Page 1

Dual-Channel
Arbitrary Waveform Generator
User Manual
FG-30802T
FG-31602T
FG-32502T
Page 2

General Warranty
We warrant that the product will be free from defects in materials and workmanship
for a period of 3 years from the date of purchase of the product by the original
purchaser from our company. The warranty period for accessories such as probes,
battery is 12 months. This warranty only applies to the original purchaser and is not
transferable to a third party.
If the product proves defective during the warranty period, we will either repair the
defective product without charge for parts and labour, or will provide a replacement
in exchange for the defective product. Parts, modules and replacement products
used by our company for warranty work may be new or reconditioned like new. All
replaced parts, modules and products become the property of our company.
In order to obtain service under this warranty, the customer must notify our
company of the defect before the expiration of the warranty period. Customer shall
be responsible for packaging and shipping the defective product to the designated
service centre, a copy of the customers proof of purchase is also required.
This warranty shall not apply to any defect, failure or damage caused by improper
use or improper or inadequate maintenance and care. We shall not be obligated to
furnish service under this warranty a) to repair damage resulting from attempts by
personnel other than our company representatives to install, repair or service the
product; b) to repair damage resulting from improper use or connection to
incompatible equipment; c) to repair any damage or malfunction caused by the use
of not our supplies; or d) to service a product that has been modified or integrated
with other products when the effect of such modification or integration increases
the time or difficulty of servicing the product.
Please contact the nearest Sales and Service Offices for services.
Excepting the after-sales services provided in this summary or the applicable warranty
statements, we will not offer any guarantee for maintenance definitely declared or hinted,
including but not limited to the implied guarantee for marketability and special-purpose
acceptability. We should not take any responsibilities for any indirect, special or
consequent damages.
Page 3

i
Table of Contents
1. General Safety Requirement ................................................................ 1
2. Safety Terms and Symbols .................................................................... 2
3. Quick start ............................................................................................ 3
Front panel .................................................................................................................................. 3
Rear Panel ................................................................................................................................... 5
Power On ..................................................................................................................................... 6
User Interface .............................................................................................................................. 7
Use Build-in Help ......................................................................................................................... 8
4. Panel Operation ................................................................................... 9
Channel Setting ........................................................................................................................... 9
Select the channel for configuration .................................................................................. 9
Turn On/Off Channel Output .............................................................................................. 9
Channel Copy ...................................................................................................................... 9
Waveform Setting........................................................................................................................ 9
Output Sine Wave ............................................................................................................. 10
Set the frequency/period ......................................................................................... 10
Set the amplitude ..................................................................................................... 11
Set the offset ............................................................................................................. 11
Set the high level....................................................................................................... 11
Set the low level ........................................................................................................ 11
Set the start phase .................................................................................................... 12
Output Square Wave ......................................................................................................... 12
Output Ramp Wave ........................................................................................................... 13
Set the symmetry ...................................................................................................... 13
Output Pulse Wave ........................................................................................................... 14
Set the pulse width/duty cycle ................................................................................. 17
Set the rising/falling time ......................................................................................... 18
Output Noise Wave ........................................................................................................... 18
Output Arbitrary Wave ..................................................................................................... 19
Choose build-in waves .............................................................................................. 20
Output Harmonic Wave .................................................................................................... 25
Harmonic wave function overview ........................................................................... 25
Select the harmonic type .......................................................................................... 25
Set the harmonic times ............................................................................................. 26
Set the harmonic number ......................................................................................... 26
Set the harmonic amplitude ..................................................................................... 26
Set the harmonic phase ............................................................................................ 26
Output the modulated waves ................................................................................................... 27
Amplitude Modulation(AM) ............................................................................................. 27
Page 4

ii
Frequency Modulation (FM) ............................................................................................. 29
Phase Modulation (PM) .................................................................................................... 31
Pulse Width Modulation (PWM) ...................................................................................... 32
Amplitude shift keying (ASK) ............................................................................................ 33
Phase Shift Keying (PSK).................................................................................................... 35
Frequency Shift Keying (FSK) ............................................................................................ 37
Hexadecimal frequency shift keying (3FSK) .............................................................................. 38
Quaternary frequency shift keying (4FSK) ................................................................................ 39
Binary phase shift keying (BPSK) ............................................................................................... 40
Oscillating keying (OSK)............................................................................................................. 41
Output the sweep frequency (Sweep) ...................................................................................... 43
Output the burst (Burst) ........................................................................................................... 44
Set N cycle burst ............................................................................................................... 45
Set the gated burst ........................................................................................................... 46
Counter...................................................................................................................................... 47
Utility function setting .............................................................................................................. 48
Display Setting ................................................................................................................... 48
Brightness Control..................................................................................................... 48
Screen Saver .............................................................................................................. 49
Separator ................................................................................................................... 49
Date ........................................................................................................................... 49
CH1/2 Settings................................................................................................................... 49
Synchronize ............................................................................................................... 49
Output Setting ................................................................................................................... 50
Set the load ............................................................................................................... 50
Interface Setting ................................................................................................................ 51
System Setting ................................................................................................................... 52
Select the language ................................................................................................... 52
Buzzer ........................................................................................................................ 52
Clock source .............................................................................................................. 52
Clock Output ............................................................................................................. 53
Firmware update ....................................................................................................... 53
Restore to factory setting ......................................................................................... 53
Edit the Arbitrary Wave (Edit) .................................................................................................. 57
File system (Store)..................................................................................................................... 58
Save Current Arbitrary Wave ............................................................................................ 59
Bring up arbitrary wave files in internal/external memory .............................................. 59
Clear waveform from memory ......................................................................................... 60
Save/recall instrument settings (Preset) .................................................................................. 60
Use build-in help (Help) ............................................................................................................ 61
5. Communicate with PC ........................................................................ 62
Using USB Port .......................................................................................................................... 62
Using LAN Port .......................................................................................................................... 62
Page 5

iii
Connect Directly ................................................................................................................ 62
Connect through a Router ................................................................................................ 63
6. Troubleshooting ................................................................................. 65
7. Specification ....................................................................................... 66
8. Appendix ............................................................................................ 73
Appendix A: Accessories ........................................................................................................... 73
Appendix B: Maintenance and cleaning ................................................................................... 73
Page 6

1.General Safety Requirement
1. General Safety Requirement
Before use, please read the following safety precautions to avoid any possible
bodily injury and to prevent this product or any other connected products from
damage. In order to avoid any contingent danger, ensure this product is only used
within the range specified.
Only the qualified technicians can implement the maintenance.
To avoid Fire or Personal Injury:
Use Proper Power Cord. Use only the power cord supplied with the product
and certified to use in your country.
Product Grounded. This instrument is grounded through the power cord
grounding conductor. To avoid electric shock, the grounding conductor must
be grounded. The product must be grounded properly before any
connection with its input or output terminal.
Check all Terminal Ratings. To avoid fire or shock hazard, check all ratings
and markers of this product. Refer to the user's manual for more information
about ratings before connecting to the instrument.
Do not operate without covers. Do not operate the instrument with covers
or panels removed.
Use Proper Fuse. Use only the specified type and rating fuse for this
instrument.
Avoid exposed circuit. Do not touch exposed junctions and components
when the instrument is powered.
Do not operate if in any doubt. If you suspect damage occurs to the
instrument, have it inspected by qualified service personnel before further
operations.
In well-ventilated area. Make sure the instrument installed with proper
ventilation, refer to the user manual for more details.
Do not operate in wet conditions.
Do not operate in an explosive atmosphere.
Keep product surfaces clean and dry.
1
Page 7

2.Safety Terms and Symbols
2. Safety Terms and Symbols
Safety Terms
Terms in this manual. The following terms may appear in this manual:
Warning: Warning indicates the conditions or practices that could result in
injury or loss of life.
Caution : Caution indicates the conditions or practices that could result in
damage to this product or other property.
Terms on the product. The following terms may appear on this product:
Danger: It indicates an injury or hazard may immediately happen.
Warning: It indicates an injury or hazard may be accessible potentially.
Caution: It indicates a potential damage to the instrument or other property might
occur.
Safety Symbols
Symbols on the product. The following symbol may appear on the product:
2
Page 8
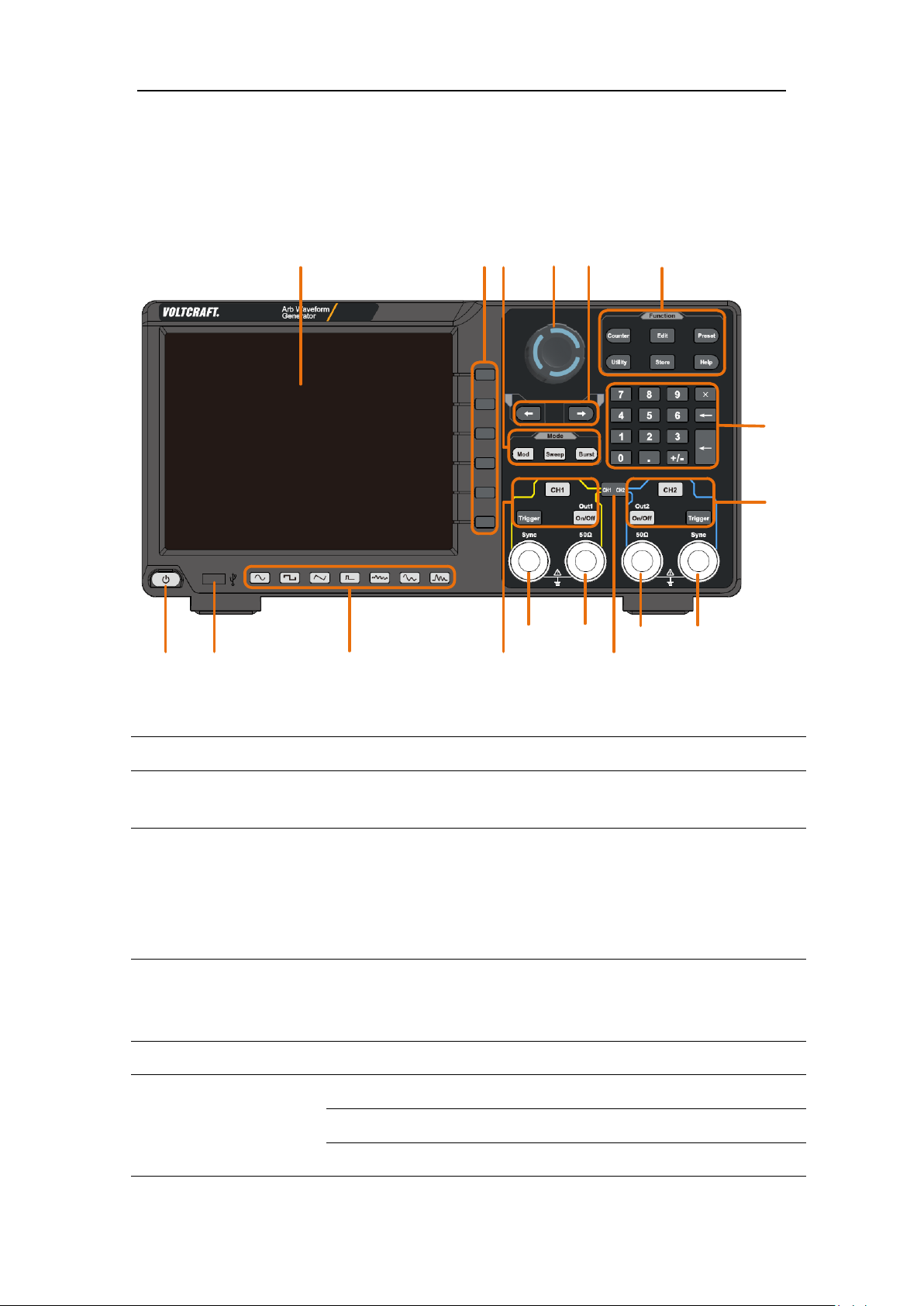
3. Quick start
17
4
9
16
1
2
15
7
6
13
12
10
5
11
8
3
14
1
Display Area
Display user interface
2
Menu Selection
Button
Includes 6 buttons to select the corresponding menu softkey
3
Mode Button
Modulation (Mod): Output modulation waveform
wave, pulse wave, or arbitrary wave.
4
Knob
Change the currently selected value, also used to select the
location or file
name is entered.
5
Direction Button
Move the cursor of the selected parameter
6
Function Button
Counter: Enter the frequency meter interface
Wave Edit (Edit): enter the waveform editing interface
Preset: Enter the preset menu, set the reset parameters or
Front panel
3.Quick start
Area
Area
Figure 3-1 Front Panel overview
Sweep: Scan a sine wave, square wave, ramp wave or
arbitrary wave
Burst: A burst that produces a sine wave, square wave, ramp
character in the soft keyboard when the file
3
Page 9

3.Quick start
power-on parameters; save or read the settings file.
Utility: Set the auxiliary system function
Store: Save/recall arbitrary waveform data
Help: To get context help for any front panel button or menu
you need help.
7
Numerical Keypad
Input the parameter
8
CH2 Button Area
CH2 key: Enter the waveform interface and select the CH2
channel (the backlight of the button lights up). After
selecting, the waveform and parameters of CH2 can be set.
Blue Trigger button: CH2 manual trigger button. In sweep or
burst mode, when the trigger source is selected as “Manual”,
each press of this button will initiate a trigger.
On/Off key: Turns the output of the CH2 channel on or off.
lights up.
9
CH2 Sync Output
turned on, this
terminal outputs a sync signal that matches the current
configuration of CH2.
10
CH2 Output
Termnial
Output CH2 signal
11
CH1⇌CH2 Button
Display channel copy menu and menu of frequency
chronization, phase
alignment, etc.
12
CH1 Output
Terminal
Output CH1 signal
13
CH1 Sync Output
turned on, this
the current
configuration of CH1.
14
CH1 Button Area
CH1 key: Enter the waveform interface and select the CH1
channel (the backlight of the button lights up). After
selecting, the waveform and parameters of CH1 can be set.
Yellow Trigger button: CH1 manual trigger button. In sweep
trigger source is selected as
“Manual”, each press of this button will initiate a trigger.
On/Off key: Turns the output of the CH1 channel on or off.
softkey, press the button and then press the button for which
Terminal
Terminal
When the output is turned on, the backlight of the button
When Utility → CH1/2 Set → CH2 Sync
synchronization, amplitude syn
When Utility → CH1/2 Set → CH1 Sync
terminal outputs a sync signal that matches
or burst mode, when the
When the output is turned on, the backlight of the button
4
Page 10
3.Quick start
lights up.
15
Waveform
Including: sine , square , ramp , pulse
, the corresponding
backlight will be lit.
16
USB Interface
Connect to an external USB Host device, such as a USB flash
drive.
17
Power Button
Turn on/off the waveform generator
8
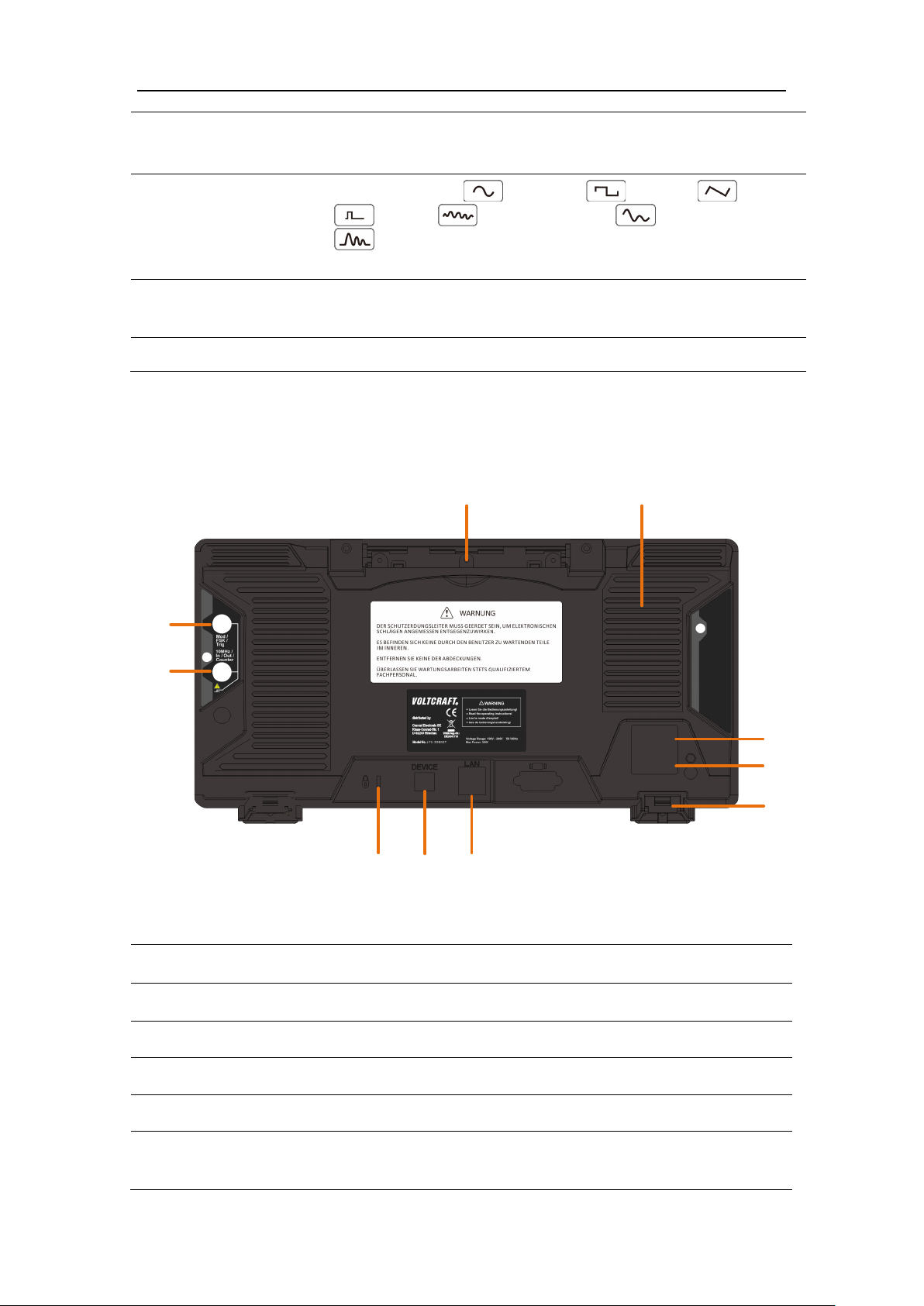
7
6
10
9
1
2
5
3
4
1
Retractable Handle
2
Vents
3
Power Input Socket
AC power input interface.
4
Fuse Box
The place to install the fuse.
5
Stool
Tilting the signal generator for easy operation.
6
LAN Interface
The signal generator is connected to the local area
network through this interface for remote control.
Selection Area
Rear Panel
, noise , arbitrary wave , harmonic waves
. When one waveform is selected
Figure 3-2 Rear Panel Overview
5
Page 11
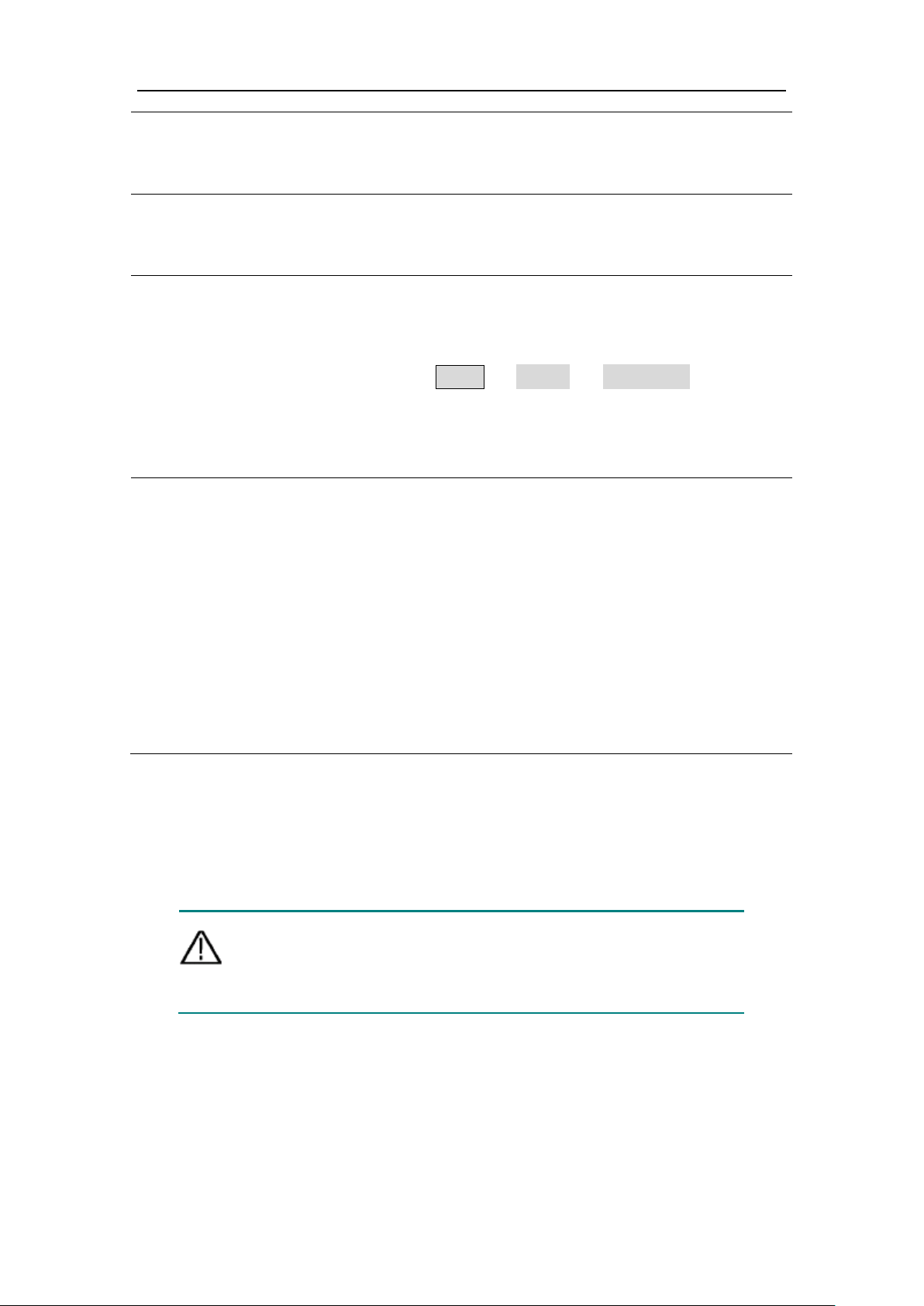
7
USB Device Interface
Used to connect a USB type B controller. The PC
generator through the host computer software.
8
Keyhole
A safety lock (please buy it yourself) can be used
to lock the instrument in a fixed position to secure
the instrument.
9
10MHz
In/Out/Counter(Reference
The default is to receive the frequency meter input
signal. Used to receive a 10MHz clock signal when
the instrument is set to an internal clock source
used to receive an external 10MHz clock signal
source.
10
Mod/FSK/Trig
When modulating the waveform, outputting the
sweep frequency, and the burst, the signal
Note: If one channel turns on AM, FM, PM, PWM
and the other channel turns on ASK, FSK,
PSK, sweep or burst, and both channels are set to
external trigger, then the channel that sets the
trigger source can be set later. With an external
trigger, the other channel automatically cancels
ger because of the different
external modulation signal types.
To prevent electric shock, make sure the instrument is properly
grounded.
clock input / output /
frequency meter input)
connector
(modulation/trigger
input) connector
3.Quick start
can be connected to communicate with the signal
and Utility → System → CLK output is On; it is
when the instrument is set to an external clock
accessed here can be used as an external source.
Power On
(1) Connect the instrument to an AC power source using the power cord supplied
with the accessory
Warning:
(2) Press the power button on the front panel and the screen will display the
booting screen.
or OSK,
the external trig
6
Page 12
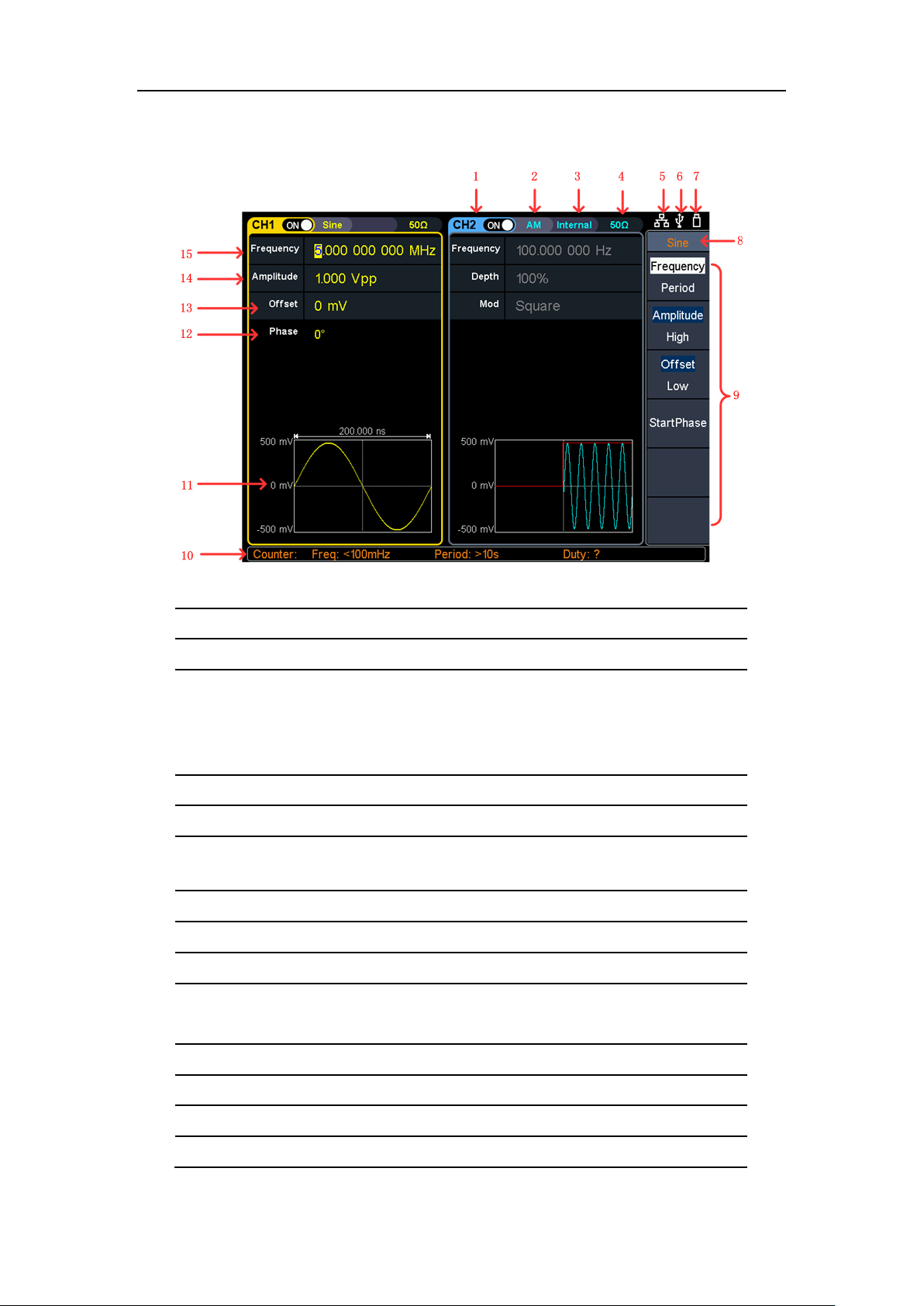
User Interface
1
2
3
4
5
This icon is lit when the network is connected through the LAN
6
This icon is lit when connected to the USB Host via the USB DEVICE
7
8
9
10
information, displays the frequency value,
12
13
14
3.Quick start
Figure 3-3 User Interface
Display channel name and channel status
Current waveform or current mode
Trigger source.
Internal: internal modulation or internal trigger source
External: external modulation or external trigger source
Manual: manual trigger source
Load, High Z indicates high resistance
interface.
When the instrument detects the USB flash drive, the icon lights.
Current menu name
Current waveform or mode setting menu
Frequency meter brief
period and the duty value
Display a schematic of the current waveform
11
Display the current starting phase
Offset / low level, depending on the right highlighted menu item
Amplitude / high level, depending on the right highlighted menu item
7
Page 13

3.Quick start
15
Frequency/cycle, depending on the right highlighted menu item
Use Build-in Help
(1) To get help on any front panel button or menu softkey, press the front panel
Help function button first, then press the button you need help.
(2) Press the Help function key again to exit the help interface.
8
Page 14

4.Panel Operation
4. Panel Operation
Channel Setting
Select the channel for configuration
Before configuring waveform parameters, you must select the channel you want to
configure. Press CH1 or CH2 to select the corresponding channel, and the
corresponding channel area in the user interface will light up
Turn On/Off Channel Output
Press the front panel CH1 On/Off or CH2 On/Off button to turn the output of the
corresponding channel on/off. When the output is turned on, the backlight of the
button lights up.
Channel Copy
(1) Press CH1⇌CH2 on front panel to display copy menu.
(2) Select CH2 to CH1 softkey or CH1 to CH2 softkey to copy the channel.
Waveform Setting
Sine, square, ramp, pulse, noise, arbitrary or harmonic waves can be set and output.
Press the waveform selection button on the instrument front panel: sine
square
, and enter the corresponding waveform setting interface. The waveform is
, ramp , pulse , noise , arbitrary wave , harmonic
,
different and the parameters that can be set are different.
Note: The following setting waveform uses CH1 channel as an example. If you need
to set CH2 channel, please refer to CH1 channel specific operation.
9
Page 15
4.Panel Operation
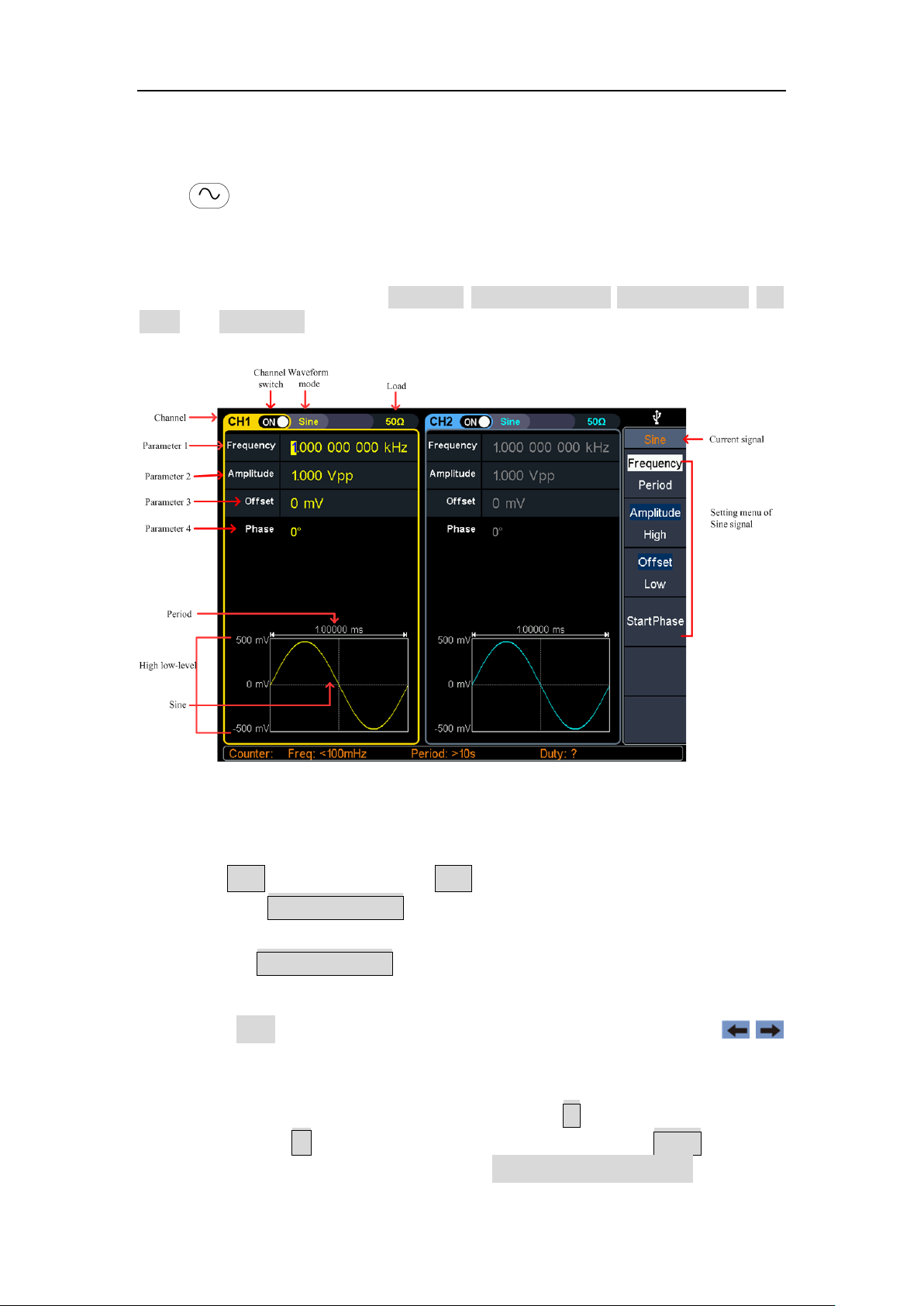
Output Sine Wave
Press , the screen displays the user interface of the sine wave. By operating the
sine wave menu on the right side of the screen, you can set the output waveform
parameters of the sine wave.
The sine wave menu includes: frequency/period, amplitude/high level, offset/low
level, and start phase. The menu can be operated by the menu selection button on
the right.
Figure 4-1: Sine wave user interface
Set the frequency/period
Press CH1, all currently selected CH1 menu items are highlighted
Press the Frequency/Period soft key, the currently selected menu item is
highlighted, and the corresponding parameter item is displayed in parameter 1.
Press the Frequency/Period softkey again to switch the frequency and period.
There are two ways to change the selected parameter value:
Turn the knob to increase or decrease the value at the cursor. Press the /
arrow key to move the cursor left or right.
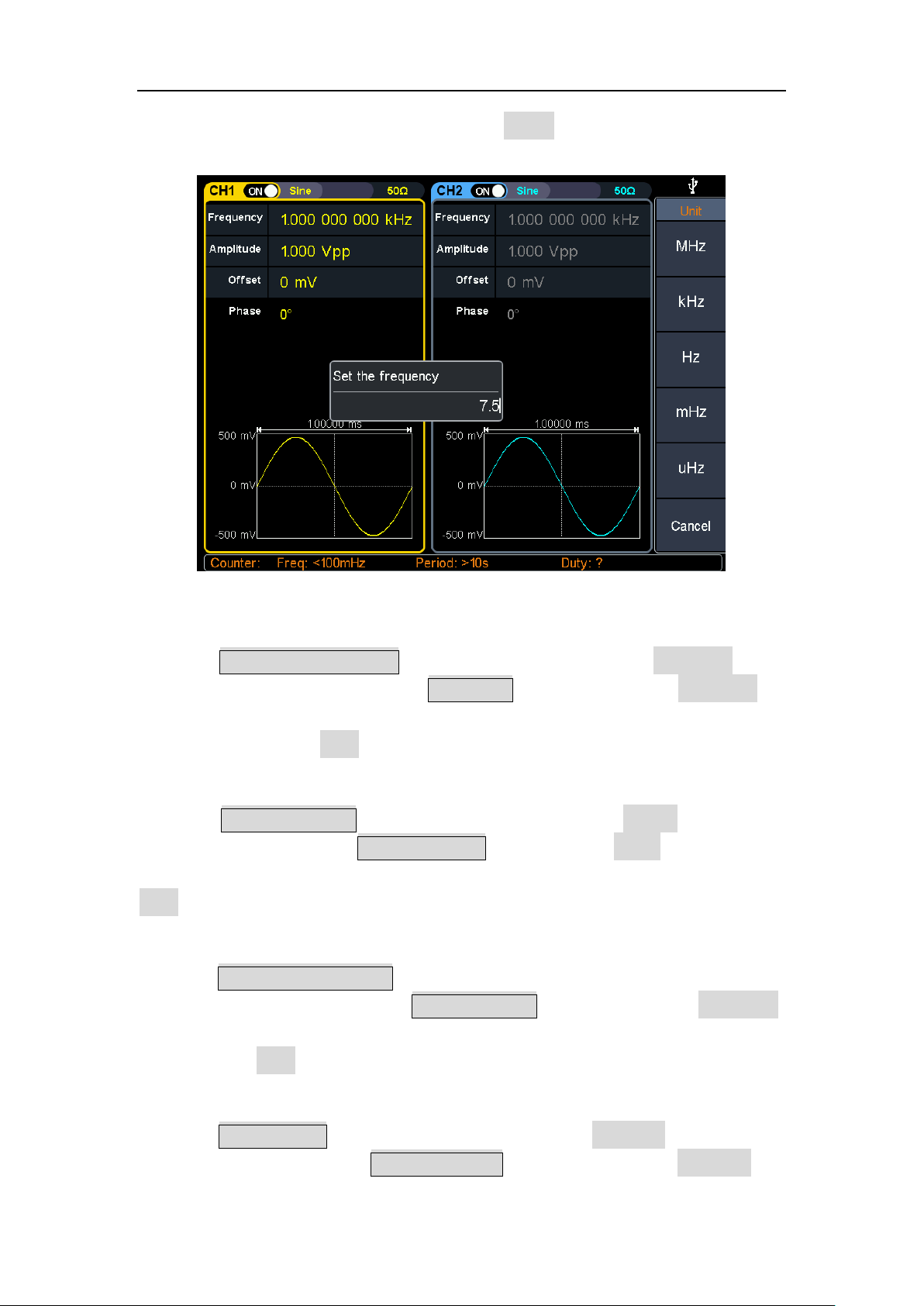
Press a number key on the numeric keypad directly, the screen will pop out the
data input box, input the desired value. Press the X soft key to delete the last
digit, press the ← soft key to cancel the input, and press the Enter soft key to
indicate the default unit input. Press the MHz, kHz, Hz, mHz, mHz soft keys to
10
Page 16
4.Panel Operation
select the unit of the parameter. Press the Cancel softkey to cancel the current
input parameter value.
Figure 4-2: Use the numeric keypad to set the frequency
Set the amplitude
Press the Amplitude/High Level softkey to confirm whether the Amplitude menu
item is highlighted; if not, press the Ampl/High button to switch to Amplitude. In
parameter 2 of Figure 5-1, the parameter value of the amplitude appears as a
blinking cursor. Use the knob or numeric keypad to set the desired value.
Set the offset
Press the Offset/Low Level softkey to confirm whether the Offset menu item is
highlighted; if not, press the Offset/Low level key to switch to Offset. In parameter 3
of Figure 5-1, the parameter value of the offset appears as a blinking cursor. Use the
knob or numeric keypad to set the desired value.
Set the high level
Press the Amplitude/High level button to confirm whether the “High level” menu
item is highlighted; if not, press the Ampl/High level button to switch to “High level”.
In parameter 2 of Figure 5-1, a high-level parameter value appears as a blinking
cursor. Use the knob or numeric keypad to set the desired value.
Set the low level
Press the Off/Low level button to confirm whether the “Low level” menu item is
highlighted; if not, press the Offset/Low level button to switch to “Low level”. In
11
Page 17
4.Panel Operation
parameter 3 of Figure 5-1, a low-level parameter value appears as a blinking cursor.
Use the knob or numeric keypad to set the desired value.
Set the start phase
Press the Start Phase softkey to confirm whether the Start Phase menu item is
highlighted; if not, press the Start Phase key. In parameter 4 of Figure 5-1, the
parameter value of the starting phase appears as a blinking cursor. Use the knob or
numeric keypad to set the desired value
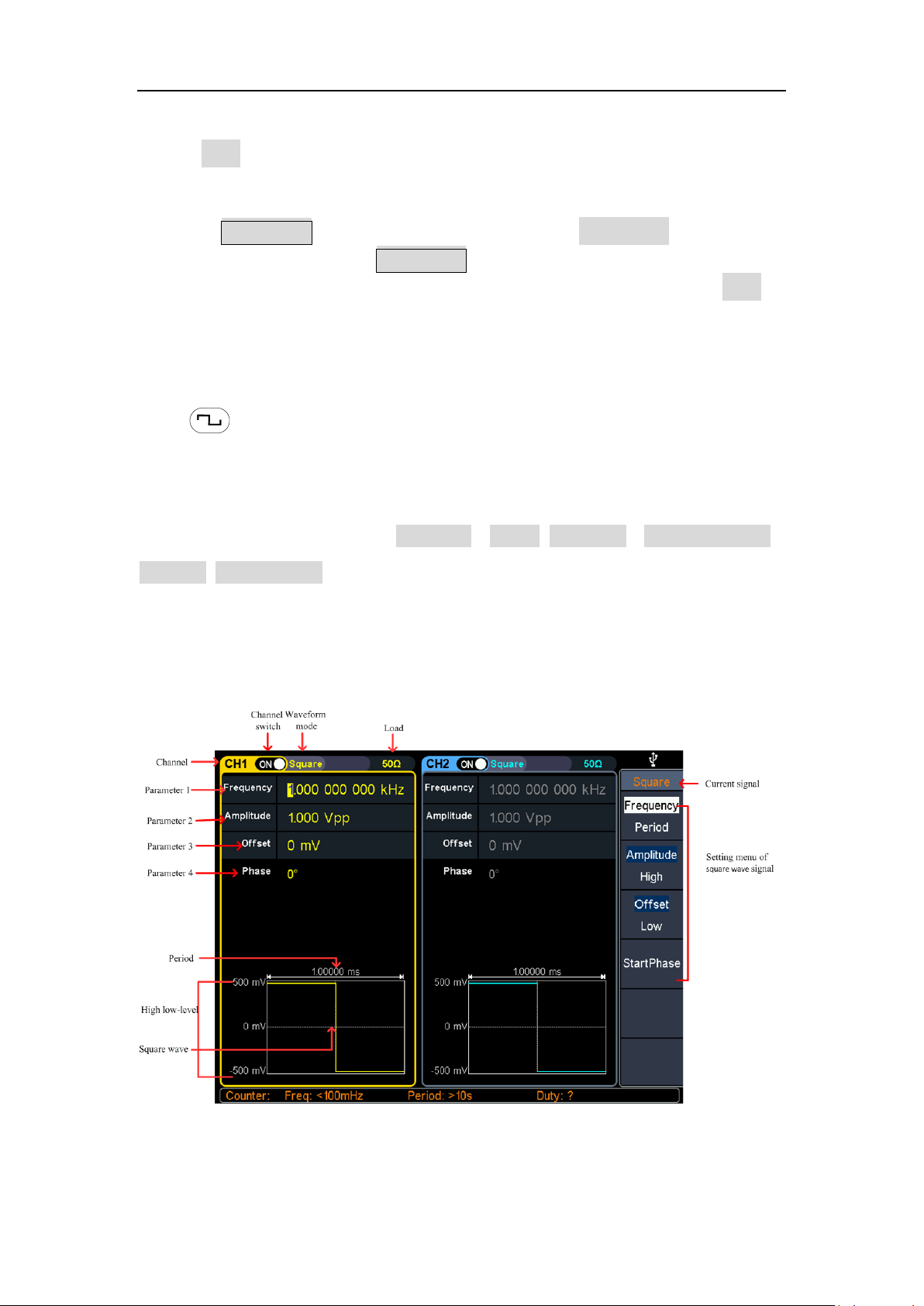
Output Square Wave
Press , the screen displays the square wave user interface. By operating the
square wave menu on the right side of the screen, you can set the square wave
output waveform parameters.
The square wave menu includes: frequency / period, amplitude / high level, offset /
low level, starting phase.
For the setting frequency/period, amplitude/high level, offset/low level, and starting
phase, please refer to Output Sine Wave on page 10.
Figure 4-3: Square wave user interface
12
Page 18
4.Panel Operation
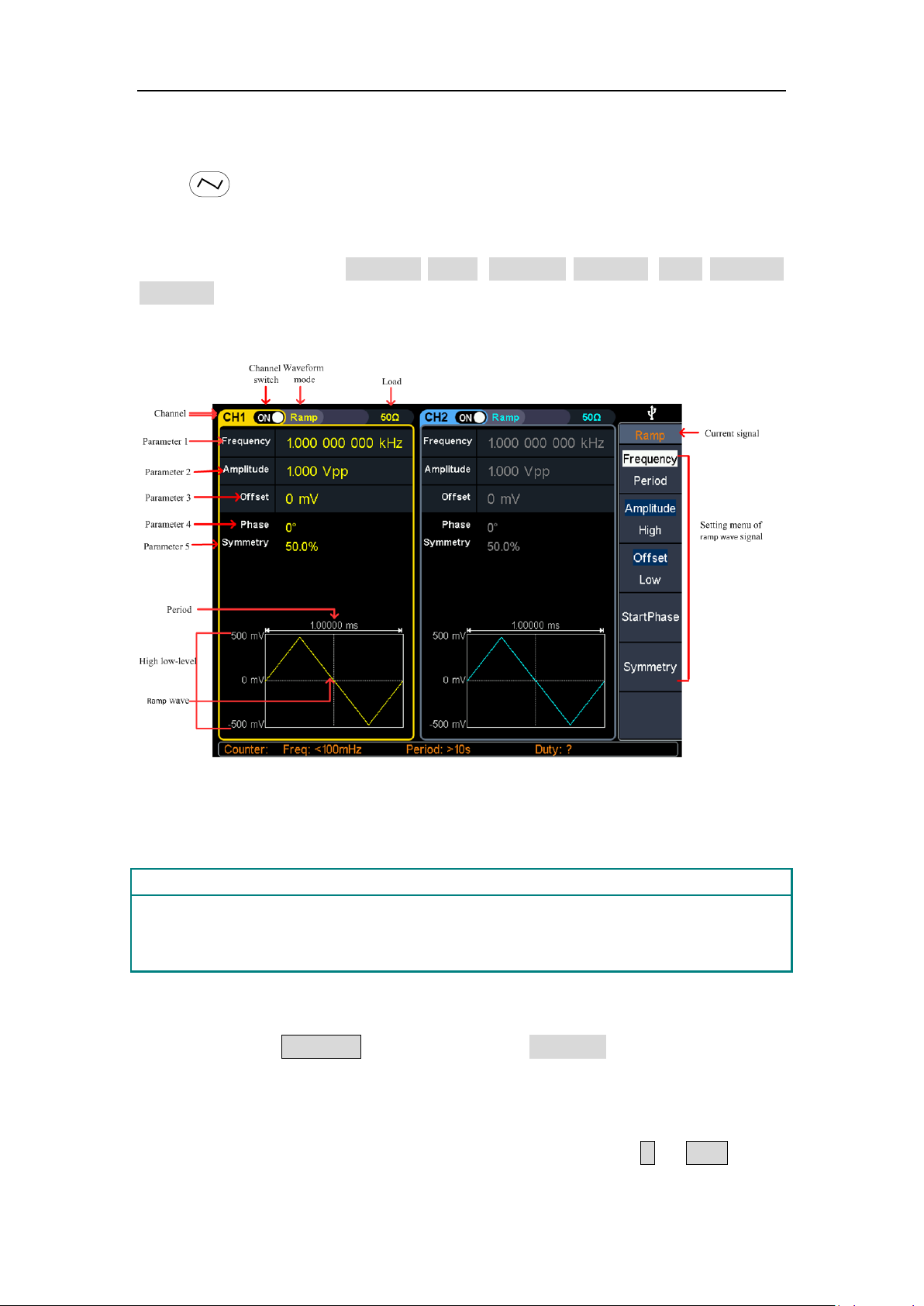
Glossary
Symmetry: Sets the percentage of the period during which the ramp waveform is
rising.
Output Ramp Wave
Press , the screen displays the user interface of the ramp wave. By operating
the ramp menu on the right side of the screen, you can set the output waveform
parameters of the ramp wave.
The ramp menu includes: frequency/period, amplitude/high level, offset/low level,
symmetry.
For the setting frequency/period, amplitude/high level, offset/low level, and starting
phase, please refer to Output Sine Wave on page 10.
Figure 4-4: Ramp wave user interface
Set the symmetry
(1) Press the Symmetry softkey to select the Symmetry menu item. Figure 5-6
Parameter 1 shows the current value of the symmetry;
(2) Use the knob to change directly, the value in parameter 1 of Figure 5-6; Or
use the numeric keypad to enter the value, press the % or Enter key to
13
Page 19
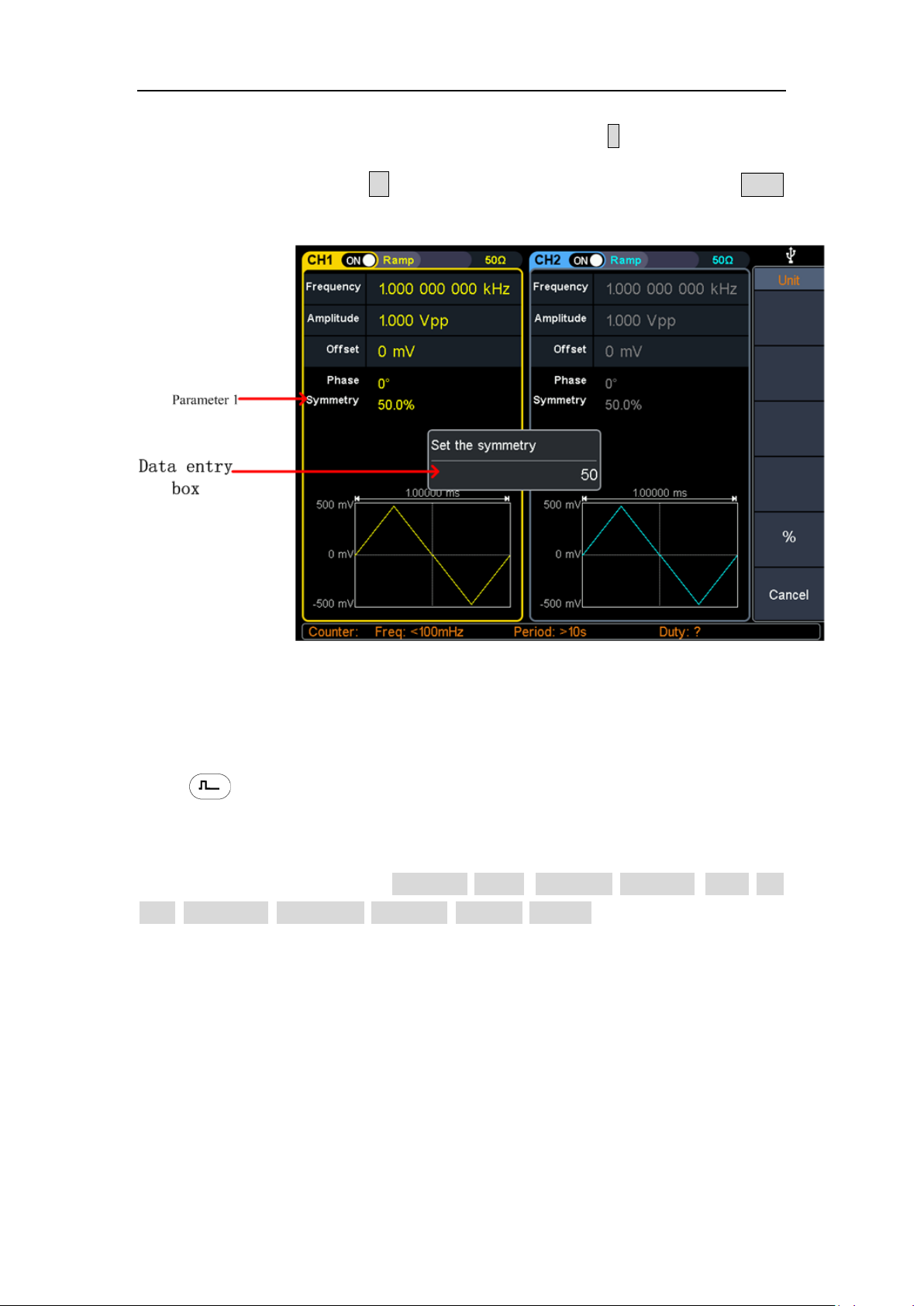
4.Panel Operation
display the symmetrical value of the input, press the X soft key to delete the
last digit, press the ← soft key to cancel the input, and press the Enter
softkey to indicate the default input.
Figure 4-5: Set the symmetry of ramp wave
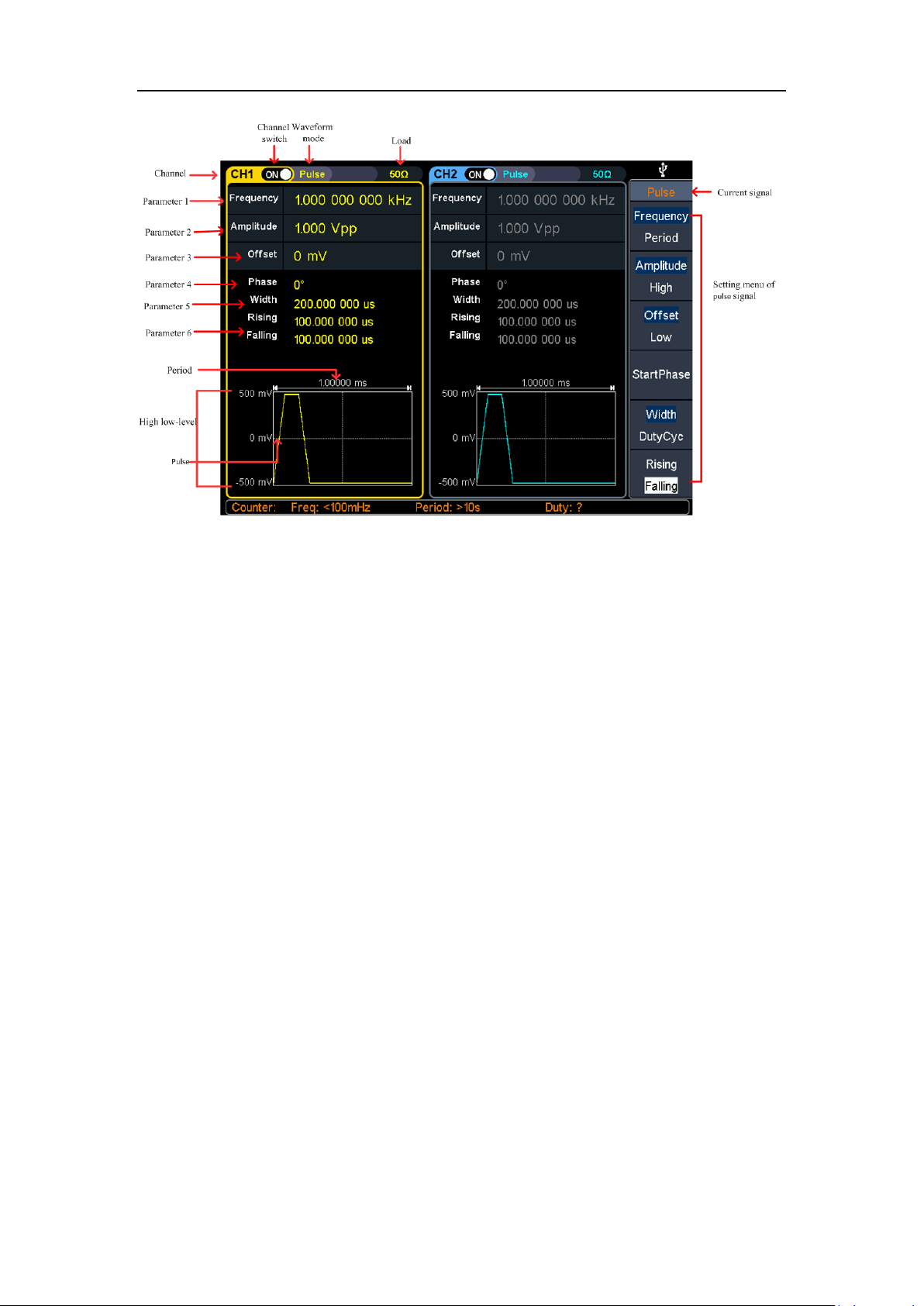
Output Pulse Wave
Press , the screen displays the user interface of the pulse wave. By operating
the pulse wave menu on the right side of the screen, the output waveform
parameters of the pulse wave can be set.
The pulse wave menu includes: frequency/period, amplitude/high level, offset/low
level, start phase, pulse width/duty cycle, rise time/fall time.
For the setting frequency/period, amplitude/high level, offset/low level, and starting
phase, please refer to Output Sine Wave on page 10.
14
Page 20
4.Panel Operation
Figure 4-6: Pulse wave user interface
15
Page 21
4.Panel Operation
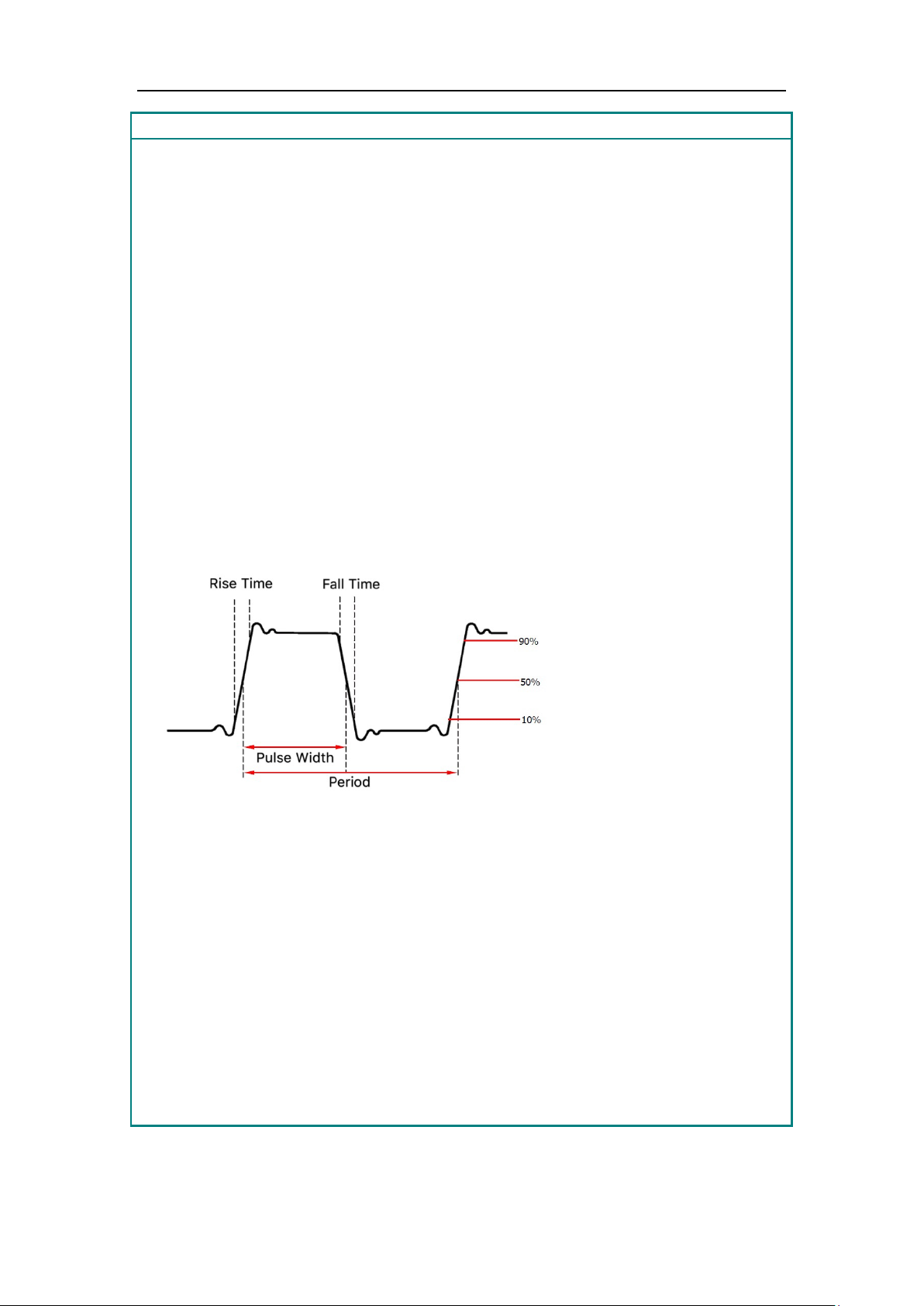
Glossary
Pulse Width
is an abbreviation for pulse width and is divided into positive pulse width and
The negative pulse width is the time interval from 50% of the falling edge to 50% of
The pulse width is determined by the period and duty cycle of the signal. The
In a series of ideal pulse sequences (such as a square wave), the ratio of the duration
50% threshold of the
ng edge of the pulse to the 50% threshold of the amplitude of
The settable range of pulse width is limited by the "minimum pulse width" and
The pulse duty cycle is defined as the pulse width as a percentage of the pulse
The pulse duty cycle is associated with the pulse width, and modifying one of the
her parameter. The pulse duty cycle
100%
PW
negative pulse width.
The positive pulse width is the time interval from 50% of the rising edge to 50% of
the adjacent falling edge.
the adjacent rising edge.
calculation formula is pulse width = period * duty cycle.
Duty Cycle
of the positive pulse to the total pulse period.
Pulse/Duty Cycle
The pulse width is defined as the time interval from the
amplitude of the risi
the next falling edge, as shown in the following figure.
"pulse period"
Pulse width ≥ minimum pulse width
Pulse width ≤ pulse period - minimum pulse width
period.
parameters will automatically modify the ot
is limited by the "minimum pulse width" and "pulse period".
Pulse duty cycle ≥ minimum pulse width ÷ pulse period × 100%
Pulse duty cycle ≤ (1 - 2 × minimum pulse width ÷ pulse period) ×
16
Page 22
4.Panel Operation
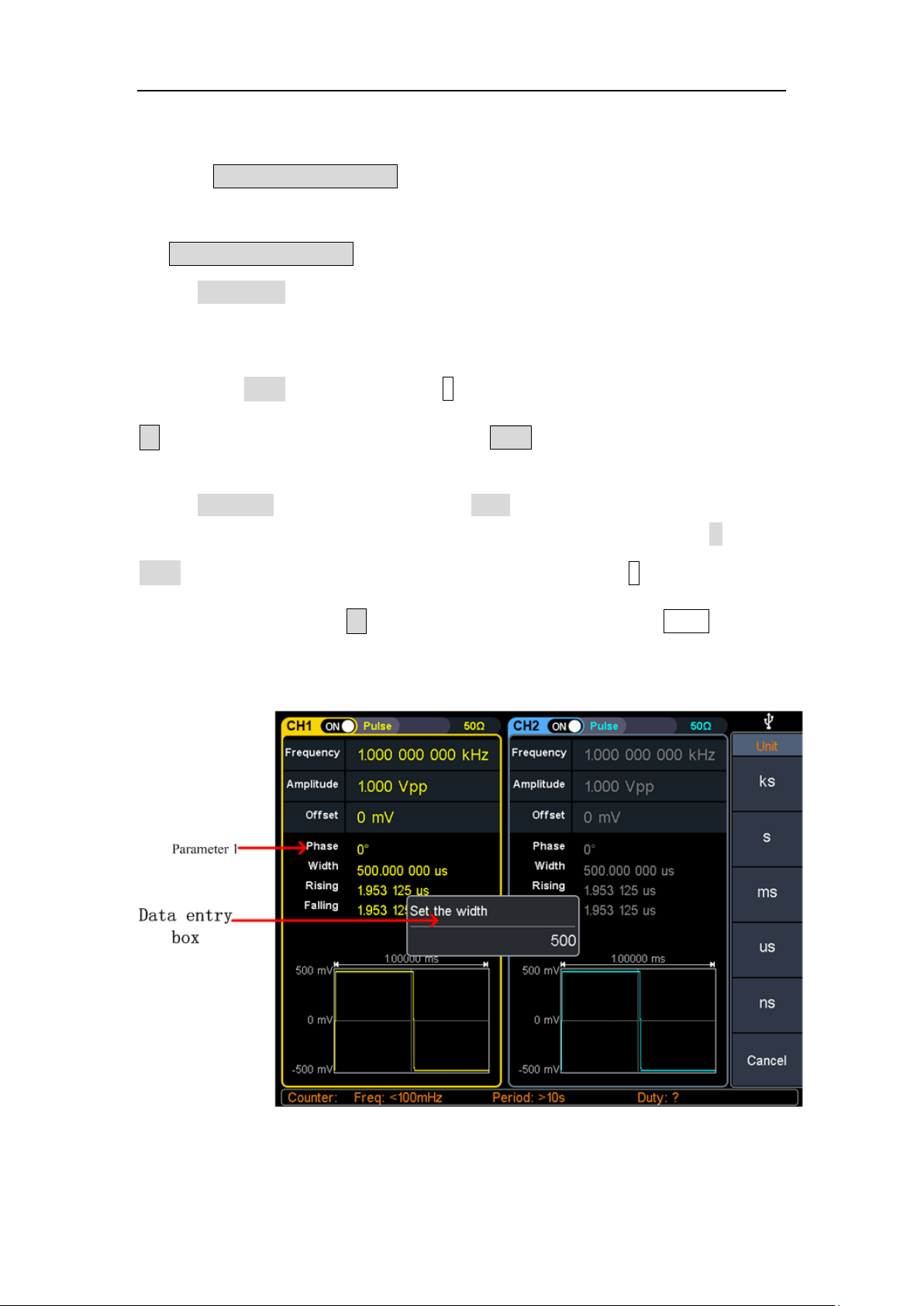
Set the pulse width/duty cycle
Press the Pulse Width/Duty Cycle softkey to select the Pulse Width menu item. As
shown in Figure 5-7, parameter 1 displays the current value of the pulse width. Press
the Pulse Width/Duty Cycle button to display the duty cycle.
Set the pulse width parameter value, use the knob to directly change the value of
the pulse width in parameter 1 of Figure 5-7; or use the numeric keypad to enter the
value, then select the desired unit from the right menu, press the desired unit (ks, s,
ms, us, ns) or Enter the value; press the X soft key to delete the last digit, press the
← soft key to cancel the input, and press the Enter soft key to indicate the default
input.
Set the duty cycle parameter value, use the knob to directly change the value of the
graph duty cycle; or use the numeric keypad to enter the value, then press % or
Enter from the right menu to enter the demand value; press the X soft key to delete
the last one. Bit, press the ← soft key to cancel the input, press the Enter soft key
to indicate the default input.
Figure 4-7: Set the pulse width
17
Page 23

4.Panel Operation
Set the rising/falling time
Press the rise time / fall time soft key to select the "rise time / fall time" menu item,
as shown in Figure 5-6, parameter 6 shows the current value of the rise/fall time;
press the rise time / fall time key to switch between the current display. Parameter
value.
Set the rise time/fall time parameter value Use the knob or use the numeric keypad
to enter the value, then select the desired unit from the right menu, press the
desired unit (ks, s, ms, us, ns) or Enter the value; press the X soft key to delete the
last digit, press the ← soft key to cancel the input, press the Enter softkey to
indicate the default input.
Output Noise Wave
The noise wave output by the system is white noise. Press , the screen displays
the user interface of the noise wave. By operating the noise wave menu on the right
side of the screen, the output waveform parameters of the noise wave can be set.
The noise wave has no frequency and periodic parameters, and the bandwidth is 120
MHz of Gaussian noise.
The menu of noise waves includes: amplitude / high level, offset / low level.
For the setting of amplitude/high level, offset/low level, please refer to Output Sine
Wave on page 10.
18
Page 24
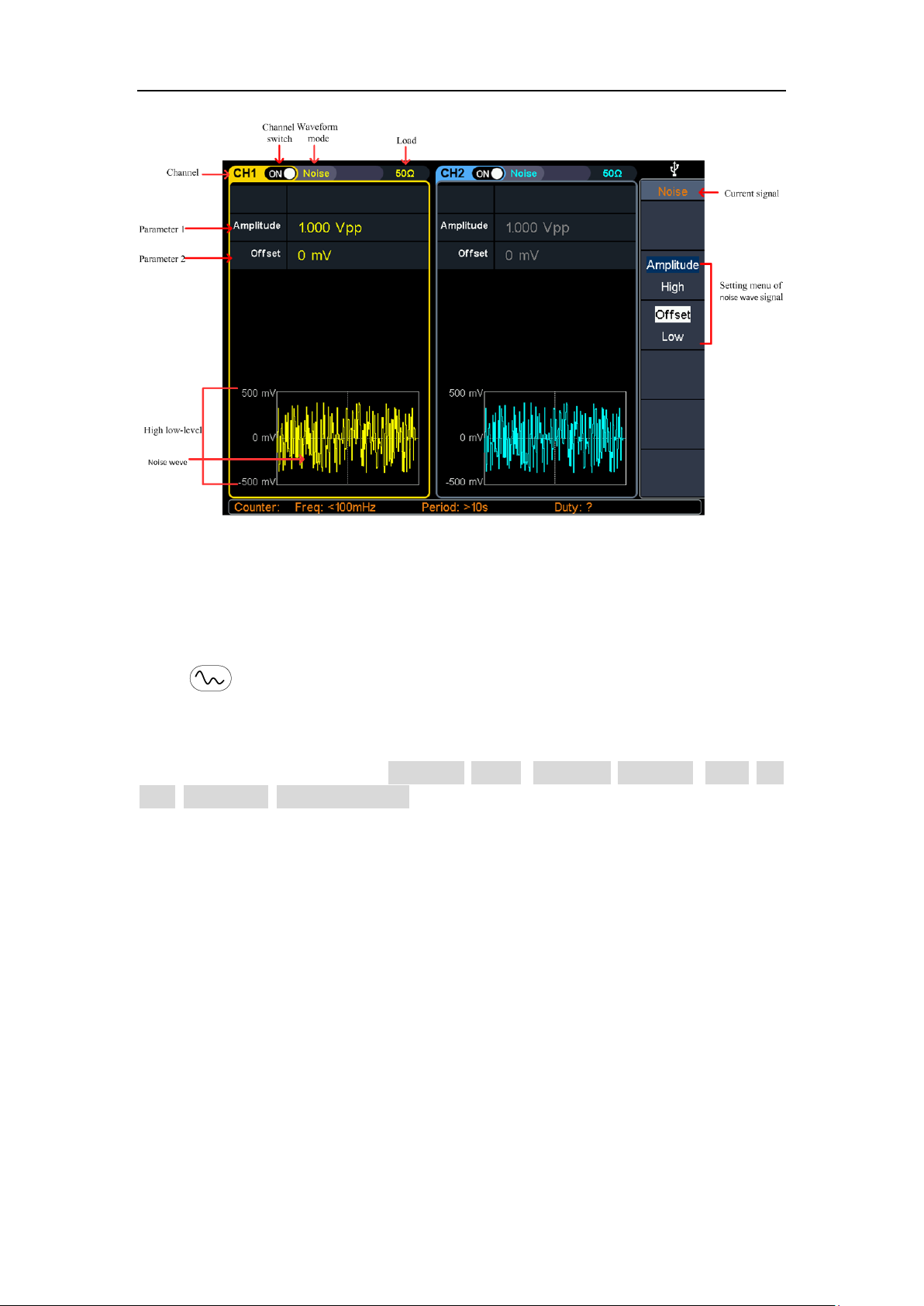
4.Panel Operation
Figure 4-8: noise wave user interface
Output Arbitrary Wave
Press , the screen displays the user interface of the arbitrary wave. By
operating the arbitrary wave menu on the right side of the screen, the output
waveform parameters of the arbitrary wave can be set.
Arbitrary wave menus include: frequency/period, amplitude/high level, offset/low
level, start phase, built-in waveform.
For the setting frequency/period, amplitude/high level, offset/low level, and starting
phase, please refer to Output Sine Wave on page 10.
Arbitrary waves include two kinds of arbitrary waveforms: system built-in waveforms
and user-edited waveforms.
19
Page 25

4.Panel Operation
Figure 4-9: Arbitrary wave user interface
Choose build-in waves
There are 152 types of waveforms built into the system, the number of waveform
points is 8192 points, and the highest upper limit frequency is 15MHz. To select a
built-in waveform, the steps are as follows:
(1) Press , then press the built-in waveform soft key to enter and select the
menu
(2) Select the type of built-in waveform by common, medical, standard, math soft
keys
Press Next menu to select the built-in waveform: Trigonometric function,
window function, engineering, and segmentation modulation.
For example, select Math to enter the interface shown below.
20
Page 26

4.Panel Operation
Name
Description
AmpALT
Gain oscillation curve
Att ALT
Attenuation oscillation curve
GaussPulse
Gauss pulse
NegRamp
Negative ramp
NPulse
Negative pluse
StairUP / UD
Stair upward/downward
Trapezia
Trapezia
Heart
Heart
Cardiac
Cardiac
LFPulse
(3) Turn the knob to select the desired waveform, for example, select Airy. Press the
OK soft key to enter the Airy function.
Buld-in wave list
Common
DC Direct current
AbsSine Absolute sine
AbsSineHalf Absolute half-sine
PPulse Positive pluse
SineTra Sine-Tra wave
SineVer Sine-Ver wave
StairDn Stair downward
Medical
Tens 1 Neuroelectric stimulation therapy waveform 1
Tens 2 Neuroelectric stimulation therapy waveform 2
Tens 3 Neuroelectric stimulation therapy waveform 3
EOG Electrooculogram
Low frequency pulse electrotherapy waveform
21
Page 27

4.Panel Operation
Ignition
TP2A
ISP
Automobile starting profile with oscillation
VR
TP1
Automotive transients due to power cuts
TP2B
P4
SCR SCR
Sintering temperature release map
Surge
Surge signal
Airy Airy function
Besselj
Type I Bessel function
Bessely
Type II Bessel function
ErfcInv
Anti-complement error function
ErfInv
Inverse error function
Dirichlet
Dirichlet function
ExpFall
Exponential decline function
ExpRise
Exponential rise function
Laguerre
Four Laguerre polynomials
Log Base 10 logarithmic function
LogNormal
Lognormal distribution
Lorentz
Lorentz function
Maxwell
Maxwell distribution
Rayleigh
Rayleigh distribution
Versiera
Tongue line
EEG electroencephalogram
Pulseilogram Ordinary pulse curve
ResSpeed Ordinary expiratory flow rate curve
Standard
Automobile internal combustion engine ignition waveform
Automotive transients due to inductance in the wiring
Working voltage profile of the car when resetting
TP5A
TP5B
Car transients due to startup switching off
Car working profile during start-up
Car transients due to the power cut of battery
Car transients due to the power cut of battery
Math
Cauchy Cauchy distribution
X^3 Cubic function
Erf Error function
Erfc Remnant error function
Laplace Laplace distribution
Legend Five Legendre polynomials
Gauss
HaverSine Semi-positive function
Gaussian distribution, also known as the normal distribution
Weibull Weber distribution
Ln(x) Natural logarithmic waveform
X^2 Square function
Round Round wave
22
Page 28

4.Panel Operation
CosH
Hyperbolic cosine
Cot
Cotangent function
CotH
Hyperbolic cotangent
CotHCon
Concave hyperbolic cotangent
CotHPro
Raised hyperbolic cotangent
CscCon
Recessed cosecant
Csc
CscPro
CscHPro
Raised hyperbolic cosecant
RecipCon
Reciprocal of the depression
RecipPro
Raised countdown
SecCon
Depression secant
SecPro
Raised secant
SecH
Hyperbolic secant
Sinc
SinH
TanH
Hyperbolic tangent
ACos
Inverse cosine function
ACosH
Inverse hyperbolic cosine function
ACot
Anti-cotangent function
ACotCon
Inverse cotangent function
ACotPro
Raised inverse cotangent function
ACotH
ACotHCon
ACscCon
Concave inverse cosecting function
ACscPro
Raised anti-cosecting function
AcscH
Anti-hyperbolic cosecant
ACscHCon
Inverse hyperbolic cotangent function
ACscHPro
Raised inverse hyperbolic cosecant function
Asec
Inverse cut function
ASecCon
ASecPro
Chirp Linear frequency modulation
Rhombus Diamond wave
Trigonometric function
CscH
CscHCon
Sqrt
Tan
ACotHPro
Acsc
ASecH
ASin
Cosecant
Raised cosecant
Hyperbolic cosecant
Depressed hyperbolic cosecant
Sinc function
Hyperbolic sine
Square root function
Tangent function
Inverse hyperbolic cotangent function
Inverse hyperbolic cotangent function
Raised inverse hyperbolic cotangent function
Anti-cosecting function
Inverse tangent function
Raised arctangent function
Inverse hyperbolic secant function
Inverse sine function
23
Page 29

4.Panel Operation
Window Function
Bartlett
Bartlett window
BarthannWin
Modified Bartlett window
Blackman
Blackman window
BlackmanH
BlackmanH window
BohmanWin
BohmanWin window
Boxcar
ChebWin
Hanning
Hanning window
Kaiser
Kaiser window
NuttallWin
The smallest four Blackman-Harris windows
ParzenWin
Parzen window
TaylorWin
Tay l a o r window
Triang
Triangle window, also call Fejer window
TukeyWin
Engineering Window
CPulse
C-Pulse signal
CWPulse
CW pulse signal
RoundHalf
Half-round wave
BandLimited
Band limited signal
BlaseiWave
Chebyshev1
Type I Chebyshev filter
Chebyshev2
DampedOsc
GateVibar
Gate self-vibration signal
LFMPulse
Chirp signal
MCNoise
Mechanical construction noise
Discharge
NiMH battery discharge curve
Quake
Seismic wave
Radar
Radar signal
Ripple
RoundsPM
ASinH
ATan
ATanH
FlattopWin
Hamming
Inverse hyperbolic sine function
Arc tangent function
Inverse hyperbolic tangent function
Rectangular window
Chebyshev window
Flat top window
Hamming window
Tukey window
Butterworth
Combin
DualTone
Gamma
StepResp
SwingOsc
Butterworth filter
Combined function
Blasting vibration "time-vibration speed" curve
Type II Chebyshev filter
Damped oscillation "time-displacement" curve
Dual audio signal
Gamma signal
Ripple
RoundsPM wave
Step response signal
Swing oscillation kinetic energy-time curve
24
Page 30

4.Panel Operation
Segement Modulation
AM
Sinusoidal segmented AM wave
FM
Sinusoidal segmented FM wave
PM
Sinusoidal segmented PM wave
PWM
Pulse width segmented PWM wave
TV
Voice
TV signal
Voice signal
Output Harmonic Wave
Press to display the harmonic user interface. You can set the harmonic output
waveform parameters by operating the harmonic menu on the right side of the
screen.
Harmonic menus include: frequency/period, amplitude/high level, offset/low level,
start phase, harmonic type, harmonic order, sequence number, harmonic amplitude,
harmonic phase.
For the setting frequency/period, amplitude/high level, offset/low level, and starting
phase, please refer to Output Sine Wave on page 10.
Harmonic wave function overview
According to the Fourier transform theory, the time domain waveform is a superposition of a
series of sine waves, expressed by the following equation:
f
(t) = A1 sin(2πf1t
Generally, the component of frequency
frequency,
frequency of each component is usually an integer multiple of the fundamental frequency, which
is called harmonic. A component whose frequency is an odd multiple of the fundamental
frequency is called an odd harmonic, and a component whose frequency is an even multiple of
the fundamental frequency is called an even harmonic.
This signal source can output up to 16 harmonic orders. After selecting CH1 or CH2, press the
front panel
the fundamental, select the type of output harmonics, specify the maximum number of output
harmonics, and the amplitude and phase of each harmonic.
A
1
+
ϕ
) + A2 sin(2πf2t
1
is the fundamental amplitude, and
button to enter the harmonic setting menu. You can set the parameters of
+
ϕ
) + A3 sin(2πf3t
2
f
is called the fundamental wave,
1
ϕ
is the fundamental phase. In addition, the
1
+
ϕ
3
) + ......
f
is the fundamental
1
Select the harmonic type
This signal source can output even harmonics, odd harmonics, all harmonics or user-defined
harmonics. Enter the harmonic setting menu and press the harmonic type softkey to select the
desired harmonic type.
Even harmonic
25
Page 31

4.Panel Operation
Press the Harmonic Type softkey menu and the instrument outputs the fundamental and even
harmonics.
Odd harmonic
Press the Harmonic Type softkey menu and the instrument outputs the fundamental and odd
harmonics.
Order harmonic
Press the Harmonic Type softkey menu and the instrument outputs the fundamental and
harmonics in sequence.
customize
Press the Harmonic Type softkey to customize the number of times the harmonics are output.
The maximum number of times is 16. The 16-bit binary data is used to represent the output state
of the 16th harmonic, respectively, 1 means the output of the corresponding subharmonic is
turned on, and 0 means the output of the corresponding subharmonic is turned off. The user
only needs to use the numeric keypad to modify the value of each data bit (note: the leftmost bit
indicates the fundamental wave, fixed to X, and modification is not allowed). For example, set
16-bit data to X001 0000 0000 0001, indicating the output fundamental, 4th harmonic, and 16th
harmonic. Note: The harmonics of the actual output are limited by the currently specified
“harmonic times”.
Set the harmonic times
Press the Next soft key to enter the next page, and then press the Harmonic Times softkey to
confirm whether the “Harmonic Times” menu item is highlighted; if not, press the Harmonic
Times softkey. In parameter 5 of Figure 5-11, the parameter value of the harmonic order appears
as a blinking cursor. Use the knob or numeric keypad to set the desired value, which can be set
from 2 to 16 times.
Set the harmonic number
Press the Next soft key to enter the next page, and then press the Sequence soft key to confirm
whether the “Number” menu item is highlighted; if not, press the Sequence soft key. In
parameter 6 of Figure 5-11, the parameter value of the serial number appears as a blinking cursor.
Use the knob or numeric keypad to set the desired value, which can be set from 2 to 16 times.
Set the harmonic amplitude
Press the Next soft key to enter the next page, and then press the Harmonic Amplitude softkey
to confirm whether the “Harmonic Amplitude” menu item is highlighted; if not, press the
Harmonic softkey soft key. In parameter 7 of Figure 5-11, the parameter value of the harmonic
amplitude appears as a blinking cursor. Use the knob or numeric keypad to set the desired value.
Set the harmonic phase
Press Next to enter the next page, and then press the Harmonic Phase softkey to confirm
whether the “Harmonic Phase” menu item is highlighted; if not, press the Harmonic Phase
softkey. In parameter 8 of Figure 5-11, the parameter value of the harmonic phase appears as a
blinking cursor. Use the knob or numeric keypad to set the desired value.
26
Page 32

4.Panel Operation
Figure 4-10 harmonic wave user interface
Output the modulated waves
After pressing the Mod function key, press the F1 key to select the modulation type
to output the modulated waveform. Types that can be modulated include: AM
(amplitude modulation), FM (frequency modulation), PM (phase modulation), PWM
(pulse width modulation), ASK (amplitude shift keying), PSK (phase shift keying), FSK
(frequency) Shift keying), 3FSK (ternary frequency shift keying), 4FSK (quadrature
frequency shift keying), BPSK (biphase phase shift keying), OSK (oscillating keying).
Note: The following output modulation waveform uses CH1 channel as an example.
If you need to set CH2 channel, please refer to CH1 channel specific operation.
Amplitude Modulation(AM)
The output modulation waveform consists of a carrier wave and a modulated wave.
The carrier wave can be a sine wave, a square wave, a ramp wave, or an arbitrary
wave. In amplitude modulation, the amplitude of the carrier varies with the
instantaneous voltage of the modulation waveform. The user interface for amplitude
modulation is shown below.
27
Page 33

4.Panel Operation
Figure 4-11: Amplitude modulation user interface
How to set the parameters of amplitude modulation
(1) After pressing the Mod function key, press the Modulation type soft key, use
the knob to select, the modulation type is AM, press the OK soft key.
(2) Press to display the waveform and parameters of the current carrier. You
can change the parameters of the carrier. For details, please refer to Output Sine
Wave on page 10. Press or Mod to return to the modulation mode
interface.
(3) Press Source to select the source. If External is selected, the external signal
source is connected to the Ext Mod In interface on the rear panel, and the
setting is completed; if you select Internal, continue with the following steps.
(4) Press Modulation Waveform to select the modulation waveform. You can select
Sine, Square, Ramp, Noise, or Arb.
(5) Press the AM frequency button to set the AM frequency. The amplitude
modulation range is from 2 mHz to 100 kHz (for internal sources only).
(6) Press Modulation Depth to set the modulation depth. The modulation depth
ranges from 0% to 100%.
28
Page 34

4.Panel Operation
Glossary
AM frequency: the frequency of the modulation waveform.
100% modulation, the output amplitude is equal to the specified value. For external
+1 V corresponds to the currently selected depth of 100%.
Modulation Depth:The range of amplitude variations of the output modulation
waveform. At 0% modulation, the output amplitude is half of the set amplitude. At
sources, the AM depth is controlled by the signal level on the Ext Mod In connect o r.
Frequency Modulation (FM)
The output modulation waveform consists of a carrier wave and a modulated wave.
The carrier wave can be a sine wave, a square wave, a ramp wave, or an arbitrary
wave. In frequency modulation, the frequency of the carrier varies with the
instantaneous voltage of the modulation waveform. The user interface for frequency
modulation is shown below.
Figure 4-12: frequency modulation user interface
Steps to set the frequency modulation
(1) After pressing the Mod function key, press the Modulation type soft key, select
the knob to select, the modulation type is FM, press the OK soft key.
(2) Press to display the waveform and parameters of the current carrier. You
29
Page 35

4.Panel Operation
can change the parameters of the carrier. For details, please refer to Output Sine
Wave on page 10. Press or Mod to return to the modulation mode
interface.
(3) Press Source to select the source. If External is selected, connect the external
signal source to the Ext Mod In interface on the rear panel and skip to step (5).
If you select Internal, continue with the following steps.
(4) Press Modulation Waveform to select the modulation waveform type. You can
select Sine, Square, Ramp, Noise, or Arb.
(5) Press Modulation Frequency to set the modulation frequency value. The
modulation frequency ranges from 2 mHz to 100 kHz (for internal sources only).
(6) Press the Frequency Offset softkey to set the frequency offset value. Frequency
offset range: 2 mHz ≤ offset ≤ min (min is the carrier frequency or carrier
maximum frequency - carrier frequency) by default, the smaller of the two.
30
Page 36

4.Panel Operation
Phase Modulation (PM)
The output modulation waveform consists of a carrier wave and a modulated wave.
The carrier wave can be a sine wave, a square wave, a ramp wave, or an arbitrary
wave. In phase modulation, the phase of the carrier varies with the instantaneous
voltage of the modulation waveform. The phase modulation user interface is shown
below
Figure 4-13: Phase modulation user interface
Steps to set phase modulation
(1) After pressing the Mod function key, press the Modulation type soft key, use
the knob to select, the modulation type PM, and press the OK soft key.
(2) Press to display the waveform and parameters of the current carrier. You
can change the parameters of the carrier. For details, please refer to Output Sine
Wave on page 10. Press or Mod to return to the modulation mode
interface.
(3) Press Source to select the source. If External is selected, connect the external
signal source to the Ext Mod In interface on the rear panel and skip to step (5).
If you select Internal, continue with the following steps.
(4) Press Modulation Waveform to select the modulation waveform. You can select
Sine, Square, Ramp, Noise, or Arb.
31
Page 37

4.Panel Operation
(5) Press the Phase Modulation Frequency softkey to set the phase modulation
frequency. The range is from 2 mHz to 100 kHz (for internal sources only).
(6) Press Phase Deviation to set the phase deviation, which is the offset of the
phase, ranging from 0° to 180°.
Pulse Width Modulation (PWM)
The output modulation waveform consists of a carrier wave and a modulated wave.
The pulse width modulation function can only be applied to the modulated pulse
wave, so the carrier can only be a pulse wave. In pulse width modulation, the pulse
width of a carrier (pulse wave) varies with the instantaneous voltage of the
modulation waveform.
Figure 4-14 Pulse width modulation user interface
Steps to set pulse width modulation
(1) First set the carrier to pulse wave, press Mod to enter PWM modulation mode.
(2) After pressing the Mod function button, press the Modulation Type so f tkey, use
the knob to select the modulation type as PWM, and press the Enter sof t key.
(3) Press to display the waveform and parameters of the current carrier. You
can change the parameters of the carrier. For details, please refer to Output Sine
Wave on page 10. Press or Mod to return to the modulation mode
interface.
32
Page 38

4.Panel Operation
(4) Press Source to select the source. If External is selected, connect the external
signal source to the Ext Mod In interface on the rear panel and skip to step (6). If
you select Internal, continue with the following steps.
(5) Press Modulation Waveform to select the modulation waveform. You can select
Sine, Square, Ramp, Noise, or Arb.
(6) Press the PWM Rate softkey to set the PWM rate, which can be set from 2 mHz
to 100 kHz (for internal sources only).
(7) Press the Duty Cycle Deviation softkey to set the duty cycle deviation (depending
on the non-modulation mode, the pulse wave setting menu is pulse width or
duty cycle). The maximum value of the duty cycle deviation is: 0 to 99%. [pulse
wave duty ratio, 100% - pulse wave duty ratio]
Amplitude shift keying (ASK)
The output modulation waveform consists of a carrier wave and a modulated wave.
The carrier wave can be a sine wave, a square wave, a ramp wave, or an arbitrary
wave. In phase modulation, the phase of the carrier varies with the instantaneous
voltage of the modulation waveform. The user interface for phase modulation is
shown below.
Figure 4-15 Amplitude shift keying user interface
Steps to set frequency shift keying modulation
33
Page 39

4.Panel Operation
(1) After pressing the Mod function key, press the Modulation type soft key,
use the knob to select, the modulation type is ASK, press the Enter soft ke y.
(2) Press to display the waveform and parameters of the current carrier.
You can change the parameters of the carrier. For details, please refer to
Output Sine Wave on page 10. Press or Mod to return to the
modulation mode interface.
(3) Press Source to select the source. If external is selected, connect the
external signal source to the Ext Trig/Burst/Fsk In interface on the rear panel
and skip to step (5). If you select internal, continue with the following steps.
(4) Note: When the source selects external, the slope is set to “positive”, then
the larger of the carrier amplitude and modulation amplitude is output
when the logic is high level, and the carrier amplitude and modulation
amplitude are output when the logic low level is input. The smaller one.
When the slope is "negative", the opposite is true.
(5) Press the ASK Rate softkey to set the ASK rate, which can be set from 2 mHz
to 1 MHz (for internal sources only).
(6) Press the Amplitude softkey to set the amplitude, ie the modulation
amplitude, which can be set from 0 mVpp to 1 Vpp.
34
Page 40

4.Panel Operation
Phase Shift Keying (PSK)
The output modulation waveform consists of a carrier wave and a modulated wave. The carrier
wave can be a sine wave, a square wave, a ramp wave, or an arbitrary wave. In phase modulation,
the phase of the carrier varies with the instantaneous voltage of the modulation waveform. The
phase modulation user interface is shown below
Figure 4-16 Phase shift keying user interface
Steps to set phase shift keying modulation
(1) After pressing the Mod function key, press the Modulation type soft key, use
the knob to select, the modulation type is PSK, press the Enter s oft key. The
carrier waveform can be selected as needed. The following is a sine wave.
(2) Press to display the waveform and parameters of the current carrier. You
can change the parameters of the carrier. For details, please refer to
Wave on page 10. Press or Mod to return to the modulation mode
interface.
(3) Press Source to select the source. If external is selected, connect the external
signal source to the Ext Trig/Burst/Fsk In interface on the rear panel and skip to
step (5). If you select internal, continue with the following steps.
Note: When the source selects external, set the slope to “positive”, then output
the carrier phase when input logic low level, and output the modulation phase
Output Sine
35
Page 41

4.Panel Operation
when input logic high level. When the slope is "negative", the opposite is true.
(4) Press the PSK softkey to set the PSK rate, which can be set from 2 mHz to 1 MHz
(for internal sources only).
(5) Press Phase Deviation to set the phase deviation. The range is from 0° to 360°.
The default is 0°.
36
Page 42

4.Panel Operation
Frequency Shift Keying (FSK)
Using frequency shift keying modulation, the output frequency is shifted between
two preset frequency values (carrier frequency and hopping frequency). The
frequency at which the output moves between the two frequencies is determined
by the internal frequency generator (internal source) or the signal level (external
source) on the rear panel Ext Trig/Burst/Fsk In interface. The carrier wave can be a
sine wave, a square wave, a ramp wave, or an arbitrary wave. The user interface of
the frequency shift keying modulation is shown below.
Figure 4-17: Frequency shift keying user interface
Steps to set frequency shift keying modulation
(1) After pressing the Mod function key, press the Modulation type soft key, use
the knob to select, the modulation type is PSK, press the OK soft key. Th e
carrier waveform can be selected as needed. The following is a sine wave.
(2) Press to display the waveform and parameters of the current carrier.
You can change the parameters of the carrier. For details, please refer to
Output Sine Wave on page 10. Press or Mod to return to the
modulation mode interface.
(3) Press Source to select the source. If external is selected, connect the external
signal source to the Ext Trig/Burst/Fsk In interface on the rear panel and skip
to step (5). If you select internal, continue with the following steps.
Note: When the source selects external, set the slope to “positive”, then
37
Page 43

4.Panel Operation
output the carrier frequency when input logic low level, and output the
frequency hopping frequency when input logic high level. When the slope is
"negative", the opposite is true.
(4) Press the FSK Rate softkey to set the FSK rate, which can be set from 2 mHz to
1 MHz (for internal sources only).
(5) Press the Frequency Hopping softkey to set the frequency hopping, which is
the alternating frequency.
Hexadecimal frequency shift keying (3FSK)
Using ternary frequency shift keying modulation, the output frequency is shifted
between three preset frequency values ("carrier frequency" and 2 "hopping
frequencies"). The frequency at which this output moves between three frequencies
is determined by the internal frequency generator (internal source). The carrier wave
can be a sine wave, a square wave, a ramp wave, or an arbitrary wave. The user
interface of ternary frequency shift keying modulation is shown in the figure belo w.
Figure 4-18 Hexadecimal frequency shift keying user interface
Steps to set frequency shift keying modulation
(1) After pressing the Mod function key, press the modulation type s oft key, us e
the knob to select, the modulation type is 3FSK, press the enter key. The
carrier waveform can be selected as needed. The following is a sine wave.
38
Page 44

4.Panel Operation
(2) Press to display the waveform and parameters of the current carrier.
You can change the parameters of the carrier. For details, please refer to
Output Sine Wave on page 10. Press or Mod to return to the
modulation mode interface.
(3) Press the FSK Rate softkey to set the 3FSK rate, which can be set from 2 mHz
to 1 MHz.
(4) Press the Frequency Hopping 1 Frequency Hopping 2 softkey to select the
setting frequency hopping, which is the alternating frequency.
Quaternary frequency shift keying (4FSK)
Using quaternary frequency shift keying modulation, the output frequency is shifted
between four preset frequency values ("carrier frequency" and 3 "hopping
frequencies"). The frequency at which the output moves between the four
frequencies is determined by the internal frequency generator (internal source). The
carrier wave can be a sine wave, a square wave, a ramp wave, or an arbitrary wave.
The user interface of quaternary frequency shift keying modulation is shown in the
figure below.
Figure 4-19 Quaternary frequency shift keying user interface
Steps to set frequency shift keying modulation
39
Page 45

4.Panel Operation
(1) After pressing the Mod function key, press the modulation type s oft key, use
the knob to select, the modulation type is 4FSK, press the enter key. The
carrier waveform can be selected as needed. The following is a sine wave.
(2) Press to display the waveform and parameters of the current carrier.
You can change the parameters of the carrier. For details, please refer to
Output Sine Wave on page 10. Press or Mod to return to the
modulation mode interface.
(3) Press FSK Rate to set the 4FSK rate from 2 mHz to 1 MHz.
(4) Press Frequency Hopping 1 Frequency Hopping 2 Frequency Hopping 3 Soft
Key to select the setting frequency hopping, which is the alternating
frequency.
Binary phase shift keying (BPSK)
The use of binary phase shift keying modulation shifts the output phase between
preset frequency values ("carrier phase" and "modulation phase"). The frequency at
which the output moves between the two phases is determined by the internal
frequency generator (internal source). The carrier wave can be a sine wave, a square
wave, a ramp wave, or an arbitrary wave. The user interface of the two-phase phase
shift keying modulation is shown in the figure below.
Figure 4-20 Binary phase shift keying user interface
40
Page 46

4.Panel Operation
Steps to set frequency shift keying modulation
(1) After pressing the Mod function key, press the modulation type s oft key, us e
the knob to select the modulation type as BPSK, and press the ENTER key.
The carrier waveform can be selected as needed. The following is a sine wave.
(2) Press to display the waveform and parameters of the current carrier.
You can change the parameters of the carrier. For details, please refer to
Output Sine Wave on page 10. Press or Mod to return to the
modulation mode interface.
(3) Press Code Rate to set the code rate. The range is from 2 mHz to 1 MHz.
(4) Press Phase Deviation to select the phase deviation. The range is from 0° to
360°.
(5) Press Data Source to select the setting data source, including (01 code, 10
code, PN15 code, PN21 code).
Oscillating keying (OSK)
The output modulation waveform consists of a carrier wave and a modulated wave.
The carrier can only be a sine wave. In phase modulation, the phase of the carrier
varies with the keying frequency of the modulated waveform. The user interface for
the oscillating keying modulation is shown below.
Figure 4-21 Oscillating keying user interface
41
Page 47

4.Panel Operation
Steps to set frequency shift keying modulation
(1) After pressing the Mod function key, press the Modulation type soft key, use
the knob to select the modulation type as OSK, and press the enter key. The
carrier waveform can be selected as needed. The following is a sine wave.
(2) Press to display the waveform and parameters of the current carrier.
You can change the parameters of the carrier. For details, please refer to
Output Sine Wave on page 10. Press or Mod to return to the
modulation mode interface.
(3) Press the key frequency. The soft key sets the key rate. The range is from 2
mHz to 1 MHz.
(4) Press Vibration Time to select the vibration time, ranging from 8ns to
499.75μs.
42
Page 48

4.Panel Operation
Output the sweep frequency (Sweep)
In the sweep mode, the frequency is output from the start frequency to the end
frequency according to the sweep type change frequency within the specified sweep
time. Sweeping can only be performed using sine, square, ramp or arbitrary waves.
Figure 4-22: Sweep mode user interface
Steps to set the scan mode
(1) In the sine wave, square wave, ramp wave or arbitrary wave interface, press the
Sweep function key to enter the scan mode.
(2) Press 、
、
when selecting a sine wave, press to display the scan waveform and
parameters, and change the parameters. For details, please refer to Output Sine
Wave on page 10.
(3) Press Sweep Time to set the scan time, which is the number of seconds from
the start frequency to the stop frequency. The range is from 1ms to 500s.
(4) Press the Linear Sweep/Logarithmic Scan softkey to switch the scan type. When
or to select the sweep waveform. For example,
linear sweep is selected, the output frequency changes linearly during the scan;
when logarithmic sweep is selected, the logarithm of the output frequency
changes during the scan.
43
Page 49

4.Panel Operation
Glossary
Burst:
d together is called a "burst". The various signal
Contains a specific number of waveform cycles, each of which is initiated by a trigger
active
(5) Press the Start Frequency / Center Frequency softkey to select the start
frequency or center frequency and set the corresponding value, as shown in
Figure 1.
(6) Press the End Frequency/Frequency Range softkey to select the end frequency
or frequency range and set the corresponding value. See Figure 1 for details.
Wave type
Parameter
Minimum start/stop frequency 1uHz
Maximum start/stop frequency 200MHz
Sine Square Ramp Arbitrary
50MHz 5MHz 15MHz (Bulid-in waves)
50MHz (User customized waves)
Table 1
(7) Press the Trigger Source softkey to select the trigger source. The internal is the
internal signal source; the external is the external source of the Ext
Trig/Burst/Fsk In interface on the rear panel. Under the external signal source,
the slope can be selected as positive/negative (Positive: Select to output the
trigger signal when rising. Negative: Select to output the trigger signal when
falling.); manually select manual trigger, each time you press the front panel
knob in the sweep interface, it will start a scan.
Output the burst (Burst)
Press Burst function key, that is burst, to generate burst waveform output of various
waveform functions. The burst can last for a specific number of waveform cycles
(N-cycle bursts) or be controlled by an external gate signal (gated burst). Sine, square,
ramp, pulse, or arbitrary wave functions can be used (this function is not available for
noise waves and harmonics).
The set of pulses transmitte
generators are commonly referred to as the BURST function.
N cycle burst:
event.
Gated burst:
Use external department signals to control when waveform burst waveforms are
44
Page 50

Set N cycle burst
4.Panel Operation
Figure 4-23: N cycle burst user interface
(1) In the sine wave, rectangular wave, ramp wave, pulse wave or arbitrary
waveform interface, press the Burst function key to burst.
(2) Press , , , or
to select the waveform function.
For example, when selecting a sine wave, press to display the
waveform and parameters, and change the parameters. For details, please
refer to Output Sine Wave on page 10, and then press to return to
the burst mode interface.
Note: Before configuring the waveform parameters, you must first select
the channel you want to configure. Press CH1 or CH2 to select the
corresponding channel, and the corresponding channel area in the user
interface will light up.
(3) Press the N Cycle/Gate softkey to switch to the N cycle.
(4) Press the Trigger Period softkey to set the burst period, which can be set
from 10 ns to 500 s (Min = Cycles * Period).
(5) Press the Cycles/Infinite softkey to set the number of cycles, which is the
number of waveform cycles to be output for each N-cycle pulse train. The
range is from 1 to 50,000 cycles. When Infinite is selected, a continuous
45
Page 51

4.Panel Operation
waveform is output until a trigger event is received.
Note: In Burst mode, the upper limit of the carrier frequency is half of the
maximum frequency of the original carrier. Taking a sine wave as an
example, the maximum carrier frequency is 200MHz. Press to set
the carrier to 200MHz. Then press the Burst softkey menu, then press or
Burst to display the original carrier frequency to 100MHz.
Warning:
If necessary, the burst period will increase to accommodate the specified
number of cycles.
For infinite count bursts, an external or manual trigger source start pulse train
(except internally) is required.
(6) Press Source to select the source. The internal is the internal signal source;
the external is the external source of the Ext Trig/Burst/Fsk In interface on
the rear panel. Under the external signal source, the slope can be selected
as positive/negative. (Positive: Select the trigger signal when rising) ;
negative: select to output the trigger signal when falling); manually select
manual trigger, in the N cycle burst interface, press the Trigger under the
current channel of the front panel to output a burst.
Set the gated burst
46
Page 52

4.Panel Operation
Figure 4-24: gated burst user interface
(1) In the sine wave, square wave, ramp wave, pulse wave or arbitrary waveform
interface, press the Burst function key.
(2) Press 、 、 、 or to select the waveform function. For
example, when selecting a sine wave, press
to display the waveform and
parameters, and change the parameters. For details, please refer to Output
Sine Wave on page 10.
Note: Before configuring the waveform parameters, you must first select the
channel you want to configure. Press CH1 or CH2 to select the corresponding
channel, and the corresponding channel area in the user interface will light up.
(3) Press the N Cycle/Gate softkey to switch to the gate.
(4) Press the Polarity softkey to select the gate signal “Positive” or “Negative”. The
default is positive. The gate polarity is only available in gated burst mode. The
instrument outputs a pulse train when the gate signal on the [Ext Trig/Burst/Fsk
In] connector on the rear panel is "High" or "Low".
Counter
The frequency meter measures signals in the frequency range from 100 mHz
to 200 MHz. The [10MHz In/Out/Counter] connector on the rear panel is used
by default to receive the frequency meter input signal. The frequency meter
works from the start, unless the connector is set to an external clock input or
clock output.
(1) Press the front panel Counter function key to enter the frequency meter
interface.
(2) Connect the signal to be tested to the [10MHz In/Out/Counter] connector
on the rear panel.
(3) Set the counter:
Press the Coupling soft key to switch AC or DC to set the coupling mode of
the input signal.
Press the Sensitivity softkey to toggle low, medium or high.
For small amplitude signals, the sensitivity is selected to be medium or high.
47
Page 53

4.Panel Operation
For low frequency large signals or signals with slow rising edges, low
sensitivity is selected and the measurement results are more accurate.
Press the HF Suppression softkey to toggle ON or OFF high frequency
rejection.
High-frequency rejection can be used to filter high-frequency components
when measuring low-frequency signals, improving measurement accuracy.
When measuring low frequency signals with a frequency less than 1 kHz,
turn on high frequency rejection to filter out high frequency noise
interference; turn off high frequency rejection when measuring high
frequency signals with frequencies greater than 1 kHz.
Press the Trigger Level softkey. Turn the knob to change the current cursor
position value, press the arrow keys to move the cursor left or right; or use
the numeric keypad to enter a value and then select the desired unit from
the right menu. The trigger level ranges from -2.5 V to 2.5 V.
After the setting is completed, the frequency meter will measure the signal
to be tested at the current setting. If the reading is unstable, repeat the
above adjustment until the display is stable.
(4) The frequency, period, duty cycle, positive pulse width, and negative pulse
width can be viewed on the frequency meter interface
Utility function setting
Press the Utility function key to enter the system options menu. The user can set the
display parameters of the signal generator, CH1/2 settings, interface settings, and
system parameters. Press Utility again to exit the system options menu.
Display Setting
Brightness Control
(1) Press the Utility softkey, select Display Settings, and press the Backlight softkey
to select Backlight.
(2) Turn the knob to change the current cursor position value, press the /
arrow key to move the cursor left or right, or use the numeric keypad to enter
the brightness percentage. The brightness range is from 0% to 100%.
48
Page 54

4.Panel Operation
Screen Saver
If there is no operation during the set screen saver time, the screen enters the
protection mode (the screen display is turned off, that is, the black screen). Press any
key to redisplay the operation interface.
(1) Press the Utility softkey, select Display Settings, and press the Screen Saver
softkey to select the On/Off screen saver.
(2) When the screen saver is turned on, the screen saver time can be set. Turn the
knob to change the current cursor position value, press the / arrow key
to move the cursor left or right, or use the numeric keypad to enter the time in
minutes, and the screen saver time range is 1 to 999 minutes.
Separator
The user can set the separator of the screen display data.
(1) Press the Utility softkey, select Display Settings, and press the Delimiter
(2) Press the Separator softkey to toggle between commas, spaces, and none.
Taking the frequency parameter as an example:
softkey.
Comma
Space
None
Date
(1) Press the Utility softkey, select Display Settings, and then press the Date softkey
to select Date.
(2) Turn the knob to change the current cursor position value, press the /
arrow key to move the cursor left or right.
CH1/2 Settings
Synchronize
Our instruments can output basic waveforms (except noise), arbitrary waveforms
(except DC), harmonics, sweep waveforms, burst waveforms, and synchronized
waveforms of modulated waveforms from a single channel or simultaneously from
49
Page 55

4.Panel Operation
two channels. This signal is output from the front panel [Sync] connector.
(1) Sync Switch
Enable or disable the sync signal on the [Sync] connector. Press Utility to set CH1
sync/CH2 sync and select “On” or “Off” sync signal output. The default is "on",
which sends the sync signal to the [Sync] connector. The output level on the
[Sync] connector is a logic low when the sync signal is turned off.
(2) Synchronization signal of various waveforms
For sine, square, ramp and pulse waves, the sync signal is a square wave with a 50%
duty cycle. When the waveform output is positive, the sync signal is TTL high with
respect to the 0V voltage (or DC offset value). When the waveform output is negative,
the sync signal is TTL low relative to the 0V voltage (or DC offset value).
For an arbitrary waveform, the sync signal is a square wave with a variable duty cycle.
When the output waveform amplitude reaches a certain value, the sync signal is TTL
high.
For harmonics, the sync signal is referenced to the harmonic order and is a square wave
with a variable duty cycle. When the output waveform amplitude is positive, the sync
signal is TTL high.
For AM, FM, PM, and PWM, for internal modulation, the sync signal is referenced to
the modulation frequency, and the sync signal is a square wave with a 50% duty cycle.
In the first half of the modulation waveform, the sync signal is TTL high. When external
modulation is performed, there is no sync signal output.
For ASK, FSK, PSK, BPSK, 3FSK, 4FSK, the synchronization signal is referenced to the
keying frequency, and the synchronization signal is a square wave with a duty cycle of
50%. There is no sync signal output during external modulation.
For OSK, the sync signal is referenced to the keyed frequency and the sync signal is a
square wave with a 50% duty cycle. When the internal crystal oscillator starts, the sync
signal is TTL high.
For N-cycle bursts, the sync signal is TTL high at the beginning of the burst. At the end
of the specified number of cycles, the sync signal is TTL low (if the waveform has an
associated start phase, it may not be a zero crossing). For an infinite count pulse train,
the sync signal is the same as the sync signal of the continuous waveform.
For external gated bursts, the sync signal follows its gate signal. Note: This signal does
not become TTL low until the end of the last cycle (if the waveform has an associated
starting phase, it may not be a zero crossing).
Output Setting
Set the load
For each of the two channels of the front panel, the signal generator has a fixed
series output impedance of 50 Ω. If the actual load impedance is different from the
specified value, the displayed amplitude and offset level will not match the voltage
50
Page 56

4.Panel Operation
level of the part under test. The load impedance settings provided are only for the
convenience of the user to match the display voltage to the desired load.
The step to set the CH1 or CH2 load value is as follows:
(1) Press the Utility function button to select the CH1/2 setting. Press CH1 Load to
select CH1 load, or press CH2 Load to select CH2 load; press again to switch to
high impedance or *ohm ("*" represents a value).
(2) To change the resistance value, after selecting *ohm in the previous step, turn
the knob to change the current cursor position value, press the / arrow
key to move the cursor left or right, or use the numeric keypad to input the
value. The input load range is from 1 ohm to 10k ohm.
Warning:
Each output of the front panel has a fixed 50 Ω series output impedance, regardless
of the value specified for this parameter. If the actual load is different from the
specified value, the displayed voltage level does not match the actual level.
Interface Setting
(1) Press the Utility function key, select the interface setting, and press the USB
device soft key to switch the USB device.
Set the communication protocol type of the USB Device interface on the
rear panel.
PC: This is the internal communication protocol. Select this option when
connecting to the ultrawave host computer software via the USB Device
interface.
USBTMC: Select this when you need to use the USBTMC communication
protocol standard.
(2) Press the Network Settings button and select Network Settings to go to the next
level menu: IP Address, Gateway, Subnet Mask, Port. The physical address
displayed on the interface cannot be modified. After setting the network
parameters such as the IP address of the user-defined signal generator, you
need to wait for 2S or more to restart the machine.
Press IP Address to select the IP address. Use the numeric keypad and the
rotary keys to enter the desired IP address. The format of the IP address is
nnn.nnn.nnn.nnn. The first nnn ranges from 1 to 223 (except 127), and the
51
Page 57

4.Panel Operation
other three nnn ranges from 0 to 255. It is recommended to ask your
network administrator for an available IP address.
Press Gateway and select Gateway. Use the numeric keypad and knob keys
to enter the desired gateway address. The default gateway format is
nnn.nnn.nnn.nnn. The first nnn ranges from 1 to 223 (except 127), and the
other three nnn ranges from 0 to 255. It is recommended to consult your
network administrator for an available IP address.
Press the Subnet Mask softkey to select the subnet mask. Use the numeric
keypad and knob keys to enter the desired subnet mask address. The
default gateway format is nnn.nnn.nnn.nnn. Where nnn ranges from 0 to
255. It is recommended to ask your network administrator for an available
IP address.
Press Port to select the port. Use the numeric keypad and knob keys to
enter the desired port value, which ranges from 0001 to 4000.
System Setting
Select the language
Press the Utility function key to select System Settings and press the Language
softkey to switch the display language.
Buzzer
Press the Utility function button, select System Settings, and press the beep soft key
to select the “on” or “off” buzzer.
Clock source
An internal clock source is provided, an external clock source from the [10MHz In/Out/Counter]
input on the rear panel is also accepted, and a clock source can be output from the [Ref Clk Out]
connector for use by other devices.
Warning:
The amplitude of the [10MHz In/Out/Counter] input signal must be above 1 V.
Press the Utility function key, select System Settings, press the Clock Source softkey to select the
52
Page 58

4.Panel Operation
Error Code
Error Information
2
File too large
3
Error reading firmware file
4
Verify firmware file error
5
Firmware type flag error
6
Instrument version cannot be upgraded to
firmware file version
7
Instrument model does not match firmware file
model
clock source, and then press the soft key to switch. Internal/External
Warning:
The clock source defaults to the internal clock source. When an external clock source is required,
this function is switched to the outside. At this time, the clock source forcibly outputs the output.
When the clock source output selection is turned on, the clock source must be switched to
internal, and the frequency meter function stops after the clock output is turned on.
Clock Output
Press the Utility function key, select System Settings , select the Clock Output soft key, press the
Clock Output menu, and then press the soft key to toggle on/off.
Firmware update
Press the Utility softkey to select System Setup.
Plug the USB storage device into the USB connector on the front panel of the
instrument. (Note: If the USB storage device is not plugged in, the Firmware Upgrade
menu will be disabled)
Select the Firmware Upgrade softkey, press the firmware upgrade menu, use the
front panel knob to select USBDEVICE, press to enter the softkey, and enter the USB
storage device to browse the file.
Use the front panel knob to select the downloaded firmware file and press the
Execute softkey to perform the firmware upgrade.
Note: The firmware file name is as follows: xxx model _Vx.x.x version.upp.
Note: If the firmware update fails, an error code will be displayed on the screen. The
error message corresponding to the error code can be found in Schedule 2.
Restore to factory setting
Press the Preset function key, press the reset soft key, and then press the Enter to
restore the instrument's settings to the factory default values (Note: “Reset Settings”
Table 2
53
Page 59

4.Panel Operation
Output Configuration
Factory Setting
CH1 signal output switch
OFF
CH2 signal output switch
OFF
Function
Sine
Frequency
1 kHz
Amplitude/offset
1 Vpp / 0 Vdc
Waveform Configuration
Factory Setting
Frequency
1.000kHz
Period
1.000ms
Amplitude
1.000Vpp
Offset
0.000V
High Level
500mV
Low Level
-500mV
Start Phase
0deg
Symmetry
50%
Pulse Width
500.000us
Duty Cycle
50.00%
Rising Time
1.953125us
Falling Time
1.953125us
Build-in Wave
X^2
Harmonic Wave Type
Even harmonic
Harmonic Wave Times
2
Number
2
Harmonic Wave Amplitude
1.000Vpp
Harmonic Wave Phase
0deg
Modulation Waveform
Factory Setting
Modulation type
AM
Modulated waveform
Sine
Amplitude modulation
frequency
100.000Hz
menu is “Factory Settings” to press the “Reset” soft key for factory setting. ). The
factory default parameter values are as follows
54
Page 60

4.Panel Operation
Modulation depth
100%
Source
Internal
Frequency modulation
frequency
100.000Hz
Frequency offset
100.000Hz
Phase modulation frequency
100.000Hz
Phase deviation
0deg
PWM rate
100.000Hz
Duty cycle deviation
0.0%
ASK rate
100.000Hz
ASK amplitude
1.000Vpp
PSK rate
100.000Hz
PSK phase deviation
0deg
FSK rate
100.000Hz
Frequency hopping
100.000Hz
Frequency hopping 1
100.000Hz
Frequency hopping 2
100.000Hz
Frequency hopping 3
100.000Hz
Code rate
100.000Hz
BPSK phase deviation
180deg
Data source
PN15 code
Key frequency
100.000Hz
Vibration time
100.000us
Sweep
Factory Setting
Sweeping time
1.000s
Sweeping method
Linear Sweep
Starting frequency
100.000Hz
Termination frequency
1.000kHz
Center frequency
550.000Hz
Frequency range
900.000Hz
Trigger source
Internal
Slope
Positive
Burst
Factory Setting
55
Page 61

4.Panel Operation
Trigger interval
1.000s
Burst mode
N cycle
Number of cycles
1
Trigger source
Internal
Slope
Positive
Polarity
Positive
Counter
Factory Setting
Coupling
Sensitivity
High frequency suppression
Trigger level
Edit
Factory Setting
Number of waveform points
Interpolation
Tem pl ate
Factory Setting
Reset settings
Factory setting
AC
Low
ON
0.000V
1000
Off
Blank
Save/recall instrument settings
Power-on setting Last time setting
user settings Setup0
56
Page 62

4.Panel Operation
Backlight
100%
Screen saver
turn on
Screen saver time
30Minute
Separator
Space
CH1 synchronization
shut down
CH2 synchronization
shut down
CH1 load
50ohm
CH2 load
50ohm
USB device
USBTMC
IP address
192.168.1.99
Gateway
192.168.1.1
Subnet mask
255.255.255.000
Port
3000
Language
Subject to the actual machine
Buzzer
turn on
Clock source
internal
Accessibility Factory Setting
Between Channels Factory Setting
Frequency lock
Amplitude lock
Off
Off
Edit the Arbitrary Wave (Edit)
Press the front panel Edit function key to enter the arbitrary wave editing
interface.
(1) Set the number of waveform points: Press the number of waveform
points softkey, use the knob to change the value directly or use the
numeric keypad to input and select the unit softkey. The number of points
ranges from 2 to 100,000.
(2) Set interpolation: Press the Interpolate softkey to toggle the interpolation
on/off. Select On to connect each waveform point with a straight line;
select Off, the voltage level between each waveform point remains the
same, creating a waveform similar to the step.
57
Page 63

4.Panel Operation
(3) Select a template: Press the Template softkey to select blank, sine,
square, ramp, and noise.
(4) Edit Waveform Point: Press to edit the waveform point to enter the Edit
Waveform Point menu.
Select the number of points and enter the number of the point you want to set.
Select the voltage and enter the voltage value to be set at this point.
Repeat this step to set all the points you want to set.
Press Store to enter the file system interface.
If you want to save the waveform to the built-in memory, check INTER and press
to enter the softkey. Tu rn the knob to select one of the USER files (EditMemory
cannot be selected) and press the Save softkey. (The file size is displayed on the
right side of the USER file. If 0B is displayed, it means the file is empty.)
Description: EditMemory is a temporary data space created, saved, edited or
recalled by any arbitrary wave. Saving the waveform is to save the data of this
space to the user-specified location (EditMemory is in the memory and never
empty). The data in this space is changed after an arbitrary waveform is called, a
new waveform is created, or a related programming command is received.
If you want to save to a USB storage device, you need to plug the USB storage device
into the front panel USB interface. Turn the knob to select USBDEVICE. Press to enter
the softkey and the instrument will list the directories of the folders and files in the
USB storage device. You can turn the knob to select a folder or file. Press to enter the
softkey to enter the currently selected folder. To return to the parent directory, press
the Back soft key.
After selecting the storage path, press the Save As softkey and the input keyboard
appears on the screen. Turn the knob to select a character. Press the
uppercase/lowercase softkey to toggle the case of keyboard characters. Press the
Select soft key to enter the current character. Press the Delete soft key to delete the
last character that has been entered. Press the Finish soft key to finish editing, and
the waveform will be saved in the current path with the file suffixed by bin.
File system (Store)
File system memory is divided into internal memory (INTER) and removable memory
(USBDEVICE). When a USB device is connected, the main interface displays INTER and
USBDEVICE. If no USB device is connected, only the internal memory INTER is
displayed. The internal memory can store 32 arbitrary waveform data.
Press the front panel Store function key to enter the file system.
58
Page 64

4.Panel Operation
Save Current Arbitrary Wave
(1) Press the button to enter the Arbitrary Wave menu and configure the
waveform parameters.
(2) Press the front panel Store function key to enter the file system.
If you want to save the current arbitrary waveform to the built-in
memory, select INTER and press to enter the soft key. Turn the knob to
select one of the USER files (EditMemory cannot be selected) and
press the Save softkey. (The file size is displayed on the right side of
the USER file. If 0B is displayed, it means the file is empty.)
Description: EditMemory is a temporary data space created, saved,
edited or recalled by any arbitrary wave. Saving the waveform is to
save the data of this space to the user-specified location (EditMemory
is in the memory and never empty). The data in this space is changed
after an arbitrary waveform is called, a new waveform is created, or a
related programming command is received.
If you want to save to a USB storage device, you need to plug the USB
storage device into the front panel USB interface. Turn the knob to
select USBDEVICE. Press to enter the softkey and the instrument will
list the directories of the folders and files in the USB storage device.
You can turn the knob to select a folder or file. Press to enter the
softkey to enter the currently selected folder. To return to the parent
directory, press the Back soft key.
After selecting the storage path, press the Save As softkey and the
input keyboard appears on the screen. Turn the knob to select a
character. Press the uppercase/lowercase softkey to toggle the case of
keyboard characters. Press the Select soft key to enter the current
character. Press the Delete soft key to delete the last character that
has been entered. Press the Finish soft key to finish editing, and the
waveform will be saved in the current path in a file format such as bin.
Bring up arbitrary wave files in internal/external memory
Press the front panel Store function key to enter the file system.
59
Page 65

4.Panel Operation
To c a l l up the waveform file in the internal memory, select INTER under the
memory selection interface and press to enter the soft key. Turn the knob to
select a file and press to call up the softkey. If the reading is successful, the
screen will prompt “File Read Successful”.
Note: The file size is displayed on the right side of the file. If 0B is displayed,
the file is empty.
To recall the waveform file in the USB storage device, turn the knob to select
USBDEVICE in the memory selection interface. Press to enter the softkey and
the instrument will list the directories of the folders and files in the USB
storage device. Turn the knob to select a folder or file. Select the file with
the suffix of bin and press to call up the softkey. If the reading is successful,
the screen will prompt “File Read Successful”. Press the Save As soft key, a
soft keyboard will appear on the screen interface. We can use the front
panel knob to rotate left or right or the right menu soft key to create and
name files.
Note:The screen will output the waveform file <500kB, which can be directly
previewed in the lower right corner of the screen. If the knob is named,
press the knob once to confirm it. If you press and hold the button (greater
than 2s), the button will be saved when it is popped up. The current screen
interface in bmp format to the u disk specific path ((model) / IMAGE /
xx.bmp).
Copy the waveform file from the USB storage device to the internal memory:
After the waveform file in the USB storage device is called up according to
the previous step, press the Back soft key to return to the upper directory.
After returning to the memory selection interface, turn the knob to select
INTER and press to enter the soft key. Turn the knob to select a USER file and
press the Save button to copy the waveform file to the internal memory.
Note:In the arbitrary waveform interface, Shape displays the storage location or
waveform name of the current arbitrary waveform. USER indicates the internal
memory, External indicates the USB storage device, and if it is a built-in waveform,
the built-in waveform name is displayed.
Clear waveform from memory
(1) Press the front panel Store function key to enter the file system.
(2) Select INTER under the memory selection interface and press to enter the soft key.
Press the Security soft key, the screen pops up, and then press the OK soft key to clear all
waveforms in the internal memory.
Save/recall instrument settings (Preset)
The instrument settings can be saved as files in internal memory or on an external
60
Page 66

4.Panel Operation
USB storage device. Up to 16 instrument settings can be saved in the instrument's
internal memory. To save more settings, use a USB storage device. The settings file
saved to the USB storage device uses the extension CFG. The saved settings can be
restored from files in the internal memory or USB storage device.
Operation Steps:
Press the front panel Preset function key to enter the preset menu, and press the
Save/Read Settings soft key to enter the memory selection interface.
If you want to save the settings to the built-in memory, check INTER and press
the Enter soft key. Turn the knob to select a Setup file and press the Save softkey.
(The file size is displayed on the right side of the Setup file. If 0B is displayed, it
means the file is empty.)
Note: Press the Security softkey and press the OK soft key to clear all settings in
the internal memory.
If you want to save to a USB storage device, you need to plug the USB storage
device into the front panel USB interface. Turn the knob to select USBDEVICE.
Press to enter the softkey and the instrument will list the directories of the
folders and files in the USB storage device. You can turn the knob to select a
folder or file. Press to enter the softkey to enter the currently selected folder. To
return to the parent directory, press the Back soft key.
After selecting the storage path, press the Save As softkey and the input
keyboard appears on the screen. Turn the knob to select a character. Press the
uppercase/lowercase softkey to toggle the case of keyboard characters. Press
the Select soft key to enter the current character. Press the Delete soft key to
delete the last character that has been entered. Press the Finish soft key to
complete the editing. The current instrument settings will be saved in the
current path in the cfg file format.
To recall the settings, select the desired file and press to call up the softkey.
Use build-in help (Help)
(1) To get help for any front panel buttons or menu softkeys, first press the front
panel Help softkey, then press the button you need help with.
(2) Press the Help softkey again to exit the help interface.
61
Page 67

5.Communicate with PC
5. Communicate with PC
Supports communication with a computer via a USB port or a LAN port. Using the
Waveform Editor software installed on the computer, the signal generator can be
operated on the computer to control the output of the signal generator.
Here's how to connect to a computer. First, install the Waveform Editor software on
the CD-ROM on your computer. Then, there are several connection options to choose
from.
Using USB Port
(1) Set the USB device protocol type of the signal generator: Press Utility → I/O
Setup → USBDEV , switch to PC.
(2) Connection: Connect the USB Device interface on the rear panel of the signal
generator to the USB interface of the computer with a USB cable.
(3) Install the driver: Run Waveform Editor software on the computer, press F1 to
view the built-in help documentation. Follow the instructions to install the driver.
The path of the driver is the USBDRV folder in the directory where the Waveform
Editor communication software is located.
(4) Host computer communication port setting: Open the Waveform Editor
software, click “Communications” in the menu bar, select “Ports-Settings”, i n t h e
setting dialog box, select the communication port as “USB”. After the connection
is successful, the connection status prompt in the lower right corner of the
software interface turns green.
Using LAN Port
Connect Directly
(1) Connection. Plug one end of the network cable into the LAN connector on the
rear panel of the signal generator; the other end is plugged into the LAN
interface of the computer.
(2) Set the network parameters of the computer. Since the signal generator does
not support automatic IP address acquisition, you need to specify the IP you rs elf.
Here we set the IP address to 192.168.1.71.
(3) Set the network parameters of the host computer. Run Waveform Editor
software on the computer. In the "Communications" menu, under
"Ports-Settings", select the communication port as "LAN", the IP is set to be the
same as the first three fields of the computer's network IP in step (2), and the
last field has a different IP address. It is "192.168.1.99"; the port can be set to
62
Page 68

5.Communicate with PC
any value from 0 to 4000. However, since ports below 2000 are often occupied,
it is recommended to set it to 2000 or higher. Here, it is set to "3000".
Figure 5-1 Setting the network parameters of the host computer
(4) Set the network parameters of the signal generator. In the signal generator,
press Utility → I/O Setup → Network setting to enter the submenu. Set the IP
address and port to the IP and port in the PC software port settings in step (3).
After the shutdown and restart, if the data can be obtained normally in the PC
software, the connection is successful.
Connect through a Router
(1) Connection. Connect the LAN interface on the rear panel of the signal generator
to the router with a network cable. The computer is also connected to the
ro u te r.
(2) Set the network parameters of the computer. Since the signal generator does
not support automatic IP address acquisition, you need to specify the IP yoursel f.
The default gateway and subnet mask settings must match the settings of the
router. For example, the IP address is set to 192.168.1.71, the subnet mask is set
to 255.255.255.0, and the default gateway is set to 192.168.1.1.
(3) Set the network parameters of the host computer. Run Waveform Editor
software on the computer. In the "Communications" menu, under
"Ports-Settings", select the communication port as "LAN", the IP is set to be the
same as the first three fields of the computer's network IP in step (2), and the
last field has a different IP address. It is "192.168.1.99"; the port can be set to
any value from 0 to 4000. However, since ports below 2000 are often occupied,
it is recommended to set it to 2000 or higher. Here, it is set to "3000".
Figure 5-2 Set the network parameters of the host computer
63
Page 69

5.Communicate with PC
(4) Set the network parameters of the signal generator. In the signal generator,
press Utility → I/O Setup → Network setting to enter the submenu. Set the IP
address and port to the IP and port in the PC software port settings in step (3).
The gateway settings need to be the same as the gateway settings of the router.
After the shutdown and restart, if the data can be obtained normally in the PC
software, the connection is successful.
For the specific operation method of Waveform Editor software, please press F1 to
view the built-in help documentation.
64
Page 70

6.Troubleshooting
6. Troubleshooting
1. If the instrument is still black and there is no display when you press the power
switch, please follow the steps below:
Check if the power connector is connected.
Check that the voltage selector is in the correct gear position.
Check that the fuse at the power connector meets the specified type and
rating and is blown (can be opened with a flat-blade screwdriver).
After completing the above checks, restart the instrument.
If you still cannot use this product, please contact us and let us serve you.
2. The measured value of the output signal amplitude does not match the
displayed value:
Check that the actual load value of the signal is consistent with the load value set by
the system. For details, please refer to Set the load on page 50.
If you encounter other problems, please try resetting the settings (see Clock source
on page 52) or reboot. If you still cannot use this product, please contact us and let
us serve you.
65
Page 71

7.Specification
Waveform
Sine wave, square wave, ramp wave, pulse wave,
noise, arbitrary wave, harmonic
Arbitrary waveform
Sinc, exponential rise, exponential decline,
150 kinds
Sampling Rate
1.25GSa/s
Number of channels
2
Number of digits
14bits
Frequency Feature
Frequency aging rate: ±1 ppm per year.
Sine wave
FG-32502T
1 μHz—250 MHz
FG-31602T
1 μHz—160 MHz
FG-30802T
1 μHz—80 MHz
Square wave
FG-32502T
FG-31602T
FG-30802T
1 μHz—30 MHz
Ramp wave
1 μHz—5 MHz
Pulse wave
1 μHz—25 MHz
Noise wave
120 MHz bandwidth (-3dB) (Gaussian white noise)
Arbitrary wave
1 μHz—15MHz (Bulid-in waves);
1 μHz—50MHz (User customized waves)
Harmonic wave
FG-32502T
1 μHz—125 MHz
FG-31602T
1 μHz—80 MHz
FG-30802T
1 μHz—40 MHz
Amplitude characteristics (not specifically labeled, the load defaults to 50Ω)
2mVpp to 20Vpp (≤ 40MHz)
2mVpp to 2Vpp (≤250MHz)
7. Specification
All specifications apply to this product unless otherwise stated. The signal generator
must be operated continuously for more than 30 minutes at the specified operating
temperature to meet these specifications.
In addition to the specifications marked with the word "Typical", the specifications
used are guaranteed.
Standard Waveform
electrocardiogram, Gaussian, semi-positive,
Lorentz, dual audio, DC voltage totaling more than
Frequency resolution: 1 μHz or 10 significant figures;
Frequency stability: ±1 ppm at 0-40C;
1 μHz—50 MHz
Output amplitude
High
Resistance
2mVpp to 10Vpp (≤80MHz)
2mVpp to 5Vpp (≤120MHz)
66
Page 72

7.Specification
1mVpp to 10Vpp (≤ 40MHz)
1mVpp to 1Vpp (≤250MHz)
Amplitude accuracy
±(1% of setting + 1 mVpp) (Typical value 1kHz sine, 0V
offset)
Amplitude resolution
1 mVpp or 4 digits
DC offset range (High
resistance,open circuit)
DC offset range
±(5 Vpk – Amplitude Vpp/2)
DC offset accuracy
±(1 % of |setting| + 1 mV + amplitude Vpp * 0.5%)
Offset resolution
1 mV or 4 digits
Output Impedance
50Ω (typical)
Waveform Feature
Sine
Bandwidth flatness (1 Vpp, relative to
≤10MHz: ±0.2dB
≤250MHz: ±1.5dB
Harmonic distortion
Typical (0dBm)
120MHz to 250MHz: <-45dBc
Total harmonic distortion
0.05 %, 10 Hz to 20 kHz, 1 Vpp
Non-harmonic distortion
Typical (0dBm)
>10MHz: <-70dBc + 6dB/ sound interval
Phase noise
Typical (0dBm, 10kHz offset)
10MHz: ≤-110dBc/Hz
Square
Rise/fall time
<5ns
Jitter
300ps + 100ppm
Overshoot
< 3%
Duty cycle
50.0% (fixed)
Ramp
Linearity
< 0.1% of peak output (typical 1 kHz, 1 Vpp,
symmetry 50%)
Symmetry
0% to 100%
pulse
Pulse Width
12 ns to 1000 ks
1kHz)
50 Ω
1mVpp to 5Vpp (≤80MHz)
1mVpp to 2.5Vpp (≤120MHz)
±(10 Vpk – Amplitude Vpp/2)
≤60MHz: ±0.3dB
≤100MHz: ±0.5dB
≤160MHz: ±1dB
DC to 1MHz: <-65dBc
1MHz to 10MHz: <-60dBc
10MHz to 120MHz: <-50dBc
<
≤10MHz: <-70dBc
67
Page 73

7.Specification
Duty cycle
0.3% to 99.7%
Rise and fall time
≥7ns
Overshoot
< 3%
Jitter
300ps + 100ppm
Noise
Typ es
Gaussian white noise
Bandwidth (-3dB)
120M
Arbiratry wave
Bandwidth
120M
Waveform length
2 to 1M points
Sampling rate
< = 312M (at frequency <25kHz)
1.25G (at frequency >=25kHz)
Amplitude accuracy
14 bits
Minimum rise and fall time
< 7 ns
Jitter
3 ns
Harmonic wave
Harmonic number
≤16
Frequency Range
1μHz to 100MHz
Harmonic type
Odd, even, sequential, custom
Harmonic amplitude
Each harmonic amplitude can be set
Harmonic phase
Each harmonic phase can be set
Modulated Waves
AM
Carrier
Sine wave, square wave, ramp wave, arbitrary wave
Modulated signal
source
Internal or external
Internal modulation
waveform
Sine wave, square wave, ramp wave, white noise, arbitrary
waveform
Internal amplitude
modulation frequency
2 mHz to 100 kHz
Depth
0.0% to 100.0%
FM
Carrier
Sine wave, square wave, ramp wave, arbitrary wave
Modulated signal
source
Internal or external
Internal modulation
waveform
Sine, square, ramp, white noise, and arbitrary waveforms
Internal modulation
frequency
2 mHz to 100 kHz
68
Page 74

7.Specification
Frequency offset
2 mHz ≤ offset ≤ min (carrier frequency, carrier maximum
two
PM
Carrier
Sine wave, square wave, ramp wave, arbitrary wave
Modulated signal
source
Internal or external
Internal modulation
waveform
Sine, square, ramp, white noise, and arbitrary waveforms
Internal phase
modulation frequency
2 mHz to 100 kHz
Phase deviation range
0°~180°
PWM
Carrier
Pulse wave
Modulated signal
source
Internal or external
Internal modulation
waveform
Sine, square, ramp, white noise, and arbitrary waveforms
Internal phase
modulation frequency
2 mHz to 100 kHz
Offset
0 to min (min is the smaller value of pulse wave duty cycle
and 100%-pulse wave duty cycle)
FSK
Carrier
Sine wave, square wave, ramp wave, arbitrary wave
Modulated signal
source
internal
Internal modulation
waveform
50% square wave
FSK frequency
2 mHz to 1MHz
3FSK
Carrier
Sine wave, square wave, ramp wave, arbitrary wave
Modulated signal
source
internal
Internal modulation
waveform
50% square wave
FSK frequency
2 mHz to 1MHz
4FSK
Carrier
Sine wave, square wave, ramp wave, arbitrary wave
Modulated signal
source
internal
Internal modulation
waveform
50% square wave
PSK
frequency - carrier frequency) by default, the smaller of the
69
Page 75

7.Specification
Carrier
Sine wave, square wave, ramp wave, arbitrary wave
Modulated signal
source
Internal or external
Internal modulation
waveform
50% square wave
PSK frequency
2 mHz to 1MHz
ASK
Carrier
Sine wave, square wave, ramp wave, arbitrary wave
Modulated signal
source
Internal or external
Internal modulation
waveform
50% square wave
ASK frequency
2 mHz to 1MHz
BPSK
Carrier
Sine wave, square wave, ramp wave, arbitrary wave
Modulated signal
source
internal
Internal modulation
waveform
50% square wave
BPSK frequency
2 mHz to 1MHz
OSK
Carrier
Sine wave
Modulated signal
source
internal
Internal modulation
waveform
50% square wave
Oscillation time
8ns to 499.75μs
OSK frequency
2 mHz to 1MHz
Sweep
Carrier
Sine, rectangular wave, ramp wave, arbitrary wave
Minimum/maximum
starting frequency
1uHz
Maximum/termination
Sine wave: 200MHz
in waveform) or 50MHz
(user-defined waveform)
Typ es
Linear, logarithmic
Sweep direction
Up / Down
Sweep time
1 ms to 500 s ± 0.1%
Trigger source
Internal, external, manual
Burst
frequency
Square wave: 50MHz
Ramp wave: 5MHz
Arbitrary wave: 15MHz (built-
70
Page 76

7.Specification
Waveform
Sine wave, square wave, ramp wave, pulse wave and
arbitrary wave
Typ es
Count (1 to 50,000 cycles), unlimited, gated
Trigger source
Internal, external, manual
Carrier frequency
2mHz to 100MHz
Internal cycle
10 ns to 500 s (Min = Cycles * Period)
Gate source
External trigger
Counter Specification
Measurement
function
Frequency, period, positive pulse width, negative pulse
width, duty cycle
Frequency Range
Single channel: 100 mHz to 200 MHz
Frequency resolution
7 digits
Coupling method
AC, DC
Voltage range and sensitivity (non-modulated signal)
DC coupling
DC offset range
±1.5 V
100 mHz to 100 MHz
250 mVp-p - 5 Vp-p (AC+DC)
100 MHz to 200 MHz
400 mVp-p - 5 Vp-p (AC+DC)
AC coupling
1 Hz to 100 MHz
250 mVp-p - 5 Vp-pp
100 MHz to 200 MHz
400 mVp-p - 5 Vp-p
Pulse width and duty
cycle measurement
1 Hz to 10 MHz (100 mVpp to 5 Vpp)
Input resistance
1 MΩ
Sensitivity
Can set high, medium and low three files
Trigger level range
±2.5 V
Channel coupling
1 Hz to 10 MHz (100 mVpp to 5 Vpp)
Amplitude lock, frequency lock, channel copy
Input/Output
Communication Interface
USB Host, USB Device, LAN
External modulation input
Input frequency range
DC-20 kHz
Input level range
± 1 V full scale
Input resistance
10 kΩ typical value
External trigger input
Level
TTL-compatible
Slope
Pulse Width
>100 ns
External clock input (frequency meter input)
External clock input
(frequency meter input)
impedance
Rise/fall optional
1MΩ DC coupled
71
Page 77

Input level range
Lock time
<1s
Lock range
10 MHz ± 9 kHz
External clock output
Frequency
10 MHz
Impedance
50 Ω, DC coupling
Amplitude
1.6Vpp 50Ω impedance
Sync Output
Level
TTL-compatible
Maximum frequency
1MHz
Display:
Feature
Description
Display type
8-inch color LCD display
display resolution
800 horizontal × 600 vertical pixels
Display color
65536 colors, 16 bits, TFT
Feature
Description
Voltage
100 - 240 VAC, 50/60 Hz, CATⅡ
Power consumption
Less than 50 W
Fuse
Start time
Booting for 30 mins
Feature
Description
Temperature
Working temperature: 0 °C to 40 °C
Storage temperature: -20 °C to 60 °C
Relative humidity
≤90%
Height
Operating 3,000 meters
Non-operation 12,000 meters
Cooling method
Feature
Description
Dimension
340 mm (Length) × 177 mm (Height) × 90mm (Width)
Weight
2.5 kg
7.Specification
100 mVp-p to 3.3 Vp-p
Power:
250 V, F2AL
Environment:
Smart fan cooling
Mechanical Specification:
Adjustment interval:
The recommended calibration interval is one year.
72
Page 78

8.Appendix
Warning: Before re-energizing, please confirm that the instrument has dried
out to avoid electrical short circuit or even personal injury due to
8. Appendix
Appendix A: Accessories
A power cord that meets the standards of the country where you are located
A USB communication cable
A CD
A Safety hintsheet
Two BNC/Q9 lines
Appendix B: Maintenance and cleaning
General maintenance
Do not store or place the instrument where the LCD monitor will be exposed to
direct sunlight for long periods of time.
Cautious: Do not allow sprays, liquids, and solvents to get on the instrument to
avoid damaging the instrument.
Cleaning
The instrument is often checked for usage. Follow the steps below to clean the
outer surface of the instrument:
1. Wipe the dust on the outside of the instrument with a soft cloth. When
cleaning the LCD screen, be careful not to scratch the transparent LCD screen.
2. Wipe the instrument with a soft cloth that is damp but not dripping. Please
pay attention to disconnect the power supply. It can be scrubbed with a mild
detergent or water. Do not use any abrasive chemical cleaners to avoid
damaging the instrument.
moisture.
73
 Loading...
Loading...