VMware vCenter Server - 6.7 Installation Manual

vCenter Server
Installation and Setup
17 APR 2018
VMware vSphere 6.7
vCenter Server 6.7

vCenter Server Installation and Setup
You can find the most up-to-date technical documentation on the VMware website at:
https://docs.vmware.com/
If you have comments about this documentation, submit your feedback to
docfeedback@vmware.com
VMware, Inc.
3401 Hillview Ave.
Palo Alto, CA 94304
www.vmware.com
Copyright © 2018 VMware, Inc. All rights reserved. Copyright and trademark information.
VMware, Inc. 2

Contents
About vCenter Server Installation and Setup 5
Introduction to vSphere Installation and Setup 6
1
Overview of the vSphere Installation and Setup Process 6
vCenter Server Components and Services 9
Overview of the vCenter Server Appliance 11
vCenter Server and Platform Services Controller Deployment Types 12
Understanding vSphere Domains, Domain Names, and Sites 16
Deployment Topologies with External Platform Services Controller Instances and High Availability 17
vCenter Enhanced Linked Mode 19
Deploying the vCenter Server Appliance and Platform Services Controller
2
Appliance 22
System Requirements for the vCenter Server Appliance and Platform Services Controller
Appliance 23
Preparing for Deployment of the vCenter Server Appliance and Platform Services Controller
Appliance 32
Prerequisites for Deploying the vCenter Server Appliance or Platform Services Controller
Appliance 35
GUI Deployment of the vCenter Server Appliance and Platform Services Controller Appliance 36
CLI Deployment of the vCenter Server Appliance and Platform Services Controller Appliance 60
Installing vCenter Server and Platform Services Controller on Windows 78
3
vCenter Server for Windows Requirements 79
Preparing for Installing vCenter Server and Platform Services Controller on Windows 89
Required Information for Installing vCenter Server or Platform Services Controller on Windows 111
Installing vCenter Server and Platform Services Controller on Windows 113
File-Based Backup and Restore of vCenter Server Appliance 121
4
Considerations and Limitations for File-Based Backup and Restore 122
Schedule a File-Based Backup 125
Manually Back up a vCenter Server Appliance by Using the vCenter Server Appliance
Management Interface 126
Restore a vCenter Server Appliance from a File-Based Backup 128
Image-Based Backup and Restore of a vCenter Server Environment 134
5
Considerations and Limitations for Image-Based Backup and Restore 135
Restore a vCenter Server Image-based Environment 138
VMware, Inc.
3

vCenter Server Installation and Setup
After You Install vCenter Server or Deploy the vCenter Server Appliance 143
6
Log in to vCenter Server by Using the vSphere Web Client 143
Install the VMware Enhanced Authentication Plug-in 144
Collect vCenter Server Log Files 145
Repoint vCenter Server to Another External Platform Services Controller in the Same Domain 145
Repoint vCenter Server to External Platform Services Controller in a Different Domain 147
Reconfigure a Standalone vCenter Server with an Embedded Platform Services Controller to a
vCenter Server with an External Platform Services Controller 155
Troubleshooting vCenter Server Installation or Deployment 159
7
Collecting Logs for Troubleshooting a vCenter Server Installation or Upgrade 159
Attempt to Install a Platform Services Controller After a Prior Installation Failure 161
Microsoft SQL Database Set to Unsupported Compatibility Mode Causes vCenter Server
Installation or Upgrade to Fail 162
Uninstall vCenter Server 163
8
VMware, Inc. 4
About vCenter Server Installation and Setup
vCenter Server Installation and Setup describes how to install and configure VMware vCenter Server®,
and deploy the VMware vCenter® Server Appliance™.
vSphere Installation and Setup is intended for experienced administrators who want to install and
configure vCenter Server, and deploy and configure the vCenter Server Appliance.
This information is written for experienced Windows or Linux system administrators who are familiar with
virtual machine technology and data center operations. The information about using the Image Builder
and VMware vSphere® Auto Deploy™ is written for administrators who have experience with Microsoft
PowerShell and VMware vSphere® PowerCLI™.
vSphere Web Client and vSphere Client
Instructions in this guide reflect the vSphere Client (an HTML5-based GUI). You can also use the
instructions to perform most of the tasks by using the vSphere Web Client (a Flex-based GUI).
Note In vSphere 6.7, most of the vSphere Web Client functionality is implemented in the vSphere Client.
For an up-to-date list of the unsupported functionality, see Functionality Updates for the vSphere Client.
VMware Technical Publications Glossary
VMware Technical Publications provides a glossary of terms that might be unfamiliar to you. For
definitions of terms as they are used in VMware technical documentation, go to
http://www.vmware.com/support/pubs.
VMware, Inc.
5

Introduction to vSphere
Installation and Setup 1
vSphere 6.7 provides various options for installation and setup. To ensure a successful vSphere
deployment, understand the installation and setup options, and the sequence of tasks.
The two core components of vSphere are ESXi and vCenter Server. ESXi is the virtualization platform on
which you can create and run virtual machines and virtual appliances. vCenter Server is a service that
acts as a central administrator for ESXi hosts connected in a network. vCenter Server lets you pool and
manage the resources of multiple hosts.
You can install vCenter Server on a Windows virtual machine or physical server, or deploy the
vCenter Server Appliance. The vCenter Server Appliance is a preconfigured Linux-based virtual machine
optimized for running vCenter Server and the vCenter Server components. You can deploy the
vCenter Server Appliance on ESXi hosts 6.0 or later, or on vCenter Server instances 6.0 or later.
Starting with vSphere 6.0, all prerequisite services for running vCenter Server and the vCenter Server
components are bundled in the VMware Platform Services Controller™. You can deploy vCenter Server
with an embedded or external Platform Services Controller, but you must always install or deploy the
Platform Services Controller before installing or deploying vCenter Server.
For detailed information about the ESXi installation process, see VMware ESXi Installation and Setup .
This chapter includes the following topics:
n
Overview of the vSphere Installation and Setup Process
n
vCenter Server Components and Services
n
Overview of the vCenter Server Appliance
n
vCenter Server and Platform Services Controller Deployment Types
n
Understanding vSphere Domains, Domain Names, and Sites
n
Deployment Topologies with External Platform Services Controller Instances and High Availability
n
vCenter Enhanced Linked Mode
Overview of the vSphere Installation and Setup Process
vSphere is a sophisticated product with multiple components to install and set up. To ensure a successful
vSphere deployment, understand the sequence of tasks required.
Installing vSphere includes the following tasks:
VMware, Inc.
6

Start the vSphere
installation and setup
End of the vSphere
installation and setup
Small envrionment with one
vCenter Server Instance
Large envrionment with multiple
vCenter Server Instances
Install ESXi
on at least one host
Set up ESXi
Deploy or install vCenter Server
with an embedded Platform
Services Controller
Log in to the vSphere Web
Client to create and organize
your vCenter Server inventory
Log in to the vSphere Web
Client to create and organize
your vCenter Server inventories
Start the vSphere
installation and setup
End of the vSphere
installation and setup
Install ESXi
on at least one host
Set up ESXi
Deploy or install the Platform
Services Controller instances
in a sequence
Deploy or install the vCenter Server
instances and register them with the
external Platform Services
Controller instances
vCenter Server Installation and Setup
Figure 1‑1. vSphere Installation and Setup Workflow
1 Read the vSphere release notes.
2 Install ESXi.
Note See VMware ESXi Installation and Setup for detailed information about the ESXi installation
process.
VMware, Inc. 7

vCenter Server Installation and Setup
3 Configure the ESXi boot and network settings, the direct console, and other settings. See VMware
ESXi Installation and Setup for information.
4 Consider setting up a syslog server for remote logging, to ensure sufficient disk storage for log files.
Setting up logging on a remote host is especially important for hosts with limited local storage. See
VMware ESXi Installation and Setup
5 Determine the vCenter Server and Platform Services Controller deployment model that is suitable for
your environment.
vCenter Server with an embedded Platform Services Controller deployment is suitable for small-scale
environments. vCenter Server with an external Platform Services Controller deployment is suitable for
environments with several vCenter Server instances. See vCenter Server and Platform Services
Controller Deployment Types.
6 Deploy or install vCenter Server and Platform Services Controller.
You can deploy the vCenter Server Appliance or Platform Services Controller appliance on an ESXi
host or vCenter Server instance, or you can install vCenter Server and Platform Services Controller
on a Windows virtual machine or physical server.
You can deploy or install multiple vCenter Server instances connected in Enhanced Linked Mode
configuration by registering them to a common or different joined Platform Services Controller
instances.
n
Deploy the vCenter Server Appliance or Platform Services Controller appliance.
1 Review the topics in System Requirements for the vCenter Server Appliance and Platform
Services Controller Appliance and verify that your system meets the hardware and software
requirements for deploying the appliance.
2 Determine the deployment method to use.
You can use the GUI method to deploy the appliance interactively. You can use the CLI
method to perform a silent deployment of the appliance. See GUI Deployment of the vCenter
Server Appliance and Platform Services Controller Appliance and CLI Deployment of the
vCenter Server Appliance and Platform Services Controller Appliance.
3 Use the topic Required Information for Deploying a vCenter Server Appliance or Platform
Services Controller Appliance to create a worksheet with the information you need for the
GUI deployment, or use the topic Prepare Your JSON Configuration File for CLI Deployment
to create your JSON templates for the CLI deployment.
4 Deploy the appliance.
n
Install vCenter Server or Platform Services Controller on a Windows virtual machine or physical
server.
1 Verify that your system meets the hardware and software requirements for installing
vCenter Server. See vCenter Server for Windows Requirements.
2 (Optional) Set up an external vCenter Server database. See Preparing vCenter Server
Databases for Install.
VMware, Inc. 8
vCenter Server Installation and Setup
For an environment with up to 20 hosts and 200 virtual machines, you can use the bundled
PostgreSQL database. For production and large scale environments, set up an external
database, because the migration from the embedded PostgreSQL database to an external
database is not a trivial manual process.
3 Create a worksheet with the information you need for installation. See Required Information
for Installing vCenter Server or Platform Services Controller on Windows.
4 Install vCenter Server with an embedded Platform Services Controller,
Platform Services Controller, or vCenter Server with an external Platform Services Controller.
7 Connect to vCenter Server from the vSphere Web Client. See Chapter 6 After You Install vCenter
Server or Deploy the vCenter Server Appliance.
8 Configure the vCenter Server Appliance or vCenter Server instance. See vCenter Server Appliance
Configuration and vCenter Server and Host Management.
vCenter Server Components and Services
vCenter Server provides a centralized platform for management, operation, resource provisioning, and
performance evaluation of virtual machines and hosts.
When you install vCenter Server with an embedded Platform Services Controller, or deploy the
vCenter Server Appliance with an embedded Platform Services Controller, vCenter Server, the
vCenter Server components, and the services included in the Platform Services Controller are deployed
on the same system.
When you install vCenter Server with an external Platform Services Controller, or deploy the
vCenter Server Appliance with an external Platform Services Controller, vCenter Server and the
vCenter Server components are deployed on one system, and the services included in the
Platform Services Controller are deployed on another system.
The following components are included in the vCenter Server and vCenter Server Appliance installations:
n
The VMware Platform Services Controller group of infrastructure services contains vCenter Single
Sign-On, License service, Lookup Service, and VMware Certificate Authority.
n
The vCenter Server group of services contains vCenter Server, vSphere Web Client, vSphere Auto
Deploy, and vSphere ESXi Dump Collector. vCenter Server for Windows also contains the VMware
vSphere Syslog Collector. The vCenter Server Appliance also contains the VMware vSphere Update
Manager Extension service.
Note Starting with vSphere 6.5, all vCenter Server services and some Platform Services Controller
services run as child processes of the VMware Service Lifecycle Manager service.
VMware, Inc. 9

vCenter Server Installation and Setup
Services Installed with VMware Platform Services Controller
vCenter Single Sign-On The vCenter Single Sign-On authentication service provides secure
authentication services to the vSphere software components. By using
vCenter Single Sign-On, the vSphere components communicate with each
other through a secure token exchange mechanism, instead of requiring
each component to authenticate a user separately with a directory service
like Active Directory. vCenter Single Sign-On constructs an internal security
domain (for example, vsphere.local) where the vSphere solutions and
components are registered during the installation or upgrade process,
providing an infrastructure resource. vCenter Single Sign-On can
authenticate users from its own internal users and groups, or it can connect
to trusted external directory services such as Microsoft Active Directory.
Authenticated users can then be assigned registered solution-based
permissions or roles within a vSphere environment.
vCenter Single Sign-On is required with vCenter Server.
vSphere License
Service
VMware Certificate
Authority
For information about all Platform Services Controller services and capabilities, see Platform Services
Controller Administration.
The vSphere License service provides common license inventory and
management capabilities to all vCenter Server systems that are connected
to a Platform Services Controller or multiple linked
Platform Services Controllers.
VMware Certificate Authority (VMCA) provisions each ESXi host with a
signed certificate that has VMCA as the root certificate authority, by default.
Provisioning occurs when the ESXi host is added to vCenter Server
explicitly or as part of the ESXi host installation process. All ESXi
certificates are stored locally on the host.
Services Installed with vCenter Server
These additional components are installed silently when you install vCenter Server. The components
cannot be installed separately as they do not have their own installers.
PostgreSQL A bundled version of the VMware distribution of PostgreSQL database for
vSphere and vCloud Hybrid Services.
vSphere Web Client The vSphere Web Client lets you connect to vCenter Server instances by
using a Web browser, so that you can manage your vSphere infrastructure.
VMware, Inc. 10

vCenter Server Installation and Setup
vSphere Client
vSphere ESXi Dump
Collector
VMware vSphere
Syslog Collector
The new user interface that lets you connect to vCenter Server instances
by using a Web browser. The terminology, topology, and workflow are
closely aligned with the same aspects and elements of the
vSphere Web Client user interface.
The vCenter Server support tool. You can configure ESXi to save the
VMkernel memory to a network server, rather than to a disk, when the
system encounters a critical failure. The vSphere ESXi Dump Collector
collects such memory dumps over the network.
The vCenter Server on Windows support tool that enables network logging
and combining of logs from multiple hosts. You can use the vSphere Syslog
Collector to direct ESXi system logs to a server on the network, rather than
to a local disk. The recommended maximum number of supported hosts to
collect logs from is 30. For information about configuring vSphere Syslog
Collector, see http://kb.vmware.com/kb/2021652.
The vCenter Server Appliance uses the built-in Rsyslog service of the Linux
OS. For information how to redirect the log files to another machine with the
Appliance Management Interface, see vCenter Server Appliance
Configuration.
vSphere Auto Deploy The vCenter Server support tool that can provision hundreds of physical
hosts with ESXi software. You can specify the image to deploy and the
hosts to provision with the image. Optionally, you can specify host profiles
to apply to the hosts, and a vCenter Server location (folder or cluster) for
each host.
VMware vSphere
Update Manager
Extension
Update Manager enables centralized, automated patch and version
management for VMware vSphere and offers support for VMware ESXi
hosts, virtual machines, and virtual appliances. The VMware vSphere
Update Manager Extension is an optional service of only the
vCenter Server Appliance 6.7.
Overview of the vCenter Server Appliance
The vCenter Server Appliance is a preconfigured Linux-based virtual machine that is optimized for
running vCenter Server and the associated services.
The vCenter Server Appliance reduces the deployment time of vCenter Server and the associated
services, and provides a low-cost alternative to the Windows-based vCenter Server installation.
The vCenter Server Appliance package contains the following software:
n
Project Photon OS® 1.0
n
The Platform Services Controller group of infrastructure services
n
The vCenter Server group of services
VMware, Inc. 11

vCenter Server Installation and Setup
n
PostgreSQL
n
VMware vSphere Update Manager Extension
Version 6.7 of the vCenter Server Appliance is deployed with virtual hardware version 10, which supports
64 virtual CPUs per virtual machine in ESXi.
The vCenter Server Appliance uses the embedded PostgreSQL database that has the scalability of up to
2,000 hosts and 35,000 virtual machines. During the deployment, you can choose the
vCenter Server Appliance size for your vSphere environment size and the storage size for your database
requirements.
Starting with vSphere 6.5, the vCenter Server uses the VMware vSphere Update Manager Extension
service. An external VMware Update Manager instance on Windows is no longer required for vSphere
centralized automated patch and version management. For information about the vCenter Server and
Platform Services Controller services, see vCenter Server Components and Services.
Starting with vSphere 6.5, the vCenter Server Appliance supports high availability. For information about
configuring vCenter Server Appliance in a vCenter High Availability cluster, see vSphere Availability.
Starting with vSphere 6.5, the vCenter Server Appliance and Platform Services Controller appliance
support file-based backup and restore. For information backing up and restoring, see Chapter 4 File-
Based Backup and Restore of vCenter Server Appliance.
For information about the vCenter Server Appliance maximums, see the Configuration Maximums
documentation.
vCenter Server and Platform Services Controller Deployment Types
You can deploy the vCenter Server Appliance or install vCenter Server for Windows with an embedded or
external Platform Services Controller. You can also deploy a Platform Services Controller as an appliance
or install it on Windows. If necessary, you can use a mixed operating systems environment.
Before you deploy the vCenter Server Appliance or install vCenter Server for Windows, you must
determine the deployment model that is suitable for your environment. For each deployment or
installation, you must select one of the three deployment types.
VMware, Inc. 12
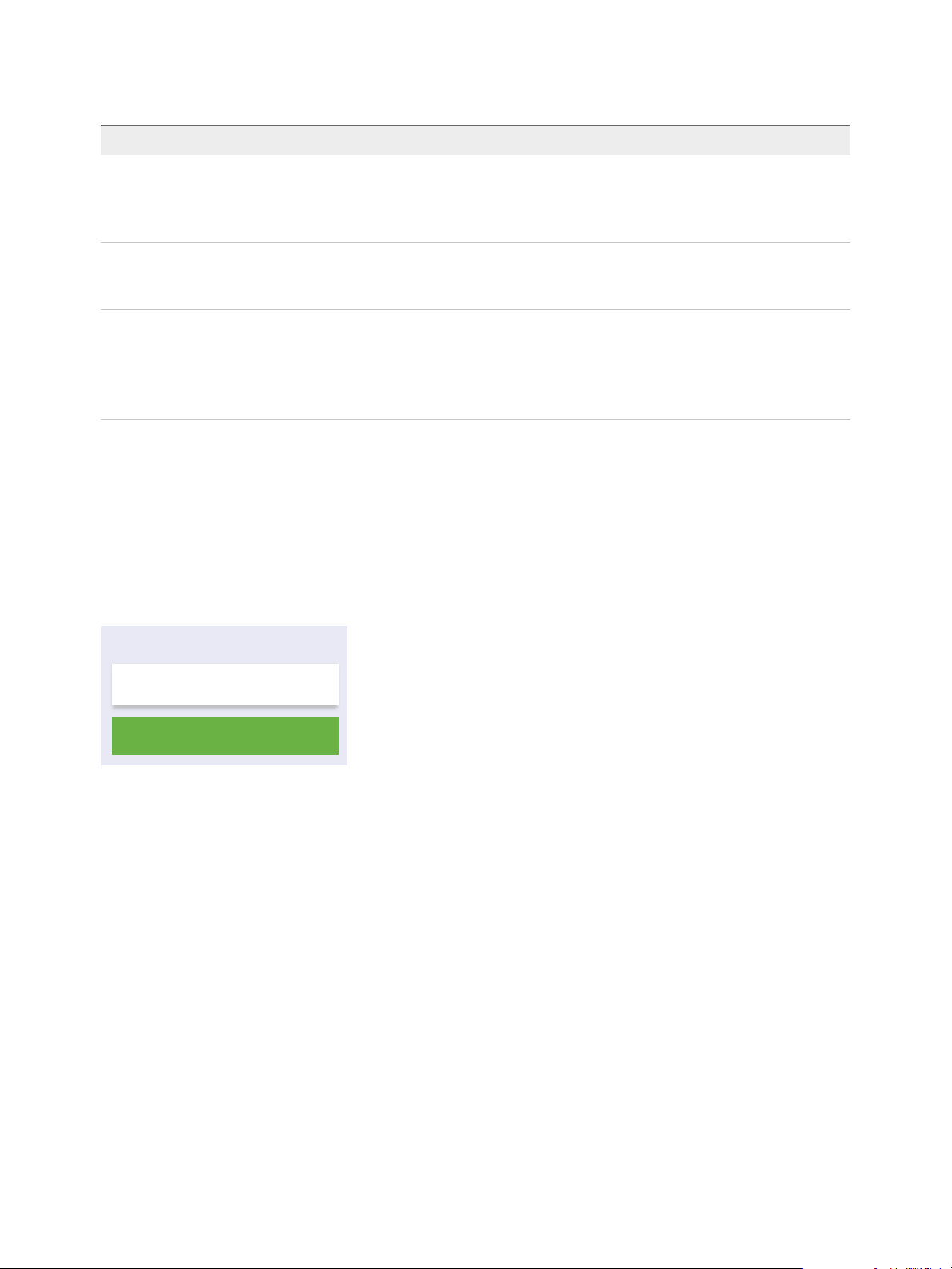
Platform Services
Controller
Virtual Machine or Physical Server
vCenter Server
vCenter Server Installation and Setup
Table 1‑1. vCenter Server and Platform Services Controller Deployment Types
Deployment Type Description
vCenter Server with an embedded Platform Services Controller All services that are bundled with the
Platform Services Controller are deployed together with the
vCenter Server services on the same virtual machine or physical
server.
Platform Services Controller Only the services that are bundled with the
Platform Services Controller are deployed on the virtual machine
or physical server.
vCenter Server with an external Platform Services Controller
(Requires external Platform Services Controller)
Only the vCenter Server services are deployed on the virtual
machine or physical server.
You must register such a vCenter Server instance with a
Platform Services Controller instance that you previously
deployed or installed.
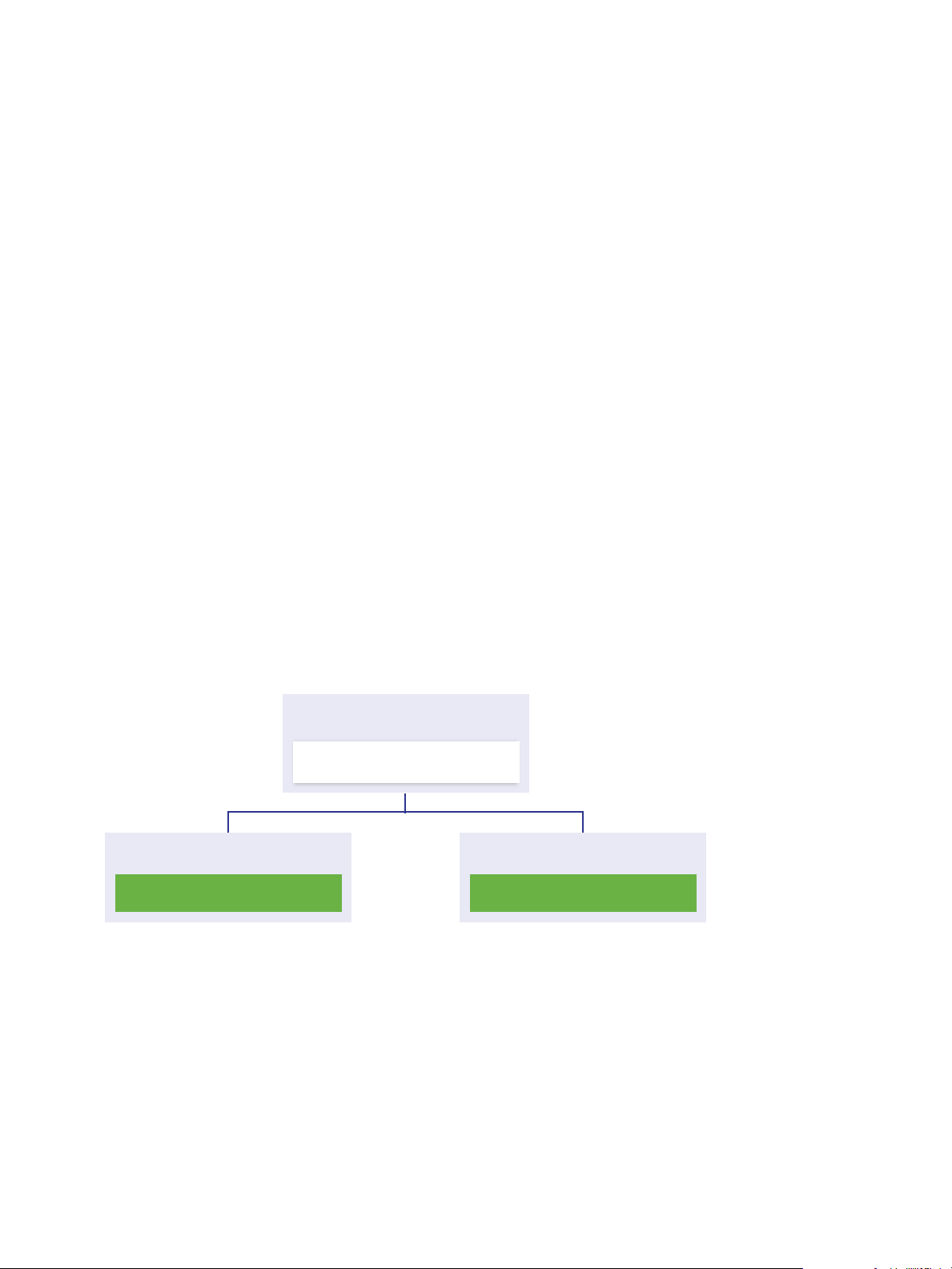
vCenter Server with an Embedded Platform Services Controller
Using an embedded Platform Services Controller results in a standalone deployment that has its own
vCenter Single Sign-On domain with a single site. vCenter Server with an embedded
Platform Services Controller is suitable for small environments. You cannot join other vCenter Server or
Platform Services Controller instances to this vCenter Single Sign-On domain.
Figure 1‑2. vCenter Server with an Embedded Platform Services Controller
Installing vCenter Server with an embedded Platform Services Controller has the following advantages:
n
The connection between vCenter Server and the Platform Services Controller is not over the network,
and vCenter Server is not prone to outages caused by connectivity and name resolution issues
between vCenter Server and the Platform Services Controller.
n
If you install vCenter Server on Windows virtual machines or physical servers, you need fewer
Windows licenses.
n
You manage fewer virtual machines or physical servers.
Installing vCenter Server with an embedded Platform Services Controller has the following
disadvantages:
n
There is a Platform Services Controller for each product which might be more than required and
which consumes more resources.
n
The model is suitable only for small-scale environments.
VMware, Inc. 13
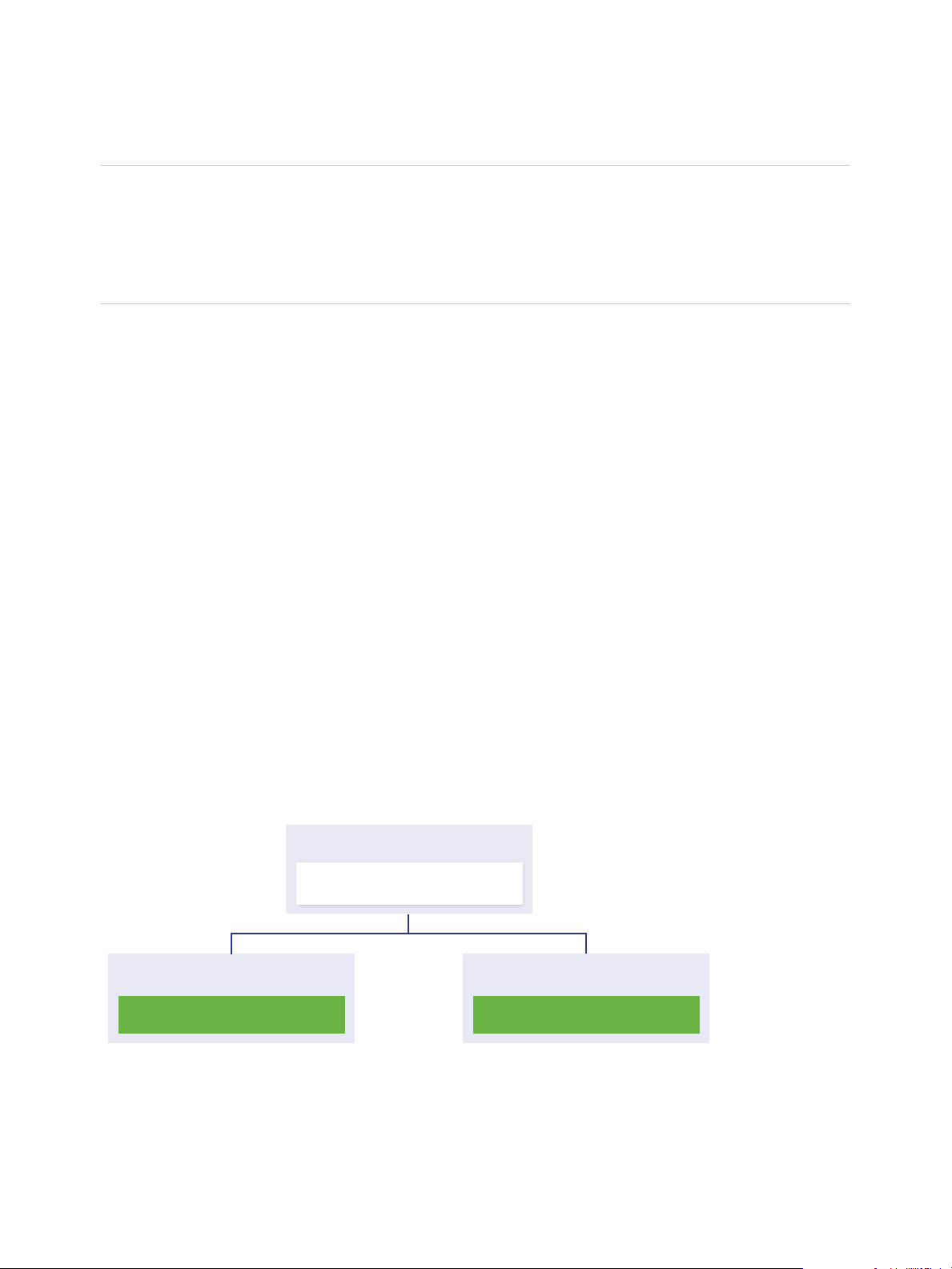
Platform Services
Controller
Virtual Machine or Physical Server
vCenter Server
Virtual Machine or Physical Server
vCenter Server
Virtual Machine or Physical Server
vCenter Server Installation and Setup
You can configure the vCenter Server Appliance with an embedded Platform Services Controller in
vCenter High Availability configuration. For information, see vSphere Availability.
Note After you deploy or install vCenter Server with an embedded Platform Services Controller, you can
reconfigure the deployment type and switch to vCenter Server with an external
Platform Services Controller.
See Reconfigure a Standalone vCenter Server with an Embedded Platform Services Controller to a
vCenter Server with an External Platform Services Controller.
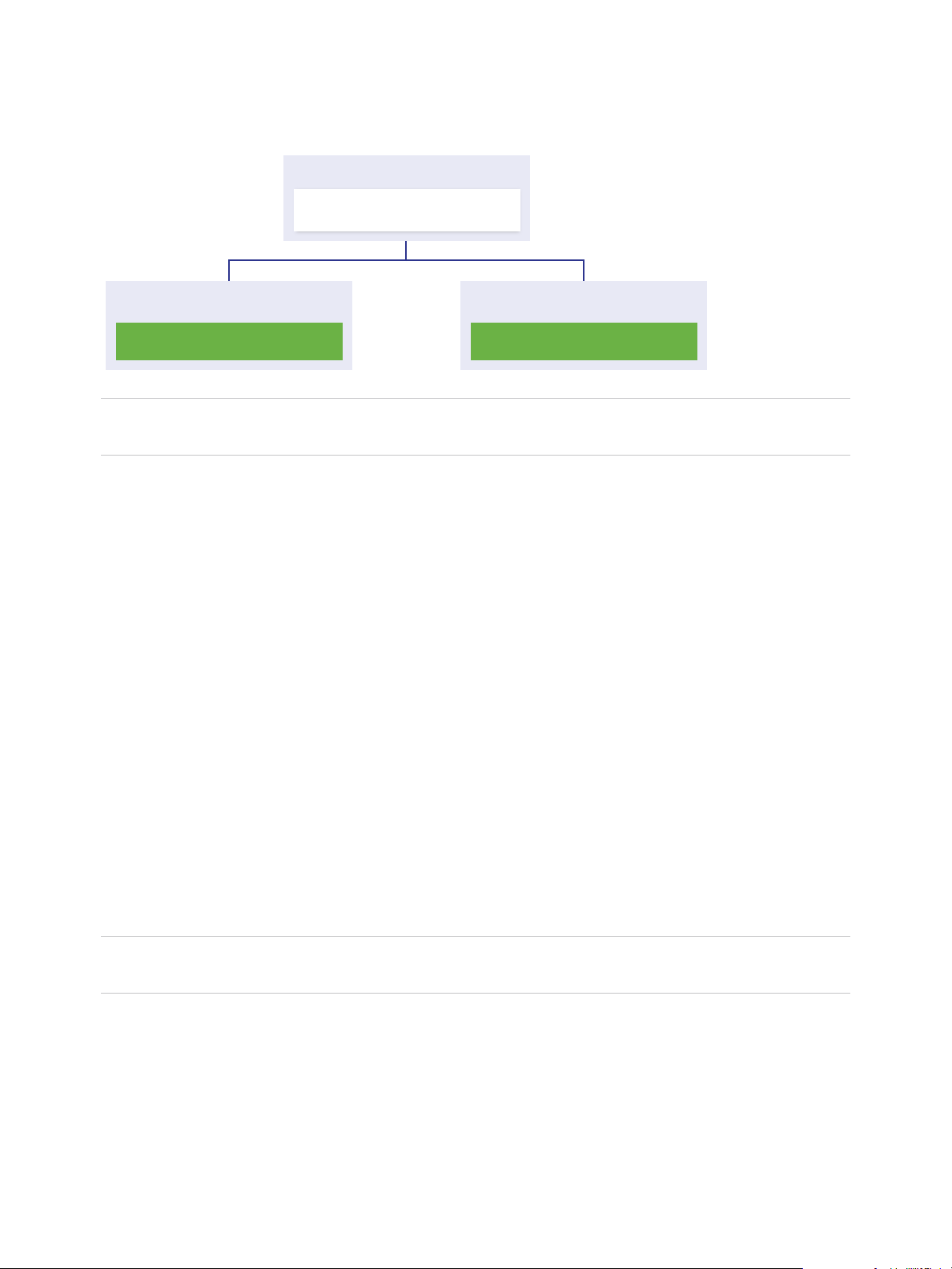
Platform Services Controller and vCenter Server with an External
Platform Services Controller
When you deploy or install a Platform Services Controller instance, you can create a vCenter Single SignOn domain or join an existing vCenter Single Sign-On domain. Joined Platform Services Controller
instances replicate their infrastructure data, such as authentication and licensing information, and can
span multiple vCenter Single Sign-On sites. For information, see Understanding vSphere Domains,
Domain Names, and Sites.
For information about managing the Platform Services Controller services, see Platform Services
Controller Administration.
You can register multiple vCenter Server instances with one common external
Platform Services Controller instance. The vCenter Server instances assume the vCenter Single Sign-On
site of the Platform Services Controller instance with which they are registered. All vCenter Server
instances that are registered with one common or different joined Platform Services Controller instances
are connected in Enhanced Linked Mode.
See Enhanced Linked Mode for vCenter Server or vCenter Server Appliance with an External Platform
Services Controller.
Figure 1‑3. Example of Two vCenter Server Instances with a Common External
Platform Services Controller
Installing vCenter Server with an external Platform Services Controller has the following advantages:
n
Fewer resources consumed by the shared services in the Platform Services Controller instances.
n
The model is suitable for large-scale environments.
VMware, Inc. 14
Platform Services
Controller on Windows
Windows Virtual Machine
or Physical Server
vCenter Server on Windows
Virtual Machine or Physical Server
vCenter Server Appliance
Virtual Machine
vCenter Server Installation and Setup
Installing vCenter Server with an external Platform Services Controller has the following disadvantages:
n
The connection between vCenter Server and Platform Services Controller might have connectivity
and name resolution issues.
n
If you install vCenter Server on Windows virtual machines or physical servers, you need more
Microsoft Windows licenses.
n
You must manage more virtual machines or physical servers.
For information about the Platform Services Controller and vCenter Server maximums, see the
Configuration Maximums documentation.
For information about the deployment topologies and Platform Services Controller high availability, see
Deployment Topologies with External Platform Services Controller Instances and High Availability.
For information about configuring the vCenter Server Appliance with an external
Platform Services Controller in vCenter High Availability configuration, see vSphere Availability.
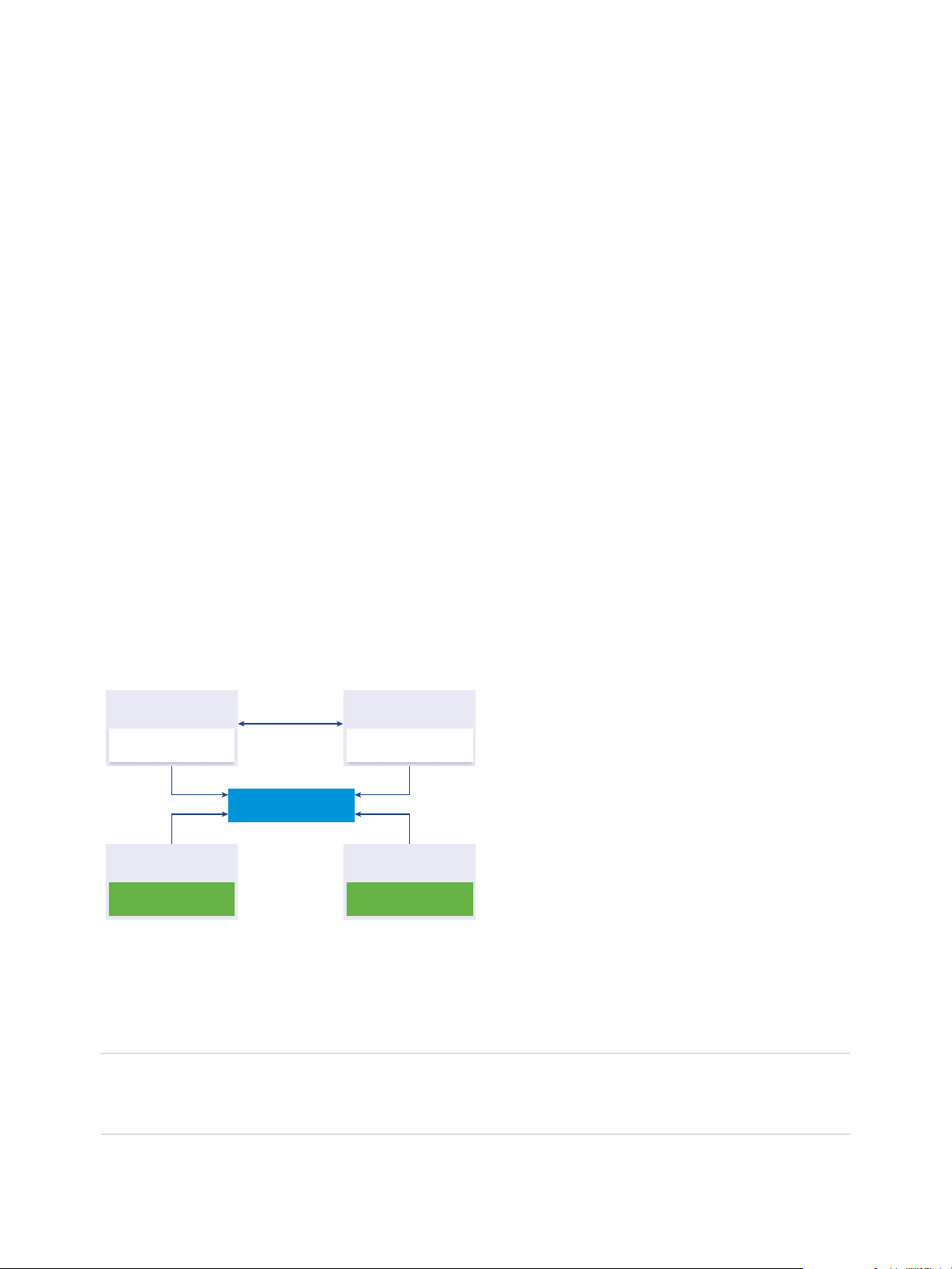
Mixed Operating Systems Environment
A vCenter Server instance installed on Windows can be registered with either a
Platform Services Controller installed on Windows or a Platform Services Controller appliance. A
vCenter Server Appliance can be registered with either a Platform Services Controller installed on
Windows or a Platform Services Controller appliance. Both vCenter Server and the
vCenter Server Appliance can be registered with the same Platform Services Controller.
Figure 1‑4. Example of a Mixed Operating Systems Environment with an External Platform
Services Controller on Windows
VMware, Inc. 15
Platform Services
Controller Appliance
Virtual Machine
vCenter Server on Windows
Virtual Machine or Physical Server
vCenter Server Appliance
Virtual Machine
vCenter Server Installation and Setup
Figure 1‑5. Example of a Mixed Operating Systems Environment with an External Platform
Services Controller Appliance
Note To ensure easy manageability and maintenance, use only appliances or only Windows installations
of vCenter Server and Platform Services Controller.
Understanding vSphere Domains, Domain Names, and Sites
Each Platform Services Controller is associated with a vCenter Single Sign-On domain. The domain
name defaults to vsphere.local, but you can change it during installation of the first
Platform Services Controller. The domain determines the local authentication space. You can split a
domain into multiple sites, and assign each Platform Services Controller and vCenter Server instance to a
site. Sites are logical constructs, but usually correspond to geographic location.
Platform Services Controller Domain
When you install a Platform Services Controller, you are prompted to create a vCenter Single Sign-On
domain or join an existing domain.
The domain name is used by the VMware Directory Service (vmdir) for all Lightweight Directory Access
Protocol (LDAP) internal structuring.
With vSphere 6.0 and later, you can give your vSphere domain a unique name. To prevent authentication
conflicts, use a name that is not used by OpenLDAP, Microsoft Active Directory, and other directory
services.
Note You cannot change the domain to which a Platform Services Controller or vCenter Server instance
belongs.
After you specify the name of your domain, you can add users and groups. It usually makes more sense
to add an Active Directory or LDAP identity source and allow the users and groups in that identity source
to authenticate. You can also add vCenter Server or Platform Services Controller instances, or other
VMware products, such as vRealize Operations, to the domain.
VMware, Inc. 16
Load Balancer
vCenter Server
Platform Services
Controller
Virtual Machine or
Physical Server
Virtual Machine or
Physical Server
vCenter Server
Platform Services
Controller
Virtual Machine or
Physical Server
Virtual Machine or
Physical Server
vCenter Server Installation and Setup
Platform Services Controller Sites
You can organize Platform Services Controller domains into logical sites. A site in the VMware Directory
Service is a logical container for grouping Platform Services Controller instances within a vCenter Single
Sign-On domain.
Starting with vSphere 6.5, sites become important. During Platform Services Controller failover, the
vCenter Server instances are affinitized to a different Platform Services Controller in the same site. To
prevent your vCenter Server instances from being affinitized to a Platform Services Controller in a distant
geographic location, you can use multiple sites.
You are prompted for the site name when you install or upgrade a Platform Services Controller. See the
vCenter Server Installation and Setup documentation.
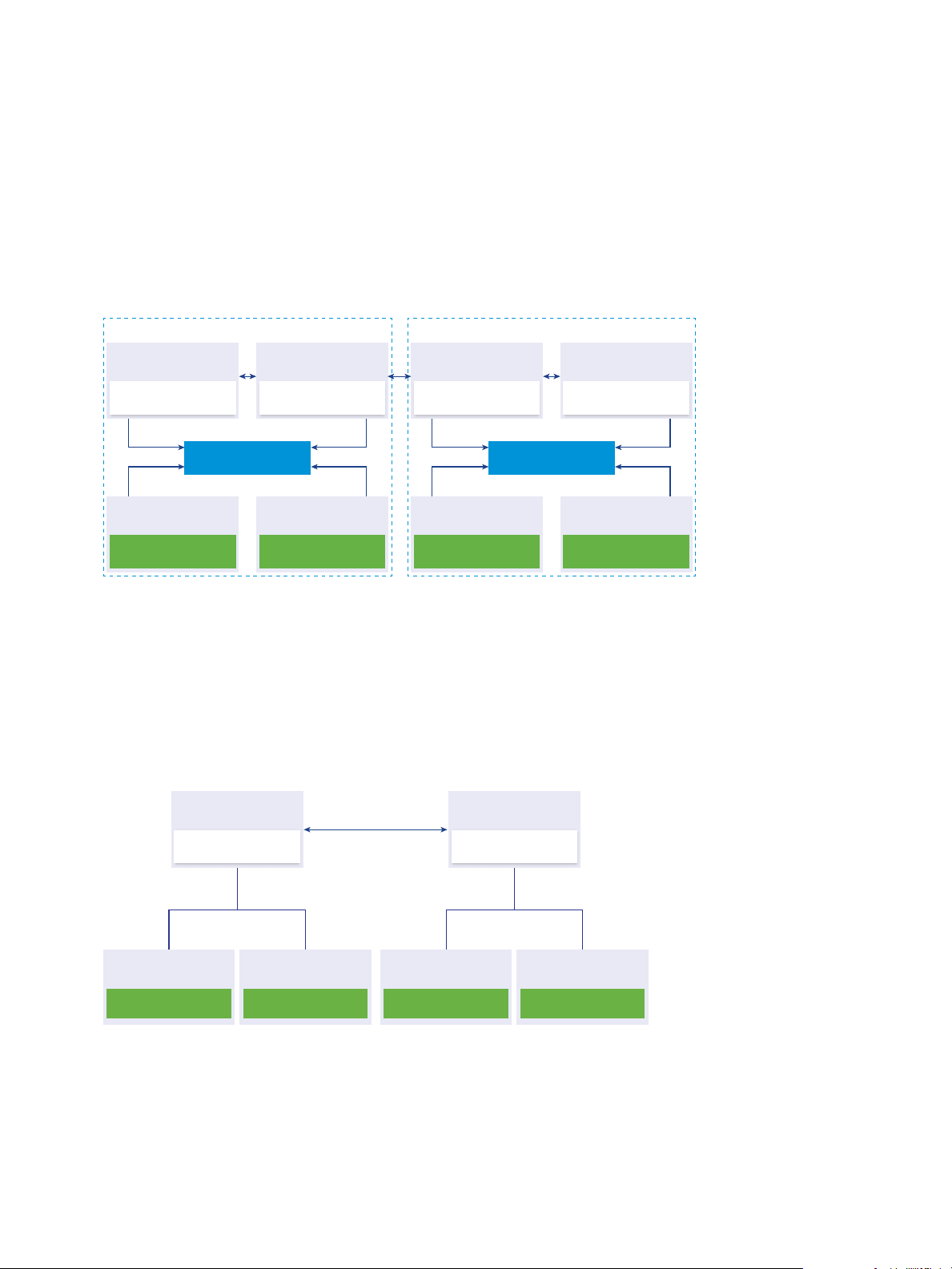
Deployment Topologies with External Platform Services Controller Instances and High Availability
To ensure Platform Services Controller high availability in external deployments, you must install or
deploy at least two joined Platform Services Controller instances in your vCenter Single Sign-On domain.
When you use a third-party load balancer, you can ensure an automatic failover without downtime.
Platform Services Controller with a Load Balancer
Figure 1‑6. Example of a Load Balanced Pair of Platform Services Controller Instances
You can use a third-party load balancer per site to configure Platform Services Controller high availability
with automatic failover for this site. For information about the maximum number of
Platform Services Controller instances behind a load balancer, see the Configuration Maximums
documentation.
Important To configure Platform Services Controller high availability behind a load balancer, the
Platform Services Controller instances must be of the same operating system type. Mixed operating
systems Platform Services Controller instances behind a load balancer are unsupported.
VMware, Inc. 17
Load Balancer
vCenter Server
Platform Services
Controller
Virtual Machine or
Physical Server
Site 1
Virtual Machine or
Physical Server
vCenter Server
Platform Services
Controller
Virtual Machine or
Physical Server
Virtual Machine or
Physical Server
Load Balancer
vCenter Server
Platform Services
Controller
Virtual Machine or
Physical Server
Virtual Machine or
Physical Server
vCenter Server
Platform Services
Controller
Virtual Machine or
Physical Server
Virtual Machine or
Physical Server
Site 2
Platform Services
Controller
Virtual Machine or
Physical Server
Virtual Machine or
Physical Server
Virtual Machine or
Physical Server
Virtual Machine or
Physical Server
vCenter Server vCenter Server vCenter Server vCenter Server
Virtual Machine or
Physical Server
Platform Services
Controller
Virtual Machine or
Physical Server
vCenter Server Installation and Setup
The vCenter Server instances are connected to the load balancer. When a Platform Services Controller
instance stops responding, the load balancer automatically distributes the load among the other functional
Platform Services Controller instances without downtime.
Platform Services Controller with Load Balancers Across vCenter
Single Sign-On Sites
Figure 1‑7. Example of Two Load Balanced Pairs of Platform Services Controller Instances
Across Two Sites
Your vCenter Single Sign-On domain might span multiple sites. To ensure Platform Services Controller
high availability with automatic failover throughout the domain, you must configure a separate load
balancer in each site.
Platform Services Controller with No Load Balancer
Figure 1‑8. Example of Two Joined Platform Services Controller Instances with No a Load
Balancer
When you join two or more Platform Services Controller instances in the same site with no load balancer,
you configure Platform Services Controller high availability with a manual failover for this site.
VMware, Inc. 18

vCenter Server
Platform Services
Controller
Virtual Machine or
Physical Server
Virtual Machine or
Physical Server
vCenter Server
Platform Services
Controller
Virtual Machine or
Physical Server
Virtual Machine or
Physical Server
vCenter Server
Platform Services
Controller
Virtual Machine or
Physical Server
Virtual Machine or
Physical Server
vCenter Server
Platform Services
Controller
Virtual Machine or
Physical Server
Virtual Machine or
Physical Server
Site 1 Site 2
vCenter Server Installation and Setup
When a Platform Services Controller instance stops responding, you must manually fail over the
vCenter Server instances that are registered to it. You fail over the instances by repointing them to other
functional Platform Services Controller instances within the same site. See Repoint vCenter Server to
Another External Platform Services Controller in the Same Domain.
Note If your vCenter Single Sign-On domain includes three or more Platform Services Controller
instances, you can manually create a ring topology. A ring topology ensures Platform Services Controller
reliability when one of the instances fails. To create a ring topology, run the /usr/lib/vmware-
vmdir/bin/vdcrepadmin -f createagreement command against the first and last
Platform Services Controller instance that you have deployed.
Platform Services Controller with No Load Balancer Across
vCenter Single Sign-On Sites
Figure 1‑9. Example of Two Joined Pairs of Platform Services Controller Instances Across
Two Sites with No Load Balancer
Your vCenter Single Sign-On domain might span multiple sites. When no load balancer is available, you
can manually repoint vCenter Server from a failed to a functional Platform Services Controller within the
same site. See Repoint vCenter Server to Another External Platform Services Controller in the Same
Domain.
vCenter Enhanced Linked Mode
vCenter Enhanced Linked Mode allows you to log in to any single instance of vCenter Server Appliance
or vCenter Server and view and manage the inventories of all the vCenter Server systems in the group.
You can join up to ten vCenter Server Appliance systems and eight vCenter Server systems with vCenter
Enhanced Linked Mode.
You can create a vCenter Enhanced Linked Mode group only during the deployment of vCenter Server
Appliance or installation of vCenter Server. You cannot create a vCenter Enhanced Linked Mode group
after you install vCenter Server or after you deploy the vCenter Server Appliance.
VMware, Inc. 19
Platform Services
Controller
Appliance
vCenter Server
Platform Services
Controller
Appliance
vCenter Server
Platform Services
Controller
Appliance
vCenter Server
Platform Services
Controller
Appliance
vCenter Server
vCenter Server Installation and Setup
vCenter Embedded Linked Mode for a vCenter Server Appliance with Embedded Platform Services Controller
vCenter Embedded Linked Mode is enhanced linked mode support for vCenter Server Appliance with an
embedded Platform Services Controller.
With vCenter Embedded Linked Mode, you can connect a vCenter Server Appliance with an embedded
Platform Services Controller together to form a domain. vCenter Embedded Linked Mode is not supported
for Windows vCenter Server installations. vCenter Embedded Linked Mode is suitable for most
deployments.
Other features of vCenter Embedded Linked Mode include:
n
No external Platform Services Controller, providing a more simplified domain architecture than
enhanced linked mode.
n
A simplified backup and restore process.
n
A simplified HA process, removing the need for load balancers.
n
Up to ten vCenter Server Appliances can be linked together using vCenter Embedded Linked Mode
and displayed in a single inventory view.
n
For a vCenter High Availability (vCenter HA) cluster, three nodes are considered one logical
vCenter Server node. This represents ten times the vCenter HA clusters in a vCenter Embedded
Linked Mode for a total of 30 VMs.
Figure 1‑10. Embedded Linked Mode
Note Embedded linked mode is not supported for Windows vCenter Server installations.
Joining a vCenter Embedded Linked Mode Domain
You can join a vCenter Server with an embedded Platform Services Controller to another embedded node
during deployment of the vCenter Server Appliance.
For example, suppose you have two vCenter Servers with embedded Platform Services Controller
systems.
If you are deploying the vCenter Server Appliances with the UI Installer:
1 For Appliance 1, deploy the vCenter Server Appliance as an instance on ESXi Host 1. Synchronize
VMware, Inc. 20
the time settings with ESXi Host 1.

vCenter Server Installation and Setup
2 For Appliance 2, deploy the vCenter Server Appliance as an instance on ESXi Host 1 and configure
the time settings so that Appliance 2 are synchronized with ESXi Host 1. In stage 2 you select to join
the vCenter Single Sign-On server of the deployed appliance on Machine 1. For specific instructions,
see Stage 2 - Set up the Newly Deployed vCenter Server Appliance with an Embedded Platform
Services Controller.
If you are deploying the vCenter Server Appliances with the CLI:
1 Configure the JSON configuration template embedded_vCSA_on_VC.json (or
embedded_vCSA_on_ESXi.json) for Appliance 1 as an instance on ESXi Host 1. See Prepare Your
JSON Configuration File for CLI Deployment for specific instructions on preparing the JSON
configuraiton file.
2 Deploy Appliance 1 by running the vcsa-cli-installer command. See Deploy a vCenter Server
Appliance or Platform Services Controller Appliance by Using the CLI for instructions.
3 Configure the JSON configuration template embedded_vCSA_replication_on_VC.json for
Appliance 2 as an instance on ESXi Host 1. Enter the hostname of the first embedded node in the
replication_partner_hostname field in the sso section.
4 Deploy Appliance 2 by running the vcsa-cli-installer command on the
embedded_vCSA_replication_on_VC.json file.
Enhanced Linked Mode for vCenter Server or vCenter Server Appliance with an External Platform Services Controller
Enhanced Linked Mode connects multiple vCenter Server systems together by using one or more
Platform Services Controllers.
Enhanced Linked Mode lets you view and search across all linked vCenter Server systems and replicate
roles, permissions, licenses, policies, and tags.
When you install vCenter Server or deploy the vCenter Server Appliance with an external
Platform Services Controller, you must first install the Platform Services Controller. During installation of
the Platform Services Controller, you can select whether to create a vCenter Single Sign-On domain or
join an existing domain. You can select to join an existing vCenter Single Sign-On domain if you have
already installed or deployed a Platform Services Controller instance and have created a vCenter Single
Sign-On domain. When you join an existing vCenter Single Sign-On domain, the infrastructure data
between the existing Platform Services Controller and the new Platform Services Controller is replicated.
With Enhanced Linked Mode, you can connect not only vCenter Server systems running on Windows but
also many vCenter Server Appliances. You can also have an environment where multiple vCenter Server
systems and vCenter Server Appliances are linked together.
If you install vCenter Server with an external Platform Services Controller, you first must deploy the
Platform Services Controller on one virtual machines or physical server and then deploy vCenter Server
on another virtual machine or physical server. While installing vCenter Server, you must select an existing
external Platform Services Controller. You cannot select an existing Platform Services Controller that is a
part of an embedded installation. For more information about the supported topologies, see vCenter
Server and Platform Services Controller Deployment Types.
VMware, Inc. 21
Deploying the
vCenter Server Appliance and
Platform Services Controller
Appliance 2
You can deploy the vCenter Server Appliance with an embedded or external Platform Services Controller
to manage your vSphere environment. You can deploy a Platform Services Controller appliance and
register external deployments and Windows installations of vCenter Server Appliance with this
Platform Services Controller appliance.
You can deploy the vCenter Server Appliance or Platform Services Controller appliance on an ESXi host
5.5 or later, or on an ESXi host or DRS cluster from the inventory of a vCenter Server instance 5.5 or
later.
For information about the software included in the vCenter Server Appliance 6.7, see Overview of the
vCenter Server Appliance.
For information about the software and hardware requirements for deploying the
vCenter Server Appliance and Platform Services Controller appliance, see System Requirements for the
vCenter Server Appliance and Platform Services Controller Appliance.
The vCenter Server Appliance installer contains executable files for GUI and CLI deployments, which you
can use alternatively.
n
The GUI deployment is a two stage process. The first stage is a deployment wizard that deploys the
OVA file of the appliance on the target ESXi host or vCenter Server instance. After the OVA
deployment finishes, you are redirected to the second stage of the process that sets up and starts the
services of the newly deployed appliance.
n
The CLI deployment method involves running a CLI command against a JSON file that you previously
prepared. The CLI installer parses the configuration parameters and their values from the JSON file
and generates an OVF Tool command that automatically deploys and sets up the appliance.
Important For topologies with external Platform Services Controller instances, you must deploy the
replicating Platform Services Controller instances in a sequence. After the successful deployment of all
Platform Services Controller instances in the domain, you can perform concurrent deployments of multiple
vCenter Server appliances that point to a common external Platform Services Controller instance.
The vCenter Server Appliance and Platform Services Controller appliance have the following default user
names:
VMware, Inc.
22
vCenter Server Installation and Setup
User Name Description
root Use this user name to log in to the appliance operating system and the Appliance
Management Interface.
You set the password while deploying the virtual appliance.
administrator@your_domain_name Use this user name for vCenter Single Sign-On login.
You set the password while creating the vCenter Single Sign-On domain. You create a
vCenter Single Sign-On domain during the deployment of a vCenter Server Appliance with an
embedded Platform Services Controller or the first Platform Services Controller instance in a
new vCenter Single Sign-On domain.
After you create a vCenter Single Sign-On domain, only the
administrator@your_domain_name user has the privileges required to log in to vCenter Single
Sign-On and vCenter Server.
The administrator@your_domain_name user can proceed as follows:
n
Add an identity source in which additional users and groups are defined to vCenter Single
Sign-On.
n
Give permissions to the users and groups.
For information about adding identity sources and giving permissions to the users and groups,
see Platform Services Controller Administration.
For information about upgrading and patching the vCenter Server Appliance and
Platform Services Controller appliance, see vSphere Upgrade.
For information about configuring the vCenter Server Appliance and Platform Services Controller
appliance, see vCenter Server Appliance Configuration.
Starting with vSphere 6.5, vCenter Server supports mixed IPv4 and IPv6 environment. If you want to set
up the vCenter Server Appliance to use an IPv6 address version, use the fully qualified domain name
(FQDN) or host name of the appliance. To set up an IPv4 address, the best practice is to use the FQDN
or host name of the appliance, because the IP address can change if assigned by DHCP.
This chapter includes the following topics:
n
System Requirements for the vCenter Server Appliance and Platform Services Controller Appliance
n
Preparing for Deployment of the vCenter Server Appliance and Platform Services Controller
Appliance
n
Prerequisites for Deploying the vCenter Server Appliance or Platform Services Controller Appliance
n
GUI Deployment of the vCenter Server Appliance and Platform Services Controller Appliance
n
CLI Deployment of the vCenter Server Appliance and Platform Services Controller Appliance
System Requirements for the vCenter Server Appliance
and Platform Services Controller Appliance
You can deploy the vCenter Server Appliance or Platform Services Controller appliance on an ESXi host
5.5 or later, or on a vCenter Server instance 5.5 or later. Your system must also meet specific software
and hardware requirements.
When you use Fully Qualified Domain Names, verify that the client machine from which you are deploying
the appliance and the network on which you are deploying the appliance use the same DNS server.
VMware, Inc. 23

vCenter Server Installation and Setup
Before you deploy the appliance, synchronize the clocks of the target server and all vCenter Server and
Platform Services Controller instances on the vSphere network. Unsynchronized clocks might result in
authentication problems and can cause the installation to fail or prevent the appliance services from
starting. See Synchronizing Clocks on the vSphere Network.
Hardware Requirements for the vCenter Server Appliance and Platform Services Controller Appliance
When you deploy the vCenter Server Appliance, you can select to deploy an appliance that is suitable for
the size of your vSphere environment. The option that you select determines the number of CPUs and the
amount of memory for the appliance. The size of the Platform Services Controller appliance is the same
for all environment sizes.
Hardware Requirements for the vCenter Server Appliance
The hardware requirements for a vCenter Server Appliance depend on the size of your vSphere
inventory.
Table 2‑1. Hardware Requirements for a vCenter Server Appliance with an Embedded or
External Platform Services Controller
Number of vCPUs Memory
Tiny environment (up to 10 hosts or 100
virtual machines)
Small environment (up to 100 hosts or
1,000 virtual machines)
Medium environment (up to 400 hosts or
4,000 virtual machine)
Large environment (up to 1,000 hosts or
10,000 virtual machines)
X-Large environment (up to 2,000 hosts or
35,000 virtual machines)
2 10 GB
4 16 GB
8 24 GB
16 32 GB
24 48 GB
Note If you want to add an ESXi host with more than 512 LUNs and 2,048 paths to the
vCenter Server Appliance inventory, you must deploy a vCenter Server Appliance for a large or x-large
environment.
Hardware Requirements for the Platform Services Controller Appliance
The hardware requirements for a Platform Services Controller appliance are 2 vCPUs and 4 GB memory.
VMware, Inc. 24
vCenter Server Installation and Setup
Storage Requirements for the vCenter Server Appliance and Platform Services Controller Appliance
When you deploy the vCenter Server Appliance or Platform Services Controller appliance, the ESXi host
or DRS cluster on which you deploy the appliance must meet minimum storage requirements. The
required storage depends not only on the size of the vSphere environment and the storage size, but also
on the disk provisioning mode.
Storage Requirements for the vCenter Server Appliance
The storage requirements are different for each vSphere environment size and depend on your database
size requirements.
Table 2‑2. Storage Requirements for a vCenter Server Appliance with an Embedded or
External Platform Services Controller
Default Storage Size Large Storage Size X-Large Storage Size
Tiny environment (up to 10
hosts or 100 virtual machines)
Small environment (up to 100
hosts or 1,000 virtual
machines)
Medium environment (up to
400 hosts or 4,000 virtual
machine)
Large environment (up to 1,000
hosts or 10,000 virtual
machines)
X-Large environment (up to
2,000 hosts or 35,000 virtual
machines)
250 GB 775 GB 1650 GB
290 GB 820 GB 1700 GB
425 GB 925 GB 1805 GB
640 GB 990 GB 1870 GB
980 GB 1030 GB 1910 GB
Note The storage requirements include the requirements for the VMware Update Manager that runs as
a service in the vCenter Server Appliance.
Storage Requirements for the Platform Services Controller Appliance
The storage requirement for a Platform Services Controller appliance is 60 GB.
Software Requirements for the vCenter Server Appliance and Platform Services Controller Appliance
The VMware vCenter Server Appliance and Platform Services Controller appliance can be deployed on
ESXi hosts 5.5 or later, or on vCenter Server instances 6.0 or later.
VMware, Inc. 25
vCenter Server Installation and Setup
You can deploy the vCenter Server Appliance or Platform Services Controller appliance by using the GUI
or CLI installer. You run the installer from a network client machine that you use to connect to the target
server and deploy the appliance on the server. You can connect directly to an ESXi 6.x host on which to
deploy the appliance. You can also connect to a vCenter Server 6.x instance to deploy the appliance on
an ESXi host or DRS cluster that resides in the vCenter Server inventory.
For information about the requirements for network client machine, see System Requirements for the
vCenter Server Appliance Installer.
Required Ports for vCenter Server and Platform Services Controller
The vCenter Server system, both on Windows and in the appliance, must be able to send data to every
managed host and receive data from the vSphere Web Client and the Platform Services Controller
services. To enable migration and provisioning activities between managed hosts, the source and
destination hosts must be able to receive data from each other.
If a port is in use or is blacklisted, the vCenter Server installer displays an error message. You must use
another port number to proceed with the installation. There are internal ports that are used only for interprocess communication.
VMware uses designated ports for communication. Additionally, the managed hosts monitor designated
ports for data from vCenter Server. If a built-in firewall exists between any of these elements, the installer
opens the ports during the installation or upgrade process. For custom firewalls, you must manually open
the required ports. If you have a firewall between two managed hosts and you want to perform source or
target activities, such as migration or cloning, you must configure a means for the managed hosts to
receive data.
Note In Microsoft Windows Server 2008 and later, firewall is enabled by default.
Table 2‑3. Ports Required for Communication Between Components
Used for Node-to-Node
Port Protocol Description Required for
22 TCP System port for SSHD. Appliance deployments
of
n
vCenter Server
n
Platform Services
Controller
53 DNS service Windows installations
and appliance
deployments of
Platform Services
Controller
Communication
No
No
VMware, Inc. 26
vCenter Server Installation and Setup
Table 2‑3. Ports Required for Communication Between Components (Continued)
Used for Node-to-Node
Port Protocol Description Required for
Communication
80 TCP vCenter Server requires port 80 for direct
HTTP connections. Port 80 redirects
requests to HTTPS port 443. This
redirection is useful if you accidentally
use http://server instead of https://server.
WS-Management (also requires port 443
to be open).
If you use a Microsoft SQL database that
is stored on the same virtual machine or
physical server as the vCenter Server,
port 80 is used by the SQL Reporting
Service. When you install or upgrade
vCenter Server, the installer prompts you
to change the HTTP port for
vCenter Server. Change the
vCenter Server HTTP port to a custom
value to ensure a successful installation
or upgrade.
Important You can change this port
number during the vCenter Server and
Platform Services Controller installations
on Windows.
88 TCP Active Directory server. This port must be
open for host to join Active Directory. If
you use native Active Directory, the port
must be open on both vCenter Server
and Platform Services Controller.
Windows installations
and appliance
deployments of
n
vCenter Server
n
Platform Services
Controller
Windows installations
and appliance
deployments of
Platform Services
Controller
No
No
389 TCP/UDP This port must be open on the local and
all remote instances of vCenter Server.
This is the LDAP port number for the
Directory Services for the vCenter Server
group. If another service is running on
this port, it might be preferable to remove
it or change its port to a different port.
You can run the LDAP service on any
port from 1025 through 65535.
If this instance is serving as the Microsoft
Windows Active Directory, change the
port number from 389 to an available port
from 1025 through 65535.
Windows installations
and appliance
deployments of
Platform Services
Controller
n
vCenter Server to
Platform Services
Controller
n
Platform Services
Controller to
Platform Services
Controller
VMware, Inc. 27
vCenter Server Installation and Setup
Table 2‑3. Ports Required for Communication Between Components (Continued)
Used for Node-to-Node
Port Protocol Description Required for
Communication
443 TCP The default port that the vCenter Server
system uses to listen for connections
from the vSphere Web Client. To enable
the vCenter Server system to receive
data from the vSphere Web Client, open
port 443 in the firewall.
The vCenter Server system also uses
port 443 to monitor data transfer from
SDK clients.
This port is also used for the following
services:
n
WS-Management (also requires port
80 to be open)
n
Third-party network management
client connections to vCenter Server
n
Third-party network management
clients access to hosts
Important You can change this port
number during the vCenter Server and
Platform Services Controller installations
on Windows.
514 TCP/UDP vSphere Syslog Collector port for
vCenter Server on Windows and vSphere
Syslog Service port for
vCenter Server Appliance
Important You can change this port
number during the vCenter Server and
Platform Services Controller installations
on Windows.
Windows installations
and appliance
deployments of
n
vCenter Server
n
Platform Services
Controller
Windows installations
and appliance
deployments of
n
vCenter Server
n
Platform Services
Controller
n
vCenter Server to
vCenter Server
n
vCenter Server to
Platform Services
Controller
n
Platform Services
Controller to
vCenter Server
No
636 TCP vCenter Single Sign-On LDAPS
For backward compatibility with vSphere
6.0 only.
VMware, Inc. 28
Windows installations
and appliance
deployments of
Platform Services
Controller
During upgrade from
vSphere 6.0 only.
vCenter Server 6.0 to
Platform Services
Controller 6.5
vCenter Server Installation and Setup
Table 2‑3. Ports Required for Communication Between Components (Continued)
Used for Node-to-Node
Port Protocol Description Required for
Communication
902 TCP/UDP The default port that the vCenter Server
system uses to send data to managed
hosts. Managed hosts also send a
regular heartbeat over UDP port 902 to
the vCenter Server system. This port
must not be blocked by firewalls between
the server and the hosts or between
hosts.
Port 902 must not be blocked between
the VMware Host Client and the hosts.
The VMware Host Client uses this port to
display virtual machine consoles
Important You can change this port
number during the vCenter Server
installations on Windows.
1514 TCP vSphere Syslog Collector TLS port for
vCenter Server on Windows and vSphere
Syslog Service TLS port for
vCenter Server Appliance
Important You can change this port
number during the vCenter Server and
Platform Services Controller installations
on Windows.
Windows installations
and appliance
deployments of
vCenter Server
Windows installations
and appliance
deployments of
n
vCenter Server
n
Platform Services
Controller
No
No
2012 TCP Control interface RPC for vCenter Single
Sign-On
Windows installations
and appliance
deployments of
Platform Services
Controller
2014 TCP RPC port for all VMCA (VMware
Certificate Authority) APIs
Important You can change this port
number during the
Platform Services Controller installations
Windows installations
and appliance
deployments of
Platform Services
Controller
on Windows.
2015 TCP DNS management Windows installations
and appliance
deployments of
Platform Services
Controller
n
vCenter Server to
Platform Services
Controller
n
Platform Services
Controller to
vCenter Server
n
Platform Services
Controller to
Platform Services
Controller
n
vCenter Server to
Platform Services
Controller
n
Platform Services
Controller to
vCenter Server
Platform Services
Controller to
Platform Services
Controller
VMware, Inc. 29
vCenter Server Installation and Setup
Table 2‑3. Ports Required for Communication Between Components (Continued)
Used for Node-to-Node
Port Protocol Description Required for
Communication
2020 TCP/UDP Authentication framework management
Important You can change this port
number during the vCenter Server and
Platform Services Controller installations
on Windows.
5480 TCP Appliance Management Interface
Open endpoint serving all HTTPS,
XMLRPS and JSON-RPC requests over
HTTPS.
6500 TCP/UDP ESXi Dump Collector port
Important You can change this port
number during the vCenter Server
installations on Windows.
6501 TCP Auto Deploy service
Important You can change this port
number during the vCenter Server
installations on Windows.
6502 TCP Auto Deploy management
Important You can change this port
number during the vCenter Server
installations on Windows.
Windows installations
and appliance
deployments of
n
vCenter Server
n
Platform Services
Controller
Appliance deployments
of
n
vCenter Server
n
Platform Services
Controller
Windows installations
and appliance
deployments of
vCenter Server
Windows installations
and appliance
deployments of
vCenter Server
Windows installations
and appliance
deployments of
vCenter Server
n
vCenter Server to
Platform Services
Controller
n
Platform Services
Controller to
vCenter Server
No
No
No
No
7080,
12721
TCP Secure Token Service
Note Internal ports
7081 TCP VMware Platform Services Controller
Web Client
Note Internal port
8200,
8201,
8300,
TCP Appliance management
Note Internal ports
8301
8084 TCP vSphere Update Manager SOAP port
The port used by vSphere Update
Manager client plug-in to connect to the
vSphere Update Manager SOAP server.
Windows installations
and appliance
deployments of
Platform Services
Controller
Windows installations
and appliance
deployments of
Platform Services
Controller
Appliance deployments
of
n
vCenter Server
n
Platform Services
Controller
Appliance deployments
of vCenter Server
No
No
No
No
VMware, Inc. 30
 Loading...
Loading...