Page 1

Page 2

Page 3

1 Notices.....................................................................................................................9
Revision Table.....................................................................................................................................................9
Hearing Aid Compatibility....................................................................... ..............................................................9
UL/CSA Safety Compliance...................................................................................................................................9
Docmentation Disclosure......................................................................................................................................9
FCC Statement....................................................................................................................................................10
CE Declaration of Conformity................................................................................................................................10
Environment .......................................................................................................................................................10
Copyright Notice..................................................................................................................................................10
Trademarks.........................................................................................................................................................11
2 Product Configuration................................................................................................16
LAN vs. WAN.......................................................................................................................................................16
Things to know about the product ........................................................................................................................20
3 System Feature Description Table...............................................................................29
Access Control - Browser .....................................................................................................................................31
Account Code......................................................................................................................................................31
Agent (UCD) Logon/Logoff................................................................... ................................................................31
Alarm .................................................................................................................................................................31
Alternate Attendant .............................................................................................................................................31
Announcement Only Mailbox ................................................................................................................................31
Answer Position...................................................................................................................................................32
Automated Attendant (Receptionist) (AA)..............................................................................................................32
Automatic Daylight Savings (NTP).........................................................................................................................32
Automatic Hold .................................. ............................ ............................. ........................................................32
Automatic Line Select (Hot Line)...........................................................................................................................33
Automatic Provisioning.........................................................................................................................................33
Automatic Route Select (ARS) ........................................................................ ......................................................33
Backlit Display.....................................................................................................................................................33
Basic Calling........................................................................................................................................................33
Busy Call Back.....................................................................................................................................................33
Busy Lamp Field (BLF).........................................................................................................................................33
Call Abandon.......................................................................................................................................................33
Call Forward........................................................................................................................................................34
Call Operator.......................................................................................................................................................34
Call Park.............................................................................................................................................................34
Call Pickup Group ................................................................................................................................................35
Call Restriction ....................................................................................................................................................35
Call Routing ........................................................................................................................................................35
Call Waiting.........................................................................................................................................................35
Caller ID.............................................................................................................................................................35
Class of Service...................................................................................................................................................35
Conference .........................................................................................................................................................36
Day & Night Service Mode....................................................................................................................................36
Daylight Savings..................................................................................................................................................36
Default Setting......................................................................................... ...........................................................36
TOC
XBLUE Networks
3
Page 4

TOC
Direct Inward Dial (DID) ......................................................................................................................................36
Direct Inward System Access (DISA).....................................................................................................................36
Direct Telephone Line Access................................................................................................................................36
Distinctive Ringing...............................................................................................................................................37
Domain Name Server (DNS).................................................................................................................................37
Emergency Call......................................................................... ...........................................................................37
Extension Password................... ..........................................................................................................................37
E-mail Delivery of Voicemail Messages....................................................... ............................................................37
FAX/Modem Detection............................................... ...........................................................................................37
Flash ..................................................................................................................................................................37
Flexible Numbering Plan................................................................. ......................................................................38
X-50
to
X-50
................................................................................................................................................38
Hot Dial Keypad...................................................................................................................................................38
Last Number Redial.................................................................................. ............................................................38
Least Cost Routing...............................................................................................................................................38
Line Group........................................................................................................... ...............................................39
Live Call Record............... ....................................................................................................................................39
Meet Me Page .....................................................................................................................................................39
Message Waiting Indication (MWI)........................................................................................................................39
Music on Hold......................................................................................................................................................39
Mutual Mailboxes (Group Mailbox) ............................. ............................. ............................ ..................................39
Navigation Keys...................................................................................................................................................39
Night Service.......................................................................................................................................................40
Numbering Plan...................................................................................................................................................40
Off Hook Preference.............................................................................................................................................40
Outside Calls.......................................................................................................................................................40
One Touch Record ...............................................................................................................................................40
Paging................................................................................................................................................................40
Pause Insertion ...................................................................................................................................................41
Phantom Mailbox (Extension) ...............................................................................................................................41
Phonebook..........................................................................................................................................................41
Power Failure Transfer..........................................................................................................................................41
Programmable Buttons.........................................................................................................................................41
Redial.................................................................................................................................................................41
Registration Server ..............................................................................................................................................42
Remote Management...........................................................................................................................................42
Service Mode.......................................................................................................................................................42
SIP Trunk.............. ..............................................................................................................................................42
Soft Interactive Keys............................................................................................................................................42
Speed Dial ......... ............................. ....................................................................................................................42
Station Lock ........................................... .............................................................................................................42
Station Message Detailed Recording (SMDR)..........................................................................................................43
System Speed Dial...............................................................................................................................................43
System Time and Date.................................... .....................................................................................................43
Time and Date in Display .....................................................................................................................................43
Toll Restriction.....................................................................................................................................................43
Transfer..............................................................................................................................................................43
4
XBLUE Networks
Page 5

Traveling Class of Service.................................................................................. ...................................................43
Trunk Group........................................................................................................................................................43
Unified Call Distribution (UDC) or Hunt Group........................................................................................................44
UCD Reroute.......................................................................................................................................................44
Virtual Extension (Phantom)....................................................... ............................ ..............................................44
Voice Mail............................. ..............................................................................................................................44
Wizard Setup ...................... ................................................................................................................................45
4 Telephone Feature Description Table...........................................................................47
Agent Log On/Off - UCD Group .................................. ..........................................................................................53
Alphanumeric Backlit Display................................................................................................................................53
Automatic Hold .................................. ............................ ............................. ........................................................54
Busy Callback................... ...................................................................................................................................54
Call Forward - Forking................. .........................................................................................................................55
Call Forward........................................................................................................................................................55
Call Hold.............................................................................................................................................................59
Call Log ..............................................................................................................................................................59
Call Park.............................................................................................................................................................60
Call Pickup..........................................................................................................................................................60
Call Waiting.........................................................................................................................................................60
Call Blocking .......................................................................................................................................................61
Conference - 3 Way.............................................................................................................................................61
Class of Service - Traveling................................................................... ................................................................62
Distinctive Ringing....................................................................................... ........................................................62
Do Not Disturb (DND)..........................................................................................................................................63
Extension Feature Reset.......................................................................................................................................63
Feature (Flexible) Button Programming.................................................................................................................64
Feature Button Reset...........................................................................................................................................66
Hold Reminder....................................................................................................................................................66
LCD & Interactive Buttons....................................................................................................................................66
Multi-Line Appearance ................ .........................................................................................................................67
Mute ..................................................................................................................................................................67
On-Hook Dialing..................................................................................................................................................68
Paging................................................................................................................................................................68
Paging Allow/Deny ..............................................................................................................................................68
Phonebook..........................................................................................................................................................69
Phone Lock/Unlock............................................................................................................. .................................71
Plug and Play......................................................................................................................................................71
Reminder Tone..................................................... ............................ ............................. ......................................71
Service Mode ......................................................................................................................................................72
Telephone Line Flash ....................................................................................................... ....................................72
Transfer..............................................................................................................................................................73
Volume Control ...................................................................................................................................................73
Web Management ...............................................................................................................................................73
TOC
XBLUE Networks
5
Page 6

5 Installation Planning..................................................................................................75
6 Getting Started..........................................................................................................81
7 Advanced Programming.............................................................................................101
TOC
Basics.................................................................................................................................................................75
Where to begin....................................................................................................................................................76
Installing the
Before Programming the
Setup Wizard..................................... ..................................................................................................................81
Setup Wizard Tabs............................................................................................. ..................................................82
WAN Port Settings ...............................................................................................................................................83
Device Information ..............................................................................................................................................103
Advanced Setup - WAN.......................................................... ..............................................................................110
Advanced - WAN..................................................................................................................................................110
Advanced - NAT...................................................................................................................................................116
Security ..............................................................................................................................................................123
Quality of Service (QoS).......................................................................................................................................132
Routing...............................................................................................................................................................136
Dynamic DNS........................................................................... ............................ ...............................................139
Universal Plug and Play (UPnP).............................................................................................................................142
File Server..................................................................... ......................................................................................143
Printer Server......................................................................................................................................................144
X-50
VoIP Telephone System ........................................... ..............................................................80
X-50
............................................................................................................................80
8 Wireless Programming...............................................................................................145
Basic ..................................................................................................................................................................146
Additional Networks.............................................................................................................................................148
Security ..............................................................................................................................................................150
Wireless Bridge....................................................................................................................................................156
Advanced............................................................................................................................................................158
Station Info.........................................................................................................................................................161
Power Saving ......................................................................................................................................................162
XBLUE Wireless Universal Adapter.........................................................................................................................163
9 Voice........................................................................................................................165
Phone Extension..................................................................................................................................................166
SIP Authentication................................................................................... ............................................................167
Extension Line Keys......................... ....................................................................................................................169
Trunk..................................................................................................................................................................171
SIP Trunks ..........................................................................................................................................................173
Direct Inward Dial.......... ......................................................................................................................................176
Trunk Groups .................................................................................................. ....................................................177
Answer Position...................................................................................................................................................179
Call Routing Rules................................................................................................................................................181
Call Restriction Rules............................................................................................................................................183
System ...............................................................................................................................................................186
Numbering Plan......................................................................................................... ..........................................187
Service Mode.......................................................................................................................................................192
6
XBLUE Networks
Page 7

Transmission.......................................................................................................................................................193
Internet Gateway Group - Voice Network ..............................................................................................................196
Station Message Detail Recording (SMDR).............................................................................................................198
SMDR Configuration.............................................................................................................................................199
SMDR View.............................. ...........................................................................................................................200
UCD Call Log.......................................................................................................................................................201
Voicemail............................................................................................................................................................202
Auto Attendant....................................................................................................................................................203
Single Digit Dialing Table......................................................................................................................................204
Voicemail............................................................................................................................................................206
House Keeping................................................................................................................ ....................................207
Phone Extension..................................................................................................................................................208
Virtual Extension .................................................................................................................................................210
Update MOH File.................................................................................................................................................211
Holiday Settings ....... ...........................................................................................................................................212
Advanced............................................................................................................................................................213
STUN..................................................................................................................................................................214
Registered Phones...............................................................................................................................................215
10 Management...........................................................................................................217
Settings..............................................................................................................................................................218
Settings..............................................................................................................................................................219
Update ...............................................................................................................................................................220
Restore Default...................................................................................................................................................221
System Log.........................................................................................................................................................222
TR-069...............................................................................................................................................................224
Time Settings.............. ............................ ............................ ................................................................................226
Access Control.....................................................................................................................................................230
Passwords...........................................................................................................................................................231
PTC Configuration.................................................................................. ..............................................................232
Update Software .................................................................................................................................................233
Reboot ...............................................................................................................................................................234
TOC
11 System Diagnostics..................................................................................................235
12 Getting to Know your Voice Mailbox..........................................................................237
Setting up your Voice Mailbox...............................................................................................................................238
Using your Voice Mailbox .....................................................................................................................................238
Remote Message Pickup...................... .................................................................................................................239
Voicemail Administration......................................................................................................................................241
13 Glossary..................................................................................................................243
Index.........................................................................................................................253
XBLUE Networks
7
Page 8

Notes:
TOC
8
XBLUE Networks
Page 9
1 Notices and Conventions
Notices
RevisionTab le
Revision Date Version Supersedes Description
September 2011 Version 1.0 Initial Release
Reproduction, publication, or duplication of this manual, or any part thereof, in any manner, mechanically, electronically, or photographically, is strictly prohibited.
HearingAidCompatibility
© Copyright 2010 by XBLUE Networks, LLC. All rights reserved.
The X2020 telephone endpoints are hearing aid compatible, as defined in section 68.316 of Part 68 FCC
Rules and Regulations.
UL/CSASafetyCompliance
The X-50 system has met all safety requires, and found to be in compliance with the Underwriters
Laboratories (UL) 60950-1
DocmentationDisclosure
The information contained in this document is subject to change without notice and should not be
construed as a commitment by XBLUE Networks, LLC. The information contained herein is supplied without
representation or warranty of any kind. XBLUE Networks, reserves the right, without notice, to make
changes to the equipment, equipment design, and documentation as advances in engineering and
manufacturing methods warrant, and assumes no responsibility and shall have no liability of any kind
arising from the supply or use of this document or the material contained herein.
Warning: This documented inf ormation is des igned to assist in the installation of the new XBLUE products.
XBLUE networks has done its best to give adequate warnings and cautions to advise both technical and
non-technical individuals, but it is very important to use common sense when installing all electrical
equiptment.
• The use of this system may result in local, long distance, Internet access or data transfer
charges, which are the sole responsibility of the user/owner of the equipment.
XBLUE Networks
9
Page 10
Notices and Conventions
ISO-9001ISO-9001
FCCStatement
This equipment generates, uses and can radiate r adio frequency energy, and if not installed and used properly , that
is, in strict accordance with the instruction manual, may cause interference to radio and television reception. This
equipment has been tested and found to comply with the limits f or a Cla ss B computing device in Subject J of P art
15 of FCC rules, which are designed to provide reasonable protection against such interference when operated.
However, there is not guarantee or warranty, written or implied, that interference will not occur in a particular
installation. If this equipment causes or receives interference or fails to operate correctly, due to radio frequency
interference (RFI) or electromagnetic interference (EMI), it will be fixed at the owners expense.
FCC Statement
FCC Information
Provide the following information to the Telephone Company prior to connection the system to the network.
TABLE 1.1 FCC Information Table
• Wireless access has been added for convenience, however, XBLUE does not warrant or guarentee,
written or implied, that the wireless will work in every location. It is the responsibility of the owner
to enable security to stop unwanted access to the network.
1
Item Specification
FCC Registration D6XIG6600
Ringer Equivalence 0.5B
Networks Address Signalling E
Service Order Code 9.0Y
Facility Interface Code 02LS2
Required Network Interface RJ11 & RJ14 & RJ45
CEDeclarationofConformity
This equipment complies with the requirements relating to electromagnetic compatibility, EN55022 class B for ITE
and EN 50082-1. This meets the essential protection requirements of the European Council Directive 89/336/EEC
on the approximation of the laws of the Member States relating to electromagnetic compatibility.
Environment
All electronic equipment must be disposed of at an approved electronic recycling center.
CopyrightNotice
10
All right reserved. No part of this publication may be reproduced, transmitted, transcribed, stored in retrieval
system, photographically or translated into any language or computer language, in any form or by any means,
electronic, mechanical, magnetic, optical, chemical, manual or otherwise, without the prior written premission of
XLBUE Networks, LLC.
XBLUE Networks
Page 11

Notices and Conventions
Trademarks
Windows Operating Systems 98/NT/2000/ME/XP/7TM are registered trademarks of Microsoft Corporation. All other
company , br and and product names, like Netscape Na vigator
of their respective owners.
TM
X-50
1. To avoid damage to yourself or the equipment read the installation instructions carefully before installing or
2. Opening the X-50 system may cause damage to the installer or the equipment as well as void the manufactures
3. Do not install any equipment in direct sunlight or expose it to excessive heat or fire.
4. Do not install any equipment where it can get wet by rain or other moistu re or water.
5. Do not install any equipment in an area where it can be subjected to high or low impact.
6. When cleaning the equipment (system and phone) use a fine damp cloth. Never use solvents such as
7. The equipment is designed to work in temperatures ranging from 32 to 100 degrees, with a relitiv e humidity of less
8. Do not install any equipment within 10 feet from a device that emits radio frequency equipment, such as TV’s,
9. Do not connect the LAN or WAN port to anything other than a ethernet network. Voltage from a telephone line may
10. Be sure that there is no power intruptions when performing a system upgrade. If the power fails during an
11. Do not work on or install the system during a lightning storm. If possible, it is a good idea to unplug all
12. It is a good idea install the equipment where it is out of re ach of children.
13. Only plug the system into a standard 120 Volts AC +
is a registered trademark of XBLUE Networks, LLC.
WARNING
powering up the system.
warranty.
trichloroethylene or acetone, which will perminately damage finish of any plastic surfaces. Never use a spray
cleaner as it may infiltrate the equipment and cause serious damage.
than 80 percent.
radios or other audio or video equipment. Other equipment to avoid is microwaves or high pulse lighting such as
photography equipment or other equipment that that may radiate electromagnetic fields.
cause serious damage, which is not covered by the warranty.
upgrade, the system may need to be returned to have the software reloaded, at the owners expense.
connections to the system during a lightning storm. Lightning damage is not covered by the manufacturer’s
warranty.
TM
and SafariTM are trademarks or registered trademarks
10%.
Trademarks
1
XBLUE Networks
11
Page 12

Notices and Conventions
Part Numbers
Below is a list of component part numbers:
TABLE 1.2 Componet Part Numbers
SKU/Part Number Description
47-9001 X-50 Telephone System Gateway
47-9002 X-2020 SIP Telephone Endpoint
47-9003 24 Button Sidecar, Electronic Dialing Module (EDM)
47-9004 8 Port 10/100 Ethernet Switch
47-9005 XBLUE Neteworks X-50 Universal Wireless Adapter
47-9006 6+ Foot Ethernet Cable
Trademarks
1
12
XBLUE Networks
Page 13

2Introduction
W
A
N
P
o
r
t
L
A
N
P
o
r
t
Telephone Lines 1 ~ 6
S
L
T
P
o
r
t
U
S
B
P
o
r
t
P
o
w
e
r
I
n
p
u
t
WPS Wireless Security Button
The X-50 IP Small Business System is a full featured Session Initiated Protocol (SIP) Voice over
Internet Protocol (VoIP) Telephone System and Gateway, with an integrated auto attendant and voice
mail system, which comes equipped with six FXO ports to accommodate six standard PSTN telephone
lines, one FXS port, to accommodate one single line (analog) telephone or FAX machine and will
support up to 24 SIP telephone endpoints. In addition, the X-50 includes all of the standard gateway
features, such as Firewall, Local Area Network (LAN) and Wide Area Network (WAN) Ports, plus an
integrated SIP server and 802.11N Wireless Access just to name a few.
X-50 Callouts - Learning the X-50 system
XBLUE Networks
13
Page 14
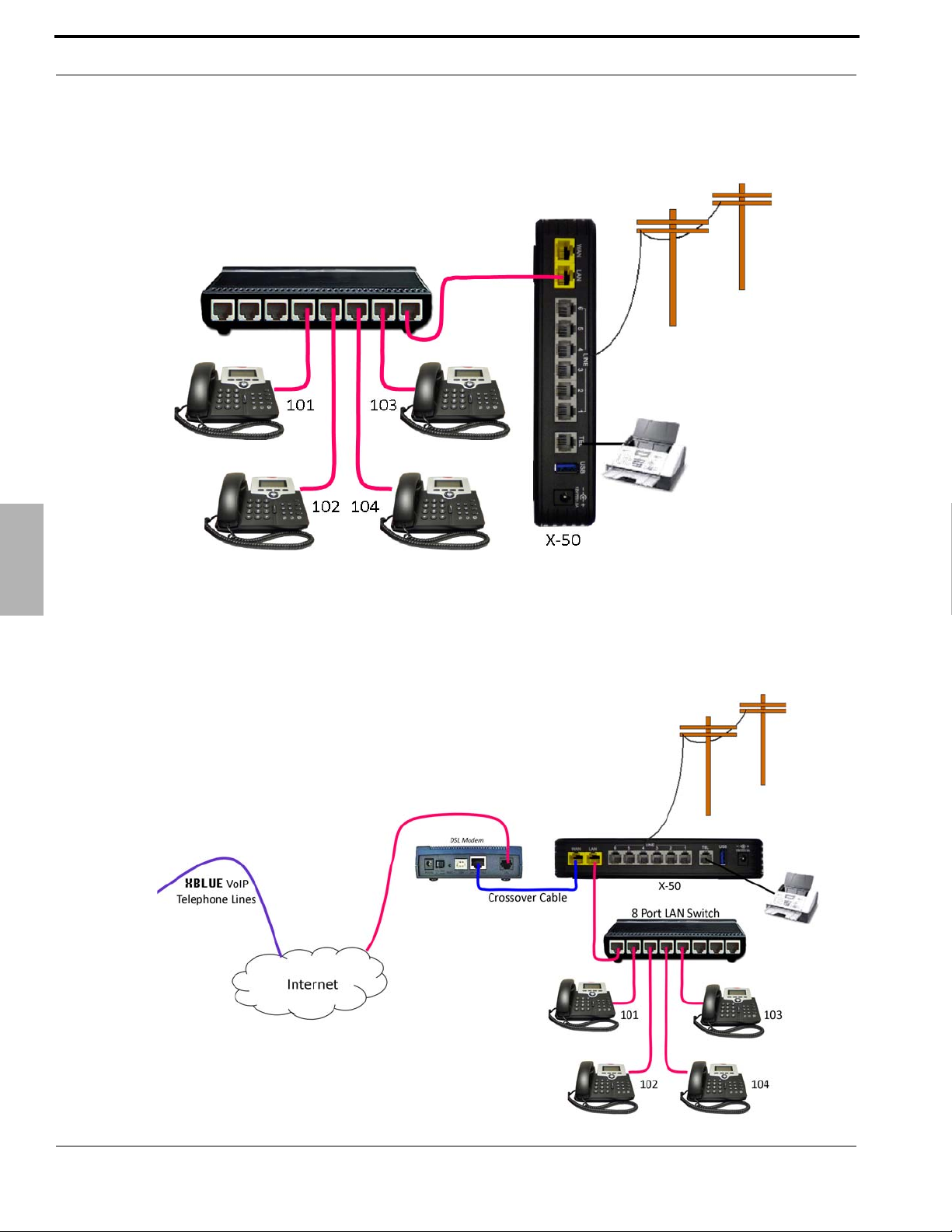
Introduction
The X-50 is extremely versatile in the way that it can be installed. It will work as a standalone small business
telephone system with no connection to an existing Network or Internet...
2
Connected to the Internet for email delivery and SIP Trunks ...
14
XBLUE Networks
Page 15
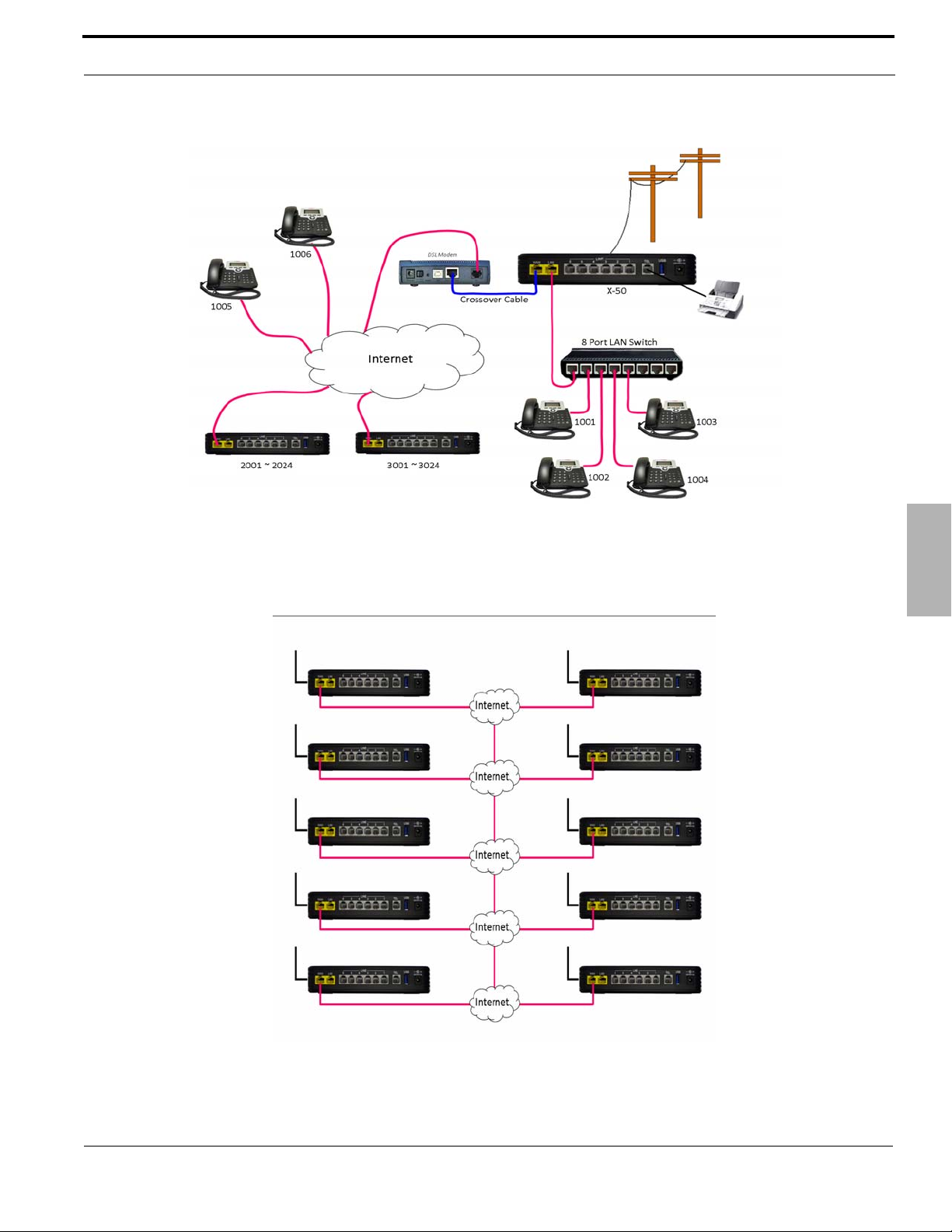
or with a static IP Address connect remote workers or create a voice (campus) network...
Introduction
And it can be connected together with nine additional X-50 systems creating a ten location voice communications
network, also known as a “Campus Environment”, each having up to 24 LAN or WAN SIP telephones endpoints.
2
With a little networking knowledge, this system should be is easy to install and program.
XBLUE Networks
15
Page 16
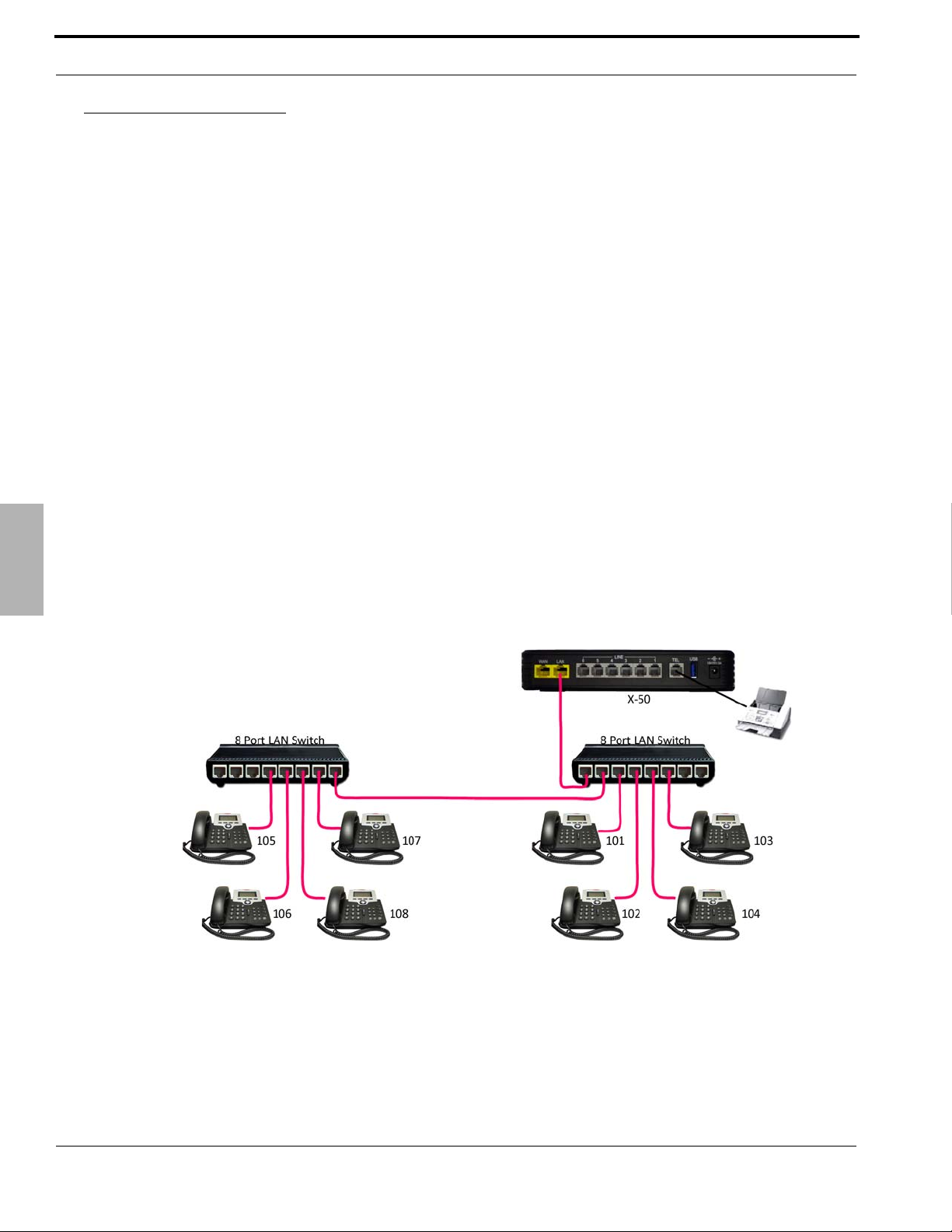
Introduction
The X-50 routes calls over a standard Intranet using a TCP/IP backbone, and does
not require or rely on the Internet.
Therefore, it is possible to use the X-50 as a standalone telephone system without
connecting it to the Internet.
ProductConfiguration
The X-50 IP small business system is a fully functional VoIP Telephone System, Auto (Receptionist) Attendant
and Voice Mail as well as a full featured Internet Gatew ay (IGW). A Gateway is used to join two dis parate netwo rks
such as a Local Area Network (LAN) and a Wide Area Network (WAN).
LANvs.WAN
In reality a “Network” is nothing more than the “network of wires”, which is used to join computing devices.
However, it has become common place to refer to the Local Area Network (LAN) as “the Network”, which includes
computers, computer devices and peripheral equiptment such as network printers. The Local Area Network is also
referred to as “the Intranet” meaning the “Internal Network”. This manual may use these terms interchangeably.
2
LAN vs. WAN
The LAN port on the X-50 is used when installing endpoints, such as the X2020 telephone or other computer
devices within the same Subnet, which is generally a small geographical area like a single building. The WAN port
is used when connecting endpoints that are not within the same Subnet, which is generally a larger geographical
area or remote location such as a home office.
LAN
A Local Area Network (LAN) or Intranet is created when two or more computing devices ar e connected together to
share information or access to another device. A network switch, or multiple network switches, can be used when
connecting more than two devices. The LAN port of a X-50 VoIP Telephone System is used to communicate with
all of the connected devices and to connect these devices to other networks such as the PSTN or other WAN
Devices.
16
XBLUE Networks
Page 17
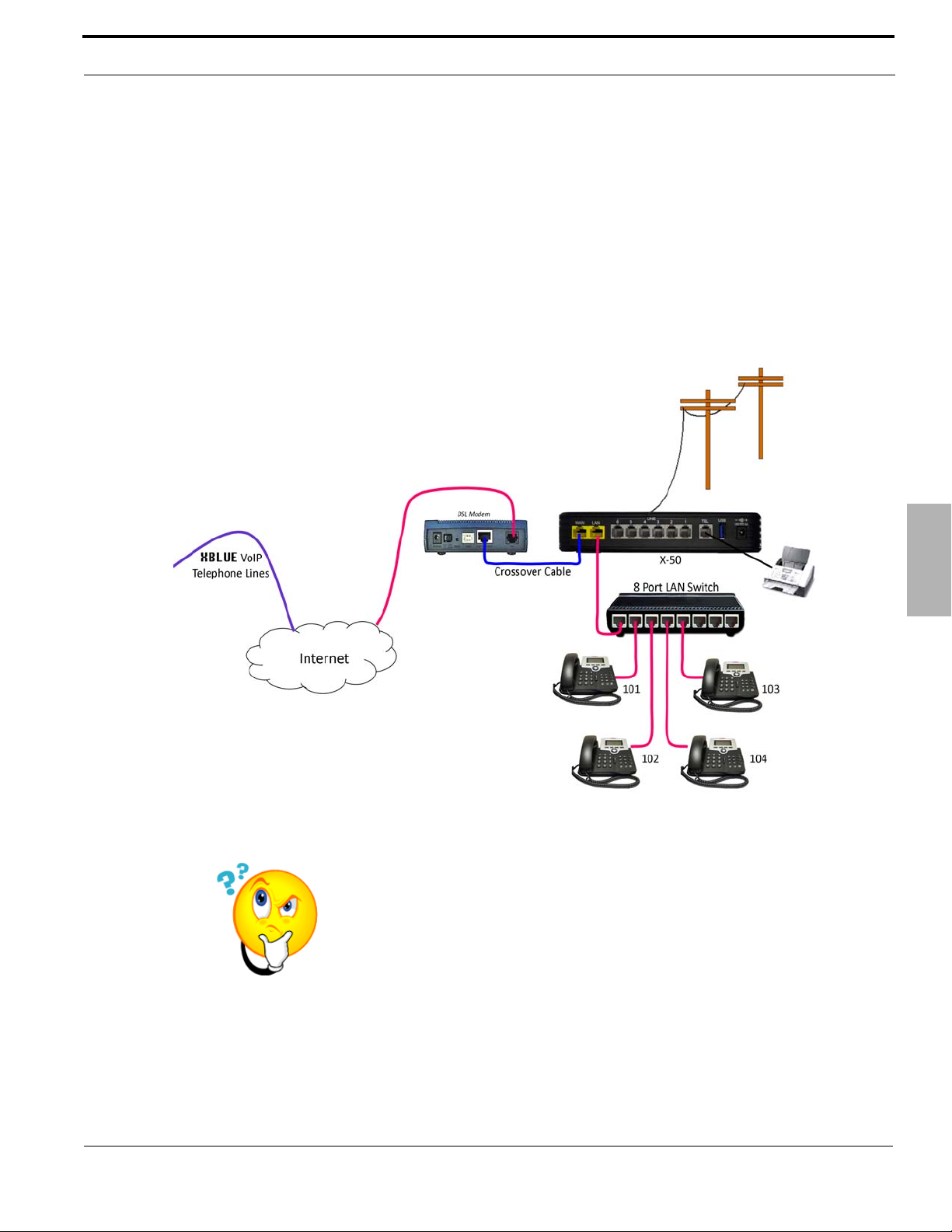
Introduction
What does that say?
The WAN port can be programmed so that it connects to the Local
Area Network (LAN), allowing it to “function” as both a WAN and LAN
port. This allows the administrator to use Network Address T r anslation
(NAT) to redirect outside Class A or B IP Addresses to an internal
locations.
WAN
The WAN port is used when connecting a Gateway to the Internet Service Provider’s (ISP) DSL/Cable modem. Once
connected the Gateway allows remote devices to communicate with local devices connected to the LAN. Connecting
the X-50 VoIP Telephone System to the ISP using a DHCP address allows SIP Trunks to authentication and other
features such as email delivery of voicemail messages. This does not require a “Fixed” or Static Class A or B IP
Address, just access to the Internet.
E-mail Delivery
When using SIP Trunks or e-mail delivery of a voice mail messages and not using remote worker or creating a voice
network, the WAN port of the X-50 VoIP Telephone System is connected to a LAN port on the existing LAN. It can
use a DHCP address or given an internal static IP Address.
LAN vs. WAN
2
XBLUE Networks
17
Page 18
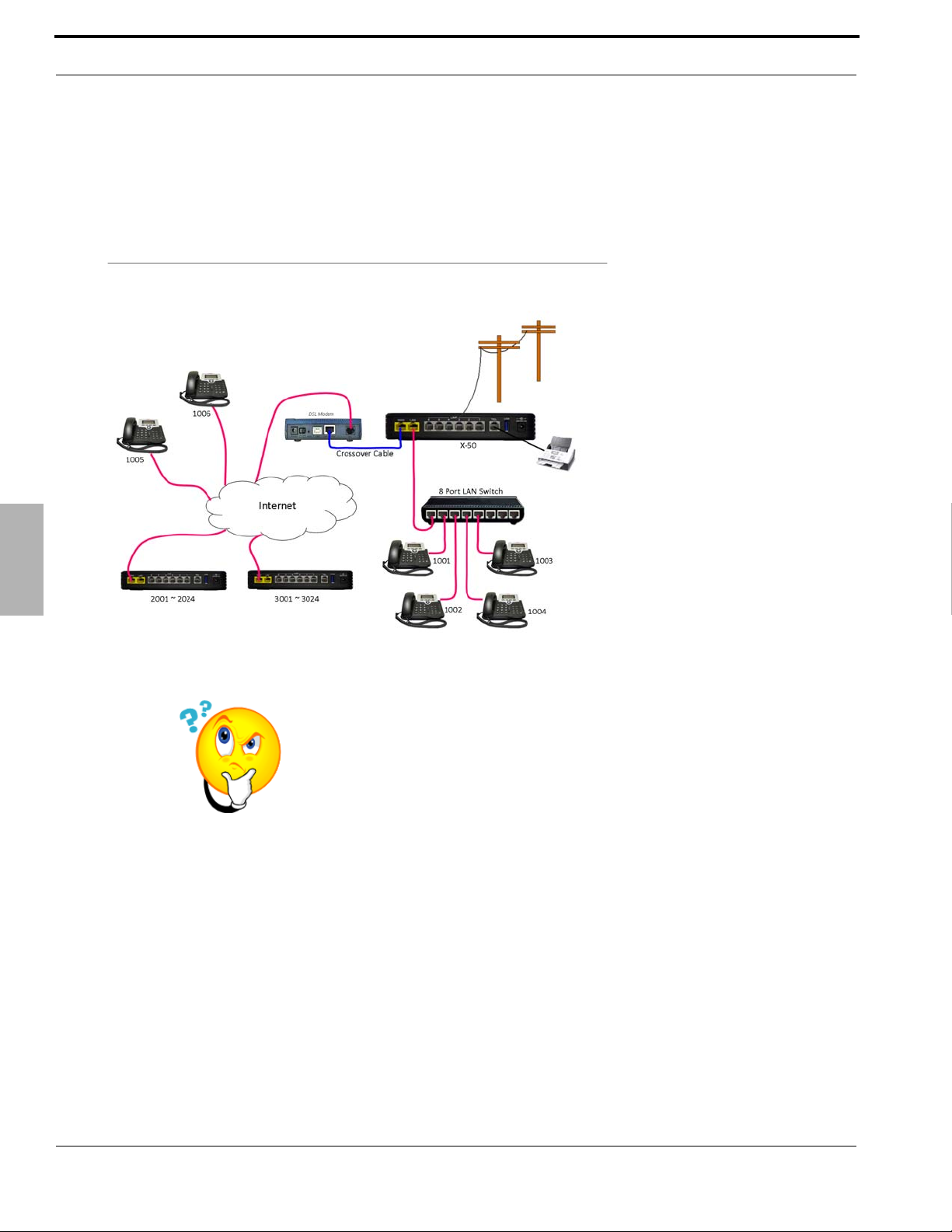
LAN vs. WAN
Remote telephones are directed
to the static IP Address of the
WAN port, which will have a
Class A or Class B IP Address.
Once registered, the WAN port
of the X-50 keeps the
telephone endpoints active by
sending “keep alive” packets to
each of the remote telephone
endpoints.
The Remote telephone should
set the Session Timer to 20
seconds.
What does that say?
The Internet Service Provider (ISP) will program their DSL/Cable
modem to be a bridge or a concurrent bridge allowing the X-50 VoIP
Telephone System to join the network parallel to the ISP’s DSL/Cable
modem. If needed, this also allows the X-50 VoIP Telephone System
to become the main router on the Local Area Network (LAN).
When connecting remote workers to a X-50 system, it must have a
static IP Address. When creating a voice network or “Campus
Environment”, only one of the X-50 systems must have a static IP
Address.
Any X-50 with a static Class A or B IP Address will support remote
workers, even if they are a node on a voice network.
Introduction
Remote Telephones
When connecting remote workers to the X-50 VoIP Telephone System it must have a fixed or static class A or B
IP Address. When creating a voice network (Campus Environment) the “Master” X-50 VoIP Telephone System
also must have a fixed or static class A or B IP Address. All other systems on the voice network can use Dynamic IP
addresses. This may require the ISP’s Gateway to be programmed as a Bridge or a concurrent bridge.
2
18
XBLUE Networks
Page 19
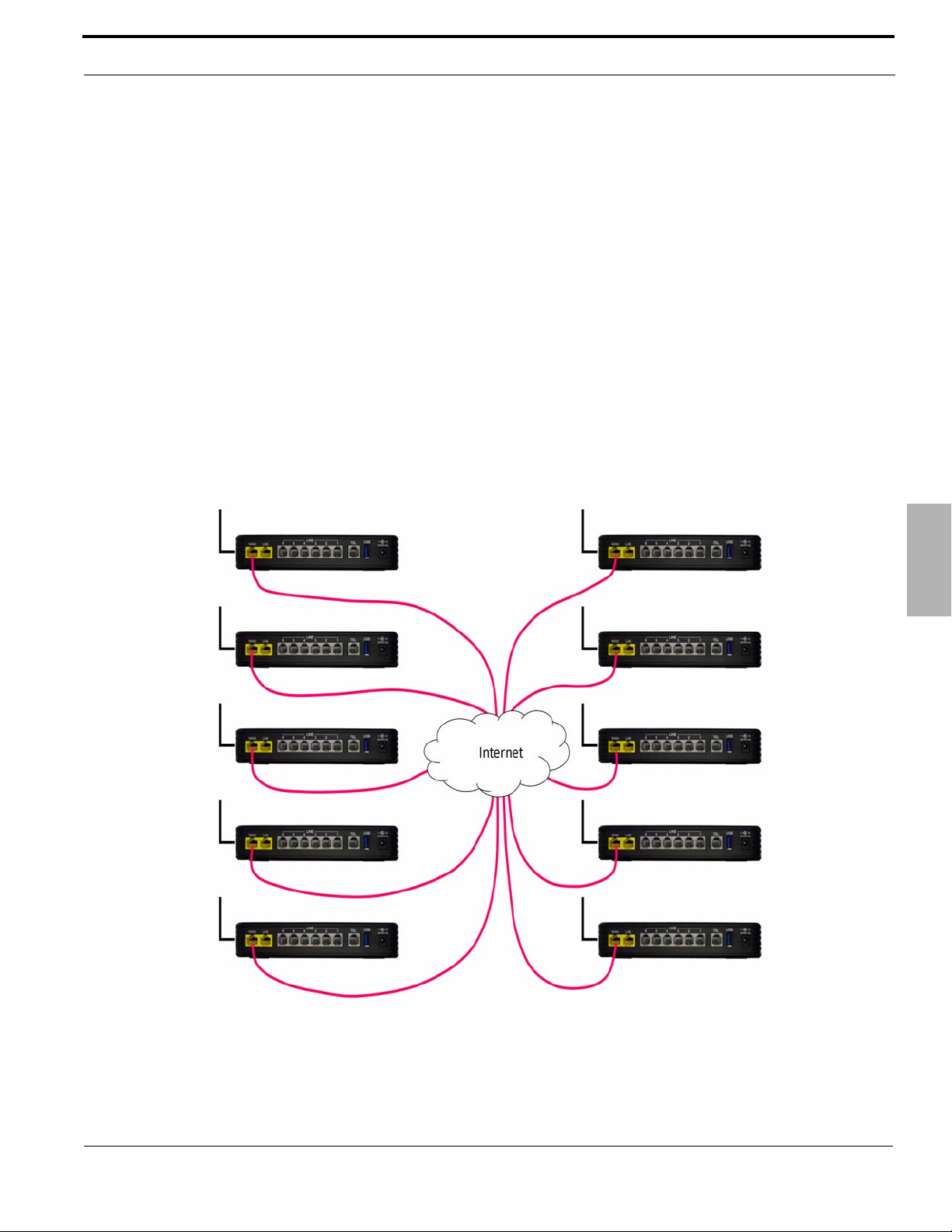
Introduction
5xxx
6xxx
7xxx
8xxx
10xx
15xx
2xxx
3xxx
4xxx 9xxx
Creating a Voice Network
Using the Internet and the WAN port, it is possible to connect multiple X-50 systems together creating one large
voice network “Campus Environment”, with 3 or 4 digit dialing between each location. To keep it cost effective, only
one X-50 VoIP Telephone System requires a static Class A or B IP Address the rest can use DHCP Addresses.
However, each location must have access to the Internet with enough bandwidth to support the number of calls to be
processed. Creating this type of voice network requires a little preplanning to ensure that there enought bandwidth
and no numbering conflicts.
Generally, it is a good idea to have a specific numbering sequence for each location. This can be as easy as routing
specifc groups of numbers, such as 100 to 149 for the “Master System”, 150 to 199 for the second location, 200 to
299 for the third location, etc., or when using 4 digit dialing the numbering plan may resemble 1000 to 1499 for the
Master System, 1500 to 1999 for the second location, 2000 to 2999 for the third location, etc. Another option is to use
a “leading Digit”, where the Master System is 1 + the extension number (1101, 1102, 1103, etc.), the second system
is 2 + the extension number (2101, 2102, 2103, etc.), the third system is 3 + the extension number (3101, 3102,
3103, 3014, etc.).
LAN vs. WAN
2
XBLUE Networks
19
Page 20

Introduction
Thingstoknowabouttheproduct
TABLE 2.1 Maximum Configuration
Things to know about the product
2
PSTN SIP Trunk SIP Extensions
6 CO Lines 8 SIP Trunks 24 SIP Extensions 1
14 Total Telephone Lines 25 Total Extensions (24 SIP and 1 Analog)
Single Line
Analog Extension
TABLE 2.2 Physical System Capacities
Capacity Interface Port Description
1 LAN RJ45 Local Area Network 10 base-T/100 base-TX
1 WAN RJ45 Wide Area Network (for remote workers or offices)
10 base-t/100 base-TX/1000 base-T Gigabit Ethernet port
1 FXS RJ11 Connected a Single Line (Analog) Telephone or FAX
6 FXO RJ11 Allowing 6 s imultaneously Telephone Calls
1 USB USB USB Interface to create a network or centralized printer
1 Wireless 802.x LAN - 802.11a, 802.11b, 802.11g and 802.11n
24 SIP RJ45 SIP telephone endpoint devices
TABLE 2.3 System Software Capacities
Capacity Interface Port Description
8 SIP Trunks Interface with up to 8 SIP Trunks
4 AA & VM Interfaces with Auto Attendant and Voice Mail with 32 hours of storage
24 LAN/WAN RJ45 Telephone Endpoints - Non Blocking
9 WAN RJ45 Additional Office to Office - Voice Network (total 10)
14 Concurrent Telephone Line Calls (PSTN and SIP Trunks)
40 Call Routing Tables
25 Voice mailboxes associated with a telephone endpoint
40 Virtual Mailbox Extension without telephone endpoint
10 Single Digit Dialing Menus with Menu Tree Routing
10 Day - Outgoing System Greeting (OGM)
10 Lunch (Noon) - Outgoing System Greeting (OGM)
10 Night - - Outgoing System Greeting (OGM)
10 Holiday - Outgoing System Greeting (OGM)
10 Temporary - Outgoing System Message (OGM)
20
XBLUE Networks
Page 21
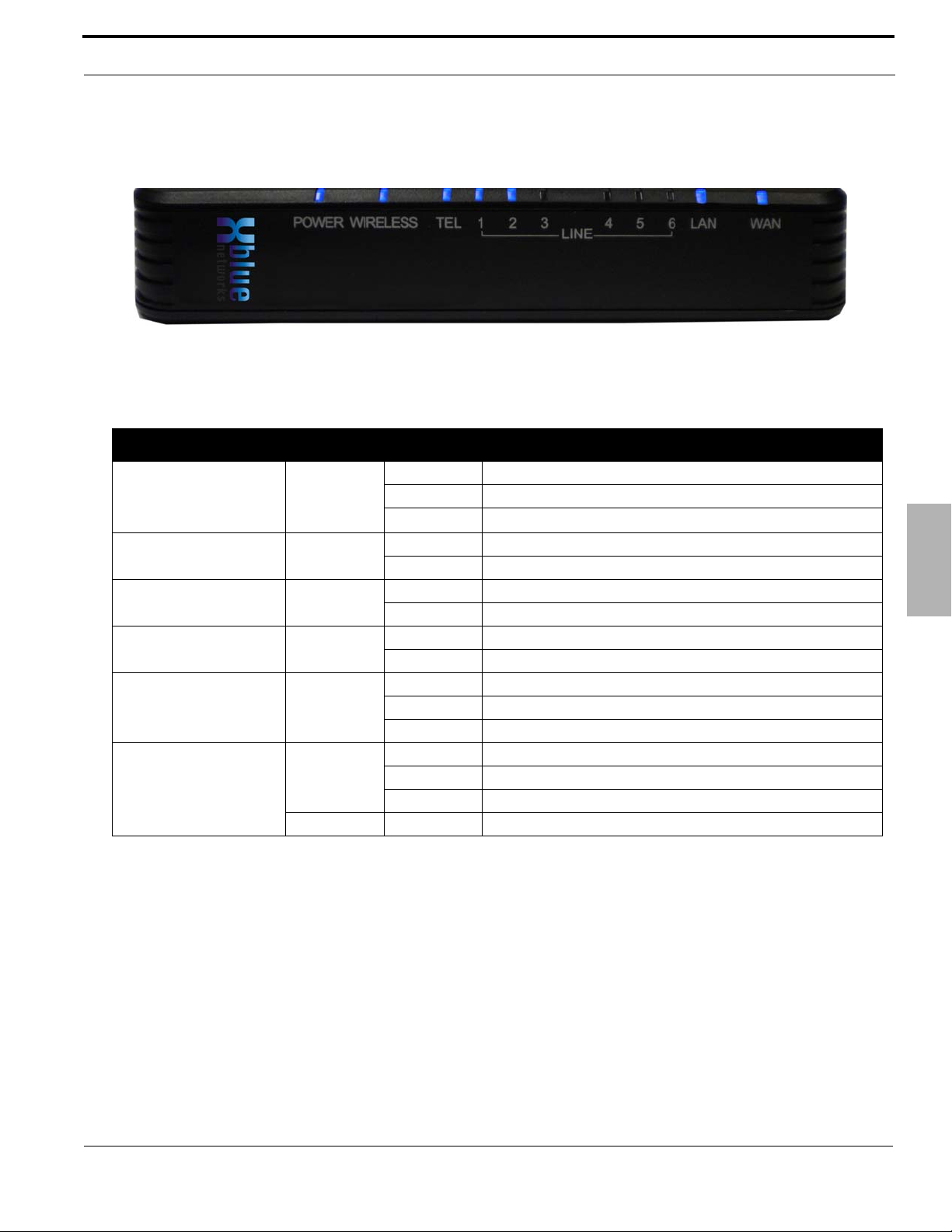
LED’s on the X-50 System
TABLE 2.4 LED Function
LED Name LED Status Description
Power Blue On Power is On
Off Power is Off
Flashing
Wireless Blue On Wireless LAN initialization successful
Off Wireless LAN not operational
“TEL” Port
SLT Telephone
Line (1 - 6) Blue On PSTN Line is Busy
LAN Blue On LAN is Connected
WAN Blue On WAN Conn ected
Blue On Single Line Telephone is Busy
Off Single Line Telephone is Idle
Off PSTN Line is Idle
Off LAN is not Connected
Blinking Active LAN Traffic
Off WAN is not Connected
Blinking Active WAN Traffic
Red ON Ping the Default Gateway fail or DHCP fail
X-50 is rebooting
Introduction
Things to know about the product
2
XBLUE Networks
21
Page 22

Things to know about the product
Introduction
Notes:
2
22
XBLUE Networks
Page 23
2 System Specifications
TABLE 2.1 System Specification
Feature
Main Processor 400 MHz Dual Core MIPS Processor Broadcom BCM6369
Processor SDRAM External 64 MB
Processor Flash ROM External 16 MB
Supplementary Processor 1x DSP Mindspeed M82351
System Flash (Voice Mail) 512 MB
Giga WAN PHY Chip Broadcom BCM5481
Standards IEEE 802.11 a/b/g/n, IEEE 802.3
Ports 1 - WAN, 1 - LAN, 1 FXS and 6 FXO
Buttons Reset, WIFI On/Off and WPS
Ports RJ-45 and RJ-11
LED’s Power, Wireless, Telephone, Lines (6), LAN and WAN
EMI/EMC FCC Part 15 Class B
TABLE 2.2 Environmental
Operating Conditions Specification
Operating Temperature 32° F to 95 ° F
Storage Temperature 32° F to 95 ° F
Operating Humidity 10% to 80% - Non Condensing
Storage Temperature 10% to 80% - Non Condensing
System Power 12 Volts - 1.5A
XBLUE Networks
23
Page 24
System Specifications
2
TABLE 2.3 IP PBX Configuration
Quantity Interface Connector Description
6 FXO RJ11 Allowing 6 simultaneously sessions
1 FXS RJ11 For analog (single line) telephone
1USBUSB Print Server
1 LAN RJ45 10/100 Local Area Network
1 WAN RJ45 100/1000 Wide Area Network (for remote workers or offices)
TABLE 2.4 WiFi
Connector Speed Port Description
Wireless 802.11 b, g and n LAN Port A Local Area Network allows network devices to share and access files
through a wireless connection using 802.1x protocol. Gener ally, a LAN uses
one DHCP Server, it is “small” in size (geographically) like a home or office,
and it does not require any external ISP to transmit data between
endpoints.
Antenna 5dbi single pole
TABLE 2.5 Default LAN and WAN Ports
IP Address Description
LAN 192.168.10.1
WAN DHCP The WAN port is set to DHCP and will connect to an existing network and
Do not use IP Address 192.168.1.254 - it is reserved for the X-50’s DSP.
Using this port will result in erratic operation.
can be set to DHCP, Static or PPPoE.
TABLE 2.6 Physical Connectors
Connector Speed Port Description
RJ45 10/100/1000
BaseT
RJ45 10/100 BaseT LAN Port A Local Area Network (LAN) allows network devices to share and access
WAN Port A Wide Area Network (WAN) allows devices to share and access files
through a series of wires known as a “Network”. A WAN is used with
multiple locations, and has no physical boundaries. It is actually possible to
have a WAN that spans the globe.
files through a series of wires known as a “Network”. Generally, a LAN uses
one DHCP Server, it is “small” in size (geogr aphically) like a home or o ffice,
and it does not require any external ISP to transmission data between
endpoints.
24
XBLUE Networks
Page 25

System Specifications
TABLE 2.7 X-50 System Capacities
Capacity Interface Port Description
6 FXO RJ11 Allowing 6 PSTN lines and simultaneously sessions
1 FXS RJ11 Connected a Single Line (Analog) Telephone
1 USB USB Connect a printer to be shared by devices on the LAN
1 Wireless LAN LAN - 802.11b, 802.11g and 802.11n
1 LAN RJ45 10/100 Local Area Network
1 WAN RJ45 100/1000 Wide Area Network (for remote workers or offices)
8 SIP Trunks Interface with up to 8 SIP Trunks
4 AA & VM Interfaces with Auto Attendant and Voice Mail allowing it to process up to 4
simultaneous calls, which is shared with all telephone lines and endpoints
24 LAN/WAN RJ45 Telephone Endpoints - Non Blocking
10 WAN RJ45 Office to Office - Voice Network (Campus Environment)
14 Concurrent Calls (Telephone Lines and SIP Trunks)
40 Call Routing Tables
25 Telephone Endpoint voice mailboxes with Personal OutGoing Message (OGM)
40 Virtual Voice mailboxes with personal OutGoing Message (OGM)
10 Single Digit Dialing Menus with Menu Tree Routing
10 Day time OutGoing Message (OGM)
10 Lunch (Noon) - OutGoing Message (OGM)
10 Night time OutGoing Message (OGM)
10 Holiday OutGoing Message (OGM)
10 Temporary Outing Message (OGM)
2
TABLE 2.8 VoIP & Signalling Protocols
Signaling Documented Protocol Description
G.168 ITU-T G.168 Echo Canceller was designed and used to address and standardize the
performance of echo cancellers in the PSTN.
G.711 ITU-T G.711 Highest Bandwidth/Lowest Compression - best voice quality. A voice
encoder that compresses 64K bit stream to an 8K per second sampling
rate, with a typical algorithmic delay of 0.125ms. G.711 is used when
transmitting Music, FAX’es and DTMF tones because it is very reliable.
G.723.1 ITU-T G.723.1 Intermediate Bandwidth/Intermediate Compression - minimal reduction in
voice qual ity. A voice encoder that compresses voice in 30ms frames, with
a look-ahead of 7.5ms, with a typical algorithmic delay of 37.5ms. G.729a
uses very low bandwidth because it samples at 8kHz/16-bit (240 Samples
for 30ms frames).
G.729.a/b ITU-T G.729a Lowest Bandwidth/Highest Compression and least complex protocol, with a
hybrid speech reproduction quality by use of an Algebraic Code Excited
Linear Predication (ACELP) that reproduces a voice encoder that
compresses voice in 10ms frames, with a look ahead of 5ms per fr ame, and
atypical algorithmic delay of 15ms, per frame. It operates at 8k bits, and
can be used with 6.4kbits and 11.8k bits, with a marginal reduction in voice
quality.
XBLUE Networks
25
Page 26
System Specifications
2
TABLE 2.8 VoIP & Signalling Protocols
Signaling Documented Protocol Description
In/out Band RFC 2833 In/Out Band is used to define the method of transporting DTMF tones to
use on RTP connections. In-Band ar e tones that ar e “hear d” by the dis tant
party, and Out of Band tones are used for signaling.
MD5 RFC 3261 Message-Digest Algorithm 5 - is a widely used Cryptographic hash function
(security) that uses 128 bit hash value.
QoS RFC 2990 Quality of Service assigns different priorities to different data packets.
Voice, for example, will receive a much higher priority than non-voice
traffic, so it receives the highest priority. Therefore, QoS is used to
prioritize specific packets, su ch as voice, within a packet -switched network.
However, it does not guarantee voice quality.
T.38 ITU-T T.38 T.38 is the standard for transporting FAX transmissions, between G3 Fax
devices, over an IP Network.
RTP RFC 1889, 3550 Real-time Transport Protocol provides end-to-end network transport
functions suitable for applications transmitting real-time data, such as
audio, video, or simulation data, over multicas t or unicast network se rvers.
RTP is a standardize protocol for delivering audio and video over the
Internet.
SDP RFC 2327 Session Description Protocol is purely a protocol that negotiates between
two endpoints to allow them to agree on a media type and format. It is
intended for describing multimedia sessions, and to on a wide range of
networks and networking environments.
SIP V2 RFC 3261 Session Initiated Protocol is an applications layer control (signaling)
protocol that is outlined in the “Internet Official Protocol Standards”
document number RFC 3261.
ToS RFC 791, 1060, 1122, 1123,
1195, 1247, 1248, 1349,
2474, 3168
DTMF RFC 4733
AF Class RFC 2597 One part of QoS, is Assured Forwarding Classes. This allows the
EC RFC 3246 Expedited Forwarding has the characteristics of low delay, low loss, and
The Type of Service octet is part of the Internet Protocol header that
specifies the priority of the attached datagram (message).
®
Dual Tone Multi-Frequency Tones - also known as touch tones
protocol for transmission of DTMF tones transmitted over a packet
switching network.
administrator to divide the IP Packets into one of 12 different Classes. In
the event that the network becomes congested, the packets with the
highest Drop rate will be dropped.
low jitter, making it suitable for Voice, Video and other real-time services.
- Defined
26
XBLUE Networks
Page 27
System Specifications
TABLE 2.9 Internet Protocol
Protocol Documentation Description
IP Address RFC 950 Defines the standards used to divide Class A, B and C using Subnets.
ARP RFC 826, 3315 Address Resolution Protocol - allows devices to find a “host” device using
the network layer (MAC Address).
RARP RFC 903 Reverse Address Resolution Protocol - allows devices to find a “host”
device using the network layer (MAC Address).
CHAP RFC 1994 Challenge-Handshake Authentication Protocol - Negotiating protocol used
with PPPoE. Also see MSCHAP and PAP
MSCHAP RFC 2433, 2759 Microsoft’s version of CHAP that allows mutual au then tica tion between
peers, by piggybacking challenge and response packets on a successful
packet.
PAP RFC 1334 Simple method for the peer to establish its identity using a 2-way un-
encrypted handshake. Passwords are sent in ASCII format with no
encryption. Also see CHAP, and MSCHAP.
DHCP
Client
DHCP
Server
DNS RFC 1912 A Domain Name System is the “Phone Book” for the Internet. It tra nslates
HTTP RFC 2616 Hypertext T r ansfer Protocol - is one of the communications protocols used
ICMP RFC 792 Internet Control Message Protocol is one of the core protocols within
IP RFC 791 Internet Protocol allows devices to communicate over a package-switched
NAT RFC 3022 Network Address Translation allows multiple hosts, on one private
NAPT RFC 2663 Network Address Port Translation increases the efficiency of NAT by
PPPoE RFC 2516 Point to Point over Ethernet allows users to “Virtually” create a direct
SNTP RFC 1305 Simple Network Time Protocol allows devices packet-switched networks to
NPT RFC 867, 868 Network Time Protocol ensures that the time is synchronized all along the
TCP RFC 793 Tr ansmission Control Pr otocol provides the r eliability that In ternet Protocol
RFC 2131 - 2132 Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol is used by client devices, to obtain
the correct settings, when joining a network.
RFC 2132 Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol is used by server devices, to obtain
or assign the correct settings, when joining a network.
“Human Relatable” names such as www.xbluenetworks.com into the
numeric IP Address. The DNS can be a local or remote server, and it is a
essential part of today’s Internet.
to transfer information over a packet-switched network, such as an
Intranet or the Internet. Typically, HTTP (at default using port 80) initiates
or receives a request/ response from a client to/from a server.
Internet Protocol (IP). This protocol is a reactionary protocol only
responding to error messages that are received.
network. This protocol provides an unreliable network, and makes no
guarantees about sending or receiving a data packa ge; it is a “best Ef fort”
protocol. Therefore, other protocols such as “TCP” were created to make
data transfer more reliable.
network, to access the Internet using one public IP Address.
translating the “transport identifier”, allowing a private host to multiplex
into the transport identifiers to appear as a single Public IP Address.
connection between two devices over an Ethernet network.
synchronize their time from a specific location.
Packet Switching Network.
(IP) does not, making it suitable for applications such as File T r ansf er and
E-mail.
2
XBLUE Networks
27
Page 28
System Specifications
TABLE 2.9 Internet Protocol
Protocol Documentation Description
Telnet RFC 2946 TELNET is a reliable connection-oriented transport protocol, which is
Client/Server based. At default TELNET uses Port 23.
TFTP RFC 2349 Trivial File Transfer Protocol is a very basic and simple protocol which is
loosely based on the FTP protocol.
UDP FRC 768 Using User Datagram Protocol networked computers can send short
messages known as datagrams. Although the delivery of a UDP packet is
faster it is not as reliable as TCP packets.
RIP v1, v2 RFC 1058, 2453 Routing Information Protocol used in Local and Wide Area Networks to
limit the number of hops allowed in a path from source to destination.
Maximum number is 15 hops.
CLIP Calling Line Identification Presentation
2
28
XBLUE Networks
Page 29
3Feature Description
SystemFeatureDescriptionTab le
TABLE 3.1 VoIP Module Features
Feature Page Feature Page
Access Control page 31 Least Cost Routing (Call Routing) page 38
Account Codes (Traveling COS) page 31 Line Group Assignment page 39
Alarm (Station) page 31 Live Call Record page 39
Alternate Attendant page 31 Meet Me Page page 39
Announcement Mailbox page 31 Message Waiting Indication page 39
Answer Position page 32 Music on Hold page 39
Automated Attendant (Receptionist) page 32 Mutual Mailboxes (Group Mailbox) page 39
Automatic Daylight Savings (Internet) page 32 Navigation Keys (Buttons) page 39
Automatic Hold page 32 Night Service (Automatic day/night) page 40
Automatic Line Select page 33 Numbering Plan page 38
Automatic Provisioning (PnP) page 33 Off Hook Preference page 40
Automatic Route Select
Backlit Display page 33 One Touch Record page 40
Basic Calling page 33 Paging (All Call and Zone) page 40
Busy Call Back page 33 Pause page 41
Busy Lamp Field (Busy Extension) page 33 Phantom Mailbox (Extension) page 41
Call Abandon page 33 Phonebook (Personal) page 41
Call Forwarding (6 types) page 34 Phonebook (Public) page 41
Call Operator page 34 Power Fail Transfer page 41
Call Park page 34 Programmable Buttons (Telephone & Sidecar) page 41
Call Pickup - Group page 35 Redial page 41
Call Restriction page 35 Registration Server page 42
Call Routing page 35 Remote (Administration) Management page 42
Call Waiting page 35 Service Mode page 42
Caller ID page 35 SIP IP Trunk (Maximum 8) page 42
Class of Service page 35 Soft (Interactive) Keys page 42
Conference page 36 Speed Dial page 42
Day & Night Service Mode page 36 Station Lock page 42
Daylight Savings Time page 36 Station Message Detailed Recording page 43
(Call Routing) page 33 Outgoing Call page 40
XBLUE Networks
29
Page 30
Feature Description
TABLE 3.1 VoIP Module Features
Feature Page Feature Page
Default Setting page 36 System Speed Dial page 42
Direct Inward Dial page 36 System T ime & Date page 43
Direct Inward System A ccess page 36 Time and Date in Display page 43
Distinctive Ringing page 37 Toll Restriction page 43
DNS Client page 37 Transfer page 43
Emergency Call page 37
Extension Password page 37 Traveling Class of Service page 43
E-mail Delivery of Voicemail Messages page 37 Trunk Group page 43
FAX Detection page 37 Uniform Distribution/Hung Group (UCD) page 44
Flexible Numbering Plan page 38 UCD - Agent Login/Logout Call Reroute page 44
X-50 to X-50
Hot Dial Keypad page 38 Voice Mail page 44
Last Number Redial page 38 Wizard Setup page 45
page 38 Virtual Mailbox (Extension) page 44
3
30
XBLUE Networks
Page 31

Feature Description
AccessControl‐Browser
For security, the X-50 is password protected with a programmable port, making it more secure. There are th ree
different password levels, User, Administrator, and Support.
TABLE 3.2 Password levels
User Name Password Description
admin2583 000000 Unrestricted access to all programming parameters
user user View configuration settings and statistics
support support Run Diagnostics with technical support engineer on the phone
Only one Administrator can log into the X-50 at one time. Additional attempts to enter the administration area will be
denied until the original administrator has exited and three minutes have elapses.
AccountCode
Also known as “Traveling Class of Service” - This allows authorized users to make calls on restricted extensions. The
systems recognizes the user when they enter a code and their password, and brings their less restrictive class of
service to the new location. The user’s Class of Service remains active for 60 seconds after the call is disconnected and
then it returns to the original Class of Service.
Access Control - Browser
Agent(UCD)Logon/Logoff
Agents (extensions) may dial a code, which temporarily takes them out of all UCD groups. Once the agent logs off,
they will not receive any additional incoming UCD calls. This can be very helpful when an agent is out of the office or
out to lunch. When the agent returns, they dial a code to log into all UCD groups. Once logged in, they start receiving
UCD calls.
Alarm
Each X2020 connected to the X-50 VoIP Telephone System can set up to three telephone alarms, which can be
programmed to play once or set to always. The user can select between 11 (0~10) different ring tones. After the
alarm is reached, it can repeat up to 10 times at an interval of once every 1 to 5 minutes.
AlternateAttendant
A second extension may be programmed as the Alternate Attendant. The alternate answering position serves as a
back up position to the primary attendant. Telephone line ringing will forw ard to the altern ate answering position after
the preprogrammed ring alternate position time.
AnnouncementOnlyMailbox
Any physical or virtual voice mailbox can be programmed to be an announcement only mailbox. An announcement
only mailbox may be used to make common announcements such as business hours, directions, mass schedules for
Church, etc. These mailboxes can be accessed from the Automated Attendant or the Attendant can transfer a call
directly to the announcement. After the announcement plays the call is disconnected.
3
XBLUE Networks
31
Page 32

Feature Description
AnswerPosition
Each of the six analog (PSTN) and eight SIP trunk lines can be programmed to ring at the Operator, Auto
Attendant, Extension or UCD hunt group for both day and night. When set to operator - callers will ring the
extension that is progra mmed as th e oper ato r in the sys tem. When set to auto at tendant - callers will ring one of
the four auto attendant ports and be answered with the appropriate day, lunch, night, holiday or temporary
outgoing message. When set to Extension - callers will ring the entered extension. When set to Universal Call
Distribution (UCD) Group - all members of the group (up to 25 members can be entered into each group) will
ring.
AutomatedAttendant(Receptionist)(AA)
3
Answer Position
The system comes standard with an integrated four port Automated Attendant (R e cept ionist) whic h can perform
up to four simultaneous tasks. All telephone lines, extensions and virtual mailboxes share these four ports. When
the Answer Position, for a telephone line, is set to “Automated Attendant” the call is immediately answered and is
played a customizable prompt. In addition, there are 10 single digit dialing menus that can be used to route
callers. Each menu has the ability to play five; day, lunch, night, holiday and temporary outgoing messages
(OGM) based on the time of day or day of week. The X-50 VoIP Telephone System also supports single digital
dialing and menu trees.
AutomaticDaylightSavings(NTP)
When the X-50 VoIP Telephone System is connected to the Internet it will automatically synchr onize the dat e an
time using Network Time Protocol (NTP). Therefore, when time changes for daylight savings, the system will
automatically change.
AutomaticHold
Automatic hold allows extension users to press a preprogrammed extension button (DSS) to announce a call
without pressing hold first. The telephone line call is automatically placed on hold. This allows busy extension
users, such as the attendant, to answer multiple calls very quickly.
32
XBLUE Networks
Page 33

Feature Description
AutomaticLineSelect(HotLine)
Users may select how their idle extension functions when lifting the handset or pressing the speaker button. An
extension can be set to access a specific outside line, a line group, or intercom (ICM) automatically when going off
hook or pressing the speaker button. In addition, Users can program a timer from 0 to 8 second, delay before the off
hook action is taken.
AutomaticProvisioning
The system comes standard with WAN Management Protocol (TR-069) which allows the system to use AutoConfiguration Server (ACS) to preform auto-configuration, provision, collection, and diagnostics.
AutomaticRouteSelect(ARS)
See Call Routing
BacklitDisplay
The X2020 SIP Telephone endpoint has a 6 line, 128 x 64 backlit display, which can be programmed go into sleep
mode, or stay lit.
BasicCalling
There are two different types of calling; Intercom which are calls within the system and telephone line to an external
location. When a dialed number is within the system numbering plan, it is considered an intercom call. If the number
is not within the system numbering plan, but matches an entry in the routing tables the call will be routed over the
appropriate telephone line or line group. Related Features: Numbering Plan and Call Routing.
BusyCallBack
Busy Call Back allows the user to dial a code when they call a busy extension to queue up for a call. When the called
extension hangs up, the calling extension will ring, when calling extension lifts the handset, the called extension will
being ringing.
BusyLampField(BLF)
Busy Lamp Field also known as Direct Station Select (DSS) is a visual indication, usually a LED on a preprogrammed
button, that shows when an extension or telephone is busy. The associated LED will be lit solid indicating that the
extension or telephone line is busy.
Automatic Line Select (Hot Line)
3
CallAbandon
Call Abandon is a timed signal which is sent from the telephone company to the system to indicate that a telephone
line had disconnected. This is especially helpful when callers disconnect the call while they are on hold. The system
receives a timed disconnect signal, which matches the preprogrammed Call Abandon Time, from the telephone line
provider and forces the telephone line on-hook.
XBLUE Networks
33
Page 34

Feature Description
CallForward
At default, all extensions are forwarded to voicemail. However, they can also use several other types of call
forwarding; Busy, Direct, Do Not Disturb, Follow me, Call forking, and Remote (External). These can be
programmed using the web interface or by dialing the call forward code.
Busy Call Forward
Busy Call Forward, forwards all incoming calls to the forwarded destination only when the extension is busy.
Extensions that are busy forwarded will not ring when a second call is presented to them. Howe ver, an alert tone
is heard indicating that a new call is being routed to the forwarded destination.
Direct (Always) Call Forward
3
Call Forward
Direct Call Forward, forwards all incoming calls to the forwarded destination as soon as it is presented to the
extension. An alert tone is heard indicating that a new call is being routed to the forwarded destination.
Do not Disturb Call Forward
DND call forward, forwards all incoming calls to the forwarded destination only when the extension is in DND. If
the extension is put into DND and it is not DND forwarding, callers will get a busy signal.
Follow me Forward
The Follow Me Forward, feature allows internal extension users to re-forward their extensions to a new location.
This is especially helpful when waiting for an important telephone call but must go to another destinat ion, such as
an impromptu meeting. An alert tone is heard indicating that a new call is being routed to the forwarded
destination.
Call Forking Forwarding
Call Forking is used to ring two destinations at the same time. This feature will work for two extension number,
without a SIP Trunk, but with a SIP Trunk, it can ring an extension and one or two external numbers.
Remote (External) Call Forward
Remote (External) Call Forward, allows extension users to forward their incoming calls to a remote destination
such as a cellular or home telephone number. The extension user can change their forwarded destination from
their extension.
CallOperator
The system supports both a primary and secondary operator which can be accessed from any SIP telephone
endpoint or the analog port by dialing “0”. Any extension, SIP telephone endpoint or FXS (analog port) can be
assigned as the primary and secondary operator. The Operators are defined in the Numbering Plan.
CallPark
Park often called orbit, is a way of placing a call on hold where anyone within the system can access that call by
dialing a park pickup code. The Park location is usually the same as the extension number.
34
XBLUE Networks
Page 35

Feature Description
CallPickupGroup
Any extension SIP telephone endpoint can dial star “*” to pick up a telephone line that is ringing at a different
extension. If multiple telephone lines are ringing the oldest ringing line will be accessed.
CallRestriction
When making a telephone line call all digits dialed will be compared to the telephone’s Class of Service and restriction
table. The Call Restriction table allows the administrator to enter a range of digits (From - To), Trunk Access, Class of
Service (COS). The X-50 VoIP Telephone System has eight classes of service zero (0) which has no restrictions and
seven which is the most restrictive. The Call Restriction Table is made up of two tables an allow table and a deny table.
Each entry into either table is associated with a Class of Server. The combination of these entries make up the allow or
deny table. There are 40 call restriction tables and they work in the following way:
1. If there are no entries in either the allow or deny tables, all calls are allowed. If there are entries in either table the calls are evaluated in the following order:
2. Deny Table - If the dialed digits match an entry in the deny table the call is denied. If the dialed digits do
not match an entry in the deny table, the call is sent to the allow table.
3. Allow Table - If the digits match an entry in the allow table, the call is allowed. If the digits do not match an
entry in the allow table, the call is denied.
Call Pickup Group
CallRouting
When making a call all digits dialed will be compared to the rules entered in the Call Routing Table. The Call Routing
Table is built using up to 40 different routing rules. Each call routing condition (rule) directs the dialed digits to a
specific route and is made up of eight parameters, which include the “From” and “To” dialed digits, “Minimum” and
“Maximum” number of digits to evaluate, number of digits to “Delete” or “Insert” before dialing the numbers over the
“Destination” route (line group).
The call routing table is used to route calls over a v oice network, which allows the administrator to route calls the most
inexpensive way. F or example, in a v oice network with locati ons in Boston, Chicago, and San Francisco calls with a 617
area code, can be routed to the Boston location, thus avoiding toll charges.
CallWaiting
The Call Waiting Flash supports the CO line flash, which allows extension users to pick up a call after receiving a call
waiting indication from the telephone line provider.
CallerID
The system is equipped to received caller ID (requires a subscription) from the telephone line provider and will at
default passed the information to a ringing telephone (SIP or Analog) extension.
3
ClassofService
Each extension in the system is assigned one day and one night class of service of service, which determines the
extension’s dialing privileges. There are eight different Classes of Service which are defined in the Call Restriction
Table. A Class of Service (COS) of seven has the most restriction whereas a COS of zero (0) has no restrictions.
XBLUE Networks
35
Page 36

Feature Description
Conference
The systems can conference, join together, multiple Telephone (PSTN or SIP) Lines or extensions, or a
combination of both, to the maximum of three connections so that multiple parties can speak together
simultaneously.
Day&NightServiceMode
The system can run in either day or night mode and can be programmed to automatically switch between day
and night mode.
DaylightSavings
Conference
3
The system supports manual or automatic synchronization of daylight savings. When set to automatic the system
will automatically change from standard to daylight savings time. When set to manual, the administrator will have
to enter the update manually.
DefaultSetting
Using the “Restore Default” feature found in “Management” the administrator can reset the system back to
factory default. This will also reset some of the SIP Te lephone endpoint parameters such as Line Keys, Call
Forward Settings, Auto Answer, Phone Lock and Call waiting. Howev er, it does not reset any system prompts t hat
have been rerecorded.
DirectInwardDial(DID)
Using the SIP Trunks, the system can support up to 50 Direct Inward Dial (DID) numbers. These numbers share
with the connected (up to eight) SIP trunk positions. The system has a special DID Ring Table which allows the
administrator to direct the incoming DID numbers to a specific extension, Auto Attendant, UCD group or voice
mailbox. In addition, some DID can also be programming as Direct Outing Dialing (DOD) which can be
programmed to send the DID number as its caller ID.
DirectInwardSystemAccess(DISA)
DISA allows an incoming caller to enter a code into the auto attendant to gain access to system resources. At
default this feature is disabled. Enabling this feature could cause unw anted long distance charges, which are the
sole responsibility of the owner of the system.
DirectTelephoneLineAccess
Each extension can program any programmable button to be a direct access to a PSTN or SIP Trunk telephone
line.
36
XBLUE Networks
Page 37

Feature Description
DistinctiveRinging
Telephone Line
Each telephone line (PSTN or SIP Trunk) can be programmed to ring with one of eleven different ring tones.
Extension
Each SIP Telephone endpoint can be programmed to ring with one of eleven different ring tones.
DomainNameServer(DNS)
A Domain Name Server is the “Phone Book” for the Internet. It translates “Human Relatable” names such as
www.google.com from the numeric IP Address 64.233.187.99. The DNS can be a local or remote server, and it is a
essential part of the Internet.
EmergencyCall
The system, regardless of Class of Service, Call Routing, Call Restriction or Phone Lock programming, will not block
any of the five emergency numbers that are programmed into the Emergency Call Table. At default, 911 is
programmed into the table.
Note:
Numbers in the Emergency Call table cannot conflict with any numbers in the numbering plan. For example, when
using 3 digit extension numbers do not use “911” as one of the extensions.
ExtensionPassword
All extensions in the system are assigned a password that is used to access voice mail and when using the phone lock/
unlock feature.
E‐mailDeliveryofVoicemailMessages
The voice mail has the ability to send a new voice mail message to a users E-mail address. The systems uses Simple
Mail T r ansport Protocol (SMTP) to send the voice mail message as a standard WAV file, which can be reviewed by most
smart phones or multimedia Personal Computers.
FAX/ModemDetection
Distinctive Ringing
3
The X-50 supports both FAX (T.38) and Modem detection and auto-fallback to G711, from an analog telephone line to
the Single Line Port.
Flash
The Flash key (or hook switch) on an analog telephone (Single Line Telephone) connected to the system can be used
to activate features such as placing a call on hold, picking up the held call, or when transferring a call to another
destination.
XBLUE Networks
37
Page 38

Feature Description
FlexibleNumberingPlan
The X-50 is preprogrammed with a default numbering plan which may be changed to suit customers’ needs.
When changing the numbering plan it is important to remember that the numbers entered cannot conflict with
the numbers entered in the Emergency Call Table.
TABLE 3.3 Default Numbering Plan
Description Default Numbers Configure
Start extension number 101
Flexible Numbering Plan
3
End extension number 125
FXS Phone Extension 125
Operator speed-dial number 0 Day/Night Alternate Day/Night
AA/Voicemail Service Number 450
Start Virtual Extension Number 830
Start PSTN Line number 701
Start IP Trunk Line Number 711
Start Trunk Group Number 80
All Paging number 400
All Paging Range LAN/WAN/Both
Paging Group Start Number 401 (1) 401, (2) 402, (3) 403
UCD Group Start Number 430 (1) 430, (2) 431, (3) 432, (4) 433
System Speed Dial 600 600 through 699
Start Call Park Number 731
X-50
to X-50
Each X-50 VoIP Telephone System can be one of ten systems that creates a voice network. Once connected,
extensions will be able to dial directly to extensions on the network. For example, if an extension (111) in Boston
wanted to call an extension (211) in San Francisco they would dial 211. In the call routing table 211 will be
directed to the San Francisco Gateway and the call will be connected. Similarly, telephone line calls can be routed
to remote gateways for cost effective call processing.
HotDialKeypad
The X2020 telephone endpoints support hot dial keypad dialing, which allows a user to dial a telephone number
without lifting the handset or pressing the speaker button.
LastNumberRedial
Last Number Redial also known as Redial is used to press one button for quick access to the last thirty numbers
dialed from that extension.
LeastCostRouting
See Call Routing
38
XBLUE Networks
Page 39

Feature Description
LineGroup
Each telephone line in the X-50 is assigned to one of four line or trunk groups, which are used to group similar trunks
together. For example, all PSTN lines in group 1 and SIP trunks in group 2, etc.
LiveCallRecord
Also known as One Touch Record feature, which allows extension users to record the current conversation. Live Call
Record is extremely helpful for remembering telephone numbers or addresses when a pen and paper are not readily
available. The recording is placed in the user’s personal mailbox so that they may listen at a more convenient time.
This feature works with local (LAN) and remote (WAN) authenticated X2020 telephones.
This feature may violate privacy laws if used in a manner that is inconsistent with requirements of these laws.
Manufacturer assumes no responsibility with regard to the use of this feature. It is provided for the virtue of ethical
use only. The User is responsible for using this feature appropriately considering all applicable laws.
MeetMePage
Meet me page allows an extension user to dial a code from any extension within the system and be connected to the
person that just completed a page. Once the call is established the paging port is released, and the two parties will
converse privately.
MessageWaitingIndication(MWI)
Whenever a new voice mail message is left of for a SIP telephone endpoint the light bar above the LCD Display will
flash rapidly and the display will update to indicate that there is a message.
MusiconHold
The system has a prerecorded music on hold file that plays whenever a telephone line or SIP trunks is placed on hold.
MutualMailboxes(GroupMailbox)
A Mutual Mailbox is a special mailbox that can appear on multiple telephone extensions. This allows a group of
extension users to share access to the same mailbox. When a new message is left in the mailbox, all extensions with
the special mailbox button will light, indicating that there is a new voicemail message.
NavigationKeys
Line Group
3
The X2020 come equipped with “cell phone like” navigation keys, which ar e used to scro ll through f eatures, list s and
programming parameters. They allow t he user to go up, down, left, right, and the center key is used to select, say OK,
or confirm the parameter entry.
XBLUE Networks
39
Page 40

Feature Description
NightService
The X-50 VoIP Telephone System can operate in two modes; day service and night service. Night service can be
used to change the extension Class of Service as well as the system ring scheme and Auto Attendant message.
Each extension is assigned a day and a night class of service, which can be used to specify day and night dialing
privileges. Thus, controlling the amount of unauthorized calls placed at night.
NumberingPlan
See Flexible Numbering Plan
OffHookPreference
Night Service
3
Similar to Automatic Line Select and Hot Line, The analog (SLT) telephone and X2020 extension users have the
ability to select how their telephone will react when they lift the handset or press the speaker button. For
example, the telephone can access a specific telephone line, line group, dial a specific or group of extensions, and
even dial an outside telephone number.
OutsideCalls
Once authenticated, an X2020 telephone can dial a telephone number without going off hook, pressing the
speaker button, or accessing a telephone line. In addition, the user can press the softkey under “Backsp” to
delete a number if it is dialed incorrectly. Once the “Dial Time-out” timer expires, or the user presses the center
navigation button (Check Button” the call is sent to the X-50 for processing. The user can also press a
preprogrammed telephone line button and dial the number directly.
OneTou chRecord
Also Known as Live Call Record - Extensions have the ability record the current conv ersation. One Touch record is
extremely helpful for remembering telephone numbers or addresses when a pen and paper are not readily
available. The recording is placed in the user’s personal mailbox so that they may listen at a more convenient
time. This feature works with local (LAN) and remote (WAN) authenticated X2020 telephones.
This feature may violate privacy laws if used in a manner that is inconsistent with requirements of these laws.
Manufacturer assumes no responsibility with regard to the use of this feature. It is provided for the virtue of
ethical use only. The User is responsible for using this feature appropriately considering all applicable laws.
Paging
All Call Page
When doing an all call page, all LAN and WAN X2020 telephones (within the same subnet) that are idle will
receive the page announcement.
Zone Page
Each extension can be placed into one or more paging zones. This allows specific areas to make a page
announcement without interrupting everyone on the system. When the page zone is dialed, all LAN and WAN
X2020 telephones (within the same subnet) that are idle will receive the page announcement.
40
XBLUE Networks
Page 41

Feature Description
PauseInsertion
Pause is a momentary delay in dialing when placing an outgoing PSTN or SIP Trunk Line from a stored number such as
a speed bin. In addition, the X-50 system will automatically enter a momentary pause when an international number
is dialed. To insert a Pause when programming a speed dial bin, use either a “P” or “p”.
PhantomMailbox(Extension)
The X-50 VoIP Telephone System has 40 special phantom or virtual mailbox extensions. They are used for personnel
that do not require a physical telephone but need to be visible within the system. They can also be used as group
mailboxes allowing multiple people to share the same mailbox.
Phonebook
There are two types of phonebook, Person al and Public. The P ersonal Phonebook is for the priv ate use of the user that
enters the number and the Public Phonebook can be accessed by all authenticated X2020 telephones.
Private
Each extension has a phonebook for their exclusive use. The phonebook holds 200 numbers that are stored
alphabetically by the name and can be grouped by Family, Friends, Colleague, and VIP. In addition, if incoming Caller
ID matches one of these entries, they can be assigned to use a distinctive ringing tone.
Public
Pause Ins ertion
3
The Public Phonebook is a list that the administrator creates and maintains in a centralized location allowing all
authenticated X2020 telephones to link to the list. Each user has the ability to import the list and have access to the
numbers.
PowerFailureTransfer
In the event of a power failure, the first PS TN line will be automatically connected to the FXS port labeled “ TEL” in the
system.
ProgrammableButtons
Each X2020 telephone has the ability to program the four button labeled 1, 2 3 and 4. At default, they are the first
four PSTN telephone lines and the optional Sidecar has twenty-four (24) buttons which at default are extensions 101
through 125. Any of the buttons on the phone or the sidecar can be programmed to be feature, telephone line, speed
bin, etc.
Redial
Redial also known as Last Number Redial is used to press one button for quick access to the last thirty numbers dialed
from that extension.
XBLUE Networks
41
Page 42

Feature Description
RegistrationServer
The X-50 VoIP Telephone System acts like a registrar server for both SIP telephone endpoints and SIP trunks,
which eliminates any possibility of a numbering conflict.
RemoteManagement
The X-50 VoIP Telephone System combines both Proxy and Registrar servers in its application. For a Registrar
server, it acts as the front end to the location service for a domain, reading and writing mappings based on the
contents of the Register requests. The location service is then typically constructed by a proxy server.
3
Registration Server
ServiceMode
There are three service modes; Day, Night and Time. When the system is in day mode, the day greeting will play
and the day class of service will be referenced when an extensions dials a number. Night mode, the night greeting
will play and the night class of service will be referenced when an extension dials a number. If the system is set
to Time mode, it will automatically switch between day and night modes and the associated classes of service,
day and night.
SIPTrunk
The system can support up to 8 SIP uplink servers, known as SIP Trunks. These trunks, once authenticated, are
treated as any other trunk (telephone line) in the system. In addition, to the normal programming such as
Answer Position, Call Routing, Call Restriction, and Trunk Groups, the X-50 also supports provisioning for Direct
Inward Dial (DID) numbers over SIP trunks. SIP Trunks are also required when using the Call Forward feature
Forking.
SoftInteractiveKeys
There are four buttons under the X2020 telephone display that change their f unction, to assist the user, as they
use the telephone. For example, when the phone is idle, the left soft key shows “Menu”, which changes when the
speaker button is pressed to “NUM” and the third key shows “SPD”.
SpeedDial
The X2020 telephone has a special location with quick access for frequently dialed numbers. Unlike the
Phonebook, these numbers are stored by location number 0~9 and can be accessed by pressing the down
navigation key from an idle telephone.
StationLock
Using an extension’s password, users can lock their telephones. This helps reduce unauthoriz ed users from using
an extension that may have an unrestricted toll restriction. The use of station lock, may cause that extension to
be restricted from calling 911!
42
XBLUE Networks
Page 43

Feature Description
StationMessageDetailedRecording(SMDR)
This feature is used to monitor and report on incoming and/or outgoing telephone line (PSTN or SIP Trunk) calls and
displays it chronologically by extension number. The SMDR information stores telephone line used, extension number,
time and date, and the length of each call.
SystemSpeedDial
See Phonebook Public
SystemTimeandDate
When connected to the Internet the system uses Network Time Protocol (NTP) to synchronize the time and date. In
addition, the date and time can be set manually.
TimeandDateinDisplay
The first line on the LCD of an idle X2020 telephone shows the date and time. The Time format can be changed from
the default, “USA Time 12 Hour” to “USA Time 24 Hour” or “European 12 and 24 Hour” format. When using the
European format, the date will also change, after 1 minute, from MM/DD/YY to DD/MM/YY format.
TollRestriction
The Call Restriction Table is used to define up to eight different classes of service which is used by both SIP telephone
endpoints and SIP trunks. The Call Restriction Table is built “created” by using up to 40 different allow tables. Each
table uses a “from” digit and a “to” digit to define the approved digits. If a number is dialed that is not between the
“from” and the “to” digits, the call is denied and will not be placed.
Transfer
Calls that are answered by a SIP telephone endpoint may be transferred to another destination, such as a different
extension, voicemail or an extension on another system within the voice network.
TravelingClassofService
Also known as “Account Codes” - This allows authorized users to make calls on restricted extensions. The systems
recognizes the user when they enter a code and their password, and brings their less restrictive class of service to the
new location. The user’s Class of Service remains active for 60 seconds after the call is disconnected and then it
returns to the original Class of Service.
Station Message Detailed Recording
3
TrunkGroup
All trunks are automatically placed into one of four trunk groups, which are used to group trunks (PSTN or SIP) with
“like” programming such a local and long distance.
XBLUE Networks
43
Page 44

Feature Description
UnifiedCallDistribution(UDC)orHuntGroup
The system has four Uniformed Call Distribution (UCD) Groups (Hunt Groups), each can support up to 25
extensions. Each UCD can be programmed as an all ring, li near or distributiv e ring group and if unanswered calls
can be rerouted to another destination such as a different menu and greeting, or directly to a voice mailbox.
Unified Call Distribution (UDC) or Hunt
UCD Agent Logon and Logoff
Agents (extensions) may dial a code, which temporarily takes them out of all UCD groups. Once the agent logs
off, they will not receive any additional incoming UCD calls. This can be very helpful when an agent is out of the
office or out to lunch. When the agent returns, they dial a code to log into all UCD groups. Once logged in, they
start receiving UCD calls.
• All Ring - Rings all extensions simultaneously
• Linear - The call is placed into queue and the system attempts to ring the first programmed member,
if that member is busy, the next programmed extension is tired. If that one is busy, the third programmed member is tried and so on.
• Distributive - The call is placed into queue and the system finds the agent that is on-hook an d idle the
longest, and rings that member first.
3
UCDReroute
AllUCDgroupshavetheabilitytorerouteunansweredcallstoaMenu,Voicemail,PhoneorVirtual
Extension.Inaddition,avoicemailboxcanbesettobeanannouncementonlysothatitplaysames‐
sagetothecallerandthendisconnectsthecall.
VirtualExtension(Phantom)
The X-50 VoIP Telephone System has 40 special virtual mailbox or phantom extensions. They are used for
personnel that do not require a physical telephone but need to be visible within the system. They can also be
used as group mailboxes allowing multiple people to share the same mailbox.
Voi c eMail
The system has an integrated Auto Attendant and voice mail system with 32 hours of message storage. Each
authenticated extension, plus any virtual extension, has access to a password protected voice mailbox. For
extensions that should or would not use a voice mailbox, it can be disabled. In addition, the administrator can
program each voice mailbox to have e-mail delivery of a voice mail message. After a message is successfully sent,
the mailbox can be programmed to save the message as new, save it as old or delete the message completely.
44
XBLUE Networks
Page 45

Feature Description
WizardSetup
The X-50 system, at factory default, starts with a step by step setup wizard. From the wizard screen, the
administrator can load an existing configuration or select to use the step by step questions and answers. There are
eight programming parameters that make up the setup wizard.
• WAN Settings
• LAN Setting s
• Wireless Basic
• Internet or manual time setting
• Numbering plan
• IP Trunk
• Trunk DID Table (SIP Trunks required)
• Call Routing Table
Wizard Setup
3
XBLUE Networks
45
Page 46

Feature Description
Notes:
Wizard Setup
3
46
XBLUE Networks
Page 47

4 Telephone Feature
Description Table
Tele pho neFeatureDescriptionTabl e
Although the X-50 system uses standard SIP protocol it also has some special fe atures t hat only work
with the X2020 SIP Telephone Endpoints. Several of these features can be programmed or changed
using either the Telephone or System Graphical User Interface (GUI)
• If the feature is programmed using the System GUI - the column labeled GUI will have an
“S”
• If the feature is pr ogr a mmed using t he Telephone GUI - the column labeled GUI will have a
“T”
• If the feature cannot be programmed using the GUI - the column labeled GUI will have a “N”
XBLUE Networks
47
Page 48

Telephone Feature Description Table
Feature Programming Sequence Page GUI
Agent Log on/off - UCD Group Log On *91
Log Off **91
Alphanumeric Display Phone Specific page 53 N
Automatic Hold X2020 only page 54 S
page 53 N
4
Busy Callback Call ext + 6
Cancel *66
Call Forking (Requires SIP Trunk) *26 + t + Ext
t=
0=ICM
1=Outside
2=Both
Ext = Extension Number
Cancel **26
Call Forward - Direct *21+t+D
t=
0=ICM
1=Outside
2=Both
page 54 N
page 55 T
page 55 T
D=
EXT or Voicemail or UCD
Cancel **21
Call Forward - Busy *22 + t + D
t=
0=ICM
1=Outside
2=Both
D=
EXT or VVA or UCD
Cancel **22
48
XBLUE Networks
page 55 T
Page 49

Telephone Feature Description Table
Feature Programming Sequence Page GUI
Call Forward - No Answer *23 + t + D
t=
0=ICM
1=Outside
2=Both
D=
EXT or Voicemail or UCD
Cancel **23
Call Forward - DND *24 + t + D
t=
page 55 T
page 55 T
Call Forward - Follow Me - From the new
extension....
0=ICM
1=Outside
2=Both
D=
EXT or Voicemail or UCD
Cancel **24
*25 + t + Ext + * + pswd
t=
0=ICM
1=Outside
2=Both
Ext=
The Extension Number
pswd
The voicemail password
Default is 0000
4
page 55 N
Cancel **25 + Ext + * + pswd
XBLUE Networks
49
Page 50

Telephone Feature Description Table
Feature Programming Sequence Page GUI
Call Forward Remote *21 + t + * + pswd + * + O
*22 + t + * + pswd + * + O
*23 + t + * + pswd + * + O + * + T
*24 + t + * + pswd + * + O
*25 + t + * + pswd + * + O
t=
0=ICM
1=Outside
2=Both
pswd = VM Password
page 55 T
4
O=
Outside number
T=
Time to wait
Cancel
**2x
x= 1~5
Call Hold Hold Button page 59 N
Call Log X2020 only page 59 T
Call Park/Call Park Answer Defined by Numbering Plan (The
default is 731, 732, 733 and 734)
Call Pickup *53 + Extension page 60 T
Call Waiting *98
Cancel **98
Call Block page 61 T
page 60 T
page 60 T
50
XBLUE Networks
Page 51

Telephone Feature Description Table
Feature Programming Sequence Page GUI
Class of Service - Traveling *55 + ext + pswd
ext=
extension
pswd=
extension password
Conference (3 way) Press Hold while on a call
Press the down navigation key
Make second call
Press the Conference button
Distinctive Ringing Use Ring Type (Admin Menu or Web) page 62 T
page 62 N
page 61 N
Do Not Disturb (DND) * 4
Cancel **4
Extension Feature Reset *69 + Extension or Administrator Pass-
word
Feature Button Programming *70 + BN + FT
BN=
Telephone - 01~04
Sidecar 05~28)
FT=
Feature Type:
00=Null
01=Extension (Virtual) Number
02=Trunk Number (PSTN or SIP
Trunk)
03=Call Park Dial Code
04=Feature Key (Feature Access
Code)
05=Others (such as outside num-
ber)
06=Do Not Disturb)
07=Live Record
page 63 T
page 63 T
page 64 T
4
08=Virutal Mailbox
Extension Feature Reset *69 + ad-pswd
ad-pswd=
admin password
XBLUE Networks
page 63 T
51
Page 52

Telephone Feature Description Table
Feature Programming Sequence Page GUI
Feature Button Reset *68 + pswd
pswd=
extension password
LCD interactive X2020 only page 66 N
Multi-Line Appearance See Feature Button Programming page 67 T
Mute Mute Button page 67 N
On Hook dialing X2020 only page 68 N
page 66 S
4
Page Answer (Meet Me Page) - X2020
only
Page Allow/Deny *99 Page denied
Phonebook GUI Only page 69 T
Phone Lock/Unlock *97 + pswd
Plug & Play (PnP) X2020 only page 71 N
Reminder Tone (Stutter Dial Tone) Whenever a feature is enabled page 71 N
Service Mode (attendant only) *790 - Toggle between each mode
Telephone Line Flash page 72 N
Transfer Recall page 73 N
Volume Control page 73 T
Press “Answer” button under LCD page 68 N
page 68 N
**99 Page Allowed
page 71 N
**97 + pswd
pswd=
extension password
page 72 N
Go directly to a Mode
*791 - Day Mode
*792 - Night Mode
*793 - Time Mode
Web management page 73 Y
Some features require two buttons, one to activate and one to cancel a feature.
52
XBLUE Networks
Page 53

Telephone Feature Description Table
AgentLogOn/Off‐UCDGroup
• *91 - Agent log On
• **91 - Agent Log Out
Description:
Any extension programmed into a UCD group is considered an “Agent”. At times, an extension may want to stop
their extension from ringing so they can simply “Log Out” of the UCD Group.
Operation:
From an Idle X2020 Telephone Dial **91 to log out of a UCD group, dial *91 to log back into the UCD group.
Notes:
1. Only extension programmed as a member of one or more UCD Groups can use this feature.
2. When an agent logs out, they log out of all UCD groups.
3. When an agent logs in, they log out of all groups
4. There is no visual indication (lamp or LCD) when an agent is logged off.
Agent Log On/Off - UCD Group
AlphanumericBacklitDisplay
Description
The XBLUE X2020 telephone comes standard with a backlit graphic LCD display that supports 64 alphanumeric
characters.
Operation:
N/A
Notes:
N/A
4
XBLUE Networks
53
Page 54

Telephone Feature Description Table
AutomaticHold
Description:
This feature helps simplify the call handling process by allowing the user to answer a call and then press a
preprogrammed extension button without pressing the hold button first. The answered call will automatically be
placed on hold. To pickup the held call the user will press the hold button or another extension can press the
preprogrammed telephone line button.
Operation:
This is an automatic feature in the X2020 telephone.
Automatic Hold
4
Notes:
1. This will work when the user is on a Telephone Line or Intercom call
2. Automatic Hold can be disabled by the administrator in the X-50 system. It is found in the
“Programmable Line Key” parameter in the “Voice” --> “Phone Section”.
BusyCallback
Description:
The X2020 supports busy callback to an extension. This allows the user to dial 6 when they call an extension and
gets a busy signal. Once Busy Callback is activated, the called extension will ring calling parties extension when it
becomes idle. The calling extension can also cancel the Callback by dialing *66.
Operation:
A confirmation tone is heard once the busy callback feature is enabled.
The User may dial *66 to cancel a busy callback.
Notes:
1. Busy callback will not work if the called extension has busy call forward enabled.
54
XBLUE Networks
Page 55

Telephone Feature Description Table
This feautre requires SIP Trunks - It will not work with PSTN Lines.
CallForward‐Forking
Description:
This feature will allow a transferred telephone line or intercom call to ring at two simultaneous destinations, such
as an extension (LAN/WAN) or a cellular telephone. When one party answers the call the other ring te lephone will
stop ringing.
Operation:
To activate:
• *26 + t + Extension Number
• * + 26 + t + * + (pswd) + * + Outside Number
Call Forward - Forking
• t= 0 for intercom
• 1 for outside line
• 2 for both intercom and outside line
To cancel
• **26
Notes:
1. This feature will not work when the extension is programmed as the attendant or alternate attendant.
2. This feature will not work for a call that rings to a UCD group.
3. Telephone line calls must be transferred to activate this feature.
4. This feature will only work with one or more SIP Trunks.
CallForward
Description:
There are fout different types of call forwarding; Always (Direct), Busy, No Answer, and DND each call can be
forwarded to an internal extension, Voicemail, UCD or to an external telephone number such as a cellular
telephone. This allows the user to customize how calls to their extension will forwarded. In addition, intercom and
telephone line calls can be programmed to go to the same or different locations.
4
Operation:
There are two programming procedures. One for internal and one for external. These can also be programmed
using a standard Internet Web Browser.
XBLUE Networks
55
Page 56

Telephone Feature Description Table
Call Forward - Internal
Internal Procedure - * + CFW + t + DDD
• CFW =
• 21 = Always (Direct) Forward
• 22 = Busy Call Forward
• 23 = No Answer Call Forward
• * + CFW + t + DDD + T
• 24 = Do Not Disturb (DND)
• t =
Call Forward
• 0 for intercom
• 1 for outside line
• 2 for both intercom and outside line
4
• DDD =
• Extension - Real or Virtual
• Auto Attendant
• UCD Group
• T = Wait Time (0 - 60 seconds)
Examples:
*21 2 450 - Direct Forward to VM, *22 2 124 - Busy call forward to extension 124
To Cancel the Forwarding any Forwarding Dial - ** + CFW
Cancel Example
** 21 - Cancel Direct Call Forward
56
XBLUE Networks
Page 57

Telephone Feature Description Table
Call Forward - Follow Me
Follow Me Forward allows the user to use a different telephone extension and still receive their calls. Go to the
new location and enter the following information. Don’t forget to dial the “*” before the password or the entry will
not work.
Follow Me Forward - * 25 + t + EXT + * + pswd
• t =
• 0 for intercom
• 1 for outside line
• 2 for both intercom and outside line
• EXT = The Extension Number
• pswd =
• The extension password (Default 0000)
To Disable enter ** + 25 + Extension Number + * + Password
Call Forward
4
XBLUE Networks
57
Page 58

Telephone Feature Description Table
Call Forward - External
External Procedure - * + CFW + t + * + pswd + * + Outside Number
• CFW =
• 21 = Always (Direct) Forward
• 22 = Busy Call Forward
• 23 = No Answer Call Forward
• *23 + CFW + t+ * pswd + * + Outside Number + T
• 24 = Do Not Disturb (DND)
• t =
Call Forward
• 0 for intercom
• 1 for outside line
• 2 for both intercom and outside line
4
• pswd =
• Extension Password (Default 0000)
• Outside Number =
• Any 7 or 10 digit number such as a home or cellular telephone
• T = (No Answer time delay
• Waiting Time (0 - 60 seconds)
To Cancel the Forwarding any External Forwarding Dial - ** + CFW
Notes:
1. Follow me forward is an intercom function only.
2. Direct call forward overrides all other forwarding, followed by DND and then busy/no answer f orw arding.
58
XBLUE Networks
Page 59

Telephone Feature Description Table
CallHold
Description:
Both intercom and telephone line calls (PSTN or SIP Trunk) can be placed on hold. Once on hold the held party will
receive Music on Hold (MOH).
Operation:
While on a call the user presses the hold button .
Use the flash key on an analog (Single Line) telephone to place a call on hold.
Notes:
1. When using an analog (Single Line) telephone without a “Flash” key may cause erratic operation.
2. Music on Hold is a file that is stored in the X-50 System and not in the telephone. If using the
X2020 telephone on a different gateway, Music on Hold may not work the same way.
CallLog
Description:
The X2020 stores a list of missed, received and dialed calls, which the user may use to make or return calls.
Operation:
Press the “Menu” softkey and then press the check button , Call Log will be highlighted. Press the Check
button , and scroll down
button twice to recall or callback the selected number.
to select the desired call log. Select the desired number and press the check
Notes:
1. The call log numbers will reference the extension’s class of service, call restriction and call routing
rules before the call is placed.
2. The systems local area code must be programmed into the Call Routing Tables in the X-50 system.
Call Hold
4
XBLUE Networks
59
Page 60

Telephone Feature Description Table
CallPark
Description:
Call Park often referred to as “putting a call into orbit” allows extensions to place a call into a special holding area
that can be retrieved by any other extension in the system by dialing the park answer call.
Operation:
While on a telephone line call, the extension pressed a preprogrammed call park button to park the call. Any other
extension in the system can dial the park code or press their preprogrammed call park button to retrieve the call.
Notes:
1. Only extensions with a programmed Call Park button is allowed to park a call.
2. Any extension that dials the park code while a call is in the park location, is able to retrieve a call.
Call Park
3. A Call placed into a park location will recieve Music on Hold.
CallPickup
4
Description:
This feature allows the user to pickup a call that is ringing at another extension.
Operation:
While a call is ringing at another extension, press the preprogrammed Call Pickup call or dial the call pickup code, *
53 + extension number.
Notes:
1. Call pickup does not work with analog telephones
CallWaiting
Description:
The X2020 SIP telephone can be programmed to receive special alert ring whenever a second call rings at the
user’s extension. If the user would would not line to received the special ringing - just disable Call Waiting. If
disabled, calls to the Intercom calls to the user’s extension will receive a busy tone or follow the “Busy Forward” if
programmed.
Operation:
To enable call waiting - allows a second call to ring at the user’s extension - dial *98
To disable call waiting - does not allow a second call to ring at their extension - dial **98
Notes:
1. This feature is only available for the X2020 SIP telephone.
60
XBLUE Networks
Page 61

Telephone Feature Description Table
CallBlocking
Description:
The X2020 has the ability to block up to 10 different telephone numbers.
Operation:
Using a calls’ inbound caller ID the X2020 telephone allows the user to block up to 10 different telephone
numbers, each can contain up to 31 digits. When using Caller Blocking Settings, it is important to use as many
digits of the number to be blocked as possible. This will avoid inadvertently blocking large groups of numbers. For
example, if the user only enters “913”, then all calls with the area code 913 (Kansas) will be blocked.
• Enable Call Block: - Click on the Check Box to enable all 10 of the call Blocking Entries.
• Caller Blocking Entry x: (x = 0 - 9: - The user will enter the telephone numbers that they would like to
block. Remember, to minimize errors the user should use as much of the telephone number as they
can.
This parameter can be programmed using a standard Internet Web Browser.
Notes:
1. This feature is only available for the X2020.
Conference‐3Way
Description:
The conference feature allows the user to connect two additional callers in a single conversation. There are two
types of conference, supervised and unsupervised. A supervised conference is when the initiator (the person
creating the conference) remains in the confer ence. An unsupervised conf er ence is when the initiator (the person
creating the conference) disconnects from the conference.
Operation:
Use the following steps to create a conference
• While on a call press the hold button
• Press the down navigation key. This will open a second communications path, allowing the user to
place a second internal or external call.
• Dial the desired telephone number
• After the second call is answered and when the user is ready to establish the conference, press the
Call Blocking
4
Notes:
conference button, and all three parties will be joined in a single conversation.
1. This feature is accessed through the menu on the LCD Display.
2. When using PSTN lines, the dB (Volume) level may be lower when in a conference.
XBLUE Networks
61
Page 62

Telephone Feature Description Table
ClassofService‐Traveling
Description:
This feature allows the user to roam from one extension to another and retaining their dialing privileges, regardless
of the telephone’s programmed Class of Service.
Operation:
4
Class of Service - Traveling
When making a call from a telephone with a more restrictive class of service, enter * 55 + the user’s extension
number + the user’s voicemail password (Default is 0000) and then the user may place their call. This extension
retains the new Class of Service for one minute after the call has been disconnected.
Notes:
DistinctiveRinging
Description:
At default all of the X2020 extensions ring in the same way. However, each user may select from eleven (11)
different ring tones making it easier to determine when their telephone is ringing. In addition, each telephone line
(PSTN or SIP trunk) can be programmed with a distinctive Ring tone making it easier to determine which line is
ringing.
Operation:
This can be programmed using the telephone menu or using a standard Internet Web Browser.
Notes:
1. In the event that both a telephone line and a telephone is set to have a distinctive ring, the telephone
line ring assignment takes precedence.
2. Priority of distinctive ringing:
3. Caller ID Ring type is referenced first
4. Telephone line ringing is referenced second
5. Telephone extension is referenced third
62
XBLUE Networks
Page 63

Telephone Feature Description Table
DoNotDisturb(DND)
Description:
When Do Not Disturb (DND) is active all calls to the telephone is blocked. When DND call forward is set, calls will
forward to the DND destination such as voice mail. If not, the call will receive a busy signal.
Operation:
From an idle extension dial * 4 to enable DND
From an idle extension dial **4 to disable DND
Notes:
1. DND forwarding overrides all other forwarding, when DND is enabled, except Direct Call Forward
2. This feature can be disabled by the system administrator
3. When DND is enabled, the user will receive stutter dial tone when they go off hook.
4. When DND is enabled a special ICON will be displayed showing that the extension is in DND.
5. Other extensions will not recieve an indication that an extension is in DND until they call the extension
Do Not Disturb (DND)
ExtensionFeatureReset
Description:
This feature is a quick way to deactivate several features that have been changed from factory default.
Operation:
From the extension dial *69 + the extensions voicemail passowrd or the administrator password
The following will be set back to factory default:
• Call Waiting
• Paging Accept
• All programmed buttons are returned to default
• Phone Lock is disabled
• All programmed call forwarding is removed
• DND is disabled
• The extension (Agent) is logged into all programmed groups
• Auto Answer is disabled
• All programmed Distribution List are deleted
4
Notes:
1. This is good when troubleshooting extension anomalies
XBLUE Networks
63
Page 64

Telephone Feature Description Table
Feature(Flexible)ButtonProgramming
Description:
4
Feature (Flexible) Button Programming
The four buttons on the X2020 and any of the buttons on the Sidecar (DSS Console) can be reprogrammed to
accommodate a telephone PSTN or SIP Trunk Line, a feature or another extension. At default, the four buttons on
the telephone are set to the first four PSTN telephone lines (701, 702, 703, and 704) and all of the buttons on the
Sidecar are set to extensions 101~124.
Operation:
These features can be programmed using these codes or using a standard Internet Web Browser.
• Dial *70 + BN + FT
• BN = the button to be programmed; 01 - 04 on the telephone and 05 through 28 on the DSS Console,
going vertically down the left side, and then the right.
• FT = the numeric value for the next 6 feature types:
• 00=Blank button
• 01=Extension; can be a physical LAN telephone
• 02=Trunk; can be either a PSTN or SIP Trunk or Trunk Group
• 03=Call Park; enter the call park dial code
• 04=Feature Key; enter the feature code such as *91 Agent log on
• 05=Others; such as a WAN extension, a speed dial number or a specific outside telephone number
• 06=Do Not Disturb; No need to enter *4 (Administrator can disable this feature)
• 07=Live Record
• 08=Virtual Mailbox (Virtual (Phantom) Extension - Group Mailbox)
Notes:
1. Most features can be programmed on a button
2. Some features require one button to enable and another to disable the feature
Examples:
Enter the following code to create a page button on button 4 - on the telephone:
TABLE 4.1 Dialing Codes
BN Program BN Number Others Page Code
*70 04 05 400
Enter the following code to create a Call Park button on button 1 - on the telephone:
TABLE 4.2 Dialing Codes
BN Program BN Number Call Park Park Location Code
*70 01 03 731
64
XBLUE Networks
Page 65

Telephone Feature Description Table
Enter the following code to create a SIP IP Trunk button (SIP Trunk 1 = 711) on button 17 - on the Sidecar Upper Right - first button:
TABLE 4.3 Dialing Codes
BN Program BN Number Trunk Page Code
*70 13 02 711
Enter the following code to create an Agent Log Off button on button 15 and an Agent Log On button on button 16
- on the Sidecar - Last two on the Lower Left buttons:
TABLE 4.4 Dialing Codes
BN Program BN Number Feature Log on/off Code Feature
*70 15 04 **91 Log Off
*70 16 04 *91 Log On
Enter the following code to create a Do Not Disturb button on button 28 - on the sidecar - Lower Right - last
button:
TABLE 4.5 Dialing Codes
BN Program BN Number DND No Code needed
*70 28 06
Enter the following code to create a DND Call Forwrad button on button 4 - on the telephone - the forward
destination is voicemail (450):
TABLE 4.6 Dialing Codes
BN Program BN Number Others DND Forward Code Type - Both Destination Voicemail
*70 04 04 *24 2 450
Enter the following code to create a DND Call Forward button on button 4 - on the telephone - to an Outside
Number such as a cellular telephone:
TABLE 4.7 Dialing Codes
BN
Program
*70 04 04 *24 2 * 0000 * 5992583
BN
Number
Others
DND
Forward Code
Type - Both
Outside
Indicator
VM
Password
Confirm
Password
Outside
Number
The Operator (The extension that rings when 0 is dialed) can create a button to manually switch from Day to
Night mode. Enter the following code to create a Service Mode button on button 5 of the Operator’s Sidecar This
will be the top button, on the left side:
Feature (Flexible) Button Programming
4
TABLE 4.8 Dialing Codes
BN Program BN Number Feature Buttons Feature Code
*70 05 04 *790
XBLUE Networks
65
Page 66

Telephone Feature Description Table
FeatureButtonReset
Description:
The feature is used to bring the programmed buttons back to factory default. If the X2020 is connected to the X-
50 system the telephone will reference the X-50 for the currrent default button settings.
Operation:
Dial *68 + the extension (mailbox) password to default the programmable feature button
4
Feature Button Reset
Notes:
HoldReminder
Description:
Each time the programmable “Hold Reminder” timer is exceeded, a reminder tone will be heard at the extension that
placed the call on hold.
Operation:
Each extension can enable or disable the Hold Reminder as well as adjust the length of the timer.
Notes:
1. These features can be programmed using the telephone or using a standard Internet Web Browser.
LCD&InteractiveButtons
Description:
The X2020 has four interactive “Soft Buttons” that changes as the phone is being used. These soft buttons will
assist the user with the operation and programming of their telephone.
Operation:
Notes:
66
XBLUE Networks
Page 67

Telephone Feature Description Table
Multi‐LineAppearance
Description:
At default, all of the X2020 telephones are programmed with the first four PSTN lines (701, 702,70 3 and 704). All
telephone lines can also be programmed on the Sidecar.
The button, once programmed, uses the LED to indicate the current state of the telephone line. For example,
when the line is busy, the light will be lit solid.
TABLE 4.9 Telephone Line status
LED Description
Dark Idle
Fast Flash Ringing
Slow Flash Line is on hold
Wink Flash Call is recalling
Lit Solid Line is Busy
Operation:
When making an outside call, the user may press one of the progr ammed telephone line button and then dial the
desired telephone number or just dial the telephone number and let the X-50 system automatically route the call.
Notes:
Mute
Description:
Each X2020 has a mute button that is used to temporarily disable the telephone’s microphone.
Operation:
Press the Mute button to disable the telephone’s microphone, which will light R ed. Press the Mute but ton again to
disable Mute and continue the conversation. When Mute is disabled, the LED will not be lit.
Notes:
1. The Mute button may not mute a headset
Multi-Line Appearance
4
XBLUE Networks
67
Page 68

Telephone Feature Description Table
On‐HookDialing
Description:
On hook dialing, also known as Hot Keypad, allo ws t he us er to dial a number without lifting the handset or pressing
the speaker button.
Operation:
Simply dial an extension or outside telephone number without lifting the handset or pressing the speaker button.
The user may, lift the handset, press the check button or wait 5 seconds (programmable) for the system to
evaluate the dialed number and then process it according to any routing rules.
4
On-Hook Dialing
Notes:
Paging
Description:
There are two types of paging; All Call Paging and Group Paging. All Call Page, allows an extension to dial a single
code and broadcast a message to all idle X2020 telephone within the same subnet. There are three Group Paging
groups, each can have up to 24 extensions. When the group number is dialed all idle extensions within the group
and Subnet, will receive a broadcast message.
Operation:
Both All Call Page and Group Paging can be set to either LAN, WAN and both. When the All Call or Group Page code
or button is pressed, all idle X2020 telephones will receive the page. X2020 telephones users can press the soft
button under the word “Answer” to connect directly to the extension performing the page.
Notes:
1. With the paging parameter the “WAN” refers to any phone connected to the WAN port, but within the
same subnet
PagingAllow/Deny
Description:
This feature allows the user to enter a code to allow or deny paging at their extension.
Operation:
To enable paging deny (thus block paging) dial *99
To disable paging deny (thus allowing paging) dial **99
Notes:
68
XBLUE Networks
Page 69

Telephone Feature Description Table
Phonebook
Description:
Each extension has a personal and public phonebook that contains the contact name, phone number, ringing tone,
and group.
Operation:
Each telephone has a Private and Public Phonebook. The Private Phonebook is for the user’s personal use, and
the Public Phonebook is synchronize with a CSV file, which can be located in a centralized location. Currently, the
Phonebook feature does not support Microsoft Excel’s CSV files.
Private:
The Private Phonebook is for the user’s personal use, and can be enter individually or they may use a CSV File to
upload them all at once.
Phonebook
Enter the four parameters and then press the “Add” button, to add new entries.
• User Name: - Enter the user name that will be associated with this entry.
• Phone Number: - Enter the phone number (up to 64) digits.
• Ring Type: - There are eleven different ring tones that can be used to differentiate the entered
telephone number when it calls into the system.
• Select the Group that will be associated with the entered telephone number. Select between Family,
Friends, Colleague, VIP or None.
It is a good idea to create a back up of the configuration file once all of the numbers are entered. The user can
create a back up by clicking on the “SW Upgrade” tab and then click on the “Backup” button. Be sure to locate the
file where it is easy to locate should it be needed.
Click on the “Backup Button” and save it in a location that is easy to locate when needed.
4
XBLUE Networks
69
Page 70

Telephone Feature Description Table
Create a backup
Public
The Public phonebook gets linked to a CSV file in a centralled location, allowing an administrator to update all
phones connected to the system with a single file. There are several ways to create a CSV file. One way is to use the
backup created from the personal phonebook. Another way to create the file is using Windows Notepad. Once
created save it with a name such as “Publicphonebook.csv, and place it in a location that is easily found.
Phonebook
4
The format of this file is very important:
Name,Number,Ring,Group,
Anne Sweeney,1924020842,0,family,
Alan Booker,769011,0,Friends,
Bob Smith,12122641501,0,Colleague,
Donald Kilroy,18752250474,0,VIP,
One the file is ready to be uploaded, click on the “SW Upgrade” tab.
• Locate the “Public Phonebook File:” and click on the Browse... button
• Locate the saved file
• Click on the Update button
Notes:
70
• Click on “OK” to complete the the upload or “Cancel” to stop the upload.
• Click on the Phonebook tab, and then the Public Page t ab. If the file format is correct, the inf ormaiotn will
be visible. If the numbers are not visible recheck the file format.
XBLUE Networks
Page 71

Telephone Feature Description Table
PhoneLock/Unlock
Description:
The phone Lock/Unlock feature allows the user to lock th eir extension to prevent someone from making
unauthorized calls from their extension. The phone lock/unlock feature does not block intercom or emergency
calls, it only blocks telephone line (PSTN or SIP Trunk) calls.
Operation:
• To lock the phone dial *97 + extension (mailbox) password
• To unlock the phone dial **97 + extension (mailbox) password
Notes:
1. Locked extensions can only make intercom or emergency calls
PlugandPlay
Description:
When connecting an X2020 to the X-50 system over the LAN it will automaticall y aut henticate and be assigned
an extension number and activate the mailbox. An extension connecting over the WAN port will also automatically
authenticate, be assigned an extension number, and activate the mailbox but requires some basic programming.
Operation:
Connect the X2020 telephone to the LAN port, no other programming is required. When Connecting over the
WAN port, there are four parameters that need to be programmed; the SIP Proxy Server, Outbound Proxy Server,
Registrar Server, Registrar Outbound Server. This programming can be done using the telephone menu or using a
standard Internet Web Browser.
Notes:
1. Although WAN extensions will automatically received an extension number it is a good idea to enter
their extensions manually to make them more perminate. It has been found that after a power outage,
for example, the extension numbers may change.
ReminderTon e
Description:
When the extension goes off hook, speaker or handset, stutter dial tone will be heard when DND, MWI or Call
Forward is enabled.
Phone Lock/Unlock
4
Operation:
This is an automatic feature
Notes:
XBLUE Networks
71
Page 72

Telephone Feature Description Table
ServiceMode
Description:
The Operator has the ability to change the mode of the sy stem from day mode to night mode or timed mode. When
the system is set to day mode, the Auto Attendant will only play the day greeting and extensions will use the day
Class of Service for dialing privileges. When the system is in night mode, the Auto Attendant will only play the night
greeting and extensions will use the night Class of Service for dialing privileges. When the system is in timed mode
the system will automatically switch between day, lunch and night modes using the service mode settings in the X-
50 system.
Operation:
Only the attendant has the ability to swap between the service modes:
Service Mode
4
• Dial: *790 - displays the current mode
• Dial: *791 - changes the system into Day mode
• Dial: *792 - changes the system into Night mode
• Dial: *793 - changes the system into time mode to automatically change between modes.
Notes:
1. This feature only works with the attendant extension
TelephoneLineFlash
Description:
The flash command is used to activate a telephone line feature, such as call waiting or three way calling.
Operation:
While on a telephone line call, X2020 telephone users may press the software button under the word “Flash”.
Notes:
1. When using an analog (Single Line) telephone without a “Flash” key may cause erratic operation.
2. Use *790 when programming a button to toggle between day and night modes.
72
XBLUE Networks
Page 73

Telephone Feature Description Table
Transfer
Description:
Calls can be transferred from an extension to another destination, such as another extension, voice mail, or an
outside number. In addition, transfers can be blind, without announcing the call, supervised, listening for call
supervision, or screened where the transferring extension can announce the call.
Operation:
• While on a telephone line call press the transfer button
• Press the preprogrammed DSS button or dial the desired destination
• Hang up to release the call, or remain on the line to announce the call
Notes:
1. If the receiving extension is forwarded, the transferred call will follow the forwarding
2. If the receiving extension is not forwarded, and goes unanswered, it will recall at the extension that
transferred the call
Vol u me Control
Description:
The X2020 system is equipped to adjust the volume levels of the following settings:
• Ringing (extension and telephone line)
• Handset
• speaker
• Headset
Operation:
Press the volume up to increase or down to decrease the volume of the currently used feature. For example,
while the telephone is ringing use the volume button to increase or decrease the ringing volume.
Notes:
WebManagement
Description:
Transfer
4
The X2020 can be programmed using the L CD menu or using a standard Internet W eb Brow ser, such as Windows
Internet Explorer.
Operation:
Enter the IP Address in the browser address bar to access the Web interface page for programming.
Notes:
XBLUE Networks
73
Page 74

Telephone Feature Description Table
Notes:
Web Management
4
74
XBLUE Networks
Page 75

5Installation
InstallationPlanning
This chapter will show how to prepare and install the X-50 system and basic networking setup and
protocol.
Basics
1. Never perform any wiring in a wet location, while standing in water or during a lightning storm.
2. The X-50 should be installed in a well lit location with proper ventilation, having an optimum
temperature range from 40
3. The X-50 should not be installed where it will be exposed to direct sunlight or heat.
4. Do not install the X-50 close to or in a strong magnetic field, such as those generated by heavy
motors, televisions, copy machines or some kitchen appliances. Ideally, the X-50 should be
installed in an electrically noise-free environment to avoid interference.
5. Be careful when connecting any type of antenna or power through a cable that will be connected directly or indirectly to the X-50.
° to 95° F and a relative humidity range of 20 to 80 percent.
Note:
The manufacturer Warranty does not cover damage caused by abuse, electrical or telephone line
power surges or lightning damage.
XBLUE Networks
75
Page 76

Where to begin
Installation
Wheretobegin
The X-50 can be mounted in one of three different ways, virticall, horizontally, or wall mounted. See “Wall
Mount Template” for wall mounting in structions
Vertically
Horizontally
5
For best results;
• If using PSTN telephone lines the X-50 should be installed near where they enter the building,
which is called the “RJ21X”.
• The X-50 should be installed in a server room or anywhere that is a computer might be placed.
It should be placed on a clean hard service or mounted on a wall.
• The X-50 should be connected to all devices using Category 5, Category 5E or Category 6
cables.
• The X-50 should be in a location that is easily accessible by anyone who may need to perform
maintenance on the unit.
• The “TEL” port (analog telephone port) on the X-50 may be connected directly to a standard
corded, cordless telephone or FAX machine.
• The X-50 should be placed on a line condition Uninterrupted Power Supply (UPS) system which
will provide line conditioning and battery back up during a power outage. To minimize the number of UPS systems needed, power all telephone endpoints using Power of the Ethernet (PoE).
76
XBLUE Networks
Page 77

Installation
The X-50 VoIP Telephone
System must have a static
Class A or B IP Address when
connecting multiple systems
or remote workers.
Logical
1. Will this system be a standalone system or part of a voice network? This will help determine the numbering plan and the LAN/WAN requirements. If the X-50 is going to be a
standalone system, the default numbering plan should be fine. However, if the system is going to be connected to
a voice network, the numbering plan may need to be modified to allow direct dialing to specific locations. See
“
Numbering Plan” on page 91. In addition, a standalone system may not need to be connected to the Internet, so
there is no need to set up the “WAN” port, and the system’s location is a lot more flexible.
2. Will this system be the “Master” system in a Voice Network? If this system is part of a voice network, will it be the master system? If so, it will require a “Static IP Address”. If
not, it can use a DHCP Address, because it will be programmed to synchronize with the master system.
3. Will this system have any remote workers? A remote worker is someone who uses the telephone system’s resources but does not reside in the same building
or physical area. Connecting remote workers requires a static Class A or B IP Address and the ISP’s DSL/Cable
modem should be programmed as a bridge or concurrent bridge.
Where to begin
5
4. Will the system be connected to PSTN Lines?
This may determine where the system will be located. If PSTN lines are being used it is a good idea to locate the
X-50 VoIP Telephone System close to where they enter the building.
XBLUE Networks
77
Page 78

Where to begin
Installation
5. Will the system join an existing network or will it be on it’s own network?
If joining an existing network, Connect the WAN port of the X-50 to the current network. It will then act as
both a WAN and a LAN. Also, if there is more than one wireless device make sure that they are not all using
the same channel.
Joining an existing Local Area Network
5
If the system is going to be a standalone system, with isolated cables for VoIP, there is no need to connect it
to the Internet, except for remote programming.
78
XBLUE Networks
Page 79

A standalone Voice network.
Installation
Where to begin
Physical
1. Locate where the PSTN telephone and DSL/Cable lines enter the building. The X-50 has six FXO ports, which supports standar Public Switched T elephone Network (PSTN) telephone lines.
In addition, it has both a LAN and a WAN port, which may be connected to an existing network as well as a
Wireless LAN. Therefore, the X-50 will need to be located in an area that will allow it to be connected to both the
PSTN telephone lines and any existing network switch, router or gateway.
When using PSTN lines, it is a good idea to install the X-50 close to where the telephone lines enter the office or
building. However, if only “SIP Trunks” are going to be used, which is not recommended because of power
outages and emergencies, the system can be located near where the Internet Service Provider’s ( ISP) DSL/Cable
modem enters the building.
2. Verify tha t all cables, between data devices, are Category 5, 5E or 6. All devices connected to the X-50 must use a Category 5, 5E or 6 high speed Ethernet cable. This will ensure the
best data transfer rates. Failure to use the correct cable will cause spotty results in voice communication.
3. Cables between the FXS Port, labeled “TEL” (Analog Telepone Port) or PSTN telephone lines can be Category 3, 5, 5E or 6. It is acceptable to use Category 3 cabling when connecting the FXO (Telephone Lines) and the FXS (Single Line Telephone).
5
XBLUE Networks
79
Page 80

Installing the X-50 VoIP Telephone Sys-
Installation
Installingthe X-50VoIP TelephoneSystem
1. Remove all of the components from the box.
2. Wall Mount - locate the supplied wall template and secure it to the wall. Drill starter holes and place the
supplied anchors into the holes. Position the supplied screws into the anchors and secure them. It will be
necessary to back the screws out about 1/4 of an inch to securely hold the system on the wall.
3. Table or shelf Mount - There are two ways to mount the system on a table or shelf, vertical and horizontal, neither has an advantage over the other.
Vertical Installation - the system comes with a special weighted base stand designed to secure the X-50
VoIP Telephone System in a vertical position.
Horizontal Installation - the system also comes equipped with “Rubber” feet at the bottom of the unit so
that it can be placed on a table or shelf with a low profile. The Antenna, for the Wireless LAN, will bend at 90
degrees so that it can be tilted upward.
The X-50 is designed to operate either vertically or horizontally.
5
BeforeProgrammingthe X-50
Because the X-50 is a complete Gateway and Router, including a DHCP server it is a good idea to do some basic
programming before connecting it to an existing network. Connect a PC to the X-50 LAN Port, using the supplied
Patch Cable and then power up the X-50 system. If the user’s PC is set to DHCP, it will connect to the X-50 and
the two devices will become a network. The Gateway’s default IP Address is 192.168.10.1.
80
XBLUE Networks
Page 81

6 Programming Wizard
GettingStarted
The X-50 is a fully functioning Voice over Internet Protocol (VoIP) Gateway and router, which is
programmed using a standard Internet browser such as Microsoft’s Internet Explorer
with a Network Interface Card (NIC), connected to a TCP/IP network, can be used to program the X-
50 VoIP Telephone System.
SetupWizard
Once the administrator logs in and authenticates the first time, the programming wizard will walk the
administrator through the programming process. The next time the administrator logs into the X-50,
after the programming wizard is completed, the administrator will be sent to the main programming
landing page which shows the current status of the X-50 VoIP Telephone System.
There are two ways to begin programming the X-50 system; manually or restore from a backup.
®
. Any computer
If restoring a backup, Click the next button and then locate the backup file and click on the Update
Settings button. The update will take about 2 minutes.
The system will reboot after uploading the configuraiton file.
XBLUE Networks
81
Page 82

Programming Wizard
Before beginning the installation process it is a good idea to gather as much networking
information as possible. This includes IP Addresses for the LAN, WAN, Default Gateway,
Subnet, etc. It is also a good idea to make a note of all MAC Addresses for all wireless
devices as well as system or voice network numbing plan, SIP trunk information and how
dialed numbers will be routed.
The Setup Wizard guides the administrator through the required setup parameters to make the X-50
operational. The Setup Wizard must be completed at least once, before gaining access to the “Advanced Setup”
programming area. If any of the parameters are unknown, just press “Next” and continue. All o f these
parameters can be adjusted later using the “Advanced Setup” area.
Setup Wizard Tabs
SetupWizardTa bs
6
• WAN Settings (See “WAN Port Settings” on page 83.)
• LAN Settings (See “LAN Port Settings” on page 87.)
• Wireless Basic (See “Wireless Basics” on page 89.)
• Internet Time (See “Internet Time” on page 90.)
• Numbering Plan (See “Numbering Plan” on page 91.)
• IP Trunks (if needed) (See “SIP Trunks” on page 94.)
• DID Trunks (Requires IP TRunk) (See “SIP Trunks” on page 94.)
• Call Routing Tab le (See “Call Routing Table” on page 97.)
82
XBLUE Networks
Page 83

Programming Wizard
WAN PortSettings
The WAN Settings Tab is automatically selected and the default page in the Setup Wizard. Unlike a LAN port, the
WAN port can be used to redirect class A or B IP Addresses from an external location, such as the Internet, to a
specific internal Port. This process is called Network Address Translation or NAT.
WAN Port Settings
IP Settings (Default)
• At default, the “WAN Port Settings” are set to Automatic Configuration - DHCP. Dynamic Host
Configuration Protocol (DHCP) allows the WAN port of the system to automatically receive an IP and
Subnet Mask Addresses from the Internet Service Provider (ISP).
• The system can use either dynamic (automatically assigned) or Static DNS settings. Unless required
by the ISP it is probably easier to leave this set to automatic.
WAN Services
• Enable Firewall - Although nothing is 100% safe against malicious network attacks, keeping the
firewall enabled, should minimize the effectiveness of these attacks.
6
XBLUE Networks
83
Page 84

Programming Wizard
WAN Port Settings
6
84
XBLUE Networks
Page 85

IP Settings (Static IP Address)
Programming Wizard
WAN Port Settings
Depending on the installation it may be possible to configure the WAN port to use a “Static IP Address”, which can be
used by some ISP’s but generally is used when the system is not part of a voice network or supporting remote
workers. For example, when using e-mail delivery or NA T for r emote to progr amming. This par amete r makes it e asier
for network administrators to enter a specific IP Address, which they often reserve for printers, servers, routers, and
gateways.
• Internet IP Address - Enter the IP address that will be used to identify the X-50 system.
• Subnet Mask - when using “Static IP Address” the Subnet Mask will have to be entered by the
administrator. If there is a single Subnet, the entry will be 255.255.255.0.
• Gateway - The Default Gate way refers to the Gatewa y devic e t hat connec ts the Intranet (LAN) to the
Internet. Basically, it is the window to the Internet.
• Static DNS 1 & 2 - The Domain Name System (DNS) the Internet’s phone book, and is used to
translate IP Addresses to something that is easy to remember such as “xbluenetworks.com”. Some
Internet Service Providers (ISP) require Static DNS when using static IP Addresses.
WAN Services
• Enable Firewall - Although nothing is 100% safe against malicious network attacks, keeping the
firewall enabled should minimize the effectiveness of these attacks.
6
XBLUE Networks
85
Page 86

Programming Wizard
Point-to-Point Protocol over Ethernet (PPPOE)
WAN Port Settings
6
The WAN Port of the X-50 can also be set to PPPoE. In this case, the Internet Service Pro vider (ISP) will supply
the administrator with a User Name and Password (most likely it will be case sensitive), which is required when
connecting the WAN port to the Internet. The ISP’ s mo dem/gatewa y must be set as a bridge, allowing the X-50
system to authenticate direc tly with the ISP.
• Automatic (Auto) - This will automatically negotiate the correct authentication protocol.
• Password Authentication Protocol (PAP) - This will send the authentication un-encrypted.
• Challenge Handshake Authentication (CHAP) - This is more secure than the af or ementioned PAP,
and sends the authentication encrypted.
• Microsoft’s version of CHAP that allows mutual authentication between peers, by piggybacking
challenge and response packets on a successful packet.
• Static DNS 1 & 2 - The Domain Name System (DNS) the Internet’s phone book, and is used to
translate IP Addresses to something that is easy to remember such as “xbluenetworks.com”.
Some Internet Service Providers (ISP) require Static DNS when using static IP Addresses.
WAN Services
• Enable Firewall - Although nothing is 100% safe against malicious network attacks, keeping the
firewall enabled, should minimize the effectiveness of these attacks.
86
XBLUE Networks
Page 87

LAN Port Settings
The X-50 system is a gateway, which joins two or more different
types of networks together, such as WAN, LAN and PSTN. If the
X-50 system is connected to the ISP through a bridge to allow for
connecting to external devices. The LAN Address will be set to
192.168.10.1 and it is set to be the network’s DHCP Server.
However, if the X-50 is only using email delivery and remote
programming then the WAN port can be set to join
as a node or client on the existing Local Area
Network.
When connecting the WAN port of the X-50 to an
existing LAN, the LAN port of the X-50 must be
given a different IP address such as
(192.168.100.1). The LAN of the X-50 is then
considered “Down Stream” from the existing LAN.
When establishing any network numbering plan,
do not use the IP address x.x.x.254 becasue this
address is reservered for the system’s DSP and
will cause erratic operation.
Programming Wizard
WAN Port Settings
Once the WAN port settings are complete, press next to get to the Local Area Network (LAN) Port Settings page. At
default the LAN IP Address is set to 192.168.10.1 and Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP) serv er is enabled.
6
XBLUE Networks
87
Page 88

Programming Wizard
Configure IP Address and Subnet Mask for LAN Interface
WAN Port Settings
6
• LAN IP Address - at default the L AN IP Address is set to 192.168.10.1, but can be customized to
accommodate any valid IP Address. In addition, the LAN IP Address is considered the default
gateway for any of the SIP telephone endpoints connected within the LAN. When establishing
any network numbering plan, do not use the IP address x.x.x.254 becasue this address is
reservered for the system’s DSP and will cause erratic operation.
• Subnet Mask - when using the “Static IP Address” setting, the Subnet Mask will have to be
Manually entered. If there is a single Subnet, the entry will be 255.255.255.0.
• Universal Plug and Play (UPnP) - When enabled, the X-50 will recognize any device that is
connected to the LAN port and begins broadcast UPnP protocol.
• Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP) Server - When enabled the X-50 can be used to
automatically assign client devices an IP Address. In addition, the administrator can grant a
specific range of valid IP Addresses. At default the DHCP is enabled and will allow from
192.168.10.2 to 192.168.10.25 but can be expaned to 192.168.10.253. When disabled, every
device connected to the network will have to be manually configur ed with an IP Address, which is
good for security but creates a lot of extra work for the administrator. When establishing any
network numbering plan, do not use the IP address x.x.x.254 becasue this address is reservered
for the system’s DSP and will cause erratic operation.
• Leased Time - The amount of time that each dynamically assigned IP Address will be assigned to
any one device before it is renewed. If the device is still connected and active the device will
probably continue with the same IP Address. However, if the device has been removed and
inactive for more than the lease time, it may be assigned a dif ferent IP Addr ess the next time it is
connected.
88
XBLUE Networks
Page 89

Wireless Basics
Programming Wizard
WAN Port Settings
The X-50 is equipped with a wireless router, which allows wireless devices to connect using 802.11b, 802.11g and
802.11n protocol speeds.
• Enable Wireless - The wireless router is enabled at default, and can be disabled by un-checking this
parameter.
• Hide Access P oint - Check t his parameter t o “hide” the X-50 wireless signal. This stops the SSID from
being broadcast, making it harder for unauthorized endpoints to access the Wireless Access Point
(WAP). When SSID is disabled, the uer must enter the specific IP Address of the X-50 to connected
wirelessly.
• SSID - Service Set IDentifier - This is the name that will be broadcast to make it easier for authorized
endpoints to connect to the X-50 wirelessly.
• BSSID - Basic Service Set IDentifier - uniquely identifies each Basic Service Set (BSS), which is the
building block for all 802.11(x) devices. The BSSID is a locally administered MAC Address of the
Wireless Access Point (WAP).
• The Country parameter determines the frequencies and r estricts based on country requirements.
6
XBLUE Networks
89
Page 90

Programming Wizard
Internet Time
WAN Port Settings
6
The X-50 can be set to synchronize its date and time with specific sites found on the internet. This is referred to
as “Network Time Protocol (NTP)”.
• The X-50 allows for up to five different time server locations to be used to synchronize the time.
Therefore, if one or more servers fail, the time will not be lost. It is a good idea to select at least
one primary and one secondary time server, however, only the primary is required. Use the drop
down menu, to select the desired timer server.
• Time Zone Offset - This is the amount of time added or deducted from Greenwich Mean Time
(GMT)
If the system is not connected to the Internet, click on “Manual Date and Time Settings” to enter the time
manually. Do not reset the system after the date and time is set manually, it may cause the system time to
adjust erraticlly.
90
XBLUE Networks
Page 91

Numbering Plan
Programming Wizard
WAN Port Settings
The numbering plan establishes the “dial plan” that will be used for the X-50 system. It defines the start extension
number (101) and the ending extension number (125), as well as the day and night oper ator extension or extensions.
In addition, the X-50 includes one FXS (Single Line - analog - T e lephone) which has a default number of 125 and the
number to be dialed to ring the operator (0); all of which can be customized.
The SIP Authentication area is where the extension telephone numbers and passwords are established. These
numbers are used by the SIP telephone endpoints to authenticate to the X-50 system. It is important to keep in
mind if this system is going to be part of a larger voice network, the whole network must have one unified numbering
plan. For example, a system in Boston may have extensions numbered 1001 - 1025, in Chicago 1501 - 1525, Las
Vegas 2001 - 2025 and in San Fr ancisco 3001 - 3025, etc. This will allow an extension to dial 4 digits (3 digits number
plans will also work) and speak to someone at a different location. For example, someone in Boston dials 2021 and
speaks to an extension user in Las Vegas without using a telephone line. Tables “Suggested 4-Digit Numbing Plan” on
page 92 and “Suggested 3-Digit Numbing Plan” on page 93 show some suggestions extension numbering plans.
Note:
When entering a new numbering plan do not use 311, 411 and 911 as extension numbers.
6
XBLUE Networks
91
Page 92

Programming Wizard
WAN Port Settings
6
TABLE 6.1 Suggested 4-Digit Numbing Plan
Single System Voice Network Numbering Plan
AlonePSWD 12345678910
Primary
101 101101 1001 1501 2001 3001 4001 5001 6001 7001 8001 9001
102 102102 1002 1502 2002 3002 4002 5002 6002 7002 8002 9002
103 103103 1003 1503 2003 3003 4003 5003 6003 7003 8003 9003
104 104104 1004 1504 2004 3004 4004 5004 6004 7004 8004 9004
105 105105 1005 1505 2005 3005 4005 5005 6005 7005 8005 9005
106 106106 1006 1506 2006 3006 4006 5006 6006 7006 8006 9006
107 107107 1007 1507 2007 3007 4007 5007 6007 7007 8007 9007
108 108108 1008 1508 2008 3008 4008 5008 6008 7008 8008 9008
109 109109 1009 1509 2009 3009 4009 5009 6009 7009 8009 9009
110 110110 1010 1510 2010 3010 4010 5010 6010 7010 8010 9010
111 111111 1011 1511 2011 3011 4011 5011 6011 7011 8011 9011
112 112112 1012 1512 2012 3012 4012 5012 6012 7012 8012 9012
113 113113 1013 1513 2013 3013 4013 5013 6013 7013 8013 9013
114 114114 1014 1514 2014 3014 4014 5014 6014 7014 8014 9014
115 115115 1015 1515 2015 3015 4015 5015 6015 7015 8015 9015
116 116116 1016 1516 2016 3016 4016 5016 6016 7016 8016 9016
117 117117 1017 1517 2017 3017 4017 5017 6017 7017 8017 9017
118 118118 1018 1518 2018 3018 4018 5018 6018 7018 8018 9018
119 119119 1019 1519 2019 3019 4019 5019 6019 7019 8019 9019
120 120120 1020 1520 2020 3020 4020 5020 6020 7020 8020 9020
121 121121 1021 1521 2021 3021 4021 5021 6021 7021 8021 9021
122 122122 1022 1522 2022 3022 4022 5022 6022 7022 8022 9022
123 123123 1023 1523 2023 3023 4023 5023 6023 7023 8023 9023
124 124124 1024 1524 2024 3024 4024 5024 6024 7024 8024 9024
125 125125 1025 1525 2025 3025 4025 5025 6025 7025 8025 9025
92
XBLUE Networks
Page 93

Programming Wizard
TABLE 6.2 Suggested 3-Digit Numbing Plan
Single System Voice Network Numbering Plan
AlonePSWD 12345678910
Primary
101 101101 101 151 201 301 401 501 601 701 801 901
102 102102 102 152 202 302 402 502 602 702 802 902
103 103103 103 153 203 303 403 503 603 703 803 903
104 104104 104 154 204 304 404 504 604 704 804 904
105 105105 105 155 205 305 405 505 605 705 805 905
106 106106 106 156 206 306 406 506 606 706 806 906
107 107107 107 157 207 307 407 507 607 707 807 907
108 108108 108 158 208 308 408 508 608 708 808 908
109 109109 109 159 209 309 409 509 609 709 809 909
110 110110 110 160 210 310 410 510 610 710 810 910
111 111111 111 161 211 312 412 511 611 711 811 912
112 112112 112 162 212 313 413 512 612 712 812 913
113 113113 113 163 213 314 414 513 613 713 813 914
114 114114 114 164 214 315 415 514 614 714 814 915
115 115115 115 165 215 316 416 515 615 715 815 916
116 116116 116 166 216 317 417 516 616 716 816 917
117 117117 117 167 217 318 418 517 617 717 817 918
118 118118 118 168 218 319 419 518 618 718 818 919
119 119119 119 169 219 320 420 519 619 719 819 920
120 120120 120 170 220 321 421 520 620 720 820 921
121 121121 121 171 221 322 422 521 621 721 821 922
122 122122 122 172 222 323 423 522 622 722 822 923
123 123123 123 173 223 324 424 523 623 723 823 924
124 124124 124 174 224 325 425 524 624 724 824 925
125 125125 125 175 225 326 426 525 625 725 825 965
WAN Port Settings
6
• Day and Night Operator - at default the Single Line (Analog) Telephone, extension 125, is
programmed to be the day and night operator.
• Operator spee d dia l is t he numbe r that wil l be dial ed to ring the operator. Generallly this is set to zero
(0).
• Phone Number & passwords to authenticate each SIP telephone endpoint. Although, remote workers
will automatically authenticate it is a good idea to manually enter the extension number and password
of all remote workers. Because the WAN port authenticates first, remote workers may change their
extension number when the system is reset.
XBLUE Networks
93
Page 94

Programming Wizard
SIP Trunks
WAN Port Settings
6
The X-50 comes equipped to support eight SIP IP Trunks and fifty Direct Inward Dial (DID) numbers. SIP
T runks are not physically connected, they authenticate over the Internet. Thus, the voice quality of these line are
directly related to the ISP speed. There are several SIP IP Trunk providers on the market and the integration
should be standardized. However, this may not always be the case, and although we do our best to integrate all
SIP Trunks, there is no guarantee, written or implied, that every SIP IP Trunk provider will work with the X-50.
94
XBLUE Networks
Page 95

Programming Wizard
A Proxy Server is a “Go Between” that makes request on behalf of other
clients. Its primary roll is to route packets the fastest way possible and enforce
routing policies, even if it has to rewrite specific parts of the request before
forwarding the packet.
A Register Server sends a Registrar Server requests so that it will place vital
information in a location for the Domain Server. Some SIP IP Trunk providers
require that a Registrar Server be reference in order to keep the connection working correctly.
An Outbound Proxy is often used as a central location for security verification before
connecting two devices. This is commonly used as an additional layer of security.
The settings will be provided by the SIP IP Trunk Provider; please contact the provider if any ajustments are needed
to integrate their SIP Trunk.
• Phone number - The assigned phone number which will be provided by the SIP IP Trunk provider.
• User Name - The SIP IP Trunk provider will provide the user name. Depending on the provider, the
user name may be an account number, telephone number or reference number.
• Auth ID - Authentication ID - The SIP IP T runk provider will provide the Authentication ID. Depending
on the provider, the Auth ID may be an account number, telephone number or reference number.
• Auth Password - Authentication Password - The SIP IP Trunk provider will provide the Authentication
Password. Depending on the provider, the Auth Password may be an account number, telephone
number or reference number.
WAN Port Settings
• SIP Proxy - The SIP IP Trunk Provider will provide the SIP Proxy. The SIP Proxy can be either a class
A or B IP Address, or must likely will be a specific Uniform (Universal) Resource Locator (URL)
Address.
• Port - 5060 is one of the “Well Known Ports” that is used for the transmission of both TCP or UDP SIP
Packets. Some providers may require this to be changed, but most will not.
• Outbound Proxy - The SIP IP Trunk Provider will provide the Outbound Proxy. The Outbound Proxy’s
Address can be either a class A or B IP Address, or must likely will be a specific Uniform (Universal)
Resource Locator (URL) Address.
• Port - 5060 is one of the “Well Known Ports” that is used for the transmission of both TCP or UDP SIP
Packets. Some providers may require this to be changed, but most will not.
• Register Server - The SIP IP Trunk Provider will provide the Registrar Server. The Registrar Server’s
address can be either a class A or B IP Address, or must likely will be a specific Uniform (Universal)
Resource Locator (URL) Address.
• Port - 5060 is one of the “Well Known Ports” that is used for the transmission of both TCP or UDP SIP
Packets. Some providers may require this to be changed, but most will not.
• SIP Domain - The SIP IP Trunk Provider will provide the SIP Domain. The SIP Domain can be either a
class A or B IP Address, or must likely will be a specific Uniform (Universal) Resource Locator (URL)
Address.
• Register Expires - If “Register Status” is set to “On” this timer will be referenced and it is how often
the X-50 will send a signal to the Registrar Server in order to keep the information current. If there
is no reply within the programmed time, at default 60 seconds, the connection is terminated.
• Register Status - When Set to “On” the Register Expires will be reference d, otherwise it will not be
referenced. The SIP IP Trunk provider will provide the proper settings for this parameter.
6
XBLUE Networks
95
Page 96

Programming Wizard
Direct Inward Dial (DID)
WAN Port Settings
• Support E.164 - This protocol was defined by ITU-T, to standardize international
telecommunications numbering plan, used over the Public Switched Telephone Network (PSTN).
For proper dialing formats, some SIP IP Trunk Providers may require this to be enabled. At
default, it is disabled.
6
• DID Number - Enter the DID numbers that will be received from the SIP Trunks.
• Destination - Enter the destination of the receiving DID number, valid entries are a physical,
virtual extension or a UCD group.
• Outgoing Caller ID - Enter the telephone number that the SIP Trunk will send when the entered
DID extension makes an outoing call.
• Display Name - Enter the name that the SIP Trunk will send when the entered DID extension
makes an outgoing call.
96
XBLUE Networks
Page 97

Call Routing Table
Programming Wizard
WAN Port Settings
Once programmed, the Call Routing Table will automatically route calls through the proper telephone line or group of
lines (line group). Each entry may contain up to ten digits and has a “From” (start evaluation) and a “To” (end
evaluation) digit or set of digits. In addition, dialed numbers can be automatically modified to ensure that they are
sent through the most cost effective route. For example, if the main number of another system on the voice network
is dialed, that number can be deleted, and a new number can be inserted. The Call Routing Tables are also used to
direct three or four digit dialing between X-50 VoIP Telephone Systems.
6
XBLUE Networks
97
Page 98

Programming Wizard
For proper operation of Call Log - Dialed, Missed, and Received Calls, the home area
code, and automatic long distance insert, must be programmed into the Call Routing
Table.
Enter the home area code, where the system is loc ated, such as 913 in the “From” and
“To”, then the maximum and minimum digits dialed will be 10, in both, then enter 3
digits to be deleted by the system before the number is dialed. Do not enter any digits
into the “Delete” parameter if all 10 digits should be dialed. Therefore, when a number
in the entered area code is dialed, the area code if there is an entry in the delete
parameter, in the example, 913, will be delete. The remaining 7 digits will be dialed.
The second entry will automatically enter a 1 for all other 10 digit numbers. Enter
“From 2”, “To 9”, Min=10, Max=10, Insert=1, and “Group” default is 1. When any
number that begins with 2 through 9, except 913, will receive a 1, when it is sent to
the telephone line.
Kansas
In Scottsdale Arizona, for example, any 10 digit number that is dialed with 480 as the
first three digits, 480 will be deleted. Any 10 digit number that has 602 and 623 as an
area code, all 10 digits will be dialed. All other 10 digit numbers regardless of area
code will receive a 1 before sending the call to the telephone line.
Scottsdale, AZ
6
WAN Port Settings
98
XBLUE Networks
Page 99

Programming Wizard
Calls can automatically be routed to a specific telephone (PSTN) or
Group of lines, a specific SIP IP Trunk or group of SIP IP Trunks or to
another X-50.
Using the routing table eliminates the need for users to remember, what
can be, complex dialing plans.
The “To” entry must be a greater number than the “From” entry, or
the rule will be invalid.
• The “From” entry, works in conjunction with the “To” entry, and where the digit evaluation begins.
This entry can contain up to ten digits. When a dialed number falls within the “From” and the “To”
entries the call will be routed through the programmed destination.
WAN Port Settings
6
• The “To” entry, works in conjunction with the “From” entry, and where the digit evaluation ends. This
entry can contain up to ten digits. When a dialed number falls within the “From” and the “To” entries
the call will be routed through the programmed destination.
• The “Min” entry, works in conjunction with the “Max” entry, and determines the minimum number of
digits required to be considered for evaluation.
• The “Max” entry, works in conjunction with the “Min” entry, and determines the maximum number of
digits that will be evaluated. Any digits that exceeds this number will not be evaluated.
• The “del” (delete digits) column is the number of digits that will be deleted when the dialed digits
match the “From” and the “To” entry.
• The maximum number of digits that can be inserted, from the insert column is ten.
• Calls can be routed to a specific telephone line, 1 through 6, a SIP IP Line, 1 through 8, between
other X-50 systems using the IGW group, or a group can be created using either telephone lines or
SIP IP Trunk Lines, or a combination of both.
XBLUE Networks
99
Page 100

Programming Wizard
Complete the Setup Wizard by selecting the “Save & Reboot” to save the changes or “Exit & Reboot” to discard
the changes. Select the “Back” button to modify any parameters that may need to be changed before completing
the wizard.
WAN Port Settings
6
100
XBLUE Networks
 Loading...
Loading...