Page 1

VMware vFabric Data Director
Administrator and User Guide
vFabric Data Director 2.5
This document supports the version of each product listed and
supports all subsequent versions until the document is replaced
by a new edition. To check for more recent editions of this
document, see http://www.vmware.com/support/pubs.
EN- 001078-00
Page 2

VMware vFabric Data Director Administrator and User Guide
You can find the most up-to-date technical documentation on the VMware Web site at:
http://www.vmware.com/support/
The VMware Web site also provides the latest product updates.
If you have comments about this documentation, submit your feedback to:
docfeedback@vmware.com
Copyright © 2012 VMware, Inc. All rights reserved. This product is protected by U.S. and international copyright and intellectual
property laws. VMware products are covered by one or more patents listed at http://www.vmware.com/go/patents.
VMware is a registered trademark or trademark of VMware, Inc. in the United States and/or other jurisdictions. All other marks
and names mentioned herein may be trademarks of their respective companies.
VMware, Inc.
3401 Hillview Ave.
Palo Alto, CA 94304
www.vmware.com
2 VMware, Inc.
Page 3

Contents
About VMware vFabric Data Director Administrator and User Guide 7
VMware vFabric Data Director Overview 9
1
Data Director System Architecture 9
VMware Data Director Components 10
Data Director User Management Modes 10
About Data Director Administration 11
Data Director Supported Databases 12
Managing Data Director Resources 15
2
Resource Management Overview 15
Resource Bundles and Resource Pools 16
System Resource Bundle 17
Resource Assignment 17
vSphere Resource Pools and Data Director 18
Viewing Resource Information 20
Create the System Resource Pool 21
Create the System Resource Bundle 22
Monitor Resource Usage 22
Create a Resource Pool 23
Create a Resource Bundle 24
Assign a Resource Bundle to an Organization 25
Perform Advanced Cluster Configuration 26
VMware, Inc.
Managing Users and Roles 27
3
User Management Overview 27
Authenticating Users 28
Role-Based Access Control 29
Predefined Roles 30
Privileges 31
Propagation of Permissions and Roles 32
Organization Privileges and Permissions 32
Add Users to Your Organization 33
Add Roles to an Organization 33
Grant a Permission to a User 34
Modify Organization Security Settings 34
Building DBVMs and Base DB Templates 37
4
Database Virtual Machine OVA Files 39
Deploy a DBVM OVA File 39
Build a SLES and Oracle Base Database Virtual Machine 40
3
Page 4

VMware vFabric Data Director Administrator and User Guide
Build a Custom RHEL and Oracle Database Template 44
Install the Operating System and Database Software in a Blank DBVM 49
Requirements for the Kickstart File 49
Database Update Configuration 52
Configure a vFabric Postgres Update Chain 53
Update an Oracle Database 54
Managing Organizations 61
5
Organization Structure 61
Operating Organizations 62
Managing Resources For Organizations 63
Managing Organization Users 64
Create a Data Director Organization 64
Bind a vCloud Director Organization to Data Director 65
IP Whitelists 67
6
Create an Organization IP Whitelist 67
Apply IP Whitelists to Databases 68
Create Custom IP Whitelists 68
Managing Database Groups 71
7
Database Group Management Overview 71
Managing Resources for Database Groups 72
Storage Reservation 73
Database Groups and Security 73
Create a Database Group 73
Managing Database Templates 75
8
Introduction to Database Templates 75
Enable a Base DB Template 76
Create a DB Parameter Group 77
Create a Resource Template 77
Modify a Resource Template 78
Create a Backup Template 79
Modify a Backup Template 80
Managing Databases 83
9
Database Lifecycle 83
Requirements for Creating Databases 85
Database Creation 86
Using Tags 96
Managing the Organization Catalog 97
Batch Operations and Scheduled Tasks 99
Updating Databases 100
Database Administration 101
Cloning Databases 107
10
Clone Types 107
4 VMware, Inc.
Page 5

Cloning Customizations 109
Clone a Database 109
Managing Post-Clone Scripts 113
Managing a Cloned Database Refresh 117
Contents
Managing Database Entities 121
11
Database Entity Management 121
SQL Management 126
Safeguarding Data 129
12
Backup Strategies 130
Backup Types 130
Backup Template Settings 132
Preconfigured Backup Templates 133
Select a Database Backup Template 133
Schedule Regular Database Backups 134
Recover a Database 135
Import Backups 136
Use VMware Data Recovery to Back Up Data Director 136
Database End of Life and Backups 138
Perform Point-in-time Recovery of Management Server Database 139
Add Pre-Action and Post-Action Scripts to the DBVM for Selected Agents 139
Monitoring the Data Director Environment 141
13
Explore Monitoring Customization and Filtering 141
Monitoring for System Administrators 142
Monitoring for Organization Administrators 146
Explore Database Monitoring 150
Working with Alarms 151
About aurora_mon Configuration 153
aurora_mon Configuration Parameters 154
Managing Licenses 159
14
License Management Overview 159
Counting Data Director Licenses 161
About Evaluation Licenses 161
Add License Keys 162
View License Information 162
View License Usage Information 163
Change the vFabric Postgres Database Usage Type 163
Remove License Keys 164
IP Pool Management 165
15
Add an IP Pool 165
Edit IP Pool 166
Delete an IP Pool 166
VMware, Inc. 5
Page 6

VMware vFabric Data Director Administrator and User Guide
VMware vCloud Director Integration 169
16
Enable vCloud Director Integration in Setup 170
Enable vCloud Director Integration after Setup 170
Edit or Disable vCloud Director Integration 171
Add a vCloud Director Organization Administrator 171
Reconfiguring Data Director Networks 173
17
Change the vCenter IP Address 173
Reconfigure the Web Console Network Mapping or Network Adapter 174
Reconfigure the vCenter Network Mapping 175
Reconfigure the vCenter Network Adapter Settings 175
Reconfigure the DB Name Service Network or DB Name Service Network Adapter 176
Reconfigure the Internal Network or Internal Network Adapter Mapping 177
Verify Network Settings in Data Director 178
Reconfigure the Database Access Network Used by a Database Group 178
Modify IP Pool Settings 179
Managing SSL Keys and Certificates 181
18
Regenerate Management Server Key and Certificate 181
Import Management Server Key and Certificate 182
Edit Management Server Certificate 183
Regenerate DB Name Server Key and Certificate 183
Import DB Name Server Key and Certificate 184
Edit DB Name Server Certificate 184
Regenerate DBVM Key and Certificate 185
Import DBVM Key and Certificate 185
Edit DBVM Certificate 186
Data Director Troubleshooting 187
19
vCenter Server Stops Responding 187
Resource Bundles Become Unusable Because DRS Is Disabled 188
Missing Resource Pool 188
Troubleshooting for SSL Communication 189
Database Cannot Be Connected Using the JDBC Connection String 189
Index 191
6 VMware, Inc.
Page 7

About VMware vFabric Data Director Administrator and User Guide
The VMware vFabric Data Director Administrator and User Guide describes the features of VMware® vFabric Data
Director.
VMware vFabric Data Director is an enterprise class database-as-a-service (DBaaS) solution on VMware
vSphere that provides self-service lifecycle management for heterogeneous databases. The solution includes
the following features.
n
Database creation, cloning, backup, and restore.
n
Flexible, policy-based resource management.
n
Resource isolation within organizations and within databases.
n
Security policy implementation through role-based access control.
n
Database ingestion.
Self-service database lifecycle management enables administrators to create databases, manage schemas,
configure backups, perform restores, clone databases for testing and development, scale up database sizes,
and decommission databases. Administrators can assign permissions to perform these functions to others,
such as application developers, QA (test), and production engineers.
Customizable templates for database configuration and backups simplifies database creation and resource
allocation, enabling administrators to control database parameters and enforce resource allocation policies.
Administrators perform the following types of tasks.
n
Create organizations and database groups.
n
Allocate resources.
n
Create database templates.
n
Create, clone, backup and restore databases.
n
Monitor the Data Director environment.
Administrators also manage users and roles by assigning various permissions to enable users to perform
specific database management tasks.
Intended Audience
This document is for administrators any user to whom an administrator might grant database permissions.
n
System administrators use this document to learn how to manage and monitor a Data Director
environment.
n
Organization administrators use this document to learn how to manage and monitor database groups and
databases.
VMware, Inc.
7
Page 8

VMware vFabric Data Director Administrator and User Guide
n
Application developers use this document to learn how to create, manage and monitor databases.
n
Application developers, QA and production engineers, and others use this document to learn how to
perform functions for which they have been granted permissions.
8 VMware, Inc.
Page 9

VMware vFabric Data Director
Overview 1
VMware vFabric Data Director is a software solution that powers Database-as-a-service in your cloud. It
enables you to implement database-aware virtualization on vSphere and provides self-service lifecycle
management for heterogeneous databases.
This chapter includes the following topics:
n
“Data Director System Architecture,” on page 9
n
“VMware Data Director Components,” on page 10
n
“Data Director User Management Modes,” on page 10
n
“About Data Director Administration,” on page 11
n
“Data Director Supported Databases,” on page 12
Data Director System Architecture
vFabric Data Director automates deployment, management, and governance of thousands of databases and
enables policy-based self-service database management for application developers.
Data Director supports the following databases.
n
Oracle 11gR2 Enterprise and Standard editions.
n
Oracle 10gR2 Enterprise and Standard editions.
n
Microsoft SQL Server 2012 Enterprise and Standard editions.
n
Microsoft SQL Server 2008 R2 Enterprise and Standard editions.
n
vFabric Postgres 9.0 and 9.1, a VMware vSphere optimized relational database based on PostgreSQL.
Data Director provides flexible, policy-based resource management at the system level, and isolation at the
organization and database level. Data Director system administrators can implement security policies through
role-based access control to restrict system access to authorized users. System administrators use database
templates to guarantee corporate compliance to standardization, and carry out important database lifecycle
management tasks such as provisioning, backup, snapshots, point-in-time recovery, cloning, updating,
monitoring, and so on.
Database administrators and authorized users can configure databases by using customizable parameters.
Resource and backup templates simplify database creation. After an administrator assigns appropriate
permissions, users can create databases and allocate resources to them. Users can schedule backups, perform
restores, and clone databases to use in testing and development environments. They can scale up databases
according to system needs, and decommission databases when they are no longer required.
VMware, Inc.
9
Page 10

VMware vFabric Data Director Administrator and User Guide
VMware Data Director Components
The Data Director hierarchy consists of organizations, each with its own discrete database groups and
databases. Currently supported databases include vFabric Postgres, Microsoft SQL Server, and Oracle.
System administrators perform management tasks at the system level, which is the top level of the hierarchy.
To edit system-level settings you must have system privileges, but having system privileges does not
automatically allow you to make changes at the other levels.
A system can contain multiple organizations, each with multiple database groups. A database group can
contain multiple databases. You can create database groups only within organizations. Databases can exist
only within database groups.
Figure 1-1. Data Director System Hierarchy
System administrators manage Data Director resources at the system and organization levels. System
administrators create resource bundles from vSphere resource pools (CPU and memory resources) and storage
and network resources, and allocate one or more resource bundles to each organization.
Organization administrators assign resources from the given resource bundles to database groups for
consumption by databases.
Data Director User Management Modes
Data Director user management modes control how users are assigned and managed among different
organizations. Data Director has two user management modes: Global mode (for enterprises) and By
Organization mode (for service providers). Global user management mode is the default.
User management mode must be set to By Organization for VMware vCloud Director integration. See
“Organization Structure,” on page 61.
By Organization user management mode has the following characteristics.
n
Organizations are set up as separate, isolated enterprises with no visibility into other organizations.
n
The Data Director system user list is not visible to organizations.
n
No organization can see another organization's user list.
n
Organization administrators send email to invite users to join their organization, or register users directly.
n
Users can navigate to the Data Director web console URL and register for an account, pending approval
from the organization administrator.
10 VMware, Inc.
Page 11

Global user management mode has the following characteristics.
n
Organizations are set up as separate departments, business units, or groups within one enterprise, such
as a corporation's HR and Finance departments.
n
All Data Director users are visible to all organizations within Data Director.
n
Organization administrators grant access to users to the organization or grant access directly from the
system user list.
n
Users can navigate to the Data Director web console URL and register for an account, pending approval
from the organization administrator.
About Data Director Administration
Data Director system administrators perform Data Director administration on the system level. Organization
administrators perform Data Director administration on the organization level.
You create the initial account for the Data Director system administrator during Data Director setup. That
system administrator creates the system resource bundle, base database virtual machines (base DBVMs), and
base database templates.
By default, users do not have roles or permissions and cannot access any organizations. Organization
administrators assign roles and permissions to users and grant them access to specific organizations.
Chapter 1 VMware vFabric Data Director Overview
System administrators perform system-level operations for Data Director or for an entire organization. System
administrators perform the following tasks.
Table 1-1. System-Level Operations
Operation Type Examples
Resource management operations
User and organization
management operations
n
Creating and managing the system resource bundle.
n
Creating and managing resource bundles.
n
Creating and managing database virtual machines (DBVMs).
n
Managing base database templates.
n
Assigning base database templates to resource bundles.
n
Assigning resource bundles to organizations.
n
Creating and managing resource templates.
n
Creating and managing backup templates.
n
Creating system users.
n
Creating system administrators.
n
Creating organizations.
n
Creating organization administrators.
n
Designating existing users as organization administrators.
Organization administrators perform organization-level operations within their organizations. Organization
administrators perform the following tasks.
VMware, Inc. 11
Page 12

VMware vFabric Data Director Administrator and User Guide
Table 1-2. Organization-Level Operations
Operation Type Examples
Resource management operations
User management operations
By default, Data Director system administrators do not have access to organizations. Organization
administrators have access to only their own organization. They can create organization users and can grant
access to existing Data Director users.
Data Director system administrators can create users, but only organization administrators can grant those
users access to organizations.
n
Creating database groups.
n
Enabling base database templates in resource bundles.
n
Creating resource templates.
n
Creating backup templates.
n
Allocating resources to database groups within the organization.
n
Creating and managing organization users.
n
Granting organization access to existing Data Director users.
n
Assigning organization roles to users in the organization.
n
Creating and managing organization roles and granting roles to
organization user.
n
Defining organization permissions and granting permissions to
organization users.
Data Director Supported Databases
Data Director supports self-service database provisioning and automation through a web interface and
compatible client tools and drivers.
Data Director supports the following databases.
n
“VMware vFabric Postgres databases,” on page 13
n
“Oracle databases,” on page 13
n
“Microsoft SQL Server databases,” on page 13
Database administrators and application developers administer databases within their organizations.
Database administration includes the following tasks.
n
Creating databases and allocating resources to them.
n
Cloning databases.
n
Managing database users, roles, privileges, and permissions.
n
Maintenance such as performing backups and restores.
n
Scaling up databases.
n
Updating databases.
n
Monitoring database usage and performance.
n
Monitoring database alarms.
n
Decommissioning databases.
12 VMware, Inc.
Page 13

Chapter 1 VMware vFabric Data Director Overview
Oracle databases
As a system administrator, you upload, test, and manage the Oracle base database templates that organization
administrators, DBAs, and application developers use to create Oracle databases.
The recommended practice for using Oracle with Data Director is to set up a dedicated vSphere ESXi cluster
for hosting Oracle resources, including operating system, Oracle database server, and client tools. You create
Oracle base database virtual machines (DBVMs) using the dedicated Oracle resources in vSphere, then upload
the DBVMs to Data Director to use as database templates.
Data Director supports the following Oracle versions.
n
Oracle 11gR2 on SUSE, RHEL, or Oracle Linux.
n
Oracle 10gR2 on SUSE, RHEL, or Oracle Linux.
VMware vFabric Postgres databases
Data Director provides self-service database provisioning and automation with vFabric Postgres databases.
vFabric Postgres is built on the open source Postgres database.
vFabric Postgres is compatible with pSQL and the PostgreSQL tools and client drivers. vFabric Postgres
databases are fully compliant with ACID and ANSI SQL. The ACID properties, Atomicity, Consistency,
Isolation, and Durability, guarantee that database transactions are processed reliably.
For information about the Postgres database features for Data Director, see the Using VMware vFabric Postgres
for Data Director.
Microsoft SQL Server databases
As a Data Director system administrator you upload and manage the SQL Server base database templates that
organization administrators, DBAs, and application developers use to provision SQL Server databases.
Use SQL Server with Data Director to set up a dedicated vSphere ESXi cluster for hosting SQL Server resources,
including operating system, SQL Server database server, and client tools. You create SQL Server base database
virtual machines (DBVMs) using the dedicated SQL Server resources in vSphere, and upload the DBVMs to
Data Director to use as database templates from which you can provision SQL Server databases.
Data Director supports the following SQL Server versions.
n
SQL Server 2012 Enterprise and Standard editions.
n
SQL Server 2008 R2 Enterprise and Standard editions.
Provisioning Support for SQL Server
Data Director supports the creation of a stand-alone SQL Server instance using the default (unnamed) instance
name. The default instance name is the same as the host name. You can have only one default instance per
virtual machine.
NOTE A SQL Server instance is either a default, unnamed instance, or it is a named instance. When SQL Server
is installed as a default instance, it does not require a client to specify the name of the instance to make a
connection. The client only has to know the server name.
The Data Director provisioning process prepares and configures the SQL Server software as described in the
following list.
n
The SQL Server DBVM can join an existing Windows domain during provisioning. You must provide a
Windows Active Directory credential with sufficient privileges to join the domain. If a SQL Server DBVM
joins a domain, Windows authentication is the authentication method. The user-supplied domain account
is added to the sysadmin role of the SQL Server instance.
VMware, Inc. 13
Page 14

VMware vFabric Data Director Administrator and User Guide
n
If the DBVM does not join a domain, Data Director uses mixed authentication, and prompts for the SQL
Server System Administrator (SA) password.
n
No user databases are created when provisioning within Data Director.
Data Director Support for SQL Server
Data Director supports the creation of new, empty SQL Server databases. To learn more about creating a SQL
Server database, see “Create an Empty SQL Server Database,” on page 88.
The following Data Director features are not currently supported.
n
Database backup and recovery.
n
Database cloning.
n
Adding databases to the organization catalog.
n
Database ingestion.
n
Use of IP whitelists.
n
Changing disk size.
n
DBVM reporting.
n
Editing database resources.
n
Adding database owners.
n
Base DB template validation.
n
High availability (HA).
n
Upgrading.
NOTE When using Data Director to monitor and manage SQL Server databases, the user interface controls for
the above listed features are not visible in the administration console.
14 VMware, Inc.
Page 15

Managing Data Director Resources 2
System administrators manage CPU, memory, storage, and networking resources, as well as system-wide
database and backup configuration templates. Organization administrators manage resources for database
groups and for databases and enable database templates for their organizations.
This chapter includes the following topics:
n
“Resource Management Overview,” on page 15
n
“Resource Bundles and Resource Pools,” on page 16
n
“System Resource Bundle,” on page 17
n
“Resource Assignment,” on page 17
n
“vSphere Resource Pools and Data Director,” on page 18
n
“Viewing Resource Information,” on page 20
n
“Create the System Resource Pool,” on page 21
n
“Create the System Resource Bundle,” on page 22
n
“Monitor Resource Usage,” on page 22
n
“Create a Resource Pool,” on page 23
n
“Create a Resource Bundle,” on page 24
n
“Assign a Resource Bundle to an Organization,” on page 25
n
“Perform Advanced Cluster Configuration,” on page 26
Resource Management Overview
System administrators allocate resources to organizations. These virtual resources come directly from the
physical resources of the cluster on which Data Director runs. Organization administrators assign organization
resources to database groups and databases.
A vSphere cluster consists of several ESXi hosts that provide the physical CPU and memory resources for the
databases managed by Data Director. As part of installation, you create the cluster and enable vSphere High
Availability (HA) and vSphere Distributed Resource Management (DRS) for the cluster. Data Director can take
advantage of the vSphere HA and vSphere DRS functionality because Data Director runs on top of the cluster.
See the vSphere Availability and the vSphere Resource Management documentation for details.
A Data Director resource bundle includes CPU, memory, storage, and networking resources. The CPU and
memory resources come from a resource pool in the vSphere cluster. The storage and networking resources
are assigned to Data Director during installation or at a later time. Data Director includes a set of VLANs to
carry different types of network traffic.
VMware, Inc.
15
Page 16

VMware vFabric Data Director Administrator and User Guide
Data Director provides the following types of resource bundles.
n
System resource bundle. Data Director system administrators create one system resource bundle at the
Data Director system level. In addition to providing virtual resources, the system resource bundle contains
the database virtual machines (DBVMs) and base database templates that support creating and
provisioning databases. See “System Resource Bundle,” on page 17.
n
Resource bundle. Data Director system administrators create one or more resource bundles to provide
operating resources to organizations.
When system administrators create an organization, they can assign virtual resources to the organization as
resource bundles. When organization administrators create a database group, they assign virtual resources to
the database group. These virtual resources are backed by the physical resources of one or more clusters.
vSphere clusters provide failover protection and support efficient use of physical resources.
System administrators can assign resources when they create an organization (see “Create a Data Director
Organization,” on page 64) or assign resources to an existing organization (see “Assign a Resource Bundle
to an Organization,” on page 25). Organization administrators can assign resources when they create a
database group or assign resources to existing database groups.
If you chose the Express installation in the Data Director Setup wizard and enabled Create defaults, a system
resource bundle and Default resource bundle is already created. A Default organization and Default database
group is also created, and the Default resource bundle is assigned to the Default organization.
To help you specify the resources associated with a database template, Data Director includes a calculator that
computes the optimum resource configuration based on the anticipated usage patterns. When you create
databases from the template, the specified resources are allocated.
Resource Bundles and Resource Pools
A resource bundle is a set of compatible IT resources for provisioning databases. To assign the appropriate
amount of resources to each organization, system administrators create resource bundles and assign them to
organizations. System administrators specify a resource pool and storage and networking resources when they
create a resource bundle. If Create defaults was selected in Express installation, a Default resource bundle is
created and assigned to a Default organization.
Resource Pool
Storage Resources
DB Access Networks
All CPU and memory resources of a resource bundle come from a vSphere
resource pool that is created in the vSphere Client with reservation equal to
limit. See “Create a Resource Pool,” on page 23.
Each resource bundle includes storage resources for data and storage resources
for backup. The storage resources must be visible to all hosts that use the
resource bundle.
DB Access Networks provide communication for databases. A DB Access
Network corresponds to a vSphere port group. Each network must be visible
to all hosts that use the resource bundle. DHCP or IP Pool is required. See
Chapter 15, “IP Pool Management,” on page 165
Selecting one or more DB Access Networks allows you to isolate different
database groups from one another, for example, to isolate a QA database group
from a Production database group. When no DB Access Networks have been
assigned in the environment, select the network that is mapped to the Web
Console Network. Do not select internal networks for DB Access Network
traffic.
The figure shows how Data Director resources come from vSphere resource pools, datastores, and port groups.
When administrators create a resource bundle, the resources are always coming from the underlying vSphere
environment.
16 VMware, Inc.
Page 17
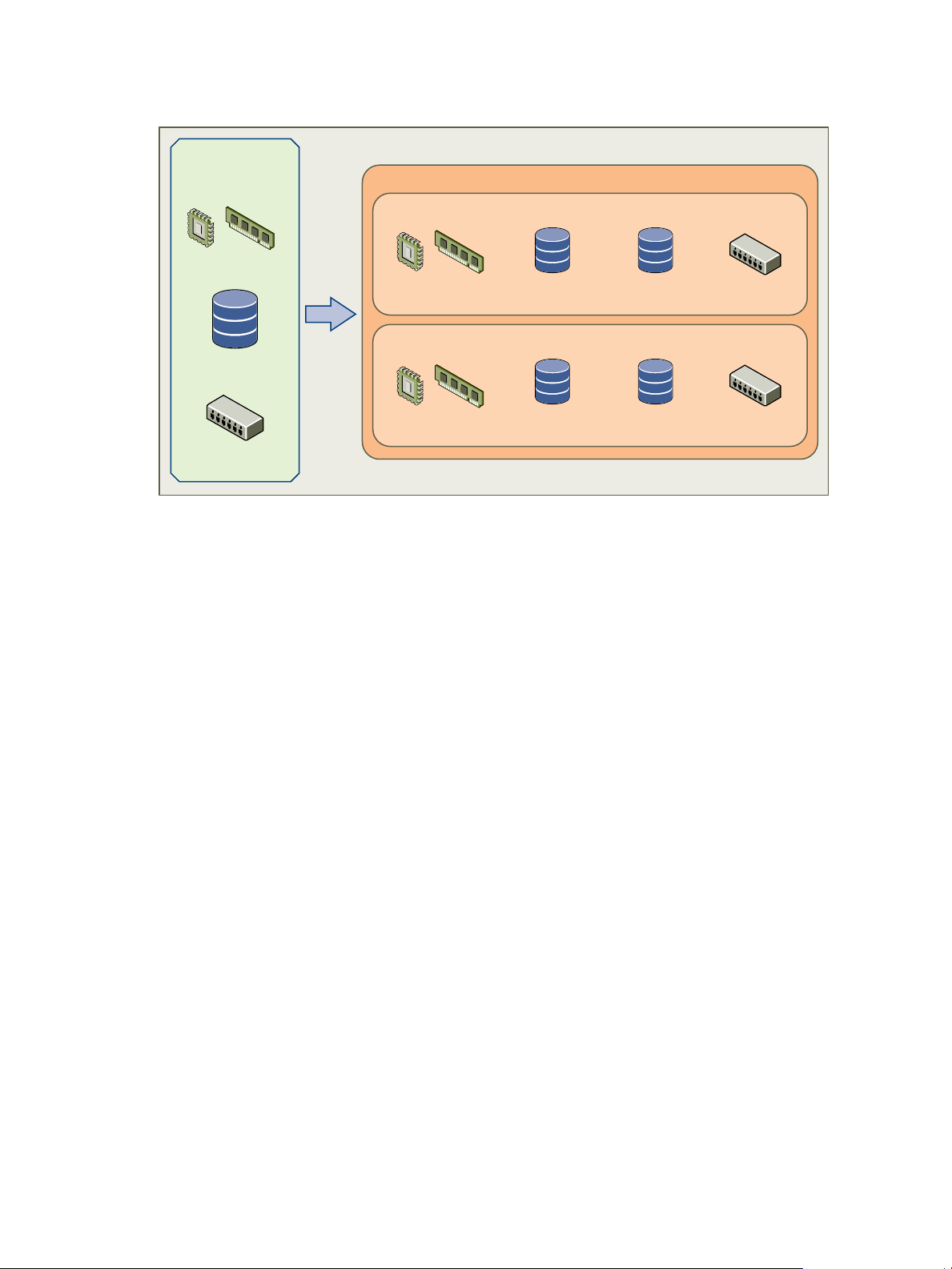
Figure 2-1. Resources in vSphere and Data Director
vSphere
source RPs
source datastores
source port groups
CPU & memory
database
storage
network
backup
storage
resource bundle
CPU & memory
database
storage
network
backup
storage
Data Director
resource bundle
Chapter 2 Managing Data Director Resources
“Resource Assignment,” on page 17 explains how resource assignment differs for the different levels of the
hierarchy.
System Resource Bundle
The system resource bundle provides CPU, memory, network, and storage resources for the base database
virtual machines (base DBVMs) and base database templates that you use to create and provision databases.
Each Data Director installation must have one system resource bundle. If you chose Create defaults in the
Express installation, a system resource bunde is created automatically.
Data Director system administrators create the system resource bundle before setting up other Data Director
entities and populate it with base database templates and base DBVMs.
The Data Director system administrator creates the system resource bundle at the system level. This ensures
that the CPU, memory, storage, and networking resources, base database templates, and base DBVMs apply
to the entire Data Director platform. The system administrator creates resource bundles and assigns base
database templates to them, and assigns the resource bundles to organizations. The organization administrator
enables base database templates for use in that organization.
See “Create the System Resource Bundle,” on page 22.
Resource Assignment
Resource assignment differs for organizations, database groups, and databases.
Resource Assignment for Organizations
VMware, Inc. 17
System administrators can assign multiple resource bundles to each organization. System administrators can
assign a particular base database template to multiple resource bundles. Organization administrators allocate
the resource bundles to database groups and enable base DB templates. When you create databases, they draw
on the resources assigned to the database group and the base database templates enabled in the organization.
This resource isolation guarantees that different organizations and different database groups have control over
their resources.
Page 18

VMware vFabric Data Director Administrator and User Guide
If you chose the Express installation and enabled Create defaults in the Data Director Setup wizard, a system
resource bundle and Default resource bundle are created during setup. A Default organization with a Default
database group within that organization is also created, and the Default resource bundle is assigned to the
Default organization.
Resource Assignment for Database Groups
When you create a database group, you assign a resource bundle that specifies the resources for that group.
You cannot assign more than one resource bundle to one database group. Multiple database groups can share
one resource bundle.
When you assign a resource bundle to a database group, you can specify how to allocate each resource.
n
CPU priority or reservation.
n
Memory priority or reservation.
n
Storage allocation.
n
Storage reservation percentage.
n
A network for the database group. You cannot divide the network. You can select only one network when
you create a database group even if several networks are associated with the resource bundle.
If you do not specify the CPU or memory allocation, Data Director sets the reservation to zero but sets
expandable reservations to true. If expandable reservations is set to true, the CPU or memory can expand
beyond the specified value.
Resource Assignment for Databases
A database consumes the resources assigned to its database group.
n
You can specify the number of virtual CPUs, the memory size, and CPU and memory priority for each
database that you create.
n
You cannot specify storage allocation. All databases consume the data and the backup storage allocated
to their parent database group. You can specify the size of data or PITR disk of each database.
n
Each database uses the network assigned to the database group as the DB access network.
vSphere Resource Pools and Data Director
A vSphere resource pool is a logical abstraction for flexible management of CPU and memory resources.You
add CPU and memory resources to Data Director resource bundles by adding a vSphere resource pool to the
bundle.
Data Director has the following types of resource pools.
Resource Pools for
Databases
System Resource Pool
vSphere administrators create one or more resource pools to enable Data
Director users to create databases. Resource pools for databases require
configuration settings such as DRS and HA enabled, and CPU and memory
limits equal to reservation.
There is one system resource pool for one Data Director instance. vSphere
administrators can deploy database virtual machine (DBVM) OVA files into
the system resource pool at any time. The configuration settings for the system
resource pool are different from the configuration settings for database
resource pools. You do not have to enable HA, and CPU, and memory limits
do not have to equal reservations. The reservation must be greater than 0.
18 VMware, Inc.
Page 19

Chapter 2 Managing Data Director Resources
You can also enable expandable CPU and memory. See “Create the System
Resource Pool,” on page 21.
CAUTION Data Director can use only resource pools for creating databases if the corresponding cluster is
enabled for DRS and HA. Do not disable DRS. If you do, Data Director cannot use the resource pools even if
you reenable DRS. See “Resource Bundles Become Unusable Because DRS Is Disabled,” on page 188.
Resource pools allow you to group available CPU and memory resources. You can allocate resources explicitly,
or use the resource pool share mechanism. You can hierarchically partition available CPU and memory
resources by grouping resource pools into hierarchies. You can allow different organizations access to different
resource pools. For example, a QA department might need large amounts of CPU and memory for running
tests while the marketing department might require smaller amounts.
Data Director expects you to group the hosts that provide the CPU and memory resources into clusters. Each
cluster owns the resources of all hosts. You can create one or more resource pools for the cluster, which has an
invisible root resource pool. Each resource pool owns some of the cluster's resources. If necessary, you can
create child resource pools. Child resource pools represent successively smaller amounts of CPU and memory.
CAUTION To use Oracle with Data Director, create a cluster specifically for Oracle use. To avoid licensing issues,
assign only resources from your dedicated Oracle cluster to organizations that create and provision Oracle
databases and DBVMs.
How you allocate CPU and memory resources to database groups differs from how you allocate those resources
to databases.
Creating Resource Pools for Databases
You create resource pools for databases by using a vSphere Client connected to a vCenter Server system. Specify
the following resource pool settings to ensure that Data Director always receives all of its allocated resources
and does not have different amounts of CPU and memory available if the cluster is experiencing a light or a
heavy load.
NOTE If you do not configure your resource pool with these settings, problems with resource bundle creation
or other Data Director tasks might result. Resource pools with incorrect settings do not appear in the list of
available resource pools when you create a resource bundle.
Set the Limit equal to the
Reservation.
Set Expandable
Reservation to checked
or unchecked.
Set Unlimited to
unchecked.
After you create the resource pool, you create resource bundles. Each resource bundle uses one resource pool.
If the system never allocates more resources than you reserved, you do not
experience resource fluctuations.
If the system does not attempt to allocate more resources than you reserved,
you do not experience resource fluctuations.
Data Director requires this setting to avoid a resource bundle taking more than
its share of the resource pool.
See “Create a Resource Pool,” on page 23 and “Create a Resource Bundle,” on page 24.
VMware, Inc. 19
Page 20

VMware vFabric Data Director Administrator and User Guide
Allocating CPU and Memory Resources to Database Groups
When you create a database group and set its CPU and memory allocation, Data Director creates a child
resource pool of the resource pool that you select. Data Director configures the resource pool with the allocation
that you specify. Having a different resource pool for each database group isolates the database group's
allocation and makes different groups independent.
n
If you specify the CPU and memory allocation, Data Director uses the following settings for the resource
pool it creates.
n
Reservation is set to the value you specify.
n
Expandable reservation is set to False.
n
Limit is set to unlimited.
n
If you do not specify CPU or memory allocation, Data Director uses the following settings for the resource
pool it creates.
n
Reservation is set to 0.
n
Expandable reservation is set to True, allowing the database group to consume resources as they are
available.
n
Limit is set to unlimited.
Allocating CPU and Memory Resources to Databases
In the Data Director environment, a database is a virtual machine that consumes resources from the database
group. You can specify the CPU and memory allocation for the database. Data Director always sets the limit
to unlimited.
Viewing Resource Information
Data Director system administrators can view resource usage information for an organization from the Data
Director Manage & Monitor tab.
When you log in to Data Director as a system administrator, you can view information about the resource
usage of the different organizations and about the resource bundle or resource bundles that are being used by
each organization.
n
The Organizations pane allows you to manage organizations. You can view organization information,
assign and unassign resource bundles, delete the organization, and view the organization's properties.
n
The Resource Bundles pane allows you to view all resource bundles currently created for this instance of
Data Director. You can display either allocation information or vCenter Server Object information.
n
You can click on an item in the heading, such as Organization, to re-sort the table based on that
column. Right-click any resource bundle name and choose Properties to see detailed information
about each resource bundle.
n
If you select vCenter Server Objects, Data Director displays the names of resource pools, datastores,
and networks that you see in the vSphere Client UI.
n
The Datastore Usage pane shows datastore usage for the main datastore and the backup datastore. You
can see how resource bundles map to datastores and examine storage allocation information for each
datastore.
See Chapter 13, “Monitoring the Data Director Environment,” on page 141 for details on using the monitoring
interface.
20 VMware, Inc.
Page 21

Create the System Resource Pool
vSphere administrators create one system resource pool from a vSphere Client connected to a vCenter Server
system. vSphere Administrators deploy the Data Director database virtual machine (DBVM) OVAs to the
system resource pool.
Prerequisites
n
Connect to the vCenter Server system by using a vSphere Client. You cannot create resource pools if the
client is connected directly to a host.
n
Verify that you have permissions sufficient to create a resource pool.
n
Choose a location for the resource pool. Data Director cannot use resource pools at the top level.
n
See vSphere Resource Management for information about resource pools.
n
Before you create any resource pools, you must prepare a cluster. You must have at least one host in the
cluster. See the vFabric Data Director Installation Guide for information.
Procedure
1 In the vSphere Client, select Home > Inventory > Hosts and Clusters.
2 Select the cluster to which all Data Director hosts have been assigned.
Chapter 2 Managing Data Director Resources
3 Specify the settings for the system resource pool.
Option Description
Name
CPU Shares
CPU Reservation
Expandable Reservation
CPU Limit
Unlimited
Memory Shares
Memory Reservation
Expandable Reservation
Memory Limit
Unlimited
Name of the resource pool.
Leave CPU shares set to Normal.
CPU resources to allocate to this resource pool. Set CPU reservation equal to
CPU limit value. Must be greater than 0.
Can be checked or unchecked.
Maximum CPU resources available to this resource pool. Set CPU limit equal
to CPU reservation value.
Leave unchecked.
Leave memory shares set to Normal.
Memory resources to allocate to this resource pool. Must be greater than 0.
Can be checked or Unchecked.
Maximum memory resources available to this resource pool. Because this is
the system resource pool, limit does not have to equal reservation.
Unchecked.
After the system resource pool is set up, you can deploy Data Director OVA files and point to the system
resource pool when you create the Data Director system resource bundle.
What to do next
Create the system resource bundle. See “Create the System Resource Bundle,” on page 22.
VMware, Inc. 21
Page 22

VMware vFabric Data Director Administrator and User Guide
Create the System Resource Bundle
The system resource bundle resides at the Data Director system level, and enables you to create, test, and run
base database virtual machines.
Prerequisites
n
Create a resource pool to use for allocating CPU and memory resources. See “Create a Resource Pool,” on
page 23.
n
Determine the storage resources that you want to include in the system resource bundle. Plan for storage
resources for database storage and resources for backup storage.
n
Determine the networking resource that you want to include in the system resource bundle. You can assign
only one network to the system resource bundle. The networking resource is used by the base DBVMs for
building base database templates.
NOTE If you do not configure your resource pool with these settings, you might have problems with system
resource bundle creation or other Data Director tasks.
Procedure
1 Log in to Data Director with system administrator privileges.
2 Select System, and click System Settings.
3 ClickSystem Resource Bundle in the left pane.
4 ClickCreate System Resource Bundle
5 Specify the following information about the resource bundle in the wizard.
Wizard screen Action
Name and Description
CPU and Memory
Storage
Networks
Type a name and optional description and click Next.
Select the resource pool from which you want to assign CPU and memory
resources and click Next.
Click Edit to select a datastore, and allocate the number of gigabytes to use
with Data Director, or allocate all unallocated space. Repeat the process for
backup storage.
NOTE Do not select a datastore that is in a datastore cluster.
Select the networks that you want to have available to this resource bundle.
These networks provide the public network for the organization's databases.
Resource bundles must use a database network when available.
The resource bundle is created.
What to do next
Create a base DBVM. See Chapter 4, “Building DBVMs and Base DB Templates,” on page 37.
Monitor Resource Usage
System administrators can view usage information for resource bundles and datastores and can reassign
resource bundles from the Manage & Monitor tab.
The focus of this task is on monitoring, not on changing current settings.
Prerequisites
n
Log in to Data Director as a user with system administrator privileges.
22 VMware, Inc.
Page 23

Chapter 2 Managing Data Director Resources
n
Verify that one or more organizations exist in your environment.
n
Verify that resource bundles and datastores have been assigned to the organizations.
Procedure
1 In Data Director, click the System tab, and click the Manage & Monitor tab.
The Organizations panel displays resource allocation information about each organization.
2 Click one of the columns, for example Total Memory, to reorder the rows of the table.
3 Click one of the organizations to display resource bundle information for the selected organization.
4 Click Resource Bundles to display the Resource Bundles pane.
5 Click Datastore Usage to display information about available datastores, their capacity, and the allocated
and unallocated storage for each.
6 Click one of the datastores to display the associated resource bundles and their storage allocation.
What to do next
You can change the resource bundle information by clicking the Actions icon and selecting Properties. If
properties are dimmed, you do not have permissions to change them.
Create a Resource Pool
You allocate CPU and memory resources to Data Director by creating one or more resource pools from a
vSphere Client connected to a vCenter Server system. From the Data Director user interface, you can then
assign the resources from those resource pools to database groups and databases.
Before you create the resource pools, you must prepare a cluster. Enable the cluster for HA and DRS, and add
all Data Director hosts to the cluster. See the vFabric Data Director Installation Guide for information.
Prerequisites
n
Connect to the vCenter Server system by using a vSphere Client. You cannot create resource pools if the
client is connected directly to a host.
n
Verify that you have permissions sufficient to create a resource pool.
n
Choose a location for the resource pool. Data Director cannot use resource pools at the vApp top level.
For information about resource pools, see the vSphere Resource Management documentation .
Procedure
1 In the vSphere Client, select Home > Inventory > Hosts and Clusters.
2 Select the cluster to which all Data Director hosts were assigned.
3 Configure the resource pool.
Option Description
Name
CPU Shares
CPU Reservation
Expandable Reservation
CPU Limit
Unlimited
Memory Shares
Memory Reservation
Name of the resource pool.
Do not specify CPU shares. Instead, specify the CPU reservation.
CPU resources to allocate to this resource pool. Must be greater than 0.
Checked or unchecked.
Maximum CPU resources available to this resource pool. Set Limit to be equal
to CPU Reservation.
Unchecked.
Do not specify memory shares. Instead, specify a memory reservation.
Memory resources to allocate to this resource pool. Must be greater than 0.
VMware, Inc. 23
Page 24

VMware vFabric Data Director Administrator and User Guide
Option Description
Expandable Reservation
Memory Limit
Unlimited
After you create and configure the resource pool, you can point to the resource pool when you create the Data
Director resource bundle.
What to do next
Create a resource bundle. See “Create a Resource Bundle,” on page 24.
Create a Resource Bundle
Resource bundles allow you to bundle CPU, memory, storage, database template, and networking resources.
You create resource bundles using the Data Director user interface.
When you create a resource bundle, the wizard displays only resource pools with a parent cluster that meets
the following requirements.
n
vSphere DRS and vSphere HA are enabled.
Checked or Unchecked.
Maximum memory resources available to this resource pool. Set Limit to be
equal to Memory Reservation.
Unchecked.
n
VM Monitoring is set to VM and Application Monitoring.
n
VM Restart Priority is not disabled for any of the virtual machines.
n
Host monitoring and admission control are enabled.
See “Perform Advanced Cluster Configuration,” on page 26 for details on recommended settings.
Prerequisites
n
Create a resource pool to use for allocating CPU and memory resources. See “Create a Resource Pool,” on
page 23.
n
Decide on the storage resources that you want to include in the resource bundle. Plan for storage resources
for database storage and resources for backup storage.
n
Decide on the database templates (base DB templates) that you want to assign to the resource bundle.
Organization users can create and provision databases only when base DB templates are assigned to, and
enabled in, an organization's resource bundle(s). You can assign additional base DB templates to resource
bundles at any time.
n
Decide on the networking resources that you want to include in the resource bundle. The resource bundle's
networking resources are used for the DB access network for databases in an organization.
NOTE If you do not configure your resource pool with these settings, you might have problems with resource
bundle creation or other Data Director tasks.
Procedure
1 Log in to Data Director with system administrator privileges.
2 Select System, and click Manage & Monitor.
3 Click Resource Bundles.
4 Click the plus (+) icon.
24 VMware, Inc.
Page 25

Chapter 2 Managing Data Director Resources
5 Specify the following information about the resource bundle in the wizard.
Wizard Screen Action
Name and Description
Resource Pool
Storage
Base Database Templates
DB Access Networks
Type a name and optional description and click Next.
Select the resource pool from which you want to assign CPU and memory
resources and click Next.
a Click Edit to select a Datastore, and allocate the number of gigabytes to
use with Data Director, or allocate all unallocated space. Repeat the
process for backup storage.
NOTE Do not select a datastore that is in a datastore cluster.
b Specify the storage reservation. The default is 100%. The minimum
storage reservation is the lower bound of the storage reservations of
database groups created under the resource bundle. System
administrators typically use this reserve to control how much storage
over allocation can be allotted by organization administrators with this
resource bundle. See Chapter 7, “Managing Database Groups,” on
page 71 for more information about storage reservation.
Select the base Database templates available in this resource bundle. Users
create and provision databases using these templates. You can assign base
database templates to resource bundles at any time.
Select the networks that you want to have available to this resource bundle.
These networks provide the public network for the organization's databases.
Resource bundles must use a database network when available.
What to do next
System administrators can assign additional base database templates to resource bundles, and allocate the
resource bundles to organizations. Organization administrators can assign resources to their database groups.
Assign a Resource Bundle to an Organization
System administrators can assign a resource bundle to an organization when they create an organization. You
can also assign a resource bundle to an organization at a later time.
Prerequisites
Log in to Data Director as a system administrator or a user who can assign resource bundles to organizations.
Procedure
1 Click the Manage & Monitor tab and, click Organizations.
2 Right-click the organization that you want to assign a resource bundle to, and select Assign Resource
Bundle.
3 Select the resource bundle that you want to assign from the list of resource bundles and click OK.
What to do next
System administrators can assign additional base DB templates to the resource bundle. Organization
administrators can enable base DB templates for their organizations and create one or more database groups
and databases. See Chapter 9, “Managing Databases,” on page 83 and “Create a Database Group,” on
page 73.
VMware, Inc. 25
Page 26

VMware vFabric Data Director Administrator and User Guide
Perform Advanced Cluster Configuration
During installation, you configure the Data Director cluster with vSphere DRS and vSphere HA enabled, and
with certain monitoring settings. You can later edit the Data Director cluster configuration to change the
monitoring sensitivity for virtual machines.
As part of the installation process, you configure the Data Director cluster. See the vFabric Data Director
Installation Guide. After installation, you can customize the cluster to work in your environment. See the vSphere
Availability documentation and the vSphere Resource Management documentation for background information.
Not all changes that you can make to a vSphere cluster are compatible with Data Director. You must make
sure that the cluster settings remain compatible with Data Director. Data Director checks the following settings.
n
DRS must be enabled. DRS automation level can be any of the supported options. Partially automated
works best with Data Director in most situations.
n
HA, host monitoring, and admission control must be enabled.
n
VM Monitoring is set to VM and Application Monitoring.
If cluster settings are not compatible with Data Director, and if you create a resource pool in the cluster, you
cannot import the resource pool to a Data Director resource bundle.
If you change cluster settings from Data Director compatible to Data director incompatible, Data Director
displays alerts but does not revert the settings. You must revert the settings to make the cluster compatible
again.
CAUTION Do not disable DRS, because you lose all resource pools. Reenabling DRS does not restore the resource
pools. See “Resource Bundles Become Unusable Because DRS Is Disabled,” on page 188.
If you customize the HA settings for a virtual machine, and if those settings are not compatible with Data
Director, an alert appears. You must make the cluster compatible again.
Prerequisites
Verify that you have log-in privileges and privileges for cluster modification for the vCenter Server system on
which the Data Director cluster runs.
Procedure
1 Log in to a vSphere Client that is connected to the vCenter Server on which the Data Director cluster runs.
2 Right-click the cluster and click Edit Settings.
3 Click VM Monitoring.
4 Select the Custom check box and specify custom settings.
These are the lowest acceptable settings. Values can be higher.
Option Description
Failure interval
Minimum uptime
Maximum Per-VM resets
Maximum resets time window
30 seconds
120 seconds
3
Within 1 hour
5 Click OK.
26 VMware, Inc.
Page 27

Managing Users and Roles 3
User management controls the users that can log in to Data Director and what they can see and do after they
log in.
This chapter includes the following topics:
n
“User Management Overview,” on page 27
n
“Authenticating Users,” on page 28
n
“Role-Based Access Control,” on page 29
n
“Predefined Roles,” on page 30
n
“Privileges,” on page 31
n
“Propagation of Permissions and Roles,” on page 32
n
“Organization Privileges and Permissions,” on page 32
n
“Add Users to Your Organization,” on page 33
n
“Add Roles to an Organization,” on page 33
n
“Grant a Permission to a User,” on page 34
n
“Modify Organization Security Settings,” on page 34
User Management Overview
System and organization administrators use a combination of user logins, privileges, permissions, and roles
(role-based access control) to manage Data Director users. Role-based access control provides management of
users and the tasks that they can perform on objects. You can grant and revoke roles and permissions at the
system level, on organizations, and on database groups, databases, and templates within organizations.
Roles are sets of permissions required to perform particular jobs. Jobs are sets of tasks that a user with a
particular role is responsible for performing, such as the set of tasks that are the responsibility of a database
administrator. System and organization administrators define roles as part of defining security policies, and
grant the roles to users. To change the permissions and tasks associated with a particular job, the system or
organization administrator updates the role settings. The updated settings take effect for all users associated
with the role.
n
To add a user to a job, the system or organization administrator grants the role to the user.
n
To remove a user from a job, the system or organization administrator revokes the role from the user.
Changes are effective immediately.
VMware, Inc.
27
Page 28
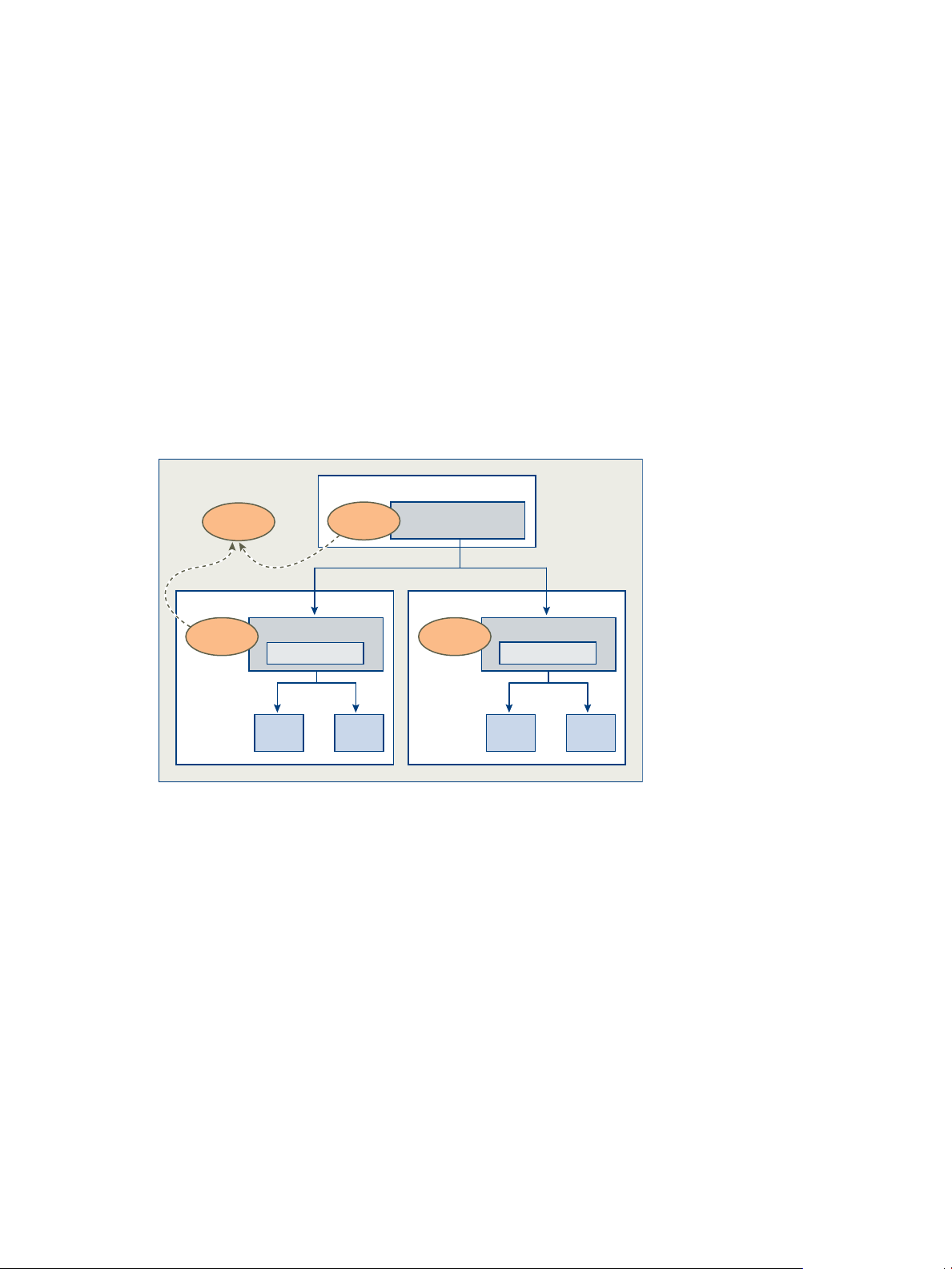
User Namespace
Bob
role domain
System
(user) Alliance
DBG DBGDBGDBG
role domain role domain
(user) Benefits
DBAdmin
SysAdmin
DBAdmin
Organization
Organization
VMware vFabric Data Director Administrator and User Guide
Roles apply only to the organization in which they are created. For example, an organization administrator
creates a database administrator role that includes permission to add and remove database users, start and
stop databases, and perform backups for a specific database in that organization. Users that are granted the
database administrator role in that organization can perform database administrator tasks only within that
organization.
Organization administrators usually manage role and permission assignments for their organizations.
However, any user that has the permission to grant and revoke permissions on an object can grant all
permissions on that object to any user or any role. Organization administrators can also grant permissions
directly to users.
Each user's login account is unique in the system. Managing access, roles, and permissions for each user is
based on their user login account. The organization administrator can grant users access to one or more
organizations. Within those organizations, each user can be granted multiple roles and permissions.
Users who cannot view or access certain objects or cannot perform certain operations were not granted the
permissions to do so.
The following figure illustrates the scope of users and roles in Data Director.
Figure 3-1. Scope of users and roles in Data Director
In the figure, user Bob is logged in to Data Director and has been granted access to the system and to the
organization Alliance. Bob is also granted the SysAdmin role at the system level, and the DBAdmin role in the
organization Alliance. Bob's SysAdmin role applies to the system level. The SysAdmin role does not propagate
to any organizations. The role DBAdmin in organization Alliance and the role DBAdmin in organization
Benefits are separate roles that apply only within their organizations. Bob has the DBAdmin role in the Alliance
organization but does not have access to the Benefits organization.
Authenticating Users
28 VMware, Inc.
User authentication is based on user login and password.
User login accounts and credentials are unique in Data Director. This enables managing credentials, roles,
permissions, and privileges for each user based on the user login account.
Create users and passwords in the following ways.
n
A system or organization administrator creates the user account and assigns a password.
n
A user registers for a Data Director account and specifies a password as part of the registration request.
Page 29

Data Director encrypts the password and stores it with the user information. When the user logs in, that user's
credentials are stored in an HTTP session. Data Director uses the credentials to validate that the user is
authorized to view organization objects (database groups and databases) and to perform tasks.
Role-Based Access Control
Role-based access control enables system and organization administrators to control user access to Data
Director and to control what users can do after they log in. To implement role-based access control, system
and organization administrators associate (or revoke) privileges, permissions, and roles with (or from) user
login accounts.
Chapter 3 Managing Users and Roles
Users
Privileges
Permissions
Roles
User logins (users) are unique accounts that enable users to access Data
Director. They include a password and identifying information such as name,
email address, and phone number. Because user login accounts are unique,
system and organization administrators can control each user's access and
actions by granting or revoking privileges, permissions, and roles to or from
the user's login account.
Users can be active or inactive. Inactive users cannot log in.
Privileges control all actions in Data Director. They define the allowable actions
within an organization. Privileges apply to particular types of Data Director
objects. For example, you can apply the Stop Database privilege to
organizations, database groups, and databases and apply the Create
Database privilege to organizations and database groups. Privileges by
themselves are not associated with specific objects within an organization.
Permissions associate a user and privilege pair with an object in Data Director.
Examples are granting a user permission to start or stop a specific database, to
modify an organization's backup templates, or to create other users in an
organization.
You can grant permissions to users by assigning a role to a user, or by granting
permissions directly to the user.
Roles are collections of permissions that can be associated with or granted to
users. Roles provide a convenient way to package all the permissions required
to perform a job, such as that of database administrator. Roles apply only to
the entity in which they are created. If you create a role at the system level, it
applies only to the system. If you create a role in an organization, it applies only
to the organization. Organizations have no visibility into each others' roles. If
two organizations in the same Data Director data cloud each have a role that
has the same name, those roles are distinct within each organization.
One user can have multiple roles within an organization. Users can have access
to multiple organizations and can have multiple roles in each organization.
A user can have different roles for different objects. For example, if you have
two database groups in your organization, DBG1 and DBG2, you can grant the
Database Admin role to a particular user on DBG1 and grant that user the DB
User role on DBG2. These assignments might allow the user to perform
administrative tasks in DBG1, but not in DBG2.
VMware, Inc. 29
Page 30

VMware vFabric Data Director Administrator and User Guide
Predefined Roles
Data Director provides the predefined roles of system administrator, user administrator, and organization
administrator. Predefined roles provide a starting point for administering Data Director users and roles and
for defining custom roles. You can also create custom roles.
Organization
administrator role
Organization adminstrators manage their organizations. They control which
users can access the organizations, how users request access to the
organizations, and what those users can see and do within the organization.
This role has all privileges on the organization for which it is created.
Organization administrators invite users to join the organization, grant access,
roles, and permissions to users in the organization, create database groups, and
can create databases. You can choose to create an administrator user when you
create a new organization, or you can select an existing user as the new
organization administrator.
Organization administrators perform all user management tasks within their
organizations, including the following.
n
Add users to organizations, database groups, and databases.
n
Modify user settings.
n
Remove users from organizations, database groups, and databases.
n
Create roles.
n
Grant privileges and permissions to roles and to individual users.
n
View users, roles, and permissions granted to users and roles.
Organization administrators can view, grant, and revoke privileges on all
objects within their organizations, including database groups, databases, and
templates. Privileges include Create Database Groups and Modify Database
Configuration Templates.
System administrator
role
Template user role
User administrator role
System administrators operate Data Director. The first system administrator
user is created during Data Director installation. This role has all system-level
privileges, including managing resources for the system and for organizations.
System administrators can see, grant, and revoke permissions at the system
level. The first system administrator configures Data Director, creates other
system administrators and system-level users, and creates initial organizations.
System administrators manage users at the system level. By default they do not
have access to organizations unless an organization administrator grants access
to them.
Template users can use any resource templates and backup templates when
creating databases.
The User administrator role manages users at the system level, including
creating, editing settings for, and deleting system users.
30 VMware, Inc.
Page 31

Privileges
Privileges define the allowable actions on objects in vFabric Data Director. You associate privileges with a user
login and a Data Director object to define permissions.
For example, the Start and Stop Database privilege indicates that in general, Data Director users can start and
stop databases. But the privilege by itself does not indicate which users can start and stop databases, or the
databases that they can start and stop. To provide context, you associate the privilege with a user login and a
Data Director object. The combination of privilege, user login, and Data Director object is a permission. You
can group related permissions into roles to package all the permissions required to perform a job, such as that
of database administrator.
Chapter 3 Managing Users and Roles
System
Organizations
Database Group
Databases
System privileges relate to Data Director management, such as Manage
Resources and Manage System Settings. These privileges apply only to the
system. System privileges do not propagate to organizations.
Privileges on organizations relate to organization management, such as
Manage Organization Settings and Manage Registration. Organization
privileges apply only to organizations. They do not propagate beyond
organization boundaries.
Privileges on database groups relate to database group management, such as
Create Databases and Import Backups. Database group privileges apply only
within the organization and to the organization's database groups.
Organization administrators and users with database group management
privileges grant and revoke privileges on database groups, and enable users to
access a database group by adding the database group to the user's account.
Privileges on databases relate to database management, such as Start and Stop
Database and Edit Database Info. Database privileges apply only to databases,
database groups, and organizations. If a database-related privilege is on a
database group, that privilege applies to all databases within that database
group. If the database-related privilege is on an organization, it applies to every
database group and database in the organization.
Organization administrators and users with database management privileges
grant and revoke these privileges and permissions on databases. To gain access
to databases, the databases must be added to a user's account.
Resource Templates,
Backup Templates, and
Base DB Templates
VMware, Inc. 31
Privileges on templates relate to template management, such as edit template
and view and user template. Edit template applies only to the organization.
View and user template applies to individual templates or to the organization.
If a template privilege is on an organization, it applies to all templates within
that organization.
Organization administrators and users with template management privileges
grant and revoke template privileges and permissions. To gain access to
templates, the templates must be added to a user's account.
Page 32

VMware vFabric Data Director Administrator and User Guide
Propagation of Permissions and Roles
How permissions and roles propagate through an organization depends on where and on what types of objects
they are granted. Understanding how permissions and roles propagate can help you to assign them to users
appropriately.
Permission and role propagation stops at the organization boundary. Permissions granted within an
organization propagate only within that organization. Permissions granted at the system level do not
propagate to organizations.
Permissions (and their associated privileges) that apply to an organization are inherited by that organization's
database groups and databases. Users or roles can have permissions on specific database groups, and those
permissions propagate to databases within the database groups.
Roles apply only to the organization in which they are defined. If a role is defined at the system level, it applies
only to the system and is not visible to organizations. If a role is defined within an organization, it applies only
to that organization and is not visible to the system or to other organizations.
You can grant permissions and roles on objects within an organization, such as on a database group, on a
database, or on a template. For example, granting the Start/Stop Database permission on a database group
means that the user or role has the Start/Stop Database permission on all databases within that database group.
If a user is granted the Start/Stop Database permission on a database group, that user can start and stop any
databases within that database group. However, permissions that apply only to certain types of objects do not
propagate to other objects. For example, granting the database group permission Create Database on a database
is meaningless.
Organization Privileges and Permissions
Organization administrators grant privileges and permissions to users and roles in their organizations. Those
privileges and permissions propagate to database groups, base DB templates, and databases in the
organization.
You can grant the following types of privileges and permissions to users and roles on organizations.
n
User and permission management, such as manage roles and registration and grant/revoke permissions.
n
Organization management, such as manage organization settings, database configuration and backup
templates, and import databases.
n
Database group management, such as manage database groups, create databases, and import backups.
n
Database management, such as edit database information, resource, and backup settings, modify database
users, upgrade databases.
n
Database operations, such as enable/disable databases, delete databases, start and stop databases, and
restart databases.
n
Database backup and recovery, such as create and delete snapshots, create and delete external backups,
clone databases, and recover databases.
n
Templates, such as use templates.
n
View and monitor, such as viewing reports and monitoring resource usage.
32 VMware, Inc.
Page 33

Add Users to Your Organization
Users can self-register to login to Data Director, but cannot access Data Director organizations, database groups,
or databases until organization administrators grant access to them. You must add the users to your
organization to grant them access.
Prerequisites
n
Verify that you have Manage Registration permission for the organization.
n
Verify that the system setting Allow Public Registration is on.
Procedure
1 Log in as an organization administrator.
2 Click the Organization Settings tab, expand Users and Roles, and click Users.
3 Click the plus (+) icon.
4 Complete the user information in the Credentials and Contact Information sections.
5 Grant roles and permissions now or choose to grant roles and permissions later.
6 Click OK.
Chapter 3 Managing Users and Roles
If the Email Validation system setting is on, users receive an activation email that contains a link that they click
to activate their account. The new users' status is Pending and the users cannot log in until they activate the
account.
The new user appears in the Users list.
Add Roles to an Organization
Roles enable you to group the permissions required to perform tasks associated with a job, such as the job of
database administrator. You can then grant the role to users rather than granting individual permissions
needed for each task. You can add custom roles to your organization and grant them to the users who are
responsible for performing particular jobs.
Prerequisites
n
You are logged in to Data Director.
n
You have the OrgAdmin role with permissions on all objects in the organization, or permissions for the
organization in which to create the role.
n
You have grant and revoke permissions on objects.
Procedure
1 Click the Organization Settings tab.
2 Expand Users and Roles and click Roles.
The OrgAdmin role appears in the list.
3 Click the plus (+) icon.
4 Type a name for the role.
5 (Optional) Enter a description
VMware, Inc. 33
Page 34

VMware vFabric Data Director Administrator and User Guide
6 Right-click Status.
n
Select Enable to activate the role.
n
Select Disable to deactivate the role.
7 In the Permissions section, select the permissions to grant to this role.
You can grant permissions to the role on the organization, database groups within the organization,
databases within the organization's database groups, and on organization templates.
8 Click OK.
The new role appears in the Roles list.
What to do next
Grant this role to organization users.
Create other roles and grant permissions to them.
Grant a Permission to a User
If a user requires only limited privileges in your organization, you can grant just those privileges to the user
instead of granting a role to that user.
Prerequisites
You are logged in to a Data Director organization as an organization administrator.
Procedure
1 Click the Organization Settings tab, then click Users.
2 Select a user name.
3 Use one of the following methods to access the Edit Permissions window.
n
Select the user name, click the gear icon, and select Edit Direct User Permissions.
n
Right-click the user name and select Edit Direct User Permissions.
n
Left-click the user name, select Grant direct user permissions now, then click Edit.
4 Grant privileges to the user.
n
To grant a category of privileges to the user, click the All privileges check box.
n
To grant a specific privilege to the user, click the privilege's check box.
5 Click OK.
What to do next
Use the Edit Permissions window to grant the user access to database groups, databases, and templates within
the organization.
Modify Organization Security Settings
Organization security settings determine whether your organization allows open registration or users must
be invited to register, and whether or not the system administrator can access your organization. You can
change the security settings at any time.
Prerequisites
Log in as organization administrator or as a user with the Manage Organization Settings permission.
34 VMware, Inc.
Page 35

Chapter 3 Managing Users and Roles
Procedure
1 Click the Organization Settings tab.
2 Click Settings, then click Security.
3 (By Organization user management mode only) Choose one of the following Allow public registration
settings.
Setting Description
No
Yes
User registration is by invitation only.
Users can see the organization and register themselves.
4 Choose one of the following Allow System Administrator to log into Org settings.
Setting Description
No
Yes
Do not allow the system addministrator to log into the organization.
Allow the system administrator to log into the organization.
5 Click Apply to accept the settings.
VMware, Inc. 35
Page 36

VMware vFabric Data Director Administrator and User Guide
36 VMware, Inc.
Page 37

Building DBVMs and Base DB
Templates 4
Data Director enables administrators to quickly provision databases, such as Oracle and vFabric Postgres,
using database templates. Administrators prepare templates that let users create databases in Data Director.
Data Director uses base database templates (base DB templates) to create databases. A base DB template is a
virtual machine that contains all the required software to create a database. Required software includes the
operating system (OS), database, and system software configurations. The base DB template can also contain
third-party tools that are required for a particular environment.
You create a base database virtual machine (DBVM) and install the operating system and database software
required to create databases.You create a base DB template from a base DBVM. A DBVM is a virtual machine
with a disk layout that contains the seven virtual machine disks (VMDK) required for base DBVMs to work in
Data Director.
Base DBVMs contain the virtual hardware, structure, and the required files and configuration information
necessary to build base DB templates and to create and operate databases. Base DB templates provide the
blueprints for creating databases in Data Director.
Data Director supports vFabric Postgres, and the following OS and Oracle database versions.
n
OS: SUSE Linux Enterprise Server (SLES) 11 SP1; Red Hat Enterprise Linux (RHEL) 5.4 and later (6.0 is
not supported); Oracle Linux 5.4 and later (5.7 and 6.0 are not supported).
n
Database software: Oracle 11gR2, Oracle 10gR2.
Data Director supports the following SQL Server versions on the Windows Server 2008R2 OS.
n
SQL Server 2008R2 Enterprise and Standard editions.
n
SQL Server 2012 Enterprise and Standard editions.
The DBVM workflow shows the roles for building a DBVM, preparing the base DB template, and creating
databases.
VMware, Inc.
37
Page 38

Install Data Director
Create System
Resource Pool (SRP)
Download OVA and
deploy into SRP
Install OS and database
Create resource pools
Create system resource bundle
Convert DBVM to
Base DBVM Template
Optionally run validate
Create resource bundle
Create organization
vSphere
System Administrator
Data Director
System Administrator
Data Director
Org Administrator
Create organization
roles and users
Enable Base DBVM Template
Assign Base DBVM Template
to resource bundle
VMware vFabric Data Director Administrator and User Guide
Figure 4-1. DBVM Workflow
To prepare DBVMs for use, vSphere administrators perform the following tasks.
n
Download the DBVM template OVA files into a directory the vSphere Client can access.
n
Create a system resource pool to contain the DBVM templates. See “Create the System Resource Pool,”
on page 21.
n
Use vCenter to deploy each DBVM template OVA file into the system resource pool. Deploy the OVA files
one at a time. See vSphere Virtual Machine Administration for information about deploying OVA files.
n
If required for your business environment, install the operating system and database software into a blank
DBVM to customize a database template.
To prepare base DB templates for use, Data Director system administrators perform the following tasks.
n
Create one system resource bundle to contain base DBVM templates. See “System Resource Bundle,” on
page 17
n
Convert the DBVMs to base DB templates.
n
Assign the base DB templates to the resource bundle for an organization.
n
Optionally validate the base DB template to ensure it built successfully.
Organization administrators enable base DB templates in their resource bundles. After a base DB template is
enabled, organization users can use the base DB template to create databases.
38 VMware, Inc.
Page 39

This chapter includes the following topics:
n
“Database Virtual Machine OVA Files,” on page 39
n
“Deploy a DBVM OVA File,” on page 39
n
“Build a SLES and Oracle Base Database Virtual Machine,” on page 40
n
“Build a Custom RHEL and Oracle Database Template,” on page 44
n
“Install the Operating System and Database Software in a Blank DBVM,” on page 49
n
“Requirements for the Kickstart File,” on page 49
n
“Database Update Configuration,” on page 52
n
“Configure a vFabric Postgres Update Chain,” on page 53
n
“Update an Oracle Database,” on page 54
Database Virtual Machine OVA Files
Data Director provides downloadable database virtual machine (DBVM) templates as OVA files.
Downloadable OVA Files
Chapter 4 Building DBVMs and Base DB Templates
vFabric Data Director
vPostgres 9.0 (VMwareData-Director-SLES11vPostgres 90-BaseDBVM-<build#>.ova)
vFabric Data Director
vPostgres 9.1 (VMwarevFabric-Data-DirectorSLES11-vPostgres 91Base-DBVM<build#>.ova)
vFabric SUSE Linux
operating system
(VMware-Data-DirectorSLES11-Base-DBVM<build#>.ova)
Custom (blank) VM
Template (VMware-DataDirector-Blank-BaseDBVM-<build#>.ova)
Includes virtual hardware and the SUSE Linux Enterprise Server with
vFabric Postgres 9.0 database software installed with default parameters.
Includes virtual hardware and the SUSE Linux Enterprise Server with
vFabric Postgres 9.1 database software installed with default parameters.
Includes virtual hardware and the SUSE Linux Enterprise Server with no
database software installed.
Contains only virtual hardware, no operating system or database components.
Also called the custom or empty DBVM. The blank DBVM template has the
disk layout required for Data Director database virtual machines. Use the blank
DBVM template to build custom database environments. For example, use the
blank DBVM template to build a custom DBVM with the Red Hat Enterprise
Linux operating system and Oracle 11g database software.
Deploy a DBVM OVA File
As a vSphere administrator, you deploy the provided DBVM template OVA files to the system resource pool
for Data Director.
Prerequisites
n
Verify that you have vSphere administrator privileges.
n
Verify that you can log in to the console as root.
VMware, Inc. 39
Page 40

VMware vFabric Data Director Administrator and User Guide
n
Verify that Data Director is installed.
n
Verify that the Data Director DBVM template OVA files are downloaded to a directory that you can access
from vSphere.
n
Verify that the system resource pool is created in vSphere.
n
Verify the network mapping or determine how to map the networks configured for Data Director to the
DBVM template's networks. See the vFabric Data Director Installation Guide and the vFabric Data Director
Worksheets.
Procedure
1 In the vSphere Client Inventory view, click the system resource pool.
2 Click File, and select Deploy OVF Template.
3 In the Source page, choose the DBVM template OVA file and click Next.
4 click Next.
5 Type a unique name for the template, select the cluster, and click Next.
6 choose a datastore that has at least 100GB of available space and click Next.
7 Map the DBVM template networks listed to the networks configured for Data Director.
8 (Optional) In the Disk Format page, select Thin Provision and click Next.
9 Click Next, review the settings, and click Finish.
The DBVM is deployed in the system resource pool.
What to do next
Deploy another DBVM template OVA file, or install operating system and database software to the DBVM.
Build a SLES and Oracle Base Database Virtual Machine
Data Director provides a base DBVM with SLES. You can install Oracle into the SLES DBVM to provide an
environment for proof-of-concept projects or to allow non-Oracle DBAs to explore Oracle.
Prerequisites
n
Verify that you can log in to vSphere as an administrator.
n
Verify that Data Director is installed.
n
Verify that the SLES DBVM is deployed to the system resource pool in vSphere.
n
Verify that the Data Director system resource bundle is set up.
Procedure
1 Install Oracle in the SLES Base DBVM on page 41
As a vSphere administrator, you can provide an SLES and Oracle database environment by installing
the Oracle database software in a DBVM with the SLES operating system already installed.
2 Create a Base DBVM on page 41
You can create a base DBVM and install the operating system and database software required to create
databases. The blank base DBVM contains the structure for installing an operating system and database
software combination not provided by preconfigured base DBVMs.
40 VMware, Inc.
Page 41

Chapter 4 Building DBVMs and Base DB Templates
3 Convert a Base DBVM into a Base DB Template on page 42
Data Director system administrators convert base DBVMs into base DB templates to provide the
blueprints for creating databases.
4 Validate a Base DB Template on page 43
As a Data Director system administrator, you can validate a base DB template to confirm that it built
correctly. You can validate a base DB template at any time.
5 Assign a Base DB Template to a Resource Bundle on page 43
As a Data Director system administrator, you assign base DB templates to resource bundles as part of
providing organizations with access to the base DB templates.
Install Oracle in the SLES Base DBVM
As a vSphere administrator, you can provide an SLES and Oracle database environment by installing the Oracle
database software in a DBVM with the SLES operating system already installed.
Prerequisites
n
Open a console in vSphere and log in as root.
n
Deploy vFabric Data Director SLES 11 DBVM Template (VMware-Data-Director-SLES11-Base-DBVM<build#>.ova) to the system resource pool.
n
Verify that the deployed DBVM can access the Oracle installation bits.
Procedure
1 Log in to the vSphere Client as a administrator.
2 In the Data Director system resource pool, right-click the SLES Base DBVM and click Open Console.
3 Log in to the console as root.
4 Type the following command to run the Oracle installation script.
/opt/aurora/installation/install.sh
n
NFS PATH FOR Oracle is the full pathname of the NFS server where the Oracle installation files reside.
n
Oracle version is the full version number of the Oracle installation.
[NFS PATH FOR ORACLE][Oracle version]
When the message Oracle installation finished appears on the console, the installation is complete and
your SLES Oracle base DBVM is built on the vSphere Client.
What to do next
Go to “Convert a Base DBVM into a Base DB Template,” on page 42
Create a Base DBVM
You can create a base DBVM and install the operating system and database software required to create
databases. The blank base DBVM contains the structure for installing an operating system and database
software combination not provided by preconfigured base DBVMs.
Prerequisites
Create the system resource bundle.
Ensure there is adequate free space on the datastore.
Procedure
1 Log in to Data Director as a system administrator.
VMware, Inc. 41
Page 42

VMware vFabric Data Director Administrator and User Guide
2 In the System tab, click Manage and Monitor.
3 Expand Templates and select Base DBVMs.
4 Click the plus (+) icon to start the Create Base DBVM wizard and enter the appropriate information.
Option Description
Name
Database type
Database version
Installer ISO
Operating system
OS installer ISO
Data Director installs the OS, copies the Oracle or SQL Server files, installs the virtual machine tools and agents,
and invokes Windows sysprep. The base DBVM appears in the Base DBVMs list with the status Creating. The
process can take a few minutes. The status changes to Running when creation finishes.
Enter a unique name for the base DBVM.
Select a database type, or select Empty to create a blank base DBVM.
Select a version.
Type the path to the ISO file on the datastore in the cluster. The path must
be of the form[datastore]folder/DB .iso. Ensure that the database version
matches the database type you selected.
Select an operating system from the drop-down menu of supported
operating systems.
Type the path to the IOS file on the datastore in the cluster. The path must
be of the form[datastore]folder/OS.iso.
What to do next
Go to “Convert a Base DBVM into a Base DB Template,” on page 42.
Convert a Base DBVM into a Base DB Template
Data Director system administrators convert base DBVMs into base DB templates to provide the blueprints
for creating databases.
Prerequisites
You have installed the operating system and database software into the base DBVM.
Procedure
1 Log in to Data Director as a system administrator.
2 Click the Manage and Monitor tab and expand Templates.
3 Select Base DBVMs.
4 Select the base DBVM to convert.
5 Click the gear icon and select Convert to Base DB Template.
6 In the Convert to Base DB Template wizard, provide the appropriate information.
Option Action
Name
Description
Save the source DBVM (clone before
converting)
7 Click OK.
Enter a unique name for the base DB template.
(Optional) Enter a description of the base DB template.
Click the checkbox to retain the source base DBVM for future use.
When conversion is finished, the base DB template appears in the Base DB Templates list.
42 VMware, Inc.
Page 43

Chapter 4 Building DBVMs and Base DB Templates
What to do next
For Oracle and vFabric Postgres BDVMs, go to “Validate a Base DB Template,” on page 43. Template
validation is optional. Validation is not supported for SQL Server.
Validate a Base DB Template
As a Data Director system administrator, you can validate a base DB template to confirm that it built correctly.
You can validate a base DB template at any time.
Prerequisites
Complete the step “Convert a Base DBVM into a Base DB Template,” on page 42.
Procedure
1 Log in to Data Director with system administrator privileges.
2 Click Manage and Monitor, expand Templates and click Base DB Templates.
3 Right-click a base DB template and select Validate.
4 Select the organization and database group in which to validate the base DB template and click OK.
What to do next
If validation does not succeed, troubleshoot the base DB template in vSphere. Contact your VMware
representative for assistance. After you have validated a base DB template, see “Assign a Base DB Template
to a Resource Bundle,” on page 43.
Assign a Base DB Template to a Resource Bundle
As a Data Director system administrator, you assign base DB templates to resource bundles as part of providing
organizations with access to the base DB templates.
As a best practice, run validation before assigning a template to an organization. See “Validate a Base DB
Template,” on page 43.
Prerequisites
n
Complete the task “Convert a Base DBVM into a Base DB Template,” on page 42.
Procedure
1 Log in to Data Director as a user with system administrator privileges.
2 In Manage and Monitor, select Resource Bundles.
3 Right-click a resource bundle, and select Assign Base DB Templates.
4 Select one or more templates.
5 Click OK.
The base DB template is available to the resource bundle.
What to do next
Assign the resource bundle to an organization. See “Assign a Resource Bundle to an Organization,” on
page 25.
VMware, Inc. 43
Page 44

VMware vFabric Data Director Administrator and User Guide
Build a Custom RHEL and Oracle Database Template
Data Director system administrators can build custom DBVMs to enable organization users to create databases
with a specific operating system and database combination.
To build a template that includes RHEL 5.5 and Oracle 11gR2, you must meet Oracle and Data Director
prerequisites.
Prerequisites
n
Verify that Data Director is installed and the system resource bundle is set up.
n
Verify that you have access to a RHEL 5.5 installation ISO image
n
You have prepared a custom KS.cfg file for the Linux and Oracle. See “Requirements for the Kickstart
File,” on page 49.
n
Verify that you have access to Oracle installation bits. The installation bits must be available on an NFS
share.
Procedure
1 Deploy the base database VM into the System Resource Pool on page 44
You can use a blank base database VM to build a custom database template.
2 Repackage the Linux ISO Image on page 45
Because the original Red Hat ISO image is not Data Director compliant and does not distribute Data
Director related scripts, repackage your custom kickstart file with Red Hat ISO image
3 Install Linux on a Blank Virtual Machine on page 45
You can install Linux as the operating system on the blank virtual machine.
4 Initialize the Virtual Machine to Make It Oracle and Data Director Compliant on page 46
You can initialize the base database virtual machine to ensure that the Oracle and Data Director
requirements are met.
5 Install Oracle 11g R2 Software on page 47
You can use a provided script that will install Oracle Home in the correct disk.
6 Convert a Base DBVM into a Base DB Template on page 47
Data Director system administrators convert base DBVMs into base DB templates to provide the
blueprints for creating databases.
7 Validate a Base DB Template on page 48
As a Data Director system administrator, you can validate a base DB template to confirm that it built
correctly. You can validate a base DB template at any time.
8 Assign a Base DB Template to a Resource Bundle on page 48
As a Data Director system administrator, you assign base DB templates to resource bundles as part of
providing organizations with access to the base DB templates.
Deploy the base database VM into the System Resource Pool
You can use a blank base database VM to build a custom database template.
Prerequisites
Verify that the system resource pool has sufficient resources.
44 VMware, Inc.
Page 45

Chapter 4 Building DBVMs and Base DB Templates
Procedure
1 Log in to vSphere Client as a system administrator and connect to the vCenter server.
2 2. Deploy the VMware-Data-Director-Blank-Base-DBVM-<build#>.ova file into the system resource pool.
When deployment completes, the virtual machine appears in the system resource pool. This virtual
machine is known as the base VM.
3 Power on the base VM.
Repackage the Linux ISO Image
Because the original Red Hat ISO image is not Data Director compliant and does not distribute Data Director
related scripts, repackage your custom kickstart file with Red Hat ISO image
Prerequisites
The repackage scripts run on a Linux OS with the sed and mkisofs commands.
Procedure
1 Obtain a working Linux environment with sufficient storage to repackage the Linux ISO image.
If you mount the RHEL ISO from an NFS server, 8GB is sufficient. You need 12GB if you upload the ISO
to your local disk.
2 Ensure that you have a discoverable path to the working Linux environment for the original RHEL ISO
image, local directory, or NFS path.
3 Download the ISO image from the VMware product download page.
4 Mount the ISO image by typing the following command, substituting your build number for <build#> .
mount –o loop /mnt/Data-Director-Initialize-Base-DBVM-
build#
.iso /tmp/mnt
5 To repackage the RHEL ISO image, mount the NFS manually, then type the following command.
/tmp/mnt/Tools/repack_rhel_iso.sh
REDHAT_ISO_PATH Output_folder
For example, the command
/tmp/mnt/Tools/repack_rhel_iso.sh rhel5.5.iso ./
specifies the original Linux ISO image as the source ISO image. The command repackages the ISO image,
which can pick up the kickstart file automatically from the floppy device.
REDHAT_ISO_LOCAL_FILE_PATH must be a local path. If the Red Hat ISO is on an NFS volume, mount
it to the local directory before using this command.
A RHEL ISO image is created, with its own kickstart file.
Install Linux on a Blank Virtual Machine
You can install Linux as the operating system on the blank virtual machine.
Prerequisites
Deploy the base database virtual machine into the system resource pool. See “Deploy the base database VM
into the System Resource Pool,” on page 44.
Repackage the Linux ISO image. See “Repackage the Linux ISO Image,” on page 45.
A floppy image containing the ks.cfg file (unless you have packaged your own customized ks.cfg file into
the ISO.
A CDROM device containing the OS ISO.
VMware, Inc. 45
Page 46

VMware vFabric Data Director Administrator and User Guide
A CDROM device containing the database binary ISO.
A CDROM device containing the initialized ISO.
Procedure
1 In the vSphere Client, select the blank virtual machine that you deployed.
2 Click Edit Settings.
3 Click the Hardware tab, and select CD/DVD drive in the hardware list.
4 In the right panel, click Datastore ISO file and click Browse.
5 Enter the path of the repackaged Linux ISO image.
You can alternatively use the client device to connect the local ISO when the virtual machine is running.
6 In the Device Status pane, click Connected and click Connected at Power On.
7 Click Save.
8 Power on the virtual machine if it is not running, and open a console to observe.
The virtual machine will start to bootstrap, and install Linux as specified in the custom kickstart file.
Linux is installed. The kickstart file brings up the installaiion for the database binary and orhter required
pacakges from the CDROM.
What to do next
Initialize the same base virtual machine by installing the required software components and scripts, to ensure
that it is Oracle and Data Director compliant.
Initialize the Virtual Machine to Make It Oracle and Data Director Compliant
You can initialize the base database virtual machine to ensure that the Oracle and Data Director requirements
are met.
Prerequisites
You have installed Linux on the virtual machine.
Procedure
1 In vSphere Client, right-click the base database virtual machine and open the console.
2 Log in as root and type password when prompted for the password.
The password value is defined in the kickstart file, and appears at the top of virtual machine console. T
3 Click the CD/DVD drive icon, and select the datastore ISO file from the storage disk.
4 Type the following command to mount the CDROM to the local directory.
mount /dev/cdrom/mnt/cdrom
5 As root, type the following command from the local directory.
./install.sh –i
This command installs scripts for Oracle install, VMware Tools, and Python 2.6 runtime.
When the installation completes, the base database virtual machine is Oracle and Data Director compliant.
What to do next
Install Oracle 11g R2 in the base database virtual machine.
46 VMware, Inc.
Page 47

Chapter 4 Building DBVMs and Base DB Templates
Install Oracle 11g R2 Software
You can use a provided script that will install Oracle Home in the correct disk.
Prerequisites
Verify that you have initialized the virtual machine to make it Oracle and Data Director compliant.
Procedure
1 Log in to the OS as root.
2 Type the following command to install Oracle.
/opt/aurora/installation/install.sh
NFS_PATH_FOR_Oracle_binary_folder Oracle_version
NFS_PATH_FOR_Oracle_binary_folder is the full path of the NFS server where you store your Oracle
installation software components.
Oracle_version is the full version number of the Oracle software.
3 Power off the virtual machine when the Oracle installation finishes.
4 Remove the CD/DVD devices.
The Oracle EE binary is installed.
What to do next
Convert the base database virtual machine into a database template. See “Convert a Base DBVM into a Base
DB Template,” on page 42You can, optionally, install third party tools to ensure that all necessary tools are
installed on the binary disk.
Convert a Base DBVM into a Base DB Template
Data Director system administrators convert base DBVMs into base DB templates to provide the blueprints
for creating databases.
Prerequisites
You have installed the operating system and database software into the base DBVM.
Procedure
1 Log in to Data Director as a system administrator.
2 Click the Manage and Monitor tab and expand Templates.
3 Select Base DBVMs.
4 Select the base DBVM to convert.
5 Click the gear icon and select Convert to Base DB Template.
6 In the Convert to Base DB Template wizard, provide the appropriate information.
Option Action
Name
Description
Save the source DBVM (clone before
converting)
Enter a unique name for the base DB template.
(Optional) Enter a description of the base DB template.
Click the checkbox to retain the source base DBVM for future use.
7 Click OK.
VMware, Inc. 47
Page 48

VMware vFabric Data Director Administrator and User Guide
When conversion is finished, the base DB template appears in the Base DB Templates list.
What to do next
For Oracle and vFabric Postgres BDVMs, go to “Validate a Base DB Template,” on page 43. Template validation
is optional. Validation is not supported for SQL Server.
Validate a Base DB Template
As a Data Director system administrator, you can validate a base DB template to confirm that it built correctly.
You can validate a base DB template at any time.
Prerequisites
Complete the step “Convert a Base DBVM into a Base DB Template,” on page 42.
Procedure
1 Log in to Data Director with system administrator privileges.
2 Click Manage and Monitor, expand Templates and click Base DB Templates.
3 Right-click a base DB template and select Validate.
4 Select the organization and database group in which to validate the base DB template and click OK.
What to do next
If validation does not succeed, troubleshoot the base DB template in vSphere. Contact your VMware
representative for assistance. After you have validated a base DB template, see “Assign a Base DB Template
to a Resource Bundle,” on page 43.
Assign a Base DB Template to a Resource Bundle
As a Data Director system administrator, you assign base DB templates to resource bundles as part of providing
organizations with access to the base DB templates.
As a best practice, run validation before assigning a template to an organization. See “Validate a Base DB
Template,” on page 43.
Prerequisites
n
Complete the task “Convert a Base DBVM into a Base DB Template,” on page 42.
Procedure
1 Log in to Data Director as a user with system administrator privileges.
2 In Manage and Monitor, select Resource Bundles.
3 Right-click a resource bundle, and select Assign Base DB Templates.
4 Select one or more templates.
5 Click OK.
The base DB template is available to the resource bundle.
What to do next
Assign the resource bundle to an organization. See “Assign a Resource Bundle to an Organization,” on
page 25.
48 VMware, Inc.
Page 49

Chapter 4 Building DBVMs and Base DB Templates
Install the Operating System and Database Software in a Blank DBVM
vSphere users with access to the Data Director DBVMs, install the operating system and database software in
the blank DBVM as part of building a custom base DBVM template.
Prerequisites
n
Verify that you can log in to vSphere as an administrator.
n
Verify that Data Director is installed.
n
Verify that the blank DBVM is deployed to the system resource pool in vSphere.
n
Verify that the Data Director system resource bundle is set up.
Procedure
1 Log in to the vSphere Client.
2 Run the installation script as instructed by your VMware representative.
The installation script creates a directory with a name such as /opt/aurora/agent2/plugin. The directory
contains files such as the following examples.
n
config.py contains one line that indicates the active plugin.
n
vdd-vpg vPostgres plug-in.
n
vdd-SUSE-oracle-11 SUSE Linux Enterprise Server (SLES) SUSE Oracle 11 plug-in.
n
XML files contains database configuration parameters.
3 (Optional) Customize the XML database parameter file and database plug-in.
4 Edit the config.py file to indicate the active plug-in.
5 (Optional) Modify the active plug-in as required for your installation or write your own plug-in to suit
your requirements.
What to do next
Convert the base DBVM to a base DB template. See “Convert a Base DBVM into a Base DB Template,” on
page 42.
Requirements for the Kickstart File
The kickstart installation method is used primarily by the RHEL to perform unattended operation system
installation and configuration automatically. To customize a base DB template for Data Director, the kickstart
file must be fully compliant with Data Director and the target database.
Kickstart Options
Go to the Red Hat Web site for Red Hat documentation on kickstart options.
Kickstart Options Required for Data Director
The following content is required in your kickstart file to be compliant with Data Director.
1. # Disk partitioning information
2. part / --bytes-per-inode=4096 --fstype="ext3" --grow --ondisk=sda --size=1
3. part /opt/aurora/oracle --bytes-per-inode=4096 --fstype="ext3" --grow \
--ondisk=sdb --size=1
4. part /opt/aurora/archive --bytes-per-inode=4096 --fstype="ext3" --grow \
VMware, Inc. 49
Page 50

VMware vFabric Data Director Administrator and User Guide
--ondisk=sdc --size=1
5. part /var --bytes-per-inode=4096 --fstype="ext3" --grow --ondisk=sdd --size=1
6. part /opt/aurora/dbg --bytes-per-inode=4096 --fstype="ext3" --grow \
--ondisk=sde --size=1
7. %packages
8. @core
9. @base
10. @development-tools
12. @legacy-software-development
13. @editors
14. unixODBC
15. libaio-devel
16. libXtst-devel
17. libXp-devel
18. libXau-devel
19. sysstat
20. iptables*
21. httpd
22. httpd
23. openldap-clients
24. %post
25. /bin/cat > /root/firstboot.sh <<EOF
26. mkdir /mnt/cdrom2 /mnt/cdrom3
27. mount -o loop /dev/cdrom-hdb /mnt/cdrom2
28. mount -o loop /dev/cdrom-hdc /mnt/cdrom3
29. /mnt/cdrom2/Redhat/install.sh -i -o /mnt/cdrom3 -v 11.2.0.1.0
30. umount /mnt/cdrom2
31. umount /mnt/cdrom3
32. sed -i '/^#FIRSTBOOT_START#/,/^#FIRSTBOOT_END#/d' /etc/rc.local
33. EOF
34. chmod a=x /root/firstboot.sh
35. /bin/cat >> /etc/rc.local >> EOF
36. #FIRSTBOOT_START#
37. echo "Initializing base vm and install Oracle, you can find log in \
38. /root/VMware-Data-Director-Install.log."
39. /root/firstboot.sh
40. #FIRSTBOOT_END#
41. EOF
NOTE Lines 14 through 18 are fields required by Oracle and the original equipment manufacturer (OEM).
Sample Kickstart file
This is a sample kickstart file.
#platform=x86, AMD64, or Intel EM64T
key --skip
# System authorization information
auth --useshadow --enablemd5
# System bootloader configuration
bootloader --location=mbr
# Clear the Master Boot Record
zerombr
# Partition clearing information
clearpart --all --initlabel
# Use text mode install
50 VMware, Inc.
Page 51

Chapter 4 Building DBVMs and Base DB Templates
text
# Firewall configuration
firewall --disabled
# Run the Setup Agent on first boot
firstboot --disable
# System keyboard
keyboard us
# System language
lang en_US
# Installation logging level
logging --level=info
# Use CDROM installation media
# Network information
cdrom
network --bootproto dhcp --device eth0
network --bootproto dhcp --device eth1
# Reboot after installation
reboot
#Root password
rootpw --iscrypted $1$X0Hs3tQw$Zw7.vM.MQfnmRlU4qs9zP/
# SELinux configuration
selinux --enforcing
# System timezone
timezone Etc/GMT
# Install OS instead of upgrade
install
# X Window System configuration information
xconfig --defaultdesktop=GNOME --depth=8 --resolution=800x600
# Disk partitioning information
part / --bytes-per-inode=4096 --fstype "ext3" --grow --ondisk=sda --size=1
part /opt/aurora/oracle --bytes-per-inode=4096 --fstype "ext3" --grow \
--ondisk=sdb --size=1
part /opt/aurora/archive --bytes-per-inode=4096 --fstype "ext3" --grow \
--ondisk=sdc --size=1
part /var --bytes-per-inode=4096 --fstype "ext3" --grow --ondisk=sdd \
-size=1
part /opt/aurora/dbg --bytes-per-inode=4096 --fstype "ext3" --grow \
--ondisk=sde --size=1
%post
/bin/cat >> /etc/issue <<EOF
root login password -- password
EOF
/bin/cat > /root/firstboot.sh <<EOF
mkdir /mnt/cdrom2 /mnt/cdrom3
mount -o loop /dev/cdrom-hdb /mnt/cdrom2
mount -o loop /dev/cdrom-hdc /mnt/cdrom3
/mnt/cdrom2/Redhat/install.sh -i -o /mnt/cdrom3 -v 10.2.0.1.0
umount /mnt/cdrom2
umount /mnt/cdrom3
sed -i '/^#FIRSTBOOT_START#/,/^#FIRSTBOOT_END#/d' /etc/rc.local
EOF
chmod a+x /root/firstboot.sh
/bin/cat >> /etc/rc.local <<EOF
#FIRSTBOOT_START#
echo "Initializing base vm and install Oracle, you can find log in /root/ \
VMware, Inc. 51
Page 52

VMware vFabric Data Director Administrator and User Guide
VMware-Data-Director-Install.log."
/root/firstboot.sh
#FIRSTBOOT_END#
EOF
%packages
@core
@base
@development-tools
@legacy-software-development
@development-libs
@editors
sysstat
iptables*
openldap-clients
unixODBC
libaio-devel
httpd
mod_ssl
libXtst-devel
libXp-devel
libXau-devel
Database Update Configuration
You update databases to take advantage of features in new releases or upgrades of database software. Also,
to incorporate enhancements to a database virtual machine (DBVM) or to third party software tools. System
administrators manage the base DB template update chain to ensure that users update databases based on
templates that comply with defined update policies.
Updates apply enhancements to a DBVM that are not necessarily database software upgrades. You can create
a base DB template from an existing version of a database and add third party software tools to the new base
DB template. You can then apply the new base DB template to multiple databases by performing a batch update.
Update Chain Management
The update chain is a property of base DB templates, and determines which base DB templates can be updated
from or updated to the current base DB template. You can assign templates with the same database engine
(Oracle or vFabric Postgres) to the current template chain. You set the update mode when configuring the
template chain.
Update Mode
In-place update
Determines how databases are updated. You select an update mode according
to the capability and update scenario of the destination base DB template. There
are two update modes.
Modifies the original database files. No additional storage is required and no
new files are created during the in-place update process. You use the in-place
update mode when updating within the same vFabric Postgres version, that is,
when updating from 9.0 to 9.0, or from 9.1 to 9.1.
Dump-restore update
Requires additional storage to finish the update. The process moves the original
database to a separate location, and then restores the files to the updated
database instance
52 VMware, Inc.
Page 53

Chapter 4 Building DBVMs and Base DB Templates
User Defined Upgrade Scripts for Oracle databases
In the update process, Data Director attempts to run two user defined scripts, the source base DB template
preupgrade script, and the target base DB template postupgrade script. To achieve customization in the update
process, you must upload a script to the base DBVM before converting it to a base DB template.
Table 4-1. Upgrade Scripts
Upgrade Script Scope Description
Preupgrade script Source base DB template Preupgrade scripts run in the original
database before updating. Scripts are
located at ${AgentHome}/plugin/$
{ActivatedPluginFolder}/upgrade
_script/preupgrade_script.
For Oracle 11 template, the full path
is
/opt/aurora/agent2/plugin/vfdd_
linux_oracle_11/upgrade_scrip
t/pretupgrade_script.
Postupgrade script Target base DB template Postupgrade script run in the staging
database after the system applies
updates, such as new third party tools
or database software upgrades. The
database instance is started after the
post-upgrade script finishes. Scripts are
located at ${AgentHome}/plugin/$
{ActivatedPluginFolder}/upgrade
_script/postupgrade_script.
For Oracle 11 template, the full path
is
/opt/aurora/agent2/plugin/vfdd_
linux_oracle_11/upgrade_scrip
t/postupgrade_script.
Permission To Scripts
The directory upgrade_script must be accessible and writable to system database administrator users. The
script files preupgrade_script and postupgrade_script must be readable and executable to system database
administrator users.
Configure a vFabric Postgres Update Chain
You configure an update chain to enable database users to update databases based on templates the comply
with update policies.
Prerequisites
• Verify that Data Director has one vFabric Postgres 9.1 db template.
• Verify that Data Director has one vFabric Postgres 9.0 db template.
NOTE You must upgrade vFabric Postgres 9.0 on Data Director 1.0 to vFabric Postgres 9.0 on Data Director
2.x before you upgrade to vFabric Postgres 9.1 on Data Director 2.x.
Procedure
1 Log in to Data Director as a system administrator.
2 Click the Manage and Monitor tab.
VMware, Inc. 53
Page 54

VMware vFabric Data Director Administrator and User Guide
3 Click the Base DB Templates in the left pane.
4 Right-click vPostgres 9.1, and select Properties.
5 Click the Update From tab.
6 Check the box for a vFabric Postgres 9.0 template, and select dump-restore.
7 Click OK.
Update an Oracle Database
You update an Oracle database to take advantage of features available in the latest release of the database
software, or to incorporate enhancements to a database virtual machine (DBVM) or to third party software
tools. Updating an Oracle database is referred to as patching.
Prerequisites
Verify that you have Oracle databases that require upgrading in Data Director.
Procedure
1 Identify Existing Target DBVM on page 55
To create a template with the required patches, determine whether a base database virtual machine of
the Oracle database that you intend to patch is available.
2 Create a Base Database VM from an Existing Template on page 55
You create a base database VM to correspond with a base database template so you can make patches to
an Oracle database.
3 Apply a Patch to the Base Database Virtual Machine on page 55
You apply a patch to an Oracle database to update it to the latest release of the database software.
4 Convert a Base DBVM into a Base DB Template on page 56
Data Director system administrators convert base DBVMs into base DB templates to provide the
blueprints for creating databases.
5 Validate a Base DB Template on page 57
As a Data Director system administrator, you can validate a base DB template to confirm that it built
correctly. You can validate a base DB template at any time.
6 Assign a Base DB Template to a Resource Bundle on page 57
As a Data Director system administrator, you assign base DB templates to resource bundles as part of
providing organizations with access to the base DB templates.
7 Enable a Base DB Template on page 58
Organization administrators enable a base DB template on the underlying resource bundles so that
organization users can provision databases based on the base DB template. Only organization
administrators and users with Manage base DB templates privileges can enable, disable, and edit base
DB templates.
8 Configure an Oracle Update Chain on page 58
You configure an update chain to enable database users to update databases based on templates that
comply with update policies.
9 Update a Database on page 59
You can update a database to apply enhancements or software upgrades.
54 VMware, Inc.
Page 55

Chapter 4 Building DBVMs and Base DB Templates
Identify Existing Target DBVM
To create a template with the required patches, determine whether a base database virtual machine of the
Oracle database that you intend to patch is available.
Prerequisites
Verify that you have Oracle databases that required upgrading in Data Director.
Procedure
1 Log in to Data Director as an organization administrator.
2 Click the Manage and Monitor tab.
3 Double-click a database group in the left pane.
4 Right-click the database that you intend to patch and select Properties.
5 Write down the name of the template in the Base DB template text box for your reference when you create
a base database virtual machine.
What to do next
You can create a base database virtual machine. See “Create a Base Database VM from an Existing
Template,” on page 55
Create a Base Database VM from an Existing Template
You create a base database VM to correspond with a base database template so you can make patches to an
Oracle database.
Prerequisites
You have identified the base database VM of the Oracle database you intend to patch.
Procedure
1 Log in to Data Director as a system administrator.
2 Click the Manage and Monitor tab.
3 Click Base DB Templates in the left pane.
4 Right-click the Oracle template you identified previously and select Export to Base DBVM.
5 When the task completes, click Base DB Templates in the left pane.
The template will appear in the list. Depending on whether you selected the option Save the source DBVM
(clone before converting) when you converted the base database VM to a template, the base VM might
already be available.
What to do next
Apply a patch to the base database VM.
Apply a Patch to the Base Database Virtual Machine
You apply a patch to an Oracle database to update it to the latest release of the database software.
This procedure uses PSU 12419378 as an example.
VMware, Inc. 55
Page 56

VMware vFabric Data Director Administrator and User Guide
Prerequisites
Verify that a base database virtual machine of the Oracle database is available.
Configure the update chain.
Procedure
1 Connect to the Base DBVM console.
You can connect from the vSphere client or other SSH terminals.
2 Download the PSU 12419378 package from the Oracle Web site.
3 Upload p5880880_112000_Linux-x86-64.zip to the /tmp directory in the database virtual machine.
4 Upgrade the patch according to README.txt.
5 Apply PSU 12419378 according to README.html.
Refer to the patch post-installation instructions in the Patch Set Update README material.
6 Create a post upgrade script in this DBVM.
The file is located in /opt/aurora/agent2/plugin/vdd_linux_oracle_11/upgrade_script. Rename the file
postupgrade_script.
7 Set file privileges to 777 to make this file readable and executable.
8 Copy the script to the postupgrade_script file.
The following is a sample script to be executed.
#!/bin/bash
sqlplus / as sysdba << EOF
startup
@$ORACLE_HOME/rdbms/admin/catbundle.sql cpu apply
quit
EOF
You updated the base database virtual machine with PSU 12419378
What to do next
You can convert the base database virtual machine to a target database template. See “Convert a Base DBVM
into a Base DB Template,” on page 42.
Convert a Base DBVM into a Base DB Template
Data Director system administrators convert base DBVMs into base DB templates to provide the blueprints
for creating databases.
Prerequisites
You have installed the operating system and database software into the base DBVM.
Procedure
1 Log in to Data Director as a system administrator.
2 Click the Manage and Monitor tab and expand Templates.
3 Select Base DBVMs.
4 Select the base DBVM to convert.
5 Click the gear icon and select Convert to Base DB Template.
56 VMware, Inc.
Page 57

Chapter 4 Building DBVMs and Base DB Templates
6 In the Convert to Base DB Template wizard, provide the appropriate information.
Option Action
Name
Description
Save the source DBVM (clone before
converting)
Enter a unique name for the base DB template.
(Optional) Enter a description of the base DB template.
Click the checkbox to retain the source base DBVM for future use.
7 Click OK.
When conversion is finished, the base DB template appears in the Base DB Templates list.
What to do next
For Oracle and vFabric Postgres BDVMs, go to “Validate a Base DB Template,” on page 43. Template validation
is optional. Validation is not supported for SQL Server.
Validate a Base DB Template
As a Data Director system administrator, you can validate a base DB template to confirm that it built correctly.
You can validate a base DB template at any time.
Prerequisites
Complete the step “Convert a Base DBVM into a Base DB Template,” on page 42.
Procedure
1 Log in to Data Director with system administrator privileges.
2 Click Manage and Monitor, expand Templates and click Base DB Templates.
3 Right-click a base DB template and select Validate.
4 Select the organization and database group in which to validate the base DB template and click OK.
What to do next
If validation does not succeed, troubleshoot the base DB template in vSphere. Contact your VMware
representative for assistance. After you have validated a base DB template, see “Assign a Base DB Template
to a Resource Bundle,” on page 43.
Assign a Base DB Template to a Resource Bundle
As a Data Director system administrator, you assign base DB templates to resource bundles as part of providing
organizations with access to the base DB templates.
As a best practice, run validation before assigning a template to an organization. See “Validate a Base DB
Template,” on page 43.
Prerequisites
n
Complete the task “Convert a Base DBVM into a Base DB Template,” on page 42.
Procedure
1 Log in to Data Director as a user with system administrator privileges.
2 In Manage and Monitor, select Resource Bundles.
3 Right-click a resource bundle, and select Assign Base DB Templates.
4 Select one or more templates.
VMware, Inc. 57
Page 58

VMware vFabric Data Director Administrator and User Guide
5 Click OK.
The base DB template is available to the resource bundle.
What to do next
Assign the resource bundle to an organization. See “Assign a Resource Bundle to an Organization,” on
page 25.
Enable a Base DB Template
Organization administrators enable a base DB template on the underlying resource bundles so that
organization users can provision databases based on the base DB template. Only organization administrators
and users with Manage base DB templates privileges can enable, disable, and edit base DB templates.
Prerequisites
System administrators have assigned at least one base DB template to the resource bundles of the underlying
organization.
Log in to Data Director as an organization administrator or as an administrator with privileges to enable base
DB templates.
Procedure
1 Click the Organization Settings tab.
2 In the left pane, click Base DB Templates.
3 In the center pane, right-click a base DB template and select Enable on Resource Bundles.
4 Click Enable.
Wait for the base DB template to be enabled.
5 Click Close.
Configure an Oracle Update Chain
You configure an update chain to enable database users to update databases based on templates that comply
with update policies.
Prerequisites
Verify that you have successfully converted a Base DBVM containing a patch to a new Base DB Template.
Procedure
1 Log in to Data Director as a system administrator.
2 Click Manage and Monitor.
3 Click Base DB Templates in the left pane.
4 Right-click Oracle 11g and select Properties.
5 Click the Update From tab, and click one Oracle 10 template.
6 Check the box for an Oracle 10g template and select dump-restore.
7 Click OK.
What to do next
Update the Oracle database. See “Updating Databases,” on page 100.
58 VMware, Inc.
Page 59

Update a Database
You can update a database to apply enhancements or software upgrades.
Prerequisites
Verify that the following conditions are met.
n
The system administrator has built and converted a base DBVM with proper update scripts and binary
updates, such as new third-party tools or database software upgrades.
n
The system administrator has enabled the base DB template on the resource bundle where the target
databases exist, and properly configured the base DB templates update chain.
n
You have appropriate privileges to access and update databases.
n
You have existing databases that require the updates contained in the new base DB template.
Procedure
1 Log in to an organization as a user with database privileges.
2 Click the Manage and Monitor tab.
3 On the Databases tab, right-click one or more databases and select Update.
Chapter 4 Building DBVMs and Base DB Templates
The Update page shows the current base DB template and its version.
4 On the Update page, provide the following information.
Option Description
Update to
DB parameter group
Keep existing values when possible
Take a snapshot before starting the
upgrade
Automatically cancel if update fails
Schedule Action
The new template from which to update the database.
Database configuration parameters to apply to the updated database.
If the new template does not require new database parameter values and you
prefer to retain the current values, select the Keep existing values when
possible check box.
Select whether to take a snapshot backup of the database before updating.
The default is to take a snapshot backup.
The task is canceled if the update fails.
Schedule the update for a specific date and time.
If you did not schedule the update, the database update proceeds immediately. If you scheduled the update,
the database update proceeds at the specified date and time. A database can have only one pending update
task.
VMware, Inc. 59
Page 60

VMware vFabric Data Director Administrator and User Guide
60 VMware, Inc.
Page 61

Managing Organizations 5
The basic component of Data Director is the organization. Data Director system administrators create
organizations, assign the initial organization administrator, and allocate resources to the organization.
This chapter includes the following topics:
n
“Organization Structure,” on page 61
n
“Operating Organizations,” on page 62
n
“Managing Resources For Organizations,” on page 63
n
“Managing Organization Users,” on page 64
n
“Create a Data Director Organization,” on page 64
n
“Bind a vCloud Director Organization to Data Director,” on page 65
Organization Structure
The structure of organizations depends on the user management mode: Global mode or By Organization mode.
User management mode is set by the system administrator during Data Director deployment and cannot be
changed.
Global Mode
By Organization Mode
VMware, Inc. 61
In Global mode, all users in the Data Director system are visible to all
organizations. Global mode is best for operating Data Director for a single
enterprise in which organizations represent business units or departments
within the enterprise. Organization administrators can see the global user list
and grant access to any user to their organization.
Global mode does not support integration with VMware vCloud Director.
In By Organization mode, Data Director operates as a service and each
organization is a distinct enterprise. Organizations are not visible to each other
in By Organization mode. Each organization has its own distinct user list that
is not visible to any other organization. Users must either send a request to
register to an organization and be approved by the organization administrator,
or the organization administrator can invite a user to join the organization.
By Organization mode supports integration with VMware vCloud Director. If
integration with VMware vCloud Director is enabled, you can provide access
to vCloud Director organizations by binding them to Data Director. The
vCloud Director organizations remain distinct from Data Director
organizations. vCloud Director organizations and users can be managed only
from vCloud Director.
Page 62

VMware vFabric Data Director Administrator and User Guide
Organizations contain one or more database groups (DBGs) that in turn contain one or more databases, as
shown in the following figure.
Figure 5-1. Data Director Organization Structure
Organization names must be unique within Data Director. Organizations cannot be nested.
Organization roles, policies, and templates apply only within that organization. Resources allocated to an
organization are reserved for that organization and cannot be shared among multiple organizations, whether
in Global or By Organization mode. This restriction enhances security and ensures resource isolation among
organizations.
See Chapter 2, “Managing Data Director Resources,” on page 15 for details about resource management in
Data Director.
Operating Organizations
Organization operations include system-level tasks such as creating and assigning resources to organizations,
and organization-level tasks such as managing organization users, defining and granting roles, and creating
database groups.
System administrators perform tasks such as the following.
n
Create an organization. See “Create a Data Director Organization,” on page 64.
n
If vCloud Director integration is enabled, bind vCloud Director organizations to Data Director. See “Bind
a vCloud Director Organization to Data Director,” on page 65.
n
View all organizations within Data Director
n
Create organization administrators
n
Create database virtual machines (DBVMs) and convert them to base database templates
n
Assign base database templates to resource bundles
n
Allocate resources to organizations
n
Revoke resource bundles from existing organizations
n
Implement user authorization and authentication rules (security policies)
n
Edit organization properties such as the organization name and description
n
Delete disabled organizations
62 VMware, Inc.
Page 63

By default, system administrators cannot access organizations. Organization administrators can grant access
database
backup
database database
resource
bundle
resource
bundle
Cloud
org org org
database group database group
templates
database database
resource
bundle
resource
bundle
to system administrators by modifying a security setting for their organization.
Organization administrators perform tasks such as the following.
n
Manage organization users, roles, privileges, and permissions
n
Create other organization administrators
n
Grant access to the organization to existing users
n
Enable base database templates for the organization
n
Allocate organization resources to database groups
n
Implement organization security and backup policies
n
Define roles
n
Define database configuration and database backup templates
n
Monitor organization performance, resource usage, and alarms
Managing Resources For Organizations
Organizations get their resources from vSphere resource pools and from networking and storage resources.
These resources are allocated to the organization by Data Director system administrators.
Chapter 5 Managing Organizations
Organizations manage resource bundles on behalf of their database groups and databases. Resource bundles
are composed of vSphere resource pools (CPU and memory), storage, and networking resources, and provide
the resources and base templates used to provision databases.
Resource pools initially created in vSphere are allocated to the Data Director system, where Data Director
system administrators use them to create resource bundles. System administrators allocate resource bundles
to organizations, and organization administrators can then assign resources to their database groups.
Figure 5-2. Resource Bundles, Organizations, and Database Groups
VMware, Inc. 63
Page 64

VMware vFabric Data Director Administrator and User Guide
One or more resource bundles can be assigned to an organization, but a resource bundle cannot be shared
across organizations. This restriction provides resource isolation, enhances security, and helps to ensure
compliance with Oracle licensing requirements by enabling organizations with Oracle databases to use only
the vSphere resources dedicated for Oracle use. Organizations do not compete for available resources and do
not have access to each others' CPU, memory, storage, and network resources.
Storage resources are the datastores and allocation amounts for database data and backups. Network resources
are the network or networks that are available to the resource bundle and that provide the network(s) for
databases. Data Director system administrators can set up separate networks to provide database isolation.
Organization administrators can subdivide resource bundles across several database groups within their
organization.
Databases draw their resources from their parent database groups, which draw their resources from their
parent organizations. Organizations draw their resources from the Data Director system.
Managing Organization Users
Data Director organization administrators control user access, roles, permissions, and privileges within their
organizations.
Organization administrators control which users can access their organizations and what those users can do.
Only organization administrators can grant access to their organizations and assign roles to users within their
organizations.
NOTE vCloud Director organizations and users can be managed only from vCloud Director. See the vCloud
Director documentation for details.
Users can belong to multiple organizations and can be granted multiple roles within those organizations in
either By Organization or Global mode systems.
n
In a By Organization system, each organization has a distinct user list that is not visible to other
organizations. To join an organization, users send a request to the organization administrator, or the
organization administrator can invite a user to join.
n
In a Global system, the user list for the system is visible to all organizations. All users belong to all
organizations. Organization administrators grant roles to users to enable them to perform tasks in the
organization.
Organization administrators can grant any roles defined within their organizations to organization users. In
By Organization mode, the user must be on the organization's user list.
Organization administrators control what users can do in their organizations by defining roles, privileges, and
permissions within their organizations, then granting them to organization users. Roles are specific to the
organization in which they are created and are not visible to other organizations.
See Chapter 3, “Managing Users and Roles,” on page 27.
Create a Data Director Organization
The Data Director system administrator creates organizations to allow organization administrators
independent management of their database groups and databases.
Prerequisites
n
Resource bundle(s) must be created and available for allocation.
n
You are logged in as a Data Director system administrator.
Procedure
1 With System selected, click Manage & Monitor.
64 VMware, Inc.
Page 65

2 Click Organizations in the left pane.
3 Click the plus (+) icon to start the Create Organization wizard.
4 Click Create New Data Director Organization.
5 Enter the organization information.
Wizard screen Action
Name and Description
Organization Administrator
Resource Bundles
Specify a name and optional description and click Next.
To create a new organization administrator user, perform the following
tasks.
a Click Create a new user.
b Specify the user name, password, first and last name, and optionally,
phone number.
c Click Next.
To use an existing user, perform the following tasks.
a Click Choose an existing user.
b Select the user from the list.
c Click Next.
You can assign resource bundles at any time after creating the organization.
To skip the assign resource bundles step, click Assign resource bundles
later. To select a resource bundle now, click Choose an existing resource
bundle and select a resource bundle from the list. Click Finish.
Chapter 5 Managing Organizations
The new organization appears in the Organizations list.
What to do next
Create resource bundles and assign them to the organization. See “Create a Resource Bundle,” on page 24.
Bind a vCloud Director Organization to Data Director
Data Director system administrators can integrate vCloud Director organizations and users with Data Director
by binding to the vCloud Director organizations.
Prerequisites
n
vCloud Director integration is enabled.
n
Resource bundle(s) are created and available for allocation.
n
You are logged in as a Data Director system administrator.
Procedure
1 With System selected, click Manage & Monitor.
2 Click Organizations in the left pane.
3 Click the plus (+) icon to start the Create Organization wizard.
4 Click Bind to vCloud Director Organization.
Data Director connects to vCloud Director. This may take a minute.
5 Select a vCloud Director organization from the Organization drop down list and click Next.
VMware, Inc. 65
Page 66

VMware vFabric Data Director Administrator and User Guide
6 Enter the appropriate information.
Wizard screen Action
Organization Administrator
Resource Bundles
The vCloud Director organization appears in the Organizations list.
What to do next
Create resource bundles and assign them to the organization. See “Create a Resource Bundle,” on page 24.
Select the vCloud Director organization administrator.
You can assign resource bundles at any time after binding the organization.
To skip the assign resource bundles step, click Assign resource bundles
later. To select a resource bundle now, click Choose an existing resource
bundle and select a resource bundle from the list. Click Finish.
66 VMware, Inc.
Page 67

IP Whitelists 6
Organization administrators and users with appropriate permissions can add a level of security to database
connection requests by creating IP whitelists and applying them to individual databases. By default, all users
with valid credentials can connect to a database. By applying one or more IP whitelists to a database, you
ensure that only connection requests from trusted IP addresses are accepted by that database.
Organization administrators and users with Manage IP Whitelists and Edit information and storage
permissions can create IP whitelists at either the organization level or the individual database level.
Organization level IP whitelists, known as organization IP whitelists, can be applied to any database in that
organization. Database level IP whitelists, known as custom IP whitelists, can be applied to a specific database.
IP whitelists contain one or more IP address ranges as well as one or more single IP addresses.
You can add, update, and apply IP whitelists during or after database creation.
This chapter includes the following topics:
n
“Create an Organization IP Whitelist,” on page 67
n
“Apply IP Whitelists to Databases,” on page 68
n
“Create Custom IP Whitelists,” on page 68
Create an Organization IP Whitelist
Organization administrators and users with Manage IP Whitelists permission can create IP whitelists. IP
whitelists ensure that databases accept connections only from trusted IP addresses.
Procedure
1 Log in to Data Director as an organization administrator or as a user with Manage IP Whitelists
permissions.
2 Click the Organization Settings tab, and click Security.
3 Click the IP Whitelists tab, and click the plus (+) icon to start the Create IP Whitelist wizard.
4 Enter the appropriate information.
Option Description
Name
Description
IP Ranges
VMware, Inc.
The unique name for the IP whitelist.
(Optional) A description for the IP whitelist.
Click the plus (+) icon to add IP addresses.
n
To add one IP address, select Single IP and enter the IP address.
n
To add a block of IP addresses, select IP Range and enter the beginning
and ending IP addresses of the IP address range.
67
Page 68

VMware vFabric Data Director Administrator and User Guide
5 Click OK.
The IP whitelist appears in the IP Whitelist list.
Apply IP Whitelists to Databases
You can apply IP whitelists to a database to ensure that the database accepts connection requests only from
trusted IP addresses.
Prerequisites
n
Verify that your organization administrator or user with Manage IP Whitelist and Edit information and
storage permissions has created IP whitelists.
n
Create a database to which you want to apply an IP whitelist.
Procedure
1 Log in to Data Director as an organization user with database management privileges.
2 Click the organization Manage & Monitor tab, and select your database group.
3 Click the Databases tab.
4 Right-click your database and select Properties.
5 Click the IP Whitelists tab.
6 Select Only allow connections from the selected IP whitelists.
7 Click the appropriate IP whitelist check box.
8 Click OK.
Data Director reconfigures the database to accept connections only from the selected IP whitelists' IP addresses.
Create Custom IP Whitelists
Users with Manage IP Whitelist and database management privileges can create one or more custom IP
whitelists to apply to databases.
Prerequisites
Create a database to which you want to apply custom IP whitelists.
Procedure
1 Log in to your Data Director organization as a user with database management permissions.
2 Click your organization's Manage & Monitor tab, and select your database group.
3 Click the Databases tab.
4 Right-click your database and select Properties.
5 In the Properties window, click the IP Whitelists tab.
6 Select Only allow connections from the selected IP whitelists.
7 Click the plus (+) icon to start the Custom IP Whitelists wizard and enter the appropriate information.
Option Description
Name
Single IP
68 VMware, Inc.
Enter a unique name for the custom IP whitelist.
Select to enter a single trusted IP address.
Page 69

Chapter 6 IP Whitelists
Option Description
IP Range
Description
(Default) Enter a range of trusted IP addresses. Enter a beginning and ending
IP address.
(Optional) A description of the custom IP whitelist.
8 Repeat Step 7 to continue adding custom IP whitelists.
9 Click OK.
Data Director reconfigures the database to accept connections from the custom IP whitelists' IP addresses.
What to do next
Click the IP Whitelists tab to modify or delete custom IP whitelists.
VMware, Inc. 69
Page 70

VMware vFabric Data Director Administrator and User Guide
70 VMware, Inc.
Page 71

Managing Database Groups 7
Database groups contain sets of databases within organizations. Database groups allow organization
administrators to provide the resources for operating and provisioning databases and to apply access and
authorization rules (security policies) to those databases. Grouping databases enables subdivision of resources
from the organization's allocated resources.
This chapter includes the following topics:
n
“Database Group Management Overview,” on page 71
n
“Managing Resources for Database Groups,” on page 72
n
“Storage Reservation,” on page 73
n
“Database Groups and Security,” on page 73
n
“Create a Database Group,” on page 73
Database Group Management Overview
Organization administrators create database groups to enable efficient management of databases.
Organization administrators also allocate the resources required to provision, operate, and control database
groups.
VMware, Inc.
The databases within a database group are usually related. For example, in Global user management mode,
where organizations represent business units in a single enterprise, database groups can group databases for
departments within the business unit. In By Organization user management mode, where each organization
represents a unique enterprise, database groups can group databases for business units within that enterprise.
Each database group can contain one or more databases. Databases must reside in one database group and
cannot be divided among database groups.
Database groups must reside in one organization and cannot be nested.
The following figure shows the relationship between organizations and database groups.
71
Page 72

database
backup
database database
resource
bundle
resource
bundle
Cloud
org org org
database group database group
templates
database database
resource
bundle
resource
bundle
VMware vFabric Data Director Administrator and User Guide
Figure 7-1. Database Groups in the Data Director Architecture
Managing Resources for Database Groups
Database groups require CPU, memory, storage, and networking resources to enable database operation,
provisioning, and backup. To provide database groups with the required resources, you allocate resource
bundles to their database groups.
Resource bundles consist of CPU, memory, storage, and networking resources. Multiple database groups in
an organization can share the same resource bundle. The organization administrator can allocate part of the
resource bundle to each database group, or assign a resource bundle exclusively to one database group.
Organization administrators assign resources when they create database groups and can add or expand
resources as required. Each database group has exclusive use of its assigned resources to ensure resource
isolation. Resource isolation ensures that database groups and the databases that they contain do not compete
for resources or have visibility into the resources of other organizations.
When organization administrators create database groups, they optionally specify how much unused CPU
and memory to reserve for the database groups. The organization administrator also assigns the database
group's priority for distribution of unreserved resources. The priority options are high, medium, or low.
Organization administrators allocate storage for the database groups, and assign a storage reservation for the
database groups. The storage reservation determines the percentage of the total database storage allocation
that is initially committed to a database group. It is reserved even if the storage is not used yet. See “Storage
Reservation,” on page 73.
Because system administrators allocate resources to organizations and then organization administrators assign
resources to database groups within organizations, each database must be contained within one database
group. You cannot split databases among database groups, and you cannot move a database to a different
database group after the database is created.
Use the following guidelines to estimate the resources that you need for a database group.
n
Calculate the storage allocation based on the expected number of databases that the database group will
contain, the amount of storage allocated for each of those databases, and room for growth.
(Number of DBs) X (Avg. storage for each DB) + (Room for growth)
72 VMware, Inc.
Page 73

n
Determine the size of the backup storage allocation to support the external backups for each database in
the database group plus the Point-in-Time Recovery allocation for each database.
Storage Reservation
Organization administrators use storage reservation to control whether they can allocate more storage than is
available to databases in a database group. Administrators set a limit on how much storage can be
overallocated.
Storage reservation determines the percentage of the total database storage allocation that is initially committed
to the database group. The storage is reserved, although it is not used yet.
For example, if the organization administrator sets database storage at 100GBs and storage reservation at 20%,
a total of 500GBs is allocated for all databases in the database group. If a user then creates one database in the
group, the single database can allocate up to 500GBs of data storage but commit 100GBs. If a user instead
creates five databases in the group, each database can allocate up to 100GBs of data storage but can commit
20GBs. You cannot add more databases to the group because all 100GBs are committed. For example, 500GBs
are allocated, 100GBs are the capacity, and 400GBs are over allocated.
In practice, data storage is always less than the maximum 500GBs, because total allocation includes space for
overhead for the operating system, bin, snapshots, and so on.
Database Groups and Security
Chapter 7 Managing Database Groups
Role-based access control and direct user permissions form the security policies that determine which users
can access particular database groups and the actions that the users can perform. Database groups inherit
security policies from their organizations.
Organization administrators define the security policies for their organization, including user roles,
permissions, and privileges.
For example, an organization administrator creates a user role with permissions on database groups. These
permissions include create database, take database snapshots, and start or stop database. Those roles and their
associated permissions apply to each database group within the organization, and to each database within
each database group.
Chapter 3, “Managing Users and Roles,” on page 27 discusses the Data Director security model and explains
how you can use roles for fine-grained permission management.
Create a Database Group
Database groups contain sets of databases within an organization. Database groups enable grouping related
databases and provide efficient use of resources needed to provision and operate databases.
Prerequisites
n
Verify that at least one resource bundle is allocated to the database group's organization. See “Create a
Resource Bundle,” on page 24 if no resource bundle is available.
n
Verify that at least one base DB template is enabled in the organization.
n
Log in as an organization administrator or have permissions to create or modify database groups.
Procedure
1 Click the Manage & Monitor tab.
2 Click the Database Groups tab.
3 Click the plus (+) icon to create a database group.
VMware, Inc. 73
Page 74

VMware vFabric Data Director Administrator and User Guide
4 Specify the following information in the Create Database Group wizard.
Wizard page Action
Name and Description
Resource Bundle
Enable Templates (Conditional)
Resources
Type a name and optional description and click Next.
Select a resource bundle from the list and click Next.
If no base DB template is enabled on the resource bundle, you must enable
one.
a Click Next, and select one or more base DB templates.
b Click Enable.
c When Status is refreshed to Enabled, click Next.
Select one or more base DB templates and click Enable. When Status is
refreshed to Enabled, click Next.
Specify the resources for this database group.
Network
CPU & Memory
Storage
Select the network from the drop-down menu.
n
Assign the priority (High, Medium, or Low).
n
(Optional) Select the Reserve resources for this
database group check box and enter the
reservation amounts for CPU and memory.
Enter the amount of database and backup storage to
allocate to the database group, in gigabytes, in the
Database Storage Allocation and Backup Storage
Allocation text boxes.
Enter the percentage of database group storage to
reserve for each of the database group's databases in
the Storage Reservation text box.
5 Click Finish.
The new database group appears in the database group list.
What to do next
Click the database group name to open the database group. You can view and edit its properties.
74 VMware, Inc.
Page 75

Managing Database Templates 8
Data Director database templates allow organization administrators to enable database templates, and to
standardize database creations and their backup policies. Database templates in Data Director also impose
limits on resource consumption. Database administrators can create and back up databases consistently by
using templates and can create, clone, and customize templates.
This chapter includes the following topics:
n
“Introduction to Database Templates,” on page 75
n
“Enable a Base DB Template,” on page 76
n
“Create a DB Parameter Group,” on page 77
n
“Create a Resource Template,” on page 77
n
“Modify a Resource Template,” on page 78
n
“Create a Backup Template,” on page 79
n
“Modify a Backup Template,” on page 80
Introduction to Database Templates
Data Director includes database templates to help administrators streamline resource allocation and
standardize database setup and backup setup. Templates help database administrators to quickly provision a
database and to select a backup process.
Data Director supports base DB templates, resource templates, and backup templates. Included with Data
Director are several optimized templates. When system administrators create an organization, they must assign
base DB templates to the organization. Data Director copies the system-defined templates, resource templates,
and backup templates to the new organization. Organization administrators can modify only the resource and
backup template instances or configure new templates.
You can enable base DB templates, create DB parameter groups associated with base DB templates, and create
resource templates and publish them immediately or publish them later. When a template is not published,
you can view or manage it, but you cannot use it for provisioning or for other purposes.
Base DB Templates
System administrators prepare base DB templates. The templates are not visible to organizations until system
administrators assign them to the resource bundles of underlying organizations. When the base DB templates
become visible, organization administrators must enable them on the resource bundles before database users
can provision database from them.
VMware, Inc.
75
Page 76

VMware vFabric Data Director Administrator and User Guide
DB parameter groups are associated with base DB templates and contain the database configuration settings
used to provision database instances. DB parameter groups specify database configurations that vary from db
engines. For vFabric Postgres, this includes parameters such as connection, memory, IO, WAL, checkpoint,
logging, and so on. When organization administrators enable a base DB template, they can use the default DB
parameter group for the template. They can also create a new DB parameter group or copy from another
template, so that database users can choose a parameter group based on actual need when provisioning
databases.
Resource Templates
Database Resource templates define the computing and storage resources for creating a database, the database
parameter group, and the high availability settings.
Resource Settings
You can create different templates for different situations. For example, you can define a resource template for
engineering with a small memory size and have high availability disabled. You can define the resource template
for QA with a larger memory size and with high availability enabled.
When you create a template, you can specify the number of virtual CPUs,
memory size, and recommended database storage allocation. You can enable
high availability for the template and all corresponding databases. You can also
choose the CPU and memory priority, which affects the allocation of resources
for all databases in the database group. The levels (high, medium, and low)
give certain databases higher priority than other databases in the same
database group. The CPU reservation and Memory reservation text boxes let
you reserve resources for each database that you create from the template.
If you make changes to a template, databases that are already created from the
template are not affected.
Backup Templates
Backup templates define backup settings for databases. You can associate a backup template with a database
when you create the database, or you can associate a backup template with a database at a later time. See
“Select a Database Backup Template,” on page 133.
You can use one of the predefined backup templates for consistency across your organization. See “Backup
Template Settings,” on page 132.
You can also clone and customize an existing template and associate the custom template with your database.
You can customize frequency, start time, and retention for snapshots and for external backup. You can also
enable and customize point-in-time recovery, and you can specify a backup label. See “Create a Backup
Template,” on page 79.
Enable a Base DB Template
Organization administrators enable a base DB template on the underlying resource bundles so that
organization users can provision databases based on the base DB template. Only organization administrators
and users with Manage base DB templates privileges can enable, disable, and edit base DB templates.
Prerequisites
System administrators have assigned at least one base DB template to the resource bundles of the underlying
organization.
Log in to Data Director as an organization administrator or as an administrator with privileges to enable base
DB templates.
76 VMware, Inc.
Page 77

Procedure
1 Click the Organization Settings tab.
2 In the left pane, click Base DB Templates.
3 In the center pane, right-click a base DB template and select Enable on Resource Bundles.
4 Click Enable.
Wait for the base DB template to be enabled.
5 Click Close.
Create a DB Parameter Group
Organization administrators and users with Manage base DB templates privileges can configure the DB
parameter group for base DB templates.
Prerequisites
System administrators have assigned at least one base DB template to the resource bundles of the underlying
organization.
You are logged in to Data Director as an organization administrator or as an administrator with privileges to
create, edit, and delete DB parameter groups.
Chapter 8 Managing Database Templates
Procedure
1 Click the Organization Settings tab.
2 In the left pane, click Base DB templates.
3 Right-click a base DB template in the table, and select Properties.
4 Click the DB Parameter Group tab.
5 Click the plus (+) icon.
6 Type a name and description for your parameter group.
7 Scroll through the parameters associated with the base DB templates, and select the Override box to
override default values for individual parameters.
8 Click OK.
A DB parameter is created and associated to the base DB template.
Create a Resource Template
You can create a resource template by cloning a template or by configuring a new template. In both cases, you
can specify the resource settings and the database settings for the template.
Only organization administrators or users with Manage Resource Templates or Manage Backup
Templates privileges can create, edit, and delete templates.
Prerequisites
Log in to Data Director as an organization administrator or as an administrator with privileges to create and
modify templates.
Procedure
1 Click the Organization Settings tab.
2 Click Templates, and click Resource Templates.
VMware, Inc. 77
Page 78

VMware vFabric Data Director Administrator and User Guide
3 Create a template or clone a template.
Creation Method Action
New template
Clone
4 In the Create Resource Template wizard, type a name and description.
5 Specify whether you want to publish the template, and click Next.
When a template is not published, you can view or manage it, but you cannot use it to create databases.
6 Enter resource settings for the template and click Finish.
Option Description
vCPUs
High availability
Memory size
Recommended DB storage
allocation
CPU and memory priority
Explicitly reserve resources for
databases created by this template
CPU reservation
Memory reservation
Click the green plus icon above the menu bar.
Right-click an existing template and choose Clone.
Number of virtual CPUs the database virtual machine will use.
Select Enable to protect the database with vSphere High Availability. See the
vSphere Availability documentation.
Amount of memory the database virtual machine will use.
Specify recommended storage allocation for this database.
Select Automatic to allow the vCenter Server system to allocate CPU and
memory to the virtual machine. If you select another value, the CPU priority
determines how unreserved CPU and memory resources are assigned to this
database as compared to other databases in this database group.
If selected, you can reserve resources for running databases. Reservations
guarantee that the database has the specified amount of CPU and memory
available.
Number of MHz to reserve for this database.
Number of MB to reserve for this database.
Modify a Resource Template
If the requirements for resources or other aspects of your environment change, you can modify existing
resource templates. Databases that you create from the new template use the new settings.
Prerequisites
Log in to Data Director as an organization administrator or as an administrator with privileges to manage
resource templates.
Procedure
1 In your organization, click the Organization Settings tab.
2 Click Resource Templates in the left pane.
3 Right-click the template that you want to modify, and perform one of the supported actions.
Action Description
Clone
Delete
Unpublish
Creates a copy of this template. When you clone a template, the Create
Database Resource Template wizard opens, and you can configure the
resource settings for the clone.
Deletes the selected template.
Disables provisioning and other capabilities for this template. When a
template is not published, you can view or manage, but cannot be used for
provisioning or other purposes.
78 VMware, Inc.
Page 79

Action Description
Edit Permissions
Properties
You can create databases with the new settings from the modified template. Databases that you previously
created from the template do not change.
Create a Backup Template
Backup templates include frequently used backup settings. You can use one of the existing templates, clone
and customize a template, or create a template. You can then associate the backup template with a database
that you create.
The system-defined backup templates use recommended settings for different situations. See “Backup
Template Settings,” on page 132 for information about system-defined templates.
Prerequisites
Chapter 8 Managing Database Templates
Allows you to specify who can use this template, and what each user can do.
You can change the permissions for an existing user, remove an existing user,
and add a role. Users who can create a database from the template do not
automatically have permissions to modify the template.
Allows you to modify the settings that you specified when you created the
template. See “Create a Resource Template,” on page 77 for a discussion of
the properties you can change.
Log in to Data Director as an organization administrator or as an administrator with Manage Resource
Templates or Manage Backup Templates privileges.
Procedure
1 Click the Organization Settings tab.
2 Click Backup Templates in the left pane.
3 Create a template or clone a template.
Creation Method Action
New template
Clone
Click the green plus sign above the menu bar.
Right-click one of the existing templates and select Clone.
4 In the Backup Template wizard, type a name and description for the template.
5 Specify whether you want to publish the template, and click Next.
When a template is not published, you can view or manage it, but you cannot use it to backup databases.
6 Specify the snapshot settings in the Backup Settings panel.
Option Action
Frequency
Start Time
Retention
Select one of the options from the menu. Select Never if you do not want
backups for databases that use this backup template.
Select Automatic to allow the system to control the start time, or enter a start
time. The system initiates a backup within two minutes of the target start
time, depending on system load.
Enter the number of hours or the number of copies to retain.
VMware, Inc. 79
Page 80

VMware vFabric Data Director Administrator and User Guide
7 Specify the external backup settings.
Option Action
Frequency
Start Time
Retention
Extended retention
8 Select the general backup settings.
Option Action
Point-In-Time recovery
Backup label
9 Click Finish to finish creating the template.
Select one of the options from the menu. Select Never if you do not want
backups for databases that use this backup template.
Select Automatic to allow the system to control the start time, or enter a start
time. The system initiates a backup within two minutes of the target start
time, depending on system load.
Select a proper retention period from the options.
Check the box to enable extended retention, then specify a retention value.
Click to enable point-in-time recovery, and enter a value in Recommended
PITR storage allocation.
Select Suspend database or Automatically adjust PITR retention if storage
runs out.
The start time for point-in-time recovery is right after point-in-time recovery
is enabled, when the system creates a baseline backup or snapshot. You
cannot remove the baseline backup. If you do, the start time for point-in-time
recovery changes.
The time range for point-in-time recovery is from the time of your oldest
automatic backup to the present. The oldest backup can be an external
backup or a snapshot. Backups with extended retention are not supported
as oldest backups.
Point-in-time recovery consumes space in the backup storage area.
Depending on database load and retention lengths, this feature might require
a significant amount of storage.
Type the first part of the name of the backup.
Defaults to user-specified label-date_and_time-dbname. For your database
named db1, if you entered testbackup as the label and the backup starts at
12:30:45 on May 30, 2011, the full name is
testbackup-2013-05-30-12-30-45-db1.
If you do not specify a label, the system uses snapshot-data_and_time-dbname
or backup-data_and_time-dbname.
What to do next
You can assign the template to databases.
Modify a Backup Template
If the requirements for backups in your environment change, you can modify existing backup templates.
Prerequisites
Log in to Data Director as an organization administrator or as an administrator with privileges to manage
backup templates.
Procedure
1 In your organization, click the Organization Settings tab.
2 Click Backup Templates in the left pane.
80 VMware, Inc.
Page 81

Chapter 8 Managing Database Templates
3 Right-click the template that you want to modify and perform one of the supported actions.
Action Description
Clone
Delete
Unpublish
Edit Permissions
Properties
Creates a copy of this template. When you clone a template, the Create
Backup Template wizard opens and you can configure the backup settings
for the clone.
Deletes the selected template.
Disables provisioning and other capabilities for this template. When a
template is not published, you can view or manage it, but you cannot use it
for backup or other purpose.
Lets you change the permissions for an existing user, to remove an existing
user, and to add a role.
Lets you modify the settings you specified when you created the backup
template.
You can create databases with the new settings from the modified template. Databases that you created from
the template do not change.
VMware, Inc. 81
Page 82

VMware vFabric Data Director Administrator and User Guide
82 VMware, Inc.
Page 83

Managing Databases 9
Database administrators and application developers manage database lifecycles from creation to
decommissioning. Database administrators manage databases from a central management perspective.
Application developers focus on how databases can help with application development as a service.
This chapter includes the following topics:
n
“Database Lifecycle,” on page 83
n
“Requirements for Creating Databases,” on page 85
n
“Database Creation,” on page 86
n
“Using Tags,” on page 96
n
“Managing the Organization Catalog,” on page 97
n
“Batch Operations and Scheduled Tasks,” on page 99
n
“Updating Databases,” on page 100
n
“Database Administration,” on page 101
Database Lifecycle
In Data Director, database lifecycle includes preparing base database templates from database virtual
machines, database creation and resource allocation, managing the database schema and data, performing
backup and recovery tasks, ingesting databases into Data Director, and decommissioning databases. System
administrators, database administrators, and application developers perform the database lifecycle tasks.
For information about backup and recovery tasks, see Chapter 12, “Safeguarding Data,” on page 129.
Prepare base database
templates
VMware, Inc. 83
Base database templates (base DB templates) reside at the Data Director system
level. They provide the virtual hardware, operating system, database software,
and other required files and configuration information needed to create
databases in Data Director. System administrators create database virtual
machines (DBVMs) at the system level, convert them to base DB templates,
assign the base DB templates to one or more resource bundles, and assign the
Page 84

VMware vFabric Data Director Administrator and User Guide
resource bundles to organizations. Organization administrators must enable
at least one base database template in their organization resource bundle(s) to
allow organization users to create databases. See Chapter 4, “Building DBVMs
and Base DB Templates,” on page 37.
Create databases
Manage schema
Backup and restore
Update database
Create and allocate resources to a new database using base database templates,
database resource templates, and parameter groups. Database resource
templates specify resource limits. Parameter groups specify sets of database
parameters, such as maximum connections allowed, encoding, and checkpoint
timeout. Application developers can perform do-it-yourself database creation
using the predefined base database templates, resource templates, and
parameter groups. See “Requirements for Creating Databases,” on page 85.
Administrators can grant permissions to their users to create databases from
resource templates, but not allow users to modify the resource templates or
change the default resource allocations. This restriction provides resource limit
enforcement and allows administrators to retain control of resource and
security policies. See Chapter 8, “Managing Database Templates,” on page 75.
Manage vFabric Postgres database schemas and add data. You can create
tables, designate primary and foreign keys and indexes, and create views,
sequences, triggers, and other database entities.
NOTE Data Director supports managing schemas for vFabric Postgres
databases only.
Safeguard your data by taking regular backups and testing your backups. See
Chapter 12, “Safeguarding Data,” on page 129.
Choose the database version to update within Data Director to meet IT policies
or application requirements.
Clone
Scale up
Monitor performance
and usage
Stop and restart the
database
Decommission the
database
Add databases to the
organization catalog
Ensure access to consistent, yet isolated databases by cloning the database for
specific purposes such as development or quality assurance. See Chapter 10,
“Cloning Databases,” on page 107.
Dynamically increase the database size as required during the development,
test, and production phases.
Use the Data Director user interface to monitor resource usages, recent alarms,
tasks and events. See Chapter 13, “Monitoring the Data Director
Environment,” on page 141.
Stop and restart, for example, to perform maintenance tasks.
Disable and then delete databases. Free up the resources when they are no
longer needed.
Add any Data Director database to the organization catalog. Organization
users can create databases using the catalog databases when they need a
database with known characteristics and preloaded data, for example, for
testing SQL scripts or usage scenarios.
84 VMware, Inc.
Page 85

Chapter 9 Managing Databases
Ingest external
databases into Data
Director
Ingest a backup of an external database into Data Director. You can ingest a
one time clone, or you can refresh an existing database from an external
database. Ingested databases are accessible only from the organization
database catalog and can be refreshed only by an additional backup from the
source database. You cannot use ingested databases directly in Data Director.
Perform common
operations and schedule
tasks in batches
Perform common tasks and schedule database operations to run on multiple
databases in a database group, for example, run restart, stop, repair, enable,
and add whitelists tasks, and schedule upgrade and backup operations on
multiple databases.
Every database requires an administrator account that can perform all schema management operations. This
account is specific to the database and cannot log in to Data Director. You can add database owner accounts
after database creation. Data Director database users must log in with their database-specific credentials to
view the database, its entities, and its data or to perform database management tasks.
Database administrators and application developers can manage databases only if they have appropriate
permissions and roles granted to them by the organization administrator. The administrator must grant
permissions and roles on the database group or on the database. These permissions and roles apply only within
the organization in which they are granted.
Requirements for Creating Databases
You must have certain permissions to create databases, and you must calculate the storage needed for database
and related data.
Permissions Required for Creating Databases
To create databases, you need Create Databases permission on the database group that will contain the
database, Use Templates permission on at least one database template, and permission to at least one resource
template and one backup template.
It is useful to have the following permissions on the database group and on the database.
n
Create snapshots.
n
Create external backups.
n
Delete snapshots, including editing their retention time.
n
Clone the database.
n
Recover the database from a backup or snapshot.
n
Manage IP Whitelists
The organization administrator can create a role with these permissions and assign organization users to the
role.
Calculating Database Storage Allocation
During the database creation process, you specify database storage allocation, point-in-time recovery storage
allocation, and the database group for the database. The database group provides the CPU, memory, storage,
and network resources required to run the database. The storage and point-in-time recovery allocations specify
how much of the database group's resources to use for this database. See “Storage Reservation,” on page 73.
When you calculate the amount of storage to allocate to the database, proceed as follows.
n
Estimate how much data will be stored in the database.
n
Consider the number of users and average expected number of transactions in a particular time period
and allow for the number to increase.
VMware, Inc. 85
Page 86

VMware vFabric Data Director Administrator and User Guide
n
If you plan to enable point-in-time recovery, calculate additional storage to accommodate the point-intime recovery write-ahead logs (WALs). The size of the allocation depends on the expected volume of
transactions on the database.
Every database requires a certain amount of storage overhead for the operating system, database software,
swap space, log files, snapshots, and so on. The storage for overhead is explicitly allocated and does not count
against database storage allocation. Database storage allocation is for the database schema and data only. You
must have enough resources available to cover the database allocation and to cover any overhead.
Even if the database group has enough free space for creating a database, database creation does not finish if
you do not have enough resources for the overhead. If the free space is less than the following calculation, Data
Director cannot create the database.
(storage allocation * storage reservation %) + overhead
Database Creator Permissions
After database creation finishes, the following permissions on the new database are granted to the database
creator.
Edit information and
storage
Manage IP whitelists
Modify administrator
accounts
Start database and Stop
database
View properties
Edit settings
Monitor status
Database Creation
As a DBA or application developer, you create databases to serve your project or application requirements.
Data Director provides several methods for creating and provisioning databases.
n
“Create an Empty vFabric Postgres or Oracle Database,” on page 87. Use a resource template to create
an empty database. Use this method when developing a new application or the database characteristics
or data are not important to the current phase of your project.
Enables the database creator to edit database properties such as the name,
description, and size of the database.
Enables the database creator to assign IP whitelists to this database and to create
custom IP whitelists for this database.
Enables the database creator to add or modify database users for this database.
Database users are granted full permission on this database.
Enables the database creator to start and stop.
Enables the database creator to view the database.
Enables database creators to edit database parameters, database ingestion, and
refresh settings and SSL certificates.
Enables database creators to monitor dashboards, events, tasks, reports, and
logs. You can also define, monitor, and acknowledge alarms.
n
“Create a Database from a Catalog,” on page 89. Use this method when you require a database with
known characteristics and pre-loaded data. Catalog databases are read-only and cannot be modified or
powered on by users, though the data in the catalog database can be refreshed periodically from the source
database.
n
Create a database by cloning an existing database. Use this method to create a database in a pristine state,
with pre-loaded data and configuration settings, for testing and development purposes. See Chapter 10,
“Cloning Databases,” on page 107.
86 VMware, Inc.
Page 87

Chapter 9 Managing Databases
n
“Ingest an External Database,” on page 93. Use this method to reproduce a state from a production or
other type of environment. With ingestion, you can create a one-time clone, create a "golden clone", which
cannot be modified within Data Director, or refresh a database from an external database, also known as
in-place refresh. A golden clone can be refreshed only by an additional backup from the source database.
You can make clones of a golden clone within Data Director.
Create an Empty vFabric Postgres or Oracle Database
When you need an empty database for a new application, you can create it with a database resource template.
The template is configured to allocate resources to the database.
Prerequisites
n
Verify that you have access to the organization and database group in which to create the new database.
n
Verify that you have Clone permission on the catalog database and Create databases permission on the
database group in which you create the database.
n
Verify that you have Use template permission on at least one resource template, backup template.
Procedure
1 Navigate to the organization and to the database group in which to create the database.
2 Click the Manage & Monitor tab.
3 Click the Databases tab.
4 Click the plus (+) icon to start the Create Database wizard.
5 View the summary, and click Finish.
Field Option
Creation Type
Name and Description
Database Type
Base DB Template
Database Group
Resource template
Data disk allocation
Parameter group
Backup template
PITR disk allocation
Administrator user name
Password
Confirm password
Click Create new database.
Type a name and, optionally, a description of the database.
Select a database type from the drop-down menu. For example, Oracle or
vPostgres.
Select a base database template from which to create the database from the
drop-down menu. For example, Oracle 11.2.0.3
If you selected a database group, this field is filled in for you.
Select a database resource template from the drop-down menu. For example,
tiny, giant, and so on.
Select the data storage allocation for this database. The minimum is 1GB for
vFabric Postgres and SQL Server, and 2GB for Oracle.
Select a parameter group for the database or accept the default parameter
group. Parameter groups contain database configuration settings such as
checkpoint timeout, write-ahead log buffers, encoding, and shared buffers.
(Optional) Select a backup template from the drop-down menu. You can
select a backup template for specific purposes, such as development, or select
no backups (Disabled).
Select the number of gigabytes to allocate for point-in-time recovery
operations. The minimum is 1GB.
Type an administrator account for the database. Each database requires an
administrator that can perform all schema management operations. The
administrator account is specific to the database and cannot log in to Data
Director.
Type an owner account password.
Confirm the owner account password.
VMware, Inc. 87
Page 88

VMware vFabric Data Director Administrator and User Guide
Field Option
Expiration
Tags
Snapshot
IP Whitelist
The database appears in the Databases List with a status of Creating. The process can take a few minutes. The
status changes to Running when creation finishes successfully.
What to do next
You can load the database data and use the database.
Create an Empty SQL Server Database
You can create an empty SQL Server database for a new application with a database resource template. The
template is configured to allocate resources to the database
Select a date and time at which the database expires. Then select an action
upon expiration, or no expiration.
(Optional) Select one or more tags for this database. Use tags to filter the list
of databases that you view in an organization's Databases tab, for example,
all your customer relationship databases can have a tag called CRM.
(Optional) Select the check box to take a snapshot backup of the database
when creation and provisioning finishes.
Select Allow all connections to the database. Optionally, select Only allow
connections from selected IP whitelists (next page), and select an
organization IP whitelist or create a custom IP whitelist..
Prerequisites
n
Verify that you have access to the organization and database group in which to create the new database.
n
Verify that you have Clone permission on the catalog database and Create databases permission on the
database group in which you create the database.
n
Verify that you have Use template permission on at least one resource template, backup template.
Procedure
1 Navigate to the organization and to the database group in which to create the database.
2 Click the Manage & Monitor tab.
3 Click the Databases tab.
4 Click the plus (+) icon to start the Create Database wizard.
5 Click Create new database, and provide the appropriate information.
Option Description
Name and description
Database type
Base DB template
Database group
Resource template
Data disk allocation
Parameter group
Domain
Type the NETBIOS name for the Windows machine and, optionally, a
description of the database.
Select SQL Server.
Select Template-sql server from the drop-down menu.
Select a database group.
Select a resource template.
Type a data storage allocation value for this database. The minimum is 1GB
for SQL Server.
Select a parameter group for the database or accept the default parameter
group.
To use Windows authentication, click Join machine to domain and type a
domain name, user name, and password.
To use mixed authentication, click Do not join domain.
88 VMware, Inc.
Page 89

Chapter 9 Managing Databases
Option Description
Administrator
Options
Tags
If you joined the machine to a domain, type a domain user name for the SQL
Server administration.
If you did not join the machine to a domain, enter a password for the builtin SQL Server Administrator account, and a password for the Local Windows
Administrator.
Click No expiration, or click Expires on and select an expiration date and
time and an action upon expiration.
(Optional) Select one or more tags for this database. Use tags to filter the list
of databases that you view in an organization's Databases tab. For example,
you can tag all your customer relationship databases as CRM.
6 Confirm your selections, and click Finnish.
You have a running SQL Server instance.
What to do next
You can add the database data and begin to use the database.
Create a Database from a Catalog
You create a database from a catalog when your application requires a database with known characteristics
and data.
Prerequisites
n
Verify that you have access to the organization and database group in which to create the new database.
n
Verify that you have Clone permission on the catalog database and Create databases permission on the
database group in which you create the database.
n
Verify that you have Use template permission on at least one resource template, backup template.
Procedure
1 Navigate to the organization and to the database group in which to create the database.
2 Click the Manage & Monitor tab.
3 Click the Databases tab.
4 Click the plus (+) icon to start the Create Database wizard.
5 Select Create Database from the Catalog and click Next.
6 Select a database from the catalog, click Full clone or Linked clone, and click Next.
7 Enter the following information.
Option Action
Name and Description
Database type
Base DB template
Database group
Resource template
DB storage allocation
Type a name and, optionally, a description of the database.
The database type is the same as the catalog database you selected.
The database template is the same as the template for the catalog database
you selected.
If you selected a database group, this text box is completed for you. Click
Next.
Click Clone from source database and, optionally, view the settings, or select
a database resource template from the drop-down menu. For example, tiny,
giant, and so on.
You cannot change this value when creating a database from the catalog.
VMware, Inc. 89
Page 90

VMware vFabric Data Director Administrator and User Guide
Option Action
Database parameters
Backup template
PITR disk allocation
Post-clone Script
Expiration
Tags
IP whitelists
8 View the summary to confirm your selections, and click Finish.
The database appears in the Databases List with the status Creating. The process can take a few minutes. The
status changes to Running when creation finishes successfully.
Click Clone from source database and, optionally edit the parameters, or
select a parameter group from the drop-down menu.
Click Clone from source database and, optionally, view the settings, or select
a backup template from the drop-down menu.
You cannot change this value when creating a database from the catalog.
Click Next.
Select an SQL script to run after database is created or, optionally, click the
plus (+) icon to create a new script and name it as post-clone scripts. You can
click Edit to modify a script.
Select a date and time at which the database expires and select an action upon
expiration., or select no expiration.
(Optional) Select one or more tags for this database. Use tags to filter the list
of databases that you view in an organization's Databases tab, for example,
all your customer relationship databases can have a tag called CRM.
Select Allow all connections to the database. Optionally, select Only allow
connections from selected IP whitelists (next page), and select an
organization IP whitelist or create a custom IP whitelist. Click Next.
Requirements for Ingesting External Databases
To ingest a database is to take Oracle backup files, generated by the Oracle RMAN utility on an external, or
source, database, and restore them to a new, or target, database in Data Director.
The Oracle backup files are hosted on an NFS server for Data Director to consume. As the source database
evolves, the refresh process can take incremental backup files from the source and apply them to target, so any
changes after ingestion can be synced to the target database, regularly or on demand.
You can use ingestion to reproduce a production environment, or to create a one-time clone or golden clone,
or refresh an existing database in place.The imported database is a clone of a physical database that exists
outside of Data Director.
System Requirements
To ingest an external database, you need the following versions of Oracle, and Linux.
n
Oracle: 11g Release 2 Linux x86-64 Enterprise/Standard Edition.
n
Oracle: 10g Release 2 Linux x86-64 Enterprise/Standard Edition.
n
OS: Linux x86-64.
Backup Operation Requirement
You must comply with the following rules when backing up the source database.
n
Turn on control file auto backup and use the default control file auto backup format for device type disk
('%F').
n
If the database is in archive log mode and open, you must include archive logs in the backup. For example,
backup INCREMENTAL LEVEL 0 database plus archivelog
90 VMware, Inc.
Page 91

Chapter 9 Managing Databases
Otherwise, do not include an archive log in the backup. If the database is in nonarchive mode, the refresh
from external database feature does not support point in time refresh. The absolute path of any control
files, data files, redo log files, or temporary files of source database cannot contain any space, tab, carriage
return, asterisk, question mark, backslash, quote or line feed characters.
n
The database must be included in the backup. You cannot back up only the archive logs.
n
For golden clone ingestion and golden clone refresh, you must supply a LIST file containing information
about the backup operation. See next section for the name convention and format of LIST file.
n
For a one-time clone (in-place refresh), a full backup or one level 0 incremental backup plus several
optional level 1 subsequent incremental backups is required. You can optionallly do several subsequent
level 1 incremental backups (L0+nL1). For a point in time refresh, record the modify time so you can refresh
to the specified time. For a golden clone, a level 0 incremental backup is required for ingestion, and a level
0 or level 1 (either differential or cumulative) incremental backup is required for a refresh.
n
You must have an spfile in the control file backup set if you do not specify a pfile.
n
The database name must be the SID.
n
If network speed is limited or the database is very large, the ingestion-refresh process can take a long time.
If you use DHCP for the database virtual machine, ensure that the DHCP lease time is long enough so that
the IP address does not change during the ingestion and refresh process.
Additional Requirements
You must comply with the following additional requirements when backing up the source database.
n
The NFS server must be accessible to the DB Access Network or the Internal Network when ingestion and
refresh is running, and the backup files, LIST file and pfile must be readable.
n
You must allocate sufficient storage when ingesting, and estimate future expansion when ingesting a
golden clone.
Supported Oracle Features
The following Oracle features are supported.
n
Backup set.
n
Different block size for various data files.
n
BLOB data type.
n
Compressed backup.
Unsupported Oracle Features
The following Oracle features are not supported.
n
Image copy backup.
n
External file.
n
Encrypted backup.
n
OEM (Oracle Enterprise Manager) is not supported on ingested database.
VMware, Inc. 91
Page 92

VMware vFabric Data Director Administrator and User Guide
File Based Conventions
During the ingestion and refresh process, coordinate your operations with external programs, such as third
party backup software, or with manual operations. Familiarize yourself with the backup files, and observe
these file based conventions.
n
Backup files for each ingestion or refresh operation should have their own directory. The directory should
be beneath the exported directory.
n
For a golden clone ingestion and golden clone refresh, you must supply a LIST file that contains
information about the backup. The naming convention for a LIST file is database.LIST, where database is
the name of the database. The content of the LIST file is a series of key-value pairs, as in this example LIST
file.
controlfile=o1 mf_s_774019590_71hv06jn_.bkp
pfile=sales.pfile
NOTE The level value, required in previous versions of Data Director, is no longer needed. The agent
automatically checks the bakup level during ingestion and refresh. The optional catalogstart property
specifies the location to load the backup files. This means the control file directory and the catalog start directory
can be different. The value of catalogstart is a directory relative to the LIST file. If no catalogstart is provided,
the directory of the LIST file is used. When you upgrade from Data Director 2.0, make sure your old LIST file
works as expected. Otherwise, provide a catalogstart value.
In this LIST file, the controlfile field specifies the control backup file in the backup set. The value is a file
relative to the LIST file. It can be in the same directory as the LIST file, or in another directory. Other backup
files must be in the same directory as the control backup file.
The pfile field is optional.
To illustrate how to organize the LIST file, a pfile, and backup files, assume that you take a level 0 backup on
Sunday and a level 1 backup on all other days. In this case, you would create a backup directory with a LIST
file and a pfile in it, for example, sales.LIST and sales.pfile. Also in that directory, you would create
subdirectories for each day of the week, with a backup file, LIST file and pfile in each of them.
On Sunday, the sales.LIST file will look like this.
controlfile=Sun/o1_mf_s_774019590_7lhv06jn_.bkp
catalogstart=Sun
pfile=sales.pfile
level=0
NOTE For backwards compatibility, you can retain the level value, as shown for Sunday.
On Monday, the sales.LIST file will look like this.
controlfile=Mon/o1_mf_s_774002607_7lhbfhrm_.bkp
catalogstart=Mon
pfile=sales.pfile
level=1
Ensure that the level information in the LIST file is correct. Information at the wrong level will result in failure
of the refresh process. If you retain the level value for backwards compatibility, set it as shown for Monday.
In the directory containing the backup files, a LOCK file is generated during the ingestion and refresh processes
to coordinate the operation with external programs. The LOCK file uses the same naming convention as the
LIST file. If the LOCK exists at the beginning of an ingestion or refresh process, the process aborts.
92 VMware, Inc.
Page 93

Chapter 9 Managing Databases
Ingest an External Database
You ingest a database to reproduce a production environment and create a one-time (golden) clone. The
imported database is a clone of a physical database that exists outside of Data Director.
Prerequisites
n
Verify that you have access to the organization and database group in which to create the new database.
n
Verify that you have Ingest databases permission on the database group in which you create the new
database.
n
Verify that you have Use template permission on at least one resource template and backup template.
Procedure
1 Configure the Database Refresh Profile on page 93
The database refresh profile determines how, and how often, to refresh database data.
2 Configure the Ingestion Process Settings on page 94
The ingestion process settings specify the source of the database to ingest, the ingestion schedule, and
the maximum network bandwidth the ingestion process can use.
3 Enter General Database Information on page 95
Specify general information about the database, including name, database type and template, parameter
group, Point-In-Time Recovery allocation, and whether to take a snapshot backup after database creation
completes.
4 Refresh a Data Director Database from an External Database on page 95
You can refresh a database in Data Director from an external backup database. This is also known as an
in-place refresh.
Configure the Database Refresh Profile
The database refresh profile determines how, and how often, to refresh database data.
Procedure
1 Navigate to the organization and to the database group in which to create the database.
a Click the Manage & Monitor tab.
b Click the Databases tab.
c Click the plus (+) icon to start the Create Database wizard.
d Select Ingest external database and click Next.
2 Select One-time clone or Golden clone in catalog.
Option Description
One-time clone
Golden clone in catalog
One-time clones are not linked to the source database. After the database is
ingested, it is open and running, and you can modify data as required. You
can also refresh it froman external database by performing an in-place
refresh, but the original database will be removed.
A golden clone, once ingested, is marked as a catalog database and the virtual
machine is powered off. You cannot use it directly but must provision a
database from it. You can then refresh the target database from the source
database manually, or by scheduling incremental backups at regular
intervals.
VMware, Inc. 93
Page 94

VMware vFabric Data Director Administrator and User Guide
3 (Optional) If you selectGolden clone in catalog, you can select Take a snapshot before refreshing, and
select Automatic refresh and specify a refresh frequency and start time.
What to do next
Click Next to configure Ingestion Process Settings or click Back to make changes.
Configure the Ingestion Process Settings
The ingestion process settings specify the source of the database to ingest, the ingestion schedule, and the
maximum network bandwidth the ingestion process can use.
You can ingest an external database from backup files that reside in NFS shared storage.
Prerequisites
Complete the refresh profile configuration settings.
Procedure
1 (Optional) If you selected One-time clone in the Refresh Profile, enter the following information.
Field Option
NFS share name
Catalog start
Control file
Optional pfile
Refresh point
2 In the Scheduling Window section, select Run this action now to ingest the external database
immediately, or specify the ingestion start date and time.
(Required) NFS share containing the RMAN backup of the source database.
Root folder that contains the RMAN backup set. This is the relative path to
NFS Share. All backups under this directory are used for ingestion and
refresh. For example, if the daily backups for a database are stored under a
specific folder in the NFS share, catalog start should point to it.
(Required) Relative path to NFS Share. This is the control file used to restore
the database. It is a control file backup that includes a copy of the control file
and spfile.
Custom pfile.
Select Most recent backup or specify a point in time for the ingestion. For a
point in time ingestion, the backup set under the catalog start directory must
include a level 1 incremental backup.
3 Specify the maximum network bandwidth the ingestion process can use.
4 (Optional) If you selected Golden clone in catalog, enter the backup storage information, including the
NFS share name and relative path.
Data Director checks the specified NFS information to verify that the NFS server is accessible.
What to do next
Click Next to enter general database information.
94 VMware, Inc.
Page 95

Chapter 9 Managing Databases
Enter General Database Information
Specify general information about the database, including name, database type and template, parameter group,
Point-In-Time Recovery allocation, and whether to take a snapshot backup after database creation completes.
Procedure
1 Enter the following information.
Field Option
Name and Description
Database Type
Base DB Template
Database Group
Resource template
Data disk allocation
Backup template
PITR disk allocation
Expiration
Tags
Snapshot
IP Whitelist
2 On the Summary page, review the database information.
Type a name and, optionally, a description of the database.
Select a database type from the drop-down menu. For example, Oracle or
vFabric Postgres.
Select a base database template from which to create the database from the
drop-down menu. For example, Oracle 11.2.0.3
If you selected a database group, this field is filled in for you.
Select a database resource template from the drop-down menu. For example,
tiny, giant, and so on.
Select the data storage allocation for this database. The minimum is 1GB for
vFabric Postgres and 2GB for Oracle.
(Optional) Select a backup template from the drop-down menu. You can
select a backup template for specific purposes, such as development, or select
no backups (Disabled).
Select the number of gigabytes to allocate for point-in-time recovery
operations. The minimum is 1GB.
Select a date and time at which the database expires. Then select an action
upon expiration, or no expiration.
(Optional) Select one or more tags for this database. Use tags to filter the list
of databases that you view in an organization's Databases tab, for example,
all your customer relationship databases can have a tag called CRM.
(Optional) Select the check box to take a snapshot backup of the database
when creation and provisioning finishes.
Select Allow all connections to the database. Optionally, select Only allow
connections from selected IP whitelists (next page), and select an
organization IP whitelist or create a custom IP whitelist..
3 Click Finish to ingest the database.
If the ingested database is a one-time clone, the database appears in the databases list with a status of Creating.
The status changes to Running when the database is created. The process can take a few minutes. If the ingested
database is a golden clone, the database is added to the organization catalog with a status of Creating. The
status changes to Ready when the database is created.
Refresh a Data Director Database from an External Database
You can refresh a database in Data Director from an external backup database. This is also known as an inplace refresh.
Prerequisites
Verify that you have Create database permissions on the group.
Procedure
1 Click the Manage and Monitor tab in your organization.
VMware, Inc. 95
Page 96

VMware vFabric Data Director Administrator and User Guide
2 Right-click a database and select Refresh.
3 Enter the following information.
Field Option
NFS share name
Catalog start
Control file
Optional pfile
Refresh point
4 Click Refresh.
The database is refreshed, the original database is removed, and the database name (SID) of new database
becomes the database name (SID) of the external backup database.
(Required) NFS share containing the RMAN backup of the source database.
Root folder that contains the RMAN backup set. This is the relative path to
NFS Share. All backups under this directory are used for ingestion and
refresh. For example, if the daily backups for a database are stored under a
specific folder in the NFS share, catalog start should point to it.
(Required) Relative path to NFS Share. This is the control file used to restore
the database. It is a control file backup that includes a copy of the control file
and spfile.
Custom pfile.
Select Most recent backup or specify a point in time for the ingestion. For a
point in time ingestion, the backup set under the catalog start directory must
include a level 1 incremental backup.
Using Tags
Tags are text labels that users create and associate with databases. Users can create tags on any databases that
are visible to them. Tags provide a simple way to search for databases in a particular database group or
organization.
Users can see only the tags that they create.
Tags enable filtering on the list of databases that appear in an organization under theDatabases tab. For
example, a user can create a tag called HR and associate the tag with all of the HR databases in an organization.
When that user views the Databases tab, filtering on the HR tag displays only the databases with that tag.
You can associate a tag with a database during database creation. See “Create an Empty vFabric Postgres or
Oracle Database,” on page 87. You can also associate tags with an existing database.
Create a Tag
Tags provide a simple way to search for databases in a database group or organization.
Procedure
1 Log in to Data Director as an organization administrator.
2 Click the Manage and Monitor tab.
3 Click the Tags tab.
4 Click the plus (+) icon.
5 Type the name of the tag in the Create Tag dialog box and click OK.
96 VMware, Inc.
Page 97

Associate a Tag with an Existing Database
Tags support searches for databases. You can associate a tag with a database to help with searches for databases.
Procedure
1 Log in to Data Director as an organization administrator or as a user with Edit information and storage
permission.
2 Click the Manage & Monitor tab.
3 Click the Databases tab.
4 Right-click a database to display the Actions menu and select Properties.
5 Click the General tab, select a tag in the Tags field, and click Edit.
6 Click the check box for the tag or tags to associate with the database and click OK.
Managing the Organization Catalog
Organization administrators can add Data Director databases to the organization catalog. Organization users
create databases from the catalog when they need a database with known characteristics and preloaded data,
for example, when they test SQL scripts or usage scenarios.
Chapter 9 Managing Databases
Users cannot directly modify databases in the catalog and databases cannot power on. Organization
administrators can remove catalog databases when the databases are no longer needed.
Add a database to the organization catalog in one of the following ways.
n
Select a database from a database group's Databases tab.
n
Add a database using the organization's Catalog tab.
As part of the cataloging process, you choose whether to clone the database and add the clone to the catalog
or move the database into the catalog.
n
Clone the database to allow refreshing the catalog database from the source database. You can create a
full clone or a linked clone.
n
Move the database when you want to preserve the database in its current state with its current data.
Add a Database to the Catalog
You can add an existing Data Director database to the database group catalog, and use the catalog database to
create other databases with known characteristics and preloaded data. You cannot directly modify or power
on catalog databases.
Prerequisites
Verify that you have Create catalog items and Clone privileges at the organization or database group level.
Procedure
1 Log in to Data Director.
2 On the organization Manage and Monitor tab, select the database group.
3 Click Databases.
4 Right-click the database and select Add to Catalog.
VMware, Inc. 97
Page 98

VMware vFabric Data Director Administrator and User Guide
5 In the Add Databases to Catalog window, enter the following information.
Option Description
Source Database
Name
Description
Add Action
The default is the database that you selected . To add a different database to
the catalog, click Edit and select a database from the list.
Type a name for the catalog database. The default is the name of the database
that you entered earlier.
(Optional) Type a description of the catalog database.
To allow refreshing the catalog database from the source database, select
Clone source to catalog, and then select Full Clone or Linked Clone. To
disallow refreshing to the catalog database, select Move Source to Catalog.
You can move only a stopped database to the catalog.
6 Click OK.
The database is added to the database group catalog with the status Ready. You can now use it to create
databases.
Add a Database to the Catalog Using the Catalog Tab
You can add a database to the organization catalog, then create other databases from it.
Prerequisites
Verify that you have organization privileges.
Procedure
1 Click the organization Manage and Monitor tab and click the Catalog tab.
2 Click the plus (+) icon.
3 In the Add Databases to Catalog window, enter the following information.
Option Description
Source Database
Name
Description
Add Action
The default is the database that you selected . To add a different database to
the catalog, click Edit and select a database from the list.
Type a name for the catalog database. The default is the name of the database
that you entered earlier.
(Optional) Type a description of the catalog database.
To allow refreshing the catalog database from the source database, select
Clone source to catalog, and then select Full Clone or Linked Clone. To
disallow refreshing to the catalog database, select Move Source to Catalog.
You can move only a stopped database to the catalog.
4 Click OK.
The database is added to the database group catalog with the status Ready. You can now use it to create
databases.
Remove a Database From the Organization Catalog
Organization administrators can remove a database from the organization catalog, for example, when the
database becomes obsolete.
Prerequisites
Verify that you have organization and database privileges.
98 VMware, Inc.
Page 99

Procedure
1 Log in as an organization administrator or user with organization and database privileges.
2 In the organization Manage & Monitor tab, select Catalog.
3 Right-click the database and select Delete.
The database is removed from the organization catalog.
Batch Operations and Scheduled Tasks
You can run common database operations in batches, schedule common database operations to run in batches
on multiple databases, and schedule an operation to run on a single database at a particular time.
n
Batch operations start immediately and operate on multiple databases.
n
Scheduled batch operations start at a time that you specify and operate on multiple databases.
n
Scheduled operations start at a time that you specify and operate on a single database.
Batch operations and batch scheduled operations let you quickly perform the same action on multiple
databases. Scheduling operations singly or in batches allows you to run long or CPU-intensive processes at
optimum times for the system load.
You can perform batch processing with the following operations and tasks.
Chapter 9 Managing Databases
n
Start, stop, and restart databases.
n
Add databases to Favorites.
n
Schedule external and snapshot backups.
n
Batch recover databases from last state.
n
Perform updates.
n
Enable-Disable databases.
You can schedule a start time window for each task, but the order in which tasks run is not guaranteed. You
cannot schedule operations on a recurring basis.
Run Basic Batch Operations
Organization administrators and users with appropriate privileges can select multiple databases, and then run
an operation on the selected databases.
Prerequisites
Verify that you have appropriate database operations and management privileges for the operations that you
plan to perform.
Procedure
1 Log in to Data Director.
2 In the Manage & Monitor tab, select the database group.
3 In the Databases tab, select the databases on which to run an operation.
4 Right-click the selected database or databases and select the operation.
5 Perform actions as appropriate for the selected operation.
The operation runs on each of the selected databases.
VMware, Inc. 99
Page 100

VMware vFabric Data Director Administrator and User Guide
Schedule Actions
Organization administrators and users with appropriate privileges can schedule actions to run on one or more
databases.
Prerequisites
Verify that you have appropriate database operations and management privileges for the tasks that you plan
to schedule.
Procedure
1 Log in to Data Director.
2 In the Manage & Monitor tab, select the database group.
3 In the Databases tab, select one or more databases for which to schedule an operation.
4 Right-click the selected database or databases, select Schedule Action, and select the task.
5 Enter the schedule information in the scheduling window.
The operation runs on the selected database or databases at the scheduled time.
Updating Databases
Update Data Director databases to use features available in the latest release of your database software
(upgrade) or to incorporate enhancements to a database virtual machine (DBVM) or to its third-party tools.
Users with database permissions can update databases from the database group's Databases tab. You can take
a snapshot of the database before proceeding with an update, and you can choose to automatically cancel it if
the update fails.
Updates apply enhancements to a DBVM that are not necessarily database software upgrades. For example,
you can create a base DB template from an existing version and add third-party tools to the new base DB
template. You can apply the new base DB template to multiple databases by performing a batch update.
System administrators can define an update chain from one database template to another to allow database
users to perform updates. System administrators also can indicate how to update databases. Database update
modes include In-place update and Dump-restore update.
Update a Database
You can update a database to apply enhancements or software upgrades.
Prerequisites
Verify that the following conditions are met.
n
The system administrator has built and converted a base DBVM with proper update scripts and binary
updates, such as new third-party tools or database software upgrades.
n
The system administrator has enabled the base DB template on the resource bundle where the target
databases exist, and properly configured the base DB templates update chain.
n
You have appropriate privileges to access and update databases.
n
You have existing databases that require the updates contained in the new base DB template.
Procedure
1 Log in to an organization as a user with database privileges.
100 VMware, Inc.
 Loading...
Loading...