Page 1

Using VMware vCenter Orchestrator
Plug-Ins
vCenter Orchestrator 4.2
This document supports the version of each product listed and
supports all subsequent versions until the document is replaced
by a new edition. To check for more recent editions of this
document, see http://www.vmware.com/support/pubs.
EN-000422-00
Page 2

Using VMware vCenter Orchestrator Plug-Ins
You can find the most up-to-date technical documentation on the VMware Web site at:
http://www.vmware.com/support/
The VMware Web site also provides the latest product updates.
If you have comments about this documentation, submit your feedback to:
docfeedback@vmware.com
Copyright © 2011 VMware, Inc. All rights reserved. This product is protected by U.S. and international copyright and intellectual
property laws. VMware products are covered by one or more patents listed at http://www.vmware.com/go/patents.
VMware is a registered trademark or trademark of VMware, Inc. in the United States and/or other jurisdictions. All other marks
and names mentioned herein may be trademarks of their respective companies.
VMware, Inc.
3401 Hillview Ave.
Palo Alto, CA 94304
www.vmware.com
2 VMware, Inc.
Page 3

Contents
Using VMware vCenter Orchestrator Plug-Ins 7
Introduction to Orchestrator Plug-Ins 9
1
Orchestrator Architecture 9
Default Orchestrator Plug-Ins 10
Access the Orchestrator API Explorer 12
Using the vCenter Server 4.1 Plug-In 15
2
Configure the vCenter Server 4.1 Plug-In 15
vCenter Server 4.1 Plug-In Scripting API 16
vCenter Server Scripting Examples 16
Using the vCenter Server 4.1 Plug-In Inventory 18
Access the vCenter Server 4.1 Plug-In Workflow Library 18
vCenter Server 4.1 Plug-In Workflow Library 19
Using the vCO Library Plug-In 29
3
vCO Library Plug-In Workflows 29
Using the Database Plug-In 31
4
Database Plug-In Scripting API 31
Connection Class 31
JDBCConnection Class 31
PreparedStatement Class 32
ResultSet Class 32
Running the JDBC Sample Workflows 33
Generate a JDBC URL 33
Test a JDBC Connection 34
Create a Table by Using JDBC 34
Insert a Row into a JBCD Table 35
Select Rows from a JDBC Table 35
Delete an Entry from a JDBC Table 36
Delete All Entries from a JDBC Table 36
Drop a JDBC Table 37
Run a Complete JDBC Cycle 37
VMware, Inc.
Using the SSH Plug-In 39
5
Configure the SSH Plug-In 39
SSH Plug-In Scripting API 40
SSH:File Type 40
SSH:Folder Type 40
SSH:RootFolder Type 40
3
Page 4

Using VMware vCenter Orchestrator Plug-Ins
SSH:SshConnection Type 40
KeyPairManager Class 40
SSHCommand Class 41
SSHFile Class 42
SSHFolder Class 42
SSHSession Class 43
Running the SSH Plug-In Sample Workflows 44
Generate a Key Pair 44
Change the Key Pair Passphrase 45
Register an Orchestrator Public Key on an SSH Host 45
Run an SSH Command 46
Copy a File from an SSH Host 46
Copy a File to an SSH Host 47
Using the XML Plug-In 49
6
XML Plug-In Scripting API 49
XMLDocument Class 49
XMLElement Class 50
XMLManager Class 51
XMLNamedNodeMap Class 51
XMLNode Class 52
XMLNodeList Class 53
Running the XML Plug-In Sample Workflows 53
Create a Simple XML Document 53
Find an Element in an XML Document 54
Modify an XML Document 54
Create an Example Address Book from XML 55
Using the Mail Plug-In 57
7
Define the Default SMTP Connection 57
Mail Plug-In Scripting API 58
EmailMessage Class 58
Email Scripting Examples 58
Using the Mail Plug-In Sample Workflows 59
Access the Mail Plug-In Sample Workflows 59
Mail Plug-In Sample Workflows 59
Test an Example Interaction with Email 60
Using the Net Plug-In 61
8
Net Plug-In Scripting API 61
FTPClient Class 61
POP3Client Class 62
POP3Message Class 63
TelnetClient Class 63
Using the Enumeration Plug-In 65
9
Enumeration Plug-In Scrpting API 65
Time Zone Codes 66
4 VMware, Inc.
Page 5

Index 69
Contents
VMware, Inc. 5
Page 6

Using VMware vCenter Orchestrator Plug-Ins
6 VMware, Inc.
Page 7

Using VMware vCenter Orchestrator Plug-Ins
The Using VMware vCenter Orchestrator Plug-Ins provides information and instructions about configuring and
using the official set of plug-ins installed with VMware® vCenter Orchestrator.
Intended Audience
This information is intended for advanced vSphere administrators and experienced system administrators
who are familiar with virtual machine technology and datacenter operations.
VMware, Inc. 7
Page 8

Using VMware vCenter Orchestrator Plug-Ins
8 VMware, Inc.
Page 9

Introduction to Orchestrator Plug-Ins 1
Plug-ins allow you to use Orchestrator to access and control external technologies and applications. Exposing
an external technology in an Orchestrator plug-in allows you to incorporate objects and functions in workflows
that access the objects and functions of that external technology.
The external technologies that you can access by using plug-ins can include virtualization management tools,
email systems, databases, directory services, and remote control interfaces.
Orchestrator provides a set of standard plug-ins to allow you to incorporate such technologies as the VMware
vCenter Server API and email capabilities into workflows. In addition, the Orchestrator open plug-in
architecture allows you to develop plug-ins to access other applications. Orchestrator implements open
standards, to simplify integration with external systems. For information about developing custom content,
see Developing with VMware vCenter Orchestrator.
Plug-ins extend the Orchestrator scripting engine with new object types and methods, and plug-ins publish
notification events from the external system that trigger events in Orchestrator and in the plugged-in
technology. Plug-ins provide an inventory of JavaScript objects that you can access on the Orchestrator
Inventory tab. Each plug-in can provide one or more packages of workflows and actions that you can run on
the objects in the inventory to automate the typical use cases of the integrated product.
This chapter includes the following topics:
n
“Orchestrator Architecture,” on page 9
n
“Default Orchestrator Plug-Ins,” on page 10
n
“Access the Orchestrator API Explorer,” on page 12
Orchestrator Architecture
Orchestrator contains a workflow library and a workflow engine to allow you to create and run workflows
that automate orchestration processes. You run workflows on the objects of different technologies that
Orchestrator accesses through a series of plug-ins.
Orchestrator provides a standard set of plug-ins, including a plug-in for vCenter Server, to allow you to
orchestrate tasks in the different environments that the plug-ins expose.
Orchestrator also presents an open architecture to allow you to plug in external third-party applications to the
orchestration platform. You can run workflows on the objects of the plugged-in technologies that you define
yourself. Orchestrator connects to a directory services server to manage user accounts, and to a database to
store information from the workflows that it runs. You can access Orchestrator, the Orchestrator workflows,
and the objects it exposes through the Orchestrator client interface, through a Web browser, or through Web
services.
VMware, Inc.
9
Page 10
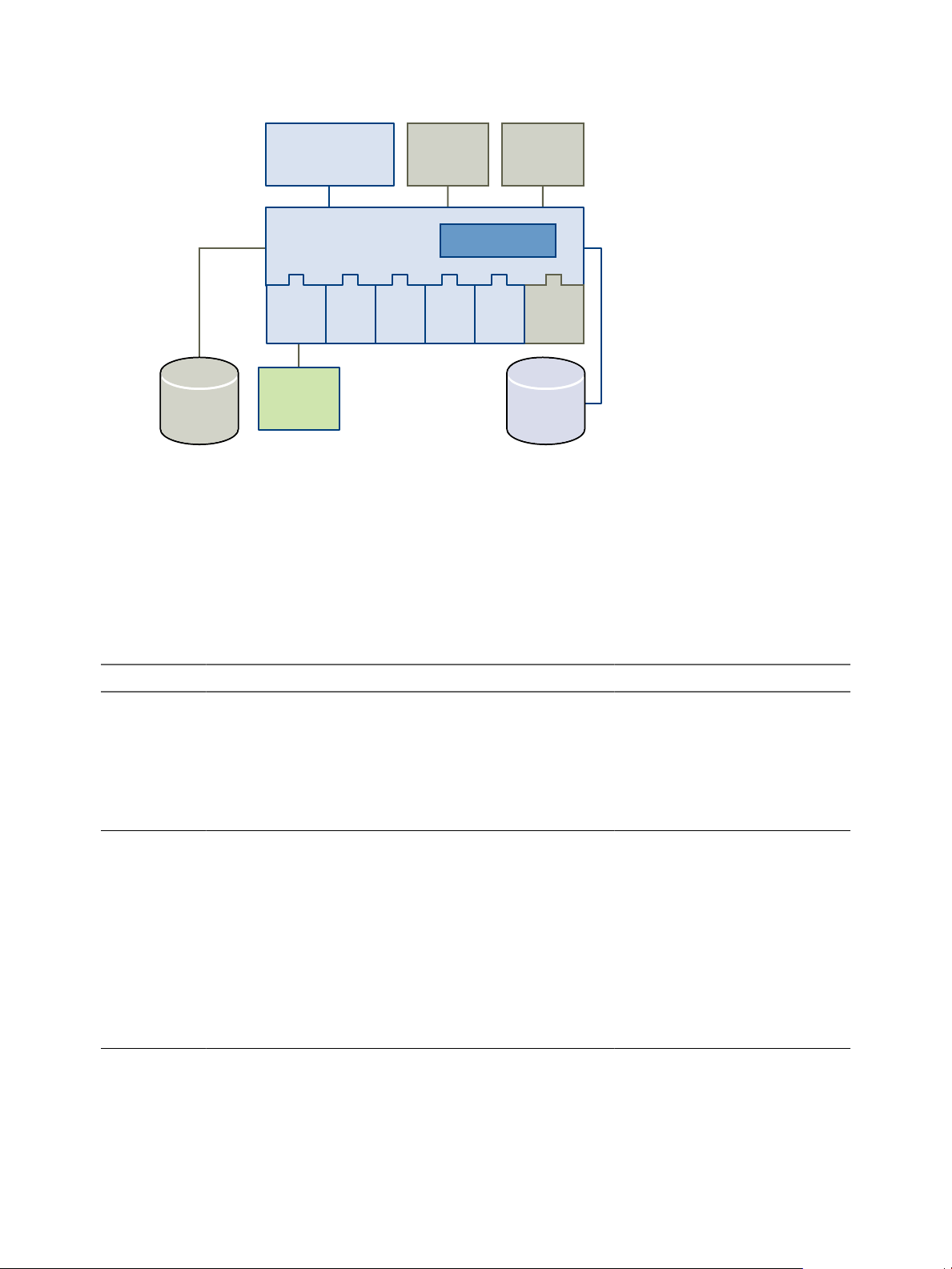
Orchestrator
database
workflow library
vCenter
Server
XML SSH JDBC SMTP
3rd-party
plug-in
directory
services
workflow engine
web
service
browser
access
vCenter
Orchestrator
Client application
vCenter
Server
Using VMware vCenter Orchestrator Plug-Ins
Figure 1-1. VMware vCenter Orchestrator Architecture
Default Orchestrator Plug-Ins
Orchestrator includes a collection of plug-ins. Each plug-in exposes an external product API to the Orchestrator
platform. Plug-ins provide inventory classes, extend the scripting engine with new object types, and publish
notification events from the external system. Each plug-in can also provide a library of workflows that
represents the typical use cases of the integrated product in an automated fashion.
You can see the list of available plug-ins from the Plug-ins tab in the Orchestrator configuration interface. Plug-
ins that require configuration add separate tabs to the interface.
Table 1-1. Plug-Ins Installed with Orchestrator by Default
Plug-In Purpose Configuration Input Types Scripting Objects Inventory
vCenter Server
4.1
vCO Library Provides workflows that act
Provides access to the
vCenter Server 4.1 API, so
that you can incorporate all
of the vCenter Server objects
and functions into the
management processes that
you use Orchestrator to
automate.
as basic building blocks for
customization and
automation of client
processes. The workflow
library includes templates
for lifecycle management,
provisioning, disaster
recovery, hot backup, and
many other standard
processes. Sources of library
processes are accessible and
can be copied and edited.
See “Configure
the vCenter
Server 4.1 PlugIn,” on page 15.
None See Developing
See
http://www.vmw
are.com/suppor
t/orchestrator/do
c/vco_vsphere41
_api/index.html.
with VMware
vCenter
Orchestrator,
Using the
Orchestrator API.
See
http://www.vmware.co
m/support/orchestrato
r/doc/vco_vsphere41_ap
i/index.html.
See Developing with
VMware vCenter
Orchestrator, Using the
Orchestrator API.
Exposes all
vCenter
Server
objects.
Exposes
nothing in
the
inventory.
10 VMware, Inc.
Page 11

Chapter 1 Introduction to Orchestrator Plug-Ins
Table 1-1. Plug-Ins Installed with Orchestrator by Default (Continued)
Plug-In Purpose Configuration Input Types Scripting Objects Inventory
Database Java Database Connectivity
(JDBC) API is the industry
standard for databaseindependent connectivity
between the Java
programming language and
a wide range of databases.
The databases include SQL
databases and other tabular
data sources, such as
spreadsheets or flat files. The
JDBC API provides a calllevel API for SQL-based
database access from
workflows.
SSH Provides an implementation
of the Secure Shell v2 (SSH-2)
protocol. Allows remote
command and file transfer
sessions with password and
public key-based
authentication in workflows.
Optionally, the SSH plug-in
can provide remote file
system browsing directly in
the vCO inventory.
XML A complete Document
Object Model (DOM) XML
parser that you can
implement in workflows.
Alternatively, you can use
the ECMAScript for XML
(E4X) implementation in the
Orchestrator JavaScript API.
Mail Uses Simple Mail Transfer
Protocol (SMTP) to send
email from workflows.
Net Wraps the Jakarta Apache
Commons Net Library.
Provides implementations of
Telnet, FTP, and POP3. The
POP3 part allows reading
email. In combination with
the Mail plug-in, the Net
plug-in provides full email
sending and receiving
capabilities in workflows.
None None
See “Configure
the SSH PlugIn,” on page 39.
File
Folder
RootFolder
SshConnection
None None
Set the default
None
values for the
EmailMessage
object to use.
See “Define the
Default SMTP
Connection,” on
page 57.
None None
Connection
JDBCConnection
PreparedStatement
ResultSet
KeyPairManager
SSHCommand
SSHFile
SSHFolder
SSHSession
XMLDocument
XMLElement
XMLManager
XMLNameNodeMap
XMLNode
XMLNodeList
EmailMessage
FTPClient
POP3Client
POP3Message
TelnetClient
Exposes
nothing in
the
inventory.
Can expose
objects in the
inventory.
Exposes
nothing in
the
inventory.
Exposes
nothing in
the
inventory.
Exposes
nothing in
the
inventory.
VMware, Inc. 11
Page 12

Using VMware vCenter Orchestrator Plug-Ins
Table 1-1. Plug-Ins Installed with Orchestrator by Default (Continued)
Plug-In Purpose Configuration Input Types Scripting Objects Inventory
Enumeration Provides common
vCO
WebOperator
enumerated types that can be
used in workflows by other
plug-ins.
A Web view that allows you
to access the workflows in
the Orchestrator library and
interact with them across a
network by using a Web
browser. See Administering
VMware vCenter Orchestrator,
Weboperator Web View.
Plug-In Components
Each plug-in is a DAR file package. The DAR files are stored in
server\server\vmo\plugins on the Orchestrator server system. The components of each plug-in, such as
workflow categories and API modules, can use different naming conventions.
Table 1-2. Names of Plug-In Components
Plug-In Name in the
Configuration UI DAR Name
vCenter Server 4.1
vCO Library
Database
SSH
XML
Mail
Net
Common
enumerated types
vCO WebOperator
o11nplugin-vsphere41.dar
o11nplugin-library.dar
o11nplugin-jdbc.dar
o11nplugin-ssh.dar
o11nplugin-xml.dar
o11nplugin-mail.dar
o11nplugin-jakartacommonsnet.dar
o11nplugin-enums.dar
o11nplugin-weboperator.dar
None JavaScript
Enumerations
None None None Exposes
Orchestrator_installation_path
Workflow
Categories API Module
vCenter
Locking
Orchestrator
Troubleshooting
JDBC
SSH
XML
Mail
None
None
None N/A
None Exposes
nothing in
the
inventory.
nothing in
the
inventory.
\app-
VC
N/A
Database
SSH
XML
Mail
Net
Enums
Access the Orchestrator API Explorer
Orchestrator provides an API Explorer to allow you to search the Orchestrator API and see the documentation
for JavaScript objects that you can use in scripted elements.
You can consult an online version of the Scripting API for the vCenter Server plug-in on the Orchestrator
documentation home page.
12 VMware, Inc.
Page 13

Chapter 1 Introduction to Orchestrator Plug-Ins
Procedure
u
Access the API Explorer from either the Orchestrator client or from the Scripting tabs of the workflow,
policy, and action editors.
n
To access the API Explorer from the Orchestrator client, click Tools > API Explorer in the Orchestrator
client tool bar.
n
To access the API Explorer from the Scripting tabs of the workflow, policy, and action editors, click
Search API on the left.
The API Explorer appears, allowing you to search all the objects and functions of the Orchestrator API.
What to do next
Use the API Explorer to write scripts for scriptable elements.
VMware, Inc. 13
Page 14

Using VMware vCenter Orchestrator Plug-Ins
14 VMware, Inc.
Page 15

Using the vCenter Server 4.1 Plug-In 2
You can use the vCenter Server 4.1 plug-in to manage multiple vCenter Server hosts. You can create workflows
that use the vCenter Server plug-in API to automate tasks in your vCenter Server environment.
The vCenter Server plug-in maps the vCenter Server API to the JavaScript that you can use in workflows. It
also provides actions that perform individual vCenter Server tasks that you can include in workflows.
The vCenter Server plug-in provides a library of standard workflows that automate vCenter Server operations.
For example, you can run workflows that create, clone, migrate, or delete virtual machines.
This chapter includes the following topics:
n
“Configure the vCenter Server 4.1 Plug-In,” on page 15
n
“vCenter Server 4.1 Plug-In Scripting API,” on page 16
n
“vCenter Server Scripting Examples,” on page 16
n
“Using the vCenter Server 4.1 Plug-In Inventory,” on page 18
n
“Access the vCenter Server 4.1 Plug-In Workflow Library,” on page 18
n
“vCenter Server 4.1 Plug-In Workflow Library,” on page 19
Configure the vCenter Server 4.1 Plug-In
Orchestrator uses the vCenter Web Service API to control vCenter Server. You can set the parameters to enable
Orchestrator to connect to your vCenter Sever instances.
Prerequisites
Import the SSL certificates for each vCenter Server instance you define. For more information, see Installing
and Configuring VMware vCenter Orchestrator.
Procedure
1 Log in to the Orchestrator configuration interface as vmware.
2 Click vCenter Server 4.1.
3 Click New vCenter Server Host.
4 From the Available drop-down menu, select Enabled.
5 In the Host text box, type the IP address or the DNS name of the vCenter Server host.
6 In the Port text box, retain the default value, 443.
7 (Optional) Select the Secure channel check box to establish a secure connection to your vCenter Server
host.
VMware, Inc.
15
Page 16

Using VMware vCenter Orchestrator Plug-Ins
8 In the Path text box, retain the default value, /sdk.
This is the location of the SDK that you use to connect to your vCenter Server instance.
9 In the User name and Password text boxes, type the credentials for Orchestrator to use to establish the
connection to the vCenter Server host.
The user that you select must be a valid user with administrative privileges on your vCenter Server,
preferably at the top of the vCenter Server tree structure. Orchestrator uses these credentials to monitor
the vCenter Web service (typically to operate Orchestrator system workflows). All other requests inherit
the credentials of the user who triggers an action.
10 Specify the method you use to manage user access on the vCenter Server host.
Option Action
Share a unique session
Session per user
11 Click Apply changes.
Select this option to allow Orchestrator to create only one connection to
vCenter Server. Type the credentials of a user who is a vCenter Server
administrator.
Select this option if your vCenter Server is in an Active Directory domain.
Make sure that the user has the necessary permissions to perform the
required operations.
CAUTION Each user who logs in to Orchestrator creates a new session to
vCenter Server. This might rapidly use CPU, memory, and bandwidth.
The URL to the newly configured vCenter Server host is added to the list of defined hosts.
12 Repeat Step 3 through Step 11 for each vCenter Server instance.
vCenter Server 4.1 Plug-In Scripting API
The VC scripting API contains classes, with their respective attributes, methods, and constructors that allow
interaction between vCenter Orchestrator and vCenter Server. You can use the API to develop custom
workflows.
For a list of available API objects, see
http://www.vmware.com/support/orchestrator/doc/vco_vsphere41_api/index.html.
vCenter Server Scripting Examples
Workflow scripted elements can include scripting of common vCenter Server tasks. You can cut, paste, and
adapt these examples into your scripted elements.
Access Managed Object Types
The following JavaScript example allows Orchestrator to use scripting to access vCenter Server managed
objects through the vCenter Server plug-in.
var vm = ...;
// Get the property 'name'
var name = vm.name; // returns a string
// return a VcEnvironmentBrowser managed object
var environmentBrowser = vm.environmentBrowser;
16 VMware, Inc.
Page 17

Chapter 2 Using the vCenter Server 4.1 Plug-In
Access Managed Object Reference Types
The following JavaScript example allows Orchestrator to access data objects with the return type
ManagedObjectReference. Getters and setters that end with
List<ManagedObjects>
// virtualMachine is a workflow input parameter
var virtualMachineSnapshotInfo = virtualMachine.snapshot;
var virtualMachineSnapshot = virtualMachineSnapshotInfo.currentSnapshot;
// The reverse operation
virtualMachineSnapshotInfo.currentSnapshot = virtualMachineSnapshot;
.
_ManagedOjects
return
ManagedObject
In versions of Orchestrator earlier than 4.1, you must use the toManagedObject() method to convert object
references, for example workflow input parameter objects, to managed objects. The following JavaScript
operation works in Orchestrator 4.1, but it is no longer necessary.
// vCenter Server 4.0 plug-in code
var virtualMachineSnapshot = VcPlugin.toManagedObject(
virtualMachine, virtualMachineSnapshot);
Handle Enumeration Types
or
The following JavaScript example allows Orchestrator to use scripting to handle vCenter Server enumerations
through the vCenter Server plug-in.
// a VcSharesLevel FINDER ENUMERATION TYPE, for example
// received from an input parameter
var sharesLevel = ...
// get the String value of the FINDER ENUMERATION TYPE
var sharesLevelString = sharesLevel.value;
// Assign to a DataObject
var sharesInfo = new VcSharesInfo();
sharesInfo.level = sharesLevel;
Discover Host Machines and Virtual Machines
The following JavaScript example allows Orchestrator to use scripting to find host machines and virtual
machines through the vCenter Server plug-in.
var sdkConnections = VcPlugin.allSdkConnections;
System.log(sdkConnections.length + " SdkConnections found");
for (var i = 0; i < sdkConnections.length; i++) {
var sdkConnection = sdkConnections[i];
System.log("SdkConnection '" + sdkConnection.id + "'");
// Hierarchy entry point
var rootFolder = sdkConnection.rootFolder;
// Get the property 'name'
var name = rootFolder.name;
System.log("--- Root folder '" + name + "'");
// Get the folder's data centers
VMware, Inc. 17
Page 18

Using VMware vCenter Orchestrator Plug-Ins
var datacenters = rootFolder.datacenter;
if (datacenters != null) {
for (var j = 0; j < datacenters.length; j++) {
var datacenter = datacenters[j];
System.log("--- Datacenter '" + datacenter.id + "'");
}
}
// Method to get all the virtual machines in a vCenter Server host
var vms = sdkConnection.getAllVirtualMachines();
if (vms != null) {
for (var j = 0; j < vms.length; j++) {
var vm = vms[j];
System.log("--- VM '" + vm.id + "'");
System.log("--- VM '" + vm.name + "'");
var guestInfo = vm.guest;
System.log("--- VM guestInfo '" + guestInfo + "'");
if (guestInfo != null) {
System.log("--- VM guestInfo.guestFamily '" + guestInfo.guestFamily + "'");
}
}
}
}
Set vCenter Server Option Values
The following JavaScript example allows Orchestrator to set vCenter VcOptionManager option values.
var myVcOptionValue = new VcOptionValue();
myVcOptionValue.key = VimAdvancedOptionKey;
myVcOptionValue.value_LongValue = VimAdvancedOptionValue;
You can set the following optional value types as VcOptionValue attributes.
value
value_FloatValue
value_IntValue
value_LongValue
Attribute is a string value.
Attribute value is a float value.
Attribute value is an integer value.
Attribute value is a long value.
Using the vCenter Server 4.1 Plug-In Inventory
The vCenter Server plug-in exposes all objects of the connected vCenter Server hosts in the Inventory view.
You can use the Inventory view to add authorization elements or to run workflows on vCenter Server objects.
If the Use contextual menu in inventory option is enabled, all of the workflows that you can run on the selected
inventory object appear in a contextual menu.
Access the vCenter Server 4.1 Plug-In Workflow Library
You must use the Orchestrator client to access the elements from the vCenter Server 4.1 plug-in workflow
library.
Prerequisites
n
The vCenter Server 4.1 plug-in must be enabled and configured in the Orchestrator configuration interface.
18 VMware, Inc.
Page 19

n
You must be logged in to the Orchestrator client as a user who can run vCenter workflows.
Procedure
1 Click the Workflows view in the Orchestrator client.
2 Expand the hierarchical list to Library > vCenter.
What to do next
Review the workflow library.
vCenter Server 4.1 Plug-In Workflow Library
The vCenter Server 4.1 plug-in workflow library contains workflows that allow you to run automated processes
related to the management of vCenter Server.
Batch Workflows
You access these workflows from Library > vCenter > Batch.
Chapter 2 Using the vCenter Server 4.1 Plug-In
Fill batch configuration
elements
Run a workflow on a
selection of objects
Populates the configuration elements that the Run a workflow on a selection
of objects workflow uses. Resets the BatchObject and BatchAction
configuration elements. Fills the BatchObject configuration element with all of
the workflows that have only one input parameter. Fills the BatchAction
configuration element with all of the actions that have no input parameters or
one input parameter and that have an array as the returnType.
Runs a workflow on a selection of vCenter Server objects, taking one action as
input. This is the action that retrieves the list of objects on which to run the
workflow. To return the objects without running the selected workflow, run
the workflow in simulation mode.
Cluster and Compute Resource Workflows
You access these workflows from Library > vCenter > Cluster and Compute Resource.
Create cluster
Delete cluster
Disable HA on cluster
Enable HA on cluster
Rename cluster
Creates a new cluster in a given host folder.
Deletes a given cluster.
Disables high availability on a given cluster.
Enables high availability on a given cluster.
Renames a given cluster.
Custom Attribute Workflows
You access these workflows from Library > vCenter > Custom Attributes.
Add custom attribute to
a virtual machine
Add custom attribute to
multiple virtual
machines
Get custom attribute
VMware, Inc. 19
Adds a custom attribute to a given virtual machine.
Adds a custom attribute to a selection of virtual machines.
Gets a custom attribute for a given virtual machine in vCenter Server.
Page 20

Using VMware vCenter Orchestrator Plug-Ins
Datacenter Workflows
You access these workflows from Library > vCenter > Datacenter.
Create datacenter
Delete datacenter
Reload datacenter
Rename a datacenter
Rescan datacenter
HBAs
Creates a new datacenter in a given datacenter folder and returns the new
datacenter.
Deletes a given datacenter.
Forces vCenter Server to reload data from a datacenter.
Renames a given datacenter and waits for the task to complete.
Scans the hosts in a datacenter and initiates a rescan on the host's HBAs to
discover new storage.
Datastore and Files Workflows
You access these workflows from Library > vCenter > Datastore and Files.
Delete all files
Delete all unused
datastore files
Export unused datastore
files
Find unused files in
datastores
Deletes a list of files.
Searches all datastores in the vCenter Server environment and deletes all
unused files.
Searches all datastores and creates and XML descriptor file that lists all unused
files.
Searches the vCenter Server environment for all unused disks (*.vmdk), virtual
machines (*.vmx), and template (*.vmtx) files that are not associated with any
vCenter Server instances that are registered with Orchestrator.
Get all configuration,
template, and disk files
from virtual machines
Log all datastore files
Log unused datastore
files
Creates a list of all virtual machine descriptor files and a list of all virtual
machine disk files, for all datastores.
Creates a log for every virtual machine configuration file and every virtual
machine file found in all datastores.
Searches the vCenter Server environment for unused files that are registered
on virtual machines and exports a log of the files in a text file.
Datacenter FolderManagementWorkflows
You access these workflows from Library > vCenter > Folder management > Datacenter folder.
Create datacenter folder
Delete datacenter folder
Rename datacenter
folder
Creates a datacenter folder and returns it.
Deletes a datacenter folder and waits for the task to complete.
Renames a datacenter folder and waits for the task to complete.
20 VMware, Inc.
Page 21

Chapter 2 Using the vCenter Server 4.1 Plug-In
Host FolderManagementWorkflows
You access these workflows from Library > vCenter > Folder management > Host folder.
Create host folder
Delete host folder
Rename host folder
Creates a host folder and returns it.
Deletes a host folder and waits for the task to complete.
Renames a host folder and waits for the task to complete.
Virtual Machine FolderManagementWorkflows
You access these workflows from Library > vCenter > Folder management > VM folder.
Create virtual machine
folder
Delete virtual machine
folder
Rename virtual machine
folder
Creates a virtual machine folder.
Deletes a virtual machine folder and waits for the task to complete.
Renames a virtual machine folder and waits for the task to complete.
Basic HostManagementWorkflows
You access these workflows from Library > vCenter > Host management > Basic.
Enter maintenance
mode
Exit maintenance mode
Puts the host into maintenance mode. The task can be canceled.
Exits maintenance mode. The task can be canceled.
Move host into cluster
Move host to folder
Reload host
Moves an existing host into a cluster. The host must be part of the same
datacenter, and if the host is part of a cluster, the host must be in maintenance
mode.
Moves a host into a folder as a standalone host (ComputeResource). The host
must be part of a ClusterComputeResource in the same datacenter and the host
must be in maintenance mode.
Forces vCenter Server to reload data from an ESX host.
Host Management Power Workflows
You access these workflows from Library > vCenter > Host management > Power.
Reboot host
Shut down host
Reboots a host. If the Orchestrator client is connected directly to the host, it
does not receive any indication of success in the returned task, but rather loses
the connection to the host if the operation succeeds.
Shuts down a host. If the Orchestrator client is connected directly to the host,
it does not receive any indication of success in the returned task, but rather
loses the connection to the host if the operation succeeds.
VMware, Inc. 21
Page 22

Using VMware vCenter Orchestrator Plug-Ins
Host Management Registration Workflows
You access these workflows from Library > vCenter > Host management > Registration.
Add host to cluster
Add standalone host
Disconnect host
Reconnect host
Reconnect host with all
information
Remove host
Adds a host to the cluster. This workflow fails if it cannot authenticate the SSL
certificate of the host system.
Registers a host as a standalone host (ComputeResource).
Disconnects a host from vCenter Server.
Reconnects a disconnected host by providing only the host information.
Reconnects a disconnected host by providing all information about the host.
Removes a host and unregisters it from vCenter Server. If the host is part of a
cluster, you must put it into maintenance mode before attempting to remove
it.
Resource Pool Workflows
You access these workflows from Library > vCenter > Resource Pool.
Create resource pool
Create resource pool
with specified values
Creates a resource pool with the default CPU and memory allocation values.
To create a resource pool in a cluster, the cluster must be with VMware DRS
enabled.
Creates a resource pool with the specified CPU and memory allocation values.
To create a resource pool in a cluster, the cluster must be with VMware DRS
enabled.
Delete resource pool
Get resource pool
information
Reconfigure resource
pool
Rename resource pool
Deletes a resource pool and waits for the task to complete.
Returns CPU and memory information about a given resource pool.
Reconfigures CPU and memory allocation configuration for a given resource
pool.
Renames a resource pool and waits for the task to complete.
Storage Workflows
You access these workflows from Library > vCenter > Storage.
Create VMFS for all
available disks
Display all datastores
and disks
Creates a VMFS volume for all available disks of a given host.
Displays the existing datastores and available disks.
22 VMware, Inc.
Page 23

Chapter 2 Using the vCenter Server 4.1 Plug-In
Basic Virtual Machine Management Workflows
You access these workflows from Library > vCenter > Virtual Machine management > Basic.
Create custom virtual
machine
Create simple
dvPortGroup virtual
machine
Create simple virtual
machine
Delete virtual machine
Mark as template
Mark as virtual machine
Move virtual machine to
folder
Move virtual machine to
resource pool
Move virtual machines to
folder
Move virtual machines to
resource pool
Creates a virtual machine with the specified configuration options and
additional devices.
Creates a simple virtual machine. The network used is a Distributed Virtual
Port Group.
Creates a virtual machine with the most common devices and configuration
options.
Removes a virtual machine from the inventory and datastore.
Converts an existing virtual machine to a template, not allowing it to start. You
can use templates to create new virtual machines.
Converts an existing template to a virtual machine, allowing it to start.
Moves a virtual machine to a specified virtual machine folder.
Moves a virtual machine to a resource pool. If the target resource pool is not in
the same cluster, you must use the migrate or relocate workflows.
Moves several virtual machines to a specified virtual machine folder.
Moves several virtual machines to a resource pool.
Register virtual machine
Reload virtual machine
Rename virtual machine
Set virtual machine
performance
Unregister virtual
machine
Upgrade VM Hardware
(force if required)
Upgrade virtual machine
Wait for task and answer
virtual machine question
Registers a virtual machine. The virtual machine files must be stored in an
existing datastore and must not be already registered.
Forces vCenter Server to reload a virtual machine.
Renames an existing virtual machine on the vCenter Server system, or host and
not on the datastore.
Changes performance settings such as shares, min/max values, shaping for
network, and disk access of a virtual machine.
Removes an existing virtual machine from the inventory.
Upgrades the virtual machine hardware to the latest revision that is supported
by the host. This workflow forces the upgrade to continue, even if VMware
Tools is out of date. If VMware Tools is out of date, forcing the upgrade to
continue reverts the guest network settings to the default settings. To avoid
this, upgrade VMware Tools before running the workflow.
Upgrades the virtual hardware to the latest revision that is supported by the
host. An input parameter allows a forced upgrade even if VMware Tools is out
of date.
Waits for a vCenter Server task to complete or for the virtual machine to ask a
question. If the virtual machine requires an answer, accepts user input and
answers the question.
VMware, Inc. 23
Page 24

Using VMware vCenter Orchestrator Plug-Ins
Clone Workflows
You access these workflows from Library > vCenter > Virtual Machine management > Clone.
Clone virtual machine
from properties
Clone virtual machine,
no customization
Customize virtual
machine from properties
Clones virtual machines by using properties as input parameters.
Clones a virtual machine without changing anything except the virtual
machine UUID.
Customizes a virtual machine by using properties as input parameters.
Linked Clone Workflows
You access these workflows from Library > vCenter > Virtual Machine management > Clone > Linked
Clone.
Restore virtual machine
from linked clone
Set up virtual machine
for linked clone
Linked clone, Linux with
multiple NICs
Linked clone, Linux with
single NIC
Linked clone, Windows
with multiple NICs and
credential
Removes a virtual machine from a linked clone setup.
Prepares a virtual machine to be link cloned.
Creates a linked clone of a Linux virtual machine, performs the guest operating
system customization, and configures up to four virtual network cards.
Creates a linked clone of a Linux virtual machine, performs the guest operating
system customization, and configures one virtual network card.
Creates a linked clone of a Windows virtual machine and performs the guest
operating system customization. Configures up to four virtual network cards
and a local administrator user account.
Linked clone, Windows
with single NIC and
credential
Linked clone, no
customization
Creates a linked clone of a Windows virtual machine and performs the guest
operating system customization. Configures one virtual network card and a
local administrator user account.
Creates the specified number of linked clones of a given virtual machine.
Linux Customization Clone Workflows
You access these workflows from Library > vCenter > Virtual Machine management > Clone > Linux
Customization.
Clone, Linux with
multiple NICs
Clone, Linux with single
NIC
Clones a Linux virtual machine, performs the guest operating system
customization, and configures up to four virtual network cards.
Clones a Linux virtual machine, performs the guest operating system
customization, and configures one virtual network card.
24 VMware, Inc.
Page 25

Chapter 2 Using the vCenter Server 4.1 Plug-In
Tools Clone Workflows
You access these workflows from Library > vCenter > Virtual Machine management > Clone > Tools.
Get Linux customization
Get NIC setting map
Get Windows
customization, Sysprep
with Unattended.txt
Get Windows
customization, Sysprep
with credentials
Get Windows
customization for
Sysprep
Get a
VirtualEthernetCard to
change the network
Get multiple
VirtualEthernetCard
device changes
Returns the Linux customization preparation.
Returns the setting map for virtual network card by using
VimAdapterMapping.
Returns customization information for the Microsoft Sysprep process using an
Unattended.txt file. Workflows for cloning Windows virtual machines use this
workflow.
Returns customization information for the Microsoft Sysprep process, with
credentials. Workflows for cloning Windows virtual machines use this
workflow.
Returns customization information for the Microsoft Sysprep process.
Workflows for cloning Windows virtual machines use this workflow.
Returns a new ethernet card to update a virtual device. Contains only the device
key of the given virtual device and the new network.
Returns an array of VirtualDeviceConfigSpec objects for add and remove
operations on VirtualEthernetCard objects.
Windows Customization Clone Workflows
You access these workflows from Library > vCenter > Virtual Machine management > Clone > Windows
Customization.
Customize, Windows
with single NIC and
credential
Clone thin provisioned,
Windows with single NIC
and credential
Clone, Windows
Sysprep with single NIC
and credential
Clone, Windows with
multiple NICs and
credential
Clone, Windows with
single NIC
Clone, Windows with
single NIC and credential
Performs guest operating system customization, configures one virtual
network card and a local administrator user account on a Windows virtual
machine.
Clones a Windows virtual machine performing the guest operating system
customization. Specifies virtual disk thin provisioning policy and configures
one virtual network card and a local administrator user account. Sysprep tools
must be available on the vCenter Server system.
Clones a Windows virtual machine performing the guest operating system
customization. Configures one virtual network card and a local administrator
user account. Sysprep tools must be available on the vCenter Server system.
Clones a Windows virtual machine performing the guest operating system
customization. Configures the local administrator user account and up to four
virtual network cards. Sysprep tools must be available on the vCenter Server
system.
Clones a Windows virtual machine performing the guest operating system
customization and configures one virtual network card. Sysprep tools must be
available on the vCenter Server system.
Clones a Windows virtual machine performing the guest operating system
customization. Configures one virtual network card and a local administrator
user account. Sysprep tools must be available on the vCenter Server system.
VMware, Inc. 25
Page 26

Using VMware vCenter Orchestrator Plug-Ins
Device Management Workflows
You access these workflows from Library > vCenter > Virtual Machine management > Device
Management.
Add CD-ROM
Add disk
Change RAM
Convert disks to thin
provisioning
Convert independent
disks
Disconnect all
detachable devices from
a running virtual
machine
Mount floppy disk drive
Adds a virtual CD-ROM to a virtual machine. If the virtual machine has no IDE
controller, the workflow creates one.
Adds a virtual disk to a virtual machine.
Changes the amount of RAM of a virtual machine.
Converts thick-provisioned disks of virtual machines to thin-provisioned
disks.
Converts all independent virtual machine disks to normal disks by removing
the independent flag from the disks.
Disconnects floppy disks, CD-ROM drives, parallel ports, and serial ports from
a running virtual machine.
Mounts a floppy disk drive FLP file from the ESX datastore.
Move and Migrate Workflows
You access these workflows from Library > vCenter > Virtual Machine management > Move and Migrate.
Mass migrate virtual
machines with storage
vMotion
Uses Storage vMotion to migrate a single virtual machine, a selection of virtual
machines, or all available virtual machines.
Mass migrate virtual
machines with vMotion
Migrate virtual machine
with vMotion
Move virtual machine to
another vCenter Server
Quick migrate multiple
virtual machines
Quick migration of
virtual machine
Relocate virtual machine
disks
Uses vMotion, Storage vMotion, or both vMotion and Storage vMotion to
migrate a single virtual machine, a selection of virtual machines, or all available
virtual machines.
Migrates a virtual machine from one host to another by using the
MigrateVM_Task operation from the vSphere API.
Moves a list of virtual machines to another vCenter Server system.
Suspends the virtual machines if they are powered on and migrates them to
another host using the same storage.
Suspends the virtual machine if it is powered on and migrates it to another host
using the same storage.
Relocates virtual machine disks to another host or datastore while the virtual
machine is powered off by using the RelocateVM_Task operation from the
vSphere API.
26 VMware, Inc.
Page 27

Chapter 2 Using the vCenter Server 4.1 Plug-In
Other Workflows
You access these workflows fromLibrary > vCenter > Virtual Machine management > Others.
Extract virtual machine
information
Find orphaned virtual
machines
Returns the virtual machine folder, host system, resource pool, compute
resource, datastore, hard drive sizes, CPU and memory, network, and IP
address for a given virtual machine. Might require VMware Tools.
Lists all virtual machines in an orphaned state in the Orchestrator inventory.
Lists the VMDK and VMTX files for all datastores in the Orchestrator inventory
that have no association with any virtual machines in the Orchestrator
inventory. Sends the lists by email (optional).
Power Management Workflows
You access these workflows fromLibrary > vCenter > Virtual Machine management > Power Management.
Power off virtual
machine and wait
Reboot guest OS
Reset virtual machine
and wait
Resume virtual machine
and wait
Set guest OS to standby
Powers off a virtual machine and waits for the process to complete.
Reboots the virtual machine's guest operating system. Does not reset nonpersistent virtual machines. VMware Tools must be running.
Resets a virtual machine and waits for the process to complete.
Resumes a suspended virtual machine and waits for the process to complete.
Sets the guest operating system to standby mode. VMware Tools must be
running.
Shut down and delete
virtual machine
Shut down guest OS and
wait
Start virtual machine and
wait
Suspend virtual machine
and wait
Shuts down a virtual machine and deletes it from the inventory and disk.
Shuts down a guest operating system and waits for the process to complete.
Starts a virtual machine and waits for VMware Tools to start.
Suspends a virtual machine and waits for the process to complete.
Snapshot Workflows
You access these workflows from Library > vCenter > Virtual Machine management > Snapshot.
Create a snapshot
Create snapshots of all
virtual machines in a
resource pool
Remove all snapshots
Remove excess
snapshots
Creates a snapshot and returns it.
Creates a snapshot of each virtual machine in a resource pool.
Removes all existing snapshots without reverting to a previous snapshot.
Finds virtual machines with more than a given number of snapshots and
optionally deletes the oldest snapshots. Sends the results by email.
VMware, Inc. 27
Page 28

Using VMware vCenter Orchestrator Plug-Ins
Remove old snapshots
Gets all snapshots that are older than a given number of days and prompts the
user to select which ones to delete.
Remove snapshots of a
given size
Revert to current
Gets all snapshots that are larger than a given size and prompts the user to
confirm deletion.
Reverts to the current snapshot.
snapshot
Revert to snapshot and
Reverts to a specific snapshot. Does not delete the snapshot.
wait
VMware Tools Workflows
You access these workflows from Library > vCenter > Virtual Machine management > VMware Tools.
Mount tools installer
Set console screen
resolution
Turn on time
synchronization
Unmount tools installer
Upgrade tools
Mounts the VMware Tools installer on the virtual CD-ROM.
Sets the console window's resolution. The virtual machine must be powered
on.
Turns on time synchronization between the virtual machine and the ESX server
in VMware Tools.
Unmounts the VMware Tools CD-ROM.
Upgrades VMware Tools on a virtual machine.
Upgrade tools at next
reboot
Upgrades VMware Tools on a virtual machine without performing an
automatic reboot.
28 VMware, Inc.
Page 29

Using the vCO Library Plug-In 3
You can use the vCO Library plug-in workflows as templates for customization and automation of client
processes, and to troubleshoot Orchestrator.
vCO Library Plug-In Workflows
The vCO Library plug-in provides the workflows in the Locking, Orchestrator, and Troubleshooting workflow
categories.
Locking Workflows
You access these workflows from Library > Locking.
Display all locks
Locking test
Locking test (x5)
Release all locks
Shows all locks.
A test workflow that creates a lock.
A test workflow that creates five locks.
Releases all locks.
Orchestrator Workflows
You access these workflows from Library > Orchestrator.
Create recurrent task
Create task
Start workflows in a
series
Start workflows in
parallel
Creates a recurrent task an returns the newly created task.
Schedules a workflow to run at a later time and date, as a task.
Runs a workflow multiple times in a series, one instance after the other. You
provide workflow parameters in an array, providing a property list, with one
property per workflow input, for each instance of the workflow that starts. The
number of properties in the array define the number of workflow runs.
Runs a workflow multiple times, with different parameters. You provide
workflow parameters in an array, providing a property list, with one property
per workflow input, for each instance of the workflow that starts. The number
of properties in the array define the number of workflow runs.
VMware, Inc. 29
Page 30

Using VMware vCenter Orchestrator Plug-Ins
Troubleshooting Workflows
You access these workflows from Library > Troubleshooting.
Export logs and
application settings
Generates a ZIP archive of troubleshooting information that contains
configuration files, server, configuration, wrapper, and installation log files.
The output directory must exist and write access must be permitted.
30 VMware, Inc.
Page 31

Using the Database Plug-In 4
You can use the API that the Database plug-in provides to implement connectivity to SQL databases and other
tabular data sources, such as spreadsheets or flat files.
The Database plug-in API which is based on JDBC, provides a call-level API for SQL-based database access.
The Database plug-in also provides sample workflows that demonstrate how to use the API in workflows.
This chapter includes the following topics:
n
“Database Plug-In Scripting API,” on page 31
n
“Running the JDBC Sample Workflows,” on page 33
Database Plug-In Scripting API
The Database scripting API contains classes, with their respective methods, that enable interaction between
vCenter Orchestrator and SQL-based databases. You can use the API to create workflows that read data from
and write data to SQL-based databases.
Connection Class
The Connection class contains methods that control the connection to a database.
The Connection class defines the following methods.
Method Returns Description
close():Object Object
createStatement():Object Object
prepareCall(string):PreparedSta
tement
prepareStatement(string):Prepar
edStatement
JDBCConnection Class
The JDBCConnection class contains a method that specifies the URL and credentials for a connection to a
database.
The Connection class defines the following method.
VMware, Inc.
PreparedStatement
PreparedStatement
Releases the database and JDBC
resources for a Connection object.
Creates a Statement object for sending
SQL statements to the database.
Creates a CallableStatement object
for calling database stored procedures.
Creates a PreparedStatement object
for sending parameterized SQL
statements to the database.
31
Page 32

Using VMware vCenter Orchestrator Plug-Ins
Method Returns Description
getConnection(string,string,str
ing):Connection
PreparedStatement Class
The PreparedStatement class represents a precompiled SQL statement.
The PreparedStatement class defines the following methods.
Method Returns Description
execute():boolean Boolean
executeQuery():ResultSet ResultSet
executeUpdate():number Number
setDate(number,object):Object Object
setString(number,object):Object Object
setTimestamp(number,object):Obj
ect
Connection
Object
The three strings represent URL, user
name, and password.
Runs an SQL statement in the
PreparedStatement object.
Runs an SQL query in the
PreparedStatement object and returns
the ResultSet object generated by the
query.
Runs an SQL INSERT, UPDATE, or
DELETE statement, or an SQL
statement that returns nothing, in the
PreparedStatement object.
Sets a designated parameter to the given
Date value.
Sets a designated parameter to the given
String value.
Sets a designated parameter to the given
Timestamp value.
ResultSet Class
The ResultSet class is the result of a run of an executeQuery method.
The ResultSet class defines the following methods.
Method Returns Description
afterLast():Object Object
beforeFirst():Object Object
first():boolean Boolean
getDate(string):Object Object
getDateAt(number):Object Object
getNumber(string):number Number
Moves the cursor to the end of the
ResultSet object, after the last row.
This method has no effect if the result
set contains no rows.
Moves the cursor to the front of the
ResultSet object, before the first row.
This method has no effect if the result
set contains no rows.
Moves the cursor to the first row in the
ResultSet object. Returns true if the
cursor is on a valid row, and false if
there are no rows in the result set.
Returns the Date value of a given
column name.
Returns the Date value of a given
column index.
Returns the Number value of a given
column name.
32 VMware, Inc.
Page 33

Chapter 4 Using the Database Plug-In
Method Returns Description
getNumberAt(number):number Number
getString(string):Object String
getStringAt(number):Object String
getTimestamp(string):Object Object
getTimestampAt(number):Object Object
last():boolean Boolean
next():boolean Boolean
previous():boolean Boolean
wasNull():boolean Boolean
Returns the Number value of a given
column index.
Returns the String value of a given
column name.
Returns the String value of a given
column index.
Returns the Timestamp value of a given
column name.
Returns the Timestamp value of a given
column index.
Moves the cursor to the last row in the
ResultSet object. Returns true if the
cursor is on a valid row, and false if
there are no rows in the result set.
Moves the cursor down one row.
Returns true if the cursor is on a valid
row, and false if there are no more
rows.
Moves the cursor to the previous row in
the ResultSet object. Returns true if
the cursor is on a valid row, and false
if it is off the result set.
Reports whether the last column read
had a value of SQL NULL.
Running the JDBC Sample Workflows
You can run the Database plug-in sample workflows from the Orchestrator client to test SQL-based database
operations.
Generate a JDBC URL
You can run a workflow from the Orchestrator client to generate a JDBC connection URL.
Prerequisites
n
The Database plug-in must be enabled in the Orchestrator configuration interface.
n
You must be logged in to the Orchestrator client as a user who can run JDBC workflows.
Procedure
1 Click the Workflows view in the Orchestrator client.
2 In the workflows hierarchical list, open Library > JDBC to navigate to the JDBC URL generator workflow.
3 Right-click the JDBC URL generator workflow and select Start workflow.
4 Select the type of database for which to generate a URL.
NOTE If you use a Microsoft database, you might need to provide the database instance name and database
user domain name.
5 Provide the required information to generate a database URL.
a Type a database server name or IP address.
b Type a database name.
VMware, Inc. 33
Page 34

Using VMware vCenter Orchestrator Plug-Ins
c (Optional) Type a database port number.
If you do not specify a port number, the workflow uses a default port number.
d Type a user name to access the database.
e Type a password to access the database.
6 Click Submit to run the workflow.
Test a JDBC Connection
You can run a workflow from the Orchestrator client to test the connection to a database.
Prerequisites
n
The Database plug-in must be enabled in the Orchestrator configuration interface.
n
You must be logged in to the Orchestrator client as a user who can run JDBC workflows.
Procedure
1 Click the Workflows view in the Orchestrator client.
2 In the workflows hierarchical list, open Library > JDBC > JDBC Examples to navigate to the JDBC
connection example workflow.
3 Right-click the JDBC connection example workflow and select Start workflow.
4 Provide the required information to test a database connection.
a Type a user name to access the database.
b Type the URL to test.
c Type a password to access the database.
5 Click Submit to run the workflow.
Create a Table by Using JDBC
You can run a workflow from the Orchestrator client to test the creation of a database.
Prerequisites
n
The Database plug-in must be enabled in the Orchestrator configuration interface.
n
You must be logged in to the Orchestrator client as a user who can run JDBC workflows.
Procedure
1 Click the Workflows view in the Orchestrator client.
2 In the workflows hierarchical list, open Library > JDBC > JDBC Examples to navigate to the JDBC create
table example workflow.
3 Right-click the JDBC create table example workflow and select Start workflow.
4 Provide the required information to create a table.
a Type a password to access the database.
b Type a JDBC connection URL.
34 VMware, Inc.
Page 35

Chapter 4 Using the Database Plug-In
c Type a user name to access the database.
d Type an SQL create statement.
An example syntax is:
CREATE TABLE "table_name"
("column1" "data_type_for_column1",
"column2" "data_type_for_column2")
5 Click Submit to run the workflow.
Insert a Row into a JBCD Table
You can run a workflow from the Orchestrator client to test the insertion of a row into a JDBC table.
Prerequisites
n
The Database plug-in must be enabled in the Orchestrator configuration interface.
n
You must be logged in to the Orchestrator client as a user who can run JDBC workflows.
Procedure
1 Click the Workflows view in the Orchestrator client.
2 In the workflows hierarchical list, open Library > JDBC > JDBC Examples to navigate to the JDBC insert
into table example workflow.
3 Right-click the JDBC insert into table example workflow and select Start workflow.
4 Provide the required information to insert a row into a table.
a Type a JDBC connection URL.
b Type a user name to access the database.
c Type a password to access the database.
d Type an SQL insert statement.
An example syntax is:
INSERT INTO "table_name" ("column1", "column2")
VALUES ("value1", "value2")
e Type the values to insert into the row.
5 Click Submit to run the workflow.
Select Rows from a JDBC Table
You can run a workflow from the Orchestrator client to test the selection of rows from a JDBC table.
Prerequisites
n
The Database plug-in must be enabled in the Orchestrator configuration interface.
n
You must be logged in to the Orchestrator client as a user who can run JDBC workflows.
Procedure
1 Click the Workflows view in the Orchestrator client.
2 In the workflows hierarchical list, open Library > JDBC > JDBC Examples to navigate to the JDBC select
from table example workflow.
3 Right-click the JDBC select from table example workflow and select Start workflow.
VMware, Inc. 35
Page 36

Using VMware vCenter Orchestrator Plug-Ins
4 Provide the required information to select rows from a table.
a Type a JDBC connection URL.
b Type a user name to access the database.
c Type a password to access the database.
d Type an SQL select statement.
An example syntax is:
SELECT * FROM "table_name"
5 Click Submit to run the workflow.
Delete an Entry from a JDBC Table
You can run a workflow from the Orchestrator client to test the deletion of an entry from a JDBC table.
Prerequisites
n
The Database plug-in must be enabled in the Orchestrator configuration interface.
n
You must be logged in to the Orchestrator client as a user who can run JDBC workflows.
Procedure
1 Click the Workflows view in the Orchestrator client.
2 In the workflows hierarchical list, open Library > JDBC > JDBC Examples to navigate to the JDBC delete
entry from table example workflow.
3 Right-click the JDBC delete entry from table example workflow and select Start workflow.
4 Provide the required information to delete an entry from a table.
a Type the first name of the user entry to be deleted.
b Type a user name to access the database.
c Type a JDBC connection URL.
d Type the last name of the user entry to be deleted.
e Type a password to access the database.
f Type an SQL delete statement.
An example syntax is:
DELETE FROM "table_name" where ("column1" = ?, "column2" = ?)
5 Click Submit to run the workflow.
Delete All Entries from a JDBC Table
You can run a workflow from the Orchestrator client to test the deletion of all entries from a JDBC table.
Prerequisites
n
The Database plug-in must be enabled in the Orchestrator configuration interface.
n
You must be logged in to the Orchestrator client as a user who can run JDBC workflows.
Procedure
1 Click the Workflows view in the Orchestrator client.
36 VMware, Inc.
Page 37

Chapter 4 Using the Database Plug-In
2 In the workflows hierarchical list, open Library > JDBC > JDBC Examples to navigate to the JDBC delete
all from table example workflow.
3 Right-click the JDBC delete all from table example workflow and select Start workflow.
4 Provide the required information to delete all all entries from a table.
a Type a JDBC connection URL.
b Type a user name to access the database.
c Type a password to access the database.
d Type an SQL delete statement.
An example syntax is:
DELETE FROM "table_name"
5 Click Submit to run the workflow.
Drop a JDBC Table
You can run a workflow from the Orchestrator client to test the dropping of a JDBC table.
Prerequisites
n
The Database plug-in must be enabled in the Orchestrator configuration interface.
n
You must be logged in to the Orchestrator client as a user who can run JDBC workflows.
Procedure
1 Click the Workflows view in the Orchestrator client.
2 In the workflows hierarchical list, open Library > JDBC > JDBC Examples to navigate to the JDBC drop
table example workflow.
3 Right-click the JDBC drop table example workflow and select Start workflow.
4 Provide the required information to drop a table from the database.
a Type a password to access the database.
b Type a JDBC connection URL.
c Type a user name to access the database.
d Type an SQL drop statement.
An example syntax is:
DROP TABLE "table_name"
5 Click Submit to run the workflow.
Run a Complete JDBC Cycle
You can run a workflow from the Orchestrator client to test all JDBC example workflows in one full cycle.
Prerequisites
n
The Database plug-in must be enabled in the Orchestrator configuration interface.
n
You must be logged in to the Orchestrator client as a user who can run JDBC workflows.
Procedure
1 Click the Workflows view in the Orchestrator client.
VMware, Inc. 37
Page 38

Using VMware vCenter Orchestrator Plug-Ins
2 In the workflows hierarchical list, open Library > JDBC > JDBC Examples to navigate to the Full JDBC
cycle example workflow.
3 Right-click the Full JDBC cycle example workflow and select Start workflow.
4 Provide the required information to run a complete database cycle.
a Type a JDBC connection URL.
b Type a user name to access the database.
c Type a password to access the database.
d Type the values to be used as entries in the database.
5 Click Submit to run the workflow.
38 VMware, Inc.
Page 39

Using the SSH Plug-In 5
You can use the SSH plug-in workflows to run SSH commands on a remote host that supports SSH and transfer
files between an Orchestrator server and a remote host through a secure connection.
This chapter includes the following topics:
n
“Configure the SSH Plug-In,” on page 39
n
“SSH Plug-In Scripting API,” on page 40
n
“Running the SSH Plug-In Sample Workflows,” on page 44
Configure the SSH Plug-In
You can set up the SSH plug-in to ensure encrypted connections.
Procedure
1 Log in to the Orchestrator configuration interface as vmware.
2 Click SSH.
3 Click New connection.
VMware, Inc.
4 In the Host name text box, enter the host to access with SSH through Orchestrator.
NOTE The username and password are not required because Orchestrator uses the credentials of the
currently logged-in user to run SSH commands. You must reproduce the accounts you want to work on
SSH on target hosts from the LDAP server.
5 Click Apply changes.
The host is added to the list of SSH connections.
6 (Optional) Configure an entry path on the server.
a Click New root folder.
b Enter the new path and click Apply changes.
The SSH host is available in the Inventory view of the Orchestrator client.
39
Page 40

Using VMware vCenter Orchestrator Plug-Ins
SSH Plug-In Scripting API
The SSH scripting API contains classes, with their respective attributes, methods, and constructors, that allow
Orchestrator to perform SSH operations from workflows. You can use the API to develop custom workflows
that access a remote server through SSH.
SSH:File Type
The SSH:File type uses the SSHFile class as its scripting object.
The SSH:File type contains the following properties.
n
path
n
name
n
hostname
n
port
SSH:Folder Type
The SSH:Folder type uses the SSHFolder class as its scripting object.
The SSH:File type contains the following properties.
n
path
n
name
n
hostname
n
port
SSH:RootFolder Type
The SSH:RootFolder type uses the SSHFolder class as its scripting object.
The SSH:RootFile type contains the following property.
n
name
SSH:SshConnection Type
The SSH:SshConnection type uses the FinderResult class as its scripting object.
The SSH:SshConnection type contains the following properties.
n
name
n
userName
KeyPairManager Class
The KeyPairManager class contains a set of functions to manage private and public SSH keys.
The KeyPairManager class defines the following methods.
40 VMware, Inc.
Page 41

Method Returns Description
changePassphrase(Path,SecureStr
ing,SecureString):Object
generateKeyPair(string,Path,Sec
ureString,number,
string):string
Object
String
SSHCommand Class
The SSHCommand class is the main class for running SSH commands from workflows.
The SSHCommand class defines the following constructors.
Constructor Description
SSHCommand(string,string,SecureString):SSHCommand
SSHCommand(string,string,string,number):SSHCommand
The SSHCommand class defines the following attributes.
Attribute Returns Description
cmd String
error String
exitCode Number
output String
state String
Creates a new SSHCommand.
Creates a new SSHCommand.
Chapter 5 Using the SSH Plug-In
Changes the passphrase of a private
key.
Generates a pair of a public and a
private key. Returns the generated key
fingerprint.
Command to run
Command error, if any
NOTE The error message depends on
your operating system. The operating
system returns a string from the error
messages buffer.
Exit code of the last command
NOTE The exit code depends on your
operating system. Refer to your
operating system's documentation for
descriptions.
Command output, if any
Run state
The SSHCommand class defines the following methods.
Method Returns Description
disconnect():Object Object
execute():Object Object
executeAndLog(string):Object Object
executeCommand(string,boolean):
string
findAll(string,string):string[]
VMware, Inc. 41
String
Array of String Searches recursively and returns files
Disconnects the current session.
Runs a single command and returns
immediately. Leaves an open session.
You can disconnect the session
manually.
Runs a single command and waits until
it is completed.
Runs a single command, waits until it is
completed, and returns the stdout
result, if synchronous. Leaves an open
session. You can disconnect the session
manually.
and directories that match a pattern.
Leaves an open session. You can
disconnect the session manually.
Page 42

Using VMware vCenter Orchestrator Plug-Ins
Method Returns Description
findDir(string,string):string[]
findFile(string,string):string[
]
getFile(string,string):number Number
listAll(string):string[]
listDir(string):string[]
listFile(string):string[]
putFile(string,string):number Number
Array of String Searches recursively and returns
directories that match a pattern. Leaves
an open session. You can disconnect the
session manually.
Array of String Searches recursively and returns files
that match a pattern. Leaves an open
session. You can disconnect the session
manually.
Copies a file from a remote host to the
Orchestrator server. Leaves an open
session. You can disconnect the session
manually. Returns 0 if successful, -1 if
an error has occured, and -2 if a fatal
error has occured.
Array of String Lists files and directories in a path.
Leaves an open session. You can
disconnect the session manually.
Array of String Lists directories in a path. Leaves an
open session. You can disconnect the
session manually.
Array of String Lists files in a path. Leaves an open
session. You can disconnect the session
manually.
Copies a file from the Orchestrator
server to a remote host. The destination
directory must exist. Returns 0 if
successful, or -1 if an error has occured.
SSHFile Class
The SSHFile class contains attributes for SSH access to files on a remote file system.
The SSHFile class defines the following attributes.
Attribute Returns Description
fileName String
hostname String
name String
path String
port Number
File name
SSH host name
File name
Full file path
SSH port
SSHFolder Class
The SSHFolder class contains attributes for SSH access to folders on a remote file system.
The SSHFolder class defines the following attributes.
Attribute Returns Description
folderName String
hostname String
name String
Folder name
SSH host name
Folder name
42 VMware, Inc.
Page 43

Attribute Returns Description
path String
port Number
SSHSession Class
The SSHSession class is the main class for SSH session management.
The SSHSession class defines the following constructors.
Constructor Description
SSHSession(string,string):SSHSession
SSHSession(string,string,number):SSHSession
The SSHSession class defines the following attributes.
Attribute Returns Description
cmd String
error String
exitCode Number
output String
pty Boolean
state String
terminal String
Creates a new SSHSession.
Creates a new SSHSession.
Chapter 5 Using the SSH Plug-In
Full folder path
SSH port
Command to run
Command error, if any
NOTE The error message depends on
your operating system. The operating
system returns a string from the error
messages buffer.
Exit code of the last command
NOTE The exit code depends on your
operating system. Refer to your
operating system's documentation for
descriptions.
Command output, if any
Requesting a pseudo-terminal
Run state
Terminal type
The SSHSession class defines the following methods.
Method Returns Description
addEnvironment(string,string):O
bject
connectWithIdentity(Path,Secure
String):Object
connectWithPassword(SecureStrin
g):Object
connectWithPasswordOrIdentity
(boolean,SecureString,Path):Obj
ect
disconnect():Object Object
execute():Object Object
VMware, Inc. 43
Object
Object
Object
Object
Fills a property list of environment
variables that are set prior to opening a
channel.
Connects the session using public key
authentication.
Connects the session using simple
password authentication.
Connects the session using either
password or public key authentication.
Disconnects the current session.
Runs a single command and returns
immediately. Leaves an open session.
You can disconnect the session
manually.
Page 44

Using VMware vCenter Orchestrator Plug-Ins
Method Returns Description
executeAndLog(string):Object Object
executeCommand(string,boolean):
string
findAll(Path,string):string[]
findDir(Path,string):string[]
findFile(Path,string):string[]
getFile(Path,Path):number Number
listAll(Path):string[]
listDir(Path):string[]
listFile(Path):string[]
putFile(Path,Path):number Number
Runs a single command and waits until
it is completed.
String
Array of String Searches recursively and returns files
Array of String Searches recursively and returns
Array of String Searches recursively and returns files
Array of String Lists files and directories in a path.
Array of String Lists directories in a path. Leaves an
Array of String Lists files in a path. Leaves an open
Runs a single command, waits until it is
completed, and returns the stdout
result, if synchronous. Leaves an open
session. You can disconnect the session
manually.
and directories that match a pattern.
Leaves an open session. You can
disconnect the session manually.
directories that match a pattern. Leaves
an open session. You can disconnect the
session manually.
that match a pattern. Leaves an open
session. You can disconnect the session
manually.
Copies a file from a remote host to the
Orchestrator server. Leaves an open
session. You can disconnect the session
manually. Returns 0 if successful, -1 if
an error has occured, and -2 if a fatal
error has occured.
Leaves an open session. You can
disconnect the session manually.
open session. You can disconnect the
session manually.
session. You can disconnect the session
manually.
Copies a file from the Orchestrator
server to a remote host. The destination
directory must exist. Returns 0 if
successful, or -1 if an error has occured.
Running the SSH Plug-In Sample Workflows
You can run the SSH plug-in sample workflows from the Orchestrator client to test the connection between
the Orchestrator server and the SSH host.
Generate a Key Pair
You can run a workflow from the Orchestrator client to generate a key pair. You can use the key pair to connect
to an SSH host without a password.
A key pair consists of a public key and a private key. Orchestrator can use the private key to connect to the
public key on an SSH host. You can use a passphrase to improve security.
CAUTION All Orchestrator users with the right set of privileges can read, use, and overwrite your private key.
44 VMware, Inc.
Page 45

Chapter 5 Using the SSH Plug-In
Prerequisites
n
The SSH plug-in must be enabled and configured in the Orchestrator configuration interface.
n
You must be logged in to the Orchestrator client as a user who can run SSH workflows.
Procedure
1 Click the Workflows view in the Orchestrator client.
2 In the workflows hierarchical list, open Library > SSH to navigate to the Generate key pair workflow.
3 Right-click the Generate key pair workflow and select Start workflow.
4 Provide the required information.
a Select the key type.
b Select the key size.
c (Optional) Type a passphrase.
NOTE You can change the passphrase later.
d (Optional) Type a comment.
5 Click Submit to run the workflow.
If a key pair exists, the new key pair overwrites it.
Change the Key Pair Passphrase
You can run a workflow from the Orchestrator client to change the passphrase for the key pair that you
generated last.
Prerequisites
n
The SSH plug-in must be enabled and configured in the Orchestrator configuration interface.
n
You must be logged in to the Orchestrator client as a user who can run SSH workflows.
Procedure
1 Click the Workflows view in the Orchestrator client.
2 In the workflows hierarchical list, open Library > SSH to navigate to the Change key pair passphrase
workflow.
3 Right-click the Change key pair passphrase workflow and select Start workflow.
4 Reset the key pair passphrase.
a Type the current passphrase.
b Type the new passphrase.
5 Click Submit to run the workflow.
Register an Orchestrator Public Key on an SSH Host
You can use a public key instead of a password. To register an Orchestrator public key on an SSH host, you
can run a workflow from the Orchestrator client.
Prerequisites
n
The SSH plug-in must be enabled and configured in the Orchestrator configuration interface.
n
You must be logged in to the Orchestrator client as a user who can run SSH workflows.
VMware, Inc. 45
Page 46

Using VMware vCenter Orchestrator Plug-Ins
Procedure
1 Click the Workflows view in the Orchestrator client.
2 In the workflows hierarchical list, open Library > SSH to navigate to the Register vCO public key on host
workflow.
3 Right-click the Register vCO public key on host workflow and select Start workflow.
4 Provide the host and authentication information.
NOTE You must provide credentials that are registered on the SSH host.
5 Click Submit to run the workflow.
You can use public key authentication instead of password authentication when you connect to the SSH host
as the registered user.
Run an SSH Command
You can run a workflow from the Orchestrator client to run SSH commands on a remote ESX host.
Prerequisites
n
The SSH plug-in must be enabled and configured in the Orchestrator configuration interface.
n
You must be logged in to the Orchestrator client as a user who can run SSH workflows.
Procedure
1 Click the Workflows view in the Orchestrator client.
2 In the workflows hierarchical list, open Library > SSH to navigate to the Run SSH command workflow.
3 Right-click the Run SSH command workflow and select Start workflow.
4 Provide the required information.
a Type an SSH host name or IP.
b Type an SSH command to run.
NOTE The default SSH command is uptime. It shows how long the server has been active and the
user load for that period.
c (Optional) Select Yes to use password authentication.
NOTE The default option is to use key file authentication.
d Type the authentication information.
5 Click Submit to run the workflow.
Copy a File from an SSH Host
You can run a workflow from the Orchestrator client to copy files from an SSH host to the Orchestrator server.
The SSH plug-in uses the Java JCraft library, which implements SFTP. The SCP get command workflow
transfers files by using SFTP.
Prerequisites
n
The SSH plug-in must be enabled and configured in the Orchestrator configuration interface.
n
You must be logged in to the Orchestrator client as a user who can run SSH workflows.
46 VMware, Inc.
Page 47

Chapter 5 Using the SSH Plug-In
Procedure
1 Click the Workflows view in the Orchestrator client.
2 In the workflows hierarchical list, open Library > SSH to navigate to the SCP get command workflow.
3 Right-click the SCP get command workflow and select Start workflow.
4 Provide the required information.
a Type an SSH host name or IP address.
b Type the SSH authentication information.
c Type the path to the directory on the Orchestrator server into which to copy the file.
d Type the path to the file to get from the remote SSH host.
5 Click Submit to run the workflow.
Copy a File to an SSH Host
You can run a workflow from the Orchestrator client to copy files from the Orchestrator server to an SSH host.
The SSH plug-in uses the Java JCraft library, which implements SFTP. The SCP put command workflow
transfers files by using SFTP.
Prerequisites
n
The SSH plug-in must be enabled and configured in the Orchestrator configuration interface.
n
You must be logged in to the Orchestrator client as a user who can run SSH workflows.
Procedure
1 Click the Workflows view in the Orchestrator client.
2 In the workflows hierarchical list, open Library > SSH to navigate to the SCP put command workflow.
3 Right-click the SCP put command workflow and select Start workflow.
4 Provide the required information.
a Type an SSH host name or IP address.
b Type the SSH authentication information.
c Type the path to the file that you want to copy from the local Orchestrator server to the remote SSH
host.
d Type the path to the directory on the remote SSH host into which to copy the file.
5 Click Submit to run the workflow.
VMware, Inc. 47
Page 48

Using VMware vCenter Orchestrator Plug-Ins
48 VMware, Inc.
Page 49

Using the XML Plug-In 6
You can use the XML plug-in to run workflows that create and modify XML documents.
The XML plug-in adds an implementation of a Document Object Model (DOM) XML parser to the Orchestrator
JavaScript API. The XML plug-in also provides some sample workflows to demonstrate how you can create
and modify XML documents from workflows.
Alternatively, you can use the ECMAScript for XML (E4X) implementation in the Orchestrator JavaScript API
to process XML documents directly in JavaScript. For an E4X scripting example, see Developing with VMware
vCenter Orchestrator.
For information about E4X, go to the Web site of the organization that maintains the ECMA-357 standard.
This chapter includes the following topics:
n
“XML Plug-In Scripting API,” on page 49
n
“Running the XML Plug-In Sample Workflows,” on page 53
XML Plug-In Scripting API
The XML scripting API contains classes, with their respective attributes and methods, that allow vCenter
Orchestrator to manage XML documents. You can use the API to develop custom workflows.
XMLDocument Class
The XMLDocument class is the main XML class.
The XMLDocument class defines the following methods.
Method Returns Description
appendChild(XMLNode):Object Object
cloneNode(boolean):Object Object
createCDATASection(Object):XMLN
ode
createComment(String):XMLNode XMLNode
createElement(String):XMLElementXMLElement
createProcessingInstruction(Str
ing,String):XMLNode
VMware, Inc. 49
XMLNode
XMLNode
Adds a newChild node to the end of the
list of child nodes of this node. If the
newChild node exists in the tree, it is
first removed.
Clones a node.
Creates a CDATA node.
Creates a comment node.
Creates an element with a given name.
Creates a ProcessingInstruction node
with specified name and data strings.
Page 50

Using VMware vCenter Orchestrator Plug-Ins
Method Returns Description
createTextNode(String):XMLNode XMLNode
getChildNodes():Object Object
getDocumentElement():XMLElement XMLElement
getElementsByTagName(String):Ob
ject
insertBefore(XMLNode,XMLNode):O
bject
normalize():Object Object
removeChild(XMLNode):Object Object
replaceChild(XMLNode,XMLNode):O
bject
Object
Object
Object
Creates a text node.
Gets all child nodes.
Allows direct access to the child node
that is at the root element of the
document.
Returns an XMLNodeList of all elements
with a given tag name in the order in
which they are encountered in a preordered traversal of the XMLDocument
tree.
Inserts a newChild node before the
existing child node refChild. If
refChild is null, the newChild node is
inserted at the end of list of child nodes.
If the newChild node exists in the tree,
it is first removed.
Normalizes the document.
Removes the child node indicated by
oldChild from the list of child nodes
and returns it.
Replaces the oldChild node with a
newChild node in the list of child nodes
and returns the oldChild node. If the
newChild node exists in the tree, it is
first removed.
XMLElement Class
The XMLElement class is the main element class.
The XMLElement class defines the following attributes.
Attribute Returns Description
tagName String
textContent String
The XMLElement class defines the following methods.
Method Returns Description
appendChild(XMLNode):Object Object
cloneNode(boolean):Object Object
getAttributes():Object Object
getChildNodes():XMLNodeList XMLNodeList
getElementsByTagName(String):Ob
ject
Object
The tag name
The text content
Adds a newChild node to the end of the
list of child nodes of this node. If the
newChild node exists in the tree, it is
first removed.
Clones a node.
Contains the attributes of an element.
Gets all child nodes.
Returns an XMLNodeList of all elements
with a given tag name in the order in
which they are encountered in a preordered traversal of the current element
tree.
50 VMware, Inc.
Page 51

Method Returns Description
hasAttribute(String):boolean Boolean
insertBefore(XMLNode,XMLNode):O
bject
normalize():Object Object
removeAttribute(String):Object Object
removeChild(XMLNode):Object Object
replaceChild(XMLNode,XMLNode):O
bject
setAttribute(String,String):Obj
ect
Object
Object
Object
Returns true if the attribute exists.
Inserts a newChild node before the
existing child node refChild. If
refChild is null, the newChild node is
inserted at the end of list of child nodes.
If the newChild node exists in the tree,
it is first removed.
Normalizes the node.
Removes an attribute with a given
name.
Removes the child node indicated by
oldChild from the list of child nodes
and returns it.
Replaces the oldChild node with a
newChild node in the list of child nodes
and returns the oldChild node. If the
newChild node exists in the tree, it is
first removed.
Sets a new attribute.
Chapter 6 Using the XML Plug-In
XMLManager Class
The XMLManager class is the main class for creation of XML document parsers.
The XMLManager class defines the following methods.
Method Returns Description
fromString(String):XMLDocument XMLDocument
getDocumentContent(XMLDocument)
:string
loadDocument(String,boolean):XM
LDocument
loadDocumentWithEncoding
(String,String,boolean):XMLDocu
ment
newDocument():XMLDocument XMLDocument
saveDocument(XMLDocument,String
,String,String):Object
saveDocumentWithEncoding
(XMLDocument,String,String,Stri
ng,String):Object
validateDocument(XMLDocument,St
ring,String):Object
String
XMLDocument
XMLDocument
Object
Object
Object
Gets a document for a given string
content.
Gets a document as a string.
Gets a document for a given path using
the default character encoding.
Gets a document for a given path using
the specified character encoding.
Creates an empty XML document.
Saves a document to a given path using
the default character encoding.
Saves a document to a given path using
the specified character encoding.
Validates a document without saving it.
XMLNamedNodeMap Class
The XMLNamedNodeMap class is the main class for node maps, usually used for attributes of an element.
The XMLNamedNodeMap class defines the following attribute.
VMware, Inc. 51
Page 52

Using VMware vCenter Orchestrator Plug-Ins
Attribute Returns Description
length Number
The XMLNamedNodeMap class defines the following methods.
Method Returns Description
getNamedItem(string):XMLNode XMLNode
item(number):XMLNode XMLNode
XMLNode Class
The XMLNode class is the main node class.
The XMLNode class defines the following attributes.
Attribute Returns Description
nodeName String
nodeValue String
parentNode Object
The length of a list
Retrieves a node specified by name.
Retrieves a child node at index.
The node name
The node value
The parent node (XMLNode)
The XMLNode class defines the following methods.
Method Returns Description
appendChild(XMLNode):Object Object
cloneNode(boolean):Object Object
getChildNodes():XMLNodeList XMLNodeList
insertBefore(XMLNode,XMLNode):O
bject
normalize():Object Object
removeChild(XMLNode):Object Object
insertBefore(XMLNode,XMLNode):O
bject
replaceChild(XMLNode,XMLNode):O
bject
Object
Object
Object
Adds a newChild node to the end of the
list of child nodes of this node. If the
newChild node exists in the tree, it is
first removed.
Clones a node.
Gets all child nodes.
Inserts a newChild node before the
existing child node refChild. If
refChild is null, the newChild node is
inserted at the end of list of child nodes.
If the newChild node exists in the tree,
it is first removed.
Normalizes the node.
Removes the child node indicated by
oldChild from the list of child nodes
and returns it.
Inserts a newChild node before the
existing child node refChild. If
refChild is null, the newChild node is
inserted at the end of list of child nodes.
If the newChild node exists in the tree,
it is first removed.
Replaces the oldChild node with a
newChild node in the list of child nodes
and returns the oldChild node. If the
newChild node exists in the tree, it is
first removed.
52 VMware, Inc.
Page 53

XMLNodeList Class
The XMLNodeList class is the main class for node lists.
The XMLNodeList class defines the following attribute.
Attribute Returns Description
length Number
The XMLNodeList class defines the following method.
Method Returns Description
item(number):Object Object
Running the XML Plug-In Sample Workflows
You can run the XML plug-in sample workflows from the Orchestrator client to create and modify XML
documents for testing purposes.
Because the workflows can create, read, or modify files, you must have sufficient access rights to the working
directory.
Chapter 6 Using the XML Plug-In
The length of a list
Retrieves a child node at index.
Orchestrator has read, write, and execute rights to a folder named orchestrator, at the root of the server system.
Although workflows have permission to read, write, and execute in this folder, you must create the folder on
the server system.
You can allow access to other folders by changing the settings for server file system access from workflows
and JavaScript. See Administering VMware vCenter Orchestrator, Setting Server File System Access from Workflows
and JavaScript.
Create a Simple XML Document
You can run a workflow from the Orchestrator client to create a simple XML document for testing purposes.
Prerequisites
n
The XML plug-in must be enabled from the Orchestrator configuration interface.
n
You must be logged in to the Orchestrator client as a user who can run XML workflows.
n
Verify that you created the c:/orchestrator folder at the root of the Orchestrator server system or set
access rights to another folder.
Procedure
1 Click the Workflows view in the Orchestrator client.
2 In the workflows hierarchical list, open Library > XML > Samples XML (Simple) to navigate to the Create
a simple XML document workflow.
3 Right-click the Create a simple XML document workflow and select Start workflow.
4 Type the filepath to the XML document to create.
For example, c:/orchestrator/
filename
.xml.
5 Click Submit to run the workflow.
The workflow creates an XML document that contains a list of users. The attributes for each entry are user
ID and name.
VMware, Inc. 53
Page 54

Using VMware vCenter Orchestrator Plug-Ins
Find an Element in an XML Document
You can run a workflow from the Orchestrator client to find an element in the XML created by the Create a
simple XML document workflow.
Prerequisites
n
The XML plug-in must be enabled from the Orchestrator configuration interface.
n
You must be logged in to the Orchestrator client as a user who can run XML workflows.
n
Verify that you created the c:/orchestrator folder at the root of the Orchestrator server system or set
access rights to another folder.
Procedure
1 Click the Workflows view in the Orchestrator client.
2 In the workflows hierarchical list, open Library > XML > Samples XML (Simple) to navigate to the Find
element in document workflow.
3 Right-click the Find element in document workflow and select Start workflow.
4 Type the filepath to the XML document.
For example, c:/orchestrator/
filename
.xml.
5 Click Submit to run the workflow.
The workflow searches for an element and displays the result in the system log.
What to do next
To view the result, select the completed workflow run in the Orchestrator client and click Logs on the
Schema tab.
Modify an XML Document
You can run a workflow from the Orchestrator client to modify the XML that the Create a simple XML
document workflow creates.
Prerequisites
n
The XML plug-in must be enabled from the Orchestrator configuration interface.
n
You must be logged in to the Orchestrator client as a user who can run XML workflows.
n
Verify that you created the c:/orchestrator folder at the root of the Orchestrator server system or set
access rights to another folder.
Procedure
1 Click the Workflows view in the Orchestrator client.
2 In the workflows hierarchical list, open Library > XML > Samples XML (Simple) to navigate to the Modify
XML document workflow.
3 Right-click the Modify XML document workflow and select Start workflow.
54 VMware, Inc.
Page 55

4 Provide the input and output filepaths.
a Type the filepath to the XML document to modify.
Chapter 6 Using the XML Plug-In
For example, c:/orchestrator/
filename
.xml.
b Type the filepath to the modified XML document.
For example, c:/orchestrator/
filename
.xml.
NOTE If you type the same filepath in both fields, the workflow overwrites the original file with the
modified file. If you type an output filepath to a file that does not exist, the workflow creates a modified
file.
5 Click Submit to run the workflow.
The workflow searches for an element and modifies the entry where the element is found.
Create an Example Address Book from XML
You can run a workflow from the Orchestrator client to create an address book for testing purposes.
Prerequisites
n
The XML plug-in must be enabled from the Orchestrator configuration interface.
n
You must be logged in to the Orchestrator client as a user who can run XML workflows.
n
Verify that you created the c:/orchestrator folder at the root of the Orchestrator server system or set
access rights to another folder.
Procedure
1 Click the Workflows view in the Orchestrator client.
2 In the workflows hierarchical list, open Library > XML > Samples XML (Address Book) to navigate to
the Full address book test workflow.
3 Right-click the Full address book test workflow and select Start workflow.
4 Type the path to the address book folder.
For example, c:/orchestrator/
foldername
.
The workflow automatically creates the folder if it does not exist.
5 Click Submit to run the workflow.
The workflow creates a DTD, an XML, and a CSS file, appends the stylesheet, and stores the files in the specified
folder.
VMware, Inc. 55
Page 56

Using VMware vCenter Orchestrator Plug-Ins
56 VMware, Inc.
Page 57

Using the Mail Plug-In 7
You can send email messages from workflows by using the Mail plug-in, which uses the Simple Mail Transfer
Protocol (SMTP). For example, you can create a workflow to send an email to a given address if the workflow
requires user interaction or when it completes its run.
This chapter includes the following topics:
n
“Define the Default SMTP Connection,” on page 57
n
“Mail Plug-In Scripting API,” on page 58
n
“Email Scripting Examples,” on page 58
n
“Using the Mail Plug-In Sample Workflows,” on page 59
Define the Default SMTP Connection
The Mail plug-in is installed with Orchestrator Server and is used for email notifications. The only option
available for this plug-in is to use default values for new mail messages. You can set the default email account.
Avoid load balancers when configuring mail in Orchestrator. You might receive SMTP_HOST_UNREACHABLE error.
Procedure
VMware, Inc.
1 Log in to the Orchestrator configuration interface as vmware.
2 Click Mail.
3 Select the Define default values check box and fill in the required text boxes.
Text box Description
SMTP host
SMTP port
User name
Password
From name and address
Enter the IP address or domain name of your SMTP server.
Enter a port number to match your SMTP configuration.
The default SMTP port is 25.
Enter a valid email account.
This is the email account Orchestrator uses to send emails.
Enter the password associated with the user name.
Enter the sender information to appear in all emails sent by Orchestrator.
4 Click Apply changes.
57
Page 58

Using VMware vCenter Orchestrator Plug-Ins
Mail Plug-In Scripting API
The Mail scripting API contains one class, with its respective attributes and methods, that allow vCenter
Orchestrator workflows to send email messages. You can use the API to develop custom workflows.
EmailMessage Class
The EmailMessage class is the main class for creating email messages that you want to send from workflows.
The EmailMessage class defines the following attributes.
Attribute Returns Description
bccAddress String
ccAddress String
fromAddress String
fromName String
password String
smtpHost String
smtpPort Number
subject String
toAddress String
username String
Comma-separated list of blind carbon
copy email address entries
Comma-separated list of carbon copy
email address entries
Sender's email address
Sender's name
Password for authentication
SMTP host name or IP address
SMTP port number (default is 25)
Email subject
Comma-separated list of email address
entries
User name for authentication
The EmailMessage class defines the following methods.
Method Returns Description
addMimePart(Object,String):void Void
sendMessage():void Void
Email Scripting Examples
Workflow scripted elements can include scripting of common email-related tasks. You can cut, paste, and adapt
these examples into your scripted elements.
When you run a mail workflow, it uses the default mail server configuration that you set in the Orchestrator
configuration interface. You can override the default values by using input parameters, or by defining custom
values in workflow scripted elements.
Obtain an Email Address
The following JavaScript example obtains the email address of the current owner of a running script.
var emailAddress = Server.getRunningUser().emailAddress ;
Adds a MIME part to the message.
Sends an email message.
58 VMware, Inc.
Page 59

Send an Email
The following JavaScript example sends an email to the defined recipient, through an SMTP server, with the
defined content.
var message = new EmailMessage() ;
message.smtpHost = "smtpHost" ;
message.subject= "my subject" ;
message.toAddress = "receiver@vmware.com" ;
message.fromAddress = "sender@vmware.com" ;
message.addMimePart("This is a simple message","text/html") ;
message.sendMessage() ;
Using the Mail Plug-In Sample Workflows
You can call the sample workflows of the Mail plug-in from custom workflows to implement email
functionality. You can run an example workflow to test interaction with email.
Access the Mail Plug-In Sample Workflows
You must use the Orchestrator client to access the Mail plug-in sample workflows.
Chapter 7 Using the Mail Plug-In
Prerequisites
n
The Mail plug-in must be enabled and configured in the Orchestrator configuration interface.
n
You must be logged in to the Orchestrator client as a user who can run Mail workflows.
Procedure
1 Click the Workflows view in the Orchestrator client.
2 Expand the hierarchical list to Library > Mail.
What to do next
Review the sample workflows.
Mail Plug-In Sample Workflows
You can integrate the sample Mail plug-in workflows in custom workflows.
Workflow Name Description
Retrieve messages Retrieves the messages of a given email account by using the POP3 protocol.
Send interaction Sends an email to answer a user interaction. The email body contains both the direct answer URL,
and an interaction URL to process this request. If optional parameters are not specified, the workflow
uses the default values set in the Orchestrator configuration interface.
Send notification Sends an email with specified content to a given email address. If optional parameters are not
specified, the workflow uses the default values set in the Orchestrator configuration interface.
Send notification to
mailing list
Sends an email with specified content to a given email address list, CC list, and BCC list. If optional
parameters are not specified, the workflow uses the default values set in the Orchestrator
configuration interface.
VMware, Inc. 59
Page 60

Using VMware vCenter Orchestrator Plug-Ins
Test an Example Interaction with Email
You can run a workflow from the Orchestrator client to send an email to respond to a query, known as a user
interaction.
The workflow uses the default mail server configuration that you set in the Orchestrator configuration
interface. See “Define the Default SMTP Connection,” on page 57.
Prerequisites
n
The Mail plug-in must be enabled and configured in the Orchestrator configuration interface.
n
You must be logged in to the Orchestrator client as a user who can run Mail workflows.
Procedure
1 Click the Workflows view in the Orchestrator client.
2 In the workflows hierarchical list, open Library > Mail to navigate to the Example interaction with email
workflow.
3 Right-click the Example interaction with email workflow and select Start workflow.
4 Provide the required information.
a Type a recipient address.
b Select an LDAP group of users who are authorized to answer the query.
5 Click Submit to run the workflow.
The workflow suspends its run and sends an email to the given address. The email body contains a link to the
weboperator Web view. If weboperator is running, the user can answer the request for interaction directly in
weboperator, allowing the workflow to finish its run.
60 VMware, Inc.
Page 61

Using the Net Plug-In 8
You can use the Net plug-in to implement the Telnet, FTP, and POP3 protocols in workflows. The POP3 part
allows reading email. In combination with the Mail plug-in, the Net plug-in provides full email sending and
receiving capabilities in workflows.
Net Plug-In Scripting API
The Net scripting API contains classes, with their respective attributes, methods, and constructors, that allow
vCenter Orchestrator workflows to implement Telnet, POP3, and FTP functionality. You can use the API to
develop custom workflows.
FTPClient Class
The FTPClient class is the main class for implementing FTP funtionality into workflows.
The FTPClient class defines the FTPClient():FTPClient constructor.
The FTPClient class defines the following attributes.
Attribute Returns Description
cwd String
output String
replyCode Number
soLinger Number
state String
tcpNoDelay Boolean
timeout Number
Current working directory
Command output if any
Last reply code
Socket SO Linger (null if disabled)
Run state
Socket TCP no delay
Socket timeout
The FTPClient class defines the following methods.
Method Returns Description
connect(String,number):Object Object
disconnect():Object Object
enableSSL(boolean):Object Object
executeCommand(String,String):n
umber
VMware, Inc. 61
Number
Connects the client to a host.
Logs out and disconnects the current
session if open.
Enables SSL.
Runs a command.
Page 62

Using VMware vCenter Orchestrator Plug-Ins
Method Returns Description
getFile(String,String):Number Number
getString(String):String String
listAll(String):String[]
listDir(String):String[]
listFile(String):String[]
login(String,String,String):boo
lean
putFile(String,String):Number Number
putString(String,String):Number Number
POP3Client Class
The POP3Client class is the main class for implementing POP3 funtionality into workflows.
The POP3Client class defines the POP3Client():POP3Client constructor.
The POP3Client class defines the following attributes.
Copies a file from a remote host to the
Orchestrator server.
Gets the content of a remote file.
Array of String Lists all files and directories in a path.
Array of String Lists directories in a path.
Array of String Lists files in a path.
Boolean
Logs in on an FTP server.
Copies a file from the Orchestrator
server to a remote host.
Puts a string of content to a remote file.
Attribute Returns Description
output String
soLinger Number
state String
tcpNoDelay Boolean
timeout Number
Command output if any
Socket SO Linger (null if disabled)
Connection state
Socket TCP no delay
Socket timeout
The POP3Client class defines the following methods.
Method Returns Description
connect(String,number):Object Object
disconnect():Object Object
enableSSL(boolean):Object Object
listMessages():POP3Message[]
login(String,String):boolean Boolean
loginWithSecret(String,String,S
tring):boolean
logout():Object Object
Array of POP3Message Lists all messages. If there are no
Boolean
Connects the client to a host.
Disconnects the client from the server.
Enables SSL.
messages, the method returns a zero
length array. If the operation fails, the
method returns null.
Logs in on POP3 server with the given
user name and password. You must first
connect to the server with the
connect() method, before attempting
to log in.
Logs in on POP3 server with the given
user name and authentication
information.
Logs out of the POP3 server. To fully
disconnect from the server, you must
call the disconnect() method.
62 VMware, Inc.
Page 63

Method Returns Description
noop():Object Object
reset():Object Object
POP3Message Class
The POP3Message class provides POP3 email funtionality.
The POP3Message class defines the following attributes.
Attribute Returns Description
body String
from String
id Number
subject String
to String
Chapter 8 Using the Net Plug-In
Sends a NOOP command to the POP3
server. This is useful for keeping the
connection alive.
Resets the POP3 session. This is useful
for undoing any message deletions that
might have been performed.
Message body
Sender
Message ID in current session
Message subject
Recepient
The POP3Message class defines the following methods.
Method Returns Description
deleteFromServer():Object Object
getHeader(String):string String
Deletes a message from the POP3
server. The server marks the message
for deletion but does not delete it
immediately. If you decide to unmark
the message, you must use call the
reset() command from the
POP3Client class. The server deletes all
messages marked for deletion when
you call the logout() command from
the POP3Client class.
Gets the header value.
TelnetClient Class
The TelnetClient class is the main class for implementing Telnet funtionality into workflows.
The TelnetClient class defines the TelnetClient(String):TelnetClient constructor.
The TelnetClient class defines the following attributes.
Attribute Returns Description
soLinger Number
tcpNoDelay Boolean
timeout Number
Socket SO Linger (null if disabled)
Socket TCP no delay
Socket timeout
The TelnetClient class defines the following methods.
VMware, Inc. 63
Page 64

Using VMware vCenter Orchestrator Plug-Ins
Method Returns Description
connect(String,number):Object Object
disconnect():Object Object
enableSSL(boolean):Object Object
receiveAsBinary():Object[]
receiveAsString():string String
sendBinary(Object[]):Object Object
sendString(String):Object Object
waitForData(Number):boolean Boolean
Connects the client to a host.
Disconnects the client.
Enables SSL.
Array of Object Gets a response as an array of numbers.
Gets a response as a string.
Sends binary information as an array of
numbers.
Sends a string command.
Waits for data to become available and
returns true if data is available or
false if the request times out.
64 VMware, Inc.
Page 65

Using the Enumeration Plug-In 9
You can use the Enumeration plug-in to implement common enumerated types in workflows.
This chapter includes the following topics:
n
“Enumeration Plug-In Scrpting API,” on page 65
n
“Time Zone Codes,” on page 66
Enumeration Plug-In Scrpting API
The Enums scripting API contains common enumerated types.
Table 9-1. Common Enumerated Types
Enumeration Name Possible Values Description
Enums:Backup
Enums:Disk
Enums:Environment
Enums:MSTimeZone
All: Configuration file and all disks
Config: Configuration file only
None: No backup at all
System: Configuration file and first
disk
0: No disk
2: 2 GB
4: 4 GB
8: 8 GB
12: 12 GB
16: 16 GB
20: 20 GB
60: 60 GB
80: 80 GB
100: 100 GB
120: 120 GB
160: 160 GB
Validation: Validation
environments
Test: Test environments
Development: Development
environments
Production: Production
environments
See “Time Zone Codes,” on page 66. Time zones
Kind of backup
Possible disk sizes
Type of deployment environment
VMware, Inc. 65
Page 66

Using VMware vCenter Orchestrator Plug-Ins
Table 9-1. Common Enumerated Types (Continued)
Enumeration Name Possible Values Description
Enums:Performance
Enums:RAM
Enums:vCPU
Low: Low (20%)
Medium: Medium (60%)
High: High (80%)
128: 128 MB
256: 256 MB
512: 512 MB
1024: 1 GB
2048: 2 GB
3584: 3.5 GB (ESX 2 maximum)
4096: 4 GB
6144: 6 GB
8192: 8 GB
10240: 10 GB
12288: 12 GB
14336: 14 GB
16384: 16 GB
1: Virtual machine with 1 virtual CPU
2: Virtual machine with 2 virtual CPUs
3: Virtual machine with 3 virtual CPUs
4: Virtual machine with 4 virtual CPUs
5: Virtual machine with 5 virtual CPUs
6: Virtual machine with 6 virtual CPUs
7: Virtual machine with 7 virtual CPUs
8: Virtual machine with 8 virtual CPUs
Type of performance
Possible RAM sizes
Number of virtual CPUs
Time Zone Codes
You can use the time zone codes as possible values for the Enums:MSTimeZone enumeration.
Time Zone Code Time Zone Name Description
000 Dateline Standard Time (GMT-12:00) International Date Line
001 Samoa Standard Time (GMT-11:00) Midway Island, Samoa
002 Hawaiian Standard Time (GMT-10:00) Hawaii
003 Alaskan Standard Time (GMT-09:00) Alaska
004 Pacific Standard Time (GMT-08:00) Pacific Time (US and
010 Mountain Standard Time (GMT-07:00) Mountain Time (US and
013 Mexico Standard Time 2 (GMT-07:00) Chihuahua, La Paz,
015 U.S. Mountain Standard Time (GMT-07:00) Arizona
020 Central Standard Time (GMT-06:00) Central Time (US and
025 Canada Central Standard Time (GMT-06:00) Saskatchewan
West
Canada); Tijuana
Canada)
Mazatlan
Canada)
66 VMware, Inc.
Page 67

Chapter 9 Using the Enumeration Plug-In
Time Zone Code Time Zone Name Description
030 Mexico Standard Time (GMT-06:00) Guadalajara, Mexico City,
Monterrey
033 Central America Standard Time (GMT-06:00) Central America
035 Eastern Standard Time (GMT-05:00) Eastern Time (US and
Canada)
040 U.S. Eastern Standard Time (GMT-05:00) Indiana (East)
045 S.A. Pacific Standard Time (GMT-05:00) Bogota, Lima, Quito
050 Atlantic Standard Time (GMT-04:00) Atlantic Time (Canada)
055 S.A. Western Standard Time (GMT-04:00) Caracas, La Paz
056 Pacific S.A. Standard Time (GMT-04:00) Santiago
060 Newfoundland and Labrador
Standard Time
(GMT-03:30) Newfoundland and
Labrador
065 E. South America Standard Time (GMT-03:00) Brasilia
070 S.A. Eastern Standard Time (GMT-03:00) Buenos Aires,
Georgetown
073 Greenland Standard Time (GMT-03:00) Greenland
075 Mid-Atlantic Standard Time (GMT-02:00) Mid-Atlantic
080 Azores Standard Time (GMT-01:00) Azores
083 Cape Verde Standard Time (GMT-01:00) Cape Verde Islands
085 GMT Standard Time (GMT) Greenwich Mean Time : Dublin,
Edinburgh, Lisbon, London
090 Greenwich Standard Time (GMT) Casablanca, Monrovia
095 Central Europe Standard Time (GMT+01:00) Belgrade, Bratislava,
Budapest, Ljubljana, Prague
100 Central European Standard Time (GMT+01:00) Sarajevo, Skopje, Warsaw,
Zagreb
105 Romance Standard Time (GMT+01:00) Brussels, Copenhagen,
Madrid, Paris
110 W. Europe Standard Time (GMT+01:00) Amsterdam, Berlin, Bern,
Rome, Stockholm, Vienna
113 W. Central Africa Standard Time (GMT+01:00) West Central Africa
115 E. Europe Standard Time (GMT+02:00) Bucharest
120 Egypt Standard Time (GMT+02:00) Cairo
125 FLE Standard Time (GMT+02:00) Helsinki, Kyiv, Riga,
Sofia, Tallinn, Vilnius
130 GTB Standard Time (GMT+02:00) Athens, Istanbul, Minsk
135 Israel Standard Time (GMT+02:00) Jerusalem
140 South Africa Standard Time (GMT+02:00) Harare, Pretoria
145 Russian Standard Time (GMT+03:00) Moscow, St. Petersburg,
Volgograd
150 Arab Standard Time (GMT+03:00) Kuwait, Riyadh
155 E. Africa Standard Time (GMT+03:00) Nairobi
158 Arabic Standard Time (GMT+03:00) Baghdad
160 Iran Standard Time (GMT+03:30) Tehran
VMware, Inc. 67
Page 68

Using VMware vCenter Orchestrator Plug-Ins
Time Zone Code Time Zone Name Description
165 Arabian Standard Time (GMT+04:00) Abu Dhabi, Muscat
170 Caucasus Standard Time (GMT+04:00) Baku, Tbilisi, Yerevan
175 Transitional Islamic State of
180 Ekaterinburg Standard Time (GMT+05:00) Ekaterinburg
185 West Asia Standard Time (GMT+05:00) Islamabad, Karachi,
190 India Standard Time (GMT+05:30) Chennai, Kolkata,
193 Nepal Standard Time (GMT+05:45) Kathmandu
195 Central Asia Standard Time (GMT+06:00) Astana, Dhaka
200 Sri Lanka Standard Time (GMT+06:00) Sri Jayawardenepura
201 N. Central Asia Standard Time (GMT+06:00) Almaty, Novosibirsk
203 Myanmar Standard Time (GMT+06:30) Yangon (Rangoon)
205 S.E. Asia Standard Time (GMT+07:00) Bangkok, Hanoi, Jakarta
207 North Asia Standard Time (GMT+07:00) Krasnoyarsk
210 China Standard Time (GMT+08:00) Beijing, Chongqing, Hong
215 Singapore Standard Time (GMT+08:00) Kuala Lumpur, Singapore
220 Taipei Standard Time (GMT+08:00) Taipei
225 W. Australia Standard Time (GMT+08:00) Perth
227 North Asia East Standard Time (GMT+08:00) Irkutsk, Ulaan Bataar
230 Korea Standard Time (GMT+09:00) Seoul
235 Tokyo Standard Time (GMT+09:00) Osaka, Sapporo, Tokyo
240 Yakutsk Standard Time (GMT+09:00) Yakutsk
245 A.U.S. Central Standard Time (GMT+09:30) Darwin
250 Cen. Australia Standard Time (GMT+09:30) Adelaide
255 A.U.S. Eastern Standard Time (GMT+10:00) Canberra, Melbourne,
260 E. Australia Standard Time (GMT+10:00) Brisbane
265 Tasmania Standard Time (GMT+10:00) Hobart
270 Vladivostok Standard Time (GMT+10:00) Vladivostok
275 West Pacific Standard Time (GMT+10:00) Guam, Port Moresby
280 Central Pacific Standard Time (GMT+11:00) Magadan, Solomon
285 Fiji Islands Standard Time (GMT+12:00) Fiji Islands, Kamchatka,
290 New Zealand Standard Time (GMT+12:00) Auckland, Wellington
300 Tonga Standard Time (GMT+13:00) Nuku'alofa
(GMT+04:30) Kabul
Afghanistan Standard Time
Tashkent
Mumbai, New Delhi
Kong SAR, Urumqi
Sydney
Islands, New Caledonia
Marshall Islands
68 VMware, Inc.
Page 69

Index
A
API Explorer, accessing 12
audience 7
D
Database plug-in
scripting API 31
usage 31
Database plug-in API
connecting to a database 31
Connection class 31
database connection parameters 31
JDBCConnection class 31
precompiled SQL statement 32
PreparedStatement class 32
ResultSet class 32
Database plug-in sample workflows 33
default plug-ins 10
E
Enumeration plug-in
Enums:MSTimeZone values 66
scrpting API 65
usage 65
I
introduction 9
J
JDBC connection, testing 34
JDBC dropping, testing 37
JDBC entry deletion, testing 36
JDBC full cycle, testing 37
JDBC plug-in, usage 31
JDBC row insertion, testing 35
JDBC row selection, testing 35
JDBC sample workflows 33
JDBC table creation, testing 34
JDBC URL generator 33
L
load balancing 57
M
Mail plug-in
sample workflows access 59
scripting API 58
usage 57
Mail plug-in API, EmailMessage class 58
Mail plug-in sample workflows 59
Mail plug-in workflows, example interaction with
email 60
N
Net plug-in
scripting API 61
usage 61
Net plug-in API
FTPClient class 61
POP3Client class 62
POP3Message class 63
TelnetClient class 63
O
Orchestrator architecture 9
overview of
Database plug-in 10
Enumeration plug-in 10
Mail plug-in 10
Net plug-in 10
overview of 10
SSH plug-in 10
vCenter Server 4.1 plug-in 10
vCO Library plug-in 10
vCO Weboperator plug-in 10
XML plug-in 10
P
plug-ins configuration
Mail plug-in 57
SSH plug-in 39
vCenter Server plug-in 15
S
scripting
email examples 58
vCenter Server examples 16
SFTP 46, 47
SMTP connection 57
SSH commands, running 46
VMware, Inc. 69
Page 70

Using VMware vCenter Orchestrator Plug-Ins
SSH file copy
SCP get command 46
SCP put command 47
SSH plug-in
scripting API 40
usage 39
SSH plug-in API
KeyPairManager class 40
managing private and public SSH keys 40
SSH:File type 40
SSH:Folder type 40
SSH:RootFolder type 40
SSH:SshConnection type 40
SSHCommand class 41
SSHFile class 42
SSHFolder class 42
SSHSession class 43
SSH plug-in sample workflows 44
SSH workflows
changing a key pair passphrase 45
generating a key pair 44
registering a public key 45
V
vCenter Server 4.1 plug-in
Inventory 18
scripting API 16
usage 15
workflow library 19
workflow library access 18
vCO Library plug-in
usage 29
workflows 29
X
XML
DOM 49
E4X 49
XML plug-in
scripting API 49
usage 49
XML plug-in API
XMLDocument class 49
XMLElement class 50
XMLManager class 51
XMLNamedNodeMap class 51
XMLNode class 52
XMLNodeList class 53
XML plug-in sample workflows
creating a simple XML document 53
creating an address book 55
finding an element 54
modifying an XML document 54
70 VMware, Inc.
 Loading...
Loading...