Page 1

AS480 AUTOMATIC VOLTAGE
REGULATOR (AVR)
SPECIFICATION INSTALLATION AND ADJUSTMENTS
General description
The AS480 is a half wave phase controlled AVR which forms
part of the excitation system of the brushless generator. The
design employs Surface Mount Technology (SMT), custom
mouldings and heatsinks to produce a compact AVR assembly.
The AVR also incorporates an interface to the optional Excitation
Boost System (EBS) for use where short-circuit current
maintenance is required.
The AVR is linked with the main stator windings and the exciter
field windings to provide closed loop control of the output voltage
with load regulation of +/- 1.0%. The AVR voltage sensing
terminals continuously sample the output windings for voltage
control purposes. In response to this sample voltage, the AVR
controls the power fed to the exciter field, and hence the main
field, to maintain the machine output voltage within the specified
limits, compensating for load, speed, temperature and power
factor of the generator.
Positive voltage build up from residual levels is ensured by the
use of efficient semiconductors in the power circuitry of the AVR.
A frequency measuring circuit continually monitors the
generator output frequency and provides under-speed protection
of the excitation system. This is done by reducing the output
voltage proportionally with speed below a pre-settable threshold.
A manual adjustment is provided for factory setting of the under
frequency roll off point, (UFRO). This can be changed to 60Hz
(or 50Hz) in the field by push-on link selection.
A wide range of stability settings are available to compensate for
machine sizes and applications. A ‘slow’ setting is available for
applications involving single/twin cylinder engines and where
lamp-flicker could be a problem.
Provision is made for the connection of a remote voltage
trimmer, allowing the user fine control of the generator’s output
voltage.
Operation with 110Vac sensing is possible, replace the hand
trimmer link with fixed resistor. The hand trimmer option cannot
be used in this configuration. The generator overload capability
is reduced in 110V operation.
The AVR has the facility for droop CT connection, to allow
parallel running with other similarly equipped generators.
Over excitation conditions are limited to a safe period by a
protection circuit within the AVR. Once activated by a sustained
over-excitation condition, the generator voltage is reduced to a
low level until reset. Stopping the generator or removing power
from the AVR will perform the necessary reset.
Connections are provided to interface to the optional Excitation
Boost System. This incorporates a small externally mounted
rotary power supply which provides excitation power in the event
of heavy overloads or short circuits. The EBS is short term rated
and responds to signals from the AVR to deliver excitation power
when required. A separate overload protection system within the
EBS electronic module protects the generator against sustained
overloads.
© Cummins 2008 1 TD_AS480 AVR_04.08_02_GB
Technical specification
SENSING and POWER INPUT
Voltage 100-264 V ac 1 phase
Frequency 50-60 Hz nominal
OUTPUT
Voltage 82 V d.c. @ 200 Va.c power input.
Voltage 45 V d.c. @ 110 Va.c power input.
Current continuous 5A (see note 1).
transient 7.5A for 10 secs.
Resistance 15 ohms min
REGULATION
+/- 1.0% (see note 2)
THERMAL DRIFT
0.03% per deg. C change in AVR ambient (see note 3)
TYPICAL SYSTEM RESPONSE
AVR response 20ms
Field current to 90% 80 ms
Machine Volts to 97% 300ms
EXTERNAL VOLTAGE ADJUSTMENT
+/-10% with 1 k ohm 1 watt trimmer (see note 4)
Increasing resistance lowers voltage.
Fixed 15kOhm resistor enables 110V sensing
UNDER FREQUENCY PROTECTION
Set point 94 -98% Hz (see note 5)
UNIT POWER DISSIPATION
12 watts maximum
BUILD UP VOLTAGE
4 Volts @ AVR terminals
QUADRATURE DROOP INPUT
10 ohms burden
Max. sensitivity: 0.07 A for 5% droop 0PF
Max. input: 0.33 A
OVER EXCITATION PROTECTION
Set point 67 Vdc +/-3% (fixed)
Time delay 10-15 seconds (fixed)
ENVIRONMENTAL
Vibration 20-100 Hz 50mm/sec
100Hz – 2kHz 3.3g
Operating temperature -40 to +70C (note 6)
Relative Humidity 0-70C 95% (note 7)
Storage temperature -55 to +80C
NOTES
1. De-rate by 20% if mounted external to generator.
2. Inclusive of 4% engine governing.
3. After 2 minutes warm-up.
4. Generator de-rate may apply. Check with factory.
5. Factory set, semi-sealed, jumper selectable.
6. De-rate output current by 5% per deg. C above 60C.
7. Non condensing.
Page 2
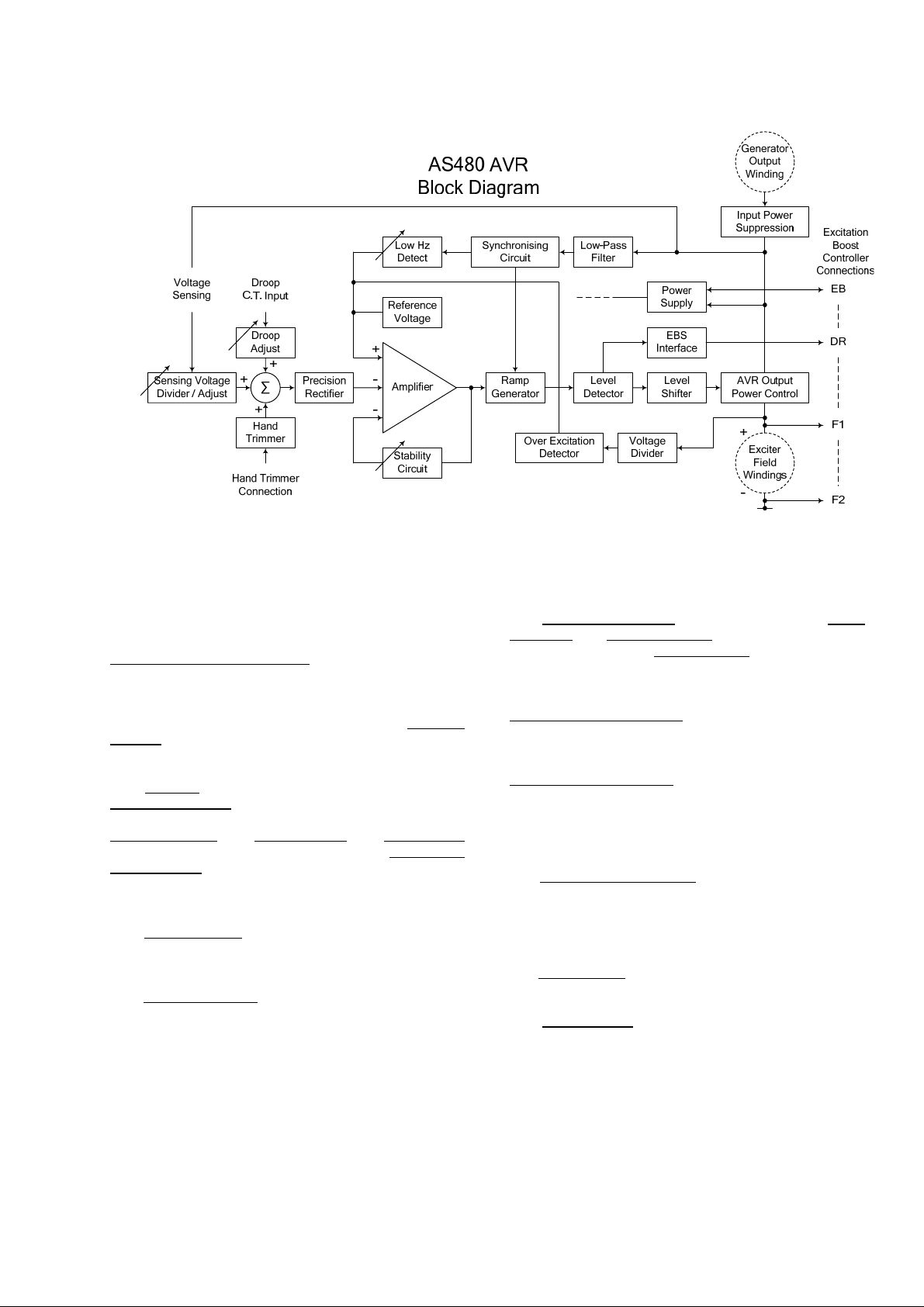
The AVR Circuit Description
The main functions of the AVR are:
Sensing Voltage Divider / Adjust
generator output voltage and attenuates it. The potential
divider is adjustable by the AVR Volts potentiometer and
external hand trimmer (when fitted). The output from the
droop CT is also added to this signal. A Precision
Rectifier converts the a.c. input signal into d.c. for further
processing.
The Amplifier
Reference Voltage
provide a controlling signal for the power devices. The
Ramp Generator
infinitely control the conduction period of the AVR Output
Power Control devices. This provides the exciter field
windings with the variable power necessary to maintain
the generator voltage within specified limits.
The Stability Circuit
ensure good steady state and transient performance of
the control system.
The Low Hz Detector
electrical cycle and causes the reference voltage to be
reduced approximately linearly with speed below a presettable threshold. A Light Emitting Diode gives indication
that the circuit is activated by the low-speed running
condition.
compares the sensed voltage to the
and amplifies the difference (error) to
and Level Detector and Level Shifter
provides adjustable feedback to
measures the period of each
takes a proportion of the
The Synchronising circuit is used to keep the Ramp
Generator and Low Hz Detector locked to the generator
waveform period. The Low Pass Filter
waveforms affecting the operation of the AVR control
circuit.
AVR Output Power Control
exciter field current in response to the error signal
produced by the Amplifier.
Input Power Suppression
prevent load generated voltage transients from damaging
the AVR components and also to reduce the amount of
conducted radio-frequency noise on the generator
terminals.
The Over Excitation Detector
exciter field voltage and provides the signal required to
collapse the output voltage. This protection circuit
triggers only if an over excitation condition persists for a
specific amount of time.
The Power Supply
AVR circuitry.
The EBS Interface
control the excitation boost generator (EBG). The EBG
responds to the level of excitation provided by the AVR
and supplies additional power as it is needed to support
the overload.
provides the required voltages for the
provides the signals necessary to
devices vary the amount of
components are included to
continuously monitors the
prevents distorted
© Cummins 2008 2 TD_AS480 AVR_04.08_02_GB
Page 3

AS480 AVR – Links and Adjustments
refer to the generator wiring diagram for all connection details
Operation at 110Vac (optional)
- remove link(*) before fitting
- connect the 15k/1W sensing link
- the hand trimmer cannot be used in this mode
- Overload performance is limited in this mode.
> 100kW
connections for
excitation boost
unit
Stability Linking
< 100kW
Slow
Link BDLink BC
< 100kW
50Hz 60Hz
UFRO Linking
Fast
No Link
VOLTS
DROOP
D
C
B
50
HZ
60
DR
LED
EB
F2
F1
2
1
S2
S1
F2
F1
STABILITY
UFRO
7
8
Hand
Trimmer
(optional)
Raise
1k / 1W
Droop
C/T
(optional)
Remove link
before fitting
Control Function Direction
VOLTS Generator output voltage setting Clockwise raises voltage
STABILITY Output voltage stability Clockwise increases stabilisation effect
DROOP Voltage droop for paralleling Clockwise increases drooping effect
UFRO Under-frequency 'Knee' point Clockwise decreases 'Knee' point
Refer to the Generator Wiring Diagrams for all Connection detail
© Cummins 2008 3 TD_AS480 AVR_04.08_02_GB
Page 4

ADJUSTMENT OF AVR CONTROLS
VOLTAGE ADJUSTMENT
The generator output voltage is set at the factory but can
be altered by adjustment of the VOLTS control on the AVR
board or by the external hand trimmer if fitted. Before
adjusting the generator output voltage , note the following
warnings.
WARNING! Do not increase the voltage above the
rated generator voltage shown on the rating plate
mounted on the generator case.
WARNING! Do not ground any of the external hand
trimmer terminals. Failure to observe this could cause
equipment damage.
To adjust the generator output voltage, proceed as follows:
1. Before running the generator set, turn the [VOLTS]
control fully anti-clockwise. Turn the [STABILITY] control
to its midway position and the external hand trimmer (if
fitted) to its midway position.
2. Connect a suitable voltmeter (0-300Vac) across Line
and Neutral of the generator.
3. Start the generator set, and run on no load at nominal
frequency e.g. 50Hz (or 60Hz).
4. If the red Light Emitting Diode (LED) is illuminated, refer
to the section on Under-Frequency-Roll-Off adjustment.
5. Carefully turn the [VOLTS] control clockwise until the
required voltage is reached.
6. If instability is present at rated voltage, refer to the
section on Stability adjustment.7. Voltage adjustment is
now completed.
STABILITY ADJUSTMENT
The AVR includes an optimised stability circuit to provide
good steady state and transient performance of the
generator. Links are provided to change the response of
the stability circuit to suit different frame size generators
and applications. A slow response setting is more
appropriate on small generator sets and will prove helpful
in reducing lamp flicker.
The correct setting of the Stability adjustment can be found
by running the generator at no load and slowly turning the
stability control anti-clockwise until the generator voltage
starts to become unstable. The optimum position for the
control is slightly clockwise from this point (i.e. where the
machine volts are stable but close to the unstable region).
UNDER-FREQUENCY-ROLL-OFF ADJUSTMENT:
(UFRO)
The AVR incorporates an under-speed protection
circuit which produces a volts/Hz characteristic when
the generator frequency falls below a preset threshold
- known as the "knee" point. The red Light Emitting
Diode (LED) gives indication that the UFRO circuit is
operating in the low frequency region.
The UFRO adjustment is preset and sealed and only
requires the selection of 50Hz or 60Hz operation
using the jumper link.
For normal operation, the LED should illuminate as
the frequency falls just below 95% of nominal.
i.e. 47Hz on 50Hz systems or 57Hz on 60Hz systems.
DROOP ADJUSTMENT
Generators intended for parallel operation should be
fitted with a quadrature droop C.T. The C.T. is
connected to S1, S2 on the AVR and provides a
power factor dependent signal for the AVR voltage
sensing circuit. This allows the control of generator
reactive current when two or more generators are
operated in parallel.
The DROOP adjustment is normally preset in the
works to give 5% voltage droop at full load zero
power-factor.
Clockwise increases the amount of C.T. signal
injected into the AVR and increases the amount of
voltage droop. With the control fully anti-clockwise
there is no droop.
OVER EXCITATION TRIP
The over-excitation trip level is set at the works at
65Vdc and cannot be altered. An over excitation
condition is indicated on the LED (which also indicates
under speed running).
The over-excitation is allowed to exist for
approximately eight seconds to prevent nuisance
tripping and to support normal transients and shortterm overloads. The generator voltage falls to low
levels when the trip is activated. The generator must
be stopped to reset an over-excitation shutdown
condition.
EXCITATION BOOST SYSTEM
There are no user adjustments on the EBS
module just connect the unit and it is ready for
use.
© Cummins 2008 4 TD_AS480 AVR_04.08_02_GB
Page 5

EBS - Circuit description:
The EBS comprises an add-on permanent magnet
generator (EBG) with embedded control electronics
(the EBC module).
The main functions of the EBC are as follows:
The Input Rectifier and Power-Supply
supplies to the internal control parts of the EBC.
The Micro-controller measures the drive signal
(DR) generated by the AVR and determines the
© Cummins 2008 5 TD_AS480 AVR_04.08_02_GB
provides
need for excitation power support. As this support is
required it is delivered at low, medium or high levels to the
exciter field. The AVR control function
maintains generator voltage within broad limits until both
AVR and EBS are fully conducting.
The micro processor contains three timer functions: to
prevent actinnnvation on generator run up, operation below
30Hz and to disconnect the booster power after a period of
boost operation i.e. preventing the generator from
overheating. This function is designed to follow
the approximate thermal state (temperature) of the machine
windings.
Page 6

The output characteristic of the EBS is as shown
below. The high-speed interaction between the EBS
output and AVR demand is effectively ‘smoothed’ by
the connected generators excitation component
time-constants.
Barnack Road • Stamford • Lincolnshire • PE9 2NB
Tel: 00 44 (0)1780 484000 • Fax: 00 44 (0)1780 484100
POWER INPUT
Voltage 90-130 Vac 3 phase
Frequency 100-120 Hz nominal
OUTPUT
Voltage 120 Vd.c. @ 100 Va.c power input.
Current continuous 6A
Resistance 15 ohms min
TYPICAL SYSTEM RESPONSE
EBC response 20ms
INTERNAL TIMERS
Start-up timer 5sec nominal
Overload protection timer 5sec nominal
UNIT POWER DISSIPATION
12 watts maximum
© Cummins 2008 6 TD_AS480 AVR_04.08_02_GB
 Loading...
Loading...