Page 1

vCloud Air Platform Programmer's
Guide
vCloud Air OnDemand 5.7
This document supports the version of each product listed and
supports all subsequent versions until the document is
replaced by a new edition. To check for more recent editions
of this document, see http://www.vmware.com/support/pubs.
EN-001712-00
Page 2

vCloud Air Platform Programmer's Guide
You can find the most up-to-date technical documentation on the VMware Web site at:
http://www.vmware.com/support/
The VMware Web site also provides the latest product updates.
If you have comments about this documentation, submit your feedback to:
docfeedback@vmware.com
Copyright © 2015 VMware, Inc. All rights reserved. Copyright and trademark information.
VMware, Inc.
3401 Hillview Ave.
Palo Alto, CA 94304
www.vmware.com
2 VMware, Inc.
Page 3

Contents
About This Programmer's Guide 5
About the vCloud Air Platform APIs 7
1
The VMware APIs for Virtual Private Cloud OnDemand 8
Service-Oriented Architecture Explained 8
About Plans, Instances, and the Compute Service 9
Media Support - JSON and XML 11
API Versioning 12
Authentication and Authorization 12
Roles for the APIs for Cloud Automation 13
Error Codes and Error Handling 13
Filter Expressions 15
vCloud Air Platform APIs Schema Reference 15
About the Examples in This Programmer's Guide 16
Hello vCloud Air: A Simplified RESTful Workflow 17
2
Log In and Receive Access Token 18
List Available Plans and Instances 19
Managing Users 23
3
About User Management 23
List Users 25
Add a User 28
Update a User 30
Delete a User 33
Retrieve Forgotten Password 34
Metering and Billing for Resource Usage 37
4
About Resource Usage Metering and Billing 37
Workflow for Using the Metering GET Operations 38
Summary of Metering and Billing Requests 39
Index 41
VMware, Inc. 3
Page 4

vCloud Air Platform Programmer's Guide
4 VMware, Inc.
Page 5

About This Programmer's Guide
The vCloud Air Platform Programmer's Guide provides information about APIs for vCloud Air
Virtual Private Cloud OnDemand (formerly known as the vCloud Air API Extensions).
VMware provides many different APIs and SDKs for applications and goals. This guide provides
information about vCloud Air Platform APIs for developers who create RESTful clients for vCloud Air
Virtual Private Cloud OnDemand.
Intended Audience
This guide is intended for software developers who are building interactive clients of vCloud Air
Virtual Private Cloud OnDemand. This guide discusses Representational State Transfer (REST) and RESTful
programming conventions, and vCloud Air technology. You must be familiar with these and other widely
deployed technologies such as XML, HTTP, and the Windows or Linux operating system.
Related Documentation
The vCloud Air – Virtual Private Cloud OnDemand User's Guide and the vCloud Air Compute Service
Programming Guide (API Version 9.0) contain detailed information about many of the objects and
operations referred to in this guide.
VMware Technical Publications Glossary
VMware Technical Publications provides a glossary of terms that might be unfamiliar to you. For definitions
of terms as they are used in VMware technical documentation, go to
http://www.vmware.com/support/pubs.
VMware, Inc.
5
Page 6

vCloud Air Platform Programmer's Guide
6 VMware, Inc.
Page 7

About the vCloud Air Platform APIs 1
The vCloud Air Platform APIs provide programmatic access to vCloud Air
Virtual Private Cloud OnDemand.
Virtual Private Cloud OnDemand is an infrastructure-as-a-service (IaaS) platform that allows customers to
consume specific compute, storage, and networking resources as incremental pay-as-you-go services.
Virtual Private Cloud OnDemand leverages a resource pool-based delivery model. Customers pay for only
the resources they actually used, on a metered, charge-back basis, under flexible service agreements, as
opposed to fixed-term contracts. Customers can increase or decrease capacity based on demands and
budget.
Customers consume Virtual Private Cloud OnDemand like any software-defined data center. Because
Virtual Private Cloud OnDemand is built on the vSphere and vCloud platforms, customers consume it the
same way that they consume their existing on-premises vSphere environments.
For more information about the features of vCloud Air – Virtual Private Cloud OnDemand, see Introducing
Virtual Private Cloud OnDemand in the vCloud Air – Virtual Private Cloud OnDemand User's Guide.
This chapter includes the following topics:
“The VMware APIs for Virtual Private Cloud OnDemand,” on page 8
n
“Service-Oriented Architecture Explained,” on page 8
n
VMware, Inc.
“About Plans, Instances, and the Compute Service,” on page 9
n
“Media Support - JSON and XML,” on page 11
n
“API Versioning,” on page 12
n
“Authentication and Authorization,” on page 12
n
“Roles for the APIs for Cloud Automation,” on page 13
n
“Error Codes and Error Handling,” on page 13
n
“Filter Expressions,” on page 15
n
“vCloud Air Platform APIs Schema Reference,” on page 15
n
“About the Examples in This Programmer's Guide,” on page 16
n
7
Page 8

Schema Docs
Network
Compute
Metering
Identity
Management
Service
Controller
REST API
vCloud Air
vCloud Air Platform Programmer's Guide
The VMware APIs for Virtual Private Cloud OnDemand
The vCloud Air Platform APIs provides support for developers who are building interactive clients of
vCloud Air using a RESTful application development style.
vCloud Air clients and vCloud Air servers communicate over HTTP, exchanging representations of
vCloud Air objects. These representations take the form of XML elements. vCloud Air clients make HTTP
requests to the server and retrieve the information the clients need from the server's responses.
Customers manage and consume Virtual Private Cloud OnDemand resources by using public APIs. The
public APIs provide management of cloud resources including virtual data center management,
configuration of network services, and virtual machine instance lifecycle management, as well as access to
resource usage metrics.
Complete programmatic access to the VMware APIs for Virtual Private Cloud OnDemand is accomplished
by utilizing the following VMware APIs:
vCloud Air Platform APIs, version 5.7: Build client applications that discover and access vCloud Air
n
services (such as Virtual Private Cloud OnDemand), manage users for
Virtual Private Cloud OnDemand, and automate resource usage metering and billing.
In addition to this guide, see the vCloud Air Platform APIs Schema Reference , 5.7.
vCloud Air Compute Service APIs: Build client applications that access the API endpoint for the
n
vCloud Compute Service, which exposes compute (vRAM and vCPU resources for virtual machines),
storage, and networking functionality in the public cloud on a pay-as-you-go basis.
For information, see the following documentation:
vCloud Air Compute Service Programming Guide (API Version 9.0)
n
vCloud API 9.0 Schema Reference
n
Service-Oriented Architecture Explained
The vCloud Air Platform APIs are designed to work with the service-oriented architecture on which
Virtual Private Cloud OnDemand is built.
Understanding the service-oriented architecture is essential to creating API clients to automate operations.
The extensibility of the service-oriented architecture supports the discovery and consumption of services
through public APIs, allowing for a common framework, and loosely-coupled services based on a common
message bus.
Figure 1‑1. Components of the Service-Oriented Architecture
8 VMware, Inc.
Page 9

Chapter 1 About the vCloud Air Platform APIs
Table 1‑1. API Surfaces for Virtual Private Cloud OnDemand
Component Capabilities API URI
Identify
Management
Service Controller
Metering Service Metering data collection and aggregation with an
Compute Service Exposure of compute (vRAM and vCPU resources for
Networking Service The pay-as-you-go network services—gateways,
Authentication and single sign on between
n
services
User identity lifecycle management
n
Authorization, such as access control
n
For information about the APIs for authentication and
authorization, see Chapter 2, “Hello vCloud Air: A
Simplified RESTful Workflow,” on page 17.
For information about the APIs for user management,
see Chapter 3, “Managing Users,” on page 23.
vCloud Air plan and instance management,
n
including the instance lifecycle
Exposure of the service-oriented architecture that
n
is available for consumption
Discovery of plans and instances by customers
n
Registry for information related to plans and
n
instances
For information about the APIs for the Service
Controller, see Chapter 2, “Hello vCloud Air: A
Simplified RESTful Workflow,” on page 17.
interface to your My VMware account for billing data
For information about the APIs for the Metering
Service, see Chapter 4, “Metering and Billing for
Resource Usage,” on page 37.
virtual machines), storage, and networking
functionality in the public cloud on a pay-as-you-go
basis
For information about the APIs for the vCloud
Compute Service, see vCloud Air Compute Service
Programming Guide (API Version 9.0).
networks, vApp/VM networks, firewall and NAT
rules
For information about the APIs for the Networking
Service, see Network Administration in the vCloud Air
Compute Service Programming Guide.
NOTE External networks and network pools are
system resources managed by vCloud Air
administrators with VMware or your authorized
service provider.
/api/iam/login
/api/iam/Users
/api/sc/plans
/api/sc/instances
/api/metering
/api/billing
/api/compute
For the list of API surfaces for
provisioning within the vCloud
Compute Service, see Summary of
vCloud API Provisioning Requests in the
vCloud Air Compute Service Programming
Guide (API Version 9.0).
/api/admin/edgeGateway
/api/admin/vdc/id/networks
About Plans, Instances, and the Compute Service
To work with the service-oriented architecture on which Virtual Private Cloud OnDemand is built, you
need to understand the following resources and how they interact.
Plans
n
VMware, Inc. 9
Page 10

vCloud Air Platform Programmer's Guide
A plan abstracts the infrastructure and platform functionality for Virtual Private Cloud OnDemand.
You can think of a plan as a template because it defines how you consume resources provided in the
VMware public cloud. For example, the plan for Virtual Private Cloud OnDemand allows customers to
create virtual machines configured with 2.6GHz vCPUs. Other plans for vCloud Air might allow
customers to create virtual machines configured with a different vCPU speed.
NOTE Each location can have different plans provisioned; if multiple locations are offering the same
plan, the plans in each location have the same plan name.
For information about how Virtual Private Cloud OnDemand is available in different locations, see
Geographical Locations in the vCloud Air – Virtual Private Cloud OnDemand User's Guide.
Instances
n
An instance is a consumable instance of a given plan. After account creation, you initialize an instance
in a chosen location.
Compute Service
n
A user in vCloud Air can access the vCloud API through the vCloud Compute Service. The vCloud
Compute Service is the service that exposes the compute, networking, and storage functionality that is
available to customers of Virtual Private Cloud OnDemand.
For information about the APIs to develop client applications that access the API endpoint for the
vCloud Compute Service, see the vCloud Air Compute Service Programming Guide (API Version 9.0).
A plan, which is a complex type, has the following structure:
<xs:element name="Plan" type="service:PlanType"/>
<xs:complexType name="PlanType">
<xs:complexContent>
<xs:extension base="common:ResourceType">
<xs:sequence>
<xs:element name="region" type="common:NonEmptyString"/>
<xs:element name="description" type="common:NonEmptyString" minOccurs="0"/>
<xs:element name="planVersion" type="common:NonEmptyString"/>
<xs:element name="planAttributes" type="common:NonEmptyString" minOccurs="0"/>
<xs:element name="instanceSpec" type="common:NonEmptyString" minOccurs="0"/>
<xs:element name="planPolicy" type="service:PlanPolicyType" minOccurs="0"/>
</xs:sequence>
</xs:extension>
</xs:complexContent>
</xs:complexType>
<xs:element name="PlanList" type="service:PlanListType"/>
<xs:complexType name="PlanListType">
<xs:sequence>
<xs:element name="plans" type="service:PlanType" minOccurs="0" maxOccurs="unbounded"/>
</xs:sequence>
</xs:complexType>
An instance has the following (complex type) structure:
<xs:element name="Instance" type="instance:InstanceType"/>
<xs:complexType name="InstanceType">
<xs:complexContent>
<xs:extension base="common:ResourceType">
<xs:sequence>
<xs:element name="description" type="common:NonEmptyString" minOccurs="0"/>
<xs:element name="region" type="common:NonEmptyString"/>
<xs:element name="serviceName" type="common:NonEmptyString"/>
10 VMware, Inc.
Page 11

Chapter 1 About the vCloud Air Platform APIs
<xs:element name="instanceVersion" type="common:NonEmptyString" minOccurs="0"/>
<xs:element name="planId" type="common:NonEmptyString"/>
<xs:element name="serviceGroupId" type="common:NonEmptyString"/>
<xs:element name="apiUrl" type="xs:anyURI"/>
<xs:element name="dashboardUrl" type="xs:anyURI"/>
<xs:element name="instanceAttributes" type="common:NonEmptyString" minOccurs="0"/>
</xs:sequence>
</xs:extension>
</xs:complexContent>
</xs:complexType>
The instance, as shown in the example, has the following attributes:
serviceName: The name of the service offering for the plan
n
The serviceName attribute can be used to distinguish whether a plan or instance belongs to the Compute
Service or another vCloud Air service.
planId: The plan associated with the creation of an instance
n
serviceGroupId: Service group ID associated with the creation of the instance
n
When you sign up for Virtual Private Cloud OnDemand, VMware creates your account and assigns a
service group ID to your account. VMware uses your service group ID as part of its billing system. The
service group ID indicates which billing account to charge for resource usage.
Each instance created for Virtual Private Cloud OnDemand contains one vCloud Compute Service. The
vCloud Compute Service exposes compute (vRAM and vCPU resources for virtual machines), storage, and
networking functionality in the public cloud on a pay-as-you-go basis.
Media Support - JSON and XML
The vCloud Air Platform APIs support XML and JSON data input and output formats. Whether you specify
JSON or XML in a request, the data structure returned in the response is equivalent for both formats; the
only difference is the data encoding differs by format.
Request Headers
In HTTP requests, API clients must specify in the Content-Type header the format in which data is
submitted:
Content-Type: application/xml
Content-Type: application/json
For HTTP responses, specifying the media type and subtype is optional.
For HTTP responses, the vCloud Air Platform APIs support specifying in the Accept header the following
media types and subtypes:
Accept: application/xml
Accept: application/json
Accept: application/*
Accept: */*
When you do not specify a media type or subtype or you specify wildcards in an Accept header, the
vCloud Air Platform APIs provide the HTTP response by using application/xml. To receive a response
using JSON, you must explicitly specify application/json in the Accept header.
VMware, Inc. 11
Page 12

vCloud Air Platform Programmer's Guide
Table 1‑2. Media Type and Subtype Support
Type Media Range
Application media type and JSON subtype Accept:application/json;class=mediatype
Application media type and XML subtype Accept:application/xml;class=mediatype
Wildcard media type and subtype
API Versioning
The vCloud Air Platform APIs follow an API version scheme to ensure standardization throughout the API
surface and to provide backward compatibility with future releases.
To specify the API version for content negotiation, include the vCloud Air Platform APIs version in the
Accept header as an extension parameter (;version=5.7).
The API versions the entire information model except for the media classes. (The media class for a resource
is optional and does not include versioning information.)
Accept:application/*;class=mediatype
n
Accept: */*;class=mediatype
n
Media type defaults to “application”
n
Subtype defaults “xml”
n
NOTE Specifying the media class for a resource is optional
and does not include versioning information.
NOTE
If you specify version=* in the Accept header, the API uses the latest API version.
n
When omitting the version from the Accept header, the API performs the operations by using the most
n
recent API version supported for the vCloud Air Platform APIs.
In HTTP responses, the API returns the version in the Content-Type header as an extension parameter.
Authentication and Authorization
HTTP communications between vCloud Air clients and servers are secured with SSL. In addition to SSL
encryption, vCloud Air implements authentication and authorization for secure API access.
Authentication with vCloud Air
vCloud Air implements Basic HTTP authentication, as defined by RFC 2617, which enables a client to
authenticate by including an Authorization header in the request. The Authorization header sends a user
name and password as basic credentials in MIME Base64 encoding:
Authorization: Basic UserName@domain.com:password
The vCloud Air Identity Management Service authenticates the user credentials for
Virtual Private Cloud OnDemand and returns an OAuth 2.0 Access token that is signed and formatted using
Base64 encoded JSON.
Response:
201 Created
vchs-authorization:vchs-OAuth-token
NOTE Before you can receive an OAuth token in a response, you must log in to
Virtual Private Cloud OnDemand using the Web UI and accept the Terms of Service.
12 VMware, Inc.
Page 13

Chapter 1 About the vCloud Air Platform APIs
Authorization with vCloud Air and vCloud
The returned OAuth token contains the necessary user attributes, such as user name, user ID, company
name, company ID, and user permissions, for API clients to access each functional boundary surfaced by the
API and to receive an authorization token from vCloud.
All requests from clients must include the OAuth token the Authorization header:
Authorization: Bearer OAuth_token
After the client authenticates, vCloud Air retrieves a SAML session token (x-vcloud-authorization) and
authenticates with the vCloud instance to perform Compute Service operations.
The response codes indicate whether requests succeeded or how they failed. When a request is successful,
the server returns HTTP response code 201 Created because logging in to the API requires a POST call. If an
Authentication header is missing, the server returns HTTP response code 403. If the credentials supplied in
an Authentication header are invalid, or if the token has expired, the server returns HTTP response code
401.
NOTE OAuth tokens expire 15 minutes after their issue times (even when API clients are active). You cannot
revoke OAuth tokens. If an API client's session terminates and the OAuth token has expired, the client must
re-authenticate with a user name and password.
Roles for the APIs for Cloud Automation
vCloud Air includes predefined roles. Each of these roles includes a set of default rights.
For information about the rights available for each predefined role in vCloud Air, see Role-based User
Account Management in the vCloud Air Virtual Private Cloud OnDemand User's Guide.
The following roles have access to the vCloud Air API:
Virtual Infrastructure Administrator – allows management of virtual data centers, virtual machines,
n
and backup settings
Read-only Administrator – read access to all administration objects
n
End User role – read and write access to virtual machines
n
These vCloud Air roles map to the following roles in the vCloud API for the Compute Service as follows:
Table 1‑3. vCloud Air Roles Mapped to vCloud API Roles
vCloud Air vCloud API for the Compute Service
Virtual Infrastructure Administrator VPC Administrator
Read-Only Administrator Read-Only VPC Administrator
End User VPC User
Each of the vCloud API roles—VPC Administrator, Read-Only VPC Administrator, and VPC User—provide
access to vCloud functionality. For the access list for each of the vCloud API roles, see vCloud Air Roles and
vCloud Director Rights in the vCloud Air Compute Service Programming Guide.
Error Codes and Error Handling
The following API functional boundaries for vCloud Air are designed to use standardized error handling:
Identity Management Service (IAM)
n
Service Controller (SC)
n
VMware, Inc. 13
Page 14

vCloud Air Platform Programmer's Guide
Metering Service (M/B)
n
For information about the errors returned by the Compute Service, see vCloud API REST Responses in the
vCloud Air Compute Service Programming Guide.
When an API client receives a response containing HTTP status code 400 and higher for any resource, the
response body includes the following attributes:
A standard error message type
n
The class of the error, which matches the HTTP status code
n
The specific error code from the error code list for the vCloud Air Platform APIs
n
A detailed error message
n
Additional information (when available), such as a link to details about the error
n
Table 1‑4. Description of the Error Codes that the API Returns
Code Possible Causes Components
CLIENT ERRORS
400 The request body is malformed, incomplete, or otherwise invalid. IAM, SC, M/B
401 Unable to authenticate: Provided credentials are not valid.
n
n
403
404
405 The HTTP method specified in the request is not supported for this
409
412 A precondition failed:
413 The requested entity is too large.
SERVER ERRORS
500 The request was received but could not be completed because of an
501 The requested operation is not supported. IAM
503 The server is busy performing a long running operation. SC
n
n
n
n
n
n
n
object. (The links applicable to a resource are returned as a part of the
resource.)
n
n
n
n
{"maxOperations": 1000,
"maxPayload": 1048576}
internal server error or a timeout.
The credentials supplied in an Authentication header are invalid.
The OAuth token has expired.
The Authentication header is missing.
The server does not support the requested operation.
One or more objects specified in the request could not be found in
the specified container.
The user is not authenticated or does not have adequate privileges to
access one or more objects specified in the request.
The user's session has expired.
The specified resource does not exist.
The request URL or request body is malformed.
The object state is not compatible with the requested operation.
A duplicate exists. All resources are uniquely identified by an ID
field.
If received when logging in, the precondition failed because the user
did not accepted the Terms of Service.
A resource could not be updated because the resource changed on
the server since the last time it was retrieved.
IAM, SC, M/B
IAM, SC, M/B
IAM, SC, M/B
SC
IAM, SC
IAM
IAM
IAM, SC, M/B
14 VMware, Inc.
Page 15

Filter Expressions
You can filter results using string matching or numeric comparison operations. A filter comprises one or
more subexpressions drawn from the following set of operators.
When using filtering with the API, the following conditions apply:
All collection APIs use standardized filtering.
n
Only one query parameter is supported for filtering named as "filter".
n
Filter expressions use the following format: filter={expression}
n
NOTE Only the Service Controller APIs (/api/sc/plans and /api/sc/instances) support filter expressions.
Table 1‑5. Supported Filter Operators
Operator Example Operation
== attribute==value
!= attribute!=value
; attribute1==value1;attribute2!
=value2
, attribute1==value1,attribute2=
=value2
Chapter 1 About the vCloud Air Platform APIs
Matches
The example evaluates to true if attribute has a value that
matches value in a case-sensitive comparison.
NOTE Asterisk (*) characters that appear anywhere in value are
treated as wildcards that match any character string. When
value includes wildcards, the comparison with attribute
becomes case insensitive.
Does not match
The example evaluates to true if attribute has a value that does
not match value in a case-sensitive comparison. Wildcard
characters are not allowed.
Logical AND
The example evaluates to true only if attribute1 has a value
that matches value1 and attribute2 has a value that does not
match value2 in a case-sensitive comparison.
Logical OR
The example evaluates to true if attribute1 has a value that
matches value1 or attribute2 has a value that matches value2
in a case-sensitive comparison.
vCloud Air Platform APIs Schema Reference
The schema reference includes detailed information about the XML representations of all vCloud Air API
objects and HTTP requests that operate on those objects.
The API represents objects in a cloud as XML documents in which object properties are contained in
elements and attributes that have typed values, and an explicit object hierarchy defined by an XML schema.
The schema reference includes reference material for all elements, types, and operations in vCloud Air.
Clients of RESTful Web services must be able to request object representations from the server, parse the
server's responses to extract the information contained in the responses, and compose requests that are
based on the information extracted from the responses.
vCloud Air uses a validating XML parser that requires elements in XML documents to agree in order and
number with the schema. Required elements must appear in requests. All elements that appear in requests
must appear in the order established by the schema, and with content that conforms to the type constraint
specified in the schema.
The schema reference is available in HTML format in the vCloud Air Documentation Center. See vCloud
Air Platform REST APIs Schema Reference.
VMware, Inc. 15
Page 16

vCloud Air Platform Programmer's Guide
The schema reference includes the schema definition files. To download the complete set of schemas for the
vCloud Air Platform APIs, see Download an Archive in the vCloud Air Documentation Center.
About the Examples in This Programmer's Guide
The examples in this guide of HTTP requests and responses illustrate the workflow and content that is
associated with automating login to vCloud Air, user management, and obtaining metering data for
resource usage.
NOTE The vCloud Air Platform APIs support XML and JSON data input and output formats. This
programmer's guide provides examples for requests and responses by using JSON and XML format
interchangeably.
Example request headers follow these conventions:
Header names and values are case-insensitive, and can be submitted or returned in any character case.
n
HTTP headers (such as Date, Content-Length, and Server) are omitted when they are not relevant to the
n
specifics of the example.
Example responses follow these conventions:
Responses show only those elements and attributes that are relevant to the operation being explained.
n
Ellipses (…) indicate omitted content within responses.
Object IDs shown in href attribute values appear as small integers, for example vca-2 for compute-uuid
n
or vdc-7 for vdc-uuid. In the API, object IDs are universal unique identifiers (UUIDs) as defined by RFC
4122, for example f5e185a4-7c00-41f1-8b91-0e552d538101.
16 VMware, Inc.
Page 17

Hello vCloud Air: A Simplified
RESTful Workflow 2
vCloud Air clients and servers communicate over HTTPS, exchanging XML or JSON representations of
vCloud API objects for the Compute Service. This simplified example of a RESTful workflow includes
logging in to Virtual Private Cloud OnDemand and requesting service details from the Service Controller.
Using the plan and instance data returned from the Service Controller, you can create a vCloud session to
obtain the list of virtual data centers for a Compute Service. For the steps to create a vCloud session to access
the vCloud Compute Service, see the Access the vCloud API Through the vCloud Compute Service in
vCloud Air in vCloud Air Compute Service Programming Guide.
These tasks assume that you have registered for Virtual Private Cloud OnDemand and have received your
user account information.
For information about signing up for Virtual Private Cloud OnDemand, see Create Your Account in
vCloud Air – Virtual Private Cloud OnDemand Getting Started.
This guide documents how to use the vCloud Air Platform APIs to retrieve information about the
Virtual Private Cloud OnDemand plans and for customers to retrieve information about their instances.
A user in vCloud Air can access the vCloud API through the vCloud Compute Service. The vCloud
Compute Service is the service that exposes the compute, networking, and storage functionality that is
available to customers of Virtual Private Cloud OnDemand.
VMware, Inc.
1 Log In and Receive Access Token on page 18
vCloud Air requires login requests to be authenticated. Begin the workflow with a login request that
supplies user credentials in the MIME Base64 encoding format as specified in RFC 1421.
2 List Available Plans and Instances on page 19
To programmatically access the vCloud Compute Service, you must discover the plans and instances
available in Virtual Private Cloud OnDemand.
17
Page 18

Client
Client
IAM
IAM
alt
POST api/iam/login
Authentication failed
Response 401 unauthorized
Response 412 TOS not accepted
Success & TOS accepted
Store SAML token in database
Generate OAuth 2.0 access token
Response 201 Created (token in Response header)
vCloud Air Platform Programmer's Guide
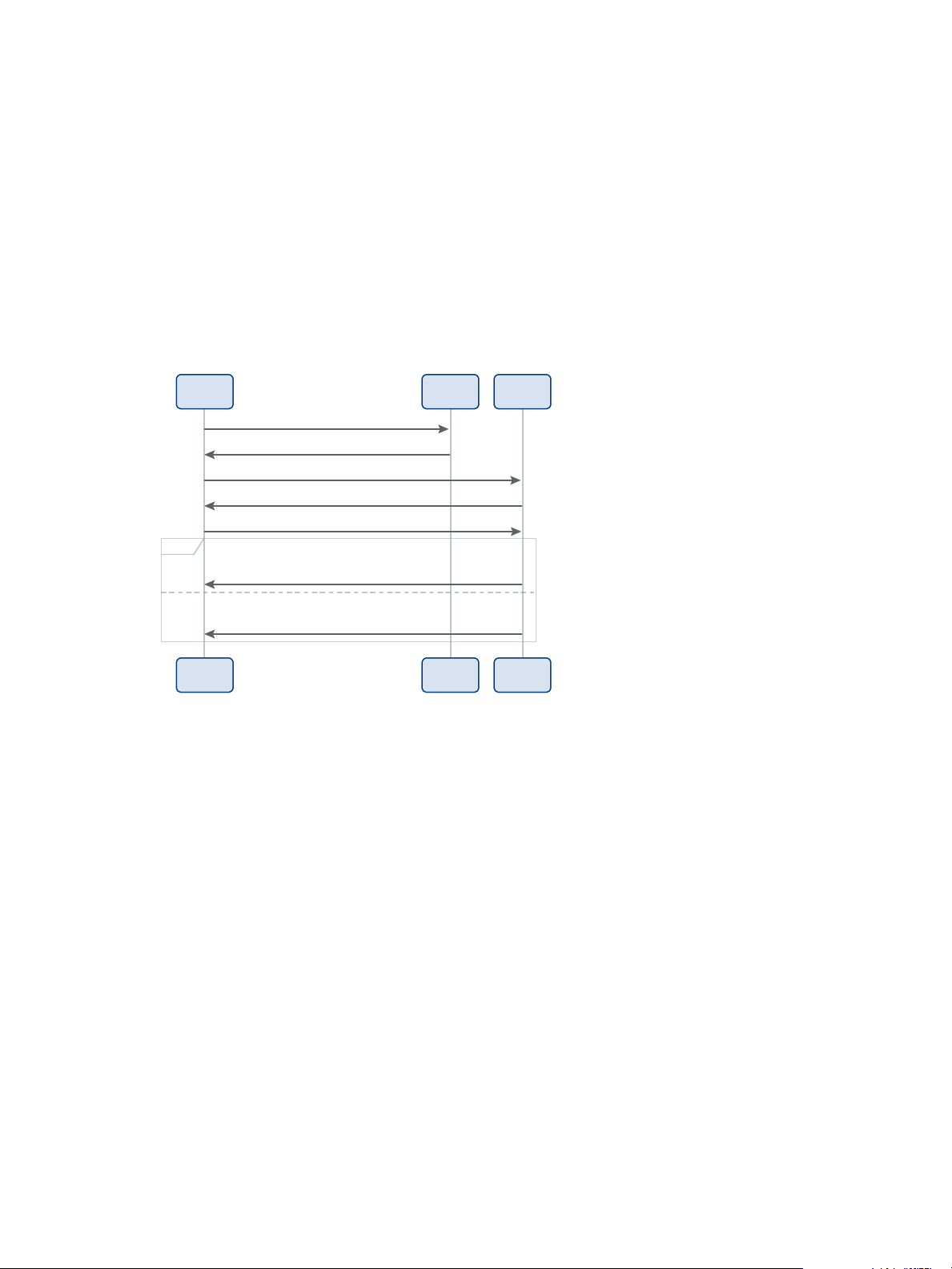
Log In and Receive Access Token
vCloud Air requires login requests to be authenticated. Begin the workflow with a login request that
supplies user credentials in the MIME Base64 encoding format as specified in RFC 1421.
Figure 2‑1. Log in and Accept Terms of Service Sequence Diagram
Prerequisites
You have signed up and registered for Virtual Private Cloud OnDemand and received an email with a
n
user name and password for an Account Administrator.
See Create Your Account in vCloud Air – Virtual Private Cloud OnDemand Getting Started for information.
Using the URL in the confirmation email, you have logged in to Virtual Private Cloud OnDemand
n
using the Web UI, set your password, and accepted the Terms of Service.
Procedure
POST a request that includes your user name and password in a MIME Base64 encoding:
u
POST https://vca.vmware.com/api/iam/login
The initial POST requires that you enter the Authorization header with an encoded Base64
username:password value as shown:
Authorization: Basic HelloUser@example.com:password
Wherein HelloUser@example.com:password is encoded.
If the request is successful, the server returns HTTP response code 201 Created and a response that
contains the vchs-authorization.
Example: Request and Response to Log In
Request Header
POST https://vca.vmware.com/api/iam/login
Accept: application/json;version=5.7
Authorization Basic cHhzdXNlcjFAdm13YXJlLmNvbTpQYXNzQDEyMw==…
18 VMware, Inc.
Request body not required.
Page 19
Response
alt
Client
Client
IAM
IAM SC
SC
POST api/iam/login
Response 201 Created
GET api/sc/plans
Response 200 OK (list of plans)
GET api/sc/instances
[Response OK]
Response with 404 - Not Found
[No instances]
Response 200 OK (list of instances)
HTTP/1.1 201 Created
Header:
Content-Type: application/json;version=5.7
vchs-authorization: eyJhbGciOiJIUzI1NiJ9.eyJqdGkiOiJmOTF…
Body:
{"serviceGroupIds":["89a6da00-0d15-48e9-8fed-6c87dfca5c0e"]}
List Available Plans and Instances
To programmatically access the vCloud Compute Service, you must discover the plans and instances
available in Virtual Private Cloud OnDemand.
Figure 2‑2. Log in and List Available Plans and Instance Sequence Diagram
Chapter 2 Hello vCloud Air: A Simplified RESTful Workflow
Prerequisites
You have signed up and registered for Virtual Private Cloud OnDemand and received an email with a
n
user name and password for an Account Administrator.
Using the URL in the confirmation email, you have logged in to Virtual Private Cloud OnDemand
n
using the Web UI, set your password, and accepted the Terms of Service.
Procedure
1 POST a request that includes your user name and password in a MIME Base64 encoding:
POST https://vca.vmware.com/api/iam/login
The initial POST requires that you enter the Authorization header with an encoded Base64
username:password value as shown:
Authorization: Basic HelloUser@example.com:password
Wherein HelloUser@example.com:password is encoded.
If the request is successful, the server returns HTTP response code 201 Created and a response that
contains the vchs-authorization.
2 Issue a request to get the list of service plans for your account:
GET https://vca.vmware.com/api/sc/plans
VMware, Inc. 19
Page 20

vCloud Air Platform Programmer's Guide
In the request, include the OAuth token:
Authorization: Bearer OAuth_token
Include the OAuth token in all subsequent API requests as a request header.
The returned response includes the list of plans for your account. Each plan consists of the following
elements:
Element Description
id
name
region
description
planVersion
serviceUri
instanceSpec
planAttributes
planPolicy
The ID of the plan
The name of the plan
The geographical location where the plan is offered
Description about the plan
The version of the plan
The API endpoint of the service offering for the plan
Custom values to create an instance
When instanceSpec is specified, default values are not used when the
instance is created.
The attributes associated with a given plan
Policy information for the plan
The planPolicy element enables functionality for future releases.
3 Issue a request to get a list of all the instances:
GET https://vca.vmware.com/api/sc/instances
The response includes your list of all instances. Each instance has the following elements:
Element Description
description
region
instanceVersion
planId
serviceGroupId
apiUrl
dashboardUrl
instanceAttributes
id
name
Description of the instance
The geographical location where the instance was created
The version of the instance
The plan associated with the creation of the instance
The service group ID associated with the creation of the instance
The API endpoint to access the instance
You use the value in the apiUrl to log in to the Compute Service for
Virtual Private Cloud OnDemand.
The URL to access the Compute Service by using the Web UI
The attributes associated with a given instance
The ID of the instance
The name of the instance
Example: Request and Response to List Plans and Instances
Request Header – Log in
POST https://vca.vmware.com/api/iam/login
Accept: application/json;version=5.7
Authorization: Basic cHhzdXNlcjFAdm13YXJlLmNvbTpQYXNzQDEyMw==…
Request body not required.
20 VMware, Inc.
Page 21

Chapter 2 Hello vCloud Air: A Simplified RESTful Workflow
Response – Log in
HTTP/1.1 201 Created
Header:
vchs-authorization: eyJhbGciOiJIUzI1NiJ9.eyJqdGkiOiJmOTF…
Body:
{"serviceGroupIds":["37"]}
Request Header – Get plans
GET https://vca.vmware.com/api/sc/plans
Accept: application/json;version=5.7
Authorization: Bearer eyJhbGciOiJIUzI1NiJ9.eyJqdGkiOiJmOTF…
Response body not required.
Response Body – Get plans
{
{
"plans": [{
"link": [],
"region": "LVG",
"serviceName": "com.vmware.vchs.compute",
"description": "Create virtual machines, and scale as your needs change.",
"planVersion": "1.0",
"instanceSpec": "",
"planAttributes": "attributes",
"planPolicy": {
"canCreateInstance": true,
"canCreateBinding": true,
"maxInstanceCount": 1
},
"id": "6",
"name": "Virtual Private Cloud OnDemand"
}]
}
Request Header – Get instances
GET https://vca.vmware.com/api/sc/instances
Accept: application/json;version=5.7
Authorization: Bearer eyJhbGciOiJIUzI1NiJ9.eyJqdGkiOiJmOTF…
Response Body – Get instances
{
"instances": [{
"link": [],
"description": "Create virtual machines, and scale as your needs change.",
"region": "LVG",
"instanceVersion": "1.0",
"planId": "24",
"serviceGroupId": "37",
"apiUrl": "https://example_host.vmware.com/api/compute/api/org/17",
"dashboardUrl": "https://example_host.vmware.com/api/compute/compute/ui?
orgName=42&serviceInstanceId=17",
"instanceAttributes":
"{\"orgName\":\"42\",\"sessionUri\":\"https://example_host.vmware.com/api/compute/api/sessions\"}
",
VMware, Inc. 21
Page 22

vCloud Air Platform Programmer's Guide
"id": "71",
"name": "Virtual Private Cloud OnDemand"
}]
}
22 VMware, Inc.
Page 23

Managing Users 3
Administrators add users for Virtual Private Cloud OnDemand and assign one or more roles to them. User
roles have a default group of privileges. Administrators can manage users and their details.
This chapter includes the following topics:
“About User Management,” on page 23
n
“List Users,” on page 25
n
“Add a User,” on page 28
n
“Update a User,” on page 30
n
“Delete a User,” on page 33
n
“Retrieve Forgotten Password,” on page 34
n
About User Management
vCloud Air includes APIs for full, user lifecycle management.
Schema for User Management Resources
vCloud Air implements user management by using attributes from the common System for Cross-Domain
Identity Management (SCIM) specification, which is designed for managing user identity in cloud-based
applications, and adds schema extensions for functions unique to vCloud Air.
Table 3‑1. Common Elements from the SCIM Schema
Element Description
email
familyName
givenName
VMware, Inc. 23
Email address for the user
NOTE The userName and email attributes must contain the same values.
Family name or last name for the user
First name of the user
Page 24

vCloud Air Platform Programmer's Guide
Table 3‑1. Common Elements from the SCIM Schema (Continued)
Element Description
roles
name
Table 3‑2. Schema Extensions for User Management
Extension Description
state
id
companyId
customerNumber
serviceGroupIds
tosAccepted
tosAcceptDate
userName
The roles to which the user is assigned
Name of the roles assigned to the user
You can assign a user to the following roles:
Account Administrator
n
Virtual Infrastructure Administrator
n
Network Administrator
n
Read-Only Administrator
n
End User
n
The roles are mutually exclusive with the exception of the Network Administrator
and Virtual Infrastructure Administrator roles; meaning, you can assign a user to the
Network Administrator and Virtual Infrastructure Administrator roles, or the
Account Administrator, Read-Only Administrator, or End User role.
For information about the rights available for each predefined role in vCloud Air, see
Role-based User Account Management in the vCloud Air
Virtual Private Cloud OnDemand User's Guide.
State of the user—active or inactive
Unique ID of the user
Created automatically when you create the user.
ID of the company to which the user belongs
Created automatically when VMware creates your Virtual Private Cloud OnDemand
account.
Not used by the API
The service group ID associated with the user
When you sign up for Virtual Private Cloud OnDemand, VMware creates your
account and assigns a service group ID to your account. VMware uses your service
group ID as part of its billing system. The service group ID indicates which billing
account to charge for resource usage.
Whether the Terms of Service has been accepted by the user
NOTE You cannot update the tosAccepted element for a user.
When the user accepted the Terms of Service
NOTE You cannot update the tosAcceptDate element for a user.
Name of the user in email format
NOTE The userName and email attributes must contain the same values.
Summary of User Management Operations
As shown in the following sequence diagram, the APIs for Virtual Private Cloud OnDemand include the
common CRUD (create, read, update, and delete) methods for the user management operations.
24 VMware, Inc.
Page 25

Figure 3‑1. User Management API Sequence Diagram
PUT api/iam/Users/{user-id} (update user name)
GET api/iam/Users
POST api/iam/login
Response 201 Created
Response 200 OK (list of all users)
GET api/iam/Users?self=1
Response 200 OK (user “self” details)
Response 204 No Content
Response 200 OK
Response 204 No Content
Response 201 Created
POST api/iam/Users (create user with Response body)
GET api/iam/Users/{user-id}
DELETE api/iam/Users/{user-id} (delete user)
Client
Client IAM
IAM
Chapter 3 Managing Users
Additionally, the APIs include an operation to handle a forgotten password. See “Retrieve Forgotten
Password,” on page 34 for information.
List Users
Use these operations to retrieve a list of all users created to access Virtual Private Cloud OnDemand or to
retrieve the details for a specified user.
Prerequisites
You have signed up and registered for Virtual Private Cloud OnDemand and received an email with a
n
user name and password for an Account Administrator.
Using the URL in the confirmation email, you have logged in to Virtual Private Cloud OnDemand
n
using the Web UI, set your password, and accepted the Terms of Service.
You have logged in as an administrator using the /api/IAM/login API and received an OATH token.
n
See “Log In and Receive Access Token,” on page 18 for information.
VMware, Inc. 25
Procedure
1 Issue a request to get the list of users for your account:
GET https://vca.vmware.com/api/IAM/Users
In the request, include the OATH token and the Accept header:
Accept: application/json;version=5.7
Authorization: Bearer OAuth_token
Include the OATH token in all subsequent API requests as a request header.
The returned response includes the list of users added for your account.
2 To get the details for a specific user, issue the following request:
GET https://vca.vmware.com/api/IAM/Users/userId
Where userId is the ID you received in step 1.
Page 26

vCloud Air Platform Programmer's Guide
Example: Requests and Responses to List Users
This example shows how to request a list of all users for your account and then request details for a specific
user.
Request Header – List all users
GET https://vca.vmware.com/api/IAM/Users
Accept: application/json;version=5.7
Authorization: Bearer eyJhbGciOiJSUzI1NiJ9.eyJqdGkiOiJiN2VjNjUyZi1mZmUzLTRh…
Request body not required.
Response Body – List all users
{"users":[
"meta": {
"created":1402527010108,
"modified":1402527010108
},
"schemas": [
"urn:scim:schemas:core:1.0"
],
"state": "Active",
"id": "790ee208-6c7d-4177-b6c6-212bdbe1a66b",
"companyId": "e9b1f777-ab16-493d-a0af-ad3474e13cd2",
"customerNumber": null,
"email": "test994@sample.com",
"familyName": "samplefamily1",
"givenName": "Jane",
"roles": {
"roles": [
{
"description": "Allows creation and management of VMs.",
"name": "End User",
"id": "6"
}
]
},
"serviceGroupIds": {
"serviceGroupIds": []
},
"tosAcceptDate": null,
"tosAccepted": false,
"userName": "test994@sample.com"
},
{
"meta": {
"created":1402527205542
"modified":1402527205542
},
"schemas": [
"urn:scim:schemas:core:1.0"
],
"state": "Active",
"id": "021cd2ab-c727-45f0-bbaf-1bb2f4af4b72",
"companyId": "e9b1f777-ab16-493d-a0af-ad3474e13cd2",
26 VMware, Inc.
Page 27

"customerNumber": null,
"email": "1925test@sample.com",
"familyName": "FamilyName",
"givenName": "John",
"roles": {
"roles": [
{
"description": "Allows user management and account settings.",
"name": "Account Administrator",
"id": "1"
}
]
},
"serviceGroupIds": {
"serviceGroupIds": []
},
"tosAcceptDate": null,
"tosAccepted": false,
"userName": "1925test@sample.com"
}
]
}
Chapter 3 Managing Users
Request Header – Get user
GET https://vca.vmware.com/api/iam/Users/790ee208-6c7d-4177-b6c6-212bdbe1a66b
Request body not required.
Response Body – Get user
{"users":[
"meta": {
"created":1402527010108,
"modified":1402527010108
},
"schemas": [
"urn:scim:schemas:core:1.0"
],
"state": "Active",
"id": "790ee208-6c7d-4177-b6c6-212bdbe1a66b",
"companyId": "e9b1f777-ab16-493d-a0af-ad3474e13cd2",
"customerNumber": null,
"email": "test994@sample.com",
"familyName": "samplefamily1",
"givenName": "Jane",
"roles": {
"roles": [
{
"description": "Allows creation and management of VMs.",
"name": "End User",
"id": "6"
}
]
},
"serviceGroupIds": {
"serviceGroupIds": []
},
VMware, Inc. 27
Page 28

vCloud Air Platform Programmer's Guide
"tosAcceptDate": null,
"tosAccepted": false,
"userName": "test994@sample.com"
}
Add a User
You can add users and assign privileges to them in Virtual Private Cloud OnDemand.
The company attribute is present in the OAuth token vCloud Air that sends as a part of the Authorization
header. The new user is created using the company value of the administrator who logged in to create the
user.
Prerequisites
You have signed up and registered for Virtual Private Cloud OnDemand and received an email with a
n
user name and password for an Account Administrator.
Using the URL in the confirmation email, you have logged in to Virtual Private Cloud OnDemand
n
using the Web UI, set your password, and accepted the Terms of Service.
You have logged in as an administrator using the /api/iam/login API and received an OAuth token.
n
See “Log In and Receive Access Token,” on page 18 for information.
Procedure
Issue a request to create a user for your account:
u
POST https://vca.vmware.com/api/iam/Users
In the request, include the OAuth token and the Accept header:
Accept: application/json;version=5.7
Authorization: Bearer OAuth_token
Include the following elements in the request body:
Table 3‑3. Required Elements to Create a User
Element Description
state
email
familyName
givenName
roles
State of the user—active or inactive
Email address for the user
NOTE The userName and email attributes must contain the same values.
Family name or last name for the user
First name of the user
The roles to which the user is assigned
28 VMware, Inc.
Page 29

Table 3‑3. Required Elements to Create a User (Continued)
Element Description
name
userName
Name of the roles assigned to the user
You can assign a user to the following roles:
Account Administrator
n
Virtual Infrastructure Administrator
n
Network Administrator
n
Read-Only Administrator
n
End User
n
The roles are mutually exclusive with the exception of the Network Administrator and
Virtual Infrastructure Administrator roles; meaning, you can assign a user to the Network
Administrator and Virtual Infrastructure Administrator roles, or the Account
Administrator, Read-Only Administrator, or End User role.
For information about the rights available for each predefined role in vCloud Air, see
Role-based User Account Management in the vCloud Air Virtual Private Cloud OnDemand
User's Guide.
Name of the user in email format
NOTE The userName and email attributes must contain the same values.
Example: Request and Response to Add a User
Chapter 3 Managing Users
Request Header – Add user
POST https://vca.vmware.com/api/iam/Users
Accept: application/json;version=5.7
Authorization: Bearer eyJhbGciOiJSUzI1NiJ9.eyJqdGkiOiJiN2VjNjUyZi1mZmUzLTRh…
Request Body – Add user
{
"schemas": [
"urn:scim:schemas:core:1.0"
],
"state": "Active",
"email": "test12345@sample.com",
"familyName": "test12345",
"givenName": "Jill",
"roles": {
"roles": [
{
"name": "End User"
}
]
},
"userName": "test12345@iamtest2242014.com"
}
Response – Add user
Header:
Status: 201 CREATED
Body:
{
"meta": {
"created": 1400665149048,
"modified": 1400665149048
},
VMware, Inc. 29
Page 30

vCloud Air Platform Programmer's Guide
"schemas": [
"urn:scim:schemas:core:1.0"
],
"state": "Active",
"id": "7179ba2e-6d49-485f-b54e-16e3b8ea3058",
"companyId": "422ca48d-a8e6-4b71-9f8f-5aa78362f98e",
"customerNumber": null,
"email": "test12345@sample.com",
"familyName": "test12345",
"givenName": "Jill",
"roles": {
"roles": [
{
"description": "Allows creation and management of VMs.",
"name": "End User",
"id": "6"
}
]
},
"serviceGroupIds": {
"serviceGroupIds": []
},
"tosAcceptDate": null,
"tosAccepted": false,
"userName": "test12345@iamtest2242014.com"
}
Update a User
To update a user's profile in Virtual Private Cloud OnDemand, issue a PUT request for a specific user's ID.
All elements are required and omitting elements will cause an error. VMware recommends you issue a GET
request to retrieve the user's profile, modify the profile, then submit the changes by sending a PUT request.
You can update the following elements for a user:
givenName
n
familyName
n
state
n
name within the roles element
n
You can update the name to one of the following values: Account Administrator, Read-Only
Administrator, End User, Virtual Infrastructure Administrator, Network Administrator .
NOTE Role updates do not rely on IDs. Change the role name field. The API ignores any changes you
make to the id or description attributes.
email
n
The API partially supports updating this element. Update the email element to change the address that
VMware uses when sending Virtual Private Cloud OnDemand messages to the user.
NOTE Updating the email element does not change the value for the userName element.
You cannot update the following attributes for a user:
userName
n
30 VMware, Inc.
Page 31

Chapter 3 Managing Users
companyId
n
userId
n
tosAccepted
n
tosAcceptDate
n
Meta fields
n
Schema field
n
Prerequisites
You have signed up and registered for Virtual Private Cloud OnDemand and received an email with a
n
user name and password for an Account Administrator.
Using the URL in the confirmation email, you have logged in to Virtual Private Cloud OnDemand
n
using the Web UI, set your password, and accepted the Terms of Service.
You have logged in as an administrator and received an OAuth token. See “Log In and Receive Access
n
Token,” on page 18 for information.
Procedure
1 (Optional) Issue a request to get the ID and elements for the user that you want to update:
GET https://vca.vmware.com/api/iam/Users
In the request, include the OAuth token and the Accept header:
Accept: application/json;version=5.7
Authorization: Bearer OAuth_token
Include the OAuth token in all subsequent API requests as a request header.
The returned response includes the list of users added for your account.
2 Issue the following request to update the user's profile:
PUT https://vca.vmware.com/api/iam/Users/userId
In the request, include the OAuth token and the Accept header:
Accept: application/json;version=5.7
Authorization: Bearer OAuth_token
In the request body, include the required elements for the user.
NOTE All elements are required and omitting elements will cause an error. VMware recommends you
issue a GET request to retrieve the user's profile, modify the profile, then submit the changes by
sending a PUT request.
See “About User Management,” on page 23 for a description of each element.
Example: Requests and Responses to Update a User
This example shows how to request the profile of a specific user and update the values for familyName and
roles. The elements and values returned in the GET userId response are provided and updated in the
update user request body as follows:
familyName updated from “samplefamily1” to “newName”
n
roles updated from End User to Account Administrator.
n
VMware, Inc. 31
Page 32

vCloud Air Platform Programmer's Guide
Request Header – Get userId 790ee208-6c7d-4177-b6c6-212bdbe1a66b
GET https://vca.vmware.com/api/iam/Users/790ee208-6c7d-4177-b6c6-212bdbe1a66b
Accept: application/json;version=5.7
Authorization: Bearer eyJhbGciOiJSUzI1NiJ9.eyJqdGkiOiJiN2VjNjUyZi1mZmUzLTRh…
Request body not required.
Response Body – Get userId 790ee208-6c7d-4177-b6c6-212bdbe1a66b
{"users":[
"meta": {
"created":1402527010108,
"modified":1402527010108
},
"schemas": [
"urn:scim:schemas:core:1.0"
],
"state": "Active",
"id": "790ee208-6c7d-4177-b6c6-212bdbe1a66b",
"companyId": "e9b1f777-ab16-493d-a0af-ad3474e13cd2",
"customerNumber": null,
"email": "test994@sample.com",
"familyName": "samplefamily1",
"givenName": "Jane",
"roles": {
"roles": [
{
"description": "Allows creation and management of VMs.",
"name": "End User",
"id": "6"
}
]
},
"serviceGroupIds": {
"serviceGroupIds": []
},
"tosAcceptDate": null,
"tosAccepted": false,
"userName": "test994@sample.com"
}
Request Header – Update user
PUT https://vca.vmware.com/api/iam/Users/790ee208-6c7d-4177-b6c6-212bdbe1a66b
Accept: application/json;version=5.7
Authorization: Bearer eyJhbGciOiJSUzI1NiJ9.eyJqdGkiOiJiN2VjNjUyZi1mZmUzLTRh…
Request Body – Update user
{"users":[
"meta": {
"created":1402527010108,
"modified":1402527010108
},
"schemas": [
"urn:scim:schemas:core:1.0"
],
"state": "Active",
32 VMware, Inc.
Page 33

"id": "790ee208-6c7d-4177-b6c6-212bdbe1a66b",
"companyId": "e9b1f777-ab16-493d-a0af-ad3474e13cd2",
"customerNumber": null,
"email": "test994@sample.com",
"familyName": "newName",
"givenName": "Jane",
"roles": {
"roles": [
{
"description": "Allows creation and management of VMs.",
"name": "Account Administrator",
"id": "6"
}
]
},
"serviceGroupIds": {
"serviceGroupIds": []
},
"tosAcceptDate": null,
"tosAccepted": false,
"userName": "test994@sample.com"
}
Chapter 3 Managing Users
Response Header – Update user
Status: 204 NO CONTENT
Connection: close
Content-Length: 0
Content-Type: text/plain; charset=UTF-8
Date: Fri, 06 Jun 2014 06:53:40 GMT
Server: Apache-Coyote/1.1
Response body not returned.
Delete a User
When users leave your company, you might want to delete their user profile from
Virtual Private Cloud OnDemand.
You can delete users from Virtual Private Cloud OnDemand to revoke their access to the service. In this
way, you can recover any resources that were assigned to the user. If you delete users who are signed in at
the time, their sessions will be forcibly terminated and they will be signed out. The user is deleted and does
not appear in the user list. The end user's resources (such as any virtual machines that they own) are moved
to the administrator who deleted the user.
To temporarily suspend a user's account, you can change the user's state from active to inactive. See
“Update a User,” on page 30 for information.
Prerequisites
You have signed up and registered for Virtual Private Cloud OnDemand and received an email with a
n
user name and password for an Account Administrator.
Using the URL in the confirmation email, you have logged in to Virtual Private Cloud OnDemand
n
using the Web UI, set your password, and accepted the Terms of Service.
You have logged in as an administrator using the /api/iam/login API and received an OATH token.
n
See “Log In and Receive Access Token,” on page 18 for information.
VMware, Inc. 33
Page 34

vCloud Air Platform Programmer's Guide
Procedure
1 If necessary, issue a request to get the ID for the user who you want to delete:
GET https://vca.vmware.com/api/iam/Users
In the request, include the OAuth token and the Accept header:
Accept: application/json;version=5.7
Authorization: Bearer OAuth_token
Include the OAuth token in all subsequent API requests as a request header.
The returned response includes the list of users for your account.
2 Issue the request to delete the user:
DELETE https://vca.vmware.com/api/iam/Users/user_id
Example: Request and Response to Delete a User
Request Header – Delete user
DELETE https://vca.vmware.com/api/iam/Users/aef1ee7e-c645-49db-83ae-ce9ad164df53
Accept: application/json;version=5.7
Authorization: Bearer eyJhbGciOiJSUzI1NiJ9.eyJqdGkiOiJiN2VjNjUyZi1mZmUzLTRh…
Request body not required.
Response Header – Delete user
Status: 204 NO CONTENT
Connection: close
Content-Length: 0
Content-Type: text/plain; charset=UTF-8
Date: Thu, 26 Jun 2014 05:30:20 GMT
Server: Apache-Coyote/1.1
Response body not returned.
Retrieve Forgotten Password
When a user forgets a password, you can use the API to send the user an email with links to change the
password. The email is sent to the email address in the element userName.
Prerequisites
You have signed up and registered for Virtual Private Cloud OnDemand and received an email with a
n
user name and password for an Account Administrator.
Using the URL in the confirmation email, you have logged in to Virtual Private Cloud OnDemand
n
using the Web UI, set your password, and accepted the Terms of Service.
You have logged in as an administrator using the /api/iam/login API and received an OAuth token.
n
See “Log In and Receive Access Token,” on page 18 for information.
Procedure
1 If necessary, issue a request to get the user name for the user who has forgotten a password:
GET https://vca.vmware.com/api/iam/Users/userId
In the request, include the OAuth token and the Accept header:
Accept: application/json;version=5.7
Authorization: Bearer OAuth_token
34 VMware, Inc.
Page 35

Include the OAuth token in all subsequent API requests as a request header.
The returned response includes elements for the specified users.
2 Issue a request to send a link to reset the user password:
PUT https://vca.vmware.com/api/iam/Users/userName/password/forgot
Accept: application/json;version=5.7
Authorization: Bearer OAuth_token
Example: Request and Response to Retrieve Forgotten Password
Request Header – Retrieve password
PUT https://vca.vmware.com/iam/Users/1234user@sample.com/password/forgot
Accept: application/json;version=5.7
Authorization: Bearer eyJhbGciOiJSUzI1NiJ9.eyJqdGkiOiJiN2VjNjUyZi1mZmUzLTRh…
Request body not required.
Response Header
Status: 202 ACCEPTED
Content-Length: 0
Date: Mon, 19 May 2014 09:38:30 GMT
Server: Apache-Coyote/1.1
Chapter 3 Managing Users
Response body not returned.
VMware, Inc. 35
Page 36

vCloud Air Platform Programmer's Guide
36 VMware, Inc.
Page 37

Metering and Billing for Resource
Usage 4
With Virtual Private Cloud OnDemand, customers pay nothing up front. They pay for only the services they
actually used, on a metered, charge-back basis, under flexible service agreements, as opposed to fixed-term
contracts.
You can use the vCloud Air Platform APIs to retrieve read-only information about current unbilled resource
usage and billed usage for Virtual Private Cloud OnDemand.
For information about how VMware meters and bills resource usage for Virtual Private Cloud OnDemand,
see Metering Resource Usage in the vCloud Air – Virtual Private Cloud OnDemand User's Guide.
This chapter includes the following topics:
“About Resource Usage Metering and Billing,” on page 37
n
“Workflow for Using the Metering GET Operations,” on page 38
n
“Summary of Metering and Billing Requests,” on page 39
n
About Resource Usage Metering and Billing
To utilize the metering API to obtain metering and billing data for Virtual Private Cloud OnDemand, the
Metering Service requires the context for metering data collection.
The Metering Service must map resource usage for a specific instance to a service group. The Service
Controller requires a mapping between serviceGroupId and instance id. The Metering Service passes the
instance id to the Service Controller and the Service Controller responds with the serviceGroupId for that
instance id. The Compute Service maintains the metering events for the instance id.
See “About Plans, Instances, and the Compute Service,” on page 9 for information about how an instance
contains the serviceGoupId element.
Metering Object Hierarchy
The Metering Service operates using the following object hierarchy (with an ID for each object) to map a
customer's company to their billed usage.
– Company Entity that VMware bills for resource usage; for vCloud Air, a customer is equivalent to a company
– Service
Group
– Service A consumable instance of a given plan; initialized in a chosen location
– L2 Container for L1 entities; a virtual data center in the Compute Service
Part of the VMware billing system—indicates which billing account to charge for resource usage
VMware, Inc. 37
Page 38
vCloud Air Platform Programmer's Guide
– L1 Primary container for a metered entity; a virtual machine or a gateway in the Compute
Service
– Billable Usage Metered resource usage
Metered Entities > L2 and L1
Metered entities provide a container for measurements and are directly managed by the Metering Service.
The Metering Service defines two abstract containers for metering—L2 and L1. These containers correspond
to entities in the Compute Service. An L1 entity is a primary container that the Metering Service monitors;
an L2 entity is a container of L1 entities.
In the Compute Service, a virtual machine and a gateway are L1 entities and the virtual data center (VDC)
that contains them is the corresponding L2 entity.
Current Versus Billed Usage in the API
Current usage includes mid-cycle usage when an account is in between billing statements; you query for
current usage by using date ranges. The Metering Service returns data for bill-to-date usage.
Billed usage includes usage, rates, and cost as invoiced by VMware. You query for billed usage by using the
anniversary (month and year) date.
Getting current and billed usage across the same date range involves issuing separate calls to the current
and billed usage endpoints with appropriate input dates.
Workflow for Using the Metering GET Operations
Retrieving read-only metering and billing information for your Virtual Private Cloud OnDemand account
by using the APIs for the vCloud Air Compute Service and vCloud Air Platform APIs uses the following
workflow:
1 Issue a login request that supplies user credentials in the MIME Base64 encoding format as specified in
RFC 1421.
See “Log In and Receive Access Token,” on page 18 for information.
2 To access the vCloud Compute Service, discover the instance accessible to you in
Virtual Private Cloud OnDemand.
See “List Available Plans and Instances,” on page 19 for information.
3 Access the Compute Service through the vCloud API.
See Access the vCloud API Through the vCloud Compute Service in vCloud Air in the vCloud Air
Compute Service Programming Guide for information.
4 Issue a request to get the virtual data center attributes for the Org you have logged into.
See Find a Catalog and a VDC in the vCloud Air Compute Service Programming Guide for information.
The response contains the virtual data center ID you need for the metering API GET operations. The
response also contains the vApp Container href to navigate to specific virtual machines for which to get
metering data.
5 Retrieve a virtual machine ID by using the discovered virtual machine href.
See Deploying and Operating vApps and Virtual Machines in the vCloud Air Compute Service
Programming Guide.
6 Issue a metering GET operation to retrieve resource usage data for the virtual data center or virtual
machine you have navigated to.
38 VMware, Inc.
Page 39

See “Summary of Metering and Billing Requests,” on page 39 for information.
Summary of Metering and Billing Requests
The vCloud Air Platform APIs include the following GET operations that you can use to retrieve metering
and billing information for your Virtual Private Cloud OnDemand account.
Table 4‑1. Resource Usage API Operations for Virtual Private Cloud OnDemand
Request Response Parameters Description
GET /api/metering/servicegroup/{service-group-id}/billable-costs
GET /api/metering/serviceinstance/{service-instance-id}/billableusage
GET /api/metering/serviceinstance/{service-instance-id}/l1/{l1id}/billable-usage
GET /api/metering/serviceinstance/{service-instance-id}/l2/{l2id}/billable-usage
GET /api/billing/service-groups ServiceGroups — Returns all service groups for a
GET /api/billing/service-group/{servicegroup-id}
GET /api/billing/service-group/{servicegroup-id}/billed-costs
GET /api/billing/service-group/{servicegroup-id}/billed-usage
BilledCosts
BilledUsage
BilledUsage
BilledUsage
n
n
n
n
n
n
n
n
n
month=..
year=....
month=..
year=....
level=....
month=..
year=....
month=..
year=....
ServiceGroup — Returns service group details:
BillableCosts — Returns the costs associated with a
BillableUsage
n
n
start=
end= or
duration=...
Chapter 4 Metering and Billing for Resource Usage
Returns the billable value of cost items
associated with a service group:
Support Cost
n
Service Credit
n
Returns all billable usage for an
instance. The response includes rolledup usage for all L2 entities associated
with the instance. Usage can be rolled
up over a period of hours, days, or
months, or for a specified time.
Returns all billable usage for an L1
entity. This request returns aggregated
usage data. Usage can be aggregated
over a period of hours, days, or
months, or for a specified time.
Returns all billable usage for an L2
entity. This request returns rolled-up
usage for all L1 entities associated with
the L2 entity. Usage can be rolled up
over a period of hours, days, or
months, or for a specified time.
company:
Company details
n
Service group
n
Billing currency
n
Spend threshold and other
n
billing attributes
Anniversary dates
n
The OAuth token determines the
company for which service group
details are returned.
Billing currency
n
Spend threshold and other billing
n
attributes
Anniversary dates
n
service group for a billing cycle:
Support Cost
n
Service Credit
n
Returns all billed usage for a service
group post invoicing. This request
returns all rolled-up usage for all L1
entities and L2 entities associated with
the service group ID.
VMware, Inc. 39
Page 40

vCloud Air Platform Programmer's Guide
Table 4‑1. Resource Usage API Operations for Virtual Private Cloud OnDemand (Continued)
Request Response Parameters Description
GET /api/billing/serviceinstance/{service-instance-id}/l1/{l1id}/billed-usage
GET /api/billing/serviceinstance/{service-instance-id}/l2/{l2id}/billed-usage
BillableUsage
BillableUsage
start=
n
end= or
n
duration=...
start=
n
end= or
n
duration=...
Returns all billed usage for an L1 entity
post invoicing. Usage can be
aggregated over a billing month or for
a specified time.
Returns all billed usage for an L2 entity
post invoicing. This request returns
rolled-up usage for all L1 entities
associated with the L2 entity. Usage
can be rolled up over a billing month or
for a specified time.
40 VMware, Inc.
Page 41

Index
A
Accept header 11, 12
API
components 8
Compute Service 8
Compute Service endpoint 9
Networking Service 8
sign-up requirement 17
user roles 13
version 11
audiences, defined 8
authentication, requirements 18
Authentication header, error 13
Authorization header 12, 18
B
basic auth 18
C
company attribute, from Oauth token 28
Compute Service
authorization 12
documentation 8
errors 13
metering entities 37
Web URL 19
Content-Type header 11
D
data format, shown in examples 16
documentation set
complete 8
Compute Service 8
vCloud API 8
G
glossary 5
H
headers
Accept 11, 12
Authorization 12, 18
Content-Type 11
shown in examples 16
HTTP, status codes 13
I
IDs
company 23
deleting users 33
instances 19
metering object hierarchy 37
objects 16
plans 19
roles 23
service groups 19
updating users 30
users 23
UUIDs 16
virtual data center 38
virtual machines 38
infrastructure-as-a-service, defined 7
initialize, vCloud Air service 9
instances, elements of 19
intended audience 5
L
L1 entities, defined 37
L2 entities, defined 37
locations, vCloud Air 9
M
media classes 12
media type, support 11
metering data, read-only 37
Metering Service, GET operations 39
MIME Base64 encoding 18
N
Networking Service, API 8
numeric comparison operations 15
O
Oauth token
company attribute in 28
errors 13
expiration 12
operators 15
P
planId, defined 9
plans, elements of 19
VMware, Inc. 41
Page 42

vCloud Air Platform Programmer's Guide
R
request, errors 13
resources
recover from users 33
usage calculation 37
usage metering 37
S
SAML session token 12, 18
schema
downloading 15
reference documentation 8
Service Controller
API 17
filtering 15
service-oriented architecture, defined 8
serviceGroupIds
defined 9
metering requirement 37
serviceName, defined 9
sessions, users terminated 33
SSL encryption 12
string matching 15
T
terms of service
accepting 18
users accepting 23, 30
tokens
Oauth 12
SAML session 12
type constraints 15
virtual data center ID, discovery 38
X
XMLschema
definition files 15
parser 15
U
users
deactivating 30
discovering ID 25
elements of 23, 25
email 34
updating email 30
UUIDs 16
V
vCloud Air
API access 13
billing system 37
locations 9
resources 9
service-oriented architecture 8
terms of service 18
user roles 23
vCloud API
roles mapping 13
session 17
Virtual Private Cloud OnDemand, features of 7
42 VMware, Inc.
 Loading...
Loading...