Page 1

vCloud Director Installation and
Configuration Guide
vCloud Director 1.5
This document supports the version of each product listed and
supports all subsequent versions until the document is replaced
by a new edition. To check for more recent editions of this
document, see http://www.vmware.com/support/pubs.
EN-000582-01
Page 2

vCloud Director Installation and Configuration Guide
You can find the most up-to-date technical documentation on the VMware Web site at:
http://www.vmware.com/support/
The VMware Web site also provides the latest product updates.
If you have comments about this documentation, submit your feedback to:
docfeedback@vmware.com
Copyright © 2010, 2011 VMware, Inc. All rights reserved. This product is protected by U.S. and international copyright and
intellectual property laws. VMware products are covered by one or more patents listed at
http://www.vmware.com/go/patents.
VMware is a registered trademark or trademark of VMware, Inc. in the United States and/or other jurisdictions. All other marks
and names mentioned herein may be trademarks of their respective companies.
VMware, Inc.
3401 Hillview Ave.
Palo Alto, CA 94304
www.vmware.com
2 VMware, Inc.
Page 3

Contents
VMware vCloud Director Installation and Configuration Guide 5
Overview of vCloud Director Installation and Configuration 7
1
vCloud Director Architecture 7
Configuration Planning 8
vCloud Director Hardware and Software Requirements 9
Creating a vCloud Director Server Group 25
2
Install and Configure vCloud Director Software on Any Member of a Server Group 26
Configure Network and Database Connections 27
Start or Stop vCloud Director Services 31
Install vCloud Director Software on Additional Servers 31
Create a Microsoft Sysprep Deployment Package 32
Uninstall vCloud Director Software 33
Upgrading vCloud Director 35
3
Use the Cell Management Tool to Quiesce and Shut Down A Server 36
Upgrade vCloud Director Software on Any Member of a Server Group 38
Upgrade the vCloud Director Database 40
Upgrade vCenter and ESX/ESXi Hosts 42
Upgrade vShield Manager 42
Reverting an Upgrade 43
vCloud Director Setup 45
4
Review the License Agreement 46
Enter the License Key 46
Create the System Administrator Account 46
Specify System Settings 46
Ready to Log In to vCloud Director 47
Index 49
VMware, Inc. 3
Page 4

vCloud Director Installation and Configuration Guide
4 VMware, Inc.
Page 5

VMware vCloud Director Installation and Configuration Guide
The VMware vCloud Director Installation and Configuration Guide provides information about installing
VMware vCloud Director software and configuring it to work with VMware vCenter™ to provide VMwareready VMware vCloud® services.
Intended Audience
This book is intended for anyone who wants to install and configure VMware vCloud Director software. The
information in this book is written for experienced system administrators who are familiar with Linux,
Windows, IP networks, and VMware vSphere®.
VMware, Inc. 5
Page 6

vCloud Director Installation and Configuration Guide
6 VMware, Inc.
Page 7

Overview of vCloud Director
Installation and Configuration 1
A VMware vCloud® combines a vCloud Director server group with the vSphere platform. You create a
vCloud Director server group by installing vCloud Director software on one or more servers, connecting the
servers to a shared database, and integrating the vCloud Director server group with vSphere.
VMware vCloud Director builds on the VMware vSphere® foundation and exposes virtualized shared
infrastructure as multitenant virtual datacenters that are decoupled from the underlying hardware and isolated
from one another. You can expose virtual datacenters to users through a Web-based portal and define and
expose a catalog of services that you can deploy within the virtual datacenter.
This chapter includes the following topics:
n
“vCloud Director Architecture,” on page 7
n
“Configuration Planning,” on page 8
n
“vCloud Director Hardware and Software Requirements,” on page 9
vCloud Director Architecture
A vCloud Director server group consists of one or more vCloud Director servers. These servers share a common
database, and are linked to an arbitrary number of vCenter servers and ESX/ESXi hosts. vShield Manager
servers provide network services to vCenter and vCloud Director.
VMware, Inc.
A simple cloud architecture might contain a vCloud Director server group comprising multiple servers. Each
server can run a collection of services called a vCloud Director cell. All servers in the group share a single
database. The group connects to multiple vCenter servers and the ESX/ESXi hosts that they manage. Each
vCenter server connects to a vShield Manager server.
7
Page 8
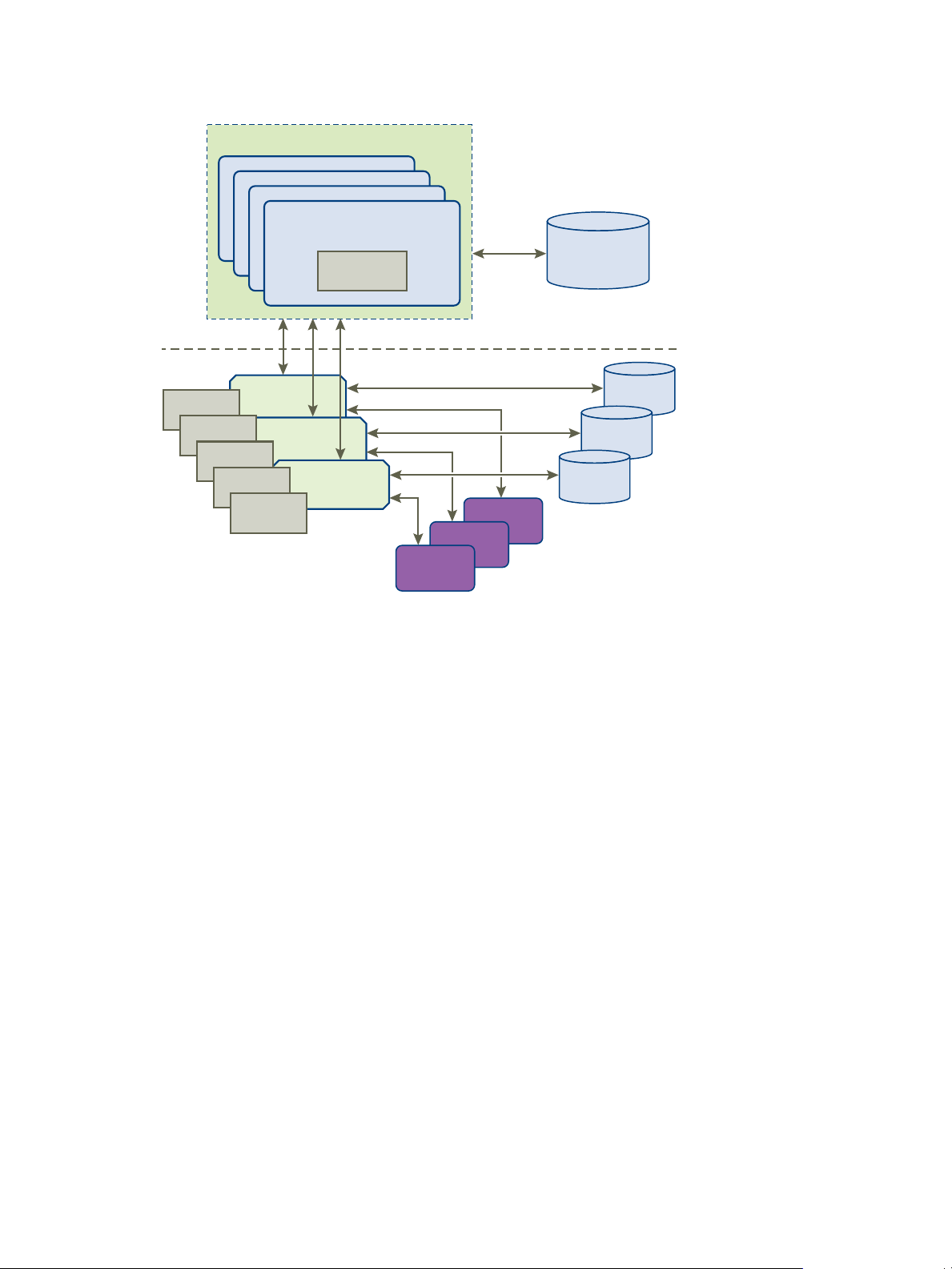
vCloud Director Server Group
vCloud Director
Server
Cell
vCloud Director
Database
VMware vCloud Director
VMware vSphere
vCenter
Database
vShield
ger
vShield
ger
vShield
Manager
vCenter
Database
vCenter
Database
vCenter
vCenter
vCenter
ESX/ESXi
ESX/ESXi
ESX/ESXi
ESX/ESXi
ESX/ESXi
vCloud Director Installation and Configuration Guide
Figure 1-1. vCloud Director Architecture Diagram
The vCloud Director installation and configuration process creates the cells, connects them to the shared
database, and establishes the first connections to a vCenter server, vShield Manager, and ESX/ESXi hosts. A
system administrator can then use the vCloud Director Web console to connect additional vCenter servers,
vShield Manager servers, and ESX/ESXi servers to the vCloud Director server group at any time.
Configuration Planning
vSphere provides storage, compute, and networking capacity to vCloud Director. Before you begin installation,
consider how much vSphere and vCloud Director capacity you need, and plan a configuration that can support
it.
Configuration requirements depend on many factors, including the number of organizations in the cloud, the
number of users in each organization, and the activity level of those users. The following guidelines can serve
as a starting point for most configurations:
n
Allocate one vCloud Director server (cell) for each vCenter server that you want to make accessible in
your cloud.
n
Be sure that all vCloud Director servers meet at least the minimum requirements for memory, CPU, and
storage detailed in “vCloud Director Hardware and Software Requirements,” on page 9.
n
Configure the vCloud Director database as described in “Installing and Configuring a vCloud Director
Database,” on page 15.
8 VMware, Inc.
Page 9

Chapter 1 Overview of vCloud Director Installation and Configuration
vCloud Director Hardware and Software Requirements
Each server in a vCloud Director server group must meet certain hardware and software requirements. In
addition, a supported database must be accessible to all members of the group. Each server group requires
access to a vCenter server, a vShield Manager server, and one or more ESX/ESXi hosts.
Supported vCenter, ESX/ESXi, and vShield Manager Versions
IMPORTANT The most current information about supported versions of ESX/ESXi and vCenter Server is
available from the VMware Product Interoperability Matrixes at
http://partnerweb.vmware.com/comp_guide/sim/interop_matrix.php.
Table 1-1. Supported vCenter Versions
vCenter Version Notes
4.0 Update 2
4.0 Update 3
4.1
4.1 Update 1
5.0 Required for Fast Provisioning, Hardware Version 8, and VPN support
Table 1-2. Supported ESX/ESXi Versions
ESX or ESXi Version Notes
4.0 Update 2
4.0 Update 3
4.1
4.1 Update 1
5.0 Required for Fast Provisioning and Hardware Version 8 support
Table 1-3. Supported vShield Manager Versions
vShield Manager Version Notes
1.0
1.0 Update 1
5.0 Required for static routing and VPN support
vSphere Configuration Requirements
vCenter servers and ESX/ESXi hosts intended for use with vCloud Director must meet specific configuration
requirements.
n
vCenter networks intended for use as vCloud Director external networks or network pools must be
available to all hosts in any cluster intended for vCloud Director to use. Making these networks available
to all hosts in a datacenter simplifies the task of adding new vCenter servers to vCloud Director.
n
DVS must be used for cross-host fencing and network pool allocation.
n
vCenter clusters used with vCloud Director must be configured to use automated DRS. Automated DRS
requires shared storage attached to all hosts in a DRS cluster.
n
vCenter 5 clusters used with vCloud Director must not enable storage DRS.
VMware, Inc. 9
Page 10

vCloud Director Installation and Configuration Guide
n
vCenter servers must trust their ESX/ESXi hosts.
vSphere Licensing Requirements
vCloud Director requires the following vSphere licenses:
n
VMware DRS, licensed by vSphere Enterprise and Enterprise Plus.
n
VMware Distributed Switch and dvFilter, licensed by vSphere Enterprise Plus. This license enables
creation and use of vCloud Director isolated networks.
Supported vCloud Director Server Operating Systems
Table 1-4. Supported vCloud Director Server Operating Systems
Operating System
Red Hat Enterprise Linux 5 (64 bit), Update 4
Red Hat Enterprise Linux 5 (64 bit), Update 5
Red Hat Enterprise Linux 5 (64 bit), Update 6
Disk Space
Requirements
Memory Requirements
Each vCloud Director server requires approximately 950MB of free space for
the installation and log files.
Each vCloud Director server must be provisioned with at least 1GB of memory.
2GB is recommended.
The required packages are typically installed by default with the operating system software. If any packages
are missing, the installer fails with a diagnostic message.
Table 1-5. Required Software Packages
Package Name Package Name Package Name
alsa-lib libICE module-init-tools
bash libSM net-tools
chkconfig libstdc pciutils
coreutils libX11 procps
findutils libXau redhat-lsb
glibc libXdmcp sed
grep libXext tar
initscripts libXi which
krb5-libs libXt
libgcc libXtst
Supported vCloud Director Databases
vCloud Director supports Oracle and Microsoft SQL Server databases. The most current information about
supported databases is available from the VMware Product Interoperability Matrixes at
http://partnerweb.vmware.com/comp_guide/sim/interop_matrix.php.
For recommended database server configurations, see “Installing and Configuring a vCloud Director
Database,” on page 15.
10 VMware, Inc.
Page 11

Chapter 1 Overview of vCloud Director Installation and Configuration
Supported LDAP Servers
Table 1-6. Supported LDAP Servers
Platform LDAP Server Authentication Methods
Windows Server 2003 Active Directory Simple, Simple SSL, Kerberos, Kerberos SSL
Windows Server 2008 Active Directory Simple
Windows 7 (2008 R2) Active Directory Simple, Simple SSL, Kerberos, Kerberos SSL
Linux OpenLDAP Simple, Simple SSL
Guest OS Support
vCloud Director supports virtual machines running the following guest operating systems.
Table 1-7. Guest OS Support
Guest OS ESX 4.0 U2 ESX 4.0 U3 ESX 4.1 ESX 4.1 U1 ESX 5.0
Windows Server 2008 R2 (x64) YES YES YES YES YES
Windows Server 2008 YES YES YES YES YES
Window 7 YES YES YES YES YES
Windows Vista YES YES YES YES YES
Windows XP/Embedded YES YES YES YES YES
Windows Server 2003 YES YES YES YES YES
Windows Server 2000 YES YES YES YES YES
Windows NT YES YES YES YES YES
CentOS 4/5 YES YES YES YES YES
SLES 11 YES YES No YES YES
SLES 10 YES YES YES YES
SLES 8,9 YES YES YES YES YES
Asianux 4 No No No No YES
Asianux 3 YES YES YES YES YES
RHEL 6 YES YES YES YES YES
RHEL 5 YES YES YES YES YES
RHEL 4 YES YES YES YES YES
RHEL 3 YES YES YES YES YES
RHEL 2 (x32) YES YES YES YES YES
Debian GNU/Linux 6 No No No No YES
Debian GNU/Linux 5 YES YES YES YES YES
Debian GNU/Linux 4 YES YES YES YES YES
Ubuntu YES YES YES YES YES
Oracle Enterprise Linux 4/5 YES YES No YES YES
Other 2.6.x Linux YES YES YES YES YES
Other 2.4.x Linux YES YES YES YES YES
Solaris 10 YES YES YES YES YES
VMware, Inc. 11
Page 12

vCloud Director Installation and Configuration Guide
Browsers That vCloud Director Supports
The vCloud Director Web Console is compatible with many versions of the Firefox and Internet Explorer Web
browsers.
NOTE The vCloud Director Web Console is compatible only with 32-bit browsers. Where a browser is listed
as supported on a 64-bit platform, use of a 32-bit browser on the 64-bit platform is implied.
Browsers Supported on Microsoft Windows Platforms
Table 1-8. Browser Support and Operating System Compatibility on Microsoft Windows Platforms
Internet
Platform
Windows XP Pro 32-bit YES YES No YES YES
Windows XP Pro 64-bit YES YES No YES YES
Windows Server 2003 Enterprise
Edition 32-bit
Windows Server 2003 Enterprise
Edition 64-bit
Windows Server 2008 YES YES YES YES N/A
Windows Server 2008 R2 No YES YES YES N/A
Windows Vista 32-bit YES YES YES YES YES
Windows Vista 64-bit YES YES YES No YES
Windows 7 32-bit No YES YES YES YES
Windows 7 64-bit No YES YES YES YES
Explorer 7.x
YES YES No YES YES
YES YES No YES YES
Internet
Explorer 8.x
Internet
Explorer 9.x
Firefox 3.6,
4.x Firefox 5.x
Browsers Supported Linux Platforms
Table 1-9. Browser Support and Operating System Compatibility on Linux Platforms
Platform Firefox 3 Firefox 4.x Firefox 5.x
Red Hat Enterprise Linux 5 (32 bit), Update6No YES YES
Red Hat Enterprise Linux 6 (32 bit) No YES YES
Red Hat Enterprise Linux 6 (64 bit) No YES YES
SLES 11 32-bit No YES YES
Ubuntu 10.10 32-bit No YES YES
Ubuntu 10.10 64-bit No YES YES
Supported Versions of Adobe Flash Player
The vCloud Director Web Console requires Adobe Flash Player version 10.2 or later. Only the 32-bit version
is supported.
Supported Versions of Java
vCloud Director clients must have JRE 1.6.0 update 10 or later installed and enabled. Only the 32-bit version
is supported.
12 VMware, Inc.
Page 13

Chapter 1 Overview of vCloud Director Installation and Configuration
Supported TLS and SSL Protocol Versions and Cipher Suites
vCloud Director requires clients to use SSL. Supported versions include SSL 3.0 and TLS 1.0. Supported cipher
suites include those with RSA, DSS, or Elliptic Curve signatures and DES3, AES-128, or AES-256 ciphers.
Summary of Network Configuration Requirements
Secure, reliable operation of vCloud Director depends on a secure, reliable network that supports forward and
reverse lookup of hostnames, a network time service, and other services. Your network must meet these
requirements before you begin installing vCloud Director.
The network that connects vCloud Director servers, the database server, vCenter servers, and vShield Manager
servers, must meet several requirements:
IP addresses
Console Proxy Address
Network Time Service
Hostname Resolution
Each vCloud Director server requires two IP addresses, so that it can support
two different SSL connections. One connection is for the HTTP service. The
other is for the console proxy service. You can use IP aliases or multiple network
interfaces to create these addresses. You cannot use the Linux ip addr add
command to create the second address .
The IP address configured as the console proxy address must not be located
behind an SSL-terminating load balancer or reverse proxy. All console proxy
requests must be relayed directly to the console proxy IP address.
You must use a network time service such as NTP to synchronize the clocks of
all vCloud Director servers, including the database server. The maximum
allowable drift between the clocks of synchronized servers is 2 seconds.
All host names that you specify during vCloud Director and vShield Manager
installation and configuration must be resolvable by DNS using forward and
reverse lookup of the fully qualified domain name or the unqualified hostname.
For example, for a host named mycloud.example.com, both of the following
commands must succeed on a vCloud Director host:
nslookup mycloud
nslookup mycloud.example.com
In addition, if the host mycloud.example.com has the IP address 192.168.1.1, the
following command must return mycloud.example.com:
nslookup 192.168.1.1
Transfer Server Storage
To provide temporary storage for uploads and downloads, an NFS or other
shared storage volume must be accessible to all servers in a vCloud Director
cluster. This volume must have write permission for root. Each host must
mount this volume at $VCLOUD_HOME/data/transfer,
typically /opt/vmware/vcloud-director/data/transfer. Uploads and
downloads occupy this storage for a few hours to a day. Transferred images
can be large, so allocate at least several hundred gigabytes to this volume.
VMware, Inc. 13
Page 14

vCloud Director Installation and Configuration Guide
Network Security Recommendations
Secure operation of vCloud Director requires a secure network environment. Configure and test this network
environment before you begin installing vCloud Director
Connect all vCloud Director servers to a network that is secured and monitored. vCloud Director network
connections have several additional requirements:
n
Do not connect vCloud Director directly to the public Internet. Always protect vCloud Director network
connections with a firewall. Only port 443 (HTTPS) must be open to incoming connections. Ports 22 (SSH)
and 80 (HTTP) can also be opened for incoming connections if needed. All other incoming traffic from a
public network must be rejected by the firewall.
Table 1-10. Ports That Must Allow Incoming Packets From vCloud Director Hosts
Port Protocol Comments
111 TCP, UDP NFS portmapper used by transfer service
920 TCP, UDP NFS rpc.statd used by transfer service
61611 TCP ActiveMQ
61616 TCP ActiveMQ
Do not connect the ports used for outgoing connections to the public network.
Table 1-11. Ports That Must Allow Outgoing Packets From vCloud Director Hosts
Port Protocol Comments
25 TCP, UDP SMTP
53 TCP, UDP DNS
111 TCP, UDP NFS portmapper used by transfer service
123 TCP, UDP NTP
389 TCP, UDP LDAP
443 TCP vCenter and ESX connections
514 UDP Optional. Enables syslog use
902 TCP vCenter and ESX connections
903 TCP vCenter and ESX connections
920 TCP, UDP NFS rpc.statd used by transfer service
1433 TCP Default Microsoft SQL Server database port
1521 TCP Default Oracle database port
5672 TCP, UDP Optional. AMQP messages for task extensions
61611 TCP ActiveMQ
61616 TCP ActiveMQ
n
Do not connect physical host computers to physical networks that are uplinks for the vNetwork distributed
switches that back vCloud Director network pools.
n
Route traffic between vCloud Director servers and the vCloud Director database server over a dedicated
private network if possible.
n
Virtual switches and distributed virtual switches that support provider networks must be isolated from
each other. They cannot share the same level 2 physical network segment.
14 VMware, Inc.
Page 15

Chapter 1 Overview of vCloud Director Installation and Configuration
Installing and Configuring a vCloud Director Database
vCloud Director cells use a database to store shared information. This database must exist before you can
complete installation and configuration of vCloud Director software.
NOTE Regardless of the database software you choose, you must create a separate, dedicated database schema
for vCloud Director to use. vCloud Director cannot share a database schema with any other VMware product.
Configure an Oracle Database
Oracle databases have specific configuration requirements when you use them with vCloud Director. Install
and configure a database instance and create the vCloud Director database user account the before you install
vCloud Director.
Procedure
1 Configure the database server.
A database server configured with 16GB of memory, 100GB storage, and 4 CPUs should be adequate for
most vCloud Director clusters.
2 Create the database instance.
Use commands of the following form to create separate data (CLOUD_DATA) and index (CLOUD_INDX)
tablespaces:
Create Tablespace CLOUD_DATA datafile '$ORACLE_HOME/oradata/cloud_data01.dbf' size 1000M
autoextend on;
Create Tablespace CLOUD_INDX datafile '$ORACLE_HOME/oradata/cloud_indx01.dbf' size 500M
autoextend on;
3 Create the vCloud Director database user account.
The following command creates database user name vcloud with password vcloudpass.
Create user $vcloud identified by $vcloudpass default tablespace CLOUD_DATA;
NOTE When you create the vCloud Director database user account, you must specify CLOUD_DATA as
the default tablespace.
4 Configure database connection, process, and transaction parameters.
The database must be configured to allow at least 75 connections per vCloud Director cell plus about 50
for Oracle's own use. You can obtain values for other configuration parameters based on the number of
connections, where C represents the number of cells in your vCloud Director cluster.
Oracle Configuration Parameter Value for C Cells
CONNECTIONS
PROCESSES
SESSIONS
TRANSACTIONS
OPEN_CURSORS
75*C+50
= CONNECTIONS
= PROCESSES*1.1+5
= SESSIONS*1.1
= SESSIONS
VMware, Inc. 15
Page 16

vCloud Director Installation and Configuration Guide
5 Create the vCloud Director database user account.
Do not use the Oracle system account as the vCloud Director database user account. You must create a
dedicated user account for this purpose. Grant the following system privileges to the account:
n
CONNECT
n
RESOURCE
n
CREATE TRIGGER
n
CREATE TYPE
n
CREATE VIEW
n
CREATE MATERIALIZED VIEW
n
CREATE PROCEDURE
n
CREATE SEQUENCE
6 Note the database service name so you can use it when you configure network and database connections.
To find the database service name, open the file $ORACLE_HOME/network/admin/tsnames.ora on the database
server and look for an entry of the following form:
(SERVICE_NAME = orcl.example.com)
Configure a Microsoft SQL Server Database
SQL Server databases have specific configuration requirements when you use them with vCloud Director.
Install and configure a database instance, and create the vCloud Director database user account before you
install vCloud Director.
vCloud Director database performance is an important factor in overall vCloud Director performance and
scalability. vCloud Director uses the SQL Server tmpdb file when storing large result sets, sorting data, and
managing data that is being concurrently read and modified. This file can grow significantly when
vCloud Director is experiencing heavy concurrent load. It is a good practice to create the tmpdb file on a
dedicated volume that has fast read and write performance. For more information about the tmpdb file and
SQL Server performance, see http://msdn.microsoft.com/en-us/library/ms175527.aspx.
Prerequisites
n
You must be familiar with Microsoft SQL Server commands, scripting, and operation.
n
To configure Microsoft SQL Server, log on to the SQL Server host computer using administrator
credentials. You can configure SQL server to run with the LOCAL_SYSTEM identity, or any identity with
the privilege to run a Windows service.
Procedure
1 Configure the database server.
A database server configured with 16GB of memory, 100GB storage, and 4 CPUs should be adequate for
most vCloud Director clusters.
2 Specify Mixed Mode authentication during SQL Server setup.
Windows Authentication is not supported when using SQL Server with vCloud Director.
16 VMware, Inc.
Page 17

Chapter 1 Overview of vCloud Director Installation and Configuration
3 Create the database instance.
The following script creates the database and log files, specifying the proper collation sequence.
USE [master]
GO
CREATE DATABASE [vcloud] ON PRIMARY
(NAME = N'vcloud', FILENAME = N'C:\vcloud.mdf', SIZE = 100MB, FILEGROWTH = 10% )
LOG ON
(NAME = N'vcdb_log', FILENAME = N'C:\vcloud.ldf', SIZE = 1MB, FILEGROWTH = 10%)
COLLATE Latin1_General_CS_AS
GO
The values shown for SIZE are suggestions. You might need to use larger values.
4 Set the transaction isolation level.
The following script sets the database isolation level to READ_COMMITTED_SNAPSHOT.
USE [vcloud]
GO
ALTER DATABASE [vcloud] SET SINGLE_USER WITH ROLLBACK IMMEDIATE;
ALTER DATABASE [vcloud] SET ALLOW_SNAPSHOT_ISOLATION ON;
ALTER DATABASE [vcloud] SET READ_COMMITTED_SNAPSHOT ON WITH NO_WAIT;
ALTER DATABASE [vcloud] SET MULTI_USER;
GO
For more about transaction isolation, see http://msdn.microsoft.com/en-us/library/ms173763.aspx.
5 Create the vCloud Director database user account.
The following script creates database user name vcloud with password vcloudpass.
USE [vcloud]
GO
CREATE LOGIN [vcloud] WITH PASSWORD = 'vcloudpass', DEFAULT_DATABASE =[vcloud],
DEFAULT_LANGUAGE =[us_english], CHECK_POLICY=OFF
GO
CREATE USER [vcloud] for LOGIN [vcloud]
GO
6 Assign permissions to the vCloud Director database user account.
The following script assigns the db_owner role to the database user created in Step 5.
USE [vcloud]
GO
sp_addrolemember [db_owner], [vcloud]
GO
Create SSL Certificates
vCloud Director requires SSL to secure communications between clients and servers. Before you install and
configure a vCloud Director server group, you must create two certificates for each member of the group and
import the certificates into host keystores.
Each vCloud Director server that you intend to use in a vCloud Director cluster requires two SSL certificates,
one for each of its IP addresses.
NOTE All directories in the pathname to the SSL certificates must be readable by the user vcloud.vcloud. This
user is created by the vCloud Director installer.
VMware, Inc. 17
Page 18

vCloud Director Installation and Configuration Guide
Procedure
1 List the IP addresses for this server.
Use a command like ifconfig to discover this server's IP addresses.
2 For each IP address, run the following command to retrieve the fully qualified domain name to which the
IP address is bound.
nslookup
ip-address
3 Make a note of each IP address, the fully qualified domain name associated with it, and whether
vCloud Director should use the address for the HTTP service or the console proxy service.
You need the fully qualified domain names when you create the certificates, and the IP addresses when
you configure network and database connections.
4 Create the certificates.
You can use certificates signed by a trusted certification authority, or self-signed certificates. Signed
certificates provide the highest level of trust.
Create and Import a Signed SSL Certificate
Signed certificates provide the highest level of trust for SSL communications.
Each vCloud Director server requires two SSL certificates, one for each of its IP addresses, in a Java keystore
file. You must create two SSL certificates for each server that you intend to use in your vCloud Director server
group. You can use certificates signed by a trusted certification authority, or self-signed certificates. Signed
certificates provide the highest level of trust.
To create and import self-signed certificates, see “Create a Self-Signed SSL Certificate,” on page 20.
Prerequisites
n
Generate a list of fully-qualified domain names and their associated IP addresses on this server, along
with a service choice for each IP address. See “Create SSL Certificates,” on page 17.
n
Verify that you have access to a computer that has a Java version 6 runtime environment, so that you can
use the keytool command to create the certificate. The vCloud Director installer places a copy of
keytool in /opt/vmware/vcloud-director/jre/bin/keytool, but you can perform this procedure on any
computer that has a Java version 6 runtime environment installed. Certificates created with a keytool from
any other source are not supported for use with vCloud Director. Creating and importing the certificates
before you install and configure vCloud Director software simplifies the installation and configuration
process. These command-line examples assume that keytool is in the user's path. The keystore password
is represented in these examples as passwd.
Procedure
1 Create an untrusted certificate for the HTTP service.
This command creates an untrusted certificate in a keystore file named certificates.ks.
passwd
keytool -keystore certificates.ks -storetype JCEKS -storepass
alias http
-genkey -keyalg RSA -
2 Answer the keytool questions.
When keytool asks for your first and last name, type the fully qualified domain name associated with the
IP address you want to use for the HTTP service.
18 VMware, Inc.
Page 19

Chapter 1 Overview of vCloud Director Installation and Configuration
3 For the remaining questions, provide answers appropriate for your organization and location, as shown
in this example.
What is your first and last name? [Unknown]:mycloud.example.com
What is the name of your organizational unit? [Unknown]:Engineering
What is the name of your organization? [Unknown]:Example Corporation
What is the name of your City or Locality? [Unknown]:Palo Alto
What is the name of your State or Province? [Unknown]:California
What is the two-letter country code for this unit? [Unknown]:US
Is CN=mycloud.example.com, OU=Engineering, O="Example Corporation", L="Palo Alto",
ST=California, C=US correct?[no]:yes
Enter key password for <http> (RETURN if same as keystore password):
4 Create a certificate signing request for the HTTP service.
This command creates a certificate signing request in the file http.csr.
keytool -keystore certificates.ks -storetype JCEKS -storepass
file http.csr
passwd
-certreq -alias http -
5 Create an untrusted certificate for the console proxy service.
This command adds an untrusted certificate to the keystore file created in Step 1.
keytool -keystore certificates.ks -storetype JCEKS -storepass
alias consoleproxy
passwd
-genkey -keyalg RSA -
6 When keytool asks for your first and last name, type the fully-qualified domain name associated with the
IP address you want to use for the console proxy service.
7 For the remaining questions, provide answers appropriate for your organization and location, as shown
in the example in Step 1.
8 Create a certificate signing request for the console proxy service.
This command creates a certificate signing request in the file consoleproxy.csr.
passwd
keytool -keystore certificates.ks -storetype JCEKS -storepass
consoleproxy -file consoleproxy.csr
-certreq -alias
9 Send the certificate signing requests to your Certification Authority.
10 When you receive the signed certificates, import them into the keystore file.
a Import the Certification Authority's root certificate into the keystore file.
This command imports the root certificate from the root.cer file to the certificates.ks keystore file.
keytool -storetype JCEKS -storepass
-file root.cer
passwd
-keystore certificates.ks -import -alias root
b (Optional) If you received intermediate certificates, import them into the keystore file.
This command imports intermediate certificates from the intermediate.cer file to the
certificates.ks keystore file.
keytool -storetype JCEKS -storepass
intermediate -file intermediate.cer
VMware, Inc. 19
passwd
-keystore certificates.ks -import -alias
Page 20

vCloud Director Installation and Configuration Guide
c Import the certificate for the HTTP service.
This command imports the certificate from the http.cer file to the certificates.ks keystore file.
keytool -storetype JCEKS -storepass
-file http.cer
passwd
-keystore certificates.ks -import -alias http
d Import the certificate for the console proxy service.
This command imports the certificate from the consoleproxy.cer file to the certificates.ks keystore
file.
keytool -storetype JCEKS -storepass
consoleproxy -file consoleproxy.cer
passwd
-keystore certificates.ks -import -alias
11 To verify that all the certificates are imported, list the contents of the keystore file.
keytool -storetype JCEKS -storepass
passwd
-keystore certificates.ks -list
12 Repeat steps Step 1 through Step 11 on each of the remaining vCloud Director servers.
What to do next
If you created the certificates.ks keystore file on a computer other than the server on which you generated
the list of fully qualified domain names and their associated IP addresses, copy the keystore file to that server
now. You will need the keystore path name when you run the configuration script. See “Configure Network
and Database Connections,” on page 27.
NOTE Because thevCloud Director configuration script does not run with a privileged identity, the keystore
file and the directory in which it is stored must be readable by any user.
Create a Self-Signed SSL Certificate
Self-signed certificates can provide a convenient way to configure SSL for vCloud Director in environments
where trust concerns are minimal.
Each vCloud Director server requires two SSL certificates, one for each of its IP addresses, in a Java keystore
file. You must create two SSL certificates for each server that you intend to use in your vCloud Director server
group. You can use certificates signed by a trusted certification authority, or self-signed certificates. Signed
certificates provide the highest level of trust.
To create and import signed certificates, see “Create and Import a Signed SSL Certificate,” on page 18.
Prerequisites
n
Generate a list of fully-qualified domain names and their associated IP addresses on this server, along
with a service choice for each IP address. See “Create SSL Certificates,” on page 17.
n
Verify that you have access to a computer that has a Java version 6 runtime environment, so that you can
use the keytool command to create the certificate. The vCloud Director installer places a copy of
keytool in /opt/vmware/vcloud-director/jre/bin/keytool, but you can perform this procedure on any
computer that has a Java version 6 runtime environment installed. Certificates created with a keytool from
any other source are not supported for use with vCloud Director. Creating and importing the certificates
before you install and configure vCloud Director software simplifies the installation and configuration
process. These command-line examples assume that keytool is in the user's path. The keystore password
is represented in these examples as passwd.
20 VMware, Inc.
Page 21

Chapter 1 Overview of vCloud Director Installation and Configuration
Procedure
1 Create an untrusted certificate for the HTTP service.
This command creates an untrusted certificate in a keystore file named certificates.ks.
keytool -keystore certificates.ks -storetype JCEKS -storepass
alias http
passwd
-genkey -keyalg RSA -
2 Create an untrusted certificate for the console proxy service.
This command adds an untrusted certificate to the keystore file created in Step 1.
keytool -keystore certificates.ks -storetype JCEKS -storepass
alias consoleproxy
passwd
-genkey -keyalg RSA -
3 To verify that all the certificates are imported, list the contents of the keystore file.
keytool -storetype JCEKS -storepass
passwd
-keystore certificates.ks -list
4 Repeat Step 1 through Step 3 on each of the remaining vCloud Director servers.
What to do next
If you created the certificates.ks keystore file on a computer other than the server on which you generated
the list of fully qualified domain names and their associated IP addresses, copy the keystore file to that server
now. You will need the keystore path name when you run the configuration script. See “Configure Network
and Database Connections,” on page 27.
NOTE Because thevCloud Director configuration script does not run with a privileged identity, the keystore
file and the directory in which it is stored must be readable by any user.
Installing and Configuring vShield Manager
vCloud Director depends on vShield Manager to provide network services to the cloud. Install and configure
vShield Manager before you begin installing vCloud Director.
You must associate each vCenter Server that you add to vCloud Director with a unique instance of vShield
Manager. For information about the network requirements and supported versions of vShield Manager, see
“vCloud Director Hardware and Software Requirements,” on page 9.
IMPORTANT This procedure applies only to new installations of vCloud Director. If you are upgrading an
existing installation of vCloud Director, you can optionally upgrade its associated vShield Manager
installation. A new release of vShield Manager cannot work with an existing release of vCloud Director. See
“Upgrade vShield Manager,” on page 42.
Procedure
1 Use the vSphere Client to log in to your vCenter Server.
2 Select File > Deploy OVF Template.
3 Browse to the location of the vShield Manager.ovf file and follow the prompts to deploy the OVF file.
4 After the OVF file is deployed, power on the vShield Manager virtual machine and open the console.
5 Log in to the console with the user name admin and password default.
6 At the manager prompt, type enable.
7 At the Password prompt, type default to enable setup mode.
When setup mode is enabled, the prompt string changes to manager#.
8 At the manager# prompt, type setup to begin the setup procedure.
VMware, Inc. 21
Page 22

vCloud Director Installation and Configuration Guide
9 Enter the IP address, subnet mask, and default gateway for the vShield Manager virtual machine.
You need this information to attach a vCenter Server to Cloud Director.
10 Type exit to log out.
11 Close the console and leave the virtual machine running.
It is not necessary to synchronize vShield Manager with vCenter or register the vShield Manager as a
vSphere Client plug-in when you use vShield Manager with vCloud Director.
Installing and Configuring an AMQP Broker
AMQP, the Advanced Message Queuing Protocol, is an open standard for message queuing that supports
flexible messaging for enterprise systems. vCloud Director includes an AMQP service that you can configure
to work with an AMQP broker, such as RabbitMQ, to provide cloud operators with a stream of notifications
about events in the cloud. If you want to use this service, you must install and configure an AMQP broker.
Procedure
1 Download the RabbitMQ Server from http://info.vmware.com/content/12834_rabbitmq.
2 Follow the RabbitMQ installation instructions to install RabbitMQ on any convenient host.
The RabbitMQ server host must be reachable on the network by each vCloud Director cell.
3 During the RabbitMQ installation, make a note of the values that you will need to supply when configuring
vCloud Director to work with this RabbitMQ installation.
n
The fully-qualified domain name of the RabbitMQ server host, for example amqp.example.com.
n
A username and password that are valid for authenticating with RabbitMQ.
n
The port at which the broker listens for messages. The default is 5672.
n
The RabbitMQ virtual host. The default is "/".
What to do next
By default, the vCloud Director AMQP service sends unencrypted messages. If you configure it to encrypt
these messages using SSL, it verifies the broker's certificate by using the default JCEKS trust store of the Java
runtime environment on the vCloud Director server. The Java runtime environment is typically located in the
$JRE_HOME/lib/security/cacerts directory.
To use SSL with the vCloud Director AMQP service, select Use SSL on the AMQP Broker Settings section of
the Blocking Tasks page of the vCloud Director Web console provide an SSL certificate pathname or JCEKS
trust store pathname and password. If you do not want to validate certificates, because you trust all the
computers that connect to the vCloud Director AMQP service, you can select Accept all certificates.
Download and Install the VMware Public Key
The installation file is digitally signed. To verify the signature, you must download and install the VMware
public key.
You can use the Linux rpm tool and the VMware public key to verify the digital signature of the
vCloud Director installation file, or any other signed downloaded file from vmware.com. If you install the public
key on the computer where you plan to install vCloud Director, the verification happens as part of the
installation or upgrade. You can also manually verify the signature before you begin the installation or upgrade
procedure, then use the verified file for all installations or upgrades.
NOTE The download site also publishes a checksum value for the download. The checksum is published in
two common forms. Verifying the checksum verifies that the file contents that you downloaded are the same
as the contents that were posted. It does not verify the digital signature.
22 VMware, Inc.
Page 23

Chapter 1 Overview of vCloud Director Installation and Configuration
Procedure
1 Obtain and import the VMware Packaging Public Keys.
a Create a directory to store the VMware Packaging Public Keys.
b Use a Web browser to download all of the VMware Public Packaging Public Keys from the
http://packages.vmware.com/tools/keys directory.
c Save the key files to the directory that you created.
d For each key that you download, run the following command to import the key.
# rpm --import /
key_path/key_name
key_path is the directory in which you saved the keys.
key_name is the filename of a key.
2 (Optional) Use the Linux rpm tool to verify the digital signature of the downloaded file.
# rpm --checksig
installation-file
After you verify the digital signature of the file, you can use it to install or upgrade vCloud Director on
any server, without having to install the public key on that server. The installer warns you if no key is
installed. You can ignore the warning if you already verified the signature of the file.
VMware, Inc. 23
Page 24

vCloud Director Installation and Configuration Guide
24 VMware, Inc.
Page 25

Creating a vCloud Director Server
Group 2
A vCloud Director server group consists of one or more vCloud Director servers. Each server in the group runs
a collection of services called a vCloud Director cell. To create a server group, you install vCloud Director
software on each server, configure its network and database connections, and start its vCloud Director services.
Prerequisites for Creating a vCloud Director Server Group
IMPORTANT This procedure is for new installation only. If you are upgrading an existing vCloud Director
installation, see Chapter 3, “Upgrading vCloud Director,” on page 35
Before you begin installing and configuring vCloud Director, complete all of the following tasks.
1 Verify that a supported vCenter server is running and properly configured for use with
vCloud Director. For supported versions and configuration requirements, see “Supported vCenter,
ESX/ESXi, and vShield Manager Versions,” on page 9.
2 Verify that a supported vShield Manager server is running and properly configured for use with
vCloud Director. For supported versions, see “Supported vCenter, ESX/ESXi, and vShield Manager
Versions,” on page 9. For installation and configuration details, see “Installing and Configuring vShield
Manager,” on page 21.
VMware, Inc.
3 Verify that you have at least one supported vCloud Director server platform running and configured with
an appropriate amount of memory and storage. For supported platforms and configuration requirements,
see “Supported vCloud Director Server Operating Systems,” on page 10.
n
Each member of a server group requires two IP addresses: one to support an SSL connection for the
HTTP service and another for the console proxy service.
n
Each server must have an SSL certificate for each IP address. All directories in the pathname to the
SSL certificates must be readable by the uservcloud.vcloud. This user is created by the
vCloud Director installer. See “Create SSL Certificates,” on page 17.
n
For the transfer service, each server must mount an NFS or other shared storage volume at
$VCLOUD_HOME/data/transfer, typically /opt/vmware/vcloud-director/data/transfer. This volume
must have write permission for root.
n
Each server should have access to a Microsoft Sysprep deployment package. See “Create a Microsoft
Sysprep Deployment Package,” on page 32.
4 Verify that you have created a vCloud Director database and that it is accessible to all servers in the group.
For a list of supported database software, see “Supported vCloud Director Databases,” on page 10.
n
Verify that you have an account for the vCloud Director database user and the required system
privileges. See “Installing and Configuring a vCloud Director Database,” on page 15.
n
Verify that the database service starts when the database server is rebooted.
25
Page 26

vCloud Director Installation and Configuration Guide
5 Verify that all vCloud Director servers, the database server, and all vCenter and vShield Manager servers
can resolve each other's names as described in “Summary of Network Configuration Requirements,” on
page 13.
6 Verify that all vCloud Director servers and the database server are synchronized to a network time server.
7 If you plan to import users or groups from an LDAP service, verify that the service is accessible to each
vCloud Director server.
8 Open firewall ports as shown in “Network Security Recommendations,” on page 14. Port 443 must be
open between vCloud Director and vCenter servers.
This chapter includes the following topics:
n
“Install and Configure vCloud Director Software on Any Member of a Server Group,” on page 26
n
“Configure Network and Database Connections,” on page 27
n
“Start or Stop vCloud Director Services,” on page 31
n
“Install vCloud Director Software on Additional Servers,” on page 31
n
“Create a Microsoft Sysprep Deployment Package,” on page 32
n
“Uninstall vCloud Director Software,” on page 33
Install and Configure vCloud Director Software on Any Member of a Server Group
The vCloud Director installer verifies that the target server meets all prerequisites and installs
vCloud Director software on it.
vCloud Director software is distributed as a digitally signed Linux executable file named vmware-vcloud-
director-1.5.0-nnnnnn.bin, where nnnnnn represents a build number. After the software is installed on the
target server, you must run a script that configures the server's network and database connections.
Prerequisites
n
Verify that the target server and the network it connects to meet the requirements specified in “Summary
of Network Configuration Requirements,” on page 13.
n
Verify that you have superuser credentials for the target server.
n
If you intend to create a vCloud Director server group that includes multiple servers, verify that the target
server mounts the shared transfer service storage at $VCLOUD_HOME/data/transfer.
n
If you want the installer to verify the digital signature of the installation file, download and install the
VMware public key on the target server. If you have already verified the digital signature of the installation
file, you do not need to verify it again during installation. See “Download and Install the VMware Public
Key,” on page 22.
Procedure
1 Log in to the target server as root.
2 Download the installation file to the target server.
If you purchased the software on a CD or other media, copy the installation file to a location that is
accessible to all target servers.
26 VMware, Inc.
Page 27

Chapter 2 Creating a vCloud Director Server Group
3 Verify that the checksum of the download matches the one posted on the download page.
Values for both MD5 and SHA1 checksums are posted on the download page. Use the appropriate tool
to verify that the checksum of the downloaded installation file matches the one shown on the download
page. A command of the following form validates the checksum for installation-file using the MD5
checksum-value copied from the download page.
md5sum -c
checksum-value installation-file
4 Ensure that the installation file is executable.
The installation file requires execute permission. To be sure that it has this permission, open a console,
shell, or terminal window and run the following command, where installation-file is the full pathname to
the vCloud Director installation file.
chmod u+x
installation-file
5 In a console, shell, or terminal window, run the installation file.
To run the installation file, type its full pathname, for example ./
installation-file
. The file includes an
installation script and an embedded RPM package.
NOTE You cannot run the installation file from a directory whose pathname includes any embedded space
characters.
The installer verifies that the host meets all requirements, verifies the digital signature on the installation
file, unpacks the vCloud Director RPM package, and installs the software. The installer prints a warning
of the following form if you have not installed the VMware public key on the target server.
warning:
installation-file
.rpm: Header V3 RSA/SHA1 signature: NOKEY, key ID 66fd4949
After the software is installed, the installer prompts you to run the configuration script. The script
configures the server's network and database connections.
6 Decide when to run the configuration script.
Option Description
Run the configuration script now
Run the configuration script later
Type y and press Enter.
Type n and press Enter to exit to the shell.
For more information about running the configuration script, see “Configure Network and Database
Connections,” on page 27.
Configure Network and Database Connections
After vCloud Director software is installed on the server, the installer prompts you to run a script that
configures network and database connection details.
You must install vCloud Director software on the server before you can run the configuration script. The
installer prompts you to run the script after installation is complete, but you can run it later. To run the script
as a separate operation after the vCloud Director software is installed, log in as root, open a console, shell, or
terminal window, and type:
/opt/vmware/vcloud-director/bin/configure
The configuration script creates network and database connections for a single vCloud Director server. The
script also creates a response file that preserves database connection information for use in subsequent server
installations.
VMware, Inc. 27
Page 28

vCloud Director Installation and Configuration Guide
Prerequisites
n
Verify that a database of a supported type is accessible from the vCloud Director server. See “Installing
and Configuring a vCloud Director Database,” on page 15 and “vCloud Director Hardware and Software
Requirements,” on page 9.
n
Have the following information available:
n
Location and password of the keystore file that includes the SSL certificates for this server. See “Create
and Import a Signed SSL Certificate,” on page 18. The configuration script does not run with a
privileged identity, so the keystore file and the directory in which it is stored must be readable by
any user.
n
Password for each SSL certificate.
n
Hostname or IP address of the database server.
n
Database name and connection port.
n
Database user credentials (user name and password). This user must have specific database
privileges. See “Installing and Configuring a vCloud Director Database,” on page 15.
Procedure
1 Specify the IP addresses to use for the HTTP and console proxy services running on this host.
Each member of a server group requires two IP addresses, so that it can support two different SSL
connections: one for the HTTP service an another for the console proxy service. To begin the configuration
process, choose which of the IP addresses discovered by the script should be used for each service.
Please indicate which IP address available on this machine should be used
for the HTTP service and which IP address should be used for the remote console proxy.
The HTTP service IP address is used for accessing the user interface and the REST API.
The remote console proxy IP address is used for all remote console (VMRC) connections
and traffic.
Please enter your choice for the HTTP service IP address:
1: 10.17.118.158
2: 10.17.118.159
Choice [default=1]:2
Please enter your choice for the remote console proxy IP address
1: 10.17.118.158
Choice [default=1]:
2 Specify the full path to the Java keystore file.
Please enter the path to the Java keystore containing your SSL certificates and
private keys:/opt/keystore/certificates.ks
3 Type the keystore and certificate passwords.
Please enter the password for the keystore:
Please enter the private key password for the 'http' SSL certificate:
Please enter the private key password for the 'consoleproxy' SSL certificate:
28 VMware, Inc.
Page 29

Chapter 2 Creating a vCloud Director Server Group
4 Configure audit message handling options.
Services in each vCloud Director cell log audit messages to the vCloud Director database, where they are
preserved for 90 days. To preserve audit messages longer, you can configure vCloud Director services to
send audit messages to the syslog utility in addition to the vCloud Director database.
Option Action
To log audit messages to both
syslog and the vCloud Director
database.
To log audit messages only to the
vCloud Director database
Type the syslog hostname or IP address.
Press Enter.
If you would like to enable remote audit logging to a syslog
host please enter the hostname or IP address of the syslog server. Audit logs are stored by
vCloud Director for 90 days. Exporting logs via syslog will enable you to
preserve them for as long as necessary.
Syslog host name or IP address [press Enter to skip]:10.150.10.10
5 Specify the port on which the syslog process monitors the specified server.
The default is port 514.
What UDP port is the remote syslog server listening on? The
standard syslog port is 514. [default=514]:
Using default value "514" for syslog port.
6 Specify the database type, or press Enter to accept the default value.
The following database types are supported:
1. Oracle
2. Microsoft SQL Server
Enter the database type [default=1]:
Using default value "1" for database type.
7 Specify database connection information.
The information that the script requires depends on your choice of database type. This example shows the
prompts that follow specification of an Oracle database. Prompts for other database types are similar.
a Type the hostname or IP address of the database server.
Enter the host (or IP address) for the database:10.150.10.78
b Type the database port, or press Enter to accept the default value.
Enter the database port [default=1521]:
Using default value "1521" for port.
c Type the database service name.
Enter the database service name [default=oracle]:orcl.example.com
If you press Enter, the configuration script uses a default value, which might not be correct for some
installations. For information about how to find the database service name for an Oracle database,
see “Configure an Oracle Database,” on page 15.
d Type the database user name and password.
Enter the database username:vcloud
Enter the database password:
VMware, Inc. 29
Page 30

vCloud Director Installation and Configuration Guide
The script validates the information you supplied, then continues with three more steps.
1 It initializes the database and connects this server to it.
2 It offers to start vCloud Director services on this host.
3 It displays a URL at which you can connect to the Setup wizard after vCloud Director service starts.
This fragment shows a typical completion of the script.
Connecting to the database: jdbc:oracle:thin:vcloud/vcloud@10.150.10.78:1521/vcloud
...........
Database configuration complete.
Once the vCloud Director server has been started you will be able to
access the first-time setup wizard at this URL:
http://vcloud.example.com
Would you like to start the vCloud Director service now? If you choose not
to start it now, you can manually start it at any time using this command:
service vmware-vcd start
Start it now? [y/n]:y
Starting the vCloud Director service (this may take a moment).
The service was started; it may be several minutes before it is ready for use.
Please check the logs for complete details.
vCloud Director configuration is now complete. Exiting...
What to do next
NOTE Database connection information and other reusable responses you supplied during configuration are
preserved in a file located at /opt/vmware/vcloud-director/etc/responses.properties on this server. This file
contains sensitive information that you must reuse when you add more servers to a server group. Preserve the
file in a secure location, and make it available only when needed.
To add more servers to this group, see “Install vCloud Director Software on Additional Servers,” on
page 31.
After vCloud Director services are running on all servers, you can open the Setup wizard at the URL displayed
when the script completes. See Chapter 4, “vCloud Director Setup,” on page 45.
Protecting and Reusing the Response File
Network and database connection details that you supply when you configure the first vCloud Director server
are saved in a response file. This file contains sensitive information that you must reuse when you add more
servers to a server group. Preserve the file in a secure location, and make it available only when needed.
The response file is created at /opt/vmware/vcloud-director/etc/responses.properties on the first server for
which you configure network and database connections. When you add more servers to the group, you must
use a copy of the response file to supply configuration parameters that all servers share.
Procedure
1 Protect the response file.
Save a copy of the file in a secure location. Restrict access to it, and make sure it is backed up to a secure
location. When you back up the file, avoid sending cleartext across a public network.
30 VMware, Inc.
Page 31

2 Reuse the response file.
Copy the file to a location accessible to the servers you are ready to configure. The file must be owned by
vcloud.vcloud and have read and write permission for the owner, as shown in this example, or the
configuration script cannot use it.
% ls -l responses.properties
-rw------- 1 vcloud vcloud 418 Jun 8 13:42
responses.properties
What to do next
After you configure the additional servers, delete the copy of the response file you used to configure them.
Start or Stop vCloud Director Services
After you complete installation and database connection setup on a server, you can start vCloud Director
services on it. You can also stop these services if they are running.
The configuration script prompts you to start vCloud Director services. You can let the script start these services
for you, or you can start the services yourself later. These services must be running before you can complete
and initialize the installation.
vCloud Director services start whenever you reboot a server.
Chapter 2 Creating a vCloud Director Server Group
IMPORTANT If you are stopping vCloud Director services as part of a vCloud Director software upgrade, you
must download and use the cell management tool. This tool allows you to quiesce the cell before stopping
services. See “Use the Cell Management Tool to Quiesce and Shut Down A Server,” on page 36.
Procedure
1 Log in to the target server as root.
2 Start or stop services.
Option Action
Start services
Stop services when the cell is in use
Stop services when the cell is not in
use
Open a console, shell, or terminal window and run the following command.
service vmware-vcd start
Use the cell management tool. See “Use the Cell Management Tool to Quiesce
and Shut Down A Server,” on page 36
Open a console, shell, or terminal window and run the following command.
service vmware-vcd stop
Install vCloud Director Software on Additional Servers
You can add servers to a vCloud Director server group at any time. All servers in a server group must be
configured with the same database connection details. To ensure that this requirement is met, use the response
file that the first server installation creates to supply this information when you install additional servers.
Prerequisites
A copy of the response file created when you installed the first server in this installation must be accessible to
any additional servers that you add to the group. See “Protecting and Reusing the Response File,” on
page 30.
Procedure
1 Log in to the target server as root.
VMware, Inc. 31
Page 32

vCloud Director Installation and Configuration Guide
2 Download the installation file to the target server.
If you purchased the software on a CD or other media, copy the installation file to a location that is
accessible to all target servers.
3 Ensure that the installation file is executable.
The installation file requires execute permission. To be sure that it has this permission, open a console,
shell, or terminal window and run the following command, where installation-file is the full pathname to
the vCloud Director installation file.
chmod u+x
installation-file
4 Run the installation file, supplying the pathname of the response file.
Specify the -r option on the installation command line, and supply the full pathname to the response file
as the argument to that option.
installation-file
-r
path-to-response-file
5 (Optional) Repeat this procedure for any additional servers to add to this installation.
The installer requests network connection information and sets up network and database connections using
the responses from the response file.
What to do next
After the configuration script finishes and vCloud Director services are running on all servers, you can open
the Setup wizard at the URL that appears when the script completes. See Chapter 4, “vCloud Director
Setup,” on page 45.
Create a Microsoft Sysprep Deployment Package
Before vCloud Director can perform guest customization on virtual machines with certain Windows guest
operating systems, you must create a Microsoft Sysprep deployment package on each cloud cell in your
installation.
During installation, vCloud Director places some files in the sysprep folder on the vCloud Director server host.
Do not overwrite these files when you create the Sysprep package.
Prerequisites
Access to the Sysprep binary files for Windows 2000, Windows 2003 (32- and 64-bit), and Windows XP (32and 64-bit).
Procedure
1 Copy the Sysprep binary files for each operating system to a convenient location on a vCloud Director
server host.
Each operating system requires its own folder.
NOTE Folder names are case-sensitive.
Guest OS Copy Destination
Windows 2000 SysprepBinariesDirectory /win2000
Windows 2003 (32-bit) SysprepBinariesDirectory /win2k3
Windows 2003 (64-bit) SysprepBinariesDirectory /win2k3_64
32 VMware, Inc.
Page 33

Guest OS Copy Destination
Windows XP (32-bit) SysprepBinariesDirectory /winxp
Windows XP (64-bit) SysprepBinariesDirectory /winxp_64
SysprepBinariesDirectory represents a location you choose to which to copy the binaries.
2 Run the /opt/vmware/cloud-director/deploymentPackageCreator/createSysprepPackage.sh
SysprepBinariesDirectory command.
For example, /opt/vmware/cloud-
director/deploymentPackageCreator/createSysprepPackage.sh /root/MySysprepFiles.
3 Use the service vmware-vcd restart command to restart the cloud cell.
4 If you have multiple cloud cells, copy the package and properties file to all cloud cells.
scp /opt/vmware/cloud-director/guestcustomization/vcloud_sysprep.properties
/opt/vmware/cloud-director/guestcustomization/windows_deployment_package_sysprep.cab
root@
next_cell_IP
:/opt/vmware/cloud-director/guestcustomization
5 Restart each cloud cell to which you copy the files.
Uninstall vCloud Director Software
Chapter 2 Creating a vCloud Director Server Group
Use the Linux rpm command to uninstall vCloud Director software from an individual server.
Procedure
1 Log in to the target server as root.
2 Unmount the transfer service storage, typically mounted at /opt/vmware/vcloud-
director/data/transfer.
3 Open a console, shell, or terminal window and run the rpm command.
rpm -e vmware-vcloud-director
VMware, Inc. 33
Page 34

vCloud Director Installation and Configuration Guide
34 VMware, Inc.
Page 35

Upgrading vCloud Director 3
To upgrade vCloud Director to a new version, install the new version on each server in the vCloud Director
server group, upgrade the vCloud Director database, and restart vCloud Director services.
After you upgrade a vCloud Director server, you must also upgrade its vCloud Director database. The database
stores information about the runtime state of the server, including the state of all vCloud Director tasks it is
running. To ensure that no invalid task information remains in the database after an upgrade, you must ensure
that no tasks are active on the server before you shut it down for the upgrade.
The upgrade preserves the following artifacts:
n
Local and global properties files are copied to the new installation.
n
Microsoft sysprep files used for guest customization are copied to the new installation.
n
In-progress uploads of OVF packages and media images are suspended before the upgrade begins and
resumed after the upgrade is complete.
If your cloud uses a load balancer, you can upgrade a subset of the server group while keeping existing services
available on the others. If you do not have a load balancer, the upgrade requires sufficient vCloud Director
downtime to upgrade the database and at least one server.
Upgrading a vCloud Director Server Group
VMware, Inc.
1 Use the cell management tool to quiesce all cells in the server group and shut down vCloud Director
services on each server. See “Use the Cell Management Tool to Quiesce and Shut Down A Server,” on
page 36.
2 Upgrade vCloud Director software on all members of the server group. See “Upgrade vCloud Director
Software on Any Member of a Server Group,” on page 38. You can upgrade the servers individually or
in parallel, but do not restart vCloud Director services on any member of the group before you upgrade
the vCloud Director database.
3 Upgrade the vCloud Director database. See “Upgrade the vCloud Director Database,” on page 40.
4 Restart vCloud Director on the upgraded servers. See “Start or Stop vCloud Director Services,” on
page 31.
35
Page 36

vCloud Director Installation and Configuration Guide
Using a Load Balancer to Reduce Service Downtime
If you are using a load balancer or other tool that can force requests to go to specific servers, you can upgrade
a subset of the server group while keeping existing services available on the remaining subset. This approach
reduces vCloud Director service downtime to the length of time required to upgrade the vCloud Director
database.
1 Use the load balancer to redirect vCloud Director requests to a subset of the servers in the group. Follow
the procedures recommended by your load balancer.
2 Use the cell management tool to quiesce the cells that are no longer handling requests and shut down
vCloud Director services on those servers. See “Use the Cell Management Tool to Quiesce and Shut Down
A Server,” on page 36.
3 Upgrade vCloud Director software on the members of the server group on which you have stopped
vCloud Director, but do not restart those services. See “Upgrade vCloud Director Software on Any
Member of a Server Group,” on page 38.
4 Use the cell management tool to quiesce the cells that you have not yet upgraded and shut down
vCloud Director services on those servers.
5 Upgrade the vCloud Director database. See “Upgrade the vCloud Director Database,” on page 40.
6 Restart vCloud Director on the upgraded servers. See “Start or Stop vCloud Director Services,” on
page 31.
7 Use the load balancer to redirect vCloud Director requests to the upgraded servers.
8 Upgrade vCloud Director software on the remaining servers in the group, and restart vCloud Director on
those servers as the upgrades complete. See “Upgrade vCloud Director Software on Any Member of a
Server Group,” on page 38.
This chapter includes the following topics:
n
“Use the Cell Management Tool to Quiesce and Shut Down A Server,” on page 36
n
“Upgrade vCloud Director Software on Any Member of a Server Group,” on page 38
n
“Upgrade the vCloud Director Database,” on page 40
n
“Upgrade vCenter and ESX/ESXi Hosts,” on page 42
n
“Upgrade vShield Manager,” on page 42
n
“Reverting an Upgrade,” on page 43
Use the Cell Management Tool to Quiesce and Shut Down A Server
Before you upgrade a vCloud Director server, use the cell management tool to quiesce and shut down
vCloud Director services on the server's cell.
vCloud Director creates a task object to track and manage each asynchronous operation that a user requests.
Information about all running and recently completed tasks is stored in the vCloud Director database. Because
a database upgrade invalidates this task information, you must be sure that no tasks are running when you
begin the upgrade process.
With the cell management tool, you can suspend the task scheduler so that new tasks cannot be started, then
check the status of all active tasks. You can wait for running tasks to complete or log in to vCloud Director as
a system administrator and cancel them. See “Cell Management Tool Reference,” on page 37. When no tasks
are running, you can use the cell management tool to stop vCloud Director services.
36 VMware, Inc.
Page 37

Chapter 3 Upgrading vCloud Director
Prerequisites
n
Before you can run the tool on a vCloud Director 1.0 or 1.0.1 server, you must download the tool and
install it. See http://kb.vmware.com/kb/1033575.
n
Verify that you have superuser credentials for the target server.
n
Verify that you have vCloud Director system administrator credentials.
Procedure
1 Log in to the target server as root.
2 Use the cell management tool to gracefully shut down the cell.
a Retrieve the current job status.
The following cell-management-tool command line supplies system administrator credentials and
returns the count of running jobs.
[root@cell1 /opt/vmware/vclouddirector/bin]# ./cell-management-tool -u administrator -p Pa55w0rd cell --status
Job count = 3
Is Active = true
b Stop the task scheduler to quiesce the cell.
Use a cell-management-tool command of the following form.
[root@cell1 /opt/vmware/vclouddirector/bin]# ./cell-management-tool -u administrator -p Pa55w0rd cell --quiesce true
This command prevents new jobs from being started. Existing jobs continue to run until they complete
or are cancelled. To cancel a job, use the vCloud Director Web Console or the REST API.
c When the Job count is 0 and Is Active is false, it is safe to shut down the cell.
Use a cell-management-tool command of the following form.
[root@cell1 /opt/vmware/vclouddirector/bin]# ./cell-management-tool -u administrator -p Pa55w0rd cell --shutdown
What to do next
After the cell management tool stops vCloud Director services on this server, you can upgrade the server's
vCloud Director software.
Cell Management Tool Reference
You can use the cell management tool to suspend the task scheduler so that new tasks cannot be started, to
check the status of active tasks, and to shut down the cell gracefully.
The cell management tool is installed in /opt/vmware/vcloud-director/bin/cell-management-tool. It is the
recommended way to stop services on a cell.
Logging In and Getting Help
The cell management tool requires you to log in with the credentials of the vCloud Director system
administrator. After you log in to the tool, you can use its subcommands to manage the cell.
VMware, Inc. 37
Page 38

vCloud Director Installation and Configuration Guide
Table 3-1. Cell Management Tool Options and Arguments, login and help
Option Argument Description
--help (-h) None Displays a usage message.
--username (-u) vCloud Director system
--password (-p) vCloud Director system
Managing a Cell
To manage a cell, use the cell subcommand.
Table 3-2. Cell Management Tool Options and Arguments, cell Subcommand
Option Argument Description
--quiesce (-q) true or false Quiesces activity on the cell. The
--shutdown (-s) None Shuts down vCloud Director
--status (-t) None Displays information about the
administrator user name
administrator password
You must have system
administrator credentials to
manage the task scheduler and
view task status.
If you omit this argument, the tool
prompts for the password.
argument true suspends the
scheduler. The argument false
restarts the scheduler.
services on the server.
number of jobs running on the cell
and the status of the cell.
Example: Getting Task Status
The following cell-management-tool command line supplies system administrator credentials and returns the
count of running jobs. When the Job count is 0 and Is Active is false, you can safely shut down the cell.
[root@cell1 /opt/vmware/vcloud-director/bin]# ./cell-management-tool -u administrator -p Pa55w0rd
cell --status
Job count = 3
Is Active = true
Upgrade vCloud Director Software on Any Member of a Server Group
The vCloud Director installer verifies that the target server meets all upgrade prerequisites and upgrades the
vCloud Director software on the server.
vCloud Director software is distributed as a Linux executable file named vmware-vcloud-director-1.5.0-
nnnnnn.bin, where nnnnnn represents a build number. After the upgrade is installed on a member of a server
group, you must run a tool that upgrades the vCloud Director database that the group uses before you can
restart vCloud Director services on the upgraded server.
Prerequisites
n
Verify that you have superuser credentials for the target server.
n
If you want the installer to verify the digital signature of the installation file, download and install the
VMware public key on the target server. If you have already verified the digital signature of the installation
file, you do not need to verify it again during installation. See “Download and Install the VMware Public
Key,” on page 22.
n
Use the cell management tool to quiesce and shut down vCloud Director services on the server's cell.
38 VMware, Inc.
Page 39

Chapter 3 Upgrading vCloud Director
Procedure
1 Log in to the target server as root.
2 Download the installation file to the target server.
If you purchased the software on a CD or other media, copy the installation file to a location that is
accessible to all target servers.
3 Verify that the checksum of the download matches the one posted on the download page.
Values for both MD5 and SHA1 checksums are posted on the download page. Use the appropriate tool
to verify that the checksum of the downloaded installation file matches the one shown on the download
page. A command of the following form validates the checksum for installation-file using the MD5
checksum-value copied from the download page.
md5sum -c
checksum-value installation-file
4 Ensure that the installation file is executable.
The installation file requires execute permission. To be sure that it has this permission, open a console,
shell, or terminal window and run the following command, where installation-file is the full pathname to
the vCloud Director installation file.
chmod u+x
installation-file
5 Use the cell management tool to quiesce the cell and shut down vCloud Director services on the server.
See “Use the Cell Management Tool to Quiesce and Shut Down A Server,” on page 36.
6 In a console, shell, or terminal window, run the installation file.
To run the installation file, type its full pathname, for example ./
installation-file
. The file includes an
installation script and an embedded RPM package.
NOTE You cannot run the installation file from a directory whose pathname includes any embedded space
characters.
If the installer detects a version of vCloud Director installed on this server that is equal to or later than the
version in the installation file, it displays an error message and exits. Otherwise, it prompts you to confirm
that you are ready to upgrade this server.
Checking architecture...done
Checking for a supported Linux distribution...done
Checking for necessary RPM prerequisites...done
Checking free disk space...done
An older version of VMware vCloud Director has been detected. Would you like
to upgrade it to 1.5.0? The installer will stop the vmware-vcd service,
back up any configuration files from the previous release and migrate the
product configuration as necessary.
7 Respond to the upgrade prompt.
Option Action
Continue the upgrade.
Exit to the shell without making any
changes in the current installation.
Type y.
Type n.
VMware, Inc. 39
Page 40

vCloud Director Installation and Configuration Guide
After you confirm that you are ready to upgrade the server, the installer verifies that the host meets all
requirements, unpacks the vCloud Director RPM package, stops vCloud Director services on the server,
and upgrades the installed vCloud Director software.
Would you like to upgrade now? (y/n) y
Extracting vmware-vcloud-director ......done
Upgrading VMware vCloud Director...
Installing the VMware vCloud Director
Preparing... ##################################################
vmware-vcloud-director ##################################################
Migrating settings and files from previous release...done
Migrating in-progress file transfers to /opt/vmware/vcloud-director/data/transfer...done
Uninstalling previous release...done
The installer prints a warning of the following form if you did not install the VMware public key on the
target server.
warning:
installation-file
.rpm: Header V3 RSA/SHA1 signature: NOKEY, key ID 66fd4949
8 (Optional) Update logging properties.
After an upgrade, new logging properties are written to the file /opt/vmware/vcloud-
director/etc/log4j.properties.rpmnew.
Option Action
If you did not change existing
logging properties
If you changed logging properties
Copy this file to /opt/vmware/vclouddirector/etc/log4j.properties.
Merge /opt/vmware/vclouddirector/etc/log4j.properties.rpmnew file with the
existing /opt/vmware/vcloud-director/etc/log4j.properties.
Merging these files preserves your changes.
When the vCloud Director software upgrade is complete, the installer displays a message indicating where
the old configuration files are stored, then reminds you to run the database upgrade tool.
What to do next
n
If you have not already done so, upgrade the vCloud Director database that this server uses.
n
If you already upgraded the vCloud Director database that this server group uses, you can restart the
upgraded server. See “Start or Stop vCloud Director Services,” on page 31.
Upgrade the vCloud Director Database
After you upgrade a server in your vCloud Director server group, you must upgrade the group's
vCloud Director database before you restart vCloud Director services on the server.
Prerequisites
IMPORTANT Back up your existing database before you upgrade it. Use the procedures that your database
software vendor recommends.
n
Verify that no vCloud Director servers are using the database. See “Use the Cell Management Tool to
Quiesce and Shut Down A Server,” on page 36
40 VMware, Inc.
Page 41

Chapter 3 Upgrading vCloud Director
Procedure
1 Open a console, shell, or terminal window, and type the following command to run the database upgrade
script.
/opt/vmware/vcloud-director/bin/upgrade
2 Respond to the database upgrade prompt.
Welcome to the vCloud Director upgrade utility
This utility will apply several updates to the database. Please
ensure you have created a backup of your database prior to continuing.
Do you wish to upgrade the product now? [Y/N]: y
Option Action
Continue the upgrade.
Exit to the shell without making any
changes in the current
vCloud Director database.
Type y.
Type n.
The database upgrade tool runs and displays progress messages.
Examining database at URL: jdbc:oracle:thin:@10.26.50.54:1521/orcl
Applying 1 upgrade batches
Executing upgrade batch: 1.0 to 1.5
Executing SQL statements from file: cc-tool-uninstall-graceful.sql
......................................
Executing SQL statements from file: Upgrade.sql []
......................................
Executing SQL statements from file: Upgrade_Data.sql []
......................................
Executing SQL statements from file: NewInstall_Indexes.sql []
......................................
Executing SQL statements from file: Upgrade_UUID.sql []
......................................
Executing SQL statements from file: NewInstall_Funcs.sql []
......................................
Successfully applied upgrade batch: 1.0 to 1.5
Running 2 upgrade tasks
Successfully ran upgrade task
Successfully ran upgrade task
Applying 1 upgrade batches
Executing upgrade batch: 1.0 to 1.5 cleanup
Executing SQL statements from file: NewInstall_Funcs.sql []
......................................
Executing SQL statements from file: Upgrade_UUID_Clean.sql []
......................................
Executing SQL statements from file: Upgrade_Clean.sql []
......................................
Successfully applied upgrade batch: 1.0 to 1.5 cleanup
Database upgrade complete
++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++
VMware, Inc. 41
Page 42

vCloud Director Installation and Configuration Guide
Upgrade vCenter and ESX/ESXi Hosts
After you upgrade vCloud Director and its database, you can upgrade the vCenter servers and ESX/ESXi hosts
attached to your cloud to enable new vCloud Director features.
This upgrade is optional, but several vCloud Director features depend on it. For a list of vCloud Director
features that depend on new versions of vCenter and ESX/ESXi, see “vCloud Director Hardware and Software
Requirements,” on page 9.
Procedure
1 Upgrade the vCenter server.
2 Upgrade each ESX/ESXi host that the upgraded vCenter server supports.
a Use vCenter to put the host into maintenance mode and allow all the virtual machines on that host
to migrate to another host.
b Upgrade the host.
c Take the host out of maintenance mode.
NOTE To ensure that you have enough upgraded host capacity to support the virtual machines in your
cloud, upgrade hosts in small batches. When you do this, host agent upgrades can complete in time to
allow virtual machines to migrate back to the upgraded host.
After the host is upgraded, vCloud Director detects the new version and upgrades the host agent.
Upgrade vShield Manager
After you upgrade vCloud Director and its database, you can upgrade the vShield Manager servers attached
to your cloud to enable new vCloud Director features.
IMPORTANT A new installation of vShield Manager cannot work with an existing version of vCloud Director.
After you upgrade a vCenter server attached to vCloud Director, you can upgrade the vShield Manager server
associated with the upgraded vCenter server. Although this upgrade is optional, several vCloud Director
features depend on it. For a list of vCloud Director features that depend on the new release of vShield Manager,
see “vCloud Director Hardware and Software Requirements,” on page 9.
Upgrading vShield Manager interrupts access to vShield Manager administrative functions, but does not
interrupt network services. Upgrading a vShield Edge appliance briefly interrupts service on the networks
that the appliance protects.
Prerequisites
At least one upgraded cell in your vCloud Director installation must be running before you begin this upgrade.
The cell is responsible for writing data about the upgraded vShield Manager to the vCloud Director database.
Procedure
1 Upgrade vShield Manager.
Follow the procedure in the vShield Quick Start Guide. After this upgrade completes, vShield Manager
notifies vCloud Director that it has a new version. It can take several minutes before vShield Manager
sends the notification and vCloud Director processes it.
42 VMware, Inc.
Page 43

2 Upgrade all vShield Edge appliances that the upgraded vShield Manager manages.
Use the vShield Manager user interface to manage this upgrade.
NOTE If you use the vCloud Director Web console or REST API to reset a network that vShield Edge
protects, this upgrade occurs automatically. Using the vShield Manager user interface to manage the
vShield Edge provides better administrative control over the upgrade process and related network
downtime.
Reverting an Upgrade
To undo an upgrade and revert to a previous version of vCloud Director, you must stop vCloud Director
services, restore the vCloud Director database from backup media, uninstall vCloud Director on all members
of the server group, and install the previous vCloud Director version.
Procedure
1 Stop vCloud Director services on all servers to downgrade.
2 Restore the appropriate vCloud Director database by using database vendor tools.
3 Uninstall vCloud Director from all servers to downgrade.
4 Install the version of vCloud Director that matches the restored vCloud Director database.
Chapter 3 Upgrading vCloud Director
VMware, Inc. 43
Page 44

vCloud Director Installation and Configuration Guide
44 VMware, Inc.
Page 45

vCloud Director Setup 4
After you configure all servers in the vCloud Director server group and connect them to the database, you can
initialize the server group's database with a license key, system administrator account, and related information.
When this process is complete, you can use the vCloud Director Web Console to complete the initial
provisioning of your cloud.
Before you can run the vCloud Director Web Console, you must run the Setup wizard, which gathers the
information that the Web Console requires before it can start. After the wizard is finished, the Web Console
starts and displays the login screen. The vCloud Director Web Console provides a set of tools for provisioning
and managing a cloud. It includes a Quickstart feature that guides you through steps like attaching
vCloud Director to vCenter and creating an organization.
Prerequisites
n
Complete the installation of all vCloud Director servers, and verify that vCloud Director services have
started on all servers.
n
Verify that you have the URL that the configuration script displays when it completes.
NOTE To discover the URL of the Setup wizard after the script exits, look up the fully qualified domain
name associated with the IP address you specified for the HTTP service during installation of the first
server and use it to construct a URL of the form https://fully-qualified-domain-name, for example,
https://mycloud.example.com. You can connect to the wizard at that URL.
VMware, Inc.
Complete the installation of all vCloud Director servers, and verify that vCloud Director services have started
on all servers.
Procedure
1 Open a Web browser and connect to the URL that the configuration script displays when it completes.
2 Follow the prompts to complete the setup.
This chapter includes the following topics:
n
“Review the License Agreement,” on page 46
n
“Enter the License Key,” on page 46
n
“Create the System Administrator Account,” on page 46
n
“Specify System Settings,” on page 46
n
“Ready to Log In to vCloud Director,” on page 47
45
Page 46

vCloud Director Installation and Configuration Guide
Review the License Agreement
Before you can configure a vCloud Director server group, you must review and accept the end user license
agreement.
Procedure
1 Review the license agreement.
2 Accept or reject the agreement.
Option Action
To accept the license agreement.
To reject the license agreement
If you reject the license agreement, you cannot proceed with vCloud Director configuration.
Enter the License Key
Each vCloud Director cluster requires a license to run. The license is specified as a product serial number. The
product serial number is stored in the vCloud Director database.
Click Yes, I accept the terms in the license agreement.
No, I do not accept the terms in the license agreement.
The vCloud Director product serial number is not the same as the vCenter server license key. To operate a
vCloud, you must have a vCloud Director product serial number and a vCenter server license key. You can
obtain both types of license keys from the VMware License Portal.
Procedure
1 Obtain a vCloud Director product serial number from the VMware License Portal.
2 Type the product serial number in the Product serial number text box.
Create the System Administrator Account
Specify the user name, password, and contact information for the vCloud Director system administrator.
The vCloud Director system administrator has superuser privileges throughout the cloud. You create the initial
system administrator account during vCloud Director setup. After installation and configuration is complete,
this system administrator can create additional system administrator accounts as needed.
Procedure
1 Type the system administrator's user name.
2 Type the system administrator's password and confirm it.
3 Type the system administrator's full name.
4 Type the system administrator's email address.
Specify System Settings
You can specify the system settings that control how vCloud Director interacts with vSphere and vShield
Manager.
The configuration process creates a folder in vCenter for vCloud Director to use and specifies an installation
ID to use when you create MAC addresses for virtual NICs.
Procedure
1 Type a name for the vCloud Director vCenter folder in the System name field.
46 VMware, Inc.
Page 47

2 Use the Installation ID field to specify the installation ID for this installation of vCloud Director.
If a datacenter includes multiple installations of vCloud Director, each installation must specify a unique
installation ID.
Ready to Log In to vCloud Director
After you provide all of the information that the Setup Wizard requires, you can confirm your settings and
complete the wizard. After the wizard finishes, the login screen of the vCloud Director Web Console appears.
The Ready to Log In page lists all the settings you have provided to the wizard. Review the settings carefully.
Prerequisites
Verify that you have access to vCenter and vShield Manager. The vCloud Director Web Console requires access
to the installations of vCenter and vShield Manager that you want to configure as part of this
vCloud Director. These installations must be running and configured to work with each other before you finish
this task. For more information, see “vCloud Director Hardware and Software Requirements,” on page 9.
Procedure
n
To change a setting, click Back until you get to the page where the setting originated.
n
To confirm all settings and complete the configuration process, click Finish.
Chapter 4 vCloud Director Setup
When you click Finish, the wizard applies the settings you specified, then starts the vCloud Director Web
Console and displays its login screen.
What to do next
Log in to the vCloud Director Web Console using the user name and password you provided for the system
administrator account. After you have logged in, the console displays a set of Quickstart steps that you must
complete before you can use this cloud. When the steps are complete, the Guided Tasks are enabled, and your
cloud is ready for use.
VMware, Inc. 47
Page 48

vCloud Director Installation and Configuration Guide
48 VMware, Inc.
Page 49

Index
A
AMQP broker, to install and configure 22
B
browsers, supported 12
C
cell management tool, options 37
certificate
self-signed 20
signed 18
configuration, confirm settings and complete 47
D
database
about 15
connection details 27
Oracle 15
SQL Server 16
supported platforms 9
to upgrade 40
E
ESX/ESXi, to upgrade 42
F
firewall, ports and protocols 14
G
guest customization, preparing 32
I
installation
of first server 26
of more servers 31
to configure 45
uninstalling 33
Installation
and capacity planning 8
architecture diagram 7
overview of 7
to create 25
Installation ID, to specify 46
K
keystore 17
L
license agreement 46
M
Microsoft Sysprep 32
N
network
configuration requirements 13
security of 14
P
product serial number
to enter 46
to obtain 46
R
RPM file, to verify digital signature 22
S
services, to start 31
System Administrator account, to create 46
System Name, to specify 46
U
upgrade
database 40
of first server 38
to undo 43
upgrading, workflows for 35
V
vCenter
supported releases 9
to upgrade 42
vShield manager, to upgrade 42
vShield Manager
installing and configuring 21
supported releases 9
J
Java, required JRE version 12
VMware, Inc. 49
Page 50

vCloud Director Installation and Configuration Guide
50 VMware, Inc.
 Loading...
Loading...