
DFC155 & DWC155c Service Manual & Spare Parts Catalogue
602E52970Important Note
This is a first edition of the Service Manual and Spare Parts Catalogue.
To read the manual Adobe Acrobat 3.0 is needed as the .pdf files are not 2.1 compatible.
In the contents section there is a reference to remote diagnostics in chapter 5.
The section on this has been removed, as remote diagnostics are not legal in all countries.
Additionally a master unit is required. This master unit is no longer sold.
There are no references to the Linkfax softswitches in section 4 (DWC155c only). These will
be included in the next revision of the manual.

DFC155
DWC155c
SERVICE MANUAL
Part Number 602E52970

PUBLICATION ISSUED BY:
Xerox Limited Technical Centre
Bessemer Road
Welwyn garden City
Herts AL7 1HE
United Kingdom
WARNING
Danger of explosion if battery is incorrectly replaced.
Replace only with the same or equivalent type
recommended by the manufacturer.
Dispose of used batteries according to the manufacturer's instructions.

PREFACE
This manual, intended for service engineers responsible for installing, servicing and
repairing the facsimile machines described herein, consists of eight chapters covering:
• Chapter 1: the General Features and Technical Specifications
• Chapter 2: the facsimile machine's Internal and external structure
• Chapter 3: the Installation and setup procedures
• Chapter 4: how to set the Software Parameters
• Chapter 5: the Diagnostic and testing procedures
• Chapter 6: the Settings and adjustments
• Chapter 7: the Maintenance and replacement procedures
• Chapter 8: the Optional devices
DISTRIBUTION: General (G)
FIRST EDITION: January 1998
REFERENCES: User Manual
Spare parts catalogue

602E52970 v
CONTENTS
1. INTRODUCTION .......................................................... 1-1
1.1 MAIN FEATURES .......................................................................... 1-1
1.2 TECHNICAL SPECIFICATIONS ................................................... 1-2
1.3 QUICK REFERENCE GUIDE ........................................................ 1-5
1.3.1 Sending a Fax............................................................................................... 1-5
1.3.2 Receiving a Fax ............................................................................................ 1-5
1.3.3 Using the Facsimile Machine as a Photocopier ........................................... 1-5
2. GENERAL DESCRIPTION ........................................... 2-1
2.1 EXTERNAL PARTS ....................................................................... 2-1
2.1.1 Console ........................................................................................................ 2-2
2.1.2 Functions of the console keys ...................................................................... 2-3
2.2 ELECTROMECHANICAL PARTS ................................................. 2-6
2.2.1 Motors, elctromagnet and loudspeaker ....................................................... 2-6
2.2.2 Sensors ........................................................................................................ 2-7
2.3 ELECTRONIC PARTS ................................................................... 2-8
2.3.1 General Block Diagram ................................................................................ 2-9
2.3.2 Block Diagram of the Motherboard ............................................................ 2-10
2.3.3 Block Diagram of the Network Control Unit Board..................................... 2-13
2.3.4 Block Diagram of the Power Supply Board ................................................ 2-14
2.3.5 Printer Unit ................................................................................................. 2-16
2.3.6 Paper Feeding ............................................................................................ 2-18
3. INSTALLATION AND INITIALIZATION
PROCEDURES ............................................................ 3-1
3.1 PRELIMINARY OPERATIONS ...................................................... 3-1
3.1.1 Unpacking the Facsimile Machine ................................................................ 3-1
3.1.2 Connecting the Power Cord ......................................................................... 3-2
3.1.3 Inserting the paper support extension ......................................................... 3-2
3.1.4 Paper Supply ................................................................................................ 3-2
3.1.5 Installing the Print Head ............................................................................... 3-3
3.1.6 Connecting to the Telephone Line ................................................................ 3-8
3.1.7 Connecting the Handset ............................................................................... 3-9

vi 602E52970
3.2 INSTALLING AND SETTING UP THE MACHINE ........................ 3-10
3.2.1 Organization of the Installation and Setup Parameters ............................. 3-10
3.2.2 Setting the Country Parameters................................................................. 3-13
3.2.3 Storing the User's Number and Name ....................................................... 3-14
3.2.4 Setting Up the Telephone Line ................................................................... 3-15
3.2.5 Completing Installation ............................................................................... 3-17
3.2.6 Resetting the Fax Machine......................................................................... 3-19
4. SERVICE SWITCHES .................................................. 4-1
4.1 SERVICE SWITCH TABLES .......................................................... 4-3
5. DIAGNOSTICS ............................................................. 5-1
5.1 SELF-DIAGNOSTICS .................................................................... 5-1
5.1.1 Description of the Self-Diagnostic Program ................................................. 5-2
5.2 ERROR CODES ............................................................................ 5-3
5.2.1 Meaning of Protocol Signal Codes ............................................................... 5-4
5.2.2 Meaning of Error Codes ............................................................................... 5-6
5.2.3 Printing the Communication Protocol ........................................................... 5-9
5.3 REPORTS .................................................................................... 5-11
5.3.1 Transmission Report (LAST TX REPORT) ................................................ 5-11
5.3.2 Journal (ACTIVITY REPORT) .................................................................... 5-13
5.3.4 Loss of Mains Power Supply Report .......................................................... 5-13
5.4 REMOTE DIAGNOSTICS .............................................................5-15
5.4.1 Enabling the Facsimile Machine as a "Slave Station" ................................ 5-15
6. SYSTEM TEST AND ADJUSTMENTS ......................... 6-1
6.1 SYSTEM TEST .............................................................................. 6-1
6.1.1 ALIGNMENT TEST ...................................................................................... 6-2
6.1.2 NOZZLES TEST ........................................................................................... 6-4
6.1.3 PRINT CHART .............................................................................................. 6-5
6.1.4 ASF TEST ..................................................................................................... 6-8
6.1.5 ADF TEST .................................................................................................... 6-8
6.1.6 LOAD DEFAULT ........................................................................................... 6-9
6.1.7 SCANNER SHADING ................................................................................... 6-9
6.1.8 CARRIAGE TEST ....................................................................................... 6-10

602E52970 vii
6.2 CHECKS AND ADJUSTMENTS .................................................. 6-11
6.2.1 Checking the Direct Voltages ..................................................................... 6-11
7. MAINTENANCE AND REPLACEMENT
PROCEDURES ............................................................ 7-1
7.1 MAINTENANCE ............................................................................ 7-1
7.1.1 OUT OF INK Message ................................................................................. 7-1
7.1.2 Replacing the rechargeable Ink Cartridge ................................................... 7-2
7.1.3 Replacing the Print Head ............................................................................. 7-2
7.1.4 Cleaning the Print Head ............................................................................... 7-2
7.1.5 Cleaning the Electrical Contacts .................................................................. 7-3
7.1.6 Cleaning the Print Head Cleaning Pad ........................................................ 7-4
7.1.7 Cleaning the Optical Unit ............................................................................. 7-5
7.2 DISASSEMBLY AND REPLACEMENT PROCEDURES ............... 7-6
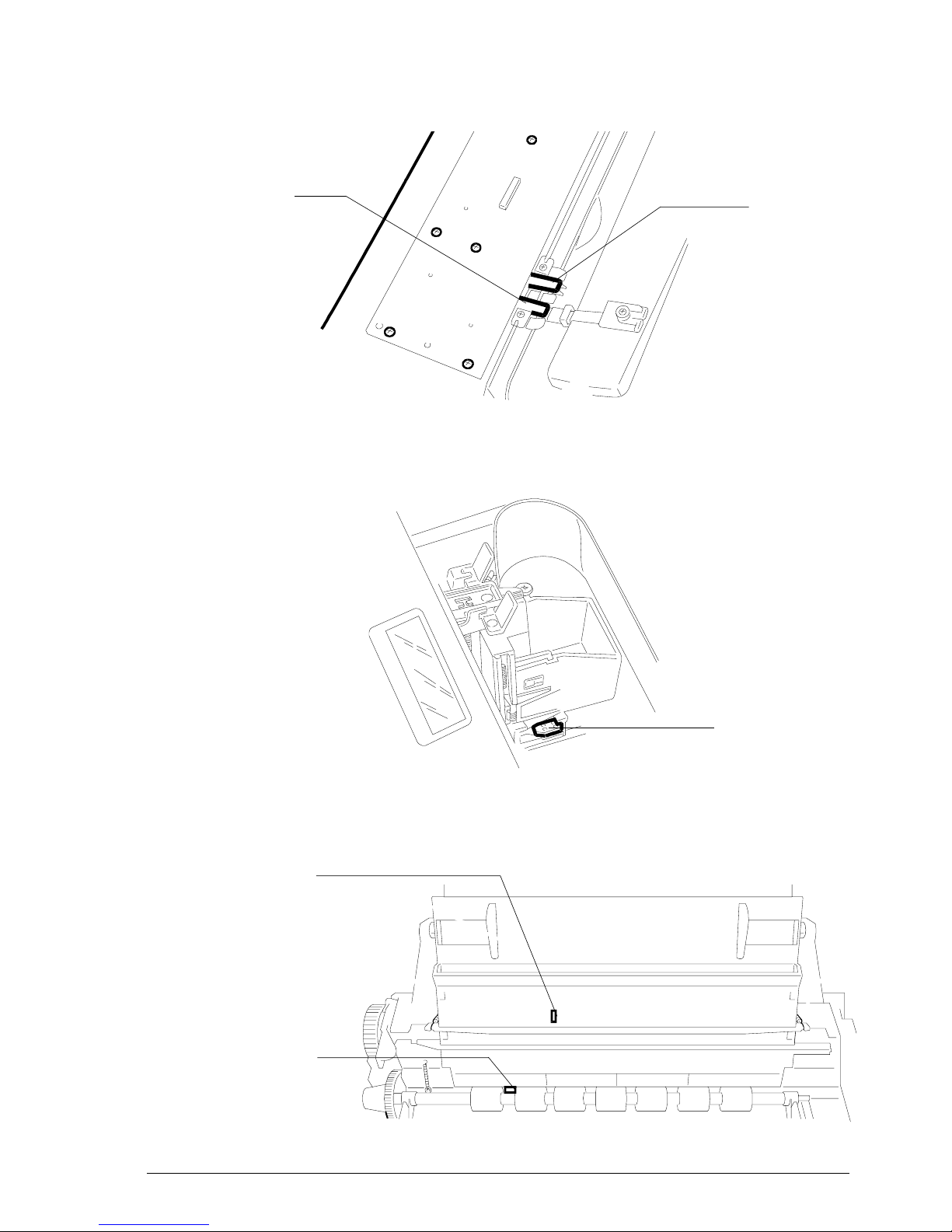
7.2.1 Wirings .......................................................................................................... 7-6
7.2.2 Removing the Casing ................................................................................... 7-8
7.2.3 Disassembling the base ............................................................................... 7-9
7.2.4 Replacing the motherboard and the NCU Board ....................................... 7-11
7.2.5 Replacing System Software ....................................................................... 7-13
7.2.6 Replacing the Power Supply Board ............................................................ 7-13
7.2.7 Replacing the Loudspeaker ........................................................................ 7-15
7.2.8 Replacing the Print Head Cleaner Electromagnet ..................................... 7-15
7.2.9 Replacing the Scanning/Interline Motor ..................................................... 7-16
7.2.10 Replacing the Carriage Motor .................................................................... 7-21
7.2.11 Replacing the Print Head Pad .................................................................... 7-22
7.2.12 Replacing the Carriage............................................................................... 7-22
7.2.13 Replacing the Forward Driving Rollers ....................................................... 7-25
7.2.14 Replacing Paper Shifter Rollers ................................................................. 7-26
7.2.15 Replacing Rear Driver Rollers .................................................................... 7-26
7.2.16 Replacing the Optical Unit (CIS) ................................................................ 7-29
7.2.17 Replacing the Document Sensor ............................................................... 7-29
7.2.18 Replacing the Paper Sensor ...................................................................... 7-30
7.2.19 Replacing the Console Board .................................................................... 7-31
7.2.20 Replacing the Display ................................................................................. 7-32
7.2.21 Restoring the Facsimile Machine ............................................................... 7-33
8. OPTIONAL DEVICES .................................................. 8-1
8.1 SETTING UP A BACK TO BACK CONNECTION .......................... 8-2
8.2 CONNECTING A TELEPHONE ANSWERING DEVICE OR AN
EMERGENCY PHONE SET .......................................................... 8-2

1-1602E52970
1. INTRODUCTION
This device is a desktop fax machine with inkjet printing, complying with the ITU-TS
G3 standard for the transmission and reception of documents.
1.1 MAIN FEATURES
• Bubble ink jet printing
Allows the use of normal paper with individual sheets of A4, Letter and Legal
format.
• Memory capacity
The fax machine has a memory which enables operations such as One-touch
Dialling, Speed Code Dialling and Substitute Reception, as well as the storage
of parameters, data and documents. This memory is powered by a backup battery
in the event of a power failure.
• Half tones
In the scanning of documents, a scale of 64 half tones can be used for a higher
quality reproduction of photographs and pictures.
• Automatic Document Feeder (ADF)
The fax machine allows automatic feeding of up to 5 documents in A4, Letter or
Legal format, with a maximum thickness of 0.1 mm/sheet.
1-2 602E52970
(1) with the document output tray >>
Desktop transceiver
359 x 264 (+ 841) x 193 (+ 1381) mm
5 kg
2 lines of 16 characters
- 15 function keys of which 4 are dual function and
two are triple function
- 12 dual-function keys for normal dialling and user
name setting
- 10 one-touch dialling keys
- 1 light indicator
220-240V, 50/60Hz
6W (in standby); max 30W
Public telephone network (PSTN) or private branch
exchange (PBX)
ITU-TS G3 standard
CCITT V29 / V27ter
2400 / 4800 / 7200 / 9600 bps
Half duplex
MH, MR (DFC 155)
MH, MR, MMR (DWC155c)
About 15 s for ITU-TS test sheet n°1 (Slerexe Letter)
at 9600 bps in standard resolution
• Telephone answering device (TAD)
The model without a built-an TAD can be connected to an external one.
1.2 TECHNICAL SPECIFICATIONS
Physical characteristics
Type
Dimensions (L, D, H)
Weight
Operator console
Display
Keypad
Power supply
Operating range
Absorption
Communication characteristics
Type of connection
Compatibility
Type of modulation
Transmission speed
Type of communication
Coding methods
Transmission time
1-3602E52970
>>
Contact Sensor (CIS)
Vertical: 3.85 (standard) / 7.7 (fine) lines/mm
Horizontal: 8 dots/mm
From 210 x 148 mm (minimum length) to 216 x 600 mm
(maximum length)
Horizontal: 216 mm
Vertical: within 2 mm of the edge of the document
Capacity: 5 sheets of A4 / US Letter / Legal format
(max thickness 0.1 mm/sheet)
Sheet thickness: min 0.06 mm, max 0.12 mm
The facsimile machine can emphasize the contrast of text
areas and reproduce pictures with 64 half tones.
Three levels are handled: dark, normal and light
Bubble ink jet on plain paper
ITU-TS test sheet n°1 (Slerexe Letter) / about 40 s
Capacity: 40 sheets of A4 / US Letter/ Legal format
(weight 70-90g/m2)
300 x 300 dpi
208 x 290 (A4) / 273 (Letter US) / 349 (Legal) mm
512 kbytes, of which about 450 available to the user,
powered by a backup battery
Pulse and tone
The number can be dialled directly on the facsimile
machine's keypad
Scanner
Scanning system
Resolution
Document size (width x length)
Actual scanning area
Automatic document feeder
(ADF)
Half tones
Contrast
Printer
Printing method
Printing speed
Automatic sheet feeder
Print resolution
Actual printing area
Memory
Capacity
Dialling
Dialling mode
Dialling on facsimile machine
1-4 602E52970
Redialling
One-touch dialling
Speed code dialling
Other features
Automatic reception
Polling
Reports
Environmental conditions
Temperature
Relative humidity
A number can be redialled in automatic or manual mode
10 numerical keys (0 ÷ 9) are available
32 memory locations are available, and each may be assigned a facsimile or telephone number ID
The facsimile machine can be set to receive a document
automatically
Polling is available both for transmission and reception
Various kinds of reports may be printed (transmission,
activity, etc.)
Operating: from 5°C to 35°C
Storage:from 0°C to +45°C
Transport:from -15°C to +45°C
Operating: from 15% to 85 % (without condensation)
Storage: from 15% to 85 % (without condensation)
Transport: from 5% to 95 % (without condensation)
1-5602E52970
1.3 QUICK REFERENCE GUIDE
1.3.1 Sending a Fax
1. Insert the document into the automatic document
feeder.
2. Press the HOOK key and dial the correspondent's
number on the numeric keypad.
1.3.2 Receiving a Fax
1. The facsimile machine is normally set for automatic
reception: the message AUTOMATIC RX is dis-
played.
2. If you want to receive a fax in manual mode, press
the RX MODE key: the message MANUAL RX will
be displayed.
1.3.3 Using the Facsimile Machine as a Photocopier
1. Insert the document (max 5 sheets) into the automatic document feeder
2. Type on the numeric keypad the number of copies
to make (max. 9 copies)
3. If necessary, set contrast (C), resolution (R) and
enlargement or reduction rate (I)
4. Press the COPY key.
n
Õ
Ó
Ò
Õ
Ð
Ð
Ð
,
5
&
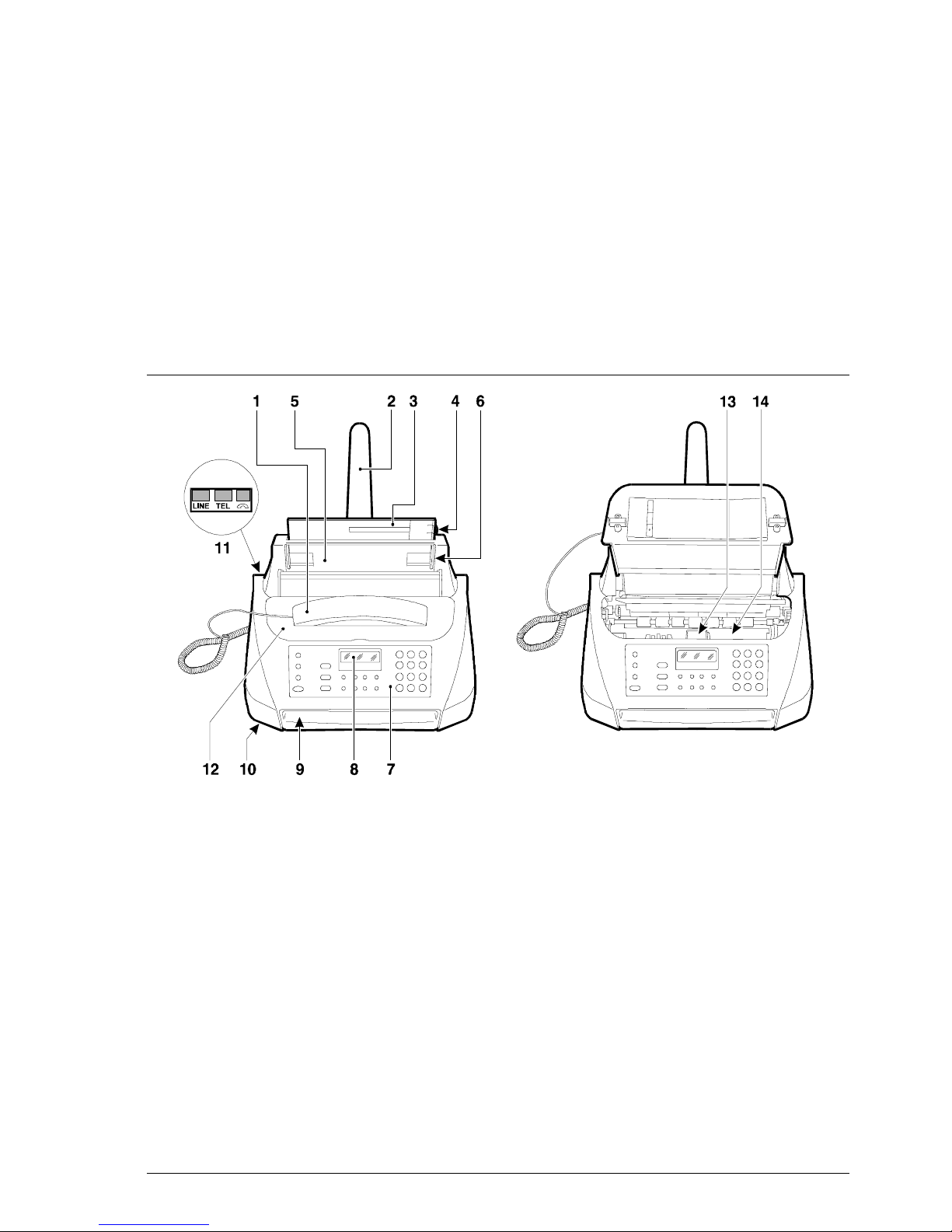
602E52970 2-1
2. GENERAL DESCRIPTION
2.1 EXTERNAL PARTS
The figure shows the main external parts, of the facsimile machine.
1. Handset 8. Display
2. Paper support extension 9. Outlet for original documents and
documents received or copied
3. Automatic sheet feeder (ASF)
10. Loudspeaker
4. Paper format adjustment lever
11. Connection sockets
5. Automatic document feeder (ADF) 12. Printer lid
6. Document guides 13. Print carriage
7. Console 14. Optical reader
Fig. 2-1 External parts of the facsimile machine
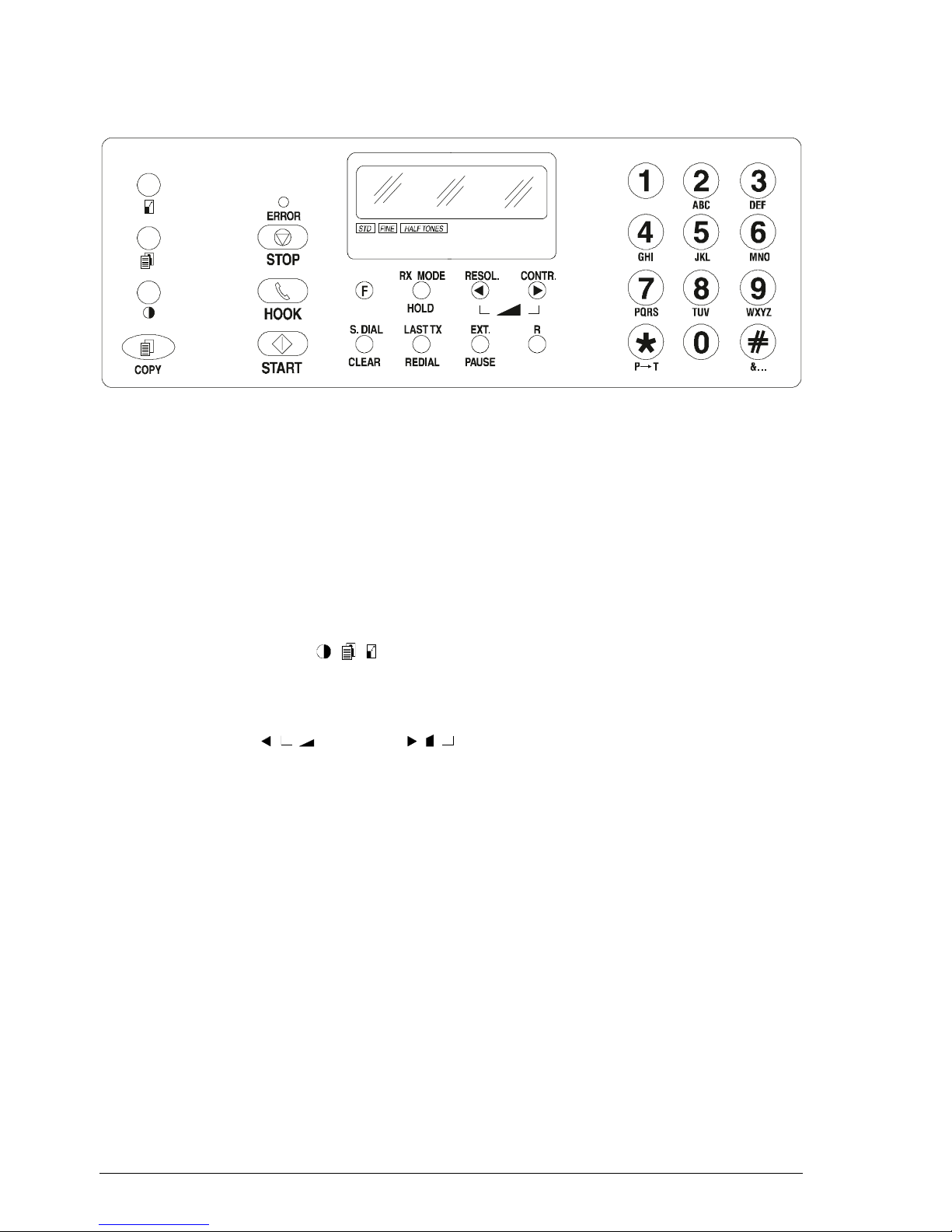
2-2
602E52970
2.1.1 Console
Fig. 2-2 Console layout
The console comprises:
• a display consisting of 2 lines of 16 characters each
• a keypad consisting of:
- 15 function keys (
- - - COPY - STOP - HOOK - START - F - RX/STANDBY
MODE - RESOL. - CONTR. - S. DIAL/CLEAR - LAST TX/REDIAL - EXT./
PAUSE - R) of which 4 are dual function keys (RX/STANDBY MODE - S.DIAL/
CLEAR - LAST TX/REDIAL - EXT./PAUSE) and two are triple function keys
(RESOL. / / - CONTR./ / )
- 12 triple-function keys: for normal dialling (0 - 1 - 2- 3- 4- 5 - 6 - 7 - 8 - 9 - *
- #), for user name setting (ABD - DEF - GHI - JKL - MNO - PQRS - TUV -
WXYZ - I→T - &...), for one-touch dialling (0 - 1 - 2 - 3 - 4 - 5 - 6 - 7 - 8 - 9)
or, in pairs, for speed dialling
- 1 LED for indicating ERROR conditions.
602E52970 2-3
2.1.2 Functions of the Console Keys
Some keys perform different functions according to the current operating mode of the
facsimile machine:
Stand-by mode with document on the ADF
Stand-by mode without document on the ADF
Function mode (activated by pressing the FUNCTION key), irrespective of
the presence of a document on the ADF
Hook mode (activated by pressing the Hook key or lifting the handset).
Key Mode Functions
Used for dialling numbers.
Number keys Select alphanumeric characters for setting the users name.
P→T In pulse dialling mode, changes the dialling mode to tone.
In tone dialling mode, emits a tone on line for special network
services.
«
In tone dialling mode, emits a tone on line for special network
services.
« Scrolls forward through the special characters and sym-
bols for the users name; selects the + character for the users
telephone number; used to dial remote control codes.
# In tone dialling mode, emits a tone on line for special network
services.
&...
Scrolls backwards through the special characters and
symbols available for the mnemonic ID.
F Provides access to operator selection menus and
submenus.
RX MODE Changes the reception mode: automatic, manual, FAX/
TEL, FAX/TAD.
HOLD During a telephone conversation, puts the call on hold.
RESOL. Selects the type of resolution of the document to be trans-
mitted.
Moves the cursor left during entry of the user's name and
number.
Reduces the volume of the speaker.
>>

2-4
602E52970
Key Mode Functions
CONTR. Selects the type of contrast of the document to be transmit-
ted.
Moves the cursor right during entry of the user's name and
number.
Increases the volume of the speaker.
S. DIAL Enables the setting of a two-digit code for speed dialling.
CLEAR Clears wrong settings.
LAST TX Pressed once, displays the result of the last transmission.
REDIAL Pressed twice, redials the last number.
EXT. When the facsimile machine is connected to a private branch
exchange, enables access to the public line.
PAUSE Inserts a pause in dialling the number of the called party.
R Enables to access the special functions made available by the
network operator and commonly known as REGISTER RECALL.
Switches off the ERROR LED.
Stops copying, sending or receiving a document.
STOP
Sets the facsimile machine in standby mode.
HOOK Enables the user to dial the number without lifting the
receiver and to monitor the tones through the speaker.
Starts manual reception (with the handset lifted)
After the number has been dialled, starts sending the
document on the ADF.
START After the handset is lifted, it places the facsimile in manual
reception mode.
Confirms menus, submenus, parameters and values.
Sets the facsimile in manual reception mode.
>>

602E52970 2-5
Key Mode Functions
Selects the enlargement (140%) or the reduction (70%) of
the document to be copied.
Selects the type of resolution of the document to be copied.
Selects the type of contrast of the document to be copied.
COPY Starts copying the document inserted in ADF.
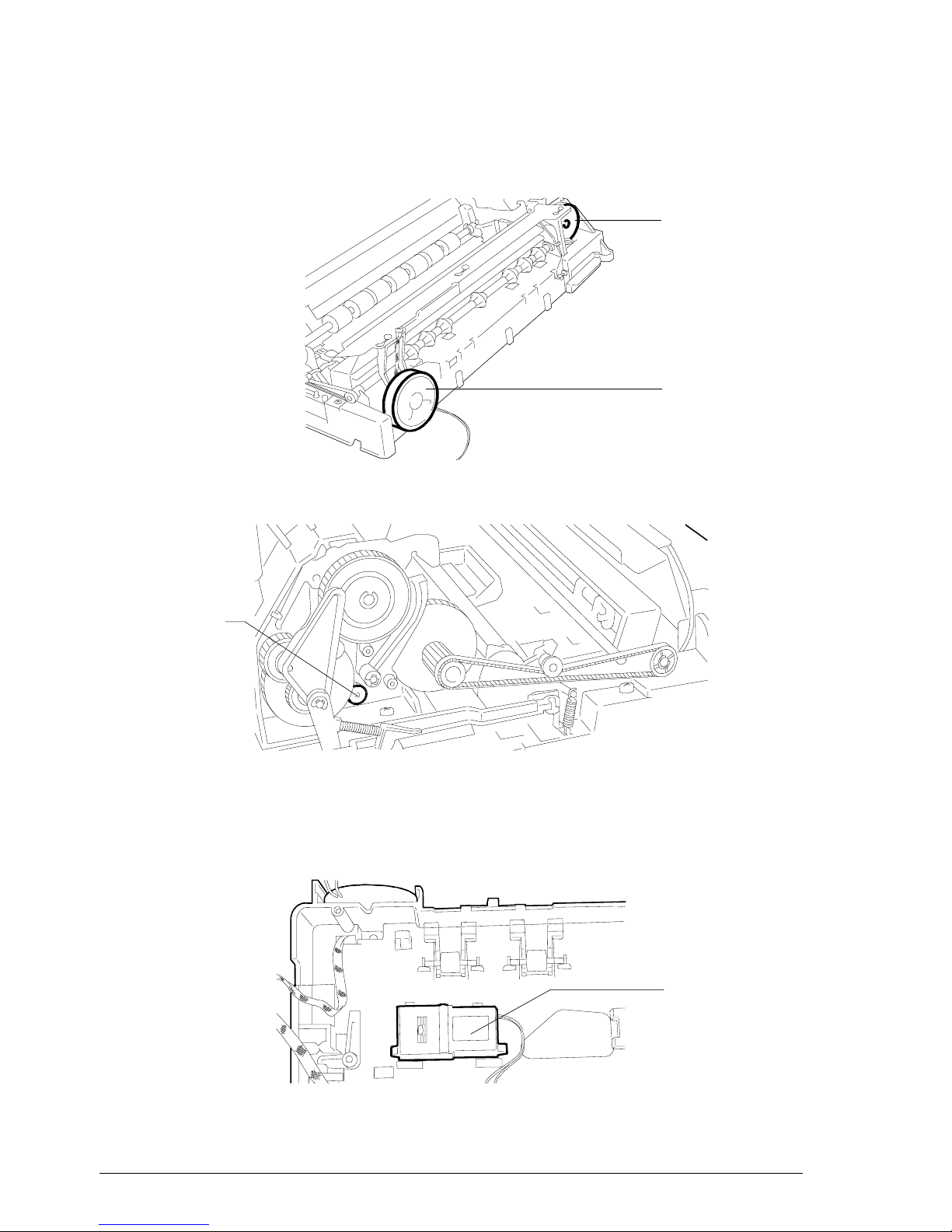
2-6
602E52970
2.2 ELECTROMECHANICAL PARTS
2.2.1 Motors, Electromagnet and Loudspeaker
Behind the front side
Loudspeaker
Carriage motor
Rear left-hand side
Paper and
scanner motor
Fig. 2-3 Locating the motors
Underneath the scanning plane
Fig. 2-4 Locating the Head clearing E.M.
Head clearing
E.M.
602E52970 2-7
2.2.2 Sensors
console
sensor
(under the
console)
receiver
sensor
(under the
console)
Fig. 2-5 Locating the paper and printer sensors
Fig. 2-6 Locating the carriage sensor
paper edge
sensor
Fig. 2-7 Locating the paper sensors
document
sensor (under
the ADF plane)
paper sensor
(under scanning
plane)

2-8
602E52970
2.3 ELECTRONIC PARTS
Figure 2-8 shows the boards assembled on the facsimile machine.
Fig. 2-8 Locating the boards
1. Contact Sensor (CIS)
2. Power supply board
3. Motherboard
4. Network Control Unit board
1
2
3
4
602E52970 2-9
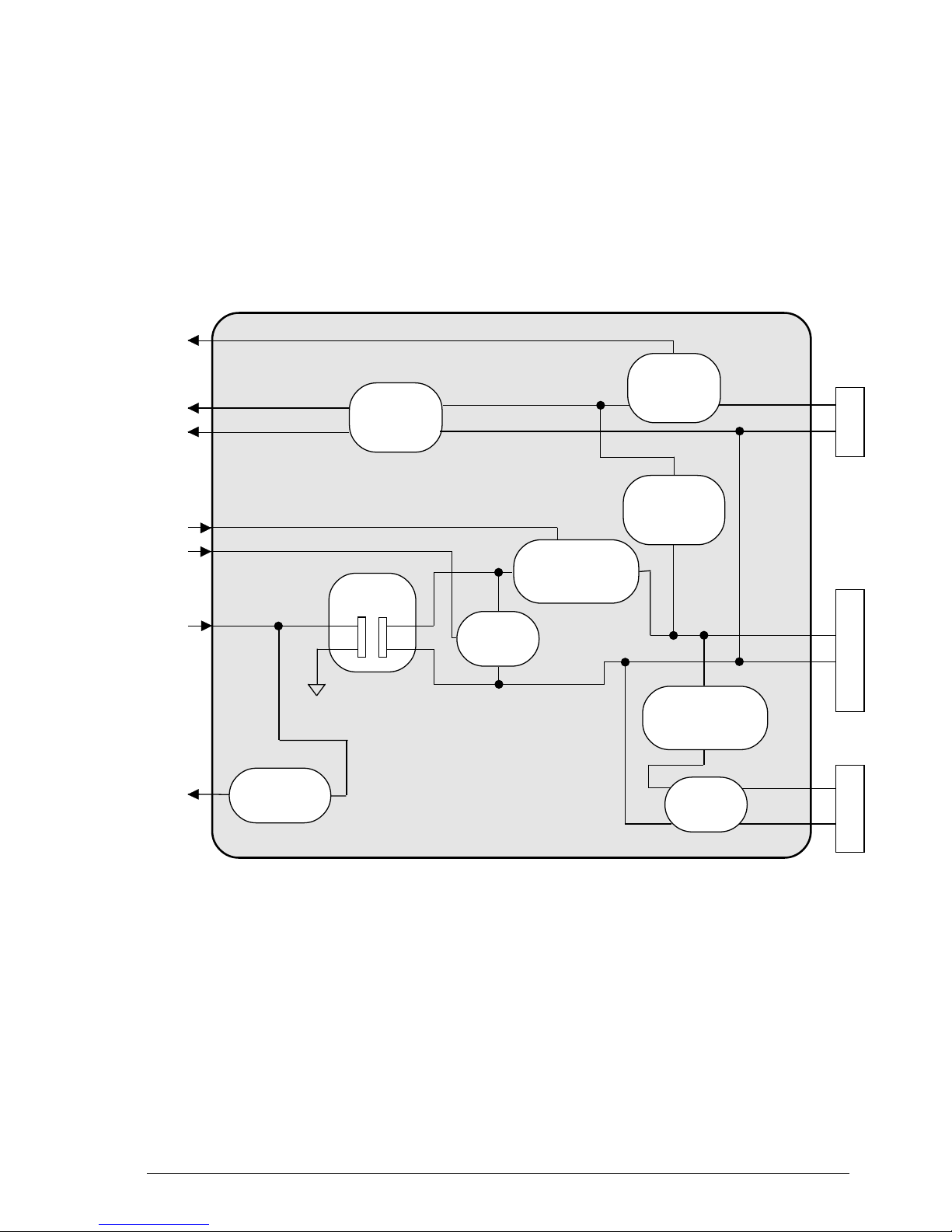
2.3.1 General Block Diagram
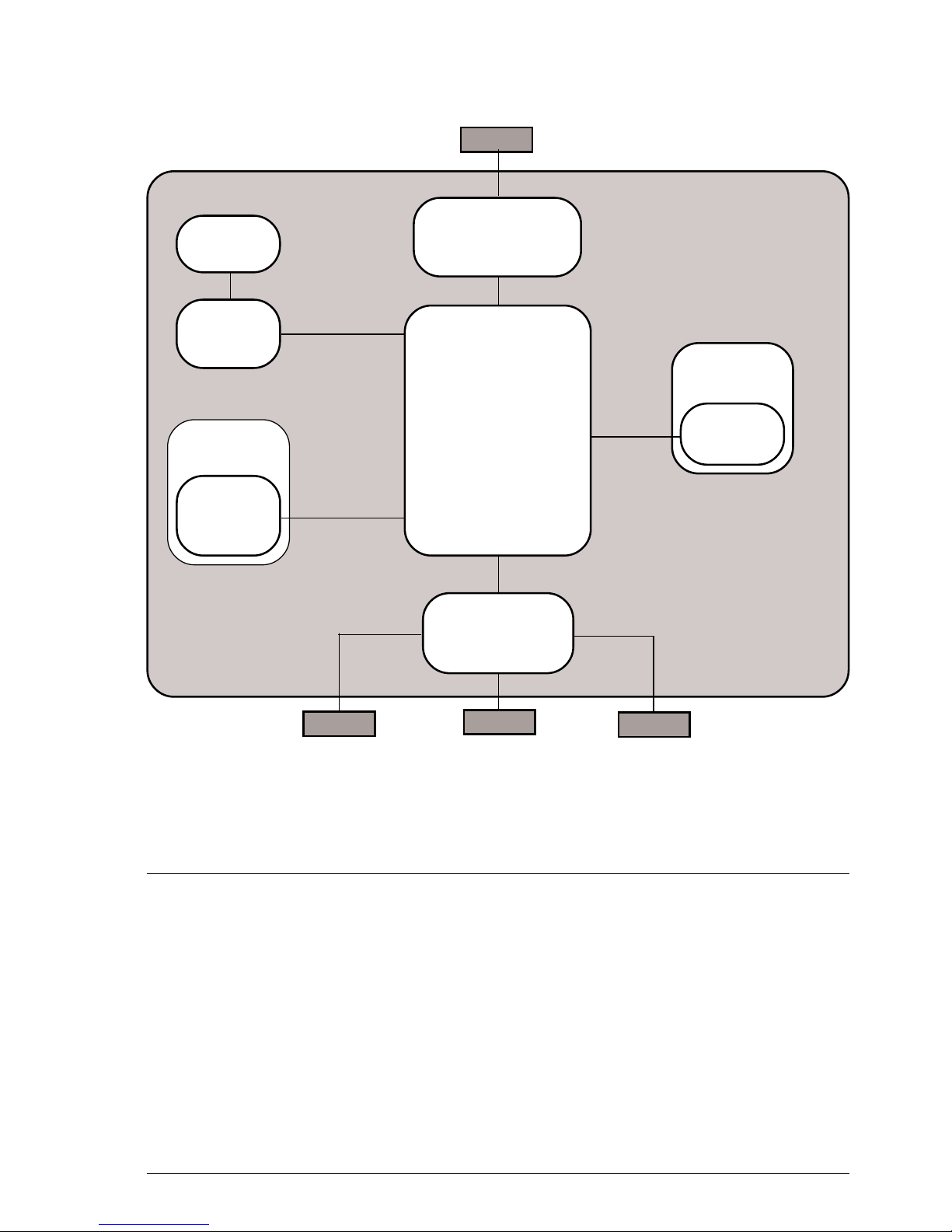
Fig. 2-9 General block diagram
The facsimile machine comprises the following main units:
• Motherboard
• Network Control Unit (NCU) board,
which also includes the integrated
phone circuit
• Console board, with the display
• Power supply board
• Optical unit, consisting of the scan-
ner unit and CIS board
• Printer unit, comprising the carriage
and the carriage drive mechanism.
Console
board
Telephone
network
Display
Power supply
board
Mains voltage
Motherboard
Print
carriage
Optical
unit
Scanner
unit
(CIS)
NCU
board
Print unit
Handset
TAD

2-10
602E52970
2.3.2 Block Diagram of the Motherboard
The motherboard controls the entire machine by means of a central processing unit
(CPU) which uses special circuits to handle four main functional units: the image
processor (for processing the scanned document), the motors and the E.M. (for
activating all the mechanical parts), the print head (for printing both received and copied
documents) and the modem (for controlling the signals to and from the telephone
network).
CPU
Modem
I/O channel
controller
Image
processor
to NCU
board
to console
board
Custom
component
ASIC
Step motor
driver
Step motor
driver
256 kB
EPROM
8 kB
static
memory
512 kB
dynamic
memory
to print
head
to print
head driver
to carriage
motor
to paper
and
scanning
motor
to the head
clearing
E.M.
Fig. 2-10 Block diagram of the motherboard
to contact
sensor
Telephone
network
Handset
602E52970 2-11
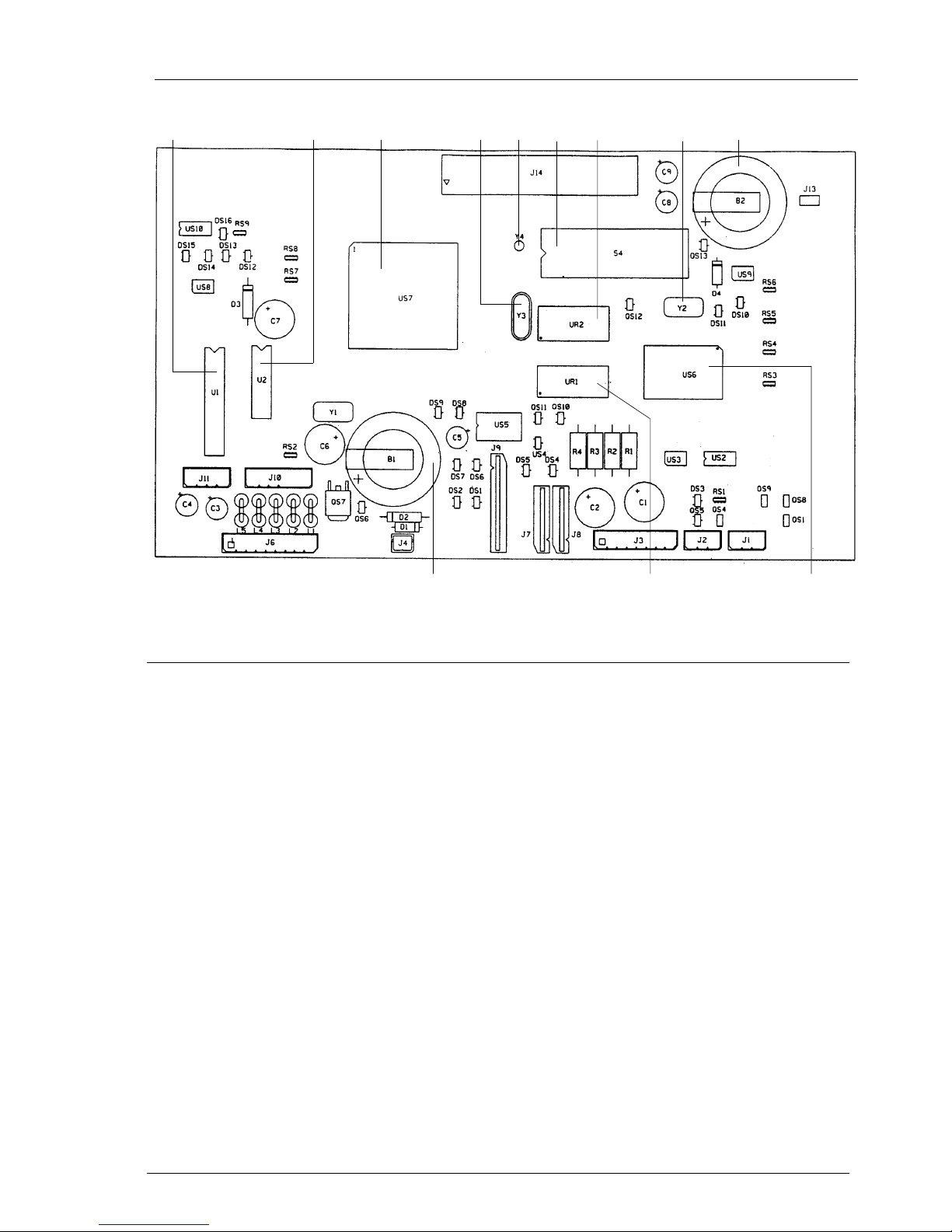
12354 9867
12 11 10
Fig. 2-10a Locating the motherboard components
8 QUARTZ CRYSTAL FOR ASIC
(16 MHz)
9 BACK-UP RECHARGEABLE
BATTERY FOR DYNAMIC RAM
(Li, 3 Volts, 72 hour duration)
10 CUSTOM COMPONENT ASIC
11 DYNAMIC RAM (512 kbytes)
12 SYSTEM BATTERY (Lithium, 3
volts, 5-year duration)
1 CARRIAGE MOTOR DRIVER
2 PAPER AND SCANNING MOTOR
DRIVER
3 CPU (WITH BUILT-IN MODEM AND
IMAGE PROCESSOR)
4 QUARTZ CRYSTAL FOR MODEM
CLOCK (20.736 MHz)
5 QUARTZ CRYSTAL FOR RTC
(32.768 kHz)
6 SYSTEM FIRMWARE EPROM
(256 kbytes)
7 STATIC RAM (8 X 8 kbytes)
2-12
602E52970
The memory block, divided into the following three sections, is an integral part of the
motherboard:
• EPROM (256 Kbytes), this memory contains the system firmware, the default
settings of the software parameters and the messages in the various languages
• STATIC RAM (8 kbytes), this memory contains:
- the current user and service software parameters
- the calibration settings (alignment settings)
- the telephone number list (one-touch dialling numbers and speed code
dialling numbers)
- the power failure report with the memory erasure report if needed.
• DYNAMIC RAM (512 kbytes), this memory contains:
- the compression and decompression buffer
- the scanning buffer
- the print buffer
- the transaction memory (activity reports)
- the user memory (documents to send, documents received in the memory).
The data is retained in the dynamic memory even during a power failure by a backup
battery capable of powering the system for 72 hours. The facsimile machine must be
left powered for 24 hours to recharge this battery.
The data is retained in the static memory by the 5-year duration system battery.
Static
RAM
EPROM
Dynamic
RAM
602E52970 2-13
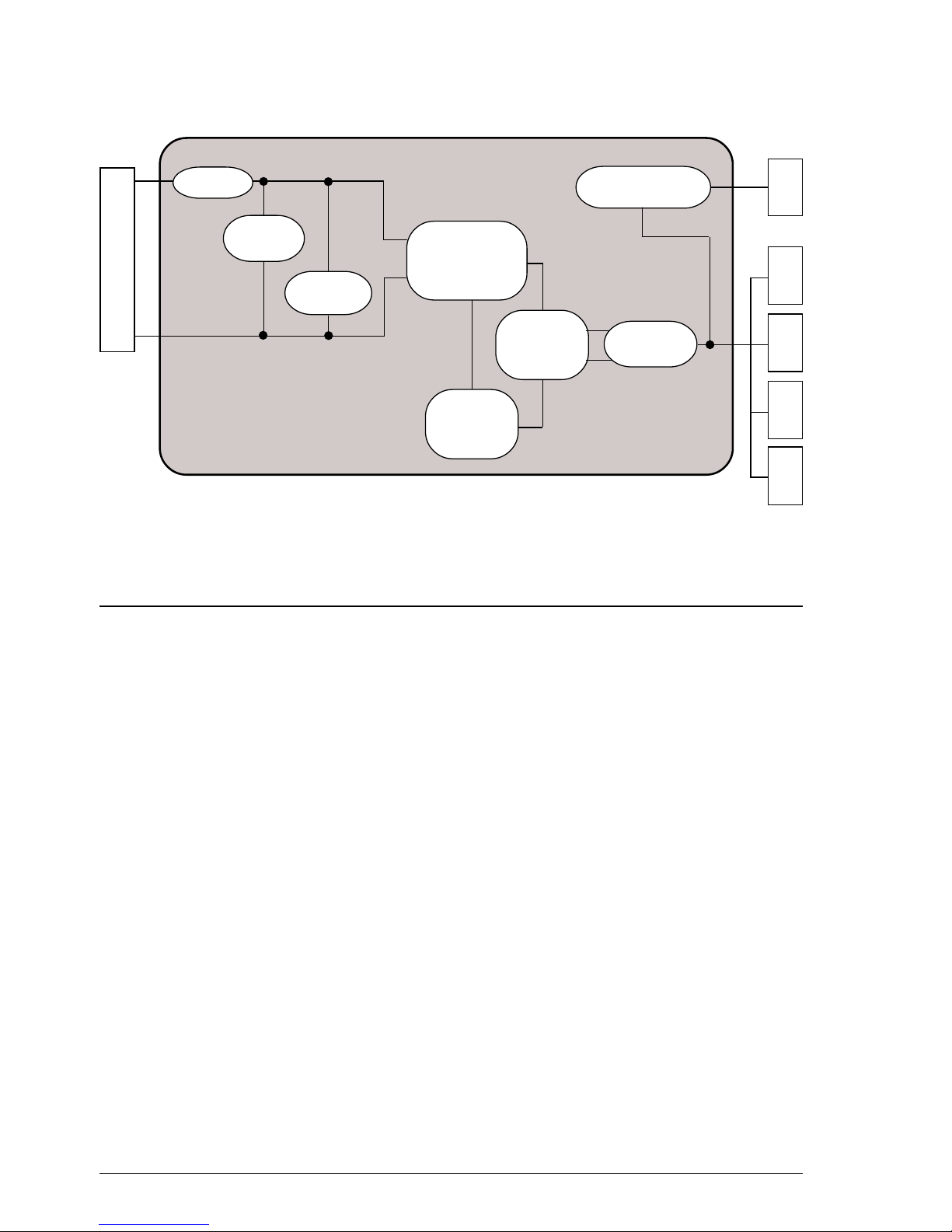
2.3.3 Block Diagram of the Network Control Unit Board
The NCU (Network Control Unit) board acts as the physical interface with the
telephone line. The NCU board is available in several versions, to suit the specific needs
of each country.
The NCU board also contains the integrated phone circuitry.
Fig. 2-11 Block diagram of a generic NCU board
Amplifier
Selector
relay
Line
transf.
Call
detector
Current
detector
TX
RX
Handset
TAD
Selector and
modem-line
connection relay
Motherboard
Telephone line
Telephone-line
connection relay
Receiver
detector
relay
Telephone
circuit
2-14
602E52970
2.3.4 Block Diagram of the Power Supply Board
Fig. 2-12 Block diagram of the power supply board
The power supply board provides a maximum power of 30 Watts and supplies, via
the switching circuit, the following direct voltages:
- +28 VDC (±10%), for the motors, variable according to the load
- +24 VDC (±2%), for CIS and the print head
- +12 VDC (±10%), for NCU and logic circuits
- -12 VDC (+10% -15%), for logic circuits
- +5 VDC (±5%) for CSI sensors and logic circuits.
Fuse
Mains voltage
Voltage reg.
+24 V
2 A
Mains
filter
Primary
rectifier
Switching
transformer
Switching
controller
MOS
Rectif.
diodes
-12 V
+12 V
+5 V
+28 V
Prim./sec.
optical
coupler
602E52970 2-15
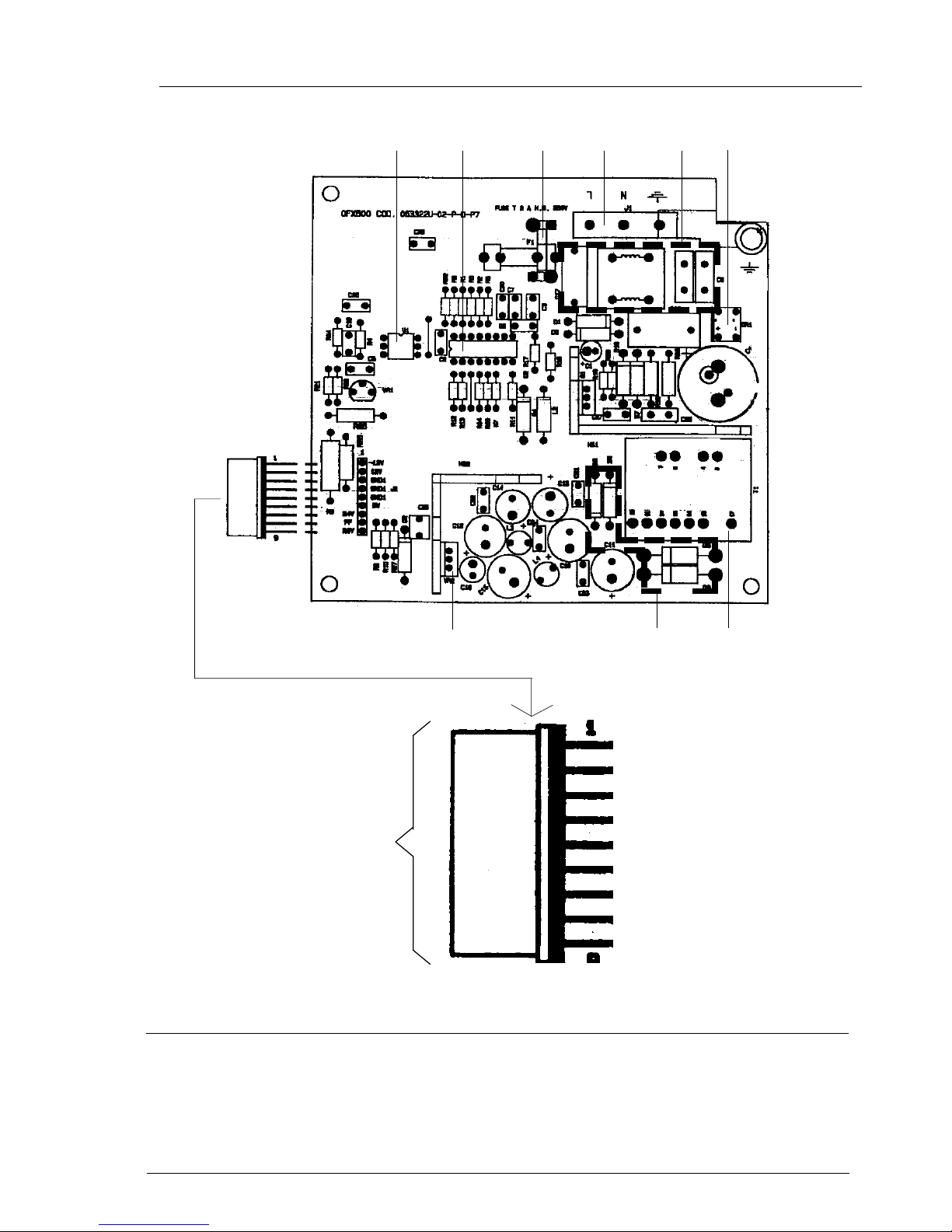
Fig. 2-12a Locating the power supply components
1 Prim/sec optical coupler
2 Switching controller MOS
3 Fuse (2A)
4 Mains connector
5 Mains filter
6 Stabiliser
7 Transformer
8 Diode rectifier
9 +24 V regulator
4321
6
5
7
89
-12 V
+12 V
GND
GND
GND
+5 V
+24 V
PF
+28 V
to motherboard
2-16
602E52970
2.3.5 Printer Unit
The facsimile machine has a bubble ink jet system which uses a special head and
prints on plain paper.
The bubble ink jet print head consists of an interchangeable cartridge, which contains
a sponge soaked with liquid ink, which is ejected from 50 nozzles made of a nickel and
gold component, under the control of the signals that reach an electrical circuit
consisting of 50 resistors (Fig. 2-13).
cartridge
nozzles
electrical
circuit
sponge
Each nozzle generates a drop of ink
when the corresponding resistor is powered (+24 Volt) for a few microseconds.
The resistor is heated and the ink that is
in direct contact with it evaporates, expanding like a bubble and pressing the rest
of the ink against the nozzle.
nozzle
+24V
+24V
ink
Fig. 2-13 Composition of the print head
resistor
bubble
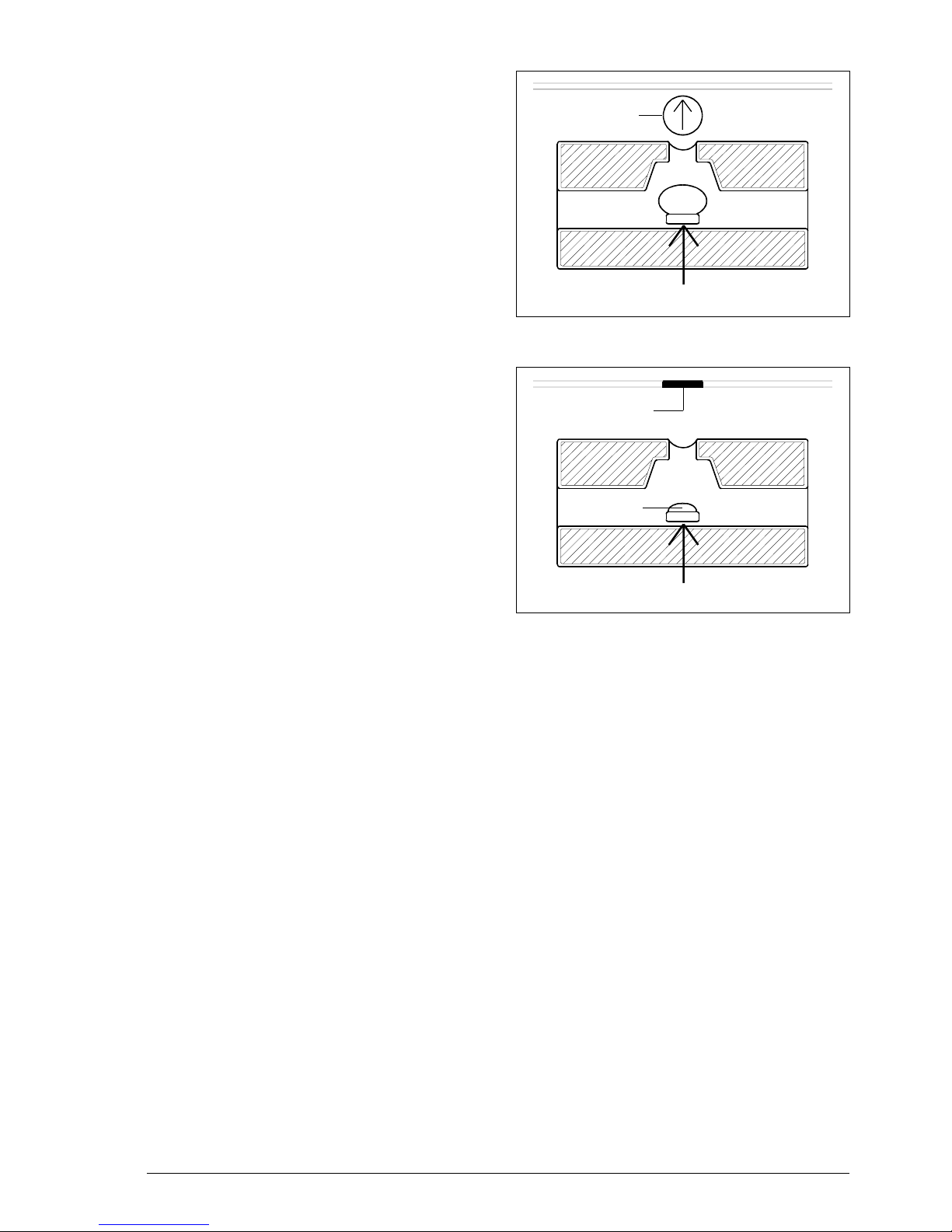
602E52970 2-17
As a result, a drop of ink is ejected from
the nozzle at a speed of 15 metres a
second until it strikes the paper on which it
makes a dot.
When the resistor is powered off, the
bubble collapses quickly, drawing from the
sponge a quantity of ink equal to the amount
ejected. 800 microseconds after the ink
has been ejected, the nozzle is ready to
eject another drop.
+24V
15 m/s
0V
drop
dot
bubble
2-18
602E52970
2.3.6 Paper Feeding
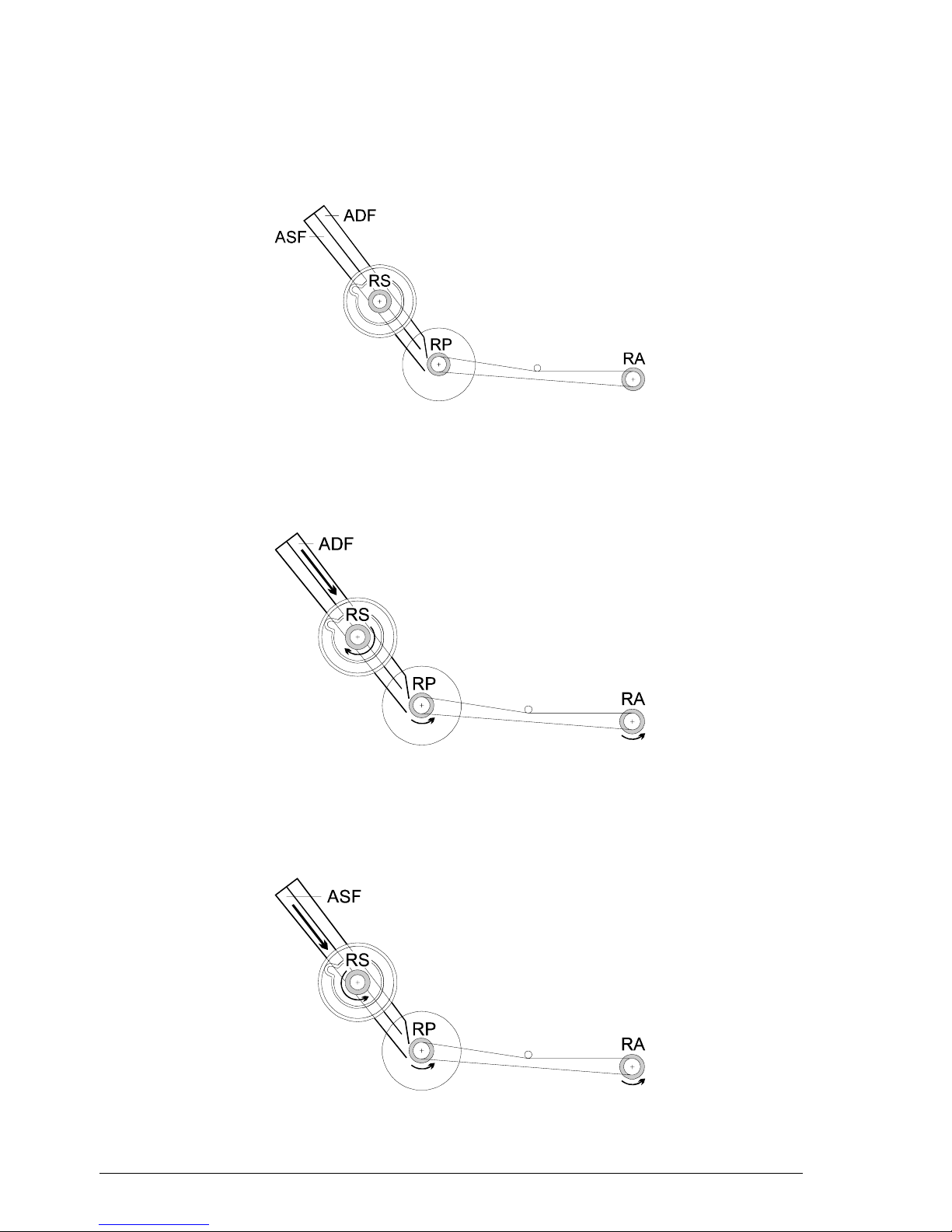
The fax machine feeds both the originals (placed in the ADF) and the documents
received or copied (in the ASF) through a single series of rollers RS which conveys them
towards a single outlet, comprising rear RP and front RA rollers (fig. 2-14):
Fig. 2-14 Paper path
A single motor, able to rotate in both directions, can feed the originals (clockwise
rotation of the RS rollers) (fig. 2-15):
Fig. 2-15 Original document feeding
... or received or copied documents (counter-clockwise rotation of the RS rollers)
(fig. 2-16):
Fig. 2-16 Received or copied document feeding

602E52970 2-19
The RS roller shaft comprises (fig. 2-17):
Fig. 2-17 RS roller shaft
• two series of symmetrical cams C1 and C2, integral with the shaft, which:
- through the upper profile PS move the ADF (or ASF) away from the RS rollers
- through the lower profile PI at the same time allow the ASF (or ADF) to come
in contact with the RS rollers
• two oscillating rockers O1 and O2, moved in the shaft rotation, which maintain the
ADF (or ASF) in the position detached from the RS rollers, respectively through
steps A or P).
Rotation to the RS shaft is imparted by motor M through a series of gear wheels,
rocker B1 and feeler pin T2 which supports rocker B2 (Fig. 2-18):
Fig. 2-18 Paper feed mechanisms

2-20
602E52970
A paper feeding cycle is started by the carriage against the left side. In this position,
the motion shown in fig. 2-19 is started, which frees cam CRS (integral to the RS roller
shaft) from feeler pin T1 of the rocker B1, and simultaneously accomplishes the
connection between motor M and the cam (in detail) thus allowing the shaft to rotate:
&56
%
0
&56
%
0
Fig. 2-19 Paper feeding cycle start
Paper feeding conditions in the case of the ADF and in the case of the ASF are
described separately below.
Original document feeding (ADF)
Motor M rotates counter-clockwise so that the CRS cam (and thus the RS roller
shaft) rotates clockwise, allowing the original documents contained in the ADF to be fed
(Fig. 2-20):
Fig. 2-20 Original document feeding

602E52970 2-21
During the first 360° of rotation of the CRS cam, the original is aligned against rear
rollers RP which are still stationary because, thanks to feeler pin T2, neither one of the
wheels R1 and R2 of the rocker B2 is engaged with the remaining mechanisms (Fig.
2-21):
Fig. 2-21 Original document alignment
Subsequently, the feeler T2 allows rocker B2, which is set in motion by friction, to
transmit the motion to the rear rollers RP thanks to its wheel R2 (Fig. 2-22):
Fig. 2-22 Original document ejection

2-22
602E52970
Received or copied document feeding (ASF)
Motor M rotates clockwise, so that cam CRS (and thus the RS roller shaft) rotates
counter-clockwise, allowing the paper in the ASF to be fed (Fig. 2-23):
Fig. 2-23 Received or copied document feeding
In this case as well, during the first 360° of rotation of the CRS cam, the paper is
aligned against the rear rollers RP. Subsequently, feeler pin T2 allows rocker B2 to
transmit motion to rear rollers RP thanks to its wheel R1. Note that rotation of the RP
rollers is always counter-clockwise (Fig. 2-24):
Fig. 2-24 Received or copied document ejection
n

602E52970 3-1
3. INSTALLATION AND INITIALIZATION
PROCEDURES
Installation of the facsimile machine consists of three separate phases:
1. PRELIMINARY OPERATIONS, or fitting together the parts supplied in
the packaging and subsequent connection of the facsimile machine and
telephone, if present, to the telephone network
2. INSTALLATION, or setting the parameters indispensable for the facsimile machine's operation.
3. SETUP, or setting the customization parameters.
3.1 PRELIMINARY OPERATIONS
3.1.1 Unpacking the Facsimile Machine
Having removed the facsimile machine and the other parts from the packaging,
check that the following elements are present:
• the facsimile machine (complete with power cord)
• a packet containing the print head
• the telephone cable (with two international RJ11 connectors)
• the handset (complete with connection cord)
• the telephone plug
• the paper support extension
• three clear films with back sheet to use as holders for documents in non-standard
formats
• the "User Guide", complete with the "Quick Reference Guide".

3-2
602E52970
3.1.2 Connecting the Power Cord
Plug the power cord into the wall socket. The fax machine performs a brief self-test
and then shows the following message on the display:
CAUTION
: If the message does not appear in your language, carry out the
country setup procedure described in section 3.2.2 and continue
with this procedure starting from the next step.
3.1.3 Inserting the Paper Support Extension
Insert the paper support extension in its slot pushing downward until you hear the
latching click.
3.1.4 Paper Supply
When supplying the paper to print received and copied documents, always pay
attention to the following two factors, which must always coincide to guarantee that
the print is properly contained within the width of the sheet in use:
AUTOMATIC RX
CHECK PRINT HEAD

602E52970 3-3
- paper format, i.e. width of the sheet in use
- print format, i.e. the value of the FORMAT parameter in the PRINT PARAMETERS menu (see sect. 3.2.1).
1) Insert the sheets without going beyond the maximum quantity indicator notch,
letting them fall into the tray without bending or forcing them.
2) Push the sheets against the left side of the tray using the adjustment lever.
CAUTION:When you need to add paper in the tray, insert the sheets under those
already present.
3) Set the FORMAT parameter of the PRINT PARAMETERS menu to the value
corresponding to the format of the paper (see sect. 3.2.1)
3.1.5 Installing the Print Head
1) Flip open the printer lid

3-4
602E52970
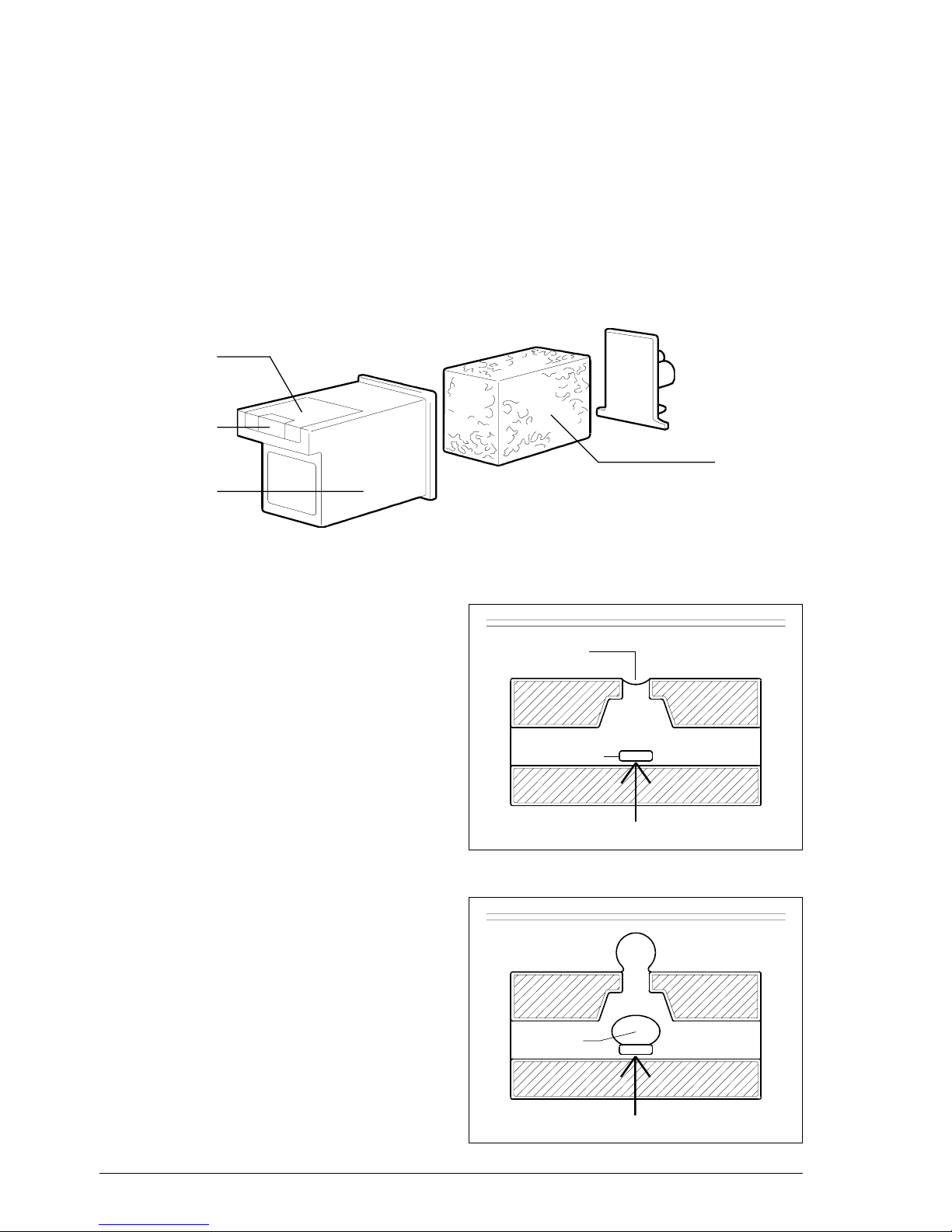
2) Open the print head packet and remove the sealed box containing the print head.
3) Open the box and remove the print head, holding it by the grip, then remove the
label covering the nozzles.
WARNING: do not touch the electrical contacts or the print head
nozzles
In addition, if the print head has an interchangeable cartridge, do
not separate the cartridge from the print head
4) Tilt the printer cover, then insert the print head in position with the electrical
contacts facing the front of the machine.

602E52970 3-5
5) Taking care not to obstruct the hole on the top, insert your index finger in the
recess on the print head and pull it until you hear it clearly click into
position.
6) Having inserted the print head, close the printer cover
WARNING: if a disposable print head has been inserted, the following
message generally appears:
Set the value 1.
7) If the CHECK PRINT HEAD appears again, remove the print head pulling the
small levers forward:
NEW PRINT HEAD?
1=YES 0=NO

3-6
602E52970
and visually check for the presence of a particle on the print nib: if so, remove the
particle with care, without touching the electrical contacts. If not, the facsimile
machine automatically loads a sheet of paper and starts the nozzle cleaning
and checking procedure, which ends by:
• printing out the following print chart on the automatically loaded sheet
(*)
which contains:
− a numbered scale, for checking the flow of ink and the electrical
circuits controlling the print head nozzles
− a section of graphics and text, for evaluating print quality
numbered scale
black areas

602E52970 3-7
(*) only if bit 2 of SW09 is set to 1.
• the following message appears
8) Analyse the print chart as follows:
• Check that there are no gaps in the numbered scale and that there are no
horizontal white lines in the black areas: under these conditions, which
indicate that the print head has been inserted correctly and is in perfect
working order, type 1: the facsimile machine returns to stand-by and is
ready for use
• If there are gaps or white lines, type 0 to repeat the nozzle cleaning
procedure: if the new print chart is still unsatisfactory, repeat the procedure
again
• If the printing quality is still not up to the required standard after the proce-
dure has been performed three times, proceed as follows until a satisfactory
print chart is obtained:
- Make a copy of a document with the desired type of graphics and text
and assess its quality.
- Change the type of paper (the paper you are using may be too porous)
and repeat the procedure.
- Remove and reinsert the print head.
- Remove the print head and check that there is no foreign body on the
printing nib; if there is, remove it with care, taking care not to touch the
electrical contacts; slide the print carriage to the right, then clean the
print head cleaning pad using a cotton swab soaked in water, taking
care not to leave any fluff;
CHECK PRINTOUT
1=EXIT 0=REPEAT

3-8
602E52970
Reinsert the print head.
- Remove the print head and clean the contacts with a piece of felt, pressing firmly;
Clean the contacts on the print carriage with a soft, dry cloth;
Reinsert the print head.
- Replace the print head
- Replace the print carriage (see section 7.2.15).
3.1.6 Connecting to the Telephone Line
CAUTION: check that the power cable is plugged into the power outlet,
before connecting the facsimile machine to the telephone line.
To connect the facsimile machine to the telephone line, plug one end of the
telephone cable to the line socket (LINE) on the facsimile machine and the other end
into a wall socket (a) or using the adapter if necessary (b).

602E52970 3-9
CAUTION: If the telephone exchange the fax machine is inserted on is of the type
with multiple sockets in series, then the telephone cord must be plugged
into the primary socket.
3.1.7 Connecting the Handset
Insert the handset cord into the fax machine socket bearing the corresponding
symbol, then place the handset in its cradle.
Handset socket
b)
a)
Line Socket

3-10
602E52970
The procedures used for installing and setting up the machine may be divided into
indispensable procedures (marked by the background ) and procedures that
depend on the characteristics of the telephone exchange or the user's requirements (marked by the background ).
3.2.1 Organization of the Installation and Setup Parameters
The installation and setup parameters are organized into menus and submenus,
shown on the display as follows:
top line
DISPLAY
bottom line
- the top line is used for displaying:
· menu and submenu items, which represent the operating selections available
on the facsimile machine
· parameters, to which a value is to be assigned to make an operating selection
- the bottom line is used for displaying the keys that handle the items indicated
on the top line, that is:
F for selecting menu and submenu items, which can be scrolled
cyclically forwards only, i.e. from the first to the last and then
skipping straight back to the first again
(START) for confirming menu and submenu items, parameters and
values:
· by confirming a menu, you access the corresponding submenu
· by confirming a submenu, you access the corresponding
parameters
· by confirming a parameter or its value, you access the next
parameter
3.2 INSTALLING AND SETTING UP THE MACHINE

602E52970 3-11
The figure that follows provides a detailed illustration of the organization of the
installation and setup parameters.
A schematic diagram of parameter management is provided below:
for selecting the values of a parameter, scrolling forwards and
backwards through those available on the machine, or for moving
along the characters that make up the parameter value. In the latter
case, the value must then be set using the numeric keypad
(STOP) for exiting from installation or setup mode.
)F
)F
)F
)F
VALUES
SUBMENU
MENU
OPERATING SELECTION PARAMETER SETTING
SETTING OF
VALUE
PARAMETERS
PARAMETER
SELECTION
EXIT FROM
MODE
F
)
)
)
)

3-12
602E52970
TX FROM MEMORY
PRINT OUT REPORT
FAX SET-UP
DELAYED TX
POLLING RX
POLLING TX
INSTALLATION
MENU
HEAD MAINTENANCE
CLEANING
SUBMENU
INSTALLATION
TEL. LINE SET-UP
LANGUAGE
STATION NAME
PHONE NUMBER
DIAGNOSTICS
PRINT INSTALL.
SERVICE PARAM.
STATION NAME
TYPE YOUR NAME
PARAMETERS
TEL. LINE SET-UP
PUBL. LINE (PSTN) (*)
PRIV. LINE (PBX) (*)
PBX DIAL
PSTN DIAL.
EXT. LINE
REMOTE START
RING COUNT (*)
FAX/TEL TIMER
SILENCE LAPSE (*)
LANGUAGE
ITALIAN
ENGLISH
etc.
PHONE NUMBER (*)
TYPE YOUR NUMBER
DIAGNOSTICS
REMOTE DIAG.
LINE MONITOR
SERVICE PARAM.
TYPE PASSWORD
COUNTRY SET-UP
SERVICE SWITCHES
SYSTEM TEST
PRINT SERV. SW
PRINT PROT. DUMP
PRINT COUNTERS
ONE TOUCH DIAL
TYPE ONE TOUCH
NUMBER
SPEED
OVERSEAS
NAME
EDIT ANOTHER
CODED SPEED DIAL
TYPE SPEED NO.
NUMBER
SPEED
OVERSEAS
NAME
EDIT ANOTHER
PRINTOUT SET -UP
PRINT SETTINGS
PRINT: ONE TOUCH
PRINT: SPEED DIAL
PRINT: EXIT
VARIOUS SETTINGS
ECM
FAILED TX REPORT
BROADC. REP.
DELAY LIST
TX SPEED
HEADER
RETRANS.DOC.
CONF. TEL. NUM.
COPY/TX RES.
BUZZER VOL.
PARAMETERS
SUBMENU
FAX SET-UP
VARIOUS SETTINGS
PRINTER PARAMET.
DATE AND TIME
ONE TOUCH DIAL
CODED SPEED DIAL
PRINT OUT SET-UP
HEAD MAINTENANCE
PRINTER PARAMET.
SIZE
REDUCTION
SURPLUS
DATE AND TIME
FORMAT: DD/MM/YY
FORMAT: 24H
(*) These parameters
are not displayed in
some national versions.

602E52970 3-13
3.2.2 Setting the Country Parameters
This procedure enables you to adapt some specific parameters automatically to the
values preset for a particular country.
Setting
a) The facsimile machine is in stand-by mode
b) Press F to access the main menu
c) Select the SERVICE SWITCHES submenu of the IN-
STALLATION menu.
d) Press
e) Enter the number 5 0 0 and press to enter "service"
mode
f) Press
to confirm the COUNTRY SETUP item
g) Select the desired country (for example, U.K.), and then
press
: the values for the selected country are automatically loaded, then the facsimile machine returns to standby mode.
WARNING: After setting the country parameters it
is possible, whenever necessary, to
reload the default values for the current country, by means of the following
simplified procedure;
- press in rapid sequence
# #
AUTOMATIC RX
09-05-95 14:58
Display
FAX SET-UP
(F)/ /
SERVICE SWITCHES
(F)/ /
TYPE PASSWORD
z
COUNTRY SETUP
/ /¬/®
U.K.
/ /¬/®
AUTOMATIC RX
09-05-95 14:58
AMERICA
/ /¬/®
COUNTRY SETUP
/ /¬/®

3-14
602E52970
Setting
a) The facsimile machine is in stand-by mode
b) Access the main menu and select the STATION NAME
item on the INSTALLATION menu
c) Press
d) Enter the user's mnemonic ID:
- you can use a maximum of 16 alphanumeric charac-
ters
- select one character at a time using the numeric keys,
as shown below:
key 0 characters: 0
key 2, characters: 2ABC
key 3, characters: 3DEF
key 4, characters: 4GHI
key 5, characters: 5JKL
key 6, characters: 6MNO
key 7, characters: 7PRS
key 8, characters: 8TUV
key 9, characters: 9WXY
key 0, characters: 0QZ
key *, characters: symbols (selected "forwards")
key #, characters: symbols (selected "backwards")
- each key selects the characters cyclically, starting
from the numeric character and displaying each of the
other characters when pressed
- confirm the character selected by pressing the
key:
the cursor will move one place to the right
- to correct an error, move the cursor to the character to
be changed using the and keys, and select the
desired character
- to delete the entire entry, press CLEAR.
>>
TYPE YOUR NAME
JOHN
Example
Display
STATION NAME
(F)/ /
TYPE YOUR NAME
z
3.2.3 Storing the User's Number and Name
AUTOMATIC RX
09-05-95 14:58

602E52970 3-15
Display
Setting
- having made the entry, press
to access the PHONE
NUMBER item
e) Press
f) Enter your number:
- you can enter a maximum of 16 characters using the
numeric keys (0 :
9), the * key (to enter the + character)
and the > key (to enter a space)
- to correct or delete, proceed as for the mnemonic ID
- having made the entry, press
g) Press to return to stand-by mode.
TYPE YOUR NUMBER
+39 125 524598
Example
AUTOMATIC RX
09-05-95 14:58
DIAGNOSTICS
(F)/ /
PHONE NUMBER
(F)/ /
TYPE YOUR NUMBER
z
3.2.4 Setting Up the Telephone Line
According to the type of network to which the facsimile machine is connected
(PUBLIC NETWORK or PRIVATE BRANCH EXCHANGE), the following specific
parameters must be set:
- type of dialling (established by the Telephone Service Manager):
· tone (or multifrequency) (PBX/PSTN DIAL: TONE)
· pulse (PBX/PSTN DIAL: PULSE)
- type of access from private line to public line:
· numeric prefix (EXT. LINE: PREFIX)
· earth pulse (EXT. LINE: EARTH)
· flash pulse (EXT. LINE: FLASH).

3-16
602E52970
In addition to these indispensable parameters, the following parameters may also be
set:
- enabling of extension telephone for activating the facsimile machine ( REMOTE
START), by means of a one-digit code (0-9)
- number of rings after which the facsimile machine prepares for automatic
reception (RING COUNT: 01 / 02 / 04 / 08)
- time (in seconds) after which the facsimile machine with the fax/phone feature
enabled switches to fax mode (FAX/TEL TIMER: 15 / 20 / 30 / 40)
- time (in seconds) after which the facsimile machine connected to an external
telephone answering machine switches to fax mode, when there is no incoming
message (SILENCE LAPSE: 3 / 4 / 6 / 8 / 10 / NO).
Display
Setting
a) The facsimile machine is in stand-by mode
b) Access the main menu and select the TEL.LINE SETUP
submenu of the INSTALLATION menu.
c) Press
d) Set the parameters to the desired values, following the
explanatory flow chart shown below:
AUTOMATIC RX
09-05-95 14:58
TEL.LINE SETUP
(F)/ /
PUBL.LINE (PSTN)
/ /¬/®
TYPE PREFIX
PRIV. LINE (PBX) PUBL. LINE (PSTN)
PBX DIAL:PULSE PBX DIAL:TONE
EXT.LINE:PREFIX EXT.LINE EARTH EXT.LINE: FLASH
PSTN DIAL:PULSE PSTN DIAL:TONE
REMOTE START:ON REMOTE START:OFF
TYPE CODE
RING COUNT: 01 RING COUNT 02 RING COUNTY:04 RING COUNT:08
FAX/TEL/FAX: 15 FAX/TEL TIMER: 20 FAX/TEL TIMER: 30 FAX/TEL TIMER: 40
SILENCE LAPSE: 4 SILENCE LAPSE: 6 SILENCE LAPSE 8 SILENCE LAPSE: 10
TEL.LINE SET UP
E LAPSE: 3 SILENCE LAP

602E52970 3-17
3.2.5 Completing Installation
Installation may be completed by setting the FAX SET-UP to suit the user's needs.
See the User Manual for a description of the procedure to be followed.
Various parameters
• ECM (error correction mode): allows to enable (YES) or disable (NO) the function
for correcting errors caused by line interference; this function is effective if it is
enabled on both connected fax machines.
• TX FAILURE REPORT: allows to enable (TX REPORT: ALWAYS) or disable (TX
REPORT: NO) the automatic transmission report print in case of failed
transmission.
• DELAYED LIST: allows to enable (YES) or disable (NO) the automatic print of
the delayed transmission parameters after they have been set.
• SPEED: allows to define transmission speed (9600 bps / 4800 bps).
• HEADER: allows the sender to choose how to send the line with his/her
identification data:
- INT, as the internal part of the document to be transmitted (in which case, the
header is overlaid onto the contents of the document)
- EXT, as the external part of the document to be transmitted (in which case,
the header is transmitted before the document)
• RESOLUTION: allows to define the current degree of transmission resolution
(STD / FINE). The resolution can be changed momentarily at any instant
afterwards, using the RESOL. key.
• VOLUME: it allows to change the volume of the sound indications (LOW /
HIGH).
Print Parameters
• FORMAT: allows to define the format of the sheets to be used for reception and
copying (A4 / LETTER / LEGAL).
• REDUCTION: allows to reduce automatically the size of the printed docu-
ment (always received in A4 format) into the following percentages: 94% / 80%
/ 76% / 70%, or to leave it unchanged (NO).

3-18
602E52970
• EXCESS: allows to define how to print a received document, whose length
exceeds that of the paper in use on the fax machine.
- YES, on multiple consecutive sheets
- NO, losing the part of document that exceeds the length of the paper in use
- AUTO, if the document exceeds the format of the paper in use by a quantity
exceeding that set through the software parameter SW03, bit 7 (8 mm / 12
mm), then it is printed on multiple consecutive sheets; otherwise, the
excess part is lost.
• COPY: allows to define print quality when copying (HIGH QUAL. / NORMAL).
Date and time
• FORMAT: allows to define the order in which the three components of the date
are displayed (MM/GG/AA - AA/MM/GG - GG/MM/AA).
• TIME FORMAT: allows to define how the time is to be displayed:
- 24 H; the time is expressed over 24 hours (e.g. 17:35)
- 12 H, the time is expressed over 12 hours differentiating ante meridian hours
(preceded by the letter a; for instance, a 09:47) from the post-meridian hours;
for instance, p 11:05).

602E52970 3-19
3.2.6 Resetting the Fax Machine
Having installed the machine, if it does not work properly in reception and transmission, reset the parameters to restore the default values and repeat the installation
procedure from the start.
Setting
a) The facsimile machine is in stand-by mode
b) Access the main menu and select the SERVICE
SWITCHES submenu of the INSTALLATION menu.
c) Press
d) Enter the number 5 0 0 and press START to enter
"service" mode
e) Select the SYSTEM TEST item and press
f) Select LOAD DEFAULT and press twice: the default
values for U.K./SOUTH AFRICA are loaded automatically in place of those set previously
g) Press
to return to stand-by mode.
h) Perform fax machine nationalisation and reset installa-
tion and configuration parameters.
Display
TYPE PASSWORD
z
AUTOMATIC RX
09-05-95 14:58
SERVICE SWITCHES
(F)/ /
COUNTRY SETUP
/ /¬/®
SYSTEM TEST
/ /¬/®
LOAD DEFAULT
/ /¬/®
AUTOMATIC RX
09-05-95 14:58
n
WARNING: having installed the machine successfully, never repeat the
reset procedure or you will have to reset all personal data set by
the user.

602E52970 4-1
4. SERVICE SWITCHES
The term service switches is intended to mean parameters that cannot be
accessed by the user and that can only be accessed by service technicians with
the facsimile machine in "service" mode (see section 3.2.2).
These parameters are given default values which depend on the country specifications made by the telephone network manager. As a result, the technician should only
change these values in order to correct the functioning of the machine or to adapt it to
particular local features.
Before changing any of the service switch settings, it is advisable to print them, as
described below:
Setting
a) The facsimile machine is in standby mode
b) Access the main menu and select the SERVICE
SWITCHES submenu of the INSTALLATION menu
c) Press
d) Enter the number 5 0 0 and press to enter "service
mode"
e) Select the PRINT SERV. SW option
f) Press the key: the current default values will be
printed (see fig. 4-1)
g) Press
to return to standby mode.
Display
AUTOMATIC RX
09-05-95 14:58
SERVICE SWITCHES
(F)/ /
TYPE PASSWORD
z
COUNTRY SETUP
/ /¬/®
PRINT SERV. SW
/ /¬/®
PRINTING...
STOP
AUTOMATIC RX
09-05-95 14:58

4-2
602E52970
Fig. 4-1 Example of a printout of the service switch settings
Two types of service switches are available in the SERVICE SWITCHES menu:
- SW01 - SW11: these switches consist of 8 bits and can
be programmed either individually or in group
bit no. 76543210
- SWA - SWR: these switches consist of a value ranging
from 1 to 3 digits
Warning: 1) Whenever no value is printed in correspondence with a service
switch SWA-SWR, this means that the value is 0 (zero).
2) Some of the service switches can be set by the user; in these cases,
the user setting takes priority over the service setting. The
parameters concerned are:
User parameter Software parameter
RING COUNT SWB
FAX/TEL TIMER SWM
SILENCE LAPSE SWO
SERVICE SWITCHES
SW01 01010101
SERVICE SWITCHES
SWR 120

602E52970 4-3
4.1 SERVICE SWITCH TABLES
The tables that follow describe the functions carried out by the bits and combinations
of bits for each service switch. In order to correctly interpret some of the functions
required, a knowledge of the communication protocol is required. The default values
may undergo some modifications due to both homologation and user's peculiarities.
For this reason, you are recommended to print out the service switches of the facsimile
machine to be serviced, always before modifying them.
Switch SW01
bit Function set to 1 set to 0
7 Error code generated YES NO
on failed reception
Next page sent from the ADF
or resent from memory
6 despite bad reception signal YES NO
(RTN) from the receiver
Multifrequency bit 5 4 = 0 0, -11 / -9
5 output level bit 5 4 = 0 1, -8 / -6
4 (dBm) bit 5 4 = 1 0, -12 / -10
bit 5 4 = 1 1, -6 / -4
Cable equalizer bit 3 2 = 0 0, 0 km (0 dB)
3 in reception bit 3 2 = 0 1, 1.8 km (4 dB)
2 (*) bit 3 2 = 1 0, 3.6 km (8 dB)
bit 3 2 = 1 1, 5.6 km (12 dB)
Cable equalizer bit 1 0 = 0 0, 0 km (0 dB)
1 in transmission bit 1 0 = 0 1, 1.8 km (4 dB)
0 (*) bit 1 0 = 1 0, 3.6 km (8 dB)
bit 1 0 = 1 1, 5.6 km (12 dB)
(*) Distances refer to a cable radius = 0.4 mm. With smaller or greater cable
radii, distances respectively decrease or increase, with equal attenuation.

4-4
602E52970
Switch SW02
bit Function set to 1 set to 0
7 Answer to second
signal from the receiver YES NO
(anti-echo device)
6 Tone duration / pause bit 6 5 4 = 0 0 0, 70 / 70
5 in tone dialling bit 6 5 4 = 0 0 1, 70 / 140
4 (ms / ms) bit 6 5 4 = 0 1 0, 87 / 87
bit 6 5 4 = 0 1 1, 120 / 120
bit 6 5 4 = 1 0 0, 200 / 200
3 Disable non standard YES NO
features (NSF)
2 Reception 9600-2400 4800-2400
start speed (V.29,V.27ter) (V.27ter only)
bit 1 0 = 0 0, 9600 bps
1 Transmission bit 1 0 = 0 1, 7200 bps
0 start speed bit 1 0 = 1 0, 4800 bps
bit 1 0 = 1 1, 2400 bps

602E52970 4-5
Switch SW03
bit Function set to 1 set to 0
7 Page loss when 12 mm 8 mm
SURPLUS = AUTO
Automatic transmission in
6 HOOK mode without pressing YES NO
START at the end of dialling
Transmission of the tone
5 emitted by the receiver NO YES
during reception (CED)
4 Anti-echo protect tone YES NO
in transmission
3 Reception sensitivity -47 dBm -43 dBm
bit 2 1 = 0 0, 35 s (*)
2 Wait time for signal from bit 2 1 = 0 1, 60 s (*)
1 receiver during transmission bit 2 1 = 1 0, 90 s (*)
bit 2 1 = 1 1, 130 s (*)
Frequency of the tone
0 emitted by the receiver 1100 Hz 2100 Hz
during reception (CED)
(*) In some countries these bits are set to a single specific value.

4-6
602E52970
Switch SW04
bit Function set to 1 set to 0
bit 7 6 = 0 0, strict
7 Reception channel bit 7 6 = 0 1, average
6 evaluation criteria bit 7 6 = 1 0, moderate
bit 7 6 = 1 1, loose
5 Pause between digits 800 ms 900 ms
in pulse dialling
4 Dial pulses bit 4 3 = 0 0, N
3 (N = digits dialled) bit 4 3 = 0 1, N + 1
bit 4 3 = 1 0, 10 - N
2 Pulse dialling frequency 20 p/s (*) 10 p/s
1 Report printing inhibited always (**)
0 PBX dialling tone YES NO
detection
(*) only valid if the value of switch SWP is halved.
(**) as programmed via TX REPORT user parameter.

602E52970 4-7
Switch SW05
bit Function set to 1 set to 0
7 Earth pulse duration 100 ms 300 ms
6 Flash pulse duration 110 ms 270 ms
bit 5 4 = 0 0, 2 s
5 Pause time bit 5 4 = 0 1, 3 s
4 bit 5 4 = 1 0, 4 s
bit 5 4 = 1 1, 5 s
3 PAUSE key enabling NO YES
2 Limit to the number of unlimited for 11 s
pauses that may be inserted number max
bit 1 0 = 0 0, 1 s
1 Predialling pause bit 1 0 = 0 1, 2 s
0 (*) bit 1 0 = 1 0, 3 s
bit 1 0 = 1 1, 4 s
(*) only valid if dial tone detection is not enabled (SW06, bit 2 = 0).

4-8
602E52970
Switch SW06
bit Function set to 1 set to 0
bit 7 6 = 0 0, 320 / 570 Hz
7 Dialling tone bit 7 6 = 0 1, 360 / 520 Hz
6 frequency range bit 7 6 = 1 0, 300 / 640 Hz
bit 7 6 = 1 1, 300 / 640 Hz
bit 5 4 3 = 0 0 0, 400 ms
5 bit 5 4 3 = 0 0 1, 800 ms
4 Dialling tone bit 5 4 3 = 0 1 0, 900 ms
3 detection time bit 5 4 3 = 0 1 1, 1200 ms
bit 5 4 3 = 1 0 0, 1800 ms
bit 5 4 3 = 1 0 1, 2000 ms
2 PSTN dialling tone YES NO
detection
Shortcircuit
1 between digits YES NO
in pulse dialling
Shortcircuit time
0 on relay, before and after 260 / 70 ms 86 / 48 ms
dialling pulse

602E52970 4-9
Switch SW07
bit Function set to 1 set to 0
Busy tone
7 detected after YES NO
dialling
Exchange tones detected
6 during preliminary YES NO
phase of reception
5 Rapid preamble recognition YES NO
during the handshake phase
4 Reserved 128 kbytes 17 kbytes
3 Report always printed YES NO
on failed transmission
2 Busy tone seek time 20 s standard
after dialling (*)
1 Frequency range of 1120:1160 Hz as for the 1st
second dialling tone Belgian type dialling tone
0 Dialling tone 40 s 10 s
wait time
(*) i.e., as established by the couple of bits 1 and 2 of switch SW03

4-10
602E52970
Switch SW08
bit Function set to 1 set to 0
7 Full line monitoring YES NO
6 Not used
Dialling tone bit 5 4 = 0 0, -40 dBm
4 detection bit 5 4 = 0 1, -30 dBm
5 threshold bit 5 4 = 1 0, -26 dBm
bit 5 4 = 1 1, -35 dBm
3 R Key function REGISTER REGISTER
RECALL (*) RECALL (**)
2 Exit from HOOK mode after 1 h after 1 min
1 Busy tone detected YES NO
before dialling
0 Busy tone sequence 4 sequences 2 sequences
(*) by Earth pulse
(**) by Flash pulse

602E52970 4-11
Switch SW09
bit Function set to 1 set to 0
7 Switching off manual automatic
ERROR LED after 1 min
Maximum bit 6 5 = 0 0, 8 min
5 reception/transmission bit 6 5 = 0 1, 16 min
6 time for one page bit 6 5 = 1 0, 32 min
bit 6 5 = 1 1, unlimited
4 Size of data block 64 bytes 256 bytes
packets in ECM (*)
3 Compression method MR & MH MH
2 Print chart enabled YES NO
1 Frequency and sequence of Type B Type A
answer tone in FAX/TEL mode (**) (***)
0 Extended error codes YES NO
(*) only to be used on lines with interference
(**) Frequency: 425 Hz
Sequence: 1 s 4 s
(***) Frequency: 700 Hz
Sequence:
0.1 s 0.1 s 0.1 s 0.1 s 0.1 s 2 s

4-12
602E52970
Switch SW10 (to enable / disable user-level functions)
bit Function set to 1 set to 0
Change in dialling mode
7 by pressing the YES NO
¬ key disabled
6 Not used
5 Enable remote diagnostics YES NO
4 Set number of rings(*) YES NO
3 Enable pulse mode YES NO
during dialling
2 Set silence time detection YES NO
1 FAX/TEL switch YES NO
0 Set call time YES NO
in FAX/TEL mode
(*) if this is set to zero the customer cannot set the number of rings

602E52970 4-13
Switch SW11 (to enable / disable user-level functions)
bit Function set to 1 set to 0
7 Enable FAX/TAD NO YES
6 Not used
5 Reserved
4 Protection for YES NO
telephone credit card (*)
3 Reserved
2 Linking between fixed to 1
letters and numeric keys (never set to 0)
1 Disable "second tone" NO YES
function of HOLD - 2.TONE key
0 Enable entry of YES NO
sender's number
(*) In order to prevent the secret card code from being either
displayed or printed, only the last 10 digits of the telephone
number are displayed or printed.

4-14
602E52970
Switch SWA
Format Function
1 digit Time before answering
(0 :
9) (in seconds)
Switch SWB
Format Function
2 digits Number of rings before answering
(01 :
10)
Switch SWC
Format Function
max 3 digits First ring detection time (in tens of ms)
(001 :
255)
Switch SWD
Format Function
max 3 digits Second ring detection time
(001 :
255) (in tens of ms)
Switch SWE
Format Function
max 3 digits Ring reset time (in hundreds of ms)
(001 : 255)

602E52970 4-15
Switch SWF
Format Function
Maximum percentage of
max 2 digits incorrect lines on a page
(00 :
15) without an error message
(00 = function disabled)
Switch SWG
Format Function
Maximum number of
max 2 digits incorrect lines on a page
(00 :
15) without an error message
(00 = function disabled)
Switch SWH
Format Function
max 2 digits Transmission level code
(00 :
15) (*) (in dBm)
(*) 03 : 15 for Italy.
Switch SWI
Format Function
max 3 digits Minimum ring duration (Max Freq)
(010 :
100) (in ms)
Switches I and J set the ring frequency detection range NOT the duration of
the ring.
Switch SWJ
Format Function
max 3 digits Maximum ring duration (Min Freq)
(010 :
100) (in ms)

4-16
602E52970
Switch SWK
Format Function
max 2 digits Number rings before answering
(00 :
99) in manual reception mode
(00 = no answer in manual RX)
Switch SWL
Format Function
max 2 digits Wait time of the tone emitted by the
(01 : 99) sender before alarm to the operator
in FAX/TEL mode (in seconds)
Switch SWM
Format Function
max 2 digits Alarm duration
(01 :
99) in FAX/TEL mode (in seconds)
Switch SWN
Format Function
max 2 digits Reserved
(01 :
99)
Switch SWO
Format Function
max 2 digits Silence recognition time in
(01 :
59) FAX/TAD mode (in seconds)

602E52970 4-17
Switch SWP
Format Function
max 2 digits Break time
(50 :
80) in pulse dialling (in ms) (*)
(*) with a pulse dialling frequency of 20 p/s, halve the value used with
the 10 p/s frequency.
Switch SWQ
Format Function
max 2 digits Number of redials
(00 :
99)
Switch SWR
Format Function
max 3 digits Time between redials (in seconds)
(000 :
999) (000 = no redials)
n

602E52970 5-1
5. DIAGNOSTICS
5.1 SELF-DIAGNOSTICS
The facsimile machine automatically runs a diagnostic program (SELFDIAGNOSTIC TEST) the first time it is powered on and on reactivation after a power
failure or disconnection from the mains:
- if the self-diagnostic test is passed, the facsimile machine enters standby
mode
- If instead the self-diagnostic test is failed, the fax machine shows an error code
on the display (SYSTEM ERROR xx). In this case, the fax machine needs to be
disconnected from the power supply socket before eliminating the related
problem.
The self-diagnostic routine tests the following components:
• EPROM
• static RAM
• printer.

5-2 602E52970
The self-diagnostic test stops at the first test in which a fault is detected.
5.1.1 Description of the Self-Diagnostic Program
Diagnostic step Error message
1) The facsimile machine is powered on: the error LED lights up
2) The EPROM is tested
3) The static RAM is tested
4) Printer startup: check that the
print carriage is reset.
5) The paper edge sensor is tested.
6) Self-diagnostic program ended
successfully: error LED switches
off.
(1) To solve this problem, replace the EPROM.
(2) This error means that the data of the static memory have been damaged, so U.K./
S. AFRICA country software parameters have automatically been loaded. To solve
this problem, proceed as follows:
- disconnect and reconnect the fax machine from the power supply socket: if the
error message persists, replace first the rechargeable battery then, if the error
still persists, replace the motherboard. If instead the message disappears,
proceed as follows:
- perform LOAD DEFAULT (see sect. 6.1.7), ALIGNMENT TEST (see sect. 6.1.1)
and SCANNER SHADING (see sect. 6.1.8) procedures
- perform fax machine nationalisation and reset installation and configuration
parameters (see sect. 3.2).
(3) This problem could be caused by the absence of the carriage limit stop plate (right
side), by the paper edge sensor (replace carriage) or by a failure in the carriage
motor (replace the defective part: motor, belt, etc.).
4) This problem could be caused by the absence of the carriage limit stop plate (right
SYSTEM ERROR 93
SYSTEM ERROR 16
SYSTEM ERROR 03
SYSTEM ERROR 04
AUTOMATIC RX
09-05-95 14:58
(1)
(2)
(4)
(3)

602E52970 5-3
side) or by the paper edge sensor (replace the carriage).
5.2 ERROR CODES
The error codes are printed on the journals (see section 5.3).
The format of these error codes, excluding those referring to the self-diagnostic test
(described in section 5.1.1), may be:
- one group of two digits (xx)
- two groups of two digits separated by a dot (xx.xx); this extended format:
• indicates the category to which the error belongs, by means of the first
group,:
01 Document incorrectly positioned
02 Unable to connect
03 No answer from correspondent
04 Failed transmission
05 Incomplete transmission
07 Document too long
08 Document jam
10 Failed or incomplete reception
11 No reception due to memory full
13 Failed polling reception
16 Power failure
• provides more detailed information about the error, by means of the
second group, and may be requested by the technician with the machine in
"service" mode (see section 3.2.2), by setting bit 0 of switch SW09 to 1 (see
section 4.1).
In the tables that follow, the error codes are indicated in their extended format and
in ascending numeric order.
For an explanation of the meaning of the protocol signal codes that appear in the
description of the causes of errors, see the next section (5.2.1).
Important: to ensure correct identification of the cause of the error, we recom-

5-4 602E52970
mend you always print the communication protocol (PROTOCOL
DUMP, see section 5.2.3).
5.2.1 Meaning of Protocol Signal Codes
Code Name Type of signal
CRP Command Repeat GENERIC
CED Called (Station Identification)
CIG Calling (Subscriber Identification)
CSI Called asubscriber Identification
DIS Digital Identification Signal
NSC Non-Standard Command INITIAL
IDENTIFICATION
NSF Non-Standard Facilities
NSS Non-Standard Set-up
TCF Training Check Frame
TSI Transmitting Subscriber Identification
DTC Digital Transmit Command POLLING
COMMANDS
DCS Digital Command Signal TRANSMISSION
COMMANDS
CFR Confirmation To Receive PRE-MESSAGE
ANSWERS
FTT Failure To Train
CTC Continue To Correct
EOM End-of-Message
EOP End-of-Procedure
EOR End-of-Retransmission POST-MESSAGE COMMANDS
MPS Multipage Signal

602E52970 5-5
PPS Partial Page signal
>>
PRI Procedure Interrupt
RR Receive Ready
CTR Response to CTC
ERR Response to EOR
MCF Message Confirmation
PIN Procedure Interrupt Negative
PIP Procedure Interrupt Positive POST-MESSAGE ANSWERS
PPR Partial Page Request
RNR Receive Not ready
RTN Retrain Negative
RTP Retrain Positive

5-6 602E52970
DCN Disconnect DISCONNECTION
5.2.2 Meaning of Error Codes
Code Cause of Error Action
02.00 No dial tone Check telephone connection
03.00 No answer from correspondent Call again manually
04.00 No connection due to Print and analyse protocol dump
disconnected correspondent
(DCN received)
04.01 No connection due to incompatible Print and analyse protocol dump
correspondent
(during handshake phase)
04.02 No connection due to incompatible Print and analyse protocol dump
correspondent
04.03 No connection due to incompatible Print and analyse protocol dump
correspondent
(incompatible confirmation signal)
04.04 No connection due to incompatible Print and analyse protocol dump
correspondent
(DCN instead of confirmation signal)
04.05 Line error as no further speed Print and analyse protocol dump
fall-back is possible
04.06 No connection due to problems Call again manually
on receiver's side (no answer)
04.07 No answer during Print and analyse protocol dump
post-message phase
04.08 Answer not allowed during Print and analyse protocol dump
post-message phase
04.09 No development of protocol Print and analyse protocol dump

602E52970 5-7
04.10 Answer not allowed during Print and analyse protocol dump
post-message phase in ECM
>>
Code Cause of Error Action
04.11 No answer during Call again
post-message phase in ECM
04.12 Insufficient memory Call again
on receiver's side
05.00 Transmission incomplete Call back and send missing pages again
due to RTN reception
07.00 Transmission duration Call again
exceeding time set with SW09, bit 5-6
08.00 Document jam Remove document
09.00 STOP pressed during TX or RX None
10.00 Text coding error Print and analyse protocol dump
at start of message
10.01 No connection due to Print and analyse protocol dump
incompatible correspondent
10.02 No reception due to no answer Print and analyse protocol dump
from correspondent during
handshake, or at the end of the block, or at
the end of a page with change in resolution
10.03 Line error due to incompatible Print and analyse protocol dump
speed
10.04 No commands received Print and analyse protocol dump
from correspondent
10.05 Text coding error Print and analyse protocol dump
(5 seconds without data)
10.06 No signal during Print and analyse protocol dump
reception of the message
>>

5-8 602E52970
10.07 No commands received Print and analyse protocol dump
from correspondent at start of message
Code Cause of Error Action
10.08 No document present on Print and analyse protocol dump
polling request
10.09 Page received incorrectly Print and analyse protocol dump
(RTN transmitted)
10.10 No commands received from Print and analyse protocol dump
correspondent at start of message
(in ECM)
10.11 Page received incorrectly in ECM Print and analyse protocol dump
(ERR sent)
10.12 Busy tone recognized Print and analyse protocol dump
during handshake
10.13 Text coding error during Print and analyse protocol dump
reception of the message
11.00 Reception incomplete due to Clear unwanted documents
user memory full from the memory
11.10 Reception incomplete due to Clear unwanted documents
user memory full in ECM from the memory
13.00 Failed polling reception Call again

602E52970 5-9
5.2.3 Printing the Communication Protocol
Setting Display
1) The facsimile machine is in standby mode.
b) Enter "service" mode and select PRINT PROT. DUMP
c) Make sure that there is paper in the ASFand then press
: the data shown in fig. 5-1 will be printed and then the
facsimile machine will return to standby mode.
Fig. 5-1
The protocol status is presented, session by session, by means of the following fields:
TIMER Indicates the times, in minutes : seconds, at which the signals were
exchanged during the session
LOCAL Indicates the signals, represented by a hexadecimal code and a
mnemonic code, sent by the local facsimile machine
REMOTE Indicates the signals sent by the correspondent's facsimile machine
FIF Indicates the structure of the signals (FIF = Facsimile Information
Field) in hexadecimal code.
AUTOMATIC RX
09-05-95 14:58
PRINT PROT DUMP
/ /¬/®
PRINT PROT.DUMP
/

5-10 602E52970
16.00 Power failure None
Remarks:
1) The LOCAL field, during the session in which the message was sent, indicates
the message's transmission level, followed by the word MESSAGE (fig. 5-2)
Fig. 5-2
2) If there is a data inconsistency error in any session, the LOCAL field contains the
message CRC ERROR
3) At the end of the session, the FIF indicates the extended code of the result of
the session (fig. 5-3):
Fig. 5-3
• positive result (00 00)
• positive result with document received incorrectly (00 01)
• negative result (extended error code, e.g. 10 01)
• busy status (06 00)

602E52970 5-11
• STOP key pressed status (09 00).
5.3 REPORTS
The facsimile machine controls and updates various kinds of transaction reports
which are described in this section for the technician's benefit, though a more detailed
description is provided in the Instruction manual. Some of these reports are printed
automatically and others on request by the operator:
• Transmission report (LAST TX REPORT): printed automatically and manually
• Broadcast transmission report (LAST BROAD. REP.): printed automatically and
manually
• Journal (ACTIVITY REPORT): printed automatically and manually
• Power failure report: printed automatically only.
A report is printed by selecting the PRINT OUT REPORT option on the main menu
(see section 3.2.1).
5.3.1 Transmission Report (TX REPORT)
The methods for printing the transmission report (automatically or manually) are
selected by means of the SET MISCELLANEOUS option of the FAX SET-UP menu (see
section 3.2.1):
• TX REPORT: OFF, if you do not want the report to be printed automatically
• TX REPORT: ALWAYS, if you want the report to be printed automatically after
each transmission transaction
• FAILED TX REPORT, if you want the report to be printed automatically only
when an error is detected (*).

5-12 602E52970
(*) if bit 3 of switch SW07 is set to 1 (see section 4.1), the report is always printed
when transmission is failed even if the TX REPORT: OFF option is selected.
The transmission report contains the following information (fig. 5-5):
Fig. 5-5
• Act. n. progressive number of activity or transaction (4 digits)
• Type transaction (TX / TX ECM / RX / RX ECM / POLL / POLL ECM)
• Dialled correspondent's number dialled
number
• Received correspondent's number (and name, if recorded)
Id (*)
• Date/Time date and time of start of transaction
• Duration duration of transaction (minutes : seconds)
• Page number of pages in document
• Result result of transaction (OK / error code).
(*) this is the ID recorded on the correspondent's facsimile machine, the numeric
part of which should correspond to the actual telephone number of the fac-

602E52970 5-13
simile machine: if it does not, call the correspondent and ask him/her to correct
the ID.
5.3.2 Journal (ACTIVITY REPORT)
Provides information about all transactions (transmission / reception) and is printed
automatically every 32 transactions (and the information printed is subsequently cleared from the memory) or on request by the operator (fig. 5-6):
Fig. 5-6
5.3.3 Loss of Mains Power Supply Report
When operating conditions are restored after a loss of mains power supply, the fax
machine may behave in three different ways:
• if power was lost during a transaction (transmission or reception), then a report
with the transmission data will automatically be printed (fig. 5-7):
Fig. 5-7

5-14 602E52970
or with the reception data (fig. 5-8):
Fig. 5-8
• if power was lost during reception and the received document was damaged,
the same report as in fig. 5-8 is printed, with the addition of data pertaining to the
last 16 receptions (fig. 5-9):
Fig. 5-9
• if power was lost after a substitute reception and the document still in
memory is damaged, a report is automatically printed with the data for the last
16 receptions (fig. 5-10):

602E52970 5-15
Fig. 5-10
• if power was lost after a substitute reception and the received document
is not damaged, no report is printed.
n

602E52970 6-1
6. SYSTEM TEST AND ADJUSTMENTS
6.1 SYSTEM TEST
The SYSTEM TEST is a collection of utility programs, which are not available to the
user but are provided to enable the service technician to carry out specific tests on
components and modules.
The system tests are arranged into menus under the SYSTEM TEST item (see
section 3.2.1) and can be accessed either with the machine in "service" mode (see
section 3.2.2) or pressing in rapid sequence START « «. Underlined tests cannot be
activated with a colour print head:
• PRINT OUT SET-UP (*) • RAM TEST (*)
• ALIGNMENT TEST • AGING TEST (*)
• NOZZLES TEST • FIRMWARE RELEASE (*)
• CLEANING • LOAD DEFAULT
• PRINT CHART • SCANNER SHADING
• ASF TEST • KEYBOARD TEST (*)
• ADF TEST • DISPLAY TEST (*)
• SYSTEM TEST MSG (*) • CARRIAGE TEST.
• MODEM TEST (*) • PRINT SIMULATION (*)
• KEYB. SIMULATION (*) • CLEANER TEST (*).
Warning: each test in progress can be interrupted or terminated in either of the
following ways:
- by pressing the STOP key once, if you want to stay in test mode
(the test that follows the interrupted or terminated one appears on
the display)
- by pressing the STOP key twice, if you want to exit from test mode
and return to stand-by mode.
(*) These tests are used exclusively for special production requirements or during
laboratory tests and, consequently, no description is provided in this manual.

6-2 602E52970
6.1.1 ALIGNMENT TEST (not active with a colour print head)
This test MUST be carried out after replacing: the printer unit, motherboard, carriage
or carriage motor.
Setting Display
a) The facsimile machine is in standby mode
b) Get access to the system test menu and select the
ALIGNMENT TEST option
c) Make sure that there is paper in the ASF, and then press
: the test chart shown in fig. 6-1 is printed out
d) At the end of the printout, the message VALUE 'A' xx
will appear on the display; look carefully at the scale
printed in the top left corner of the print chart (use a
magnifying lens or make an enlarged copy of the scale)
and detect the value of its length (from 0 to 15):
Subtract 5 from the value to give the correct value 'A'.
e) Enter the detected value as xx (in order to adjust the
print left margin) and press
; the message VALUE 'B'
xx will appear on the display:
- identify the best vertical alignment from the ten
shown on the test chart
- enter the number corresponding to the best alignment using the left and right arrow keys; note that an
intermediate value, which is not printed on the test
chart, may be selected as the best alignment, there
are therefore 20 values available (0−19)
- press
: the test chart in fig. 6-2 showing both the
margin alignment (the example shows VALUE 'A' = 07)
and the vertical alignment (the example shows VALUE
'B' = 11) is printed out.
AUTOMATIC RX
09-05-95 14:58
ALIGNMENT TEST
/ /¬/®
ALIGNMENT TEST
VALUE 'A' xx
/ /¬/®
VALUE 'B' xx
/ /¬/®

602E52970 6-3
Fig. 6-1
Fig. 6-2

6-4 602E52970
6.1.2 NOZZLES TEST
This test may be carried out to identify the cause of printing errors.
Setting Display
a) The facsimile machine is in standby mode
b) Get access to the system test menu and select the
NOZZLES TEST option
c) Press
: the test result is immediately displayed
d) Make sure that there is paper in the ASF, and then press
; if you have installed a monochrome print head, the
following chart is printed out (see fig. 6-3):
Fig. 6-3
The chart consists of:
(1) a numbered scale for checking the flow of ink, with the nozzles numbered
from 01 to 50
(2) a message providing the result of the test run on the electrical print head
circuits.
6.1.2.1 Checking the Ink Flow
Check the numbered scale:
- if all the lines that make up the scale are present, all the nozzles are working
- if one or more lines are missing, the fault could be due to one of the following:
• dirty printing nib: clean the rubber print head pad
AUTOMATIC RX
09-05-95 14:58
NOZZLES TEST
/ /¬/®
NOZZLES TEST OK
/
or
NOZZLES TEST OK
/
(2)
(1)

602E52970 6-5
• foreign body on printing nib: remove it taking care to avoid touching the
electrical contacts on the print head
• air bubble in the ink: carry out the CLEANING (see section 6.1.3) followed by
the PRINT CHART test (see section 6.1.4); if the fault persists, repeat the
CLEANING up to three times, and then replace the print head if this does not
have the desired effect.
6.1.2.2 Checking the Electrical Circuits
Check the message indicating the result of the test:
- ALL NOZZLES OK all the electrical circuits are working
- NOZZLES DAMAGED: circuit(s) xx (yy, zz) error: remove the print head,
xx yy zz clean the electrical contacts on the print head with
a dry swab and the electrical contacts of the print
carriage with a soft, dry cloth, then reinsert the print head and repeat the
NOZZLES TEST. If another faulty circuit is indicated, reinsert the print head
several times until the fault has been eliminated; if the fault persists on the
same circuit (xx / yy / zz) after installing a new print head, replace the print
carriage (see section 7.2.14).
6.1.3 PRINT CHART (not active with a colour print head)
This test MUST be carried out after replacing: the printer unit, motherboard, carriage,
carriage motor or paper motor.
Setting Display
a) The facsimile machine is in standby mode
AUTOMATIC RX
09-05-95 14:58
b) Get access to the system test menu and select the
PRINT CHART option
c) Make sure that there is paper in the ASF and then press
: the test chart shown in fig. 6-4 is printed out.
d) With reference to the figure, check that:
• lines 1, 10, 11 and 12 delimit the printable area on an A4-size sheet (about 208
x 290 mm)
PRINT CHART
/ /¬/®
PRINT CHART

6-6 602E52970
• area 2 is used to evaluate that the transport speed of the print carriageis uniform:
no shadings should result in the strip
• area 3 is used for checking vertical alignment; run the printer alignment test, if
necessary, to modify the alignment parameters (see section 6.1.1)
• areas 4, 5 and 7 are used for checking that the line feed mechanism is uniform:
- in area 4, groups of lines are printed close together but must never cross or
overlap (
); the groups alternate in lines corresponding to the
central nozzle on the print head (number 25)
- in area 5, groups of lines are printed one on top of another and there must be
no space between them (
); the groups alternate in lines
corresponding to the central nozzle on the print head (number 25)
- in area 7 dark grey and light grey patterns are printed forming a uniform strip,
that is, without black or white lines distributed irregularly across it; if the lines
appear at regular intervals along the strips, some of the nozzles are faulty
Faults found in areas 4, 5 and 7 indicate line feed errors
• four areas 6 are used for checking "all black" printing; check that there are no
white lines present; if there are, some print nozzles may be blocked. In this case,
run CLEANING (see section 6.1.3)
• area 8 is used for checking the printing of ASCII characters
• area 9 is used for checking printing with the nozzles spraying at maximum
frequency: there must be no white or broken lines; if there are, run the nozzles
test (see section 6.1.2).

602E52970 6-7
Fig. 6-4
line 1
line 10 line 12line 11
area 6area 6
area 6area 6
area 2
area 3
area 5
area 4
area 7
area 8
area 9

6-8 602E52970
6.1.4 ASF TEST (not active with a colour print head)
This test MUST be carried out after replacing: the paper motor or the printer unit.
Setting Display
a) The facsimile machine is in standby mode.
b) Get access to the system test menu and select the ASF
TEST option
c) Place an A4-size blank sheet of paper in the ASF and
then press : the same line is printed on both top and
bottom of sheet as in the case of the alignment test (fig.
6-2):
d) If the paper gets jammed, the message PAPER ERROR
appears on the display.
6.1.5 ADF TEST
This test MUST be carried out after replacing: the feeder rollers or the scanner unit.
Setting Display
a) The facsimile machine is in standby mode
b) Get access to the system test menu and select the ADF
TEST option
c) Place one or more sheets with text and pictures in the
automatic document feeder and then press : the
documents are scanned one at a time and, at the end of
the operation, a message appears indicating the number
of documents scanned (xx)
d) If you want to repeat the test, insert more sheets in the
feeder and press .
AUTOMATIC RX
09-05-95 14:58
ASF TEST
/ /¬/®
ASF TEST
AUTOMATIC RX
09-05-95 14:58
xx: ADF TEST
ADF TEST
/ /¬/®
PAPER ERROR
PRESS

602E52970 6-9
6.1.6 LOAD DEFAULT
This procedure is used for loading the default values of the service switches for the
current country version of the facsimile machine.
Setting Display
a) The facsimile machine is in standby mode
b) Get access to the system test menu and select the LOAD
DEFAULT option
c) Press
d) Press once again: the default values of the U.K.
service switches are automatically set in place of the
current ones, clearing the static RAM and thus deleting
all data (reports) set by the user.
6.1.7 SCANNER SHADING
This test MUST be carried out after replacing: the scanner unit, motherboard or CCD
board. It must also be carried out after making the CCD adjustment (see section 6.3).
Setting Display
a) The facsimile machine is in standby mode
b) Get access to the system test menu and select the
SCANNER SHADING option
c) Press
d) Press
e) Press
AUTOMATIC RX
09-05-95 14:58
LOAD DEFAULT
/ /¬/®
LOAD DEFAULT
/
AUTOMATIC RX
09-05-95 14:58
SCANNER SHADING
/ /¬/®
SCANNER SHADING
/
SCANNER SHADING

6-10 602E52970
6.1.8 CARRIAGE TEST
This test MUST be carried out after replacing: the carriage, carriage motor or printer
unit.
Setting Display
a) The facsimile machine is in standby mode
b) Get access to the system test menu and select the
CARRIAGE TEST option
c) Press
: the carriage starts moving from right to left and
gradually increases its field of movement until it reaches
the left-hand side of the machine, and then it repeats this
procedure.
AUTOMATIC RX
09-05-95 14:58
CARRIAGE TEST
CARRIAGE TEST
/ /¬/®

602E52970 6-11
6.2 CHECKS AND ADJUSTMENTS
6.2.1 Checking the Direct Voltages
1) Remove the power supply/NCU assembly (see section 7.2.3) without disconnecting it from the motherboard
2) Measure the direct voltages at connector J2 on the power supply board.
Fig. 6-5
-12 V
+12 V
GND
GND
GND
+5 V
+24 V
PF
+28 V
n

602E52970 7-1
7.1 MAINTENANCE
The facsimile machine's maintenance includes periodic preventive procedures
(such as optical unit cleaning), and action to be taken following a message on the
display (such as the ink out message): the procedures are normally carried out by the
user so they will be described in detail in the User Guide. Here only a brief description
is provided.
7.1.1 OUT OF INK Message
The facsimile machine has a built-in counter for keeping track of ink consumption,
so as to provide an ink out message at the right time. When the ink present in the
cartridge runs out, the display shows the following message:
OUT OF INK
to prompt the operator to:
- replace the ink cartridge, if the print head is of the rechargeable type
- replace the entire print head, if it is of the disposable type.
If a rechargeable print head is used, the ink cartridge can be replaced several times.
When a deterioration in the printing quality is observed, after several replacements,
this means that the entire print head is to be replaced.
While replacing the cartridge only, but not the entire print head, a little ink may be
ejected, to prevent the printing area from getting dirty, when the out of ink message
appears, a sheet of paper is automatically inserted under the print carriage.
7. MAINTENANCE AND REPLACEMENT
PROCEDURES

7-2 602E52970
7.1.2 Replacing the rechargeable Ink Cartridge
1. Tilt the printer cover.
2. Remove the used cartridge, without removing the print head, by pressing the
catch.
3. Remove the new cartridge from its sealed packing and peel the protective film off
the ink supply hole.
4.Insert the cartridge in its housing immediately and press it in until the catch clicks
into place to indicate that the cartridge is correctly inserted.
5.Close the printer cover: if the head cleaning feature is enabled (bit 2 of software
parameter SW09 =1, see section 4.1), the facsimile machine automatically starts
the nozzle cleaning and testing procedure (see section 3.1.5, step 7). If it is not,
the sheet of paper is unloaded.
`
WARNING
Do not touch the inked area!
7.1.3 Replacing the Print Head
See section 3.1.5 (starting from step 4).
7.1.4 Cleaning the Print Head
If print quality deteriorates, the print nozzles need to be tested first (see sect. 6.1.2)
to determine whether it is necessary to perform the print head CLEARING procedure,
which entails drawing ink to free the print head from any air bubbles it may contain.
HEAD MAINTENANCE
(F)/ /
AUTOMATIC RX
09-05-95 14:58
Setting
1) The facsimile machine is in stand-by mode
2) Access the main menu and select the HEAD MAINTE-
NANCE submenu of the FAX SETUP menu
3) Press
twice to start procedure.
Display
PRINTING

602E52970 7-3
7.1.5 Cleaning the Electrical Contacts
If a deterioration of the print quality is observed, it may be necessary to clean the
electrical contacts on the print head
1) Unplug the power cable from the mains socket and tilt the printer cover
2) Remove the print head and clean the electrical contacts using a dry cotton swab
(see figure 7-1)
Warning: Do not touch the printing nib.
Fig. 7-1
3) Clean also the electrical contacts on the print carriage using a dry soft cloth (see
figure 7-2).
Fig. 7-2
4) After reinserting the print head, close the printer cover.
electrical
contacts
on carriage

7-4 602E52970
7.1.6 Cleaning the Print Head Cleaning Pad
1) Unplug the power cord from the mains socket and flip open the printer lid.
2) Remove the print head and move the carriage against the left side (figure 7-3).
Fig. 7-3
3) Clean the print head cleaning pad using a dry cotton swab (fig. 7-4), then re-install
the print head and close the printer lid.
Fig. 7-4
print head
cleaning pad
 Loading...
Loading...