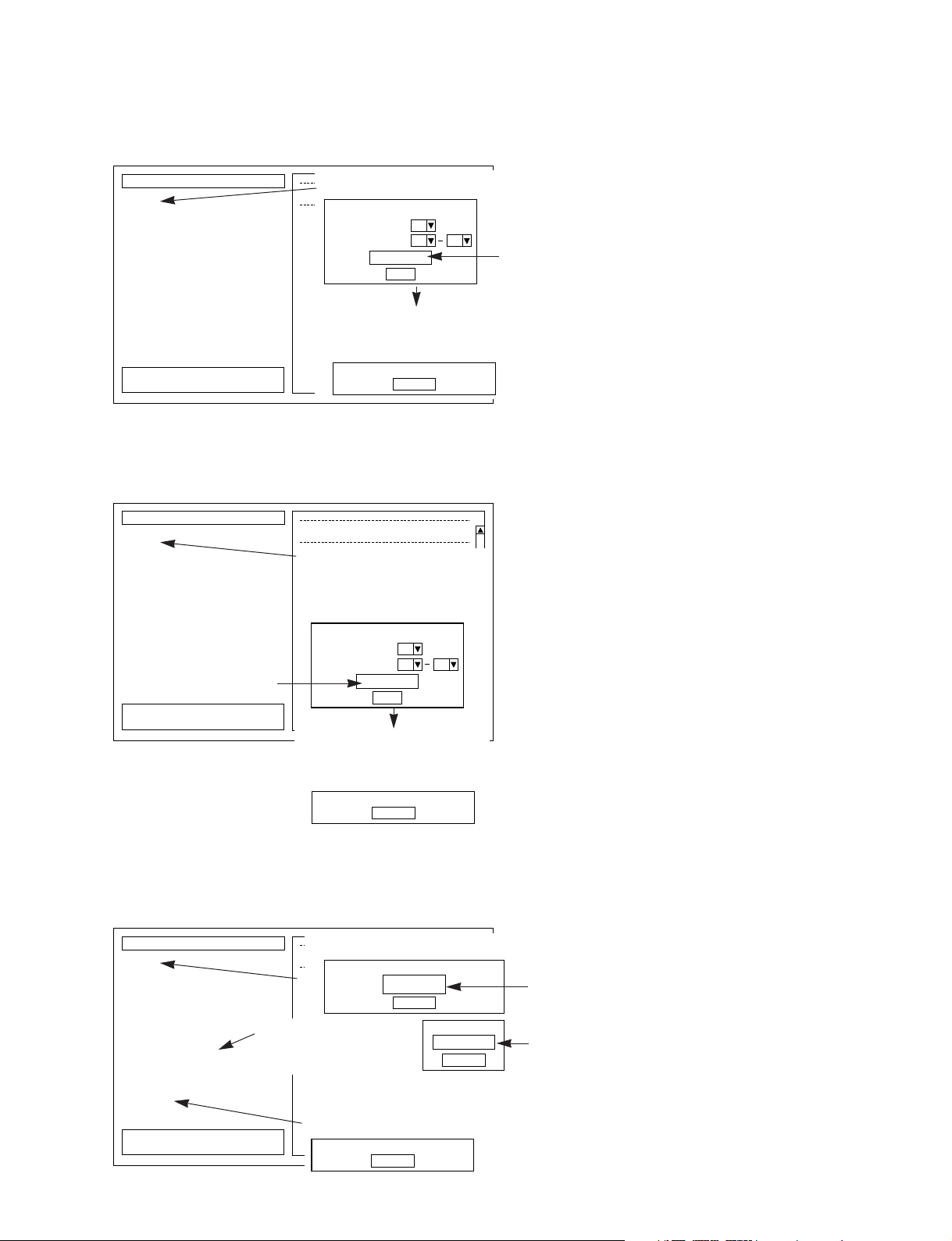
DSP1D-JK1 (INPUT x) Test
OK
10-1. DSP1D-JK1 (INPUT 1) Test
DIR2(IC112): OK
SI: OK
RQ: OK
AK: OK
W.CLK: OK
CONTROL: OK
ID: OK
MSB/LSB:
2CH/4CH:
OK
OK
OK
* DIR2
OK* SI
OK* RQ
OK* AK
OK* W.CLK
OK* CONTROL
OK* ID
OK
OK
* MSB/LSB
* 2CH/4CH
In
Out
110
Please select 68pin ports to check
[OUTPUTPort]
1
[INPUTPort]
OK
The Output port used for the input check is
selected from the pull-down list.
Connect [OUTPUT 1] to[INPUT 1].
OK
Fixed to the port selected for the output side;
the input connections are changed in order.
When changing to the next port, a pop-up
box like the one below is displayed.
Change [MSB/LSB line] to low level.
OK
In the MSB/LSB, 2CH/4CH items, the
following pop-up menu will be displayed.
Set the switches on the ID conversion jig so
that the corresponding signal will become
low and click the OK button.
ID change jig DIP
switch settings
10. DSP1D-JK1 (INPUT x) TEST
This test checks the JK1 board with loopback connections. These items are repeated for just the specified range of Inputs 1-10. The
11-1.DSP1D-JK4(TO CONSOLE 1) INPUT
OK
11-1. DSP1D-JK4 (TO CONSOLE 1) INPUT Test
DIR2(IC112): OK
SI: OK
W.CLK: OK
ID: OK
MSB/LSB: OK
OK
* DIR2
OK* SI
OK* W.CLK
OK* ID
OK* MSB/LSB
In
Out
Connect [OUTPUT 1] to [TO CONSOLE 1]
OK
The Output port used for the TO CONSOLE
check is selected from the pull-down list.
(The port selected in Test 10 is displayed as
the default. Normally, the input cable that has
been connected and reconnected sequentially in
10. can just be reconnected to TO CONSOLE.
Fixed to the port selected for the output side;
the TO CONSOLE connections are changed
in order.
When changing to the next port, a pop-up
box like the one below is displayed.
12
Please select 68pin ports to check
[OUTPUT Port]
1
[To CONSOLE Port]
OK
Change [MSB/LSB line] to low level.
OK
In the MSB/LSB items, the following popup menu will be displayed. Set the
switches on the ID conversion jig so that
the corresponding signal will become low
and click the OK button.
ID change jig DIP switch
settings
11. DSP1D-JK4 (TO CONSOLE x) Input Test
This test checks the JK4 port input direction communications. These items are repeated for the specified range of TO CONSOLE 1-2.
9-1.
DSP1D-Connection (PDB) Test
OK
9-1. DSP1D-Connection (PDB) Test
PDB->IDB1: OK
PDB->IDB2: OK
PDB->GDB: OK
PDB->EDB: OK
IDB1->PDB: OK
IDB2->PDB: OK
GDB->PDB: OK
EDB->PDB: OK
OK
Now Checking …
EDB -> PDB
NG example
ICxxx[xxxxx] – ICxxx[xxxxx]
* PDB -> IDB1 xxx/xxx
xxx/xxx
xxx/xxx
xxx/xxx
xxx/xxx
xxx/xxx
xxx/xxx
xxx/xxx
OK* PDB -> IDB2
OK* PDB -> GDB
OK* PDB -> EDB
OK* IDB1 -> PDB
OK* IDB2 -> PDB
OK* GDB -> PDB
OK* EDB -> PDB
9-1.
DSP1D-Connection (PDB) Test
9-1. DSP1D-Connection (PDB) Test
PDB->IDB1: NG
PDB->IDB2:
ICxxx[xxxxx] – ICxxx[xxxxx]
NG
PDB->GDB:
ICxxx[xxxxx] – ICxxx[xxxxx]
NG
PDB->EDB:
ICxxx[xxxxx] – ICxxx[xxxxx]
NG
IDB1->PDB:
ICxxx[xxxxx] – ICxxx[xxxxx]
NG
IDB2->PDB:
ICxxx[xxxxx] – ICxxx[xxxxx]
NG
GDB->PDB:
ICxxx[xxxxx] – ICxxx[xxxxx]
NG
ICxxx[xxxxx] – ICxxx[xxxxx]
ICxxx[xxxxx] – ICxxx[xxxxx]
EDB->PDB: NG
NG
* PDB -> IDB1 xxx/xxx
xxx/xxx
xxx/xxx
xxx/xxx
xxx/xxx
xxx/xxx
xxx/xxx
xxx/xxx
NG* PDB -> IDB2
NG* PDB -> GDB
NG* PDB -> EDB
NG* IDB1 -> PDB
NG* IDB2 -> PDB
NG* GDB -> PDB
NG* EDB -> PDB
9-1. DSP1D-Connection (PDB) Test
Checks the connections between the PDB and the other boards.
Displays which pin numbers
are NG between which ICs
Basically, the same
as up till here
NG sample
Please refer to page 49, 51, 52 for NG charts.
NG sample
Please refer to page 49, 51, 52 for NG charts.
Page 12
DSP1D
55
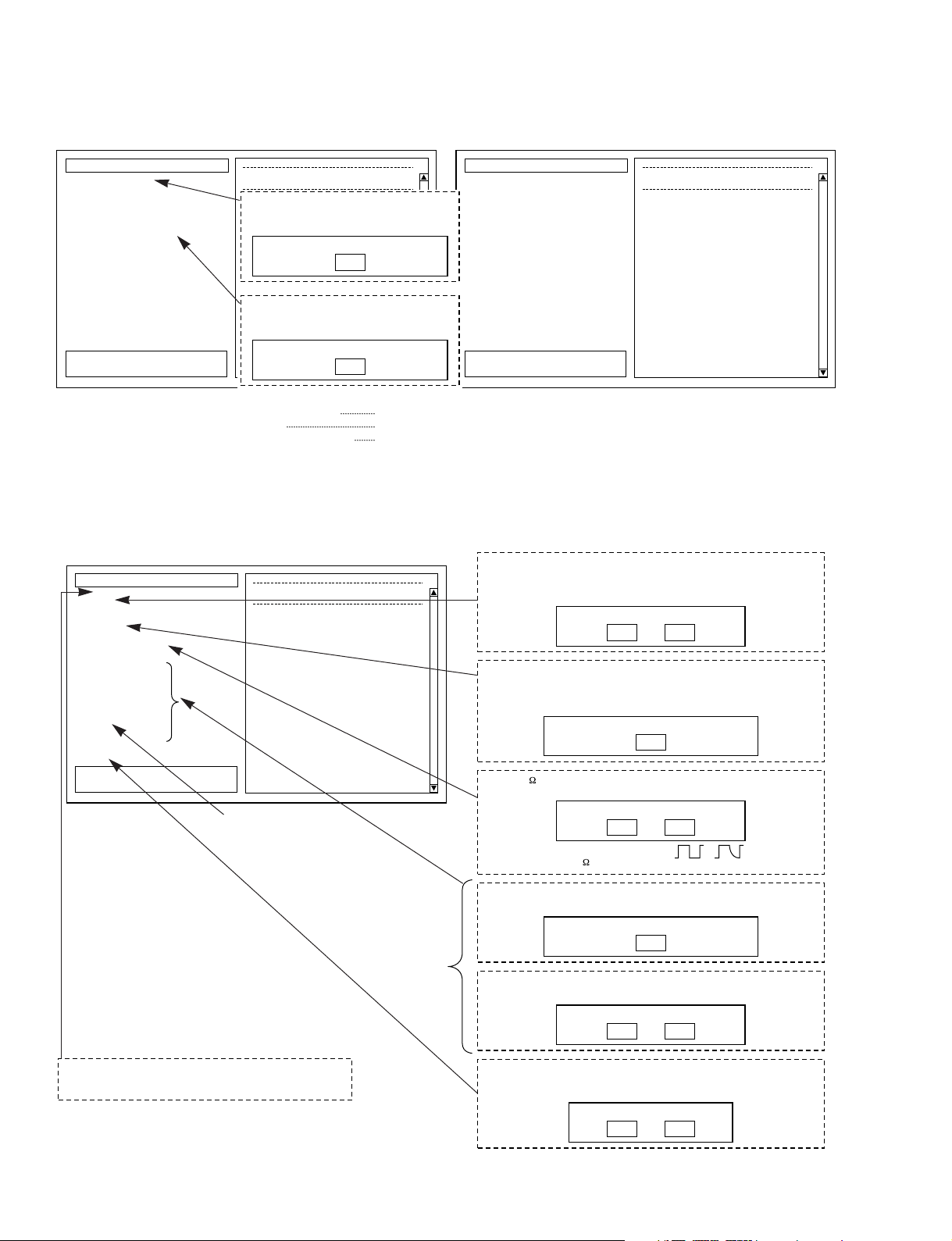
13-1.DSP1D-JK4(TO CONSOLE 1)OUTPUT
OK
13-1. DSP1D-JK4 (TO CONSOLE 1) OUTPUT Test
SO: OK
OK* SO
Connect [INPUT 1] to [TO CONSOLE 1].
OK
The Input port used for the TO CONSOLE
check is selected from the pull-down list.
(The port selected in Test 12 is displayed as
the default. Normally, the input cable that has
been connected and reconnected sequentially in
12. can just be reconnected to TO CONSOLE.)
Fixed to the port selected for the input side;
the TO CONSOLE connections are changed
in order.
When changing to the next port, a pop-up
box like the one below is displayed.
12
Please select 68pin ports to check
[INPUT Port]
1
[
TO CONSOLEPort
]
OK
For this item, the DIP switch
setting does not matter, so it
can be ignored
13. DSP1D-JK4 (TO CONSOLE x) Output Test
This test checks the JK4 port output direction communications. For this item, use either the altered TO CONSOLE (OUTPUT) ID
change jig or the altered special cable.
12-1. DSP1D-JK2 (OUTPUT 1) Test
OK
12-1. DSP1D-JK2 (OUTPUT 1) Test
SO:
RQ:
AK:
W.CLK:
OK
* SO
OK* RQ
OK* AK
OK
OK
* W.CLK
* CONTROL
OK
OK
OK
* ID
* MSB/LSB
* 2CH/4CH
In
Out
In
Out
ID:
Connect [INPUT 1] to [OUTPUT 1].
OK
The INPUT port used for the output check is
selected from the pull-down list.
Fixed to the port selected for the input side;
the output connections are changed in order.
When changing to the next port, a pop-up
box like the one below is displayed.
16
Please select 68pin ports to check
[INPUT Port]
1
[OUTPUT Port]
OK
ID change jig DIP
switch settings
12. DSP1D-JK2 (OUTPUT x) Test
This test checks the JK2 port with loopback connections. These items are repeated only for INPUT1-10. The output ID change jig is
used for Item 12.
14. DSP1D-JK3 (CASCADE) Test
OK
14. DSP1D-JK3 (CASCADE) Test
OK
OK* DIR2
OK
OK
OK
OK
OK
OK
DIR2(IC110,126):
OK
OK
OK
OK
OK
OK
SI/SO:
W.CLK:
CONTROL:
* SI/SO
* W.CLK
* CONTROL
* ID (CASCADE IN)
In
Out
* ID (CASCADE OUT)
* MSB/LSB
In
Out
ID(CASCADE IN):
ID(CASCADE OUT):
MSB/LSB:
Change DipSW.
OK
Connect [CASCADE OUT] to [CASCADE OIN].
OK
A pop-up box is displayed asking you to change
the connections and DIP switch settings.
Change [MSB/LSB line] to low level.
OK
In the MSB/LSB items, the following popup menu will be displayed. Set the
switches on the ID conversion jig so that
the corresponding signal will become low
and click the OK button.
ID change jig DIP
switch settings
ID change jig DIP
switch settings
The pop-up box below is
displayed just before the ID
(CASCADE out), so change the
ID change jig DIP switch settings.
14. DSP1D-JK3 (CASCADE) Test
This test checks the JK3 port with loopback connections. For this test, use either the Cascade ID change jig.
NG sample
Please refer to page 49, 51, 52 for NG charts.
NG sample
Please refer to page 49, 51, 52 for NG charts.
NG sample
Please refer to page 49, 51, 52 for NG charts.
Page 13
DSP1D
56
Connect USBport[HostPCtoDSP1D].Push OK button.
OK
A pop-up box appears verifying that D24 has gone into playback status through
MIDI THRU. The inspector judges OK/NG, but since the MIDI OUT/IN loopback
check is carried out at the same time, if a problem is found in the loopback check,
even though the inspector presses OK, NG appears.
When the pop-up box asking you to make the connections for the USB check
appears, connect the USB cable.
(If you connect the cable before requested, the software is not loaded properly.)
(The USB check driver must be installed before hand.)
Please check [D24].
NGOK
ON OFF
Please prepare for [48kHz + 6% W.CLK].
OK
For the 75 switch item, the pop-up box below is displayed, so send any clock
with the function generator and judge visually with the oscilloscope.
The pop-up box below is displayed for items requiring connection changes. Press
OK to start the check.
Please check [Jitter (48kHz)].
NGOK
Please check [WordClock 75ohm SW].
NGOK
After the check is started with the above pop-up box, a pop-up box is displayed
for the inspector to enter the results of their visual check, OK or NG.
Please check [LED].
NGOK
The pop-up box below is displayed for the DSP1D front LED check. Judge the
LEDs visually. The six LEDs should light up in order so when you have verified
that they do so, press OK.
A pop-up box is displayed asking you to stop D24. If the inspections
have all been normal up to this point, D24 should already be stopped,
but if it has not been stopped, press the Stop button.
Normal oscilloscope behavior
for 75 switch
16.DSP1D-JK6,LED2 Test OK
16. DSP1D-JK6,LED2 Test
OK
OK* MIDI
OK
OK
OK
OK
OK
MIDI
OK
OK
OK
OK
OK
RS232C:
USB:
W.CLK 75ohm SW:
* RS232C
* USB
* W.CLK 75ohm SW
* W.CLK
* LED2
In 48 kHz + 6%
In 44.1kHz - 10%
Jitter 48 kHz
Jitter 44.1kHz
DIR2
In/Out
LED2:
W.CLK:
16. DSP1D-JK6 Test
This test checks the JK6 port and LED2. For details on how to change the connections, see Page 45.
15. DSP1D-JK5 Test OK
15. DSP1D-JK5 Test
OK
OK
Now Checking …
ETHER
NG example
* REMOTE (CROSS)
OK
OK
OK
OK
REMOTE(CROSS)
OK
OK
OK
OK
GPI:
TC:
REMOTE(STRAIGHT)
* GPI
* TC
* REMOTE (STRAIGHT)
* ETHER
CH1
CH2
ETHER:
CH1:
CH2:
OK
OK
15. DSP1D-JK5 Test
15. DSP1D-JK5 Test
NG
NG* REMOTE (CROSS)
NG
NG
NG
NG
REMOTE(CROSS)
NG
NG
NG
NG
GPI:
TC:
REMOTE(STRAIGHT)
* GPI
* TC
* REMOTE (STRAIGHT)
* ETHER
CH1
CH2
ETHER:
CH1:
CH2:
NG
NG
Please stop [D24] and connect it by [Cross…].
OK
A pop-up box is displayed asking you to stop D24.
At this point, normally D24 should already be
stopped and you can just verify this.
Replace [Cross] serial cable with [Straight] one.
OK
Instructions appear to replace the serial cross cable
with a straight cable, so change the cable as
instructed, then press OK.
• Normal behavior for each inspection item
REMOTE (CROSS)
TC
REMOTE (STRAIGHT)
D24 playback (TC send)
TC check from D24
D24 stop
15. DSP1D-JK5 Test
This test checks the JK5 port.
Detects PLL for valid detection
(IC301 of IFC3 sheet).
Page 14

DSP1D
ERROR MESSAGES
• If both ENGINE ID A and B indicators are flash-ing:
There is a malfunction in the internal board (PDB, GDB, IDB1/2, EDB, EMB, or CIB). Or the necessary board does not exist.
• If either ENGINE ID A or B indicator is flashing:
During the Mirror mode operation, the ENGINE ID indicator for the unused DSP1D/DSP1D-EX flashes, indicating that the
unit is in standby mode.
If Indicator A is flashing, unit A is in standby mode. If Indicator B is flashing, unit B is in standby mode.
• If the CONTROL I/O 1 indicator is flashing:
Communication between the CS1D control surface and the DSP1D is not established.The CONSOLE 1, 2 IN OUT jacks or the
PC CON-TROL port is not connected correctly.
• If the INPUT CONFIGURATION 48CH is flashing:
The signal is not locking to the word clock.
57
Page 15
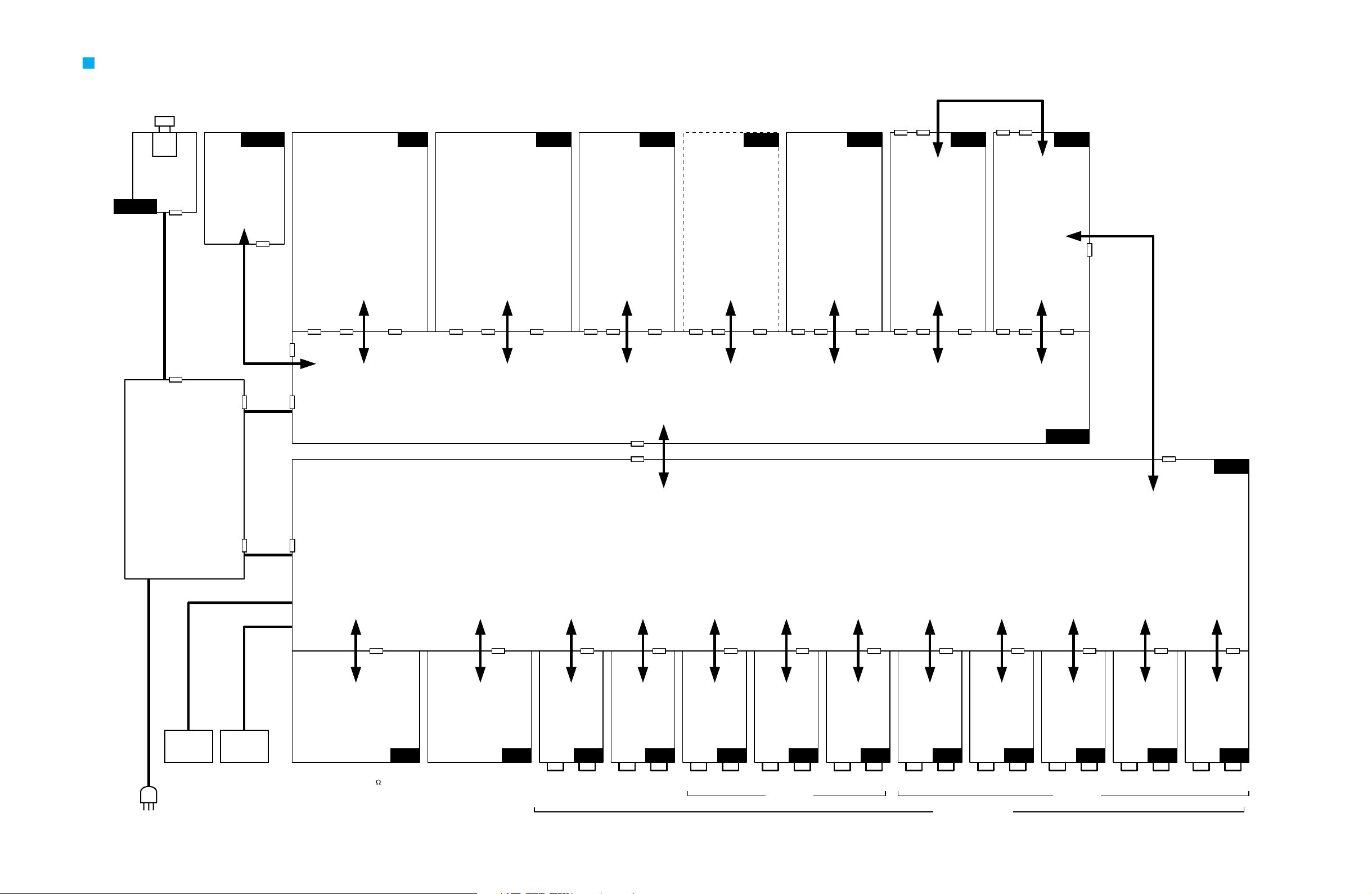
POWER UNIT
FANFAN
[1][2][3][5][6][7] [4][8][9][10][1][2][3][4][5]
[6]
[IN]
[OUT][1][2]
[INPUT]
[OUTPUT]
[CASCADE]
[CONSOLE I/O]
[DIGITAL I/O]
[ON/OFF]
[POWER]
FOR DSP1D-EX
[CONTROL I/O]
[CONSOLE]
[1]
[IN]
[OUT]
[2]
[IN]
[OUT]
[REMOTE]
[RS-422]
[GPI]
[TIME CODE IN]
[MIDI]
[IN]
[OUT]
[THRU]
[PC CONTROL]
[RS-232-C]
[USB]
[WORD CLOCK]
[IN]
[OUT]
[75 ] [ON]
[OFF]
P.66
P.67 P.68 P.69 P.69 P.69 P.70 P.71
P.66
P.65 P.60
P.59
PSB2
CN200
CN10
CN3~7
CN4~7,9 CN105,305,
405,505,605
CN104,204,304,
404,504,604
CN803
CN101
CN104,304,504,
604,801,802
CN105,305,505,
605,803,804
CN103
CN703
CN102
CN702
CN101
CN701
CN103
CN603
CN102
CN602
CN101
CN601
CN625
CN503
CN651
CN502
CN650
CN501
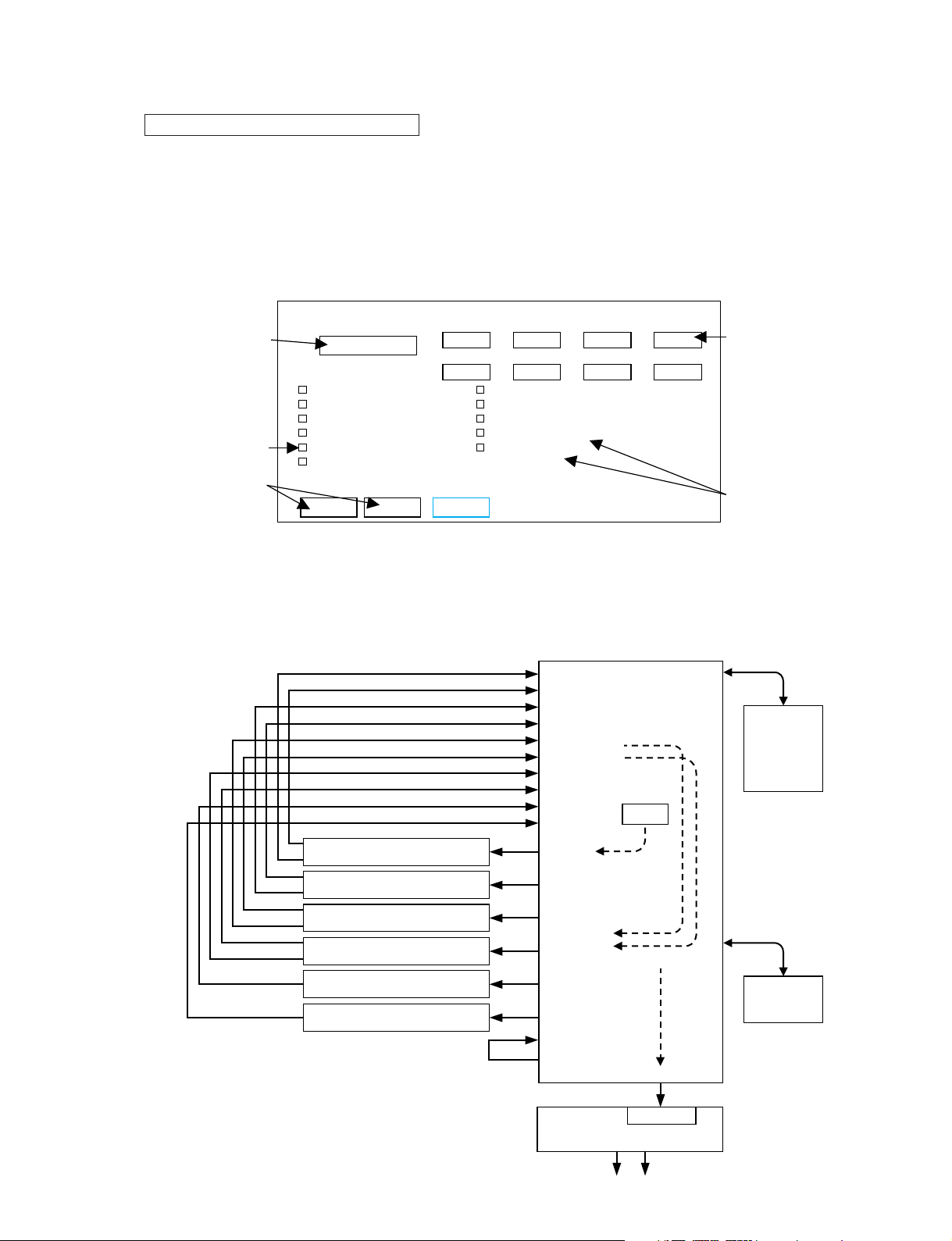
LED2 CIB EMB EDB IDB GDB PDBIDB
CN3
CN403
CN2
CN402
CN1
CN401
CN3
CN303
CN2
CN302
CN1
CN301
CN100
CN102
CN904
CN203
CN903
CN202
CN901 CN900
CN902
CN201
CN902
CN103
CN901
CN102
CN950 CN952
CN900
CN101
CN801,802,
805~808
CN951,953,
954,955,
956,957
MB11
IFC1
JK1
WHOLE
P.60
CN101
CN102
JK1
P.60
CN102
CN102
JK1
P.60
CN103
CN102
JK1
P.60
CN104
CN102
JK1
P.61
CN104
CN102
JK2
P.61
CN201
CN102
JK2
P.61
CN203
CN102
JK2
P.62
CN301
CN102
JK3
P.63P.64
CN302
CN102
JK4
CN303
CN100
JK5
CN304
CN100
JK6
DSP1D
BLOCK DIAGRAM
KEC-92538-2
58
Page 16

CONNECTOR
USB
GPI
REMOTE(RS-422)
CONTROL I/O
TIME CODE
FPGA
(CLOCK SYSTEM,I/O CONTROL)
DIR2 x 2
(CLOCK
GENERATOR)
XTAL
(22.5792Mz)
WC(X21)
XI
WC
LOCK
DIR2
(VALID
DETECTOR)
INPUT,OUTPUT CONTROL I/O
XI
WC
LOCK
CASCADE CONTROL I/O
LOCK
BUFFER & TRANSCEIVER
INPUT,OUTPUT CONTROL I/O
IFC
INPUT,OUTPUT CONTROL I/O
CASCADE CONTROL I/OCASCADE CONTROL I/O
CONNECTOR
OUTPUT 1,2,3,4,5,6 AUDIO
INPUT 1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9,10 AUDIO
CASCADE IN,OUT AUDIO
CONSOLE I/O 1,2 AUDIO
BUFFER
256FS,etc.
CONNECTOR
BUFFER & TRANSCEIVER
IC707~716 20pin
REMOTE(RS-422)
TIME CODE
CONTROL I/O
WC
LOCK
CONNECTOR
INPUT 9 AUDIO
INPUT 9 CONTROL I/O
256FS,etc.
INPUT 9 WC
INPUT 7 AUDIO
INPUT 8 CONTROL I/O
INPUT 7 WC
FS
INPUT 10 CONTROL I/O
INPUT 10 AUDIO
INPUT 10 WC
INPUT 7 CONTROL I/O
INPUT 8 AUDIO
INPUT 8 WC
INPUT 5 AUDIO
INPUT 6 CONTROL I/O
INPUT 5 WC
INPUT 5 CONTROL I/O
INPUT 6 AUDIO
INPUT 6 WC
INPUT 3 AUDIO
INPUT 4 CONTROL I/O
INPUT 3 WC
INPUT 3 CONTROL I/O
INPUT 4 AUDIO
INPUT 4 WC
INPUT 1 AUDIO
INPUT 2 CONTROL I/O
INPUT 1 WC
INPUT 1 CONTROL I/O
INPUT 2 AUDIO
INPUT 2 WC
JK
CASCADE OUT WC
OUTPUT 6 CONTROL I/O
CASCADE OUT CONTROL I/O
CONSOLE I/O 2 AUDIO IN
256FS,etc.
CONSOLE I/O 2 WC
CASCADE IN AUDIO
OUTPUT 6 WC
CONSOLE I/O 1 AUDIO IN
CONSOLE I/O 2 AUDIO OUT
CONSOLE I/O 1 AUDIO OUT
CONSOLE I/O 1 WC
CASCADE IN CONTROL I/O
CASCADE OUT AUDIO
CASCADE IN WC
OUTPUT 5 CONTROL I/O
OUTPUT 5 WC
OUTPUT 4 CONTROL I/O
OUTPUT 4 WC
OUTPUT 3 CONTROL I/O
OUTPUT 3 WC
OUTPUT 2 CONTROL I/O
OUTPUT 2 WC
OUTPUT 1 CONTROL I/O
OUTPUT 1 AUDIO
OUTPUT 1 WC
OUTPUT 2 AUDIO
OUTPUT 3 AUDIO
OUTPUT 4 AUDIO
OUTPUT 5 AUDIO
OUTPUT 6 AUDIO
JK
GPI
USB
PC CONTROL(RS-232-C)
MIDI IN,OUT
IFC
IFC
MIDI IN,OUT
PC CONTROL(RS-232-C)
256FS,etc.
P.66
XTAL
(24.576Mz)
IFC1
MB11
IC701~706, IC717
20pin
171,173
215
3
214
97
100
110
99
109
36
12
103,10515
36
12
15
3
IC503
240pin
IC605,IC606
44pin
44pin
IC604
IC608,
IC609,
IC610
P.71
PDB
CONNECTOR
P.60
JK1
CONNECTOR
P.60
JK1
CONNECTOR
P.60
JK1
CONNECTOR
P.60
JK1
CONNECTOR
P.60
JK1
CONNECTOR
P.61
JK2
CONNECTOR
P.61
JK2
CONNECTOR
P.61
JK2
CONNECTOR
P.62
JK3
CONNECTOR
P.63
JK4
P.64
JK5
P.65
JK6
DSP1D
59
KEC-92538-3
Page 17

CONNECTOR
BUFFER & TRANSCEIVER
JK
INPUT2 CONTROL I/O
INPUT2
AUDIO
INPUT2
AUDIO
INPUT2
AUDIO
INPUT2
WC
256FS
,etc.
256FS,etc.
INPUT2
CONTROL
I/O
JK
INPUT2 AUDIO
256FS,etc.
ID
ID
INPUT1 AUDIO
INPUT2 WCINPUT2 WC
INPUT1 WC
LOCK
JK
INPUT1 CONTROL I/O
RECEIVER & BUFFER
DIR2
I/O PORT
I/O PORT
INPUT1
AUDIO
INPUT1
AUDIO
INPUT1
AUDIO
INPUT1
WC
256FS
,etc.
256FS,etc.
INPUT1
CONTROL
I/O
ID
ID
INPUT1 WC
ATSC X2
(PHASE ADJUSTER
& FORMAT
CONVERTER)
MUTE
LOCK
MUTE
MUTE
[INPUT]
[1] ([3],[5],[7],[9])
CONNECTOR(DSUB 68P)
[INPUT]
[2] ([4],[6],[8],[10])
CONNECTOR(DSUB 68P)
INPUT2 CONTROL I/O
INPUT1 CONTROL I/O
FS
FS
P.59
JK1
IFC1
IC122~124, IC129 20pin
IC100
9
8
MUTE
IC100
12
11
IC103~108 16pin IC127,128,130~133 20pin
RECEIVER & BUFFER
IC113~118 16pin IC127,128,130~133 20pin
(256FS,etc.
GENERATOR,
WC DETECTOR)
IC112 44pin
DIR2
(256FS,etc.
GENERATOR,
WC DETECTOR)
IC121 44pin
IC109, IC110
80pin
ATSC X2
(PHASE ADJUSTER
& FORMAT
CONVERTER)
IC119, IC120
80pin
78
78
KEC-92538-4
DSP1D
60
Page 18

P.59
IFC1
JK2
CONNECTOR
BUFFER & TRANSCEIVER
JK
OUTPUT2 CONTROL I/O
OUTPUT2
AUDIO
OUTPUT2
AUDIO
OUTPUT2
AUDIO
OUTPUT2
WC
256FS,etc.
OUTPUT2
CONTROL
I/O
JK
OUTPUT2 AUDIO
256FS,etc.
ID
ID
OUTPUT1 AUDIO
OUTPUT2 WC
OUTPUT2 WC
OUTPUT1 WC
LOCK
JK
DRIVER & BUFFER
OUTPUT1
AUDIO
OUTPUT1
AUDIO
OUTPUT1
AUDIO
OUTPUT1
WC
256FS,etc.
ID
ID
OUTPUT1 WC
ATSC X2
FORMAT CONVERTER
LOCK
MUTE
MUTE
[1]([3],[5])
[OUTPUT]
CONNECTOR(D-SUB Half Pitch 68P)
[2]([4],[6])
[OUTPUT]
CONNECTOR(D-SUB Half Pitch 68P)
DIR2
(WC DETECTOR)
OUTPUT2 CONTROL I/O
OUTPUT1 CONTROL I/O
OUTPUT1
CONTROL
I/O
OUTPUT1 CONTROL I/O
FS
FS
IC122~124 20pin IC125 16pin IC127~134 20pin
IC103, IC105~108 16pin IC131 20pin IC104 16pin
DRIVER & BUFFER
IC115, IC1117~120 16pin IC130 20pin IC116 16pin
I/O PORT
I/O PORT
IC112 44pin
IC100, IC101
80pin
ATSC X2
FORMAT CONVERTER
IC113, IC114
80pin
15
DIR2
(W
C DETECTOR)
IC121 44pin
15
KEC-92538-5
DSP1D
61
Page 19

P.59
IFC1
JK3
CONNECTOR
BUFFER & TRANSCEIVER
JK
CASCADE IN CONTROL I/O
RECEIVER & BUFFER
CASCADE
IN
AUDIO
CASCADE
IN
AUDIO
CASCADE
IN AUDIO
CASCADE
IN
WC
256FS
,etc.
256FS,etc.
CASCADE
IN
CONTROL
I/O
JK
CASCADE IN AUDIO
256FS,etc.
ID
ID
CASCADE IN WC
CASCADE IN WC
CASCADE
OUT
AUDIO
CASCADE OUT WC
JK
CASCADE OUT CONTROL I/O
DRIVER & BUFFER
DIR2
(W
C DETECTOR)
I/O PORT
I/O PORT
CASCADE
OUT
AUDIO
CASCADE
OUT
AUDIO
CASCADE
OUT
AUDIO
CASCADE
OUT
WC
CASCADE
OUT
CONTROL
I/O
ID
ID
CASCADE OUT WC
DFF
LOCK
MUTE
INV
128FS
LOCK
MUTE
MUTE
[CASCADE]
[OUT]
CONNECTOR(D-SUB Half Pitch 68P)
[CASCADE]
[IN]
CONNECTOR(D-SUB Half Pitch 68P)
CASCADE IN CONTROL
I/O
CASCADE OUT
CONTROL I/O
FS
FS
FS
IC127~129, IC131~138 20pin
IC117~119
20pin
IC126
44pin
IC120~125 16pinIC101, 102, 104~107 16pin
IC104~106
16pin
3
15
ATSC X4
(PHASE ADJUSTER
& FORMAT
CONVERTER)
IC111~IC114
80pin
DIR2
(256FS,etc.
GENERATOR,
WC DETECTOR)
IC110 44pin
78
IC108
10 9
8
KEC-92538-6
DSP1D
62
Page 20

P.59
IFC1
JK4
CONNECTOR
BUFFER & TRANSCEIVER
JK
CONNECTOR(D-SUB Half Pitch 68P)
RECEIVER & BUFFER
I/O PORT
CONSOLE
I/O 1
IN
AUDIO
CONSOLE
I/O 1
IN
AUDIO
CONSOLE
I/O 1
IN AUDIO
CONSOLE
I/O 1
WC
256FS
,etc.
256FS,etc.
JK
CONSOLE I/O 1 IN
AUDIO
256FS,etc.
ID ID
CONSOLE I/O 1 WCCONSOLE I/O 1 WC
CONSOLE I/O 1 OUT
AUDIO
CONSOLE
I/O 1
OUT
AUDIO
CONSOLE
I/O 1 OUT
AUDIO
LOCK
MUTE
MUTE
FORMAT CONVERTER
(ATSC)
X1
MUTE
[CONSOLE I/O]
[1]
[CONSOLE I/O]
[2]
SAME AS ABOVE
CONSOLE
I/O 1
OUT
AUDIO
CONSOLE I/O 2 OUT
AUDIO
CONSOLE I/O 2
IN AUDIO
CONSOLE I/O 2 WC
FS
IC103~108 16pin
IC110 80pin
ATSC
(PHASE ADJUSTER
& FORMAT
CONVERTER)
IC109
80pin
DIR2
(256FS,etc.
GENERATOR,
W
C DETECTOR)
IC112 44pin
15
IC122, 123 20pin IC127~134 20pin
KEC-92538-7
DSP1D
63
Page 21

P.59
IFC1
JK5
CONNECTOR
BUFFER & TRANSCEIVER
GPI
CONNECTOR(BNC X4)
DRIVER & RECEIVER
CONTROL I/O
CONNECTOR(9pin DSUB)
CONNECTOR(25pin DSUB)
CONNECTOR(female XLR)
DRIVER & RECEIVER
REMOTE(RS-422)
DRIVER
I/O PORT
CONTROL CONTROL
CONTROL
RECEIVER
TIME CODE TIME CODE
REMOTE(RS-422)
[CONSOLE]
[CONTROL I/O]
[IN] [1] [OUT]
[IN] [2] [OUT]
[REMOTE]
[RS-422]
[GPI]
[TIME CODE IN]
GPI
IC104 20pin IC100 14pin
IC105 20pin
IC106 3pin
IC101 16pinIC201, 301, 401, 501 16pin
KEC-92538-8
DSP1D
64
Page 22

P.59
IFC1
JK6
[OUT]
CONNECTOR
BUFFER & TRANSCEIVER
USB
CONNECTOR(MIDI X3)
RECEIVER
CONNECTOR(9pin DSUB)
CONNECTOR(USB)
CONNECTOR(BNC X2)
DRIVER & RECEIVER
PC CONTROL(RS-232-C)
USB CONTROLER &
DRIVER & RECEIVER
DRIVER & RECEIVER
[MIDI]
[THRU]
[IN]
[OUT]
[PC CONTROL]
[RS-232C]
[USB]
[WORD CLOCK]]
DRIVER
BUFFER & TRANSCEIVER
MIDI IN,OUT
USB
[IN]
WCWC
FS FS
WC
FS
DIR2
(CLOCK
GENERATOR)
LOCKLOCK
USB
MIDI OUT
MIDI IN
IC103, 104, 106 20pin IC204 20pin
4
5
15
17
6
IC202 44pin
36
15
IC200, 201 16pin
710
39
IC105
28pin
IC102 16pin
IC107,108IC101 8pin
31
42
IC106 20pin
9,11 8,12
8,9,11,12
KEC-92538-9
DSP1D
65
Page 23

P.59
LED2
LED2
MB11
MB11
IFC1
CONNECTOR
USB
PC CONTROL(RS-232-C)
CASCADE CONTROL I/O
CONTROL I/O
EM
TIME CODE
MIDI IN,OUT
REMOTE(RS-422)
GPI
CONNECTOR
IFC
INPUT,OUTPUT CONTROL I/O
EM
METER DATA TRIGGER
CONNECTOR
METER DATA TRIGGER
CONNECTOR
METER DATA TRIGGER
CONNECTOR
METER DATA TRIGGER
CONNECTOR
256FS,etc.
AUDIO
METER DATA TRIGGER
CONNECTOR
256FS,etc.
AUDIO
METER DATA TRIGGER
DPM
256FS,etc.
256FS,etc.
256FS,etc.
DPM
DPM
DPM
DPM
DPM
AUDIO
AUDIO
AUDIO
CONNECTOR
LED CONTROL
CO
NN
ECTO
R
CO
NNECTO
R
P.67
CIB
P.68
EMB
P.69
EDB
P.69
IDB
P.69
IDB
P.70
GDB
P.71
PDB
KEC-92538-10
DSP1D
66
Page 24

CONNECTOR
HI
BUFFER & TRANSCEIVER
CPU
(TIMECODE,MIDI,REMOTE,
GPI CONTROL)
TC
EM
FPGA
(CONTROL I/O)
EM
DUAL
PORT
MEMORY
FIFO
UP
DW
CPU
(PC CONTROL,
CASCADE IN,OUT CONTROL)
FLASH
MEMORY
SRAM
HI
DUAL
PORT
MEMORY
TC
USB
CASCADE CONTROL I/O
GPI
MIDI IN,OUT
CASCADE CONTROL I/O
TC
TC
CONTROL I/O CONTROL I/O
TIME CODE
PC CONTROL(RS-232-C)PC CONTROL(RS-232-C)
REMOTE(RS-422)
MIDI IN,OUT
REMOTE(RS-422)
P.66
CIB
MB11
IC105~110, IC135, IC137 20pin IC112~115 24pin IC120, 121, IC130, IC140, IC145, 146 20pin
IC133
44pin
IC139
112pin
IC126
240pin
IC129
112pin
IC132
48pin
FLASH
MEMORY
SRAM
IC143
44pin
IC142
48pin
IC136
44pin
IC122, IC123
32pin
FIFO
IC118, IC119
32pin
IC116 100pin
DUAL
PORT
MEMORY
IC127 100pin
IC138 100pin
KEC-92538-11
DSP1D
67
Page 25

IC137~146 20pin IC102~104 20pin IC109~112 20pin IC147 20pin
P.66
EMB
MB11
CONNECTOR
BUFFER & TRANSCEIVER
CPU
(SCENE,METER CONTORL)
EM
EM
EM
METER DATA TRIGGER METER DATA TRIGGER
DPM DPM
FPGA
(DUAL PORT MEMORY
CONTROL)
BATTERY
(BUCK UP)
UI
CPU
(DIGITAL I/O CONTROL)
UI
DUAL
PORT
MEMORY
IFC
INPUT,OUTPUT
CONTROL I/O INPUT,OUTPUT CONTROL I/O
FPGA
(UI BUS CONTROL)
OUT
PORT
EM
LED CONTROLLED CONTROL
FLASH
MEMORY
SRAM
IC131
44pin
SRAM
IC119,120
44pin
IC124,125
32pin
IC127 112pin
IC135 100pin
IC133 100pin
IC114 144pin
IC130
48pin
FLASH
MEMORY
IC118
48pin
IC126 100pin
DUAL
PORT
MEMORY
IC113 100pin
KEC-92538-12
DSP1D
68
Page 26

P.66
EDBIDB
MB11
CONNECTOR
BUFFER & TRANSCEIVER
DSP SECTION
METER DATA TRIGGER
AUDIO
256FS,etc.
AUDIO
DPM
256FS,etc.
:See P.74-93
DSP
FPGA
(DSP ACCESS & W
AIT CONTORL
,DUAL PORT MEMORY CONTROL)
CPU
(DSP,DUAL PORT MEMORY
CONTROL)
FLASH
MEMORY
SRAM
DSP
METER DATA TRIGGER
TRANSCEIVER
DSP
CONTROL
WAIT
WAIT
IC250~253 20pin
IC100 112pin
IC254 144pin
IC255~260 20pin IC600~606 20pin
EDB
IDB
:See P.92,93
31 140
IC103
44pin
IC104
48pin
IC101 20pin
KEC-92538-13
DSP1D
69
Page 27

P.66
P.71
GDB
PDB
MB11
CONNECTOR
DSP
BUFFER & TRANSCEIVER
DSP SECTION
FPGA
(DSP ACCESS & WAIT CONTORL,
DUAL PORT MEMORY CONTROL)
CPU
FLASH
MEMORY
SRAM
DSP
METER DATA TRIGGER
METER DATA TRIGGER
TRANSCEIVER
DSP
BUFFER
CONNECTOR
AUDIO
AUDIO
AUDIO
256FS,etc.
AUDIO
DPM
See P.84-88
CONTROL
256FS,etc.
WAIT
WAIT
IC102 20pin
IC220~229 20pin
IC850~871 20pin
IC103
44pin
IC104
48pin
IC100
112pin
IC200
144pin
(DSP,DUAL PORT MEMORY
CONTROL)
14031
KEC-92538-14
DSP1D
70
Page 28

P.66
P.70
PDB
GDB
MB11
CONNECTOR
DSP
BUFFER & TRANSCEIVER
FPGA
(DSP ACCESS & WAIT CONTORL
,DUAL PORT MEMORY CONTROL)
CPU
(DSP,DUAL PORT MEMORY
CONTROL)
FLASH
MEMORY
SRAM
DSP
METER DATA TRIGGER METER DATA TRIGGER
TRANSCEIVER
DSP
AUDIO
AUDIO
AUDIO
256FS,
etc.
256FS,etc.
AUDIO
DPM
CONTROL
AUDIO
AUDIO
CONNECTOR
BUFFER
P.66
IFC1
CONNECTOR
BUFFER
WAIT
WAIT
IC812~817,
IC852,853,861,862
20pin
IC800~810, IC817
IC855~860,862,869
20pin
IC902~904 20pin
IC105 20pin
DSP SECTION
See P.72,73
89,90,91
IC106,IC110~112,IC200~202,IC204~206 20pin
IC811,IC817~822,IC850,851,854,IC863~868,
IC870~872,IC900,901 20pin
IC107
44pin
IC114
48pin
IC203
144pin
IC101
112pin
31 140
KEC-92538-15
DSP1D
71
Page 29

INSERT IN ST IN 3-4
INPUT 1-4
INPUT 5-8
INPUT 9-12
INPUT 13-16
INPUT 17-20
INPUT 21-24
INPUT 25-28
INPUT 29-32
INPUT 33-36
INPUT 37-40
INPUT 41-44
INPUT 45-48
INPUT 49-52
INPUT 53-56
INPUT 57-60
INPUT 61-64
INPUT 65-68
INPUT 69-72
INPUT 73-76
INPUT 77-80
INPUT 81-84
INPUT 85-88
INPUT 89-92
INPUT 93-96
INPUT 97-100
INPUT 101-104
INPUT 105-108
INPUT 109-112
INPUT 113-116
INPUT 117-120
INPUT 121-124
INPUT 125-128
INPUT 129-132
INPUT 133-136
INPUT 137-140
INPUT 141-144
INPUT 145-148
INPUT 149-152
INPUT 153-156
INPUT 157-160
INPUT 161-164
INPUT 165-168
INPUT 169-172
INPUT 173-176
INPUT 177-180
INPUT 181-184
INPUT 185-188
INPUT 189-192
CH IN 1-4
CH IN 17-20
CH IN 21-24
PARALLEL BUS
INSERT IN CH 1-4
INSERT IN CH 5-8
INSERT IN CH 9-12
INSERT IN CH 13-16
INSERT IN CH 17-20
INSERT IN CH 21-24
INSERT IN CH 25-28
INSERT IN CH 29-32
INSERT IN CH 33-36
INSERT IN CH 37-40
INSERT IN CH 41-44
INSERT IN CH 45-48
DSP5
P.74
FUNCTION: INPUT PATCH, PEAK METER
IN:40
OUT:17
IN:40
OUT:15
CH IN 25-28
CH IN 29-32
CH IN 33-36
CH IN 37-40
CH IN 41-44
CH IN 45-48
CH IN 49-52
CH IN 53-56
CH IN 57-60
CH IN 61-64
CH IN 65-68
CH IN 69-72
INPUT 193-196
INPUT 197-200
INPUT 201-204
INPUT 205-208
P.73
01
02
03
04
05
06
07
08
09
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
21
22
00
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
01
02
03
04
05
06
07
08
09
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
00
20
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
INPUT 241-244
INPUT 245-248
INPUT 249-252
INPUT 253-256
INPUT 257-260
INPUT 261-264
INPUT 265-268
INPUT 269-272
INPUT 273-276
INPUT 277-280
INPUT 281-284
INPUT 285-288
INPUT 289-292
INPUT 293-296
INPUT 297-300
INPUT 301-304
INPUT 305-308
INPUT 309-312
INPUT 313-316
INPUT 317-320
INSERT IN CH 57-60
INSERT IN CH 61-64
INSERT IN CH 65-68
INSERT IN CH 69-72
INSERT IN CH 49-52
INSERT IN CH 53-56
IN:28
OUT:14
INPUT 209-212
INPUT 213-216
INPUT 217-220
INPUT 221-224
INPUT 225-228
INPUT 229-232
INPUT 233-236
INPUT 237-240
CH IN 5-8
CH IN 9-12
CH IN 13-16
P.75 P.76
KEY IN 1-4
P.76
P.85
P.89
2TR IN 1-2(LR)
INSERT IN ST IN 1-2
ST IN 1-2
ST IN 3-4
INSERT IN ST IN 5-6
ST IN 5-6
2TR IN 3-4(LR)
2TR IN 5-6(LR) KEY IN 1-4
KEY IN 1-4
KEY IN 1-4
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
44
45
46
47
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
P.88
48
OUT PATCH TEST 1
OUT PATCH TEST 2
OUT PATCH TEST 3
OUT PATCH TEST 4
01
02
03
00
OUT PATCH TEST 5
OUT PATCH TEST 6
04
05
06
07
44
45
46
C1 TALKBACK A-B,RESERVED
P.92,93
EFFECT RETURN 1-2(LR)
EFFECT RETURN 3-4(LR)
EFFECT RETURN 5-6(LR)
EFFECT RETURN 7-8(LR)
ANALYZER SOURCE 1
ANALYZER SOURCE 2
C1 2TR IN 1-2(LR)
C1 2TR IN 3-4(LR)
C1 2TR IN 5-6(LR)
KEY IN 1-4
P.125
[CONSOLE I/O]
C2 TALKBACK A-B,RESERVED
C2 2TR IN 1-2(LR)
C2 2TR IN 3-4(LR)
C2 2TR IN 5-6(LR)
47
GEQ RETURN 1-4(LR)
GEQ RETURN 5-8(LR)
GEQ RETURN 9-12(LR)
GEQ RETURN 13-16(LR)
GEQ RETURN 17-20(LR)
GEQ RETURN 21-24(LR)
08
09
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
CASCADE IN TB,COMM.,SUB IN
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
44
45
46
47
IC250 IC251 IC300
[2]
[1]
DSP5
DSP5
P.74
[DIGITAL I/O]
[INPUT]
[1]-[5]
[DIGITAL I/O]
[INPUT]
[6]-[10]
PDB
KEC-92538-16
72
DSP1D
Page 30
PDB
CH IN 73-76
CH IN 77-80
CH IN 81-84
CH IN 85-88
CH IN 89-92
CH IN 93-96
INSERT IN CH 73-76
INSERT IN CH 77-80
INSERT IN CH 81-84
INSERT IN CH 85-88
INSERT IN CH 89-92
INSERT IN CH 93-96
FUNCTION: INPUT PATCH, PEAK METER
P.72
INSERT IN MIX 1-4
INSERT IN MIX 9-12
INSERT IN MIX 13-16
INSERT IN MIX 17-20
INSERT IN MIX 21-24
INSERT IN MIX 25-28
INSERT IN MIX 29-32
INSERT IN MIX 33-36
INSERT IN MIX 37-40
INSERT IN MIX 41-44
INSERT IN MIX 45-48
INSERT IN MIX 5-8 INSERT IN MATRIX 5-8
INSERT IN MATRIX 1-4
INSERT IN MATRIX 9-12
INSERT IN MATRIX 13-16
INSERT IN MATRIX 17-20
INSERT IN MATRIX 21-24
SUB IN 1(LR),DIRECT IN 1(LR)
P.85
INSERT STEREO A-B
INPUT 1-4
INPUT 5-8
INPUT 9-12
INPUT 13-16
INPUT 17-20
INPUT 21-24
INPUT 25-28
INPUT 29-32
INPUT 33-36
INPUT 37-40
INPUT 41-44
INPUT 45-48
INPUT 49-52
INPUT 53-56
INPUT 57-60
INPUT 61-64
INPUT 65-68
INPUT 69-72
INPUT 73-76
INPUT 77-80
INPUT 81-84
INPUT 85-88
INPUT 89-92
INPUT 93-96
INPUT 97-100
INPUT 101-104
INPUT 105-108
INPUT 109-112
INPUT 113-116
INPUT 117-120
PARALLEL BUS
P.77
IN:40
OUT:14
IN:40
OUT:14
INPUT 193-196
INPUT 197-200
INPUT 201-204
INPUT 205-208
01
02
03
04
05
06
07
08
09
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
21
22
00
01
02
03
04
05
06
07
08
09
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
00
20
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
INPUT 209-212
INPUT 213-216
INPUT 217-220
INPUT 221-224
INPUT 225-228
INPUT 229-232
INPUT 233-236
INPUT 237-240
INSERT IN ST IN 7-8
ST IN 7-8
TALKBACK A-B,COMM. A-B
SUB IN 2,DIRECT IN 2
P.74,76
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
INPUT 121-124
INPUT 125-128
INPUT 129-132
INPUT 133-136
INPUT 137-140
INPUT 141-144
INPUT 145-148
INPUT 149-152
INPUT 153-156
INPUT 157-160
INPUT 161-164
INPUT 165-168
INPUT 169-172
INPUT 173-176
INPUT 177-180
INPUT 181-184
INPUT 185-188
INPUT 189-192
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
INPUT 241-244
INPUT 245-248
INPUT 249-252
INPUT 253-256
INPUT 257-260
INPUT 261-264
INPUT 265-268
INPUT 269-272
INPUT 273-276
INPUT 277-280
INPUT 281-284
INPUT 285-288
INPUT 289-292
INPUT 293-296
INPUT 297-300
INPUT 301-304
INPUT 305-308
INPUT 309-312
INPUT 313-316
INPUT 317-320
P.74,76
P.89
IN PATCH TEST 1
IN PATCH TEST 2
IN PATCH TEST 3
IN PATCH TEST 4
IN PATCH TEST 5
P.90
DSP5
IN:28
OUT:15
01
02
03
04
05
06
07
08
09
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
00
CASCADE IN TB,COMM.,SUB IN(LR)
OUT PATCH TEST 1
OUT PATCH TEST 2
OUT PATCH TEST 3
OUT PATCH TEST 4
OUT PATCH TEST 5
OUT PATCH TEST 6
C1 TALKBACK A-B,RESERVED
EFFECT RETURN 1-2(LR)
EFFECT RETURN 3-4(LR)
EFFECT RETURN 5-6(LR)
EFFECT RETURN 7-8(LR)
ANALYZER SOURCE 1
ANALYZER SOURCE 2
C1 2TR IN 1-2(LR)
C1 2TR IN 3-4(LR)
C1 2TR IN 5-6(LR)
KEY IN 1-4
C2 TALKBACK A-B,RESERVED
C2 2TR IN 1-2(LR)
C2 2TR IN 3-4(LR)
C2 2TR IN 5-6(LR)
GEQ RETURN 1-4(LR)
GEQ RETURN 5-8(LR)
GEQ RETURN 9-12(LR)
GEQ RETURN 13-16(LR)
GEQ RETURN 17-20(LR)
GEQ RETURN 21-24(LR)
CASCADE IN TB,COMM.,SUB
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
44
45
46
47
48 48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
44
45
46
47
FFT IN,FFT NOISE
IC301 IC350 IC351
DSP5
DSP5
P.86
KEC-92538-17
73
DSP1D
Page 31

IDB (1–48)
FUNCTION: INPUT EQ/GATE/COMP/DELAY/FADER ON
CH IN 1-4
KEY IN 1-4
<CH1>PRE EQ,PRE FADER,POST FADER,POST ON
INSERT OUT CH1-4
CH1-4 KEY IN CUE
DATA BUS(DRAM)
DSP6
P.72
INSERT IN CH 1-4 <CH2>PRE EQ,PRE FADER,POST FADER,POST ON
<CH3>PRE EQ,PRE FADER,POST FADER,POST ON
<CH4>PRE EQ,PRE FADER,POST FADER,POST ON
DIRECT OUT CH1-4
COMP KEY IN METER(CH1-4)
CH IN 5-8
<CH5>PRE EQ,PRE FADER,POST FADER,POST ON
INSERT OUT CH5-8
DATA BUS(DRAM)
P.72
INSERT IN CH 5-8
<CH6>PRE EQ,PRE FADER,POST FADER,POST ON
<CH7>PRE EQ,PRE FADER,POST FADER,POST ON
<CH8>PRE EQ,PRE FADER,POST FADER,POST ON
DIRECT OUT CH5-8
CH IN 9-12
<CH9>PRE EQ,PRE FADER,POST FADER,POST ON
INSERT OUT CH9-12
DATA BUS(DRAM)
P.72
INSERT IN CH 9-12
<CH10>PRE EQ,PRE FADER,POST FADER,POST ON
<CH11>PRE EQ,PRE FADER,POST FADER,POST ON
<CH12>PRE EQ,PRE FADER,POST FADER,POST ON
DIRECT OUT CH9-12
CH IN 13-16
<CH13>PRE EQ,PRE FADER,POST FADER,POST ON
INSERT OUT CH13-16
DATA BUS(DRAM)
IN:4
OUT:8
INSERT IN CH 13-16
<CH14>PRE EQ,PRE FADER,POST FADER,POST ON
<CH15>PRE EQ,PRE FADER,POST FADER,POST ON
<CH16>PRE EQ,PRE FADER,POST FADER,POST ON
DIRECT OUT CH13-16
ST IN 1-2
<ST IN 1(L)>PRE EQ,PRE FADER,POST FADER,POST ON
INSERT OUT ST IN 1-2
DATA BUS(DRAM)
P.72
INSERT IN ST IN1-2
<ST IN 1(R)>PRE EQ,PRE FADER,POST FADER,POST ON
<ST IN 2(L)>PRE EQ,PRE FADER,POST FADER,POST ON
<ST IN 2(R)>PRE EQ,PRE FADER,POST FADER,POST ON
DIRECT OUT ST IN 1-2
COMP KEY IN METER(ST IN 1-2)
CH IN 21-24
<CH21>PRE EQ,PRE FADER,POST FADER,POST ON
INSERT OUT CH21-24
DATA BUS(DRAM)
P.72
INSERT IN CH 21-24
<CH22>PRE EQ,PRE FADER,POST FADER,POST ON
<CH23>PRE EQ,PRE FADER,POST FADER,POST ON
<CH24>PRE EQ,PRE FADER,POST FADER,POST ON
DIRECT OUT CH21-24
CH IN 17-20
<CH17>PRE EQ,PRE FADER,POST FADER,POST ON
INSERT OUT CH17-20
P.72
INSERT IN CH 17-20
<CH18>PRE EQ,PRE FADER,POST FADER,POST ON
<CH19>PRE EQ,PRE FADER,POST FADER,POST ON
<CH20>PRE EQ,PRE FADER,POST FADER,POST ON
DIRECT OUT CH17-20
P.78
P.90
P.78
P.90
P.78
P.90
P.78
P.90
IN:4
OUT:8
IN:4
OUT:8
IN:4
OUT:8
P.78
P.90
P.78
P.90
P.75
P.72
IN:3
OUT:8
IN:4
OUT:8
IN:4
OUT:8
DRAM
1M x 16
(16Mbit)
DATA BUS(DRAM)
P.78
P.90
COMP KEY IN METER(CH5-8)
COMP KEY IN METER(CH9-12)
COMP KEY IN METER(CH13-16)
COMP KEY IN METER(CH17-20)
COMP KEY IN METER(CH21-24)
00
1
22
1
3
4
5
6
7
3
0
1
2
0
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
3
0
1
2
0
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
0
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
0
1
2
3
0
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
1
2
3
0
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
0
1
2
3
0
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
0
1
2
3
IN:4
OUT:6
DATA BUS(DRAM 32bit)
3
CH5-8 KEY IN CUE
CH9-12 KEY IN CUE
CH13-16 KEY IN CUE KEY CH 20 PRE GATE,CH17-20 KEY IN CUE
KEY ST IN 2 PRE GATE,CH21-24 KEY IN CUE
KEY ST IN 2 PRE GATE,ST IN1-2 KEY IN CUE
P.75
4
4
4
4
4
@ PRE COMP METER x 4
@ GATE KEY IN METER x 4
P.73
SUB IN 1(LR),DIRECT IN 1(LR)
TALKBACK A-B,COMM. A-B
0
1
SUB IN 1(LR),DIRECT IN 1(LR)
A(TB,TB/OSC,OSC,COMM.)
P.89
P.84
P.90
P.880
1
ADDRESS,RW CONTROL
0
P.75
2
CASCADE IN TB,COMM,SUB IN(LR)
2
CASCADE OUT TB,COMM.,SUB IN(LR)
3
SUB IN 2(LR),DIRECT IN 2(LR)
4
5
6
7
5
6
7
5
6
7
5
6
7
5
6
7
5
6
7
4
5
6
7
4
5
6
7
KEY 1-4 OUT(CH IN1-24)
PRE EQ METER 1
KEY IN METER 1
3
4
5
6
7
P.80
P.88
IC250
DSP6
DSP6
DSP6
DSP6
DSP6
DSP6
DSP6
IC255
IC300
IC301
IC351
IC400
IC401
IC350
IC251
IC252
[DIGITAL I/O] [CASCADE] [OUT]
P.80
P.80
P.80
P.80
P.80
P.80
P.80
KEC-92538-18
74
DSP1D
Page 32

IDB (1–48)
FUNCTION: INPUT EQ/GATE/COMP/DELAY/FADER ON
CH IN 25-28
KEY IN 1-4 <CH25>PRE EQ,PRE FADER,POST FADER,POST ON
INSERT OUT CH25-28
DATA BUS(DRAM)
P.72
INSERT IN CH 25-28
<CH26>PRE EQ,PRE FADER,POST FADER,POST ON
<CH27>PRE EQ,PRE FADER,POST FADER,POST ON
<CH28>PRE EQ,PRE FADER,POST FADER,POST ON
DIRECT OUT CH25-28
COMP KEY IN METER(CH25-28)
CH IN 29-32
<CH29>PRE EQ,PRE FADER,POST FADER,POST ON
INSERT OUT CH29-32
DATA BUS(DRAM)
P.72
INSERT IN CH 29-32
<CH30>PRE EQ,PRE FADER,POST FADER,POST ON
<CH31>PRE EQ,PRE FADER,POST FADER,POST ON
<CH32>PRE EQ,PRE FADER,POST FADER,POST ON
DIRECT OUT CH29-32
COMP KEY IN METER(CH29-32)
CH IN 33-36
<CH33>PRE EQ,PRE FADER,POST FADER,POST ON
INSERT OUT CH33-36
DATA BUS(DRAM)
P.72
INSERT IN CH 33-36
<CH34>PRE EQ,PRE FADER,POST FADER,POST ON
<CH35>PRE EQ,PRE FADER,POST FADER,POST ON
<CH36>PRE EQ,PRE FADER,POST FADER,POST ON
DIRECT OUT CH33-36
COMP KEY IN METER(CH33-36)
CH IN 37-40
<CH37>PRE EQ,PRE FADER,POST FADER,POST ON
INSERT OUT CH37-40
DATA BUS(DRAM)
IN:5
OUT:8
INSERT IN CH 37-40
<CH38>PRE EQ,PRE FADER,POST FADER,POST ON
<CH39>PRE EQ,PRE FADER,POST FADER,POST ON
<CH40>PRE EQ,PRE FADER,POST FADER,POST ON
DIRECT OUT CH37-40
COMP KEY IN METER(CH37-40)
ST IN 3-4
<ST IN 3(L)>PRE EQ,PRE FADER,POST FADER,POST ON
INSERT OUT ST IN 3-4
DATA BUS(DRAM)
P.72
INSERT IN ST IN3-4
<ST IN 3(R)>PRE EQ,PRE FADER,POST FADER,POST ON
<ST IN 4(L)>PRE EQ,PRE FADER,POST FADER,POST ON
<ST IN 4(R)>PRE EQ,PRE FADER,POST FADER,POST ON
DIRECT OUT ST IN 3-4
COMP KEY IN METER(ST IN 3-4)
CH IN 45-48
<CH45>PRE EQ,PRE FADER,POST FADER,POST ON
INSERT OUT CH45-48
DATA BUS(DRAM)
P.72
INSERT IN CH 45-48
<CH46>PRE EQ,PRE FADER,POST FADER,POST ON
<CH47>PRE EQ,PRE FADER,POST FADER,POST ON
<CH48>PRE EQ,PRE FADER,POST FADER,POST ON
DIRECT OUT CH45-48
COMP KEY IN METER(CH45-48)
CH IN 41-44
<CH41>PRE EQ,PRE FADER,POST FADER,POST ON
INSERT OUT CH41-44
P.72
INSERT IN CH 41-44
<CH42>PRE EQ,PRE FADER,POST FADER,POST ON
<CH43>PRE EQ,PRE FADER,POST FADER,POST ON
<CH44>PRE EQ,PRE FADER,POST FADER,POST ON
DIRECT OUT CH41-44
COMP KEY IN METER(CH41-44)
P.78
P.90
P.78
P.90
P.78
P.90
P.78
P.90
IN:5
OUT:8
IN:5
OUT:8
IN:5
OUT:8
P.78
P.90
P.78
P.90
IN:5
OUT:8
IN:5
OUT:8
IN:5
OUT:8
DRAM
P.78
P.90
KEY CH24 PRE GATE
SUB IN 2,DIRECT IN 2(LR)
DATA BUS(DRAM)
SUB IN 1,DIRECT IN 1
B(TB,TB/OSC,OSC,COMM.)
IN:8
OUT:7
TALKBACK A-B,COMM. A-B
P.89
3
0
1
20
1
2
3
4
5
7
6
3
0
1
2
0
1
2
3
4
5
7
6
3
0
1
2
0
1
2
3
4
5
7
6
3
0
1
2
0
1
2
3
4
5
7
6
3
0
1
2
0
1
2
3
4
5
7
6
3
0
1
2
0
1
2
3
4
5
7
6
3
0
1
2
0
1
2
3
4
5
7
6
0
1
0
1 P.84
P.90
P.88
KEY CH28 PRE GATE,CH25-28 KEY IN CUE
KEY CH32 PRE GATE,CH29-32 KEY IN CUE
KEY CH36 PRE GATE,CH33-36 KEY IN CUE
KEY CH40 PRE GATE,CH37-40 KEY IN CUE
KEY CH44 PRE GATE,CH41-44 KEY IN CUE
KEY CH48 PRE GATE,CH45-48 KEY IN CUE
KEY ST IN 2 PRE GATE
KEY ST IN 4 PRE GATE,ST IN3-4 KEY IN CUE
P.74
KEY CH48 PRE GATE
2
3
KEY ST IN 4 PRE GATE
CH48 PRE EQ,PRE GATE
P.80
2
4
4
4
4
4
ST IN 2 PRE EQ
4
CH48 PRE EQ
4
ST IN 4 PRE EQ
5
ST IN 4 PRE EQ,PRE GATE
3
CH24 PRE EQ
4
ADDRESS,RW CONTROL
CASCADE IN TB,COMM,SUB IN(LR)
6
P.74
4
SUB IN 2,DIRECT IN 2
7
5
6
7
5
6
7
5
6
7
5
6
7
5
6
7
5
6
7
5
6
7
KEY 1-4 OUT(CH IN25-48,ST IN3-4)
PRE EQ METER 2
5
6
7
KEY IN METER 2
P.88
1M x 16
(16Mbit)
DATA BUS(DRAM 32bit)
P.76
DSP6
DSP6
DSP6
DSP6
DSP6
DSP6
DSP6
DSP6
IC450
IC453
IC500
IC501 IC550
IC551
IC600
IC601
@ PRE COMP METER x 4
@ GATE KEY IN METER x 4
IC451
IC452
P.74
P.72
P.80
P.80
P.80
P.80
P.80
P.80
P.80
KEC-92538-19
75
DSP1D
Page 33

IDB (49–96)
FUNCTION: INPUT EQ/GATE/COMP/DELAY/FADER ON
CH IN 49-52
KEY IN 1-4
<CH49>PRE EQ,PRE FADER,POST FADER,POST ON
INSERT OUT CH49-52
KEY CH52 PRE GATE,CH49-52 KEY IN CUE
DATA BUS(DRAM)
P.72
INSERT IN CH 49-52 <CH50>PRE EQ,PRE FADER,POST FADER,POST ON
<CH51>PRE EQ,PRE FADER,POST FADER,POST ON
<CH52>PRE EQ,PRE FADER,POST FADER,POST ON
DIRECT OUT CH49-52
COMP KEY IN METER(CH49-52)
CH IN 53-56
<CH53>PRE EQ,PRE FADER,POST FADER,POST ON
INSERT OUT CH53-56
DATA BUS(DRAM)
P.72
INSERT IN CH 53-56
<CH54>PRE EQ,PRE FADER,POST FADER,POST ON
<CH55>PRE EQ,PRE FADER,POST FADER,POST ON
<CH56>PRE EQ,PRE FADER,POST FADER,POST ON
DIRECT OUT CH53-56
CH IN 57-60
<CH57>PRE EQ,PRE FADER,POST FADER,POST ON
INSERT OUT CH57-60
DATA BUS(DRAM)
P.72
INSERT IN CH 57-60
<CH58>PRE EQ,PRE FADER,POST FADER,POST ON
<CH59>PRE EQ,PRE FADER,POST FADER,POST ON
<CH60>PRE EQ,PRE FADER,POST FADER,POST ON
DIRECT OUT CH57-60
CH IN 61-64
<CH61>PRE EQ,PRE FADER,POST FADER,POST ON
INSERT OUT CH61-64
DATA BUS(DRAM)
IN:4
OUT:8
INSERT IN CH 61-64
<CH62>PRE EQ,PRE FADER,POST FADER,POST ON
<CH63>PRE EQ,PRE FADER,POST FADER,POST ON
<CH64>PRE EQ,PRE FADER,POST FADER,POST ON
DIRECT OUT CH61-64
ST IN 5-6
<ST IN 5(L)>PRE EQ,PRE FADER,POST FADER,POST ON
INSERT OUT ST IN 5-6
DATA BUS(DRAM)
P.72
INSERT IN ST IN5-6
<ST IN 5(R)>PRE EQ,PRE FADER,POST FADER,POST ON
<ST IN 6(L)>PRE EQ,PRE FADER,POST FADER,POST ON
<ST IN 6(R)>PRE EQ,PRE FADER,POST FADER,POST ON
DIRECT OUT ST IN 5-6
COMP KEY IN METER(ST IN 5-6)
CH IN 69-72
<CH69>PRE EQ,PRE FADER,POST FADER,POST ON
INSERT OUT CH69-72
DATA BUS(DRAM)
P.72
INSERT IN CH 69-72
<CH70>PRE EQ,PRE FADER,POST FADER,POST ON
<CH71>PRE EQ,PRE FADER,POST FADER,POST ON
<CH72>PRE EQ,PRE FADER,POST FADER,POST ON
DIRECT OUT CH69-72
CH IN 65-68
<CH65>PRE EQ,PRE FADER,POST FADER,POST ON
INSERT OUT CH65-68
P.72
INSERT IN CH 65-68 <CH66>PRE EQ,PRE FADER,POST FADER,POST ON
<CH67>PRE EQ,PRE FADER,POST FADER,POST ON
<CH68>PRE EQ,PRE FADER,POST FADER,POST ON
DIRECT OUT CH65-68
P.81
P.90
P.81
P.90
P.81
P.90
P.81
P.90
IN:4
OUT:8
IN:4
OUT:8
IN:4
OUT:8
P.81
P.90
P.81
P.90
P.77
P.72
IN:3
OUT:8
IN:4
OUT:8
IN:4
OUT:8
DRAM
1M x 16
(16Mbit)
DATA BUS(DRAM)
P.81
P.90
COMP KEY IN METER(CH53-56)
COMP KEY IN METER(CH57-60)
COMP KEY IN METER(CH61-64)
COMP KEY IN METER(CH65-68)
COMP KEY IN METER(CH69-72)
00
1
22
1
3
4
5
6
7
3
0
1
2
0
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
3
0
1
2
0
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
0
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
0
1
2
3 0
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
0
1
2
3
0
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
0
1
2
3
0
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
0
1
2
3
IN:4
OUT:3
DATA BUS(DRAM 32bit)
3
KEY CH56 PRE GATE,CH53-56 KEY IN CUE
KEY CH60 PRE GATE,CH57-60 KEY IN CUE
KEY CH64 PRE GATE,CH61-64 KEY IN CUE KEY CH68 PRE GATE,CH65-68 KEY IN CUE
KEY CH72 PRE GATE,CH69-72 KEY IN CUE
KEY ST IN 6 PRE GATE,ST IN5-6 KEY IN CUE
P.77
4
4
4
4
4
ADDRESS,RW CONTROL
CH48 PRE EQ,PRE GATE
P.75
P.75
ST IN 4 PRE EQ,PRE GATE
P.77
P.73
SUB IN 1,DIRECT IN 1(LR)
TALKBACK A-B,COMM. A-B
CASCADE IN TB,COMM.,SUB
SUB IN 2,DIRECT IN 2(LR)
4
5
6
7
5
6
7
5
6
7
5
6
7
5
6
7
5
6
7
4
5
6
7
0
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
KEY 1-4 OUT(CH IN49-72,ST IN5-6)
PRE EQ METER 3
KEY IN METER 3
P.83
5
6
7
DSP6
DSP6
DSP6
DSP6
DSP6
DSP6
DSP6
DSP6
IC250
IC255
IC300
IC301 IC350
IC351
IC400
IC401
@ PRE COMP METER x 4
@ GATE KEY IN METER x 4
IC251
IC252
P.83
P.83
P.83
P.83
P.83
P.83
P.83
(FOR DSP1D-EX)
KEC-92538-20
76
DSP1D
Page 34

IDB (49–96)
(FOR DSP1D-EX)
FUNCTION: INPUT EQ/GATE/COMP/DELAY/FADER ON
CH IN 73-76
KEY IN 1-4 <CH73>PRE EQ,PRE FADER,POST FADER,POST ON
INSERT OUT CH73-76
DATA BUS(DRAM)
P.73
INSERT IN CH 73-76
<CH74>PRE EQ,PRE FADER,POST FADER,POST ON
<CH75>PRE EQ,PRE FADER,POST FADER,POST ON
<CH76>PRE EQ,PRE FADER,POST FADER,POST ON
DIRECT OUT CH73-76
COMP KEY IN METER(CH73-76)
CH IN 77-80
<CH77>PRE EQ,PRE FADER,POST FADER,POST ON
INSERT OUT CH77-80
DATA BUS(DRAM)
P.73
INSERT IN CH 77-80
<CH78>PRE EQ,PRE FADER,POST FADER,POST ON
<CH79>PRE EQ,PRE FADER,POST FADER,POST ON
<CH80>PRE EQ,PRE FADER,POST FADER,POST ON
DIRECT OUT CH77-80
COMP KEY IN METER(CH77-80)
CH IN 81-84
<CH81>PRE EQ,PRE FADER,POST FADER,POST ON
INSERT OUT CH81-84
DATA BUS(DRAM)
P.73
INSERT IN CH 81-84
<CH82>PRE EQ,PRE FADER,POST FADER,POST ON
<CH83>PRE EQ,PRE FADER,POST FADER,POST ON
<CH84>PRE EQ,PRE FADER,POST FADER,POST ON
DIRECT OUT CH81-84
COMP KEY IN METER(CH81-84)
CH IN 85-88
<CH85>PRE EQ,PRE FADER,POST FADER,POST ON
INSERT OUT CH85-88
DATA BUS(DRAM)
IN:5
OUT:8
INSERT IN CH 85-88
<CH86>PRE EQ,PRE FADER,POST FADER,POST ON
<CH87>PRE EQ,PRE FADER,POST FADER,POST ON
<CH88>PRE EQ,PRE FADER,POST FADER,POST ON
DIRECT OUT CH85-88
COMP KEY IN METER(CH85-88)
ST IN 7-8
<ST IN 7(L)>PRE EQ,PRE FADER,POST FADER,POST ON
INSERT OUT ST IN 7-8
DATA BUS(DRAM)
P.73
INSERT IN ST IN7-8
<ST IN 7(R)>PRE EQ,PRE FADER,POST FADER,POST ON
<ST IN 8(L)>PRE EQ,PRE FADER,POST FADER,POST ON
<ST IN 8(R)>PRE EQ,PRE FADER,POST FADER,POST ON
DIRECT OUT ST IN 7-8
COMP KEY IN METER(ST IN 7-8)
CH IN 93-96
<CH93>PRE EQ,PRE FADER,POST FADER,POST ON
INSERT OUT CH93-96
DATA BUS(DRAM)
P.73
INSERT IN CH 93-96
<CH94>PRE EQ,PRE FADER,POST FADER,POST ON
<CH95>PRE EQ,PRE FADER,POST FADER,POST ON
<CH96>PRE EQ,PRE FADER,POST FADER,POST ON
DIRECT OUT CH93-96
COMP KEY IN METER(CH93-96)
CH IN 89-92 <CH89>PRE EQ,PRE FADER,POST FADER,POST ON
INSERT OUT CH89-92
P.73
INSERT IN CH 89-92
<CH90>PRE EQ,PRE FADER,POST FADER,POST ON
<CH91>PRE EQ,PRE FADER,POST FADER,POST ON
<CH92>PRE EQ,PRE FADER,POST FADER,POST ON
DIRECT OUT CH89-92
COMP KEY IN METER(CH89-92)
P.81
P.90
P.81
P.90
P.81
P.90
P.81
P.90
IN:5
OUT:8
IN:5
OUT:8
IN:5
OUT:8
P.81
P.90
P.81
P.90
P.73
IN:5
OUT:8
IN:5
OUT:8
IN:5
OUT:8
DRAM
1M x 16
(16Mbit)
DATA BUS(DRAM 32bit)
P.81
P.90
CH72 PRE GATE
DATA BUS(DRAM)
IN:8
OUT:3
3
0
1
20
1
2
3
4
5
7
6
3
0
1
2
0
1
2
3
4
5
7
6
3
0
1
2
0
1
2
3
4
5
7
6
3
0
1
2
0
1
2
3
4
5
7
6
3
0
1
2
0
1
2
3
4
5
7
6
3
0
1
2
0
1
2
3
4
5
7
6
3
0
1
2
0
1
2
3
4
5
7
6
0
1
KEY CH76 PRE GATE,CH73-76 KEY IN CUE
KEY CH80 PRE GATE,CH77-80 KEY IN CUE
KEY CH84 PRE GATE,CH81-84 KEY IN CUE
KEY CH88 PRE GATE,CH85-88 KEY IN CUE KEY CH92 PRE GATE,PRE COMP,KEY IN CUE(LR)
KEY CH96 PRE GATE,CH93-96 KEY IN CUE
KEY ST IN 6 PRE GATE
KEY ST IN 8 PRE GATE,ST IN7-8 KEY IN CUE
P.76
KEY CH96 PRE GATE
2
3
KEY ST IN 8 PRE GATE
4
4
4
4
4
ST IN 6 PRE EQ
4
CH96 PRE EQ
4
ST IN 8 PRE EQ
5
CH72 PRE EQ
4
@ PRE COMP METER x 4
@ GATE KEY IN METER x 4
ADDRESS,RW CONTROL
6
7
SUB IN 1,DIRECT IN 1
TALKBACK A-B,COMM. A-B
CASCADE IN TB,COMM,SUB IN
P.76
SUB IN 2,DIRECT IN 2
5
6
7
5
6
7
5
6
7
5
6
7
5
6
7
5
6
7
5
6
7
KEY 1-4 OUT(CH73-96,ST IN7-8)
PRE EQ METER 4
KEY IN METER 4
P.83
5
6
7
4
3
2
1
0
DSP6
DSP6
DSP6
DSP6
DSP6
DSP6
DSP6
DSP6
IC450
IC453
IC500
IC501 IC550
IC551
IC600
IC601
IC451
IC452
P.76
P.83
P.83
P.83
P.83
P.83
P.83
P.83
KEC-92538-21
77
DSP1D
Page 35

IDB (1–48)
P.84P.84
FUNCTION: <CH1-48,ST IN1-4>PAN,MIX/STEREO/CUE/KEY IN,METER
<CH1>PRE EQ,PRE FADER,POST FADER,POST ON
P.74
MIX 1-4
MIX 5-8
DSP5
IN:56
OUT:2
<CH2>PRE EQ,PRE FADER,POST FADER,POST ON
<CH3>PRE EQ,PRE FADER,POST FADER,POST ON
<CH4>PRE EQ,PRE FADER,POST FADER,POST ON
<CH5>PRE EQ,PRE FADER,POST FADER,POST ON
<CH6>PRE EQ,PRE FADER,POST FADER,POST ON
<CH7>PRE EQ,PRE FADER,POST FADER,POST ON
<CH8>PRE EQ,PRE FADER,POST FADER,POST ON
<CH9>PRE EQ,PRE FADER,POST FADER,POST ON
<CH10>PRE EQ,PRE FADER,POST FADER,POST ON
<CH11>PRE EQ,PRE FADER,POST FADER,POST ON
<CH12>PRE EQ,PRE FADER,POST FADER,POST ON
<CH13>PRE EQ,PRE FADER,POST FADER,POST ON
<CH14>PRE EQ,PRE FADER,POST FADER,POST ON
<CH15>PRE EQ,PRE FADER,POST FADER,POST ON
<CH16>PRE EQ,PRE FADER,POST FADER,POST ON
<CH17>PRE EQ,PRE FADER,POST FADER,POST ON
<CH18>PRE EQ,PRE FADER,POST FADER,POST ON
<CH19>PRE EQ,PRE FADER,POST FADER,POST ON
<CH20>PRE EQ,PRE FADER,POST FADER,POST ON
<CH21>PRE EQ,PRE FADER,POST FADER,POST ON
<CH22>PRE EQ,PRE FADER,POST FADER,POST ON
<CH23>PRE EQ,PRE FADER,POST FADER,POST ON
<CH24>PRE EQ,PRE FADER,POST FADER,POST ON
<CH25>PRE EQ,PRE FADER,POST FADER,POST ON
<CH26>PRE EQ,PRE FADER,POST FADER,POST ON
<CH27>PRE EQ,PRE FADER,POST FADER,POST ON
<CH28>PRE EQ,PRE FADER,POST FADER,POST ON
<CH29>PRE EQ,PRE FADER,POST FADER,POST ON
<CH30>PRE EQ,PRE FADER,POST FADER,POST ON
<CH31>PRE EQ,PRE FADER,POST FADER,POST ON
<CH32>PRE EQ,PRE FADER,POST FADER,POST ON
<CH33>PRE EQ,PRE FADER,POST FADER,POST ON
<CH34>PRE EQ,PRE FADER,POST FADER,POST ON
<CH35>PRE EQ,PRE FADER,POST FADER,POST ON
<CH36>PRE EQ,PRE FADER,POST FADER,POST ON
<CH37>PRE EQ,PRE FADER,POST FADER,POST ON
<CH38>PRE EQ,PRE FADER,POST FADER,POST ON
<CH39>PRE EQ,PRE FADER,POST FADER,POST ON
<CH40>PRE EQ,PRE FADER,POST FADER,POST ON
<CH41>PRE EQ,PRE FADER,POST FADER,POST ON
<CH42>PRE EQ,PRE FADER,POST FADER,POST ON
<CH43>PRE EQ,PRE FADER,POST FADER,POST ON
<CH44>PRE EQ,PRE FADER,POST FADER,POST ON
<CH45>PRE EQ,PRE FADER,POST FADER,POST ON
<CH46>PRE EQ,PRE FADER,POST FADER,POST ON
<CH47>PRE EQ,PRE FADER,POST FADER,POST ON
<CH48>PRE EQ,PRE FADER,POST FADER,POST ON
<ST IN 1(L)>PRE EQ,PRE FADER,POST FADER,POST ON
<ST IN 1(R)>PRE EQ,PRE FADER,POST FADER,POST ON
<ST IN 2(L)>PRE EQ,PRE FADER,POST FADER,POST ON
<ST IN 2(R)>PRE EQ,PRE FADER,POST FADER,POST ON
<ST IN 3(L)>PRE EQ,PRE FADER,POST FADER,POST ON
<ST IN 3(R)>PRE EQ,PRE FADER,POST FADER,POST ON
<ST IN 4(L)>PRE EQ,PRE FADER,POST FADER,POST ON
<ST IN 4(R)>PRE EQ,PRE FADER,POST FADER,POST ON
P.75
MIX 9-12
MIX 13-16
DSP5
IN:56
OUT:2
MIX 17-20
MIX 21-24
DSP5
P.84
IN:56
OUT:2
P.79
01
60
02
03
04
05
06
07
08
09
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
00
61
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
01
60
02
03
04
05
06
07
08
09
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
00
61
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
01
60
02
03
04
05
06
07
08
09
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
00
61
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
IC650 IC651 IC700
KEC-92538-22
78
DSP1D
Page 36

IDB (1–48)
MIX 25-28
MIX 29-32
P.84P.84
FUNCTION: <CH1-48,ST IN1-4>PAN,MIX/STEREO/CUE/KEY IN,METER
<CH1>PRE EQ,PRE FADER,POST FADER,POST ON MIX 33-36
MIX 37-40
DSP5
IN:56
OUT:2
<CH2>PRE EQ,PRE FADER,POST FADER,POST ON
<CH3>PRE EQ,PRE FADER,POST FADER,POST ON
<CH4>PRE EQ,PRE FADER,POST FADER,POST ON
<CH5>PRE EQ,PRE FADER,POST FADER,POST ON
<CH6>PRE EQ,PRE FADER,POST FADER,POST ON
<CH7>PRE EQ,PRE FADER,POST FADER,POST ON
<CH8>PRE EQ,PRE FADER,POST FADER,POST ON
<CH9>PRE EQ,PRE FADER,POST FADER,POST ON
<CH10>PRE EQ,PRE FADER,POST FADER,POST ON
<CH11>PRE EQ,PRE FADER,POST FADER,POST ON
<CH12>PRE EQ,PRE FADER,POST FADER,POST ON
<CH13>PRE EQ,PRE FADER,POST FADER,POST ON
<CH14>PRE EQ,PRE FADER,POST FADER,POST ON
<CH15>PRE EQ,PRE FADER,POST FADER,POST ON
<CH16>PRE EQ,PRE FADER,POST FADER,POST ON
<CH17>PRE EQ,PRE FADER,POST FADER,POST ON
<CH18>PRE EQ,PRE FADER,POST FADER,POST ON
<CH19>PRE EQ,PRE FADER,POST FADER,POST ON
<CH20>PRE EQ,PRE FADER,POST FADER,POST ON
<CH21>PRE EQ,PRE FADER,POST FADER,POST ON
<CH22>PRE EQ,PRE FADER,POST FADER,POST ON
<CH23>PRE EQ,PRE FADER,POST FADER,POST ON
<CH24>PRE EQ,PRE FADER,POST FADER,POST ON
<CH25>PRE EQ,PRE FADER,POST FADER,POST ON
<CH26>PRE EQ,PRE FADER,POST FADER,POST ON
<CH27>PRE EQ,PRE FADER,POST FADER,POST ON
<CH28>PRE EQ,PRE FADER,POST FADER,POST ON
<CH29>PRE EQ,PRE FADER,POST FADER,POST ON
<CH30>PRE EQ,PRE FADER,POST FADER,POST ON
<CH31>PRE EQ,PRE FADER,POST FADER,POST ON
<CH32>PRE EQ,PRE FADER,POST FADER,POST ON
<CH33>PRE EQ,PRE FADER,POST FADER,POST ON
<CH34>PRE EQ,PRE FADER,POST FADER,POST ON
<CH35>PRE EQ,PRE FADER,POST FADER,POST ON
<CH36>PRE EQ,PRE FADER,POST FADER,POST ON
<CH37>PRE EQ,PRE FADER,POST FADER,POST ON
<CH38>PRE EQ,PRE FADER,POST FADER,POST ON
<CH39>PRE EQ,PRE FADER,POST FADER,POST ON
<CH40>PRE EQ,PRE FADER,POST FADER,POST ON
<CH41>PRE EQ,PRE FADER,POST FADER,POST ON
<CH42>PRE EQ,PRE FADER,POST FADER,POST ON
<CH43>PRE EQ,PRE FADER,POST FADER,POST ON
<CH44>PRE EQ,PRE FADER,POST FADER,POST ON
<CH45>PRE EQ,PRE FADER,POST FADER,POST ON
<CH46>PRE EQ,PRE FADER,POST FADER,POST ON
<CH47>PRE EQ,PRE FADER,POST FADER,POST ON
<CH48>PRE EQ,PRE FADER,POST FADER,POST ON
<ST IN 1(L)>PRE EQ,PRE FADER,POST FADER,POST ON
<ST IN 1(R)>PRE EQ,PRE FADER,POST FADER,POST ON
<ST IN 2(L)>PRE EQ,PRE FADER,POST FADER,POST ON
<ST IN 2(R)>PRE EQ,PRE FADER,POST FADER,POST ON
<ST IN 3(L)>PRE EQ,PRE FADER,POST FADER,POST ON
<ST IN 3(R)>PRE EQ,PRE FADER,POST FADER,POST ON
<ST IN 4(L)>PRE EQ,PRE FADER,POST FADER,POST ON
<ST IN 4(R)>PRE EQ,PRE FADER,POST FADER,POST ON
DSP5
IN:56
OUT:2
01
60
02
03
04
05
06
07
08
09
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
00
61
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
01
60
02
03
04
05
06
07
08
09
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
00
61
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
P.80
P.78
P.84
MIX 41-44
MIX 45-48
DSP5
IN:56
OUT:2
01
60
02
03
04
05
06
07
08
09
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
00
61
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
IC701 IC750 IC751
KEC-92538-23
79
DSP1D
Page 37

IDB (1–48)
FUNCTION:<CH1-48,ST IN1-4>PAN,MIX/STEREO/CUE/KEY IN,METER
<CH1>PRE EQ,PRE FADER,POST FADER,POST ON
STEREO A-B
DSP5
P.84
IN:57
OUT:2
<CH2>PRE EQ,PRE FADER,POST FADER,POST ON
<CH3>PRE EQ,PRE FADER,POST FADER,POST ON
<CH4>PRE EQ,PRE FADER,POST FADER,POST ON
<CH5>PRE EQ,PRE FADER,POST FADER,POST ON
<CH6>PRE EQ,PRE FADER,POST FADER,POST ON
<CH7>PRE EQ,PRE FADER,POST FADER,POST ON
<CH8>PRE EQ,PRE FADER,POST FADER,POST ON
<CH9>PRE EQ,PRE FADER,POST FADER,POST ON
<CH10>PRE EQ,PRE FADER,POST FADER,POST ON
<CH11>PRE EQ,PRE FADER,POST FADER,POST ON
<CH12>PRE EQ,PRE FADER,POST FADER,POST ON
<CH13>PRE EQ,PRE FADER,POST FADER,POST ON
<CH14>PRE EQ,PRE FADER,POST FADER,POST ON
<CH15>PRE EQ,PRE FADER,POST FADER,POST ON
<CH16>PRE EQ,PRE FADER,POST FADER,POST ON
<CH17>PRE EQ,PRE FADER,POST FADER,POST ON
<CH18>PRE EQ,PRE FADER,POST FADER,POST ON
<CH19>PRE EQ,PRE FADER,POST FADER,POST ON
<CH20>PRE EQ,PRE FADER,POST FADER,POST ON
<CH21>PRE EQ,PRE FADER,POST FADER,POST ON
<CH22>PRE EQ,PRE FADER,POST FADER,POST ON
<CH23>PRE EQ,PRE FADER,POST FADER,POST ON
<CH24>PRE EQ,PRE FADER,POST FADER,POST ON
<CH25>PRE EQ,PRE FADER,POST FADER,POST ON
<CH26>PRE EQ,PRE FADER,POST FADER,POST ON
<CH27>PRE EQ,PRE FADER,POST FADER,POST ON
<CH28>PRE EQ,PRE FADER,POST FADER,POST ON
<CH29>PRE EQ,PRE FADER,POST FADER,POST ON
<CH30>PRE EQ,PRE FADER,POST FADER,POST ON
<CH31>PRE EQ,PRE FADER,POST FADER,POST ON
<CH32>PRE EQ,PRE FADER,POST FADER,POST ON
<CH33>PRE EQ,PRE FADER,POST FADER,POST ON
<CH34>PRE EQ,PRE FADER,POST FADER,POST ON
<CH35>PRE EQ,PRE FADER,POST FADER,POST ON
<CH36>PRE EQ,PRE FADER,POST FADER,POST ON
<CH37>PRE EQ,PRE FADER,POST FADER,POST ON
<CH38>PRE EQ,PRE FADER,POST FADER,POST ON
<CH39>PRE EQ,PRE FADER,POST FADER,POST ON
<CH40>PRE EQ,PRE FADER,POST FADER,POST ON
<CH41>PRE EQ,PRE FADER,POST FADER,POST ON
<CH42>PRE EQ,PRE FADER,POST FADER,POST ON
<CH43>PRE EQ,PRE FADER,POST FADER,POST ON
<CH44>PRE EQ,PRE FADER,POST FADER,POST ON
<CH45>PRE EQ,PRE FADER,POST FADER,POST ON
<CH46>PRE EQ,PRE FADER,POST FADER,POST ON
<CH47>PRE EQ,PRE FADER,POST FADER,POST ON
<CH48>PRE EQ,PRE FADER,POST FADER,POST ON
<ST IN 1(L)>PRE EQ,PRE FADER,POST FADER,POST ON
<ST IN 1(R)>PRE EQ,PRE FADER,POST FADER,POST ON
<ST IN 2(L)>PRE EQ,PRE FADER,POST FADER,POST ON
<ST IN 2(R)>PRE EQ,PRE FADER,POST FADER,POST ON
<ST IN 3(L)>PRE EQ,PRE FADER,POST FADER,POST ON
<ST IN 3(R)>PRE EQ,PRE FADER,POST FADER,POST ON
<ST IN 4(L)>PRE EQ,PRE FADER,POST FADER,POST ON
<ST IN 4(R)>PRE EQ,PRE FADER,POST FADER,POST ON
KEY 1-4 OUT(CH49-96)
DSP5
P.84
IN:34
OUT:2
COMP KEY IN METER(CH1-4)
COMP KEY IN METER(CH5-8)
COMP KEY IN METER(CH9-12)
COMP KEY IN METER(CH13-16)
COMP KEY IN METER(CH17-20)
COMP KEY IN METER(CH21-24)
COMP KEY IN METER(ST IN 1-2)
P.109
COMP KEY IN METER(CH25-28)
COMP KEY IN METER(CH29-32)
COMP KEY IN METER(CH33-36)
COMP KEY IN METER(CH37-40)
COMP KEY IN METER(CH41-44)
COMP KEY IN METER(CH45-48)
COMP KEY IN METER(ST IN 3-4)
P.110
01
60
02
03
04
05
06
07
08
09
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
00
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
01
60
02
03
04
05
06
07
08
09
10
00
11
12
13
CH1-4 KEY IN CUE
CH5-8 KEY IN CUE
CH9-12 KEY IN CUE
CH13-16 KEY IN CUE
CH17-20 KEY IN CUE
CH21-24 KEY IN CUE
CH25-28 KEY IN CUE
CH29-32 KEY IN CUE
ST IN1-2 KEY IN CUE
CH33-36 KEY IN CUE
CH37-40 KEY IN CUE
CH41-44 KEY IN CUE
CH45-48 KEY IN CUE
ST IN3-4 KEY IN CUE
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
KEY IN CUE
61
P.109
P.110
CUE A-B
61
P.79
57
58
59
KEY 1-4 OUT(CH1-24)
PRE EQ METER 1
KEY IN METER 1
P.109
KEY 1-4 OUT(CH25-48)
PRE EQ METER 2
KEY IN METER 2
P.110
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
IC800
IC801
KEC-92538-24
80
DSP1D
Page 38

IDB (49–96)
(FOR DSP1D-EX)
P.84P.84
FUNCTION: <CH49-96,ST IN5-8>PAN,MIX/STEREO/CUE/KEY IN,METER
<CH49>PRE EQ,PRE FADER,POST FADER,POST ON
P.76
MIX 1-4
MIX 5-8
DSP5
IN:56
OUT:2
<CH50>PRE EQ,PRE FADER,POST FADER,POST ON
<CH51>PRE EQ,PRE FADER,POST FADER,POST ON
<CH52>PRE EQ,PRE FADER,POST FADER,POST ON
<CH53>PRE EQ,PRE FADER,POST FADER,POST ON
<CH54>PRE EQ,PRE FADER,POST FADER,POST ON
<CH55>PRE EQ,PRE FADER,POST FADER,POST ON
<CH56>PRE EQ,PRE FADER,POST FADER,POST ON
<CH57>PRE EQ,PRE FADER,POST FADER,POST ON
<CH58>PRE EQ,PRE FADER,POST FADER,POST ON
<CH59>PRE EQ,PRE FADER,POST FADER,POST ON
<CH60>PRE EQ,PRE FADER,POST FADER,POST ON
<CH61>PRE EQ,PRE FADER,POST FADER,POST ON
<CH62>PRE EQ,PRE FADER,POST FADER,POST ON
<CH63>PRE EQ,PRE FADER,POST FADER,POST ON
<CH64>PRE EQ,PRE FADER,POST FADER,POST ON
<CH65>PRE EQ,PRE FADER,POST FADER,POST ON
<CH66>PRE EQ,PRE FADER,POST FADER,POST ON
<CH67>PRE EQ,PRE FADER,POST FADER,POST ON
<CH68>PRE EQ,PRE FADER,POST FADER,POST ON
<CH69>PRE EQ,PRE FADER,POST FADER,POST ON
<CH70>PRE EQ,PRE FADER,POST FADER,POST ON
<CH71>PRE EQ,PRE FADER,POST FADER,POST ON
<CH72>PRE EQ,PRE FADER,POST FADER,POST ON
<CH73>PRE EQ,PRE FADER,POST FADER,POST ON
<CH74>PRE EQ,PRE FADER,POST FADER,POST ON
<CH75>PRE EQ,PRE FADER,POST FADER,POST ON
<CH76>PRE EQ,PRE FADER,POST FADER,POST ON
<CH77>PRE EQ,PRE FADER,POST FADER,POST ON
<CH78>PRE EQ,PRE FADER,POST FADER,POST ON
<CH79>PRE EQ,PRE FADER,POST FADER,POST ON
<CH80>PRE EQ,PRE FADER,POST FADER,POST ON
<CH81>PRE EQ,PRE FADER,POST FADER,POST ON
<CH82>PRE EQ,PRE FADER,POST FADER,POST ON
<CH83>PRE EQ,PRE FADER,POST FADER,POST ON
<CH84>PRE EQ,PRE FADER,POST FADER,POST ON
<CH85>PRE EQ,PRE FADER,POST FADER,POST ON
<CH86>PRE EQ,PRE FADER,POST FADER,POST ON
<CH87>PRE EQ,PRE FADER,POST FADER,POST ON
<CH88>PRE EQ,PRE FADER,POST FADER,POST ON
<CH89>PRE EQ,PRE FADER,POST FADER,POST ON
<CH90>PRE EQ,PRE FADER,POST FADER,POST ON
<CH91>PRE EQ,PRE FADER,POST FADER,POST ON
<CH92>PRE EQ,PRE FADER,POST FADER,POST ON
<CH93>PRE EQ,PRE FADER,POST FADER,POST ON
<CH94>PRE EQ,PRE FADER,POST FADER,POST ON
<CH95>PRE EQ,PRE FADER,POST FADER,POST ON
<CH96>PRE EQ,PRE FADER,POST FADER,POST ON
<ST IN 5(L)>PRE EQ,PRE FADER,POST FADER,POST ON
<ST IN 5(R)>PRE EQ,PRE FADER,POST FADER,POST ON
<ST IN 6(L)>PRE EQ,PRE FADER,POST FADER,POST ON
<ST IN 6(R)>PRE EQ,PRE FADER,POST FADER,POST ON
<ST IN 7(L)>PRE EQ,PRE FADER,POST FADER,POST ON
<ST IN 7(R)>PRE EQ,PRE FADER,POST FADER,POST ON
<ST IN 8(L)>PRE EQ,PRE FADER,POST FADER,POST ON
<ST IN 8(R)>PRE EQ,PRE FADER,POST FADER,POST ON
P.77
MIX 9-12
MIX 13-16
DSP5
IN:56
OUT:2
MIX 17-20
MIX 21-24
DSP5
P.84
IN:56
OUT:2
P.82
01
60
02
03
04
05
06
07
08
09
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
00
61
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
01
60
02
03
04
05
06
07
08
09
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
00
61
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
01
60
02
03
04
05
06
07
08
09
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
00
61
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
IC650 IC651 IC700
KEC-92538-25
81
DSP1D
Page 39

IDB (49–96)
(FOR DSP1D-EX)
MIX 25-28
MIX 29-32
P.84P.84
FUNCTION: <CH49-96,ST IN5-8>PAN,MIX/STEREO/CUE/KEY IN,METER
<CH49>PRE EQ,PRE FADER,POST FADER,POST ON MIX 33-36
MIX 37-40
DSP5
IN:56
OUT:2
<CH50>PRE EQ,PRE FADER,POST FADER,POST ON
<CH51>PRE EQ,PRE FADER,POST FADER,POST ON
<CH52>PRE EQ,PRE FADER,POST FADER,POST ON
<CH53>PRE EQ,PRE FADER,POST FADER,POST ON
<CH54>PRE EQ,PRE FADER,POST FADER,POST ON
<CH55>PRE EQ,PRE FADER,POST FADER,POST ON
<CH56>PRE EQ,PRE FADER,POST FADER,POST ON
<CH57>PRE EQ,PRE FADER,POST FADER,POST ON
<CH58>PRE EQ,PRE FADER,POST FADER,POST ON
<CH59>PRE EQ,PRE FADER,POST FADER,POST ON
<CH60>PRE EQ,PRE FADER,POST FADER,POST ON
<CH61>PRE EQ,PRE FADER,POST FADER,POST ON
<CH62>PRE EQ,PRE FADER,POST FADER,POST ON
<CH63>PRE EQ,PRE FADER,POST FADER,POST ON
<CH64>PRE EQ,PRE FADER,POST FADER,POST ON
<CH65>PRE EQ,PRE FADER,POST FADER,POST ON
<CH66>PRE EQ,PRE FADER,POST FADER,POST ON
<CH67>PRE EQ,PRE FADER,POST FADER,POST ON
<CH68>PRE EQ,PRE FADER,POST FADER,POST ON
<CH69>PRE EQ,PRE FADER,POST FADER,POST ON
<CH70>PRE EQ,PRE FADER,POST FADER,POST ON
<CH71>PRE EQ,PRE FADER,POST FADER,POST ON
<CH72>PRE EQ,PRE FADER,POST FADER,POST ON
<CH73>PRE EQ,PRE FADER,POST FADER,POST ON
<CH74>PRE EQ,PRE FADER,POST FADER,POST ON
<CH75>PRE EQ,PRE FADER,POST FADER,POST ON
<CH76>PRE EQ,PRE FADER,POST FADER,POST ON
<CH77>PRE EQ,PRE FADER,POST FADER,POST ON
<CH78>PRE EQ,PRE FADER,POST FADER,POST ON
<CH79>PRE EQ,PRE FADER,POST FADER,POST ON
<CH80>PRE EQ,PRE FADER,POST FADER,POST ON
<CH81>PRE EQ,PRE FADER,POST FADER,POST ON
<CH82>PRE EQ,PRE FADER,POST FADER,POST ON
<CH83>PRE EQ,PRE FADER,POST FADER,POST ON
<CH84>PRE EQ,PRE FADER,POST FADER,POST ON
<CH85>PRE EQ,PRE FADER,POST FADER,POST ON
<CH86>PRE EQ,PRE FADER,POST FADER,POST ON
<CH87>PRE EQ,PRE FADER,POST FADER,POST ON
<CH88>PRE EQ,PRE FADER,POST FADER,POST ON
<CH89>PRE EQ,PRE FADER,POST FADER,POST ON
<CH90>PRE EQ,PRE FADER,POST FADER,POST ON
<CH91>PRE EQ,PRE FADER,POST FADER,POST ON
<CH92>PRE EQ,PRE FADER,POST FADER,POST ON
<CH93>PRE EQ,PRE FADER,POST FADER,POST ON
<CH94>PRE EQ,PRE FADER,POST FADER,POST ON
<CH95>PRE EQ,PRE FADER,POST FADER,POST ON
<CH96>PRE EQ,PRE FADER,POST FADER,POST ON
<ST IN 5(L)>PRE EQ,PRE FADER,POST FADER,POST ON
<ST IN 5(R)>PRE EQ,PRE FADER,POST FADER,POST ON
<ST IN 6(L)>PRE EQ,PRE FADER,POST FADER,POST ON
<ST IN 6(R)>PRE EQ,PRE FADER,POST FADER,POST ON
<ST IN 7(L)>PRE EQ,PRE FADER,POST FADER,POST ON
<ST IN 7(R)>PRE EQ,PRE FADER,POST FADER,POST ON
<ST IN 8(L)>PRE EQ,PRE FADER,POST FADER,POST ON
<ST IN 8(R)>PRE EQ,PRE FADER,POST FADER,POST ON
DSP5
IN:56
OUT:2
01
60
02
03
04
05
06
07
08
09
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
00
61
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
01
60
02
03
04
05
06
07
08
09
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
00
61
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
P.81
P.83
P.84
MIX 41-44
MIX 45-48
DSP5
01
60
02
03
04
05
06
07
08
09
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
00
61
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
IN:56
OUT:2
IC701 IC750 IC751
KEC-92538-26
82
DSP1D
Page 40

IDB (49–96)
(FOR DSP1D-EX)
FUNCTION: <CH49-96,ST IN5-8>PAN,MIX/STEREO/CUE/KEY IN,METER
<CH49>PRE EQ,PRE FADER,POST FADER,POST ON STEREO A-B
DSP5
P.84
IN:57
OUT:2
<CH50>PRE EQ,PRE FADER,POST FADER,POST ON
<CH51>PRE EQ,PRE FADER,POST FADER,POST ON
<CH52>PRE EQ,PRE FADER,POST FADER,POST ON
<CH53>PRE EQ,PRE FADER,POST FADER,POST ON
<CH54>PRE EQ,PRE FADER,POST FADER,POST ON
<CH55>PRE EQ,PRE FADER,POST FADER,POST ON
<CH56>PRE EQ,PRE FADER,POST FADER,POST ON
<CH57>PRE EQ,PRE FADER,POST FADER,POST ON
<CH58>PRE EQ,PRE FADER,POST FADER,POST ON
<CH59>PRE EQ,PRE FADER,POST FADER,POST ON
<CH60>PRE EQ,PRE FADER,POST FADER,POST ON
<CH61>PRE EQ,PRE FADER,POST FADER,POST ON
<CH62>PRE EQ,PRE FADER,POST FADER,POST ON
<CH63>PRE EQ,PRE FADER,POST FADER,POST ON
<CH64>PRE EQ,PRE FADER,POST FADER,POST ON
<CH65>PRE EQ,PRE FADER,POST FADER,POST ON
<CH66>PRE EQ,PRE FADER,POST FADER,POST ON
<CH67>PRE EQ,PRE FADER,POST FADER,POST ON
<CH68>PRE EQ,PRE FADER,POST FADER,POST ON
<CH69>PRE EQ,PRE FADER,POST FADER,POST ON
<CH70>PRE EQ,PRE FADER,POST FADER,POST ON
<CH71>PRE EQ,PRE FADER,POST FADER,POST ON
<CH72>PRE EQ,PRE FADER,POST FADER,POST ON
<CH73>PRE EQ,PRE FADER,POST FADER,POST ON
<CH74>PRE EQ,PRE FADER,POST FADER,POST ON
<CH75>PRE EQ,PRE FADER,POST FADER,POST ON
<CH76>PRE EQ,PRE FADER,POST FADER,POST ON
<CH77>PRE EQ,PRE FADER,POST FADER,POST ON
<CH78>PRE EQ,PRE FADER,POST FADER,POST ON
<CH79>PRE EQ,PRE FADER,POST FADER,POST ON
<CH80>PRE EQ,PRE FADER,POST FADER,POST ON
<CH81>PRE EQ,PRE FADER,POST FADER,POST ON
<CH82>PRE EQ,PRE FADER,POST FADER,POST ON
<CH83>PRE EQ,PRE FADER,POST FADER,POST ON
<CH84>PRE EQ,PRE FADER,POST FADER,POST ON
<CH85>PRE EQ,PRE FADER,POST FADER,POST ON
<CH86>PRE EQ,PRE FADER,POST FADER,POST ON
<CH87>PRE EQ,PRE FADER,POST FADER,POST ON
<CH88>PRE EQ,PRE FADER,POST FADER,POST ON
<CH89>PRE EQ,PRE FADER,POST FADER,POST ON
<CH90>PRE EQ,PRE FADER,POST FADER,POST ON
<CH91>PRE EQ,PRE FADER,POST FADER,POST ON
<CH92>PRE EQ,PRE FADER,POST FADER,POST ON
<CH83>PRE EQ,PRE FADER,POST FADER,POST ON
<CH94>PRE EQ,PRE FADER,POST FADER,POST ON
<CH95>PRE EQ,PRE FADER,POST FADER,POST ON
<CH96>PRE EQ,PRE FADER,POST FADER,POST ON
<ST IN 5(L)>PRE EQ,PRE FADER,POST FADER,POST ON
<ST IN 5(R)>PRE EQ,PRE FADER,POST FADER,POST ON
<ST IN 6(L)>PRE EQ,PRE FADER,POST FADER,POST ON
<ST IN 6(R)>PRE EQ,PRE FADER,POST FADER,POST ON
<ST IN 7(L)>PRE EQ,PRE FADER,POST FADER,POST ON
<ST IN 7(R)>PRE EQ,PRE FADER,POST FADER,POST ON
<ST IN 8(L)>PRE EQ,PRE FADER,POST FADER,POST ON
<ST IN 8(R)>PRE EQ,PRE FADER,POST FADER,POST ON
KEY 1-4 OUT(CH1-48)
DSP5
P.84
IN:34
OUT:2
COMP KEY IN METER(CH49-52)
COMP KEY IN METER(CH53-56)
COMP KEY IN METER(CH57-60)
COMP KEY IN METER(CH61-64)
COMP KEY IN METER(CH65-68)
COMP KEY IN METER(CH69-72)
COMP KEY IN METER(ST IN 5-6)
P.76
COMP KEY IN METER(CH73-76)
COMP KEY IN METER(CH77-80)
COMP KEY IN METER(CH81-84)
COMP KEY IN METER(CH85-88)
COMP KEY IN METER(CH89-92)
COMP KEY IN METER(CH93-96)
COMP KEY IN METER(ST IN 7-8)
P.77
01
60
02
03
04
05
06
07
08
09
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
00
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
01
60
02
03
04
05
06
07
08
09
10
00
11
12
13
CH49-52 KEY IN CUE
CH53-56 KEY IN CUE
CH57-60 KEY IN CUE
CH61-64 KEY IN CUE
CH65-68 KEY IN CUE
CH69-72 KEY IN CUE
CH73-76 KEY IN CUE
CH77-80 KEY IN CUE
ST IN5-6 KEY IN CUE
CH81-84 KEY IN CUE
CH85-88 KEY IN CUE
CH89-92 KEY IN CUE
CH93-96 KEY IN CUE
ST IN7-8 KEY IN CUE
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
KEY IN CUE
61
P.76
P.77
61
CUE A-B
P.82
57
58
59
KEY 1-4 OUT(CH49-72,ST IN5-6)
PRE EQ METER 3
KEY IN METER 3
P.76
KEY 1-4 OUT(CH73-96,ST IN7-8)
PRE EQ METER 4
KEY IN METER 4
P.77
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
IC800
IC801
KEC-92538-27
83
DSP1D
Page 41

GDB
FUNCTION: MIX/STEREO/CUE/KEY IN
MIX 1-4
P.78
MIX PRE 1-4
MIX 5-8
MIX 9-12
EFFECT RETURN 1-2(LR)
EFFECT RETURN 3-4(LR)
EFFECT RETURN 5-6(LR)
EFFECT RETURN 7-8(LR)
ANALYZER SOURCE 1
ANALYZER SOURCE 2
MIX 1-4
P.81
MIX 5-8
MIX 9-12
MIX PRE 5-8
MIX PRE 9-12
P.92
DSP5
P.85
MIX PRE 33-36
DSP5
P.86
IN:34
OUT:7
IN:24
OUT:8
A(TB,TB/OSC,OSC,COMM.)
P.74
MIX 13-16
MIX 17-20
MIX 21-24
MIX 13-16
MIX 17-20
MIX 21-24
P.79
MIX 33-36
EFFECT RETURN 1-2(LR)
EFFECT RETURN 3-4(LR)
EFFECT RETURN 5-6(LR)
EFFECT RETURN 7-8(LR)
ANALYZER SOURCE 1
ANALYZER SOURCE 2
P.82
MIX 33-36
A(TB,TB/OSC,OSC,COMM.)
MIX 37-40
MIX 41-44
MIX 45-48
MIX 37-40
MIX 41-44
MIX 45-48
MIX PRE 13-16
MIX PRE 17-20
MIX PRE 21-24
MIX PRE 37-40
MIX PRE 41-44
MIX PRE 45-48
STEREO A-B
STEREO A-B
STEREO PRE A-B
KEY 1-4 OUT(CH1-48)
KEY 1-4 OUT(CH49-96)
CUE PRE A-B
P.88
KEY 1-4 OUT(CH1-96)
MIX 1-4 to STEREO
MIX 5-8 to STEREO
MIX 9-12 to STEREO
MIX 13-16 to STEREO
MIX 17-20 to STEREO
MIX 21-24 to STEREO
MIX 25-28 to STEREO
MIX 29-32 to STEREO
MIX 33-36 to STEREO
MIX 37-40 to STEREO
MIX 41-44 to STEREO
MIX 45-48 to STEREO
P.87
01
02
03
04
05
06
07
08
09
10
11
12
13
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
00
01
02
03
04
05
06
07
08
09
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
00
30
31
32
33
48
49
50
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
CUE A-B
CUE A-B
MIX 25-28
MIX 25-28
MIX PRE 25-28
MIX 29-32
MIX 29-32
14
15
MIX PRE 29-32
P.80
P.83
23
51
52
53
54
B(TB,TB/OSC,OSC,COMM.)
B(TB,TB/OSC,OSC,COMM.)
34
35
IC250 IC251
P.79
P.82
P.93
P.75
P.80
P.83
KEC-92538-28
84
DSP1D
Page 42

GDB
FUNCTION: MIX EQ/COMP/DELAY/FADER ON
MIX PRE 1-4
KEY IN 1-4
<MIX1>PRE EQ,PRE FADER,POST FADER,POST ON
INSERT OUT MIX 1-4
KEY MIX4 PRE EQ,MIX 1-4 KEY IN CUE
DATA BUS(DRAM)
DSP6
INSERT IN MIX 1-4 <MIX2>PRE EQ,PRE FADER,POST FADER,POST ON
<MIX3>PRE EQ,PRE FADER,POST FADER,POST ON
<MIX4>PRE EQ,PRE FADER,POST FADER,POST ON
KEY 1-4 OUT(MIX 1-4)
MIX PRE 5-8
<MIX5>PRE EQ,PRE FADER,POST FADER,POST ON
INSERT OUT MIX 5-8
DATA BUS(DRAM)
DSP6
INSERT IN MIX 5-8
<MIX6>PRE EQ,PRE FADER,POST FADER,POST ON
<MIX7>PRE EQ,PRE FADER,POST FADER,POST ON
<MIX8>PRE EQ,PRE FADER,POST FADER,POST ON
KEY 1-4 OUT(MIX 5-8)
MIX PRE 29-32
<MIX29>PRE EQ,PRE FADER,POST FADER,POST ON
INSERT OUT MIX 29-32
DATA BUS(DRAM)
DSP6
INSERT IN MIX 29-32
<MIX30>PRE EQ,PRE FADER,POST FADER,POST ON
<MIX31>PRE EQ,PRE FADER,POST FADER,POST ON
<MIX32>PRE EQ,PRE FADER,POST FADER,POST ON
KEY 1-4 OUT(MIX 29-32)
MIX PRE 25-28
<MIX25>PRE EQ,PRE FADER,POST FADER,POST ON
INSERT OUT MIX 25-28
DSP6
INSERT IN MIX 25-28
<MIX26>PRE EQ,PRE FADER,POST FADER,POST ON
<MIX27>PRE EQ,PRE FADER,POST FADER,POST ON
<MIX28>PRE EQ,PRE FADER,POST FADER,POST ON
KEY 1-4 OUT(MIX 25-28)
P.87
P.90
IN:5
OUT:8
IN:5
OUT:8
IN:5
OUT:8
IN:5
OUT:8
DRAM
1M x 16
(16Mbit)
DATA BUS(DRAM 32bit)
P.87
P.87
P.87
0
1
2
3
4
5
6
0
1
2
0
1
2
3
4
5
6
0
1
2
3
0
1
2
3
4
5
6
0
1
2
3
0
1
2
3
4
5
6
0
1
2
3
P.73
DRAM
P.84
3
P.84
P.73
P.90
KEY MIX8 PRE EQ,MIX 5-8 KEY IN CUE
MIX PRE 13-16
<MIX13>PRE EQ,PRE FADER,POST FADER,POST ON
DSP6
INSERT IN MIX 13-16
<MIX14>PRE EQ,PRE FADER,POST FADER,POST ON
<MIX15>PRE EQ,PRE FADER,POST FADER,POST ON
<MIX16>PRE EQ,PRE FADER,POST FADER,POST ON
KEY 1-4 OUT(MIX 13-16)
DSP6
IN:5
OUT:8
P.90
IN:5
OUT:8
P.87
P.87
0
1
2
3
4
5
6
0
1
2
3 0
1
2
3
4
5
6
0
1
2
3
P.84
P.73
INSERT OUT MIX 13-16
KEY MIX16 PRE EQ,MIX 13-16 KEY IN CUE
P.90
P.84
P.73
P.84
P.73
KEY MIX28 PRE EQ,MIX 25-28 KEY IN CUE
P.90
P.84
P.73
P.90
KEY MIX32 PRE EQ,MIX 29-32 KEY IN CUE
DATA BUS(DRAM)
DATA BUS(DRAM)
DSP6
MIX PRE 21-24
<MIX21>PRE EQ,PRE FADER,POST FADER,POST ON
INSERT OUT MIX 21-24
DSP6
INSERT IN MIX 21-24
<MIX22>PRE EQ,PRE FADER,POST FADER,POST ON
<MIX23>PRE EQ,PRE FADER,POST FADER,POST ON
<MIX24>PRE EQ,PRE FADER,POST FADER,POST ON
KEY 1-4 OUT(MIX 21-24)
IN:5
OUT:8
IN:5
OUT:8
P.87
P.87
0
1
2
3
4
5
6
0
1
2
3
0
1
2
3
4
5
6
0
1
2
3
P.90
P.84
P.73
KEY MIX24 PRE EQ,MIX 21-24 KEY IN CUE
P.90
DATA BUS(DRAM)
MIX PRE 9-12
INSERT IN MIX 9-12
P.84
P.73
<MIX9>PRE EQ,PRE FADER,POST FADER,POST ON
<MIX10>PRE EQ,PRE FADER,POST FADER,POST ON
<MIX11>PRE EQ,PRE FADER,POST FADER,POST ON
<MIX12>PRE EQ,PRE FADER,POST FADER,POST ON
KEY 1-4 OUT(MIX 9-12)
INSERT OUT MIX 9-12
KEY MIX12 PRE EQ,MIX 9-12 KEY IN CUE
MIX PRE 17-20
INSERT IN MIX 17-20
<MIX17>PRE EQ,PRE FADER,POST FADER,POST ON
INSERT OUT MIX 17-20
<MIX18>PRE EQ,PRE FADER,POST FADER,POST ON
<MIX19>PRE EQ,PRE FADER,POST FADER,POST ON
<MIX20>PRE EQ,PRE FADER,POST FADER,POST ON
KEY 1-4 OUT(MIX 17-20)
KEY MIX20 PRE EQ,MIX 17-20 KEY IN CUE
CASCADE IN MIX 1-4
4
CASCADE OUT MIX 1-4
7
CASCADE OUT MIX 5-8
7
CASCADE IN MIX 5-8
4
CASCADE IN MIX 9-12
4
CASCADE OUT MIX 9-12
7
CASCADE OUT MIX 13-16
7
CASCADE IN MIX 13-16
4
CASCADE IN MIX 17-20
4
CASCADE OUT MIX 17-20
7
CASCADE OUT MIX 21-24
7
CASCADE IN
MIX 21-24
4
CASCADE IN
MIX 25-28
4
CASCADE OUT MIX 25-28
7
CASCADE OUT MIX 29-32
7
CASCADE IN
MIX 29-32
4
ADDRESS,RW CONTROL
ADDRESS,RW CONTROL
IC400
P.86
7
5
6
7
5
6
7
5
6
7
5
6
7
5
6
7
5
6
7
5
6
7
5
6
1M x 16
(16Mbit)
DATA BUS(DRAM 32bit)
to DRAM(RW,ADDRESS)
IC300
IC305
IC350
IC351 IC400
IC403
IC450
IC451
IC401
IC402
IC301
IC302
[DIGITAL I/O]
[CASCADE]
[IN]
[DIGITAL I/O]
[CASCADE]
[IN]
[DIGITAL I/O]
[CASCADE]
[IN]
[DIGITAL I/O]
[CASCADE]
[IN]
[DIGITAL I/O]
[CASCADE]
[OUT]
[DIGITAL I/O]
[CASCADE]
[OUT]
[DIGITAL I/O]
[CASCADE]
[OUT]
[DIGITAL I/O]
[CASCADE]
[IN]
[DIGITAL I/O]
[CASCADE]
[OUT]
P.73
[DIGITAL I/O]
[CASCADE]
[OUT]
P.88
P.88
P.88
P.88
P.88
P.88
P.88
P.88
KEC-92538-29
85
DSP1D
Page 43

<STEREO A(L)>PRE EQ,PRE FADER,POST FADER,POST ON
<STEREO A(R)>PRE EQ,PRE FADER,POST FADER,POST ON
<STEREO B(L)>PRE EQ,PRE FADER,POST FADER,POST ON
<STEREO B(R)>PRE EQ,PRE FADER,POST FADER,POST ON
GDB
FUNCTION: MIX EQ/COMP/DELAY/FADER ON
MIX PRE 33-36
KEY IN 1-4
<MIX33>PRE EQ,PRE FADER,POST FADER,POST ON
INSERT OUT MIX 33-36
DATA BUS(DRAM)
DSP6
INSERT IN MIX 33-36 <MIX34>PRE EQ,PRE FADER,POST FADER,POST ON
<MIX35>PRE EQ,PRE FADER,POST FADER,POST ON
<MIX36>PRE EQ,PRE FADER,POST FADER,POST ON
KEY 1-4 OUT(MIX 33-36)
MIX PRE 37-40
<MIX37>PRE EQ,PRE FADER,POST FADER,POST ON
INSERT OUT MIX 37-40
DATA BUS(DRAM)
DSP6
INSERT IN MIX 37-40
<MIX38>PRE EQ,PRE FADER,POST FADER,POST ON
<MIX39>PRE EQ,PRE FADER,POST FADER,POST ON
<MIX40>PRE EQ,PRE FADER,POST FADER,POST ON
KEY 1-4 OUT(MIX 37-40)
MIX PRE 41-44
<MIX41>PRE EQ,PRE FADER,POST FADER,POST ON
INSERT OUT MIX 41-44
DSP6
INSERT IN MIX 41-44
<MIX42>PRE EQ,PRE FADER,POST FADER,POST ON
<MIX43>PRE EQ,PRE FADER,POST FADER,POST ON
<MIX44>PRE EQ,PRE FADER,POST FADER,POST ON
KEY 1-4 OUT(MIX 41-44)
P.90
IN:5
OUT:8
IN:5
OUT:8
IN:5
OUT:8
P.87
P.87
KEY MIX32 PRE EQ
0
1
2
3
4
5
6
0
1
2
3
0
1
2
3
4
5
6
0
1
2
3
0
1
2
3
4
5
6
0
1
2
3
STEREO PRE A-B(LR)
INSERT OUT STEREO A,B
DSP6
INSERT IN STEREO A,B
KEY 1-4 OUT(STEREO A,B)
IN:5
OUT:8
P.87
0
1
2
3
4
5
6
0
1
2
3
DRAM
P.84
P.73
KEY MIX36 PRE EQ,MIX 33-36 KEY IN CUE
P.90
KEY MIX40 PRE EQ,MIX 37-40 KEY IN CUE
P.87
P.84
P.73
P.84
P.73
KEY MIX44 PRE EQ,MIX 41-44 KEY IN CUE
P.90
P.84
KEY STEREO B(R) PRE EQ,STEREO A-B KEY IN CUE
P.90
MIX PRE 45-48
<MIX45>PRE EQ,PRE FADER,POST FADER,POST ON
INSERT OUT MIX 45-48
DSP6
INSERT IN MIX 45-48
<MIX46>PRE EQ,PRE FADER,POST FADER,POST ON
<MIX47>PRE EQ,PRE FADER,POST FADER,POST ON
<MIX48>PRE EQ,PRE FADER,POST FADER,POST ON
KEY 1-4 OUT(MIX 45-48)
IN:5
OUT:8
0
1
2
3
4
5
6
0
1
2
3
P.84
P.73
KEY MIX48 PRE EQ,MIX 45-48 KEY IN CUE
P.90
CASCADE OUT MIX 33-36
7
CASCADE OUT MIX 37-40
CASCADE IN MIX 33-36
4
CASCADE IN MIX 37-40
4
CASCADE IN MIX 41-44
4
CASCADE OUT MIX 41-44
CASCADE OUT MIX 45-48
CASCADE IN MIX 45-48
4
CASCADE IN
STEREO A-B
4
CASCADE OUT STEREO A,B
DRAM
256K x 16
(4Mbit)
DATA BUS(DRAM)
7
7
7 7
P.87
ADDRESS,RW CONTROL
ADDRESS,RW CONTROL
P.85
P.73
7
5
6
7
5
6
7
5
6
7
5
6
7
5
6
1M x 16
(16Mbit)
DATA BUS(DRAM 32bit)
IC500
IC503
IC550
IC551 IC600
IC601
IC602
IC501
IC502
[DIGITAL I/O]
[CASCADE]
[IN]
[DIGITAL I/O]
[CASCADE]
[OUT]
[DIGITAL I/O]
[CASCADE]
[OUT]
[DIGITAL I/O]
[CASCADE]
[IN]
[DIGITAL I/O]
[CASCADE]
[IN]
[DIGITAL I/O]
[CASCADE]
[IN]
[DIGITAL I/O]
[CASCADE]
[IN]
P.88
P.88
P.88
P.88
P.88
KEC-92538-30
86
DSP1D
Page 44

GDB
FUNCTION: MATRIX,CUE/MONITOR ADD.,KEY IN
<MIX1>PRE EQ,PRE FADER,POST FADER,POST ON
P.85
MATRIX PRE 1-4
MATRIX PRE 5-8
MATRIX PRE 9-12
DSP5
P.89
IN:52
OUT:9
<MIX2>PRE EQ,PRE FADER,POST FADER,POST ON
<MIX3>PRE EQ,PRE FADER,POST FADER,POST ON
<MIX4>PRE EQ,PRE FADER,POST FADER,POST ON
<MIX5>PRE EQ,PRE FADER,POST FADER,POST ON
<MIX6>PRE EQ,PRE FADER,POST FADER,POST ON
<MIX7>PRE EQ,PRE FADER,POST FADER,POST ON
<MIX8>PRE EQ,PRE FADER,POST FADER,POST ON
<MIX9>PRE EQ,PRE FADER,POST FADER,POST ON
<MIX10>PRE EQ,PRE FADER,POST FADER,POST ON
<MIX11>PRE EQ,PRE FADER,POST FADER,POST ON
<MIX12>PRE EQ,PRE FADER,POST FADER,POST ON
<MIX13>PRE EQ,PRE FADER,POST FADER,POST ON
<MIX14>PRE EQ,PRE FADER,POST FADER,POST ON
<MIX15>PRE EQ,PRE FADER,POST FADER,POST ON
<MIX16>PRE EQ,PRE FADER,POST FADER,POST ON
<MIX17>PRE EQ,PRE FADER,POST FADER,POST ON
<MIX18>PRE EQ,PRE FADER,POST FADER,POST ON
<MIX19>PRE EQ,PRE FADER,POST FADER,POST ON
<MIX20>PRE EQ,PRE FADER,POST FADER,POST ON
<MIX21>PRE EQ,PRE FADER,POST FADER,POST ON
<MIX22>PRE EQ,PRE FADER,POST FADER,POST ON
<MIX23>PRE EQ,PRE FADER,POST FADER,POST ON
<MIX24>PRE EQ,PRE FADER,POST FADER,POST ON
<MIX25>PRE EQ,PRE FADER,POST FADER,POST ON
<MIX26>PRE EQ,PRE FADER,POST FADER,POST ON
<MIX27>PRE EQ,PRE FADER,POST FADER,POST ON
<MIX28>PRE EQ,PRE FADER,POST FADER,POST ON
<MIX29>PRE EQ,PRE FADER,POST FADER,POST ON
<MIX30>PRE EQ,PRE FADER,POST FADER,POST ON
<MIX31>PRE EQ,PRE FADER,POST FADER,POST ON
<MIX32>PRE EQ,PRE FADER,POST FADER,POST ON
<MIX33>PRE EQ,PRE FADER,POST FADER,POST ON
<MIX34>PRE EQ,PRE FADER,POST FADER,POST ON
<MIX35>PRE EQ,PRE FADER,POST FADER,POST ON
<MIX36>PRE EQ,PRE FADER,POST FADER,POST ON
<MIX37>PRE EQ,PRE FADER,POST FADER,POST ON
<MIX38>PRE EQ,PRE FADER,POST FADER,POST ON
<MIX39>PRE EQ,PRE FADER,POST FADER,POST ON
<MIX40>PRE EQ,PRE FADER,POST FADER,POST ON
<MIX41>PRE EQ,PRE FADER,POST FADER,POST ON
<MIX42>PRE EQ,PRE FADER,POST FADER,POST ON
<MIX43>PRE EQ,PRE FADER,POST FADER,POST ON
<MIX44>PRE EQ,PRE FADER,POST FADER,POST ON
<MIX45>PRE EQ,PRE FADER,POST FADER,POST ON
<MIX46>PRE EQ,PRE FADER,POST FADER,POST ON
<MIX47>PRE EQ,PRE FADER,POST FADER,POST ON
<MIX48>PRE EQ,PRE FADER,POST FADER,POST ON
<STEREO A(L)>PRE EQ,PRE FADER,POST FADER,POST ON
<STEREO A(R)>PRE EQ,PRE FADER,POST FADER,POST ON
<STEREO B(L)>PRE EQ,PRE FADER,POST FADER,POST ON
<STEREO B(R)>PRE EQ,PRE FADER,POST FADER,POST ON
MIX 1-4 to STEREO
MIX 5-8 to STEREO
MIX 9-12 to STEREO
MIX 13-16 to STEREO
MIX 17-20 to STEREO
MIX 21-24 to STEREO
P.84
P.88
MATRIX PRE 13-16
DSP5
IN:52
OUT:9
MATRIX PRE 17-20
MATRIX PRE 21-24
P.89
MIX 25-28 to STEREO
MIX 29-32 to STEREO
MIX 33-36 to STEREO
MIX 37-40 to STEREO
MIX 41-44 to STEREO
MIX 45-48 to STEREO
P.84
PARALLEL BUS
MIX OUT 1-4
DSP5
IN:52
OUT:12
P.90
MIX OUT 5-8
MIX OUT 9-12
MIX OUT 13-16
MIX OUT 17-20
MIX OUT 21-24
MIX OUT 25-28
MIX OUT 29-32
MIX OUT 33-36
MIX OUT 37-40
MIX OUT 41-44
MIX OUT 45-48
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
00
01
02
04
05
06
07
08
09
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
00
01
02
04
05
06
07
08
09
10
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
00
01
02
03
04
05
06
07
08
09
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
10
03 03
IC650 IC651 IC750
P.86
KEC-92538-31
87
DSP1D
Page 45

GDB
FUNCTION: MATRIX,CUE/MONITOR ADD.,KEY IN
<MIX1>PRE EQ,PRE FADER,POST FADER,POST ON
DSP5
IN:52
OUT:2
KEY 1-4
<MIX2>PRE EQ,PRE FADER,POST FADER,POST ON
<MIX3>PRE EQ,PRE FADER,POST FADER,POST ON
<MIX4>PRE EQ,PRE FADER,POST FADER,POST ON
<MIX5>PRE EQ,PRE FADER,POST FADER,POST ON
<MIX6>PRE EQ,PRE FADER,POST FADER,POST ON
<MIX7>PRE EQ,PRE FADER,POST FADER,POST ON
<MIX8>PRE EQ,PRE FADER,POST FADER,POST ON
<MIX9>PRE EQ,PRE FADER,POST FADER,POST ON
<MIX10>PRE EQ,PRE FADER,POST FADER,POST ON
<MIX11>PRE EQ,PRE FADER,POST FADER,POST ON
<MIX12>PRE EQ,PRE FADER,POST FADER,POST ON
<MIX13>PRE EQ,PRE FADER,POST FADER,POST ON
<MIX14>PRE EQ,PRE FADER,POST FADER,POST ON
<MIX15>PRE EQ,PRE FADER,POST FADER,POST ON
<MIX16>PRE EQ,PRE FADER,POST FADER,POST ON
<MIX17>PRE EQ,PRE FADER,POST FADER,POST ON
<MIX18>PRE EQ,PRE FADER,POST FADER,POST ON
<MIX19>PRE EQ,PRE FADER,POST FADER,POST ON
<MIX20>PRE EQ,PRE FADER,POST FADER,POST ON
<MIX21>PRE EQ,PRE FADER,POST FADER,POST ON
<MIX22>PRE EQ,PRE FADER,POST FADER,POST ON
<MIX23>PRE EQ,PRE FADER,POST FADER,POST ON
<MIX24>PRE EQ,PRE FADER,POST FADER,POST ON
<MIX25>PRE EQ,PRE FADER,POST FADER,POST ON
<MIX26>PRE EQ,PRE FADER,POST FADER,POST ON
<MIX27>PRE EQ,PRE FADER,POST FADER,POST ON
<MIX28>PRE EQ,PRE FADER,POST FADER,POST ON
<MIX29>PRE EQ,PRE FADER,POST FADER,POST ON
<MIX30>PRE EQ,PRE FADER,POST FADER,POST ON
<MIX31>PRE EQ,PRE FADER,POST FADER,POST ON
<MIX32>PRE EQ,PRE FADER,POST FADER,POST ON
<MIX33>PRE EQ,PRE FADER,POST FADER,POST ON
<MIX34>PRE EQ,PRE FADER,POST FADER,POST ON
<MIX35>PRE EQ,PRE FADER,POST FADER,POST ON
<MIX36>PRE EQ,PRE FADER,POST FADER,POST ON
<MIX37>PRE EQ,PRE FADER,POST FADER,POST ON
<MIX38>PRE EQ,PRE FADER,POST FADER,POST ON
<MIX39>PRE EQ,PRE FADER,POST FADER,POST ON
<MIX40>PRE EQ,PRE FADER,POST FADER,POST ON
<MIX41>PRE EQ,PRE FADER,POST FADER,POST ON
<MIX42>PRE EQ,PRE FADER,POST FADER,POST ON
<MIX43>PRE EQ,PRE FADER,POST FADER,POST ON
<MIX44>PRE EQ,PRE FADER,POST FADER,POST ON
<MIX45>PRE EQ,PRE FADER,POST FADER,POST ON
<MIX46>PRE EQ,PRE FADER,POST FADER,POST ON
<MIX47>PRE EQ,PRE FADER,POST FADER,POST ON
<MIX48>PRE EQ,PRE FADER,POST FADER,POST ON
<STEREO A(L)>PRE EQ,PRE FADER,POST FADER,POST ON
DSP5
IN:53
OUT:4
<STEREO A(R)>PRE EQ,PRE FADER,POST FADER,POST ON
<STEREO B(L)>PRE EQ,PRE FADER,POST FADER,POST ON
<STEREO B(R)>PRE EQ,PRE FADER,POST FADER,POST ON
SUB IN 1,DIRECT IN 1
MONITOR PRE A,B
P.89
PARALLEL BUS
2TR IN 1 1-2(LR)
MATRIX 1-4 to CUE
MATRIX 5-8 to CUE
MATRIX 9-12 to CUE
MATRIX 13-16 to CUE
MATRIX 17-20 to CUE
MATRIX 21-24 to CUE
MATRIX 1-4 to MONITOR
MATRIX 5-8 to MONITOR
MATRIX 9-12 to MONITOR
MATRIX 13-16 to MONITOR
MATRIX 17-20 to MONITOR
MATRIX 21-24 to MONITOR
CUE PRE A-B
KEY 1-4 OUT(MIX 1-4)
KEY 1-4 OUT(MIX 5-8)
KEY 1-4 OUT(MIX 9-12)
KEY 1-4 OUT(MIX 13-16)
KEY 1-4 OUT(MIX 17-20)
KEY 1-4 OUT(MIX 21-24)
KEY 1-4 OUT(MIX 25-28)
KEY 1-4 OUT(MIX 29-32)
KEY 1-4 OUT(MIX 33-36)
KEY 1-4 OUT(MIX 37-40)
KEY 1-4 OUT(MIX 41-44)
KEY 1-4 OUT(MIX 45-48)
STEREO OUT A,B
P.90
P.72
P.87
KEY 1-4 OUT(STEREO A,B)
P.90
P.74
P.89
P.84
P.85
2TR IN 1 3-4(LR)
2TR IN 1 5-6(LR)
MIX 1-4 KEY IN CUE
MIX 5-8 KEY IN CUE
MIX 9-12 KEY IN CUE
MIX 13-16 KEY IN CUE
MIX 17-20 KEY IN CUE
MIX 21-24 KEY IN CUE
MIX 25-28 KEY IN CUE
MIX 29-32 KEY IN CUE
MIX 33-36 KEY IN CUE
MIX 37-40 KEY IN CUE
MIX 41-44 KEY IN CUE
MIX 45-48 KEY IN CUE
STEREO A-B KEY IN CUE
SUB IN 2,DIRECT IN 2
CUE SUB OUT A-B
00
01
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
00
01
02
03
04
GDSP to PDSP TEST1
GDSP to PDSP TEST2
05
56
57
A(TB,TB/OSC,OSC,COMM.)
B(TB,TB/OSC,OSC,COMM.)
58
59
60
61
62
63
GEQ RETURN 1-4
GEQ RETURN 5-8
GEQ RETURN 9-12
GEQ RETURN 13-16
GEQ RETURN 17-20
GEQ RETURN 21-24
P.92
8
KEY 1-4 OUT(CH1-96)
P.84
9
10
11
IC751
IC800
Except CUE Signal
CUE Signal
P.86
P.85
P.86
P.75
P.74
P.75
P.93
KEC-92538-32
88
DSP1D
Page 46

KEY MATRIX8 PRE EQ,POST EQ
KEY MATRIX16 PRE EQ,POST EQ
CASCADE OUT MONITOR A-B(LR)
KEY MATRIX24 PRE EQ,POST EQ
PDB
FUNCTION: MATRIX EQ/COMP/DELAY/FADER ON,MONITOR DELAY
DSP6
IN:4
OUT:7
MATRIX PRE 5-8
P.87
INSERT IN MATRIX 5-8
MATRIX OUT 5-8
MATRIX 5-8 TEMP.
INSERT OUT MATRIX 5-8
P.90
DATA BUS(DRAM)
DSP6
IN:4
OUT:7
MATRIX PRE 9-12
INSERT IN MATRIX 9-12
MATRIX OUT 9-12
INSERT OUT MATRIX 9-12
DATA BUS(DRAM)
DSP6
DSP6
IN:4
OUT:7
IN:4
OUT:7
MATRIX PRE 17-20
INSERT IN MATRIX 17-20
DSP6
IN:4
OUT:7
MATRIX PRE 13-16
INSERT IN MATRIX 13-16
MATRIX OUT 13-16
INSERT OUT MATRIX 13-16
MATRIX OUT 17-20
INSERT OUT MATRIX 17-20
P.90
MATRIX OUT 21-24
INSERT OUT MATRIX 21-24
MATRIX PRE 21-24
P.87
INSERT IN MATRIX 21-24MATRIX 9-12 TEMP.
MATRIX 21-24 TEMP.
MATRIX 17-20 TEMP.
MATRIX 13-16 TEMP.
MATRIX PRE 1-4
KEY IN 1-4
MATRIX OUT 1-4
DATA BUS(DRAM)
DSP6
P.87
INSERT IN MATRIX 1-4 MATRIX 1-4 TEMP.
INSERT OUT MATRIX 1-4
IN:3
OUT:7
MATRIX 1-4 to CUE
MATRIX 1-4 to MONITOR
MATRIX 5-8 to CUE
MATRIX 5-8 to MONITOR
MATRIX 9-12 to CUE
MATRIX 9-12 to MONITOR
MATRIX 13-16 to CUE
MATRIX 13-16 to MONITOR MATRIX 17-20 to CUE
MATRIX 17-20 to MONITOR
MATRIX 21-24 to CUE
MATRIX 21-24 to MONITOR
MONITOR PRE A,B
A(TB,TB/OSC,OSC,COMM.)
MONITOR A-B
DSP6
P.90
IN:6
OUT:5
P.88
P.74
P.88
P.88
P.88
0
1
3
2
0
1
2
3
4
5
00
1
30
1
2
3
4
5
0
1
2
30
1
2
3
4
5
0
1
2
0
5
1
2
30
1
2
3
4
0
5
1
2
3
0
1
2
3
4
0
1
2
3
0
1
2
3
4
DRAM
1M x 16
(16Mbit)
DATA BUS(DRAM 32bit)
P.73
DRAM
1M x 16
(16Mbit)
DATA BUS(DRAM 32bit)
KEY MATRIX4 PRE EQ,POST EQ
6
KEY 1-4 OUT(MATRIX1-4)
P.73
6
KEY 1-4 OUT(MATRIX5-8)
6
KEY 1-4 OUT(MATRIX9-12)
KEY MATRIX12 PRE EQ,POST EQ
P.87
P.73
P.87
P.73
P.87
P.73
6
KEY 1-4 OUT(MATRIX13-16)
6
KEY 1-4 OUT(MATRIX17-20)
KEY MATRIX20 PRE EQ,POST EQ
6
KEY 1-4 OUT(MATRIX21-24)
5
B(TB,TB/OSC,OSC,COMM.)
2
P.73
CUE SUB OUT A-B
3
CASCADE IN MONITOR A-B(LR)
4
1
2
CUE A-B
DATA BUS(DRAM)
ADDRESS,RW CONTROL
ADDRESS,RW CONTROL
CASCADE IN CUE A-B(LR)
5
CASCADE OUT CUE A-B(LR)
3
4
MONITOR A-B TEMP.
4
5
6
7
4
5
6
7
4
5
6
7
4
5
6
7
4
5
6
7
4
5
6
7
6
7
IC500
IC505
IC550
IC551 IC600
IC603
IC650
IC601
IC602
CUE Signal Except CUE Signal
IC501
IC502
[DIGITAL I/O]
[CASCADE]
[OUT]
[DIGITAL I/O]
[CASCADE]
[IN]
P.91
P.90
P.90
P.90
P.91
P.91
P.75
P.91
P.90
P.90
P.88
P.91
P.90
P.90
P.88
P.91
P.90
P.90
P.88
P.91
P.90
P.72
KEC-92538-33
89
DSP1D
Page 47

D. SUB OUT 1-4
D. SUB OUT 5-8
D. SUB OUT 9-12
D. SUB OUT 13-16
D. SUB OUT 17-20
D. SUB OUT 21-24
D. SUB OUT 25-28
D. SUB OUT 29-32
D. SUB OUT 33-36
D. SUB OUT 37-40
D. SUB OUT 41-44
D. SUB OUT 45-48
D. SUB OUT 49-52
D. SUB OUT 53-56
D. SUB OUT 57-60
D. SUB OUT 61-64
D. SUB OUT 65-68
D. SUB OUT 69-72
D. SUB OUT 73-76
D. SUB OUT 77-80
D. SUB OUT 81-84
D. SUB OUT 85-88
OUT PATCH TEST 1
OUT PATCH TEST 2
D. SUB OUT 97-100
D. SUB OUT 105-108
D. SUB OUT 109-112
D. SUB OUT 113-116
D. SUB OUT 117-120
D. SUB OUT 121-124
D. SUB OUT 125-128
D. SUB OUT 101-104
D. SUB OUT 173-176
D. SUB OUT 129-132
D. SUB OUT 133-136
D. SUB OUT 137-140
D. SUB OUT 141-144
D. SUB OUT 145-148
D. SUB OUT 149-152
D. SUB OUT 153-156
D. SUB OUT 157-160
D. SUB OUT 161-164
D. SUB OUT 165-168
D. SUB OUT 169-172
DIGITAL STEREO OUT A-B
PDB
FUNCTION: OUTPUT PATCH, PEAK METER
MIX OUT 1-4
MIX OUT 5-8
MIX OUT 9-12
MIX OUT 13-16
MIX OUT 17-20
MIX OUT 21-24
MIX OUT 25-28
MIX OUT 29-32
MIX OUT 33-36
MIX OUT 37-40
MIX OUT 41-44
MIX OUT 45-48
DSP5
IN:40
OUT:24
P.87
MATRIX OUT 1-4
MATRIX OUT 5-8
MATRIX OUT 9-12
MATRIX OUT 13-16
MATRIX OUT 17-20
MATRIX OUT 21-24
P.89
D. SUB OUT 89-92
D. SUB OUT 93-96
INSERT OUT CH1-4
INSERT OUT CH5-8
INSERT OUT CH9-12
INSERT OUT CH13-16
INSERT OUT CH17-20
INSERT OUT CH21-24
INSERT OUT CH25-28
INSERT OUT CH29-32
INSERT OUT CH33-36
INSERT OUT CH37-40
INSERT OUT CH41-44
INSERT OUT CH45-48
DSP5
IN:40
OUT:24
INSERT OUT CH49-52
INSERT OUT MIX 1-4
INSERT OUT MIX 5-8
INSERT OUT MIX 9-12
INSERT OUT MIX 13-16
INSERT OUT MIX 17-20
INSERT OUT MIX 21-24
INSERT OUT MIX 25-28
INSERT OUT MIX 29-32
INSERT OUT MIX 33-36
INSERT OUT MIX 37-40
INSERT OUT MIX 41-44
INSERT OUT MIX 45-48
INSERT OUT STEREO A,B
INSERT OUT MATRIX 1-4
INSERT OUT MATRIX 5-8
INSERT OUT MATRIX 9-12
INSERT OUT MATRIX 13-16
INSERT OUT MATRIX 17-20
INSERT OUT MATRIX 21-24
P.74
P.89
PARALLEL BUS
PARALLEL BUS
INSERT OUT ST IN1-2
INSERT OUT ST IN3-4
01
02
03
04
05
06
07
08
09
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
00
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
01
57
02
03
04
05
06
07
08
09
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
00
58
59
60
30
32
33
34
35
36
37
54
55
56
61
52
53
50
51
48
49
57
58
59
60
54
55
56
61
52
53
50
51
48
49
38
A(TB,TB/OSC,OSC,COMM.)
39
31
B(TB,TB/OSC,OSC,COMM.)
P.74
P.91
P.91
DIRECT OUT CH1-4
DIRECT OUT CH5-8
DIRECT OUT CH9-12
DIRECT OUT CH13-16
DIRECT OUT CH17-20
DIRECT OUT CH21-24
GEQ RETURN 1-4
GEQ RETURN 9-12
GEQ RETURN 13-16
GEQ RETURN 17-20
GEQ RETURN 21-24
P.92
GEQ RETURN 5-8
DIRECT OUT ST IN1-2
DIRECT OUT CH25-28
DIRECT OUT CH29-32
DIRECT OUT CH33-36
DIRECT OUT CH37-40
DIRECT OUT CH41-44
DIRECT OUT CH45-48
P.74
DIRECT OUT ST IN3-4
P.85
INSERT OUT CH53-56
INSERT OUT CH57-60
44
45
46
47
44
45
46
47
38
39
P.74
43
42
41
40
62
63
62
63
43
42
41
40
IN PATCH TEST 1
IN PATCH TEST 2
P.73
IN PATCH TEST 3
IN PATCH TEST 4
P.73
OUT PATCH TEST 3
OUT PATCH TEST 4
P.72
P.72
STEREO OUT A,B
MONITOR A-B
KEY 1-4 OUT(MATRIX1-4)
P.88
CUE A-B
KEY 1-4 OUT(MATRIX4-8)
KEY 1-4 OUT(MATRIX9-12)
KEY 1-4 OUT(MATRIX13-16)
KEY 1-4 OUT(MATRIX17-20)
KEY 1-4 OUT(MATRIX21-24)
P.89
KEY 1-4
KEY MATRIX24 POST EQ
D. SUB OUT 177-180
D. SUB OUT 181-184
D. SUB OUT 185-188
D. SUB OUT 189-192
DSP5
IN:40
OUT:23
DIRECT OUT CH49-52
DIRECT OUT CH53-56
DIRECT OUT CH57-60
DIRECT OUT CH61-64
DIRECT OUT CH65-68
DIRECT OUT CH69-72
DIRECT OUT CH73-76
DIRECT OUT CH77-80
DIRECT OUT CH81-84
DIRECT OUT CH85-88
DIRECT OUT CH89-92
DIRECT OUT CH93-96
P.77
P.91
MONITOR OUT A-B
KEY IN 1-4
EFFECT SEND 1-2(LR)
P.92
GEQ SEND 1-4
GEQ SEND 5-8
GEQ SEND 9-12
GEQ SEND 13-16
GEQ SEND 17-20
GEQ SEND 21-24
PARALLEL BUS
01
02
03
04
05
06
07
08
09
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
00
CUE OUT A-B
P.72
INSERT OUT CH61-64
INSERT OUT CH65-68
INSERT OUT CH69-72
INSERT OUT CH73-76
INSERT OUT CH77-80
INSERT OUT CH81-84
INSERT OUT CH85-88
INSERT OUT CH89-92
INSERT OUT CH93-96
INSERT OUT ST IN7-8
INSERT OUT ST IN5-6
DIRECT OUT ST IN5-6
DIRECT OUT ST IN7-8
57
58
59
54
55
56
52
53
50
51
48
49
IN PATCH TEST 5
FFT IN,FFT NOISE
28
29
30
31
32
33
44
45
46
47
34
35
RESERVED A-B
36
37
38
39
43
42
41
40
GDSP to PDSP TEST1
GDSP to PDSP TEST2
P.73
OUT PATCH TEST 5
OUT PATCH TEST 6
P.72
60
61
62
EFFECT SEND 3-4(LR)
EFFECT SEND 5-6(LR)
EFFECT SEND 7-8(LR)
ANALYZER SEND 1
ANALYZER SEND 2
P.76
IC400 IC401 IC450
[DIGITAL I/O]
[CONSOLEI/O]
[1]
[2]
P.93
P.92
P.93
P.75
P.93
P.75
P.75
P.86
P.76
P.77
P.76
KEC-92538-34
90
DSP1D
Page 48

DITHER 1-4
DITHER 5-8
DITHER 9-12
DITHER 13-16
DITHER 17-20
DITHER 21-24
DITHER 25-28
DITHER 29-32
DITHER 33-36
DITHER 37-40
DITHER 41-44
DITHER 45-48
DITHER 49-52
DITHER 53-56
DITHER 57-60
DITHER 61-64
DIGITAL OUT 1-4
DIGITAL OUT 5-8
DIGITAL OUT 9-12
DIGITAL OUT 13-16
DIGITAL OUT 17-20
DIGITAL OUT 21-24
DIGITAL OUT 25-28
DIGITAL OUT 29-32
DIGITAL OUT 33-36
DIGITAL OUT 37-40
DIGITAL OUT 41-44
DIGITAL OUT 45-48
DIGITAL OUT 49-52
DIGITAL OUT 53-56
DIGITAL OUT 57-60
DIGITAL OUT 61-64
DIGITAL OUT 65-68
DIGITAL OUT 69-72
DIGITAL OUT 73-76
DIGITAL OUT 77-80
DIGITAL OUT 81-84
DIGITAL OUT 85-88
DIGITAL OUT 89-92
DIGITAL OUT 93-96
DIGITAL OUT 133-136
DIGITAL OUT 137-140
DIGITAL OUT 141-144
DIGITAL OUT 145-148
DIGITAL OUT 149-152
DIGITAL OUT 153-156
DIGITAL OUT 157-160
DIGITAL OUT 129-132
DIGITAL OUT 125-128
DIGITAL OUT 121-124
DIGITAL OUT 117-120
DIGITAL OUT 113-116
DIGITAL OUT 109-112
DIGITAL OUT 105-108
DIGITAL OUT 101-104
DIGITAL OUT 97-100
DIGITAL OUT 161-164
DIGITAL OUT 165-168
DIGITAL OUT 169-172
DIGITAL OUT 176-180
DIGITAL OUT 181-184
DIGITAL OUT 185-188
DIGITAL OUT 189-192
DIGITAL OUT 173-175
PDB
FUNCTION: DITHER
D. SUB OUT 65-68
DSP5
IN:40
OUT:24
D. SUB OUT 69-72
D. SUB OUT 73-76
D. SUB OUT 77-80
D. SUB OUT 81-84
D. SUB OUT 85-88
D. SUB OUT 89-92
D. SUB OUT 93-96
DSP6
IN:4
OUT:8
1
0
2
3
4
5
6
7
1
0
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
P.90
DSP5
IN:40
OUT:24
1
0
2
3
4
5
6
7
D. SUB OUT 97-100
D. SUB OUT 101-104
D. SUB OUT 105-108
D. SUB OUT 109-112
D. SUB OUT 113-116
D. SUB OUT 117-120
D. SUB OUT 121-124
D. SUB OUT 125-128
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
D. SUB OUT 129-132
P.90
D. SUB OUT 133-136
D. SUB OUT 137-140
D. SUB OUT 141-144
D. SUB OUT 145-148
D. SUB OUT 149-152
D. SUB OUT 153-156
D. SUB OUT 157-160
D. SUB OUT 161-164
D. SUB OUT 165-168
D. SUB OUT 169-172
D. SUB OUT 173-176
D. SUB OUT 177-180
D. SUB OUT 181-184
D. SUB OUT 185-188
D. SUB OUT 189-192
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
D. SUB OUT 1-4
D. SUB OUT 5-8
D. SUB OUT 9-12
D. SUB OUT 13-16
D. SUB OUT 17-20
D. SUB OUT 21-24
D. SUB OUT 25-28
D. SUB OUT 29-32
D. SUB OUT 33-36
D. SUB OUT 37-40
D. SUB OUT 41-44
D. SUB OUT 45-48
D. SUB OUT 49-52
D. SUB OUT 53-56
D. SUB OUT 57-60
D. SUB OUT 61-64
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
54
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
44
40
41
42
43
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
DSP6
IN:3
OUT:8
1
0
2
3
4
5
6
7
DITHER 1-4
DITHER 5-8
DITHER 9-12
DITHER 13-16
DITHER 17-20
DITHER 21-24
DITHER 25-28
DITHER 29-32
DITHER 33-36
DITHER 37-40
DITHER 41-44
DITHER 45-48
DITHER 49-52
DITHER 53-56
DITHER 57-60
DITHER 61-64
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
DITHER 1-4
DITHER 5-8
DITHER 9-12
DITHER 13-16
DITHER 17-20
DITHER 21-24
DITHER 25-28
DITHER 29-32
DITHER 33-36
DITHER 37-40
DITHER 41-44
DITHER 45-48
DITHER 49-52
DITHER 53-56
DITHER 57-60
DITHER 61-64
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
54
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
44
40
41
42
43
MATRIX 1-4 TEMP.
MATRIX 5-8 TEMP.
MATRIX 9-12 TEMP.
MATRIX 13-16 TEMP.
P.89
0
1
2
3
MATRIX 17-20 TEMP.
MATRIX 21-24 TEMP.
MONITOR A-B TEMP.
P.89
0
1
2
4
5
6
7
4
5
6
7
3
IC750 IC751
IC701
IC700
[DIGITAL I/O]
[OUTPUT]
[4]-[6]
[DIGITAL I/O]
[OUTPUT]
[1]-[3]
KEC-92538-35
91
DSP1D
Page 49

EFFECT RETURN 3-4(LR)
GEQ RETURN 5-8
EFFECT RETURN 1-2(LR)
GEQ RETURN 1-4
EFFECT RETURN 5-6(LR) EFFECT RETURN 7-8(LR)
EDB
FUNCTION: EFFECT,GEQ
EFFECT SEND
1-2(LR)
DSP6
P.90
IN:2
OUT:2
GEQ SEND 1-4
DSP6
P.72
IN:4
OUT:2
DSP6
IN:2
OUT:2
GEQ SEND 5-8
DSP6
IN:4
OUT:2
DATA BUS(DRAM 32bit)
256K x 16
(4Mbit)
DRAM
DRAM
DRAM
P.84
0
1
2
3
0
1
0
1
0
1
2
3
0
1
0
1
0
1
P.90
P.72
P.84
P.90
DSP6
IN:2
OUT:2
GEQ SEND 9-12
DSP6
P.72
IN:4
OUT:2
GEQ RETURN 9-12
DSP6
IN:2
OUT:2
GEQ SEND 13-16
DSP6
IN:4
OUT:2
GEQ RETURN 13-16
DRAM
DRAM
DRAM
DRAM
P.84
0
1
2
3
0
1
0
1
0
1
2
3
0
1
0
1
0
1P.90
P.72
P.84
P.90
P.72
P.72
P.72
P.72
2
3
4
5
6
7
P.90
4
5
6
7
2
3
4
5
6
7
4
5
6
7
2
3
4
5
6
7
P.90
4
5
6
7
P.90
2
3
4
5
6
7
0
1
0
1
EFFECT SEND
3-4(LR)
EFFECT SEND
7-8(LR)
EFFECT SEND
5-6(LR)
P.88
P.88
P.88
P.88
DATA BUS(DRAM 32bit)
256K x 16
(4Mbit)
DATA BUS(DRAM 32bit)
256K x 16
(4Mbit)
DATA BUS(DRAM 32bit)
DRAM
256K x 16
(4Mbit)
DATA BUS(DRAM 32bit)
256K x 16
(4Mbit)
DATA BUS(DRAM 32bit)
256K x 16
(4Mbit)
DATA BUS(DRAM 32bit)
256K x 16
(4Mbit)
DATA BUS(DRAM 32bit)
256K x 16
(4Mbit)
IC300 IC304 IC350 IC354
IC400 IC404 IC450 IC454
IC301
IC302
IC303
IC305
IC351
IC352
IC353
IC355
IC453
IC455
IC451
IC452
IC403
IC405
IC401
IC402
KEC-92538-36
92
DSP1D
Page 50

EDB
FUNCTION: EFFECT,GEQ
ANALYZER SEND 1
DSP6
P.90
IN:4
OUT:2
GEQ SEND 17-20
ANALYZER 1 LOOP A
GEQ RETURN 17-18
DSP6
P.123
IN:4
OUT:4
ANALYZER SOURCE 1
GEQ RETURN 17-20
DSP6
P.90
IN:4
OUT:2
GEQ SEND 21-24
ANALYZER 2 LOOP A
GEQ RETURN 21-22
DSP6
P.90
IN:4
OUT:4
ANALYZER SOURCE 2
GEQ RETURN 21-24
DRAM
DATA BUS(DRAM)
DRAM
DATA BUS(DRAM)
P.117
P.84
2
3
0
1
0
1
0
1
0
1
2
3
0
1
0
1
0
1
0
1
2
3
2
3
2
3
2
3
P.105
P.72
P.72
P.105
4
5
6
7
4
5
6
7
4
5
6
7
4
5
6
7
ANAKYZER SEND 2
P.88P.121
DATA BUS(DRAM 32bit)
256K x 16
(4Mbit)
DATA BUS(DRAM 32bit)
256K x 16
(4Mbit)
ANALYZER 2 LOOP B
ANALYZER 1 LOOP C
ANALYZER 2 LOOP C
ANALYZER 1 LOOP B
IC500
IC503 IC553
IC550
IC501
IC502
IC551
IC552
KEC-92538-37
93
DSP1D
 Loading...
Loading...